User login
Development of Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Following Treatment With Upadacitinib for Atopic Dermatitis
Development of Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Following Treatment With Upadacitinib for Atopic Dermatitis
To the Editor:
A 22-year-old man presented to our clinic with a history of longstanding widespread recalcitrant atopic dermatitis (AD) since early childhood. He had been treated by an outside physician with topical steroids and nonsteroidal medications without notable improvement as well as with dupilumab, which was discontinued due to the development of severe head and neck dermatitis. Given the severity of his AD on presentation, we initiated treatment with upadacitinib 15 mg/d, which resulted in partial improvement. The dose was increased to 30 mg/d at 3 months with further clinical improvement.
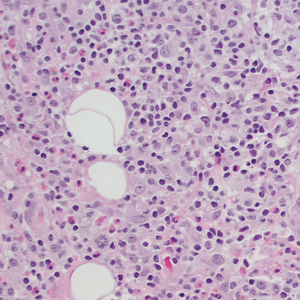
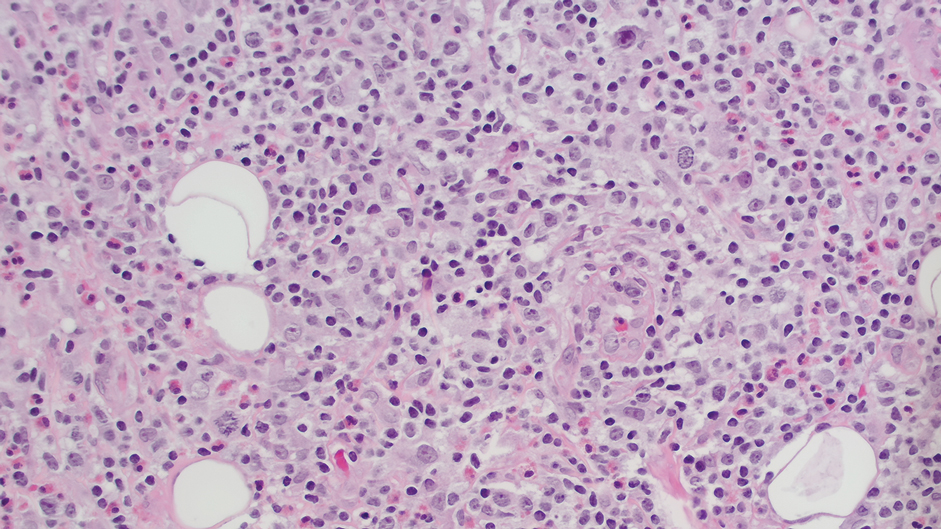
Ten months after the patient was started on upadacitinib, he presented for a follow-up evaluation and reported a new nontender nodule on the scalp. A punch biopsy revealed a dense dermal and subcutaneous lymphoid infiltrate (Figure 1) composed of many large atypical CD2+/CD5+/CD45+ T cells with partial loss of CD3 expression (Figure 2). The atypical cells demonstrated diffuse CD30+ expression (Figure 3) and a CD4:CD8 ratio of greater than 50:1 (Figures 4 and 5). He was diagnosed with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and the upadacitinib was discontinued. No additional therapies directed toward ALCL were initiated.
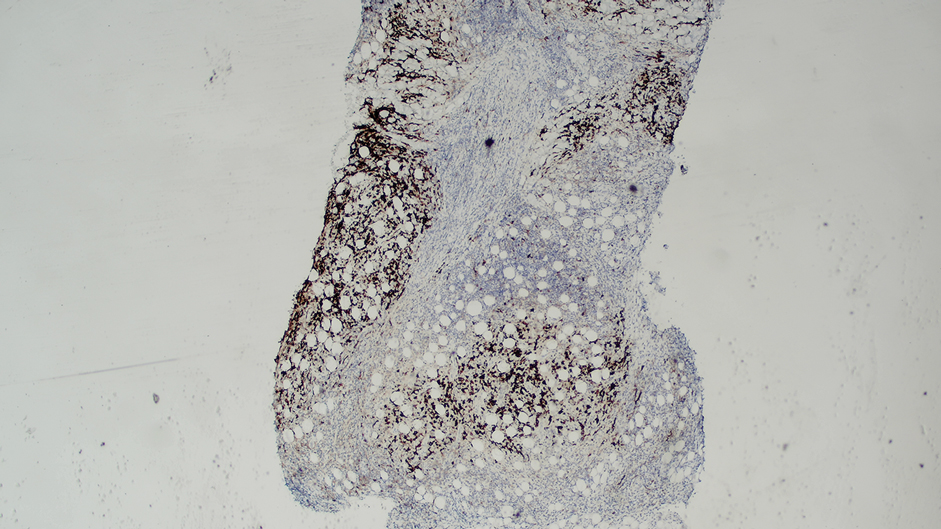
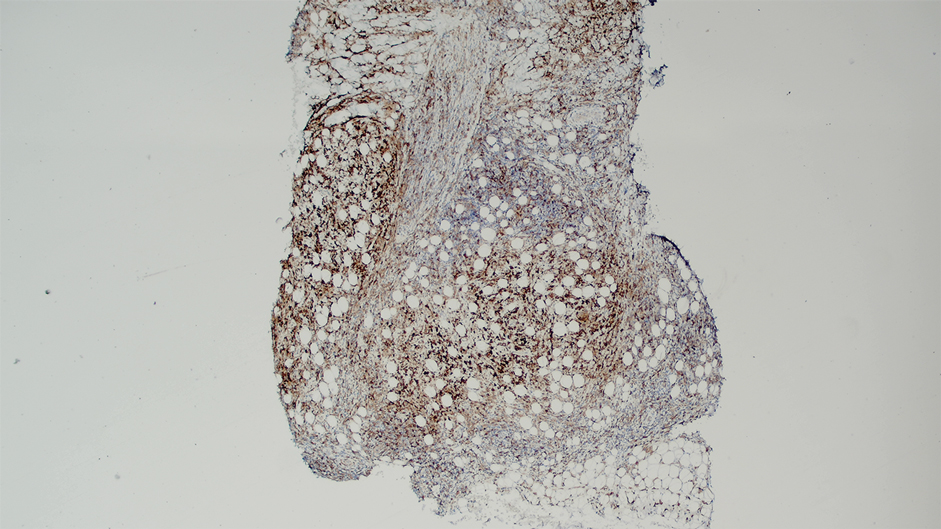
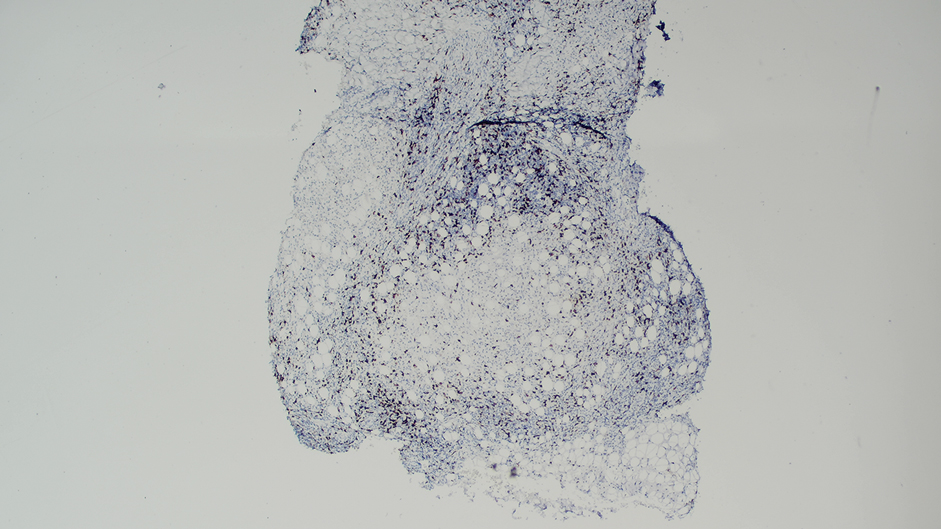
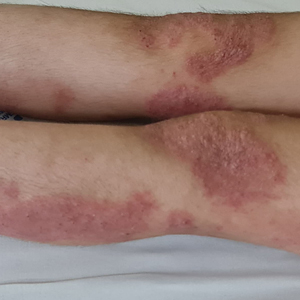
Over the next 2 weeks, the patient developed additional nodules on the postauricular skin and trunk that demonstrated similar histopathology and immunophenotype to the original scalp nodule. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies demonstrated shared clonal peaks in these subsequent nodules. A concurrent biopsy of an eczematous plaque on the back showed spongiotic dermatitis without evidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; gene rearrangement studies from this site were negative. A positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan showed mildly hypermetabolic cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes, which were favored to be reactive. Narrow-band UVB phototherapy was initiated for management of the AD, and no additional nodules developed over the subsequent months.
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are immunomodulatory small molecules that interfere with JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling involving 1 or more isoforms (eg, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, tyrosine kinase 2) and have been used to treat various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, axial spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and AD.1 Upadacitinib is an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older.2 A search of PubMed using the terms upadacitinib or Rinvoq and anaplastic large cell lymphoma did not identify any cases of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib. However, a case of lymphomatoid papulosis after initiation of upadacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in a 74-year-old Japanese woman has been described,3 and the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway has been implicated in the development of other CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders.4,5
An association between JAK inhibitors and aggressive B-cell lymphomas has been described. In an observational study of 626 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Porpaczy et al,6 4 of 69 (5.8%) patients treated with JAK inhibitors developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma, whereas only 2 of 557 (0.36%) patients who did not receive JAK-inhibitor therapy developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma. In contrast, a retrospective analysis of 2583 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Pemmaraju et al7 found no significant increase in lymphoma rates in the JAK inhibitor–treated population as compared with the non-JAK inhibitor–treated group; 9 (0.56%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 1617 patients with myelofibrosis, of which 6 had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy and 3 had no exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy (P=.082) and 5 (0.52%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 966 patients with essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera, none of whom had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy.Finally, some evidence suggests the use of JAK inhibitors may be associated with an elevated risk of malignancies overall. The ORAL Surveillance study found the incidence of all cancers, excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), in patients treated with tofacitinib to be 4.2% (122/2911) compared with 2.9% (42/1451) in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors; it should be noted that the patients in this study were restricted to adults aged 50 years and older who were undergoing treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.8 In a safety profile study for upadacitinib, a higher rate of malignancies, excluding NMSC, was found in patients with AD treated with upadacitinib 30 mg/d than in patients treated with 15 mg/d; however, the overall rates of malignancies, excluding NMSC, in patients treated with upadacitinib were comparable to the standard incidence rates of malignancies in the general population derived from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data.9
In summary, we present a case of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib for AD. While some literature suggests AD may independently predispose patients to the development of CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders, the onset of our patient’s cutaneous ALCL 10 months after initiation of upadacitinib is suggestive of an association between his lymphoproliferative disorder and JAK inhibition. Further studies are needed to better characterize the risk of lymphoproliferative disorders and other malignancies in patients treated with JAK inhibitors.
- Strangfeld A, Hierse F, Rau R, et al. Risk of incident or recurrent malignancies among patients with rheumatoid arthritis exposed to biologic therapy in the German biologics register RABBIT. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R5. doi:10.1186/ar2904
- Rinvoq. Highlights of prescribing information. Abbvie Inc; 2024. Accessed January 31, 2026. https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/rinvoq_pi.pdf
- Iinuma S, Hayashi K, Noguchi A, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis during upadacitinib treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Dermatol. 2022;32:142-143. doi:10.1684/ejd.2022.4238
- Quesada AE, Zhang Y, Ptashkin R, et al. Next generation sequencing of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphomas reveals a novel STAT3-JAK2 fusion among other activating genetic alterations within the JAK-STAT pathway. Breast J. 2021;27:314-321. doi:10.1111/tbj.14205
- Maurus K, Appenzeller S, Roth S, et al. Recurrent oncogenic JAK and STAT alterations in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2023-2031.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.02.019
- Porpaczy E, Tripolt S, Hoelbl-Kovacic A, et al. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas in patients with myelofibrosis receiving JAK1/2 inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2018;132:694-706. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-10-810739
- Pemmaraju N, Kantarjian H, Nastoupil L, et al. Characteristics of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms with lymphoma, with or without JAK inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2019;133:2348-2351. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-01-897637
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109927
- Burmester GR, Cohen SB, Winthrop KL, et al. Safety profile of upadacitinib over 15 000 patient-years across rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and atopic dermatitis. RMD Open. 2023;9:E002735. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002735
To the Editor:
A 22-year-old man presented to our clinic with a history of longstanding widespread recalcitrant atopic dermatitis (AD) since early childhood. He had been treated by an outside physician with topical steroids and nonsteroidal medications without notable improvement as well as with dupilumab, which was discontinued due to the development of severe head and neck dermatitis. Given the severity of his AD on presentation, we initiated treatment with upadacitinib 15 mg/d, which resulted in partial improvement. The dose was increased to 30 mg/d at 3 months with further clinical improvement.
Ten months after the patient was started on upadacitinib, he presented for a follow-up evaluation and reported a new nontender nodule on the scalp. A punch biopsy revealed a dense dermal and subcutaneous lymphoid infiltrate (Figure 1) composed of many large atypical CD2+/CD5+/CD45+ T cells with partial loss of CD3 expression (Figure 2). The atypical cells demonstrated diffuse CD30+ expression (Figure 3) and a CD4:CD8 ratio of greater than 50:1 (Figures 4 and 5). He was diagnosed with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and the upadacitinib was discontinued. No additional therapies directed toward ALCL were initiated.





Over the next 2 weeks, the patient developed additional nodules on the postauricular skin and trunk that demonstrated similar histopathology and immunophenotype to the original scalp nodule. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies demonstrated shared clonal peaks in these subsequent nodules. A concurrent biopsy of an eczematous plaque on the back showed spongiotic dermatitis without evidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; gene rearrangement studies from this site were negative. A positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan showed mildly hypermetabolic cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes, which were favored to be reactive. Narrow-band UVB phototherapy was initiated for management of the AD, and no additional nodules developed over the subsequent months.
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are immunomodulatory small molecules that interfere with JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling involving 1 or more isoforms (eg, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, tyrosine kinase 2) and have been used to treat various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, axial spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and AD.1 Upadacitinib is an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older.2 A search of PubMed using the terms upadacitinib or Rinvoq and anaplastic large cell lymphoma did not identify any cases of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib. However, a case of lymphomatoid papulosis after initiation of upadacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in a 74-year-old Japanese woman has been described,3 and the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway has been implicated in the development of other CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders.4,5
An association between JAK inhibitors and aggressive B-cell lymphomas has been described. In an observational study of 626 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Porpaczy et al,6 4 of 69 (5.8%) patients treated with JAK inhibitors developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma, whereas only 2 of 557 (0.36%) patients who did not receive JAK-inhibitor therapy developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma. In contrast, a retrospective analysis of 2583 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Pemmaraju et al7 found no significant increase in lymphoma rates in the JAK inhibitor–treated population as compared with the non-JAK inhibitor–treated group; 9 (0.56%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 1617 patients with myelofibrosis, of which 6 had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy and 3 had no exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy (P=.082) and 5 (0.52%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 966 patients with essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera, none of whom had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy.Finally, some evidence suggests the use of JAK inhibitors may be associated with an elevated risk of malignancies overall. The ORAL Surveillance study found the incidence of all cancers, excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), in patients treated with tofacitinib to be 4.2% (122/2911) compared with 2.9% (42/1451) in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors; it should be noted that the patients in this study were restricted to adults aged 50 years and older who were undergoing treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.8 In a safety profile study for upadacitinib, a higher rate of malignancies, excluding NMSC, was found in patients with AD treated with upadacitinib 30 mg/d than in patients treated with 15 mg/d; however, the overall rates of malignancies, excluding NMSC, in patients treated with upadacitinib were comparable to the standard incidence rates of malignancies in the general population derived from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data.9
In summary, we present a case of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib for AD. While some literature suggests AD may independently predispose patients to the development of CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders, the onset of our patient’s cutaneous ALCL 10 months after initiation of upadacitinib is suggestive of an association between his lymphoproliferative disorder and JAK inhibition. Further studies are needed to better characterize the risk of lymphoproliferative disorders and other malignancies in patients treated with JAK inhibitors.
To the Editor:
A 22-year-old man presented to our clinic with a history of longstanding widespread recalcitrant atopic dermatitis (AD) since early childhood. He had been treated by an outside physician with topical steroids and nonsteroidal medications without notable improvement as well as with dupilumab, which was discontinued due to the development of severe head and neck dermatitis. Given the severity of his AD on presentation, we initiated treatment with upadacitinib 15 mg/d, which resulted in partial improvement. The dose was increased to 30 mg/d at 3 months with further clinical improvement.
Ten months after the patient was started on upadacitinib, he presented for a follow-up evaluation and reported a new nontender nodule on the scalp. A punch biopsy revealed a dense dermal and subcutaneous lymphoid infiltrate (Figure 1) composed of many large atypical CD2+/CD5+/CD45+ T cells with partial loss of CD3 expression (Figure 2). The atypical cells demonstrated diffuse CD30+ expression (Figure 3) and a CD4:CD8 ratio of greater than 50:1 (Figures 4 and 5). He was diagnosed with anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and the upadacitinib was discontinued. No additional therapies directed toward ALCL were initiated.





Over the next 2 weeks, the patient developed additional nodules on the postauricular skin and trunk that demonstrated similar histopathology and immunophenotype to the original scalp nodule. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement studies demonstrated shared clonal peaks in these subsequent nodules. A concurrent biopsy of an eczematous plaque on the back showed spongiotic dermatitis without evidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; gene rearrangement studies from this site were negative. A positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan showed mildly hypermetabolic cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes, which were favored to be reactive. Narrow-band UVB phototherapy was initiated for management of the AD, and no additional nodules developed over the subsequent months.
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are immunomodulatory small molecules that interfere with JAK–signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling involving 1 or more isoforms (eg, JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, tyrosine kinase 2) and have been used to treat various inflammatory conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, axial spondyloarthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and AD.1 Upadacitinib is an oral selective JAK1 inhibitor approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for treatment of moderate to severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older.2 A search of PubMed using the terms upadacitinib or Rinvoq and anaplastic large cell lymphoma did not identify any cases of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib. However, a case of lymphomatoid papulosis after initiation of upadacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in a 74-year-old Japanese woman has been described,3 and the JAK/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway has been implicated in the development of other CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders.4,5
An association between JAK inhibitors and aggressive B-cell lymphomas has been described. In an observational study of 626 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Porpaczy et al,6 4 of 69 (5.8%) patients treated with JAK inhibitors developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma, whereas only 2 of 557 (0.36%) patients who did not receive JAK-inhibitor therapy developed an aggressive B-cell lymphoma. In contrast, a retrospective analysis of 2583 patients with myeloproliferative neoplasia by Pemmaraju et al7 found no significant increase in lymphoma rates in the JAK inhibitor–treated population as compared with the non-JAK inhibitor–treated group; 9 (0.56%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 1617 patients with myelofibrosis, of which 6 had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy and 3 had no exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy (P=.082) and 5 (0.52%) cases of lymphoma occurred in 966 patients with essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera, none of whom had exposure to JAK inhibitor therapy.Finally, some evidence suggests the use of JAK inhibitors may be associated with an elevated risk of malignancies overall. The ORAL Surveillance study found the incidence of all cancers, excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), in patients treated with tofacitinib to be 4.2% (122/2911) compared with 2.9% (42/1451) in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors; it should be noted that the patients in this study were restricted to adults aged 50 years and older who were undergoing treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.8 In a safety profile study for upadacitinib, a higher rate of malignancies, excluding NMSC, was found in patients with AD treated with upadacitinib 30 mg/d than in patients treated with 15 mg/d; however, the overall rates of malignancies, excluding NMSC, in patients treated with upadacitinib were comparable to the standard incidence rates of malignancies in the general population derived from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data.9
In summary, we present a case of cutaneous ALCL arising after treatment with upadacitinib for AD. While some literature suggests AD may independently predispose patients to the development of CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorders, the onset of our patient’s cutaneous ALCL 10 months after initiation of upadacitinib is suggestive of an association between his lymphoproliferative disorder and JAK inhibition. Further studies are needed to better characterize the risk of lymphoproliferative disorders and other malignancies in patients treated with JAK inhibitors.
- Strangfeld A, Hierse F, Rau R, et al. Risk of incident or recurrent malignancies among patients with rheumatoid arthritis exposed to biologic therapy in the German biologics register RABBIT. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R5. doi:10.1186/ar2904
- Rinvoq. Highlights of prescribing information. Abbvie Inc; 2024. Accessed January 31, 2026. https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/rinvoq_pi.pdf
- Iinuma S, Hayashi K, Noguchi A, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis during upadacitinib treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Dermatol. 2022;32:142-143. doi:10.1684/ejd.2022.4238
- Quesada AE, Zhang Y, Ptashkin R, et al. Next generation sequencing of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphomas reveals a novel STAT3-JAK2 fusion among other activating genetic alterations within the JAK-STAT pathway. Breast J. 2021;27:314-321. doi:10.1111/tbj.14205
- Maurus K, Appenzeller S, Roth S, et al. Recurrent oncogenic JAK and STAT alterations in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2023-2031.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.02.019
- Porpaczy E, Tripolt S, Hoelbl-Kovacic A, et al. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas in patients with myelofibrosis receiving JAK1/2 inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2018;132:694-706. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-10-810739
- Pemmaraju N, Kantarjian H, Nastoupil L, et al. Characteristics of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms with lymphoma, with or without JAK inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2019;133:2348-2351. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-01-897637
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109927
- Burmester GR, Cohen SB, Winthrop KL, et al. Safety profile of upadacitinib over 15 000 patient-years across rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and atopic dermatitis. RMD Open. 2023;9:E002735. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002735
- Strangfeld A, Hierse F, Rau R, et al. Risk of incident or recurrent malignancies among patients with rheumatoid arthritis exposed to biologic therapy in the German biologics register RABBIT. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R5. doi:10.1186/ar2904
- Rinvoq. Highlights of prescribing information. Abbvie Inc; 2024. Accessed January 31, 2026. https://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/rinvoq_pi.pdf
- Iinuma S, Hayashi K, Noguchi A, et al. Lymphomatoid papulosis during upadacitinib treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Dermatol. 2022;32:142-143. doi:10.1684/ejd.2022.4238
- Quesada AE, Zhang Y, Ptashkin R, et al. Next generation sequencing of breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphomas reveals a novel STAT3-JAK2 fusion among other activating genetic alterations within the JAK-STAT pathway. Breast J. 2021;27:314-321. doi:10.1111/tbj.14205
- Maurus K, Appenzeller S, Roth S, et al. Recurrent oncogenic JAK and STAT alterations in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140:2023-2031.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.02.019
- Porpaczy E, Tripolt S, Hoelbl-Kovacic A, et al. Aggressive B-cell lymphomas in patients with myelofibrosis receiving JAK1/2 inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2018;132:694-706. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-10-810739
- Pemmaraju N, Kantarjian H, Nastoupil L, et al. Characteristics of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms with lymphoma, with or without JAK inhibitor therapy. Blood. 2019;133:2348-2351. doi:10.1182/blood-2019-01-897637
- Ytterberg SR, Bhatt DL, Mikuls TR, et al. Cardiovascular and cancer risk with tofacitinib in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:316-326. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109927
- Burmester GR, Cohen SB, Winthrop KL, et al. Safety profile of upadacitinib over 15 000 patient-years across rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and atopic dermatitis. RMD Open. 2023;9:E002735. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002735
Development of Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Following Treatment With Upadacitinib for Atopic Dermatitis
Development of Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Following Treatment With Upadacitinib for Atopic Dermatitis
Practice Points
- Janus kinase inhibitors are immunomodulators used for the treatment of various inflammatory conditions, including atopic dermatitis.
- Treatment with Janus kinase inhibitors may be associated with the development of CD3012+ lymphoproliferative disorders such as cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma.
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition associated with skin barrier impairment and immune system dysregulation.1 Development of AD in young children can present challenges in determining appropriate treatment regimens. Natural remedies for AD often are promoted on social media over traditional treatments, including topical corticosteroids (TCSs), which can contribute to corticophobia.2 Dermatologists play a critical role not only in optimizing topical therapy but also addressing patient interest in natural approaches to AD, including diet-related questions. This article outlines the role of diet and probiotics in pediatric AD and reviews the topical treatments currently approved for this patient population.
Diet and Probiotics
With a growing focus on natural therapies for AD, dietary interventions have come to the forefront. A prevalent theme among patients and their families is addressing gut health and allergic triggers. Broad elimination diets have not shown clinical benefit in patients with AD regardless of age,3 and in children, they may result in nutritional deficiencies, poor growth, and increased risk for IgE-mediated food allergies.4 If a true food allergy is identified based on positive IgE and an acute clinical reaction, elimination of the allergen may provide some benefit.5
The link between gut microbiota and skin health has driven an interest in the role of probiotics in the treatment of pediatric AD. A meta-analysis of 20 articles concluded that, whether administered to infants or breastfeeding mothers, use of probiotics overall led to a significant reduction in AD risk in infants (P=.001). Lactobacillus and mixed strains were effective.6 While broad elimination diets are not used to treat AD, probiotic supplementation can be considered for prevention of AD.
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are the cornerstone of AD treatment; however, corticophobia among patients is on the rise, leading to poor adherence and suboptimal control of AD.7 Mild cutaneous adverse effects (AEs) including skin atrophy, striae, and telangiectasias may occur. Rarely, systemic AEs occur due to absorption of TCSs into the bloodstream, mainly with application of potent steroids over large body surface areas or under occlusion.8 When the optimal potency of a TCS is chosen and used appropriately, incidence of AEs from TCS use is very low.9
Counseling parents about risk factors that can lead to AEs during treatment with TCSs and formulating regimens that minimize these risks while maintaining efficacy increases adherence and outcomes. Pulse maintenance dosing of TCSs typically involves application 1 to 2 times weekly to areas of the skin that are prone to frequent outbreaks. Pulse maintenance dosing can reduce the incidence of AD flares while also decreasing the total amount of topical medication needed as compared to the reactive approach alone, thereby reducing risk for AEs.8
Steroid-Sparing Topical Treatments
Although TCSs are considered first-line agents, recently there has been an advent of steroid-sparing topical agents approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for pediatric patients with AD, including topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCIs), phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors, a Janus kinase inhibitor, and aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Offering steroid-sparing agents in these patients can help ease parental anxiety regarding TCS overuse.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors—Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% are approved for patients aged 2 years and older and have anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects equivalent to low-potency TCS. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for patients aged 16 years and older with similar efficacy to a midpotency TCSs. Pimecrolimus cream 1% and tacrolimus ointment 0.03% often are used off-label in children younger than 2 years, as supported by clinical trials showing their safety and efficacy.10
Topical calcineurin inhibitors can replace or supplement TCSs, making TCIs a desirable option for avoidance of steroid-related AEs. The addition of a TCI to spot treatment or a pulse regimen in a young patient can reassure them and their caregivers that the provider is proactively reducing the risk of TCS overuse. The largest barrier to TCI use is the FDA’s black box warning based on the oral formulation of tacrolimus, citing a potential increased risk for lymphoma and skin cancer; however, there is no evidence for substantial systemic absorption of topical pimecrolimus or tacrolimus.11 Large task-force reviews have found no association between TCI use and development of malignancy.12,13 Based on the current data, counseling patients and their caregivers that this risk primarily is theoretical may help them more confidently integrate TCIs into their treatment regimen. Burning and tingling may occur in a minority of pediatric patients using TCIs for AD. Applying the medication to open wounds or inflamed skin increases the risk for stinging, but pretreatment with a short course of TCSs before transitioning to a TCI may boost tolerance.14
Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitors—Crisaborole ointment 2%, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, is approved for children aged 3 months and older with mild to moderate AD. Its use has been more limited than TCSs and TCIs, as local irritation including stinging and burning can occur in up to 50% of patients.15 One study comparing crisaborole 2% with tacrolimus 0.03% revealed greater improvement with tacrolimus.16 A second phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor approved for once-daily use in children aged 6 years and older with mild to moderate AD is roflumilast cream 0.15%. Roflumilast reduces eczema severity and pruritus, with AEs also limited to application-site stinging and burning.17
Janus Kinase Inhibitor—Ruxolitinib cream 1.5%, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has been approved by the FDA since 2023 for twice-daily use in children aged 12 years and older with AD. Similar to TCIs, ruxolitinib cream carries a black box warning. Short-term safety data on ruxolitinib cream have revealed low levels of ruxolitinib concentration in plasma18; however, long-term studies on topical Janus kinase inhibitors for AD in pediatric and adult populations are lacking. To reduce the risk for systemic absorption, recommendations include limiting usage to 60 g per week and limiting treatment to less than 20% of the body surface area.19 Ruxolitinib has efficacy similar to or possibly superior to triamcinolone 0.1%.20 Ruxolitinib is emerging as a promising nonsteroidal option that potentially is highly efficacious and well tolerated without cutaneous AEs.
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist—Tapinarof cream 1% is an aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist that has been approved by the FDA since 2024 for children aged 2 years and older as a once-daily treatment for moderate to severe AD. Adverse events include folliculitis, nasopharyngitis, and headache, which are mostly mild or moderate.21
Final Thoughts
Topical management of pediatric AD includes traditional therapy with TCSs and newer steroid-sparing agents, which can help address corticophobia. Anticipatory guidance regarding the safety and long-term effects of individual therapies is critical to ensuring patient adherence to treatment regimens. Probiotics may help prevent pediatric AD, but future studies are needed to determine their role in treatment.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
- Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, et al. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:1.
- Voillot P, Riche B, Portafax M, et al. Social media platforms listening study on atopic dermatitis: quantitative and qualitative findings. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24:E31140.
- Bath-Hextall F, Delamere FM, Williams HC. Dietary exclusions for improving established atopic eczema in adults and children: systematic review. Allergy. 2009;64:258-264.
- Rustad AM, Nickles MA, Bilimoria SN, et al. The role of diet modification in atopic dermatitis: navigating the complexity. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:27-36.
- Khan A, Adalsteinsson J, Whitaker-Worth DL. Atopic dermatitis and nutrition. Clin Dermatol. 2022;40:135-144.
- Chen L, Ni Y, Wu X, et al. Probiotics for the prevention of atopic dermatitis in infants from different geographic regions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33:2931-2939.
- Herzum A, Occella C, Gariazzo L, et al. Corticophobia among parents of children with atopic dermatitis: assessing major and minor risk factors for high TOPICOP scores. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6813.
- Eichenfield LF, Tom WL, Berger TG, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis: section 2. management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:116-132.
- Callen J, Chamlin S, Eichenfield LF, et al. A systematic review of the safety of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:203-221.
- Reitamo S, Rustin M, Ruzicka T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus ointment compared with that of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in adult patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;109:547-555.
- Thaçi D, Salgo R. Malignancy concerns of topical calcineurin inhibitors for atopic dermatitis: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2010;28:52-56.
- Berger TG, Duvic M, Van Voorhees AS, et al. The use of topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology: safety concerns. report of the AAD Association Task Force. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:818-823.
- Fonacier L, Spergel J, Charlesworth EN, et al. Report of the Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Task Force of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:1249-1253.
- Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M, et al. Safety and efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:495-504.
- Lin CPL, Gordon S, Her MJ, et al. A retrospective study: application site pain with the use of crisaborole, a topical phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80:1451-1453.
- Ryan Wolf J, Chen A, Wieser J, et al. Improved patient- and caregiver-reported outcomes distinguish tacrolimus 0.03% from crisaborole in children with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:1364-1372.
- Simpson EL, Eichenfield LF, Alonso-Llamazares J, et al. Roflumilast cream, 0.15%, for atopic dermatitis in adults and children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Dermatol. 2024;160:1161-1170.
- Papp K, Szepietowski JC, Kircik L, et al. Long-term safety and disease control with ruxolitinib cream in atopic dermatitis: results from two phase 3 studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;88:1008-1016.
- Sidbury R, Alikhan A, Bercovitch L, et al. Guidelines of carefor the management of atopic dermatitis in adults with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:E1-E20.
- Sadeghi S, Mohandesi NA. Efficacy and safety of topical JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis in paediatrics and adults: a systematic review. Exp Dermatol. 2023;32:599-610.
- Silverberg JI, Eichenfield LF, Hebert AA, et al. Tapinarof cream 1% once daily: significant efficacy in the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children down to 2 years of age in the pivotal phase 3 ADORING trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2024;91:457-465.
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Update on Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Children
Epidemiologic and Clinical Evaluation of the Bidirectional Link Between Molluscum Contagiosum and Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Epidemiologic and Clinical Evaluation of the Bidirectional Link Between Molluscum Contagiosum and Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), which is caused by a DNA virus in the Poxviridae family, is a common viral skin infection that primarily affects children.1-4 The reported incidence and prevalence of MC exhibit notable geographic variation. Worldwide, annual incidence rates per 1000 individuals range from 3.1 to 25, and prevalence ranges from 0.27% to 34.6%.2-7
Molluscum contagiosum is diagnosed clinically and typically manifests as smooth, flesh-colored papules measuring 2 to 6 mm in diameter with central umbilication. It can manifest as a single lesion or multiple clustered lesions, or in a disseminated pattern. The primary mode of transmission is through contact with skin, lesions, or contaminated personal items, or via self-inoculation. The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but in some patients, MC may be associated with pruritus, tenderness, erythema, or irritation. When present, secondary bacterial infections can cause localized inflammation and pain.1,3,4 The pathogenesis hinges on MC virus replication within keratinocytes, disrupting cellular differentiation and keratinization. The virus persists in the host by influencing the immune response through various mechanisms, including interference with signaling pathways, apoptosis inhibition, and antigen presentation disruption.3,4
Molluscum contagiosum typically follows a self-limiting trajectory, resolving over several months to 2 years.3,4 The resolution timeframe is intricately linked to variables such as the patient’s immune profile, lesion burden, and treatment approach. For symptomatic lesions, a variety of treatment options have been described, including physical ablation (eg, cryotherapy, curettage) and topical agents such as potassium hydroxide, cantharidin, imiquimod, and salicylic acid.3,4,8,9
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic relapsing inflammatory skin disorder. In the United States, its prevalence ranges from 15% to 30% in children and from 2% to 10% in adults, with ongoing evidence of a growing global incidence.10-14 While AD can emerge at any age, typical onset is during early childhood. The clinical manifestation of AD includes a spectrum of eczematous features, often accompanied by persistent itching. The pathogenesis is multifactorial, involving a complex interplay of genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors. Key contributors to this multifaceted process encompass a compromised epidermal barrier, alterations in the skin microbiome, and an immune dysregulation promoting a type 2 immune response. Epidermal barrier dysfunction can be attributed to various factors, including diminished ceramide production, altered lipid composition, the release of inflammatory mediators, and mechanical damage from the persistent itch-scratch cycle.10-13,15 These factors or their interplay may enhance the susceptibility of patients with AD to infections.
Several studies conducted across various geographic regions examining the relationship between MC and AD have reported variable findings.2,6,7,16-21 Published studies have reported a prevalence of AD in children with MC ranging from 13.2% to 43%.2,6,7,16-21 Although some studies suggest a higher rate of atopy in patients with MC, not all research has confirmed this association.16,21 Dohil et al2 reported a greater number of MC lesions in children with AD than those without an atopic background. Silverberg20 reported that in 10% (5/50) of children with MC, the onset of AD was triggered, and in 22% (11/50) MC was associated with flares of pre-existing AD.
In this study, we aimed to assess MC infection rates in children with AD, analyze the epidemiologic aspects and severity differences between atopic children with and without MC infection, and compare data from atopic and nonatopic children with MC.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed the medical records of pediatric patients diagnosed with MC, AD, or both conditions at an outpatient dermatology practice in Netanya, HaSharon, Israel, from September 2013 to August 2022. Data were collected from the electronic medical records and included patient demographics, the clinical presentation of MC and/or AD at diagnosis, and the duration of both conditions. Only patients with complete data and at least 6 months of follow-up were included. Key epidemiologic characteristics assessed included patient sex, age at the initial visit, and age at the onset of MC and/or AD. Diagnoses of MC and AD were established through clinical examinations conducted by dermatologists. The clinical evaluation of AD encompassed the assessment of body surface area involvement (categorized as <5%, 5%-10%, or >10%). Atopic dermatitis severity was classified as mild, moderate, or severe using the validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis.22 Clinical evaluation of MC included assessment of the number of lesions (categorized as ≤4, 5-9, or ≥10), presence of inflammatory lesions, and resolution times for individual lesions (categorized as <1 week, several weeks, or unknown), as well as the overall resolution time for all lesions (categorized as <6 months, 6-12 months, 13-18 months, or >18 months). The temporal relationship between the appearance of MC and AD also was assessed.
Statistical Analysis—Numbers and percentages were used for categorical variables. Continuous variables were represented by mean and standard deviation. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 test, and continuous variables between groups were compared using the Student t test. All statistical tests were 2-sided, with statistical significance defined as P≤.05. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 28 (IBM).
Results
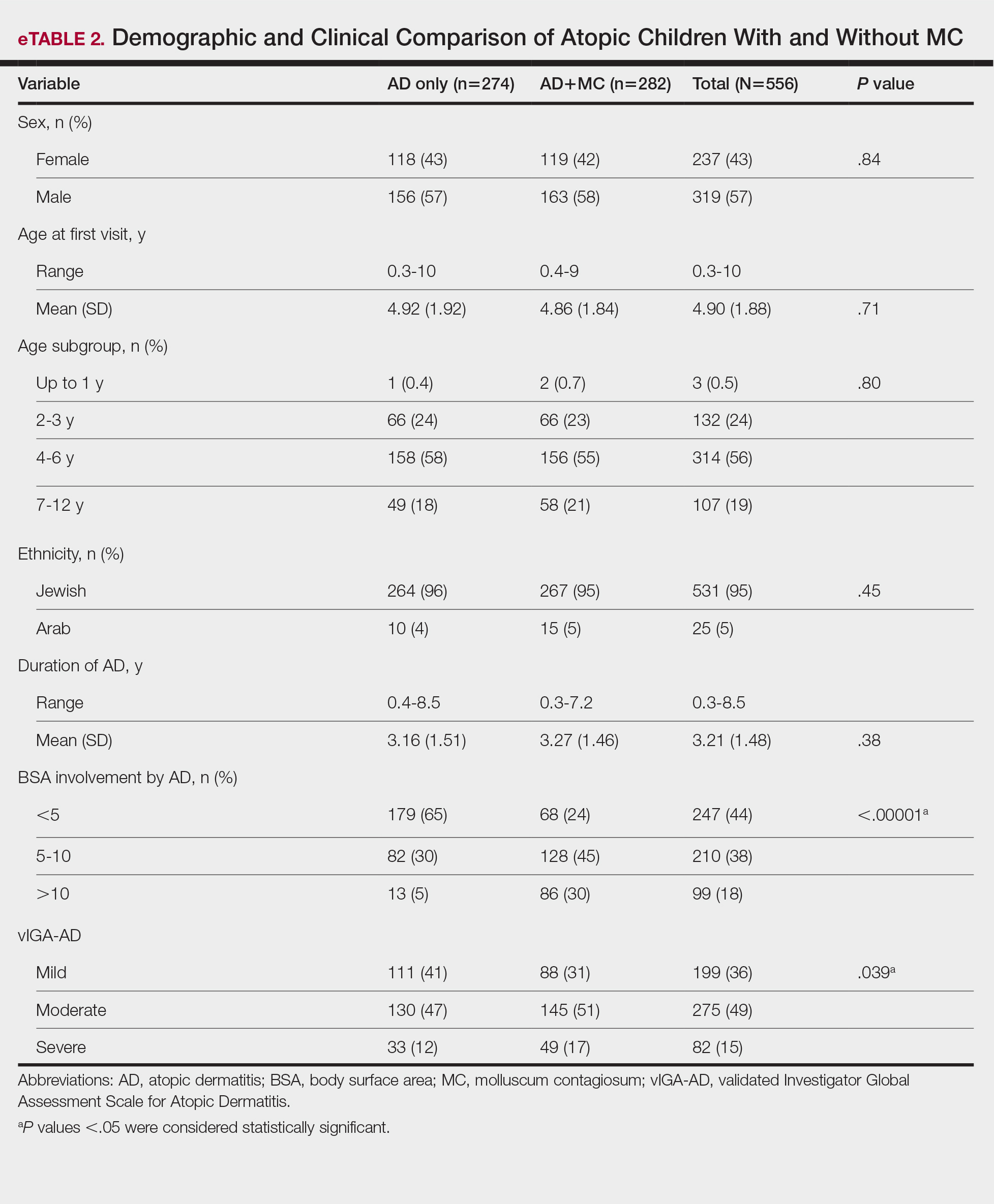
Study Population—A total of 610 children were included in the study; 263 (43%) were female and 347 (57%) were male. The patients ranged in age from 4 months to 10 years, with a mean (SD) age of 4.87 (1.82) years. Five hundred fifty-six (91%) patients had AD, and 336 (55%) had MC. Within this cohort, 274 (45%) children had AD only, 54 (9%) had MC only, and 282 (46%) had both AD and MC. Regarding the temporal sequence, among the 282 children who had both AD and MC, AD preceded MC in 203 (72%) cases, both conditions were diagnosed concomitantly in 43 (15%) cases, and MC preceded AD in 36 (13%) cases. For cases in which the MC diagnosis followed the diagnosis of AD, the mean (SD) time between each diagnosis was 3.17 (1.5) years.
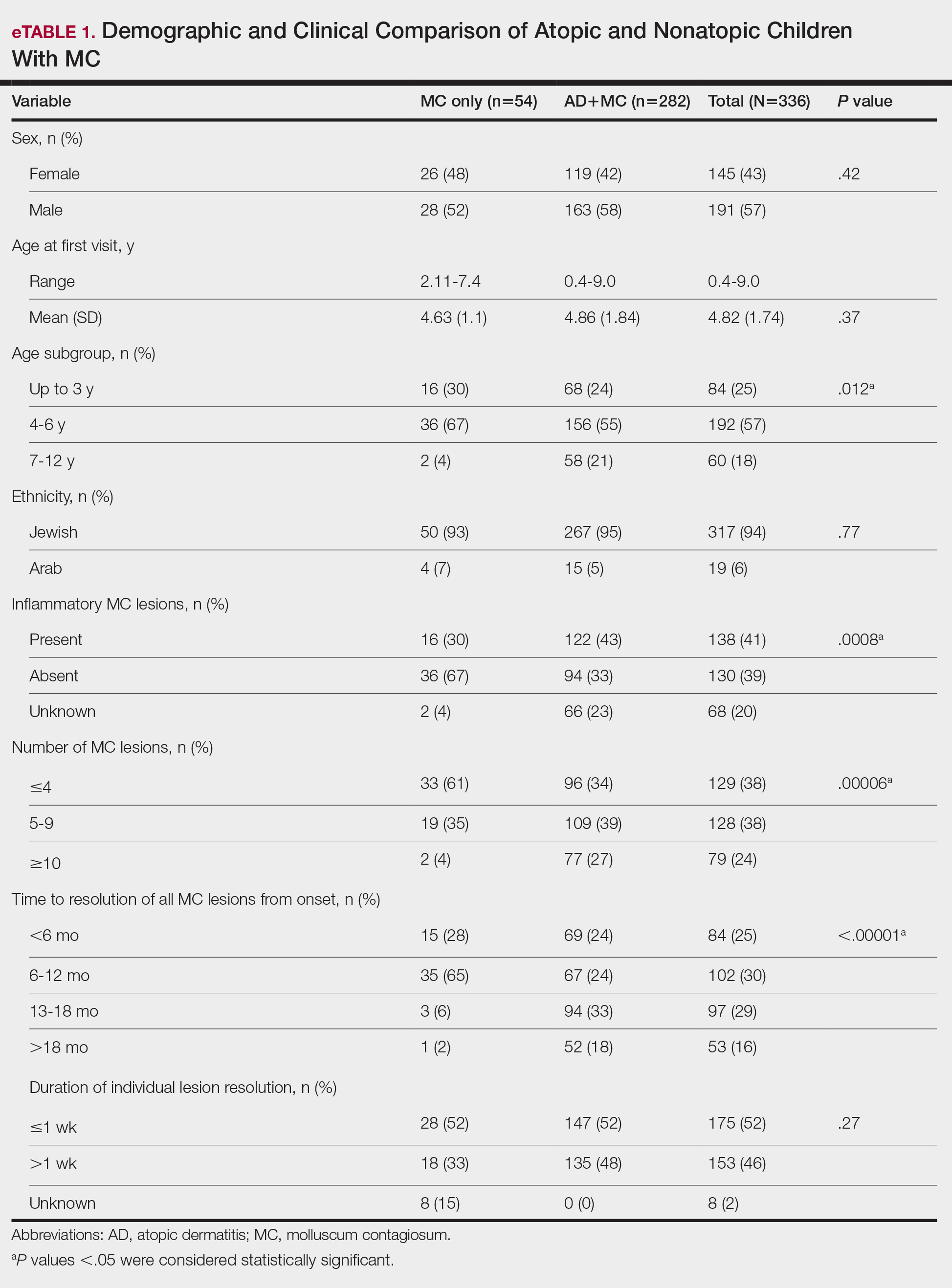
Comparison of Atopic and Nonatopic Children With MC—Although a higher proportion of males were diagnosed with MC (with or without concurrent AD), the differences in sex distribution between the 2 groups did not reach statistical significance. Among all children with MC, the majority (81.5% [274/336]) were aged 1 to 6 years at presentation. Patients with MC as their sole diagnosis had a similar mean age compared with those with concurrent AD. However, a detailed age subgroup analysis revealed a notable distinction: in the group with MC as the sole diagnosis, the majority (95% [51/54]) were younger than 7 years. In contrast, in the combined MC and AD group, MC manifested across a wider age range, with 21% (58/282) of patients being older than 7 years. In MC cases associated with AD, a notably higher lesion count and increased local inflammatory response were observed compared to those without AD. The time for complete resolution of all MC lesions was substantially prolonged in patients with comorbid AD. Specifically, 93% (50/54) of patients with MC without comorbid AD achieved full resolution within 1 year, whereas 52% (146/282) of patients with comorbid AD required more than 1 year for resolution (eTable 1).
Comparison of Atopic Children With and Without MC—Sex, age distribution, and disease duration showed no differences between atopic patients with and without MC. Atopic patients with MC exhibited greater body surface area involvement and higher validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis scores compared to atopic patients without MC (eTable 2).
Comment
This study examined the relationship between MC and AD in pediatric patients, revealing a notable correlation and yielding valuable epidemiologic and clinical insights. Consistent with previous research, our study demonstrated a high prevalence of AD in children with MC.2,6,7,16-21 Previous studies indicated AD rates of 13% to 43% in pediatric patients with MC, whereas our study found a higher prevalence (84%), signifying a substantial majority of patients with MC in our cohort had AD. This discrepancy arises from factors such as demographic, genetic, and environmental differences, along with differences in access to medical care, referral practices, and diagnostic approaches across health care systems.14
Our temporal analysis of MC and AD diagnoses offers important insights. In the majority (72% [203/282]) of cases, the diagnosis of AD preceded MC, supporting previous research suggesting that the underlying pathophysiology of AD heightens susceptibility to MC.15,17-20 Less frequently, MC was diagnosed before or concurrently with AD, indicating that MC may occasionally trigger or exacerbate milder or undiagnosed AD, as previously proposed.20
A notable finding in our study was the expanded age range for MC onset in patients with AD, encompassing older age groups compared to patients with MC as their sole diagnosis, possibly due to persistent immune dysregulation. To the best of our knowledge, this specific observation has not been systematically reported or documented in prior cohort studies. Visible skin lesions of MC may have a psychological impact on patients, influencing self-consciousness and causing embarrassment and emotional distress. This may be more pronounced in older children, who are more aware of their appearance and social perceptions.23-25 These considerations should play a role in the management of MC.
Our study revealed that children with AD and MC displayed higher lesion counts, increased local inflammatory responses, and a more protracted resolution period compared to nonatopic children. In more than 50% of children with AD, MC took more than 1 year for resolution, whereas the majority of those without AD achieved resolution within 1 year. These findings may be attributed to AD-related immune dysregulation, influencing the natural course of MC. Consequently, it suggests that while nonatopic children with MC usually are managed through observation, atopic patients may benefit from an intervention-oriented approach.
Comparing atopic patients with and without MC showed a heightened occurrence of severe and extensive AD among those with concurrent MC. Several factors could contribute to this observation. On one hand, there could be a direct association between the extent and severity of AD, leading to an elevated susceptibility to MC. Conversely, MC might exacerbate immunologic dysregulation and intensify skin inflammation in atopic individuals.20 Additionally, itching related to both disorders may exacerbate inflammation and compromise the epidermal barrier, facilitating the spread of MC. This interplay suggests that each condition exacerbates the other in a self-reinforcing cycle. The importance of patient and caregiver education is underscored by recognizing these interactions. To manage both conditions effectively, health care providers should counsel patients and caregivers on maintaining proper skin care practices such as gentle cleansing with mild, fragrance-free products, regular moisturization, and avoidance of irritants, encourage them to avoid scratching, and recommend adopting an active treatment approach.
Our study had notable strengths. Firstly, a substantial sample size enhanced the statistical reliability of our findings. Additionally, valuable insights into the epidemiology and clinical aspects of AD and MC were obtained by utilizing real-world data from an outpatient dermatology practice. In our study, clinical evaluations covered body surface area involvement and disease severity for AD while also assessing lesion counts and the presence of inflammatory lesions for MC. This comprehensive approach facilitated a thorough analysis of both conditions. The extended data collection period not only allowed for observation of their clinical course and duration, but also enabled a detailed assessment of their interplay.
Our study also had several limitations. Primarily, its retrospective design relied on the accuracy and comprehensiveness of medical records, which may have introduced bias. The exclusion of some patients due to incomplete data further increased the potential for selection bias. Additionally, this study was conducted in a single outpatient dermatology practice in Israel, resulting in a study population composed predominantly of Jewish patients (94%), with a minority (6%) of Arab patients. Other ethnic groups, including Black, Asian, and Hispanic populations, were not represented. This reflects the country’s demographic composition rather than an intentional selection bias. However, the limited ethnic diversity reduces the generalizability of our findings. Differences in demographics, coding practices, health care utilization (eg, timeliness of seeking care, access to dermatology services), and treatment strategies also may impact the observed prevalence, clinical characteristics, and patient outcomes. Furthermore, while our study highlighted the potential advantages of a proactive treatment approach for atopic children with MC, it did not evaluate specific treatment protocols. Future research should aim to confirm the most efficacious therapeutic strategies for managing MC in atopic individuals and to include a more diverse population to better understand the applicability of findings across various ethnic groups.
Conclusion
Our study found a high prevalence of AD in children with MC and a strong bidirectional relationship between these conditions. Pediatric patients with AD display a broader age range for MC, greater lesion burden, increased local inflammatory responses, prolonged resolution times, and more extensive and severe AD.
Recognizing the interplay between MC and AD is crucial, highlighting the importance of health care providers educating patients and caregivers. Emphasizing skin hygiene, discouraging scratching, and implementing proactive treatment approaches can enhance the outcomes of both conditions. Further research into the underlying mechanisms of this association and effective therapeutic strategies for MC in atopic individuals is warranted.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank Zvi Segal, MD (Tel Hashomer, Israel) for his insightful contribution to the statistical analysis of the results. We would like to express our appreciation to the dedicated team of the dermatology practice in Netanya for the support throughout the performance of the study. Additionally, we thank all study participants and their parents for their participation and contribution to our research.
- Han H, Smythe C, Yousefian F, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus evasion of immune surveillance: a review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22182-189.
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54.
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305;E1;E2.
- Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on management. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:504-515.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Piguet V, et al. Epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2014;31:130-136.
- Kakourou T, Zachariades A, Anastasiou T, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in Greek children: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:221-223.
- Osio A, Deslandes E, Saada V, et al. Clinical characteristics of molluscum contagiosum in children in a private dermatology practice in the greater Paris area, France: a prospective study in 661 patients. Dermatology. 2011;222:314-320.
- Hebert AA, Bhatia N, Del Rosso JQ. Molluscum contagiosum: epidemiology, considerations, treatment options, and therapeutic gaps. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2023;16(8 Suppl 1):S4-S11.
- Chao YC, Ko MJ, Tsai WC, et al. Comparative efficacy of treatments for molluscum contagiosum: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:587-597.
- Garg N, Silverberg JI. Epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:281-288.
- Hale G, Davies E, Grindlay DJC, et al. What’s new in atopic eczema? an analysis of systematic reviews published in 2017. part 2: epidemiology, etiology, and risk factors. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:868-873.
- Tracy A, Bhatti S, Eichenfield LF. Update on pediatric atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2020;106:143-146.
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396:345-360.
- Silverberg JI. Public health burden and epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:283-289.
- Manti S, Amorini M, Cuppari C, et al. Filaggrin mutations and molluscum contagiosum skin infection in patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119446-451.
- Seize M, Ianhez M, Cestari S. A study of the correlation between molluscum contagiosum and atopic dermatitis in children. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:663-668.
- Ren Z, Silverberg JI. Association of atopic dermatitis with bacterial, fungal, viral, and sexually transmitted skin infections. Dermatitis. 2020;31:157-164.
- Olsen JR, Piguet V, Gallacher J, et al. Molluscum contagiosum and associations with atopic eczema in children: a retrospective longitudinal study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2016;66:E53-E58.
- Han JH, Yoon JW, Yook HJ, et al. Evaluation of atopic dermatitis and cutaneous infectious disorders using sequential pattern mining: a nationwide population-based cohort study. J Clin Med. 2022;11:3422.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Hayashida S, Furusho N, Uchi H, et al. Are lifetime prevalence of impetigo, molluscum and herpes infection really increased in children having atopic dermatitis? J Dermatol Sci. 2010;60:173-178.
- Simpson E, Bissonnette R, Eichenfield LF, et al. The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD): the development and reliability testing of a novel clinical outcome measurement instrument for the severity of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:839-846.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195.
- Ðurovic´ MR, Jankovic´ J, Spiric´ VT, et al. Does age influence the quality of life in children with atopic dermatitis? PLoS One. 2019;14:E0224618.
- Chernyshov PV. Stigmatization and self-perception in children with atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:159-166.
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), which is caused by a DNA virus in the Poxviridae family, is a common viral skin infection that primarily affects children.1-4 The reported incidence and prevalence of MC exhibit notable geographic variation. Worldwide, annual incidence rates per 1000 individuals range from 3.1 to 25, and prevalence ranges from 0.27% to 34.6%.2-7
Molluscum contagiosum is diagnosed clinically and typically manifests as smooth, flesh-colored papules measuring 2 to 6 mm in diameter with central umbilication. It can manifest as a single lesion or multiple clustered lesions, or in a disseminated pattern. The primary mode of transmission is through contact with skin, lesions, or contaminated personal items, or via self-inoculation. The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but in some patients, MC may be associated with pruritus, tenderness, erythema, or irritation. When present, secondary bacterial infections can cause localized inflammation and pain.1,3,4 The pathogenesis hinges on MC virus replication within keratinocytes, disrupting cellular differentiation and keratinization. The virus persists in the host by influencing the immune response through various mechanisms, including interference with signaling pathways, apoptosis inhibition, and antigen presentation disruption.3,4
Molluscum contagiosum typically follows a self-limiting trajectory, resolving over several months to 2 years.3,4 The resolution timeframe is intricately linked to variables such as the patient’s immune profile, lesion burden, and treatment approach. For symptomatic lesions, a variety of treatment options have been described, including physical ablation (eg, cryotherapy, curettage) and topical agents such as potassium hydroxide, cantharidin, imiquimod, and salicylic acid.3,4,8,9
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic relapsing inflammatory skin disorder. In the United States, its prevalence ranges from 15% to 30% in children and from 2% to 10% in adults, with ongoing evidence of a growing global incidence.10-14 While AD can emerge at any age, typical onset is during early childhood. The clinical manifestation of AD includes a spectrum of eczematous features, often accompanied by persistent itching. The pathogenesis is multifactorial, involving a complex interplay of genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors. Key contributors to this multifaceted process encompass a compromised epidermal barrier, alterations in the skin microbiome, and an immune dysregulation promoting a type 2 immune response. Epidermal barrier dysfunction can be attributed to various factors, including diminished ceramide production, altered lipid composition, the release of inflammatory mediators, and mechanical damage from the persistent itch-scratch cycle.10-13,15 These factors or their interplay may enhance the susceptibility of patients with AD to infections.
Several studies conducted across various geographic regions examining the relationship between MC and AD have reported variable findings.2,6,7,16-21 Published studies have reported a prevalence of AD in children with MC ranging from 13.2% to 43%.2,6,7,16-21 Although some studies suggest a higher rate of atopy in patients with MC, not all research has confirmed this association.16,21 Dohil et al2 reported a greater number of MC lesions in children with AD than those without an atopic background. Silverberg20 reported that in 10% (5/50) of children with MC, the onset of AD was triggered, and in 22% (11/50) MC was associated with flares of pre-existing AD.
In this study, we aimed to assess MC infection rates in children with AD, analyze the epidemiologic aspects and severity differences between atopic children with and without MC infection, and compare data from atopic and nonatopic children with MC.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed the medical records of pediatric patients diagnosed with MC, AD, or both conditions at an outpatient dermatology practice in Netanya, HaSharon, Israel, from September 2013 to August 2022. Data were collected from the electronic medical records and included patient demographics, the clinical presentation of MC and/or AD at diagnosis, and the duration of both conditions. Only patients with complete data and at least 6 months of follow-up were included. Key epidemiologic characteristics assessed included patient sex, age at the initial visit, and age at the onset of MC and/or AD. Diagnoses of MC and AD were established through clinical examinations conducted by dermatologists. The clinical evaluation of AD encompassed the assessment of body surface area involvement (categorized as <5%, 5%-10%, or >10%). Atopic dermatitis severity was classified as mild, moderate, or severe using the validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis.22 Clinical evaluation of MC included assessment of the number of lesions (categorized as ≤4, 5-9, or ≥10), presence of inflammatory lesions, and resolution times for individual lesions (categorized as <1 week, several weeks, or unknown), as well as the overall resolution time for all lesions (categorized as <6 months, 6-12 months, 13-18 months, or >18 months). The temporal relationship between the appearance of MC and AD also was assessed.
Statistical Analysis—Numbers and percentages were used for categorical variables. Continuous variables were represented by mean and standard deviation. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 test, and continuous variables between groups were compared using the Student t test. All statistical tests were 2-sided, with statistical significance defined as P≤.05. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 28 (IBM).
Results
Study Population—A total of 610 children were included in the study; 263 (43%) were female and 347 (57%) were male. The patients ranged in age from 4 months to 10 years, with a mean (SD) age of 4.87 (1.82) years. Five hundred fifty-six (91%) patients had AD, and 336 (55%) had MC. Within this cohort, 274 (45%) children had AD only, 54 (9%) had MC only, and 282 (46%) had both AD and MC. Regarding the temporal sequence, among the 282 children who had both AD and MC, AD preceded MC in 203 (72%) cases, both conditions were diagnosed concomitantly in 43 (15%) cases, and MC preceded AD in 36 (13%) cases. For cases in which the MC diagnosis followed the diagnosis of AD, the mean (SD) time between each diagnosis was 3.17 (1.5) years.
Comparison of Atopic and Nonatopic Children With MC—Although a higher proportion of males were diagnosed with MC (with or without concurrent AD), the differences in sex distribution between the 2 groups did not reach statistical significance. Among all children with MC, the majority (81.5% [274/336]) were aged 1 to 6 years at presentation. Patients with MC as their sole diagnosis had a similar mean age compared with those with concurrent AD. However, a detailed age subgroup analysis revealed a notable distinction: in the group with MC as the sole diagnosis, the majority (95% [51/54]) were younger than 7 years. In contrast, in the combined MC and AD group, MC manifested across a wider age range, with 21% (58/282) of patients being older than 7 years. In MC cases associated with AD, a notably higher lesion count and increased local inflammatory response were observed compared to those without AD. The time for complete resolution of all MC lesions was substantially prolonged in patients with comorbid AD. Specifically, 93% (50/54) of patients with MC without comorbid AD achieved full resolution within 1 year, whereas 52% (146/282) of patients with comorbid AD required more than 1 year for resolution (eTable 1).

Comparison of Atopic Children With and Without MC—Sex, age distribution, and disease duration showed no differences between atopic patients with and without MC. Atopic patients with MC exhibited greater body surface area involvement and higher validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis scores compared to atopic patients without MC (eTable 2).

Comment
This study examined the relationship between MC and AD in pediatric patients, revealing a notable correlation and yielding valuable epidemiologic and clinical insights. Consistent with previous research, our study demonstrated a high prevalence of AD in children with MC.2,6,7,16-21 Previous studies indicated AD rates of 13% to 43% in pediatric patients with MC, whereas our study found a higher prevalence (84%), signifying a substantial majority of patients with MC in our cohort had AD. This discrepancy arises from factors such as demographic, genetic, and environmental differences, along with differences in access to medical care, referral practices, and diagnostic approaches across health care systems.14
Our temporal analysis of MC and AD diagnoses offers important insights. In the majority (72% [203/282]) of cases, the diagnosis of AD preceded MC, supporting previous research suggesting that the underlying pathophysiology of AD heightens susceptibility to MC.15,17-20 Less frequently, MC was diagnosed before or concurrently with AD, indicating that MC may occasionally trigger or exacerbate milder or undiagnosed AD, as previously proposed.20
A notable finding in our study was the expanded age range for MC onset in patients with AD, encompassing older age groups compared to patients with MC as their sole diagnosis, possibly due to persistent immune dysregulation. To the best of our knowledge, this specific observation has not been systematically reported or documented in prior cohort studies. Visible skin lesions of MC may have a psychological impact on patients, influencing self-consciousness and causing embarrassment and emotional distress. This may be more pronounced in older children, who are more aware of their appearance and social perceptions.23-25 These considerations should play a role in the management of MC.
Our study revealed that children with AD and MC displayed higher lesion counts, increased local inflammatory responses, and a more protracted resolution period compared to nonatopic children. In more than 50% of children with AD, MC took more than 1 year for resolution, whereas the majority of those without AD achieved resolution within 1 year. These findings may be attributed to AD-related immune dysregulation, influencing the natural course of MC. Consequently, it suggests that while nonatopic children with MC usually are managed through observation, atopic patients may benefit from an intervention-oriented approach.
Comparing atopic patients with and without MC showed a heightened occurrence of severe and extensive AD among those with concurrent MC. Several factors could contribute to this observation. On one hand, there could be a direct association between the extent and severity of AD, leading to an elevated susceptibility to MC. Conversely, MC might exacerbate immunologic dysregulation and intensify skin inflammation in atopic individuals.20 Additionally, itching related to both disorders may exacerbate inflammation and compromise the epidermal barrier, facilitating the spread of MC. This interplay suggests that each condition exacerbates the other in a self-reinforcing cycle. The importance of patient and caregiver education is underscored by recognizing these interactions. To manage both conditions effectively, health care providers should counsel patients and caregivers on maintaining proper skin care practices such as gentle cleansing with mild, fragrance-free products, regular moisturization, and avoidance of irritants, encourage them to avoid scratching, and recommend adopting an active treatment approach.
Our study had notable strengths. Firstly, a substantial sample size enhanced the statistical reliability of our findings. Additionally, valuable insights into the epidemiology and clinical aspects of AD and MC were obtained by utilizing real-world data from an outpatient dermatology practice. In our study, clinical evaluations covered body surface area involvement and disease severity for AD while also assessing lesion counts and the presence of inflammatory lesions for MC. This comprehensive approach facilitated a thorough analysis of both conditions. The extended data collection period not only allowed for observation of their clinical course and duration, but also enabled a detailed assessment of their interplay.
Our study also had several limitations. Primarily, its retrospective design relied on the accuracy and comprehensiveness of medical records, which may have introduced bias. The exclusion of some patients due to incomplete data further increased the potential for selection bias. Additionally, this study was conducted in a single outpatient dermatology practice in Israel, resulting in a study population composed predominantly of Jewish patients (94%), with a minority (6%) of Arab patients. Other ethnic groups, including Black, Asian, and Hispanic populations, were not represented. This reflects the country’s demographic composition rather than an intentional selection bias. However, the limited ethnic diversity reduces the generalizability of our findings. Differences in demographics, coding practices, health care utilization (eg, timeliness of seeking care, access to dermatology services), and treatment strategies also may impact the observed prevalence, clinical characteristics, and patient outcomes. Furthermore, while our study highlighted the potential advantages of a proactive treatment approach for atopic children with MC, it did not evaluate specific treatment protocols. Future research should aim to confirm the most efficacious therapeutic strategies for managing MC in atopic individuals and to include a more diverse population to better understand the applicability of findings across various ethnic groups.
Conclusion
Our study found a high prevalence of AD in children with MC and a strong bidirectional relationship between these conditions. Pediatric patients with AD display a broader age range for MC, greater lesion burden, increased local inflammatory responses, prolonged resolution times, and more extensive and severe AD.
Recognizing the interplay between MC and AD is crucial, highlighting the importance of health care providers educating patients and caregivers. Emphasizing skin hygiene, discouraging scratching, and implementing proactive treatment approaches can enhance the outcomes of both conditions. Further research into the underlying mechanisms of this association and effective therapeutic strategies for MC in atopic individuals is warranted.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank Zvi Segal, MD (Tel Hashomer, Israel) for his insightful contribution to the statistical analysis of the results. We would like to express our appreciation to the dedicated team of the dermatology practice in Netanya for the support throughout the performance of the study. Additionally, we thank all study participants and their parents for their participation and contribution to our research.
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), which is caused by a DNA virus in the Poxviridae family, is a common viral skin infection that primarily affects children.1-4 The reported incidence and prevalence of MC exhibit notable geographic variation. Worldwide, annual incidence rates per 1000 individuals range from 3.1 to 25, and prevalence ranges from 0.27% to 34.6%.2-7
Molluscum contagiosum is diagnosed clinically and typically manifests as smooth, flesh-colored papules measuring 2 to 6 mm in diameter with central umbilication. It can manifest as a single lesion or multiple clustered lesions, or in a disseminated pattern. The primary mode of transmission is through contact with skin, lesions, or contaminated personal items, or via self-inoculation. The majority of cases are asymptomatic, but in some patients, MC may be associated with pruritus, tenderness, erythema, or irritation. When present, secondary bacterial infections can cause localized inflammation and pain.1,3,4 The pathogenesis hinges on MC virus replication within keratinocytes, disrupting cellular differentiation and keratinization. The virus persists in the host by influencing the immune response through various mechanisms, including interference with signaling pathways, apoptosis inhibition, and antigen presentation disruption.3,4
Molluscum contagiosum typically follows a self-limiting trajectory, resolving over several months to 2 years.3,4 The resolution timeframe is intricately linked to variables such as the patient’s immune profile, lesion burden, and treatment approach. For symptomatic lesions, a variety of treatment options have been described, including physical ablation (eg, cryotherapy, curettage) and topical agents such as potassium hydroxide, cantharidin, imiquimod, and salicylic acid.3,4,8,9
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic relapsing inflammatory skin disorder. In the United States, its prevalence ranges from 15% to 30% in children and from 2% to 10% in adults, with ongoing evidence of a growing global incidence.10-14 While AD can emerge at any age, typical onset is during early childhood. The clinical manifestation of AD includes a spectrum of eczematous features, often accompanied by persistent itching. The pathogenesis is multifactorial, involving a complex interplay of genetic, immunologic, and environmental factors. Key contributors to this multifaceted process encompass a compromised epidermal barrier, alterations in the skin microbiome, and an immune dysregulation promoting a type 2 immune response. Epidermal barrier dysfunction can be attributed to various factors, including diminished ceramide production, altered lipid composition, the release of inflammatory mediators, and mechanical damage from the persistent itch-scratch cycle.10-13,15 These factors or their interplay may enhance the susceptibility of patients with AD to infections.
Several studies conducted across various geographic regions examining the relationship between MC and AD have reported variable findings.2,6,7,16-21 Published studies have reported a prevalence of AD in children with MC ranging from 13.2% to 43%.2,6,7,16-21 Although some studies suggest a higher rate of atopy in patients with MC, not all research has confirmed this association.16,21 Dohil et al2 reported a greater number of MC lesions in children with AD than those without an atopic background. Silverberg20 reported that in 10% (5/50) of children with MC, the onset of AD was triggered, and in 22% (11/50) MC was associated with flares of pre-existing AD.
In this study, we aimed to assess MC infection rates in children with AD, analyze the epidemiologic aspects and severity differences between atopic children with and without MC infection, and compare data from atopic and nonatopic children with MC.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we analyzed the medical records of pediatric patients diagnosed with MC, AD, or both conditions at an outpatient dermatology practice in Netanya, HaSharon, Israel, from September 2013 to August 2022. Data were collected from the electronic medical records and included patient demographics, the clinical presentation of MC and/or AD at diagnosis, and the duration of both conditions. Only patients with complete data and at least 6 months of follow-up were included. Key epidemiologic characteristics assessed included patient sex, age at the initial visit, and age at the onset of MC and/or AD. Diagnoses of MC and AD were established through clinical examinations conducted by dermatologists. The clinical evaluation of AD encompassed the assessment of body surface area involvement (categorized as <5%, 5%-10%, or >10%). Atopic dermatitis severity was classified as mild, moderate, or severe using the validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis.22 Clinical evaluation of MC included assessment of the number of lesions (categorized as ≤4, 5-9, or ≥10), presence of inflammatory lesions, and resolution times for individual lesions (categorized as <1 week, several weeks, or unknown), as well as the overall resolution time for all lesions (categorized as <6 months, 6-12 months, 13-18 months, or >18 months). The temporal relationship between the appearance of MC and AD also was assessed.
Statistical Analysis—Numbers and percentages were used for categorical variables. Continuous variables were represented by mean and standard deviation. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 test, and continuous variables between groups were compared using the Student t test. All statistical tests were 2-sided, with statistical significance defined as P≤.05. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 28 (IBM).
Results
Study Population—A total of 610 children were included in the study; 263 (43%) were female and 347 (57%) were male. The patients ranged in age from 4 months to 10 years, with a mean (SD) age of 4.87 (1.82) years. Five hundred fifty-six (91%) patients had AD, and 336 (55%) had MC. Within this cohort, 274 (45%) children had AD only, 54 (9%) had MC only, and 282 (46%) had both AD and MC. Regarding the temporal sequence, among the 282 children who had both AD and MC, AD preceded MC in 203 (72%) cases, both conditions were diagnosed concomitantly in 43 (15%) cases, and MC preceded AD in 36 (13%) cases. For cases in which the MC diagnosis followed the diagnosis of AD, the mean (SD) time between each diagnosis was 3.17 (1.5) years.
Comparison of Atopic and Nonatopic Children With MC—Although a higher proportion of males were diagnosed with MC (with or without concurrent AD), the differences in sex distribution between the 2 groups did not reach statistical significance. Among all children with MC, the majority (81.5% [274/336]) were aged 1 to 6 years at presentation. Patients with MC as their sole diagnosis had a similar mean age compared with those with concurrent AD. However, a detailed age subgroup analysis revealed a notable distinction: in the group with MC as the sole diagnosis, the majority (95% [51/54]) were younger than 7 years. In contrast, in the combined MC and AD group, MC manifested across a wider age range, with 21% (58/282) of patients being older than 7 years. In MC cases associated with AD, a notably higher lesion count and increased local inflammatory response were observed compared to those without AD. The time for complete resolution of all MC lesions was substantially prolonged in patients with comorbid AD. Specifically, 93% (50/54) of patients with MC without comorbid AD achieved full resolution within 1 year, whereas 52% (146/282) of patients with comorbid AD required more than 1 year for resolution (eTable 1).

Comparison of Atopic Children With and Without MC—Sex, age distribution, and disease duration showed no differences between atopic patients with and without MC. Atopic patients with MC exhibited greater body surface area involvement and higher validated Investigator Global Assessment Scale for Atopic Dermatitis scores compared to atopic patients without MC (eTable 2).

Comment
This study examined the relationship between MC and AD in pediatric patients, revealing a notable correlation and yielding valuable epidemiologic and clinical insights. Consistent with previous research, our study demonstrated a high prevalence of AD in children with MC.2,6,7,16-21 Previous studies indicated AD rates of 13% to 43% in pediatric patients with MC, whereas our study found a higher prevalence (84%), signifying a substantial majority of patients with MC in our cohort had AD. This discrepancy arises from factors such as demographic, genetic, and environmental differences, along with differences in access to medical care, referral practices, and diagnostic approaches across health care systems.14
Our temporal analysis of MC and AD diagnoses offers important insights. In the majority (72% [203/282]) of cases, the diagnosis of AD preceded MC, supporting previous research suggesting that the underlying pathophysiology of AD heightens susceptibility to MC.15,17-20 Less frequently, MC was diagnosed before or concurrently with AD, indicating that MC may occasionally trigger or exacerbate milder or undiagnosed AD, as previously proposed.20
A notable finding in our study was the expanded age range for MC onset in patients with AD, encompassing older age groups compared to patients with MC as their sole diagnosis, possibly due to persistent immune dysregulation. To the best of our knowledge, this specific observation has not been systematically reported or documented in prior cohort studies. Visible skin lesions of MC may have a psychological impact on patients, influencing self-consciousness and causing embarrassment and emotional distress. This may be more pronounced in older children, who are more aware of their appearance and social perceptions.23-25 These considerations should play a role in the management of MC.
Our study revealed that children with AD and MC displayed higher lesion counts, increased local inflammatory responses, and a more protracted resolution period compared to nonatopic children. In more than 50% of children with AD, MC took more than 1 year for resolution, whereas the majority of those without AD achieved resolution within 1 year. These findings may be attributed to AD-related immune dysregulation, influencing the natural course of MC. Consequently, it suggests that while nonatopic children with MC usually are managed through observation, atopic patients may benefit from an intervention-oriented approach.
Comparing atopic patients with and without MC showed a heightened occurrence of severe and extensive AD among those with concurrent MC. Several factors could contribute to this observation. On one hand, there could be a direct association between the extent and severity of AD, leading to an elevated susceptibility to MC. Conversely, MC might exacerbate immunologic dysregulation and intensify skin inflammation in atopic individuals.20 Additionally, itching related to both disorders may exacerbate inflammation and compromise the epidermal barrier, facilitating the spread of MC. This interplay suggests that each condition exacerbates the other in a self-reinforcing cycle. The importance of patient and caregiver education is underscored by recognizing these interactions. To manage both conditions effectively, health care providers should counsel patients and caregivers on maintaining proper skin care practices such as gentle cleansing with mild, fragrance-free products, regular moisturization, and avoidance of irritants, encourage them to avoid scratching, and recommend adopting an active treatment approach.
Our study had notable strengths. Firstly, a substantial sample size enhanced the statistical reliability of our findings. Additionally, valuable insights into the epidemiology and clinical aspects of AD and MC were obtained by utilizing real-world data from an outpatient dermatology practice. In our study, clinical evaluations covered body surface area involvement and disease severity for AD while also assessing lesion counts and the presence of inflammatory lesions for MC. This comprehensive approach facilitated a thorough analysis of both conditions. The extended data collection period not only allowed for observation of their clinical course and duration, but also enabled a detailed assessment of their interplay.
Our study also had several limitations. Primarily, its retrospective design relied on the accuracy and comprehensiveness of medical records, which may have introduced bias. The exclusion of some patients due to incomplete data further increased the potential for selection bias. Additionally, this study was conducted in a single outpatient dermatology practice in Israel, resulting in a study population composed predominantly of Jewish patients (94%), with a minority (6%) of Arab patients. Other ethnic groups, including Black, Asian, and Hispanic populations, were not represented. This reflects the country’s demographic composition rather than an intentional selection bias. However, the limited ethnic diversity reduces the generalizability of our findings. Differences in demographics, coding practices, health care utilization (eg, timeliness of seeking care, access to dermatology services), and treatment strategies also may impact the observed prevalence, clinical characteristics, and patient outcomes. Furthermore, while our study highlighted the potential advantages of a proactive treatment approach for atopic children with MC, it did not evaluate specific treatment protocols. Future research should aim to confirm the most efficacious therapeutic strategies for managing MC in atopic individuals and to include a more diverse population to better understand the applicability of findings across various ethnic groups.
Conclusion
Our study found a high prevalence of AD in children with MC and a strong bidirectional relationship between these conditions. Pediatric patients with AD display a broader age range for MC, greater lesion burden, increased local inflammatory responses, prolonged resolution times, and more extensive and severe AD.
Recognizing the interplay between MC and AD is crucial, highlighting the importance of health care providers educating patients and caregivers. Emphasizing skin hygiene, discouraging scratching, and implementing proactive treatment approaches can enhance the outcomes of both conditions. Further research into the underlying mechanisms of this association and effective therapeutic strategies for MC in atopic individuals is warranted.
Acknowledgments—The authors thank Zvi Segal, MD (Tel Hashomer, Israel) for his insightful contribution to the statistical analysis of the results. We would like to express our appreciation to the dedicated team of the dermatology practice in Netanya for the support throughout the performance of the study. Additionally, we thank all study participants and their parents for their participation and contribution to our research.
- Han H, Smythe C, Yousefian F, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus evasion of immune surveillance: a review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22182-189.
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54.
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305;E1;E2.
- Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on management. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:504-515.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Piguet V, et al. Epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2014;31:130-136.
- Kakourou T, Zachariades A, Anastasiou T, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in Greek children: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:221-223.
- Osio A, Deslandes E, Saada V, et al. Clinical characteristics of molluscum contagiosum in children in a private dermatology practice in the greater Paris area, France: a prospective study in 661 patients. Dermatology. 2011;222:314-320.
- Hebert AA, Bhatia N, Del Rosso JQ. Molluscum contagiosum: epidemiology, considerations, treatment options, and therapeutic gaps. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2023;16(8 Suppl 1):S4-S11.
- Chao YC, Ko MJ, Tsai WC, et al. Comparative efficacy of treatments for molluscum contagiosum: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:587-597.
- Garg N, Silverberg JI. Epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:281-288.
- Hale G, Davies E, Grindlay DJC, et al. What’s new in atopic eczema? an analysis of systematic reviews published in 2017. part 2: epidemiology, etiology, and risk factors. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:868-873.
- Tracy A, Bhatti S, Eichenfield LF. Update on pediatric atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2020;106:143-146.
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396:345-360.
- Silverberg JI. Public health burden and epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:283-289.
- Manti S, Amorini M, Cuppari C, et al. Filaggrin mutations and molluscum contagiosum skin infection in patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119446-451.
- Seize M, Ianhez M, Cestari S. A study of the correlation between molluscum contagiosum and atopic dermatitis in children. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:663-668.
- Ren Z, Silverberg JI. Association of atopic dermatitis with bacterial, fungal, viral, and sexually transmitted skin infections. Dermatitis. 2020;31:157-164.
- Olsen JR, Piguet V, Gallacher J, et al. Molluscum contagiosum and associations with atopic eczema in children: a retrospective longitudinal study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2016;66:E53-E58.
- Han JH, Yoon JW, Yook HJ, et al. Evaluation of atopic dermatitis and cutaneous infectious disorders using sequential pattern mining: a nationwide population-based cohort study. J Clin Med. 2022;11:3422.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Hayashida S, Furusho N, Uchi H, et al. Are lifetime prevalence of impetigo, molluscum and herpes infection really increased in children having atopic dermatitis? J Dermatol Sci. 2010;60:173-178.
- Simpson E, Bissonnette R, Eichenfield LF, et al. The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD): the development and reliability testing of a novel clinical outcome measurement instrument for the severity of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:839-846.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195.
- Ðurovic´ MR, Jankovic´ J, Spiric´ VT, et al. Does age influence the quality of life in children with atopic dermatitis? PLoS One. 2019;14:E0224618.
- Chernyshov PV. Stigmatization and self-perception in children with atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:159-166.
- Han H, Smythe C, Yousefian F, et al. Molluscum contagiosum virus evasion of immune surveillance: a review. J Drugs Dermatol. 2023;22182-189.
- Dohil MA, Lin P, Lee J, et al. The epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:47-54.
- Silverberg NB. Pediatric molluscum: an update. Cutis. 2019;104:301-305;E1;E2.
- Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Molluscum contagiosum: review and update on management. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017;34:504-515.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Piguet V, et al. Epidemiology of molluscum contagiosum in children: a systematic review. Fam Pract. 2014;31:130-136.
- Kakourou T, Zachariades A, Anastasiou T, et al. Molluscum contagiosum in Greek children: a case series. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:221-223.
- Osio A, Deslandes E, Saada V, et al. Clinical characteristics of molluscum contagiosum in children in a private dermatology practice in the greater Paris area, France: a prospective study in 661 patients. Dermatology. 2011;222:314-320.
- Hebert AA, Bhatia N, Del Rosso JQ. Molluscum contagiosum: epidemiology, considerations, treatment options, and therapeutic gaps. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2023;16(8 Suppl 1):S4-S11.
- Chao YC, Ko MJ, Tsai WC, et al. Comparative efficacy of treatments for molluscum contagiosum: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2023;21:587-597.
- Garg N, Silverberg JI. Epidemiology of childhood atopic dermatitis. Clin Dermatol. 2015;33:281-288.
- Hale G, Davies E, Grindlay DJC, et al. What’s new in atopic eczema? an analysis of systematic reviews published in 2017. part 2: epidemiology, etiology, and risk factors. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019;44:868-873.
- Tracy A, Bhatti S, Eichenfield LF. Update on pediatric atopic dermatitis. Cutis. 2020;106:143-146.
- Langan SM, Irvine AD, Weidinger S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2020;396:345-360.
- Silverberg JI. Public health burden and epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2017;35:283-289.
- Manti S, Amorini M, Cuppari C, et al. Filaggrin mutations and molluscum contagiosum skin infection in patients with atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;119446-451.
- Seize M, Ianhez M, Cestari S. A study of the correlation between molluscum contagiosum and atopic dermatitis in children. An Bras Dermatol. 2011;86:663-668.
- Ren Z, Silverberg JI. Association of atopic dermatitis with bacterial, fungal, viral, and sexually transmitted skin infections. Dermatitis. 2020;31:157-164.
- Olsen JR, Piguet V, Gallacher J, et al. Molluscum contagiosum and associations with atopic eczema in children: a retrospective longitudinal study in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2016;66:E53-E58.
- Han JH, Yoon JW, Yook HJ, et al. Evaluation of atopic dermatitis and cutaneous infectious disorders using sequential pattern mining: a nationwide population-based cohort study. J Clin Med. 2022;11:3422.
- Silverberg NB. Molluscum contagiosum virus infection can trigger atopic dermatitis disease onset or flare. Cutis. 2018;102:191-194.
- Hayashida S, Furusho N, Uchi H, et al. Are lifetime prevalence of impetigo, molluscum and herpes infection really increased in children having atopic dermatitis? J Dermatol Sci. 2010;60:173-178.
- Simpson E, Bissonnette R, Eichenfield LF, et al. The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD): the development and reliability testing of a novel clinical outcome measurement instrument for the severity of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:839-846.
- Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:190-195.
- Ðurovic´ MR, Jankovic´ J, Spiric´ VT, et al. Does age influence the quality of life in children with atopic dermatitis? PLoS One. 2019;14:E0224618.
- Chernyshov PV. Stigmatization and self-perception in children with atopic dermatitis. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:159-166.
Epidemiologic and Clinical Evaluation of the Bidirectional Link Between Molluscum Contagiosum and Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Epidemiologic and Clinical Evaluation of the Bidirectional Link Between Molluscum Contagiosum and Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Practice Points
- There is a high prevalence of atopic dermatitis (AD) in children with molluscum contagiosum, with a strong bidirectional relationship between these conditions.
- Children with AD display a broader age range for molluscum contagiosum, greater lesion burden, increased local inflammatory responses, prolonged resolution time, and more extensive and severe disease.
Sniffing Out Skin Disease: Odors in Dermatologic Conditions
Sniffing Out Skin Disease: Odors in Dermatologic Conditions
Humans possess the ability to recognize and distinguish a large range of odors that can be utilized in a wide range of applications. For example, sommeliers can classify more than 88 smells specific to the roughly 800 volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in wine. Thorough physical examination is essential in dermatology, and although sight and touch play the most important diagnostic roles, the sense of smell often is overlooked. Dermatologists are rigorously trained on the many visual aspects of skin disease and have a plethora of terms to describe these features while there is minimal characterization of odors. Research on odors and the role of olfaction in dermatologic practice is limited.1,2 We conducted a literature review of PubMed and Google Scholar for peer-reviewed articles discussing the role of odors in dermatologic diseases. Keywords included odor + dermatology, smell + dermatology, cutaneous odor, odor + diagnosis, and disease odor. Relevant studies were identified by screening their abstracts, followed by a full-text review. A total of 38 articles written in English that presented information on the odor associated with dermatologic diseases were included. Articles that were unrelated to the topic or written in a language other than English were excluded.
Common Skin Odors
The human body emits odorants—small VOCs—in various forms (skin/sweat, breath, urine, reproductive fluids). Human odor originates from the oxidation and bacterial metabolism of sweat and sebum on the skin.3 While many odors are physiologic and not cause for concern, others can signal underlying dermatologic pathologies.4 Odor-producing conditions can be categorized broadly into infectious diseases, disorders of keratinization and acantholysis, metabolic disorders, and organ dysfunction (Table). Infectious causes include bacterial infections and chronic wounds, which commonly emit characteristic offensive odors. For example, coryneform infections produce methanethiol, causing a cheesy odor of putrid fruit, and pseudomonal pyoderma infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor.
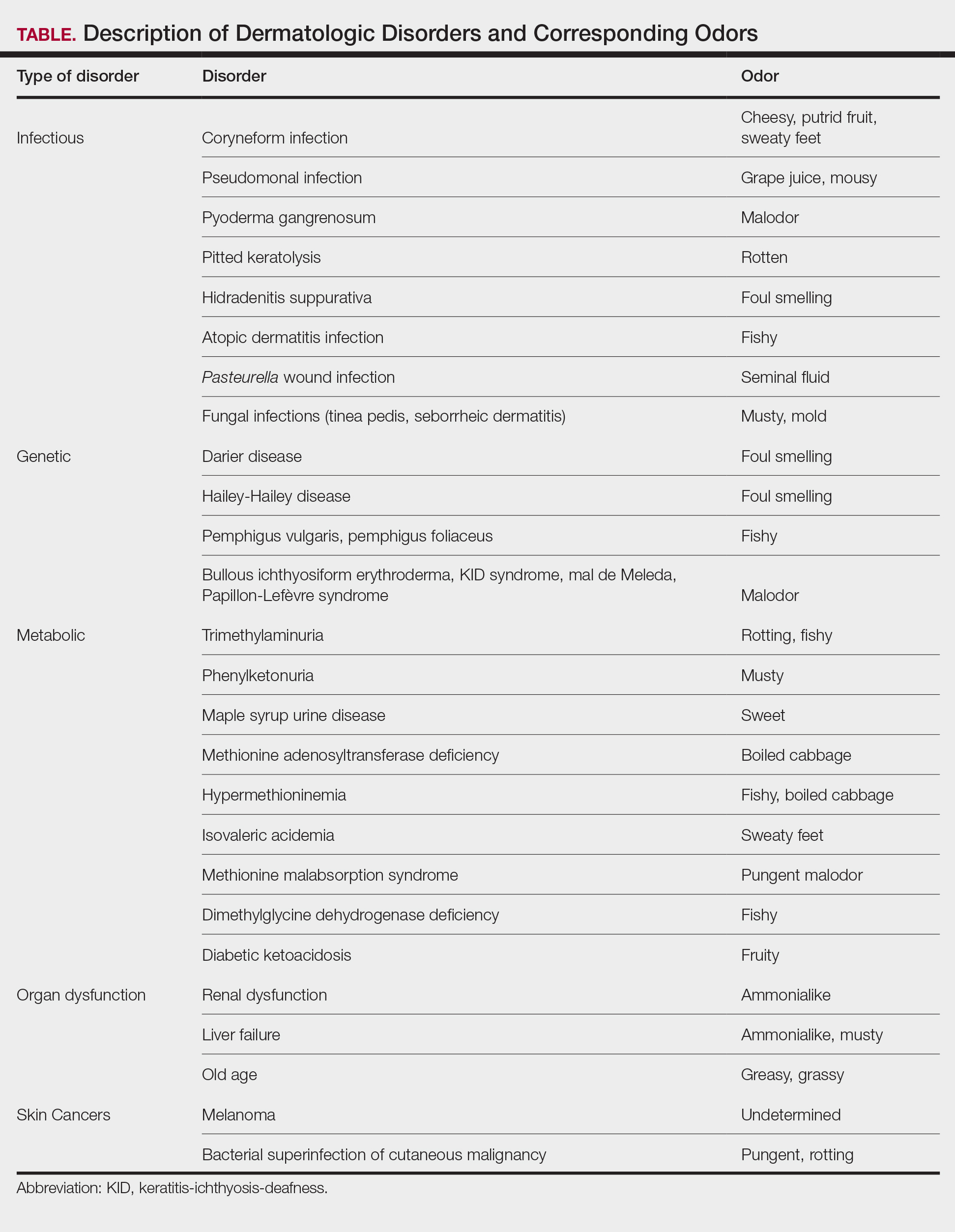
Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacterial and fungal infections often have distinct smells. Coryneform infections emit an odor of sweaty feet, pseudomonal infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor, and trichomycosis infections (caused by Corynebacterium tenuis) present with malodor.5 Pseudomonas can infect pyoderma gangrenosum lesions, producing a characteristic malodor.5 These smells can be clues for infectious etiology and guide further workup.
Pitted keratolysis, a malodorous pitted rash characterized by infection of the stratum corneum by Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, or Corynebacterium species, is associated with a rotten smell. Its pungent odor, clinical location, and characteristic appearance often are enough to make a diagnosis. The amount of bacteria maintained in the stratum corneum is correlated with the extent of the lesion. Controlling excessive moisture in footwear, aluminum chloride, and topical microbial agents work together to eliminate the skin eruption.6
Hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic inflammatory disease of apocrine gland–containing skin, can manifest with abscesses, draining sinuses, and nodules that produce a foul-smelling, purulent discharge. The disease can be debilitating, largely impacting patients’ quality of life, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.7,8 Therapy is dependent on disease severity and includes topical antibiotics, systemic therapies, and biologics.8
Patients with atopic dermatitis often experience bacterial superinfection with Staphylococcus aureus. A case report described a patient who developed a fishy odor in this setting that resolved with antibiotic treatment, implicating S aureus in the etiology of the smell.9
A seminal fluid odor has been reported in cases of Pasteurella wound infection. In such cases, Pasteurella multocida subspecies septica was identified in the wounds caused by a dog scratch and a cat bite. The seminal fluid–like odor was apparent hours after the inciting incident and resolved after treatment with antibiotics.10
Fungal infections frequently emit musty or moldy odors. Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) is the most prevalent cutaneous fungal infection. The presence of tinea pedis is associated with an intense foul-smelling odor, itching, fissuring, scaling, or maceration of the interdigital regions. The rash and odor resolve with use of topical antifungal agents.11,12 Seborrheic dermatitis, a prevalent and chronic dermatosis, is characterized by yellow greasy scaling on an erythematous base. In severe cases, a greasy crust with an offensive odor can cover the entire scalp.13 The specific cause of this odor is unclear, but it is thought that sebum production and the immunological response to specific Malassezia yeast species may play a role.14
Genetic and Metabolic Disorders
An array of disorders of keratinization and acantholysis can manifest with distinctive smells that dermatologists frequently encounter. For example, Darier disease, characterized by keratotic papules progressing to crusted plaques, has a signature foul-smelling odor associated with cutaneous bacterial colonization.15 Similarly, Hailey-Hailey disease, an autosomal-dominant disorder with crusted erosions in skinfold areas, produces a distinct foul smell.16 Disorders such as pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus emit a peculiar fishy odor that can be helpful in making a diagnosis.17 Additionally, bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma, keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome, mal de Meleda, and Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome are all associated with malodor.5
Certain metabolic disorders can manifest and present initially with identifiable odors. Trimethylaminuria is a psychologically disabling disease known for its rotting fishy smell due to high amounts of trimethylamine appearing in affected individuals’ sweat, urine, and breath. Previously considered to be very rare, Messenger et al18 reported the disorder is likely underdiagnosed in those with idiopathic malodor production. Detection and treatment can greatly improve patient quality of life.
Phenylketonuria is an autosomal-recessive inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism that produces a musty body and urine odor as well as other neurologic and dermatologic symptoms.19,20 Patients can present with eczematous rashes, fair skin, and blue eyes. Phenylacetic acid produces the characteristic odor in the bodily fluids, and the disease is treated with a phenylalanine-free diet.21
Maple syrup urine disease is a disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, leucine, and isoleucine (branched-chain amino acids) characterized by urine that smells sweet, resembling maple syrup, in afflicted individuals. The odor also can be present in other bodily secretions, such as sweat. Patients present early in infancy with poor feeding and vomiting as well as neurologic symptoms, eventually leading to intellectual disability. These individuals must avoid the branched-chain amino acids in their diets.21
Other metabolic storage disorders linked with specific odors are methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency (boiled cabbage), hypermethioninemia (fishy, boiled cabbage), isovaleric acidemia (sweaty feet), methionine malabsorption syndrome (pungent malodor), and dimethylglycine dehydrogenase deficiency (fishy).5,21,22
In diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication of diabetes, the excess of ketone bodies produced causes patients to have a distinct fruity breath and urine odor, as well as fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia, nausea, and vomiting.22 Although patients with type 1 diabetes typically comprise the cohort of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, patients with type 2 diabetes can exhibit cutaneous manifestations such as infection, xerosis, and inflammatory skin diseases.23,24
Organ Dysfunction
A peculiar body odor can be a sign of organ dysfunction. Renal dysfunction may present with both an odor and dermatologic manifestations. Patients with end-stage renal disease can have an ammonialike uremic breath odor as the result of excessive nitrogenous waste products and increased concentrations of urea in their saliva.4,22 These patients also can exhibit pruritus, xerosis, pigmentation changes, nail changes, other dermatoses, and rarely uremic frost with white urate crystals present on the skin.25,26
Liver failure has been associated with an ammonialike musty breath odor termed fetor hepaticus. Shimamoto et al27 reported notably higher levels of breath ammonia levels in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, indicating that excess ammonia is responsible for the odor. Fetor hepaticus has unique characteristics that can permit a diagnosis of liver disease, though it has been reported in cases in which a liver injury could not be identified.28
Aging patients typically have a distinctive smell. Haze et al29 analyzed the body odor of patients aged 26 to 75 years and discovered the compound 2-nonenal—an unsaturated aldehyde with a smell described as greasy and grassy—was found only in patients older than 40 years. The researchers’ analysis of skin-surface lipids also revealed that the presence of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids and lipid peroxides increased with age. They concluded that 2-nonenal is generated from the oxidative degradation of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids by lipid peroxides, suggesting that 2-nonenal may be a cause of the odor of old age.29
Cutaneous Malignancies
Research shows that the profiles of the body’s continuously released VOCs change in the presence of malignancy. Some studies suggest that melanoma may have a unique odor. Willis et al30 reported that after a 13-month training period, a dog was able to correctly identify melanoma and distinguish it from basal cell carcinoma, benign nevi, and healthy skin based on olfaction alone. Additional cases have been reported in which dogs have been able to identify melanoma based on smell, suggesting that canine olfactory detection of melanoma could possibly aid in the diagnosis of skin cancer, which warrants further investigation.31,32 There is limited evidence on the specific odors of other cutaneous malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Bacterial superinfection of cutaneous malignancy can secrete pungent odors. An offensive rotting odor has been associated with necrotic malignant ulcers of the vagina. This malodor likely is a result of the formation of putrescine, cadaverine, short-chain fatty acids (isovaleric and butyric acids) and sulfur-containing compounds by bacteria.33 Recognition of similar smells may aid in management of these infections.
Diagnostic Techniques
Evaluating human skin odor is challenging, as the components of VOCs are complicated and typically found at trace levels. Studies indicate that gas chromatography–mass spectrometry is the most effective way to analyze human odor. This method separates, quantifies, and analyzes VOCs from samples containing odors.34 Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, however, has limitations, as the time for analysis is lengthy, the equipment is large, and the process is expensive.3 Research supports the usefulness and validity of quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry to detect odorants and evaluate odor activity of VOCs in various samples.35 With this technique, human assessors act in place of more conventional detectors, such as mass spectrometers. This method has been used to evaluate odorants in human urine with the goal of increasing understanding of metabolization and excretion processes.36 However, gas chromatography–olfactometry typically is used in the analysis of food and drink, and future research should be aimed at applying this method to medicine.
Zheng et al3 proposed a wearable electronic nose as a tool to identify human odor to emulate the odor recognition of a canine’s nose. They developed a sensor array based on the composites of carbon nanotubes and polymers able to examine and identify odors in the air. Study participants wore the electronic nose on the arm with the sensory array facing the armpits while they walked on a treadmill. Although many issues regarding odor measurement were not addressed in this study, the research suggests further studies are warranted to improve analysis of odor.3
Clinical Cases
Patient 1—Arseculeratne et al37 described a 41-year-old man who presented with a fishy odor that others had noticed since the age of 13 years but that the patient could not smell himself. Based on his presentation, he was worked up for trimethylaminuria and found to have elevated levels of urinary trimethylamine (TMA) with a raised TMA/TMA-oxidase ratio. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of primary trimethylaminuria, and the patient was referred to a dietician for counseling on foods that contain low amounts of choline and lecithin. Initially his urinary TMA level fell but then rose again, indicating possible relaxation of his diet. He then took a 10-day course of metronidazole, which helped reduce some of the malodor. The authors reported that the most impactful therapy for the patient was being able to discuss the disorder with his friends and family members.37 This case highlighted the importance of confirming the diagnosis and early initiation of dietary and pharmacologic interventions in patients with trimethylaminuria. In patients reporting a persistent fishy body odor, trimethylaminuria should be on the differential.
Patient 2—In 1999, Schissel et al6 described a 20-year-old active-duty soldier who presented to the dermatology department with smelly trench foot and tinea pedis. The soldier reported having this malodorous pitted rash for more than 10 years. He also reported occasional interdigital burning and itching and noted no improvement despite using various topical antifungals. Physical examination revealed an “overpowering pungent odor” when the patient removed his shoes. He had many tender, white, and wet plaques with scalloped borders coalescing into shallow pits on the plantar surface of the feet and great toes. Potassium hydroxide preparation of the great toe plaques and interdigital web spaces were positive for fungal elements, and bacterial cultures isolated moderate coagulase-negative staphylococcal and Corynebacterium species. Additionally, fungal cultures identified Acremonium species. The patient was started on clotrimazole cream twice daily, clindamycin solution twice daily, and topical ammonium chloride nightly. Two weeks later, the patient reported resolution of symptoms, including the malodor.6 In pitted keratolysis, warm and wet environments within boots or shoes allow for the growth of bacteria and fungi. The extent of the lesions is related to the amount of bacteria within the stratum corneum. The diagnosis often is made based on odor, location, and appearance of the rash alone. The most common organisms implicated as causal agents in the condition are Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, and species of Corynebacterium and Actinomyces. It is thought that these organisms release proteolytic enzymes that degrade the horny layer, releasing a mixture of thiols, thioesters, and sulfides, which cause the pungent odor. Familiarity with the characteristic odor aids in prompt diagnosis and treatment, which will ultimately heal the skin eruption.
Patient 3—Srivastava et al32 described a 43-year-old woman who presented with a nevus on the back since childhood. She noticed that it had changed and grown over the past few years and reported that her dog would often sniff the lesion and try to scratch and bite the lesion. This reaction from her dog led the patient to seek out evaluation from a dermatologist. The patient had no personal history of skin cancer, bad sunburns, tanning bed use, or use of immunosuppressants. She reported that her father had a history of basal cell carcinoma. Physical examination revealed a 1.2×1.5-cm brown patch with an ulcerated nodule located on the lower aspect of the lesion. The patient underwent a wide local excision and sentinel lymph node biopsy with pathology showing a 4-mm-thick melanoma with positive lymph nodes. She then underwent a right axillary lymphadenectomy and was diagnosed with stage IIIB malignant melanoma. Following the surgery, the patient’s dog would sniff the back and calmly rest his head in her lap. She has not had a recurrence and credits her dog for saving her life.32 Canine olfaction may play a role in detecting skin cancers, as evidenced by this case. Patients and dermatologists should pay attention to the behavior of dogs toward skin lesions. Harnessing this sense into a method to noninvasively screen for melanoma in humans should be further investigated.
Patient 4—Matthews et al38 described a 32-year-old woman who presented to an emergency eye clinic with a white “lump” on the left upper eyelid of 6 months’ duration. Physical examination revealed 3 nodular and cystic lesions oozing a thick yellow-white discharge. Cultures were taken, and the patient was started on chloramphenicol ointment once daily to the skin. At follow-up, the lesions had not changed, and the cultures were negative. The patient reported an intermittent malodorous discharge and noted multiple similar lesions on her body. Excisional biopsy demonstrated histologic findings including dyskeratosis, papillomatosis, and suprabasal acantholysis associated with focal underlying chronic inflammatory infiltrate. She was referred to a dermatologist and was diagnosed with Darier disease. She was started on clobetasone butyrate when necessary and adapalene nocte. Understanding the smell associated with Darier disease in conjunction with the cutaneous findings may aid in earlier diagnosis, improving outcomes for affected patients.38
Conclusion
The sense of smell may be an overlooked diagnostic tool that dermatologists innately possess. Odors detected when examining patients should be considered, as these odors may help guide a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are important in many dermatologic diseases, so it is imperative to consider all diagnostic clues. Although physician olfaction may aid in diagnosis, its utility remains challenging, as there is a lack of consensus and terminology regarding odor in disease. A limitation of training to identify disease-specific odors is the requirement of engaging in often unpleasant odors. Methods to objectively measure odor are expensive and still in the early stages of development. Further research and exploration of olfactory-based diagnostic techniques is warranted to potentially improve dermatologic diagnosis.
- Stitt WZ, Goldsmith A. Scratch and sniff: the dynamic duo. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:997-999.
- Delahunty CM, Eyres G, Dufour JP. Gas chromatography-olfactometry. J Sep Sci. 2006;29:2107-2125.
- Zheng Y, Li H, Shen W, et al. Wearable electronic nose for human skin odor identification: a preliminary study. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2019;285:395-405.
- Mogilnicka I, Bogucki P, Ufnal M. Microbiota and malodor—etiology and management. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:2886. doi:10.3390/ijms21082886
- Ravindra K, Gandhi S, Sivuni A. Olfactory diagnosis in skin. Clin Derm Rev. 2018;2:38-40.
- Schissel DJ, Aydelotte J, Keller R. Road rash with a rotten odor. Mil Med. 1999;164:65-67.
- Buyukasik O, Osmanoglu CG, Polat Y, et al. A life-threatening multilocalized hidradenitis suppurativa case. MedGenMed. 2005;7:19.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Hon KLE, Leung AKC, Kong AYF, et al. Atopic dermatitis complicated by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Natl Med Assoc. 2008;100:797-800.
- Arashima Y, Kumasaka K, Tutchiya T, et al. Two cases of pasteurellosis accompanied by exudate with semen-like odor from the wound. Article in Japanese. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1999;73:623-625.
- Goldstein AO, Smith KM, Ives TJ, et al. Mycotic infections. Effective management of conditions involving the skin, hair, and nails. Geriatrics. 2000;55:40-42, 45-47, 51-52.
- Kircik LH. Observational evaluation of sertaconazole nitrate cream 2% in the treatment of pruritus related to tinea pedis. Cutis. 2009;84:279-283.
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019.
- Sameen K. A clinical study on the efficacy of homoeopathic medicines in the treatment of seborrhiec eczema. Int J Hom Sci. 2022;6:209-212.
- Burge S. Management of Darier’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24:53-56.
- Nanda KB, Saldanha CS, Jacintha M, et al. Hailey-Hailey disease responding to thalidomide. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:190-192.
- Kanwar AJ, Ghosh S, Dhar S, et al. Odor in pemphigus. Dermatology. 1992;185:215.
- Messenger J, Clark S, Massick S, et al. A review of trimethylaminuria: (fish odor syndrome). J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:45-48.
- Stone WL, Basit H, Los E. Phenylketonuria. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535378/
- Williams RA, Mamotte CDS, Burnett JR. Phenylketonuria: an inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism. Clin Biochem Rev. 2008;29:31-41.
- Cone TE Jr. Diagnosis and treatment: some diseases, syndromes, and conditions associated with an unusual odor. Pediatrics. 1968;41:993-995.
- Shirasu M, Touhara K. The scent of disease: volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J Biochem. 2011;150:257-266.
- Ghimire P, Dhamoon AS. Ketoacidosis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534848/
- Duff M, Demidova O, Blackburn S, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of diabetes mellitus. Clin Diabetes. 2015;33:40-48.
- Raina S, Chauhan V, Sharma R, et al. Uremic frost. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 1):S58.
- Blaha T, Nigwekar S, Combs S, et al. Dermatologic manifestations in end stage renal disease. Hemodial Int. 2019;23:3-18.
- Shimamoto C, Hirata I, Katsu K. Breath and blood ammonia in liver cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:443-445.
- Butt HR, Mason HL. Fetor hepaticus: its clinical significance and attempts at chemical isolation. Gastroenterology. 1954;26:829-845.
- Haze S, Gozu Y, Nakamura S, et al. 2-nonenal newly found in human body odor tends to increase with aging. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:520-524.
- Willis CM, Britton LE, Swindells MA, et al. Invasive melanoma in vivo can be distinguished from basal cell carcinoma, benign naevi and healthy skin by canine olfaction: a proof-of-principle study of differential volatile organic compound emission. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1020-1029.
- Campbell LF, Farmery L, George SMC, et al. Canine olfactory detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013008566. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-008566
- Srivastava R, John JJ, Reilly C, et al. Sniffing out malignant melanoma: a case of canine olfactory detection. Cutis. 2019;104:E4-E6.
- Fleck CA. Fighting odor in wounds. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2006;19:242-244.
- Gallagher M, Wysocki CJ, Leyden JJ, et al. Analyses of volatile organic compounds from human skin. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:780-791.
- Campo E, Ferreira V, Escudero A, et al. Quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry and chemical quantitative study of the aroma of four Madeira wines. Anal Chim Acta. 2006;563:180-187.
- Wagenstaller M, Buettner A. Characterization of odorants in human urine using a combined chemo-analytical and human-sensory approach: a potential diagnostic strategy. Metabolomics. 2012;9:9-20.
- Arseculeratne G, Wong AKC, Goudie DR, et al. Trimethylaminuria (fish-odor syndrome): a case report. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:81-84.
- Mathews D, Perera LP, Irion LD, et al. Darier disease: beware the cyst that smells. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:206-207.
Humans possess the ability to recognize and distinguish a large range of odors that can be utilized in a wide range of applications. For example, sommeliers can classify more than 88 smells specific to the roughly 800 volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in wine. Thorough physical examination is essential in dermatology, and although sight and touch play the most important diagnostic roles, the sense of smell often is overlooked. Dermatologists are rigorously trained on the many visual aspects of skin disease and have a plethora of terms to describe these features while there is minimal characterization of odors. Research on odors and the role of olfaction in dermatologic practice is limited.1,2 We conducted a literature review of PubMed and Google Scholar for peer-reviewed articles discussing the role of odors in dermatologic diseases. Keywords included odor + dermatology, smell + dermatology, cutaneous odor, odor + diagnosis, and disease odor. Relevant studies were identified by screening their abstracts, followed by a full-text review. A total of 38 articles written in English that presented information on the odor associated with dermatologic diseases were included. Articles that were unrelated to the topic or written in a language other than English were excluded.
Common Skin Odors
The human body emits odorants—small VOCs—in various forms (skin/sweat, breath, urine, reproductive fluids). Human odor originates from the oxidation and bacterial metabolism of sweat and sebum on the skin.3 While many odors are physiologic and not cause for concern, others can signal underlying dermatologic pathologies.4 Odor-producing conditions can be categorized broadly into infectious diseases, disorders of keratinization and acantholysis, metabolic disorders, and organ dysfunction (Table). Infectious causes include bacterial infections and chronic wounds, which commonly emit characteristic offensive odors. For example, coryneform infections produce methanethiol, causing a cheesy odor of putrid fruit, and pseudomonal pyoderma infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor.

Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacterial and fungal infections often have distinct smells. Coryneform infections emit an odor of sweaty feet, pseudomonal infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor, and trichomycosis infections (caused by Corynebacterium tenuis) present with malodor.5 Pseudomonas can infect pyoderma gangrenosum lesions, producing a characteristic malodor.5 These smells can be clues for infectious etiology and guide further workup.
Pitted keratolysis, a malodorous pitted rash characterized by infection of the stratum corneum by Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, or Corynebacterium species, is associated with a rotten smell. Its pungent odor, clinical location, and characteristic appearance often are enough to make a diagnosis. The amount of bacteria maintained in the stratum corneum is correlated with the extent of the lesion. Controlling excessive moisture in footwear, aluminum chloride, and topical microbial agents work together to eliminate the skin eruption.6
Hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic inflammatory disease of apocrine gland–containing skin, can manifest with abscesses, draining sinuses, and nodules that produce a foul-smelling, purulent discharge. The disease can be debilitating, largely impacting patients’ quality of life, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.7,8 Therapy is dependent on disease severity and includes topical antibiotics, systemic therapies, and biologics.8
Patients with atopic dermatitis often experience bacterial superinfection with Staphylococcus aureus. A case report described a patient who developed a fishy odor in this setting that resolved with antibiotic treatment, implicating S aureus in the etiology of the smell.9
A seminal fluid odor has been reported in cases of Pasteurella wound infection. In such cases, Pasteurella multocida subspecies septica was identified in the wounds caused by a dog scratch and a cat bite. The seminal fluid–like odor was apparent hours after the inciting incident and resolved after treatment with antibiotics.10
Fungal infections frequently emit musty or moldy odors. Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) is the most prevalent cutaneous fungal infection. The presence of tinea pedis is associated with an intense foul-smelling odor, itching, fissuring, scaling, or maceration of the interdigital regions. The rash and odor resolve with use of topical antifungal agents.11,12 Seborrheic dermatitis, a prevalent and chronic dermatosis, is characterized by yellow greasy scaling on an erythematous base. In severe cases, a greasy crust with an offensive odor can cover the entire scalp.13 The specific cause of this odor is unclear, but it is thought that sebum production and the immunological response to specific Malassezia yeast species may play a role.14
Genetic and Metabolic Disorders
An array of disorders of keratinization and acantholysis can manifest with distinctive smells that dermatologists frequently encounter. For example, Darier disease, characterized by keratotic papules progressing to crusted plaques, has a signature foul-smelling odor associated with cutaneous bacterial colonization.15 Similarly, Hailey-Hailey disease, an autosomal-dominant disorder with crusted erosions in skinfold areas, produces a distinct foul smell.16 Disorders such as pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus emit a peculiar fishy odor that can be helpful in making a diagnosis.17 Additionally, bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma, keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome, mal de Meleda, and Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome are all associated with malodor.5
Certain metabolic disorders can manifest and present initially with identifiable odors. Trimethylaminuria is a psychologically disabling disease known for its rotting fishy smell due to high amounts of trimethylamine appearing in affected individuals’ sweat, urine, and breath. Previously considered to be very rare, Messenger et al18 reported the disorder is likely underdiagnosed in those with idiopathic malodor production. Detection and treatment can greatly improve patient quality of life.
Phenylketonuria is an autosomal-recessive inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism that produces a musty body and urine odor as well as other neurologic and dermatologic symptoms.19,20 Patients can present with eczematous rashes, fair skin, and blue eyes. Phenylacetic acid produces the characteristic odor in the bodily fluids, and the disease is treated with a phenylalanine-free diet.21
Maple syrup urine disease is a disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, leucine, and isoleucine (branched-chain amino acids) characterized by urine that smells sweet, resembling maple syrup, in afflicted individuals. The odor also can be present in other bodily secretions, such as sweat. Patients present early in infancy with poor feeding and vomiting as well as neurologic symptoms, eventually leading to intellectual disability. These individuals must avoid the branched-chain amino acids in their diets.21
Other metabolic storage disorders linked with specific odors are methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency (boiled cabbage), hypermethioninemia (fishy, boiled cabbage), isovaleric acidemia (sweaty feet), methionine malabsorption syndrome (pungent malodor), and dimethylglycine dehydrogenase deficiency (fishy).5,21,22
In diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication of diabetes, the excess of ketone bodies produced causes patients to have a distinct fruity breath and urine odor, as well as fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia, nausea, and vomiting.22 Although patients with type 1 diabetes typically comprise the cohort of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, patients with type 2 diabetes can exhibit cutaneous manifestations such as infection, xerosis, and inflammatory skin diseases.23,24
Organ Dysfunction
A peculiar body odor can be a sign of organ dysfunction. Renal dysfunction may present with both an odor and dermatologic manifestations. Patients with end-stage renal disease can have an ammonialike uremic breath odor as the result of excessive nitrogenous waste products and increased concentrations of urea in their saliva.4,22 These patients also can exhibit pruritus, xerosis, pigmentation changes, nail changes, other dermatoses, and rarely uremic frost with white urate crystals present on the skin.25,26
Liver failure has been associated with an ammonialike musty breath odor termed fetor hepaticus. Shimamoto et al27 reported notably higher levels of breath ammonia levels in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, indicating that excess ammonia is responsible for the odor. Fetor hepaticus has unique characteristics that can permit a diagnosis of liver disease, though it has been reported in cases in which a liver injury could not be identified.28
Aging patients typically have a distinctive smell. Haze et al29 analyzed the body odor of patients aged 26 to 75 years and discovered the compound 2-nonenal—an unsaturated aldehyde with a smell described as greasy and grassy—was found only in patients older than 40 years. The researchers’ analysis of skin-surface lipids also revealed that the presence of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids and lipid peroxides increased with age. They concluded that 2-nonenal is generated from the oxidative degradation of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids by lipid peroxides, suggesting that 2-nonenal may be a cause of the odor of old age.29
Cutaneous Malignancies
Research shows that the profiles of the body’s continuously released VOCs change in the presence of malignancy. Some studies suggest that melanoma may have a unique odor. Willis et al30 reported that after a 13-month training period, a dog was able to correctly identify melanoma and distinguish it from basal cell carcinoma, benign nevi, and healthy skin based on olfaction alone. Additional cases have been reported in which dogs have been able to identify melanoma based on smell, suggesting that canine olfactory detection of melanoma could possibly aid in the diagnosis of skin cancer, which warrants further investigation.31,32 There is limited evidence on the specific odors of other cutaneous malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Bacterial superinfection of cutaneous malignancy can secrete pungent odors. An offensive rotting odor has been associated with necrotic malignant ulcers of the vagina. This malodor likely is a result of the formation of putrescine, cadaverine, short-chain fatty acids (isovaleric and butyric acids) and sulfur-containing compounds by bacteria.33 Recognition of similar smells may aid in management of these infections.
Diagnostic Techniques
Evaluating human skin odor is challenging, as the components of VOCs are complicated and typically found at trace levels. Studies indicate that gas chromatography–mass spectrometry is the most effective way to analyze human odor. This method separates, quantifies, and analyzes VOCs from samples containing odors.34 Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, however, has limitations, as the time for analysis is lengthy, the equipment is large, and the process is expensive.3 Research supports the usefulness and validity of quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry to detect odorants and evaluate odor activity of VOCs in various samples.35 With this technique, human assessors act in place of more conventional detectors, such as mass spectrometers. This method has been used to evaluate odorants in human urine with the goal of increasing understanding of metabolization and excretion processes.36 However, gas chromatography–olfactometry typically is used in the analysis of food and drink, and future research should be aimed at applying this method to medicine.
Zheng et al3 proposed a wearable electronic nose as a tool to identify human odor to emulate the odor recognition of a canine’s nose. They developed a sensor array based on the composites of carbon nanotubes and polymers able to examine and identify odors in the air. Study participants wore the electronic nose on the arm with the sensory array facing the armpits while they walked on a treadmill. Although many issues regarding odor measurement were not addressed in this study, the research suggests further studies are warranted to improve analysis of odor.3
Clinical Cases
Patient 1—Arseculeratne et al37 described a 41-year-old man who presented with a fishy odor that others had noticed since the age of 13 years but that the patient could not smell himself. Based on his presentation, he was worked up for trimethylaminuria and found to have elevated levels of urinary trimethylamine (TMA) with a raised TMA/TMA-oxidase ratio. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of primary trimethylaminuria, and the patient was referred to a dietician for counseling on foods that contain low amounts of choline and lecithin. Initially his urinary TMA level fell but then rose again, indicating possible relaxation of his diet. He then took a 10-day course of metronidazole, which helped reduce some of the malodor. The authors reported that the most impactful therapy for the patient was being able to discuss the disorder with his friends and family members.37 This case highlighted the importance of confirming the diagnosis and early initiation of dietary and pharmacologic interventions in patients with trimethylaminuria. In patients reporting a persistent fishy body odor, trimethylaminuria should be on the differential.
Patient 2—In 1999, Schissel et al6 described a 20-year-old active-duty soldier who presented to the dermatology department with smelly trench foot and tinea pedis. The soldier reported having this malodorous pitted rash for more than 10 years. He also reported occasional interdigital burning and itching and noted no improvement despite using various topical antifungals. Physical examination revealed an “overpowering pungent odor” when the patient removed his shoes. He had many tender, white, and wet plaques with scalloped borders coalescing into shallow pits on the plantar surface of the feet and great toes. Potassium hydroxide preparation of the great toe plaques and interdigital web spaces were positive for fungal elements, and bacterial cultures isolated moderate coagulase-negative staphylococcal and Corynebacterium species. Additionally, fungal cultures identified Acremonium species. The patient was started on clotrimazole cream twice daily, clindamycin solution twice daily, and topical ammonium chloride nightly. Two weeks later, the patient reported resolution of symptoms, including the malodor.6 In pitted keratolysis, warm and wet environments within boots or shoes allow for the growth of bacteria and fungi. The extent of the lesions is related to the amount of bacteria within the stratum corneum. The diagnosis often is made based on odor, location, and appearance of the rash alone. The most common organisms implicated as causal agents in the condition are Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, and species of Corynebacterium and Actinomyces. It is thought that these organisms release proteolytic enzymes that degrade the horny layer, releasing a mixture of thiols, thioesters, and sulfides, which cause the pungent odor. Familiarity with the characteristic odor aids in prompt diagnosis and treatment, which will ultimately heal the skin eruption.
Patient 3—Srivastava et al32 described a 43-year-old woman who presented with a nevus on the back since childhood. She noticed that it had changed and grown over the past few years and reported that her dog would often sniff the lesion and try to scratch and bite the lesion. This reaction from her dog led the patient to seek out evaluation from a dermatologist. The patient had no personal history of skin cancer, bad sunburns, tanning bed use, or use of immunosuppressants. She reported that her father had a history of basal cell carcinoma. Physical examination revealed a 1.2×1.5-cm brown patch with an ulcerated nodule located on the lower aspect of the lesion. The patient underwent a wide local excision and sentinel lymph node biopsy with pathology showing a 4-mm-thick melanoma with positive lymph nodes. She then underwent a right axillary lymphadenectomy and was diagnosed with stage IIIB malignant melanoma. Following the surgery, the patient’s dog would sniff the back and calmly rest his head in her lap. She has not had a recurrence and credits her dog for saving her life.32 Canine olfaction may play a role in detecting skin cancers, as evidenced by this case. Patients and dermatologists should pay attention to the behavior of dogs toward skin lesions. Harnessing this sense into a method to noninvasively screen for melanoma in humans should be further investigated.
Patient 4—Matthews et al38 described a 32-year-old woman who presented to an emergency eye clinic with a white “lump” on the left upper eyelid of 6 months’ duration. Physical examination revealed 3 nodular and cystic lesions oozing a thick yellow-white discharge. Cultures were taken, and the patient was started on chloramphenicol ointment once daily to the skin. At follow-up, the lesions had not changed, and the cultures were negative. The patient reported an intermittent malodorous discharge and noted multiple similar lesions on her body. Excisional biopsy demonstrated histologic findings including dyskeratosis, papillomatosis, and suprabasal acantholysis associated with focal underlying chronic inflammatory infiltrate. She was referred to a dermatologist and was diagnosed with Darier disease. She was started on clobetasone butyrate when necessary and adapalene nocte. Understanding the smell associated with Darier disease in conjunction with the cutaneous findings may aid in earlier diagnosis, improving outcomes for affected patients.38
Conclusion
The sense of smell may be an overlooked diagnostic tool that dermatologists innately possess. Odors detected when examining patients should be considered, as these odors may help guide a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are important in many dermatologic diseases, so it is imperative to consider all diagnostic clues. Although physician olfaction may aid in diagnosis, its utility remains challenging, as there is a lack of consensus and terminology regarding odor in disease. A limitation of training to identify disease-specific odors is the requirement of engaging in often unpleasant odors. Methods to objectively measure odor are expensive and still in the early stages of development. Further research and exploration of olfactory-based diagnostic techniques is warranted to potentially improve dermatologic diagnosis.
Humans possess the ability to recognize and distinguish a large range of odors that can be utilized in a wide range of applications. For example, sommeliers can classify more than 88 smells specific to the roughly 800 volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in wine. Thorough physical examination is essential in dermatology, and although sight and touch play the most important diagnostic roles, the sense of smell often is overlooked. Dermatologists are rigorously trained on the many visual aspects of skin disease and have a plethora of terms to describe these features while there is minimal characterization of odors. Research on odors and the role of olfaction in dermatologic practice is limited.1,2 We conducted a literature review of PubMed and Google Scholar for peer-reviewed articles discussing the role of odors in dermatologic diseases. Keywords included odor + dermatology, smell + dermatology, cutaneous odor, odor + diagnosis, and disease odor. Relevant studies were identified by screening their abstracts, followed by a full-text review. A total of 38 articles written in English that presented information on the odor associated with dermatologic diseases were included. Articles that were unrelated to the topic or written in a language other than English were excluded.
Common Skin Odors
The human body emits odorants—small VOCs—in various forms (skin/sweat, breath, urine, reproductive fluids). Human odor originates from the oxidation and bacterial metabolism of sweat and sebum on the skin.3 While many odors are physiologic and not cause for concern, others can signal underlying dermatologic pathologies.4 Odor-producing conditions can be categorized broadly into infectious diseases, disorders of keratinization and acantholysis, metabolic disorders, and organ dysfunction (Table). Infectious causes include bacterial infections and chronic wounds, which commonly emit characteristic offensive odors. For example, coryneform infections produce methanethiol, causing a cheesy odor of putrid fruit, and pseudomonal pyoderma infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor.

Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacterial and fungal infections often have distinct smells. Coryneform infections emit an odor of sweaty feet, pseudomonal infections emit a grape juice–like or mousy odor, and trichomycosis infections (caused by Corynebacterium tenuis) present with malodor.5 Pseudomonas can infect pyoderma gangrenosum lesions, producing a characteristic malodor.5 These smells can be clues for infectious etiology and guide further workup.
Pitted keratolysis, a malodorous pitted rash characterized by infection of the stratum corneum by Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, or Corynebacterium species, is associated with a rotten smell. Its pungent odor, clinical location, and characteristic appearance often are enough to make a diagnosis. The amount of bacteria maintained in the stratum corneum is correlated with the extent of the lesion. Controlling excessive moisture in footwear, aluminum chloride, and topical microbial agents work together to eliminate the skin eruption.6
Hidradenitis suppurativa, a chronic inflammatory disease of apocrine gland–containing skin, can manifest with abscesses, draining sinuses, and nodules that produce a foul-smelling, purulent discharge. The disease can be debilitating, largely impacting patients’ quality of life, making early diagnosis and treatment critical.7,8 Therapy is dependent on disease severity and includes topical antibiotics, systemic therapies, and biologics.8
Patients with atopic dermatitis often experience bacterial superinfection with Staphylococcus aureus. A case report described a patient who developed a fishy odor in this setting that resolved with antibiotic treatment, implicating S aureus in the etiology of the smell.9
A seminal fluid odor has been reported in cases of Pasteurella wound infection. In such cases, Pasteurella multocida subspecies septica was identified in the wounds caused by a dog scratch and a cat bite. The seminal fluid–like odor was apparent hours after the inciting incident and resolved after treatment with antibiotics.10
Fungal infections frequently emit musty or moldy odors. Tinea pedis (athlete’s foot) is the most prevalent cutaneous fungal infection. The presence of tinea pedis is associated with an intense foul-smelling odor, itching, fissuring, scaling, or maceration of the interdigital regions. The rash and odor resolve with use of topical antifungal agents.11,12 Seborrheic dermatitis, a prevalent and chronic dermatosis, is characterized by yellow greasy scaling on an erythematous base. In severe cases, a greasy crust with an offensive odor can cover the entire scalp.13 The specific cause of this odor is unclear, but it is thought that sebum production and the immunological response to specific Malassezia yeast species may play a role.14
Genetic and Metabolic Disorders
An array of disorders of keratinization and acantholysis can manifest with distinctive smells that dermatologists frequently encounter. For example, Darier disease, characterized by keratotic papules progressing to crusted plaques, has a signature foul-smelling odor associated with cutaneous bacterial colonization.15 Similarly, Hailey-Hailey disease, an autosomal-dominant disorder with crusted erosions in skinfold areas, produces a distinct foul smell.16 Disorders such as pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus emit a peculiar fishy odor that can be helpful in making a diagnosis.17 Additionally, bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma, keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome, mal de Meleda, and Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome are all associated with malodor.5
Certain metabolic disorders can manifest and present initially with identifiable odors. Trimethylaminuria is a psychologically disabling disease known for its rotting fishy smell due to high amounts of trimethylamine appearing in affected individuals’ sweat, urine, and breath. Previously considered to be very rare, Messenger et al18 reported the disorder is likely underdiagnosed in those with idiopathic malodor production. Detection and treatment can greatly improve patient quality of life.
Phenylketonuria is an autosomal-recessive inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism that produces a musty body and urine odor as well as other neurologic and dermatologic symptoms.19,20 Patients can present with eczematous rashes, fair skin, and blue eyes. Phenylacetic acid produces the characteristic odor in the bodily fluids, and the disease is treated with a phenylalanine-free diet.21
Maple syrup urine disease is a disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of valine, leucine, and isoleucine (branched-chain amino acids) characterized by urine that smells sweet, resembling maple syrup, in afflicted individuals. The odor also can be present in other bodily secretions, such as sweat. Patients present early in infancy with poor feeding and vomiting as well as neurologic symptoms, eventually leading to intellectual disability. These individuals must avoid the branched-chain amino acids in their diets.21
Other metabolic storage disorders linked with specific odors are methionine adenosyltransferase deficiency (boiled cabbage), hypermethioninemia (fishy, boiled cabbage), isovaleric acidemia (sweaty feet), methionine malabsorption syndrome (pungent malodor), and dimethylglycine dehydrogenase deficiency (fishy).5,21,22
In diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening complication of diabetes, the excess of ketone bodies produced causes patients to have a distinct fruity breath and urine odor, as well as fatigue, polyuria, polydipsia, nausea, and vomiting.22 Although patients with type 1 diabetes typically comprise the cohort of patients presenting with diabetic ketoacidosis, patients with type 2 diabetes can exhibit cutaneous manifestations such as infection, xerosis, and inflammatory skin diseases.23,24
Organ Dysfunction
A peculiar body odor can be a sign of organ dysfunction. Renal dysfunction may present with both an odor and dermatologic manifestations. Patients with end-stage renal disease can have an ammonialike uremic breath odor as the result of excessive nitrogenous waste products and increased concentrations of urea in their saliva.4,22 These patients also can exhibit pruritus, xerosis, pigmentation changes, nail changes, other dermatoses, and rarely uremic frost with white urate crystals present on the skin.25,26
Liver failure has been associated with an ammonialike musty breath odor termed fetor hepaticus. Shimamoto et al27 reported notably higher levels of breath ammonia levels in patients with hepatic encephalopathy, indicating that excess ammonia is responsible for the odor. Fetor hepaticus has unique characteristics that can permit a diagnosis of liver disease, though it has been reported in cases in which a liver injury could not be identified.28
Aging patients typically have a distinctive smell. Haze et al29 analyzed the body odor of patients aged 26 to 75 years and discovered the compound 2-nonenal—an unsaturated aldehyde with a smell described as greasy and grassy—was found only in patients older than 40 years. The researchers’ analysis of skin-surface lipids also revealed that the presence of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids and lipid peroxides increased with age. They concluded that 2-nonenal is generated from the oxidative degradation of ω7 unsaturated fatty acids by lipid peroxides, suggesting that 2-nonenal may be a cause of the odor of old age.29
Cutaneous Malignancies
Research shows that the profiles of the body’s continuously released VOCs change in the presence of malignancy. Some studies suggest that melanoma may have a unique odor. Willis et al30 reported that after a 13-month training period, a dog was able to correctly identify melanoma and distinguish it from basal cell carcinoma, benign nevi, and healthy skin based on olfaction alone. Additional cases have been reported in which dogs have been able to identify melanoma based on smell, suggesting that canine olfactory detection of melanoma could possibly aid in the diagnosis of skin cancer, which warrants further investigation.31,32 There is limited evidence on the specific odors of other cutaneous malignancies, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
Bacterial superinfection of cutaneous malignancy can secrete pungent odors. An offensive rotting odor has been associated with necrotic malignant ulcers of the vagina. This malodor likely is a result of the formation of putrescine, cadaverine, short-chain fatty acids (isovaleric and butyric acids) and sulfur-containing compounds by bacteria.33 Recognition of similar smells may aid in management of these infections.
Diagnostic Techniques
Evaluating human skin odor is challenging, as the components of VOCs are complicated and typically found at trace levels. Studies indicate that gas chromatography–mass spectrometry is the most effective way to analyze human odor. This method separates, quantifies, and analyzes VOCs from samples containing odors.34 Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, however, has limitations, as the time for analysis is lengthy, the equipment is large, and the process is expensive.3 Research supports the usefulness and validity of quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry to detect odorants and evaluate odor activity of VOCs in various samples.35 With this technique, human assessors act in place of more conventional detectors, such as mass spectrometers. This method has been used to evaluate odorants in human urine with the goal of increasing understanding of metabolization and excretion processes.36 However, gas chromatography–olfactometry typically is used in the analysis of food and drink, and future research should be aimed at applying this method to medicine.
Zheng et al3 proposed a wearable electronic nose as a tool to identify human odor to emulate the odor recognition of a canine’s nose. They developed a sensor array based on the composites of carbon nanotubes and polymers able to examine and identify odors in the air. Study participants wore the electronic nose on the arm with the sensory array facing the armpits while they walked on a treadmill. Although many issues regarding odor measurement were not addressed in this study, the research suggests further studies are warranted to improve analysis of odor.3
Clinical Cases
Patient 1—Arseculeratne et al37 described a 41-year-old man who presented with a fishy odor that others had noticed since the age of 13 years but that the patient could not smell himself. Based on his presentation, he was worked up for trimethylaminuria and found to have elevated levels of urinary trimethylamine (TMA) with a raised TMA/TMA-oxidase ratio. These findings were consistent with a diagnosis of primary trimethylaminuria, and the patient was referred to a dietician for counseling on foods that contain low amounts of choline and lecithin. Initially his urinary TMA level fell but then rose again, indicating possible relaxation of his diet. He then took a 10-day course of metronidazole, which helped reduce some of the malodor. The authors reported that the most impactful therapy for the patient was being able to discuss the disorder with his friends and family members.37 This case highlighted the importance of confirming the diagnosis and early initiation of dietary and pharmacologic interventions in patients with trimethylaminuria. In patients reporting a persistent fishy body odor, trimethylaminuria should be on the differential.
Patient 2—In 1999, Schissel et al6 described a 20-year-old active-duty soldier who presented to the dermatology department with smelly trench foot and tinea pedis. The soldier reported having this malodorous pitted rash for more than 10 years. He also reported occasional interdigital burning and itching and noted no improvement despite using various topical antifungals. Physical examination revealed an “overpowering pungent odor” when the patient removed his shoes. He had many tender, white, and wet plaques with scalloped borders coalescing into shallow pits on the plantar surface of the feet and great toes. Potassium hydroxide preparation of the great toe plaques and interdigital web spaces were positive for fungal elements, and bacterial cultures isolated moderate coagulase-negative staphylococcal and Corynebacterium species. Additionally, fungal cultures identified Acremonium species. The patient was started on clotrimazole cream twice daily, clindamycin solution twice daily, and topical ammonium chloride nightly. Two weeks later, the patient reported resolution of symptoms, including the malodor.6 In pitted keratolysis, warm and wet environments within boots or shoes allow for the growth of bacteria and fungi. The extent of the lesions is related to the amount of bacteria within the stratum corneum. The diagnosis often is made based on odor, location, and appearance of the rash alone. The most common organisms implicated as causal agents in the condition are Kytococcus sedentarius, Dermatophilus congolensis, and species of Corynebacterium and Actinomyces. It is thought that these organisms release proteolytic enzymes that degrade the horny layer, releasing a mixture of thiols, thioesters, and sulfides, which cause the pungent odor. Familiarity with the characteristic odor aids in prompt diagnosis and treatment, which will ultimately heal the skin eruption.
Patient 3—Srivastava et al32 described a 43-year-old woman who presented with a nevus on the back since childhood. She noticed that it had changed and grown over the past few years and reported that her dog would often sniff the lesion and try to scratch and bite the lesion. This reaction from her dog led the patient to seek out evaluation from a dermatologist. The patient had no personal history of skin cancer, bad sunburns, tanning bed use, or use of immunosuppressants. She reported that her father had a history of basal cell carcinoma. Physical examination revealed a 1.2×1.5-cm brown patch with an ulcerated nodule located on the lower aspect of the lesion. The patient underwent a wide local excision and sentinel lymph node biopsy with pathology showing a 4-mm-thick melanoma with positive lymph nodes. She then underwent a right axillary lymphadenectomy and was diagnosed with stage IIIB malignant melanoma. Following the surgery, the patient’s dog would sniff the back and calmly rest his head in her lap. She has not had a recurrence and credits her dog for saving her life.32 Canine olfaction may play a role in detecting skin cancers, as evidenced by this case. Patients and dermatologists should pay attention to the behavior of dogs toward skin lesions. Harnessing this sense into a method to noninvasively screen for melanoma in humans should be further investigated.
Patient 4—Matthews et al38 described a 32-year-old woman who presented to an emergency eye clinic with a white “lump” on the left upper eyelid of 6 months’ duration. Physical examination revealed 3 nodular and cystic lesions oozing a thick yellow-white discharge. Cultures were taken, and the patient was started on chloramphenicol ointment once daily to the skin. At follow-up, the lesions had not changed, and the cultures were negative. The patient reported an intermittent malodorous discharge and noted multiple similar lesions on her body. Excisional biopsy demonstrated histologic findings including dyskeratosis, papillomatosis, and suprabasal acantholysis associated with focal underlying chronic inflammatory infiltrate. She was referred to a dermatologist and was diagnosed with Darier disease. She was started on clobetasone butyrate when necessary and adapalene nocte. Understanding the smell associated with Darier disease in conjunction with the cutaneous findings may aid in earlier diagnosis, improving outcomes for affected patients.38
Conclusion
The sense of smell may be an overlooked diagnostic tool that dermatologists innately possess. Odors detected when examining patients should be considered, as these odors may help guide a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are important in many dermatologic diseases, so it is imperative to consider all diagnostic clues. Although physician olfaction may aid in diagnosis, its utility remains challenging, as there is a lack of consensus and terminology regarding odor in disease. A limitation of training to identify disease-specific odors is the requirement of engaging in often unpleasant odors. Methods to objectively measure odor are expensive and still in the early stages of development. Further research and exploration of olfactory-based diagnostic techniques is warranted to potentially improve dermatologic diagnosis.
- Stitt WZ, Goldsmith A. Scratch and sniff: the dynamic duo. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:997-999.
- Delahunty CM, Eyres G, Dufour JP. Gas chromatography-olfactometry. J Sep Sci. 2006;29:2107-2125.
- Zheng Y, Li H, Shen W, et al. Wearable electronic nose for human skin odor identification: a preliminary study. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2019;285:395-405.
- Mogilnicka I, Bogucki P, Ufnal M. Microbiota and malodor—etiology and management. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:2886. doi:10.3390/ijms21082886
- Ravindra K, Gandhi S, Sivuni A. Olfactory diagnosis in skin. Clin Derm Rev. 2018;2:38-40.
- Schissel DJ, Aydelotte J, Keller R. Road rash with a rotten odor. Mil Med. 1999;164:65-67.
- Buyukasik O, Osmanoglu CG, Polat Y, et al. A life-threatening multilocalized hidradenitis suppurativa case. MedGenMed. 2005;7:19.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Hon KLE, Leung AKC, Kong AYF, et al. Atopic dermatitis complicated by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Natl Med Assoc. 2008;100:797-800.
- Arashima Y, Kumasaka K, Tutchiya T, et al. Two cases of pasteurellosis accompanied by exudate with semen-like odor from the wound. Article in Japanese. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1999;73:623-625.
- Goldstein AO, Smith KM, Ives TJ, et al. Mycotic infections. Effective management of conditions involving the skin, hair, and nails. Geriatrics. 2000;55:40-42, 45-47, 51-52.
- Kircik LH. Observational evaluation of sertaconazole nitrate cream 2% in the treatment of pruritus related to tinea pedis. Cutis. 2009;84:279-283.
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019.
- Sameen K. A clinical study on the efficacy of homoeopathic medicines in the treatment of seborrhiec eczema. Int J Hom Sci. 2022;6:209-212.
- Burge S. Management of Darier’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24:53-56.
- Nanda KB, Saldanha CS, Jacintha M, et al. Hailey-Hailey disease responding to thalidomide. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:190-192.
- Kanwar AJ, Ghosh S, Dhar S, et al. Odor in pemphigus. Dermatology. 1992;185:215.
- Messenger J, Clark S, Massick S, et al. A review of trimethylaminuria: (fish odor syndrome). J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:45-48.
- Stone WL, Basit H, Los E. Phenylketonuria. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535378/
- Williams RA, Mamotte CDS, Burnett JR. Phenylketonuria: an inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism. Clin Biochem Rev. 2008;29:31-41.
- Cone TE Jr. Diagnosis and treatment: some diseases, syndromes, and conditions associated with an unusual odor. Pediatrics. 1968;41:993-995.
- Shirasu M, Touhara K. The scent of disease: volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J Biochem. 2011;150:257-266.
- Ghimire P, Dhamoon AS. Ketoacidosis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534848/
- Duff M, Demidova O, Blackburn S, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of diabetes mellitus. Clin Diabetes. 2015;33:40-48.
- Raina S, Chauhan V, Sharma R, et al. Uremic frost. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 1):S58.
- Blaha T, Nigwekar S, Combs S, et al. Dermatologic manifestations in end stage renal disease. Hemodial Int. 2019;23:3-18.
- Shimamoto C, Hirata I, Katsu K. Breath and blood ammonia in liver cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:443-445.
- Butt HR, Mason HL. Fetor hepaticus: its clinical significance and attempts at chemical isolation. Gastroenterology. 1954;26:829-845.
- Haze S, Gozu Y, Nakamura S, et al. 2-nonenal newly found in human body odor tends to increase with aging. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:520-524.
- Willis CM, Britton LE, Swindells MA, et al. Invasive melanoma in vivo can be distinguished from basal cell carcinoma, benign naevi and healthy skin by canine olfaction: a proof-of-principle study of differential volatile organic compound emission. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1020-1029.
- Campbell LF, Farmery L, George SMC, et al. Canine olfactory detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013008566. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-008566
- Srivastava R, John JJ, Reilly C, et al. Sniffing out malignant melanoma: a case of canine olfactory detection. Cutis. 2019;104:E4-E6.
- Fleck CA. Fighting odor in wounds. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2006;19:242-244.
- Gallagher M, Wysocki CJ, Leyden JJ, et al. Analyses of volatile organic compounds from human skin. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:780-791.
- Campo E, Ferreira V, Escudero A, et al. Quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry and chemical quantitative study of the aroma of four Madeira wines. Anal Chim Acta. 2006;563:180-187.
- Wagenstaller M, Buettner A. Characterization of odorants in human urine using a combined chemo-analytical and human-sensory approach: a potential diagnostic strategy. Metabolomics. 2012;9:9-20.
- Arseculeratne G, Wong AKC, Goudie DR, et al. Trimethylaminuria (fish-odor syndrome): a case report. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:81-84.
- Mathews D, Perera LP, Irion LD, et al. Darier disease: beware the cyst that smells. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:206-207.
- Stitt WZ, Goldsmith A. Scratch and sniff: the dynamic duo. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:997-999.
- Delahunty CM, Eyres G, Dufour JP. Gas chromatography-olfactometry. J Sep Sci. 2006;29:2107-2125.
- Zheng Y, Li H, Shen W, et al. Wearable electronic nose for human skin odor identification: a preliminary study. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2019;285:395-405.
- Mogilnicka I, Bogucki P, Ufnal M. Microbiota and malodor—etiology and management. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:2886. doi:10.3390/ijms21082886
- Ravindra K, Gandhi S, Sivuni A. Olfactory diagnosis in skin. Clin Derm Rev. 2018;2:38-40.
- Schissel DJ, Aydelotte J, Keller R. Road rash with a rotten odor. Mil Med. 1999;164:65-67.
- Buyukasik O, Osmanoglu CG, Polat Y, et al. A life-threatening multilocalized hidradenitis suppurativa case. MedGenMed. 2005;7:19.
- Napolitano M, Megna M, Timoshchuk EA, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa: from pathogenesis to diagnosis and treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:105-115.
- Hon KLE, Leung AKC, Kong AYF, et al. Atopic dermatitis complicated by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Natl Med Assoc. 2008;100:797-800.
- Arashima Y, Kumasaka K, Tutchiya T, et al. Two cases of pasteurellosis accompanied by exudate with semen-like odor from the wound. Article in Japanese. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1999;73:623-625.
- Goldstein AO, Smith KM, Ives TJ, et al. Mycotic infections. Effective management of conditions involving the skin, hair, and nails. Geriatrics. 2000;55:40-42, 45-47, 51-52.
- Kircik LH. Observational evaluation of sertaconazole nitrate cream 2% in the treatment of pruritus related to tinea pedis. Cutis. 2009;84:279-283.
- James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, et al. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2019.
- Sameen K. A clinical study on the efficacy of homoeopathic medicines in the treatment of seborrhiec eczema. Int J Hom Sci. 2022;6:209-212.
- Burge S. Management of Darier’s disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999;24:53-56.
- Nanda KB, Saldanha CS, Jacintha M, et al. Hailey-Hailey disease responding to thalidomide. Indian J Dermatol. 2014;59:190-192.
- Kanwar AJ, Ghosh S, Dhar S, et al. Odor in pemphigus. Dermatology. 1992;185:215.
- Messenger J, Clark S, Massick S, et al. A review of trimethylaminuria: (fish odor syndrome). J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:45-48.
- Stone WL, Basit H, Los E. Phenylketonuria. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535378/
- Williams RA, Mamotte CDS, Burnett JR. Phenylketonuria: an inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism. Clin Biochem Rev. 2008;29:31-41.
- Cone TE Jr. Diagnosis and treatment: some diseases, syndromes, and conditions associated with an unusual odor. Pediatrics. 1968;41:993-995.
- Shirasu M, Touhara K. The scent of disease: volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J Biochem. 2011;150:257-266.
- Ghimire P, Dhamoon AS. Ketoacidosis. StatPearls [Internet]. Updated August 8, 2023. Accessed August 12, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534848/
- Duff M, Demidova O, Blackburn S, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of diabetes mellitus. Clin Diabetes. 2015;33:40-48.
- Raina S, Chauhan V, Sharma R, et al. Uremic frost. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(suppl 1):S58.
- Blaha T, Nigwekar S, Combs S, et al. Dermatologic manifestations in end stage renal disease. Hemodial Int. 2019;23:3-18.
- Shimamoto C, Hirata I, Katsu K. Breath and blood ammonia in liver cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:443-445.
- Butt HR, Mason HL. Fetor hepaticus: its clinical significance and attempts at chemical isolation. Gastroenterology. 1954;26:829-845.
- Haze S, Gozu Y, Nakamura S, et al. 2-nonenal newly found in human body odor tends to increase with aging. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;116:520-524.
- Willis CM, Britton LE, Swindells MA, et al. Invasive melanoma in vivo can be distinguished from basal cell carcinoma, benign naevi and healthy skin by canine olfaction: a proof-of-principle study of differential volatile organic compound emission. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1020-1029.
- Campbell LF, Farmery L, George SMC, et al. Canine olfactory detection of malignant melanoma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013008566. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-008566
- Srivastava R, John JJ, Reilly C, et al. Sniffing out malignant melanoma: a case of canine olfactory detection. Cutis. 2019;104:E4-E6.
- Fleck CA. Fighting odor in wounds. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2006;19:242-244.
- Gallagher M, Wysocki CJ, Leyden JJ, et al. Analyses of volatile organic compounds from human skin. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:780-791.
- Campo E, Ferreira V, Escudero A, et al. Quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry and chemical quantitative study of the aroma of four Madeira wines. Anal Chim Acta. 2006;563:180-187.
- Wagenstaller M, Buettner A. Characterization of odorants in human urine using a combined chemo-analytical and human-sensory approach: a potential diagnostic strategy. Metabolomics. 2012;9:9-20.
- Arseculeratne G, Wong AKC, Goudie DR, et al. Trimethylaminuria (fish-odor syndrome): a case report. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:81-84.
- Mathews D, Perera LP, Irion LD, et al. Darier disease: beware the cyst that smells. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;26:206-207.
Sniffing Out Skin Disease: Odors in Dermatologic Conditions
Sniffing Out Skin Disease: Odors in Dermatologic Conditions
PRACTICE POINTS
- Olfaction may be underutilized in making dermatologic diagnoses. Clinicians should include smell in their physical examination, as characteristic odors are associated with infectious disorders, disorders of keratinization and acantholysis, and metabolic disorders.
- Recognizing distinctive smells can help narrow the differential diagnosis and prompt targeted testing in dermatology.
- Canines and electronic noses have demonstrated the potential to detect certain malignancies, including melanoma, based on unique volatile organic compound profiles.
Upadacitinib for Treatment of Severe Atopic Dermatitis in a Child
Upadacitinib for Treatment of Severe Atopic Dermatitis in a Child
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin diseases and is characterized by age-related morphology and distribution of lesions. Although AD can manifest at any age, it often develops during childhood, with an estimated worldwide prevalence of 15% to 25% in children and 1% to 10% in adults.1 Clinical manifestation includes chronic or recurrent xerosis, pruritic eczematous lesions involving the flexural and extensor areas, and cutaneous infections. Immediate skin test reactivity and elevated total IgE levels can be found in up to 80% of patients.2
Although the pathogenesis of AD is complex, multifactorial, and not completely understood, some studies have highlighted the central role of a type 2 immune response, resulting in skin barrier dysfunction, cutaneous inflammation, and neuroimmune dysregulation.3,4 The primary goals of treatment are to mitigate these factors through improvement of symptoms and long-term disease control. Topical emollients are used to repair the epidermal barrier, and topical anti-inflammatory therapy with corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors might be applied during flares; however, systemic treatment is essential for patients with moderate to severe AD that is not controlled with topical treatment or phototherapy.5
Until recently, systemic immunosuppressant agents such as corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate were the only systemic treatment options for severe AD; however, their effectiveness is limited and they may cause serious long-term adverse events, limiting their regular usage, especially in children.6
Therapies that target type 2 immune responses include anti–IL-4/IL-13, anti–IL-13, and anti–IL-31 biologics. Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting the type 2 immune response. This biologic directly binds to IL-4Rα,which prevents signaling by both the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways. Dupilumab was the first biologic approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with demonstrated efficacy and a favorable safety profile.5
In addition to biologics, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors belong to the small-molecule class. These drugs block the JAK/STAT intracellular signaling pathway, leading to inhibition of downstream effects triggered by several cytokines related to AD pathogenesis. Upadacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2022 for treatment of severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older. This drug promotes a selective and reversible JAK-1 inhibition and has demonstrated rapid onset of action and a sustained reduction in the signs and symptoms of AD.7 We report the case of a child with recalcitrant severe AD that showed significant clinical improvement following off-label treatment with upadacitinib after showing a poor clinical response to dupilumab.
A 9-year-old girl presented to our pediatrics department with progressive worsening of severe AD over the previous 2 years. The patient had been diagnosed with AD at 6 months old, at which time she was treated with several prescribed moisturizers, topical and systemic corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors with no clinical improvement.
The patient initially presented to us for evaluation of severe pruritus and associated sleep loss at age 7 years; physical examination revealed severe xerosis and disseminated pruritic eczematous lesions. Her SCORAD (SCORing Atopic Dermatitis) score was 70 (range, 0-103), and laboratory testing showed a high eosinophil count (1.5×103/μL [range, 0-0.6×103], 13%) and IgE level (1686 κU/L [range, 0-90]); a skin prick test on the forearm was positive for Blomia tropicalis.
Following her presentation with severe AD at 7 years old, the patient was prescribed systemic treatments including methotrexate and cyclosporine. During treatment with these agents, she presented to our department with several bacterial skin infections that required oral and intravenous antibiotics for treatment. These agents ultimately were discontinued after 12 months due to the adverse effects and poor clinical improvement. At age 8 years, the patient received an initial 600-mg dose of dupilumab followed by 300 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks for 6 months along with topical corticosteroids and emollients. During treatment with dupilumab, the patient showed no clinical improvement (SCORAD score, 62). Therefore, we decided to change the dose to 200 mg every 2 weeks. The patient still showed no improvement and presented at age 9 years with moderate conjunctivitis and oculocutaneous infection caused by herpes simplex virus, which required treatment with oral acyclovir (Figure 1).
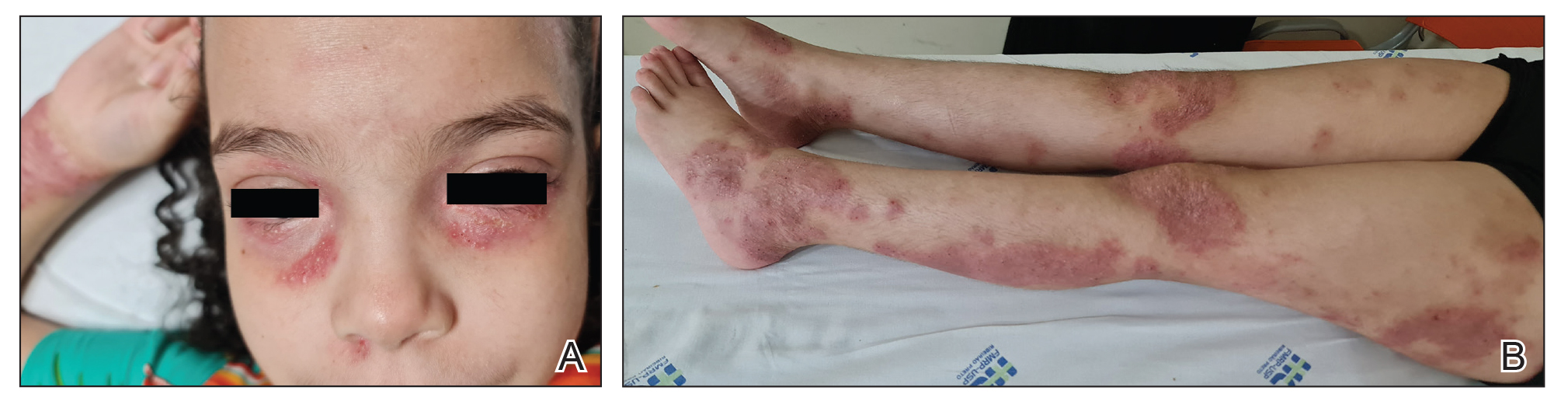
Considering the severe and refractory clinical course and the poor response to the recommended treatments for the patient’s age, oral upadacitinib was administered off label at a dose of 15 mg once daily after informed consent was obtained from her parents. She returned for follow-up once weekly for 1 month. Three days after starting treatment with upadacitinib, she showed considerable improvement in itch, and her SCORAD score decreased from 62 to 31 after 15 days. After 2 months of treatment, she reported no pruritus or sleep loss, and her SCORAD score was 4.5 (Figure 2). The results of a complete blood count, coagulation function test, and liver and kidney function tests were normal at 6-month and 12-month follow-up during upadacitinib therapy. No adverse effects were observed. The patient currently has completed 18 months of treatment, and the disease remains in complete remission.
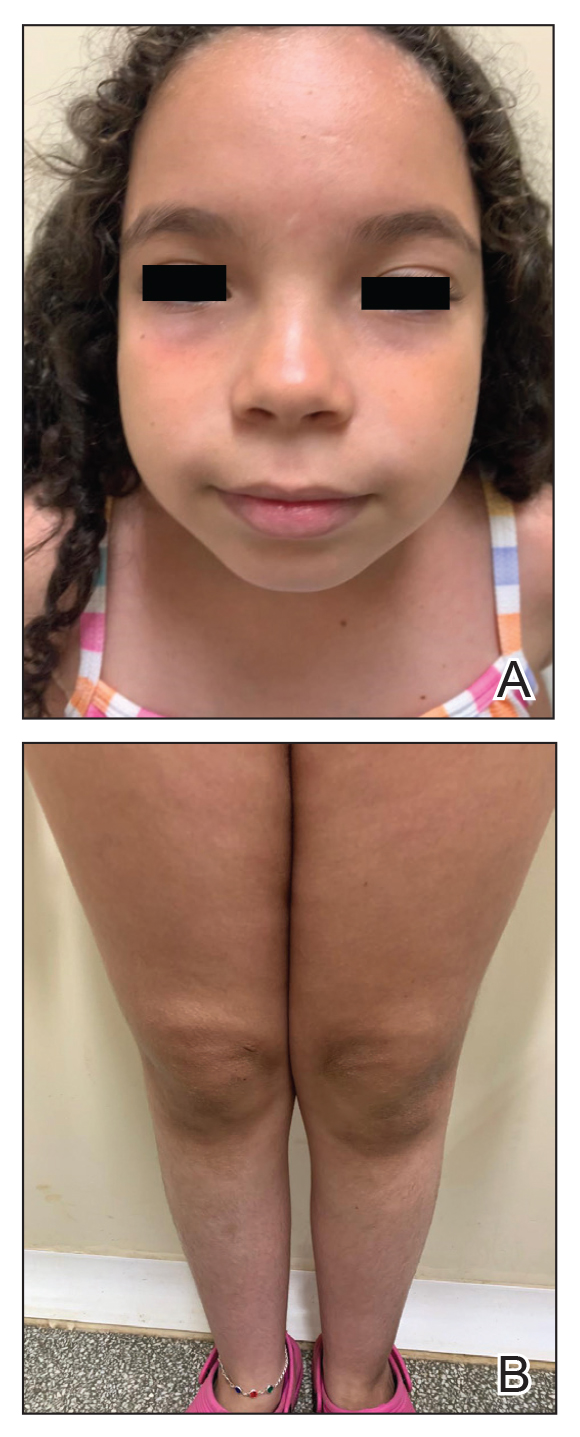
Atopic dermatitis is highly prevalent in children. According to the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood, the prevalence of eczema in 2009 was 8.2% among children aged 6 to 7 years and 5% among adolescents aged between 13 and 14 years in Brazil; severe AD was present in 1.5% of children in both age groups.8
The main systemic therapies currently available for patients with severe AD are immunosuppressants, biologics, and small-molecule drugs. The considerable adverse effects of immunosuppressants limit their application. Dupilumab is considered the first-line treatment for children with severe AD. Clinical trials and case reports have demonstrated that dupilumab is effective in patients with AD, promoting notable improvement of pruritic eczematous lesions and quality-of-life scores.9 Dupilumab has been approved by the FDA for children older than 6 months, and some studies have shown up to a 49% reduction of pruritus in this age group.9 The main reported adverse effects were mild conjunctivitis and oral herpes simplex virus infection.9,10
Upadacitinib is a reversible and selective JAK-1 inhibitor approved by the FDA for treatment of severe AD in patients aged 12 years and older. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated adolescents (12-17 years) and adults (18-75 years) with moderate to severe AD who were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive upadacitinib 15 mg, upadacitinib 30 mg, or placebo once daily for 16 weeks.11 A higher proportion of patients achieved an Eczema Area and Severity Index score of 75 at week 16 with both upadacitinib 15 mg daily (70%) and 30 mg daily (80%) compared to placebo. Improvements also were observed in both SCORAD and pruritus scores. The most commonly reported adverse events were acne, lipid profile abnormalities, and herpes zoster infection.11
Our patient was a child with severe refractory AD that demonstrated a poor treatment response to dupilumab. When switched to off-label upadacitinib, her disease was effectively controlled; the treatment also was well tolerated with no adverse effects. Reports of upadacitinib used to treat AD in patients younger than 12 years are limited in the literature. One case report described a 9-year-old child with concurrent alopecia areata and severe AD who was successfully treated off label with upadacitinib.12 A clinical trial also has evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of upadacitinib in children aged 2 to 12 years with severe AD (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03646604); although the trial was completed in 2024, at the time of this review (July 2025), the results have not been published.
Interestingly, there have been a few reports of adults with severe AD that failed to respond to treatment with immunosuppressants and dupilumab but showed notable clinical improvement when therapy was switched to upadacitinib,13,14 as we noticed with our patient. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT intracellular signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD.
Continued development of safe and efficient targeted treatment for children with severe AD is critical. Upadacitinib was a safe and effective option for treatment of refractory and severe AD in our patient; however, further studies are needed to confirm both the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in this age group.
- Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2016;387:1109-1122.
- Wollenberg A, Christen-Zäch S, Taieb A, et al. ETFAD/EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 position paper on diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults and children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34 :2717-2744.
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venererol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Nakahara T, Kido-Nakahara M, Tsuji G, et al. Basics and recent advances in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol. 2021;48:130-139.
- Wollenberg A, Kinberger M, Arents B, et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema: part I—systemic therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1409-1431.
- Chu DK, Schneider L, Asiniwasis RN, et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE– and Institute of Medicine–based recommendations. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024;132:274-312.
- Rick JW, Lio P, Atluri S, et al. Atopic dermatitis: a guide to transitioning to janus kinase inhibitors. Dermatitis. 2023;34:297-300.
- Prado E, Pastorino AC, Harari DK, et al. Severe atopic dermatitis: a practical treatment guide from the Brazilian Association of Allergy and Immunology and the Brazilian Society of Pediatrics. Arq Asma Alerg Imunol. 2022;6:432-467.
- Paller AS, Simpson EL, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;400:908-919.
- Blauvelt A, de Bruin-Weller M, Gooderham M, et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): a 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2287-2303.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021 ;397:2151-2168.
- Yu D, Ren Y. Upadacitinib for successful treatment of alopecia universalis in a child: a case report and literature review. Acta Derm Venererol. 2023;103:adv5578.
- Cantelli M, Martora F, Patruno C, et al. Upadacitinib improved alopecia areata in a patient with atopic dermatitis: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15346.
- Gambardella A, Licata G, Calabrese G, et al. Dual efficacy of upadacitinib in 2 patients with concomitant severe atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E85-E86.
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin diseases and is characterized by age-related morphology and distribution of lesions. Although AD can manifest at any age, it often develops during childhood, with an estimated worldwide prevalence of 15% to 25% in children and 1% to 10% in adults.1 Clinical manifestation includes chronic or recurrent xerosis, pruritic eczematous lesions involving the flexural and extensor areas, and cutaneous infections. Immediate skin test reactivity and elevated total IgE levels can be found in up to 80% of patients.2
Although the pathogenesis of AD is complex, multifactorial, and not completely understood, some studies have highlighted the central role of a type 2 immune response, resulting in skin barrier dysfunction, cutaneous inflammation, and neuroimmune dysregulation.3,4 The primary goals of treatment are to mitigate these factors through improvement of symptoms and long-term disease control. Topical emollients are used to repair the epidermal barrier, and topical anti-inflammatory therapy with corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors might be applied during flares; however, systemic treatment is essential for patients with moderate to severe AD that is not controlled with topical treatment or phototherapy.5
Until recently, systemic immunosuppressant agents such as corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate were the only systemic treatment options for severe AD; however, their effectiveness is limited and they may cause serious long-term adverse events, limiting their regular usage, especially in children.6
Therapies that target type 2 immune responses include anti–IL-4/IL-13, anti–IL-13, and anti–IL-31 biologics. Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting the type 2 immune response. This biologic directly binds to IL-4Rα,which prevents signaling by both the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways. Dupilumab was the first biologic approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with demonstrated efficacy and a favorable safety profile.5
In addition to biologics, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors belong to the small-molecule class. These drugs block the JAK/STAT intracellular signaling pathway, leading to inhibition of downstream effects triggered by several cytokines related to AD pathogenesis. Upadacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2022 for treatment of severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older. This drug promotes a selective and reversible JAK-1 inhibition and has demonstrated rapid onset of action and a sustained reduction in the signs and symptoms of AD.7 We report the case of a child with recalcitrant severe AD that showed significant clinical improvement following off-label treatment with upadacitinib after showing a poor clinical response to dupilumab.
A 9-year-old girl presented to our pediatrics department with progressive worsening of severe AD over the previous 2 years. The patient had been diagnosed with AD at 6 months old, at which time she was treated with several prescribed moisturizers, topical and systemic corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors with no clinical improvement.
The patient initially presented to us for evaluation of severe pruritus and associated sleep loss at age 7 years; physical examination revealed severe xerosis and disseminated pruritic eczematous lesions. Her SCORAD (SCORing Atopic Dermatitis) score was 70 (range, 0-103), and laboratory testing showed a high eosinophil count (1.5×103/μL [range, 0-0.6×103], 13%) and IgE level (1686 κU/L [range, 0-90]); a skin prick test on the forearm was positive for Blomia tropicalis.
Following her presentation with severe AD at 7 years old, the patient was prescribed systemic treatments including methotrexate and cyclosporine. During treatment with these agents, she presented to our department with several bacterial skin infections that required oral and intravenous antibiotics for treatment. These agents ultimately were discontinued after 12 months due to the adverse effects and poor clinical improvement. At age 8 years, the patient received an initial 600-mg dose of dupilumab followed by 300 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks for 6 months along with topical corticosteroids and emollients. During treatment with dupilumab, the patient showed no clinical improvement (SCORAD score, 62). Therefore, we decided to change the dose to 200 mg every 2 weeks. The patient still showed no improvement and presented at age 9 years with moderate conjunctivitis and oculocutaneous infection caused by herpes simplex virus, which required treatment with oral acyclovir (Figure 1).

Considering the severe and refractory clinical course and the poor response to the recommended treatments for the patient’s age, oral upadacitinib was administered off label at a dose of 15 mg once daily after informed consent was obtained from her parents. She returned for follow-up once weekly for 1 month. Three days after starting treatment with upadacitinib, she showed considerable improvement in itch, and her SCORAD score decreased from 62 to 31 after 15 days. After 2 months of treatment, she reported no pruritus or sleep loss, and her SCORAD score was 4.5 (Figure 2). The results of a complete blood count, coagulation function test, and liver and kidney function tests were normal at 6-month and 12-month follow-up during upadacitinib therapy. No adverse effects were observed. The patient currently has completed 18 months of treatment, and the disease remains in complete remission.

Atopic dermatitis is highly prevalent in children. According to the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood, the prevalence of eczema in 2009 was 8.2% among children aged 6 to 7 years and 5% among adolescents aged between 13 and 14 years in Brazil; severe AD was present in 1.5% of children in both age groups.8
The main systemic therapies currently available for patients with severe AD are immunosuppressants, biologics, and small-molecule drugs. The considerable adverse effects of immunosuppressants limit their application. Dupilumab is considered the first-line treatment for children with severe AD. Clinical trials and case reports have demonstrated that dupilumab is effective in patients with AD, promoting notable improvement of pruritic eczematous lesions and quality-of-life scores.9 Dupilumab has been approved by the FDA for children older than 6 months, and some studies have shown up to a 49% reduction of pruritus in this age group.9 The main reported adverse effects were mild conjunctivitis and oral herpes simplex virus infection.9,10
Upadacitinib is a reversible and selective JAK-1 inhibitor approved by the FDA for treatment of severe AD in patients aged 12 years and older. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated adolescents (12-17 years) and adults (18-75 years) with moderate to severe AD who were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive upadacitinib 15 mg, upadacitinib 30 mg, or placebo once daily for 16 weeks.11 A higher proportion of patients achieved an Eczema Area and Severity Index score of 75 at week 16 with both upadacitinib 15 mg daily (70%) and 30 mg daily (80%) compared to placebo. Improvements also were observed in both SCORAD and pruritus scores. The most commonly reported adverse events were acne, lipid profile abnormalities, and herpes zoster infection.11
Our patient was a child with severe refractory AD that demonstrated a poor treatment response to dupilumab. When switched to off-label upadacitinib, her disease was effectively controlled; the treatment also was well tolerated with no adverse effects. Reports of upadacitinib used to treat AD in patients younger than 12 years are limited in the literature. One case report described a 9-year-old child with concurrent alopecia areata and severe AD who was successfully treated off label with upadacitinib.12 A clinical trial also has evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of upadacitinib in children aged 2 to 12 years with severe AD (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03646604); although the trial was completed in 2024, at the time of this review (July 2025), the results have not been published.
Interestingly, there have been a few reports of adults with severe AD that failed to respond to treatment with immunosuppressants and dupilumab but showed notable clinical improvement when therapy was switched to upadacitinib,13,14 as we noticed with our patient. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT intracellular signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD.
Continued development of safe and efficient targeted treatment for children with severe AD is critical. Upadacitinib was a safe and effective option for treatment of refractory and severe AD in our patient; however, further studies are needed to confirm both the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in this age group.
To the Editor:
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin diseases and is characterized by age-related morphology and distribution of lesions. Although AD can manifest at any age, it often develops during childhood, with an estimated worldwide prevalence of 15% to 25% in children and 1% to 10% in adults.1 Clinical manifestation includes chronic or recurrent xerosis, pruritic eczematous lesions involving the flexural and extensor areas, and cutaneous infections. Immediate skin test reactivity and elevated total IgE levels can be found in up to 80% of patients.2
Although the pathogenesis of AD is complex, multifactorial, and not completely understood, some studies have highlighted the central role of a type 2 immune response, resulting in skin barrier dysfunction, cutaneous inflammation, and neuroimmune dysregulation.3,4 The primary goals of treatment are to mitigate these factors through improvement of symptoms and long-term disease control. Topical emollients are used to repair the epidermal barrier, and topical anti-inflammatory therapy with corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors might be applied during flares; however, systemic treatment is essential for patients with moderate to severe AD that is not controlled with topical treatment or phototherapy.5
Until recently, systemic immunosuppressant agents such as corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and methotrexate were the only systemic treatment options for severe AD; however, their effectiveness is limited and they may cause serious long-term adverse events, limiting their regular usage, especially in children.6
Therapies that target type 2 immune responses include anti–IL-4/IL-13, anti–IL-13, and anti–IL-31 biologics. Dupilumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting the type 2 immune response. This biologic directly binds to IL-4Rα,which prevents signaling by both the IL-4 and IL-13 pathways. Dupilumab was the first biologic approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of moderate to severe AD, with demonstrated efficacy and a favorable safety profile.5
In addition to biologics, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors belong to the small-molecule class. These drugs block the JAK/STAT intracellular signaling pathway, leading to inhibition of downstream effects triggered by several cytokines related to AD pathogenesis. Upadacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2022 for treatment of severe AD in adults and children aged 12 years and older. This drug promotes a selective and reversible JAK-1 inhibition and has demonstrated rapid onset of action and a sustained reduction in the signs and symptoms of AD.7 We report the case of a child with recalcitrant severe AD that showed significant clinical improvement following off-label treatment with upadacitinib after showing a poor clinical response to dupilumab.
A 9-year-old girl presented to our pediatrics department with progressive worsening of severe AD over the previous 2 years. The patient had been diagnosed with AD at 6 months old, at which time she was treated with several prescribed moisturizers, topical and systemic corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors with no clinical improvement.
The patient initially presented to us for evaluation of severe pruritus and associated sleep loss at age 7 years; physical examination revealed severe xerosis and disseminated pruritic eczematous lesions. Her SCORAD (SCORing Atopic Dermatitis) score was 70 (range, 0-103), and laboratory testing showed a high eosinophil count (1.5×103/μL [range, 0-0.6×103], 13%) and IgE level (1686 κU/L [range, 0-90]); a skin prick test on the forearm was positive for Blomia tropicalis.
Following her presentation with severe AD at 7 years old, the patient was prescribed systemic treatments including methotrexate and cyclosporine. During treatment with these agents, she presented to our department with several bacterial skin infections that required oral and intravenous antibiotics for treatment. These agents ultimately were discontinued after 12 months due to the adverse effects and poor clinical improvement. At age 8 years, the patient received an initial 600-mg dose of dupilumab followed by 300 mg subcutaneously every 4 weeks for 6 months along with topical corticosteroids and emollients. During treatment with dupilumab, the patient showed no clinical improvement (SCORAD score, 62). Therefore, we decided to change the dose to 200 mg every 2 weeks. The patient still showed no improvement and presented at age 9 years with moderate conjunctivitis and oculocutaneous infection caused by herpes simplex virus, which required treatment with oral acyclovir (Figure 1).

Considering the severe and refractory clinical course and the poor response to the recommended treatments for the patient’s age, oral upadacitinib was administered off label at a dose of 15 mg once daily after informed consent was obtained from her parents. She returned for follow-up once weekly for 1 month. Three days after starting treatment with upadacitinib, she showed considerable improvement in itch, and her SCORAD score decreased from 62 to 31 after 15 days. After 2 months of treatment, she reported no pruritus or sleep loss, and her SCORAD score was 4.5 (Figure 2). The results of a complete blood count, coagulation function test, and liver and kidney function tests were normal at 6-month and 12-month follow-up during upadacitinib therapy. No adverse effects were observed. The patient currently has completed 18 months of treatment, and the disease remains in complete remission.

Atopic dermatitis is highly prevalent in children. According to the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood, the prevalence of eczema in 2009 was 8.2% among children aged 6 to 7 years and 5% among adolescents aged between 13 and 14 years in Brazil; severe AD was present in 1.5% of children in both age groups.8
The main systemic therapies currently available for patients with severe AD are immunosuppressants, biologics, and small-molecule drugs. The considerable adverse effects of immunosuppressants limit their application. Dupilumab is considered the first-line treatment for children with severe AD. Clinical trials and case reports have demonstrated that dupilumab is effective in patients with AD, promoting notable improvement of pruritic eczematous lesions and quality-of-life scores.9 Dupilumab has been approved by the FDA for children older than 6 months, and some studies have shown up to a 49% reduction of pruritus in this age group.9 The main reported adverse effects were mild conjunctivitis and oral herpes simplex virus infection.9,10
Upadacitinib is a reversible and selective JAK-1 inhibitor approved by the FDA for treatment of severe AD in patients aged 12 years and older. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluated adolescents (12-17 years) and adults (18-75 years) with moderate to severe AD who were randomly assigned (1:1:1) to receive upadacitinib 15 mg, upadacitinib 30 mg, or placebo once daily for 16 weeks.11 A higher proportion of patients achieved an Eczema Area and Severity Index score of 75 at week 16 with both upadacitinib 15 mg daily (70%) and 30 mg daily (80%) compared to placebo. Improvements also were observed in both SCORAD and pruritus scores. The most commonly reported adverse events were acne, lipid profile abnormalities, and herpes zoster infection.11
Our patient was a child with severe refractory AD that demonstrated a poor treatment response to dupilumab. When switched to off-label upadacitinib, her disease was effectively controlled; the treatment also was well tolerated with no adverse effects. Reports of upadacitinib used to treat AD in patients younger than 12 years are limited in the literature. One case report described a 9-year-old child with concurrent alopecia areata and severe AD who was successfully treated off label with upadacitinib.12 A clinical trial also has evaluated the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of upadacitinib in children aged 2 to 12 years with severe AD (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03646604); although the trial was completed in 2024, at the time of this review (July 2025), the results have not been published.
Interestingly, there have been a few reports of adults with severe AD that failed to respond to treatment with immunosuppressants and dupilumab but showed notable clinical improvement when therapy was switched to upadacitinib,13,14 as we noticed with our patient. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT intracellular signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of AD.
Continued development of safe and efficient targeted treatment for children with severe AD is critical. Upadacitinib was a safe and effective option for treatment of refractory and severe AD in our patient; however, further studies are needed to confirm both the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in this age group.
- Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2016;387:1109-1122.
- Wollenberg A, Christen-Zäch S, Taieb A, et al. ETFAD/EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 position paper on diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults and children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34 :2717-2744.
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venererol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Nakahara T, Kido-Nakahara M, Tsuji G, et al. Basics and recent advances in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol. 2021;48:130-139.
- Wollenberg A, Kinberger M, Arents B, et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema: part I—systemic therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1409-1431.
- Chu DK, Schneider L, Asiniwasis RN, et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE– and Institute of Medicine–based recommendations. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024;132:274-312.
- Rick JW, Lio P, Atluri S, et al. Atopic dermatitis: a guide to transitioning to janus kinase inhibitors. Dermatitis. 2023;34:297-300.
- Prado E, Pastorino AC, Harari DK, et al. Severe atopic dermatitis: a practical treatment guide from the Brazilian Association of Allergy and Immunology and the Brazilian Society of Pediatrics. Arq Asma Alerg Imunol. 2022;6:432-467.
- Paller AS, Simpson EL, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;400:908-919.
- Blauvelt A, de Bruin-Weller M, Gooderham M, et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): a 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2287-2303.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021 ;397:2151-2168.
- Yu D, Ren Y. Upadacitinib for successful treatment of alopecia universalis in a child: a case report and literature review. Acta Derm Venererol. 2023;103:adv5578.
- Cantelli M, Martora F, Patruno C, et al. Upadacitinib improved alopecia areata in a patient with atopic dermatitis: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15346.
- Gambardella A, Licata G, Calabrese G, et al. Dual efficacy of upadacitinib in 2 patients with concomitant severe atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E85-E86.
- Weidinger S, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 2016;387:1109-1122.
- Wollenberg A, Christen-Zäch S, Taieb A, et al. ETFAD/EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 position paper on diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis in adults and children. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34 :2717-2744.
- Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venererol. 1980;92:44-47.
- Nakahara T, Kido-Nakahara M, Tsuji G, et al. Basics and recent advances in the pathophysiology of atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol. 2021;48:130-139.
- Wollenberg A, Kinberger M, Arents B, et al. European guideline (EuroGuiDerm) on atopic eczema: part I—systemic therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36:1409-1431.
- Chu DK, Schneider L, Asiniwasis RN, et al. Atopic dermatitis (eczema) guidelines: 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology/American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters GRADE– and Institute of Medicine–based recommendations. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024;132:274-312.
- Rick JW, Lio P, Atluri S, et al. Atopic dermatitis: a guide to transitioning to janus kinase inhibitors. Dermatitis. 2023;34:297-300.
- Prado E, Pastorino AC, Harari DK, et al. Severe atopic dermatitis: a practical treatment guide from the Brazilian Association of Allergy and Immunology and the Brazilian Society of Pediatrics. Arq Asma Alerg Imunol. 2022;6:432-467.
- Paller AS, Simpson EL, Siegfried EC, et al. Dupilumab in children aged 6 months to younger than 6 years with uncontrolled atopic dermatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2022;400:908-919.
- Blauvelt A, de Bruin-Weller M, Gooderham M, et al. Long-term management of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis with dupilumab and concomitant topical corticosteroids (LIBERTY AD CHRONOS): a 1-year, randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:2287-2303.
- Guttman-Yassky E, Teixeira HD, Simpson EL, et al. Once-daily upadacitinib versus placebo in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (Measure Up 1 and Measure Up 2): results from two replicate double-blind, randomised controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet. 2021 ;397:2151-2168.
- Yu D, Ren Y. Upadacitinib for successful treatment of alopecia universalis in a child: a case report and literature review. Acta Derm Venererol. 2023;103:adv5578.
- Cantelli M, Martora F, Patruno C, et al. Upadacitinib improved alopecia areata in a patient with atopic dermatitis: a case report. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35:E15346.
- Gambardella A, Licata G, Calabrese G, et al. Dual efficacy of upadacitinib in 2 patients with concomitant severe atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata. Dermatitis. 2021;32:E85-E86.
Upadacitinib for Treatment of Severe Atopic Dermatitis in a Child
Upadacitinib for Treatment of Severe Atopic Dermatitis in a Child
PRACTICE POINTS
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is one of the most common chronic inflammatory skin diseases in pediatric patients.
- Dupilumab is the first-line treatment for severe AD in children and is approved for use in patients aged 6 months and older. Janus kinase inhibitors are approved only for patients aged 12 years and older.
- Upadacitinib may be a safe treatment option for severe AD in children, even those younger than 12 years.
Pruritus: Diagnosing and Treating Older Adults
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic pruritus is a common problem among older individuals. During a session at the Dermatology Days of Paris 2024 conference dedicated to general practitioners, Juliette Delaunay, MD, a dermatologist and venereologist at Angers University Hospital Center in Angers, France, and Gabrielle Lisembard, MD, a general practitioner in the French town Grand-Fort-Philippe, discussed diagnostic approaches and key principles for the therapeutic management of pruritus.
Identifying Causes
“Pruritus in older people is most often linked to physiological changes in the skin caused by aging, leading to significant xerosis. However, before attributing it to aging, we need to rule out several causes,” Delaunay noted.
Beyond simple aging, one must consider autoimmune bullous dermatoses (bullous pemphigoid), drug-related causes, metabolic disorders (can occur at any age), cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, scabies, lice, and HIV infection.
Senile Pruritus
Aging-related xerosis can cause senile pruritus, often presenting as itching with scratch marks and dry skin. “This is a diagnosis of exclusion,” Delaunay insisted.
In older individuals with pruritus, initial examinations should include complete blood cell count (CBC), liver function tests, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels. Syphilis serology, HIV testing, and beta-2 microglobulin levels are secondary evaluations. Renal function analysis may also be performed, and imaging may be required to investigate neoplasia.
“Annual etiological reassessment is essential if the initial evaluation is negative, as patients may later develop or report a neoplasia or hematological disorder,” Delaunay emphasized.
Paraneoplastic pruritus can occur, particularly those linked to hematological disorders (lymphomas, polycythemia, or myeloma).
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid often begins with pruritus, which can be severe and lead to insomnia. General practitioners should consider bullous pemphigoids when there is a bullous rash (tense blisters with citrine content) or an urticarial or chronic eczematous rash that does not heal spontaneously within a few days. The first-line biologic test to confirm the diagnosis is the CBC, which may reveal significant hypereosinophilia.
The diagnosis is confirmed by a skin biopsy showing a subepidermal blister with a preserved roof, unlike intraepidermal dermatoses, where the roof ruptures.
Direct immunofluorescence revealed deposits of immunoglobulin G antibodies along the dermoepidermal junction.
Approximately 40% of cases of bullous pemphigoid are associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as stroke, parkinsonism, or dementia syndromes — occurring at a rate two to three times higher than in the general population.
It’s important to identify drugs that induce bullous pemphigoid, such as gliptins, anti-programmed cell death protein 1-programmed death-ligand 1 agents, loop diuretics (furosemide and bumetanide), anti-aldosterones (spironolactone), antiarrhythmics (amiodarone), and neuroleptics (phenothiazines).
“Stopping the medication is not mandatory if the bullous pemphigoid is well controlled by local or systemic treatments and the medication is essential. The decision to stop should be made on a case-by-case basis in consultation with the treating specialist,” Delaunay emphasized.
Treatment consists of very strong local corticosteroid therapy as the first-line treatment. If ineffective, systemic treatments based on methotrexate, oral corticosteroids, or immunomodulatory agents may be considered. Hospitalization is sometimes required.
Drug-Induced Pruritus
Drug-induced pruritus is common because older individuals often take multiple medications (antihypertensives, statins, oral hypoglycemics, psychotropic drugs, antiarrhythmics, etc.). “Sometimes, drug-induced pruritus can occur even if the medication was started several months or years ago,” Delaunay emphasized.
The lesions are generally nonspecific and scratching.
“This is a diagnosis of exclusion for other causes of pruritus. In the absence of specific lesions pointing to a dermatosis, eviction/reintroduction tests with treatments should be conducted one by one, which can be quite lengthy,” she explained.
Awareness for Scabies
Delaunay reminded attendees to consider scabies in older individuals when classic signs of pruritus flare up at night, with a rash affecting the face, scabs, or vesicles in the interdigital spaces of the hands, wrists, scrotal area, or the peri-mammary region.
“The incidence is increasing, particularly in nursing homes, where outbreaks pose a significant risk of rapid spread. Treatment involves three courses of topical and oral treatments administered on days 0, 7, and 14. All contact cases must also be treated. Sometimes, these thick lesions are stripped with 10% salicylated petroleum jelly. Environmental treatment with acaricides is essential, along with strict isolation measures,” Delaunay emphasized.
Adherent nits on the scalp or other hairy areas should raise suspicion of pediculosis.
Neurogenic and Psychogenic Origins
Neurogenic pruritus can occur during a stroke, presenting as contralateral pruritus, or in the presence of a brain tumor or following neurosurgery. Opioid-containing medications may also induce neurogenic pruritus.
The presence of unilateral painful or itchy sensations should prompt the investigation of shingles in older individuals.
Psychogenic pruritus is also common and can arise in the context of psychosis with parasitophobia or as part of anxiety-depression syndromes.
Supportive Measures
For managing pruritus, it is essential to:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Wash with cold or lukewarm water
- Use lipid-rice soaps and syndets
- Avoid irritants, including antiseptics, cologne, no-rinse cleansers, and steroidal or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Limit bathing frequency
- Avoid wearing nylon, wool, or tight clothing
- Minimize exposure to heat and excessive heating
“Alternatives to scratching, such as applying a moisturizing emollient, can be beneficial and may have a placebo effect,” explained the dermatologist. She further emphasized that local corticosteroids are effective only in the presence of inflammatory dermatosis and should not be applied to healthy skin. Similarly, antihistamines should only be prescribed if the pruritus is histamine-mediated.
Capsaicin may be useful in the treatment of localized neuropathic pruritus.
In cases of neurogenic pruritus, gabapentin and pregabalin may be prescribed, but tolerance can be problematic at this age. Other measures include acupuncture, cryotherapy, relaxation, hypnosis, psychotherapy, and music therapy. In cases of repeated therapeutic failure, patients may be treated with biotherapy (dupilumab) by a dermatologist.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Online CBT for Patients with AD: Self-Guided vs. Clinician-Guided Intervention Compared
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Alpha-Gal Syndrome: 5 Things to Know
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Alpha-gal syndrome (AGS), a tickborne disease commonly called “red meat allergy,” is a serious, potentially life-threatening allergy to the carbohydrate alpha-gal. The alpha-gal carbohydrate is found in most mammals, though it is not in humans, apes, or old-world monkeys. People with AGS can have allergic reactions when they consume mammalian meat, dairy products, or other products derived from mammals. People often live with this disease for years before receiving a correct diagnosis, greatly impacting their quality of life. The number of suspected cases is also rising.
More than 110,000 suspected AGS cases were identified between 2010 and 2022, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report.1 However, because the diagnosis requires a positive test and a clinical exam and some people may not get tested, as many as 450,000 people might be affected by AGS in the United States. Additionally, a CDC survey found that nearly half (42%) of US healthcare providers had never heard of AGS.2 Among those who had, less than one third (29%) knew how to diagnose the condition.
Here are 5 things clinicians need to know about AGS.
1. People can develop AGS after being bitten by a tick, primarily the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum), in the United States.
In the United States, AGS is primarily associated with the bite of a lone star tick, but other kinds of ticks have not been ruled out. The majority of suspected AGS cases in the United States were reported in parts of Arkansas, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, Missouri, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Virginia. The lone star tick is widely distributed with established populations in Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, and West Virginia.
While AGS is associated with tick bites, more research is needed to understand the role ticks play in starting this condition, and why certain people develop AGS. Anyone can develop AGS, but most cases have been reported in adults.
Know how to recognize the symptoms of AGS and be prepared to test, diagnose, and manage AGS, particularly in states where lone star ticks are found.
2. Tick bites are only one risk factor for developing AGS.
Many people are bitten by lone star ticks and will never develop AGS. Scientists are exploring the connection between other risk factors and developing AGS. A recent study has shown that people diagnosed with AGS may be more likely to have a family member who was also diagnosed with AGS, have another food allergy, have an allergy to stinging or biting insects, or have A or O blood types.3
Research has also shown that environmental risk factors could contribute to developing AGS,4 like living in an area with lone star ticks, remembering finding a tick on themselves, recalling multiple tick bites, living near a wooded forest, spending more time outside, or living in areas with deer, such as larger properties, wooded forests, and properties with shrubs and brush.
Ask your patient questions about other allergies and history of recent tick bites or outdoor exposure to help determine if testing for AGS is appropriate.
3. Symptoms of AGS are consistently inconsistent.
There is a spectrum of how sensitive AGS patients are to alpha-gal, and reactions are often different from person to person, which can make it difficult to diagnose. The first allergic reaction to AGS typically occurs between 1-6 months after a tick bite. Symptoms commonly appear 2-6 hours after being in contact with products containing alpha-gal, like red meat (beef, pork, lamb, venison, rabbit, or other meat from mammals), dairy, and some medications. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives or itchy rash; swelling of the lips, throat, tongue, or eyelids; gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea; heartburn or indigestion; cough, shortness of breath, or difficulty breathing; dizziness or a drop in blood pressure; or anaphylaxis.
Consider AGS if a patient reports waking up in the middle of the night with allergic symptoms after eating alpha-gal containing products for dinner, if allergic reactions are delayed, or if a patient has anaphylaxis of unknown cause, adult-onset allergy, or allergic symptoms and reports a recent tick bite.
4. Diagnosing AGS requires a combination of a blood test and a physical exam.
Diagnosing AGS requires a detailed patient history, physical exam, and a blood test to detect specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to alpha-gal (alpha-gal sIgE). Tests for alpha-gal sIgE antibodies are available at several large commercial laboratories and some academic institutions. Skin tests to identify reactions to allergens like pork or beef may also be used to inform AGS diagnosis. However, a positive alpha-gal sIgE test or skin test does not mean a person has AGS. Many people, particularly those who live in regions with lone star ticks, have positive alpha-gal specific IgE tests without having AGS.
Consider the test results along with your patient’s symptoms and risk factors.
5. There is no treatment for AGS, but people can take prevention steps and AGS can be managed.
People can protect themselves and their family from AGS by preventing tick bites. Encourage your patients to use an Environmental Protection Agency–registered insect repellent outdoors, wear permethrin-treated clothing, and conduct thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Once a person is no longer exposed to alpha-gal containing products, they should no longer experience symptoms. People with AGS should also proactively prevent tick bites. Tick bites can trigger or reactivate AGS.
For patients who have AGS, help manage their symptoms and identify alpha-gal containing products to avoid.
Dr. Kersh is Chief of the Rickettsial Zoonoses Branch, Division of Vector-Borne Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia, and disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
CDC resources:
About Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Testing and Diagnosis for Alpha-gal Syndrome | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
Clinical Resources | Alpha-gal Syndrome | CDC
References
Thompson JM et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:815-820.
Carpenter A et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:809-814. Taylor ML et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2024 Jun;132(6):759.e2-764.e2. Kersh GJ et al. Ann Allergy, Asthma & Immunol. 2023 Apr;130(4):472-478.
Topical Tapinarof Approved for Treating Atopic Dermatitis, Ages 2 and Up
An aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, tapinarof cream, 1% was first approved in May 2022 for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a press release from the manufacturer, Organon — which markets tapinarof cream, 1%, under the brand name VTAMA — the new indication for AD is based on results from the ADORING pivotal studies. In ADORING 1, the proportion of patients in the tapinarof cream, 1% treatment group who achieved a score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) and a minimum 2-grade improvement from baseline at week 8 on the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for AD was 45.4%, compared with 13.9% of patients who received vehicle alone. ADORING 2 yielded similar results (46.4% vs 18.0%, respectively; P < .0001 for both associations).
Secondary endpoints measured at week 8 also significantly favored the treatment group over the vehicle group, including the Eczema Area and Severity Index score improvement of at least 75% from baseline and achievement of a ≥ 4-point improvement in the patient-reported Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from baseline.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 1%) were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), folliculitis (9%), lower respiratory tract infection (5%), headache (4%), asthma (2%), vomiting (2%), ear infection (2%), pain in extremity (2%), and abdominal pain (1%), according to the release.
Among 728 patients in the ADORING studies who enrolled in an open-label 48-week extension trial (ADORING 3), 378 entered with or achieved complete disease clearance and discontinued treatment. In this subset of patients, the mean duration of the first treatment-free interval was approximately 80 consecutive days, according to the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, tapinarof cream, 1% was first approved in May 2022 for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a press release from the manufacturer, Organon — which markets tapinarof cream, 1%, under the brand name VTAMA — the new indication for AD is based on results from the ADORING pivotal studies. In ADORING 1, the proportion of patients in the tapinarof cream, 1% treatment group who achieved a score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) and a minimum 2-grade improvement from baseline at week 8 on the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for AD was 45.4%, compared with 13.9% of patients who received vehicle alone. ADORING 2 yielded similar results (46.4% vs 18.0%, respectively; P < .0001 for both associations).
Secondary endpoints measured at week 8 also significantly favored the treatment group over the vehicle group, including the Eczema Area and Severity Index score improvement of at least 75% from baseline and achievement of a ≥ 4-point improvement in the patient-reported Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from baseline.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 1%) were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), folliculitis (9%), lower respiratory tract infection (5%), headache (4%), asthma (2%), vomiting (2%), ear infection (2%), pain in extremity (2%), and abdominal pain (1%), according to the release.
Among 728 patients in the ADORING studies who enrolled in an open-label 48-week extension trial (ADORING 3), 378 entered with or achieved complete disease clearance and discontinued treatment. In this subset of patients, the mean duration of the first treatment-free interval was approximately 80 consecutive days, according to the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist, tapinarof cream, 1% was first approved in May 2022 for the topical treatment of plaque psoriasis in adults.
According to a press release from the manufacturer, Organon — which markets tapinarof cream, 1%, under the brand name VTAMA — the new indication for AD is based on results from the ADORING pivotal studies. In ADORING 1, the proportion of patients in the tapinarof cream, 1% treatment group who achieved a score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) and a minimum 2-grade improvement from baseline at week 8 on the Validated Investigator Global Assessment for AD was 45.4%, compared with 13.9% of patients who received vehicle alone. ADORING 2 yielded similar results (46.4% vs 18.0%, respectively; P < .0001 for both associations).
Secondary endpoints measured at week 8 also significantly favored the treatment group over the vehicle group, including the Eczema Area and Severity Index score improvement of at least 75% from baseline and achievement of a ≥ 4-point improvement in the patient-reported Peak Pruritus Numerical Rating Scale from baseline.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 1%) were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), folliculitis (9%), lower respiratory tract infection (5%), headache (4%), asthma (2%), vomiting (2%), ear infection (2%), pain in extremity (2%), and abdominal pain (1%), according to the release.
Among 728 patients in the ADORING studies who enrolled in an open-label 48-week extension trial (ADORING 3), 378 entered with or achieved complete disease clearance and discontinued treatment. In this subset of patients, the mean duration of the first treatment-free interval was approximately 80 consecutive days, according to the release.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves IL-31 Inhibitor for Atopic Dermatitis
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.