User login
Evidence Growing for Inflammation’s Role in Elevating Risk for Psychiatric Illness
New research provides more evidence that inflammation may contribute to the development of psychiatric disorders and suggests that measuring certain inflammatory biomarkers may aid in the early identification of individuals at high risk.
Using large-scale datasets, researchers found that elevated levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, particularly leukocytes, haptoglobin, and C-reactive protein (CRP), and lower levels of anti-inflammatory immunoglobulin G (IgG) were associated with an increased risk for psychiatric disorders.
Individuals with psychiatric disorders had persistently higher levels of leukocytes and haptoglobin, as well as persistently lower levels of IgG, than controls during the 30 years before diagnosis, which suggest “long-term processes and may aid in the identification of individuals at high risk,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, a higher level of leukocytes was consistently associated with increased odds of depression across different methods of Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis, “indicating a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression,” they said.
The study, with first author Yu Zeng, MSc, with the Mental Health Center and West China Biomedical Big Data Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Inflammatory Phenotype
Individuals with psychiatric disorders have been found to have elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, but prospective evidence is limited regarding the association between inflammatory biomarkers and subsequent psychiatric disorders risk.
To investigate further, the researchers employed a “triangulation” approach consisting of an exploration dataset of 585,279 adults in the Swedish AMORIS cohort with no prior psychiatric diagnoses and a measurement of at least one inflammatory biomarker, a validation dataset of 485,620 UK Biobank participants, and genetic and MR analyses using genome-wide association study summary statistics.
In the AMORIS cohort, individuals with a higher than median level of leukocytes (hazard ratio [HR], 1.11), haptoglobin (HR, 1.13), or CRP (HR, 1.02) had an elevated risk for any psychiatric disorder. In contrast, there was an inverse association for IgG level (HR, 0.92).
“The estimates were comparable for depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, specifically, and these results were largely validated in the UK Biobank,” the authors reported.
In trajectory analyses, compared with controls, individuals with psychiatric disorders had higher leukocyte and haptoglobin levels and lower IgG up to three decades before being diagnosed.
The MR analysis suggested a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression.
The underlying mechanisms for the associations of serum leukocytes, haptoglobin, CRP, and IgG with psychiatry disorders remain unclear.
“Possible explanations mainly include blood-brain barrier disruption, microglia activation, neurotransmission impairment, and other interactions between inflammations and neuropathology,” the researchers wrote.
A related paper published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry looked at trajectories of inflammation in childhood and risk for mental and cardiometabolic disorders in adulthood.
This longitudinal cohort study found that having persistently raised levels of inflammation as measured by CRP throughout childhood and adolescence, peaking at age 9 years, were associated with an increased risk of developing psychosis disorder, severe depression, and higher levels of insulin resistance.
Support for Precision Psychiatry
This study is “another strong indication that inflammation plays a role in depression,” Andrew H. Miller, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the behavioral immunology program, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“The work adds to the mounting data that there exists an inflammatory phenotype of depression that may uniquely respond to treatment and may have a unique trajectory,” Dr. Miller said.
“Eventually the field will want to embrace this novel phenotype and better understand how to recognize it and treat it. This is our entrée into precision psychiatry where we identify the right treatment for the right patient at the right time based on an understanding of the underlying cause of their illness,” Dr. Miller added.
Also weighing in, Alexander B. Niculescu III, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and medical neuroscience, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, cautioned that these biomarkers are “very nonspecific and are likely related to these subjects that go on to develop psychiatric disorders having more stressful, adverse life trajectories.”
“There are better, more specific blood biomarkers for psychiatric disorders already available,” Dr. Niculescu told this news organization.
His group recently reported that a panel of blood-based biomarkers can distinguish between depression and bipolar disorder, predict a person’s future risk for these disorders, and inform more tailored medication choices.
Notably, they observed a strong circadian clock gene component to mood disorders, which helps explain why some patients’ conditions become worse with seasonal changes. It also explains the sleep alterations that occur among patients with mood disorders, they said.
This study had no commercial funding. Yu Zeng and Dr. Miller had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Niculescu is a cofounder of MindX Sciences and is listed as inventor on a patent application filed by Indiana University.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that inflammation may contribute to the development of psychiatric disorders and suggests that measuring certain inflammatory biomarkers may aid in the early identification of individuals at high risk.
Using large-scale datasets, researchers found that elevated levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, particularly leukocytes, haptoglobin, and C-reactive protein (CRP), and lower levels of anti-inflammatory immunoglobulin G (IgG) were associated with an increased risk for psychiatric disorders.
Individuals with psychiatric disorders had persistently higher levels of leukocytes and haptoglobin, as well as persistently lower levels of IgG, than controls during the 30 years before diagnosis, which suggest “long-term processes and may aid in the identification of individuals at high risk,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, a higher level of leukocytes was consistently associated with increased odds of depression across different methods of Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis, “indicating a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression,” they said.
The study, with first author Yu Zeng, MSc, with the Mental Health Center and West China Biomedical Big Data Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Inflammatory Phenotype
Individuals with psychiatric disorders have been found to have elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, but prospective evidence is limited regarding the association between inflammatory biomarkers and subsequent psychiatric disorders risk.
To investigate further, the researchers employed a “triangulation” approach consisting of an exploration dataset of 585,279 adults in the Swedish AMORIS cohort with no prior psychiatric diagnoses and a measurement of at least one inflammatory biomarker, a validation dataset of 485,620 UK Biobank participants, and genetic and MR analyses using genome-wide association study summary statistics.
In the AMORIS cohort, individuals with a higher than median level of leukocytes (hazard ratio [HR], 1.11), haptoglobin (HR, 1.13), or CRP (HR, 1.02) had an elevated risk for any psychiatric disorder. In contrast, there was an inverse association for IgG level (HR, 0.92).
“The estimates were comparable for depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, specifically, and these results were largely validated in the UK Biobank,” the authors reported.
In trajectory analyses, compared with controls, individuals with psychiatric disorders had higher leukocyte and haptoglobin levels and lower IgG up to three decades before being diagnosed.
The MR analysis suggested a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression.
The underlying mechanisms for the associations of serum leukocytes, haptoglobin, CRP, and IgG with psychiatry disorders remain unclear.
“Possible explanations mainly include blood-brain barrier disruption, microglia activation, neurotransmission impairment, and other interactions between inflammations and neuropathology,” the researchers wrote.
A related paper published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry looked at trajectories of inflammation in childhood and risk for mental and cardiometabolic disorders in adulthood.
This longitudinal cohort study found that having persistently raised levels of inflammation as measured by CRP throughout childhood and adolescence, peaking at age 9 years, were associated with an increased risk of developing psychosis disorder, severe depression, and higher levels of insulin resistance.
Support for Precision Psychiatry
This study is “another strong indication that inflammation plays a role in depression,” Andrew H. Miller, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the behavioral immunology program, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“The work adds to the mounting data that there exists an inflammatory phenotype of depression that may uniquely respond to treatment and may have a unique trajectory,” Dr. Miller said.
“Eventually the field will want to embrace this novel phenotype and better understand how to recognize it and treat it. This is our entrée into precision psychiatry where we identify the right treatment for the right patient at the right time based on an understanding of the underlying cause of their illness,” Dr. Miller added.
Also weighing in, Alexander B. Niculescu III, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and medical neuroscience, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, cautioned that these biomarkers are “very nonspecific and are likely related to these subjects that go on to develop psychiatric disorders having more stressful, adverse life trajectories.”
“There are better, more specific blood biomarkers for psychiatric disorders already available,” Dr. Niculescu told this news organization.
His group recently reported that a panel of blood-based biomarkers can distinguish between depression and bipolar disorder, predict a person’s future risk for these disorders, and inform more tailored medication choices.
Notably, they observed a strong circadian clock gene component to mood disorders, which helps explain why some patients’ conditions become worse with seasonal changes. It also explains the sleep alterations that occur among patients with mood disorders, they said.
This study had no commercial funding. Yu Zeng and Dr. Miller had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Niculescu is a cofounder of MindX Sciences and is listed as inventor on a patent application filed by Indiana University.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that inflammation may contribute to the development of psychiatric disorders and suggests that measuring certain inflammatory biomarkers may aid in the early identification of individuals at high risk.
Using large-scale datasets, researchers found that elevated levels of certain inflammatory biomarkers, particularly leukocytes, haptoglobin, and C-reactive protein (CRP), and lower levels of anti-inflammatory immunoglobulin G (IgG) were associated with an increased risk for psychiatric disorders.
Individuals with psychiatric disorders had persistently higher levels of leukocytes and haptoglobin, as well as persistently lower levels of IgG, than controls during the 30 years before diagnosis, which suggest “long-term processes and may aid in the identification of individuals at high risk,” the researchers wrote.
In addition, a higher level of leukocytes was consistently associated with increased odds of depression across different methods of Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis, “indicating a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression,” they said.
The study, with first author Yu Zeng, MSc, with the Mental Health Center and West China Biomedical Big Data Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Inflammatory Phenotype
Individuals with psychiatric disorders have been found to have elevated levels of inflammatory biomarkers, but prospective evidence is limited regarding the association between inflammatory biomarkers and subsequent psychiatric disorders risk.
To investigate further, the researchers employed a “triangulation” approach consisting of an exploration dataset of 585,279 adults in the Swedish AMORIS cohort with no prior psychiatric diagnoses and a measurement of at least one inflammatory biomarker, a validation dataset of 485,620 UK Biobank participants, and genetic and MR analyses using genome-wide association study summary statistics.
In the AMORIS cohort, individuals with a higher than median level of leukocytes (hazard ratio [HR], 1.11), haptoglobin (HR, 1.13), or CRP (HR, 1.02) had an elevated risk for any psychiatric disorder. In contrast, there was an inverse association for IgG level (HR, 0.92).
“The estimates were comparable for depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders, specifically, and these results were largely validated in the UK Biobank,” the authors reported.
In trajectory analyses, compared with controls, individuals with psychiatric disorders had higher leukocyte and haptoglobin levels and lower IgG up to three decades before being diagnosed.
The MR analysis suggested a possible causal relationship between leukocytes and depression.
The underlying mechanisms for the associations of serum leukocytes, haptoglobin, CRP, and IgG with psychiatry disorders remain unclear.
“Possible explanations mainly include blood-brain barrier disruption, microglia activation, neurotransmission impairment, and other interactions between inflammations and neuropathology,” the researchers wrote.
A related paper published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry looked at trajectories of inflammation in childhood and risk for mental and cardiometabolic disorders in adulthood.
This longitudinal cohort study found that having persistently raised levels of inflammation as measured by CRP throughout childhood and adolescence, peaking at age 9 years, were associated with an increased risk of developing psychosis disorder, severe depression, and higher levels of insulin resistance.
Support for Precision Psychiatry
This study is “another strong indication that inflammation plays a role in depression,” Andrew H. Miller, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and director of the behavioral immunology program, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, who wasn’t involved in the study, told this news organization.
“The work adds to the mounting data that there exists an inflammatory phenotype of depression that may uniquely respond to treatment and may have a unique trajectory,” Dr. Miller said.
“Eventually the field will want to embrace this novel phenotype and better understand how to recognize it and treat it. This is our entrée into precision psychiatry where we identify the right treatment for the right patient at the right time based on an understanding of the underlying cause of their illness,” Dr. Miller added.
Also weighing in, Alexander B. Niculescu III, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and medical neuroscience, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, cautioned that these biomarkers are “very nonspecific and are likely related to these subjects that go on to develop psychiatric disorders having more stressful, adverse life trajectories.”
“There are better, more specific blood biomarkers for psychiatric disorders already available,” Dr. Niculescu told this news organization.
His group recently reported that a panel of blood-based biomarkers can distinguish between depression and bipolar disorder, predict a person’s future risk for these disorders, and inform more tailored medication choices.
Notably, they observed a strong circadian clock gene component to mood disorders, which helps explain why some patients’ conditions become worse with seasonal changes. It also explains the sleep alterations that occur among patients with mood disorders, they said.
This study had no commercial funding. Yu Zeng and Dr. Miller had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Niculescu is a cofounder of MindX Sciences and is listed as inventor on a patent application filed by Indiana University.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 Tied to Increased Risk for Mental Illness
New research adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that COVID-19 infection can be hard on mental health.
, particularly in those with severe COVID who had not been vaccinated.
Importantly, vaccination appeared to mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on mental health, the investigators found.
“Our results highlight the importance COVID-19 vaccination in the general population and particularly among those with mental illnesses, who may be at higher risk of both SARS-CoV-2 infection and adverse outcomes following COVID-19,” first author Venexia Walker, PhD, with University of Bristol, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Novel Data
“Before this study, a number of papers had looked at associations of COVID diagnosis with mental ill health, and broadly speaking, they had reported associations of different magnitudes,” study author Jonathan A. C. Sterne, PhD, with University of Bristol, noted in a journal podcast.
“Some studies were restricted to patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and some not and the duration of follow-up varied. And importantly, the nature of COVID-19 changed profoundly as vaccination became available and there was little data on the impact of vaccination on associations of COVID-19 with subsequent mental ill health,” Dr. Sterne said.
The UK study was conducted in three cohorts — a cohort of about 18.6 million people who were diagnosed with COVID-19 before a vaccine was available, a cohort of about 14 million adults who were vaccinated, and a cohort of about 3.2 million people who were unvaccinated.
The researchers compared rates of various mental illnesses after COVID-19 with rates before or without COVID-19 and by vaccination status.
Across all cohorts, rates of most mental illnesses examined were “markedly elevated” during the first month following a COVID-19 diagnosis compared with rates before or without COVID-19.
For example, the adjusted hazard ratios for depression (the most common illness) and serious mental illness in the month after COVID-19 were 1.93 and 1.49, respectively, in the prevaccination cohort and 1.79 and 1.45, respectively, in the unvaccinated cohort compared with 1.16 and 0.91 in the vaccinated cohort.
This elevation in the rate of mental illnesses was mainly seen after severe COVID-19 that led to hospitalization and remained higher for up to a year following severe COVID-19 in unvaccinated adults.
For severe COVID-19 with hospitalization, the adjusted hazard ratio for depression in the month following admission was 16.3 in the prevaccine cohort, 15.6 in the unvaccinated cohort, and 12.9 in the vaccinated cohort.
The adjusted hazard ratios for serious mental illness in the month after COVID hospitalization was 9.71 in the prevaccine cohort, 8.75 with no vaccination, and 6.52 with vaccination.
“Incidences of other mental illnesses were broadly similar to those of depression and serious mental illness, both overall and for COVID-19 with and without hospitalization,” the authors report in their paper.
Consistent with prior research, subgroup analyzes found the association of COVID-19 and mental illness was stronger among older adults and men, with no marked differences by ethnic group.
“We should be concerned about continuing consequences in people who experienced severe COVID-19 early in the pandemic, and they may include a continuing higher incidence of mental ill health, such as depression and serious mental illness,” Dr. Sterne said in the podcast.
In terms of ongoing booster vaccinations, “people who are advised that they are under vaccinated or recommended for further COVID-19 vaccination, should take those invitations seriously, because by preventing severe COVID-19, which is what vaccination does, you can prevent consequences such as mental illness,” Dr. Sterne added.
The study was supported by the COVID-19 Longitudinal Health and Wellbeing National Core Study, which is funded by the Medical Research Council and National Institute for Health and Care Research. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that COVID-19 infection can be hard on mental health.
, particularly in those with severe COVID who had not been vaccinated.
Importantly, vaccination appeared to mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on mental health, the investigators found.
“Our results highlight the importance COVID-19 vaccination in the general population and particularly among those with mental illnesses, who may be at higher risk of both SARS-CoV-2 infection and adverse outcomes following COVID-19,” first author Venexia Walker, PhD, with University of Bristol, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Novel Data
“Before this study, a number of papers had looked at associations of COVID diagnosis with mental ill health, and broadly speaking, they had reported associations of different magnitudes,” study author Jonathan A. C. Sterne, PhD, with University of Bristol, noted in a journal podcast.
“Some studies were restricted to patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and some not and the duration of follow-up varied. And importantly, the nature of COVID-19 changed profoundly as vaccination became available and there was little data on the impact of vaccination on associations of COVID-19 with subsequent mental ill health,” Dr. Sterne said.
The UK study was conducted in three cohorts — a cohort of about 18.6 million people who were diagnosed with COVID-19 before a vaccine was available, a cohort of about 14 million adults who were vaccinated, and a cohort of about 3.2 million people who were unvaccinated.
The researchers compared rates of various mental illnesses after COVID-19 with rates before or without COVID-19 and by vaccination status.
Across all cohorts, rates of most mental illnesses examined were “markedly elevated” during the first month following a COVID-19 diagnosis compared with rates before or without COVID-19.
For example, the adjusted hazard ratios for depression (the most common illness) and serious mental illness in the month after COVID-19 were 1.93 and 1.49, respectively, in the prevaccination cohort and 1.79 and 1.45, respectively, in the unvaccinated cohort compared with 1.16 and 0.91 in the vaccinated cohort.
This elevation in the rate of mental illnesses was mainly seen after severe COVID-19 that led to hospitalization and remained higher for up to a year following severe COVID-19 in unvaccinated adults.
For severe COVID-19 with hospitalization, the adjusted hazard ratio for depression in the month following admission was 16.3 in the prevaccine cohort, 15.6 in the unvaccinated cohort, and 12.9 in the vaccinated cohort.
The adjusted hazard ratios for serious mental illness in the month after COVID hospitalization was 9.71 in the prevaccine cohort, 8.75 with no vaccination, and 6.52 with vaccination.
“Incidences of other mental illnesses were broadly similar to those of depression and serious mental illness, both overall and for COVID-19 with and without hospitalization,” the authors report in their paper.
Consistent with prior research, subgroup analyzes found the association of COVID-19 and mental illness was stronger among older adults and men, with no marked differences by ethnic group.
“We should be concerned about continuing consequences in people who experienced severe COVID-19 early in the pandemic, and they may include a continuing higher incidence of mental ill health, such as depression and serious mental illness,” Dr. Sterne said in the podcast.
In terms of ongoing booster vaccinations, “people who are advised that they are under vaccinated or recommended for further COVID-19 vaccination, should take those invitations seriously, because by preventing severe COVID-19, which is what vaccination does, you can prevent consequences such as mental illness,” Dr. Sterne added.
The study was supported by the COVID-19 Longitudinal Health and Wellbeing National Core Study, which is funded by the Medical Research Council and National Institute for Health and Care Research. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that COVID-19 infection can be hard on mental health.
, particularly in those with severe COVID who had not been vaccinated.
Importantly, vaccination appeared to mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on mental health, the investigators found.
“Our results highlight the importance COVID-19 vaccination in the general population and particularly among those with mental illnesses, who may be at higher risk of both SARS-CoV-2 infection and adverse outcomes following COVID-19,” first author Venexia Walker, PhD, with University of Bristol, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online on August 21 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Novel Data
“Before this study, a number of papers had looked at associations of COVID diagnosis with mental ill health, and broadly speaking, they had reported associations of different magnitudes,” study author Jonathan A. C. Sterne, PhD, with University of Bristol, noted in a journal podcast.
“Some studies were restricted to patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and some not and the duration of follow-up varied. And importantly, the nature of COVID-19 changed profoundly as vaccination became available and there was little data on the impact of vaccination on associations of COVID-19 with subsequent mental ill health,” Dr. Sterne said.
The UK study was conducted in three cohorts — a cohort of about 18.6 million people who were diagnosed with COVID-19 before a vaccine was available, a cohort of about 14 million adults who were vaccinated, and a cohort of about 3.2 million people who were unvaccinated.
The researchers compared rates of various mental illnesses after COVID-19 with rates before or without COVID-19 and by vaccination status.
Across all cohorts, rates of most mental illnesses examined were “markedly elevated” during the first month following a COVID-19 diagnosis compared with rates before or without COVID-19.
For example, the adjusted hazard ratios for depression (the most common illness) and serious mental illness in the month after COVID-19 were 1.93 and 1.49, respectively, in the prevaccination cohort and 1.79 and 1.45, respectively, in the unvaccinated cohort compared with 1.16 and 0.91 in the vaccinated cohort.
This elevation in the rate of mental illnesses was mainly seen after severe COVID-19 that led to hospitalization and remained higher for up to a year following severe COVID-19 in unvaccinated adults.
For severe COVID-19 with hospitalization, the adjusted hazard ratio for depression in the month following admission was 16.3 in the prevaccine cohort, 15.6 in the unvaccinated cohort, and 12.9 in the vaccinated cohort.
The adjusted hazard ratios for serious mental illness in the month after COVID hospitalization was 9.71 in the prevaccine cohort, 8.75 with no vaccination, and 6.52 with vaccination.
“Incidences of other mental illnesses were broadly similar to those of depression and serious mental illness, both overall and for COVID-19 with and without hospitalization,” the authors report in their paper.
Consistent with prior research, subgroup analyzes found the association of COVID-19 and mental illness was stronger among older adults and men, with no marked differences by ethnic group.
“We should be concerned about continuing consequences in people who experienced severe COVID-19 early in the pandemic, and they may include a continuing higher incidence of mental ill health, such as depression and serious mental illness,” Dr. Sterne said in the podcast.
In terms of ongoing booster vaccinations, “people who are advised that they are under vaccinated or recommended for further COVID-19 vaccination, should take those invitations seriously, because by preventing severe COVID-19, which is what vaccination does, you can prevent consequences such as mental illness,” Dr. Sterne added.
The study was supported by the COVID-19 Longitudinal Health and Wellbeing National Core Study, which is funded by the Medical Research Council and National Institute for Health and Care Research. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Childhood Cancer Survivors Face Sexual Challenges
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Childhood cancers represent a diverse group of neoplasms, and thanks to advances in treatment, survival rates have improved significantly. Today, more than 80%-85% of children diagnosed with cancer in developed countries survive into adulthood.
This increase in survival has brought new challenges, however. Compared with the general population, childhood cancer survivors (CCS) are at a notably higher risk for early mortality, developing secondary cancers, and experiencing various long-term clinical and psychosocial issues stemming from their disease or its treatment.
Long-term follow-up care for CCS is a complex and evolving field. Despite ongoing efforts to establish global and national guidelines, current evidence indicates that the care and management of these patients remain suboptimal.
The disruptions caused by cancer and its treatment can interfere with normal physiological and psychological development, leading to issues with sexual function. This aspect of health is critical as it influences not just physical well-being but also psychosocial, developmental, and emotional health.
Characteristics and Mechanisms
Sexual functioning encompasses the physiological and psychological aspects of sexual behavior, including desire, arousal, orgasm, sexual pleasure, and overall satisfaction.
As CCS reach adolescence or adulthood, they often face sexual and reproductive issues, particularly as they enter romantic relationships.
Sexual functioning is a complex process that relies on the interaction of various factors, including physiological health, psychosexual development, romantic relationships, body image, and desire.
Despite its importance, the impact of childhood cancer on sexual function is often overlooked, even though cancer and its treatments can have lifelong effects.
Sexual Function in CCS
A recent review aimed to summarize the existing research on sexual function among CCS, highlighting assessment tools, key stages of psychosexual development, common sexual problems, and the prevalence of sexual dysfunction.
The review study included 22 studies published between 2000 and 2022, comprising two qualitative, six cohort, and 14 cross-sectional studies.
Most CCS reached all key stages of psychosexual development at an average age of 29.8 years. Although some milestones were achieved later than is typical, many survivors felt they reached these stages at the appropriate time. Sexual initiation was less common among those who had undergone intensive neurotoxic treatments, such as those diagnosed with brain tumors or leukemia in childhood.
In a cross-sectional study of CCS aged 17-39 years, about one third had never engaged in sexual intercourse, 41.4% reported never experiencing sexual attraction, 44.8% were dissatisfied with their sex lives, and many rarely felt sexually attractive to others. Another study found that common issues among CCS included a lack of interest in sex (30%), difficulty enjoying sex (24%), and difficulty becoming aroused (23%). However, comparing and analyzing these problems was challenging due to the lack of standardized assessment criteria.
The prevalence of sexual dysfunction among CCS ranged from 12.3% to 46.5%. For males, the prevalence ranged from 12.3% to 54.0%, while for females, it ranged from 19.9% to 57.0%.
Factors Influencing Sexual Function
The review identified the following four categories of factors influencing sexual function in CCS: Demographic, treatment-related, psychological, and physiological.
Demographic factors: Gender, age, education level, relationship status, income level, and race all play roles in sexual function.
Female survivors reported more severe sexual dysfunction and poorer sexual health than did male survivors. Age at cancer diagnosis, age at evaluation, and the time since diagnosis were closely linked to sexual experiences. Patients diagnosed with cancer during childhood tended to report better sexual function than those diagnosed during adolescence.
Treatment-related factors: The type of cancer and intensity of treatment, along with surgical history, were significant factors. Surgeries involving the spinal cord or sympathetic nerves, as well as a history of prostate or pelvic surgery, were strongly associated with erectile dysfunction in men. In women, pelvic surgeries and treatments to the pelvic area were commonly linked to sexual dysfunction.
The association between treatment intensity and sexual function was noted across several studies, although the results were not always consistent. For example, testicular radiation above 10 Gy was positively correlated with sexual dysfunction. Women who underwent more intensive treatments were more likely to report issues in multiple areas of sexual function, while men in this group were less likely to have children.
Among female CCS, certain types of cancer, such as germ cell tumors, renal tumors, and leukemia, present a higher risk for sexual dysfunction. Women who had CNS tumors in childhood frequently reported problems like difficulty in sexual arousal, low sexual satisfaction, infrequent sexual activity, and fewer sexual partners, compared with survivors of other cancers. Survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and those who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) also showed varying degrees of impaired sexual function, compared with the general population. The HSCT group showed significant testicular damage, including reduced testicular volumes, low testosterone levels, and low sperm counts.
Psychological factors: These factors, such as emotional distress, play a significant role in sexual dysfunction among CCS. Symptoms like anxiety, nervousness during sexual activity, and depression are commonly reported by those with sexual dysfunction. The connection between body image and sexual function is complex. Many CCS with sexual dysfunction express concern about how others, particularly their partners, perceived their altered body image due to cancer and its treatment.
Physiological factors: In male CCS, low serum testosterone levels and low lean muscle mass are linked to an increased risk for sexual dysfunction. Treatments involving alkylating agents or testicular radiation, and surgery or radiotherapy targeting the genitourinary organs or the hypothalamic-pituitary region, can lead to various physiological and endocrine disorders, contributing to sexual dysfunction. Despite these risks, there is a lack of research evaluating sexual function through the lens of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and neuroendocrine pathways.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
CBD Use in Pregnant People Double That of Nonpregnant Counterparts
Pregnant women in a large North American sample reported nearly double the rate of cannabidiol (CBD) use compared with nonpregnant women, new data published in a research letter in Obstetrics & Gynecology indicates.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the high rate of CBD use in pregnancy, especially as legal use of cannabis is increasing faster than evidence on outcomes for exposed offspring, note the researchers, led by Devika Bhatia, MD, from the Department of Psychiatry, Colorado School of Medicine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
In an accompanying editorial, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, deputy editor for obstetrics for Obstetrics & Gynecology, writes that the study “is critically important.” She points out that pregnant individuals may perceive that CBD is a safe drug to use in pregnancy, despite there being essentially no data examining whether or not this is the case.
Large Dataset From United States and Canada
Researchers used data from the International Cannabis Policy Study (2019-2021), a repeated cross-sectional survey of people aged 16-65 years in the United States and Canada. There were 66,457 women in the sample, including 1096 pregnant women.
Particularly concerning, the authors write, is the prenatal use of CBD-only products. Those products are advertised to contain only CBD, rather than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). They point out CBD-only products are often legal in North America and often marketed as supplements.
The prevalence of CBD-only use in pregnant women in the study was 20.4% compared with 11.3% among nonpregnant women, P < .001. The top reason for use by pregnant women was anxiety (58.4%). Other top reasons included depression (40.3%), posttraumatic stress disorder (32.1%), pain (52.3%), headache (35.6%), and nausea or vomiting (31.9%).
“Nonpregnant women were significantly more likely to report using CBD for pain, sleep, general well-being, and ‘other’ physical or mental health reasons, or to not use CBD for mental health,” the authors write, adding that the reasons for CBD use highlight drivers that may be important to address in treating pregnant patients.
Provider Endorsement in Some Cases
Dr. Metz, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology with the University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City, says in some cases women may be getting endorsement of CBD use from their provider or at least implied support when CBD is prescribed. In the study, pregnant women had 2.33 times greater adjusted odds of having a CBD prescription than nonpregnant women (95% confidence interval, 1.27-2.88).
She points to another cross-sectional study of more than 10,000 participants using PRAMS (Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System) data that found that “from 2017 to 2019, 63% of pregnant women reported that they were not told to avoid cannabis use in pregnancy, and 8% noted that they were advised to use cannabis by their prenatal care practitioner.”
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against prescribing cannabis products for pregnant or lactating women.
Studies that have explored THC and its metabolites have shown “a consistent association between cannabis use and decreased fetal growth,” Dr. Metz noted. “There also remain persistent concerns about the long-term neurodevelopmental effects of maternal cannabis use on the fetus and, subsequently, the newborn.”
Limitations of the study include the self-reported responses and participants’ ability to accurately distinguish between CBD-only and THC-containing products.
Because self-reports of CBD use in pregnancy may be drastically underestimated and nonreliable, Dr. Metz writes, development of blood and urine screens to help detect CBD product use “will be helpful in moving the field forward.”
Study senior author David Hammond, PhD, has been a paid expert witness on behalf of public health authorities in response to legal challenges from the cannabis, tobacco, vaping, and food industries. Other authors did not report any potential conflicts. Dr. Metz reports personal fees from Pfizer, and grants from Pfizer for her role as a site principal investigator for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and for her role as a site PI for RSV vaccination in pregnancy study.
Pregnant women in a large North American sample reported nearly double the rate of cannabidiol (CBD) use compared with nonpregnant women, new data published in a research letter in Obstetrics & Gynecology indicates.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the high rate of CBD use in pregnancy, especially as legal use of cannabis is increasing faster than evidence on outcomes for exposed offspring, note the researchers, led by Devika Bhatia, MD, from the Department of Psychiatry, Colorado School of Medicine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
In an accompanying editorial, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, deputy editor for obstetrics for Obstetrics & Gynecology, writes that the study “is critically important.” She points out that pregnant individuals may perceive that CBD is a safe drug to use in pregnancy, despite there being essentially no data examining whether or not this is the case.
Large Dataset From United States and Canada
Researchers used data from the International Cannabis Policy Study (2019-2021), a repeated cross-sectional survey of people aged 16-65 years in the United States and Canada. There were 66,457 women in the sample, including 1096 pregnant women.
Particularly concerning, the authors write, is the prenatal use of CBD-only products. Those products are advertised to contain only CBD, rather than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). They point out CBD-only products are often legal in North America and often marketed as supplements.
The prevalence of CBD-only use in pregnant women in the study was 20.4% compared with 11.3% among nonpregnant women, P < .001. The top reason for use by pregnant women was anxiety (58.4%). Other top reasons included depression (40.3%), posttraumatic stress disorder (32.1%), pain (52.3%), headache (35.6%), and nausea or vomiting (31.9%).
“Nonpregnant women were significantly more likely to report using CBD for pain, sleep, general well-being, and ‘other’ physical or mental health reasons, or to not use CBD for mental health,” the authors write, adding that the reasons for CBD use highlight drivers that may be important to address in treating pregnant patients.
Provider Endorsement in Some Cases
Dr. Metz, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology with the University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City, says in some cases women may be getting endorsement of CBD use from their provider or at least implied support when CBD is prescribed. In the study, pregnant women had 2.33 times greater adjusted odds of having a CBD prescription than nonpregnant women (95% confidence interval, 1.27-2.88).
She points to another cross-sectional study of more than 10,000 participants using PRAMS (Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System) data that found that “from 2017 to 2019, 63% of pregnant women reported that they were not told to avoid cannabis use in pregnancy, and 8% noted that they were advised to use cannabis by their prenatal care practitioner.”
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against prescribing cannabis products for pregnant or lactating women.
Studies that have explored THC and its metabolites have shown “a consistent association between cannabis use and decreased fetal growth,” Dr. Metz noted. “There also remain persistent concerns about the long-term neurodevelopmental effects of maternal cannabis use on the fetus and, subsequently, the newborn.”
Limitations of the study include the self-reported responses and participants’ ability to accurately distinguish between CBD-only and THC-containing products.
Because self-reports of CBD use in pregnancy may be drastically underestimated and nonreliable, Dr. Metz writes, development of blood and urine screens to help detect CBD product use “will be helpful in moving the field forward.”
Study senior author David Hammond, PhD, has been a paid expert witness on behalf of public health authorities in response to legal challenges from the cannabis, tobacco, vaping, and food industries. Other authors did not report any potential conflicts. Dr. Metz reports personal fees from Pfizer, and grants from Pfizer for her role as a site principal investigator for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and for her role as a site PI for RSV vaccination in pregnancy study.
Pregnant women in a large North American sample reported nearly double the rate of cannabidiol (CBD) use compared with nonpregnant women, new data published in a research letter in Obstetrics & Gynecology indicates.
Healthcare providers should be aware of the high rate of CBD use in pregnancy, especially as legal use of cannabis is increasing faster than evidence on outcomes for exposed offspring, note the researchers, led by Devika Bhatia, MD, from the Department of Psychiatry, Colorado School of Medicine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus in Aurora.
In an accompanying editorial, Torri D. Metz, MD, MS, deputy editor for obstetrics for Obstetrics & Gynecology, writes that the study “is critically important.” She points out that pregnant individuals may perceive that CBD is a safe drug to use in pregnancy, despite there being essentially no data examining whether or not this is the case.
Large Dataset From United States and Canada
Researchers used data from the International Cannabis Policy Study (2019-2021), a repeated cross-sectional survey of people aged 16-65 years in the United States and Canada. There were 66,457 women in the sample, including 1096 pregnant women.
Particularly concerning, the authors write, is the prenatal use of CBD-only products. Those products are advertised to contain only CBD, rather than tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). They point out CBD-only products are often legal in North America and often marketed as supplements.
The prevalence of CBD-only use in pregnant women in the study was 20.4% compared with 11.3% among nonpregnant women, P < .001. The top reason for use by pregnant women was anxiety (58.4%). Other top reasons included depression (40.3%), posttraumatic stress disorder (32.1%), pain (52.3%), headache (35.6%), and nausea or vomiting (31.9%).
“Nonpregnant women were significantly more likely to report using CBD for pain, sleep, general well-being, and ‘other’ physical or mental health reasons, or to not use CBD for mental health,” the authors write, adding that the reasons for CBD use highlight drivers that may be important to address in treating pregnant patients.
Provider Endorsement in Some Cases
Dr. Metz, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology with the University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City, says in some cases women may be getting endorsement of CBD use from their provider or at least implied support when CBD is prescribed. In the study, pregnant women had 2.33 times greater adjusted odds of having a CBD prescription than nonpregnant women (95% confidence interval, 1.27-2.88).
She points to another cross-sectional study of more than 10,000 participants using PRAMS (Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System) data that found that “from 2017 to 2019, 63% of pregnant women reported that they were not told to avoid cannabis use in pregnancy, and 8% noted that they were advised to use cannabis by their prenatal care practitioner.”
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends against prescribing cannabis products for pregnant or lactating women.
Studies that have explored THC and its metabolites have shown “a consistent association between cannabis use and decreased fetal growth,” Dr. Metz noted. “There also remain persistent concerns about the long-term neurodevelopmental effects of maternal cannabis use on the fetus and, subsequently, the newborn.”
Limitations of the study include the self-reported responses and participants’ ability to accurately distinguish between CBD-only and THC-containing products.
Because self-reports of CBD use in pregnancy may be drastically underestimated and nonreliable, Dr. Metz writes, development of blood and urine screens to help detect CBD product use “will be helpful in moving the field forward.”
Study senior author David Hammond, PhD, has been a paid expert witness on behalf of public health authorities in response to legal challenges from the cannabis, tobacco, vaping, and food industries. Other authors did not report any potential conflicts. Dr. Metz reports personal fees from Pfizer, and grants from Pfizer for her role as a site principal investigator for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and for her role as a site PI for RSV vaccination in pregnancy study.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Data Trends 2024: Depression and PTSD
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
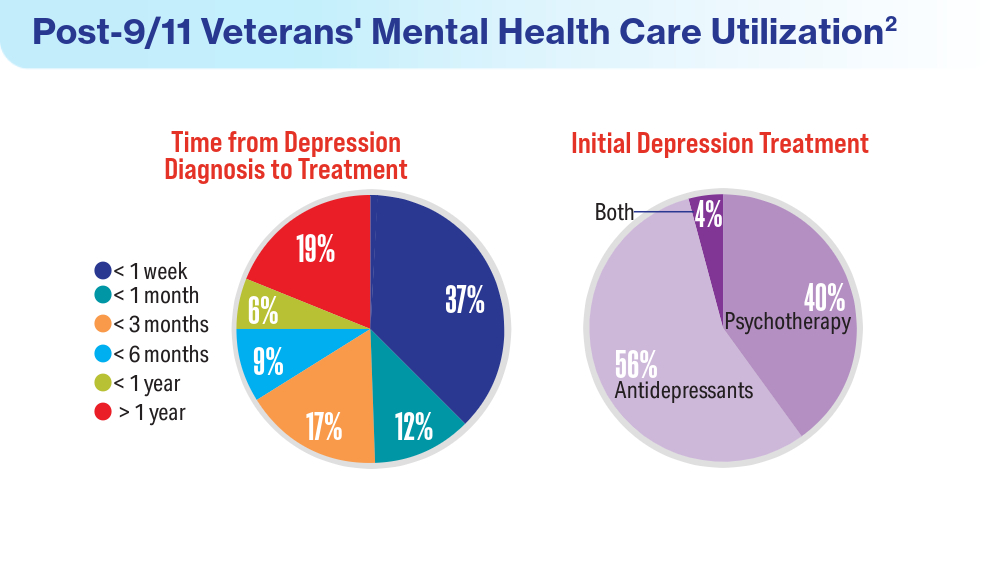
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
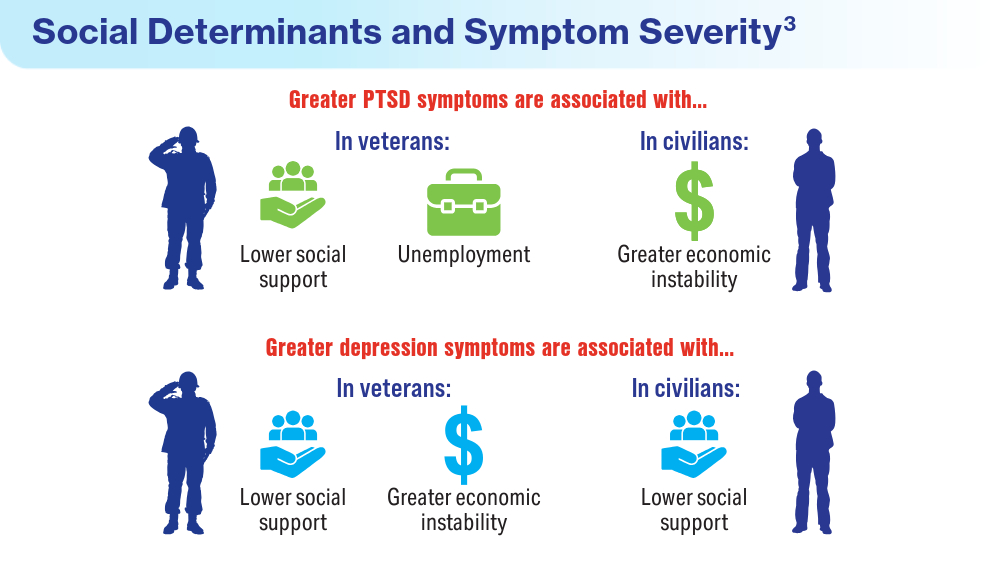
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
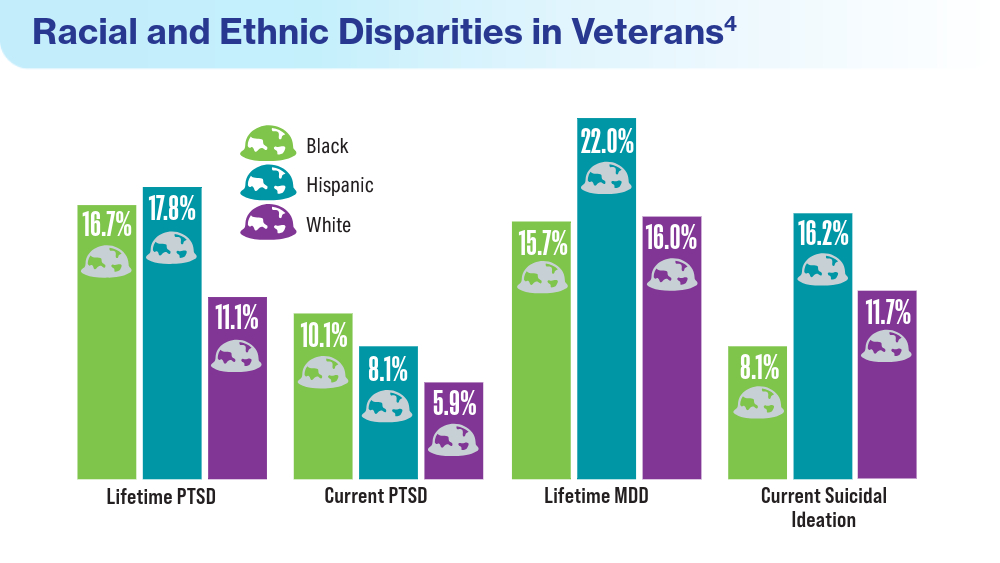
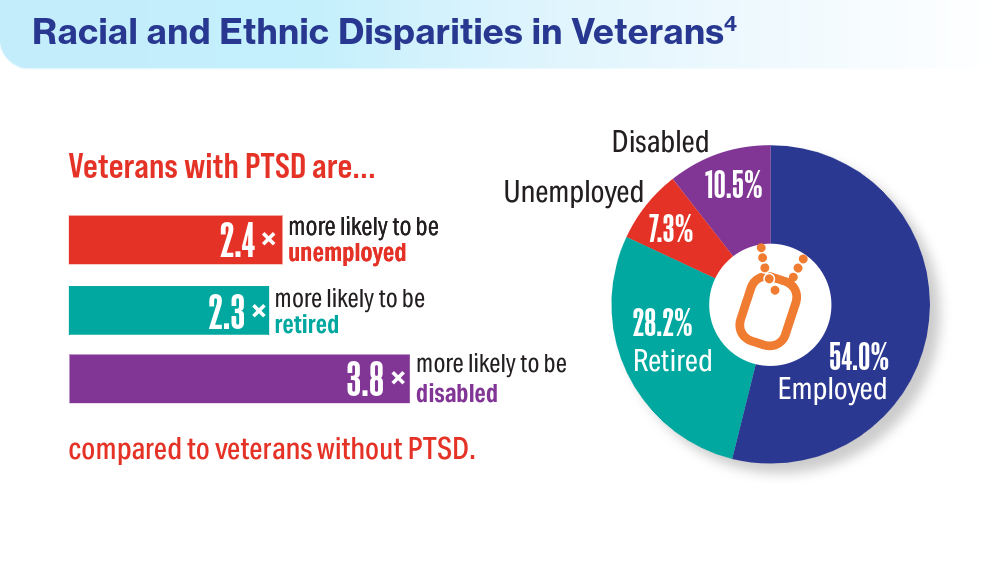
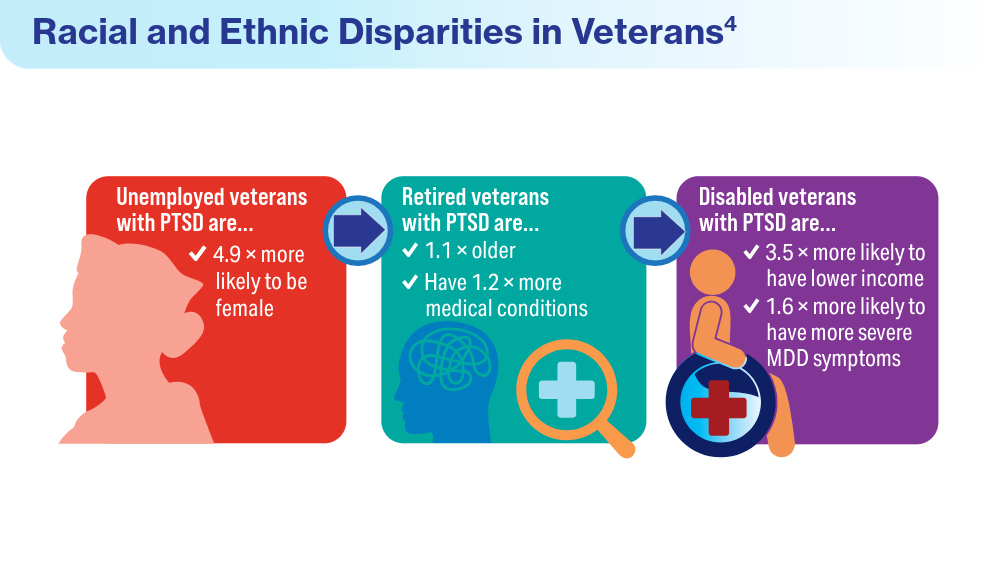
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
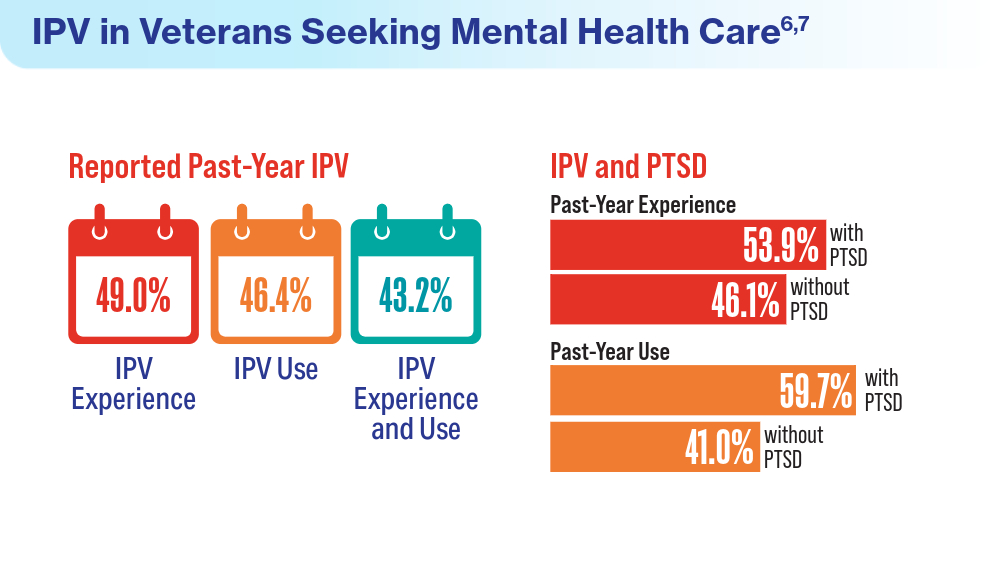
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
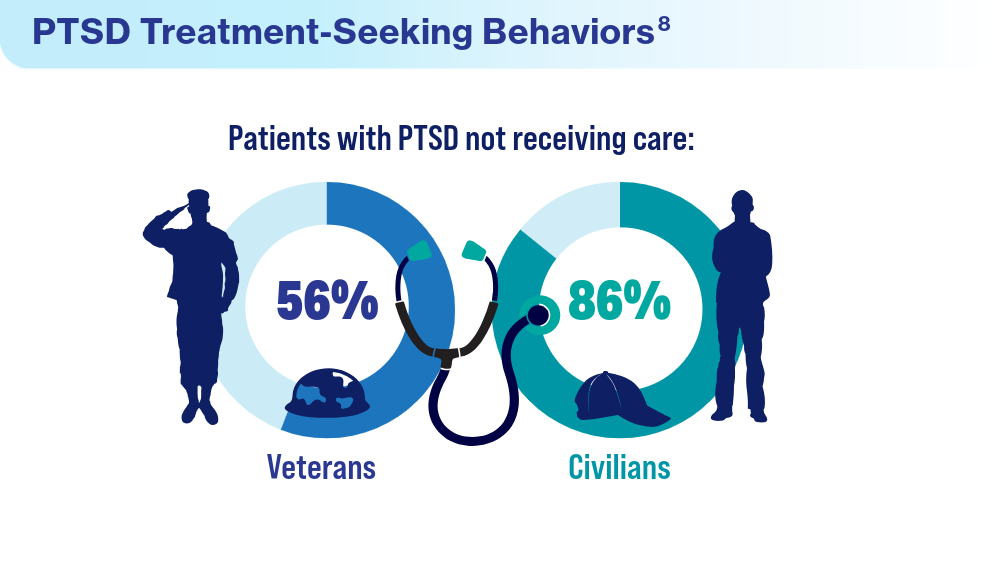
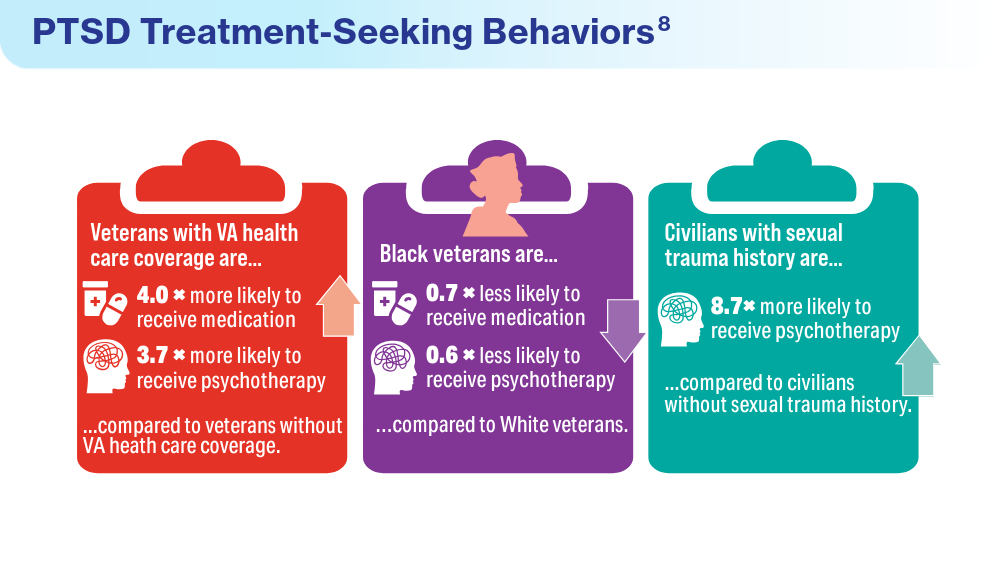
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
- Inoue C, Shawler E, Jordan CH, Moore MJ, Jackson CA. Veteran and military mental health issues. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. Updated August 17, 2023. Accessed April 1, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572092/
- Panaite V, Cohen NJ, Luter SL, et al. Mental health treatment utilization patterns among 108,457 Afghanistan and Iraq veterans with depression. Psychol Serv. 2024 Feb 1. doi:10.1037/ser0000819
- Holder N, Holliday R, Ranney RM, et al. Relationship of social determinants of health with symptom severity among veterans and non-veterans with probable posttraumatic stress disorder or depression. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2023;58(10):1523-1534. doi:10.1007/s00127-023-02478-0
- Merians AN, Gross G, Spoont MR, Bellamy CD, Harpaz-Rotem I, Pietrzak RH. Racial and ethnic mental health disparities in U.S. military veterans: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Psychiatr Res. 2023;161:71-76. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.03.005
- Fischer IC, Schnurr PP, Pietrzak RH. Employment status among US military veterans with a history of posttraumatic stress disorder: results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. J Trauma Stress. 2023;36(6):1167-1175. doi:10.1002/jts.22977
- Portnoy GA, Relyea MR, Presseau C, et al. Screening for intimate partner violence experience and use in the Veterans Health Administration. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10):e2337685. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.37685
- Cowlishaw S, Freijah I, Kartal D, et al. Intimate Partner Violence (IPV) in Military and Veteran Populations: A Systematic Review of Population-Based Surveys and Population Screening Studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(14):8853. Published 2022 Jul 21. doi:10.3390/ijerph19148853
- Ranney RM, Maguen S, Bernhard PA, et al. Treatment utilization for posttraumatic stress disorder in a national sample of veterans and nonveterans. Med Care. 2023;61(2):87-94. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000001793
Federal Health Care Data Trends 2024
More Access to Perinatal Mental Healthcare Needed
Despite federal legislation improving healthcare access, concerted efforts are still needed to increase evidence-based treatment for maternal perinatal mental health issues, a large study of commercially insured mothers suggested. It found that federal legislation had variable and suboptimal effect on mental health services use by delivering mothers.
In the cross-sectional study, published in JAMA Network Open, psychotherapy receipt increased somewhat during 2007-2019 among all mothers and among those diagnosed with perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs). The timeline encompassed periods before and after passage of the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) of 2008 and the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010.
The investigators, led by Kara Zivin, PhD, MS, MFA, a professor of psychiatry in the University of Michigan’s School of Public Health at Ann Arbor, found the results varied by policy and between the overall delivering population and the PMAD population. “We did not find a statistically significant immediate change associated with the MHPAEA or ACA in the overall delivering population, except for a steady increase in delivering women who received any psychotherapy after ACA,” Dr. Zivin and colleagues wrote.
The researchers looked at private insurance data for 837,316 deliveries among 716,052 women (64.2% White), ages 15-44 (mean 31.2), to assess changes in psychotherapy visits in the year before and after delivery. They also estimated per-visit out-of-pocket costs for the ACA in 2014 and the MHPAEA in 2010.
In the PMAD population, the MHPAEA was associated with an immediate increase in psychotherapy receipt of 0.72% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.18%; P = .002), followed by a sustained decrease of 0.05% (95% CI, 0.09%-0.02%; P = .001).
In both populations, the ACA was associated with immediate and sustained monthly increases in use of 0.77% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.27%; P = .003) and 0.07% (95% CI, 0.02%-0.12%; P = .005), respectively.
Post MHPAEA, both populations experienced a slight decrease in per-visit monthly out-of-pocket costs, while after the ACA they saw an immediate and steady monthly increase in these.
Although both policies expanded access to any psychotherapy, the greater number of people receiving visits coincided with fewer visits per person, the authors noted. “One hypothesis suggests that the number of available mental health clinicians may not have increased enough to meet the new demand; future research should better characterize this trend,” they wrote.
In addition, a lower standard cost per visit may have dampened the incentive to increase the number of mental health clinicians, they conjectured. These factors could explain why the PMAD group appeared to experience a decrease in the proportion receiving any psychotherapy after the MHPAEA’s implementation.
The findings should be reviewed in the context of the current mental health burden, the authors wrote, in which the shortage of mental health professionals means that less than 30% of mental healthcare needs are being met.
They called for more measures to mitigate the excess burden of PMADs.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zivin had no conflicts of interest. Coauthor Dr. Dalton reported personal fees from Merck, the Society of Family Planning, Up to Date, and The Medical Letter outside of the submitted work.
Despite federal legislation improving healthcare access, concerted efforts are still needed to increase evidence-based treatment for maternal perinatal mental health issues, a large study of commercially insured mothers suggested. It found that federal legislation had variable and suboptimal effect on mental health services use by delivering mothers.
In the cross-sectional study, published in JAMA Network Open, psychotherapy receipt increased somewhat during 2007-2019 among all mothers and among those diagnosed with perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs). The timeline encompassed periods before and after passage of the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) of 2008 and the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010.
The investigators, led by Kara Zivin, PhD, MS, MFA, a professor of psychiatry in the University of Michigan’s School of Public Health at Ann Arbor, found the results varied by policy and between the overall delivering population and the PMAD population. “We did not find a statistically significant immediate change associated with the MHPAEA or ACA in the overall delivering population, except for a steady increase in delivering women who received any psychotherapy after ACA,” Dr. Zivin and colleagues wrote.
The researchers looked at private insurance data for 837,316 deliveries among 716,052 women (64.2% White), ages 15-44 (mean 31.2), to assess changes in psychotherapy visits in the year before and after delivery. They also estimated per-visit out-of-pocket costs for the ACA in 2014 and the MHPAEA in 2010.
In the PMAD population, the MHPAEA was associated with an immediate increase in psychotherapy receipt of 0.72% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.18%; P = .002), followed by a sustained decrease of 0.05% (95% CI, 0.09%-0.02%; P = .001).
In both populations, the ACA was associated with immediate and sustained monthly increases in use of 0.77% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.27%; P = .003) and 0.07% (95% CI, 0.02%-0.12%; P = .005), respectively.
Post MHPAEA, both populations experienced a slight decrease in per-visit monthly out-of-pocket costs, while after the ACA they saw an immediate and steady monthly increase in these.
Although both policies expanded access to any psychotherapy, the greater number of people receiving visits coincided with fewer visits per person, the authors noted. “One hypothesis suggests that the number of available mental health clinicians may not have increased enough to meet the new demand; future research should better characterize this trend,” they wrote.
In addition, a lower standard cost per visit may have dampened the incentive to increase the number of mental health clinicians, they conjectured. These factors could explain why the PMAD group appeared to experience a decrease in the proportion receiving any psychotherapy after the MHPAEA’s implementation.
The findings should be reviewed in the context of the current mental health burden, the authors wrote, in which the shortage of mental health professionals means that less than 30% of mental healthcare needs are being met.
They called for more measures to mitigate the excess burden of PMADs.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zivin had no conflicts of interest. Coauthor Dr. Dalton reported personal fees from Merck, the Society of Family Planning, Up to Date, and The Medical Letter outside of the submitted work.
Despite federal legislation improving healthcare access, concerted efforts are still needed to increase evidence-based treatment for maternal perinatal mental health issues, a large study of commercially insured mothers suggested. It found that federal legislation had variable and suboptimal effect on mental health services use by delivering mothers.
In the cross-sectional study, published in JAMA Network Open, psychotherapy receipt increased somewhat during 2007-2019 among all mothers and among those diagnosed with perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs). The timeline encompassed periods before and after passage of the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) of 2008 and the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) of 2010.
The investigators, led by Kara Zivin, PhD, MS, MFA, a professor of psychiatry in the University of Michigan’s School of Public Health at Ann Arbor, found the results varied by policy and between the overall delivering population and the PMAD population. “We did not find a statistically significant immediate change associated with the MHPAEA or ACA in the overall delivering population, except for a steady increase in delivering women who received any psychotherapy after ACA,” Dr. Zivin and colleagues wrote.
The researchers looked at private insurance data for 837,316 deliveries among 716,052 women (64.2% White), ages 15-44 (mean 31.2), to assess changes in psychotherapy visits in the year before and after delivery. They also estimated per-visit out-of-pocket costs for the ACA in 2014 and the MHPAEA in 2010.
In the PMAD population, the MHPAEA was associated with an immediate increase in psychotherapy receipt of 0.72% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.18%; P = .002), followed by a sustained decrease of 0.05% (95% CI, 0.09%-0.02%; P = .001).
In both populations, the ACA was associated with immediate and sustained monthly increases in use of 0.77% (95% CI, 0.26%-1.27%; P = .003) and 0.07% (95% CI, 0.02%-0.12%; P = .005), respectively.
Post MHPAEA, both populations experienced a slight decrease in per-visit monthly out-of-pocket costs, while after the ACA they saw an immediate and steady monthly increase in these.
Although both policies expanded access to any psychotherapy, the greater number of people receiving visits coincided with fewer visits per person, the authors noted. “One hypothesis suggests that the number of available mental health clinicians may not have increased enough to meet the new demand; future research should better characterize this trend,” they wrote.
In addition, a lower standard cost per visit may have dampened the incentive to increase the number of mental health clinicians, they conjectured. These factors could explain why the PMAD group appeared to experience a decrease in the proportion receiving any psychotherapy after the MHPAEA’s implementation.
The findings should be reviewed in the context of the current mental health burden, the authors wrote, in which the shortage of mental health professionals means that less than 30% of mental healthcare needs are being met.
They called for more measures to mitigate the excess burden of PMADs.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Zivin had no conflicts of interest. Coauthor Dr. Dalton reported personal fees from Merck, the Society of Family Planning, Up to Date, and The Medical Letter outside of the submitted work.
FROM JAMA NETWORK NEWS
How Clinicians Can Help Patients Navigate Psychedelics/Microdosing
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Can Addressing Depression Reduce Chemo Toxicity in Older Adults?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial to evaluate whether greater reductions in grade 3 chemotherapy-related toxicities occurred with geriatric assessment-driven interventions vs standard care.
- A total of 605 patients aged 65 years and older with any stage of solid malignancy were included, with 402 randomized to the intervention arm and 203 to the standard-of-care arm.
- Mental health was assessed using the Mental Health Inventory 13, and chemotherapy toxicity was graded by the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0.
- Patients in the intervention arm received recommendations from a multidisciplinary team based on their baseline GA, while those in the standard-of-care arm received only the baseline assessment results.
- The study was conducted at City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, and patients were followed throughout treatment or for up to 6 months from starting chemotherapy.
TAKEAWAY:
- According to the authors, patients with depression had increased chemotherapy toxicity in the standard-of-care arm (70.7% vs 54.3%; P = .02) but not in the GA-driven intervention arm (54.3% vs 48.5%; P = .27).
- The association between depression and chemotherapy toxicity was also seen after adjustment for the Cancer and Aging Research Group toxicity score (odds ratio, [OR], 1.98; 95% CI, 1.07-3.65) and for demographic, disease, and treatment factors (OR, 2.00; 95% CI, 1.03-3.85).
- No significant association was found between anxiety and chemotherapy toxicity in either the standard-of-care arm (univariate OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 0.61-1.88) or the GA-driven intervention arm (univariate OR, 1.15; 95% CI, 0.78-1.71).
- The authors stated that depression was associated with increased odds of hematologic-only toxicities (OR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.13-5.56) in the standard-of-care arm.
- An analysis of a small subgroup found associations between elevated anxiety symptoms and increased risk for hematologic and nonhematologic chemotherapy toxicities.
IN PRACTICE:
“The current study showed that elevated depression symptoms are associated with increased risk of severe chemotherapy toxicities in older adults with cancer. This risk was mitigated in those in the GA intervention arm, which suggests that addressing elevated depression symptoms may lower the risk of toxicities,” the authors wrote. “Overall, elevated anxiety symptoms were not associated with risk for severe chemotherapy toxicity.”
SOURCE:
Reena V. Jayani, MD, MSCI, of Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville, Tennessee, was the first and corresponding author for this paper. This study was published online August 4, 2024, in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
The thresholds for depression and anxiety used in the Mental Health Inventory 13 were based on an English-speaking population, which may not be fully applicable to Chinese- and Spanish-speaking patients included in the study. Depression and anxiety were not evaluated by a mental health professional or with a structured interview to assess formal diagnostic criteria. Psychiatric medication used at the time of baseline GA was not included in the analysis. The study is a secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial, and it is not known which components of the interventions affected mental health.
DISCLOSURES:
This research project was supported by the UniHealth Foundation, the City of Hope Center for Cancer and Aging, and the National Institutes of Health. One coauthor disclosed receiving institutional research funding from AstraZeneca and Brooklyn ImmunoTherapeutics and consulting for multiple pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Adagene, and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. William Dale, MD, PhD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, served as senior author and a principal investigator. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Electroconvulsive Therapy Works, Now Scientists Believe They Know How
For years, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has been a lifesaving treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD), yet exactly how it works has largely remained a mystery. Now researchers believe they have uncovered the underlying mechanisms behind its therapeutic effects — a discovery that may help clinicians better predict treatment response in individual patients and quell much of the fear and stigma associated with one of psychiatry’s most effective, yet misunderstood, treatments.
Two recent papers published in Translational Psychiatry have highlighted the significance of aperiodic neural activity. The first study showed this activity increased following ECT treatment. The second study expanded on these data by demonstrating a significant increase in aperiodic activity after patients received either ECT or magnetic seizure therapy (MST), which has a better side-effect profile than ECT but lower efficacy.
Aperiodic activity is “like the brain’s background noise, and for years scientists treated it that way and didn’t pay much attention to it,” first author Sydney E. Smith, a PhD candidate at the Voytek Lab in the Neuroscience Graduate Program at the University of California San Diego (UCSD), said in a press release.
However, aperiodic activity boosts inhibitory activity in the brain, effectively slowing it down,” the investigators noted.
In an interview with this news organization, Ms. Smith used a car analogy to explain the mechanism behind ECT. “ECT might be increasing the activity levels in the brain cells that help calm it down. It taps on the brakes that tend to malfunction in depression. By restoring the balance between the gas and the brakes in the brain, some of those depressive symptoms are alleviated,” she said.
Ms. Smith added her team’s research helps demystify one of the most effective yet stigmatized treatments for severe depression.
“Aperiodic activity as a physiologically interpretable EEG metric could be a really valuable new predictive indicator for treatment response,” she added.
Fear and Stigma
ECT is primarily used for TRD and is effective in up to 80% of patients, yet it remains one of the least prescribed treatments.
Although it’s been around for almost 90 years, fear and concern about its potential cognitive side effects have contributed to its poor uptake. It is estimated that less than 1% of patients with TRD receive ECT.
Smith noted that the 1970s movie One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest still contributes to ECT’s stigma. In the film, actor Jack Nicholson’s character is forced to undergo ECT as a punishment.
It’s important for clinicians to acknowledge the stigma while advising patients that “the actual treatment doesn’t look anything like what’s in the movies,” noted Ms. Smith. Patients must give informed consent for the procedure, and it’s delivered with the lowest level of effective stimulation.
“So many steps are taken to consider comfort and efficacy for patients and to minimize how scary it can be,” she said.
ECT uses an electrical current to induce a seizure that spreads to deep subcortical structures. MST, which was developed as an alternative to ECT, uses a magnetic field to induce a more focal seizure primarily confined to the cortex.
Although MST has a better side-effect profile, experts noted it has remission rates of 30%-60% compared with ECT. Even one of MST’s inventors, Harold Sackeim, PhD, professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, is skeptical about its efficacy for TRD.
“I don’t think it works,” Dr. Sackeim, founding editor of Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation, told this news organization.
In addition to being more expensive, MST produces a peak electrical intensity at one-tenth of what a typical ECT stimulus produces. “We’re limited by electrical engineering at this point with MST. That’s my view; others are more optimistic,” he said.
A Lifesaving Treatment
One of the reasons ECT isn’t more popular is because for many patients, it’s easier and more convenient to just take a pill, senior investigator Bradley Voytek, PhD, professor of cognitive science at UCSD, said in the release.
“However, in people for whom medications don’t work, [ECT] can be lifesaving. Understanding how it works will help us discover ways to increase the benefits while minimizing side effects,” he added.
In the first study, which included nine patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), EEG results showed an increase in aperiodic activity following ECT.
The investigators then wanted to test whether these findings could be replicated in a larger study. They retrospectively assessed two previous datasets — 1 of 22 patients with MDD who received ECT and 1 of 23 patients who received MST. After treatment, both groups showed increased aperiodic activity.
“Although not directly related to clinical efficacy in this dataset, increased aperiodic activity is linked to greater amounts of neural inhibition, which is suggestive of a potential shared neural mechanism of action across ECT and MST,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers noted that this increase in aperiodic activity is a more parsimonious explanation for observations of clinical slowing than delta band power or delta oscillations for both ECT and MST.”
So why is it important to know exactly how ECT works, and is there any clinical utility to these research findings?
“It’s important for clinicians to give a patient who has questions, a meaningful understanding of what the treatment is going to do, especially with something so scary and stigmatized. The ability to tell a patient why this treatment is working could provide a level of comfort that can assuage some of these fears,” Ms. Smith said.
A New Predictor of Response?
In addition, she noted that psychiatry is becoming more focused on predictive indicators for treatment.
“It’s asking: Are there any biological measures that can be used to predict whether someone is going to respond to a treatment or not?” said Ms. Smith.
“Aperiodic activity might be a valuable asset to add to that arsenal. Maybe we can better predict which patients might respond to ECT by using this as an additional biological indicator,” she added.
Smith noted that while more studies are needed, it’s exciting that some investigators are already starting to include aperiodic activity as a variable in their research analyses on a variety of topics, such as pharmacological intervention and transcranial magnetic stimulation.
“I don’t know exactly how much utility aperiodic activity is going to have in terms of being a great biological indicator, but I hope that the research will start to play out and reveal a little bit more,” she said.
Dr. Sackeim noted that ECT is one of the most misunderstood, controversial, and infrequently used treatments in psychiatry.
“But there’s also no doubt that when you look at ECT, it saves the lives of people with psychiatric illness. Period, full stop,” he said.
He added that although restarting a patient’s heart doesn’t seem to cause unease in the public, the idea of applying electricity to the brain under anesthesia in order to provoke a seizure for therapeutic purpose causes anxiety.
Still, the benefits and harms of a treatment are more important than how it looks, Sackeim said. “If it was only about how it looks, we’d never have surgery,” he added.
‘A Huge Success Story’
ECT was first introduced by Hungarian neuropsychiatrist László Meduna in 1935, and today clinicians “know where the current goes in the brain, at what dosage, and with what path you can get 70%, 80% fully remitted,” said Dr. Sackeim.
He noted that in a randomized study published in JAMA Psychiatry, investigators compared the outcomes of MST vs ECT for major depressive episodes in 73 patients. They reported that although depression symptom scores decreased for both treatments, there was “no significant difference” between the two in response or remission rates.
However, in an opinion letter the journal published in April, Dr. Sackeim and colleagues Mark S. George, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, and William V. McCall, MD, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, strongly questioned the findings.
At less than 30%, “the ECT remission rate after acute treatment was exceptionally low, limiting confidence in the validity and/or generalizability of the findings,” they wrote.
“It’s undoubtedly the case that either if you recruited a sample from whom the treatment may not be as efficacious or if there are issues in delivering them, then you may be finding equivalence” between ECT and MST, Dr. Sackeim said.
In addition, he noted that although there have been concerns about cognitive side effects with ECT, they have improved over the years. Sackeim reported that when he entered the field, the average time for a patient to remember their name or the day of the week was 6 hours after receiving unilateral ECT and 8 hours after bilateral ECT. “With modern methods, that’s now down to 10 minutes,” he said.
“The fundamental knowledge is that this treatment can be administered far softer than it ever was in the past. Impressions from the 50s and 60s and portrayed in movies have very little to do with modern practice and with the real effects of the treatment,” Dr. Sackeim said.
As for the new studies about aperiodic activity, the investigators are “essentially saying, ‘We have a better marker’ of the process. That way of thinking had in many ways been left behind in the run to study connectivity,” Dr. Sackeim said.
He noted that years ago, while he was with Columbia University, his team found that patients who had frontal inhibition were more likely to get well after ECT.
“And that’s essentially the same thing you’re hearing from the UCSD group. They’re saying that the aperiodic measure is hopefully of clearer physiological significance than simply delta [waves] in the EEG,” Dr. Sackeim said.
“The idea that inhibition was the key to its efficacy has been around. This is saying it’s a better measure of that, and that may be true. It’s certainly an interesting contribution,” he added.
Dr. Sackeim said the takeaway message for clinicians regarding ECT today is that it can be lifesaving but is still often only used as a last resort and reserved for those who have run out of options.
However, he said, ECT is “a huge success story: Maintaining its efficacy, reducing its side effects, getting an understanding as to what the physics of it are. We have some compelling stories about ECT, but even more so, we know what’s not true. And what’s not true are most of the assumptions people have about the treatment,” he concluded.
Ms. Smith and Dr. Voytek reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Sackeim reported holding patents in ECT technology and consulting with the MECTA Corporation and SigmaStim LLC and other neuromodulation companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For years, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has been a lifesaving treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD), yet exactly how it works has largely remained a mystery. Now researchers believe they have uncovered the underlying mechanisms behind its therapeutic effects — a discovery that may help clinicians better predict treatment response in individual patients and quell much of the fear and stigma associated with one of psychiatry’s most effective, yet misunderstood, treatments.
Two recent papers published in Translational Psychiatry have highlighted the significance of aperiodic neural activity. The first study showed this activity increased following ECT treatment. The second study expanded on these data by demonstrating a significant increase in aperiodic activity after patients received either ECT or magnetic seizure therapy (MST), which has a better side-effect profile than ECT but lower efficacy.
Aperiodic activity is “like the brain’s background noise, and for years scientists treated it that way and didn’t pay much attention to it,” first author Sydney E. Smith, a PhD candidate at the Voytek Lab in the Neuroscience Graduate Program at the University of California San Diego (UCSD), said in a press release.
However, aperiodic activity boosts inhibitory activity in the brain, effectively slowing it down,” the investigators noted.
In an interview with this news organization, Ms. Smith used a car analogy to explain the mechanism behind ECT. “ECT might be increasing the activity levels in the brain cells that help calm it down. It taps on the brakes that tend to malfunction in depression. By restoring the balance between the gas and the brakes in the brain, some of those depressive symptoms are alleviated,” she said.
Ms. Smith added her team’s research helps demystify one of the most effective yet stigmatized treatments for severe depression.
“Aperiodic activity as a physiologically interpretable EEG metric could be a really valuable new predictive indicator for treatment response,” she added.
Fear and Stigma
ECT is primarily used for TRD and is effective in up to 80% of patients, yet it remains one of the least prescribed treatments.
Although it’s been around for almost 90 years, fear and concern about its potential cognitive side effects have contributed to its poor uptake. It is estimated that less than 1% of patients with TRD receive ECT.
Smith noted that the 1970s movie One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest still contributes to ECT’s stigma. In the film, actor Jack Nicholson’s character is forced to undergo ECT as a punishment.
It’s important for clinicians to acknowledge the stigma while advising patients that “the actual treatment doesn’t look anything like what’s in the movies,” noted Ms. Smith. Patients must give informed consent for the procedure, and it’s delivered with the lowest level of effective stimulation.
“So many steps are taken to consider comfort and efficacy for patients and to minimize how scary it can be,” she said.
ECT uses an electrical current to induce a seizure that spreads to deep subcortical structures. MST, which was developed as an alternative to ECT, uses a magnetic field to induce a more focal seizure primarily confined to the cortex.
Although MST has a better side-effect profile, experts noted it has remission rates of 30%-60% compared with ECT. Even one of MST’s inventors, Harold Sackeim, PhD, professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, is skeptical about its efficacy for TRD.
“I don’t think it works,” Dr. Sackeim, founding editor of Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation, told this news organization.
In addition to being more expensive, MST produces a peak electrical intensity at one-tenth of what a typical ECT stimulus produces. “We’re limited by electrical engineering at this point with MST. That’s my view; others are more optimistic,” he said.
A Lifesaving Treatment
One of the reasons ECT isn’t more popular is because for many patients, it’s easier and more convenient to just take a pill, senior investigator Bradley Voytek, PhD, professor of cognitive science at UCSD, said in the release.
“However, in people for whom medications don’t work, [ECT] can be lifesaving. Understanding how it works will help us discover ways to increase the benefits while minimizing side effects,” he added.
In the first study, which included nine patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), EEG results showed an increase in aperiodic activity following ECT.
The investigators then wanted to test whether these findings could be replicated in a larger study. They retrospectively assessed two previous datasets — 1 of 22 patients with MDD who received ECT and 1 of 23 patients who received MST. After treatment, both groups showed increased aperiodic activity.
“Although not directly related to clinical efficacy in this dataset, increased aperiodic activity is linked to greater amounts of neural inhibition, which is suggestive of a potential shared neural mechanism of action across ECT and MST,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers noted that this increase in aperiodic activity is a more parsimonious explanation for observations of clinical slowing than delta band power or delta oscillations for both ECT and MST.”
So why is it important to know exactly how ECT works, and is there any clinical utility to these research findings?
“It’s important for clinicians to give a patient who has questions, a meaningful understanding of what the treatment is going to do, especially with something so scary and stigmatized. The ability to tell a patient why this treatment is working could provide a level of comfort that can assuage some of these fears,” Ms. Smith said.
A New Predictor of Response?
In addition, she noted that psychiatry is becoming more focused on predictive indicators for treatment.
“It’s asking: Are there any biological measures that can be used to predict whether someone is going to respond to a treatment or not?” said Ms. Smith.
“Aperiodic activity might be a valuable asset to add to that arsenal. Maybe we can better predict which patients might respond to ECT by using this as an additional biological indicator,” she added.
Smith noted that while more studies are needed, it’s exciting that some investigators are already starting to include aperiodic activity as a variable in their research analyses on a variety of topics, such as pharmacological intervention and transcranial magnetic stimulation.
“I don’t know exactly how much utility aperiodic activity is going to have in terms of being a great biological indicator, but I hope that the research will start to play out and reveal a little bit more,” she said.
Dr. Sackeim noted that ECT is one of the most misunderstood, controversial, and infrequently used treatments in psychiatry.
“But there’s also no doubt that when you look at ECT, it saves the lives of people with psychiatric illness. Period, full stop,” he said.
He added that although restarting a patient’s heart doesn’t seem to cause unease in the public, the idea of applying electricity to the brain under anesthesia in order to provoke a seizure for therapeutic purpose causes anxiety.
Still, the benefits and harms of a treatment are more important than how it looks, Sackeim said. “If it was only about how it looks, we’d never have surgery,” he added.
‘A Huge Success Story’
ECT was first introduced by Hungarian neuropsychiatrist László Meduna in 1935, and today clinicians “know where the current goes in the brain, at what dosage, and with what path you can get 70%, 80% fully remitted,” said Dr. Sackeim.
He noted that in a randomized study published in JAMA Psychiatry, investigators compared the outcomes of MST vs ECT for major depressive episodes in 73 patients. They reported that although depression symptom scores decreased for both treatments, there was “no significant difference” between the two in response or remission rates.
However, in an opinion letter the journal published in April, Dr. Sackeim and colleagues Mark S. George, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, and William V. McCall, MD, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, strongly questioned the findings.
At less than 30%, “the ECT remission rate after acute treatment was exceptionally low, limiting confidence in the validity and/or generalizability of the findings,” they wrote.
“It’s undoubtedly the case that either if you recruited a sample from whom the treatment may not be as efficacious or if there are issues in delivering them, then you may be finding equivalence” between ECT and MST, Dr. Sackeim said.
In addition, he noted that although there have been concerns about cognitive side effects with ECT, they have improved over the years. Sackeim reported that when he entered the field, the average time for a patient to remember their name or the day of the week was 6 hours after receiving unilateral ECT and 8 hours after bilateral ECT. “With modern methods, that’s now down to 10 minutes,” he said.
“The fundamental knowledge is that this treatment can be administered far softer than it ever was in the past. Impressions from the 50s and 60s and portrayed in movies have very little to do with modern practice and with the real effects of the treatment,” Dr. Sackeim said.
As for the new studies about aperiodic activity, the investigators are “essentially saying, ‘We have a better marker’ of the process. That way of thinking had in many ways been left behind in the run to study connectivity,” Dr. Sackeim said.
He noted that years ago, while he was with Columbia University, his team found that patients who had frontal inhibition were more likely to get well after ECT.
“And that’s essentially the same thing you’re hearing from the UCSD group. They’re saying that the aperiodic measure is hopefully of clearer physiological significance than simply delta [waves] in the EEG,” Dr. Sackeim said.
“The idea that inhibition was the key to its efficacy has been around. This is saying it’s a better measure of that, and that may be true. It’s certainly an interesting contribution,” he added.
Dr. Sackeim said the takeaway message for clinicians regarding ECT today is that it can be lifesaving but is still often only used as a last resort and reserved for those who have run out of options.
However, he said, ECT is “a huge success story: Maintaining its efficacy, reducing its side effects, getting an understanding as to what the physics of it are. We have some compelling stories about ECT, but even more so, we know what’s not true. And what’s not true are most of the assumptions people have about the treatment,” he concluded.
Ms. Smith and Dr. Voytek reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Sackeim reported holding patents in ECT technology and consulting with the MECTA Corporation and SigmaStim LLC and other neuromodulation companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For years, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has been a lifesaving treatment for patients with treatment-resistant depression (TRD), yet exactly how it works has largely remained a mystery. Now researchers believe they have uncovered the underlying mechanisms behind its therapeutic effects — a discovery that may help clinicians better predict treatment response in individual patients and quell much of the fear and stigma associated with one of psychiatry’s most effective, yet misunderstood, treatments.
Two recent papers published in Translational Psychiatry have highlighted the significance of aperiodic neural activity. The first study showed this activity increased following ECT treatment. The second study expanded on these data by demonstrating a significant increase in aperiodic activity after patients received either ECT or magnetic seizure therapy (MST), which has a better side-effect profile than ECT but lower efficacy.
Aperiodic activity is “like the brain’s background noise, and for years scientists treated it that way and didn’t pay much attention to it,” first author Sydney E. Smith, a PhD candidate at the Voytek Lab in the Neuroscience Graduate Program at the University of California San Diego (UCSD), said in a press release.
However, aperiodic activity boosts inhibitory activity in the brain, effectively slowing it down,” the investigators noted.
In an interview with this news organization, Ms. Smith used a car analogy to explain the mechanism behind ECT. “ECT might be increasing the activity levels in the brain cells that help calm it down. It taps on the brakes that tend to malfunction in depression. By restoring the balance between the gas and the brakes in the brain, some of those depressive symptoms are alleviated,” she said.
Ms. Smith added her team’s research helps demystify one of the most effective yet stigmatized treatments for severe depression.
“Aperiodic activity as a physiologically interpretable EEG metric could be a really valuable new predictive indicator for treatment response,” she added.
Fear and Stigma
ECT is primarily used for TRD and is effective in up to 80% of patients, yet it remains one of the least prescribed treatments.
Although it’s been around for almost 90 years, fear and concern about its potential cognitive side effects have contributed to its poor uptake. It is estimated that less than 1% of patients with TRD receive ECT.
Smith noted that the 1970s movie One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest still contributes to ECT’s stigma. In the film, actor Jack Nicholson’s character is forced to undergo ECT as a punishment.
It’s important for clinicians to acknowledge the stigma while advising patients that “the actual treatment doesn’t look anything like what’s in the movies,” noted Ms. Smith. Patients must give informed consent for the procedure, and it’s delivered with the lowest level of effective stimulation.
“So many steps are taken to consider comfort and efficacy for patients and to minimize how scary it can be,” she said.
ECT uses an electrical current to induce a seizure that spreads to deep subcortical structures. MST, which was developed as an alternative to ECT, uses a magnetic field to induce a more focal seizure primarily confined to the cortex.
Although MST has a better side-effect profile, experts noted it has remission rates of 30%-60% compared with ECT. Even one of MST’s inventors, Harold Sackeim, PhD, professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, is skeptical about its efficacy for TRD.
“I don’t think it works,” Dr. Sackeim, founding editor of Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation, told this news organization.
In addition to being more expensive, MST produces a peak electrical intensity at one-tenth of what a typical ECT stimulus produces. “We’re limited by electrical engineering at this point with MST. That’s my view; others are more optimistic,” he said.
A Lifesaving Treatment
One of the reasons ECT isn’t more popular is because for many patients, it’s easier and more convenient to just take a pill, senior investigator Bradley Voytek, PhD, professor of cognitive science at UCSD, said in the release.
“However, in people for whom medications don’t work, [ECT] can be lifesaving. Understanding how it works will help us discover ways to increase the benefits while minimizing side effects,” he added.
In the first study, which included nine patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), EEG results showed an increase in aperiodic activity following ECT.
The investigators then wanted to test whether these findings could be replicated in a larger study. They retrospectively assessed two previous datasets — 1 of 22 patients with MDD who received ECT and 1 of 23 patients who received MST. After treatment, both groups showed increased aperiodic activity.
“Although not directly related to clinical efficacy in this dataset, increased aperiodic activity is linked to greater amounts of neural inhibition, which is suggestive of a potential shared neural mechanism of action across ECT and MST,” the investigators wrote.
The researchers noted that this increase in aperiodic activity is a more parsimonious explanation for observations of clinical slowing than delta band power or delta oscillations for both ECT and MST.”
So why is it important to know exactly how ECT works, and is there any clinical utility to these research findings?
“It’s important for clinicians to give a patient who has questions, a meaningful understanding of what the treatment is going to do, especially with something so scary and stigmatized. The ability to tell a patient why this treatment is working could provide a level of comfort that can assuage some of these fears,” Ms. Smith said.
A New Predictor of Response?
In addition, she noted that psychiatry is becoming more focused on predictive indicators for treatment.
“It’s asking: Are there any biological measures that can be used to predict whether someone is going to respond to a treatment or not?” said Ms. Smith.
“Aperiodic activity might be a valuable asset to add to that arsenal. Maybe we can better predict which patients might respond to ECT by using this as an additional biological indicator,” she added.
Smith noted that while more studies are needed, it’s exciting that some investigators are already starting to include aperiodic activity as a variable in their research analyses on a variety of topics, such as pharmacological intervention and transcranial magnetic stimulation.
“I don’t know exactly how much utility aperiodic activity is going to have in terms of being a great biological indicator, but I hope that the research will start to play out and reveal a little bit more,” she said.
Dr. Sackeim noted that ECT is one of the most misunderstood, controversial, and infrequently used treatments in psychiatry.
“But there’s also no doubt that when you look at ECT, it saves the lives of people with psychiatric illness. Period, full stop,” he said.
He added that although restarting a patient’s heart doesn’t seem to cause unease in the public, the idea of applying electricity to the brain under anesthesia in order to provoke a seizure for therapeutic purpose causes anxiety.
Still, the benefits and harms of a treatment are more important than how it looks, Sackeim said. “If it was only about how it looks, we’d never have surgery,” he added.
‘A Huge Success Story’
ECT was first introduced by Hungarian neuropsychiatrist László Meduna in 1935, and today clinicians “know where the current goes in the brain, at what dosage, and with what path you can get 70%, 80% fully remitted,” said Dr. Sackeim.
He noted that in a randomized study published in JAMA Psychiatry, investigators compared the outcomes of MST vs ECT for major depressive episodes in 73 patients. They reported that although depression symptom scores decreased for both treatments, there was “no significant difference” between the two in response or remission rates.
However, in an opinion letter the journal published in April, Dr. Sackeim and colleagues Mark S. George, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, and William V. McCall, MD, Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, strongly questioned the findings.
At less than 30%, “the ECT remission rate after acute treatment was exceptionally low, limiting confidence in the validity and/or generalizability of the findings,” they wrote.
“It’s undoubtedly the case that either if you recruited a sample from whom the treatment may not be as efficacious or if there are issues in delivering them, then you may be finding equivalence” between ECT and MST, Dr. Sackeim said.
In addition, he noted that although there have been concerns about cognitive side effects with ECT, they have improved over the years. Sackeim reported that when he entered the field, the average time for a patient to remember their name or the day of the week was 6 hours after receiving unilateral ECT and 8 hours after bilateral ECT. “With modern methods, that’s now down to 10 minutes,” he said.
“The fundamental knowledge is that this treatment can be administered far softer than it ever was in the past. Impressions from the 50s and 60s and portrayed in movies have very little to do with modern practice and with the real effects of the treatment,” Dr. Sackeim said.
As for the new studies about aperiodic activity, the investigators are “essentially saying, ‘We have a better marker’ of the process. That way of thinking had in many ways been left behind in the run to study connectivity,” Dr. Sackeim said.
He noted that years ago, while he was with Columbia University, his team found that patients who had frontal inhibition were more likely to get well after ECT.
“And that’s essentially the same thing you’re hearing from the UCSD group. They’re saying that the aperiodic measure is hopefully of clearer physiological significance than simply delta [waves] in the EEG,” Dr. Sackeim said.
“The idea that inhibition was the key to its efficacy has been around. This is saying it’s a better measure of that, and that may be true. It’s certainly an interesting contribution,” he added.
Dr. Sackeim said the takeaway message for clinicians regarding ECT today is that it can be lifesaving but is still often only used as a last resort and reserved for those who have run out of options.
However, he said, ECT is “a huge success story: Maintaining its efficacy, reducing its side effects, getting an understanding as to what the physics of it are. We have some compelling stories about ECT, but even more so, we know what’s not true. And what’s not true are most of the assumptions people have about the treatment,” he concluded.
Ms. Smith and Dr. Voytek reported no relevant conflicts of interest. Dr. Sackeim reported holding patents in ECT technology and consulting with the MECTA Corporation and SigmaStim LLC and other neuromodulation companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.