User login
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Atypical Intrathoracic Manifestations of Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Series
Atypical Intrathoracic Manifestations of Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Series
Prostate cancer is the most common noncutaneous cancer in men, accounting for 29% of all incident cancer cases.1 Typically, prostate cancer metastasizes to bone and regional lymph nodes.2 However, intrathoracic manifestation may occur. This report presents 3 cases of rare intrathoracic manifestations of metastatic prostate cancer with a review of the current literature.
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
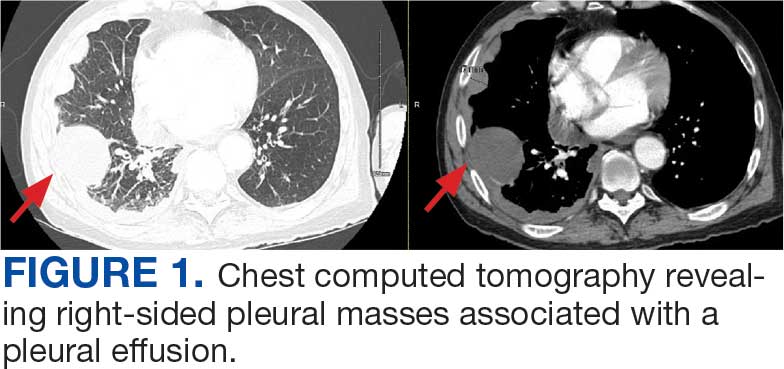
A 71-year-old male who was an active smoker and a long-standing employment as a plumber was diagnosed with rectal cancer in 2022. He completed neoadjuvant capecitabine and radiation therapy followed by a rectosigmoidectomy. Several weeks after surgery, the patient presented to the emergency department (ED) with a dry cough and worsening shortness of breath. Point-of-care ultrasound of the lungs revealed a moderate right pleural effusion with several nodular pleural masses. A chest computed tomography (CT) confirmed these findings (Figure 1). A CT of the abdomen and pelvis revealed prostatomegaly with the medial lobe of the prostate protruding into the bladder; however, no enlarged retroperitoneal, mesenteric or pelvic lymph nodes were noted. The patient underwent a right pleural fluid drainage and pleural mass biopsy. Pleural mass histomorphology as well as immunohistochemical (IHC) stains were consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. The pleural fluid cytology also was consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma.
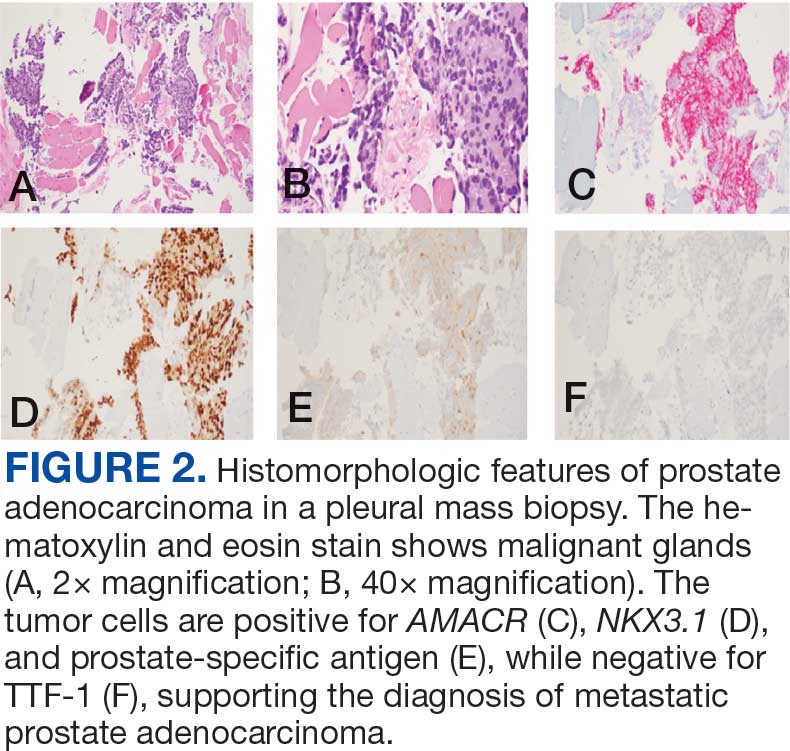
Immunohistochemistry showed weak positive staining for prostate-specific NK3 homeobox 1 gene (NKX3.1), alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase gene (AMACR), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), keratin-20, and caudal type homeobox 2 gene (CDX2) (Figure 2) 2). The patient's prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was found to be elevated at 33.9 ng/mL (reference range, < 4 ng/mL).
Case 2
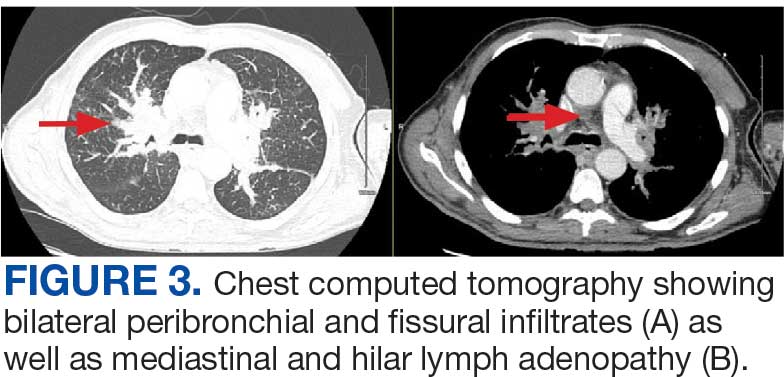
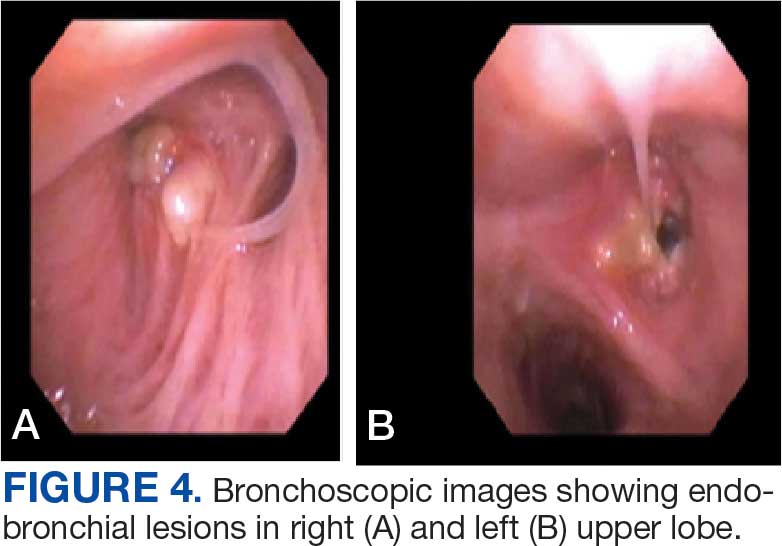
A 71-year-old male with a history of alcohol use disorder and a 30-year smoking history presented to the ED with worsening dyspnea on exertion. The patient’s baseline exercise tolerance decreased to walking for only 1 block. He reported unintentional weight loss of about 30 pounds over the prior year, no recent respiratory infections, no prior breathing problems, and no personal or family history of cancer. Chest CT revealed findings of bilateral peribronchial opacities as well as mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy (Figure 3). The patient developed hypoxic respiratory failure necessitating intubation, mechanical ventilation, and management in the medical intensive care unit, where he was treated for postobstructive pneumonia. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed endobronchial lesions in the right and left upper lobe that were partially obstructing the airway (Figure 4).
The endobronchial masses were debulked using forceps, and samples were sent for surgical pathology evaluation. Staging was completed using linear endobronchial ultrasound, which revealed an enlarged subcarinal lymph node (S7). The surgical pathology of the endobronchial mass and the subcarinal lymph node cytology were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The tumor cells were positive for AE1/AE3, PSA, and NKX3.1, but were negative for CK7 and TTF-1 (Figure 5). Further imaging revealed an enlarged heterogeneous prostate gland, prominent pelvic nodes, and left retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy, as well as sclerotic foci within the T10 vertebral body and right inferior pubic ramus. PSA was also found to be significantly elevated at 700 ng/mL.
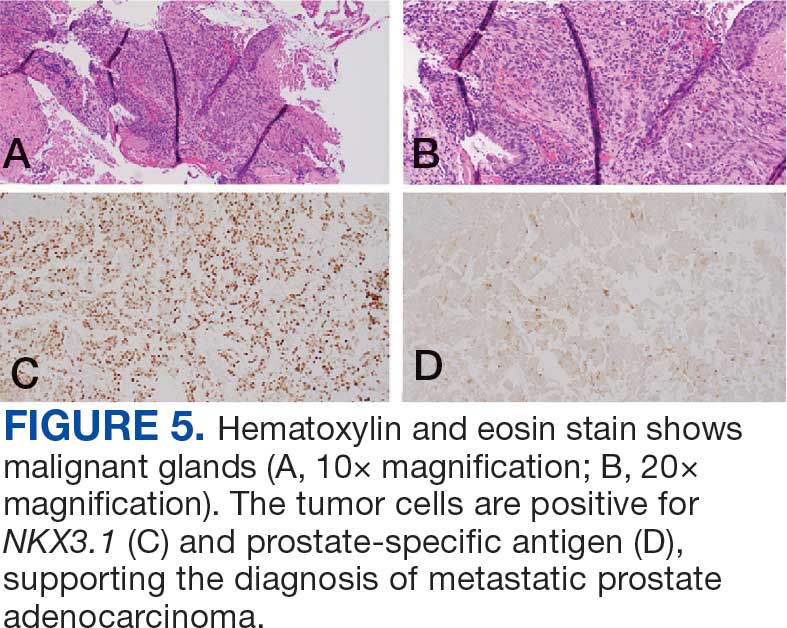
Case 3
An 80-year-old male veteran with a history of prostate cancer and recently diagnosed T2N1M0 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma was referred to the Pulmonary service for evaluation of a pulmonary nodule. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer diagnosed 12 years earlier, with an unknown Gleason score. Initial treatment included prostatectomy followed by whole pelvic radiation therapy a year after, due to elevated PSA in surveillance monitoring. This treatment led to remission. After establishing remission for > 10 years, the patient was started on low-dose testosterone replacement therapy to address complications of radiation therapy, namely hypogonadism.
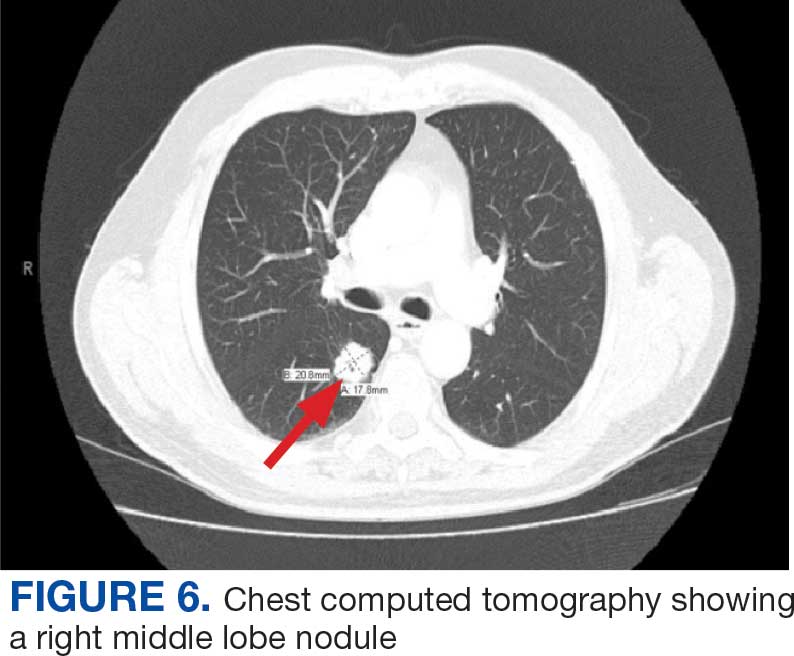
On evaluation, a chest CT was significant for a large 2-cm right middle lobe nodule (Figure 6). At that time, PSA was noted to be borderline elevated at 4.2 ng/mL, and whole-body imaging did not reveal any lesions elsewhere, specifically no bone metastasis. Biopsies of the right middle lobe lung nodule revealed adenocarcinoma consistent with metastatic prostate cancer. Testosterone therapy was promptly discontinued.
The patient initially refused androgen deprivation therapy owing to the antiandrogenic adverse effects. However, subsequent chest CTs revealed growing lung nodules, which convinced him to proceed with androgen deprivation therapy followed by palliative radiation, and chemotherapy and management of malignant pleural effusion with indwelling small bore pleural catheter for about 10 years. He died from COVID-19 during the pandemic.
DISCUSSION
These cases highlight the importance of including prostate cancer in the differential diagnoses of male patients with intrathoracic abnormalities, even in the absence of metastasis to the more common sites. In a large cohort study of 74,826 patients with metastatic prostate cancer, Gandaglia et al found that the most frequent sites of metastasis were bone (84.0%) and distant lymph nodes (10.6%).2 However, thoracic involvement was observed in 9.1% of cases, with isolated thoracic metastasis being rare. The cases described in this report exemplify exceptionally uncommon occurrences within that 9.1%.
Pleural metastases, as observed in Case 1, are a particularly rare manifestation. In a 10-year retrospective assessment, Vinjamoori et al discovered pleural nodules or masses in only 6 of 82 patients (7.3%) with atypical metastases.3 Adrenal and liver metastases accounted for 15% and 37% of cases with atypical distribution. As such, isolated pleural disease is rare even in atypical presentations.3
As seen in Case 2, endobronchial metastases producing airway obstruction are also rare, with the most common primary cancers associated with endobronchial metastasis being breast, colon, and renal cancer.4 The available literature on this presentation is confined to case reports. Hameed et al reported a case of synchronous biopsy-proven endobronchial metastasis from prostate cancer.5 These cases highlight the importance of maintaining a high level of clinical awareness when encountering endobronchial lesions in patients with prostate cancer.
Case 3 presents a unique situation of lung metastases without any involvement of the bones. It is well known—and was confirmed by Heidenreich et al—that lung metastases in prostate adenocarcinoma usually coincide with extensive osseous disease.6 This instance highlights the importance of watchful monitoring for unusual patterns of cancer recurrence.
Immunohistochemistry stains that are specific to prostate cancer include antibodies against PSA. Prostate-specific membrane antigen is another marker that is far more present in malignant than in benign prostate tissue.
The NKX3.1 gene encodes a homeobox protein, which is a transcription factor and tumor suppressor. In prostate cancer, there is loss of heterozygosity of the gene and stains for the IHC antibody to NKX3.1.7
On the other hand, lung cells stain positive for TTF-1, which is produced by surfactant-producing type 2 pneumocytes and club cells in the lung. Antibodies to TTF-1, a common IHC stain, are used to identify adenocarcinoma of lung origin and may carry a prognostic value.7
The immunohistochemistry profiles, specifically the presence of prostate-specific markers such as PSA and NKX3.1, played a vital role in making the diagnosis.
In Case 1, weak TTF-1 positivity was noted, an unusual finding in metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. Marak et al documented a rare case of TTF-1–positive metastatic prostate cancer, illustrating the potential for diagnostic confusion with primary lung malignancies.8
The 3 cases described in this report demonstrate the importance of clinical consideration, serial follow-up of PSA levels, using more prostate-specific positron emission tomography tracers (eg, Pylarify) alongside traditional imaging, and tissue biopsy to detect unusual metastases.
CONCLUSIONS
Although thoracic metastases from prostate cancer are rare, these presentations highlight the importance of clinical awareness regarding atypical cases. Pleural disease, endobronchial lesions, and isolated pulmonary nodules might be the first clinical manifestation of metastatic prostate cancer. A high index of suspicion, appropriate imaging, and judicious use of immunohistochemistry are important to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal patient management.
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Gandaglia G, Abdollah F, Schiffmann J, et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in patients with prostate cancer: a population-based analysis. Prostate. 2014;74(2):210-216. doi:10.1002/pros.22742
- Vinjamoori AH, Jagannathan JP, Shinagare AB, et al. Atypical metastases from prostate cancer: 10-year experience at a single institution. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(2):367-372. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7533
- Salud A, Porcel JM, Rovirosa A, Bellmunt J. Endobronchial metastatic disease: analysis of 32 cases. J Surg Oncol. 1996;62(4):249-252. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096- 9098(199608)62:4<249::AID-JSO4>3.0.CO;2-6
- Hameed M, Haq IU, Yousaf M, Hussein M, Rashid U, Al-Bozom I. Endobronchial metastases secondary to prostate cancer: a case report and literature review. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020;32:101326. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101326
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, et al; for the European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration- resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65(2):467- 479. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.002
- Schallenberg S, Dernbach G, Dragomir MP, et al. TTF-1 status in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is an independent predictor of relapse and survival superior to tumor grading. Eur J Cancer. 2024;197:113474. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113474
- Marak C, Guddati AK, Ashraf A, Smith J, Kaushik P. Prostate adenocarcinoma with atypical immunohistochemistry presenting with a Cheerio sign. AIM Clinical Cases. 2023;1:e220508. doi:10.7326/aimcc.2022.0508
Prostate cancer is the most common noncutaneous cancer in men, accounting for 29% of all incident cancer cases.1 Typically, prostate cancer metastasizes to bone and regional lymph nodes.2 However, intrathoracic manifestation may occur. This report presents 3 cases of rare intrathoracic manifestations of metastatic prostate cancer with a review of the current literature.
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
A 71-year-old male who was an active smoker and a long-standing employment as a plumber was diagnosed with rectal cancer in 2022. He completed neoadjuvant capecitabine and radiation therapy followed by a rectosigmoidectomy. Several weeks after surgery, the patient presented to the emergency department (ED) with a dry cough and worsening shortness of breath. Point-of-care ultrasound of the lungs revealed a moderate right pleural effusion with several nodular pleural masses. A chest computed tomography (CT) confirmed these findings (Figure 1). A CT of the abdomen and pelvis revealed prostatomegaly with the medial lobe of the prostate protruding into the bladder; however, no enlarged retroperitoneal, mesenteric or pelvic lymph nodes were noted. The patient underwent a right pleural fluid drainage and pleural mass biopsy. Pleural mass histomorphology as well as immunohistochemical (IHC) stains were consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. The pleural fluid cytology also was consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma.

Immunohistochemistry showed weak positive staining for prostate-specific NK3 homeobox 1 gene (NKX3.1), alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase gene (AMACR), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), keratin-20, and caudal type homeobox 2 gene (CDX2) (Figure 2) 2). The patient's prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was found to be elevated at 33.9 ng/mL (reference range, < 4 ng/mL).

Case 2
A 71-year-old male with a history of alcohol use disorder and a 30-year smoking history presented to the ED with worsening dyspnea on exertion. The patient’s baseline exercise tolerance decreased to walking for only 1 block. He reported unintentional weight loss of about 30 pounds over the prior year, no recent respiratory infections, no prior breathing problems, and no personal or family history of cancer. Chest CT revealed findings of bilateral peribronchial opacities as well as mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy (Figure 3). The patient developed hypoxic respiratory failure necessitating intubation, mechanical ventilation, and management in the medical intensive care unit, where he was treated for postobstructive pneumonia. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed endobronchial lesions in the right and left upper lobe that were partially obstructing the airway (Figure 4).


The endobronchial masses were debulked using forceps, and samples were sent for surgical pathology evaluation. Staging was completed using linear endobronchial ultrasound, which revealed an enlarged subcarinal lymph node (S7). The surgical pathology of the endobronchial mass and the subcarinal lymph node cytology were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The tumor cells were positive for AE1/AE3, PSA, and NKX3.1, but were negative for CK7 and TTF-1 (Figure 5). Further imaging revealed an enlarged heterogeneous prostate gland, prominent pelvic nodes, and left retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy, as well as sclerotic foci within the T10 vertebral body and right inferior pubic ramus. PSA was also found to be significantly elevated at 700 ng/mL.

Case 3
An 80-year-old male veteran with a history of prostate cancer and recently diagnosed T2N1M0 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma was referred to the Pulmonary service for evaluation of a pulmonary nodule. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer diagnosed 12 years earlier, with an unknown Gleason score. Initial treatment included prostatectomy followed by whole pelvic radiation therapy a year after, due to elevated PSA in surveillance monitoring. This treatment led to remission. After establishing remission for > 10 years, the patient was started on low-dose testosterone replacement therapy to address complications of radiation therapy, namely hypogonadism.
On evaluation, a chest CT was significant for a large 2-cm right middle lobe nodule (Figure 6). At that time, PSA was noted to be borderline elevated at 4.2 ng/mL, and whole-body imaging did not reveal any lesions elsewhere, specifically no bone metastasis. Biopsies of the right middle lobe lung nodule revealed adenocarcinoma consistent with metastatic prostate cancer. Testosterone therapy was promptly discontinued.

The patient initially refused androgen deprivation therapy owing to the antiandrogenic adverse effects. However, subsequent chest CTs revealed growing lung nodules, which convinced him to proceed with androgen deprivation therapy followed by palliative radiation, and chemotherapy and management of malignant pleural effusion with indwelling small bore pleural catheter for about 10 years. He died from COVID-19 during the pandemic.
DISCUSSION
These cases highlight the importance of including prostate cancer in the differential diagnoses of male patients with intrathoracic abnormalities, even in the absence of metastasis to the more common sites. In a large cohort study of 74,826 patients with metastatic prostate cancer, Gandaglia et al found that the most frequent sites of metastasis were bone (84.0%) and distant lymph nodes (10.6%).2 However, thoracic involvement was observed in 9.1% of cases, with isolated thoracic metastasis being rare. The cases described in this report exemplify exceptionally uncommon occurrences within that 9.1%.
Pleural metastases, as observed in Case 1, are a particularly rare manifestation. In a 10-year retrospective assessment, Vinjamoori et al discovered pleural nodules or masses in only 6 of 82 patients (7.3%) with atypical metastases.3 Adrenal and liver metastases accounted for 15% and 37% of cases with atypical distribution. As such, isolated pleural disease is rare even in atypical presentations.3
As seen in Case 2, endobronchial metastases producing airway obstruction are also rare, with the most common primary cancers associated with endobronchial metastasis being breast, colon, and renal cancer.4 The available literature on this presentation is confined to case reports. Hameed et al reported a case of synchronous biopsy-proven endobronchial metastasis from prostate cancer.5 These cases highlight the importance of maintaining a high level of clinical awareness when encountering endobronchial lesions in patients with prostate cancer.
Case 3 presents a unique situation of lung metastases without any involvement of the bones. It is well known—and was confirmed by Heidenreich et al—that lung metastases in prostate adenocarcinoma usually coincide with extensive osseous disease.6 This instance highlights the importance of watchful monitoring for unusual patterns of cancer recurrence.
Immunohistochemistry stains that are specific to prostate cancer include antibodies against PSA. Prostate-specific membrane antigen is another marker that is far more present in malignant than in benign prostate tissue.
The NKX3.1 gene encodes a homeobox protein, which is a transcription factor and tumor suppressor. In prostate cancer, there is loss of heterozygosity of the gene and stains for the IHC antibody to NKX3.1.7
On the other hand, lung cells stain positive for TTF-1, which is produced by surfactant-producing type 2 pneumocytes and club cells in the lung. Antibodies to TTF-1, a common IHC stain, are used to identify adenocarcinoma of lung origin and may carry a prognostic value.7
The immunohistochemistry profiles, specifically the presence of prostate-specific markers such as PSA and NKX3.1, played a vital role in making the diagnosis.
In Case 1, weak TTF-1 positivity was noted, an unusual finding in metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. Marak et al documented a rare case of TTF-1–positive metastatic prostate cancer, illustrating the potential for diagnostic confusion with primary lung malignancies.8
The 3 cases described in this report demonstrate the importance of clinical consideration, serial follow-up of PSA levels, using more prostate-specific positron emission tomography tracers (eg, Pylarify) alongside traditional imaging, and tissue biopsy to detect unusual metastases.
CONCLUSIONS
Although thoracic metastases from prostate cancer are rare, these presentations highlight the importance of clinical awareness regarding atypical cases. Pleural disease, endobronchial lesions, and isolated pulmonary nodules might be the first clinical manifestation of metastatic prostate cancer. A high index of suspicion, appropriate imaging, and judicious use of immunohistochemistry are important to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal patient management.
Prostate cancer is the most common noncutaneous cancer in men, accounting for 29% of all incident cancer cases.1 Typically, prostate cancer metastasizes to bone and regional lymph nodes.2 However, intrathoracic manifestation may occur. This report presents 3 cases of rare intrathoracic manifestations of metastatic prostate cancer with a review of the current literature.
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
A 71-year-old male who was an active smoker and a long-standing employment as a plumber was diagnosed with rectal cancer in 2022. He completed neoadjuvant capecitabine and radiation therapy followed by a rectosigmoidectomy. Several weeks after surgery, the patient presented to the emergency department (ED) with a dry cough and worsening shortness of breath. Point-of-care ultrasound of the lungs revealed a moderate right pleural effusion with several nodular pleural masses. A chest computed tomography (CT) confirmed these findings (Figure 1). A CT of the abdomen and pelvis revealed prostatomegaly with the medial lobe of the prostate protruding into the bladder; however, no enlarged retroperitoneal, mesenteric or pelvic lymph nodes were noted. The patient underwent a right pleural fluid drainage and pleural mass biopsy. Pleural mass histomorphology as well as immunohistochemical (IHC) stains were consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. The pleural fluid cytology also was consistent with metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma.

Immunohistochemistry showed weak positive staining for prostate-specific NK3 homeobox 1 gene (NKX3.1), alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase gene (AMACR), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), and prosaposin, and negative transcription termination factor (TTF-1), keratin-7 (CK7), keratin-20, and caudal type homeobox 2 gene (CDX2) (Figure 2) 2). The patient's prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was found to be elevated at 33.9 ng/mL (reference range, < 4 ng/mL).

Case 2
A 71-year-old male with a history of alcohol use disorder and a 30-year smoking history presented to the ED with worsening dyspnea on exertion. The patient’s baseline exercise tolerance decreased to walking for only 1 block. He reported unintentional weight loss of about 30 pounds over the prior year, no recent respiratory infections, no prior breathing problems, and no personal or family history of cancer. Chest CT revealed findings of bilateral peribronchial opacities as well as mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy (Figure 3). The patient developed hypoxic respiratory failure necessitating intubation, mechanical ventilation, and management in the medical intensive care unit, where he was treated for postobstructive pneumonia. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed endobronchial lesions in the right and left upper lobe that were partially obstructing the airway (Figure 4).


The endobronchial masses were debulked using forceps, and samples were sent for surgical pathology evaluation. Staging was completed using linear endobronchial ultrasound, which revealed an enlarged subcarinal lymph node (S7). The surgical pathology of the endobronchial mass and the subcarinal lymph node cytology were consistent with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The tumor cells were positive for AE1/AE3, PSA, and NKX3.1, but were negative for CK7 and TTF-1 (Figure 5). Further imaging revealed an enlarged heterogeneous prostate gland, prominent pelvic nodes, and left retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy, as well as sclerotic foci within the T10 vertebral body and right inferior pubic ramus. PSA was also found to be significantly elevated at 700 ng/mL.

Case 3
An 80-year-old male veteran with a history of prostate cancer and recently diagnosed T2N1M0 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma was referred to the Pulmonary service for evaluation of a pulmonary nodule. His medical history was notable for prostate cancer diagnosed 12 years earlier, with an unknown Gleason score. Initial treatment included prostatectomy followed by whole pelvic radiation therapy a year after, due to elevated PSA in surveillance monitoring. This treatment led to remission. After establishing remission for > 10 years, the patient was started on low-dose testosterone replacement therapy to address complications of radiation therapy, namely hypogonadism.
On evaluation, a chest CT was significant for a large 2-cm right middle lobe nodule (Figure 6). At that time, PSA was noted to be borderline elevated at 4.2 ng/mL, and whole-body imaging did not reveal any lesions elsewhere, specifically no bone metastasis. Biopsies of the right middle lobe lung nodule revealed adenocarcinoma consistent with metastatic prostate cancer. Testosterone therapy was promptly discontinued.

The patient initially refused androgen deprivation therapy owing to the antiandrogenic adverse effects. However, subsequent chest CTs revealed growing lung nodules, which convinced him to proceed with androgen deprivation therapy followed by palliative radiation, and chemotherapy and management of malignant pleural effusion with indwelling small bore pleural catheter for about 10 years. He died from COVID-19 during the pandemic.
DISCUSSION
These cases highlight the importance of including prostate cancer in the differential diagnoses of male patients with intrathoracic abnormalities, even in the absence of metastasis to the more common sites. In a large cohort study of 74,826 patients with metastatic prostate cancer, Gandaglia et al found that the most frequent sites of metastasis were bone (84.0%) and distant lymph nodes (10.6%).2 However, thoracic involvement was observed in 9.1% of cases, with isolated thoracic metastasis being rare. The cases described in this report exemplify exceptionally uncommon occurrences within that 9.1%.
Pleural metastases, as observed in Case 1, are a particularly rare manifestation. In a 10-year retrospective assessment, Vinjamoori et al discovered pleural nodules or masses in only 6 of 82 patients (7.3%) with atypical metastases.3 Adrenal and liver metastases accounted for 15% and 37% of cases with atypical distribution. As such, isolated pleural disease is rare even in atypical presentations.3
As seen in Case 2, endobronchial metastases producing airway obstruction are also rare, with the most common primary cancers associated with endobronchial metastasis being breast, colon, and renal cancer.4 The available literature on this presentation is confined to case reports. Hameed et al reported a case of synchronous biopsy-proven endobronchial metastasis from prostate cancer.5 These cases highlight the importance of maintaining a high level of clinical awareness when encountering endobronchial lesions in patients with prostate cancer.
Case 3 presents a unique situation of lung metastases without any involvement of the bones. It is well known—and was confirmed by Heidenreich et al—that lung metastases in prostate adenocarcinoma usually coincide with extensive osseous disease.6 This instance highlights the importance of watchful monitoring for unusual patterns of cancer recurrence.
Immunohistochemistry stains that are specific to prostate cancer include antibodies against PSA. Prostate-specific membrane antigen is another marker that is far more present in malignant than in benign prostate tissue.
The NKX3.1 gene encodes a homeobox protein, which is a transcription factor and tumor suppressor. In prostate cancer, there is loss of heterozygosity of the gene and stains for the IHC antibody to NKX3.1.7
On the other hand, lung cells stain positive for TTF-1, which is produced by surfactant-producing type 2 pneumocytes and club cells in the lung. Antibodies to TTF-1, a common IHC stain, are used to identify adenocarcinoma of lung origin and may carry a prognostic value.7
The immunohistochemistry profiles, specifically the presence of prostate-specific markers such as PSA and NKX3.1, played a vital role in making the diagnosis.
In Case 1, weak TTF-1 positivity was noted, an unusual finding in metastatic prostate adenocarcinoma. Marak et al documented a rare case of TTF-1–positive metastatic prostate cancer, illustrating the potential for diagnostic confusion with primary lung malignancies.8
The 3 cases described in this report demonstrate the importance of clinical consideration, serial follow-up of PSA levels, using more prostate-specific positron emission tomography tracers (eg, Pylarify) alongside traditional imaging, and tissue biopsy to detect unusual metastases.
CONCLUSIONS
Although thoracic metastases from prostate cancer are rare, these presentations highlight the importance of clinical awareness regarding atypical cases. Pleural disease, endobronchial lesions, and isolated pulmonary nodules might be the first clinical manifestation of metastatic prostate cancer. A high index of suspicion, appropriate imaging, and judicious use of immunohistochemistry are important to ensure accurate diagnosis and optimal patient management.
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Gandaglia G, Abdollah F, Schiffmann J, et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in patients with prostate cancer: a population-based analysis. Prostate. 2014;74(2):210-216. doi:10.1002/pros.22742
- Vinjamoori AH, Jagannathan JP, Shinagare AB, et al. Atypical metastases from prostate cancer: 10-year experience at a single institution. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(2):367-372. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7533
- Salud A, Porcel JM, Rovirosa A, Bellmunt J. Endobronchial metastatic disease: analysis of 32 cases. J Surg Oncol. 1996;62(4):249-252. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096- 9098(199608)62:4<249::AID-JSO4>3.0.CO;2-6
- Hameed M, Haq IU, Yousaf M, Hussein M, Rashid U, Al-Bozom I. Endobronchial metastases secondary to prostate cancer: a case report and literature review. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020;32:101326. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101326
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, et al; for the European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration- resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65(2):467- 479. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.002
- Schallenberg S, Dernbach G, Dragomir MP, et al. TTF-1 status in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is an independent predictor of relapse and survival superior to tumor grading. Eur J Cancer. 2024;197:113474. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113474
- Marak C, Guddati AK, Ashraf A, Smith J, Kaushik P. Prostate adenocarcinoma with atypical immunohistochemistry presenting with a Cheerio sign. AIM Clinical Cases. 2023;1:e220508. doi:10.7326/aimcc.2022.0508
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- Gandaglia G, Abdollah F, Schiffmann J, et al. Distribution of metastatic sites in patients with prostate cancer: a population-based analysis. Prostate. 2014;74(2):210-216. doi:10.1002/pros.22742
- Vinjamoori AH, Jagannathan JP, Shinagare AB, et al. Atypical metastases from prostate cancer: 10-year experience at a single institution. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(2):367-372. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7533
- Salud A, Porcel JM, Rovirosa A, Bellmunt J. Endobronchial metastatic disease: analysis of 32 cases. J Surg Oncol. 1996;62(4):249-252. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096- 9098(199608)62:4<249::AID-JSO4>3.0.CO;2-6
- Hameed M, Haq IU, Yousaf M, Hussein M, Rashid U, Al-Bozom I. Endobronchial metastases secondary to prostate cancer: a case report and literature review. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020;32:101326. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101326
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, et al; for the European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration- resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2014;65(2):467- 479. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2013.11.002
- Schallenberg S, Dernbach G, Dragomir MP, et al. TTF-1 status in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma is an independent predictor of relapse and survival superior to tumor grading. Eur J Cancer. 2024;197:113474. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113474
- Marak C, Guddati AK, Ashraf A, Smith J, Kaushik P. Prostate adenocarcinoma with atypical immunohistochemistry presenting with a Cheerio sign. AIM Clinical Cases. 2023;1:e220508. doi:10.7326/aimcc.2022.0508
Atypical Intrathoracic Manifestations of Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Series
Atypical Intrathoracic Manifestations of Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Case Series
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
For patients with cancer, the determining factor in whether they pursue mental health services is often whether their oncologist explicitly says it is a good idea, a psychologist said during the July Association of VA Hematology and Oncology (AVAHO) seminar in Long Beach, California, on treating veterans with renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Kysa Christie, PhD, of the West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center, presented findings from a 2018 study in which researchers asked Swiss patients with cancer whether their oncologist discussed their emotional health with them.
In terms of boosting intake, it did not matter if oncologists acknowledged distress or pointed out that psychosocial services existed. Instead, a direct recommendation made a difference, increasing the likelihood of using the services over a 4-month period after initial assessment (odds ratio, 6.27).
“What it took was, ‘I really recommend this. This is something that I would want you to try,’” Christie said.
Oncologists are crucial links between patients and mental health services, Christie said: “If people don’t ask about [distress], you’re not going to see it, but it’s there. Distress is the norm, right? It is not a weakness. It is something that we expect to see.”
Christie noted that an estimated 20% of cancer patients have major depressive disorder, and 35% to 40% have a diagnosable psychiatric condition. RCC shows disproportionately high rates of mental strain. According to Christie, research suggests that about three-fourths of the population report elevated levels of distress as evidenced by patients who scored ≥ 5 on the NCCN Distress Thermometer. Patients with cancer have an estimated 20% higher risk of suicide, especially during the first 12 months after diagnosis and at end of life, she added.
“Early during a diagnosis phase, where you’re having a lot of tests being done, you know something is happening. But you don’t know what,” Christie said. “It could be very serious. That’s just a lot of stress to hold and not know how to plan for.”
After diagnosis, routine could set in and lower distress, she said. Then terminal illness may spike it back up again. Does mental health treatment work in patients with cancer?
“There’s a really strong body of evidence-based treatments for depression, anxiety, adjustment disorders, and coping with different cancers,” Christie said. But it is a step too far to expect patients to ask for help while they are juggling appointments, tests, infusions, and more. “It’s a big ask, right? It’s setting people up for failure.”
To help, Christie said she is embedded with a medical oncology team and routinely talks with the staff about which patients may need help. “One thing I like to do is try to have brief visits with veterans and introduce myself when they come to clinic. I treat it like an opt-out rather than an opt-in program: I’ll just pop into the exam room. They don’t have to ask to see me.”
Christie focuses on open-ended questions and talks about resources ranging from support groups and brief appointments to extensive individual therapy.
Another approach is a strategy known as the “warm handoff,” when an oncologist directly introduces a patient to a mental health professional. “It’s a transfer of care in front of the veteran: It’s much more time-efficient than putting in a referral.”
Christie explained how this can work. A clinician will ask her to meet with a patient during an appointment, perhaps in a couple minutes.
“Then I pop into the room, and the oncologist says, ‘Thanks for joining us. This is Mr. Jones. He has been experiencing feelings of anxiety and sadness, and we’d appreciate your help in exploring some options that might help.’ I turn to the patient and ask, ‘What more would you add?’ Then I either take Mr. Jones back to my office or stay in clinic, and we’re off to the races.”
Christie reported no disclosures.
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
'Distress is the Norm': How Oncologists Can Open the Door to Patient Mental Health
Colorectal Cancer Characteristics and Mortality From Propensity Score-Matched Cohorts of Urban and Rural Veterans
Colorectal Cancer Characteristics and Mortality From Propensity Score-Matched Cohorts of Urban and Rural Veterans
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, with an estimated 52,550 deaths in 2023.1 However, the disease burden varies among different segments of the population.2 While both CRC incidence and mortality have been decreasing due to screening and advances in treatment, there are disparities in incidence and mortality across the sociodemographic spectrum including race, ethnicity, education, and income.1-4 While CRC incidence is decreasing for older adults, it is increasing among those aged < 55 years.5 The incidence of CRC in adults aged 40 to 54 years has increased by 0.5% to 1.3% annually since the mid-1990s.6 The US Preventive Services Task Force now recommends starting CRC screening at age 45 years for asymptomatic adults with average risk.7
Disparities also exist across geographical boundaries and living environment. Rural Americans faces additional challenges in health and lifestyle that can affect CRC outcomes. Compared to their urban counterparts, rural residents are more likely to be older, have lower levels of education, higher levels of poverty, lack health insurance, and less access to health care practitioners (HCPs).8-10 Geographic proximity, defined as travel time or physical distance to a health facility, has been recognized as a predictor of inferior outcomes.11 These aspects of rural living may pose challenges for accessing care for CRC screening and treatment.11-13 National and local studies have shown disparities in CRC screening rates, incidence, and mortality between rural and urban populations.14-16
It is unclear whether rural/urban disparities persist under the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health care delivery model. This study examined differences in baseline characteristics and mortality between rural and urban veterans newly diagnosed with CRC. We also focused on a subpopulation aged ≤ 45 years.
Methods
This study extracted national data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) hosted in the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI) environment. VINCI is an initiative to improve access to VA data and facilitate the analysis of these data while ensuring veterans’ privacy and data security.17 CDW is the VHA business intelligence information repository, which extracts data from clinical and nonclinical sources following prescribed and validated protocols. Data extracted included demographics, diagnosis, and procedure codes for both inpatient and outpatient encounters, vital signs, and vital status. This study used data previously extracted from a national cohort of veterans that encompassed all patients who received a group of commonly prescribed medications, such as statins, proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 blockers, acetaminophen-containing products, and hydrocortisone-containing skin applications. This cohort encompassed 8,648,754 veterans, from whom 2,460,727 had encounters during fiscal years (FY) 2016 to 2021 (study period). The cohort was used to ensure that subjects were VHA patients, allowing them to adequately capture their clinical profiles.
Patients were identified as rural or urban based on their residence address at the date of their first diagnosis of CRC. The Geospatial Service Support Center (GSSC) aggregates and updates veterans’ residence address records for all enrolled veterans from the National Change of Address database. The data contain 1 record per enrollee. GSSC Geocoded Enrollee File contains enrollee addresses and their rurality indicators, categorized as urban, rural, or highly rural.18 Rurality is defined by the Rural Urban Commuting Area (RUCA) categories developed by the Department of Agriculture and the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services.19 Urban areas had RUCA codes of 1.0 to 1.1, and highly rural areas had RUCA scores of 10.0. All other areas were classified as rural. Since the proportion of veterans from highly rural areas was small, we included residents from highly rural areas in the rural residents’ group.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All veterans newly diagnosed with CRC from FY 2016 to 2021 were included. We used the ninth and tenth clinical modification revisions of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM) to define CRC diagnosis (Supplemental materials).4,20 To ensure that patients were newly diagnosed with CRC, this study excluded patients with a previous ICD-9-CM code for CRC diagnosis since FY 2003.
Comorbidities were identified using diagnosis and procedure codes from inpatient and outpatient encounters, which were used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) at the time of CRC diagnosis using the weighted method described by Schneeweiss et al.21 We defined CRC high-risk conditions and CRC screening tests, including flexible sigmoidoscopy and stool tests, as described in previous studies (Supplemental materials).20
The main outcome was total mortality. The date of death was extracted from the VHA Death Ascertainment File, which contains mortality data from the Master Person Index file in CDW and the Social Security Administration Death Master File. We used the date of death from any cause, as cause of death was not available.
A propensity score (PS) was created to match rural (including highly rural) and urban residents at a ratio of 1:1. Using a standard procedure described in prior publications, multivariable logistic regression used all baseline characteristics to estimate the PS and perform nearest-number matching without replacement.22,23 A caliper of 0.01 maximized the matched cohort size and achieved balance (Supplemental materials). We then examined the balance of baseline characteristics between PS-matched groups.
Analyses
Cox proportional hazards regression analysis estimated the hazard ratio (HR) of death in rural residents compared to urban residents in the PS-matched cohort. The outcome event was the date of death during the study’s follow-up period (defined as period from first CRC diagnosis to death or study end), with censoring at the study’s end date (September 30, 2021). The proportional hazards assumption was assessed by inspecting the Kaplan-Meier curves. Multiple analyses examined the HR of total mortality in the PS-matched cohort, stratified by sex, race, and ethnicity. We also examined the HR of total mortality stratified by duration of follow-up.
Another PS-matching analysis among veterans aged ≤ 45 years was performed using the same techniques described earlier in this article. We performed a Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to compare mortality in PS-matched urban and rural veterans aged ≤ 45 years. The HR of death in all veterans aged ≤ 45 years (before PS-matching) was estimated using Cox proportional hazard regression analysis, adjusting for PS.
Dichotomous variables were compared using X2 tests and continuous variables were compared using t tests. Baseline characteristics with missing values were converted into categorical variables and the proportion of subjects with missing values was equalized between treatment groups after PS-matching. For subgroup analysis, we examined the HR of total mortality in each subgroup using separate Cox proportional hazards regression models similar to the primary analysis but adjusted for PS. Due to multiple comparisons in the subgroup analysis, the findings should be considered exploratory. Statistical tests were 2-tailed, and significance was defined as P < .05. Data management and statistical analyses were conducted from June 2022 to January 2023 using STATA, Version 17. The VA Orlando Healthcare System Institutional Review Board approved the study and waived requirements for informed consent because only deidentified data were used.
Results
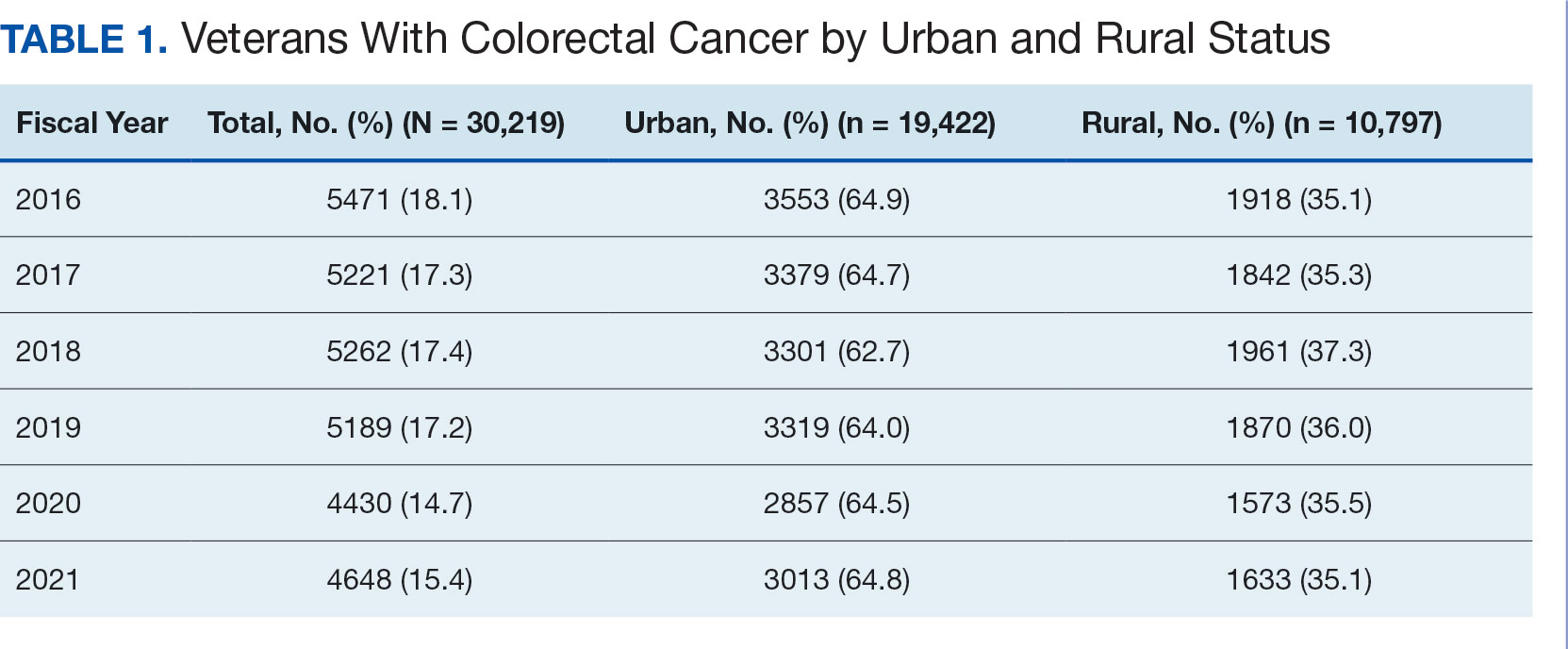
After excluding 49 patients (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0560), we identified 30,219 veterans with newly diagnosed CRC between FY 2016 to 2021 (Table 1). Of these, 19,422 (64.3%) resided in urban areas and 10,797 (35.7%) resided in rural areas (Table 2). The mean (SD) duration from the first CRC diagnosis to death or study end was 832 (640) days, and the median (IQR) was 723 (246–1330) days. Overall, incident CRC diagnoses were numerically highest in FY 2016 and lowest in FY 2020 (Figure 1). Patients with CRC in rural areas vs urban areas were significantly older (mean, 71.2 years vs 70.8 years, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be male (96.7% vs 95.7%, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be White (83.6% vs 67.8%, respectively; P < .001) and more likely to be non-Hispanic (92.2% vs 87.5%, respectively; P < .001). In terms of general health, rural veterans with CRC were more likely to be overweight or obese (81.5% rural vs 78.5% urban; P < .001) but had fewer mean comorbidities as measured by CCI (5.66 rural vs 5.90 urban; P < .001). A higher proportion of rural veterans with CRC had received stool-based (fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test) CRC screening tests (61.6% rural vs 57.2% urban; P < .001). Fewer rural patients presented with systemic symptoms or signs within 1 year of CRC diagnosis (54.4% rural vs 57.5% urban, P < .001). Among urban patients with CRC, 6959 (35.8%) deaths were observed, compared with 3766 (34.9%) among rural patients (P = .10).
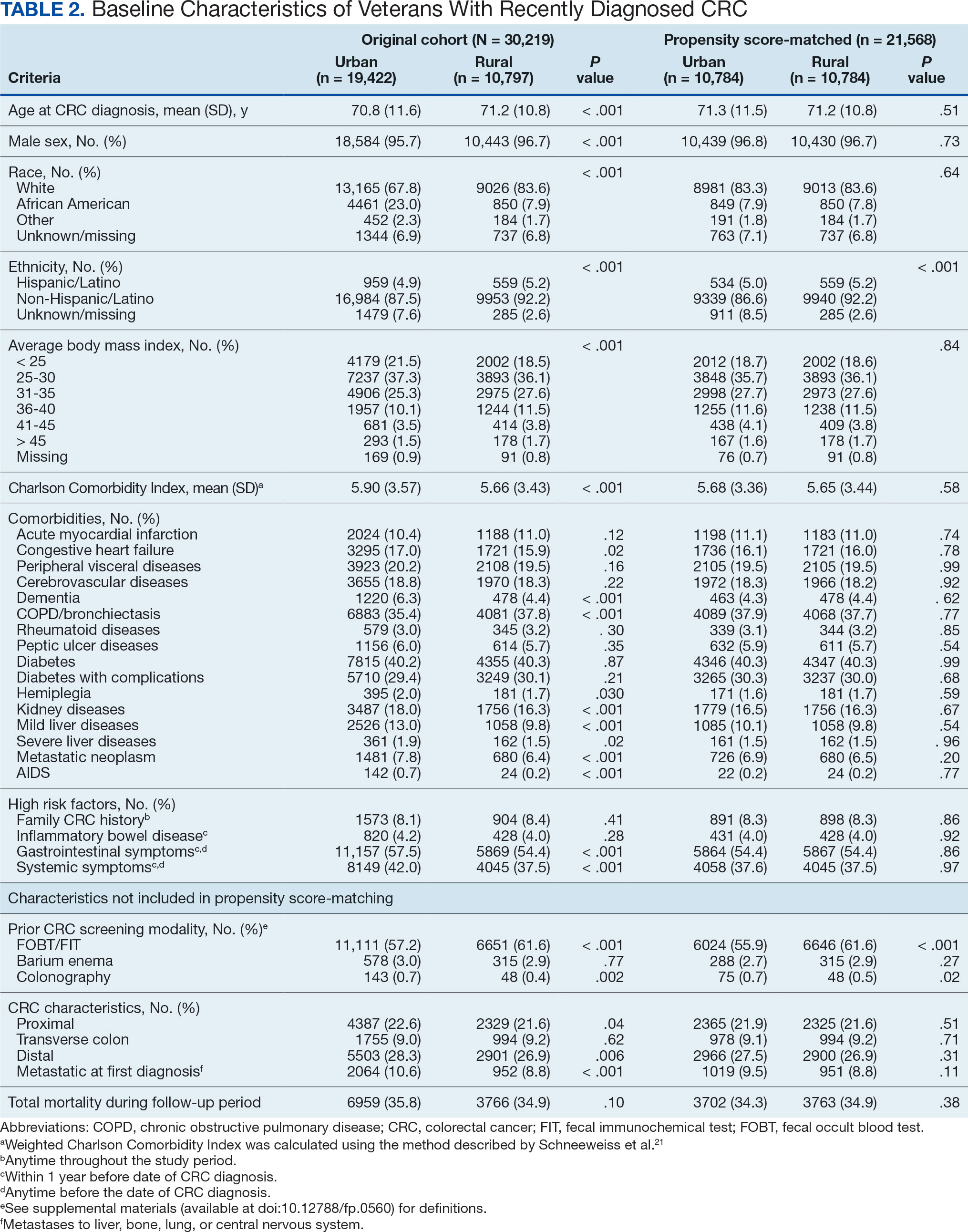
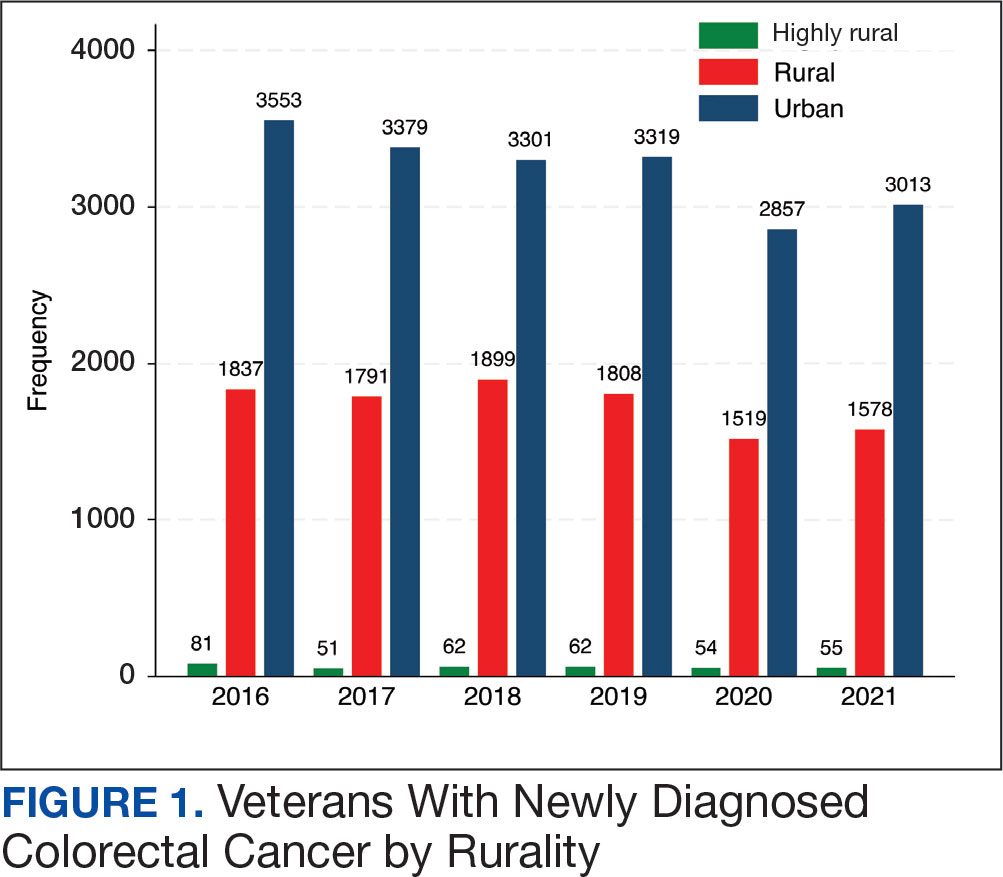
There were 21,568 PS-matched veterans: 10,784 in each group. In the PS-matched cohort, baseline characteristics were similar between veterans in urban and rural communities, including age, sex, race/ethnicity, body mass index, and comorbidities. Among rural patients with CRC, 3763 deaths (34.9%) were observed compared with 3702 (34.3%) among urban veterans. There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban CRC residents (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.97-1.06; P = .53) (Figure 2).
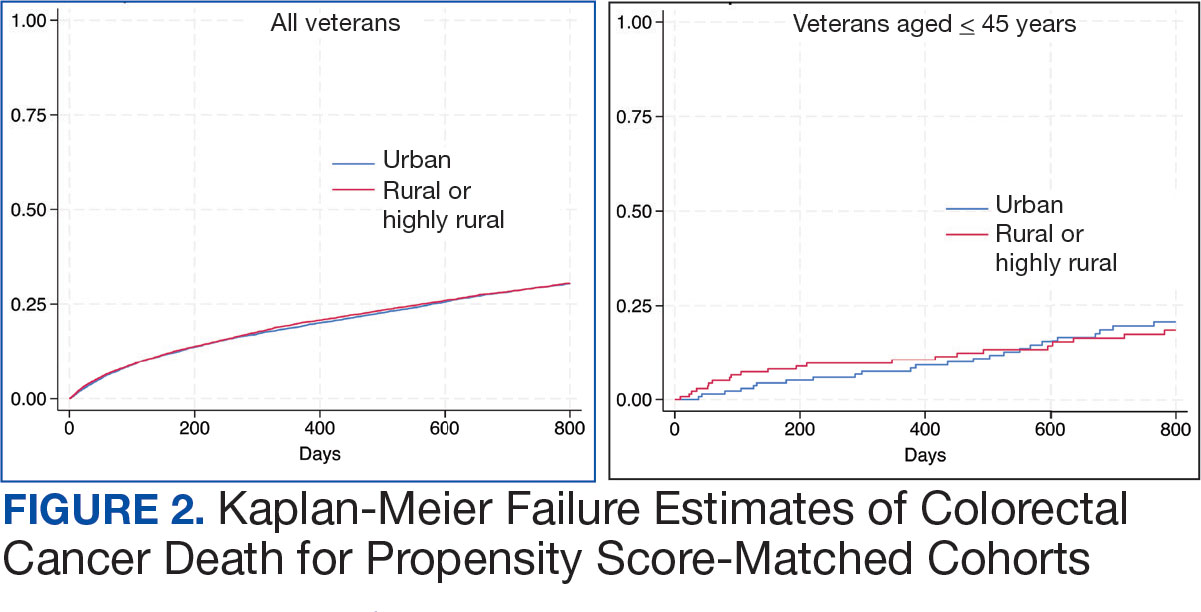
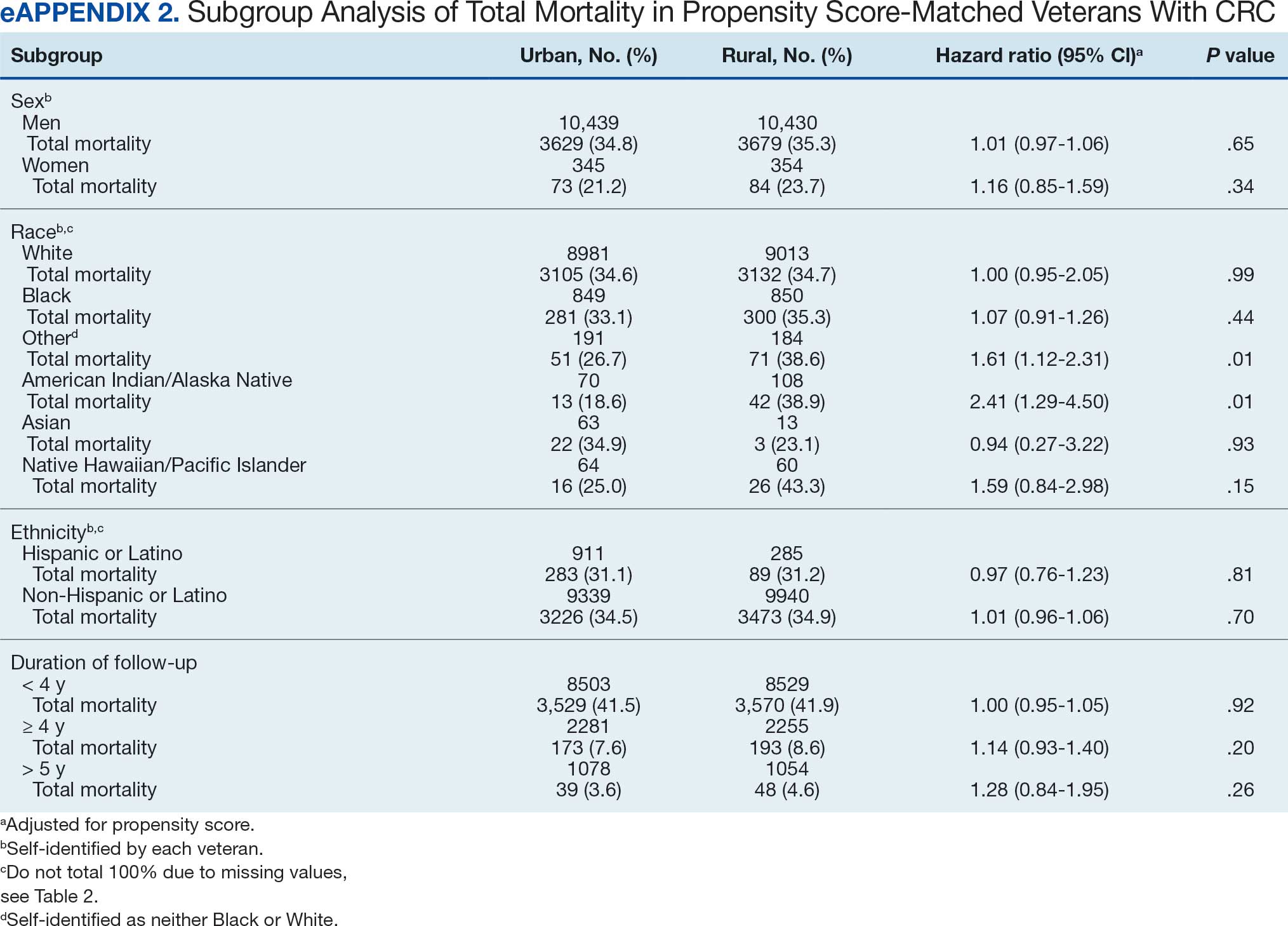
Among veterans aged ≤ 45 years, 551 were diagnosed with CRC (391 urban and 160 rural). We PS-matched 142 pairs of urban and rural veterans without residual differences in baseline characteristics (eAppendix 1). There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.57-1.63; P = .90) (Figure 2). Similarly, no difference in mortality was observed adjusting for PS between all rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.67-1.59; P = .88).
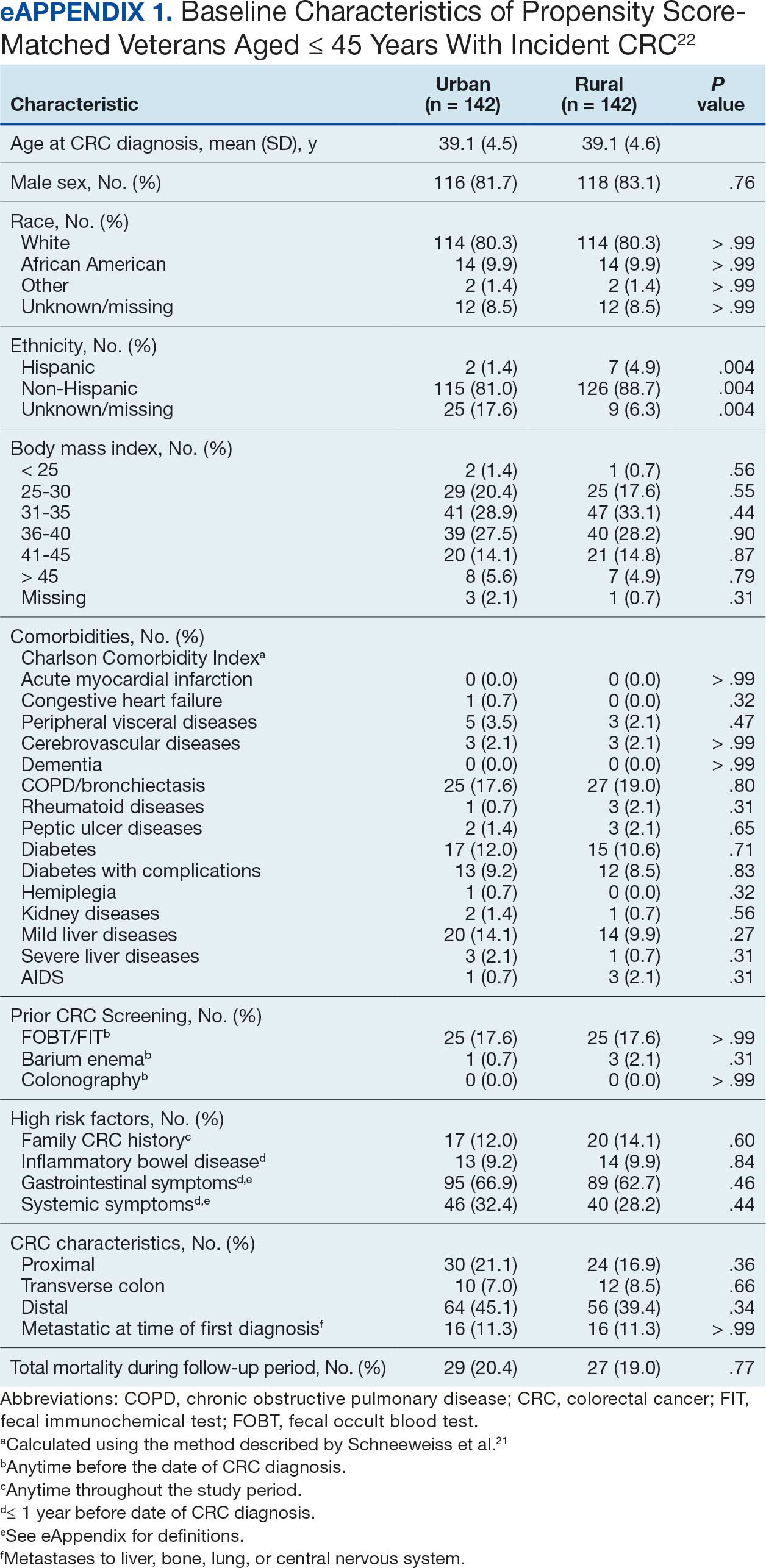
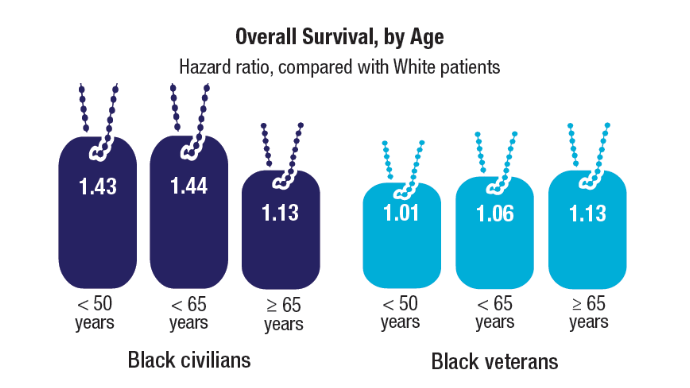
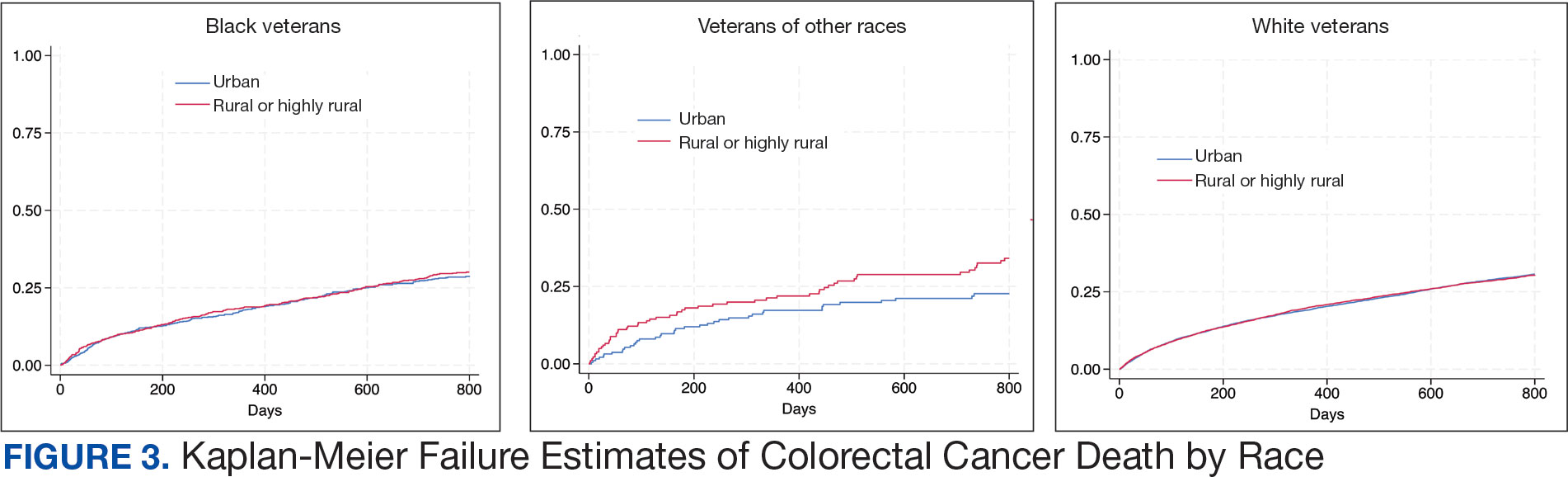
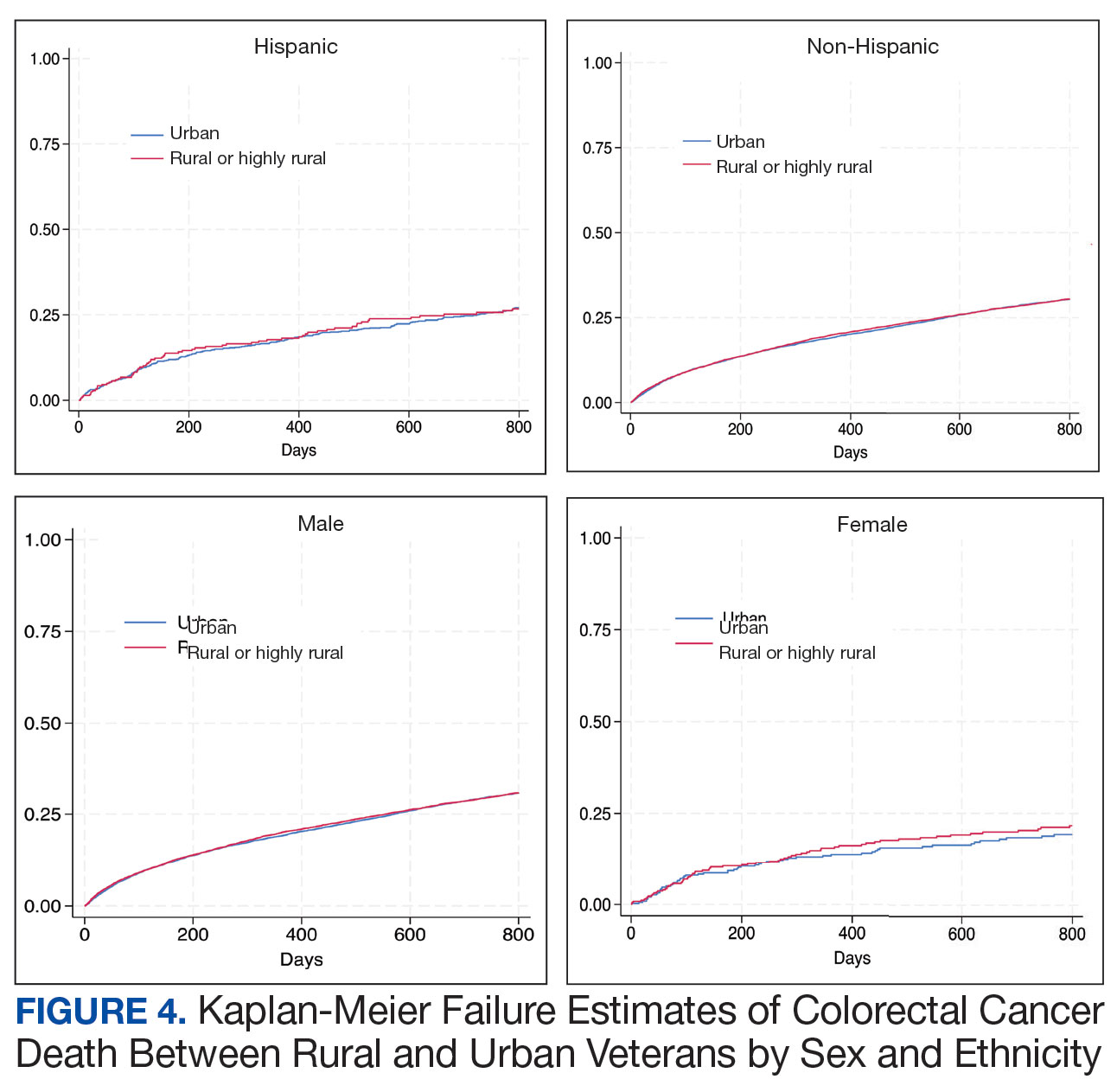
There was no difference in total mortality between rural and urban veterans in any subgroup except for American Indian or Alaska Native veterans (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006) (eAppendix 2).
Discussion
This study examined characteristics of patients with CRC between urban and rural areas among veterans who were VHA patients. Similar to other studies, rural veterans with CRC were older, more likely to be White, and were obese, but exhibited fewer comorbidities (lower CCI and lower incidence of congestive heart failure, dementia, hemiplegia, kidney diseases, liver diseases and AIDS, but higher incidence of chronic obstructive lung disease).8,16 The incidence of CRC in this study population was lowest in FY 2020, which was reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is attributed to COVID-19 pandemic disruption of health services.24 The overall mortality in this study was similar to rates reported in other studies from the VA Central Cancer Registry.4 In the PS-matched cohort, where baseline characteristics were similar between urban and rural patients with CRC, we found no disparities in CRC-specific mortality between veterans in rural and urban areas. Additionally, when analysis was restricted to veterans aged ≤ 45 years, the results remained consistent.
Subgroup analyses showed no significant difference in mortality between rural and urban areas by sex, race or ethnicity, except rural American Indian or Alaska Native veterans who had double the mortality of their urban counterparts (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006). This finding is difficult to interpret due to the small number of events and the wide CI. While with a Bonferroni correction the adjusted P value was .08, which is not statistically significant, a previous study found that although CRC incidence was lower overall in American Indian or Alaska Native populations compared to non-Hispanic White populations, CRC incidence was higher among American Indian or Alaska Native individuals in some areas such as Alaska and the Northern Plains.25,26 Studies have noted that rural American Indian/Alaska Native populations experience greater poverty, less access to broadband internet, and limited access to care, contributing to poorer cancer outcomes and lower survival.27 Thus, the finding of disparity in mortality between rural and urban American Indian or Alaska Native veterans warrants further study.
Other studies have raised concerns that CRC disproportionately affects adults in rural areas with higher mortality rates.14-16 These disparities arise from sociodemographic factors and modifiable risk factors, including physical activity, dietary patterns, access to cancer screening, and gaps in quality treatment resources.16,28 These factors operate at multiple levels: from individual, local health system, to community and policy.2,27 For example, a South Carolina study (1996–2016) found that residents in rural areas were more likely to be diagnosed with advanced CRC, possibly indicating lower rates of CRC screening in rural areas. They also had higher likelihood of death from CRC.15 However, the study did not include any clinical parameters, such as comorbidities or obesity. A statewide, population-based study in Utah showed that rural men experienced a lower CRC survival in their unadjusted analysis.16 However, the study was small, with only 3948 urban and 712 rural residents. Additionally, there was no difference in total mortality in the whole cohort (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.86-1.07) or in CRC-specific death (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.81-1.08). A nationwide study also showed that CRC mortality rates were 8% higher in nonmetropolitan or rural areas than in the most urbanized areas containing large metropolitan counties.29 However, this study did not include descriptions of clinical confounders, such as comorbidities, making it difficult to ascertain whether the difference in CRC mortality was due to rurality or differences in baseline risk characteristics.
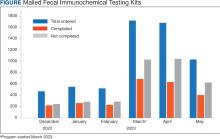
In this study, the lack of CRC-specific mortality disparities may be attributed to the structures and practices of VHA health care. Recent studies have noted that mortality of several chronic medical conditions treated at the VHA was lower than at non-VHA hospitals.30,31 One study that measured the quality of nonmetastatic CRC care based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines showed that > 72% of VHA patients received guideline-concordant care for each diagnostic and therapeutic measure, except for follow-up colonoscopy timing, which appear to be similar or superior to that of the private sector.30,32,33 Some of the VA initiative for CRC screening may bypass the urban-rurality divide such as the mailed fecal immunochemical test program for CRC. This program was implemented at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic to avoid disruptions of medical care.34 Rural patients are more likely to undergo fecal immunochemical testing when compared to urban patients in this data. Beyond clinical care, the VHA uses processes to tackle social determinants of health such as housing, food security, and transportation, promoting equal access to health care, and promoting cultural competency among HCPs.35-37
The results suggest that solutions to CRC disparities between rural and urban areas need to consider known barriers to rural health care, including transportation, diminished rural health care workforce, and other social determinants of health.9,10,27,38 VHA makes considerable efforts to provide equitable care to all enrolled veterans, including specific programs for rural veterans, including ongoing outreach.39 This study demonstrated lack of disparity in CRC-specific mortality in veterans receiving VHA care, highlighting the importance of these efforts.
Strengths and Limitations
This study used the VHA cohort to compare patient characteristics and mortality between patients with CRC residing in rural and urban areas. The study provides nationwide perspectives on CRC across the geographical spectrum and used a longitudinal cohort with prolonged follow-up to account for comorbidities.
However, the study compared a cohort of rural and urban veterans enrolled in the VHA; hence, the results may not reflect CRC outcomes in veterans without access to VHA care. Rurality has been independently associated with decreased likelihood of meeting CRC screening guidelines among veterans and military service members.38 This study lacked sufficient information to compare CRC staging or treatment modalities among veterans. Although the data cannot identify CRC stage, the proportions of patients with metastatic CRC at diagnosis and CRC location were similar between groups. The study did not have information on their care outside of VHA setting.
This study could not ascertain whether disparities existed in CRC treatment modality since rural residence may result in referral to community-based CRC care, which did not appear in the data. To address these limitations, we used death from any cause as the primary outcome, since death is a hard outcome and is not subject to ascertainment bias. The relatively short follow-up time is another limitation, though subgroup analysis by follow-up did not show significant differences. Despite PS matching, residual unmeasured confounding may exist between urban and rural groups. The predominantly White, male VHA population with high CCI may limit the generalizability of the results.
Conclusions
Rural VHA enrollees had similar survival rates after CRC diagnosis compared to their urban counterparts in a PS-matched analysis. The VHA models of care—including mailed CRC screening tools, several socioeconomic determinants of health (housing, food security, and transportation), and promoting equal access to health care, as well as cultural competency among HCPs—HCPs—may help alleviate disparities across the rural-urban spectrum. The VHA should continue efforts to enroll veterans and provide comprehensive coordinated care in community partnerships.
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Carethers JM, Doubeni CA. Causes of socioeconomic disparities in colorectal cancer and intervention framework and strategies. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(2):354-367. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.029
- Murphy G, Devesa SS, Cross AJ, Inskip PD, McGlynn KA, Cook MB. Sex disparities in colorectal cancer incidence by anatomic subsite, race and age. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(7):1668-75. doi:10.1002/ijc.25481
- Zullig LL, Smith VA, Jackson GL, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics from the Veterans Affairs central cancer registry. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016;15(4):e199-e204. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2016.04.005
- Lin JS, Perdue LA, Henrikson NB, Bean SI, Blasi PR. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence Update for the US Preventive Services Task Force. 2021. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews:Chapter 1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570917/
- Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Anderson WF, et al. Colorectal cancer incidence patterns in the United States, 1974-2013. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(8). doi:10.1093/jnci/djw322
- Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
- Hines R, Markossian T, Johnson A, Dong F, Bayakly R. Geographic residency status and census tract socioeconomic status as determinants of colorectal cancer outcomes. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(3):e63-e71. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.301572
- Cauwels J. The many barriers to high-quality rural health care. 2022;(9):1-32. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. Accessed April 24, 2025. https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/CAT.22.0254
- Gong G, Phillips SG, Hudson C, Curti D, Philips BU. Higher US rural mortality rates linked to socioeconomic status, physician shortages, and lack of health insurance. Health Aff (Millwood);38(12):2003-2010. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.00722
- Aboagye JK, Kaiser HE, Hayanga AJ. Rural-urban differences in access to specialist providers of colorectal cancer care in the United States: a physician workforce issue. JAMA Surg. 2014;149(6):537-543. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.5062
- Lyckholm LJ, Hackney MH, Smith TJ. Ethics of rural health care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001;40(2):131-138. doi:10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00139-1
- Krieger N, Williams DR, Moss NE. Measuring social class in US public health research: concepts, methodologies, and guidelines. Annu Rev Public Health. 1997;18:341-378. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.18.1.341
- Singh GK, Jemal A. Socioeconomic and racial/ethnic disparities in cancer mortality, incidence, and survival in the United States, 1950-2014: over six decades of changing patterns and widening inequalities. J Environ Public Health. 2017;2017:2819372. doi:10.1155/2017/2819372
- Adams SA, Zahnd WE, Ranganathan R, et al. Rural and racial disparities in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in South Carolina, 1996 - 2016. J Rural Health. 2022;38(1):34-39. doi:10.1111/jrh.12580
- Rogers CR, Blackburn BE, Huntington M, et al. Rural- urban disparities in colorectal cancer survival and risk among men in Utah: a statewide population-based study. Cancer Causes Control. 2020;31(3):241-253. doi:10.1007/s10552-020-01268-2
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI), VA HSR RES 13-457. https://vincicentral.vinci.med.va.gov [Source not verified]
- US Department of Veterans Affairs Information Resource Center. VIReC Research User Guide: PSSG Geocoded Enrollee Files, 2015 Edition. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research & Development Service, Information Resource Center; May. 2016. [source not verified]
- Goldsmith HF, Puskin DS, Stiles DJ. Improving the operational definition of “rural areas” for federal programs. US Department of Health and Human Services; 1993. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/pdf/improving-the-operational-definition-of-rural-areas.pdf
- Adams MA, Kerr EA, Dominitz JA, et al. Development and validation of a new ICD-10-based screening colonoscopy overuse measure in a large integrated healthcare system: a retrospective observational study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32(7):414-424. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014236
- Schneeweiss S, Wang PS, Avorn J, Glynn RJ. Improved comorbidity adjustment for predicting mortality in Medicare populations. Health Serv Res. 2003;38(4):1103-1120. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.00165
- Becker S, Ichino A. Estimation of average treatment effects based on propensity scores. The Stata Journal. 2002;2(4):358-377.
- Leuven E, Sianesi B. PSMATCH2: Stata module to perform full Mahalanobis and propensity score matching, common support graphing, and covariate imbalance testing. Statistical software components. Revised February 1, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/s432001.html.
- US Cancer Statistics Working Group. US cancer statistics data visualizations tool. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 2024. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dataviz
- Cao J, Zhang S. Multiple Comparison Procedures. JAMA. 2014;312(5):543-544. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9440
- Gopalani SV, Janitz AE, Martinez SA, et al. Trends in cancer incidence among American Indians and Alaska Natives and Non-Hispanic Whites in the United States, 1999-2015. Epidemiology. 2020;31(2):205-213. doi:10.1097/EDE.0000000000001140
- Zahnd WE, Murphy C, Knoll M, et al. The intersection of rural residence and minority race/ethnicity in cancer disparities in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4). doi:10.3390/ijerph18041384
- Blake KD, Moss JL, Gaysynsky A, Srinivasan S, Croyle RT. Making the case for investment in rural cancer control: an analysis of rural cancer incidence, mortality, and funding trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(7):992-997. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0092
- Singh GK, Williams SD, Siahpush M, Mulhollen A. Socioeconomic, rural-urban, and racial inequalities in US cancer mortality: part i-all cancers and lung cancer and part iicolorectal, prostate, breast, and cervical cancers. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;2011:107497. doi:10.1155/2011/107497
- Jackson GL, Melton LD, Abbott DH, et al. Quality of nonmetastatic colorectal cancer care in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(19):3176-3181. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7948
- Yoon J, Phibbs CS, Ong MK, et al. Outcomes of veterans treated in Veterans Affairs hospitals vs non-Veterans Affairs hospitals. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(12):e2345898. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.45898
- Malin JL, Schneider EC, Epstein AM, Adams J, Emanuel EJ, Kahn KL. Results of the National Initiative for Cancer Care Quality: how can we improve the quality of cancer care in the United States? J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(4):626-634. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3365
- Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(5):1570-1595. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.002
- Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among Veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4). doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
- Yehia BR, Greenstone CL, Hosenfeld CB, Matthews KL, Zephyrin LC. The role of VA community care in addressing health and health care disparities. Med Care. 2017;55(Suppl 9 suppl 2):S4-S5. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000768
- Wright BN, MacDermid Wadsworth S, Wellnitz A, Eicher- Miller HA. Reaching rural veterans: a new mechanism to connect rural, low-income US Veterans with resources and improve food security. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019;41(4):714-723. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdy203
- Nelson RE, Byrne TH, Suo Y, et al. Association of temporary financial assistance with housing stability among US veterans in the supportive services for veteran families program. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037047. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37047
- McDaniel JT, Albright D, Lee HY, et al. Rural–urban disparities in colorectal cancer screening among military service members and Veterans. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2019;5(1):40-48. doi:10.3138/jmvfh.2018-0013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. The rural veteran outreach toolkit. Updated February 12, 2025. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/partners/toolkit.asp
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, with an estimated 52,550 deaths in 2023.1 However, the disease burden varies among different segments of the population.2 While both CRC incidence and mortality have been decreasing due to screening and advances in treatment, there are disparities in incidence and mortality across the sociodemographic spectrum including race, ethnicity, education, and income.1-4 While CRC incidence is decreasing for older adults, it is increasing among those aged < 55 years.5 The incidence of CRC in adults aged 40 to 54 years has increased by 0.5% to 1.3% annually since the mid-1990s.6 The US Preventive Services Task Force now recommends starting CRC screening at age 45 years for asymptomatic adults with average risk.7
Disparities also exist across geographical boundaries and living environment. Rural Americans faces additional challenges in health and lifestyle that can affect CRC outcomes. Compared to their urban counterparts, rural residents are more likely to be older, have lower levels of education, higher levels of poverty, lack health insurance, and less access to health care practitioners (HCPs).8-10 Geographic proximity, defined as travel time or physical distance to a health facility, has been recognized as a predictor of inferior outcomes.11 These aspects of rural living may pose challenges for accessing care for CRC screening and treatment.11-13 National and local studies have shown disparities in CRC screening rates, incidence, and mortality between rural and urban populations.14-16
It is unclear whether rural/urban disparities persist under the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health care delivery model. This study examined differences in baseline characteristics and mortality between rural and urban veterans newly diagnosed with CRC. We also focused on a subpopulation aged ≤ 45 years.
Methods
This study extracted national data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) hosted in the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI) environment. VINCI is an initiative to improve access to VA data and facilitate the analysis of these data while ensuring veterans’ privacy and data security.17 CDW is the VHA business intelligence information repository, which extracts data from clinical and nonclinical sources following prescribed and validated protocols. Data extracted included demographics, diagnosis, and procedure codes for both inpatient and outpatient encounters, vital signs, and vital status. This study used data previously extracted from a national cohort of veterans that encompassed all patients who received a group of commonly prescribed medications, such as statins, proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 blockers, acetaminophen-containing products, and hydrocortisone-containing skin applications. This cohort encompassed 8,648,754 veterans, from whom 2,460,727 had encounters during fiscal years (FY) 2016 to 2021 (study period). The cohort was used to ensure that subjects were VHA patients, allowing them to adequately capture their clinical profiles.
Patients were identified as rural or urban based on their residence address at the date of their first diagnosis of CRC. The Geospatial Service Support Center (GSSC) aggregates and updates veterans’ residence address records for all enrolled veterans from the National Change of Address database. The data contain 1 record per enrollee. GSSC Geocoded Enrollee File contains enrollee addresses and their rurality indicators, categorized as urban, rural, or highly rural.18 Rurality is defined by the Rural Urban Commuting Area (RUCA) categories developed by the Department of Agriculture and the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services.19 Urban areas had RUCA codes of 1.0 to 1.1, and highly rural areas had RUCA scores of 10.0. All other areas were classified as rural. Since the proportion of veterans from highly rural areas was small, we included residents from highly rural areas in the rural residents’ group.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All veterans newly diagnosed with CRC from FY 2016 to 2021 were included. We used the ninth and tenth clinical modification revisions of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM) to define CRC diagnosis (Supplemental materials).4,20 To ensure that patients were newly diagnosed with CRC, this study excluded patients with a previous ICD-9-CM code for CRC diagnosis since FY 2003.
Comorbidities were identified using diagnosis and procedure codes from inpatient and outpatient encounters, which were used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) at the time of CRC diagnosis using the weighted method described by Schneeweiss et al.21 We defined CRC high-risk conditions and CRC screening tests, including flexible sigmoidoscopy and stool tests, as described in previous studies (Supplemental materials).20
The main outcome was total mortality. The date of death was extracted from the VHA Death Ascertainment File, which contains mortality data from the Master Person Index file in CDW and the Social Security Administration Death Master File. We used the date of death from any cause, as cause of death was not available.
A propensity score (PS) was created to match rural (including highly rural) and urban residents at a ratio of 1:1. Using a standard procedure described in prior publications, multivariable logistic regression used all baseline characteristics to estimate the PS and perform nearest-number matching without replacement.22,23 A caliper of 0.01 maximized the matched cohort size and achieved balance (Supplemental materials). We then examined the balance of baseline characteristics between PS-matched groups.
Analyses
Cox proportional hazards regression analysis estimated the hazard ratio (HR) of death in rural residents compared to urban residents in the PS-matched cohort. The outcome event was the date of death during the study’s follow-up period (defined as period from first CRC diagnosis to death or study end), with censoring at the study’s end date (September 30, 2021). The proportional hazards assumption was assessed by inspecting the Kaplan-Meier curves. Multiple analyses examined the HR of total mortality in the PS-matched cohort, stratified by sex, race, and ethnicity. We also examined the HR of total mortality stratified by duration of follow-up.
Another PS-matching analysis among veterans aged ≤ 45 years was performed using the same techniques described earlier in this article. We performed a Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to compare mortality in PS-matched urban and rural veterans aged ≤ 45 years. The HR of death in all veterans aged ≤ 45 years (before PS-matching) was estimated using Cox proportional hazard regression analysis, adjusting for PS.
Dichotomous variables were compared using X2 tests and continuous variables were compared using t tests. Baseline characteristics with missing values were converted into categorical variables and the proportion of subjects with missing values was equalized between treatment groups after PS-matching. For subgroup analysis, we examined the HR of total mortality in each subgroup using separate Cox proportional hazards regression models similar to the primary analysis but adjusted for PS. Due to multiple comparisons in the subgroup analysis, the findings should be considered exploratory. Statistical tests were 2-tailed, and significance was defined as P < .05. Data management and statistical analyses were conducted from June 2022 to January 2023 using STATA, Version 17. The VA Orlando Healthcare System Institutional Review Board approved the study and waived requirements for informed consent because only deidentified data were used.
Results
After excluding 49 patients (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0560), we identified 30,219 veterans with newly diagnosed CRC between FY 2016 to 2021 (Table 1). Of these, 19,422 (64.3%) resided in urban areas and 10,797 (35.7%) resided in rural areas (Table 2). The mean (SD) duration from the first CRC diagnosis to death or study end was 832 (640) days, and the median (IQR) was 723 (246–1330) days. Overall, incident CRC diagnoses were numerically highest in FY 2016 and lowest in FY 2020 (Figure 1). Patients with CRC in rural areas vs urban areas were significantly older (mean, 71.2 years vs 70.8 years, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be male (96.7% vs 95.7%, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be White (83.6% vs 67.8%, respectively; P < .001) and more likely to be non-Hispanic (92.2% vs 87.5%, respectively; P < .001). In terms of general health, rural veterans with CRC were more likely to be overweight or obese (81.5% rural vs 78.5% urban; P < .001) but had fewer mean comorbidities as measured by CCI (5.66 rural vs 5.90 urban; P < .001). A higher proportion of rural veterans with CRC had received stool-based (fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test) CRC screening tests (61.6% rural vs 57.2% urban; P < .001). Fewer rural patients presented with systemic symptoms or signs within 1 year of CRC diagnosis (54.4% rural vs 57.5% urban, P < .001). Among urban patients with CRC, 6959 (35.8%) deaths were observed, compared with 3766 (34.9%) among rural patients (P = .10).



There were 21,568 PS-matched veterans: 10,784 in each group. In the PS-matched cohort, baseline characteristics were similar between veterans in urban and rural communities, including age, sex, race/ethnicity, body mass index, and comorbidities. Among rural patients with CRC, 3763 deaths (34.9%) were observed compared with 3702 (34.3%) among urban veterans. There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban CRC residents (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.97-1.06; P = .53) (Figure 2).



Among veterans aged ≤ 45 years, 551 were diagnosed with CRC (391 urban and 160 rural). We PS-matched 142 pairs of urban and rural veterans without residual differences in baseline characteristics (eAppendix 1). There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.57-1.63; P = .90) (Figure 2). Similarly, no difference in mortality was observed adjusting for PS between all rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.67-1.59; P = .88).

There was no difference in total mortality between rural and urban veterans in any subgroup except for American Indian or Alaska Native veterans (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006) (eAppendix 2).

Discussion
This study examined characteristics of patients with CRC between urban and rural areas among veterans who were VHA patients. Similar to other studies, rural veterans with CRC were older, more likely to be White, and were obese, but exhibited fewer comorbidities (lower CCI and lower incidence of congestive heart failure, dementia, hemiplegia, kidney diseases, liver diseases and AIDS, but higher incidence of chronic obstructive lung disease).8,16 The incidence of CRC in this study population was lowest in FY 2020, which was reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is attributed to COVID-19 pandemic disruption of health services.24 The overall mortality in this study was similar to rates reported in other studies from the VA Central Cancer Registry.4 In the PS-matched cohort, where baseline characteristics were similar between urban and rural patients with CRC, we found no disparities in CRC-specific mortality between veterans in rural and urban areas. Additionally, when analysis was restricted to veterans aged ≤ 45 years, the results remained consistent.
Subgroup analyses showed no significant difference in mortality between rural and urban areas by sex, race or ethnicity, except rural American Indian or Alaska Native veterans who had double the mortality of their urban counterparts (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006). This finding is difficult to interpret due to the small number of events and the wide CI. While with a Bonferroni correction the adjusted P value was .08, which is not statistically significant, a previous study found that although CRC incidence was lower overall in American Indian or Alaska Native populations compared to non-Hispanic White populations, CRC incidence was higher among American Indian or Alaska Native individuals in some areas such as Alaska and the Northern Plains.25,26 Studies have noted that rural American Indian/Alaska Native populations experience greater poverty, less access to broadband internet, and limited access to care, contributing to poorer cancer outcomes and lower survival.27 Thus, the finding of disparity in mortality between rural and urban American Indian or Alaska Native veterans warrants further study.
Other studies have raised concerns that CRC disproportionately affects adults in rural areas with higher mortality rates.14-16 These disparities arise from sociodemographic factors and modifiable risk factors, including physical activity, dietary patterns, access to cancer screening, and gaps in quality treatment resources.16,28 These factors operate at multiple levels: from individual, local health system, to community and policy.2,27 For example, a South Carolina study (1996–2016) found that residents in rural areas were more likely to be diagnosed with advanced CRC, possibly indicating lower rates of CRC screening in rural areas. They also had higher likelihood of death from CRC.15 However, the study did not include any clinical parameters, such as comorbidities or obesity. A statewide, population-based study in Utah showed that rural men experienced a lower CRC survival in their unadjusted analysis.16 However, the study was small, with only 3948 urban and 712 rural residents. Additionally, there was no difference in total mortality in the whole cohort (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.86-1.07) or in CRC-specific death (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.81-1.08). A nationwide study also showed that CRC mortality rates were 8% higher in nonmetropolitan or rural areas than in the most urbanized areas containing large metropolitan counties.29 However, this study did not include descriptions of clinical confounders, such as comorbidities, making it difficult to ascertain whether the difference in CRC mortality was due to rurality or differences in baseline risk characteristics.
In this study, the lack of CRC-specific mortality disparities may be attributed to the structures and practices of VHA health care. Recent studies have noted that mortality of several chronic medical conditions treated at the VHA was lower than at non-VHA hospitals.30,31 One study that measured the quality of nonmetastatic CRC care based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines showed that > 72% of VHA patients received guideline-concordant care for each diagnostic and therapeutic measure, except for follow-up colonoscopy timing, which appear to be similar or superior to that of the private sector.30,32,33 Some of the VA initiative for CRC screening may bypass the urban-rurality divide such as the mailed fecal immunochemical test program for CRC. This program was implemented at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic to avoid disruptions of medical care.34 Rural patients are more likely to undergo fecal immunochemical testing when compared to urban patients in this data. Beyond clinical care, the VHA uses processes to tackle social determinants of health such as housing, food security, and transportation, promoting equal access to health care, and promoting cultural competency among HCPs.35-37
The results suggest that solutions to CRC disparities between rural and urban areas need to consider known barriers to rural health care, including transportation, diminished rural health care workforce, and other social determinants of health.9,10,27,38 VHA makes considerable efforts to provide equitable care to all enrolled veterans, including specific programs for rural veterans, including ongoing outreach.39 This study demonstrated lack of disparity in CRC-specific mortality in veterans receiving VHA care, highlighting the importance of these efforts.
Strengths and Limitations
This study used the VHA cohort to compare patient characteristics and mortality between patients with CRC residing in rural and urban areas. The study provides nationwide perspectives on CRC across the geographical spectrum and used a longitudinal cohort with prolonged follow-up to account for comorbidities.
However, the study compared a cohort of rural and urban veterans enrolled in the VHA; hence, the results may not reflect CRC outcomes in veterans without access to VHA care. Rurality has been independently associated with decreased likelihood of meeting CRC screening guidelines among veterans and military service members.38 This study lacked sufficient information to compare CRC staging or treatment modalities among veterans. Although the data cannot identify CRC stage, the proportions of patients with metastatic CRC at diagnosis and CRC location were similar between groups. The study did not have information on their care outside of VHA setting.
This study could not ascertain whether disparities existed in CRC treatment modality since rural residence may result in referral to community-based CRC care, which did not appear in the data. To address these limitations, we used death from any cause as the primary outcome, since death is a hard outcome and is not subject to ascertainment bias. The relatively short follow-up time is another limitation, though subgroup analysis by follow-up did not show significant differences. Despite PS matching, residual unmeasured confounding may exist between urban and rural groups. The predominantly White, male VHA population with high CCI may limit the generalizability of the results.
Conclusions
Rural VHA enrollees had similar survival rates after CRC diagnosis compared to their urban counterparts in a PS-matched analysis. The VHA models of care—including mailed CRC screening tools, several socioeconomic determinants of health (housing, food security, and transportation), and promoting equal access to health care, as well as cultural competency among HCPs—HCPs—may help alleviate disparities across the rural-urban spectrum. The VHA should continue efforts to enroll veterans and provide comprehensive coordinated care in community partnerships.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second-leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States, with an estimated 52,550 deaths in 2023.1 However, the disease burden varies among different segments of the population.2 While both CRC incidence and mortality have been decreasing due to screening and advances in treatment, there are disparities in incidence and mortality across the sociodemographic spectrum including race, ethnicity, education, and income.1-4 While CRC incidence is decreasing for older adults, it is increasing among those aged < 55 years.5 The incidence of CRC in adults aged 40 to 54 years has increased by 0.5% to 1.3% annually since the mid-1990s.6 The US Preventive Services Task Force now recommends starting CRC screening at age 45 years for asymptomatic adults with average risk.7
Disparities also exist across geographical boundaries and living environment. Rural Americans faces additional challenges in health and lifestyle that can affect CRC outcomes. Compared to their urban counterparts, rural residents are more likely to be older, have lower levels of education, higher levels of poverty, lack health insurance, and less access to health care practitioners (HCPs).8-10 Geographic proximity, defined as travel time or physical distance to a health facility, has been recognized as a predictor of inferior outcomes.11 These aspects of rural living may pose challenges for accessing care for CRC screening and treatment.11-13 National and local studies have shown disparities in CRC screening rates, incidence, and mortality between rural and urban populations.14-16
It is unclear whether rural/urban disparities persist under the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) health care delivery model. This study examined differences in baseline characteristics and mortality between rural and urban veterans newly diagnosed with CRC. We also focused on a subpopulation aged ≤ 45 years.
Methods
This study extracted national data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) hosted in the VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI) environment. VINCI is an initiative to improve access to VA data and facilitate the analysis of these data while ensuring veterans’ privacy and data security.17 CDW is the VHA business intelligence information repository, which extracts data from clinical and nonclinical sources following prescribed and validated protocols. Data extracted included demographics, diagnosis, and procedure codes for both inpatient and outpatient encounters, vital signs, and vital status. This study used data previously extracted from a national cohort of veterans that encompassed all patients who received a group of commonly prescribed medications, such as statins, proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 blockers, acetaminophen-containing products, and hydrocortisone-containing skin applications. This cohort encompassed 8,648,754 veterans, from whom 2,460,727 had encounters during fiscal years (FY) 2016 to 2021 (study period). The cohort was used to ensure that subjects were VHA patients, allowing them to adequately capture their clinical profiles.
Patients were identified as rural or urban based on their residence address at the date of their first diagnosis of CRC. The Geospatial Service Support Center (GSSC) aggregates and updates veterans’ residence address records for all enrolled veterans from the National Change of Address database. The data contain 1 record per enrollee. GSSC Geocoded Enrollee File contains enrollee addresses and their rurality indicators, categorized as urban, rural, or highly rural.18 Rurality is defined by the Rural Urban Commuting Area (RUCA) categories developed by the Department of Agriculture and the Health Resources and Services Administration of the US Department of Health and Human Services.19 Urban areas had RUCA codes of 1.0 to 1.1, and highly rural areas had RUCA scores of 10.0. All other areas were classified as rural. Since the proportion of veterans from highly rural areas was small, we included residents from highly rural areas in the rural residents’ group.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
All veterans newly diagnosed with CRC from FY 2016 to 2021 were included. We used the ninth and tenth clinical modification revisions of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM) to define CRC diagnosis (Supplemental materials).4,20 To ensure that patients were newly diagnosed with CRC, this study excluded patients with a previous ICD-9-CM code for CRC diagnosis since FY 2003.
Comorbidities were identified using diagnosis and procedure codes from inpatient and outpatient encounters, which were used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) at the time of CRC diagnosis using the weighted method described by Schneeweiss et al.21 We defined CRC high-risk conditions and CRC screening tests, including flexible sigmoidoscopy and stool tests, as described in previous studies (Supplemental materials).20
The main outcome was total mortality. The date of death was extracted from the VHA Death Ascertainment File, which contains mortality data from the Master Person Index file in CDW and the Social Security Administration Death Master File. We used the date of death from any cause, as cause of death was not available.
A propensity score (PS) was created to match rural (including highly rural) and urban residents at a ratio of 1:1. Using a standard procedure described in prior publications, multivariable logistic regression used all baseline characteristics to estimate the PS and perform nearest-number matching without replacement.22,23 A caliper of 0.01 maximized the matched cohort size and achieved balance (Supplemental materials). We then examined the balance of baseline characteristics between PS-matched groups.
Analyses
Cox proportional hazards regression analysis estimated the hazard ratio (HR) of death in rural residents compared to urban residents in the PS-matched cohort. The outcome event was the date of death during the study’s follow-up period (defined as period from first CRC diagnosis to death or study end), with censoring at the study’s end date (September 30, 2021). The proportional hazards assumption was assessed by inspecting the Kaplan-Meier curves. Multiple analyses examined the HR of total mortality in the PS-matched cohort, stratified by sex, race, and ethnicity. We also examined the HR of total mortality stratified by duration of follow-up.
Another PS-matching analysis among veterans aged ≤ 45 years was performed using the same techniques described earlier in this article. We performed a Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to compare mortality in PS-matched urban and rural veterans aged ≤ 45 years. The HR of death in all veterans aged ≤ 45 years (before PS-matching) was estimated using Cox proportional hazard regression analysis, adjusting for PS.
Dichotomous variables were compared using X2 tests and continuous variables were compared using t tests. Baseline characteristics with missing values were converted into categorical variables and the proportion of subjects with missing values was equalized between treatment groups after PS-matching. For subgroup analysis, we examined the HR of total mortality in each subgroup using separate Cox proportional hazards regression models similar to the primary analysis but adjusted for PS. Due to multiple comparisons in the subgroup analysis, the findings should be considered exploratory. Statistical tests were 2-tailed, and significance was defined as P < .05. Data management and statistical analyses were conducted from June 2022 to January 2023 using STATA, Version 17. The VA Orlando Healthcare System Institutional Review Board approved the study and waived requirements for informed consent because only deidentified data were used.
Results
After excluding 49 patients (Supplemental materials, available at doi:10.12788/fp.0560), we identified 30,219 veterans with newly diagnosed CRC between FY 2016 to 2021 (Table 1). Of these, 19,422 (64.3%) resided in urban areas and 10,797 (35.7%) resided in rural areas (Table 2). The mean (SD) duration from the first CRC diagnosis to death or study end was 832 (640) days, and the median (IQR) was 723 (246–1330) days. Overall, incident CRC diagnoses were numerically highest in FY 2016 and lowest in FY 2020 (Figure 1). Patients with CRC in rural areas vs urban areas were significantly older (mean, 71.2 years vs 70.8 years, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be male (96.7% vs 95.7%, respectively; P < .001), more likely to be White (83.6% vs 67.8%, respectively; P < .001) and more likely to be non-Hispanic (92.2% vs 87.5%, respectively; P < .001). In terms of general health, rural veterans with CRC were more likely to be overweight or obese (81.5% rural vs 78.5% urban; P < .001) but had fewer mean comorbidities as measured by CCI (5.66 rural vs 5.90 urban; P < .001). A higher proportion of rural veterans with CRC had received stool-based (fecal occult blood test or fecal immunochemical test) CRC screening tests (61.6% rural vs 57.2% urban; P < .001). Fewer rural patients presented with systemic symptoms or signs within 1 year of CRC diagnosis (54.4% rural vs 57.5% urban, P < .001). Among urban patients with CRC, 6959 (35.8%) deaths were observed, compared with 3766 (34.9%) among rural patients (P = .10).



There were 21,568 PS-matched veterans: 10,784 in each group. In the PS-matched cohort, baseline characteristics were similar between veterans in urban and rural communities, including age, sex, race/ethnicity, body mass index, and comorbidities. Among rural patients with CRC, 3763 deaths (34.9%) were observed compared with 3702 (34.3%) among urban veterans. There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban CRC residents (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.97-1.06; P = .53) (Figure 2).



Among veterans aged ≤ 45 years, 551 were diagnosed with CRC (391 urban and 160 rural). We PS-matched 142 pairs of urban and rural veterans without residual differences in baseline characteristics (eAppendix 1). There was no significant difference in the HR of mortality between rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.57-1.63; P = .90) (Figure 2). Similarly, no difference in mortality was observed adjusting for PS between all rural and urban veterans aged ≤ 45 years (HR, 1.03; 95% CI, 0.67-1.59; P = .88).

There was no difference in total mortality between rural and urban veterans in any subgroup except for American Indian or Alaska Native veterans (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006) (eAppendix 2).

Discussion
This study examined characteristics of patients with CRC between urban and rural areas among veterans who were VHA patients. Similar to other studies, rural veterans with CRC were older, more likely to be White, and were obese, but exhibited fewer comorbidities (lower CCI and lower incidence of congestive heart failure, dementia, hemiplegia, kidney diseases, liver diseases and AIDS, but higher incidence of chronic obstructive lung disease).8,16 The incidence of CRC in this study population was lowest in FY 2020, which was reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and is attributed to COVID-19 pandemic disruption of health services.24 The overall mortality in this study was similar to rates reported in other studies from the VA Central Cancer Registry.4 In the PS-matched cohort, where baseline characteristics were similar between urban and rural patients with CRC, we found no disparities in CRC-specific mortality between veterans in rural and urban areas. Additionally, when analysis was restricted to veterans aged ≤ 45 years, the results remained consistent.
Subgroup analyses showed no significant difference in mortality between rural and urban areas by sex, race or ethnicity, except rural American Indian or Alaska Native veterans who had double the mortality of their urban counterparts (HR, 2.41; 95% CI, 1.29-4.50; P = .006). This finding is difficult to interpret due to the small number of events and the wide CI. While with a Bonferroni correction the adjusted P value was .08, which is not statistically significant, a previous study found that although CRC incidence was lower overall in American Indian or Alaska Native populations compared to non-Hispanic White populations, CRC incidence was higher among American Indian or Alaska Native individuals in some areas such as Alaska and the Northern Plains.25,26 Studies have noted that rural American Indian/Alaska Native populations experience greater poverty, less access to broadband internet, and limited access to care, contributing to poorer cancer outcomes and lower survival.27 Thus, the finding of disparity in mortality between rural and urban American Indian or Alaska Native veterans warrants further study.
Other studies have raised concerns that CRC disproportionately affects adults in rural areas with higher mortality rates.14-16 These disparities arise from sociodemographic factors and modifiable risk factors, including physical activity, dietary patterns, access to cancer screening, and gaps in quality treatment resources.16,28 These factors operate at multiple levels: from individual, local health system, to community and policy.2,27 For example, a South Carolina study (1996–2016) found that residents in rural areas were more likely to be diagnosed with advanced CRC, possibly indicating lower rates of CRC screening in rural areas. They also had higher likelihood of death from CRC.15 However, the study did not include any clinical parameters, such as comorbidities or obesity. A statewide, population-based study in Utah showed that rural men experienced a lower CRC survival in their unadjusted analysis.16 However, the study was small, with only 3948 urban and 712 rural residents. Additionally, there was no difference in total mortality in the whole cohort (HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.86-1.07) or in CRC-specific death (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.81-1.08). A nationwide study also showed that CRC mortality rates were 8% higher in nonmetropolitan or rural areas than in the most urbanized areas containing large metropolitan counties.29 However, this study did not include descriptions of clinical confounders, such as comorbidities, making it difficult to ascertain whether the difference in CRC mortality was due to rurality or differences in baseline risk characteristics.
In this study, the lack of CRC-specific mortality disparities may be attributed to the structures and practices of VHA health care. Recent studies have noted that mortality of several chronic medical conditions treated at the VHA was lower than at non-VHA hospitals.30,31 One study that measured the quality of nonmetastatic CRC care based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines showed that > 72% of VHA patients received guideline-concordant care for each diagnostic and therapeutic measure, except for follow-up colonoscopy timing, which appear to be similar or superior to that of the private sector.30,32,33 Some of the VA initiative for CRC screening may bypass the urban-rurality divide such as the mailed fecal immunochemical test program for CRC. This program was implemented at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic to avoid disruptions of medical care.34 Rural patients are more likely to undergo fecal immunochemical testing when compared to urban patients in this data. Beyond clinical care, the VHA uses processes to tackle social determinants of health such as housing, food security, and transportation, promoting equal access to health care, and promoting cultural competency among HCPs.35-37
The results suggest that solutions to CRC disparities between rural and urban areas need to consider known barriers to rural health care, including transportation, diminished rural health care workforce, and other social determinants of health.9,10,27,38 VHA makes considerable efforts to provide equitable care to all enrolled veterans, including specific programs for rural veterans, including ongoing outreach.39 This study demonstrated lack of disparity in CRC-specific mortality in veterans receiving VHA care, highlighting the importance of these efforts.
Strengths and Limitations
This study used the VHA cohort to compare patient characteristics and mortality between patients with CRC residing in rural and urban areas. The study provides nationwide perspectives on CRC across the geographical spectrum and used a longitudinal cohort with prolonged follow-up to account for comorbidities.
However, the study compared a cohort of rural and urban veterans enrolled in the VHA; hence, the results may not reflect CRC outcomes in veterans without access to VHA care. Rurality has been independently associated with decreased likelihood of meeting CRC screening guidelines among veterans and military service members.38 This study lacked sufficient information to compare CRC staging or treatment modalities among veterans. Although the data cannot identify CRC stage, the proportions of patients with metastatic CRC at diagnosis and CRC location were similar between groups. The study did not have information on their care outside of VHA setting.
This study could not ascertain whether disparities existed in CRC treatment modality since rural residence may result in referral to community-based CRC care, which did not appear in the data. To address these limitations, we used death from any cause as the primary outcome, since death is a hard outcome and is not subject to ascertainment bias. The relatively short follow-up time is another limitation, though subgroup analysis by follow-up did not show significant differences. Despite PS matching, residual unmeasured confounding may exist between urban and rural groups. The predominantly White, male VHA population with high CCI may limit the generalizability of the results.
Conclusions
Rural VHA enrollees had similar survival rates after CRC diagnosis compared to their urban counterparts in a PS-matched analysis. The VHA models of care—including mailed CRC screening tools, several socioeconomic determinants of health (housing, food security, and transportation), and promoting equal access to health care, as well as cultural competency among HCPs—HCPs—may help alleviate disparities across the rural-urban spectrum. The VHA should continue efforts to enroll veterans and provide comprehensive coordinated care in community partnerships.
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Carethers JM, Doubeni CA. Causes of socioeconomic disparities in colorectal cancer and intervention framework and strategies. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(2):354-367. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.029
- Murphy G, Devesa SS, Cross AJ, Inskip PD, McGlynn KA, Cook MB. Sex disparities in colorectal cancer incidence by anatomic subsite, race and age. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(7):1668-75. doi:10.1002/ijc.25481
- Zullig LL, Smith VA, Jackson GL, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics from the Veterans Affairs central cancer registry. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016;15(4):e199-e204. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2016.04.005
- Lin JS, Perdue LA, Henrikson NB, Bean SI, Blasi PR. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence Update for the US Preventive Services Task Force. 2021. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews:Chapter 1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570917/
- Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Anderson WF, et al. Colorectal cancer incidence patterns in the United States, 1974-2013. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(8). doi:10.1093/jnci/djw322
- Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
- Hines R, Markossian T, Johnson A, Dong F, Bayakly R. Geographic residency status and census tract socioeconomic status as determinants of colorectal cancer outcomes. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(3):e63-e71. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.301572
- Cauwels J. The many barriers to high-quality rural health care. 2022;(9):1-32. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. Accessed April 24, 2025. https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/CAT.22.0254
- Gong G, Phillips SG, Hudson C, Curti D, Philips BU. Higher US rural mortality rates linked to socioeconomic status, physician shortages, and lack of health insurance. Health Aff (Millwood);38(12):2003-2010. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.00722
- Aboagye JK, Kaiser HE, Hayanga AJ. Rural-urban differences in access to specialist providers of colorectal cancer care in the United States: a physician workforce issue. JAMA Surg. 2014;149(6):537-543. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.5062
- Lyckholm LJ, Hackney MH, Smith TJ. Ethics of rural health care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001;40(2):131-138. doi:10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00139-1
- Krieger N, Williams DR, Moss NE. Measuring social class in US public health research: concepts, methodologies, and guidelines. Annu Rev Public Health. 1997;18:341-378. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.18.1.341
- Singh GK, Jemal A. Socioeconomic and racial/ethnic disparities in cancer mortality, incidence, and survival in the United States, 1950-2014: over six decades of changing patterns and widening inequalities. J Environ Public Health. 2017;2017:2819372. doi:10.1155/2017/2819372
- Adams SA, Zahnd WE, Ranganathan R, et al. Rural and racial disparities in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in South Carolina, 1996 - 2016. J Rural Health. 2022;38(1):34-39. doi:10.1111/jrh.12580
- Rogers CR, Blackburn BE, Huntington M, et al. Rural- urban disparities in colorectal cancer survival and risk among men in Utah: a statewide population-based study. Cancer Causes Control. 2020;31(3):241-253. doi:10.1007/s10552-020-01268-2
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI), VA HSR RES 13-457. https://vincicentral.vinci.med.va.gov [Source not verified]
- US Department of Veterans Affairs Information Resource Center. VIReC Research User Guide: PSSG Geocoded Enrollee Files, 2015 Edition. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research & Development Service, Information Resource Center; May. 2016. [source not verified]
- Goldsmith HF, Puskin DS, Stiles DJ. Improving the operational definition of “rural areas” for federal programs. US Department of Health and Human Services; 1993. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/pdf/improving-the-operational-definition-of-rural-areas.pdf
- Adams MA, Kerr EA, Dominitz JA, et al. Development and validation of a new ICD-10-based screening colonoscopy overuse measure in a large integrated healthcare system: a retrospective observational study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32(7):414-424. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014236
- Schneeweiss S, Wang PS, Avorn J, Glynn RJ. Improved comorbidity adjustment for predicting mortality in Medicare populations. Health Serv Res. 2003;38(4):1103-1120. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.00165
- Becker S, Ichino A. Estimation of average treatment effects based on propensity scores. The Stata Journal. 2002;2(4):358-377.
- Leuven E, Sianesi B. PSMATCH2: Stata module to perform full Mahalanobis and propensity score matching, common support graphing, and covariate imbalance testing. Statistical software components. Revised February 1, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/s432001.html.
- US Cancer Statistics Working Group. US cancer statistics data visualizations tool. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 2024. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dataviz
- Cao J, Zhang S. Multiple Comparison Procedures. JAMA. 2014;312(5):543-544. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9440
- Gopalani SV, Janitz AE, Martinez SA, et al. Trends in cancer incidence among American Indians and Alaska Natives and Non-Hispanic Whites in the United States, 1999-2015. Epidemiology. 2020;31(2):205-213. doi:10.1097/EDE.0000000000001140
- Zahnd WE, Murphy C, Knoll M, et al. The intersection of rural residence and minority race/ethnicity in cancer disparities in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4). doi:10.3390/ijerph18041384
- Blake KD, Moss JL, Gaysynsky A, Srinivasan S, Croyle RT. Making the case for investment in rural cancer control: an analysis of rural cancer incidence, mortality, and funding trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(7):992-997. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0092
- Singh GK, Williams SD, Siahpush M, Mulhollen A. Socioeconomic, rural-urban, and racial inequalities in US cancer mortality: part i-all cancers and lung cancer and part iicolorectal, prostate, breast, and cervical cancers. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;2011:107497. doi:10.1155/2011/107497
- Jackson GL, Melton LD, Abbott DH, et al. Quality of nonmetastatic colorectal cancer care in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(19):3176-3181. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7948
- Yoon J, Phibbs CS, Ong MK, et al. Outcomes of veterans treated in Veterans Affairs hospitals vs non-Veterans Affairs hospitals. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(12):e2345898. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.45898
- Malin JL, Schneider EC, Epstein AM, Adams J, Emanuel EJ, Kahn KL. Results of the National Initiative for Cancer Care Quality: how can we improve the quality of cancer care in the United States? J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(4):626-634. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3365
- Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(5):1570-1595. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.002
- Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among Veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4). doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
- Yehia BR, Greenstone CL, Hosenfeld CB, Matthews KL, Zephyrin LC. The role of VA community care in addressing health and health care disparities. Med Care. 2017;55(Suppl 9 suppl 2):S4-S5. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000768
- Wright BN, MacDermid Wadsworth S, Wellnitz A, Eicher- Miller HA. Reaching rural veterans: a new mechanism to connect rural, low-income US Veterans with resources and improve food security. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019;41(4):714-723. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdy203
- Nelson RE, Byrne TH, Suo Y, et al. Association of temporary financial assistance with housing stability among US veterans in the supportive services for veteran families program. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037047. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37047
- McDaniel JT, Albright D, Lee HY, et al. Rural–urban disparities in colorectal cancer screening among military service members and Veterans. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2019;5(1):40-48. doi:10.3138/jmvfh.2018-0013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. The rural veteran outreach toolkit. Updated February 12, 2025. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/partners/toolkit.asp
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Carethers JM, Doubeni CA. Causes of socioeconomic disparities in colorectal cancer and intervention framework and strategies. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(2):354-367. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.029
- Murphy G, Devesa SS, Cross AJ, Inskip PD, McGlynn KA, Cook MB. Sex disparities in colorectal cancer incidence by anatomic subsite, race and age. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(7):1668-75. doi:10.1002/ijc.25481
- Zullig LL, Smith VA, Jackson GL, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics from the Veterans Affairs central cancer registry. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2016;15(4):e199-e204. doi:10.1016/j.clcc.2016.04.005
- Lin JS, Perdue LA, Henrikson NB, Bean SI, Blasi PR. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: An Evidence Update for the US Preventive Services Task Force. 2021. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews:Chapter 1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570917/
- Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Anderson WF, et al. Colorectal cancer incidence patterns in the United States, 1974-2013. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017;109(8). doi:10.1093/jnci/djw322
- Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
- Hines R, Markossian T, Johnson A, Dong F, Bayakly R. Geographic residency status and census tract socioeconomic status as determinants of colorectal cancer outcomes. Am J Public Health. 2014;104(3):e63-e71. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2013.301572
- Cauwels J. The many barriers to high-quality rural health care. 2022;(9):1-32. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. Accessed April 24, 2025. https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/CAT.22.0254
- Gong G, Phillips SG, Hudson C, Curti D, Philips BU. Higher US rural mortality rates linked to socioeconomic status, physician shortages, and lack of health insurance. Health Aff (Millwood);38(12):2003-2010. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2019.00722
- Aboagye JK, Kaiser HE, Hayanga AJ. Rural-urban differences in access to specialist providers of colorectal cancer care in the United States: a physician workforce issue. JAMA Surg. 2014;149(6):537-543. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.5062
- Lyckholm LJ, Hackney MH, Smith TJ. Ethics of rural health care. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001;40(2):131-138. doi:10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00139-1
- Krieger N, Williams DR, Moss NE. Measuring social class in US public health research: concepts, methodologies, and guidelines. Annu Rev Public Health. 1997;18:341-378. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.18.1.341
- Singh GK, Jemal A. Socioeconomic and racial/ethnic disparities in cancer mortality, incidence, and survival in the United States, 1950-2014: over six decades of changing patterns and widening inequalities. J Environ Public Health. 2017;2017:2819372. doi:10.1155/2017/2819372
- Adams SA, Zahnd WE, Ranganathan R, et al. Rural and racial disparities in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality in South Carolina, 1996 - 2016. J Rural Health. 2022;38(1):34-39. doi:10.1111/jrh.12580
- Rogers CR, Blackburn BE, Huntington M, et al. Rural- urban disparities in colorectal cancer survival and risk among men in Utah: a statewide population-based study. Cancer Causes Control. 2020;31(3):241-253. doi:10.1007/s10552-020-01268-2
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI), VA HSR RES 13-457. https://vincicentral.vinci.med.va.gov [Source not verified]
- US Department of Veterans Affairs Information Resource Center. VIReC Research User Guide: PSSG Geocoded Enrollee Files, 2015 Edition. US Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research & Development Service, Information Resource Center; May. 2016. [source not verified]
- Goldsmith HF, Puskin DS, Stiles DJ. Improving the operational definition of “rural areas” for federal programs. US Department of Health and Human Services; 1993. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/pdf/improving-the-operational-definition-of-rural-areas.pdf
- Adams MA, Kerr EA, Dominitz JA, et al. Development and validation of a new ICD-10-based screening colonoscopy overuse measure in a large integrated healthcare system: a retrospective observational study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2023;32(7):414-424. doi:10.1136/bmjqs-2021-014236
- Schneeweiss S, Wang PS, Avorn J, Glynn RJ. Improved comorbidity adjustment for predicting mortality in Medicare populations. Health Serv Res. 2003;38(4):1103-1120. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.00165
- Becker S, Ichino A. Estimation of average treatment effects based on propensity scores. The Stata Journal. 2002;2(4):358-377.
- Leuven E, Sianesi B. PSMATCH2: Stata module to perform full Mahalanobis and propensity score matching, common support graphing, and covariate imbalance testing. Statistical software components. Revised February 1, 2018. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://ideas.repec.org/c/boc/bocode/s432001.html.
- US Cancer Statistics Working Group. US cancer statistics data visualizations tool. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. June 2024. Accessed February 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dataviz
- Cao J, Zhang S. Multiple Comparison Procedures. JAMA. 2014;312(5):543-544. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9440
- Gopalani SV, Janitz AE, Martinez SA, et al. Trends in cancer incidence among American Indians and Alaska Natives and Non-Hispanic Whites in the United States, 1999-2015. Epidemiology. 2020;31(2):205-213. doi:10.1097/EDE.0000000000001140
- Zahnd WE, Murphy C, Knoll M, et al. The intersection of rural residence and minority race/ethnicity in cancer disparities in the United States. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4). doi:10.3390/ijerph18041384
- Blake KD, Moss JL, Gaysynsky A, Srinivasan S, Croyle RT. Making the case for investment in rural cancer control: an analysis of rural cancer incidence, mortality, and funding trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26(7):992-997. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0092
- Singh GK, Williams SD, Siahpush M, Mulhollen A. Socioeconomic, rural-urban, and racial inequalities in US cancer mortality: part i-all cancers and lung cancer and part iicolorectal, prostate, breast, and cervical cancers. J Cancer Epidemiol. 2011;2011:107497. doi:10.1155/2011/107497
- Jackson GL, Melton LD, Abbott DH, et al. Quality of nonmetastatic colorectal cancer care in the Department of Veterans Affairs. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(19):3176-3181. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7948
- Yoon J, Phibbs CS, Ong MK, et al. Outcomes of veterans treated in Veterans Affairs hospitals vs non-Veterans Affairs hospitals. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(12):e2345898. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.45898
- Malin JL, Schneider EC, Epstein AM, Adams J, Emanuel EJ, Kahn KL. Results of the National Initiative for Cancer Care Quality: how can we improve the quality of cancer care in the United States? J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(4):626-634. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3365
- Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(5):1570-1595. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.02.002
- Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among Veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4). doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
- Yehia BR, Greenstone CL, Hosenfeld CB, Matthews KL, Zephyrin LC. The role of VA community care in addressing health and health care disparities. Med Care. 2017;55(Suppl 9 suppl 2):S4-S5. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000768
- Wright BN, MacDermid Wadsworth S, Wellnitz A, Eicher- Miller HA. Reaching rural veterans: a new mechanism to connect rural, low-income US Veterans with resources and improve food security. J Public Health (Oxf). 2019;41(4):714-723. doi:10.1093/pubmed/fdy203
- Nelson RE, Byrne TH, Suo Y, et al. Association of temporary financial assistance with housing stability among US veterans in the supportive services for veteran families program. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(2):e2037047. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37047
- McDaniel JT, Albright D, Lee HY, et al. Rural–urban disparities in colorectal cancer screening among military service members and Veterans. J Mil Veteran Fam Health. 2019;5(1):40-48. doi:10.3138/jmvfh.2018-0013
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rural Health. The rural veteran outreach toolkit. Updated February 12, 2025. Accessed February 18, 2025. https://www.ruralhealth.va.gov/partners/toolkit.asp
Colorectal Cancer Characteristics and Mortality From Propensity Score-Matched Cohorts of Urban and Rural Veterans
Colorectal Cancer Characteristics and Mortality From Propensity Score-Matched Cohorts of Urban and Rural Veterans
Cancer Data Trends 2025
The annual issue of Cancer Data Trends, produced in collaboration with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), highlights the latest research in some of the top cancers impacting US veterans.
In this issue:
- Access, Race, and "Colon Age": Improving CRC Screening
- Lung Cancer: Mortality Trends in Veterans and New Treatments
- Racial Disparities, Germline Testing, and Improved Overall Survival in Prostate Cancer
- Breast and Uterine Cancer: Screening Guidelines, Genetic Testing, and Mortality Trends
- HCC Updates: Quality Care Framework and Risk Stratification Data
- Rising Kidney Cancer Cases and Emerging Treatments for Veterans
- Advances in Blood Cancer Care for Veterans
- AI-Based Risk Stratification for Oropharyngeal Carcinomas: AIROC
- Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
The annual issue of Cancer Data Trends, produced in collaboration with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), highlights the latest research in some of the top cancers impacting US veterans.
In this issue:
- Access, Race, and "Colon Age": Improving CRC Screening
- Lung Cancer: Mortality Trends in Veterans and New Treatments
- Racial Disparities, Germline Testing, and Improved Overall Survival in Prostate Cancer
- Breast and Uterine Cancer: Screening Guidelines, Genetic Testing, and Mortality Trends
- HCC Updates: Quality Care Framework and Risk Stratification Data
- Rising Kidney Cancer Cases and Emerging Treatments for Veterans
- Advances in Blood Cancer Care for Veterans
- AI-Based Risk Stratification for Oropharyngeal Carcinomas: AIROC
- Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
The annual issue of Cancer Data Trends, produced in collaboration with the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), highlights the latest research in some of the top cancers impacting US veterans.
In this issue:
- Access, Race, and "Colon Age": Improving CRC Screening
- Lung Cancer: Mortality Trends in Veterans and New Treatments
- Racial Disparities, Germline Testing, and Improved Overall Survival in Prostate Cancer
- Breast and Uterine Cancer: Screening Guidelines, Genetic Testing, and Mortality Trends
- HCC Updates: Quality Care Framework and Risk Stratification Data
- Rising Kidney Cancer Cases and Emerging Treatments for Veterans
- Advances in Blood Cancer Care for Veterans
- AI-Based Risk Stratification for Oropharyngeal Carcinomas: AIROC
- Brain Cancer: Epidemiology, TBI, and New Treatments
Population vs Tailored Skin Cancer Screening: Which Is Best?
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM WCM-EADO 2025
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
VA Cancer Clinical Trials as a Strategy for Increasing Accrual of Racial and Ethnic Underrepresented Groups
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.

Improving Colorectal Cancer Screening via Mailed Fecal Immunochemical Testing in a Veterans Affairs Health System
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
AI in Mammography: Inside the Tangible Benefits Ready Now
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.