User login
Hepatitis D Virus Classified as Carcinogenic: Implications
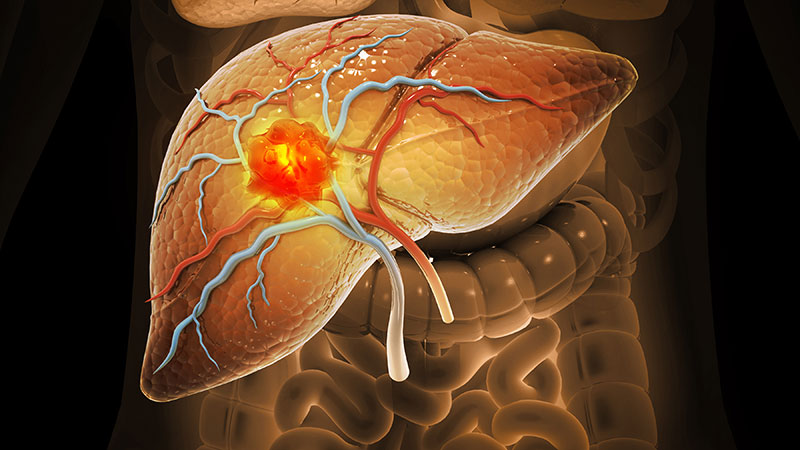
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Veterans are especially vulnerable to disordered eating because of their military backgrounds, a dietician warned US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) oncology clinicians at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology. In fact, an estimated 15% to 25% of veterans meet diagnostic criteria for eating disorders.
“Their experience in the military probably has really shaped the way that they see weight and the stigma behind it,” said Emily Fasciana, MS, RDN, LDN, a registered dietician with the VA based in Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania.
When cancer appears, the risk of eating disorders goes up even more, she said. “If we don’t catch eating disorders early on, severe medical problems can occur. In the cancer population, they’re going through enough medical problems as it is.”
Here are things to know about eating disorders in oncology.
Military Life Can Produce a ‘Perfect Storm’ of Risk Factors
Tightly controlled eating environments and food deprivation are often routine in military life. Along with trauma, these can create a “perfect storm of risk factors for eating disorders,” Fasciana said.
During service, for example, “people often will eat as much as they can when they can, sometimes followed by days of not being able to eat,” she said. These are very much like disordered eating behaviors such as binge eating and restricting, and they can place veterans at greater risk.”
She described how service members can develop specific eating patterns during service, such as “midrats” – midnight rations – “meals served during midnight shifts that were the best meal served all day long that they had access to.”
“When I hear veterans who wake up in the middle of the night, and they’re eating, I ask: ‘Did they practice something similar during their military experience?’ They associate that time of the day with enjoyable comfort foods, and that’s what they go to now.”
Vets Can be Haunted by Stigma of Excess Weight
“Making weight” – meeting weight standards – is routine in the military. The pressure to remain under a certain level can have lasting effects on how veterans think about extra pounds, said Kaitlin Ohde, PhD, a clinical health psychologist with the VA Puget Sound Health Care System in Seattle.
“I’ve heard some veterans tell me about getting kicked out of positions because of not being able to make weight. Then they carry this throughout their life, which is really sad,” Ohde said. “When they gain weight during treatment, sometimes it can be really bothersome for them.”
Regular weigh-ins can trouble patients, she said, so it’s important to explain to them why they’re getting on scales: “I’m getting your weight today because I want to see if this medication is doing XYZ.”
She advised colleagues to “make sure they explicitly know why we’re doing it [measuring weight], and how the things we’re using to treat them can impact their weight. This piece of the puzzle sometimes falls off the radar.”
Eating Disorders Can be Catastrophic in Cancer
Untreated eating disorders cause severe medical complications such as malnutrition, hormone dysregulation, low bone density or fractures, bradycardia, gastroparesis, and even anemia, Fasciana said.
There’s a New Category of Eating Disorder
Fasciana highlighted a condition that is underrecognized in oncology: Avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), which refers to patients who stay away from certain foods but not because they’re worried about body image or weight gain. “Patients with ARFID are clinically distinct from those who have anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder,” she noted.
ARFID diagnosis requires food avoidance that leads to at least 1 of these consequences: significant weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, dependence on supplements or tube feeding, or psychosocial impairment.
“Veterans might have a gagging or retching reflex at the sight or smell of certain foods,” Fasciana explained. “They might have difficulty being in the presence of another person eating a nonpreferred food.”
Some cancer patients may be averse to foods of certain temperatures. “You might need to assess why they don’t like the temperature of that food. Why are those foods something that you can’t go to? Are they hurting your teeth? What are they doing to you?”
ARFID patients may also experience social withdrawal around eating. “With a lot of our head and neck cancer patients, especially those with oral cancers and those on feeding tubes, they might feel embarrassed to be around people while eating,” Fasciana said.
She highlighted a 2021 report about 4 cancer survivors with upper abdominal cancers who developed new-onset eating disorders with malnutrition resembling ARFID.
The patients experienced malabsorption, dumping syndrome, and excessive weight loss for 12 months postoperatively without classic body-image concerns. “This is a case example of how eating disorders can evolve in the oncology population,” Fasciana said.
The report said that none of the patients “returned to a healthy weight and/or healthy eating despite extensive team input… The outcomes were poor; 1 patient died, another required admission to a specialist eating disorder admission with a subsequent relapsing-remitting course, and the remaining 2 had complicated chronic courses.”
Treatment: Start With Screening, Then Reframe Thinking
Fasciana highlighted several screening tools, such as SCOFF, BREDS, and one for ARFID.
“Any screen is going to be better than no screen at all, and any question is going to be better than no question at all,” Fasciana said.
She cautioned that “veterans are not going to be so forthcoming about some of their struggles due to stigma and shame because of their past experiences in the military.”
As for therapy, psychological care may not be required, Ohde said. And it’s especially important to “listen to your patients about what they’re going through, and give them space to share.”
For those who could be helped by psychotherapy, she said, “sometimes I introduce it as therapy that can be really brief. Maybe you just need to talk to someone for a few sessions or just get some support around coping with this.”
One strategy is to focus on bringing enjoyment back to eating, she said. For some patients, “eating becomes a chore,” a task performed without joy, alone in a hospital room.
Fasciana emphasized asking questions over time, perhaps through multiple follow-ups, without expecting answers immediately. And she coaxes patients to consider what they hold dear. “I try to get them to think about the meaning that losing or gaining weight has for them, what their values are, and what really matters to them. I link it back to health, healing, and longevity of life.”
Fasciana and Ohde reported they had no disclosures.
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Military Background Shapes Eating Disorders in VA Oncology
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
High-Risk Meds Worsen Cancer Outcomes in Veterans
TOPLINE:
High-risk medications defined by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and captured by the Geriatric Oncology Potentially Inappropriate Medication (GO-PIM) scale were prevalent in > one-third of veterans with solid and hematologic malignancies. Each additional GO-PIM was independently associated with higher risks for frailty at diagnosis, unplanned hospitalizations during follow-up, and death.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with cancer often use multiple chronic medications, raising risks for adverse events. Although several tools that identify PIMs have been developed that correlate with adverse cancer outcomes, their use is limited in busy oncology clinics. To improve implementation, researchers developed the GO-PIM scale using the NCCN’s list of high-risk medications.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the national Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and electronic health records, which included 388,113 veterans newly diagnosed with solid or hematologic malignancies (median age, 69.3 years; 97.9% men; 76.1% non-Hispanic White and 17.3% Black individuals) between 2000 and 2022.
- They identified GO-PIMs using outpatient pharmacy records in the 90 days preceding cancer diagnosis. Each prescription for a specific GO-PIM was counted as one, including both individual drugs and drug classes listed in the GO-PIM scale.
- Study outcomes were frailty, hospitalizations, and overall survival. Baseline frailty at diagnosis was measured using the Veterans Affairs Frailty Index. The score ranged from 0 to 1, and higher scores indicated greater frailty. Patients were classified as nonfrail (score, ≤ 0.2), mildly frail (score, > 0.2 to 0.3), or moderate-to-severely frail (score, > 0.3).
- Lung (23.7%), prostate (21.5%), and gastrointestinal (20.5%) cancers were the most common, and the most frequent stages were IV (25.4%) and II (24.4%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 38.0% of veterans were prescribed ≥ 1 GO-PIMs at the time of cancer diagnosis, and the proportion increased to 56.1% among those with moderate-to-severe frailty.
- The most commonly prescribed classes of PIMs were selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs; 12.0%), opioids (10.4%), benzodiazepines (9.2%), and corticosteroids (9.2%). Among individual drugs, sertraline was the most common SSRI (4.3%), tramadol the most common opioid (5.3%), lorazepam the most common benzodiazepine (2.5%), and prednisone the most common corticosteroid (4.9%). Trends over time showed a steady increase in opioid prescriptions, peaking in 2014, followed by a subsequent decline, while prescriptions of benzodiazepines declined during the later years.
- After adjusting for age, cancer type and stage, and other covariates, each additional GO-PIM was associated with a 66% higher odds of mild or moderate-to-severe frailty at diagnosis (adjusted odds ratio, 1.66).
- After adjusting for frailty and covariates, each additional GO-PIM at diagnosis was associated with increased risks for unplanned hospitalizations and death (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.08 and 1.07, respectively). These associations remained stable in sensitivity analyses that restricted GO-PIMs to scheduled medications only, focused on patients who had initiated cancer treatment, and included only those aged ≥ 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Whether prescribed for supportive oncology care or for coexisting medical conditions, high-risk medications identified as PIMs should be reviewed and optimized in patients with cancer,” the authors of the study wrote.
“GO-PIMs offers a streamlined, oncology-specific approach to identifying high-risk prescribing, and complements existing efforts to improve supportive care, especially for older, frail patients,” remarked Mostafa R. Mohamed, MBBCH, PhD, MSc, and Erika E. Ramsdale, MD, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York in an invited commentary. “The next step lies in integrating tools such as GO-PIMs into everyday practice not only to flag high risk medications but also to support actionable changes in treatment planning and patient management, such as deprescribing,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Jennifer La, PhD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
LIMITATIONS:
Prescription chronicity before or after follow-up was not measured and actual medication adherence could not be confirmed. Residual confounding by comorbidity could have existed, and the cross-sectional nature of linking GO-PIMs with frailty might have limited causal inference. Additionally, prescriptions were measured within Veterans Affairs pharmacy data, potentially underestimating GO-PIM prevalence, and the predominantly male population limited generalizability to gynecologic cancers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants and rewards from the Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Cooperative Studies Program, National Institutes of Health, and American Heart Association. Some authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants and having other ties with various sources. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High-risk medications defined by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and captured by the Geriatric Oncology Potentially Inappropriate Medication (GO-PIM) scale were prevalent in > one-third of veterans with solid and hematologic malignancies. Each additional GO-PIM was independently associated with higher risks for frailty at diagnosis, unplanned hospitalizations during follow-up, and death.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with cancer often use multiple chronic medications, raising risks for adverse events. Although several tools that identify PIMs have been developed that correlate with adverse cancer outcomes, their use is limited in busy oncology clinics. To improve implementation, researchers developed the GO-PIM scale using the NCCN’s list of high-risk medications.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the national Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and electronic health records, which included 388,113 veterans newly diagnosed with solid or hematologic malignancies (median age, 69.3 years; 97.9% men; 76.1% non-Hispanic White and 17.3% Black individuals) between 2000 and 2022.
- They identified GO-PIMs using outpatient pharmacy records in the 90 days preceding cancer diagnosis. Each prescription for a specific GO-PIM was counted as one, including both individual drugs and drug classes listed in the GO-PIM scale.
- Study outcomes were frailty, hospitalizations, and overall survival. Baseline frailty at diagnosis was measured using the Veterans Affairs Frailty Index. The score ranged from 0 to 1, and higher scores indicated greater frailty. Patients were classified as nonfrail (score, ≤ 0.2), mildly frail (score, > 0.2 to 0.3), or moderate-to-severely frail (score, > 0.3).
- Lung (23.7%), prostate (21.5%), and gastrointestinal (20.5%) cancers were the most common, and the most frequent stages were IV (25.4%) and II (24.4%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 38.0% of veterans were prescribed ≥ 1 GO-PIMs at the time of cancer diagnosis, and the proportion increased to 56.1% among those with moderate-to-severe frailty.
- The most commonly prescribed classes of PIMs were selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs; 12.0%), opioids (10.4%), benzodiazepines (9.2%), and corticosteroids (9.2%). Among individual drugs, sertraline was the most common SSRI (4.3%), tramadol the most common opioid (5.3%), lorazepam the most common benzodiazepine (2.5%), and prednisone the most common corticosteroid (4.9%). Trends over time showed a steady increase in opioid prescriptions, peaking in 2014, followed by a subsequent decline, while prescriptions of benzodiazepines declined during the later years.
- After adjusting for age, cancer type and stage, and other covariates, each additional GO-PIM was associated with a 66% higher odds of mild or moderate-to-severe frailty at diagnosis (adjusted odds ratio, 1.66).
- After adjusting for frailty and covariates, each additional GO-PIM at diagnosis was associated with increased risks for unplanned hospitalizations and death (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.08 and 1.07, respectively). These associations remained stable in sensitivity analyses that restricted GO-PIMs to scheduled medications only, focused on patients who had initiated cancer treatment, and included only those aged ≥ 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Whether prescribed for supportive oncology care or for coexisting medical conditions, high-risk medications identified as PIMs should be reviewed and optimized in patients with cancer,” the authors of the study wrote.
“GO-PIMs offers a streamlined, oncology-specific approach to identifying high-risk prescribing, and complements existing efforts to improve supportive care, especially for older, frail patients,” remarked Mostafa R. Mohamed, MBBCH, PhD, MSc, and Erika E. Ramsdale, MD, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York in an invited commentary. “The next step lies in integrating tools such as GO-PIMs into everyday practice not only to flag high risk medications but also to support actionable changes in treatment planning and patient management, such as deprescribing,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Jennifer La, PhD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
LIMITATIONS:
Prescription chronicity before or after follow-up was not measured and actual medication adherence could not be confirmed. Residual confounding by comorbidity could have existed, and the cross-sectional nature of linking GO-PIMs with frailty might have limited causal inference. Additionally, prescriptions were measured within Veterans Affairs pharmacy data, potentially underestimating GO-PIM prevalence, and the predominantly male population limited generalizability to gynecologic cancers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants and rewards from the Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Cooperative Studies Program, National Institutes of Health, and American Heart Association. Some authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants and having other ties with various sources. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
High-risk medications defined by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and captured by the Geriatric Oncology Potentially Inappropriate Medication (GO-PIM) scale were prevalent in > one-third of veterans with solid and hematologic malignancies. Each additional GO-PIM was independently associated with higher risks for frailty at diagnosis, unplanned hospitalizations during follow-up, and death.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with cancer often use multiple chronic medications, raising risks for adverse events. Although several tools that identify PIMs have been developed that correlate with adverse cancer outcomes, their use is limited in busy oncology clinics. To improve implementation, researchers developed the GO-PIM scale using the NCCN’s list of high-risk medications.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the national Veterans Affairs Cancer Registry and electronic health records, which included 388,113 veterans newly diagnosed with solid or hematologic malignancies (median age, 69.3 years; 97.9% men; 76.1% non-Hispanic White and 17.3% Black individuals) between 2000 and 2022.
- They identified GO-PIMs using outpatient pharmacy records in the 90 days preceding cancer diagnosis. Each prescription for a specific GO-PIM was counted as one, including both individual drugs and drug classes listed in the GO-PIM scale.
- Study outcomes were frailty, hospitalizations, and overall survival. Baseline frailty at diagnosis was measured using the Veterans Affairs Frailty Index. The score ranged from 0 to 1, and higher scores indicated greater frailty. Patients were classified as nonfrail (score, ≤ 0.2), mildly frail (score, > 0.2 to 0.3), or moderate-to-severely frail (score, > 0.3).
- Lung (23.7%), prostate (21.5%), and gastrointestinal (20.5%) cancers were the most common, and the most frequent stages were IV (25.4%) and II (24.4%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 38.0% of veterans were prescribed ≥ 1 GO-PIMs at the time of cancer diagnosis, and the proportion increased to 56.1% among those with moderate-to-severe frailty.
- The most commonly prescribed classes of PIMs were selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs; 12.0%), opioids (10.4%), benzodiazepines (9.2%), and corticosteroids (9.2%). Among individual drugs, sertraline was the most common SSRI (4.3%), tramadol the most common opioid (5.3%), lorazepam the most common benzodiazepine (2.5%), and prednisone the most common corticosteroid (4.9%). Trends over time showed a steady increase in opioid prescriptions, peaking in 2014, followed by a subsequent decline, while prescriptions of benzodiazepines declined during the later years.
- After adjusting for age, cancer type and stage, and other covariates, each additional GO-PIM was associated with a 66% higher odds of mild or moderate-to-severe frailty at diagnosis (adjusted odds ratio, 1.66).
- After adjusting for frailty and covariates, each additional GO-PIM at diagnosis was associated with increased risks for unplanned hospitalizations and death (adjusted hazard ratios, 1.08 and 1.07, respectively). These associations remained stable in sensitivity analyses that restricted GO-PIMs to scheduled medications only, focused on patients who had initiated cancer treatment, and included only those aged ≥ 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Whether prescribed for supportive oncology care or for coexisting medical conditions, high-risk medications identified as PIMs should be reviewed and optimized in patients with cancer,” the authors of the study wrote.
“GO-PIMs offers a streamlined, oncology-specific approach to identifying high-risk prescribing, and complements existing efforts to improve supportive care, especially for older, frail patients,” remarked Mostafa R. Mohamed, MBBCH, PhD, MSc, and Erika E. Ramsdale, MD, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, New York in an invited commentary. “The next step lies in integrating tools such as GO-PIMs into everyday practice not only to flag high risk medications but also to support actionable changes in treatment planning and patient management, such as deprescribing,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Jennifer La, PhD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, was published online in Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
LIMITATIONS:
Prescription chronicity before or after follow-up was not measured and actual medication adherence could not be confirmed. Residual confounding by comorbidity could have existed, and the cross-sectional nature of linking GO-PIMs with frailty might have limited causal inference. Additionally, prescriptions were measured within Veterans Affairs pharmacy data, potentially underestimating GO-PIM prevalence, and the predominantly male population limited generalizability to gynecologic cancers.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants and rewards from the Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Cooperative Studies Program, National Institutes of Health, and American Heart Association. Some authors declared serving as consultants or receiving grants and having other ties with various sources. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
1 in 10 Veterans Still Use Opioids Long After Cancer Surgery
TOPLINE:
About 1 in 10 veterans with early-stage cancer developed new persistent opioid use after curative‐intent surgery, though < 1% were diagnosed with opioid use disorder.
METHODOLOGY:
Although effective pain control during cancer treatment is vital, prescribing opioids in this context may contribute to unsafe, long-term use and related adverse outcomes. Veterans, who have higher-than-average rates of mental health and substance use disorders, may be at particular risk for adverse events from opioid use related to cancer treatment.
Researchers conducted a national retrospective cohort study of 9213 US veterans (98% men) with stage 0-III cancer who were opioid-naive and underwent curative-intent surgery at Veterans Affairs medical centers between 2015 and 2016. Prostate (n = 2594; 28%), colorectal (n = 2393; 26%), bladder (n = 2302; 25%), and lung (n = 1252; 14%) cancers were the most common.
Primary outcomes were the number of days of co-prescription of benzodiazepines and opioids (an indicator of unsafe opioid prescribing) and new persistent opioid use, defined as receiving ≥ 1 opioid prescription at 90-180 days postsurgery. Opioid‐related adverse effects, including opioid use disorder and opioid overdose, were also reported.
Overall, 6970 (76%) of the participants were prescribed opioids at some point during the baseline treatment period (30 days before through 14 days after surgery). The mean morphine milligram equivalent (MME) was 172.5.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, 4% of patients received co-prescriptions of benzodiazepines and opioids. The mean number of days of coprescription rose in tandem with opioid doses during the treatment period: from 0.48 days in the lowest MME quartile to 2.1 days in the highest quartile (P < .0001).
Over 1 in 10 patients (10.6%) developed new persistent opioid use. Those in the highest MME quartile had a 1.6-fold greater risk of developing new persistent opioid use than those with no opioid exposure during the treatment period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.6; P < .001). The percentage of patients with opioid prescriptions did decline over the 13-month follow-up, but among those who continued on opioids, the daily MME remained stable (median, 20 for month 1 and 30 for month 12).
Treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy increased the risk for new persistent opioid use (HR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P < .001). Additional risk factors included having bladder, colorectal, lung, or other types of cancer (vs prostate cancer); stage I-III disease (vs stage 0); age 45-64 years (vs older); lower socioeconomic status; preoperative use of nonopioid pain medication; and a baseline history of anxiety, depression, or posttraumatic stress disorder.
Over 13 months, 72 patients (0.78%) developed opioid use disorder, 3 (0.03%) experienced nonoverdose adverse events, and no opioid overdose occurred.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although a cancer diagnosis, treatment, and associated pain syndromes will require specific pain management strategies,” the authors wrote, “efforts should be taken to mitigate long‐term opioid use and its potential adverse effects in this population. They added that “both system‐level changes that involve preoperative evaluation planning as well as increased knowledge, awareness, and education among providers and patients about the risk of long‐term opioid use can guide strategies for effective and safe pain management.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Marilyn M. Schapira, MD, MPH, Center for Healthcare Evaluation, Research, and Promotion, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
Opioid prescriptions outside the Veterans Affairs system were not captured. The study was based on filled opioid prescriptions, and actual patient consumption was unknown. Outpatient methadone prescriptions were not included. The study also excluded patients with breast cancer, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs. One author reported consulting for Moderna and TriNetX. Another author reported consulting for Genetic Chemistry, Thyme Care, Biofourmis, Onc.Al, Credit Suisse, Main Street Health, ConcertAI, Medscape, and G1 Therapeutics. The other authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About 1 in 10 veterans with early-stage cancer developed new persistent opioid use after curative‐intent surgery, though < 1% were diagnosed with opioid use disorder.
METHODOLOGY:
Although effective pain control during cancer treatment is vital, prescribing opioids in this context may contribute to unsafe, long-term use and related adverse outcomes. Veterans, who have higher-than-average rates of mental health and substance use disorders, may be at particular risk for adverse events from opioid use related to cancer treatment.
Researchers conducted a national retrospective cohort study of 9213 US veterans (98% men) with stage 0-III cancer who were opioid-naive and underwent curative-intent surgery at Veterans Affairs medical centers between 2015 and 2016. Prostate (n = 2594; 28%), colorectal (n = 2393; 26%), bladder (n = 2302; 25%), and lung (n = 1252; 14%) cancers were the most common.
Primary outcomes were the number of days of co-prescription of benzodiazepines and opioids (an indicator of unsafe opioid prescribing) and new persistent opioid use, defined as receiving ≥ 1 opioid prescription at 90-180 days postsurgery. Opioid‐related adverse effects, including opioid use disorder and opioid overdose, were also reported.
Overall, 6970 (76%) of the participants were prescribed opioids at some point during the baseline treatment period (30 days before through 14 days after surgery). The mean morphine milligram equivalent (MME) was 172.5.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, 4% of patients received co-prescriptions of benzodiazepines and opioids. The mean number of days of coprescription rose in tandem with opioid doses during the treatment period: from 0.48 days in the lowest MME quartile to 2.1 days in the highest quartile (P < .0001).
Over 1 in 10 patients (10.6%) developed new persistent opioid use. Those in the highest MME quartile had a 1.6-fold greater risk of developing new persistent opioid use than those with no opioid exposure during the treatment period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.6; P < .001). The percentage of patients with opioid prescriptions did decline over the 13-month follow-up, but among those who continued on opioids, the daily MME remained stable (median, 20 for month 1 and 30 for month 12).
Treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy increased the risk for new persistent opioid use (HR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P < .001). Additional risk factors included having bladder, colorectal, lung, or other types of cancer (vs prostate cancer); stage I-III disease (vs stage 0); age 45-64 years (vs older); lower socioeconomic status; preoperative use of nonopioid pain medication; and a baseline history of anxiety, depression, or posttraumatic stress disorder.
Over 13 months, 72 patients (0.78%) developed opioid use disorder, 3 (0.03%) experienced nonoverdose adverse events, and no opioid overdose occurred.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although a cancer diagnosis, treatment, and associated pain syndromes will require specific pain management strategies,” the authors wrote, “efforts should be taken to mitigate long‐term opioid use and its potential adverse effects in this population. They added that “both system‐level changes that involve preoperative evaluation planning as well as increased knowledge, awareness, and education among providers and patients about the risk of long‐term opioid use can guide strategies for effective and safe pain management.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Marilyn M. Schapira, MD, MPH, Center for Healthcare Evaluation, Research, and Promotion, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
Opioid prescriptions outside the Veterans Affairs system were not captured. The study was based on filled opioid prescriptions, and actual patient consumption was unknown. Outpatient methadone prescriptions were not included. The study also excluded patients with breast cancer, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs. One author reported consulting for Moderna and TriNetX. Another author reported consulting for Genetic Chemistry, Thyme Care, Biofourmis, Onc.Al, Credit Suisse, Main Street Health, ConcertAI, Medscape, and G1 Therapeutics. The other authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
About 1 in 10 veterans with early-stage cancer developed new persistent opioid use after curative‐intent surgery, though < 1% were diagnosed with opioid use disorder.
METHODOLOGY:
Although effective pain control during cancer treatment is vital, prescribing opioids in this context may contribute to unsafe, long-term use and related adverse outcomes. Veterans, who have higher-than-average rates of mental health and substance use disorders, may be at particular risk for adverse events from opioid use related to cancer treatment.
Researchers conducted a national retrospective cohort study of 9213 US veterans (98% men) with stage 0-III cancer who were opioid-naive and underwent curative-intent surgery at Veterans Affairs medical centers between 2015 and 2016. Prostate (n = 2594; 28%), colorectal (n = 2393; 26%), bladder (n = 2302; 25%), and lung (n = 1252; 14%) cancers were the most common.
Primary outcomes were the number of days of co-prescription of benzodiazepines and opioids (an indicator of unsafe opioid prescribing) and new persistent opioid use, defined as receiving ≥ 1 opioid prescription at 90-180 days postsurgery. Opioid‐related adverse effects, including opioid use disorder and opioid overdose, were also reported.
Overall, 6970 (76%) of the participants were prescribed opioids at some point during the baseline treatment period (30 days before through 14 days after surgery). The mean morphine milligram equivalent (MME) was 172.5.
TAKEAWAY:
Overall, 4% of patients received co-prescriptions of benzodiazepines and opioids. The mean number of days of coprescription rose in tandem with opioid doses during the treatment period: from 0.48 days in the lowest MME quartile to 2.1 days in the highest quartile (P < .0001).
Over 1 in 10 patients (10.6%) developed new persistent opioid use. Those in the highest MME quartile had a 1.6-fold greater risk of developing new persistent opioid use than those with no opioid exposure during the treatment period (hazard ratio [HR], 1.6; P < .001). The percentage of patients with opioid prescriptions did decline over the 13-month follow-up, but among those who continued on opioids, the daily MME remained stable (median, 20 for month 1 and 30 for month 12).
Treatment with adjuvant chemotherapy increased the risk for new persistent opioid use (HR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.2-1.8; P < .001). Additional risk factors included having bladder, colorectal, lung, or other types of cancer (vs prostate cancer); stage I-III disease (vs stage 0); age 45-64 years (vs older); lower socioeconomic status; preoperative use of nonopioid pain medication; and a baseline history of anxiety, depression, or posttraumatic stress disorder.
Over 13 months, 72 patients (0.78%) developed opioid use disorder, 3 (0.03%) experienced nonoverdose adverse events, and no opioid overdose occurred.
IN PRACTICE:
“Although a cancer diagnosis, treatment, and associated pain syndromes will require specific pain management strategies,” the authors wrote, “efforts should be taken to mitigate long‐term opioid use and its potential adverse effects in this population. They added that “both system‐level changes that involve preoperative evaluation planning as well as increased knowledge, awareness, and education among providers and patients about the risk of long‐term opioid use can guide strategies for effective and safe pain management.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Marilyn M. Schapira, MD, MPH, Center for Healthcare Evaluation, Research, and Promotion, Corporal Michael J. Crescenz Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Philadelphia, was published online in Cancer.
LIMITATIONS:
Opioid prescriptions outside the Veterans Affairs system were not captured. The study was based on filled opioid prescriptions, and actual patient consumption was unknown. Outpatient methadone prescriptions were not included. The study also excluded patients with breast cancer, limiting generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by grant from the Department of Veterans Affairs. One author reported consulting for Moderna and TriNetX. Another author reported consulting for Genetic Chemistry, Thyme Care, Biofourmis, Onc.Al, Credit Suisse, Main Street Health, ConcertAI, Medscape, and G1 Therapeutics. The other authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Weekend Warrior and Regular Physical Activity Patterns Are Associated With Reduced Lung Cancer Risk
TOPLINE:
Compared with inactive patterns, weekend warrior (moderate-to-vigorous physical activity [MVPA] condensed into 1-2 days per week) and regular physical activity patterns were found to be equally effective at reducing the risk for lung cancer. Neither pattern showed significant associations with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
METHODOLOGY:
- This analysis included 80,896 participants (mean age, 55.5 years; 56% women) with valid accelerometer data collected between June 2013 and December 2015.
- Participants were classified into three groups: 32,213 active weekend warriors (≥ 150 minutes of weekly MVPA with ≥ 50% achieved in 1-2 days), 22,162 active regular participants (≥ 150 minutes of MVPA but not meeting a weekend warrior pattern), and 26,521 inactive participants (< 150 minutes of MVPA).
- Researchers tracked associations between physical activity patterns and incident cases of all types of cancer plus specific cases of prostate, breast, colorectal, and lung cancer over a median follow-up duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with inactive patterns, active weekend warrior patterns showed a significant inverse association with the risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.98).
- Active regular activity patterns demonstrated similar protective effects against lung cancer as inactive patterns (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.56-0.96).
- Neither of the physical activity patterns showed any significant association with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
IN PRACTICE:
"Physical activity condensed into one to two days per week compared with a more balanced weekly distribution was associated with similar risk reductions of incident lung cancer, while neither pattern was associated with reduced overall, prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers," the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rubén López-Bueno, Department of Physical Medicine and Nursing, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain. It was published online on September 06, 2025, in Annals of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with inactive patterns, weekend warrior (moderate-to-vigorous physical activity [MVPA] condensed into 1-2 days per week) and regular physical activity patterns were found to be equally effective at reducing the risk for lung cancer. Neither pattern showed significant associations with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
METHODOLOGY:
- This analysis included 80,896 participants (mean age, 55.5 years; 56% women) with valid accelerometer data collected between June 2013 and December 2015.
- Participants were classified into three groups: 32,213 active weekend warriors (≥ 150 minutes of weekly MVPA with ≥ 50% achieved in 1-2 days), 22,162 active regular participants (≥ 150 minutes of MVPA but not meeting a weekend warrior pattern), and 26,521 inactive participants (< 150 minutes of MVPA).
- Researchers tracked associations between physical activity patterns and incident cases of all types of cancer plus specific cases of prostate, breast, colorectal, and lung cancer over a median follow-up duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with inactive patterns, active weekend warrior patterns showed a significant inverse association with the risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.98).
- Active regular activity patterns demonstrated similar protective effects against lung cancer as inactive patterns (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.56-0.96).
- Neither of the physical activity patterns showed any significant association with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
IN PRACTICE:
"Physical activity condensed into one to two days per week compared with a more balanced weekly distribution was associated with similar risk reductions of incident lung cancer, while neither pattern was associated with reduced overall, prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers," the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rubén López-Bueno, Department of Physical Medicine and Nursing, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain. It was published online on September 06, 2025, in Annals of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with inactive patterns, weekend warrior (moderate-to-vigorous physical activity [MVPA] condensed into 1-2 days per week) and regular physical activity patterns were found to be equally effective at reducing the risk for lung cancer. Neither pattern showed significant associations with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
METHODOLOGY:
- This analysis included 80,896 participants (mean age, 55.5 years; 56% women) with valid accelerometer data collected between June 2013 and December 2015.
- Participants were classified into three groups: 32,213 active weekend warriors (≥ 150 minutes of weekly MVPA with ≥ 50% achieved in 1-2 days), 22,162 active regular participants (≥ 150 minutes of MVPA but not meeting a weekend warrior pattern), and 26,521 inactive participants (< 150 minutes of MVPA).
- Researchers tracked associations between physical activity patterns and incident cases of all types of cancer plus specific cases of prostate, breast, colorectal, and lung cancer over a median follow-up duration of 6 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with inactive patterns, active weekend warrior patterns showed a significant inverse association with the risk for lung cancer (hazard ratio [HR], 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61-0.98).
- Active regular activity patterns demonstrated similar protective effects against lung cancer as inactive patterns (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.56-0.96).
- Neither of the physical activity patterns showed any significant association with the overall risk for cancer or specific risks for prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers.
IN PRACTICE:
"Physical activity condensed into one to two days per week compared with a more balanced weekly distribution was associated with similar risk reductions of incident lung cancer, while neither pattern was associated with reduced overall, prostate, breast, and colorectal cancers," the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rubén López-Bueno, Department of Physical Medicine and Nursing, University of Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain. It was published online on September 06, 2025, in Annals of Medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Tall Cell Carcinoma with Reversed Polarity
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
Background
Tall cell carcinoma with reversed polarity (TCCRP) is a rare and distinct subtype of invasive breast carcinoma, defined by tall columnar cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and reversed nuclear polarity. TCCRP remains poorly characterized in the literature, with limited population-level evidence to guide management and prognostication. This study uses the National Cancer Database (NCDB) to examine the epidemiology, clinical features, and outcomes of this neoplasm.
Methods
A retrospective cohort analysis included 951 patients diagnosed with TCCRP (ICD-O-3 code 8509) from 2018–2020 using the NCDB. Demographic and treatment variables were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Incidence trends were assessed using linear regression, and overall survival was evaluated using Kaplan-Meier methods.
Results
Most patients were female (98.1%) with a mean age of 69.1 years. The majority were White (82.0%), followed by Black (9.0%) and Hispanic (8.7%). Primary tumor sites included overlapping breast lesions (28.5%) and the upper-inner quadrant (27.0%). Incidence remained stable (R2 = 0.0). Most patients were diagnosed at Stage I (58.4%) and had a Charlson-Deyo score of 0 (76.2%). Socioeconomically, 41.8% lived in the highest income quartile (≥$74,063), and most had Medicare (64.7%). The most common treatment settings were comprehensive community cancer programs (40.3%). Surgery was performed in 95.6% of cases, with negative margins in 91.1%. Radiation therapy (46.6%) and hormone therapy (44.3%) were frequently used. Mortality was 1.1% at 30 days and 1.7% at 90 days. Survival was 98.9% at 2 years, 97.3% at 5 years, and 94.5% at 10 years, with a mean survival of 46.4 months.
Conclusions
This is the first NCDB-based study of TCCRP, highlighting favorable outcomes and distinct clinicodemographic features. Patients were predominantly older, White, and Medicare-insured, often receiving care at community cancer programs. These findings suggest that socioeconomic factors may influence access and treatment. Results may inform strategies to promote equitable care delivery across health systems and guide further research on clinical management and survivorship in TCCRP, particularly for rare cancers within community-based settings such as the VHA.
ERCC2, KDM6A, and TERT as Key Prognostic Factors in Bladder Cancer: Insights from the AACR Project GENIE Database
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Background
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is among the top 10 frequently diagnosed cancers in the world. Mutations in FGFR3, ARID1A, and TP53 are well documented as being some of the most frequent mutations found in UC. Despite advances in treatment, survival outcomes remain poor, especially in advanced stages. To promote future pharmacotherapeutic development, the molecular understanding of UC needs to be continually updated using more recently available databases.
Methods
This study utilizes the AACR Project GENIE database from the American Association for Cancer Research to explore the mutational profiles of patients with UC. Gene mutation frequencies were calculated, and two Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn for each gene, showing one curve for patients with the mutation and one for those without. Log-Rank tests were calculated with subsequent FDR (Benjamini–Hochberg) correction applied to account for multiple hypothesis testing. Data was analyzed using R 4.4.2 and statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Results
In this study, 4525 patients had histology consistent with UC. The 5 most common mutations were TERT (n = 1714, 37.9%), TP53 (n = 1689, 37.3%), KDM6A (n = 1091, 24.1%), ARID1A (n = 872, 19.3%), and FGFR3 (n = 762, 16.8%). Mutations associated with differential survival outcomes included ERCC2 (mutated n = 387, wild type n = 3751, p < 0.0001), KDM6A (mutated n = 1091, wild type n = 3047, p < 0.0001), TERT (mutated n = 1714, wild type n = 2424), and TP53 (mutated n = 1689, wild type n = 2449, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Interestingly, while mutations in TP53 and ERCC2 were associated with shorter median survival, mutations in KDM6A and TERT were associated with longer median survival.
Communication Modality (CM) Among Veterans Using National TeleOncology (NTO) Services
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.
Background
We examined characteristics of Veterans receiving care through NTO and their CM (e.g., telephone only [T], video only [V], or both [TV]). Relevant background: In-person VA cancer care can be challenging for many Veterans due to rurality, transportation, finances, and distance to subspecialists. Such factors may impact care modality preferences.
Methods
We linked a list of all Veterans who received NTO care with Corporate Data Warehouse data to confirm an ICD-10 diagnostic code for malignancy, and to define the number of NTO interactions, latency of days between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, and demographics. The Office of Rural Health categories for rurality and NIH categories for race were used.
Data analysis
We report descriptive statistics for CM. To compare differences between Veterans by CM, we report chi-squared tests for categorical variables and ANOVAs for continuous variables.
Results
Among 13,902 NTO Veterans with CM data, most were V (9,998, 72%), few were T 2% (n= 295), and some were TV 26% (n= 3,609). There were statistically significant differences between CM in number of interactions, latency between diagnosis and first NTO interaction, age at first NTO interaction, sex, race, rurality, and cancer type. Veterans diagnosed with lung cancer were more likely to exclusively use T. Veterans with breast cancer were more likely to exclusively use V. Specifically, T were oldest (mean age = 74.3), followed by TV (69.0) and V (61.6; p < .001). Women were most represented in V (28.3%) and Rural or highly rural residence was most common among T users (54.6%), compared to V (36.8%) and TV (43.0%; p < .001). Urban users were more prevalent in the TV group (61.9%) than in the T only group (45.4%).
Implications
We identified differences in communication modality based on Veteran characteristics. This could suggest differences in Veteran or provider preference, feasibility, or acceptability, based on CM.
Significance
While V communications appear to be achievable for many Veterans, more work is needed to determine preference, feasibility, and acceptability among Veterans and their care teams regarding V and T only cancer care.