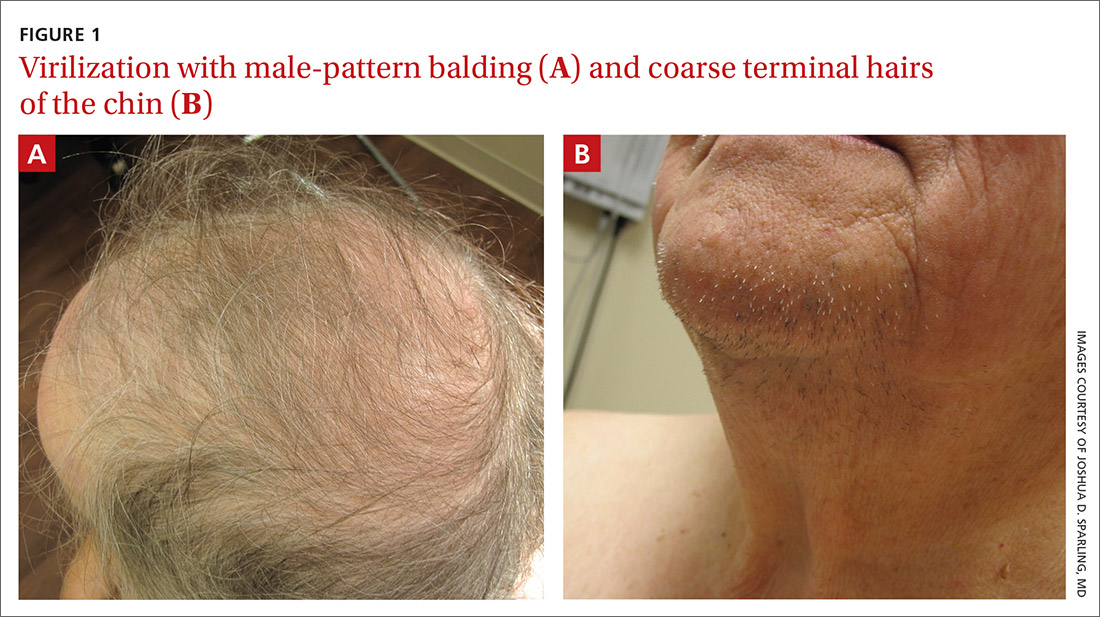
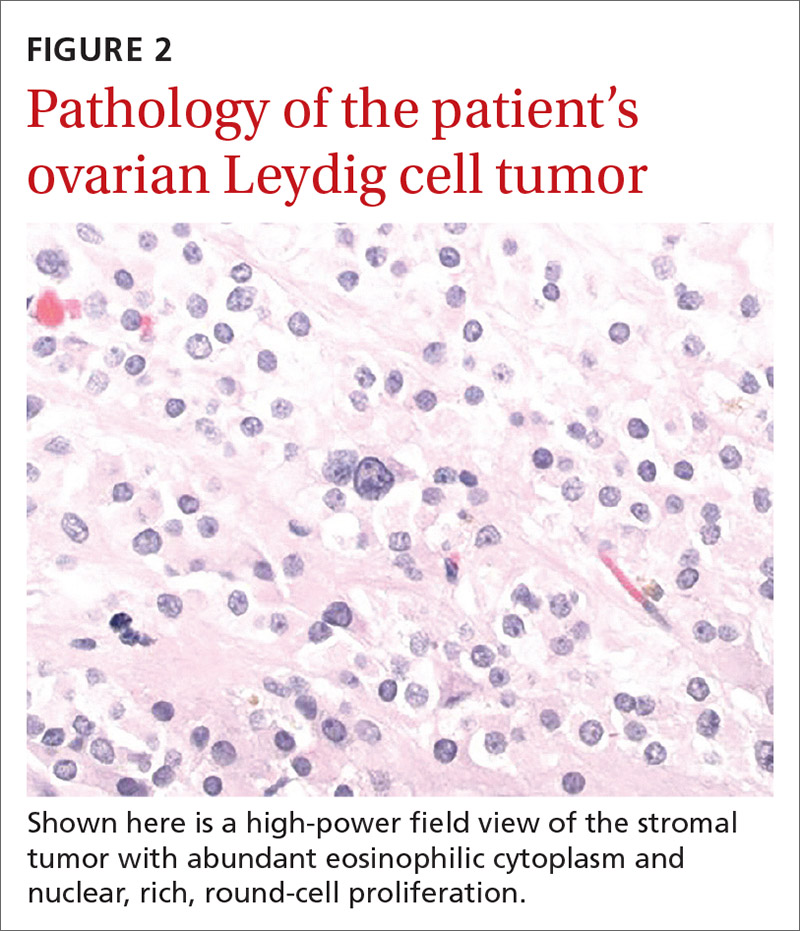
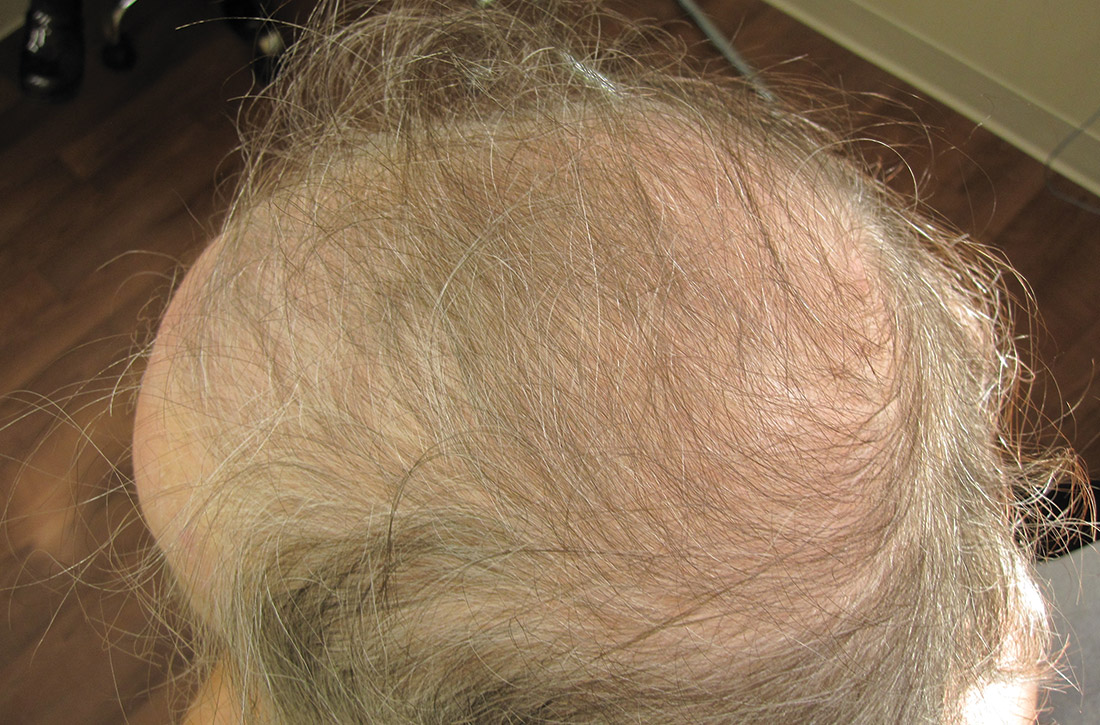
User login
Postpartum health care needs exceed those of nonpostpartum patients
Postpartum women with commercial health insurance use substantially more inpatient and outpatient care than nonpostpartum women, particularly in the first 2 months after giving birth, according to a retrospective cohort study published in the May 2021 issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“These findings are consistent with previous studies that have documented elevated postpartum ED and hospitalization rates, and we contribute new evidence that indicates postpartum health care utilization rates are significantly higher than rates of health care utilization in the general population of reproductive aged women when they are not pregnant or postpartum,” Maria W. Steenland, ScD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote. “Most notably, postpartum women were more than three times more likely to have an ED visit and eight times more likely to be hospitalized than nonpostpartum women in the early postpartum period.”
Approximately one-third of maternal deaths occur between 1 week and 1 year post partum, the authors noted in their background information. The overall U.S. maternal mortality rate was 17.4 per 100,000 live births in 2018, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“This study underscores the importance of access to health care for women, in particular in the postpartum period,” Iris Krishna, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “Maternal mortality is a public health crisis. The majority of maternal deaths are preventable and occur up to 1 year postpartum. Studies such as these are needed as the postpartum period is a critical time in the care of reproductive age women that is often overlooked.”
Using data from a large national commercial claims database, the researchers analyzed data from 149,563 women aged 18-44 years who gave birth in 2016 and from 2,048,831 women who were neither pregnant nor post partum during the same study period. In postpartum women, the researchers specifically looked at hospitalization, preventive visits, problem visits, and ED visits during three periods for postpartum women: early postpartum, defined as within 21 days of giving birth; postpartum, defined as 21-60 days after birth; and extended postpartum, defined as 61 days to 1 year after birth. These data were then compared with equivalent periods in nonpostpartum women.
“For the comparison group, we created a random start date of follow-up by generating a random variable between 0 and 365 and adding this integer to Jan. 1, 2016,” the authors explained. “These start dates correspond to the range of possible follow-up start dates among postpartum women who gave birth in 2016.”
The groups differed in age composition: 62% of the postpartum women were between 25 and 34 years old while the nonpostpartum women were more evenly distributed across the age range. A higher proportion of nonpostpartum women had a chronic disease, but median income and geographic region were similar between the groups. Just over a third of the postpartum women (36%) had a cesarean delivery, higher than the 2016 national average of 32%.
Nearly a quarter (23.7%) of postpartum women had a problem visit in the early postpartum period, compared with one in five (19.7%) nonpostpartum women in the equivalent period. This 4-point difference increased to an 4.8-point difference after adjustment for age group, chronic disease, geographic region, income, and month when follow-up began.
Postpartum women were also three times more likely to have an ED visit (3.2%) in the early postpartum period than nonpostpartum women (1%). Postpartum women’s problem visits and ED visits were most prevalent in the first 2 weeks after childbirth: 12.4% in the first week and 10.4% in the second. Complaints for these visits primarily included urinary tract infections and other genitourinary issues, hypertension, breast or breastfeeding issues, and respiratory issues, such as shortness of breath or chest pain. Hospitalization rates were also higher in the early postpartum period for postpartum women (0.8%) than nonpostpartum women (0.1%).
Problem visits showed a similar pattern during the postpartum period from 21 to 60 days after birth: 39.4% of postpartum women, compared with 30.2% of nonpostpartum women. Rate differences were narrower for ED visits (2% post partum vs. 1.9% non–post partum) and hospitalization (0.3% post partum vs. 0.2% non–post partum), but the differences remained significant, and ED visits were still 0.3 points higher after adjustment.
The biggest differences between the groups in the first 2 months occurred with preventive care. In the early postpartum period, 15% of postpartum women had a preventive visit, compared with 3.3% of nonpostpartum women. Similarly, the rates were 28.2% in postpartum women and 6.5% in nonpostpartum women in the postpartum period.
Differences between the groups evened out in the extended postpartum period, when postpartum women had slightly fewer preventive visits (42.5%) than nonpostpartum women (42.7%). ED rates (11.2% postpartum vs 11.1%) and hospitalization rates (1.4% postpartum vs. 1.6%) were similar, but postpartum women were significantly more likely to have problem visits (79.2%) in the year after childbirth than nonpostpartum women (72.8%).
“Compared with postpartum women overall, postpartum women with chronic disease, pregnancy complications, and cesarean births were more likely to receive health care of all types in the early postpartum period,” the researchers reported. “Of the three subgroups, health care use was highest among postpartum women with chronic disease, among whom 35% had at least one outpatient problem visit, 5% had an ED visit, and 1.3% were hospitalized within the first 20 days of childbirth.”
These findings as a whole point to an increased need for health care not only in the first 3 weeks after women give birth but “beyond the traditional 6-week postpartum period, which adds to the argument that the way we care for women in the postpartum period should be revised,” Dr. Krishna said.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists updated their postpartum recommendations in 2018 to advise that all postpartum women have a follow-up visit in the first 3 weeks after birth.
Dr. Krishna reiterated that postpartum patients should ideally have an initial follow-up within 3 weeks of giving birth, which the rapid expansion of telehealth has made more viable for both clinicians and mothers.
The authors similarly noted that telehealth and home visits “are promising options to promote early and consistent health care contact and reduce known barriers to postpartum care seeking such as fatigue, lack of transportation, and child care.” Predischarge guidance may also help meet postpartum patients’ health care needs.
“Health care professionals also may be able to reduce the escalation of common early postpartum problems identified in this study (e.g., respiratory problems, pain, urinary tract infections) with anticipatory postpartum counseling and care before hospital discharge such as ensuring that women have inhalers at home, developing a pain management plan, and screening for signs of urinary tract infection,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Krishna also pointed out the need to address racial inequalities in health care and material mortality.
“Black women have a maternal mortality rate two times the rate of non-Hispanic White women,” Dr. Krishna said. “One way to address health disparities between commercially insured and uninsured women is improving access to health care through Medicaid expansion for at least 1 year post partum. States that participated in the Affordable Care Acts Medicaid expansion have noted improvement in maternal mortality and a decrease in racial/ethnic inequities.”
The research was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Data was provided by Aetna, Humana, Kaiser Permanente and UnitedHealthcare. The authors and Dr. Krishna reported no disclosures.
Postpartum women with commercial health insurance use substantially more inpatient and outpatient care than nonpostpartum women, particularly in the first 2 months after giving birth, according to a retrospective cohort study published in the May 2021 issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“These findings are consistent with previous studies that have documented elevated postpartum ED and hospitalization rates, and we contribute new evidence that indicates postpartum health care utilization rates are significantly higher than rates of health care utilization in the general population of reproductive aged women when they are not pregnant or postpartum,” Maria W. Steenland, ScD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote. “Most notably, postpartum women were more than three times more likely to have an ED visit and eight times more likely to be hospitalized than nonpostpartum women in the early postpartum period.”
Approximately one-third of maternal deaths occur between 1 week and 1 year post partum, the authors noted in their background information. The overall U.S. maternal mortality rate was 17.4 per 100,000 live births in 2018, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“This study underscores the importance of access to health care for women, in particular in the postpartum period,” Iris Krishna, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “Maternal mortality is a public health crisis. The majority of maternal deaths are preventable and occur up to 1 year postpartum. Studies such as these are needed as the postpartum period is a critical time in the care of reproductive age women that is often overlooked.”
Using data from a large national commercial claims database, the researchers analyzed data from 149,563 women aged 18-44 years who gave birth in 2016 and from 2,048,831 women who were neither pregnant nor post partum during the same study period. In postpartum women, the researchers specifically looked at hospitalization, preventive visits, problem visits, and ED visits during three periods for postpartum women: early postpartum, defined as within 21 days of giving birth; postpartum, defined as 21-60 days after birth; and extended postpartum, defined as 61 days to 1 year after birth. These data were then compared with equivalent periods in nonpostpartum women.
“For the comparison group, we created a random start date of follow-up by generating a random variable between 0 and 365 and adding this integer to Jan. 1, 2016,” the authors explained. “These start dates correspond to the range of possible follow-up start dates among postpartum women who gave birth in 2016.”
The groups differed in age composition: 62% of the postpartum women were between 25 and 34 years old while the nonpostpartum women were more evenly distributed across the age range. A higher proportion of nonpostpartum women had a chronic disease, but median income and geographic region were similar between the groups. Just over a third of the postpartum women (36%) had a cesarean delivery, higher than the 2016 national average of 32%.
Nearly a quarter (23.7%) of postpartum women had a problem visit in the early postpartum period, compared with one in five (19.7%) nonpostpartum women in the equivalent period. This 4-point difference increased to an 4.8-point difference after adjustment for age group, chronic disease, geographic region, income, and month when follow-up began.
Postpartum women were also three times more likely to have an ED visit (3.2%) in the early postpartum period than nonpostpartum women (1%). Postpartum women’s problem visits and ED visits were most prevalent in the first 2 weeks after childbirth: 12.4% in the first week and 10.4% in the second. Complaints for these visits primarily included urinary tract infections and other genitourinary issues, hypertension, breast or breastfeeding issues, and respiratory issues, such as shortness of breath or chest pain. Hospitalization rates were also higher in the early postpartum period for postpartum women (0.8%) than nonpostpartum women (0.1%).
Problem visits showed a similar pattern during the postpartum period from 21 to 60 days after birth: 39.4% of postpartum women, compared with 30.2% of nonpostpartum women. Rate differences were narrower for ED visits (2% post partum vs. 1.9% non–post partum) and hospitalization (0.3% post partum vs. 0.2% non–post partum), but the differences remained significant, and ED visits were still 0.3 points higher after adjustment.
The biggest differences between the groups in the first 2 months occurred with preventive care. In the early postpartum period, 15% of postpartum women had a preventive visit, compared with 3.3% of nonpostpartum women. Similarly, the rates were 28.2% in postpartum women and 6.5% in nonpostpartum women in the postpartum period.
Differences between the groups evened out in the extended postpartum period, when postpartum women had slightly fewer preventive visits (42.5%) than nonpostpartum women (42.7%). ED rates (11.2% postpartum vs 11.1%) and hospitalization rates (1.4% postpartum vs. 1.6%) were similar, but postpartum women were significantly more likely to have problem visits (79.2%) in the year after childbirth than nonpostpartum women (72.8%).
“Compared with postpartum women overall, postpartum women with chronic disease, pregnancy complications, and cesarean births were more likely to receive health care of all types in the early postpartum period,” the researchers reported. “Of the three subgroups, health care use was highest among postpartum women with chronic disease, among whom 35% had at least one outpatient problem visit, 5% had an ED visit, and 1.3% were hospitalized within the first 20 days of childbirth.”
These findings as a whole point to an increased need for health care not only in the first 3 weeks after women give birth but “beyond the traditional 6-week postpartum period, which adds to the argument that the way we care for women in the postpartum period should be revised,” Dr. Krishna said.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists updated their postpartum recommendations in 2018 to advise that all postpartum women have a follow-up visit in the first 3 weeks after birth.
Dr. Krishna reiterated that postpartum patients should ideally have an initial follow-up within 3 weeks of giving birth, which the rapid expansion of telehealth has made more viable for both clinicians and mothers.
The authors similarly noted that telehealth and home visits “are promising options to promote early and consistent health care contact and reduce known barriers to postpartum care seeking such as fatigue, lack of transportation, and child care.” Predischarge guidance may also help meet postpartum patients’ health care needs.
“Health care professionals also may be able to reduce the escalation of common early postpartum problems identified in this study (e.g., respiratory problems, pain, urinary tract infections) with anticipatory postpartum counseling and care before hospital discharge such as ensuring that women have inhalers at home, developing a pain management plan, and screening for signs of urinary tract infection,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Krishna also pointed out the need to address racial inequalities in health care and material mortality.
“Black women have a maternal mortality rate two times the rate of non-Hispanic White women,” Dr. Krishna said. “One way to address health disparities between commercially insured and uninsured women is improving access to health care through Medicaid expansion for at least 1 year post partum. States that participated in the Affordable Care Acts Medicaid expansion have noted improvement in maternal mortality and a decrease in racial/ethnic inequities.”
The research was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Data was provided by Aetna, Humana, Kaiser Permanente and UnitedHealthcare. The authors and Dr. Krishna reported no disclosures.
Postpartum women with commercial health insurance use substantially more inpatient and outpatient care than nonpostpartum women, particularly in the first 2 months after giving birth, according to a retrospective cohort study published in the May 2021 issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
“These findings are consistent with previous studies that have documented elevated postpartum ED and hospitalization rates, and we contribute new evidence that indicates postpartum health care utilization rates are significantly higher than rates of health care utilization in the general population of reproductive aged women when they are not pregnant or postpartum,” Maria W. Steenland, ScD, of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote. “Most notably, postpartum women were more than three times more likely to have an ED visit and eight times more likely to be hospitalized than nonpostpartum women in the early postpartum period.”
Approximately one-third of maternal deaths occur between 1 week and 1 year post partum, the authors noted in their background information. The overall U.S. maternal mortality rate was 17.4 per 100,000 live births in 2018, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“This study underscores the importance of access to health care for women, in particular in the postpartum period,” Iris Krishna, MD, MPH, an assistant professor of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University, Atlanta, said in an interview. “Maternal mortality is a public health crisis. The majority of maternal deaths are preventable and occur up to 1 year postpartum. Studies such as these are needed as the postpartum period is a critical time in the care of reproductive age women that is often overlooked.”
Using data from a large national commercial claims database, the researchers analyzed data from 149,563 women aged 18-44 years who gave birth in 2016 and from 2,048,831 women who were neither pregnant nor post partum during the same study period. In postpartum women, the researchers specifically looked at hospitalization, preventive visits, problem visits, and ED visits during three periods for postpartum women: early postpartum, defined as within 21 days of giving birth; postpartum, defined as 21-60 days after birth; and extended postpartum, defined as 61 days to 1 year after birth. These data were then compared with equivalent periods in nonpostpartum women.
“For the comparison group, we created a random start date of follow-up by generating a random variable between 0 and 365 and adding this integer to Jan. 1, 2016,” the authors explained. “These start dates correspond to the range of possible follow-up start dates among postpartum women who gave birth in 2016.”
The groups differed in age composition: 62% of the postpartum women were between 25 and 34 years old while the nonpostpartum women were more evenly distributed across the age range. A higher proportion of nonpostpartum women had a chronic disease, but median income and geographic region were similar between the groups. Just over a third of the postpartum women (36%) had a cesarean delivery, higher than the 2016 national average of 32%.
Nearly a quarter (23.7%) of postpartum women had a problem visit in the early postpartum period, compared with one in five (19.7%) nonpostpartum women in the equivalent period. This 4-point difference increased to an 4.8-point difference after adjustment for age group, chronic disease, geographic region, income, and month when follow-up began.
Postpartum women were also three times more likely to have an ED visit (3.2%) in the early postpartum period than nonpostpartum women (1%). Postpartum women’s problem visits and ED visits were most prevalent in the first 2 weeks after childbirth: 12.4% in the first week and 10.4% in the second. Complaints for these visits primarily included urinary tract infections and other genitourinary issues, hypertension, breast or breastfeeding issues, and respiratory issues, such as shortness of breath or chest pain. Hospitalization rates were also higher in the early postpartum period for postpartum women (0.8%) than nonpostpartum women (0.1%).
Problem visits showed a similar pattern during the postpartum period from 21 to 60 days after birth: 39.4% of postpartum women, compared with 30.2% of nonpostpartum women. Rate differences were narrower for ED visits (2% post partum vs. 1.9% non–post partum) and hospitalization (0.3% post partum vs. 0.2% non–post partum), but the differences remained significant, and ED visits were still 0.3 points higher after adjustment.
The biggest differences between the groups in the first 2 months occurred with preventive care. In the early postpartum period, 15% of postpartum women had a preventive visit, compared with 3.3% of nonpostpartum women. Similarly, the rates were 28.2% in postpartum women and 6.5% in nonpostpartum women in the postpartum period.
Differences between the groups evened out in the extended postpartum period, when postpartum women had slightly fewer preventive visits (42.5%) than nonpostpartum women (42.7%). ED rates (11.2% postpartum vs 11.1%) and hospitalization rates (1.4% postpartum vs. 1.6%) were similar, but postpartum women were significantly more likely to have problem visits (79.2%) in the year after childbirth than nonpostpartum women (72.8%).
“Compared with postpartum women overall, postpartum women with chronic disease, pregnancy complications, and cesarean births were more likely to receive health care of all types in the early postpartum period,” the researchers reported. “Of the three subgroups, health care use was highest among postpartum women with chronic disease, among whom 35% had at least one outpatient problem visit, 5% had an ED visit, and 1.3% were hospitalized within the first 20 days of childbirth.”
These findings as a whole point to an increased need for health care not only in the first 3 weeks after women give birth but “beyond the traditional 6-week postpartum period, which adds to the argument that the way we care for women in the postpartum period should be revised,” Dr. Krishna said.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists updated their postpartum recommendations in 2018 to advise that all postpartum women have a follow-up visit in the first 3 weeks after birth.
Dr. Krishna reiterated that postpartum patients should ideally have an initial follow-up within 3 weeks of giving birth, which the rapid expansion of telehealth has made more viable for both clinicians and mothers.
The authors similarly noted that telehealth and home visits “are promising options to promote early and consistent health care contact and reduce known barriers to postpartum care seeking such as fatigue, lack of transportation, and child care.” Predischarge guidance may also help meet postpartum patients’ health care needs.
“Health care professionals also may be able to reduce the escalation of common early postpartum problems identified in this study (e.g., respiratory problems, pain, urinary tract infections) with anticipatory postpartum counseling and care before hospital discharge such as ensuring that women have inhalers at home, developing a pain management plan, and screening for signs of urinary tract infection,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Krishna also pointed out the need to address racial inequalities in health care and material mortality.
“Black women have a maternal mortality rate two times the rate of non-Hispanic White women,” Dr. Krishna said. “One way to address health disparities between commercially insured and uninsured women is improving access to health care through Medicaid expansion for at least 1 year post partum. States that participated in the Affordable Care Acts Medicaid expansion have noted improvement in maternal mortality and a decrease in racial/ethnic inequities.”
The research was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the National Institutes of Health. Data was provided by Aetna, Humana, Kaiser Permanente and UnitedHealthcare. The authors and Dr. Krishna reported no disclosures.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Quicker fertility rebound in young women with breast cancer
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HHS proposes overturning Title X ‘gag’ rule
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Department of Health & Human Services has proposed overturning rules issued during the Trump administration that effectively prohibit clinicians at Title X–funded health clinics from discussing abortion or referring patients for abortions.
HHS proposed the overhaul of the Title X regulations on April 14. The previous administration’s 2019 rules “have undermined the public health of the population the program is meant to serve,” HHS said in the introduction to its proposal.
Medical organizations and reproductive health specialists lauded the move.
“Clinicians providing care to patients must be empowered to share the full spectrum of accurate medical information necessary to ensure that their patients are able to make timely, fully informed medical decisions,” Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, said in a statement. “This means transparent, respectful, evidence-based conversations about contraception and abortion care. The proposed rule will ensure that those conversations can once again happen without restrictions, interference, or threat of financial loss.”
“Providers of comprehensive reproductive health care, including abortion care, base their relationships with their patients on trust,” Physicians for Reproductive Health President and CEO Jamila Perritt, MD, said in a statement. “The Title X gag rule went against everything we knew as providers of ethical, evidence-based health care by forcing providers at Title X funded clinics to withhold information that their patients needed and requested.”
HHS said that, since 2019, more than 1,000 Title X–funded service sites (25% of the total) have withdrawn from the program. Currently, Title X services – which include family planning, STI testing, cancer screening, and HIV testing and treatment – are not available in six states and are only available on a limited basis in six additional states. Planned Parenthood fully withdrew from Title X.
HHS said that tens of thousands fewer birth control implant procedures have been performed and that hundreds of thousands fewer Pap tests and a half-million or more fewer tests for chlamydia and gonorrhea have been conducted. In addition, the reduction in services may have led to up to 181,477 unintended pregnancies, HHS said.
The closure of sites and decreased availability of services have also exacerbated health inequities, according to the department.
The loss of services “has been especially felt by those already facing disproportionate barriers to accessing care, including the Black, Latinx and Indigenous communities that have also suffered the most harm during the COVID-19 pandemic,” agreed Dr. Phipps.
The new regulation proposes to “ensure access to equitable, affordable, client-centered, quality family-planning services for all clients, especially for low-income clients,” HHS said.
The proposed change in the rules “brings us one step closer to restoring access to necessary care for millions of low-income and uninsured patients who depend on Title X for family planning services,” American Medical Association President Susan R. Bailey, MD, said in a statement. “We are pleased that the Biden administration shares our commitment to undoing this dangerous and discriminatory ‘gag rule,’ and look forward to its elimination through any means necessary to achieve the best outcome for patients and physicians – improving the health of our nation.”
Planned Parenthood also applauded the move, and the HIV Medicine Association thanked the Biden administration for its proposal, which it called “a major step to improve #HealthEquity for all people in this country,” in a tweet.
March for Life, an antiabortion group, however, said it strongly opposed the HHS proposal. The rules “appear specifically designed to bring America’s largest abortion provider, Planned Parenthood, back into the taxpayer-funded program and keep prolife organizations out,” said the group in a tweet.
“Abortion is neither health care nor family planning, and the Title X program should not be funding it,” said the group.
The Title X program does not pay for abortions, however.
The Trump administration rules prohibit abortion referrals and impose counseling standards for pregnant patients and what the Guttmacher Institute called “unnecessary and stringent requirements for the physical and financial separation of Title X–funded activities from a range of abortion-related activities.”
The new rules would reestablish regulations from 2000, with some new additions. For instance, the program will “formally integrate elements of quality family-planning services guidelines developed by [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] and Office of Population Affairs,” tweeted Alina Salganicoff, director of women’s health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “That means that higher standards for providing family planning will be required,” she tweeted. In addition, sites that offer natural family planning and abstinence “will only be able to participate if they offer referrals to other providers that offer clients access to the contraceptive of their choice.”
The proposed rules are open for public comment for 30 days. They could be made final by the fall. The Kaiser Family Foundation reports that many sites could be ready to return to the program by then, especially since the recently passed coronavirus relief package, the American Rescue Plan, included a $50 million supplemental appropriation for Title X.
The 2019 rules remain in effect in the meantime, although the U.S. Supreme Court agreed in February to hear a challenge mounted by 21 states, the city of Baltimore, and organizations that included the AMA and Planned Parenthood. Those plaintiffs have requested that the case be dismissed, but it currently remains on the docket.
Not all medical providers are likely to support the new rules if they go into effect. The American Association of Pro-Life Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Christian Medical and Dental Associations, and the Catholic Medical Association filed motions in the Supreme Court case to defend the Trump regulations.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Feds let Illinois extend postpartum Medicaid coverage: HHS encourages other states to follow suit
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The federal government has approved a request by Illinois to extend postpartum Medicaid coverage to a full year from the current standard of 60 days.
Health & Human Services Secretary Xavier Becerra announced the approval at a press briefing on April 12, noting that it was occurring during Black Maternal Health Week. The coverage extension is aimed at decreasing maternal morbidity and mortality, particularly among women of color.
Black women are two times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women, according to HHS. Mr. Becerra noted that, in the United States, 52% of pregnancy-related deaths take place up to 1 year post partum, and that in Illinois the figure is 80%.
“The continuity of coverage available through this action will help new mothers manage chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, and it will provide access to behavioral health and other mental health care services,” he said.
Continuing Medicaid coverage for new mothers has been backed by the American Medical Association, is a priority of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and has been promoted by Republicans and Democrats in Congress and state legislatures.
Illinois is the first state to seek and win approval to extend its Medicaid coverage from the current 60-days postbirth requirement. The program was granted through an existing section 1115 waiver program. It begins today and is authorized through Dec. 31, 2025. The state estimates that some 2,500 women with incomes up to 208% of the federal poverty level will receive the year of continuous Medicaid coverage. Illinois will evaluate whether the extension improves women’s health and if it benefits the Medicaid program overall.
However, the recently passed coronavirus rescue package creates a new process that lets states more easily expand postpartum coverage, but they must act by April 2022. Mr. Becerra said the federal government is encouraging more states to follow Illinois’ lead in extending postpartum eligibility by taking advantage of the new process.
States won’t get extra money – they will receive the regular per capita–based federal match if they extend Medicaid coverage through this pathway. Even so, Mr. Becerra said there has been much interest.
“I hope that we begin to see states not only express interest but actually submit their proposals on how they would do this,” Mr. Becerra said.
Medicaid has become one of the key providers of maternal health care in the United States, as it covers 4 in 10 births, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. But postpartum coverage after the 60-day federal requirement is a patchwork. In 38 states (plus Washington, D.C.) that have expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act, mothers who earn up to 138% of the federal poverty level can continue on Medicaid; for those who earn more than that, they can get coverage through the ACA.
In the 12 states that did not expand Medicaid, new mothers have to seek Medicaid coverage after 60 days as parents, and the income limits are strict. In Texas, for example, a married mother with a newborn loses Medicaid coverage 2 months after giving birth if she and her partner have an annual income above $3,733, reports the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Coverage disruptions are harmful to mothers, said Mr. Becerra. HHS data shows that more than half of pregnant women in Medicaid experienced a coverage gap in the first 6 months postpartum and that disruptions in coverage often lead to delayed care and less preventive care.
Mr. Becerra also announced that the Health Resources and Services Administration will make $12 million available over 4 years for the Rural Maternity and Obstetrics Management Strategies program. Applicants for the new funds will be required to focus on populations that have historically suffered from poorer health outcomes, health disparities, and other inequities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stethoscope and Doppler may outperform newer intrapartum fetal monitoring techniques
For intrapartum fetal surveillance, the old way may be the best way, according to a meta-analysis involving more than 118,000 patients.
Intermittent auscultation with a Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler was associated with a significantly lower risk of emergency cesarean deliveries than newer monitoring techniques without jeopardizing maternal or neonatal outcomes, reported lead author Bassel H. Al Wattar, MD, PhD, of University of Warwick, Coventry, England, and University College London Hospitals, and colleagues.
“Over the last 50 years, several newer surveillance methods have been evaluated, with varied uptake in practice,” the investigators wrote in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, noting that cardiotocography (CTG) is the most common method for high-risk pregnancies, typically coupled with at least one other modality, such as fetal scalp pH analysis (FBS), fetal pulse oximetry (FPO), or fetal heart electrocardiogram (STAN).
“Despite extensive investment in clinical research, the overall effectiveness of such methods in improving maternal and neonatal outcomes remains debatable as stillbirth rates have plateaued worldwide, while cesarean delivery rates continue to rise,” the investigators wrote. Previous meta-analyses have relied upon head-to-head comparisons of monitoring techniques and did not take into account effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues conducted the present systematic review and meta-analysis, ultimately including 33 trials with 118,863 women who underwent intrapartum fetal surveillance, dating back to 1976. Ten surveillance types were evaluated, including intermittent auscultation with Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler, CTG with or without computer-aided decision models (cCTG), and CTG or cCTG combined with one or two other techniques, such as FBS, FPO, and STAN.
This revealed that intermittent auscultation outperformed all other techniques in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries and emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress.
Specifically, intermittent auscultation significantly reduced risk of emergency cesarean deliveries, compared with CTG (relative risk, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.97), CTG-FBS (RR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.63-0.80), CTG-lactate (RR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.64-0.92), and FPO-CTG-FBS (RR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99). Conversely, compared with IA, STAN-CTG-FBS and cCTG-FBS raised risk of emergency cesarean deliveries by 17% and 21%, respectively.
Compared with other modalities, the superiority of intermittent auscultation was even more pronounced in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress. Intermittent auscultation reduced risk by 43%, compared with CTG, 66% compared with CTG-FBS, 58%, compared with FPO-CTG, and 17%, compared with FPO-CTG-FBS. Conversely, compared with intermittent auscultation, STAN-CTG and cCTG-FBS increased risk of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress by 39% and 80%, respectively.
Further analysis showed that all types of surveillance had similar effects on neonatal outcomes, such as admission to neonatal unit and neonatal acidemia. Although a combination of STAN or FPO with CTG-FBS “seemed to improve the likelihood of reducing adverse neonatal outcomes,” the investigators noted that these differences were not significant in network meta-analysis.
“New fetal surveillance methods did not improve neonatal outcomes or reduce unnecessary maternal interventions,” Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues concluded. “Further evidence is needed to evaluate the effects of fetal pulse oximetry and fetal heart electrocardiography in labor.”
Courtney Rhoades, DO, MBA, FACOG, medical director of labor and delivery and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, suggested that the meta-analysis supports the safety of intermittent auscultation, but the results may not be entirely applicable to real-world practice.
“It is hard, in practice, to draw the same conclusion that they do in the study that the newer methods may cause too many emergency C-sections because our fetal monitoring equipment, methodology for interpretation, ability to do emergency C-sections and maternal risk factors have changed in the last 50 years,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Continuous fetal monitoring gives more data points during labor, and with more data points, there are more opportunities to interpret and act – either correctly or incorrectly. As they state in the study, the decision to do a C-section is multifactorial.”
Dr. Rhoades, who recently authored a textbook chapter on intrapartum monitoring and fetal assessment, recommended that intermittent auscultation be reserved for low-risk patients.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has endorsed intermittent auscultation for low-risk pregnancies and this study affirms their support,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Women with a low-risk pregnancy can benefit from intermittent auscultation because it allows them more autonomy and movement during labor so it should be offered to our low-risk patients.”
Dr. Al Wattar reported a personal Academic Clinical Lectureship from the U.K. National Health Institute of Research. Dr. Khan disclosed funding from the Beatriz Galindo Program Grant given to the University of Granada by the Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities of the Spanish Government.
For intrapartum fetal surveillance, the old way may be the best way, according to a meta-analysis involving more than 118,000 patients.
Intermittent auscultation with a Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler was associated with a significantly lower risk of emergency cesarean deliveries than newer monitoring techniques without jeopardizing maternal or neonatal outcomes, reported lead author Bassel H. Al Wattar, MD, PhD, of University of Warwick, Coventry, England, and University College London Hospitals, and colleagues.
“Over the last 50 years, several newer surveillance methods have been evaluated, with varied uptake in practice,” the investigators wrote in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, noting that cardiotocography (CTG) is the most common method for high-risk pregnancies, typically coupled with at least one other modality, such as fetal scalp pH analysis (FBS), fetal pulse oximetry (FPO), or fetal heart electrocardiogram (STAN).
“Despite extensive investment in clinical research, the overall effectiveness of such methods in improving maternal and neonatal outcomes remains debatable as stillbirth rates have plateaued worldwide, while cesarean delivery rates continue to rise,” the investigators wrote. Previous meta-analyses have relied upon head-to-head comparisons of monitoring techniques and did not take into account effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues conducted the present systematic review and meta-analysis, ultimately including 33 trials with 118,863 women who underwent intrapartum fetal surveillance, dating back to 1976. Ten surveillance types were evaluated, including intermittent auscultation with Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler, CTG with or without computer-aided decision models (cCTG), and CTG or cCTG combined with one or two other techniques, such as FBS, FPO, and STAN.
This revealed that intermittent auscultation outperformed all other techniques in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries and emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress.
Specifically, intermittent auscultation significantly reduced risk of emergency cesarean deliveries, compared with CTG (relative risk, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.97), CTG-FBS (RR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.63-0.80), CTG-lactate (RR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.64-0.92), and FPO-CTG-FBS (RR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99). Conversely, compared with IA, STAN-CTG-FBS and cCTG-FBS raised risk of emergency cesarean deliveries by 17% and 21%, respectively.
Compared with other modalities, the superiority of intermittent auscultation was even more pronounced in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress. Intermittent auscultation reduced risk by 43%, compared with CTG, 66% compared with CTG-FBS, 58%, compared with FPO-CTG, and 17%, compared with FPO-CTG-FBS. Conversely, compared with intermittent auscultation, STAN-CTG and cCTG-FBS increased risk of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress by 39% and 80%, respectively.
Further analysis showed that all types of surveillance had similar effects on neonatal outcomes, such as admission to neonatal unit and neonatal acidemia. Although a combination of STAN or FPO with CTG-FBS “seemed to improve the likelihood of reducing adverse neonatal outcomes,” the investigators noted that these differences were not significant in network meta-analysis.
“New fetal surveillance methods did not improve neonatal outcomes or reduce unnecessary maternal interventions,” Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues concluded. “Further evidence is needed to evaluate the effects of fetal pulse oximetry and fetal heart electrocardiography in labor.”
Courtney Rhoades, DO, MBA, FACOG, medical director of labor and delivery and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, suggested that the meta-analysis supports the safety of intermittent auscultation, but the results may not be entirely applicable to real-world practice.
“It is hard, in practice, to draw the same conclusion that they do in the study that the newer methods may cause too many emergency C-sections because our fetal monitoring equipment, methodology for interpretation, ability to do emergency C-sections and maternal risk factors have changed in the last 50 years,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Continuous fetal monitoring gives more data points during labor, and with more data points, there are more opportunities to interpret and act – either correctly or incorrectly. As they state in the study, the decision to do a C-section is multifactorial.”
Dr. Rhoades, who recently authored a textbook chapter on intrapartum monitoring and fetal assessment, recommended that intermittent auscultation be reserved for low-risk patients.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has endorsed intermittent auscultation for low-risk pregnancies and this study affirms their support,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Women with a low-risk pregnancy can benefit from intermittent auscultation because it allows them more autonomy and movement during labor so it should be offered to our low-risk patients.”
Dr. Al Wattar reported a personal Academic Clinical Lectureship from the U.K. National Health Institute of Research. Dr. Khan disclosed funding from the Beatriz Galindo Program Grant given to the University of Granada by the Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities of the Spanish Government.
For intrapartum fetal surveillance, the old way may be the best way, according to a meta-analysis involving more than 118,000 patients.
Intermittent auscultation with a Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler was associated with a significantly lower risk of emergency cesarean deliveries than newer monitoring techniques without jeopardizing maternal or neonatal outcomes, reported lead author Bassel H. Al Wattar, MD, PhD, of University of Warwick, Coventry, England, and University College London Hospitals, and colleagues.
“Over the last 50 years, several newer surveillance methods have been evaluated, with varied uptake in practice,” the investigators wrote in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, noting that cardiotocography (CTG) is the most common method for high-risk pregnancies, typically coupled with at least one other modality, such as fetal scalp pH analysis (FBS), fetal pulse oximetry (FPO), or fetal heart electrocardiogram (STAN).
“Despite extensive investment in clinical research, the overall effectiveness of such methods in improving maternal and neonatal outcomes remains debatable as stillbirth rates have plateaued worldwide, while cesarean delivery rates continue to rise,” the investigators wrote. Previous meta-analyses have relied upon head-to-head comparisons of monitoring techniques and did not take into account effects on maternal and neonatal outcomes.
To address this knowledge gap, Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues conducted the present systematic review and meta-analysis, ultimately including 33 trials with 118,863 women who underwent intrapartum fetal surveillance, dating back to 1976. Ten surveillance types were evaluated, including intermittent auscultation with Pinard stethoscope and handheld Doppler, CTG with or without computer-aided decision models (cCTG), and CTG or cCTG combined with one or two other techniques, such as FBS, FPO, and STAN.
This revealed that intermittent auscultation outperformed all other techniques in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries and emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress.
Specifically, intermittent auscultation significantly reduced risk of emergency cesarean deliveries, compared with CTG (relative risk, 0.83; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.97), CTG-FBS (RR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.63-0.80), CTG-lactate (RR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.64-0.92), and FPO-CTG-FBS (RR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.67-0.99). Conversely, compared with IA, STAN-CTG-FBS and cCTG-FBS raised risk of emergency cesarean deliveries by 17% and 21%, respectively.
Compared with other modalities, the superiority of intermittent auscultation was even more pronounced in terms of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress. Intermittent auscultation reduced risk by 43%, compared with CTG, 66% compared with CTG-FBS, 58%, compared with FPO-CTG, and 17%, compared with FPO-CTG-FBS. Conversely, compared with intermittent auscultation, STAN-CTG and cCTG-FBS increased risk of emergency cesarean deliveries because of fetal distress by 39% and 80%, respectively.
Further analysis showed that all types of surveillance had similar effects on neonatal outcomes, such as admission to neonatal unit and neonatal acidemia. Although a combination of STAN or FPO with CTG-FBS “seemed to improve the likelihood of reducing adverse neonatal outcomes,” the investigators noted that these differences were not significant in network meta-analysis.
“New fetal surveillance methods did not improve neonatal outcomes or reduce unnecessary maternal interventions,” Dr. Al Wattar and colleagues concluded. “Further evidence is needed to evaluate the effects of fetal pulse oximetry and fetal heart electrocardiography in labor.”
Courtney Rhoades, DO, MBA, FACOG, medical director of labor and delivery and assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Florida, Jacksonville, suggested that the meta-analysis supports the safety of intermittent auscultation, but the results may not be entirely applicable to real-world practice.
“It is hard, in practice, to draw the same conclusion that they do in the study that the newer methods may cause too many emergency C-sections because our fetal monitoring equipment, methodology for interpretation, ability to do emergency C-sections and maternal risk factors have changed in the last 50 years,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Continuous fetal monitoring gives more data points during labor, and with more data points, there are more opportunities to interpret and act – either correctly or incorrectly. As they state in the study, the decision to do a C-section is multifactorial.”
Dr. Rhoades, who recently authored a textbook chapter on intrapartum monitoring and fetal assessment, recommended that intermittent auscultation be reserved for low-risk patients.
“The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has endorsed intermittent auscultation for low-risk pregnancies and this study affirms their support,” Dr. Rhoades said. “Women with a low-risk pregnancy can benefit from intermittent auscultation because it allows them more autonomy and movement during labor so it should be offered to our low-risk patients.”
Dr. Al Wattar reported a personal Academic Clinical Lectureship from the U.K. National Health Institute of Research. Dr. Khan disclosed funding from the Beatriz Galindo Program Grant given to the University of Granada by the Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities of the Spanish Government.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
FDA lifts in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone
The Food and Drug Administration has lifted in-person dispensing requirements for mifepristone when used for medical termination of early pregnancy.
In an April 12, 2021, letter to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, acting commissioner of food and drugs Janet Woodcock stated that the FDA would exercise discretion to permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.
The decision follows a trial period of suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research reviewed safety and clinical outcomes data on mifepristone use when prescriptions were handled by mail or mail-order pharmacy and found that "the small number of adverse events reported to FDA during the COVID-19 public health emergency [PHE] provide no indication that any program deviation or noncompliance with the mifepristone [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program contributed to the reported adverse events," according to the letter. The analysis covers Mifeprex and the approved generic, mifepristone tablets, both 200-mg doses.
As long as other mifepristone REMS criteria are met, the FDA will continue to permit mail and mail-order prescriptions, according to the letter.
"By halting enforcement of the in-person dispensing requirement during the COVID-19 pandemic, the FDA is recognizing and responding to the available evidence - which has clearly and definitively demonstrated that the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone is unnecessary and restrictive," Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of ACOG, said in a statement in response to the FDA decision.
ACOG petitioned the FDA to suspend the in-person requirement to reduce the risk of transmission in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, given safety concerns and the potential impact on hard-hit communities, particularly communities of color, Dr. Phipps emphasized. Data from a review period with a suspension of the in-person requirement yielded no additional safety concerns with mifepristone use, and contributed to the FDA decision to lift the requirement.
"Thanks to the FDA's intent to exercise discretion in enforcing the in-person dispensing requirement, those in need of an abortion or miscarriage management will be able to do so safety and effectively by acquiring mifepristone though the mail - just as they would any other medication with a similarly strong safety profile," said Dr. Phipps. "We are pleased to see mifepristone regulated on the basis of the scientific evidence during the pandemic, rather than political bias against comprehensive reproductive health care, and we look forward to working with policy makers to ensure this principle governs postpandemic care."
CDER is communicating the decision to all approved application holders subject to the mifepristone REMS program, according to the letter.
obnews@mdedge.com
The Food and Drug Administration has lifted in-person dispensing requirements for mifepristone when used for medical termination of early pregnancy.
In an April 12, 2021, letter to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, acting commissioner of food and drugs Janet Woodcock stated that the FDA would exercise discretion to permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.
The decision follows a trial period of suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research reviewed safety and clinical outcomes data on mifepristone use when prescriptions were handled by mail or mail-order pharmacy and found that "the small number of adverse events reported to FDA during the COVID-19 public health emergency [PHE] provide no indication that any program deviation or noncompliance with the mifepristone [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program contributed to the reported adverse events," according to the letter. The analysis covers Mifeprex and the approved generic, mifepristone tablets, both 200-mg doses.
As long as other mifepristone REMS criteria are met, the FDA will continue to permit mail and mail-order prescriptions, according to the letter.
"By halting enforcement of the in-person dispensing requirement during the COVID-19 pandemic, the FDA is recognizing and responding to the available evidence - which has clearly and definitively demonstrated that the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone is unnecessary and restrictive," Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of ACOG, said in a statement in response to the FDA decision.
ACOG petitioned the FDA to suspend the in-person requirement to reduce the risk of transmission in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, given safety concerns and the potential impact on hard-hit communities, particularly communities of color, Dr. Phipps emphasized. Data from a review period with a suspension of the in-person requirement yielded no additional safety concerns with mifepristone use, and contributed to the FDA decision to lift the requirement.
"Thanks to the FDA's intent to exercise discretion in enforcing the in-person dispensing requirement, those in need of an abortion or miscarriage management will be able to do so safety and effectively by acquiring mifepristone though the mail - just as they would any other medication with a similarly strong safety profile," said Dr. Phipps. "We are pleased to see mifepristone regulated on the basis of the scientific evidence during the pandemic, rather than political bias against comprehensive reproductive health care, and we look forward to working with policy makers to ensure this principle governs postpandemic care."
CDER is communicating the decision to all approved application holders subject to the mifepristone REMS program, according to the letter.
obnews@mdedge.com
The Food and Drug Administration has lifted in-person dispensing requirements for mifepristone when used for medical termination of early pregnancy.
In an April 12, 2021, letter to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, acting commissioner of food and drugs Janet Woodcock stated that the FDA would exercise discretion to permit the dispensing of mifepristone through the mail when done by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber; or through a mail-order pharmacy under the supervision of a certified prescriber.
The decision follows a trial period of suspension of the in-person dispensing requirement in response to safety concerns for patients as well as providers associated with in-person clinic visits during the COVID-19 pandemic. The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research reviewed safety and clinical outcomes data on mifepristone use when prescriptions were handled by mail or mail-order pharmacy and found that "the small number of adverse events reported to FDA during the COVID-19 public health emergency [PHE] provide no indication that any program deviation or noncompliance with the mifepristone [Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy] program contributed to the reported adverse events," according to the letter. The analysis covers Mifeprex and the approved generic, mifepristone tablets, both 200-mg doses.
As long as other mifepristone REMS criteria are met, the FDA will continue to permit mail and mail-order prescriptions, according to the letter.
"By halting enforcement of the in-person dispensing requirement during the COVID-19 pandemic, the FDA is recognizing and responding to the available evidence - which has clearly and definitively demonstrated that the in-person dispensing requirement for mifepristone is unnecessary and restrictive," Maureen G. Phipps, MD, MPH, CEO of ACOG, said in a statement in response to the FDA decision.
ACOG petitioned the FDA to suspend the in-person requirement to reduce the risk of transmission in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, given safety concerns and the potential impact on hard-hit communities, particularly communities of color, Dr. Phipps emphasized. Data from a review period with a suspension of the in-person requirement yielded no additional safety concerns with mifepristone use, and contributed to the FDA decision to lift the requirement.
"Thanks to the FDA's intent to exercise discretion in enforcing the in-person dispensing requirement, those in need of an abortion or miscarriage management will be able to do so safety and effectively by acquiring mifepristone though the mail - just as they would any other medication with a similarly strong safety profile," said Dr. Phipps. "We are pleased to see mifepristone regulated on the basis of the scientific evidence during the pandemic, rather than political bias against comprehensive reproductive health care, and we look forward to working with policy makers to ensure this principle governs postpandemic care."
CDER is communicating the decision to all approved application holders subject to the mifepristone REMS program, according to the letter.
obnews@mdedge.com
Pregnancy after pioneering treatment for early menopause
A novel therapy combining platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with follicle-stimulating hormone that is injected directly into the ovaries has the potential to restore ovarian function for women who experience early menopause, possibly allowing for pregnancy without the need for donor eggs.
“The resumption of ovarian function in our participants means women with early menopause could have the opportunity to pursue pregnancy through IVF [in vitro fertilization] using their own eggs,” the authors of the groundbreaking pilot study report.
In the small study, published online March 29 in Menopause, menstruation resumed within a mean of about 5 weeks for 11 of 12 patients with early menopause who were treated with the technique. One patient achieved a clinical pregnancy.
In commenting on the study, Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, medical director of the North American Menopause Society, was cautious in her interpretation, noting the need for more research in larger samples.
“Any pregnancy that results from a regenerative therapy is novel,” she told this news organization. “Still, we are a long way away from this being a standard therapy for women with premature ovarian insufficiency.”
Pilot study: Platelet-rich plasma combination with FSH
Early menopause is the cessation of ovarian function at or before the age of 45 years. It is estimated that 12.2% of women experience early menopause. For these women, currently, the only chance of becoming pregnant is with donor eggs.
PRP, an autologous plasma preparation containing more than 10 times the concentration of growth factors and active metabolites than normal plasma, has recently been shown to have the potential to restore the menstrual cycles in perimenopausal women, allowing IVF. It has also been shown to benefit women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI). However, there have been few reports of pregnancies or live births.
Chao Chin Hsu, MD, PhD, of the National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, and colleagues investigated whether the combination of the activated PRP treatment with gondatrophins such as FSH could provide a more robust effect so as to sufficiently stimulate follicles. They used the intraovarian injection of the combination to treat a 38-year-old woman with POI.
The effort was successful, and the woman gave birth to healthy twins.
To further evaluate the approach, the authors conducted a pilot study involving 12 women with early menopause (mean age, 44.4 years) between November 2018 and November 2019.
The women received intraovarian injection with PRP prepared from 40 mL of autologous peripheral blood combined with recombinant FSH.
Following the treatment, 11 of the 12 women experienced resumption of menstruation within a mean of 37 days. For seven patients, menstruation resumed within a month; for three, it resumed within about 2 months; and for one, it resumed after approximately 3 months.
Of note, the menstrual cycles were mostly irregular, with an interval of about 45.6 days.
The women’s average serum FSH level dropped significantly from 70.5 IU/L at baseline to 26.2 IU/L within days of treatment, as did the average luteinizing hormone level (34.8 before and 14.3 IU/L after treatment), indicative of improved ovary function.
For six participants, 10 oocyte retrieval procedures were performed after a mean of about 2 months. Thirteen mature eggs were retrieved, and fertilization via intracytoplasmic sperm injection was attempted, resulting in 10 fertilized oocytes.
Cleavage-stage embryos were transferred into two of the participants. One achieved a clinical pregnancy, defined as a pregnancy that was confirmed by ultrasound and by the presence of a fetal heartbeat. The pregnancy ended in miscarriage at 7 weeks’ gestation.
The length of controlled ovarian stimulation necessary for follicle growth ranged from 8 to 14 days, which the authors note is similar to that seen with women of normal reproductive age.
“Although the use of PRP in reproductive medicine is considered experimental, we demonstrated the restoration of ovarian function in early menopausal women who adopted whole dimension subcortical ovarian injection of PRP/gonadotropin,” the authors write.
“Most remarkably, an early menopausal woman achieved pregnancy after the treatment followed by IVF with her mature ovulating follicle,” they report.
Mechanisms, caveats
The mechanisms thought to underlie the success of the approach include increases in ovarian vascularization and stromal cell proliferation and reductions in oxidative stress and cell death in ovaries, the authors explain.
Key caveats with the treatment include the fact that anesthesia and laparoscopy are required, and precise administration is required at 15 injection sites in 1-2 mm of the ovarian subcortical area, which can be difficult to achieve, Dr. Hsu said in an interview.
“If a new instrument could be developed in which physicians can carry out this treatment through a vaginal approach, like the transvaginal retrieval of eggs in IVF treatments,” the approach could become more acceptable, Dr. Hsu added.
The authors call for studies with larger sample sizes and say it will also be interesting to determine effects in different groups: For example, women with cancer who have undergone chemotherapy.
Dr. Faubion, who is director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health, Rochester, Minn., says the causes of early menopause could be important in determining the treatment’s efficacy.
“[The therapy’s] success may depend on the reason the woman experienced early menopause: For instance, due to chemotherapy, radiation, virus, autoimmune disease, genetic mutation, or other cause,” she said.
She also noted that cost could be an important factor.
“I don’t see a cost estimate, but it will be substantial,” she said. “So, even if the success rate improves as this technique is further studied, cost and the invasive nature of the treatment may prove to be substantial barriers to this therapy becoming mainstream,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Faubion have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel therapy combining platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with follicle-stimulating hormone that is injected directly into the ovaries has the potential to restore ovarian function for women who experience early menopause, possibly allowing for pregnancy without the need for donor eggs.
“The resumption of ovarian function in our participants means women with early menopause could have the opportunity to pursue pregnancy through IVF [in vitro fertilization] using their own eggs,” the authors of the groundbreaking pilot study report.
In the small study, published online March 29 in Menopause, menstruation resumed within a mean of about 5 weeks for 11 of 12 patients with early menopause who were treated with the technique. One patient achieved a clinical pregnancy.
In commenting on the study, Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, medical director of the North American Menopause Society, was cautious in her interpretation, noting the need for more research in larger samples.
“Any pregnancy that results from a regenerative therapy is novel,” she told this news organization. “Still, we are a long way away from this being a standard therapy for women with premature ovarian insufficiency.”
Pilot study: Platelet-rich plasma combination with FSH
Early menopause is the cessation of ovarian function at or before the age of 45 years. It is estimated that 12.2% of women experience early menopause. For these women, currently, the only chance of becoming pregnant is with donor eggs.
PRP, an autologous plasma preparation containing more than 10 times the concentration of growth factors and active metabolites than normal plasma, has recently been shown to have the potential to restore the menstrual cycles in perimenopausal women, allowing IVF. It has also been shown to benefit women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI). However, there have been few reports of pregnancies or live births.
Chao Chin Hsu, MD, PhD, of the National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, and colleagues investigated whether the combination of the activated PRP treatment with gondatrophins such as FSH could provide a more robust effect so as to sufficiently stimulate follicles. They used the intraovarian injection of the combination to treat a 38-year-old woman with POI.
The effort was successful, and the woman gave birth to healthy twins.
To further evaluate the approach, the authors conducted a pilot study involving 12 women with early menopause (mean age, 44.4 years) between November 2018 and November 2019.
The women received intraovarian injection with PRP prepared from 40 mL of autologous peripheral blood combined with recombinant FSH.
Following the treatment, 11 of the 12 women experienced resumption of menstruation within a mean of 37 days. For seven patients, menstruation resumed within a month; for three, it resumed within about 2 months; and for one, it resumed after approximately 3 months.
Of note, the menstrual cycles were mostly irregular, with an interval of about 45.6 days.
The women’s average serum FSH level dropped significantly from 70.5 IU/L at baseline to 26.2 IU/L within days of treatment, as did the average luteinizing hormone level (34.8 before and 14.3 IU/L after treatment), indicative of improved ovary function.
For six participants, 10 oocyte retrieval procedures were performed after a mean of about 2 months. Thirteen mature eggs were retrieved, and fertilization via intracytoplasmic sperm injection was attempted, resulting in 10 fertilized oocytes.
Cleavage-stage embryos were transferred into two of the participants. One achieved a clinical pregnancy, defined as a pregnancy that was confirmed by ultrasound and by the presence of a fetal heartbeat. The pregnancy ended in miscarriage at 7 weeks’ gestation.
The length of controlled ovarian stimulation necessary for follicle growth ranged from 8 to 14 days, which the authors note is similar to that seen with women of normal reproductive age.
“Although the use of PRP in reproductive medicine is considered experimental, we demonstrated the restoration of ovarian function in early menopausal women who adopted whole dimension subcortical ovarian injection of PRP/gonadotropin,” the authors write.
“Most remarkably, an early menopausal woman achieved pregnancy after the treatment followed by IVF with her mature ovulating follicle,” they report.
Mechanisms, caveats
The mechanisms thought to underlie the success of the approach include increases in ovarian vascularization and stromal cell proliferation and reductions in oxidative stress and cell death in ovaries, the authors explain.
Key caveats with the treatment include the fact that anesthesia and laparoscopy are required, and precise administration is required at 15 injection sites in 1-2 mm of the ovarian subcortical area, which can be difficult to achieve, Dr. Hsu said in an interview.
“If a new instrument could be developed in which physicians can carry out this treatment through a vaginal approach, like the transvaginal retrieval of eggs in IVF treatments,” the approach could become more acceptable, Dr. Hsu added.
The authors call for studies with larger sample sizes and say it will also be interesting to determine effects in different groups: For example, women with cancer who have undergone chemotherapy.
Dr. Faubion, who is director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health, Rochester, Minn., says the causes of early menopause could be important in determining the treatment’s efficacy.
“[The therapy’s] success may depend on the reason the woman experienced early menopause: For instance, due to chemotherapy, radiation, virus, autoimmune disease, genetic mutation, or other cause,” she said.
She also noted that cost could be an important factor.
“I don’t see a cost estimate, but it will be substantial,” she said. “So, even if the success rate improves as this technique is further studied, cost and the invasive nature of the treatment may prove to be substantial barriers to this therapy becoming mainstream,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Faubion have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A novel therapy combining platelet-rich plasma (PRP) with follicle-stimulating hormone that is injected directly into the ovaries has the potential to restore ovarian function for women who experience early menopause, possibly allowing for pregnancy without the need for donor eggs.
“The resumption of ovarian function in our participants means women with early menopause could have the opportunity to pursue pregnancy through IVF [in vitro fertilization] using their own eggs,” the authors of the groundbreaking pilot study report.
In the small study, published online March 29 in Menopause, menstruation resumed within a mean of about 5 weeks for 11 of 12 patients with early menopause who were treated with the technique. One patient achieved a clinical pregnancy.
In commenting on the study, Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, medical director of the North American Menopause Society, was cautious in her interpretation, noting the need for more research in larger samples.
“Any pregnancy that results from a regenerative therapy is novel,” she told this news organization. “Still, we are a long way away from this being a standard therapy for women with premature ovarian insufficiency.”
Pilot study: Platelet-rich plasma combination with FSH
Early menopause is the cessation of ovarian function at or before the age of 45 years. It is estimated that 12.2% of women experience early menopause. For these women, currently, the only chance of becoming pregnant is with donor eggs.
PRP, an autologous plasma preparation containing more than 10 times the concentration of growth factors and active metabolites than normal plasma, has recently been shown to have the potential to restore the menstrual cycles in perimenopausal women, allowing IVF. It has also been shown to benefit women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI). However, there have been few reports of pregnancies or live births.
Chao Chin Hsu, MD, PhD, of the National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, and colleagues investigated whether the combination of the activated PRP treatment with gondatrophins such as FSH could provide a more robust effect so as to sufficiently stimulate follicles. They used the intraovarian injection of the combination to treat a 38-year-old woman with POI.
The effort was successful, and the woman gave birth to healthy twins.
To further evaluate the approach, the authors conducted a pilot study involving 12 women with early menopause (mean age, 44.4 years) between November 2018 and November 2019.
The women received intraovarian injection with PRP prepared from 40 mL of autologous peripheral blood combined with recombinant FSH.
Following the treatment, 11 of the 12 women experienced resumption of menstruation within a mean of 37 days. For seven patients, menstruation resumed within a month; for three, it resumed within about 2 months; and for one, it resumed after approximately 3 months.
Of note, the menstrual cycles were mostly irregular, with an interval of about 45.6 days.
The women’s average serum FSH level dropped significantly from 70.5 IU/L at baseline to 26.2 IU/L within days of treatment, as did the average luteinizing hormone level (34.8 before and 14.3 IU/L after treatment), indicative of improved ovary function.
For six participants, 10 oocyte retrieval procedures were performed after a mean of about 2 months. Thirteen mature eggs were retrieved, and fertilization via intracytoplasmic sperm injection was attempted, resulting in 10 fertilized oocytes.
Cleavage-stage embryos were transferred into two of the participants. One achieved a clinical pregnancy, defined as a pregnancy that was confirmed by ultrasound and by the presence of a fetal heartbeat. The pregnancy ended in miscarriage at 7 weeks’ gestation.
The length of controlled ovarian stimulation necessary for follicle growth ranged from 8 to 14 days, which the authors note is similar to that seen with women of normal reproductive age.
“Although the use of PRP in reproductive medicine is considered experimental, we demonstrated the restoration of ovarian function in early menopausal women who adopted whole dimension subcortical ovarian injection of PRP/gonadotropin,” the authors write.
“Most remarkably, an early menopausal woman achieved pregnancy after the treatment followed by IVF with her mature ovulating follicle,” they report.
Mechanisms, caveats
The mechanisms thought to underlie the success of the approach include increases in ovarian vascularization and stromal cell proliferation and reductions in oxidative stress and cell death in ovaries, the authors explain.
Key caveats with the treatment include the fact that anesthesia and laparoscopy are required, and precise administration is required at 15 injection sites in 1-2 mm of the ovarian subcortical area, which can be difficult to achieve, Dr. Hsu said in an interview.
“If a new instrument could be developed in which physicians can carry out this treatment through a vaginal approach, like the transvaginal retrieval of eggs in IVF treatments,” the approach could become more acceptable, Dr. Hsu added.
The authors call for studies with larger sample sizes and say it will also be interesting to determine effects in different groups: For example, women with cancer who have undergone chemotherapy.
Dr. Faubion, who is director of the Mayo Clinic Women’s Health, Rochester, Minn., says the causes of early menopause could be important in determining the treatment’s efficacy.
“[The therapy’s] success may depend on the reason the woman experienced early menopause: For instance, due to chemotherapy, radiation, virus, autoimmune disease, genetic mutation, or other cause,” she said.
She also noted that cost could be an important factor.
“I don’t see a cost estimate, but it will be substantial,” she said. “So, even if the success rate improves as this technique is further studied, cost and the invasive nature of the treatment may prove to be substantial barriers to this therapy becoming mainstream,” she said.
The authors and Dr. Faubion have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bedtime soon after meals raises reflux risk in pregnancy
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
A shorter period between eating and going to sleep increased the risk of GERD during pregnancy by approximately 12%, according to data from 400 women.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common condition in pregnancy because of changes in gastrointestinal motility caused by hormonal changes, and a short meal-to-bed time (MTBT) also has been associated with increased GERD symptoms, but data on the impact of MTBT on GERD in pregnant women in particular are lacking, wrote Duc T. Quach, MD, of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, and colleagues.
In a cross-sectional study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, the researchers identified 400 pregnant women aged 18 years and older in various stages of pregnancy who were seen at a single hospital in Vietnam. A short MTBT was defined as going to bed 2 hours or less after eating. Primary outcomes were GERD, defined as troublesome heartburn and/or regurgitation at least once a week, and reflux-related insomnia, defined as trouble initiating or maintaining nighttime sleep. Participants also reported the number of days of troublesome reflux symptoms and frequency of reflux-related insomnia over the last 7 days.
A total of 154 participants had a diagnosis of GERD, for an overall prevalence of 38.5%, similar to that seen in GERD studies of GERD and pregnancy, the researchers noted, and of those with GERD, 20 participants (13.0%) reported reflux-related insomnia.
The overall prevalence of heartburn, regurgitation, nausea with or without vomiting, and epigastric pain were 11.8%, 35.8%, 30.0%, and 5.5%, respectively. A total of 139 women reported reflux symptoms on at least 2 of the past 7 days, and 40 women reported both daytime and nighttime reflux symptoms.
Short meal-to-bed time shows strongest association
A short MTBT was the strongest predictor of GERD in multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 12.73; 95% confidence interval, 2.92-55.45; P = .001); previous history of reflux symptoms (OR, 9.05; 95% CI, 5.29-15.50; P < 001) and being in the third trimester versus first or second of pregnancy (OR, 1.66, 95% CI, 1.03-2.69; P = .039) also remained significant predictors in a multivariate analysis. In addition, nighttime short MTBT (but not daytime short MTBT) was the strongest risk factor for reflux-related insomnia (OR, 4.60), although alcohol consumption and a history of reflux-related symptoms also remained significant in multivariate analysis.
“Interestingly, the number of days during which reflux symptoms were experienced during the last 7 days sequentially increased across subgroups of participants with no short MTBT, either daytime or nighttime short MTBT, and with both daytime and nighttime MTBT,” the researchers wrote. At 4-7 days, none of the patients with no short MTBT reported reflux symptoms, compared with 7.5% of those with either daytime or nighttime MTBT and 20.9% of those with both daytime and nighttime MTBT.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to accurately record participants’ diets and the potential for overestimating the odds ratio of risk factors in patients with reflux-related insomnia because of the small numbers. However, the results support findings from previous studies and suggest that dietary modifications could provide a nonpharmacological treatment target for managing GERD in pregnant women, they concluded.
Behavioral intervention may benefit pregnant women
The study is important because heartburn and regurgitation are common challenges during pregnancy, Ziad F. Gellad, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an interview. “Understanding risk factors for these conditions can be helpful in designing behavioral and pharmaceutical therapeutic interventions.”
The link between short MTBT and increased risk for GERD is well-known, said Dr. Gellad. “Lengthening the time to laying supine after a meal is a common recommendation given to patients with GERD and is included in published GERD guidelines.” Although pregnant woman may have been excluded from trials on which the guidelines and recommendations are based, “it is reasonable to expect that findings would translate to this population that is generally higher risk for reflux,” he noted.
Dr. Gellad was interested to see the dose response between MTBT and reflux, with those patients having both daytime and nighttime short MTBT experiencing reflux more often than those with short MTBT in only one of those time periods (4-7 days vs. 1-3 days).
The key message for clinicians is that, for all individuals, pregnant or not, “avoiding late night meals and short meal-to-bed time is an appropriate behavioral intervention to recommend for patients with troublesome heartburn or regurgitation,” Dr. Gellad emphasized. However, more research is needed in some areas, “implementation studies would be helpful to understand how best to educate patients on behavioral modifications known to decrease reflux symptoms.”
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Gellad had no relevant financial disclosures, but serves as a member of the GI & Hepatology News board of editors.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
Endometrial thickness could predict cancer, guide lymph node assessment
In a retrospective study of 378 patients who had hysterectomies for EIN, those with a preoperative endometrial stripe of 20 mm or greater were two times more likely to have endometrial cancer on final pathology, and those with an endometrial thickness of 15 mm or greater were 1.8 times more likely to have cancer.
“This data suggests that increasing endometrial thickness may be a useful preoperative marker to identify who’s at higher risk of concurrent endometrial cancer. It could also be considered a criterion for selectively using a sentinel lymph node algorithm in patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN. However, prospective studies are warranted to further establish this association,” said Devon Abt, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
She presented the data at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11103).
Risk of overtreatment
There are no clear consensus guidelines on lymph node assessment for patients with EIN, Dr. Abt noted. She pointed out that roughly 40% of patients with EIN are diagnosed with endometrial cancer. However, it’s usually low-stage, low-grade disease, and only about 10% of patients will have high-risk features that warrant lymph node evaluation.
“Typically, we identify patients with concurrent endometrial cancer based on intraoperative pathology, or frozen section,” Dr. Abt explained. “We then apply the Mayo criteria, which stratifies patients as high or low risk for lymph node metastasis based on pathologic criteria. ... This information helps guide our intraoperative decisions to perform, or not perform, pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy.”
Dr. Abt noted, however, that “lymphadenectomy is not benign” and increases surgical time as well as the risk of complications.
Taking these factors into account, some centers have implemented routine sentinel lymph node algorithms for staging endometrial cancers, Dr. Abt said.
What she and her colleagues wanted to determine is if there is value in this practice. Should sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy be offered routinely to all patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN?
Study details
Dr. Abt and colleagues conducted a retrospective, single-center study of 378 patients with EIN. Ultimately, 27% (n = 103) of the patients were diagnosed with endometrial cancer – 95% with stage 1a disease and 5% with stage 1b.
Increasing age, White race, and hypertension were significantly associated with the presence of endometrial cancer. Body mass index, parity, hormone therapy exposure, and baseline CA 125 were not.
The median preoperative endometrial thickness was 14 mm among patients with endometrial cancer and 11 mm in patients without cancer (P = .002).
Overall, 31% of the cancer cases were considered high risk for nodal metastases by Mayo criteria, but an endometrial stripe of 15 mm or higher increased the chance of being considered high risk.
The risk of cancer was 47% among patients with an endometrial stripe of at least 20 mm versus 21% among patients with a measurement below 15 mm.
Only 10 patients underwent lymph node evaluation, 5 with sentinel lymph node dissection and 5 with lymphadenectomy. Six of the 10 patients had endometrial cancer on final pathology, but none had positive lymph nodes.
“Given the low-grade and early-stage disease in this cohort, adherence to a routine sentinel lymph node algorithm in all patients with EIN would result in overtreatment,” Dr. Abt said.
Discussant Nicole Fleming, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said she would advocate for more selective use of sentinel lymph node biopsies in EIN as well.
Dr. Fleming said, in general, lymph node biopsy may be reasonable in settings where frozen sections are unreliable and the patient seems to be at high risk of invasive cancer. However, at academic centers with dedicated gynecologic pathologists, given the low risk of invasive cancer and the fact that lymph nodes “are probably not going to provide you a lot of useful therapeutic decision-making tools,” potentially eliminating sentinel lymph node biopsy might make sense, Dr. Fleming said.
Dr. Fleming disclosed relationships with Tesaro, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Abt reported having no relevant disclosures and did not report any study funding.
In a retrospective study of 378 patients who had hysterectomies for EIN, those with a preoperative endometrial stripe of 20 mm or greater were two times more likely to have endometrial cancer on final pathology, and those with an endometrial thickness of 15 mm or greater were 1.8 times more likely to have cancer.
“This data suggests that increasing endometrial thickness may be a useful preoperative marker to identify who’s at higher risk of concurrent endometrial cancer. It could also be considered a criterion for selectively using a sentinel lymph node algorithm in patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN. However, prospective studies are warranted to further establish this association,” said Devon Abt, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
She presented the data at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11103).
Risk of overtreatment
There are no clear consensus guidelines on lymph node assessment for patients with EIN, Dr. Abt noted. She pointed out that roughly 40% of patients with EIN are diagnosed with endometrial cancer. However, it’s usually low-stage, low-grade disease, and only about 10% of patients will have high-risk features that warrant lymph node evaluation.
“Typically, we identify patients with concurrent endometrial cancer based on intraoperative pathology, or frozen section,” Dr. Abt explained. “We then apply the Mayo criteria, which stratifies patients as high or low risk for lymph node metastasis based on pathologic criteria. ... This information helps guide our intraoperative decisions to perform, or not perform, pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy.”
Dr. Abt noted, however, that “lymphadenectomy is not benign” and increases surgical time as well as the risk of complications.
Taking these factors into account, some centers have implemented routine sentinel lymph node algorithms for staging endometrial cancers, Dr. Abt said.
What she and her colleagues wanted to determine is if there is value in this practice. Should sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy be offered routinely to all patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN?
Study details
Dr. Abt and colleagues conducted a retrospective, single-center study of 378 patients with EIN. Ultimately, 27% (n = 103) of the patients were diagnosed with endometrial cancer – 95% with stage 1a disease and 5% with stage 1b.
Increasing age, White race, and hypertension were significantly associated with the presence of endometrial cancer. Body mass index, parity, hormone therapy exposure, and baseline CA 125 were not.
The median preoperative endometrial thickness was 14 mm among patients with endometrial cancer and 11 mm in patients without cancer (P = .002).
Overall, 31% of the cancer cases were considered high risk for nodal metastases by Mayo criteria, but an endometrial stripe of 15 mm or higher increased the chance of being considered high risk.
The risk of cancer was 47% among patients with an endometrial stripe of at least 20 mm versus 21% among patients with a measurement below 15 mm.
Only 10 patients underwent lymph node evaluation, 5 with sentinel lymph node dissection and 5 with lymphadenectomy. Six of the 10 patients had endometrial cancer on final pathology, but none had positive lymph nodes.
“Given the low-grade and early-stage disease in this cohort, adherence to a routine sentinel lymph node algorithm in all patients with EIN would result in overtreatment,” Dr. Abt said.
Discussant Nicole Fleming, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said she would advocate for more selective use of sentinel lymph node biopsies in EIN as well.
Dr. Fleming said, in general, lymph node biopsy may be reasonable in settings where frozen sections are unreliable and the patient seems to be at high risk of invasive cancer. However, at academic centers with dedicated gynecologic pathologists, given the low risk of invasive cancer and the fact that lymph nodes “are probably not going to provide you a lot of useful therapeutic decision-making tools,” potentially eliminating sentinel lymph node biopsy might make sense, Dr. Fleming said.
Dr. Fleming disclosed relationships with Tesaro, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Abt reported having no relevant disclosures and did not report any study funding.
In a retrospective study of 378 patients who had hysterectomies for EIN, those with a preoperative endometrial stripe of 20 mm or greater were two times more likely to have endometrial cancer on final pathology, and those with an endometrial thickness of 15 mm or greater were 1.8 times more likely to have cancer.
“This data suggests that increasing endometrial thickness may be a useful preoperative marker to identify who’s at higher risk of concurrent endometrial cancer. It could also be considered a criterion for selectively using a sentinel lymph node algorithm in patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN. However, prospective studies are warranted to further establish this association,” said Devon Abt, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
She presented the data at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Virtual Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer (Abstract 11103).
Risk of overtreatment
There are no clear consensus guidelines on lymph node assessment for patients with EIN, Dr. Abt noted. She pointed out that roughly 40% of patients with EIN are diagnosed with endometrial cancer. However, it’s usually low-stage, low-grade disease, and only about 10% of patients will have high-risk features that warrant lymph node evaluation.
“Typically, we identify patients with concurrent endometrial cancer based on intraoperative pathology, or frozen section,” Dr. Abt explained. “We then apply the Mayo criteria, which stratifies patients as high or low risk for lymph node metastasis based on pathologic criteria. ... This information helps guide our intraoperative decisions to perform, or not perform, pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy.”
Dr. Abt noted, however, that “lymphadenectomy is not benign” and increases surgical time as well as the risk of complications.
Taking these factors into account, some centers have implemented routine sentinel lymph node algorithms for staging endometrial cancers, Dr. Abt said.
What she and her colleagues wanted to determine is if there is value in this practice. Should sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy be offered routinely to all patients with a preoperative diagnosis of EIN?
Study details
Dr. Abt and colleagues conducted a retrospective, single-center study of 378 patients with EIN. Ultimately, 27% (n = 103) of the patients were diagnosed with endometrial cancer – 95% with stage 1a disease and 5% with stage 1b.
Increasing age, White race, and hypertension were significantly associated with the presence of endometrial cancer. Body mass index, parity, hormone therapy exposure, and baseline CA 125 were not.
The median preoperative endometrial thickness was 14 mm among patients with endometrial cancer and 11 mm in patients without cancer (P = .002).
Overall, 31% of the cancer cases were considered high risk for nodal metastases by Mayo criteria, but an endometrial stripe of 15 mm or higher increased the chance of being considered high risk.
The risk of cancer was 47% among patients with an endometrial stripe of at least 20 mm versus 21% among patients with a measurement below 15 mm.
Only 10 patients underwent lymph node evaluation, 5 with sentinel lymph node dissection and 5 with lymphadenectomy. Six of the 10 patients had endometrial cancer on final pathology, but none had positive lymph nodes.
“Given the low-grade and early-stage disease in this cohort, adherence to a routine sentinel lymph node algorithm in all patients with EIN would result in overtreatment,” Dr. Abt said.
Discussant Nicole Fleming, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said she would advocate for more selective use of sentinel lymph node biopsies in EIN as well.
Dr. Fleming said, in general, lymph node biopsy may be reasonable in settings where frozen sections are unreliable and the patient seems to be at high risk of invasive cancer. However, at academic centers with dedicated gynecologic pathologists, given the low risk of invasive cancer and the fact that lymph nodes “are probably not going to provide you a lot of useful therapeutic decision-making tools,” potentially eliminating sentinel lymph node biopsy might make sense, Dr. Fleming said.
Dr. Fleming disclosed relationships with Tesaro, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Abt reported having no relevant disclosures and did not report any study funding.
FROM SGO 2021
New-onset hirsutism
A 74-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for follow-up 3 months after the surgical excision of a basal cell carcinoma on her left jawline. During this postop period, the patient developed new-onset hirsutism. She appeared to be in otherwise good health.
Family and personal medical history were unremarkable. Her medication regimen included aspirin 81 mg/d and a daily multivitamin. The patient was postmenopausal and had a body mass index of 28 and a history of acid reflux and osteoarthritis.
Physical examination of the patient’s scalp showed male-pattern alopecia (FIGURE 1A). She also had coarse terminal hairs on her forearms and back, as well as on her chin (FIGURE 1B).
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Androgen-secreting ovarian tumor
Based on the distribution of terminal hairs and marked change over 3 months, as well as the male-pattern alopecia, a diagnosis of androgen excess was suspected. Laboratory work-up, including thyroid-stimulating hormone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, complete blood count, and complete metabolic panel, was within normal limits. Pelvic ultrasound of the ovaries and abdominal computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands were also normal.
Further testing showed an elevated testosterone level of 464 ng/dL (reference range: 2-45 ng/dL) and an elevated free testosterone level of 66.8 ng/dL (reference range: 0.2-3.7 ng/dL). These levels pointed to an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor; the androgen excess was likely the cause of her hirsutism.
Hirsutism or hypertrichosis?
Hirsutism, a common disorder affecting up to 8% of women, is defined by excess terminal hairs that appear in a male pattern in women due to production of excess androgens.1 This should be distinguished from hypertrichosis, which is generalized excessive hair growth not caused by androgen excess.
Testosterone and DHEAS—produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands, respectively—contribute to the development of hirsutism.1 Hirsutism is more often associated with adrenal or ovarian tumors in postmenopausal patients.2 Generalized hypertrichosis can be associated with porphyria cutanea tarda, severe anorexia nervosa, and rarely, malignancies; it also can be secondary to certain agents, such as cyclosporin, phenytoin, and minoxidil.
While hirsutism is associated with hyperandrogenemia, its degree correlates poorly with serum levels. Notably, about half of women with hirsutism have been found to have normal levels of circulating androgens.1 Severe signs of hyperandrogenemia include rapid onset of symptoms, signs of virilization, and a palpable abdominal or pelvic mass.3
Continue to: Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal?
Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal? Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) accounts for up to three-fourths of premenopausal hirsutism.3 The likelihood of hirsutism is actually decreased in postmenopausal women because estrogen levels can drop abruptly after menopause. That said, conditions linked to hirsutism in postmenopausal women include adrenal hyperplasia, thyroid dysfunction, Cushing syndrome, and least frequently, androgen-secreting tumors (seen in this patient). (Hirsutism can also be idiopathic or iatrogenic [medications].)
Methods for detection
Research suggests that when a female patient is given a diagnosis of hirsutism, it’s important to explore possible underlying ovarian and/or adrenal tumors and adult-onset adrenal hyperplasia.1 The following tests and procedure can be helpful:
Serum testosterone and DHEAS. Levels of total testosterone > 200 ng/dL and/or DHEAS > 700 ng/dL are strongly indicative of androgen-secreting tumors.1
Imaging—including ultrasound, CT, or magnetic resonance imaging—can be used for evaluation of the adrenal glands and ovaries. However, imaging is often unable to identify these small tumors.4
Selective venous catheterization can be useful in the localization and lateralization of an androgen-secreting tumor, although a nondiagnostic result with this technique is not uncommon.4
Continue to: Dynamic hormonal testing
Dynamic hormonal testing may assist in determining the pathology of disease but not laterality.2 For example, testing for gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can be helpful because the constant administration of such agonists can lead to ovarian suppression without affecting adrenal androgen secretion.5
Testing with oral dexamethasone may induce adrenal hormonal depression of androgens and subsequent estradiol through aromatase conversion, which can help rule out an ovarian source.6 Exogenous administration of follicle-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone can further differentiate the source from ovarian theca or granulosa cell production.4
Treatment varies
The specific etiology of a patient’s hirsutism dictates the most appropriate treatment. For example, medication-induced hirsutism often requires discontinuation of the offending agent, whereas PCOS would necessitate appropriate nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic interventions.
For our patient, the elevated testosterone and free testosterone levels with normal DHEAS strongly suggested the presence of an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor. These findings led to a referral for bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The surgical gross appearance of the patient’s ovaries was unremarkable, but gross dissection and pathology of the ovaries (which were not postoperatively identified to determine laterality) showed one was larger (2.7 × 1.5 × 0.8 cm vs 3.2 × 1.4 × 1.2 cm).
The larger ovary contained an area of brown induration measuring 2.3 × 1.1 × 1.1 cm. This area corresponded to abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with nuclear, rich, round-cell proliferation, consistent with the diagnosis of a benign ovarian Leydig cell tumor (FIGURE 2). Thus, the bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy was both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Six weeks after the surgery, blood work showed normalization of testosterone and free testosterone levels. The patient’s hirsutism completely resolved over the course of the next several months.
1. Hunter M, Carek PJ. Evaluation and treatment of women with hirsutism. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:2565-2572.
2. Alpañés M, González-Casbas JM, Sánchez J, et al. Management of postmenopausal virilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2584-2588.
3. Bode D, Seehusen DA, Baird D. Hirsutism in women. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85:373-380.
4. Cohen I, Nabriski D, Fishman A. Noninvasive test for the diagnosis of ovarian hormone-secreting-neopolasm in postmenopausal women. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2016;15:12-15.
5. Gandrapu B, Sundar P, Phillips B. Hyperandrogenism in a postmenaupsal woman secondary to testosterone secreting ovarian stromal tumor with acoustic schwannoma. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2018;2018:8154513.
6. Curran DR, Moore C, Huber T. What is the best approach to the evaluation of hirsutism? J Fam Pract. 2005;54:458-473.
A 74-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for follow-up 3 months after the surgical excision of a basal cell carcinoma on her left jawline. During this postop period, the patient developed new-onset hirsutism. She appeared to be in otherwise good health.
Family and personal medical history were unremarkable. Her medication regimen included aspirin 81 mg/d and a daily multivitamin. The patient was postmenopausal and had a body mass index of 28 and a history of acid reflux and osteoarthritis.
Physical examination of the patient’s scalp showed male-pattern alopecia (FIGURE 1A). She also had coarse terminal hairs on her forearms and back, as well as on her chin (FIGURE 1B).
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Androgen-secreting ovarian tumor
Based on the distribution of terminal hairs and marked change over 3 months, as well as the male-pattern alopecia, a diagnosis of androgen excess was suspected. Laboratory work-up, including thyroid-stimulating hormone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, complete blood count, and complete metabolic panel, was within normal limits. Pelvic ultrasound of the ovaries and abdominal computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands were also normal.
Further testing showed an elevated testosterone level of 464 ng/dL (reference range: 2-45 ng/dL) and an elevated free testosterone level of 66.8 ng/dL (reference range: 0.2-3.7 ng/dL). These levels pointed to an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor; the androgen excess was likely the cause of her hirsutism.
Hirsutism or hypertrichosis?
Hirsutism, a common disorder affecting up to 8% of women, is defined by excess terminal hairs that appear in a male pattern in women due to production of excess androgens.1 This should be distinguished from hypertrichosis, which is generalized excessive hair growth not caused by androgen excess.
Testosterone and DHEAS—produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands, respectively—contribute to the development of hirsutism.1 Hirsutism is more often associated with adrenal or ovarian tumors in postmenopausal patients.2 Generalized hypertrichosis can be associated with porphyria cutanea tarda, severe anorexia nervosa, and rarely, malignancies; it also can be secondary to certain agents, such as cyclosporin, phenytoin, and minoxidil.
While hirsutism is associated with hyperandrogenemia, its degree correlates poorly with serum levels. Notably, about half of women with hirsutism have been found to have normal levels of circulating androgens.1 Severe signs of hyperandrogenemia include rapid onset of symptoms, signs of virilization, and a palpable abdominal or pelvic mass.3
Continue to: Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal?
Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal? Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) accounts for up to three-fourths of premenopausal hirsutism.3 The likelihood of hirsutism is actually decreased in postmenopausal women because estrogen levels can drop abruptly after menopause. That said, conditions linked to hirsutism in postmenopausal women include adrenal hyperplasia, thyroid dysfunction, Cushing syndrome, and least frequently, androgen-secreting tumors (seen in this patient). (Hirsutism can also be idiopathic or iatrogenic [medications].)
Methods for detection
Research suggests that when a female patient is given a diagnosis of hirsutism, it’s important to explore possible underlying ovarian and/or adrenal tumors and adult-onset adrenal hyperplasia.1 The following tests and procedure can be helpful:
Serum testosterone and DHEAS. Levels of total testosterone > 200 ng/dL and/or DHEAS > 700 ng/dL are strongly indicative of androgen-secreting tumors.1
Imaging—including ultrasound, CT, or magnetic resonance imaging—can be used for evaluation of the adrenal glands and ovaries. However, imaging is often unable to identify these small tumors.4
Selective venous catheterization can be useful in the localization and lateralization of an androgen-secreting tumor, although a nondiagnostic result with this technique is not uncommon.4
Continue to: Dynamic hormonal testing
Dynamic hormonal testing may assist in determining the pathology of disease but not laterality.2 For example, testing for gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can be helpful because the constant administration of such agonists can lead to ovarian suppression without affecting adrenal androgen secretion.5
Testing with oral dexamethasone may induce adrenal hormonal depression of androgens and subsequent estradiol through aromatase conversion, which can help rule out an ovarian source.6 Exogenous administration of follicle-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone can further differentiate the source from ovarian theca or granulosa cell production.4
Treatment varies
The specific etiology of a patient’s hirsutism dictates the most appropriate treatment. For example, medication-induced hirsutism often requires discontinuation of the offending agent, whereas PCOS would necessitate appropriate nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic interventions.
For our patient, the elevated testosterone and free testosterone levels with normal DHEAS strongly suggested the presence of an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor. These findings led to a referral for bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The surgical gross appearance of the patient’s ovaries was unremarkable, but gross dissection and pathology of the ovaries (which were not postoperatively identified to determine laterality) showed one was larger (2.7 × 1.5 × 0.8 cm vs 3.2 × 1.4 × 1.2 cm).
The larger ovary contained an area of brown induration measuring 2.3 × 1.1 × 1.1 cm. This area corresponded to abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with nuclear, rich, round-cell proliferation, consistent with the diagnosis of a benign ovarian Leydig cell tumor (FIGURE 2). Thus, the bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy was both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Six weeks after the surgery, blood work showed normalization of testosterone and free testosterone levels. The patient’s hirsutism completely resolved over the course of the next several months.
A 74-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for follow-up 3 months after the surgical excision of a basal cell carcinoma on her left jawline. During this postop period, the patient developed new-onset hirsutism. She appeared to be in otherwise good health.
Family and personal medical history were unremarkable. Her medication regimen included aspirin 81 mg/d and a daily multivitamin. The patient was postmenopausal and had a body mass index of 28 and a history of acid reflux and osteoarthritis.
Physical examination of the patient’s scalp showed male-pattern alopecia (FIGURE 1A). She also had coarse terminal hairs on her forearms and back, as well as on her chin (FIGURE 1B).
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Dx: Androgen-secreting ovarian tumor
Based on the distribution of terminal hairs and marked change over 3 months, as well as the male-pattern alopecia, a diagnosis of androgen excess was suspected. Laboratory work-up, including thyroid-stimulating hormone, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEAS), follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, prolactin, complete blood count, and complete metabolic panel, was within normal limits. Pelvic ultrasound of the ovaries and abdominal computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands were also normal.
Further testing showed an elevated testosterone level of 464 ng/dL (reference range: 2-45 ng/dL) and an elevated free testosterone level of 66.8 ng/dL (reference range: 0.2-3.7 ng/dL). These levels pointed to an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor; the androgen excess was likely the cause of her hirsutism.
Hirsutism or hypertrichosis?
Hirsutism, a common disorder affecting up to 8% of women, is defined by excess terminal hairs that appear in a male pattern in women due to production of excess androgens.1 This should be distinguished from hypertrichosis, which is generalized excessive hair growth not caused by androgen excess.
Testosterone and DHEAS—produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands, respectively—contribute to the development of hirsutism.1 Hirsutism is more often associated with adrenal or ovarian tumors in postmenopausal patients.2 Generalized hypertrichosis can be associated with porphyria cutanea tarda, severe anorexia nervosa, and rarely, malignancies; it also can be secondary to certain agents, such as cyclosporin, phenytoin, and minoxidil.
While hirsutism is associated with hyperandrogenemia, its degree correlates poorly with serum levels. Notably, about half of women with hirsutism have been found to have normal levels of circulating androgens.1 Severe signs of hyperandrogenemia include rapid onset of symptoms, signs of virilization, and a palpable abdominal or pelvic mass.3
Continue to: Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal?
Is the patient pre- or postmenopausal? Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) accounts for up to three-fourths of premenopausal hirsutism.3 The likelihood of hirsutism is actually decreased in postmenopausal women because estrogen levels can drop abruptly after menopause. That said, conditions linked to hirsutism in postmenopausal women include adrenal hyperplasia, thyroid dysfunction, Cushing syndrome, and least frequently, androgen-secreting tumors (seen in this patient). (Hirsutism can also be idiopathic or iatrogenic [medications].)
Methods for detection
Research suggests that when a female patient is given a diagnosis of hirsutism, it’s important to explore possible underlying ovarian and/or adrenal tumors and adult-onset adrenal hyperplasia.1 The following tests and procedure can be helpful:
Serum testosterone and DHEAS. Levels of total testosterone > 200 ng/dL and/or DHEAS > 700 ng/dL are strongly indicative of androgen-secreting tumors.1
Imaging—including ultrasound, CT, or magnetic resonance imaging—can be used for evaluation of the adrenal glands and ovaries. However, imaging is often unable to identify these small tumors.4
Selective venous catheterization can be useful in the localization and lateralization of an androgen-secreting tumor, although a nondiagnostic result with this technique is not uncommon.4
Continue to: Dynamic hormonal testing
Dynamic hormonal testing may assist in determining the pathology of disease but not laterality.2 For example, testing for gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can be helpful because the constant administration of such agonists can lead to ovarian suppression without affecting adrenal androgen secretion.5
Testing with oral dexamethasone may induce adrenal hormonal depression of androgens and subsequent estradiol through aromatase conversion, which can help rule out an ovarian source.6 Exogenous administration of follicle-stimulating hormone or luteinizing hormone can further differentiate the source from ovarian theca or granulosa cell production.4
Treatment varies
The specific etiology of a patient’s hirsutism dictates the most appropriate treatment. For example, medication-induced hirsutism often requires discontinuation of the offending agent, whereas PCOS would necessitate appropriate nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic interventions.
For our patient, the elevated testosterone and free testosterone levels with normal DHEAS strongly suggested the presence of an androgen-secreting ovarian tumor. These findings led to a referral for bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The surgical gross appearance of the patient’s ovaries was unremarkable, but gross dissection and pathology of the ovaries (which were not postoperatively identified to determine laterality) showed one was larger (2.7 × 1.5 × 0.8 cm vs 3.2 × 1.4 × 1.2 cm).
The larger ovary contained an area of brown induration measuring 2.3 × 1.1 × 1.1 cm. This area corresponded to abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm with nuclear, rich, round-cell proliferation, consistent with the diagnosis of a benign ovarian Leydig cell tumor (FIGURE 2). Thus, the bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy was both diagnostic and therapeutic.
Six weeks after the surgery, blood work showed normalization of testosterone and free testosterone levels. The patient’s hirsutism completely resolved over the course of the next several months.
1. Hunter M, Carek PJ. Evaluation and treatment of women with hirsutism. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:2565-2572.
2. Alpañés M, González-Casbas JM, Sánchez J, et al. Management of postmenopausal virilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2584-2588.
3. Bode D, Seehusen DA, Baird D. Hirsutism in women. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85:373-380.
4. Cohen I, Nabriski D, Fishman A. Noninvasive test for the diagnosis of ovarian hormone-secreting-neopolasm in postmenopausal women. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2016;15:12-15.
5. Gandrapu B, Sundar P, Phillips B. Hyperandrogenism in a postmenaupsal woman secondary to testosterone secreting ovarian stromal tumor with acoustic schwannoma. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2018;2018:8154513.
6. Curran DR, Moore C, Huber T. What is the best approach to the evaluation of hirsutism? J Fam Pract. 2005;54:458-473.
1. Hunter M, Carek PJ. Evaluation and treatment of women with hirsutism. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:2565-2572.
2. Alpañés M, González-Casbas JM, Sánchez J, et al. Management of postmenopausal virilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:2584-2588.
3. Bode D, Seehusen DA, Baird D. Hirsutism in women. Am Fam Physician. 2012;85:373-380.
4. Cohen I, Nabriski D, Fishman A. Noninvasive test for the diagnosis of ovarian hormone-secreting-neopolasm in postmenopausal women. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 2016;15:12-15.
5. Gandrapu B, Sundar P, Phillips B. Hyperandrogenism in a postmenaupsal woman secondary to testosterone secreting ovarian stromal tumor with acoustic schwannoma. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2018;2018:8154513.
6. Curran DR, Moore C, Huber T. What is the best approach to the evaluation of hirsutism? J Fam Pract. 2005;54:458-473.