User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
Genetically Driven Depression Tied to Increased MS Disease Activity
COPENHAGEN — , early results of a new study showed.
Unlike the previous research, the current analysis used polygenic risk scores for depression, which summarize the estimated effect of genetic variants to determine the potential association with MS disease activity, so results are less likely to be explained by reverse causality.
This study increases awareness of the link between depression and MS, said study investigator Kaarina Kowalec, PhD, assistant professor, College of Pharmacy, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. “We’re starting to understand how depression affects relapses and disability progression in MS,” she said.
The findings were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
Common Comorbidity
Depression is a common comorbidity in patients with MS and is associated with increased relapse and disability progression. Depression risk is partly polygenic in nature, involving numerous common genetic variants, said Dr. Kowalec.
The case-control study included 3420 relapsing-onset MS cases of European ancestry from four existing cohorts in three countries.
The Canadian cohort included those enrolled in a prospective longitudinal study of psychiatric comorbidity in chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID), including MS; the Swedish cohort was an MS registry (SSReg) that encompasses 64 MS clinics (the cohort was split into two groups); and the US cohort was enrolled in a clinical trial of combined therapy with interferon and glatiramer acetate (CombiRx) in patients with MS.
The median follow-up in these cohorts ranged from 3 to 5 years.
Not surprisingly, most participants were women (from 71% in one of the Swedish cohorts to 83% in the Canadian cohort), and the age at MS onset ranged from 29 years in the Canadian cohort to 35 years in one of the Swedish cohorts.
The median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score was higher in the Canadian cohort (3.5) than in the Swedish (1.5) and US (2.0) cohorts, “reflective of the Canadian cohort being slightly more progressed,” said Dr. Kowalec.
Inherited Variants
To measure depression heritability, researchers generated a polygenic risk score in whole-genome imputed genotypes. The score reflects the number of inherited common genetic variants, weighted by effect sizes.
Researchers investigated the association between depression polygenic risk scores (top 20% vs. bottom 80%) with annualized relapse rate and worsening disability in MS measured by the rate of change in EDSS score. In the US cohort, they also explored the association between depression polygenic risk scores and time to relapse and confirmed EDSS worsening.
Covariates included use of disease-modifying therapy, age, sex, and the first five genetic ancestry principal components. The latter was done to capture residual stratification by genetic ancestry, although Dr. Kowalec stressed analyses were done only in those of European ancestry.
Investigators found a higher depression polygenic risk score was associated with relapse risk (incident rate ratio, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.01-1.49).
“Essentially, for every one standard deviation increase in the depression polygenic score, we found a significant increased hazard of 23% for experiencing a relapse over the follow-up period,” said Dr. Kowalec, who is also affiliated with the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
She noted the Canadian cohort did not have many relapses, while the US and Swedish cohorts “had an increased rate.”
Other analyses examined the risk of having a relapse or worsening disability. Every one SD increase in the depression polygenic risk score was significantly associated with a 2.2 greater risk of experiencing relapse (hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.35-3.60) and a 51% increased risk for confirmed EDSS progression (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.03-2.22).
‘An Ideal Marker’
Use of polygenetic risk scores reduces the possibility of reverse causation, noted Dr. Kowalec. “These markers are fixed at birth and don’t change over your lifespan, so they’re really an ideal marker.”
The results suggest polygenetic risk scores represent a potential biomarker for risk stratification in people with MS, said Dr. Kowalec. Although depression polygenic risk scores are not currently available in clinical practice, “I would hope this would change in the next 3-4 years,” she said.
Asked by a delegate if confounding by a third variable is possible, Dr. Kowalec said because genetic markers don’t change over time, there is a hint that the direction is causal and that depression is driving the outcome. However, she added, further confirmation is needed.
Dr. Kowalec noted that there were no data on antidepressant use but noted that about half of the Canadian and US cohorts — and likely the same number in the Swedish cohorts — self-reported depression.
A limitation of the study was that it included only participants of European ancestry.
Clinical Implications Unclear
Commenting on the research, Lauren Gluck, MD, program director, Montefiore Multiple Sclerosis Center, Bronx, New York, described the study as “fascinating” but noted that it’s unclear how to use this new information in clinical practice.
“Clinicians frequently ask people with MS about mood symptoms and offer interventions like antidepressants and referrals to therapists. However, genetic testing is not routine, so we don’t yet know who to target based on these data.”
Preexisting depression or more severe depression could be viewed as a “red flag” for risk for more disease activity in the future, she said.
“This could encourage clinicians to use more highly effective therapy in these patients, similar to our strategies for people with MS with frequent attacks and more disease burden on MRIs.”
The study received support from the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs, Department of Defense.
Dr. Kowalec reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN — , early results of a new study showed.
Unlike the previous research, the current analysis used polygenic risk scores for depression, which summarize the estimated effect of genetic variants to determine the potential association with MS disease activity, so results are less likely to be explained by reverse causality.
This study increases awareness of the link between depression and MS, said study investigator Kaarina Kowalec, PhD, assistant professor, College of Pharmacy, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. “We’re starting to understand how depression affects relapses and disability progression in MS,” she said.
The findings were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
Common Comorbidity
Depression is a common comorbidity in patients with MS and is associated with increased relapse and disability progression. Depression risk is partly polygenic in nature, involving numerous common genetic variants, said Dr. Kowalec.
The case-control study included 3420 relapsing-onset MS cases of European ancestry from four existing cohorts in three countries.
The Canadian cohort included those enrolled in a prospective longitudinal study of psychiatric comorbidity in chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID), including MS; the Swedish cohort was an MS registry (SSReg) that encompasses 64 MS clinics (the cohort was split into two groups); and the US cohort was enrolled in a clinical trial of combined therapy with interferon and glatiramer acetate (CombiRx) in patients with MS.
The median follow-up in these cohorts ranged from 3 to 5 years.
Not surprisingly, most participants were women (from 71% in one of the Swedish cohorts to 83% in the Canadian cohort), and the age at MS onset ranged from 29 years in the Canadian cohort to 35 years in one of the Swedish cohorts.
The median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score was higher in the Canadian cohort (3.5) than in the Swedish (1.5) and US (2.0) cohorts, “reflective of the Canadian cohort being slightly more progressed,” said Dr. Kowalec.
Inherited Variants
To measure depression heritability, researchers generated a polygenic risk score in whole-genome imputed genotypes. The score reflects the number of inherited common genetic variants, weighted by effect sizes.
Researchers investigated the association between depression polygenic risk scores (top 20% vs. bottom 80%) with annualized relapse rate and worsening disability in MS measured by the rate of change in EDSS score. In the US cohort, they also explored the association between depression polygenic risk scores and time to relapse and confirmed EDSS worsening.
Covariates included use of disease-modifying therapy, age, sex, and the first five genetic ancestry principal components. The latter was done to capture residual stratification by genetic ancestry, although Dr. Kowalec stressed analyses were done only in those of European ancestry.
Investigators found a higher depression polygenic risk score was associated with relapse risk (incident rate ratio, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.01-1.49).
“Essentially, for every one standard deviation increase in the depression polygenic score, we found a significant increased hazard of 23% for experiencing a relapse over the follow-up period,” said Dr. Kowalec, who is also affiliated with the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
She noted the Canadian cohort did not have many relapses, while the US and Swedish cohorts “had an increased rate.”
Other analyses examined the risk of having a relapse or worsening disability. Every one SD increase in the depression polygenic risk score was significantly associated with a 2.2 greater risk of experiencing relapse (hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.35-3.60) and a 51% increased risk for confirmed EDSS progression (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.03-2.22).
‘An Ideal Marker’
Use of polygenetic risk scores reduces the possibility of reverse causation, noted Dr. Kowalec. “These markers are fixed at birth and don’t change over your lifespan, so they’re really an ideal marker.”
The results suggest polygenetic risk scores represent a potential biomarker for risk stratification in people with MS, said Dr. Kowalec. Although depression polygenic risk scores are not currently available in clinical practice, “I would hope this would change in the next 3-4 years,” she said.
Asked by a delegate if confounding by a third variable is possible, Dr. Kowalec said because genetic markers don’t change over time, there is a hint that the direction is causal and that depression is driving the outcome. However, she added, further confirmation is needed.
Dr. Kowalec noted that there were no data on antidepressant use but noted that about half of the Canadian and US cohorts — and likely the same number in the Swedish cohorts — self-reported depression.
A limitation of the study was that it included only participants of European ancestry.
Clinical Implications Unclear
Commenting on the research, Lauren Gluck, MD, program director, Montefiore Multiple Sclerosis Center, Bronx, New York, described the study as “fascinating” but noted that it’s unclear how to use this new information in clinical practice.
“Clinicians frequently ask people with MS about mood symptoms and offer interventions like antidepressants and referrals to therapists. However, genetic testing is not routine, so we don’t yet know who to target based on these data.”
Preexisting depression or more severe depression could be viewed as a “red flag” for risk for more disease activity in the future, she said.
“This could encourage clinicians to use more highly effective therapy in these patients, similar to our strategies for people with MS with frequent attacks and more disease burden on MRIs.”
The study received support from the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs, Department of Defense.
Dr. Kowalec reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
COPENHAGEN — , early results of a new study showed.
Unlike the previous research, the current analysis used polygenic risk scores for depression, which summarize the estimated effect of genetic variants to determine the potential association with MS disease activity, so results are less likely to be explained by reverse causality.
This study increases awareness of the link between depression and MS, said study investigator Kaarina Kowalec, PhD, assistant professor, College of Pharmacy, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. “We’re starting to understand how depression affects relapses and disability progression in MS,” she said.
The findings were presented at the 2024 ECTRIMS annual meeting.
Common Comorbidity
Depression is a common comorbidity in patients with MS and is associated with increased relapse and disability progression. Depression risk is partly polygenic in nature, involving numerous common genetic variants, said Dr. Kowalec.
The case-control study included 3420 relapsing-onset MS cases of European ancestry from four existing cohorts in three countries.
The Canadian cohort included those enrolled in a prospective longitudinal study of psychiatric comorbidity in chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease (IMID), including MS; the Swedish cohort was an MS registry (SSReg) that encompasses 64 MS clinics (the cohort was split into two groups); and the US cohort was enrolled in a clinical trial of combined therapy with interferon and glatiramer acetate (CombiRx) in patients with MS.
The median follow-up in these cohorts ranged from 3 to 5 years.
Not surprisingly, most participants were women (from 71% in one of the Swedish cohorts to 83% in the Canadian cohort), and the age at MS onset ranged from 29 years in the Canadian cohort to 35 years in one of the Swedish cohorts.
The median baseline Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score was higher in the Canadian cohort (3.5) than in the Swedish (1.5) and US (2.0) cohorts, “reflective of the Canadian cohort being slightly more progressed,” said Dr. Kowalec.
Inherited Variants
To measure depression heritability, researchers generated a polygenic risk score in whole-genome imputed genotypes. The score reflects the number of inherited common genetic variants, weighted by effect sizes.
Researchers investigated the association between depression polygenic risk scores (top 20% vs. bottom 80%) with annualized relapse rate and worsening disability in MS measured by the rate of change in EDSS score. In the US cohort, they also explored the association between depression polygenic risk scores and time to relapse and confirmed EDSS worsening.
Covariates included use of disease-modifying therapy, age, sex, and the first five genetic ancestry principal components. The latter was done to capture residual stratification by genetic ancestry, although Dr. Kowalec stressed analyses were done only in those of European ancestry.
Investigators found a higher depression polygenic risk score was associated with relapse risk (incident rate ratio, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.01-1.49).
“Essentially, for every one standard deviation increase in the depression polygenic score, we found a significant increased hazard of 23% for experiencing a relapse over the follow-up period,” said Dr. Kowalec, who is also affiliated with the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden.
She noted the Canadian cohort did not have many relapses, while the US and Swedish cohorts “had an increased rate.”
Other analyses examined the risk of having a relapse or worsening disability. Every one SD increase in the depression polygenic risk score was significantly associated with a 2.2 greater risk of experiencing relapse (hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.35-3.60) and a 51% increased risk for confirmed EDSS progression (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.03-2.22).
‘An Ideal Marker’
Use of polygenetic risk scores reduces the possibility of reverse causation, noted Dr. Kowalec. “These markers are fixed at birth and don’t change over your lifespan, so they’re really an ideal marker.”
The results suggest polygenetic risk scores represent a potential biomarker for risk stratification in people with MS, said Dr. Kowalec. Although depression polygenic risk scores are not currently available in clinical practice, “I would hope this would change in the next 3-4 years,” she said.
Asked by a delegate if confounding by a third variable is possible, Dr. Kowalec said because genetic markers don’t change over time, there is a hint that the direction is causal and that depression is driving the outcome. However, she added, further confirmation is needed.
Dr. Kowalec noted that there were no data on antidepressant use but noted that about half of the Canadian and US cohorts — and likely the same number in the Swedish cohorts — self-reported depression.
A limitation of the study was that it included only participants of European ancestry.
Clinical Implications Unclear
Commenting on the research, Lauren Gluck, MD, program director, Montefiore Multiple Sclerosis Center, Bronx, New York, described the study as “fascinating” but noted that it’s unclear how to use this new information in clinical practice.
“Clinicians frequently ask people with MS about mood symptoms and offer interventions like antidepressants and referrals to therapists. However, genetic testing is not routine, so we don’t yet know who to target based on these data.”
Preexisting depression or more severe depression could be viewed as a “red flag” for risk for more disease activity in the future, she said.
“This could encourage clinicians to use more highly effective therapy in these patients, similar to our strategies for people with MS with frequent attacks and more disease burden on MRIs.”
The study received support from the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs, Department of Defense.
Dr. Kowalec reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECTRIMS 2024
Considering Eating Disorder Potential When Prescribing Weight Loss Drugs to Teens
Now, with the rising popularity of medications like Ozempic for weight loss, she fears she will care for more teens with eating disorders who are seeking glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists or who have developed a disorder while taking them.
“We haven’t seen patients yet, but I’m sure they are on their way,” said Dr. Dennis, a clinical assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Illinois College of Medicine in Chicago. She is also the cofounder and chief medical officer of SunCloud Health, an outpatient eating disorder treatment center in Illinois.
Dr. Dennis’ concerns reflect a growing unease among eating disorder specialists as obesity medications gain traction for adolescent use. A recent study published in JAMA Pediatrics showed nearly 80% of teens in treatment for obesity reported symptoms of disordered eating at the outset of an intervention. These included signs of binge eating and loss of control.
The randomized clinical trial, conducted from 2018 to 2023, examined 141 adolescents with obesity undergoing interventions like low-energy diets or intermittent energy restriction. Almost half scored as having risk for an undiagnosed eating disorder, as defined by the Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDE-Q).
At the end of the intervention, many teens continued to have symptoms of disordered eating, while a smaller group was newly scored as having a risk for an eating disorder.
Weight Loss and Eating Disorders: A Balancing Act
The findings illuminate a significant challenge for pediatricians and primary care clinicians: Balancing effective weight management with the risk of exacerbating or triggering eating disorders, said Hiba Jebeile, PhD, a research dietitian at The Children’s Hospital at Westmead in Australia, and the study’s lead author. Adding weight loss medication on top of the equation can further complicate care.
“It is helpful for obesity and eating disorder services to work together, with clear referral pathways, to manage these adolescents,” Dr. Jebeile said.
The US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide for weight loss in adolescents aged 12-17 years in December 2020. One study found that the number of adolescents prescribed GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) for type 2 diabetes and weight management rose from 8722 to 60,567 between 2020 and 2023 — a nearly sevenfold increase.
“The number of adolescents taking these medications is going up because they work,” said Suzanne Cuda, MD, medical director of Alamo City Healthy Kids and Families, a medical weight management clinic in San Antonio. The medications have been shown to treat type 2 diabetes, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk for cardiovascular diseases.
“The younger you are, the better the outcome,” Dr. Cuda said.
How GLP-1 agonists may affect adolescents in the long run is not yet clear. Existing studies on GLP-1 medications in patients with eating disorders have shown mixed results. Some studies indicate that the drugs decrease binge episodes for those with binge eating disorder or bulimia nervosa. However, these studies had small sample sizes and measured only short-term effects, leaving long-term outcomes and risks unknown.
Traditional treatments for eating disorders emphasize regular eating patterns, body acceptance, addressing weight stigma, and improving attunement to hunger and fullness cues — approaches that may conflict with the effects of GLP-1 agonists. These drugs suppress appetite, alter metabolic signals, and may unintentionally reinforce weight loss as a primary goal, creating a potential disconnect between the aims of recovery from eating disorders and the biologic effects of the medication, experts said.
Dr. Cuda said she has cared for adolescents with diagnosed eating disorders in her practice who are seeking GLP-1 agonists. She said she first works with patients to treat the underlying disorder before prescribing medication.
“One of the concerns is the extreme reductions in calories that could be induced by GLP-1 RA in children and adolescents,” she said. Unlike adults, adolescents use caloric energy not just for physical activity but also for growing and developing, she said.
“They can’t catch up on that growth and development,” she added.
Advice for Screening and Monitoring
The National Eating Disorders Association raised concerns about the potential misuse of these medications and their potential to exacerbate eating disorder behaviors in people who are already at a higher risk of developing one of the conditions, including those with existing mental health disorders, stress, who have already dieted, and who have experienced weight-centric bullying.
Clinicians should be on the lookout for patients seeking GLP-1s who present with symptoms of an eating disorder that may be less apparent, such as picky eating, insomnia or difficulty sleeping, or, for girls, irregular menstrual periods, Dr. Dennis said. These patients may be more likely to go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Research also suggests that people of color are less likely to be diagnosed or receive specialty care for eating disorders.
Discussions between patients and clinicians about obesity treatment prior to prescribing provide a crucial opportunity to screen and monitor for disordered eating, which Dr. Dennis said does not universally occur currently.
Dr. Dennis recommended initial assessments using validated screening tools like the EDE-Q and the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale Revised, 10-Item Version.
Ongoing monitoring throughout treatment is essential, with initial monthly check-ins that include dietary counseling to detect subtle changes in eating behaviors or attitudes toward food and body image, Dr. Cuda said.
The Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) has stressed the importance of a collaborative approach involving connections with mental health professionals specializing in eating disorders and dietitians.
“If you have a chance to send them to an obesity medicine specialist, you should do that,” said Dr. Cuda, who coauthored the OMA statement. “It’s impractical to expect a primary care physician to do everything: Screen for dietary disorders, do a full dietary counseling, follow up on their activity.”
For patients showing signs of disordered eating, clinicians should avoid recommending restrictive dietary approaches, like cutting out food groups such as carbohydrates or a restricted calorie goal. Instead, they can suggest focusing on healthier lifestyle habits and referring to a psychotherapist, the experts said. Clinicians also should be prepared to adjust or pause GLP-1 agonists if disordered eating disorder symptoms worsen.
“I think a weight-agnostic approach where the focus of care is not weight loss but increase in health protective behaviors and nutritional intake is safest for all kids, especially those with eating disorders or eating disorder risk factors,” Dr. Dennis said.
Various authors of the eating disorder study reported receiving grants, advisory board fees, and speaker fees from entities including the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Nu-Mega Ingredients, and the National Institutes of Health, among others.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, with the rising popularity of medications like Ozempic for weight loss, she fears she will care for more teens with eating disorders who are seeking glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists or who have developed a disorder while taking them.
“We haven’t seen patients yet, but I’m sure they are on their way,” said Dr. Dennis, a clinical assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Illinois College of Medicine in Chicago. She is also the cofounder and chief medical officer of SunCloud Health, an outpatient eating disorder treatment center in Illinois.
Dr. Dennis’ concerns reflect a growing unease among eating disorder specialists as obesity medications gain traction for adolescent use. A recent study published in JAMA Pediatrics showed nearly 80% of teens in treatment for obesity reported symptoms of disordered eating at the outset of an intervention. These included signs of binge eating and loss of control.
The randomized clinical trial, conducted from 2018 to 2023, examined 141 adolescents with obesity undergoing interventions like low-energy diets or intermittent energy restriction. Almost half scored as having risk for an undiagnosed eating disorder, as defined by the Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDE-Q).
At the end of the intervention, many teens continued to have symptoms of disordered eating, while a smaller group was newly scored as having a risk for an eating disorder.
Weight Loss and Eating Disorders: A Balancing Act
The findings illuminate a significant challenge for pediatricians and primary care clinicians: Balancing effective weight management with the risk of exacerbating or triggering eating disorders, said Hiba Jebeile, PhD, a research dietitian at The Children’s Hospital at Westmead in Australia, and the study’s lead author. Adding weight loss medication on top of the equation can further complicate care.
“It is helpful for obesity and eating disorder services to work together, with clear referral pathways, to manage these adolescents,” Dr. Jebeile said.
The US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide for weight loss in adolescents aged 12-17 years in December 2020. One study found that the number of adolescents prescribed GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) for type 2 diabetes and weight management rose from 8722 to 60,567 between 2020 and 2023 — a nearly sevenfold increase.
“The number of adolescents taking these medications is going up because they work,” said Suzanne Cuda, MD, medical director of Alamo City Healthy Kids and Families, a medical weight management clinic in San Antonio. The medications have been shown to treat type 2 diabetes, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk for cardiovascular diseases.
“The younger you are, the better the outcome,” Dr. Cuda said.
How GLP-1 agonists may affect adolescents in the long run is not yet clear. Existing studies on GLP-1 medications in patients with eating disorders have shown mixed results. Some studies indicate that the drugs decrease binge episodes for those with binge eating disorder or bulimia nervosa. However, these studies had small sample sizes and measured only short-term effects, leaving long-term outcomes and risks unknown.
Traditional treatments for eating disorders emphasize regular eating patterns, body acceptance, addressing weight stigma, and improving attunement to hunger and fullness cues — approaches that may conflict with the effects of GLP-1 agonists. These drugs suppress appetite, alter metabolic signals, and may unintentionally reinforce weight loss as a primary goal, creating a potential disconnect between the aims of recovery from eating disorders and the biologic effects of the medication, experts said.
Dr. Cuda said she has cared for adolescents with diagnosed eating disorders in her practice who are seeking GLP-1 agonists. She said she first works with patients to treat the underlying disorder before prescribing medication.
“One of the concerns is the extreme reductions in calories that could be induced by GLP-1 RA in children and adolescents,” she said. Unlike adults, adolescents use caloric energy not just for physical activity but also for growing and developing, she said.
“They can’t catch up on that growth and development,” she added.
Advice for Screening and Monitoring
The National Eating Disorders Association raised concerns about the potential misuse of these medications and their potential to exacerbate eating disorder behaviors in people who are already at a higher risk of developing one of the conditions, including those with existing mental health disorders, stress, who have already dieted, and who have experienced weight-centric bullying.
Clinicians should be on the lookout for patients seeking GLP-1s who present with symptoms of an eating disorder that may be less apparent, such as picky eating, insomnia or difficulty sleeping, or, for girls, irregular menstrual periods, Dr. Dennis said. These patients may be more likely to go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Research also suggests that people of color are less likely to be diagnosed or receive specialty care for eating disorders.
Discussions between patients and clinicians about obesity treatment prior to prescribing provide a crucial opportunity to screen and monitor for disordered eating, which Dr. Dennis said does not universally occur currently.
Dr. Dennis recommended initial assessments using validated screening tools like the EDE-Q and the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale Revised, 10-Item Version.
Ongoing monitoring throughout treatment is essential, with initial monthly check-ins that include dietary counseling to detect subtle changes in eating behaviors or attitudes toward food and body image, Dr. Cuda said.
The Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) has stressed the importance of a collaborative approach involving connections with mental health professionals specializing in eating disorders and dietitians.
“If you have a chance to send them to an obesity medicine specialist, you should do that,” said Dr. Cuda, who coauthored the OMA statement. “It’s impractical to expect a primary care physician to do everything: Screen for dietary disorders, do a full dietary counseling, follow up on their activity.”
For patients showing signs of disordered eating, clinicians should avoid recommending restrictive dietary approaches, like cutting out food groups such as carbohydrates or a restricted calorie goal. Instead, they can suggest focusing on healthier lifestyle habits and referring to a psychotherapist, the experts said. Clinicians also should be prepared to adjust or pause GLP-1 agonists if disordered eating disorder symptoms worsen.
“I think a weight-agnostic approach where the focus of care is not weight loss but increase in health protective behaviors and nutritional intake is safest for all kids, especially those with eating disorders or eating disorder risk factors,” Dr. Dennis said.
Various authors of the eating disorder study reported receiving grants, advisory board fees, and speaker fees from entities including the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Nu-Mega Ingredients, and the National Institutes of Health, among others.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Now, with the rising popularity of medications like Ozempic for weight loss, she fears she will care for more teens with eating disorders who are seeking glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists or who have developed a disorder while taking them.
“We haven’t seen patients yet, but I’m sure they are on their way,” said Dr. Dennis, a clinical assistant professor in the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Illinois College of Medicine in Chicago. She is also the cofounder and chief medical officer of SunCloud Health, an outpatient eating disorder treatment center in Illinois.
Dr. Dennis’ concerns reflect a growing unease among eating disorder specialists as obesity medications gain traction for adolescent use. A recent study published in JAMA Pediatrics showed nearly 80% of teens in treatment for obesity reported symptoms of disordered eating at the outset of an intervention. These included signs of binge eating and loss of control.
The randomized clinical trial, conducted from 2018 to 2023, examined 141 adolescents with obesity undergoing interventions like low-energy diets or intermittent energy restriction. Almost half scored as having risk for an undiagnosed eating disorder, as defined by the Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDE-Q).
At the end of the intervention, many teens continued to have symptoms of disordered eating, while a smaller group was newly scored as having a risk for an eating disorder.
Weight Loss and Eating Disorders: A Balancing Act
The findings illuminate a significant challenge for pediatricians and primary care clinicians: Balancing effective weight management with the risk of exacerbating or triggering eating disorders, said Hiba Jebeile, PhD, a research dietitian at The Children’s Hospital at Westmead in Australia, and the study’s lead author. Adding weight loss medication on top of the equation can further complicate care.
“It is helpful for obesity and eating disorder services to work together, with clear referral pathways, to manage these adolescents,” Dr. Jebeile said.
The US Food and Drug Administration approved semaglutide for weight loss in adolescents aged 12-17 years in December 2020. One study found that the number of adolescents prescribed GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) for type 2 diabetes and weight management rose from 8722 to 60,567 between 2020 and 2023 — a nearly sevenfold increase.
“The number of adolescents taking these medications is going up because they work,” said Suzanne Cuda, MD, medical director of Alamo City Healthy Kids and Families, a medical weight management clinic in San Antonio. The medications have been shown to treat type 2 diabetes, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk for cardiovascular diseases.
“The younger you are, the better the outcome,” Dr. Cuda said.
How GLP-1 agonists may affect adolescents in the long run is not yet clear. Existing studies on GLP-1 medications in patients with eating disorders have shown mixed results. Some studies indicate that the drugs decrease binge episodes for those with binge eating disorder or bulimia nervosa. However, these studies had small sample sizes and measured only short-term effects, leaving long-term outcomes and risks unknown.
Traditional treatments for eating disorders emphasize regular eating patterns, body acceptance, addressing weight stigma, and improving attunement to hunger and fullness cues — approaches that may conflict with the effects of GLP-1 agonists. These drugs suppress appetite, alter metabolic signals, and may unintentionally reinforce weight loss as a primary goal, creating a potential disconnect between the aims of recovery from eating disorders and the biologic effects of the medication, experts said.
Dr. Cuda said she has cared for adolescents with diagnosed eating disorders in her practice who are seeking GLP-1 agonists. She said she first works with patients to treat the underlying disorder before prescribing medication.
“One of the concerns is the extreme reductions in calories that could be induced by GLP-1 RA in children and adolescents,” she said. Unlike adults, adolescents use caloric energy not just for physical activity but also for growing and developing, she said.
“They can’t catch up on that growth and development,” she added.
Advice for Screening and Monitoring
The National Eating Disorders Association raised concerns about the potential misuse of these medications and their potential to exacerbate eating disorder behaviors in people who are already at a higher risk of developing one of the conditions, including those with existing mental health disorders, stress, who have already dieted, and who have experienced weight-centric bullying.
Clinicians should be on the lookout for patients seeking GLP-1s who present with symptoms of an eating disorder that may be less apparent, such as picky eating, insomnia or difficulty sleeping, or, for girls, irregular menstrual periods, Dr. Dennis said. These patients may be more likely to go undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Research also suggests that people of color are less likely to be diagnosed or receive specialty care for eating disorders.
Discussions between patients and clinicians about obesity treatment prior to prescribing provide a crucial opportunity to screen and monitor for disordered eating, which Dr. Dennis said does not universally occur currently.
Dr. Dennis recommended initial assessments using validated screening tools like the EDE-Q and the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale Revised, 10-Item Version.
Ongoing monitoring throughout treatment is essential, with initial monthly check-ins that include dietary counseling to detect subtle changes in eating behaviors or attitudes toward food and body image, Dr. Cuda said.
The Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) has stressed the importance of a collaborative approach involving connections with mental health professionals specializing in eating disorders and dietitians.
“If you have a chance to send them to an obesity medicine specialist, you should do that,” said Dr. Cuda, who coauthored the OMA statement. “It’s impractical to expect a primary care physician to do everything: Screen for dietary disorders, do a full dietary counseling, follow up on their activity.”
For patients showing signs of disordered eating, clinicians should avoid recommending restrictive dietary approaches, like cutting out food groups such as carbohydrates or a restricted calorie goal. Instead, they can suggest focusing on healthier lifestyle habits and referring to a psychotherapist, the experts said. Clinicians also should be prepared to adjust or pause GLP-1 agonists if disordered eating disorder symptoms worsen.
“I think a weight-agnostic approach where the focus of care is not weight loss but increase in health protective behaviors and nutritional intake is safest for all kids, especially those with eating disorders or eating disorder risk factors,” Dr. Dennis said.
Various authors of the eating disorder study reported receiving grants, advisory board fees, and speaker fees from entities including the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Nu-Mega Ingredients, and the National Institutes of Health, among others.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
FDA’s Stricter Regulation of Lab-Developed Tests Faces Lawsuits and Lingering Concerns
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plans to scrutinize the safety and efficacy of lab-developed tests — those designed, manufactured, and used in a single laboratory — far more thoroughly in the future.
Under a rule finalized in April, the FDA will treat facilities that develop and use lab tests as manufacturers and regulate tests as medical devices. That means that most lab tests will need an FDA review before going on sale.
The FDA will also impose new quality standards, requiring test manufacturers to report adverse events and create a registry of lab tests under the new rule, which will be phased in over 4 years.
FDA officials have been concerned for years about the reliability of commercial lab tests, which have ballooned into a multibillion-dollar industry.
Consumer groups have long urged the FDA to regulate lab tests more strictly, arguing that the lack of scrutiny allows doctors and patients to be exploited by bad actors such as Theranos, which falsely claimed that its tests could diagnose multiple diseases with a single drop of blood.
“When it comes to some of these tests that doctors are recommending for patients, many doctors are just crossing their fingers and relying on the representation of the company because nobody is checking” to verify a manufacturer’s claims, said Joshua Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland.
Nearly 12,000 Labs Making Medical Tests
Although the FDA estimates there are nearly 12,000 labs manufacturing medical tests, agency officials said they don’t know how many tests are being marketed. The FDA already requires that home test kits marketed directly to consumers, such as those used to detect COVID-19, get clearance from the agency before being sold.
“There’s plenty of time for industry to get its act together to develop the data that it might need to make a premarket application,” said Peter Lurie, MD, PhD, a former associate commissioner at the FDA. In 2015, Dr. Lurie led a report outlining some of the dangers of unregulated lab tests.
For the average physician who orders lab tests, nothing is going to immediately change because of the final rule, said Dr. Lurie, now president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a nonprofit consumer watchdog.
“Tomorrow, this will look just the same as it does today,” Dr. Lurie said. “For the next 3 years, the companies will be scurrying behind the scenes to comply with the early stages of implementation. But most of that will be invisible to the average practitioner.”
Dr. Lurie predicted the FDA will focus its scrutiny on tests that pose the greatest potential risk to patients, such as ones used to diagnose serious diseases or guide treatment for life-threatening conditions. “The least significant tests will likely get very limited, if any, scrutiny,” said Dr. Lurie, adding that the FDA will likely issue guidance about how it plans to define low- and high-risk tests. “My suspicion is that it will be probably a small minority of products that are subject to full premarket approval.”
Lab Industry Groups Push Back
But imposing new rules with the potential to affect an industry’s bottom line is no easy task.
The American Clinical Laboratory Association, which represents the lab industry, said in a statement that the FDA rule will “limit access to scores of critical tests, increase healthcare costs, and undermine innovation in new diagnostics.” Another industry group, the Association for Molecular Pathology, has warned of “significant and harmful disruption to laboratory medicine.”
The two associations have filed separate lawsuits, charging that the FDA overstepped the authority granted by Congress. In their lawsuits, groups claim that lab tests are professional services, not manufactured products. The groups noted that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) already inspects lab facilities. CMS does not assess the tests’ quality or reliability.
A recent Supreme Court decision could make those lawsuits more likely to succeed, said David Simon, JD, LLM, PhD, an assistant professor of law at the Northeastern University School of Law, Boston, Massachusetts.
In the case of Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo, decided in June, justices overturned a long-standing precedent known as Chevron deference, which required courts to defer to federal agencies when interpreting ambiguous laws. That means that courts no longer have to accept the FDA’s definition of a device, Dr. Simon said.
“Because judges may have more active roles in defining agency authority, federal agencies may have correspondingly less robust roles in policymaking,” Dr. Simon wrote in an editorial coauthored with Michael J. Young, MD, MPhil, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The Supreme Court ruling could pressure Congress to more clearly define FDA’s ruling in regulating lab tests, Dr. Simon and Dr. Young wrote.
Members of Congress first introduced a bill to clarify the FDA’s role in regulating lab tests, called the VALID Act, in 2020. The bill stalled and, despite efforts to revive it, still hasn’t passed.
FDA officials have said they remain “open to working with Congress,” noting that any future legislation about lab-developed tests would supersede their current policy.
In an interview, Dr. Simon noted the FDA significantly narrowed the scope of the final rule in response to comments from critics who objected to an earlier version of the policy proposed in 2023. The final rule carves out several categories of tests that won’t need to apply for “premarket review.”
Notably, a “grandfather clause” will allow some lab tests already on the market to continue being sold without undergoing FDA’s premarket review process. In explaining the exemption, FDA officials said they did not want doctors and patients to lose access to tests on which they rely. But Dr. Lurie noted that because the FDA views all these tests as under its jurisdiction, the agency could opt to take a closer look “at a very old device that is causing a problem today.”
The FDA also will exempt tests approved by New York State’s Clinical Laboratory Evaluation Program, which conducts its own stringent reviews. And the FDA will continue to allow hospitals to develop tests for patients within their healthcare system without going through the FDA approval process, if no FDA-approved tests are available.
Hospital-based tests play a critical role in treating infectious diseases, said Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. For example, a large research hospital treating a patient with cytomegalovirus may need to develop its own test to determine whether the infection is resistant to antiviral drugs, Dr. Adalja said.
“With novel infectious disease outbreaks, researchers are able to move quickly to make diagnostic tests months and months before commercial laboratories are able to get through regulatory processes,” Dr. Adalja said.
To help scientists respond quickly to emergencies, the FDA published special guidance for labs that develop unauthorized lab tests for disease outbreaks.
Medical groups such as the American Hospital Association and Infectious Diseases Society of America remain concerned about the burden of complying with new regulations.
“Many vital tests developed in hospitals and health systems may be subjected to unnecessary and costly paperwork,” said Stacey Hughes, executive vice president of the American Hospital Association, in a statement.
Other groups, such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology, praised the new FDA policy. In comments submitted to the FDA in 2023, the cancer group said it “emphatically supports” requiring lab tests to undergo FDA review.
“We appreciate FDA action to modernize oversight of these tests and are hopeful this rule will increase focus on the need to balance rapid diagnostic innovation with patient safety and access” Everett Vokes, MD, the group’s board chair, said in a statement released after the FDA’s final rule was published.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plans to scrutinize the safety and efficacy of lab-developed tests — those designed, manufactured, and used in a single laboratory — far more thoroughly in the future.
Under a rule finalized in April, the FDA will treat facilities that develop and use lab tests as manufacturers and regulate tests as medical devices. That means that most lab tests will need an FDA review before going on sale.
The FDA will also impose new quality standards, requiring test manufacturers to report adverse events and create a registry of lab tests under the new rule, which will be phased in over 4 years.
FDA officials have been concerned for years about the reliability of commercial lab tests, which have ballooned into a multibillion-dollar industry.
Consumer groups have long urged the FDA to regulate lab tests more strictly, arguing that the lack of scrutiny allows doctors and patients to be exploited by bad actors such as Theranos, which falsely claimed that its tests could diagnose multiple diseases with a single drop of blood.
“When it comes to some of these tests that doctors are recommending for patients, many doctors are just crossing their fingers and relying on the representation of the company because nobody is checking” to verify a manufacturer’s claims, said Joshua Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland.
Nearly 12,000 Labs Making Medical Tests
Although the FDA estimates there are nearly 12,000 labs manufacturing medical tests, agency officials said they don’t know how many tests are being marketed. The FDA already requires that home test kits marketed directly to consumers, such as those used to detect COVID-19, get clearance from the agency before being sold.
“There’s plenty of time for industry to get its act together to develop the data that it might need to make a premarket application,” said Peter Lurie, MD, PhD, a former associate commissioner at the FDA. In 2015, Dr. Lurie led a report outlining some of the dangers of unregulated lab tests.
For the average physician who orders lab tests, nothing is going to immediately change because of the final rule, said Dr. Lurie, now president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a nonprofit consumer watchdog.
“Tomorrow, this will look just the same as it does today,” Dr. Lurie said. “For the next 3 years, the companies will be scurrying behind the scenes to comply with the early stages of implementation. But most of that will be invisible to the average practitioner.”
Dr. Lurie predicted the FDA will focus its scrutiny on tests that pose the greatest potential risk to patients, such as ones used to diagnose serious diseases or guide treatment for life-threatening conditions. “The least significant tests will likely get very limited, if any, scrutiny,” said Dr. Lurie, adding that the FDA will likely issue guidance about how it plans to define low- and high-risk tests. “My suspicion is that it will be probably a small minority of products that are subject to full premarket approval.”
Lab Industry Groups Push Back
But imposing new rules with the potential to affect an industry’s bottom line is no easy task.
The American Clinical Laboratory Association, which represents the lab industry, said in a statement that the FDA rule will “limit access to scores of critical tests, increase healthcare costs, and undermine innovation in new diagnostics.” Another industry group, the Association for Molecular Pathology, has warned of “significant and harmful disruption to laboratory medicine.”
The two associations have filed separate lawsuits, charging that the FDA overstepped the authority granted by Congress. In their lawsuits, groups claim that lab tests are professional services, not manufactured products. The groups noted that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) already inspects lab facilities. CMS does not assess the tests’ quality or reliability.
A recent Supreme Court decision could make those lawsuits more likely to succeed, said David Simon, JD, LLM, PhD, an assistant professor of law at the Northeastern University School of Law, Boston, Massachusetts.
In the case of Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo, decided in June, justices overturned a long-standing precedent known as Chevron deference, which required courts to defer to federal agencies when interpreting ambiguous laws. That means that courts no longer have to accept the FDA’s definition of a device, Dr. Simon said.
“Because judges may have more active roles in defining agency authority, federal agencies may have correspondingly less robust roles in policymaking,” Dr. Simon wrote in an editorial coauthored with Michael J. Young, MD, MPhil, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The Supreme Court ruling could pressure Congress to more clearly define FDA’s ruling in regulating lab tests, Dr. Simon and Dr. Young wrote.
Members of Congress first introduced a bill to clarify the FDA’s role in regulating lab tests, called the VALID Act, in 2020. The bill stalled and, despite efforts to revive it, still hasn’t passed.
FDA officials have said they remain “open to working with Congress,” noting that any future legislation about lab-developed tests would supersede their current policy.
In an interview, Dr. Simon noted the FDA significantly narrowed the scope of the final rule in response to comments from critics who objected to an earlier version of the policy proposed in 2023. The final rule carves out several categories of tests that won’t need to apply for “premarket review.”
Notably, a “grandfather clause” will allow some lab tests already on the market to continue being sold without undergoing FDA’s premarket review process. In explaining the exemption, FDA officials said they did not want doctors and patients to lose access to tests on which they rely. But Dr. Lurie noted that because the FDA views all these tests as under its jurisdiction, the agency could opt to take a closer look “at a very old device that is causing a problem today.”
The FDA also will exempt tests approved by New York State’s Clinical Laboratory Evaluation Program, which conducts its own stringent reviews. And the FDA will continue to allow hospitals to develop tests for patients within their healthcare system without going through the FDA approval process, if no FDA-approved tests are available.
Hospital-based tests play a critical role in treating infectious diseases, said Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. For example, a large research hospital treating a patient with cytomegalovirus may need to develop its own test to determine whether the infection is resistant to antiviral drugs, Dr. Adalja said.
“With novel infectious disease outbreaks, researchers are able to move quickly to make diagnostic tests months and months before commercial laboratories are able to get through regulatory processes,” Dr. Adalja said.
To help scientists respond quickly to emergencies, the FDA published special guidance for labs that develop unauthorized lab tests for disease outbreaks.
Medical groups such as the American Hospital Association and Infectious Diseases Society of America remain concerned about the burden of complying with new regulations.
“Many vital tests developed in hospitals and health systems may be subjected to unnecessary and costly paperwork,” said Stacey Hughes, executive vice president of the American Hospital Association, in a statement.
Other groups, such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology, praised the new FDA policy. In comments submitted to the FDA in 2023, the cancer group said it “emphatically supports” requiring lab tests to undergo FDA review.
“We appreciate FDA action to modernize oversight of these tests and are hopeful this rule will increase focus on the need to balance rapid diagnostic innovation with patient safety and access” Everett Vokes, MD, the group’s board chair, said in a statement released after the FDA’s final rule was published.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plans to scrutinize the safety and efficacy of lab-developed tests — those designed, manufactured, and used in a single laboratory — far more thoroughly in the future.
Under a rule finalized in April, the FDA will treat facilities that develop and use lab tests as manufacturers and regulate tests as medical devices. That means that most lab tests will need an FDA review before going on sale.
The FDA will also impose new quality standards, requiring test manufacturers to report adverse events and create a registry of lab tests under the new rule, which will be phased in over 4 years.
FDA officials have been concerned for years about the reliability of commercial lab tests, which have ballooned into a multibillion-dollar industry.
Consumer groups have long urged the FDA to regulate lab tests more strictly, arguing that the lack of scrutiny allows doctors and patients to be exploited by bad actors such as Theranos, which falsely claimed that its tests could diagnose multiple diseases with a single drop of blood.
“When it comes to some of these tests that doctors are recommending for patients, many doctors are just crossing their fingers and relying on the representation of the company because nobody is checking” to verify a manufacturer’s claims, said Joshua Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland.
Nearly 12,000 Labs Making Medical Tests
Although the FDA estimates there are nearly 12,000 labs manufacturing medical tests, agency officials said they don’t know how many tests are being marketed. The FDA already requires that home test kits marketed directly to consumers, such as those used to detect COVID-19, get clearance from the agency before being sold.
“There’s plenty of time for industry to get its act together to develop the data that it might need to make a premarket application,” said Peter Lurie, MD, PhD, a former associate commissioner at the FDA. In 2015, Dr. Lurie led a report outlining some of the dangers of unregulated lab tests.
For the average physician who orders lab tests, nothing is going to immediately change because of the final rule, said Dr. Lurie, now president of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, a nonprofit consumer watchdog.
“Tomorrow, this will look just the same as it does today,” Dr. Lurie said. “For the next 3 years, the companies will be scurrying behind the scenes to comply with the early stages of implementation. But most of that will be invisible to the average practitioner.”
Dr. Lurie predicted the FDA will focus its scrutiny on tests that pose the greatest potential risk to patients, such as ones used to diagnose serious diseases or guide treatment for life-threatening conditions. “The least significant tests will likely get very limited, if any, scrutiny,” said Dr. Lurie, adding that the FDA will likely issue guidance about how it plans to define low- and high-risk tests. “My suspicion is that it will be probably a small minority of products that are subject to full premarket approval.”
Lab Industry Groups Push Back
But imposing new rules with the potential to affect an industry’s bottom line is no easy task.
The American Clinical Laboratory Association, which represents the lab industry, said in a statement that the FDA rule will “limit access to scores of critical tests, increase healthcare costs, and undermine innovation in new diagnostics.” Another industry group, the Association for Molecular Pathology, has warned of “significant and harmful disruption to laboratory medicine.”
The two associations have filed separate lawsuits, charging that the FDA overstepped the authority granted by Congress. In their lawsuits, groups claim that lab tests are professional services, not manufactured products. The groups noted that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) already inspects lab facilities. CMS does not assess the tests’ quality or reliability.
A recent Supreme Court decision could make those lawsuits more likely to succeed, said David Simon, JD, LLM, PhD, an assistant professor of law at the Northeastern University School of Law, Boston, Massachusetts.
In the case of Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo, decided in June, justices overturned a long-standing precedent known as Chevron deference, which required courts to defer to federal agencies when interpreting ambiguous laws. That means that courts no longer have to accept the FDA’s definition of a device, Dr. Simon said.
“Because judges may have more active roles in defining agency authority, federal agencies may have correspondingly less robust roles in policymaking,” Dr. Simon wrote in an editorial coauthored with Michael J. Young, MD, MPhil, of Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The Supreme Court ruling could pressure Congress to more clearly define FDA’s ruling in regulating lab tests, Dr. Simon and Dr. Young wrote.
Members of Congress first introduced a bill to clarify the FDA’s role in regulating lab tests, called the VALID Act, in 2020. The bill stalled and, despite efforts to revive it, still hasn’t passed.
FDA officials have said they remain “open to working with Congress,” noting that any future legislation about lab-developed tests would supersede their current policy.
In an interview, Dr. Simon noted the FDA significantly narrowed the scope of the final rule in response to comments from critics who objected to an earlier version of the policy proposed in 2023. The final rule carves out several categories of tests that won’t need to apply for “premarket review.”
Notably, a “grandfather clause” will allow some lab tests already on the market to continue being sold without undergoing FDA’s premarket review process. In explaining the exemption, FDA officials said they did not want doctors and patients to lose access to tests on which they rely. But Dr. Lurie noted that because the FDA views all these tests as under its jurisdiction, the agency could opt to take a closer look “at a very old device that is causing a problem today.”
The FDA also will exempt tests approved by New York State’s Clinical Laboratory Evaluation Program, which conducts its own stringent reviews. And the FDA will continue to allow hospitals to develop tests for patients within their healthcare system without going through the FDA approval process, if no FDA-approved tests are available.
Hospital-based tests play a critical role in treating infectious diseases, said Amesh Adalja, MD, an infectious diseases specialist and senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. For example, a large research hospital treating a patient with cytomegalovirus may need to develop its own test to determine whether the infection is resistant to antiviral drugs, Dr. Adalja said.
“With novel infectious disease outbreaks, researchers are able to move quickly to make diagnostic tests months and months before commercial laboratories are able to get through regulatory processes,” Dr. Adalja said.
To help scientists respond quickly to emergencies, the FDA published special guidance for labs that develop unauthorized lab tests for disease outbreaks.
Medical groups such as the American Hospital Association and Infectious Diseases Society of America remain concerned about the burden of complying with new regulations.
“Many vital tests developed in hospitals and health systems may be subjected to unnecessary and costly paperwork,” said Stacey Hughes, executive vice president of the American Hospital Association, in a statement.
Other groups, such as the American Society of Clinical Oncology, praised the new FDA policy. In comments submitted to the FDA in 2023, the cancer group said it “emphatically supports” requiring lab tests to undergo FDA review.
“We appreciate FDA action to modernize oversight of these tests and are hopeful this rule will increase focus on the need to balance rapid diagnostic innovation with patient safety and access” Everett Vokes, MD, the group’s board chair, said in a statement released after the FDA’s final rule was published.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Psilocybin Bests SSRI for Major Depression in First Long-Term Comparison
MILAN — Psilocybin leads to a better overall outcome in the treatment of moderate to severe major depressive disorder (MDD) than the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) escitalopram, results of the first long-term comparison of the two treatments suggest.
“This is the first work to compare the long-term effects of these two drugs in the context of overall well-being, not just freedom from depression,” study investigator Tommaso Barba, PhD candidate at Imperial College London in England, said in a press release. “Psilocybin outperformed escitalopram in several measures of well-being, meaning in life, work, and social functioning.”
Findings from the 6-month follow-up study of a phase 2 double-blind, randomized, controlled trial were presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP) Congress and published simultaneously in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine
Addressing a Treatment ‘Mismatch’
The findings are important because they address “a mismatch” between what psychiatrists and what patients think is important, Mr. Barba said in an interview.
“Psychiatrists really focus on negative symptoms of depression. So, if you are not sad anymore, if your sleep or appetite is not impaired, they think you’re better. But if you look at what patients define as important, they say it’s the degree in which their life is meaningful, in which they can connect with people around them, in which they can function in everyday life,” Mr. Barba said.
“The study suggests that psilocybin therapy might be a more holistic treatment option for depression,” added co–first author David Erritzoe, MD, PhD, clinical director and deputy head of the Centre for Psychedelic Research, Imperial College London. “This could make a substantial difference in the overall happiness and daily activities of those suffering from depression, providing a more joined-up approach to mental health treatment.”
The initial single-center study included 59 adults with MDD (mean age, 41 years) who were randomized to receive either psilocybin or escitalopram over a 6-week period. The psilocybin arm (n = 30) received two 25-mg oral doses of psilocybin therapy (PT), and the escitalopram arm (n = 29) received 10-20 mg of daily escitalopram plus two (placebo-like) 1-mg doses of psilocybin (ET). Both groups received psychological support.
Based on change in depression scores on the 16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16) at week 6, the initial study results suggested noninferiority between the two treatments in terms of depressive symptoms (primary outcome), but superiority of PT for secondary outcomes including “well-being, anhedonia, social functioning, sexual functioning, and related variables, with fewer side effects compared to ET,” the researchers noted.
The new 6-month follow-up findings, with monthly questionnaires and no additional study treatment or psychiatric treatment restrictions, measured the QIDS-SR-16, plus Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Meaning in Life Questionnaire, Flourishing Scale (FS), and Watts Connectedness Scale (WCS).
Again, both groups maintained similar results on the QIDS-SR-16, with slightly greater reductions in depressive symptoms for PT in the first month (positive false discovery rate [pFDR] = 0.021), but not thereafter.
At both 3 and 6 months, there were greater improvements in WSAS scores for the PT group (pFDR < 0.001 and pFDR = 0.01, respectively), and also greater improvements in meaning in life across all follow-up timepoints (pFDR < 0.001).
There was also greater improvement in the PT group regarding WCS at both 3 and 6 months (pFDR = 0.02, and pFDR = 0.04) and comparable FS improvements for both groups across all timepoints.
Confounding follow-up interventions may have muddied the results, with 30.7% of PT participants and 43.5% of ET participants receiving an additional intervention during this period.
The researchers conclude that while a short course of SSRIs combined with intensive therapeutic support (around 20 hours) “might be enough to induce sustained antidepressant effects,” patients treated with psilocybin showed greater improvements in general functioning, connectedness, and meaning in life.
Although not reassessed in the follow-up, the initial study showed that adverse events, particularly sexual functioning, favored psilocybin, said Mr. Barba. “The two treatments seemed to go in opposite directions with psilocybin seeming to improve it and the antidepressant to suppress it. Other side effects associated with psilocybin were less diverse — mainly headaches at the end of the day — but with escitalopram they were way more diverse and more impairing.”
Although many therapists may be unfamiliar with psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy, “it’s not a difficult skill to master. It might require some specialization, but I think if you’re a good psychotherapist, you can learn how to implement psilocybin into your practice,” he said.
“Normally the journey is quite inward, so patients do not require active support during the psychedelic experience [around 6 hours]. Sometimes they do require some hand-holding, or helping them to ‘let go’, or breathing exercises. The important part is the integration work that comes afterwards,” Mr. Barba added.
He said he envisions a therapy program that involves “psychiatrists working together with psychotherapists. The psychotherapists would be more in charge of the active guiding, and the psychiatrist would do the prescribing, with the follow-up psychological support on Zoom.”
He added a word of caution for therapists that “psilocybin requires active confrontation of painful, negative emotions and people who take this drug need to be open and prepared for the idea that they are going into a state where they may probably end up crying and confronting whatever they are maybe running away from in their lives. Not everyone may want to do this.”
A New Treatment Paradigm?
In a comment, Johan Lundberg, MD, PhD, adjunct professor of psychiatry at the Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, said the study addresses a key outstanding question about the long-term effects of one or two doses of psilocybin.
“It’s a 6-month follow-up of a short treatment intervention, so in that sense, it’s of high interest. It has been talked about that psilocybin might have a long-term effect, but this is the first study that has followed this for a longer term.”
But Dr. Lundberg also pointed out that one shortcoming of the study is the diversity of treatments following the intervention.
“They didn’t have control over whether patients received other treatments or when they started. So, that is a key concern. But they transparently reported that, and we do know there was a difference in reported ability to perform activities of daily life, and that is important.”
He added that if psilocybin is eventually approved, it would likely come with an education package for providers — “which is already the case with other treatments like ECT [electroconvulsive therapy] or TMS [transcranial magnetic stimulation] — you have to learn how to do it.”
James Rucker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and senior clinical lecturer at King’s College London, who was not involved in the research, also noted that they have tended to attribute differences observed in this study to comparative differences between the drugs themselves.
However, he noted, it is also possible that the results reflect biased reporting between groups. This is more likely here because studies involving psilocybin tend to attract those with positive preconceptions about psilocybin and negative preconceptions about conventional antidepressants, and study participants were unblinded during the long-term follow-up phase, so knew which condition they were allocated to.
“This said, the nature of depression varies hugely between individuals, and this calls for the development of a similarly varied suite of treatment paradigms. Psilocybin therapy is certainly a different paradigm of treatment to escitalopram. The observation of similar levels of effectiveness to antidepressants here is encouraging to see alongside the much larger trials of psilocybin currently underway here in the UK, Europe, and the US,” Dr. Rucker added.
This work was supported by The Alexander Mosley Charitable Trust and by the founding partners of Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research.
Mr. Barba reported having received consulting fees from Adamo Bioscience. Both Dr. Lundberg and Dr. Rucker are involved in psilocybin research, but neither reported financial links.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN — Psilocybin leads to a better overall outcome in the treatment of moderate to severe major depressive disorder (MDD) than the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) escitalopram, results of the first long-term comparison of the two treatments suggest.
“This is the first work to compare the long-term effects of these two drugs in the context of overall well-being, not just freedom from depression,” study investigator Tommaso Barba, PhD candidate at Imperial College London in England, said in a press release. “Psilocybin outperformed escitalopram in several measures of well-being, meaning in life, work, and social functioning.”
Findings from the 6-month follow-up study of a phase 2 double-blind, randomized, controlled trial were presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP) Congress and published simultaneously in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine
Addressing a Treatment ‘Mismatch’
The findings are important because they address “a mismatch” between what psychiatrists and what patients think is important, Mr. Barba said in an interview.
“Psychiatrists really focus on negative symptoms of depression. So, if you are not sad anymore, if your sleep or appetite is not impaired, they think you’re better. But if you look at what patients define as important, they say it’s the degree in which their life is meaningful, in which they can connect with people around them, in which they can function in everyday life,” Mr. Barba said.
“The study suggests that psilocybin therapy might be a more holistic treatment option for depression,” added co–first author David Erritzoe, MD, PhD, clinical director and deputy head of the Centre for Psychedelic Research, Imperial College London. “This could make a substantial difference in the overall happiness and daily activities of those suffering from depression, providing a more joined-up approach to mental health treatment.”
The initial single-center study included 59 adults with MDD (mean age, 41 years) who were randomized to receive either psilocybin or escitalopram over a 6-week period. The psilocybin arm (n = 30) received two 25-mg oral doses of psilocybin therapy (PT), and the escitalopram arm (n = 29) received 10-20 mg of daily escitalopram plus two (placebo-like) 1-mg doses of psilocybin (ET). Both groups received psychological support.
Based on change in depression scores on the 16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16) at week 6, the initial study results suggested noninferiority between the two treatments in terms of depressive symptoms (primary outcome), but superiority of PT for secondary outcomes including “well-being, anhedonia, social functioning, sexual functioning, and related variables, with fewer side effects compared to ET,” the researchers noted.
The new 6-month follow-up findings, with monthly questionnaires and no additional study treatment or psychiatric treatment restrictions, measured the QIDS-SR-16, plus Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Meaning in Life Questionnaire, Flourishing Scale (FS), and Watts Connectedness Scale (WCS).
Again, both groups maintained similar results on the QIDS-SR-16, with slightly greater reductions in depressive symptoms for PT in the first month (positive false discovery rate [pFDR] = 0.021), but not thereafter.
At both 3 and 6 months, there were greater improvements in WSAS scores for the PT group (pFDR < 0.001 and pFDR = 0.01, respectively), and also greater improvements in meaning in life across all follow-up timepoints (pFDR < 0.001).
There was also greater improvement in the PT group regarding WCS at both 3 and 6 months (pFDR = 0.02, and pFDR = 0.04) and comparable FS improvements for both groups across all timepoints.
Confounding follow-up interventions may have muddied the results, with 30.7% of PT participants and 43.5% of ET participants receiving an additional intervention during this period.
The researchers conclude that while a short course of SSRIs combined with intensive therapeutic support (around 20 hours) “might be enough to induce sustained antidepressant effects,” patients treated with psilocybin showed greater improvements in general functioning, connectedness, and meaning in life.
Although not reassessed in the follow-up, the initial study showed that adverse events, particularly sexual functioning, favored psilocybin, said Mr. Barba. “The two treatments seemed to go in opposite directions with psilocybin seeming to improve it and the antidepressant to suppress it. Other side effects associated with psilocybin were less diverse — mainly headaches at the end of the day — but with escitalopram they were way more diverse and more impairing.”
Although many therapists may be unfamiliar with psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy, “it’s not a difficult skill to master. It might require some specialization, but I think if you’re a good psychotherapist, you can learn how to implement psilocybin into your practice,” he said.
“Normally the journey is quite inward, so patients do not require active support during the psychedelic experience [around 6 hours]. Sometimes they do require some hand-holding, or helping them to ‘let go’, or breathing exercises. The important part is the integration work that comes afterwards,” Mr. Barba added.
He said he envisions a therapy program that involves “psychiatrists working together with psychotherapists. The psychotherapists would be more in charge of the active guiding, and the psychiatrist would do the prescribing, with the follow-up psychological support on Zoom.”
He added a word of caution for therapists that “psilocybin requires active confrontation of painful, negative emotions and people who take this drug need to be open and prepared for the idea that they are going into a state where they may probably end up crying and confronting whatever they are maybe running away from in their lives. Not everyone may want to do this.”
A New Treatment Paradigm?
In a comment, Johan Lundberg, MD, PhD, adjunct professor of psychiatry at the Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, said the study addresses a key outstanding question about the long-term effects of one or two doses of psilocybin.
“It’s a 6-month follow-up of a short treatment intervention, so in that sense, it’s of high interest. It has been talked about that psilocybin might have a long-term effect, but this is the first study that has followed this for a longer term.”
But Dr. Lundberg also pointed out that one shortcoming of the study is the diversity of treatments following the intervention.
“They didn’t have control over whether patients received other treatments or when they started. So, that is a key concern. But they transparently reported that, and we do know there was a difference in reported ability to perform activities of daily life, and that is important.”
He added that if psilocybin is eventually approved, it would likely come with an education package for providers — “which is already the case with other treatments like ECT [electroconvulsive therapy] or TMS [transcranial magnetic stimulation] — you have to learn how to do it.”
James Rucker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and senior clinical lecturer at King’s College London, who was not involved in the research, also noted that they have tended to attribute differences observed in this study to comparative differences between the drugs themselves.
However, he noted, it is also possible that the results reflect biased reporting between groups. This is more likely here because studies involving psilocybin tend to attract those with positive preconceptions about psilocybin and negative preconceptions about conventional antidepressants, and study participants were unblinded during the long-term follow-up phase, so knew which condition they were allocated to.
“This said, the nature of depression varies hugely between individuals, and this calls for the development of a similarly varied suite of treatment paradigms. Psilocybin therapy is certainly a different paradigm of treatment to escitalopram. The observation of similar levels of effectiveness to antidepressants here is encouraging to see alongside the much larger trials of psilocybin currently underway here in the UK, Europe, and the US,” Dr. Rucker added.
This work was supported by The Alexander Mosley Charitable Trust and by the founding partners of Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research.
Mr. Barba reported having received consulting fees from Adamo Bioscience. Both Dr. Lundberg and Dr. Rucker are involved in psilocybin research, but neither reported financial links.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN — Psilocybin leads to a better overall outcome in the treatment of moderate to severe major depressive disorder (MDD) than the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) escitalopram, results of the first long-term comparison of the two treatments suggest.
“This is the first work to compare the long-term effects of these two drugs in the context of overall well-being, not just freedom from depression,” study investigator Tommaso Barba, PhD candidate at Imperial College London in England, said in a press release. “Psilocybin outperformed escitalopram in several measures of well-being, meaning in life, work, and social functioning.”
Findings from the 6-month follow-up study of a phase 2 double-blind, randomized, controlled trial were presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP) Congress and published simultaneously in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine
Addressing a Treatment ‘Mismatch’
The findings are important because they address “a mismatch” between what psychiatrists and what patients think is important, Mr. Barba said in an interview.
“Psychiatrists really focus on negative symptoms of depression. So, if you are not sad anymore, if your sleep or appetite is not impaired, they think you’re better. But if you look at what patients define as important, they say it’s the degree in which their life is meaningful, in which they can connect with people around them, in which they can function in everyday life,” Mr. Barba said.
“The study suggests that psilocybin therapy might be a more holistic treatment option for depression,” added co–first author David Erritzoe, MD, PhD, clinical director and deputy head of the Centre for Psychedelic Research, Imperial College London. “This could make a substantial difference in the overall happiness and daily activities of those suffering from depression, providing a more joined-up approach to mental health treatment.”
The initial single-center study included 59 adults with MDD (mean age, 41 years) who were randomized to receive either psilocybin or escitalopram over a 6-week period. The psilocybin arm (n = 30) received two 25-mg oral doses of psilocybin therapy (PT), and the escitalopram arm (n = 29) received 10-20 mg of daily escitalopram plus two (placebo-like) 1-mg doses of psilocybin (ET). Both groups received psychological support.
Based on change in depression scores on the 16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology–Self-Report (QIDS-SR-16) at week 6, the initial study results suggested noninferiority between the two treatments in terms of depressive symptoms (primary outcome), but superiority of PT for secondary outcomes including “well-being, anhedonia, social functioning, sexual functioning, and related variables, with fewer side effects compared to ET,” the researchers noted.
The new 6-month follow-up findings, with monthly questionnaires and no additional study treatment or psychiatric treatment restrictions, measured the QIDS-SR-16, plus Work and Social Adjustment Scale (WSAS), Meaning in Life Questionnaire, Flourishing Scale (FS), and Watts Connectedness Scale (WCS).
Again, both groups maintained similar results on the QIDS-SR-16, with slightly greater reductions in depressive symptoms for PT in the first month (positive false discovery rate [pFDR] = 0.021), but not thereafter.
At both 3 and 6 months, there were greater improvements in WSAS scores for the PT group (pFDR < 0.001 and pFDR = 0.01, respectively), and also greater improvements in meaning in life across all follow-up timepoints (pFDR < 0.001).
There was also greater improvement in the PT group regarding WCS at both 3 and 6 months (pFDR = 0.02, and pFDR = 0.04) and comparable FS improvements for both groups across all timepoints.
Confounding follow-up interventions may have muddied the results, with 30.7% of PT participants and 43.5% of ET participants receiving an additional intervention during this period.
The researchers conclude that while a short course of SSRIs combined with intensive therapeutic support (around 20 hours) “might be enough to induce sustained antidepressant effects,” patients treated with psilocybin showed greater improvements in general functioning, connectedness, and meaning in life.
Although not reassessed in the follow-up, the initial study showed that adverse events, particularly sexual functioning, favored psilocybin, said Mr. Barba. “The two treatments seemed to go in opposite directions with psilocybin seeming to improve it and the antidepressant to suppress it. Other side effects associated with psilocybin were less diverse — mainly headaches at the end of the day — but with escitalopram they were way more diverse and more impairing.”
Although many therapists may be unfamiliar with psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy, “it’s not a difficult skill to master. It might require some specialization, but I think if you’re a good psychotherapist, you can learn how to implement psilocybin into your practice,” he said.
“Normally the journey is quite inward, so patients do not require active support during the psychedelic experience [around 6 hours]. Sometimes they do require some hand-holding, or helping them to ‘let go’, or breathing exercises. The important part is the integration work that comes afterwards,” Mr. Barba added.
He said he envisions a therapy program that involves “psychiatrists working together with psychotherapists. The psychotherapists would be more in charge of the active guiding, and the psychiatrist would do the prescribing, with the follow-up psychological support on Zoom.”
He added a word of caution for therapists that “psilocybin requires active confrontation of painful, negative emotions and people who take this drug need to be open and prepared for the idea that they are going into a state where they may probably end up crying and confronting whatever they are maybe running away from in their lives. Not everyone may want to do this.”
A New Treatment Paradigm?
In a comment, Johan Lundberg, MD, PhD, adjunct professor of psychiatry at the Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, said the study addresses a key outstanding question about the long-term effects of one or two doses of psilocybin.
“It’s a 6-month follow-up of a short treatment intervention, so in that sense, it’s of high interest. It has been talked about that psilocybin might have a long-term effect, but this is the first study that has followed this for a longer term.”
But Dr. Lundberg also pointed out that one shortcoming of the study is the diversity of treatments following the intervention.
“They didn’t have control over whether patients received other treatments or when they started. So, that is a key concern. But they transparently reported that, and we do know there was a difference in reported ability to perform activities of daily life, and that is important.”
He added that if psilocybin is eventually approved, it would likely come with an education package for providers — “which is already the case with other treatments like ECT [electroconvulsive therapy] or TMS [transcranial magnetic stimulation] — you have to learn how to do it.”
James Rucker, MD, PhD, psychiatrist and senior clinical lecturer at King’s College London, who was not involved in the research, also noted that they have tended to attribute differences observed in this study to comparative differences between the drugs themselves.
However, he noted, it is also possible that the results reflect biased reporting between groups. This is more likely here because studies involving psilocybin tend to attract those with positive preconceptions about psilocybin and negative preconceptions about conventional antidepressants, and study participants were unblinded during the long-term follow-up phase, so knew which condition they were allocated to.
“This said, the nature of depression varies hugely between individuals, and this calls for the development of a similarly varied suite of treatment paradigms. Psilocybin therapy is certainly a different paradigm of treatment to escitalopram. The observation of similar levels of effectiveness to antidepressants here is encouraging to see alongside the much larger trials of psilocybin currently underway here in the UK, Europe, and the US,” Dr. Rucker added.
This work was supported by The Alexander Mosley Charitable Trust and by the founding partners of Imperial College London’s Centre for Psychedelic Research.
Mr. Barba reported having received consulting fees from Adamo Bioscience. Both Dr. Lundberg and Dr. Rucker are involved in psilocybin research, but neither reported financial links.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECNP 2024
Treating Family: Ethicist Discusses Whether It’s Appropriate
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
There’s a very interesting story in the medical press. A few years ago, a plastic surgeon named Edmond Cabbabe was preparing to do a follow-up cosmetic procedure on his wife at Mercy Hospital South, which is a big hospital in the St. Louis, Missouri, area.
He put her on the operating schedule, and he had done that when he had performed the original operation on her. On the day of the surgery, he got a call from the hospital saying the procedure was canceled. They said that the hospital’s policy, maybe a new one, would not allow doctors to operate on family members.
This physician was a past president of the Missouri State Medical Association. I think he was also on the board or president of the American Medical Association (AMA) Foundation. This was a physician not only in a skilled area where he felt confident he could take care of his wife, but also someone who was prominent in medical politics and medical policy.
The AMA forever has had a policy that says don’t treat relatives. This physician basically said, I think that policy is too restrictive, too cautious, and it doesn’t make much sense to continue to say that you can’t treat family and friends.
By implication, he was saying, I know exactly what I’m doing in my field and I know exactly what I’m doing with her procedure. I should have a right to perform it. I think I do a great job and I’d be best for her.
If you look at medical boards, every once in a while in some state, someone is brought up on a charge of doing different things with family members and saying that they’re going to get censured. They don’t usually lose their license, but they get a reprimand or get told that is just not ethical to do.
I think, in the long run, the policy about not treating your family and friends makes sense. The problem is, as is well known from the social sciences and psychology, people get biased when they deal with those they care about, love, and hold close to them.
It’s hard for the doctor to be objective when dealing with people that they really like or love. It’s also difficult for patients because they may not want to bring up something or they are uncomfortable talking with a doctor who’s a family member or close friend. They may not want to complain. They may be a little bit embarrassed about things. It just adds an emotional edge, I think, that’s difficult.
All that said, do I know doctors who regularly prescribe, say, an ointment for something that’s itchy or some kind of a pill when allergy season breaks out? I do. Do I think they’re acting in a horribly unethical manner? I don’t.
You need some judgment here. There are absolutely minor things where objectivity, fear, and anxiety are not in play. You’re going to be able to prescribe the routine thing for the routine itch without worrying too much about whether it’s a stranger, a friend, or your daughter.
What sorts of things am I really talking about when I say that minor variability ought to be allowed? It’s one thing when someone has poison ivy and they’re going to need some kind of standard medicine to treat it. A very different area that’s much more dangerous, and one I would avoid, is in the mental health field, and for that matter, the pain field.
It’s tempting to say: “Oh, my relative is just having a bad time. I’ll give her a little bit of antidepressant medicine,” or “They seem to be having pain after an operation or something, and I’m going to give them a little bit of pain meds just to get them through.”
Those areas are flying red flags. It’s easy to abuse and easy for someone to become a user and manipulate a friend or a doctor who’s a relative into getting things that another doctor wouldn’t be giving. I think that’s the space where you’ve got to exercise extreme caution.
Time and again, when those people get called up in front of the boards for treating relatives, it’s in those spaces of mental health, anxiety, and pain control. Again, when you know that there’s a likelihood of abuse, I think that’s the place where the line has to hold. Don’t treat the relative. Don’t treat the friend.
At the end of the day, I wouldn’t change the AMA policy. I think we should keep it in place and morally try to discourage doctors from caring for those they’re close to or they have emotional ties to.
At the same time, as with all ethical situations, there has to be a little bit of wiggle room for those super-minor cases where it just makes sense to say: “You don’t have to go find somebody else to do this. I can prescribe this ointment or this minor thing for you. No one’s objectivity is going to be soured, and you’re not going to feel in any way at risk because I’m going to prescribe this for you.”
Common sense ought to prevail. The default position is don’t do it; however, maybe with a tiny bit of space for what’s minor, what’s routine, and what really does just save people some inconvenience, there I might just give a little.
Dr. Caplan, Director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York City, has disclosed relationships with Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Initiative Aims to Improve Diversity in Clinical Trials
NEW YORK — Underrepresentation by gender and race in major clinical trials has been a cause for complaint for decades, but the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has drafted a regulatory solution to this issue expected to be implemented sometime in 2025.
This initiative, known as the according to Valerie M. Harvey, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor, Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Blacksburg, Virginia. These rules will be codified, she said at the 2024 Skin of Color Update.
Once the DAP is enacted, “the sponsor must specify the rationale and goals for study enrollment by age, ethnicity, sex, and race,” she said. Furthermore, the submission to the FDA must “describe the methods to meet the diversity benchmarks.”
Lack of Trial Diversity Is Common Across Medicine
Although she focused on the relevance of this initiative to dermatology, Dr. Harvey said the lack of diversity in clinical trials is pervasive throughout medicine. In one survey of randomized controlled trials, less than 60% of trials even specified the race and ethnicity of the participants. In recent psoriasis trials, only 30% met a diversity definition of ≥ 20% of patients identifying as minority (Black, Hispanic, Asian, or other non-White group), said Dr. Harvey, who practices dermatology in Newport News, Virginia.
The FDA draft guidance for the DAP was released in June 2024 and is now available for submitting comments (until September 26). The plan is expected to be published in June 2025, according to Dr. Harvey. It will pertain to all pivotal and phase 3 trials enrolling 180 days after the publication date and will be relevant to all drugs and biologics as well as certain devices.
This initiative could be a critical step toward ensuring diversity in major clinical trials after years of stagnation, Dr. Harvey said, noting that despite repeated calls for more diversity in clinical trials, the literature suggests “little progress.”
However, she said that increasing diversity in clinical trials is just one step toward gathering data about the generalizability of efficacy and safety across racial and ethnic groups. A much more complex issue involves how race and ethnicity are defined in order to understand differences, if any, for efficacy and risk.
“Race is a dynamic social construct and a poor measure for biologic variation and skin color,” Dr. Harvey said. This means that work is needed to address the more complex issue of race and ethnicity stratification that will help clinicians understand the relative benefits and risks for the drugs in these trials.
Rather than differences based on genetic or other sources of biologic differences, she said, outcomes by race alone are often suspected of reflecting disparities in access to healthcare rather than a difference in therapeutic response.
Skin Color Is Inadequate to Define Race
When stratifying patients by race or ethnicity, Dr. Harvey said that “we have to be very, very careful in considering the study purpose and what the study question is.” A study attempting to compare benefits and risks among subgroups by race or ethnicity will require descriptors beyond skin color.
The recognized limitations of measuring skin tone as a surrogate of race are one reason for widespread interest in moving away from the Fitzpatrick skin type (FST) rating that has been widely considered a standard, according to Dr. Harvey. Several alternatives have been proposed, including the Monk Skin Tone Scale, the Individual Typology Angle, and the Eumelanin Human Skin Color Scale, but she cautioned that these are less well validated and generally have the limitations of the FST.
If skin color was ever useful for grouping individuals on the basis of shared physiology, growing rates of intermarriage and immigration have made skin color increasingly irrelevant to racial identity. If the goal is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of drugs across racial groups and ethnicities, the characterization of populations will almost certainly require multiple descriptors and biomarkers, she said.
“It is very important to have many tools for characterizing patients by skin type,” Susan Taylor, MD, professor of dermatology and vice chair for diversity, equity, and inclusion for the Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview at the meeting.
The reason is “there are limitations to all of them,” she said, noting also that the questions being asked about how and if skin color and race are relevant to therapeutic options differ by the question, such as innate response or access to care.
Dr. Taylor is part of a workshop that she said is evaluating a combination of instruments for characterizing skin color and race in ways relevant to the specific question being asked.
The solutions might differ. While simple clinical assessments involving skin color might be made with methods captured on a smartphone app, Dr. Taylor acknowledged that far more complex tools might be required to document the effect of racial or ethnic differences in drug efficacy and safety in a research setting.
Outside of a research setting, any tools that might be useful for assessing race as a variable must be practical, according to Dr. Harvey. She suggested that these must be time efficient, of reasonable cost, and most importantly, reliable.
Tools meeting these criteria do not currently exist, but Dr. Harvey said the work is underway. She expects a “top-down” collaborative approach to validate alternatives to the FST. If such tools can be developed with buy-in from the FDA, they might be particularly useful for translating trial data to patient care, she added.
Dr. Harvey reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, L’Oréal, and SkinCeuticals. Dr. Taylor, president-elect of the American Academy of Dermatology, reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Underrepresentation by gender and race in major clinical trials has been a cause for complaint for decades, but the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has drafted a regulatory solution to this issue expected to be implemented sometime in 2025.
This initiative, known as the according to Valerie M. Harvey, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor, Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Blacksburg, Virginia. These rules will be codified, she said at the 2024 Skin of Color Update.
Once the DAP is enacted, “the sponsor must specify the rationale and goals for study enrollment by age, ethnicity, sex, and race,” she said. Furthermore, the submission to the FDA must “describe the methods to meet the diversity benchmarks.”
Lack of Trial Diversity Is Common Across Medicine
Although she focused on the relevance of this initiative to dermatology, Dr. Harvey said the lack of diversity in clinical trials is pervasive throughout medicine. In one survey of randomized controlled trials, less than 60% of trials even specified the race and ethnicity of the participants. In recent psoriasis trials, only 30% met a diversity definition of ≥ 20% of patients identifying as minority (Black, Hispanic, Asian, or other non-White group), said Dr. Harvey, who practices dermatology in Newport News, Virginia.
The FDA draft guidance for the DAP was released in June 2024 and is now available for submitting comments (until September 26). The plan is expected to be published in June 2025, according to Dr. Harvey. It will pertain to all pivotal and phase 3 trials enrolling 180 days after the publication date and will be relevant to all drugs and biologics as well as certain devices.
This initiative could be a critical step toward ensuring diversity in major clinical trials after years of stagnation, Dr. Harvey said, noting that despite repeated calls for more diversity in clinical trials, the literature suggests “little progress.”
However, she said that increasing diversity in clinical trials is just one step toward gathering data about the generalizability of efficacy and safety across racial and ethnic groups. A much more complex issue involves how race and ethnicity are defined in order to understand differences, if any, for efficacy and risk.
“Race is a dynamic social construct and a poor measure for biologic variation and skin color,” Dr. Harvey said. This means that work is needed to address the more complex issue of race and ethnicity stratification that will help clinicians understand the relative benefits and risks for the drugs in these trials.
Rather than differences based on genetic or other sources of biologic differences, she said, outcomes by race alone are often suspected of reflecting disparities in access to healthcare rather than a difference in therapeutic response.
Skin Color Is Inadequate to Define Race
When stratifying patients by race or ethnicity, Dr. Harvey said that “we have to be very, very careful in considering the study purpose and what the study question is.” A study attempting to compare benefits and risks among subgroups by race or ethnicity will require descriptors beyond skin color.
The recognized limitations of measuring skin tone as a surrogate of race are one reason for widespread interest in moving away from the Fitzpatrick skin type (FST) rating that has been widely considered a standard, according to Dr. Harvey. Several alternatives have been proposed, including the Monk Skin Tone Scale, the Individual Typology Angle, and the Eumelanin Human Skin Color Scale, but she cautioned that these are less well validated and generally have the limitations of the FST.
If skin color was ever useful for grouping individuals on the basis of shared physiology, growing rates of intermarriage and immigration have made skin color increasingly irrelevant to racial identity. If the goal is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of drugs across racial groups and ethnicities, the characterization of populations will almost certainly require multiple descriptors and biomarkers, she said.
“It is very important to have many tools for characterizing patients by skin type,” Susan Taylor, MD, professor of dermatology and vice chair for diversity, equity, and inclusion for the Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview at the meeting.
The reason is “there are limitations to all of them,” she said, noting also that the questions being asked about how and if skin color and race are relevant to therapeutic options differ by the question, such as innate response or access to care.
Dr. Taylor is part of a workshop that she said is evaluating a combination of instruments for characterizing skin color and race in ways relevant to the specific question being asked.
The solutions might differ. While simple clinical assessments involving skin color might be made with methods captured on a smartphone app, Dr. Taylor acknowledged that far more complex tools might be required to document the effect of racial or ethnic differences in drug efficacy and safety in a research setting.
Outside of a research setting, any tools that might be useful for assessing race as a variable must be practical, according to Dr. Harvey. She suggested that these must be time efficient, of reasonable cost, and most importantly, reliable.
Tools meeting these criteria do not currently exist, but Dr. Harvey said the work is underway. She expects a “top-down” collaborative approach to validate alternatives to the FST. If such tools can be developed with buy-in from the FDA, they might be particularly useful for translating trial data to patient care, she added.
Dr. Harvey reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, L’Oréal, and SkinCeuticals. Dr. Taylor, president-elect of the American Academy of Dermatology, reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Underrepresentation by gender and race in major clinical trials has been a cause for complaint for decades, but the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has drafted a regulatory solution to this issue expected to be implemented sometime in 2025.
This initiative, known as the according to Valerie M. Harvey, MD, MPH, associate clinical professor, Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine, Blacksburg, Virginia. These rules will be codified, she said at the 2024 Skin of Color Update.
Once the DAP is enacted, “the sponsor must specify the rationale and goals for study enrollment by age, ethnicity, sex, and race,” she said. Furthermore, the submission to the FDA must “describe the methods to meet the diversity benchmarks.”
Lack of Trial Diversity Is Common Across Medicine
Although she focused on the relevance of this initiative to dermatology, Dr. Harvey said the lack of diversity in clinical trials is pervasive throughout medicine. In one survey of randomized controlled trials, less than 60% of trials even specified the race and ethnicity of the participants. In recent psoriasis trials, only 30% met a diversity definition of ≥ 20% of patients identifying as minority (Black, Hispanic, Asian, or other non-White group), said Dr. Harvey, who practices dermatology in Newport News, Virginia.
The FDA draft guidance for the DAP was released in June 2024 and is now available for submitting comments (until September 26). The plan is expected to be published in June 2025, according to Dr. Harvey. It will pertain to all pivotal and phase 3 trials enrolling 180 days after the publication date and will be relevant to all drugs and biologics as well as certain devices.
This initiative could be a critical step toward ensuring diversity in major clinical trials after years of stagnation, Dr. Harvey said, noting that despite repeated calls for more diversity in clinical trials, the literature suggests “little progress.”
However, she said that increasing diversity in clinical trials is just one step toward gathering data about the generalizability of efficacy and safety across racial and ethnic groups. A much more complex issue involves how race and ethnicity are defined in order to understand differences, if any, for efficacy and risk.
“Race is a dynamic social construct and a poor measure for biologic variation and skin color,” Dr. Harvey said. This means that work is needed to address the more complex issue of race and ethnicity stratification that will help clinicians understand the relative benefits and risks for the drugs in these trials.
Rather than differences based on genetic or other sources of biologic differences, she said, outcomes by race alone are often suspected of reflecting disparities in access to healthcare rather than a difference in therapeutic response.
Skin Color Is Inadequate to Define Race
When stratifying patients by race or ethnicity, Dr. Harvey said that “we have to be very, very careful in considering the study purpose and what the study question is.” A study attempting to compare benefits and risks among subgroups by race or ethnicity will require descriptors beyond skin color.
The recognized limitations of measuring skin tone as a surrogate of race are one reason for widespread interest in moving away from the Fitzpatrick skin type (FST) rating that has been widely considered a standard, according to Dr. Harvey. Several alternatives have been proposed, including the Monk Skin Tone Scale, the Individual Typology Angle, and the Eumelanin Human Skin Color Scale, but she cautioned that these are less well validated and generally have the limitations of the FST.
If skin color was ever useful for grouping individuals on the basis of shared physiology, growing rates of intermarriage and immigration have made skin color increasingly irrelevant to racial identity. If the goal is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of drugs across racial groups and ethnicities, the characterization of populations will almost certainly require multiple descriptors and biomarkers, she said.
“It is very important to have many tools for characterizing patients by skin type,” Susan Taylor, MD, professor of dermatology and vice chair for diversity, equity, and inclusion for the Department of Dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in an interview at the meeting.
The reason is “there are limitations to all of them,” she said, noting also that the questions being asked about how and if skin color and race are relevant to therapeutic options differ by the question, such as innate response or access to care.
Dr. Taylor is part of a workshop that she said is evaluating a combination of instruments for characterizing skin color and race in ways relevant to the specific question being asked.
The solutions might differ. While simple clinical assessments involving skin color might be made with methods captured on a smartphone app, Dr. Taylor acknowledged that far more complex tools might be required to document the effect of racial or ethnic differences in drug efficacy and safety in a research setting.
Outside of a research setting, any tools that might be useful for assessing race as a variable must be practical, according to Dr. Harvey. She suggested that these must be time efficient, of reasonable cost, and most importantly, reliable.
Tools meeting these criteria do not currently exist, but Dr. Harvey said the work is underway. She expects a “top-down” collaborative approach to validate alternatives to the FST. If such tools can be developed with buy-in from the FDA, they might be particularly useful for translating trial data to patient care, she added.
Dr. Harvey reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, L’Oréal, and SkinCeuticals. Dr. Taylor, president-elect of the American Academy of Dermatology, reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical and cosmetic companies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SOC 2024
Should There Be a Mandatory Retirement Age for Physicians?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to pose a question: When should doctors retire? When, as practicing physicians or surgeons, do we become too old to deliver competent service?
You will be amazed to hear, those of you who have listened to my videos before — and although it is a matter of public knowledge — that I’m 68. I know it’s impossible to imagine, due to this youthful appearance, visage, and so on, but I am. I’ve been a cancer doctor for 40 years; therefore, I need to think a little about retirement.
There are two elements of this for me. I’m a university professor, and in Oxford we did vote, as a democracy of scholars, to have a mandatory retirement age around 68. This is so that we can bring new blood forward so that we can create the space to promote new professors, to bring youngsters in to make new ideas, and to get rid of us fusty old lot.
The other argument would be, of course, that we are wise, we’re experienced, we are world-weary, and we’re successful — otherwise, we wouldn’t have lasted as academics as long. Nevertheless, we voted to do that.
It’s possible to have a discussion with the university to extend this, and for those of us who are clinical academics, I have an honorary appointment as a consultant cancer physician in the hospital and my university professorial appointment, too.
I can extend it probably until I’m about 70. It feels like a nice, round number at which to retire — somewhat arbitrarily, one would admit. But does that feel right?
In the United States, more than 25% of the physician workforce is over the age of 65. There are many studies showing that there is a 20% cognitive decline for most individuals between the ages of 45 and 65.
Are we as capable as an elderly workforce as once we were? Clearly, it’s hardly individualistic. It depends on each of our own health status, where we started from, and so on, but are there any general rules that we can apply? I think these are starting to creep in around the sense of revalidation.
In the United Kingdom, we have a General Medical Council (GMC). I need to have a license to practice from the GMC and a sense of fitness to practice. I have annual appraisals within the hospital system, in which I explore delivery of care, how I’m doing as a mentor, am I reaching the milestones I’ve set in terms of academic achievements, and so on.
This is a peer-to-peer process. We have senior physicians — people like myself — who act as appraisers to support our colleagues and to maintain that sense of fitness to practice. Every 5 years, I’m revalidated by the GMC. They take account of the annual appraisals and a report made by the senior physician within my hospital network who’s a so-called designated person.
These two elements come together with patient feedback, with 360-degree feedback from colleagues, and so on. This is quite a firmly regulated system that I think works. Our mandatory retirement age of 65 has gone. That was phased out by the government. In fact, our NHS is making an effort to retain older elders in the workforce.
They see the benefits of mentorship, experience, leadership, and networks. At a time when the majority of NHS are actively seeking to retire when 65, the NHS is trying to retain and pull back those of us who have been around for that wee bit longer and who still feel committed to doing it.
I’d be really interested to see what you think. There’s variation from country to country. I know that, in Australia, they’re talking about annual appraisals of doctors over the age of 70. I’d be very interested to hear what you think is likely to happen in the United States.
I think our system works pretty well, as long as you’re within the NHS and hospital system. If you wanted to still practice, but practice privately, you would still have to find somebody who’d be prepared to conduct appraisals and so on outside of the NHS. It’s an interesting area.
For myself, I still feel competent. Patients seem to like me. That’s an objective assessment by this 360-degree thing in which patients reflected very positively, indeed, in my approach to the delivery of the care and so on, as did colleagues. I’m still publishing, I go to meetings, I cheer things, bits and bobs. I’d say I’m a wee bit unusual in terms of still having a strong academic profile in doing stuff.
It’s an interesting question. Richard Doll, one of the world’s great epidemiologists who, of course, was the dominant discoverer of the link between smoking and lung cancer, was attending seminars, sitting in the front row, and coming into university 3 days a week at age 90, continuing to be contributory with his extraordinarily sharp intellect and vast, vast experience.
When I think of experience, all young cancer doctors are now immunologists. When I was a young doctor, I was a clinical pharmacologist. There are many lessons and tricks that I learned which I do need to pass on to the younger generation of today. What do you think? Should there be a mandatory retirement age? How do we best measure, assess, and revalidate elderly physicians and surgeons? How can we continue to contribute to those who choose to do so? For the time being, as always, thanks for listening.
Dr. Kerr is professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, and professor of cancer medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom. He has disclosed ties with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers (Board of Directors); Afrox (charity; Trustee); GlaxoSmithKline and Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals (Consultant), Genomic Health; Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hidden in Plain Sight: The Growing Epidemic of Ultraprocessed Food Addiction
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Yet, even as this evidence mounted, these food items have become increasingly prominent in diets globally.
Now, recent studies are unlocking why cutting back on ultraprocessed foods can be so challenging. In their ability to fuel intense cravings, loss of control, and even withdrawal symptoms, ultraprocessed foods appear as capable of triggering addiction as traditional culprits like tobacco and alcohol.
This has driven efforts to better understand the addictive nature of these foods and identify strategies for combating it.
The Key Role of the Food Industry
Some foods are more likely to trigger addictions than others. For instance, in our studies, participants frequently mention chocolate, pizza, French fries, potato chips, and soda as some of the most addictive foods. What these foods all share is an ability to deliver high doses of refined carbohydrates, fat, or salt at levels exceeding those found in natural foods (eg, fruits, vegetables, beans).
Furthermore, ultraprocessed foods are industrially mass-produced in a process that relies on the heavy use of flavor enhancers and additives, as well as preservatives and packaging that make them shelf-stable. This has flooded our food supply with cheap, accessible, hyperrewarding foods that our brains are not well equipped to resist.
To add to these already substantial effects, the food industry often employs strategies reminiscent of Big Tobacco. They engineer foods to hit our “bliss points,” maximizing craving and fostering brand loyalty from a young age. This product engineering, coupled with aggressive marketing, makes these foods both attractive and seemingly ubiquitous.
How Many People Are Affected?
Addiction to ultraprocessed food is more common than you might think. According to the Yale Food Addiction Scale — a tool that uses the same criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders to assess ultraprocessed food addiction (UPFA) — about 14% of adults and 12% of children show clinically significant signs of addiction to such foods. This is quite similar to addiction rates among adults for legal substances like alcohol and tobacco.
Research has shown that behaviors and brain mechanisms contributing to addictive disorders, such as cravings and impulsivity, also apply to UPFA.
Many more people outside of those who meet the criteria for UPFA are influenced by their addictive properties. Picture a teenager craving a sugary drink after school, a child needing the morning cereal fix, or adults reaching for candy and fast food; these scenarios illustrate how addictive ultraprocessed foods permeate our daily lives.
From a public health standpoint, this comes at a significant cost. Even experiencing one or two symptoms of UPFA, such as intense cravings or a feeling of loss of control over intake, can lead to consuming too many calories, sugar, fat, and sodium in a way that puts health at risk.
Clinical Implications
Numerous studies have found that individuals who exhibit UPFA have more severe mental and physical health challenges. For example, UPFA is associated with higher rates of diet-related diseases (like type 2 diabetes), greater overall mental health issues, and generally poorer outcomes in weight loss treatments.
Despite the growing understanding of UPFA’s relevance in clinical settings, research is still limited on how to best treat, manage, or prevent it. Most of the existing work has focused on investigating whether UPFA is indeed a real condition, with efforts to create clinical guidelines only just beginning.
Of note, UPFA isn’t officially recognized as a diagnosis — yet. If it were, it could spark much more research into how to handle it clinically.
There is some debate about whether we really need this new diagnosis, given that eating disorders are already recognized. However, the statistics tell a different story: Around 14% of people might have UPFA compared with about 1% for binge-type eating disorders. This suggests that many individuals with problematic eating habits are currently flying under the radar with our existing diagnostic categories.
What’s even more concerning is that these individuals often suffer significant problems and exhibit distinct brain differences, even if they do not neatly fit into an existing eating disorder diagnosis. Officially recognizing UPFA could open up new avenues for support and lead to better treatments aimed at reducing compulsive eating patterns.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for UPFA are still being explored. Initial evidence suggests that medications used for treating substance addiction, such as naltrexone and bupropion, might help with highly processed food addiction as well. Newer drugs, like glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, which appear to curb food cravings and manage addictive behaviors, also look promising.
Psychosocial approaches can also be used to address UPFA. Strategies include:
- Helping individuals become more aware of their triggers for addictive patterns of intake. This often involves identifying certain types of food (eg, potato chips, candy), specific places or times of day (eg, sitting on the couch at night while watching TV), and particular emotional states (eg, anger, loneliness, boredom, sadness). Increasing awareness of personal triggers can help people minimize their exposure to these and develop coping strategies when they do arise.
- Many people use ultraprocessed foods to cope with challenging emotions. Helping individuals develop healthier strategies to regulate their emotions can be key. This may include seeking out social support, journaling, going for a walk, or practicing mindfulness.
- UPFA can be associated with erratic and inconsistent eating patterns. Stabilizing eating habits by consuming regular meals composed of more minimally processed foods (eg, vegetables, fruits, high-quality protein, beans) can help heal the body and reduce vulnerability to ultraprocessed food triggers.
- Many people with UPFA have other existing mental health conditions, including mood disorders, anxiety, substance use disorders, or trauma-related disorders. Addressing these co-occurring mental health conditions can help reduce reliance on ultraprocessed foods.
Public-policy interventions may also help safeguard vulnerable populations from developing UPFA. For instance, support exists for policies to protect children from cigarette marketing and to put clear addiction warning labels on cigarette packages. A similar approach could be applied to reduce the harms associated with ultraprocessed foods, particularly for children.
Combating this growing problem requires treating ultraprocessed foods like other addictive substances. By identifying the threat posed by these common food items, we can not only help patients with UPFA, but also potentially stave off the development of several diet-related conditions.
Dr. Gearhardt, professor of psychology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Bariatric Surgery and Weight Loss Make Brain Say Meh to Sweets
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have suggested that individuals undergoing bariatric surgery show reduced preference for sweet-tasting food post-surgery, but the mechanisms behind these changes remain unclear.
- This observational cohort study aimed to examine the neural processing of sweet taste in the reward regions of the brain before and after bariatric surgery in 24 women with obesity (mean body mass index [BMI], 47) who underwent bariatric surgery and 21 control participants with normal to overweight (mean BMI, 23.5).
- Participants (mean age about 43 years; 75%-81% White) underwent sucrose taste testing and functional MRI (fMRI) to compare the responses of the brain with sucrose solutions of 0.10 M and 0.40 M (akin to sugar-sweetened beverages, such as Coca-Cola at ~0.32 M) and Mountain Dew at ~0.35 M) versus water.
- In the bariatric surgery group, participants underwent fMRI 1-117 days before surgery, and 21 participants who lost about 20% of their weight after the surgery underwent a follow-up fMRI roughly 3-4 months later.
- The researchers analyzed the brain’s reward response using a composite activation of several reward system regions (the ventral tegmental area, ventral striatum, and orbitofrontal cortex) and of sensory regions (the primary somatosensory cortex and primary insula taste cortex).
TAKEAWAY:
- The perceived intensity of sweetness was comparable between the control group and the bariatric surgery group both before and after surgery.
- In the bariatric surgery group, the average preferred sweet concentration decreased from 0.52 M before surgery to 0.29 M after surgery (P = .008).
- The fMRI analysis indicated that women showed a trend toward a higher reward response to 0.4 M sucrose before bariatric surgery than the control participants.
- The activation of the reward region in response to 0.4 M sucrose (but not 0.1 M) declined in the bariatric surgery group after surgery (P = .042).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that both the brain reward response to and subjective liking of an innately desirable taste decline following bariatric surgery,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan Alessi, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study sample size was relatively small, and the duration of follow-up was short, with recruitment curtailed by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study did not assess the consumption of sugar or sweetened food, which could provide further insights into changes in the dietary behavior post-surgery. Participants included women only, and the findings could have been different if men were recruited.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the American Diabetes Association, Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, and National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Three authors reported financial relationships with some pharmaceutical companies outside of this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have suggested that individuals undergoing bariatric surgery show reduced preference for sweet-tasting food post-surgery, but the mechanisms behind these changes remain unclear.
- This observational cohort study aimed to examine the neural processing of sweet taste in the reward regions of the brain before and after bariatric surgery in 24 women with obesity (mean body mass index [BMI], 47) who underwent bariatric surgery and 21 control participants with normal to overweight (mean BMI, 23.5).
- Participants (mean age about 43 years; 75%-81% White) underwent sucrose taste testing and functional MRI (fMRI) to compare the responses of the brain with sucrose solutions of 0.10 M and 0.40 M (akin to sugar-sweetened beverages, such as Coca-Cola at ~0.32 M) and Mountain Dew at ~0.35 M) versus water.
- In the bariatric surgery group, participants underwent fMRI 1-117 days before surgery, and 21 participants who lost about 20% of their weight after the surgery underwent a follow-up fMRI roughly 3-4 months later.
- The researchers analyzed the brain’s reward response using a composite activation of several reward system regions (the ventral tegmental area, ventral striatum, and orbitofrontal cortex) and of sensory regions (the primary somatosensory cortex and primary insula taste cortex).
TAKEAWAY:
- The perceived intensity of sweetness was comparable between the control group and the bariatric surgery group both before and after surgery.
- In the bariatric surgery group, the average preferred sweet concentration decreased from 0.52 M before surgery to 0.29 M after surgery (P = .008).
- The fMRI analysis indicated that women showed a trend toward a higher reward response to 0.4 M sucrose before bariatric surgery than the control participants.
- The activation of the reward region in response to 0.4 M sucrose (but not 0.1 M) declined in the bariatric surgery group after surgery (P = .042).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that both the brain reward response to and subjective liking of an innately desirable taste decline following bariatric surgery,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan Alessi, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study sample size was relatively small, and the duration of follow-up was short, with recruitment curtailed by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study did not assess the consumption of sugar or sweetened food, which could provide further insights into changes in the dietary behavior post-surgery. Participants included women only, and the findings could have been different if men were recruited.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the American Diabetes Association, Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, and National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Three authors reported financial relationships with some pharmaceutical companies outside of this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have suggested that individuals undergoing bariatric surgery show reduced preference for sweet-tasting food post-surgery, but the mechanisms behind these changes remain unclear.
- This observational cohort study aimed to examine the neural processing of sweet taste in the reward regions of the brain before and after bariatric surgery in 24 women with obesity (mean body mass index [BMI], 47) who underwent bariatric surgery and 21 control participants with normal to overweight (mean BMI, 23.5).
- Participants (mean age about 43 years; 75%-81% White) underwent sucrose taste testing and functional MRI (fMRI) to compare the responses of the brain with sucrose solutions of 0.10 M and 0.40 M (akin to sugar-sweetened beverages, such as Coca-Cola at ~0.32 M) and Mountain Dew at ~0.35 M) versus water.
- In the bariatric surgery group, participants underwent fMRI 1-117 days before surgery, and 21 participants who lost about 20% of their weight after the surgery underwent a follow-up fMRI roughly 3-4 months later.
- The researchers analyzed the brain’s reward response using a composite activation of several reward system regions (the ventral tegmental area, ventral striatum, and orbitofrontal cortex) and of sensory regions (the primary somatosensory cortex and primary insula taste cortex).
TAKEAWAY:
- The perceived intensity of sweetness was comparable between the control group and the bariatric surgery group both before and after surgery.
- In the bariatric surgery group, the average preferred sweet concentration decreased from 0.52 M before surgery to 0.29 M after surgery (P = .008).
- The fMRI analysis indicated that women showed a trend toward a higher reward response to 0.4 M sucrose before bariatric surgery than the control participants.
- The activation of the reward region in response to 0.4 M sucrose (but not 0.1 M) declined in the bariatric surgery group after surgery (P = .042).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our findings suggest that both the brain reward response to and subjective liking of an innately desirable taste decline following bariatric surgery,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jonathan Alessi, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and published online in Obesity.
LIMITATIONS:
The study sample size was relatively small, and the duration of follow-up was short, with recruitment curtailed by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study did not assess the consumption of sugar or sweetened food, which could provide further insights into changes in the dietary behavior post-surgery. Participants included women only, and the findings could have been different if men were recruited.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the American Diabetes Association, Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, and National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Three authors reported financial relationships with some pharmaceutical companies outside of this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Reform School’ for Pharmacy Benefit Managers: How Might Legislation Help Patients?
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).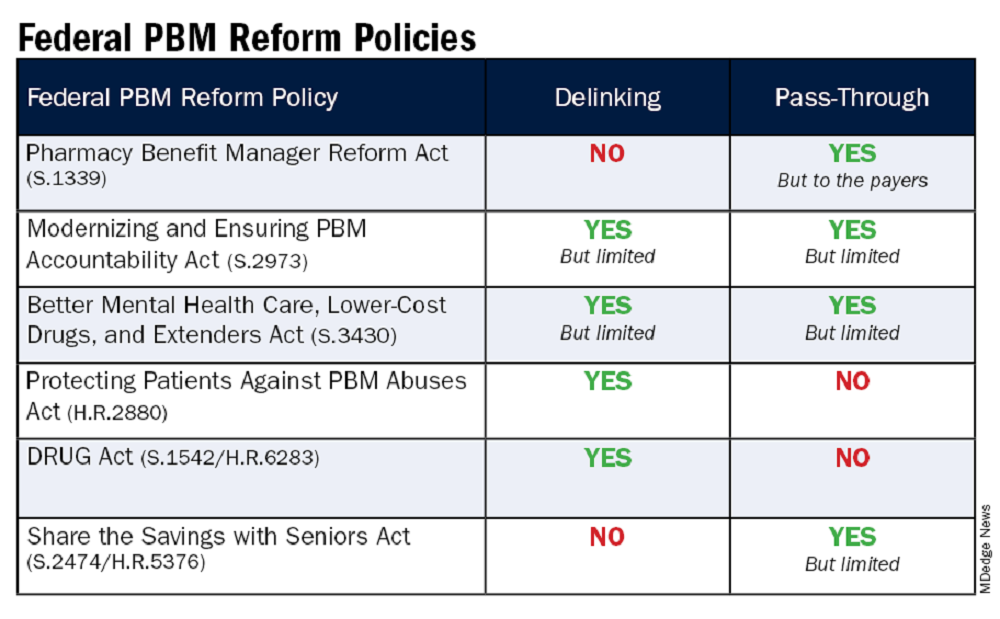
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.
The term “reform school” is a bit outdated. It used to refer to institutions where young offenders were sent instead of prison. Some argue that pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) should bypass reform school and go straight to prison. “PBM reform” has become a ubiquitous term, encompassing any legislative or regulatory efforts aimed at curbing PBMs’ bad behavior. When discussing PBM reform, it’s crucial to understand the various segments of the healthcare system affected by PBMs. This complexity often makes it challenging to determine what these reform packages would actually achieve and who they would benefit.
Pharmacists have long been vocal critics of PBMs, and while their issues are extremely important, it is essential to remember that the ultimate victims of PBM misconduct, in terms of access to care, are patients. At some point, we will all be patients, making this issue universally relevant. It has been quite challenging to follow federal legislation on this topic as these packages attempt to address a number of bad behaviors by PBMs affecting a variety of victims. This discussion will examine those reforms that would directly improve patient’s access to available and affordable medications.
Policy Categories of PBM Reform
There are five policy categories of PBM reform legislation overall, including three that have the greatest potential to directly address patient needs. The first is patient access to medications (utilization management, copay assistance, prior authorization, etc.), followed by delinking drug list prices from PBM income and pass-through of price concessions from the manufacturer. The remaining two categories involve transparency and pharmacy-facing reform, both of which are very important. However, this discussion will revolve around the first three categories. It should be noted that many of the legislation packages addressing the categories of patient access, delinking, and pass-through also include transparency issues, particularly as they relate to pharmacy-facing issues.
Patient Access to Medications — Step Therapy Legislation
One of the major obstacles to patient access to medications is the use of PBM utilization management tools such as step therapy (“fail first”), prior authorizations, nonmedical switching, and formulary exclusions. These tools dictate when patients can obtain necessary medications and for how long patients who are stable on their current treatments can remain on them.
While many states have enacted step therapy reforms to prevent stable patients from being whip-sawed between medications that maximize PBM profits (often labeled as “savings”), these state protections apply only to state-regulated health plans. These include fully insured health plans and those offered through the Affordable Care Act’s Health Insurance Marketplace. It also includes state employees, state corrections, and, in some cases, state labor unions. State legislation does not extend to patients covered by employer self-insured health plans, called ERISA plans for the federal law that governs employee benefit plans, the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. These ERISA plans include nearly 35 million people nationwide.
This is where the Safe Step Act (S.652/H.R.2630) becomes crucial, as it allows employees to request exceptions to harmful fail-first protocols. The bill has gained significant momentum, having been reported out of the Senate HELP Committee and discussed in House markups. The Safe Step Act would mandate that an exception to a step therapy protocol must be granted if:
- The required treatment has been ineffective
- The treatment is expected to be ineffective, and delaying effective treatment would lead to irreversible consequences
- The treatment will cause or is likely to cause an adverse reaction
- The treatment is expected to prevent the individual from performing daily activities or occupational responsibilities
- The individual is stable on their current prescription drugs
- There are other circumstances as determined by the Employee Benefits Security Administration
This legislation is vital for ensuring that patients have timely access to the medications they need without unnecessary delays or disruptions.
Patient Access to Medications — Prior Authorizations
Another significant issue affecting patient access to medications is prior authorizations (PAs). According to an American Medical Association survey, nearly one in four physicians (24%) report that a PA has led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care. In rheumatology, PAs often result in delays in care (even for those initially approved) and a significant increase in steroid usage. In particular, PAs in Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are harmful to Medicare beneficiaries.
The Improving Seniors’ Timely Access to Care Act (H.R.8702 / S.4532) aims to reform PAs used in MA plans, making the process more efficient and transparent to improve access to care for seniors. Unfortunately, it does not cover Part D drugs and may only cover Part B drugs depending on the MA plan’s benefit package. Here are the key provisions of the act:
- Electronic PA: Implementing real-time decisions for routinely approved items and services.
- Transparency: Requiring annual publication of PA information, such as the percentage of requests approved and the average response time.
- Quality and Timeliness Standards: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) will set standards for the quality and timeliness of PA determinations.
- Streamlining Approvals: Simplifying the approval process and reducing the time allowed for health plans to consider PA requests.
This bill passed the House in September 2022 but stalled in the Senate because of an unfavorable Congressional Budget Office score. CMS has since finalized portions of this bill via regulation, zeroing out the CBO score and increasing the chances of its passage.
Delinking Drug Prices from PBM Income and Pass-Through of Price Concessions
Affordability is a crucial aspect of accessibility, especially when it comes to medications. Over the years, we’ve learned that PBMs often favor placing the highest list price drugs on formularies because the rebates and various fees they receive from manufacturers are based on a percentage of the list price. In other words, the higher the medication’s price, the more money the PBM makes.
This practice is evident in both commercial and government formularies, where brand-name drugs are often preferred, while lower-priced generics are either excluded or placed on higher tiers. As a result, while major PBMs benefit from these rebates and fees, patients continue to pay their cost share based on the list price of the medication.
To improve the affordability of medications, a key aspect of PBM reform should be to disincentivize PBMs from selecting higher-priced medications and/or require the pass-through of manufacturer price concessions to patients.
Several major PBM reform bills are currently being considered that address either the delinking of price concessions from the list price of the drug or some form of pass-through of these concessions. These reforms are essential to ensure that patients can access affordable medications without being burdened by inflated costs.
The legislation includes the Pharmacy Benefit Manager Reform Act (S.1339); the Modernizing & Ensuring PBM Accountability Act (S.2973); the Better Mental Health Care, Lower Cost Drugs, and Extenders Act (S.3430); the Protecting Patients Against PBM Abuses Act (H.R. 2880); the DRUG Act (S.2474 / H.R.6283); and the Share the Savings with Seniors Act (S.2474 / H.R.5376).
As with all legislation, there are limitations and compromises in each of these. However, these bills are a good first step in addressing PBM remuneration (rebates and fees) based on the list price of the drug and/or passing through to the patient the benefit of manufacturer price concessions. By focusing on key areas like utilization management, delinking drug prices from PBM income, and allowing patients to directly benefit from manufacturer price concessions, we can work toward a more equitable and efficient healthcare system. Reigning in PBM bad behavior is a challenge, but the potential benefits for patient care and access make it a crucial fight worth pursuing.
Please help in efforts to improve patients’ access to available and affordable medications by contacting your representatives in Congress to impart to them the importance of passing legislation. The CSRO’s legislative map tool can help to inform you of the latest information on these and other bills and assist you in engaging with your representatives on them.
Dr. Feldman is a rheumatologist in private practice with The Rheumatology Group in New Orleans. She is the CSRO’s vice president of Advocacy and Government Affairs and its immediate past president, as well as past chair of the Alliance for Safe Biologic Medicines and a past member of the American College of Rheumatology insurance subcommittee. She has no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. You can reach her at rhnews@mdedge.com.

