User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Percentage of doctors who are Black barely changed in 120 years
according to a new study.
In 1900, 1.3% of physicians were Black. In 1940, 2.8% of physicians were Black, and by 2018 – when almost 13% of the population was Black – 5.4% of doctors were Black, reports Dan Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in a study published online April 19, 2021, in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The proportion of male Black physicians was 2.7% in 1940 and 2.6% in 2018.
Dr. Ly also found a significant wage gap. The median income earned by White doctors was $50,000 more than the median income of Black physicians in 2018. Dr. Ly based his findings on the U.S. Census Decennial Census long form, accessed via IPUMS, a free database funded by the National Institutes of Health and other organizations.
“If we care about the health of the population, particularly the health of Black patients, we should care about how small the proportion of our physicians who are Black is and the extremely slow progress we have made as a medical system in increasing that proportion,” Dr. Ly said in an interview.
Dr. Ly said he took on this research in part because previous studies have shown that Black patients are more likely to seek preventive care from Black doctors. Thus, increasing the numbers of Black physicians could narrow gaps in life expectancy between Whites and Blacks.
He also wanted to see whether progress had been made as a result of various medical organizations and the Association of American Medical Colleges undertaking initiatives to increase workforce diversity. There has been “very, very little” progress, he said.
Norma Poll-Hunter, PhD, the AAMC’s senior director of workforce diversity, said Dr. Ly’s report “was not surprising at all.”
The AAMC reported in 2014 that the number of Black men who apply to and matriculate into medical schools has been declining since 1978. That year, there were 1,410 Black male applicants and 542 Black enrollees. In 2014, there were 1,337 applicants and 515 enrollees.
Since 2014, Black male enrollment has increased slightly, rising from 2.4% in the 2014-2015 school year to 2.9% in the 2019-2020 year, the AAMC reported last year.
In addition, among other historically underrepresented minorities, “we really have seen very small progress” despite the increase in the number of medical schools, Dr. Poll-Hunter said in an interview.
The AAMC and the National Medical Association consider the lack of Black male applicants and matriculants to be a national crisis. The two groups started an alliance in 2020 aimed at finding ways to amplify and support Black men’s interest in medicine and the biomedical sciences and to “develop systems-based solutions to address exclusionary practices that create barriers for Black men and prevent them from having equitable opportunities to successfully enroll in medical school.”
Solutions include requiring medical school admissions committees and application screeners to undergo implicit bias awareness and mitigation training, adopting holistic admissions reviews, and incentivizing institutions of higher learning to partner with Black communities in urban and rural school systems to establish K-12 health sciences academies, said NMA President Leon McDougle, MD, MPH.
“There are the systems factors, and racism is a big one that we have to tackle,” said Dr. Poll-Hunter.
Diversity isn’t just about numbers, said Dr. McDougle, a professor of family medicine and associate dean for diversity and inclusion at Ohio State University, Columbus. “We know that medical school graduates who are African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native are more likely to serve those communities as practicing physicians.
“The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for more African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native physicians,” he said. “Inadequate access to culturally competent care has exacerbated existing health disparities, resulting in death and hospitalization rates up to three to four times the rates of European American or White people.”
Dr. Poll-Hunter also said that studies have shown that diversity in the classroom creates a more enriched learning environment and increases civic mindedness and cognitive complexity, “as well as helps us understand people who are different than ourselves.”
The diversity goal “is not about quotas, it’s about excellence,” she said. “We know that there’s talent that exists, and we want to make sure that everyone has an opportunity to be successful.”
Dr. Ly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study.
In 1900, 1.3% of physicians were Black. In 1940, 2.8% of physicians were Black, and by 2018 – when almost 13% of the population was Black – 5.4% of doctors were Black, reports Dan Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in a study published online April 19, 2021, in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The proportion of male Black physicians was 2.7% in 1940 and 2.6% in 2018.
Dr. Ly also found a significant wage gap. The median income earned by White doctors was $50,000 more than the median income of Black physicians in 2018. Dr. Ly based his findings on the U.S. Census Decennial Census long form, accessed via IPUMS, a free database funded by the National Institutes of Health and other organizations.
“If we care about the health of the population, particularly the health of Black patients, we should care about how small the proportion of our physicians who are Black is and the extremely slow progress we have made as a medical system in increasing that proportion,” Dr. Ly said in an interview.
Dr. Ly said he took on this research in part because previous studies have shown that Black patients are more likely to seek preventive care from Black doctors. Thus, increasing the numbers of Black physicians could narrow gaps in life expectancy between Whites and Blacks.
He also wanted to see whether progress had been made as a result of various medical organizations and the Association of American Medical Colleges undertaking initiatives to increase workforce diversity. There has been “very, very little” progress, he said.
Norma Poll-Hunter, PhD, the AAMC’s senior director of workforce diversity, said Dr. Ly’s report “was not surprising at all.”
The AAMC reported in 2014 that the number of Black men who apply to and matriculate into medical schools has been declining since 1978. That year, there were 1,410 Black male applicants and 542 Black enrollees. In 2014, there were 1,337 applicants and 515 enrollees.
Since 2014, Black male enrollment has increased slightly, rising from 2.4% in the 2014-2015 school year to 2.9% in the 2019-2020 year, the AAMC reported last year.
In addition, among other historically underrepresented minorities, “we really have seen very small progress” despite the increase in the number of medical schools, Dr. Poll-Hunter said in an interview.
The AAMC and the National Medical Association consider the lack of Black male applicants and matriculants to be a national crisis. The two groups started an alliance in 2020 aimed at finding ways to amplify and support Black men’s interest in medicine and the biomedical sciences and to “develop systems-based solutions to address exclusionary practices that create barriers for Black men and prevent them from having equitable opportunities to successfully enroll in medical school.”
Solutions include requiring medical school admissions committees and application screeners to undergo implicit bias awareness and mitigation training, adopting holistic admissions reviews, and incentivizing institutions of higher learning to partner with Black communities in urban and rural school systems to establish K-12 health sciences academies, said NMA President Leon McDougle, MD, MPH.
“There are the systems factors, and racism is a big one that we have to tackle,” said Dr. Poll-Hunter.
Diversity isn’t just about numbers, said Dr. McDougle, a professor of family medicine and associate dean for diversity and inclusion at Ohio State University, Columbus. “We know that medical school graduates who are African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native are more likely to serve those communities as practicing physicians.
“The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for more African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native physicians,” he said. “Inadequate access to culturally competent care has exacerbated existing health disparities, resulting in death and hospitalization rates up to three to four times the rates of European American or White people.”
Dr. Poll-Hunter also said that studies have shown that diversity in the classroom creates a more enriched learning environment and increases civic mindedness and cognitive complexity, “as well as helps us understand people who are different than ourselves.”
The diversity goal “is not about quotas, it’s about excellence,” she said. “We know that there’s talent that exists, and we want to make sure that everyone has an opportunity to be successful.”
Dr. Ly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a new study.
In 1900, 1.3% of physicians were Black. In 1940, 2.8% of physicians were Black, and by 2018 – when almost 13% of the population was Black – 5.4% of doctors were Black, reports Dan Ly, MD, PhD, MPP, an assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in a study published online April 19, 2021, in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
The proportion of male Black physicians was 2.7% in 1940 and 2.6% in 2018.
Dr. Ly also found a significant wage gap. The median income earned by White doctors was $50,000 more than the median income of Black physicians in 2018. Dr. Ly based his findings on the U.S. Census Decennial Census long form, accessed via IPUMS, a free database funded by the National Institutes of Health and other organizations.
“If we care about the health of the population, particularly the health of Black patients, we should care about how small the proportion of our physicians who are Black is and the extremely slow progress we have made as a medical system in increasing that proportion,” Dr. Ly said in an interview.
Dr. Ly said he took on this research in part because previous studies have shown that Black patients are more likely to seek preventive care from Black doctors. Thus, increasing the numbers of Black physicians could narrow gaps in life expectancy between Whites and Blacks.
He also wanted to see whether progress had been made as a result of various medical organizations and the Association of American Medical Colleges undertaking initiatives to increase workforce diversity. There has been “very, very little” progress, he said.
Norma Poll-Hunter, PhD, the AAMC’s senior director of workforce diversity, said Dr. Ly’s report “was not surprising at all.”
The AAMC reported in 2014 that the number of Black men who apply to and matriculate into medical schools has been declining since 1978. That year, there were 1,410 Black male applicants and 542 Black enrollees. In 2014, there were 1,337 applicants and 515 enrollees.
Since 2014, Black male enrollment has increased slightly, rising from 2.4% in the 2014-2015 school year to 2.9% in the 2019-2020 year, the AAMC reported last year.
In addition, among other historically underrepresented minorities, “we really have seen very small progress” despite the increase in the number of medical schools, Dr. Poll-Hunter said in an interview.
The AAMC and the National Medical Association consider the lack of Black male applicants and matriculants to be a national crisis. The two groups started an alliance in 2020 aimed at finding ways to amplify and support Black men’s interest in medicine and the biomedical sciences and to “develop systems-based solutions to address exclusionary practices that create barriers for Black men and prevent them from having equitable opportunities to successfully enroll in medical school.”
Solutions include requiring medical school admissions committees and application screeners to undergo implicit bias awareness and mitigation training, adopting holistic admissions reviews, and incentivizing institutions of higher learning to partner with Black communities in urban and rural school systems to establish K-12 health sciences academies, said NMA President Leon McDougle, MD, MPH.
“There are the systems factors, and racism is a big one that we have to tackle,” said Dr. Poll-Hunter.
Diversity isn’t just about numbers, said Dr. McDougle, a professor of family medicine and associate dean for diversity and inclusion at Ohio State University, Columbus. “We know that medical school graduates who are African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native are more likely to serve those communities as practicing physicians.
“The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for more African American or Black, Hispanic or Latinx, or American Indian or Alaskan Native physicians,” he said. “Inadequate access to culturally competent care has exacerbated existing health disparities, resulting in death and hospitalization rates up to three to four times the rates of European American or White people.”
Dr. Poll-Hunter also said that studies have shown that diversity in the classroom creates a more enriched learning environment and increases civic mindedness and cognitive complexity, “as well as helps us understand people who are different than ourselves.”
The diversity goal “is not about quotas, it’s about excellence,” she said. “We know that there’s talent that exists, and we want to make sure that everyone has an opportunity to be successful.”
Dr. Ly has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 infection conveys imperfect immunity in young adults
Do your patients think that getting COVID-19 is fully protective against subsequent reinfection? Tell it to the Marines.
A study of U.S. Marine recruits on their way to boot camp at Parris Island, S.C., showed that those who were seropositive at baseline, indicating prior exposure to SARS-CoV-2, remained at some risk for reinfection. They had about one-fifth the risk of subsequent infection, compared with seronegative recruits during basic training, but reinfections did occur.
The study, by Stuart C. Sealfon, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and colleagues, was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Although antibodies induced by initial infection are largely protective, they do not guarantee effective SARS-CoV-2 neutralization activity or immunity against subsequent infection,” they wrote.
An infectious disease specialist who was not involved in the study said that the findings provide further evidence about the level of immunity acquired after an infection.
“It’s quite clear that reinfections do occur, they are of public health importance, and they’re something we need to be mindful of in terms of advising patients about whether a prior infection protects them from reinfection,” Mark Siedner, MD, MPH, a clinician and researcher in the division of infectious diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study results reinforce that “not all antibodies are the same,” said Sachin Gupta, MD, an attending physician in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. “We’re seeing still that 10% of folks who have antibodies can get infected again,” he said in an interview.
CHARM initiative
Dr. Sealfon and colleagues presented an analysis of data from the ironically named CHARM (COVID-19 Health Action Response for Marines) prospective study.
CHARM included U.S. Marine recruits, most of them male, aged 18-20 years, who were instructed to follow a 2-week unsupervised quarantine at home, after which they reported to a Marine-supervised facility for an additional 2-week quarantine.
At baseline, participants were tested for SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G (IgG) seropositivity, defined as a dilution of 1:150 or more on receptor-binding domain and full-length spike protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
The recruits filled out questionnaires asking them to report any of 14 specific COVID-19–related symptoms or any other unspecified symptom, as well as demographic information, risk factors, and a brief medical history.
Investigators tested recruits for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay at weeks 0, 1, and 2 of quarantine, and any who had positive PCR results during quarantine were excluded.
Participants who had three negative swab PCR results during quarantine and a baseline serology test at the beginning of the supervised quarantine period – either seronegative or seropositive – then went on to enjoy their basic training at the Marine Corps Recruit Depot, Parris Island, S.C.
The participants were followed prospectively with PCR tests at weeks 2, 4, and 6 in both the seropositive and seronegative groups, and sera were obtained at the same time.
Holes in immunologic armor
Full data were available for a total of 189 participants who were seropositive and 2,247 who were seronegative at enrollment.
In all, 19 of 189 seropositive recruits (10%) had at least one PCR test positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection during the 6-week follow-up period. This translated into an incidence of 1.1 cases per person-year.
Of the 2,247 participants seronegative at baseline, 1,079 tested positive (6.2 cases per person-year; incidence rate ratio 0.18).
It appeared that antibodies provided some protection for seropositive recruits, as evidenced by a higher likelihood of infection among those with lower baseline full-length spike protein IgG titers than in those with higher baseline titers (hazard ratio 0.4, P < .001).
Among the seropositive participants who did acquire a second SARS-CoV-2 infection, viral loads in mid-turbinate nasal swabs were about 10-fold lower than in seronegative recruits who acquired infections during follow-up.
“This finding suggests that some reinfected individuals could have a similar capacity to transmit infection as those who are infected for the first time. The rate at which reinfection occurs after vaccines and natural immunity is important for estimating the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to suppress the pandemic,” the investigators wrote.
Baseline neutralizing antibody titers were detected in 45 of the first 54 seropositive recruits who remained PCR negative throughout follow-up, but also in 6 of 19 seropositive participants who became infected during the 6 weeks of observation.
Lessons
Both Dr. Siedner and Dr. Gupta agreed with the authors that the risks for reinfection that were observed in young, physically fit people may differ for other populations, such as women (only 10% of seropositive recruits and 8% of seronegative recruits were female), older patients, or those who are immunocompromised.
Given that the adjusted odds ratio for reinfection in this study was nearly identical to that of a recent British study comparing infection rates between seropositive and seronegative health care workers, the risk of reinfection for other young adults and for the general population may be similar, Dr. Sealfon and colleagues wrote.
Adding to the challenge of reaching herd immunity is the observation that some patients who have recovered from COVID-19 are skeptical about the need for further protection.
“There are patients who feel like vaccination is of low benefit to them, and I think these are the same people who would be hesitant to get the vaccine anyway,” Dr. Gupta said.
Although no vaccine is perfect – the vaccine failure rate from the mRNA-based vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/Biontech is about 5% – the protections they afford are unmistakable, Dr. Siedner said.
“I think it’s important to make the distinction that most postvaccination infections by and large have been very mild,” he said. “In people with normal immune systems, we have not seen an onslaught of postvaccination infections requiring hospitalization. Even if people do get infected after vaccination, the vaccines protect people from severe infection, and that’s what we want them to do.”
The investigators stated, “Young adults, of whom a high proportion are asymptomatically infected and become seropositive in the absence of known infection, can be an important source of transmission to more vulnerable populations. Evaluating the protection against subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection conferred by seropositivity in young adults is important for determining the need for vaccinating previously infected individuals in this age group.”
The study was funded by the Defense Health Agency and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Dr. Sealfon, Dr. Siedner, and Dr. Gupta have no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Gupta is a member of the editorial advisory board for this publication.
Do your patients think that getting COVID-19 is fully protective against subsequent reinfection? Tell it to the Marines.
A study of U.S. Marine recruits on their way to boot camp at Parris Island, S.C., showed that those who were seropositive at baseline, indicating prior exposure to SARS-CoV-2, remained at some risk for reinfection. They had about one-fifth the risk of subsequent infection, compared with seronegative recruits during basic training, but reinfections did occur.
The study, by Stuart C. Sealfon, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and colleagues, was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Although antibodies induced by initial infection are largely protective, they do not guarantee effective SARS-CoV-2 neutralization activity or immunity against subsequent infection,” they wrote.
An infectious disease specialist who was not involved in the study said that the findings provide further evidence about the level of immunity acquired after an infection.
“It’s quite clear that reinfections do occur, they are of public health importance, and they’re something we need to be mindful of in terms of advising patients about whether a prior infection protects them from reinfection,” Mark Siedner, MD, MPH, a clinician and researcher in the division of infectious diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study results reinforce that “not all antibodies are the same,” said Sachin Gupta, MD, an attending physician in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. “We’re seeing still that 10% of folks who have antibodies can get infected again,” he said in an interview.
CHARM initiative
Dr. Sealfon and colleagues presented an analysis of data from the ironically named CHARM (COVID-19 Health Action Response for Marines) prospective study.
CHARM included U.S. Marine recruits, most of them male, aged 18-20 years, who were instructed to follow a 2-week unsupervised quarantine at home, after which they reported to a Marine-supervised facility for an additional 2-week quarantine.
At baseline, participants were tested for SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G (IgG) seropositivity, defined as a dilution of 1:150 or more on receptor-binding domain and full-length spike protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
The recruits filled out questionnaires asking them to report any of 14 specific COVID-19–related symptoms or any other unspecified symptom, as well as demographic information, risk factors, and a brief medical history.
Investigators tested recruits for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay at weeks 0, 1, and 2 of quarantine, and any who had positive PCR results during quarantine were excluded.
Participants who had three negative swab PCR results during quarantine and a baseline serology test at the beginning of the supervised quarantine period – either seronegative or seropositive – then went on to enjoy their basic training at the Marine Corps Recruit Depot, Parris Island, S.C.
The participants were followed prospectively with PCR tests at weeks 2, 4, and 6 in both the seropositive and seronegative groups, and sera were obtained at the same time.
Holes in immunologic armor
Full data were available for a total of 189 participants who were seropositive and 2,247 who were seronegative at enrollment.
In all, 19 of 189 seropositive recruits (10%) had at least one PCR test positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection during the 6-week follow-up period. This translated into an incidence of 1.1 cases per person-year.
Of the 2,247 participants seronegative at baseline, 1,079 tested positive (6.2 cases per person-year; incidence rate ratio 0.18).
It appeared that antibodies provided some protection for seropositive recruits, as evidenced by a higher likelihood of infection among those with lower baseline full-length spike protein IgG titers than in those with higher baseline titers (hazard ratio 0.4, P < .001).
Among the seropositive participants who did acquire a second SARS-CoV-2 infection, viral loads in mid-turbinate nasal swabs were about 10-fold lower than in seronegative recruits who acquired infections during follow-up.
“This finding suggests that some reinfected individuals could have a similar capacity to transmit infection as those who are infected for the first time. The rate at which reinfection occurs after vaccines and natural immunity is important for estimating the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to suppress the pandemic,” the investigators wrote.
Baseline neutralizing antibody titers were detected in 45 of the first 54 seropositive recruits who remained PCR negative throughout follow-up, but also in 6 of 19 seropositive participants who became infected during the 6 weeks of observation.
Lessons
Both Dr. Siedner and Dr. Gupta agreed with the authors that the risks for reinfection that were observed in young, physically fit people may differ for other populations, such as women (only 10% of seropositive recruits and 8% of seronegative recruits were female), older patients, or those who are immunocompromised.
Given that the adjusted odds ratio for reinfection in this study was nearly identical to that of a recent British study comparing infection rates between seropositive and seronegative health care workers, the risk of reinfection for other young adults and for the general population may be similar, Dr. Sealfon and colleagues wrote.
Adding to the challenge of reaching herd immunity is the observation that some patients who have recovered from COVID-19 are skeptical about the need for further protection.
“There are patients who feel like vaccination is of low benefit to them, and I think these are the same people who would be hesitant to get the vaccine anyway,” Dr. Gupta said.
Although no vaccine is perfect – the vaccine failure rate from the mRNA-based vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/Biontech is about 5% – the protections they afford are unmistakable, Dr. Siedner said.
“I think it’s important to make the distinction that most postvaccination infections by and large have been very mild,” he said. “In people with normal immune systems, we have not seen an onslaught of postvaccination infections requiring hospitalization. Even if people do get infected after vaccination, the vaccines protect people from severe infection, and that’s what we want them to do.”
The investigators stated, “Young adults, of whom a high proportion are asymptomatically infected and become seropositive in the absence of known infection, can be an important source of transmission to more vulnerable populations. Evaluating the protection against subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection conferred by seropositivity in young adults is important for determining the need for vaccinating previously infected individuals in this age group.”
The study was funded by the Defense Health Agency and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Dr. Sealfon, Dr. Siedner, and Dr. Gupta have no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Gupta is a member of the editorial advisory board for this publication.
Do your patients think that getting COVID-19 is fully protective against subsequent reinfection? Tell it to the Marines.
A study of U.S. Marine recruits on their way to boot camp at Parris Island, S.C., showed that those who were seropositive at baseline, indicating prior exposure to SARS-CoV-2, remained at some risk for reinfection. They had about one-fifth the risk of subsequent infection, compared with seronegative recruits during basic training, but reinfections did occur.
The study, by Stuart C. Sealfon, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, and colleagues, was published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Although antibodies induced by initial infection are largely protective, they do not guarantee effective SARS-CoV-2 neutralization activity or immunity against subsequent infection,” they wrote.
An infectious disease specialist who was not involved in the study said that the findings provide further evidence about the level of immunity acquired after an infection.
“It’s quite clear that reinfections do occur, they are of public health importance, and they’re something we need to be mindful of in terms of advising patients about whether a prior infection protects them from reinfection,” Mark Siedner, MD, MPH, a clinician and researcher in the division of infectious diseases at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
The study results reinforce that “not all antibodies are the same,” said Sachin Gupta, MD, an attending physician in pulmonary and critical care medicine at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif. “We’re seeing still that 10% of folks who have antibodies can get infected again,” he said in an interview.
CHARM initiative
Dr. Sealfon and colleagues presented an analysis of data from the ironically named CHARM (COVID-19 Health Action Response for Marines) prospective study.
CHARM included U.S. Marine recruits, most of them male, aged 18-20 years, who were instructed to follow a 2-week unsupervised quarantine at home, after which they reported to a Marine-supervised facility for an additional 2-week quarantine.
At baseline, participants were tested for SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G (IgG) seropositivity, defined as a dilution of 1:150 or more on receptor-binding domain and full-length spike protein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
The recruits filled out questionnaires asking them to report any of 14 specific COVID-19–related symptoms or any other unspecified symptom, as well as demographic information, risk factors, and a brief medical history.
Investigators tested recruits for SARS-CoV-2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay at weeks 0, 1, and 2 of quarantine, and any who had positive PCR results during quarantine were excluded.
Participants who had three negative swab PCR results during quarantine and a baseline serology test at the beginning of the supervised quarantine period – either seronegative or seropositive – then went on to enjoy their basic training at the Marine Corps Recruit Depot, Parris Island, S.C.
The participants were followed prospectively with PCR tests at weeks 2, 4, and 6 in both the seropositive and seronegative groups, and sera were obtained at the same time.
Holes in immunologic armor
Full data were available for a total of 189 participants who were seropositive and 2,247 who were seronegative at enrollment.
In all, 19 of 189 seropositive recruits (10%) had at least one PCR test positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection during the 6-week follow-up period. This translated into an incidence of 1.1 cases per person-year.
Of the 2,247 participants seronegative at baseline, 1,079 tested positive (6.2 cases per person-year; incidence rate ratio 0.18).
It appeared that antibodies provided some protection for seropositive recruits, as evidenced by a higher likelihood of infection among those with lower baseline full-length spike protein IgG titers than in those with higher baseline titers (hazard ratio 0.4, P < .001).
Among the seropositive participants who did acquire a second SARS-CoV-2 infection, viral loads in mid-turbinate nasal swabs were about 10-fold lower than in seronegative recruits who acquired infections during follow-up.
“This finding suggests that some reinfected individuals could have a similar capacity to transmit infection as those who are infected for the first time. The rate at which reinfection occurs after vaccines and natural immunity is important for estimating the proportion of the population that needs to be vaccinated to suppress the pandemic,” the investigators wrote.
Baseline neutralizing antibody titers were detected in 45 of the first 54 seropositive recruits who remained PCR negative throughout follow-up, but also in 6 of 19 seropositive participants who became infected during the 6 weeks of observation.
Lessons
Both Dr. Siedner and Dr. Gupta agreed with the authors that the risks for reinfection that were observed in young, physically fit people may differ for other populations, such as women (only 10% of seropositive recruits and 8% of seronegative recruits were female), older patients, or those who are immunocompromised.
Given that the adjusted odds ratio for reinfection in this study was nearly identical to that of a recent British study comparing infection rates between seropositive and seronegative health care workers, the risk of reinfection for other young adults and for the general population may be similar, Dr. Sealfon and colleagues wrote.
Adding to the challenge of reaching herd immunity is the observation that some patients who have recovered from COVID-19 are skeptical about the need for further protection.
“There are patients who feel like vaccination is of low benefit to them, and I think these are the same people who would be hesitant to get the vaccine anyway,” Dr. Gupta said.
Although no vaccine is perfect – the vaccine failure rate from the mRNA-based vaccines from Moderna and Pfizer/Biontech is about 5% – the protections they afford are unmistakable, Dr. Siedner said.
“I think it’s important to make the distinction that most postvaccination infections by and large have been very mild,” he said. “In people with normal immune systems, we have not seen an onslaught of postvaccination infections requiring hospitalization. Even if people do get infected after vaccination, the vaccines protect people from severe infection, and that’s what we want them to do.”
The investigators stated, “Young adults, of whom a high proportion are asymptomatically infected and become seropositive in the absence of known infection, can be an important source of transmission to more vulnerable populations. Evaluating the protection against subsequent SARS-CoV-2 infection conferred by seropositivity in young adults is important for determining the need for vaccinating previously infected individuals in this age group.”
The study was funded by the Defense Health Agency and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. Dr. Sealfon, Dr. Siedner, and Dr. Gupta have no conflicts of interest to report. Dr. Gupta is a member of the editorial advisory board for this publication.
FROM THE LANCET RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
Vaccinating homebound patients is an uphill battle

There are about 2 million to 4 million homebound patients in the United States, according to a webinar from The Trust for America’s Health, which was broadcast in March. But many of these individuals have not been vaccinated yet because of logistical challenges.
Some homebound COVID-19 immunization programs are administering Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to their patients, but many state, city, and local programs administered the Johnson & Johnson vaccine after it was cleared for use by the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021. The efficacy of the one-shot vaccine, as well as it being easier to store and ship than the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, makes getting it to homebound patients less challenging.
“With Pfizer and Moderna, transportation is a challenge because the temperature demands and the fragility of [messenger] RNA–based vaccines,” Brent Feorene, executive director of the American Academy of Home Care Medicine, said in an interview. That’s why [the Johnson & Johnson] vaccine held such promise – it’s less fragile, [can be stored in] higher temperatures, and was a one shot.”
Other hurdles to getting homebound patients vaccinated had already been in place prior to the 10-day-pause on using the J&J vaccine that occurred for federal agencies to consider possible serious side effects linked to it.
Many roadblocks to vaccination
Although many homebound patients can’t readily go out into the community and be exposed to the COVID-19 virus themselves, they are dependent on caregivers and family members who do go out into the community.
“Their friends, family, neighbors, home health aides, and other kinds of health care workers come into the home,” said Shawn Amer, clinical program director at Central Ohio Primary Care in Columbus.
Nurses from Ms. Amer’s practice vaccinated approximately ten homebound patients with the J&J vaccine through a pilot program in March. Then on April 24, nurses from Central Ohio Primary Care vaccinated just under 40 homebound patients and about a handful of their caregivers who were not able to get their vaccines elsewhere, according to Ms. Amer. This time they used the Pfizer vaccine and will be returning to these patients’ homes on May 15 to administer the second dose.
“Any time you are getting in the car and adding miles, it adds complexity,” Ms. Amer said.
“We called patients 24 to 36 hours before coming to their homes to make sure they were ready, but we learned that just because the healthcare power of attorney agrees to a patient getting vaccinated does not mean that patient will be willing to get the vaccine when the nurse shows up," she noted.
Ms. Amer elaborated that three patients with dementia refused the vaccine when nurses arrived at their home on April 24.
“We had to pivot and find other people,” Ms. Amer. Her practice ended up having to waste one shot.
Expenses are greater
The higher costs of getting homebound patients vaccinated is an additional hurdle to getting these vulnerable individuals protected by COVID-19 shots.
Vaccinating patients in their homes “doesn’t require a lot of technology, but it does require a lot of time” and the staffing expense becomes part of the challenge, Ms. Amer noted.
For each of the two days that Central Ohio Primary Care provides the Pfizer vaccine to homebound patients, the practice needs to pay seven nurses to administer the vaccine, Ms. Amer explained.
There have also been reports of organizations that administer the vaccines – which are free for patients because the federal government is paying for them – not being paid enough by Medicare to cover staff time and efforts to vaccinate patients in their homes, Kaiser Health News reported. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they pay $40 for the administration of a single-dose COVID-19 vaccine and, for COVID-19 vaccines requiring multiple doses, Medicare pays approximately $40 for each dose in the series. These rates were implemented after March 15. Before that date, the rates were even lower, with the Medicare reimbursement rates for initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines being $16.94 and final doses being $28.39.
William Dombi, president of the National Association for Home Care & Hospice, told Kaiser Health News that the actual cost of these homebound visits are closer to $150 or $160.
“The reimbursement for the injection is pretty minimal,” Mr. Feorene said. “So unless you’re a larger organization and able to have staff to deploy some of your smaller practices, just couldn’t afford to do it.”
Many homebound patients have also been unable to get the lifesaving shots because of logistical roadblocks and many practices not being able to do home visits.
“I think that initially when the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] came out with vaccine guidance for medical providers, they offered no guidance for in-home medical providers and we had to go back and ask for that, which they did produce,” Mr. Feorene said. “And we’re grateful for that. But I think just this general understanding that there is a population of folks that are [limited to their home], that they do receive medical care and other care in the home, and that we have to remember that the medical providers who provide care in the home are also primary care providers.”
Furthermore, trying to navigate or find programs delivering vaccines to the homebound can be difficult depending on where a patient lives.
While some programs have been launched on the country or city level – the New York Fire Department launched a pilot program to bring the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to homebound seniors – other programs have been spearheaded by hospital networks like Northwell and Mount Sinai. However, many of these hospital networks only reach out to people who already have a relationship with the hospital.
Ms Amer said identifying homebound patients and reaching out to them can be tough and can contribute to the logistics and time involved in setting patients up for the vaccine.
“Reaching some of these patients is difficult,” Ms. Amer noted. “Sometimes the best way to reach them or get a hold of them is through their caregiver. And so do you have the right phone number? Do you have the right name?”
Overcoming the challenges
With the absence of a national plan targeting homebound patients, many local initiatives were launched to help these individuals get vaccinated. Local fire department paramedics have gone door to door to administer the COVID-19 vaccine in cities like Chicago, New York, and Miami. The suspension of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine resulted in the suspension of in-home vaccinations for some people in New York City. However, the program resumed after the FDA and CDC lifted the pause on April 24. 
Health systems like Mount Sinai vaccinated approximately 530 people through the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program, including patients and their caregivers, according to Peter Gliatto, MD, associate director of the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program.
“In different cities, townships, and jurisdictions, different health departments and different provider groups are approaching [the distribution of the COVID-19 vaccine] slightly differently,” Ms. Amer said. So a lot of the decisions surrounding the distribution of shots are local or dependent on local resourcing.
People who live in rural areas present a unique challenge, but Mr. Feorene said reaching out to local emergency medical services or the local health departments can provide some insight on what their town is doing to vaccinate homebound patients.
“I think understanding what a [public health department] is doing would be the very first place to start,” Mr. Feorene said in an interview.
If a patient is bedridden and is mobile enough to sit in a car, Mr. Feorene also recommends finding out if there are vaccine fairs “within a reasonable driving distance.”
Ms. Amer said continuing this mission of getting homebound patients vaccinated is necessary for public health.
“Even if it’s going to take longer to vaccinate these homebound patients, we still have to make an effort. So much of the country’s vaccine efforts have been focused on getting as many shots in as many arms as quickly as possible. And that is definitely super important,” she said.
Ms. Amer is working with her practice’s primary care physicians to try to identify all of those patients who are functionally debilitated or unable to leave their home to get vaccinated and that Central Ohio Primary Care will vaccinate more homebound patients, she added.
The experts interviewed in this article have no conflicts.
Katie Lennon contributed to this report.
This article was updated 4/29/21.

There are about 2 million to 4 million homebound patients in the United States, according to a webinar from The Trust for America’s Health, which was broadcast in March. But many of these individuals have not been vaccinated yet because of logistical challenges.
Some homebound COVID-19 immunization programs are administering Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to their patients, but many state, city, and local programs administered the Johnson & Johnson vaccine after it was cleared for use by the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021. The efficacy of the one-shot vaccine, as well as it being easier to store and ship than the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, makes getting it to homebound patients less challenging.
“With Pfizer and Moderna, transportation is a challenge because the temperature demands and the fragility of [messenger] RNA–based vaccines,” Brent Feorene, executive director of the American Academy of Home Care Medicine, said in an interview. That’s why [the Johnson & Johnson] vaccine held such promise – it’s less fragile, [can be stored in] higher temperatures, and was a one shot.”
Other hurdles to getting homebound patients vaccinated had already been in place prior to the 10-day-pause on using the J&J vaccine that occurred for federal agencies to consider possible serious side effects linked to it.
Many roadblocks to vaccination
Although many homebound patients can’t readily go out into the community and be exposed to the COVID-19 virus themselves, they are dependent on caregivers and family members who do go out into the community.
“Their friends, family, neighbors, home health aides, and other kinds of health care workers come into the home,” said Shawn Amer, clinical program director at Central Ohio Primary Care in Columbus.
Nurses from Ms. Amer’s practice vaccinated approximately ten homebound patients with the J&J vaccine through a pilot program in March. Then on April 24, nurses from Central Ohio Primary Care vaccinated just under 40 homebound patients and about a handful of their caregivers who were not able to get their vaccines elsewhere, according to Ms. Amer. This time they used the Pfizer vaccine and will be returning to these patients’ homes on May 15 to administer the second dose.
“Any time you are getting in the car and adding miles, it adds complexity,” Ms. Amer said.
“We called patients 24 to 36 hours before coming to their homes to make sure they were ready, but we learned that just because the healthcare power of attorney agrees to a patient getting vaccinated does not mean that patient will be willing to get the vaccine when the nurse shows up," she noted.
Ms. Amer elaborated that three patients with dementia refused the vaccine when nurses arrived at their home on April 24.
“We had to pivot and find other people,” Ms. Amer. Her practice ended up having to waste one shot.
Expenses are greater
The higher costs of getting homebound patients vaccinated is an additional hurdle to getting these vulnerable individuals protected by COVID-19 shots.
Vaccinating patients in their homes “doesn’t require a lot of technology, but it does require a lot of time” and the staffing expense becomes part of the challenge, Ms. Amer noted.
For each of the two days that Central Ohio Primary Care provides the Pfizer vaccine to homebound patients, the practice needs to pay seven nurses to administer the vaccine, Ms. Amer explained.
There have also been reports of organizations that administer the vaccines – which are free for patients because the federal government is paying for them – not being paid enough by Medicare to cover staff time and efforts to vaccinate patients in their homes, Kaiser Health News reported. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they pay $40 for the administration of a single-dose COVID-19 vaccine and, for COVID-19 vaccines requiring multiple doses, Medicare pays approximately $40 for each dose in the series. These rates were implemented after March 15. Before that date, the rates were even lower, with the Medicare reimbursement rates for initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines being $16.94 and final doses being $28.39.
William Dombi, president of the National Association for Home Care & Hospice, told Kaiser Health News that the actual cost of these homebound visits are closer to $150 or $160.
“The reimbursement for the injection is pretty minimal,” Mr. Feorene said. “So unless you’re a larger organization and able to have staff to deploy some of your smaller practices, just couldn’t afford to do it.”
Many homebound patients have also been unable to get the lifesaving shots because of logistical roadblocks and many practices not being able to do home visits.
“I think that initially when the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] came out with vaccine guidance for medical providers, they offered no guidance for in-home medical providers and we had to go back and ask for that, which they did produce,” Mr. Feorene said. “And we’re grateful for that. But I think just this general understanding that there is a population of folks that are [limited to their home], that they do receive medical care and other care in the home, and that we have to remember that the medical providers who provide care in the home are also primary care providers.”
Furthermore, trying to navigate or find programs delivering vaccines to the homebound can be difficult depending on where a patient lives.
While some programs have been launched on the country or city level – the New York Fire Department launched a pilot program to bring the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to homebound seniors – other programs have been spearheaded by hospital networks like Northwell and Mount Sinai. However, many of these hospital networks only reach out to people who already have a relationship with the hospital.
Ms Amer said identifying homebound patients and reaching out to them can be tough and can contribute to the logistics and time involved in setting patients up for the vaccine.
“Reaching some of these patients is difficult,” Ms. Amer noted. “Sometimes the best way to reach them or get a hold of them is through their caregiver. And so do you have the right phone number? Do you have the right name?”
Overcoming the challenges
With the absence of a national plan targeting homebound patients, many local initiatives were launched to help these individuals get vaccinated. Local fire department paramedics have gone door to door to administer the COVID-19 vaccine in cities like Chicago, New York, and Miami. The suspension of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine resulted in the suspension of in-home vaccinations for some people in New York City. However, the program resumed after the FDA and CDC lifted the pause on April 24. 
Health systems like Mount Sinai vaccinated approximately 530 people through the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program, including patients and their caregivers, according to Peter Gliatto, MD, associate director of the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program.
“In different cities, townships, and jurisdictions, different health departments and different provider groups are approaching [the distribution of the COVID-19 vaccine] slightly differently,” Ms. Amer said. So a lot of the decisions surrounding the distribution of shots are local or dependent on local resourcing.
People who live in rural areas present a unique challenge, but Mr. Feorene said reaching out to local emergency medical services or the local health departments can provide some insight on what their town is doing to vaccinate homebound patients.
“I think understanding what a [public health department] is doing would be the very first place to start,” Mr. Feorene said in an interview.
If a patient is bedridden and is mobile enough to sit in a car, Mr. Feorene also recommends finding out if there are vaccine fairs “within a reasonable driving distance.”
Ms. Amer said continuing this mission of getting homebound patients vaccinated is necessary for public health.
“Even if it’s going to take longer to vaccinate these homebound patients, we still have to make an effort. So much of the country’s vaccine efforts have been focused on getting as many shots in as many arms as quickly as possible. And that is definitely super important,” she said.
Ms. Amer is working with her practice’s primary care physicians to try to identify all of those patients who are functionally debilitated or unable to leave their home to get vaccinated and that Central Ohio Primary Care will vaccinate more homebound patients, she added.
The experts interviewed in this article have no conflicts.
Katie Lennon contributed to this report.
This article was updated 4/29/21.

There are about 2 million to 4 million homebound patients in the United States, according to a webinar from The Trust for America’s Health, which was broadcast in March. But many of these individuals have not been vaccinated yet because of logistical challenges.
Some homebound COVID-19 immunization programs are administering Moderna and Pfizer vaccines to their patients, but many state, city, and local programs administered the Johnson & Johnson vaccine after it was cleared for use by the Food and Drug Administration in February 2021. The efficacy of the one-shot vaccine, as well as it being easier to store and ship than the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines, makes getting it to homebound patients less challenging.
“With Pfizer and Moderna, transportation is a challenge because the temperature demands and the fragility of [messenger] RNA–based vaccines,” Brent Feorene, executive director of the American Academy of Home Care Medicine, said in an interview. That’s why [the Johnson & Johnson] vaccine held such promise – it’s less fragile, [can be stored in] higher temperatures, and was a one shot.”
Other hurdles to getting homebound patients vaccinated had already been in place prior to the 10-day-pause on using the J&J vaccine that occurred for federal agencies to consider possible serious side effects linked to it.
Many roadblocks to vaccination
Although many homebound patients can’t readily go out into the community and be exposed to the COVID-19 virus themselves, they are dependent on caregivers and family members who do go out into the community.
“Their friends, family, neighbors, home health aides, and other kinds of health care workers come into the home,” said Shawn Amer, clinical program director at Central Ohio Primary Care in Columbus.
Nurses from Ms. Amer’s practice vaccinated approximately ten homebound patients with the J&J vaccine through a pilot program in March. Then on April 24, nurses from Central Ohio Primary Care vaccinated just under 40 homebound patients and about a handful of their caregivers who were not able to get their vaccines elsewhere, according to Ms. Amer. This time they used the Pfizer vaccine and will be returning to these patients’ homes on May 15 to administer the second dose.
“Any time you are getting in the car and adding miles, it adds complexity,” Ms. Amer said.
“We called patients 24 to 36 hours before coming to their homes to make sure they were ready, but we learned that just because the healthcare power of attorney agrees to a patient getting vaccinated does not mean that patient will be willing to get the vaccine when the nurse shows up," she noted.
Ms. Amer elaborated that three patients with dementia refused the vaccine when nurses arrived at their home on April 24.
“We had to pivot and find other people,” Ms. Amer. Her practice ended up having to waste one shot.
Expenses are greater
The higher costs of getting homebound patients vaccinated is an additional hurdle to getting these vulnerable individuals protected by COVID-19 shots.
Vaccinating patients in their homes “doesn’t require a lot of technology, but it does require a lot of time” and the staffing expense becomes part of the challenge, Ms. Amer noted.
For each of the two days that Central Ohio Primary Care provides the Pfizer vaccine to homebound patients, the practice needs to pay seven nurses to administer the vaccine, Ms. Amer explained.
There have also been reports of organizations that administer the vaccines – which are free for patients because the federal government is paying for them – not being paid enough by Medicare to cover staff time and efforts to vaccinate patients in their homes, Kaiser Health News reported. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they pay $40 for the administration of a single-dose COVID-19 vaccine and, for COVID-19 vaccines requiring multiple doses, Medicare pays approximately $40 for each dose in the series. These rates were implemented after March 15. Before that date, the rates were even lower, with the Medicare reimbursement rates for initial doses of COVID-19 vaccines being $16.94 and final doses being $28.39.
William Dombi, president of the National Association for Home Care & Hospice, told Kaiser Health News that the actual cost of these homebound visits are closer to $150 or $160.
“The reimbursement for the injection is pretty minimal,” Mr. Feorene said. “So unless you’re a larger organization and able to have staff to deploy some of your smaller practices, just couldn’t afford to do it.”
Many homebound patients have also been unable to get the lifesaving shots because of logistical roadblocks and many practices not being able to do home visits.
“I think that initially when the [Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] came out with vaccine guidance for medical providers, they offered no guidance for in-home medical providers and we had to go back and ask for that, which they did produce,” Mr. Feorene said. “And we’re grateful for that. But I think just this general understanding that there is a population of folks that are [limited to their home], that they do receive medical care and other care in the home, and that we have to remember that the medical providers who provide care in the home are also primary care providers.”
Furthermore, trying to navigate or find programs delivering vaccines to the homebound can be difficult depending on where a patient lives.
While some programs have been launched on the country or city level – the New York Fire Department launched a pilot program to bring the Johnson & Johnson vaccine to homebound seniors – other programs have been spearheaded by hospital networks like Northwell and Mount Sinai. However, many of these hospital networks only reach out to people who already have a relationship with the hospital.
Ms Amer said identifying homebound patients and reaching out to them can be tough and can contribute to the logistics and time involved in setting patients up for the vaccine.
“Reaching some of these patients is difficult,” Ms. Amer noted. “Sometimes the best way to reach them or get a hold of them is through their caregiver. And so do you have the right phone number? Do you have the right name?”
Overcoming the challenges
With the absence of a national plan targeting homebound patients, many local initiatives were launched to help these individuals get vaccinated. Local fire department paramedics have gone door to door to administer the COVID-19 vaccine in cities like Chicago, New York, and Miami. The suspension of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine resulted in the suspension of in-home vaccinations for some people in New York City. However, the program resumed after the FDA and CDC lifted the pause on April 24. 
Health systems like Mount Sinai vaccinated approximately 530 people through the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program, including patients and their caregivers, according to Peter Gliatto, MD, associate director of the Mount Sinai Visiting Doctors Program.
“In different cities, townships, and jurisdictions, different health departments and different provider groups are approaching [the distribution of the COVID-19 vaccine] slightly differently,” Ms. Amer said. So a lot of the decisions surrounding the distribution of shots are local or dependent on local resourcing.
People who live in rural areas present a unique challenge, but Mr. Feorene said reaching out to local emergency medical services or the local health departments can provide some insight on what their town is doing to vaccinate homebound patients.
“I think understanding what a [public health department] is doing would be the very first place to start,” Mr. Feorene said in an interview.
If a patient is bedridden and is mobile enough to sit in a car, Mr. Feorene also recommends finding out if there are vaccine fairs “within a reasonable driving distance.”
Ms. Amer said continuing this mission of getting homebound patients vaccinated is necessary for public health.
“Even if it’s going to take longer to vaccinate these homebound patients, we still have to make an effort. So much of the country’s vaccine efforts have been focused on getting as many shots in as many arms as quickly as possible. And that is definitely super important,” she said.
Ms. Amer is working with her practice’s primary care physicians to try to identify all of those patients who are functionally debilitated or unable to leave their home to get vaccinated and that Central Ohio Primary Care will vaccinate more homebound patients, she added.
The experts interviewed in this article have no conflicts.
Katie Lennon contributed to this report.
This article was updated 4/29/21.
Boosting the presence of darker skin in rheumatology education
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Studies are flagging racial and ethnic disparities in rheumatology training materials, pointing to a need to boost representation of darker skin tones and better educate physicians in evaluating this cohort.
Not enough is known about these disparities in rheumatology education, despite the fact that minorities make up 40% of the population in the United States.
The problem starts with books and references used in medical schools, Lynn McKinley-Grant, MD, immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and associate professor of dermatology at Howard University, Washington, said in an interview. “In the medical literature there has been a dearth of images in skin of color in all specialties,” she said. With an increased diversity in the U.S. population, there is a need for health care providers to be able to recognize disease patterns in all skin types.” If a physician is training at an institution where there are not many patients of color in the community, the rheumatologists are even more limited in terms of their clinical experience.
This lack of training in diagnosis of disease has serious clinical repercussions, as seen in COVID cases, Dr. McKinley-Grant noted. “You end up not being able to recognize early erythema, jaundice, anemia, or hypoxemia because those conditions are a different color or pattern in the darker skin types. This can lead to errors in treatment, diagnosis, and medical care, resulting in increased morbidity and mortality.”
Studies point to education gaps
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis called attention to this issue at the American College of Rhematology’s Convergence 2020 conference.
“Patients of color with lupus are especially vulnerable as they often carry a greater disease burden, yet studies show that individuals with darker skin tones are underrepresented in medical educational materials,” Vijay Kannuthurai, MD, and colleagues wrote in their study abstract. The team surveyed 132 providers in St. Louis, Mo., on their confidence in evaluating any rash, and rashes in patients with lupus and varied skin tones.
Participating clinicians, mostly rheumatologists, dermatologists, or internists, had a higher confidence level in diagnosing any rash versus lupus rashes, but were considerably less confident in diagnosing lupus rash on darker skin, compared with those on fair skin. This represents “a disparity between provider confidence and the patient population lupus traditionally affects,” the investigators concluded.
Another recent study found evidence of disparities in clinical education resources. “The lack of dark skin representation among rheumatology educational materials contributes to the implicit bias and structural racism present in medical education by promoting White-only models of disease,” lead author Adrienne Strait, a medical student at the University of California, San Francisco, said in an interview. “Given that rheumatic diseases disproportionately impact racial and ethnic minorities, we felt it was important to examine the representation of these groups within rheumatology training resources.”
She and her colleagues gathered images of rheumatic diseases from four major databases: the American College of Rheumatology’s Image Library, UpToDate, the New England Journal of Medicine Images in Clinical Medicine and Clinical Cases filtered by “Rheumatology,” and the 9th edition of Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. They used Fitzpatrick’s skin phototypes to independently code images depicting skin as “light” (skin types I-IV), “dark” (skin types V-VI), or “indeterminate,” focusing on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis, two conditions with a known connection to racial and ethnic health disparities.
Taking into account the high incidence of sarcoidosis and SLE in Black patients when compared with White patients, the investigators did a secondary analysis that excluded these cases.
Among 1,043 patient images studied, just 13.4% represented dark skin, compared with 84% that represented light skin. More than 2% represented an indeterminate skin color. Comparing dark-skin representation in the clinical images and SLE images with the representation of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals in the United States and within lupus cases nationally, the investigators found significant underrepresentation of dark skin.
Only 4.2% of RA images had dark-skin representation, making RA one of the diseases with the lowest representation in the study, along with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the spondyloarthropathies, and Kawasaki disease. “Representation of dark skin in SLE was also lower than the proportion of Black individuals in SLE studies,” the investigators noted. Overall, representation of dark skin in SLE images was just 22.6%. Sarcoidosis comparatively had the largest representation of dark-skin images (69.6%, n = 32).
“Excluding sarcoidosis and SLE images, the overall representation of dark skin was 9.4% (n = 84), which was significantly lower than the proportion of Asian, Native American, and Black individuals within the U.S. Census population,” according to Ms. Strait and her associates. UpToDate contained the largest proportion of images of dark skin respective to other databases, whereas Kelley’s Textbook had the smallest.
Actionable steps
Many physicians are willing to improve upon their skills in identifying conditions on darker skin, as the study by Dr. Kannuthurai and associates suggests. Overall, 93% of the survey’s participants wanted to learn more about rashes in patients of color. “Future educational interventions may help practitioners improve their confidence when diagnosing rashes in lupus patients” with darker skin, they suggested.
Ms. Strait and her colleagues recommended a series of actionable steps to improve diversity and equity of dark skin tone representation in rheumatology curricula.
Editors of educational resources, for example, should make image diversity a priority for those diseases that are most commonly associated with cutaneous manifestations, such as SLE, vasculitis, inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, sarcoidosis, and psoriasis. They also called for educators in academic rheumatology programs to collaborate to improve diversity in resources used at the undergraduate and graduate medical education level.
Efforts should take place at the local, regional, and national level to publicly discuss and educate clinicians about rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. Speakers at rheumatology conferences should strive to educate learners about presentations of rheumatic diseases in individuals of color. The ACR in the meantime could establish a task force to enhance racial and ethnic diversity in their image library and other published resources.
“These steps may improve provider recognition and diagnosis of rheumatic disease manifestations in skin of color, which may in turn reduce health disparities among racial and ethnic minority groups,” Ms. Strait said.
Beth L. Jonas, MD, chair of the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues, called the findings of this study “timely and important.” The researchers highlighted a deficiency in rheumatology training materials that needs addressing, she said in an interview. “I definitely agree that ACR needs to be mindful of this. There’s no doubt that we need to take these recommendations and move along these lines.”
The ACR took a first step in 2020 with the creation of a diversity, equity, and inclusion committee. “We are undergoing a college-wide look at what we do, with an eye toward inclusion. There is a strong interest in addressing health disparities and being an equitable and inclusive community of rheumatology health care professionals,” said Dr. Jonas, chief of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology.
The American Academy of Dermatology is also working to improve the image library with images of disease in skin of color. “Everyone’s jumping on this now,” Dr. McKinley-Grant observed. The medical profession can’t afford not to. It’s a life-threatening issue when rheumatoid arthritis and other diseases in people of color aren’t diagnosed early and correctly, she added.
Technologies seek to reduce bias
While many organizations are taking steps to improve representation of darker skin images, VisualDx has taken the lead on this, she said. “They’ve been doing this for years now. There are over 14,000 images of disease in skin of color, including all the rheumatologic diseases. There’s a mobile app and desktop decision support system, and it is very popular. A majority of medical schools have this as a library resource, and hospital systems license it for EHR integration.” Doctors can also get it individually. This enables them to share images and handouts of a diagnosis and select images of patients of color, said Dr. McKinley-Grant, who uses the VisualDx smartphone app DermExpert, which is an app for nondermatologists that features an image library of skin lesions, including darker-skin images.
ProjectIMPACT, powered by VisualDx, is another effort to support reducing health care bias in darker skin. The project is a collaboration between the New England Journal of Medicine Group and the Skin Of Color Society. According to Dr. McKinley-Grant, the organizers are building awareness of the importance of reducing the educational and clinical gaps in diagnosing patients of color and trying to get students and educators to pledge to take meaningful steps and to have real-world impact.
This isn’t just exclusive to dermatology and rheumatology – it involves all medical specialties, she stressed.
ProjectIMPACT isn’t just a resource for physicians, she continued. Librarians can also use it to develop more resources on skin of color.
The Skin Of Color Society and VisualDx have also partnered with the NEJM Group to develop a comprehensive virtual series on the impact of skin color and ethnicity on clinical research. The four-part series addresses structural racism and racial bias in medicine, hair disorders in people of color, pigmentary disorders, keloids, COVID-19 comorbidities, and cutaneous manifestations of systemic diseases in children and adults.
Nuances of recognizing disease
As a medical student, Dr. McKinley-Grant said she was fortunate to attend the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Lambarene, Gabon, on a fellowship. For 3 months, she gained a wealth of experience examining only African patients with brown skin.
In her other training in medicine, “I’ve been at institutions with diverse populations, in Boston, New York, and Washington,” learning more about all different skin pigments.
This type of training should be more widely available, especially now, with COVID-19 producing new manifestations of skin lesions, she emphasized. Such efforts involve a diversification of images physicians are being trained on so that they can recognize the same disease in a person of color.
“Doctors have to be able to recognize different colors, different shades of brown and shades of white. Not all white skin is the same color,” she noted. In looking at a rash or lesion, “you have to learn how to discern differences in the background color of the skin, which is determined by melanin in the skin (Fitzpatrick skin types I-VI) and by what’s going on in the blood, such as how much oxygen and hemoglobin the patient has in their blood.” Inflammation and infection (erythema) will appear more violaceous in IV-VI skin types, for example.
At the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, a group of students and faculty have created a dermatology image library to address the deficiency in the availability of images for teaching purposes. “Our medical students recognized the gap and started this,” Dr. Jonas said. Julie Mervak, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, is spearheading this effort, with students Linnea Westerkam and Anuj Pranav Sanghvi.
“I understand that others around the country are working on similar initiatives,” Dr. Jonas said.
None of the sources for this story had any relevant disclosures.
Most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases have sufficient response to COVID-19 vaccination
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies are trouble spots
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
Although most patients with chronic inflammatory diseases mounted immune responses after two doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, glucocorticoids and B-cell–depleting therapies markedly reduced the response, according to a recently published preprint of a new study.
The study, published on MedRxiv and not yet peer reviewed, involved a prospective look at 133 patients with chronic inflammatory disease (CID) and 53 patients with healthy immune systems at Washington University, St. Louis, and the University of California, San Francisco. It is regarded as the largest and most detailed study yet in how vaccines perform in people with immune-mediated inflammatory disease. The patients were enrolled between December 2020 and March 2021, and the most common diseases were inflammatory bowel disease (32%), rheumatoid arthritis (29%), spondyloarthritis (15%), and systemic lupus erythematosus (11%).
A ‘modest’ reduction in antibody response
Senior author Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of the department of medicine at Washington University, said the overall results so far are encouraging.
“Most patients with an autoimmune disease that are on immunosuppression can mount antibody responses,” he said. “We’re seeing the majority of our subjects respond.”
The immune-healthy controls and most of the patients with CID had a robust immune response against the spike protein, although the CID group had a mean reduction in antibody titers that was three times lower than the controls (P = .0092). The CID group similarly had a 2.7-fold reduction in preventing neutralization, or halting the virus’ ability to infect (P < .0001), researchers reported.
This reduction in response is “modest,” he said.
“Is the level of reduction going to be detrimental for protection? Time will tell,” he said, adding that researchers anticipate that it won’t have a critical effect on protection because responses tended to be within the range of the immunocompetent controls, who themselves had wildly varied antibody titers across a 20-fold range. “ ‘Optimal’ isn’t necessarily the same as ‘sufficient.’ ”
Type of medication has big impact on antibody titers
But there was a wide variety of effects on the immune response depending on the medication. Glucorticoids resulted in a response that was 10 times lower than the immune-healthy controls, as well as fewer circulating plasmablasts after vaccination. Researchers found that 98% of controls were seropositive for antibody, compared with 92% of those with CID who were not taking prednisone, and 65% of CID patients on prednisone (P = .0006 and .0115, respectively). Prevention of neutralization of the virus was similarly reduced in those groups, compared with the controls. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 15 patients. These effects were seen regardless of the dose.
“We would’ve anticipated this would have been dose dependent, so this was a little bit surprising,” Dr. Kim said.
B-cell–depleting therapies, such as rituximab (Rituxan) and ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), reduced antibody titers by 36 times, compared with controls (P < .0001), with a similar reduction in preventing infection (P = .0066), the researchers found. The reduction in antibody titers was the most pronounced among those who had received B-cell–depleting therapies within the previous 6 months. Dr. Kim noted this was a small sample size, with about 10 patients.
CID study subjects taking an antimetabolite, including methotrexate, had an average of a two- to threefold reduction in antibody titers and in neutralization (P = .0006). This reduction was greatest with methotrexate, researchers found (P = .0027).
JAK inhibitors also significantly reduced antibody titers (P = .0066), but the reduction in neutralization of the virus was not significant. In addition, researchers found a reduction in antibody titers, the prevention of viral infection, and circulating plasmablasts among those on tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, compared with controls, but these were insignificant statistically except for virus neutralization.
Dr. Kim said he hopes the glucocorticoid data spur physicians to try harder to wean patients off the drugs, when possible, in keeping with recommendations already in place.
“The general culture in rheumatology has been very lax about the need to reduce glucocorticoids,” he said. “This reinvigorates that call.” Questions about possible drug holidays from glucocorticoids remain, regarding how long a holiday would be needed, he said. He noted that many patients on glucocorticoids nonetheless mounted responses.
Those on B-cell–depleting therapies present a “much more difficult” question, he said. Some patients possibly could wait a bit longer than their normal, every-6-month schedule, but it’s an individual decision, he said. Since a booster of influenza vaccine has been found to enhance the response even within the 6-month window among ocrelizumab patients, a booster of COVID-19 vaccine might also help, although this remains to be studied.
The study group has already increased its sample size and is looking at adverse reactions and long-term immune responses, Dr. Kim said.
Encouraging, rather than discouraging, results
Leonard Calabrese, DO, professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, said the findings shouldn’t discourage clinicians from encouraging vaccination.
“There’s still a preponderance of people who will develop a robust antibody vaccine response,” he said.
He cautioned that the findings look only at antibodies to the spike protein and at plasmablasts. The reduction in these titers is “of concern,” he said, but “we don’t really know with certainty what are the effects of these drugs, and these data are on the overall biologic protective effect of the vaccine. There’s much more to a vaccine response than anti–spike protein and plasmablasts,” including cell-mediated immune response.
For an individual patient, the findings “mean a lot,” he said.
“I think that people who are on significant prednisone and B-cell–depleting agents, I think you have to share with them that there’s a reasonable chance that you’re not going to be making a response similar to healthy people,” he said. “Thus, even with your vaccine, we’re not going to cut you loose to do things that are violating social distancing and group settings. … Should you be hugging your grandchildren if you’re a rituximab vaccine recipient? I think I would wait until we have a little bit more data.”
Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of ophthalmology at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, where he studies vaccinations in the immunocompromised, said that glucocorticoids tend to have little effect on vaccinations generally at low doses.
When effects are seen they can be difficult to interpret, he said.
“It’s hard to extricate that from the effect of the underlying disease,” he said. The drug can be a proxy for worse disease control.
Although it’s a small study, it’s reassuring that overall the responses were similar to healthy controls.
For B-cell–depleting therapies, his usual guidance is to not give vaccine until a patient is at least 3 months out from their last dose, and not to restart until at least 2 weeks after vaccination.
“It’s not surprising that some of these DMARDs [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs] do negatively affect vaccine response, particularly B-cell–depletion therapy. We need to do some studies to find a way to overcome that, or optimize delivery of the vaccine.”
Dr. Kim reported participating in consulting, advisory board, or speaker’s bureau for Alexion, Aurinia, Annexon Biosciences, Exagen Diagnostics, and GlaxoSmithKline, and receiving funding under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Winthrop reported receiving consulting fees from Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Novartis, and research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer. Dr. Calabrese reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM MEDRXIV
Ten reasons airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 appears airtight
The scientific evidence for airborne transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from different researchers all point in the same direction – that infectious aerosols are the principal means of person-to-person transmission, according to experts.
Not that it’s without controversy.
The science backing aerosol transmission “is clear-cut, but it is not accepted in many circles,” Trisha Greenhalgh, PhD, said in an interview.
“In particular, some in the evidence-based medicine movement and some infectious diseases clinicians are remarkably resistant to the evidence,” added Dr. Greenhalgh, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
“It’s very hard to see why, since the evidence all stacks up,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“The scientific evidence on spread from both near-field and far-field aerosols has been clear since early on in the pandemic, but there was resistance to acknowledging this in some circles, including the medical journals,” Joseph G. Allen, DSc, MPH, told this news organization when asked to comment.
“This is the week the dam broke. Three new commentaries came out … in top medical journals – BMJ, The Lancet, JAMA – all making the same point that aerosols are the dominant mode of transmission,” added Dr. Allen, associate professor of exposure assessment science at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues point to an increase in COVID-19 cases in the aftermath of so-called “super-spreader” events, spread of SARS-CoV-2 to people across different hotel rooms, and the relatively lower transmission detected after outdoor events.
Top 10 reasons
They outlined 10 scientific reasons backing airborne transmission in a commentary published online April 15 in The Lancet:
- The dominance of airborne transmission is supported by long-range transmission observed at super-spreader events.
- Long-range transmission has been reported among rooms at COVID-19 quarantine hotels, settings where infected people never spent time in the same room.
- Asymptomatic individuals account for an estimated 33%-59% of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and could be spreading the virus through speaking, which produces thousands of aerosol particles and few large droplets.
- Transmission outdoors and in well-ventilated indoor spaces is lower than in enclosed spaces.
- Nosocomial infections are reported in health care settings where protective measures address large droplets but not aerosols.
- Viable SARS-CoV-2 has been detected in the air of hospital rooms and in the car of an infected person.
- Investigators found SARS-CoV-2 in hospital air filters and building ducts.
- It’s not just humans – infected animals can infect animals in other cages connected only through an air duct.
- No strong evidence refutes airborne transmission, and contact tracing supports secondary transmission in crowded, poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
- Only limited evidence supports other means of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, including through fomites or large droplets.
“We thought we’d summarize [the evidence] to clarify the arguments for and against. We looked hard for evidence against but found none,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“Although other routes can contribute, we believe that the airborne route is likely to be dominant,” the authors note.
The evidence on airborne transmission was there very early on but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and others repeated the message that the primary concern was droplets and fomites.
Response to a review
The top 10 list is also part rebuttal of a systematic review funded by the WHO and published last month that points to inconclusive evidence for airborne transmission. The researchers involved with that review state that “the lack of recoverable viral culture samples of SARS-CoV-2 prevents firm conclusions to be drawn about airborne transmission.”
However, Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues note that “this conclusion, and the wide circulation of the review’s findings, is concerning because of the public health implications.”
The current authors also argue that enough evidence already exists on airborne transmission. “Policy should change. We don’t need more research on this topic; we need different policy,” Dr. Greenhalgh said. “We need ventilation front and center, air filtration when necessary, and better-fitting masks worn whenever indoors.”
Dr. Allen agreed that guidance hasn’t always kept pace with the science. “With all of the new evidence accumulated on airborne transmission since last winter, there is still widespread confusion in the public about modes of transmission,” he said. Dr. Allen also serves as commissioner of The Lancet COVID-19 Commission and is chair of the commission’s Task Force on Safe Work, Safe Schools, and Safe Travel.
“It was only just last week that CDC pulled back on guidance on ‘deep cleaning’ and in its place correctly said that the risk from touching surfaces is low,” he added. “The science has been clear on this for over a year, but official guidance was only recently updated.”
As a result, many companies and organizations continued to focus on “hygiene theatre,” Dr. Allen said, “wasting resources on overcleaning surfaces. Unbelievably, many schools still close for an entire day each week for deep cleaning and some still quarantine library books. The message that shared air is the problem, not shared surfaces, is a message that still needs to be reinforced.”
The National Institute for Health Research, Economic and Social Research Council, and Wellcome support Dr. Greenhalgh’s research. Dr. Greenhalgh and Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The scientific evidence for airborne transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from different researchers all point in the same direction – that infectious aerosols are the principal means of person-to-person transmission, according to experts.
Not that it’s without controversy.
The science backing aerosol transmission “is clear-cut, but it is not accepted in many circles,” Trisha Greenhalgh, PhD, said in an interview.
“In particular, some in the evidence-based medicine movement and some infectious diseases clinicians are remarkably resistant to the evidence,” added Dr. Greenhalgh, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
“It’s very hard to see why, since the evidence all stacks up,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“The scientific evidence on spread from both near-field and far-field aerosols has been clear since early on in the pandemic, but there was resistance to acknowledging this in some circles, including the medical journals,” Joseph G. Allen, DSc, MPH, told this news organization when asked to comment.
“This is the week the dam broke. Three new commentaries came out … in top medical journals – BMJ, The Lancet, JAMA – all making the same point that aerosols are the dominant mode of transmission,” added Dr. Allen, associate professor of exposure assessment science at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues point to an increase in COVID-19 cases in the aftermath of so-called “super-spreader” events, spread of SARS-CoV-2 to people across different hotel rooms, and the relatively lower transmission detected after outdoor events.
Top 10 reasons
They outlined 10 scientific reasons backing airborne transmission in a commentary published online April 15 in The Lancet:
- The dominance of airborne transmission is supported by long-range transmission observed at super-spreader events.
- Long-range transmission has been reported among rooms at COVID-19 quarantine hotels, settings where infected people never spent time in the same room.
- Asymptomatic individuals account for an estimated 33%-59% of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and could be spreading the virus through speaking, which produces thousands of aerosol particles and few large droplets.
- Transmission outdoors and in well-ventilated indoor spaces is lower than in enclosed spaces.
- Nosocomial infections are reported in health care settings where protective measures address large droplets but not aerosols.
- Viable SARS-CoV-2 has been detected in the air of hospital rooms and in the car of an infected person.
- Investigators found SARS-CoV-2 in hospital air filters and building ducts.
- It’s not just humans – infected animals can infect animals in other cages connected only through an air duct.
- No strong evidence refutes airborne transmission, and contact tracing supports secondary transmission in crowded, poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
- Only limited evidence supports other means of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, including through fomites or large droplets.
“We thought we’d summarize [the evidence] to clarify the arguments for and against. We looked hard for evidence against but found none,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“Although other routes can contribute, we believe that the airborne route is likely to be dominant,” the authors note.
The evidence on airborne transmission was there very early on but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and others repeated the message that the primary concern was droplets and fomites.
Response to a review
The top 10 list is also part rebuttal of a systematic review funded by the WHO and published last month that points to inconclusive evidence for airborne transmission. The researchers involved with that review state that “the lack of recoverable viral culture samples of SARS-CoV-2 prevents firm conclusions to be drawn about airborne transmission.”
However, Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues note that “this conclusion, and the wide circulation of the review’s findings, is concerning because of the public health implications.”
The current authors also argue that enough evidence already exists on airborne transmission. “Policy should change. We don’t need more research on this topic; we need different policy,” Dr. Greenhalgh said. “We need ventilation front and center, air filtration when necessary, and better-fitting masks worn whenever indoors.”
Dr. Allen agreed that guidance hasn’t always kept pace with the science. “With all of the new evidence accumulated on airborne transmission since last winter, there is still widespread confusion in the public about modes of transmission,” he said. Dr. Allen also serves as commissioner of The Lancet COVID-19 Commission and is chair of the commission’s Task Force on Safe Work, Safe Schools, and Safe Travel.
“It was only just last week that CDC pulled back on guidance on ‘deep cleaning’ and in its place correctly said that the risk from touching surfaces is low,” he added. “The science has been clear on this for over a year, but official guidance was only recently updated.”
As a result, many companies and organizations continued to focus on “hygiene theatre,” Dr. Allen said, “wasting resources on overcleaning surfaces. Unbelievably, many schools still close for an entire day each week for deep cleaning and some still quarantine library books. The message that shared air is the problem, not shared surfaces, is a message that still needs to be reinforced.”
The National Institute for Health Research, Economic and Social Research Council, and Wellcome support Dr. Greenhalgh’s research. Dr. Greenhalgh and Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The scientific evidence for airborne transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from different researchers all point in the same direction – that infectious aerosols are the principal means of person-to-person transmission, according to experts.
Not that it’s without controversy.
The science backing aerosol transmission “is clear-cut, but it is not accepted in many circles,” Trisha Greenhalgh, PhD, said in an interview.
“In particular, some in the evidence-based medicine movement and some infectious diseases clinicians are remarkably resistant to the evidence,” added Dr. Greenhalgh, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England).
“It’s very hard to see why, since the evidence all stacks up,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“The scientific evidence on spread from both near-field and far-field aerosols has been clear since early on in the pandemic, but there was resistance to acknowledging this in some circles, including the medical journals,” Joseph G. Allen, DSc, MPH, told this news organization when asked to comment.
“This is the week the dam broke. Three new commentaries came out … in top medical journals – BMJ, The Lancet, JAMA – all making the same point that aerosols are the dominant mode of transmission,” added Dr. Allen, associate professor of exposure assessment science at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues point to an increase in COVID-19 cases in the aftermath of so-called “super-spreader” events, spread of SARS-CoV-2 to people across different hotel rooms, and the relatively lower transmission detected after outdoor events.
Top 10 reasons
They outlined 10 scientific reasons backing airborne transmission in a commentary published online April 15 in The Lancet:
- The dominance of airborne transmission is supported by long-range transmission observed at super-spreader events.
- Long-range transmission has been reported among rooms at COVID-19 quarantine hotels, settings where infected people never spent time in the same room.
- Asymptomatic individuals account for an estimated 33%-59% of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and could be spreading the virus through speaking, which produces thousands of aerosol particles and few large droplets.
- Transmission outdoors and in well-ventilated indoor spaces is lower than in enclosed spaces.
- Nosocomial infections are reported in health care settings where protective measures address large droplets but not aerosols.
- Viable SARS-CoV-2 has been detected in the air of hospital rooms and in the car of an infected person.
- Investigators found SARS-CoV-2 in hospital air filters and building ducts.
- It’s not just humans – infected animals can infect animals in other cages connected only through an air duct.
- No strong evidence refutes airborne transmission, and contact tracing supports secondary transmission in crowded, poorly ventilated indoor spaces.
- Only limited evidence supports other means of SARS-CoV-2 transmission, including through fomites or large droplets.
“We thought we’d summarize [the evidence] to clarify the arguments for and against. We looked hard for evidence against but found none,” Dr. Greenhalgh said.
“Although other routes can contribute, we believe that the airborne route is likely to be dominant,” the authors note.
The evidence on airborne transmission was there very early on but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, World Health Organization, and others repeated the message that the primary concern was droplets and fomites.
Response to a review
The top 10 list is also part rebuttal of a systematic review funded by the WHO and published last month that points to inconclusive evidence for airborne transmission. The researchers involved with that review state that “the lack of recoverable viral culture samples of SARS-CoV-2 prevents firm conclusions to be drawn about airborne transmission.”
However, Dr. Greenhalgh and colleagues note that “this conclusion, and the wide circulation of the review’s findings, is concerning because of the public health implications.”
The current authors also argue that enough evidence already exists on airborne transmission. “Policy should change. We don’t need more research on this topic; we need different policy,” Dr. Greenhalgh said. “We need ventilation front and center, air filtration when necessary, and better-fitting masks worn whenever indoors.”
Dr. Allen agreed that guidance hasn’t always kept pace with the science. “With all of the new evidence accumulated on airborne transmission since last winter, there is still widespread confusion in the public about modes of transmission,” he said. Dr. Allen also serves as commissioner of The Lancet COVID-19 Commission and is chair of the commission’s Task Force on Safe Work, Safe Schools, and Safe Travel.
“It was only just last week that CDC pulled back on guidance on ‘deep cleaning’ and in its place correctly said that the risk from touching surfaces is low,” he added. “The science has been clear on this for over a year, but official guidance was only recently updated.”
As a result, many companies and organizations continued to focus on “hygiene theatre,” Dr. Allen said, “wasting resources on overcleaning surfaces. Unbelievably, many schools still close for an entire day each week for deep cleaning and some still quarantine library books. The message that shared air is the problem, not shared surfaces, is a message that still needs to be reinforced.”
The National Institute for Health Research, Economic and Social Research Council, and Wellcome support Dr. Greenhalgh’s research. Dr. Greenhalgh and Dr. Allen had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VEXAS syndrome: Implications for dermatologists
When I was a medical student, I always found it gratifying when there was a unifying mechanism that explained the symptoms of a disease. Part of the reason I chose dermatology as a specialty was how frequently we are able to “see” these mechanisms in the skin, both clinically and histologically. What’s even more interesting is that this condition is caused by a postzygotic somatic mutation, an apparently underrecognized cause of disease that we are just now beginning to understand. An example of a postzygotic somatic mutation causing a disease that we all learned about in medical school is paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Using a “bottom-up” approach, researchers at the National Institutes of Health and in the United Kingdom identified 25 patients with somatic UBA1 mutations and noticed that they had strikingly similar autoinflammatory syndromes. UBA1 encodes ubiquitin E1, which is part of the pathway the breaks down proteins as part of the normal cellular machine. It is localized to the X chromosome, so all 25 affected patients were males, and most were aged between 40 and 70 years. These patients had an autoinflammatory syndrome characterized by fever, chondritis (similar to relapsing polychondritis), vasculitis, and neutrophilic dermatoses. Many patients also had features of myelodysplastic syndrome and plasma cell dyscrasia. The inflammatory pattern in this condition seems to show elevations in tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
So why is this syndrome relevant to dermatology? We are often asked to evaluate patients for neutrophilic dermatosis and vasculitis, and many affected patients had clinical and histologic findings compatible with polyarteritis nodosa and Sweet syndrome. When confronted with a neutrophilic dermatosis, we’ve all been taught to evaluate for myelodysplastic syndrome, which many of these patients appeared to have, at least on the surface. When bone marrow biopsies were done, the myeloid cell precursors that give rise to neutrophils were noted to have prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles, hence the “V” in VEXAS.
In reading the article describing 25 patients with this syndrome, which was published in the New England Journal of Medicine, I was struck by how refractory they were to treatment. Most patients had been treated with systemic steroids, multiple biologics, and several nonbiologic medications that are mainstays of treatment for neutrophilic dermatosis like dapsone and colchicine. I was fortunate enough to speak to Amanda Ombrello, MD, of the National Human Genome Research Institute, one of the lead authors of the paper, who drew my attention to the supplementary appendix, which showed the marked injection-site reactions some patients had to anakinra – yet another reason why a patient might end up in a dermatology clinic. In my mind, all of these features could be a clue to a diagnosis of VEXAS syndrome.
Many patients seemed to fare poorly, with 40% of patients dying before the completion of the study. When it comes to extremely rare diseases, it seems that the more physicians who are aware of the existence of a particular syndrome, the more likely it is a patient will come under our care and be correctly diagnosed.
Dr. Saardi is a dermatologist and internist, and is director of the inpatient dermatology service at the George Washington University Hospital, Washington. He has no disclosures.
When I was a medical student, I always found it gratifying when there was a unifying mechanism that explained the symptoms of a disease. Part of the reason I chose dermatology as a specialty was how frequently we are able to “see” these mechanisms in the skin, both clinically and histologically. What’s even more interesting is that this condition is caused by a postzygotic somatic mutation, an apparently underrecognized cause of disease that we are just now beginning to understand. An example of a postzygotic somatic mutation causing a disease that we all learned about in medical school is paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Using a “bottom-up” approach, researchers at the National Institutes of Health and in the United Kingdom identified 25 patients with somatic UBA1 mutations and noticed that they had strikingly similar autoinflammatory syndromes. UBA1 encodes ubiquitin E1, which is part of the pathway the breaks down proteins as part of the normal cellular machine. It is localized to the X chromosome, so all 25 affected patients were males, and most were aged between 40 and 70 years. These patients had an autoinflammatory syndrome characterized by fever, chondritis (similar to relapsing polychondritis), vasculitis, and neutrophilic dermatoses. Many patients also had features of myelodysplastic syndrome and plasma cell dyscrasia. The inflammatory pattern in this condition seems to show elevations in tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
So why is this syndrome relevant to dermatology? We are often asked to evaluate patients for neutrophilic dermatosis and vasculitis, and many affected patients had clinical and histologic findings compatible with polyarteritis nodosa and Sweet syndrome. When confronted with a neutrophilic dermatosis, we’ve all been taught to evaluate for myelodysplastic syndrome, which many of these patients appeared to have, at least on the surface. When bone marrow biopsies were done, the myeloid cell precursors that give rise to neutrophils were noted to have prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles, hence the “V” in VEXAS.
In reading the article describing 25 patients with this syndrome, which was published in the New England Journal of Medicine, I was struck by how refractory they were to treatment. Most patients had been treated with systemic steroids, multiple biologics, and several nonbiologic medications that are mainstays of treatment for neutrophilic dermatosis like dapsone and colchicine. I was fortunate enough to speak to Amanda Ombrello, MD, of the National Human Genome Research Institute, one of the lead authors of the paper, who drew my attention to the supplementary appendix, which showed the marked injection-site reactions some patients had to anakinra – yet another reason why a patient might end up in a dermatology clinic. In my mind, all of these features could be a clue to a diagnosis of VEXAS syndrome.
Many patients seemed to fare poorly, with 40% of patients dying before the completion of the study. When it comes to extremely rare diseases, it seems that the more physicians who are aware of the existence of a particular syndrome, the more likely it is a patient will come under our care and be correctly diagnosed.
Dr. Saardi is a dermatologist and internist, and is director of the inpatient dermatology service at the George Washington University Hospital, Washington. He has no disclosures.
When I was a medical student, I always found it gratifying when there was a unifying mechanism that explained the symptoms of a disease. Part of the reason I chose dermatology as a specialty was how frequently we are able to “see” these mechanisms in the skin, both clinically and histologically. What’s even more interesting is that this condition is caused by a postzygotic somatic mutation, an apparently underrecognized cause of disease that we are just now beginning to understand. An example of a postzygotic somatic mutation causing a disease that we all learned about in medical school is paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.
Using a “bottom-up” approach, researchers at the National Institutes of Health and in the United Kingdom identified 25 patients with somatic UBA1 mutations and noticed that they had strikingly similar autoinflammatory syndromes. UBA1 encodes ubiquitin E1, which is part of the pathway the breaks down proteins as part of the normal cellular machine. It is localized to the X chromosome, so all 25 affected patients were males, and most were aged between 40 and 70 years. These patients had an autoinflammatory syndrome characterized by fever, chondritis (similar to relapsing polychondritis), vasculitis, and neutrophilic dermatoses. Many patients also had features of myelodysplastic syndrome and plasma cell dyscrasia. The inflammatory pattern in this condition seems to show elevations in tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma.
So why is this syndrome relevant to dermatology? We are often asked to evaluate patients for neutrophilic dermatosis and vasculitis, and many affected patients had clinical and histologic findings compatible with polyarteritis nodosa and Sweet syndrome. When confronted with a neutrophilic dermatosis, we’ve all been taught to evaluate for myelodysplastic syndrome, which many of these patients appeared to have, at least on the surface. When bone marrow biopsies were done, the myeloid cell precursors that give rise to neutrophils were noted to have prominent cytoplasmic vacuoles, hence the “V” in VEXAS.
In reading the article describing 25 patients with this syndrome, which was published in the New England Journal of Medicine, I was struck by how refractory they were to treatment. Most patients had been treated with systemic steroids, multiple biologics, and several nonbiologic medications that are mainstays of treatment for neutrophilic dermatosis like dapsone and colchicine. I was fortunate enough to speak to Amanda Ombrello, MD, of the National Human Genome Research Institute, one of the lead authors of the paper, who drew my attention to the supplementary appendix, which showed the marked injection-site reactions some patients had to anakinra – yet another reason why a patient might end up in a dermatology clinic. In my mind, all of these features could be a clue to a diagnosis of VEXAS syndrome.
Many patients seemed to fare poorly, with 40% of patients dying before the completion of the study. When it comes to extremely rare diseases, it seems that the more physicians who are aware of the existence of a particular syndrome, the more likely it is a patient will come under our care and be correctly diagnosed.
Dr. Saardi is a dermatologist and internist, and is director of the inpatient dermatology service at the George Washington University Hospital, Washington. He has no disclosures.
Teen tanning bed ban would prevent more than 15,000 melanoma cases
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.
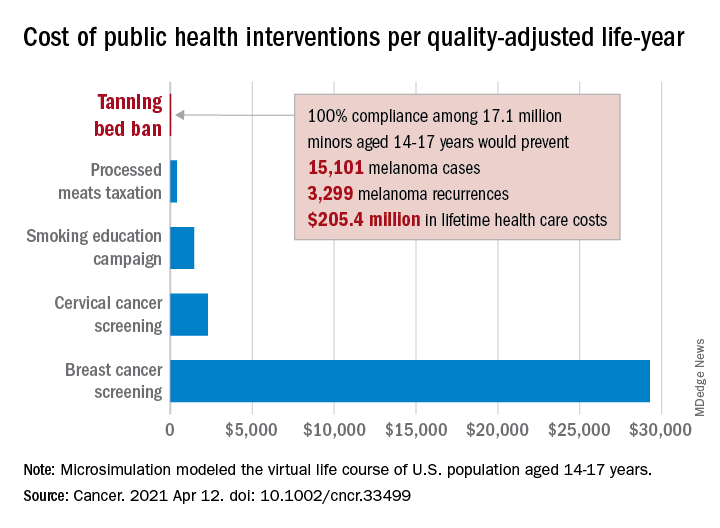
“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.

“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
and cost less than other, well-established public health interventions, according to a microsimulation of that age group’s virtual life course.

“Even with extensive sensitivity analyses on the costs of inspections, noncompliance with a ban, and the risk of developing melanoma in those who have used tanning beds, a ban can be considered highly cost effective,” Antoine Eskander, MD, ScM, of the University of Toronto, and associates said in Cancer.
Compared with no ban, such an intervention could save over $205 million in lifetime health care costs among the 17.1 million young people (based on the 2010 Census population) who would be affected, they said.
The more than 15,000 melanoma cases and 3,300 recurrences prevented would save $12 per average minor after adjusting for societal costs, such as lost productivity, formal and informal health care, economic losses to the tanning bed industry, and the need for monitoring, the investigators reported.
Switching to quality-adjusted life-years shows an improvement of 0.0002 QALYs per child for a ban, based on an overall cost of almost $24.9 per QALY, compared with no ban, they said, which makes it “more cost effective than many well-established public health interventions”:
- Processed meats taxation ($270/QALY).
- Smoking education campaign ($1,337/QALY).
- Cervical cancer screening ($2,166/QALY).
- Breast cancer screening ($29,284/QALY).
- Lung cancer screening ($49,200-$96,700/QALY).
Among the many parameters included in the microsimulation were the odds ratio of developing melanoma from exposure to tanning beds before age 25 (1.35), melanoma stage at presentation, risk of recurrence, and the cost of four annual inspections for each of the nation’s more than 13,000 tanning salons, Dr. Eskander and associates explained.
FROM CANCER
What COVID did to MD income in 2020
, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2021: The Recovery Begins.
Almost 18,000 physicians in more than 29 specialties told Medscape about their income, hours worked, greatest challenges, and the unexpected impact of COVID-19 on their compensation.
How many physicians avoided massive losses
When the pandemic started around March 2020, “a great many physicians saw reductions in volume at first,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Medscape’s survey report shows that a staggering 44% saw a 1%-25% reduction in patient volume, and 9% saw a 26%-50% decline. “That is indeed breathtaking,” Dr. Pearl says.
Several key factors saved many practices from hemorrhaging money, says Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins and Associates in Dallas. “Many physicians used the federal Paycheck Protection Program [PPP] to help keep themselves afloat,” he says. “A large percentage reduced their staff, which reduced their expenses, and many got some of their volume back by transitioning to telemedicine.”
In a 2020 survey for the Physicians Foundation, conducted by Merritt Hawkins, 48% of physicians said their practice had received PPP support, and most of those said the support was enough to allow them to stay open without reducing staff. Only 6% of practices that received PPP support did not stay open.
Telemedicine helped many practices
Early in the pandemic, Medicare reimbursements for telemedicine were equal with those for face-to-face visits. “Since telemedicine takes a third less time than an inpatient visit, doctors could see more patients,” Dr. Pearl says.
The switch was almost instantaneous in some practices. Within 3 days, a 200-provider multispecialty practice in Wilmington, N.C., went from not using telehealth to its being used by all physicians, the Medical Group Management Association reported. By late April, the practice was already back up to about 70% of normal overall production.
However, telemedicine could not help every specialty equally. “Generally, allergists can’t do their allergy testing virtually, and patients with mild problems probably put off visits,” Dr. Pearl says. Allergists experienced a large percentage decline in compensation, according to Medscape’s survey. For some, income fell from $301,000 the prior year to $274,000 this year.
Primary care struggled
Primary care physicians posted lower compensation than they did the prior year, but most rebounded to some degree. A study released in June 2020 projected that, even with telemedicine, primary care physicians would lose an average of $67,774 for the year.
However, Medscape’s survey found that internists’ average compensation declined from $251,000 in the prior year to $248,000, and average family physicians’ compensation actually rose from $234,000.
Pediatricians had a harder slog. Their average compensation sank from $232,000 to $221,000, according to the report. Even with telemedicine, parents of young children were not contacting the doctor. In May 2020, visits by children aged 3-5 years were down by 56%.
Many proceduralists recovered
Procedure-oriented specialties were particularly hard-hit at first, because many hospitals and some states banned all elective surgeries at the beginning of the pandemic.
“In March and April, ophthalmology practices were virtually at a standstill,” says John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “But by the fourth quarter, operations were back to normal. Practices were fully open, and patients were coming back in.”
Medscape’s survey shows that, by year’s end, compensation was about the same as the year before for orthopedic surgeons ($511,000 in both the 2020 and 2021 reports); cardiologists actually did better ($438,000 in our 2020 report and $459,000 in 2021); and ophthalmologists’ compensation was about the same ($378,000 in our prior report and $379,000 in 2021).
Some other proceduralists, however, did not do as well. Otolaryngologists’ compensation fell to $417,000, the second-biggest percentage drop. “This may be because otolaryngologists’ chief procedures are tonsillectomies, sinus surgery, and nasal surgery, which can be put off,” Dr. Pearl says.
Anesthesiologists, who depend on surgical volume, also did not earn as much in 2020. Their compensation declined from $398,000 in our 2020 report to $378,000 in Medscape’s 2021 report.
“Not only has 70% of our revenue disappeared, but our physicians are still working every day,” an independent anesthesiology practice in Alabama told the MGMA early in the pandemic.
Plastic surgeons now the top earners
The biggest increase in compensation by far was made by plastic surgeons, whose income rose 9.8% over the year before, to $526,000. This put them at the top of the list
Dr. Pearl adds that plastic surgeons can perform their procedures in their offices, rather than in a hospital, where elective surgeries were often canceled.
Mr. Belkin says specialties other than plastic surgery had been offering more boutique cosmetic care even before the pandemic. In 2020, nonsurgical cosmetic procedures such as neurotoxin therapy, dermal filler procedures, chemical peels, and hair removal earned $3.1 billion in revenue, according to a survey by the Aesthetic Society.
Other specialties that earned more even during COVID
In Medscape’s survey, several specialties actually earned more during the pandemic than in 2019. Some specialties, such as critical care and public health, were integral in managing COVID patients and the pandemic.
However, some specialties involved in COVID care did not see an increase. Compensation for infectious disease specialists (at $245,000) and emergency medicine specialists (at $354,000) remained basically unchanged from the prior year, and for pulmonologists, it was slightly down.
Emergency departments reported decreases in volume of 40% or more early in the pandemic, according to the American College of Emergency Physicians. It was reported that patients were avoiding EDs for fear of contracting COVID, and car accidents were down because people ventured out less.
In this year’s report, psychiatrists saw a modest rise in compensation, to $275,000. “There has been an increase in mental health visits in the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. In 2020, about 4 in 10 adults in the United States reported symptoms of anxiety or depressive disorder, up from 1 in 10 adults the prior year. In addition, psychiatrists were third on the list of Merritt Hawkins’ most requested recruiting engagements.
Oncologists saw a rise in compensation, from $377,000 to $403,000. “Volume likely did not fall because cancer patients would go through with their chemotherapy in spite of the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. “The increase in income might have to do with the usual inflation in the cost of chemotherapy drugs.” Dr. Pinto saw the same trend for retinal surgeons, whose care also cannot be delayed.
Medscape’s survey also reports increases in compensation for rheumatologists, endocrinologists, and neurologists, but it reports small declines among dermatologists, radiologists, and gastroenterologists.
Gender-based pay gap remains in place
The gender-based pay gap in this year’s report is similar to that seen in Medscape’s report for the prior year. Men earned 27% more than women in 2021, compared with 25% more the year before. Some physicians commented that more women physicians maintained flexible or shorter work schedules to help with children who could not go into school.
“Having to be a full-time physician, full-time mom, and full-time teacher during our surge was unbelievable,” a primary care pediatrician in group practice and mother of two reported in November. “I felt pulled in all directions and didn’t do anything well.”
In addition, “men dominate some specialties that seem to have seen a smaller drop in volume in the pandemic, such as emergency medicine, infectious disease, pulmonology, and oncology,” says Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, CEO of MGMA.
Employed physicians shared their employers’ pain
Employed physicians, who typically work at hospitals, shared the financial pains of their institutions, particularly in the early stages of the pandemic. In April, hospital admissions were 34.1% below prepandemic levels, according to a study published in Health Affairs. That figure had risen by June, but it was still 8.3% below prepandemic volume.
By the end of the year, many hospitals and hospital systems were in the black, thanks in large part to generous federal subsidies, but actual operations still lost money for the year. Altogether, 42% of them posted an operational loss in 2020, up from the 23% in 2019, according to a survey by Moody’s Investors Service.
Medscape’s report shows that many employed physicians lost pay in 2020, and for many, pay had not returned to pre-COVID levels. Only 28% of primary care physicians and 32% of specialists who lost pay have seen it restored, according to the report. In addition, 15% of surveyed physicians did not receive an annual raise.
Many employed doctors are paid on the basis of relative value units (RVUs), which is a measure of the value of their work. In many cases, there was not enough work to reach RVU thresholds. Would hospitals and other employers lower RVU targets to meet the problem? “I haven’t seen our clients make concessions to providers along those lines,” Mr. Belkin says.
Physicians had to work longer hours
The Medscape report also found that in 2020, physicians saw fewer patients because each visit took longer.
“With the threat of COVID, in-person visits take more time than before,” Mr. Belkin says. “Physicians and staff have to prepare the exam room after each visit, and doctors must spend more time answering patients’ questions about COVID.”
“The new protocols to keep everyone safe add time between patients, and physicians have to answer patients’ questions about the pandemic and vaccines,” Dr. Fischer-Wright says. “You might see a 20% increase in time spent just on these non–revenue-generating COVID activities.”
Physicians still like their specialty
Although 2020 was a challenging year for physicians, the percentage of those who were satisfied with their specialty choice generally did not slip from the year before. It actually rose for several specialties – most notably, rheumatology, pulmonology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and nephrology.
One specialty saw a decline in satisfaction with their specialty choice, and that was public health and preventive medicine, which plummeted 16 percentage points to 67% – putting it at the bottom of the list.
Even before the pandemic, many public health departments were chronically underfunded. This problem was possibly exacerbated by the pressures to keep up with COVID reporting and testing responsibilities.
Conclusion
Although 2020 was a wild ride for many physicians, many came out of it with only minor reductions in overall compensation, and some saw increases. Still, some specialties and many individuals experienced terrible financial stress and had to make changes in their lives and their spending in order to stay afloat.
“The biggest inhibitor to getting back to normal had to do with doctors who did not want to return because they did not want to risk getting COVID,” Dr. Pinto reports. But he notes that by February 2021 most doctors were completely vaccinated and could feel safe again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2021: The Recovery Begins.
Almost 18,000 physicians in more than 29 specialties told Medscape about their income, hours worked, greatest challenges, and the unexpected impact of COVID-19 on their compensation.
How many physicians avoided massive losses
When the pandemic started around March 2020, “a great many physicians saw reductions in volume at first,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Medscape’s survey report shows that a staggering 44% saw a 1%-25% reduction in patient volume, and 9% saw a 26%-50% decline. “That is indeed breathtaking,” Dr. Pearl says.
Several key factors saved many practices from hemorrhaging money, says Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins and Associates in Dallas. “Many physicians used the federal Paycheck Protection Program [PPP] to help keep themselves afloat,” he says. “A large percentage reduced their staff, which reduced their expenses, and many got some of their volume back by transitioning to telemedicine.”
In a 2020 survey for the Physicians Foundation, conducted by Merritt Hawkins, 48% of physicians said their practice had received PPP support, and most of those said the support was enough to allow them to stay open without reducing staff. Only 6% of practices that received PPP support did not stay open.
Telemedicine helped many practices
Early in the pandemic, Medicare reimbursements for telemedicine were equal with those for face-to-face visits. “Since telemedicine takes a third less time than an inpatient visit, doctors could see more patients,” Dr. Pearl says.
The switch was almost instantaneous in some practices. Within 3 days, a 200-provider multispecialty practice in Wilmington, N.C., went from not using telehealth to its being used by all physicians, the Medical Group Management Association reported. By late April, the practice was already back up to about 70% of normal overall production.
However, telemedicine could not help every specialty equally. “Generally, allergists can’t do their allergy testing virtually, and patients with mild problems probably put off visits,” Dr. Pearl says. Allergists experienced a large percentage decline in compensation, according to Medscape’s survey. For some, income fell from $301,000 the prior year to $274,000 this year.
Primary care struggled
Primary care physicians posted lower compensation than they did the prior year, but most rebounded to some degree. A study released in June 2020 projected that, even with telemedicine, primary care physicians would lose an average of $67,774 for the year.
However, Medscape’s survey found that internists’ average compensation declined from $251,000 in the prior year to $248,000, and average family physicians’ compensation actually rose from $234,000.
Pediatricians had a harder slog. Their average compensation sank from $232,000 to $221,000, according to the report. Even with telemedicine, parents of young children were not contacting the doctor. In May 2020, visits by children aged 3-5 years were down by 56%.
Many proceduralists recovered
Procedure-oriented specialties were particularly hard-hit at first, because many hospitals and some states banned all elective surgeries at the beginning of the pandemic.
“In March and April, ophthalmology practices were virtually at a standstill,” says John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “But by the fourth quarter, operations were back to normal. Practices were fully open, and patients were coming back in.”
Medscape’s survey shows that, by year’s end, compensation was about the same as the year before for orthopedic surgeons ($511,000 in both the 2020 and 2021 reports); cardiologists actually did better ($438,000 in our 2020 report and $459,000 in 2021); and ophthalmologists’ compensation was about the same ($378,000 in our prior report and $379,000 in 2021).
Some other proceduralists, however, did not do as well. Otolaryngologists’ compensation fell to $417,000, the second-biggest percentage drop. “This may be because otolaryngologists’ chief procedures are tonsillectomies, sinus surgery, and nasal surgery, which can be put off,” Dr. Pearl says.
Anesthesiologists, who depend on surgical volume, also did not earn as much in 2020. Their compensation declined from $398,000 in our 2020 report to $378,000 in Medscape’s 2021 report.
“Not only has 70% of our revenue disappeared, but our physicians are still working every day,” an independent anesthesiology practice in Alabama told the MGMA early in the pandemic.
Plastic surgeons now the top earners
The biggest increase in compensation by far was made by plastic surgeons, whose income rose 9.8% over the year before, to $526,000. This put them at the top of the list
Dr. Pearl adds that plastic surgeons can perform their procedures in their offices, rather than in a hospital, where elective surgeries were often canceled.
Mr. Belkin says specialties other than plastic surgery had been offering more boutique cosmetic care even before the pandemic. In 2020, nonsurgical cosmetic procedures such as neurotoxin therapy, dermal filler procedures, chemical peels, and hair removal earned $3.1 billion in revenue, according to a survey by the Aesthetic Society.
Other specialties that earned more even during COVID
In Medscape’s survey, several specialties actually earned more during the pandemic than in 2019. Some specialties, such as critical care and public health, were integral in managing COVID patients and the pandemic.
However, some specialties involved in COVID care did not see an increase. Compensation for infectious disease specialists (at $245,000) and emergency medicine specialists (at $354,000) remained basically unchanged from the prior year, and for pulmonologists, it was slightly down.
Emergency departments reported decreases in volume of 40% or more early in the pandemic, according to the American College of Emergency Physicians. It was reported that patients were avoiding EDs for fear of contracting COVID, and car accidents were down because people ventured out less.
In this year’s report, psychiatrists saw a modest rise in compensation, to $275,000. “There has been an increase in mental health visits in the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. In 2020, about 4 in 10 adults in the United States reported symptoms of anxiety or depressive disorder, up from 1 in 10 adults the prior year. In addition, psychiatrists were third on the list of Merritt Hawkins’ most requested recruiting engagements.
Oncologists saw a rise in compensation, from $377,000 to $403,000. “Volume likely did not fall because cancer patients would go through with their chemotherapy in spite of the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. “The increase in income might have to do with the usual inflation in the cost of chemotherapy drugs.” Dr. Pinto saw the same trend for retinal surgeons, whose care also cannot be delayed.
Medscape’s survey also reports increases in compensation for rheumatologists, endocrinologists, and neurologists, but it reports small declines among dermatologists, radiologists, and gastroenterologists.
Gender-based pay gap remains in place
The gender-based pay gap in this year’s report is similar to that seen in Medscape’s report for the prior year. Men earned 27% more than women in 2021, compared with 25% more the year before. Some physicians commented that more women physicians maintained flexible or shorter work schedules to help with children who could not go into school.
“Having to be a full-time physician, full-time mom, and full-time teacher during our surge was unbelievable,” a primary care pediatrician in group practice and mother of two reported in November. “I felt pulled in all directions and didn’t do anything well.”
In addition, “men dominate some specialties that seem to have seen a smaller drop in volume in the pandemic, such as emergency medicine, infectious disease, pulmonology, and oncology,” says Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, CEO of MGMA.
Employed physicians shared their employers’ pain
Employed physicians, who typically work at hospitals, shared the financial pains of their institutions, particularly in the early stages of the pandemic. In April, hospital admissions were 34.1% below prepandemic levels, according to a study published in Health Affairs. That figure had risen by June, but it was still 8.3% below prepandemic volume.
By the end of the year, many hospitals and hospital systems were in the black, thanks in large part to generous federal subsidies, but actual operations still lost money for the year. Altogether, 42% of them posted an operational loss in 2020, up from the 23% in 2019, according to a survey by Moody’s Investors Service.
Medscape’s report shows that many employed physicians lost pay in 2020, and for many, pay had not returned to pre-COVID levels. Only 28% of primary care physicians and 32% of specialists who lost pay have seen it restored, according to the report. In addition, 15% of surveyed physicians did not receive an annual raise.
Many employed doctors are paid on the basis of relative value units (RVUs), which is a measure of the value of their work. In many cases, there was not enough work to reach RVU thresholds. Would hospitals and other employers lower RVU targets to meet the problem? “I haven’t seen our clients make concessions to providers along those lines,” Mr. Belkin says.
Physicians had to work longer hours
The Medscape report also found that in 2020, physicians saw fewer patients because each visit took longer.
“With the threat of COVID, in-person visits take more time than before,” Mr. Belkin says. “Physicians and staff have to prepare the exam room after each visit, and doctors must spend more time answering patients’ questions about COVID.”
“The new protocols to keep everyone safe add time between patients, and physicians have to answer patients’ questions about the pandemic and vaccines,” Dr. Fischer-Wright says. “You might see a 20% increase in time spent just on these non–revenue-generating COVID activities.”
Physicians still like their specialty
Although 2020 was a challenging year for physicians, the percentage of those who were satisfied with their specialty choice generally did not slip from the year before. It actually rose for several specialties – most notably, rheumatology, pulmonology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and nephrology.
One specialty saw a decline in satisfaction with their specialty choice, and that was public health and preventive medicine, which plummeted 16 percentage points to 67% – putting it at the bottom of the list.
Even before the pandemic, many public health departments were chronically underfunded. This problem was possibly exacerbated by the pressures to keep up with COVID reporting and testing responsibilities.
Conclusion
Although 2020 was a wild ride for many physicians, many came out of it with only minor reductions in overall compensation, and some saw increases. Still, some specialties and many individuals experienced terrible financial stress and had to make changes in their lives and their spending in order to stay afloat.
“The biggest inhibitor to getting back to normal had to do with doctors who did not want to return because they did not want to risk getting COVID,” Dr. Pinto reports. But he notes that by February 2021 most doctors were completely vaccinated and could feel safe again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the Medscape Physician Compensation Report 2021: The Recovery Begins.
Almost 18,000 physicians in more than 29 specialties told Medscape about their income, hours worked, greatest challenges, and the unexpected impact of COVID-19 on their compensation.
How many physicians avoided massive losses
When the pandemic started around March 2020, “a great many physicians saw reductions in volume at first,” says Robert Pearl, MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University.
Medscape’s survey report shows that a staggering 44% saw a 1%-25% reduction in patient volume, and 9% saw a 26%-50% decline. “That is indeed breathtaking,” Dr. Pearl says.
Several key factors saved many practices from hemorrhaging money, says Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president at Merritt Hawkins and Associates in Dallas. “Many physicians used the federal Paycheck Protection Program [PPP] to help keep themselves afloat,” he says. “A large percentage reduced their staff, which reduced their expenses, and many got some of their volume back by transitioning to telemedicine.”
In a 2020 survey for the Physicians Foundation, conducted by Merritt Hawkins, 48% of physicians said their practice had received PPP support, and most of those said the support was enough to allow them to stay open without reducing staff. Only 6% of practices that received PPP support did not stay open.
Telemedicine helped many practices
Early in the pandemic, Medicare reimbursements for telemedicine were equal with those for face-to-face visits. “Since telemedicine takes a third less time than an inpatient visit, doctors could see more patients,” Dr. Pearl says.
The switch was almost instantaneous in some practices. Within 3 days, a 200-provider multispecialty practice in Wilmington, N.C., went from not using telehealth to its being used by all physicians, the Medical Group Management Association reported. By late April, the practice was already back up to about 70% of normal overall production.
However, telemedicine could not help every specialty equally. “Generally, allergists can’t do their allergy testing virtually, and patients with mild problems probably put off visits,” Dr. Pearl says. Allergists experienced a large percentage decline in compensation, according to Medscape’s survey. For some, income fell from $301,000 the prior year to $274,000 this year.
Primary care struggled
Primary care physicians posted lower compensation than they did the prior year, but most rebounded to some degree. A study released in June 2020 projected that, even with telemedicine, primary care physicians would lose an average of $67,774 for the year.
However, Medscape’s survey found that internists’ average compensation declined from $251,000 in the prior year to $248,000, and average family physicians’ compensation actually rose from $234,000.
Pediatricians had a harder slog. Their average compensation sank from $232,000 to $221,000, according to the report. Even with telemedicine, parents of young children were not contacting the doctor. In May 2020, visits by children aged 3-5 years were down by 56%.
Many proceduralists recovered
Procedure-oriented specialties were particularly hard-hit at first, because many hospitals and some states banned all elective surgeries at the beginning of the pandemic.
“In March and April, ophthalmology practices were virtually at a standstill,” says John B. Pinto, an ophthalmology practice management consultant in San Diego. “But by the fourth quarter, operations were back to normal. Practices were fully open, and patients were coming back in.”
Medscape’s survey shows that, by year’s end, compensation was about the same as the year before for orthopedic surgeons ($511,000 in both the 2020 and 2021 reports); cardiologists actually did better ($438,000 in our 2020 report and $459,000 in 2021); and ophthalmologists’ compensation was about the same ($378,000 in our prior report and $379,000 in 2021).
Some other proceduralists, however, did not do as well. Otolaryngologists’ compensation fell to $417,000, the second-biggest percentage drop. “This may be because otolaryngologists’ chief procedures are tonsillectomies, sinus surgery, and nasal surgery, which can be put off,” Dr. Pearl says.
Anesthesiologists, who depend on surgical volume, also did not earn as much in 2020. Their compensation declined from $398,000 in our 2020 report to $378,000 in Medscape’s 2021 report.
“Not only has 70% of our revenue disappeared, but our physicians are still working every day,” an independent anesthesiology practice in Alabama told the MGMA early in the pandemic.
Plastic surgeons now the top earners
The biggest increase in compensation by far was made by plastic surgeons, whose income rose 9.8% over the year before, to $526,000. This put them at the top of the list
Dr. Pearl adds that plastic surgeons can perform their procedures in their offices, rather than in a hospital, where elective surgeries were often canceled.
Mr. Belkin says specialties other than plastic surgery had been offering more boutique cosmetic care even before the pandemic. In 2020, nonsurgical cosmetic procedures such as neurotoxin therapy, dermal filler procedures, chemical peels, and hair removal earned $3.1 billion in revenue, according to a survey by the Aesthetic Society.
Other specialties that earned more even during COVID
In Medscape’s survey, several specialties actually earned more during the pandemic than in 2019. Some specialties, such as critical care and public health, were integral in managing COVID patients and the pandemic.
However, some specialties involved in COVID care did not see an increase. Compensation for infectious disease specialists (at $245,000) and emergency medicine specialists (at $354,000) remained basically unchanged from the prior year, and for pulmonologists, it was slightly down.
Emergency departments reported decreases in volume of 40% or more early in the pandemic, according to the American College of Emergency Physicians. It was reported that patients were avoiding EDs for fear of contracting COVID, and car accidents were down because people ventured out less.
In this year’s report, psychiatrists saw a modest rise in compensation, to $275,000. “There has been an increase in mental health visits in the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. In 2020, about 4 in 10 adults in the United States reported symptoms of anxiety or depressive disorder, up from 1 in 10 adults the prior year. In addition, psychiatrists were third on the list of Merritt Hawkins’ most requested recruiting engagements.
Oncologists saw a rise in compensation, from $377,000 to $403,000. “Volume likely did not fall because cancer patients would go through with their chemotherapy in spite of the pandemic,” Dr. Pearl says. “The increase in income might have to do with the usual inflation in the cost of chemotherapy drugs.” Dr. Pinto saw the same trend for retinal surgeons, whose care also cannot be delayed.
Medscape’s survey also reports increases in compensation for rheumatologists, endocrinologists, and neurologists, but it reports small declines among dermatologists, radiologists, and gastroenterologists.
Gender-based pay gap remains in place
The gender-based pay gap in this year’s report is similar to that seen in Medscape’s report for the prior year. Men earned 27% more than women in 2021, compared with 25% more the year before. Some physicians commented that more women physicians maintained flexible or shorter work schedules to help with children who could not go into school.
“Having to be a full-time physician, full-time mom, and full-time teacher during our surge was unbelievable,” a primary care pediatrician in group practice and mother of two reported in November. “I felt pulled in all directions and didn’t do anything well.”
In addition, “men dominate some specialties that seem to have seen a smaller drop in volume in the pandemic, such as emergency medicine, infectious disease, pulmonology, and oncology,” says Halee Fischer-Wright, MD, CEO of MGMA.
Employed physicians shared their employers’ pain
Employed physicians, who typically work at hospitals, shared the financial pains of their institutions, particularly in the early stages of the pandemic. In April, hospital admissions were 34.1% below prepandemic levels, according to a study published in Health Affairs. That figure had risen by June, but it was still 8.3% below prepandemic volume.
By the end of the year, many hospitals and hospital systems were in the black, thanks in large part to generous federal subsidies, but actual operations still lost money for the year. Altogether, 42% of them posted an operational loss in 2020, up from the 23% in 2019, according to a survey by Moody’s Investors Service.
Medscape’s report shows that many employed physicians lost pay in 2020, and for many, pay had not returned to pre-COVID levels. Only 28% of primary care physicians and 32% of specialists who lost pay have seen it restored, according to the report. In addition, 15% of surveyed physicians did not receive an annual raise.
Many employed doctors are paid on the basis of relative value units (RVUs), which is a measure of the value of their work. In many cases, there was not enough work to reach RVU thresholds. Would hospitals and other employers lower RVU targets to meet the problem? “I haven’t seen our clients make concessions to providers along those lines,” Mr. Belkin says.
Physicians had to work longer hours
The Medscape report also found that in 2020, physicians saw fewer patients because each visit took longer.
“With the threat of COVID, in-person visits take more time than before,” Mr. Belkin says. “Physicians and staff have to prepare the exam room after each visit, and doctors must spend more time answering patients’ questions about COVID.”
“The new protocols to keep everyone safe add time between patients, and physicians have to answer patients’ questions about the pandemic and vaccines,” Dr. Fischer-Wright says. “You might see a 20% increase in time spent just on these non–revenue-generating COVID activities.”
Physicians still like their specialty
Although 2020 was a challenging year for physicians, the percentage of those who were satisfied with their specialty choice generally did not slip from the year before. It actually rose for several specialties – most notably, rheumatology, pulmonology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, and nephrology.
One specialty saw a decline in satisfaction with their specialty choice, and that was public health and preventive medicine, which plummeted 16 percentage points to 67% – putting it at the bottom of the list.
Even before the pandemic, many public health departments were chronically underfunded. This problem was possibly exacerbated by the pressures to keep up with COVID reporting and testing responsibilities.
Conclusion
Although 2020 was a wild ride for many physicians, many came out of it with only minor reductions in overall compensation, and some saw increases. Still, some specialties and many individuals experienced terrible financial stress and had to make changes in their lives and their spending in order to stay afloat.
“The biggest inhibitor to getting back to normal had to do with doctors who did not want to return because they did not want to risk getting COVID,” Dr. Pinto reports. But he notes that by February 2021 most doctors were completely vaccinated and could feel safe again.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Open Notes
. While some clinicians consider it an unwelcome intrusion, advocates say it will improve communication and compliance.
Patient access to notes is not new. In many states, patients already have the ability to request copies of their charts, or to access truncated information via clinic websites. The difference is that most patients will now be able to click on a patient portal – such as MyChart, or other similar apps – and gain instantaneous, unfettered access to everything in their records.
Clinicians have traditionally thought of medical notes as private journal entries; but in the last few decades they have become an important component of the documentation necessary for billing, as well as evidence in the event of litigation. Now, with the implementation of the Cures Act, medical notes have evolved into a tool to communicate with the patient, rather than just among health care providers, lawyers, and billing departments.
Supporters contend that this change will make a big difference, because patients will be able to see exactly what their doctors have written, rather than just a list of confusing test results and diagnosis lists in “medicalese.”
OpenNotes, a think tank that has promoted the sharing of clinical notes with patients for years, calls the Cures Act legislation a “new world” where shared notes are valuable tools to improve communication between patients and physicians while strengthening their relationship. They cite evidence indicating that “when health professionals offer patients and families ready access to clinical notes, the quality and safety of care improves.”
Not all doctors are as enthusiastic. Many are concerned that patients might misinterpret what they see in their doctors’ notes, including complex descriptions of clinical assessments and decisions.
Others worry about patients having immediate access to their records, perhaps even before their physicians. The American Academy of Dermatology is working with the American Medical Association and other groups to gather real-world instances where the release of lab results, reports, or notes directly to patients before their physician could review the information with them caused emotional harm or other adverse consequences.
Undoubtedly, there are scenarios where unrestricted display of clinical notes could be problematic. One example is the issue of adolescents and reproductive health. Since parents now have access to their children’s records, some teenagers might hesitate to confide in their physicians and deny themselves important medical care.
The new rules permit blocking access to records if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or third parties. Psychotherapy counseling notes, for example, are completely exempt from the new requirements.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new federal law and block access to notes. For example, California law forbids providers from posting cancer test results without discussing them with the patient first.
Research indicates that shared notes have benefits that should outweigh the concerns of most physicians. One study showed that about 70% of patients said reviewing their notes helped them understand why medications were prescribed, which improved their compliance. This was particularly true for patients whose primary language is not English. A British study found that patients felt empowered by shared notes, and thought they improved their relationship with their physicians.
Other advantages of sharing notes include the ability of family members to review what happened at visits, which can be particularly important when dementia or other disabilities are involved. Patients will also be able to share their medical records with physicians outside of their health network, thus avoiding unnecessary or repetitious workups.
OpenNotes contends that when patients review their doctors’ notes, they gain “a newfound, deeper respect for what physicians have to understand to do their jobs.” Other predicted advantages include improved medical record accuracy and less miscommunication. In a study published in 2019 that evaluated experiences of patients who read ambulatory visit notes, only 5% were more worried after reading the notes and 3% were confused.
Alleviating worry among clinicians may be a bigger problem; but as a general principle, you should avoid judgmental language, and never write anything in a chart that you wouldn’t want your patients or their family members – or lawyers – to see.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
. While some clinicians consider it an unwelcome intrusion, advocates say it will improve communication and compliance.
Patient access to notes is not new. In many states, patients already have the ability to request copies of their charts, or to access truncated information via clinic websites. The difference is that most patients will now be able to click on a patient portal – such as MyChart, or other similar apps – and gain instantaneous, unfettered access to everything in their records.
Clinicians have traditionally thought of medical notes as private journal entries; but in the last few decades they have become an important component of the documentation necessary for billing, as well as evidence in the event of litigation. Now, with the implementation of the Cures Act, medical notes have evolved into a tool to communicate with the patient, rather than just among health care providers, lawyers, and billing departments.
Supporters contend that this change will make a big difference, because patients will be able to see exactly what their doctors have written, rather than just a list of confusing test results and diagnosis lists in “medicalese.”
OpenNotes, a think tank that has promoted the sharing of clinical notes with patients for years, calls the Cures Act legislation a “new world” where shared notes are valuable tools to improve communication between patients and physicians while strengthening their relationship. They cite evidence indicating that “when health professionals offer patients and families ready access to clinical notes, the quality and safety of care improves.”
Not all doctors are as enthusiastic. Many are concerned that patients might misinterpret what they see in their doctors’ notes, including complex descriptions of clinical assessments and decisions.
Others worry about patients having immediate access to their records, perhaps even before their physicians. The American Academy of Dermatology is working with the American Medical Association and other groups to gather real-world instances where the release of lab results, reports, or notes directly to patients before their physician could review the information with them caused emotional harm or other adverse consequences.
Undoubtedly, there are scenarios where unrestricted display of clinical notes could be problematic. One example is the issue of adolescents and reproductive health. Since parents now have access to their children’s records, some teenagers might hesitate to confide in their physicians and deny themselves important medical care.
The new rules permit blocking access to records if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or third parties. Psychotherapy counseling notes, for example, are completely exempt from the new requirements.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new federal law and block access to notes. For example, California law forbids providers from posting cancer test results without discussing them with the patient first.
Research indicates that shared notes have benefits that should outweigh the concerns of most physicians. One study showed that about 70% of patients said reviewing their notes helped them understand why medications were prescribed, which improved their compliance. This was particularly true for patients whose primary language is not English. A British study found that patients felt empowered by shared notes, and thought they improved their relationship with their physicians.
Other advantages of sharing notes include the ability of family members to review what happened at visits, which can be particularly important when dementia or other disabilities are involved. Patients will also be able to share their medical records with physicians outside of their health network, thus avoiding unnecessary or repetitious workups.
OpenNotes contends that when patients review their doctors’ notes, they gain “a newfound, deeper respect for what physicians have to understand to do their jobs.” Other predicted advantages include improved medical record accuracy and less miscommunication. In a study published in 2019 that evaluated experiences of patients who read ambulatory visit notes, only 5% were more worried after reading the notes and 3% were confused.
Alleviating worry among clinicians may be a bigger problem; but as a general principle, you should avoid judgmental language, and never write anything in a chart that you wouldn’t want your patients or their family members – or lawyers – to see.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
. While some clinicians consider it an unwelcome intrusion, advocates say it will improve communication and compliance.
Patient access to notes is not new. In many states, patients already have the ability to request copies of their charts, or to access truncated information via clinic websites. The difference is that most patients will now be able to click on a patient portal – such as MyChart, or other similar apps – and gain instantaneous, unfettered access to everything in their records.
Clinicians have traditionally thought of medical notes as private journal entries; but in the last few decades they have become an important component of the documentation necessary for billing, as well as evidence in the event of litigation. Now, with the implementation of the Cures Act, medical notes have evolved into a tool to communicate with the patient, rather than just among health care providers, lawyers, and billing departments.
Supporters contend that this change will make a big difference, because patients will be able to see exactly what their doctors have written, rather than just a list of confusing test results and diagnosis lists in “medicalese.”
OpenNotes, a think tank that has promoted the sharing of clinical notes with patients for years, calls the Cures Act legislation a “new world” where shared notes are valuable tools to improve communication between patients and physicians while strengthening their relationship. They cite evidence indicating that “when health professionals offer patients and families ready access to clinical notes, the quality and safety of care improves.”
Not all doctors are as enthusiastic. Many are concerned that patients might misinterpret what they see in their doctors’ notes, including complex descriptions of clinical assessments and decisions.
Others worry about patients having immediate access to their records, perhaps even before their physicians. The American Academy of Dermatology is working with the American Medical Association and other groups to gather real-world instances where the release of lab results, reports, or notes directly to patients before their physician could review the information with them caused emotional harm or other adverse consequences.
Undoubtedly, there are scenarios where unrestricted display of clinical notes could be problematic. One example is the issue of adolescents and reproductive health. Since parents now have access to their children’s records, some teenagers might hesitate to confide in their physicians and deny themselves important medical care.
The new rules permit blocking access to records if there is clear evidence that doing so “will substantially reduce the risk of harm” to patients or third parties. Psychotherapy counseling notes, for example, are completely exempt from the new requirements.
There are also state-level laws that can supersede the new federal law and block access to notes. For example, California law forbids providers from posting cancer test results without discussing them with the patient first.
Research indicates that shared notes have benefits that should outweigh the concerns of most physicians. One study showed that about 70% of patients said reviewing their notes helped them understand why medications were prescribed, which improved their compliance. This was particularly true for patients whose primary language is not English. A British study found that patients felt empowered by shared notes, and thought they improved their relationship with their physicians.
Other advantages of sharing notes include the ability of family members to review what happened at visits, which can be particularly important when dementia or other disabilities are involved. Patients will also be able to share their medical records with physicians outside of their health network, thus avoiding unnecessary or repetitious workups.
OpenNotes contends that when patients review their doctors’ notes, they gain “a newfound, deeper respect for what physicians have to understand to do their jobs.” Other predicted advantages include improved medical record accuracy and less miscommunication. In a study published in 2019 that evaluated experiences of patients who read ambulatory visit notes, only 5% were more worried after reading the notes and 3% were confused.
Alleviating worry among clinicians may be a bigger problem; but as a general principle, you should avoid judgmental language, and never write anything in a chart that you wouldn’t want your patients or their family members – or lawyers – to see.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.