User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Pfizer COVID vaccine antibodies may disappear in 7 months, study says
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a new study published on the bioRxiv preprint server.
In the study, which hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed or formally published in a medical journal, researchers analyzed blood samples from 46 healthy young or middle-aged adults after receiving two doses, and then 6 months after the second dose.
“Our study shows vaccination with the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine induces high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the original vaccine strain, but these levels drop by nearly 10-fold by 7 months,” the researchers told Reuters.
In about half of the adults, neutralizing antibodies were undetectable at 6 months after the second dose, particularly against coronavirus variants such as Delta, Beta, and Mu.
Neutralizing antibodies only make up part of the body’s immune defense against the virus, Reuters noted, but they are still “critically important” in protecting against coronavirus infections.
“These findings suggest that administering a booster dose at around 6 to 7 months following the initial immunization will likely enhance protection,” the study authors wrote.
BioNTech said a new vaccine formula will likely be needed by mid-2022 to protect against future mutations of the virus, according to the Financial Times.
“This year, [a different vaccine] is completely unneeded, but by mid-next year, it could be a different situation,” Ugur Sahin, MD, cofounder and CEO of BioNTech, told the news outlet.
Current variants, namely the Delta variant, are more contagious than the original coronavirus strain but not different enough to evade current vaccines, he said. But new strains may be able to evade boosters.
“This virus will stay, and the virus will further adapt,” Dr. Sahin said. “This is a continuous evolution, and that evolution has just started.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
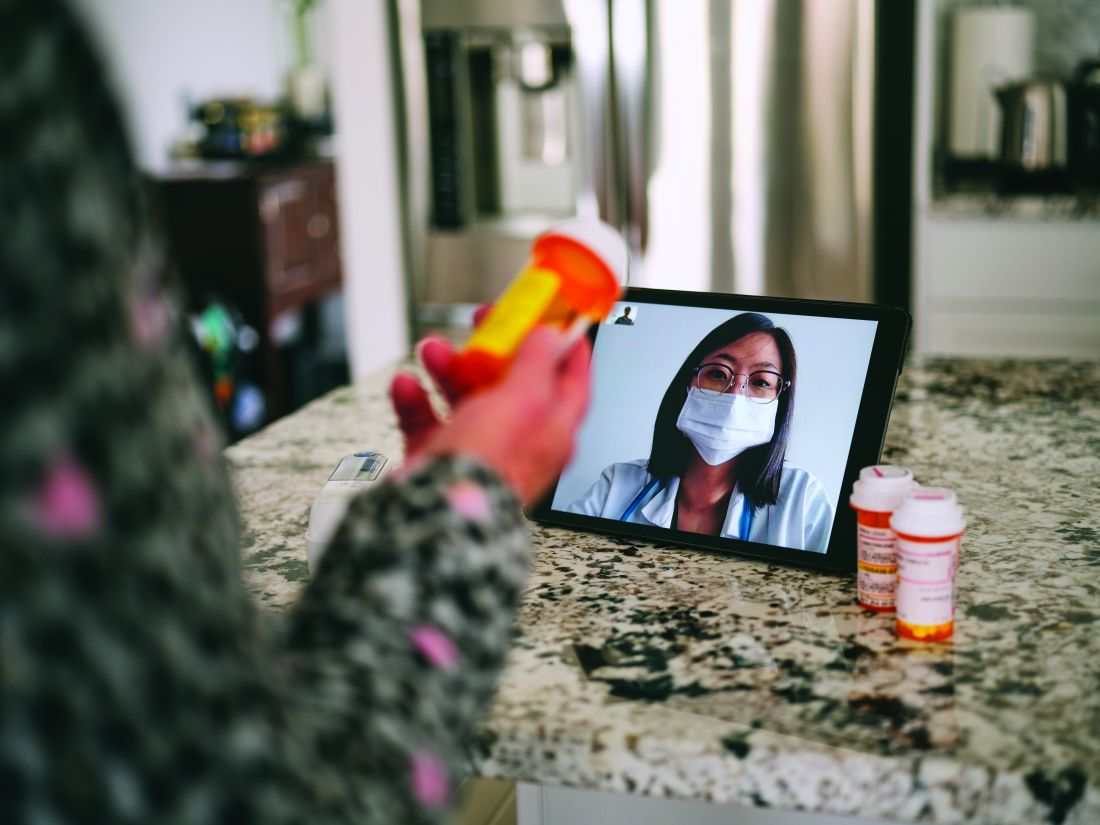
New data illustrate pandemic pivot to telehealth by patients, physicians
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth use, although much higher than before the COVID-19 pandemic, accounted for less than 20% of weekly outpatient visits 6 months into the pandemic, according to a new report from the American Medical Association. Ten percent of weekly visits were conducted via videoconferencing, and 8.1% of visits were conducted using the telephone.
Those figures may overstate the true level of telehealth use in fall 2020. A study by the Commonwealth Fund, Harvard University, Boston, and Phreesia found that in December of that year, only 8% of outpatient visits involved the use of telemedicine – and that was up from 6% in October. In contrast to the AMA results, which came from its 2020 benchmark survey of physicians, the Commonwealth Fund study used data from practice management systems and an online patient registration platform, as well as electronic health record data.
A more recent survey of hospital executives found that as of September 2021, hospital telehealth visits had leveled off at 10% to 20% of appointments. Similarly, a McKinsey survey in July showed that telehealth encounters made up 13% to 17% of evaluation and management visits across all specialties.
Big jump during pandemic
The AMA report offers a wealth of data on how physicians use telehealth and the differences between specialties in this area.
The report found that 70.3% of physicians worked in practices that used videoconferencing to provide patient visits in September 2020, compared to 14.3% of physicians in September 2018. Sixty-seven percent of physicians worked in practices that used telephone visits (the comparable figure for 2018 was unavailable).
Overall, 79% of physicians worked in a practice that used telehealth, compared to 25% in 2018.
Not every doctor in practices that utilized telehealth conducted virtual visits. In contrast to the 70.3% of doctors who were in practices that had video visits, only 59.1% of the respondents had personally conducted a videoconferencing visit in the previous week. The average numbers of weekly video and telephone visits per physician were 9.9 and 7.6, respectively, including those who did none.
There were big differences in virtual visit use among specialties as well. Eighty-five percent of psychiatrists were in practices that provided online appointments, according to the AMA survey, and three-quarters of primary care physicians said their practices offered telehealth appointments. Pediatricians were much less likely than family practice/general practice physicians (FPs/GPs) or general internists to do so.
The practices of many medical specialists were also highly likely to provide telehealth. Over 75% of practices in cardiology, endocrinology/diabetes, gastroenterology, nephrology, and neurology offered telehealth visits. About 88% of hematologists/oncologists offered video visits. Far fewer surgeons reported that their practice used virtual visits; the exceptions were urologists and dermatologists, 87% of whose practices used telehealth.
How telehealth was used
Across all specialties, 58% of physicians said clinicians in their practices used it to diagnose or treat patients; 59.2%, to manage patients with chronic disease; 50.4%, to provide acute care; and 34.3%, to provide preventive care.
Seventy-two percent of FP/GP and pediatric practices used telehealth to diagnose or treat patients. Just 64.9% of internists said their practices did so, and only 61.9% of them said their practices provided acute care via telehealth, versus 70% of FPs/GPs and pediatricians.
Among medical specialties, endocrinologists/diabetes physicians were those most likely to report the practice-level use of telehealth to diagnose or treat patients (71.9%), manage patients with chronic disease (92.1%), and provide preventive care (52.6%).
Significantly, 33% of medical specialists said their practices used remote patient monitoring. This finding was driven by high rates of use among cardiology practices (63.3%) and endocrinology practices (41.6%). Overall, the practice-level use of remote patient monitoring rose from 10.4% of practices in 2018 to 19.9% in 2020.
Virtual consults with peers
Some practices used telehealth to enable physicians to consult with colleagues. Twelve percent of respondents said their practices used telehealth to seek a second opinion from a health care professional in 2020, compared to 6.9% in 2018. Formal consultations via telehealth were also increasingly common: 17.2% of doctors said their practices did this in 2020, compared to 11.3% in 2018.
Also of note, 22.4% of physicians said their practices used telehealth for after-hours care or night calls in 2020, versus 9.9% in 2018.
The AMA report credited telehealth and expanded coverage and payment rules for enabling physician practices to keep their revenue streams positive and their practices open. However, the Commonwealth Fund study found “a substantial cumulative reduction in visits across all specialties over the course of the pandemic in 2020.” These ranged from a drop of 27% in pediatric visits to a decline of 8% in rheumatology visits during the period from March to December 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Predicted pandemic retirement of many physicians hasn’t happened
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The number of physicians who have chosen early retirement or have left medicine because of the COVID-19 pandemic may be considerably lower than previously thought, results of a new study suggest.
The research letter in the Journal of the American Medical Association, based on Medicare claims data, stated that “practice interruption rates were similar before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, except for a spike in April 2020.”
By contrast, in a Physicians Foundation Survey conducted in August 2020, 8% of physicians said they had closed their practices as a result of COVID, and 4% of the respondents said they planned to leave their practices within the next 12 months.
Similarly, a Jackson Physician Search survey in the fourth quarter of 2020 found that 54% of physicians surveyed had changed their employment plans. Of those doctors, 21% said they might hang up their white coat for early retirement. That works out to about 11% of the respondents.
The JAMA study’s authors analyzed the Medicare claims data from Jan. 1, 2019, to Dec. 30, 2020, to see how many physicians with Medicare patients had stopped filing claims for a period during those 2 years.
If a doctor had ceased submitting claims and then resumed filing them within 6 months after the last billing month, the lapse in filing was defined as “interruption with return.” If a physician stopped filing claims to Medicare and did not resume within 6 months, the gap in filing was called “interruption without return.”
In April 2020, 6.9% of physicians billing Medicare had a practice interruption, compared to 1.4% in 2019. But only 1.1% of physicians stopped practice in April 2020 and did not return, compared with 0.33% in 2019.
Physicians aged 55 or older had higher rates of interruption both with and without return than younger doctors did. The change in interruption rates for older doctors was 7.2% vs. 3.9% for younger physicians. The change in older physicians’ interruption-without-return rate was 1.3% vs. 0.34% for younger colleagues.
“Female physicians, specialists, physicians in smaller practices, those not in a health professional shortage area, and those practicing in a metropolitan area experienced greater increases in practice interruption rates in April 2020 vs. April 2019,” the study states. “But those groups typically had higher rates of return, so the overall changes in practice interruptions without return were similar across characteristics other than age.”
Significance for retirement rate
Discussing these results, the authors stressed that practice interruptions without return can’t necessarily be attributed to retirement, and that practice interruptions with return don’t necessarily signify that doctors had been furloughed from their practices.
Also, they said, “this measure of practice interruption likely misses meaningful interruptions that lasted for less than a month or did not involve complete cessation in treating Medicare patients.”
Nevertheless, “the study does capture a signal of some doctors probably retiring,” Jonathan Weiner, DPH, professor of health policy and management at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said in an interview.
But he added, “Some of those people who interrupted their practices and didn’t return may still come back. And there are probably a lot of other doctors who are leaving or changing practices that they didn’t capture.” For example, it’s possible that some doctors who went to work for other health care organizations stopped billing under their own names.
In Dr. Weiner’s view, the true percentage of physicians who have retired since the start of the pandemic is probably somewhere between the portion of doctors who interrupted their practice without return, according to the JAMA study, and the percentage of physicians who said they had closed their practices in the Physicians Foundation survey.
No mass exodus seen
Michael Belkin, JD, divisional vice president of recruiting for Merritt Hawkins, a physician search firm, said in an interview that the real number may be closer to the interruption-without-return figure in the JAMA study.
While many physician practices were disrupted in spring of 2020, he said, “it really didn’t result in a mass exodus [from health care]. We’re not talking to a lot of candidates who retired or walked away from their practices. We are talking to candidates who slowed down last year and then realized that they wanted to get back into medicine. And now they’re actively looking.”
One change in job candidates’ attitude, Mr. Belkin said, is that, because of COVID-19–related burnout, their quality of life is more important to them.
“They want to know, ‘What’s the culture of the employer like? What did they do last year during COVID? How did they handle it? Have they put together any protocols for the next pandemic?’ “
Demand for doctors has returned
In the summer of 2020, there was a major drop in physician recruitment by hospitals and health systems, partly because of fewer patient visits and procedures. But demand for doctors has bounced back over the past year, Mr. Belkin noted. One reason is the pent-up need for care among patients who avoided health care providers in 2020.
Another reason is that some employed doctors – particularly older physicians – have slowed down. Many doctors prefer to work remotely 1 or 2 days a week, providing telehealth visits to patients. That has led to a loss of productivity in many health care organizations and, consequently, a need to hire additional physicians.
Nevertheless, not many doctors are heading for the exit earlier than physicians did before COVID-19.
“They may work reduced hours,” Mr. Belkin said. “But the sense from a physician’s perspective is that this is all they know. For them to walk away from their life in medicine, from who they are, is problematic. So they’re continuing to practice, but at a reduced capacity.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study finds paying people to participate in clinical trials is not unethical
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paying people to participate in clinical trials remains controversial. But to date, most reservations are based on hypothetical scenarios or expert opinion with few real-world data to support them.
Research released this week could change that.
Investigators offered nearly 1,300 participants in two clinical trials either no payment or incentives up to $500 to partake in a smoking cessation study or an analysis of a behavioral intervention to increase ambulation in hospitalized patients.
More cash was associated with greater agreement to participate in the smoking cessation study but not the ambulation trial.
But the bigger news may be that offering payment did not appear to get people to accept more risks or skew participation to lower-income individuals, as some ethicists have warned.
“With the publication of our study, investigators finally have data that they can cite to put to rest any lingering concerns about offering moderate incentives in low-risk trials,” lead author Scott D. Halpern, MD, PhD, the John M. Eisenberg Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology, and Medical Ethics & Health Policy at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
This initial real-world data centers on low-risk interventions and more research is needed to analyze the ethics and effectiveness of paying people to join clinical trials with more inherent risk, the researchers note.
The study was published online Sept. 20 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
A good first step?
“Payments to research participants are notoriously controversial. Many people oppose payments altogether or insist on minimal payments out of concern that people might be unduly influenced to participate,” Ana S. Iltis, PhD, told this news organization when asked for comment. “Others worry that incentives will disproportionately motivate the less well-off to participate.”
“This is an important study that begins to assess whether these concerns are justified in a real-world context,” added Dr. Iltis, director of the Center for Bioethics, Health and Society and professor of philosophy at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
In an accompanying invited commentary, Sang Ngo, Anthony S. Kim, MD, and Winston Chiong, MD, PhD, write: “This work is welcome, as it presents experimental data to a bioethical debate that so far has been largely driven by conjecture and competing suppositions.”
The commentary authors, however, question the conclusiveness of the findings. “Interpreting the authors’ findings is complex and illustrates some of the challenges inherent to applying empirical data to ethical problems,” they write.
Recruitment realities
When asked his advice for researchers considering financial incentives, Dr. Halpern said: “All researchers would happily include incentives in their trial budgets if not for concerns that the sponsor or institutional review board might not approve of them.”
“By far the biggest threat to a trial’s success is the inability to enroll enough participants,” he added.
Dr. Iltis agreed, framing the need to boost enrollment in ethical terms. “There is another important ethical issue that often gets ignored, and that is the issue of studies that fail to enroll enough participants and are never completed or are underpowered,” she said.
“These studies end up exposing people to research risks and burdens without a compensating social benefit.”
“If incentives help to increase enrollment and do not necessarily result in undue influence or unfair participant selection, then there might be ethical reasons to offer incentives,” Dr. Iltis added.
Building on previous work assessing financial incentives in hypothetical clinical trials, Dr. Halpern and colleagues studied 654 participants with major depressive disorder in a smoking cessation trial. They also studied another 642 participants in a study that compared a gamification strategy to usual care for encouraging hospitalized patients to get out of bed and walk.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues randomly assigned people in the smoking cessation study to receive no financial compensation, $200, or $500. In the ambulation trial, participants were randomly allocated to receive no compensation, $100, or $300.
Key findings
A total of 22% of those offered no incentive enrolled in the smoking cessation study. In contrast, 36% offered $200 agreed, as did 47% of those offered $500, which the investigators say supports offering cash incentives to boost enrollment. The differences were significant (P < .001).
In contrast, the amount offered did not significantly incentivize more people to participate in the ambulation trial (P = .62). Rates were 45% with no compensation, 48% with $100 payment, and 43% with $300 payment.
In an analysis that adjusted for demographic differences, financial well-being, and Research Attitudes Questionnaire (RAQ-7) scores, each increase in cash incentive increased the odds of enrollment in the smoking cessation trial by 70% (adjusted odds ratio, 1.70; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-2.17).
The same effect was not seen in the ambulation trial, where each higher cash incentive did not make a significant difference (aOR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.64-1.22).
“The ambulation trial was a lower-risk trial in which patients’ willingness to participate was higher in general. So there were likely fewer people whose participation decisions could be influenced by offers of money,” Dr. Halpern said.
Inducement vs. coercion
The incentives in the study “did not function as unjust inducements, as they were not preferentially motivating across groups with different income levels or financial well-being in either trial,” the researchers note.
Dr. Halpern and colleagues also checked for any perceptions of coercion. More than 70% of participants in each smoking cessation trial group perceived no coercion, as did more than 93% of participants in each ambulation trial group, according to scores on a modified Perceived Coercion Scale of the MacArthur Admission Experience Survey.
Furthermore, perception of risks did not significantly alter the association between cash incentives and enrollment in either trial.
After collecting the findings, Dr. Halpern and colleagues informed participants about their participation in RETAIN and explained the rationale for using different cash incentives. They also let all participants know they would ultimately receive the maximum incentive – either $500 or $300, depending on the trial.
Research implications
A study limitation was reliance on participant risk perception, as was an inability to measure perceived coercion among people who chose not to participant in the trials. Another potential limitation is that “neither of these parent trials posed particularly high risks. Future tests of incentives of different sizes, and in the context of higher-risk parent trials, including trials that test treatments of serious illnesses, are warranted,” the researchers note.
“While there are many more questions to ask and contexts in which to study the effects of incentives, this study calls on opponents of incentivizing research participants with money to be more humble,” Dr. Iltis said. “Incentives might not have the effects they assume they have and which they have long held make such incentives unethical.”
“I encourage researchers who are offering incentives to consider working with people doing ethics research to assess the effects of incentives in their studies,” Dr. Halpern said. “Real-world, as opposed to hypothetical studies that can improve our understanding of the impact of incentives can improve the ethical conduct of research over time.”
Responding to criticism
The authors of the invited commentary questioned the definitions Dr. Halpern and colleagues used for undue or unjust inducement. “Among bioethicists, there is no consensus about what counts as undue inducement or an unjust distribution of research burdens. In this article, the authors have operationalized these constructs based on their own interpretations of undue and unjust inducement, which may not capture all the concerns that scholars have raised about inducement.”
Asked to respond to this and other criticisms raised in the commentary, Dr. Halpern said: “Did our study answer all possible questions about incentives? Absolutely not. But when it comes to incentives for research participation, an ounce of data is worth a pound of conjecture.”
There was agreement, however, that the findings could now put the onus on opponents of financial incentives for trial participants.
“I agree with the commentary’s authors that our study essentially shifts the burden of proof, such that, as they say, ‘those who would limit [incentives’] application may owe us an applicable criterion,’ ” Dr. Halpern said.
The authors of the invited commentary also criticized use of the study’s noninferiority design to rule out undue or unjust inducement. They note this design “may be unfamiliar to many bioethicists and can place substantial evaluative demands on readers.”
“As for the authors’ claim that noninferiority designs are difficult to interpret and unfamiliar to most clinicians and ethicists, I certainly agree,” Dr. Halpern said. “But that is hardly a reason to not employ the most rigorous methods possible to answer important questions.”
The study was supported by funding from the National Cancer Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
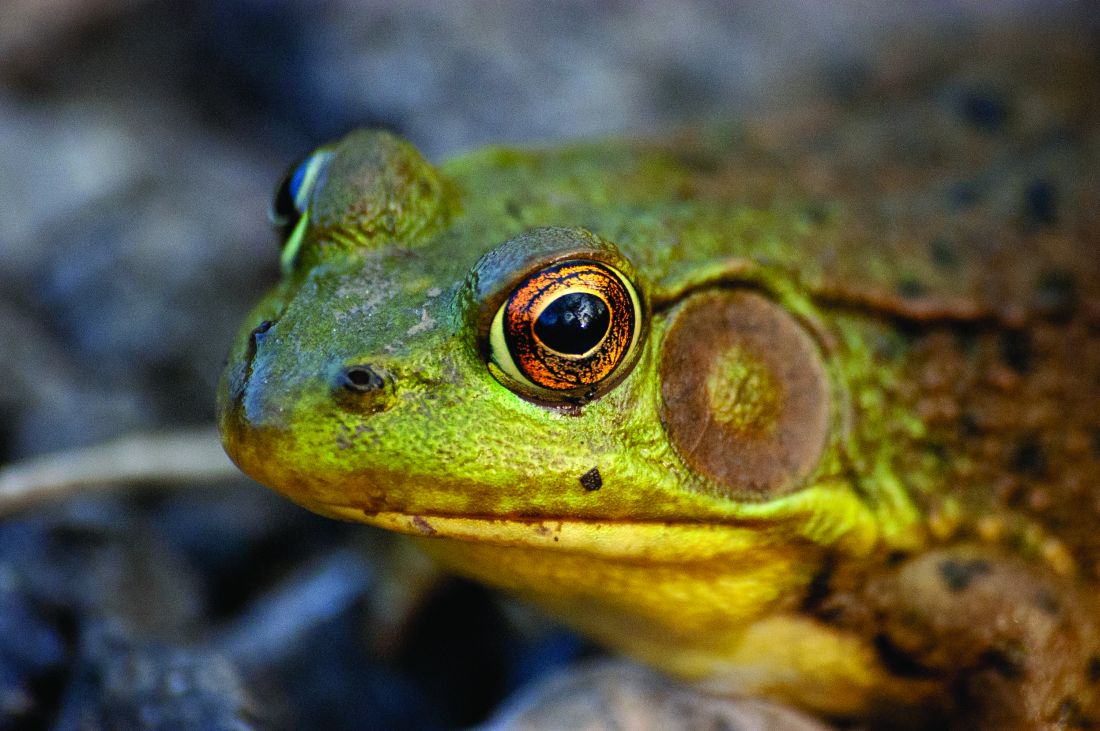
Cook your amphibians before you eat them
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!
Novel food for thought
When you were growing up, your parents probably told you to brush your teeth before you went to bed, warned you not to run with the scissors or play with matches, and punished you whenever you used the neighbor children to play Schrödinger’s cat.
They did those things for your own good, of course, and now the nation’s mother – the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – is doing the same by warning us about novel outbreak–associated foods. As in, “Put down that novel outbreak–associated food! You don’t know where it’s been!”
Seriously, you don’t know where it’s been. CDC investigators identified 28 novel foods that were linked to 36 foodborne-disease outbreaks that occurred during 2007-2016, including moringa leaf (herb/spice), tempeh (grain), frog, sprouted nut butter, and skate.
The novel foods implicated in these outbreaks were more likely to be imported, compared with 14,216 outbreaks that occurred from 1973 to 2016, and about half didn’t require refrigeration. Two-thirds did not need to be cooked after purchase. Another thing your parents wouldn’t like: Some can’t be washed, like sheep milk, sugar cane, or the aforementioned nut butter.
We wanted to get a food expert to comment on these novel foods, but our editor said that the assistant manager of our local Burger King wasn’t expert enough, so we’ve commandeered someone else’s expert. Cynthia Sears, MD, of Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, told Today.com all about the dangers of frogs: “Essentially all amphibians are contaminated, often with salmonella. Eating any amphibian that is not thoroughly cooked is a risk.”
Be sure to cook your amphibians before you eat them. Advice that your parents would be proud to share.
Dieters should stay away from diet drinks
When a drink is labeled “diet” many assume that the calorie-free beverage is the best choice. However, one of the largest studies to date on artificial sweeteners is out to set the record straight.
Artificial sweeteners, or nonnutritive sweeteners (NNS), are used in most if not all diet products to give the illusion of sweetness without the caloric guilt. Some studies say they help with weight loss for that very reason, but others say they can contribute to weight gain. So which is it?
Researchers at the University of Southern California sought to add some clarity to the research already out there.
They looked at an even-gendered split of 74 participants who drank 300 mL of drinks sweetened with NNS, table sugar, or water. The researchers then used functional MRI to see how parts of the brain responsible for appetite and cravings responded to images of high-calorie foods. They also looked at glucose, insulin, and other metabolic hormone levels, as well as how much food the participants ate at their free buffet. (In the participants’ defense, who can say no to a free buffet?)
The researchers made some interesting observations:
- Women who drank the NNS drink ate more than did the table-sugar group, but all men ate the same.
- Images of those calorie-packed goodies increased cravings and appetite for obese men and women in the NNS group, compared with the table-sugar group.
- For all participants who drank the NNS drink, there was a decrease in the hormone that tells the body it’s full.
“By studying different groups we were able to show that females and people with obesity may be more sensitive to artificial sweeteners. For these groups, drinking artificially sweetened drinks may trick the brain into feeling hungry, which may in turn result in more calories being consumed,” Kathleen Page, MD, the study’s corresponding author, said in a separate statement.
Today’s lesson? Don’t believe every label you read.
Instagram vegetables and the triumph of peer pressure
You and your family are sitting down for dinner. You’ve taken the time to prepare a healthy, nutritious meal. Vegetables, rice, seafood – all the right things. But the children around you refuse to partake. What can you do? Why, show them a highly liked photo of broccoli on Instagram!
In reality, kids will probably never like to eat their vegetables, but according to a study published in Appetite, viewing highly liked images on social media can compel adults to eat theirs.
The investigators recruited a group of 169 adults aged 18-28 (average age, 21) and showed them a series of mock Instagram posts of all sorts of food, everything from Brussels sprouts to chocolate cake, as well as nonfood images to act as a baseline. The images had a varying amount of likes. After viewing the images, study participants were offered a snack buffet consisting of grapes and cookies.
The results were a triumph of peer pressure. Those who viewed highly liked images of nutritious foods ate a significantly larger proportion of grapes, compared with those who saw highly liked images of unhealthy food or nonfood.
The authors cautioned that more research is needed, but they said that they’re onto something in the eternal struggle of getting people to eat better. If Mikey liked it, maybe you should, too. Just as long as you don’t try to encourage the eating of peas. That is a dark road none should take, and no one should ever be subjected to that cursed food.
It’s nice to share … hypertension?
You may have heard that, over time, you begin to resemble your spouse. You may have also heard that, as time goes by, your pet might start to resemble you, but that is a story for another time.
A lot of the time, it’s human nature that people partner with someone who is similar to them in physical and environmental status. If you like to go jogging at 5 a.m., you might want a spouse who does the same. A study done using data from couples in Japan and the Netherlands found that couples who had the same lifestyle had similar levels of blood pressure, cholesterol, and triglycerides. They also had similar illnesses such as hypertension and diabetes.
It’s important to note that many of the couples were not very genetically similar but had similar lifestyles. Encourage your partner to have a healthier lifestyle, so you can live on for many years to come!
Greater portal use gives patients access, doctors headaches
The use of patient portals that provide access to electronic health records has dramatically increased in the past several years, and patients whose health care practitioner encouraged them to use their online portal accessed them at a higher rate than those who were not encouraged to do so.
These were among the top-line results of a national survey of U.S. adults conducted by the National Institutes of Health from January 2020 to April 2020. Although the COVID-19 pandemic hit the United States in the middle of that period, a report on the survey by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT stated, “These findings largely reflect prepandemic rates of individuals being offered and subsequently using their online medical record, also known as a patient portal.”
But with more patient access can come additional work for physicians and other health care practitioners, ranging from an onslaught of patient communications to managing data sent to them by patients.
According to the report, 59% of individuals were offered access to their patient portal, and 38% accessed their record at least once in 2020. By comparison, in 2014, just 42% were offered access to their portal, and 25% used it. But these percentages hardly changed from 2019 to 2020.
The increase in the percentage of people who accessed portals reflects the fact that more people were offered access. In addition, there were signs of rising activity among portal users.
Among patients offered access to their patient portal, 64% accessed it at least once in 2020 – 11 percentage points more than in 2017. Twenty-seven percent of those who had access to a portal used it once or twice; 20% accessed it three to five times; and 18% used it six or more times. The latter two percentages were significantly higher than in 2017.
Of the respondents who were offered access to portals but didn’t use them, 69% said they didn’t access the portal because they preferred to speak with their health care practitioner directly. Sixty-three percent said they didn’t see a need to use their online medical record. This was similar to the percentage 3 years earlier. Other reasons included respondents’ concerns about the privacy/security of online medical records (24%), their lack of comfort with computers (20%), and their lack of Internet access (13%).
The pros and cons of patient portals, greater access
Among portal users who accessed their records through a mobile health app, 51% used the app to facilitate discussions with their health care practitioner in 2020, an 8–percentage point increase from 2017. Fifty-percent of the mobile health app users utilized it to make a decision about how to treat an illness or condition, up from 45% in 2017. And 71% of these individuals used their app to track progress on a health-related goal, just a bit more than in 2017.
Individuals who were encouraged by their health care practitioner to use their patient portal viewed clinical notes and exchanged secure messages with their practitioner at higher rates than those who had not been encouraged. This is not surprising, but it reflects an unintended result of patient portals that many physicians have found burdensome, especially during the pandemic: overflowing electronic in-boxes.
Robert Wachter, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, recently tweeted, “We’re seeing huge uptick in in-box messages for MDs during COVID – now seems like biggest driver of MD burnout. The fundamental problem: We turned on 24/7/365 access for patients (who of course like it) with no operational or business model to handle it. Crucial that we fix this.”
Steven Waldren, MD, vice president and chief medical informatics officer at the American Academy of Family Physicians, told this news organization that he agrees that this is a major challenge. “In-box management is a burden on physicians and practices,” he said. “However, it can be done better, either through a team in-box or through better use of technology.”
The team in-box he refers to is a mechanism for triaging patient messages. For example, a triage nurse can look at the messages and decide which ones can be handled by staff and which ones the doctor needs to see. Or physicians and front office staff can see the messages at the same time; a nurse can triage some messages according to protocols, and the physician can respond to any message, depending on what he or she knows about the patient.
Technology can also be enlisted in the effort, he suggested, perhaps by automating the triaging of messages such as prescription refill requests or using artificial intelligence to sort messages by content.
Making patient records portable
Nearly 40% of portal users accessed it using a smartphone app (17%) or with both their smartphone app and their computer (22%). Sixty-one percent of users relied exclusively on computers to access their portals.
About a third of patient portal users downloaded their online medical records in 2020. This proportion has nearly doubled from 17% since 2017, the ONC report noted.
Although the survey didn’t ask about multiple downloads, it appears that most people had to download their records separately from the patient portal of each practitioner who cared for them. Although the Apple Health app allows people to download records to their iPhones from multiple portals using a standard application programming interface, the ONC report says that only 5% of respondents transmitted their records to a service or app, up slightly from 3% in 2017.
Dr. Waldren hopes most patients will have the ability to download and integrate records from multiple practitioners in a few years, but he wouldn’t bet on it.
“A fair amount of work needs to be done on the business side and on figuring out how the data get connected together,” he said. “And there are still privacy concerns with apps.”
Overall, 21% of portal users transmitted their data to at least one outside party in 2020, compared with 14% in 2017. Seventeen percent of them sent their records to another health care practitioner, up from 10% in 2017. Five percent of the users transmitted their records to a caregiver, slightly more than in 2017.
Managing data is a challenge
Asked how physicians feel about portal users adding information to their record or correcting inaccurate information, Dr. Waldren says, “Doctors are already comfortable with patient-generated data. The challenge is managing it. If the patient provides data that’s not easy to put in the EHR, that’s going to add work, and they don’t want to see 100 blood pressure readings.
“You’d be hard-pressed to find a doctor who doesn’t welcome additional information about the patient’s health, but it can be onerous and can take time to enter the data,” Dr. Waldren said.
Overall, he said, “Giving patients the ability to take more ownership of their health and participate in their own care is good and can help us move forward. How this will be integrated into patient care is another question.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The use of patient portals that provide access to electronic health records has dramatically increased in the past several years, and patients whose health care practitioner encouraged them to use their online portal accessed them at a higher rate than those who were not encouraged to do so.
These were among the top-line results of a national survey of U.S. adults conducted by the National Institutes of Health from January 2020 to April 2020. Although the COVID-19 pandemic hit the United States in the middle of that period, a report on the survey by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT stated, “These findings largely reflect prepandemic rates of individuals being offered and subsequently using their online medical record, also known as a patient portal.”
But with more patient access can come additional work for physicians and other health care practitioners, ranging from an onslaught of patient communications to managing data sent to them by patients.
According to the report, 59% of individuals were offered access to their patient portal, and 38% accessed their record at least once in 2020. By comparison, in 2014, just 42% were offered access to their portal, and 25% used it. But these percentages hardly changed from 2019 to 2020.
The increase in the percentage of people who accessed portals reflects the fact that more people were offered access. In addition, there were signs of rising activity among portal users.
Among patients offered access to their patient portal, 64% accessed it at least once in 2020 – 11 percentage points more than in 2017. Twenty-seven percent of those who had access to a portal used it once or twice; 20% accessed it three to five times; and 18% used it six or more times. The latter two percentages were significantly higher than in 2017.
Of the respondents who were offered access to portals but didn’t use them, 69% said they didn’t access the portal because they preferred to speak with their health care practitioner directly. Sixty-three percent said they didn’t see a need to use their online medical record. This was similar to the percentage 3 years earlier. Other reasons included respondents’ concerns about the privacy/security of online medical records (24%), their lack of comfort with computers (20%), and their lack of Internet access (13%).
The pros and cons of patient portals, greater access
Among portal users who accessed their records through a mobile health app, 51% used the app to facilitate discussions with their health care practitioner in 2020, an 8–percentage point increase from 2017. Fifty-percent of the mobile health app users utilized it to make a decision about how to treat an illness or condition, up from 45% in 2017. And 71% of these individuals used their app to track progress on a health-related goal, just a bit more than in 2017.
Individuals who were encouraged by their health care practitioner to use their patient portal viewed clinical notes and exchanged secure messages with their practitioner at higher rates than those who had not been encouraged. This is not surprising, but it reflects an unintended result of patient portals that many physicians have found burdensome, especially during the pandemic: overflowing electronic in-boxes.
Robert Wachter, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, recently tweeted, “We’re seeing huge uptick in in-box messages for MDs during COVID – now seems like biggest driver of MD burnout. The fundamental problem: We turned on 24/7/365 access for patients (who of course like it) with no operational or business model to handle it. Crucial that we fix this.”
Steven Waldren, MD, vice president and chief medical informatics officer at the American Academy of Family Physicians, told this news organization that he agrees that this is a major challenge. “In-box management is a burden on physicians and practices,” he said. “However, it can be done better, either through a team in-box or through better use of technology.”
The team in-box he refers to is a mechanism for triaging patient messages. For example, a triage nurse can look at the messages and decide which ones can be handled by staff and which ones the doctor needs to see. Or physicians and front office staff can see the messages at the same time; a nurse can triage some messages according to protocols, and the physician can respond to any message, depending on what he or she knows about the patient.
Technology can also be enlisted in the effort, he suggested, perhaps by automating the triaging of messages such as prescription refill requests or using artificial intelligence to sort messages by content.
Making patient records portable
Nearly 40% of portal users accessed it using a smartphone app (17%) or with both their smartphone app and their computer (22%). Sixty-one percent of users relied exclusively on computers to access their portals.
About a third of patient portal users downloaded their online medical records in 2020. This proportion has nearly doubled from 17% since 2017, the ONC report noted.
Although the survey didn’t ask about multiple downloads, it appears that most people had to download their records separately from the patient portal of each practitioner who cared for them. Although the Apple Health app allows people to download records to their iPhones from multiple portals using a standard application programming interface, the ONC report says that only 5% of respondents transmitted their records to a service or app, up slightly from 3% in 2017.
Dr. Waldren hopes most patients will have the ability to download and integrate records from multiple practitioners in a few years, but he wouldn’t bet on it.
“A fair amount of work needs to be done on the business side and on figuring out how the data get connected together,” he said. “And there are still privacy concerns with apps.”
Overall, 21% of portal users transmitted their data to at least one outside party in 2020, compared with 14% in 2017. Seventeen percent of them sent their records to another health care practitioner, up from 10% in 2017. Five percent of the users transmitted their records to a caregiver, slightly more than in 2017.
Managing data is a challenge
Asked how physicians feel about portal users adding information to their record or correcting inaccurate information, Dr. Waldren says, “Doctors are already comfortable with patient-generated data. The challenge is managing it. If the patient provides data that’s not easy to put in the EHR, that’s going to add work, and they don’t want to see 100 blood pressure readings.
“You’d be hard-pressed to find a doctor who doesn’t welcome additional information about the patient’s health, but it can be onerous and can take time to enter the data,” Dr. Waldren said.
Overall, he said, “Giving patients the ability to take more ownership of their health and participate in their own care is good and can help us move forward. How this will be integrated into patient care is another question.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The use of patient portals that provide access to electronic health records has dramatically increased in the past several years, and patients whose health care practitioner encouraged them to use their online portal accessed them at a higher rate than those who were not encouraged to do so.
These were among the top-line results of a national survey of U.S. adults conducted by the National Institutes of Health from January 2020 to April 2020. Although the COVID-19 pandemic hit the United States in the middle of that period, a report on the survey by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT stated, “These findings largely reflect prepandemic rates of individuals being offered and subsequently using their online medical record, also known as a patient portal.”
But with more patient access can come additional work for physicians and other health care practitioners, ranging from an onslaught of patient communications to managing data sent to them by patients.
According to the report, 59% of individuals were offered access to their patient portal, and 38% accessed their record at least once in 2020. By comparison, in 2014, just 42% were offered access to their portal, and 25% used it. But these percentages hardly changed from 2019 to 2020.
The increase in the percentage of people who accessed portals reflects the fact that more people were offered access. In addition, there were signs of rising activity among portal users.
Among patients offered access to their patient portal, 64% accessed it at least once in 2020 – 11 percentage points more than in 2017. Twenty-seven percent of those who had access to a portal used it once or twice; 20% accessed it three to five times; and 18% used it six or more times. The latter two percentages were significantly higher than in 2017.
Of the respondents who were offered access to portals but didn’t use them, 69% said they didn’t access the portal because they preferred to speak with their health care practitioner directly. Sixty-three percent said they didn’t see a need to use their online medical record. This was similar to the percentage 3 years earlier. Other reasons included respondents’ concerns about the privacy/security of online medical records (24%), their lack of comfort with computers (20%), and their lack of Internet access (13%).
The pros and cons of patient portals, greater access
Among portal users who accessed their records through a mobile health app, 51% used the app to facilitate discussions with their health care practitioner in 2020, an 8–percentage point increase from 2017. Fifty-percent of the mobile health app users utilized it to make a decision about how to treat an illness or condition, up from 45% in 2017. And 71% of these individuals used their app to track progress on a health-related goal, just a bit more than in 2017.
Individuals who were encouraged by their health care practitioner to use their patient portal viewed clinical notes and exchanged secure messages with their practitioner at higher rates than those who had not been encouraged. This is not surprising, but it reflects an unintended result of patient portals that many physicians have found burdensome, especially during the pandemic: overflowing electronic in-boxes.
Robert Wachter, MD, chairman of the department of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, recently tweeted, “We’re seeing huge uptick in in-box messages for MDs during COVID – now seems like biggest driver of MD burnout. The fundamental problem: We turned on 24/7/365 access for patients (who of course like it) with no operational or business model to handle it. Crucial that we fix this.”
Steven Waldren, MD, vice president and chief medical informatics officer at the American Academy of Family Physicians, told this news organization that he agrees that this is a major challenge. “In-box management is a burden on physicians and practices,” he said. “However, it can be done better, either through a team in-box or through better use of technology.”
The team in-box he refers to is a mechanism for triaging patient messages. For example, a triage nurse can look at the messages and decide which ones can be handled by staff and which ones the doctor needs to see. Or physicians and front office staff can see the messages at the same time; a nurse can triage some messages according to protocols, and the physician can respond to any message, depending on what he or she knows about the patient.
Technology can also be enlisted in the effort, he suggested, perhaps by automating the triaging of messages such as prescription refill requests or using artificial intelligence to sort messages by content.
Making patient records portable
Nearly 40% of portal users accessed it using a smartphone app (17%) or with both their smartphone app and their computer (22%). Sixty-one percent of users relied exclusively on computers to access their portals.
About a third of patient portal users downloaded their online medical records in 2020. This proportion has nearly doubled from 17% since 2017, the ONC report noted.
Although the survey didn’t ask about multiple downloads, it appears that most people had to download their records separately from the patient portal of each practitioner who cared for them. Although the Apple Health app allows people to download records to their iPhones from multiple portals using a standard application programming interface, the ONC report says that only 5% of respondents transmitted their records to a service or app, up slightly from 3% in 2017.
Dr. Waldren hopes most patients will have the ability to download and integrate records from multiple practitioners in a few years, but he wouldn’t bet on it.
“A fair amount of work needs to be done on the business side and on figuring out how the data get connected together,” he said. “And there are still privacy concerns with apps.”
Overall, 21% of portal users transmitted their data to at least one outside party in 2020, compared with 14% in 2017. Seventeen percent of them sent their records to another health care practitioner, up from 10% in 2017. Five percent of the users transmitted their records to a caregiver, slightly more than in 2017.
Managing data is a challenge
Asked how physicians feel about portal users adding information to their record or correcting inaccurate information, Dr. Waldren says, “Doctors are already comfortable with patient-generated data. The challenge is managing it. If the patient provides data that’s not easy to put in the EHR, that’s going to add work, and they don’t want to see 100 blood pressure readings.
“You’d be hard-pressed to find a doctor who doesn’t welcome additional information about the patient’s health, but it can be onerous and can take time to enter the data,” Dr. Waldren said.
Overall, he said, “Giving patients the ability to take more ownership of their health and participate in their own care is good and can help us move forward. How this will be integrated into patient care is another question.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children and COVID: New cases topped 200,000 after 3 weeks of declines
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Polyethylene glycol linked to rare allergic reactions seen with mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
A common inert ingredient may be the culprit behind the rare allergic reactions reported among individuals who have received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, according to investigators at a large regional health center that was among the first to administer the shots.
Blood samples from 10 of 11 individuals with suspected allergic reactions reacted to polyethylene glycol (PEG), a component of both the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, according to a report in JAMA Network Open.
In total, only 22 individuals had suspected allergic reactions out of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered, the investigators reported, noting that the reactions were generally mild and all fully resolved.
Those findings should be reassuring to individuals who are reticent to sign up for a COVID-19 vaccine because of fear of an allergic reaction, said study senior author Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“We’re hoping that this word will get out and then that the companies could also think about making vaccines that have other products in them that don’t include polyethylene glycol,” Dr. Nadeau said in an interview.
PEG is a compound used in many products, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. In the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, PEG serves to stabilize the lipid nanoparticles that help protect and transport mRNA. However, its use in this setting has been linked to allergic reactions in this and previous studies.
No immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies to PEG were detected among the 22 individuals with suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, but PEG immunoglobulin G (IgG) was present. That suggests non-IgE mediated allergic reactions to PEG may be implicated for the majority of cases, Dr. Nadeau said.
This case series provides interesting new evidence to confirm previous reports that a mechanism other than the classic IgE-mediated allergic response is behind the suspected allergic reactions that are occurring after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, said Aleena Banerji, MD, associate professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and clinical director of the Drug Allergy Program at Massachusetts General Hospital.
“We need to further understand the mechanism of these reactions, but what we know is that IGE mediated allergy to excipients like PEG is probably not the main cause,” Dr. Banerji, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
In a recent research letter published in JAMA Internal Medicine, Dr. Banerji and coauthors reported that all individuals with immediate suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine went on to tolerate the second dose, with mild symptoms reported in the minority of patients (32 out of 159, or about 20%).
“Again, that is very consistent with not having an IgE-mediated allergy, so it seems to all be fitting with that picture,” Dr. Banerji said.
The case series by Dr. Nadeau and coauthors was based on review of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered between December 18, 2020 and January 26, 2021. Most mRNA vaccine recipients were Stanford-affiliated health care workers, according to the report.
Among recipients of those doses, they identified 148 individuals who had anaphylaxis-related ICD-10 codes recorded over the same time period. In a review of medical records, investigators pinpointed 22 individuals as having suspected allergy and invited them to participate in follow-up allergy testing.
A total of 11 individuals underwent skin prick testing, but none of them tested positive to PEG or to polysorbate 80, another excipient that has been linked to vaccine-related allergic reactions. One of the patients tested positive to the same mRNA vaccine they had previously received, according to the report.
Those same 11 individuals also underwent basophil activation testing (BAT). In contrast to the skin testing results, BAT results were positive for PEG in 10 of 11 cases (or 91%) and positive for their administered vaccine in all 11 cases, the report shows.
High levels of IgG to PEG were identified in blood samples of individuals with an allergy to the vaccine. Investigators said it’s possible that the BAT results were activated due to IgG via complement activation–related pseudoallergy, or CARPA, as has been hypothesized by some other investigators.
The negative skin prick testing results for PEG, which contrast with the positive BAT results to PEG, suggest that the former may not be appropriate for use as a predictive marker of potential vaccine allergy, according to Dr. Nadeau.
“The take-home message for doctors is to be careful,” she said. “Don’t assume that just because the person skin-tests negative to PEG or to the vaccine itself that you’re out of the woods, because the skin test would be often negative in those scenarios.”
The study was supported by a grants from the Asthma and Allergic Diseases Cooperative Research Centers, a grant from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease SARS Vaccine study, the Parker Foundation, the Crown Foundation, and the Sunshine Foundation. Dr. Nadeau reports numerous conflicts with various sources in the industry. Dr. Banerji has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A common inert ingredient may be the culprit behind the rare allergic reactions reported among individuals who have received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, according to investigators at a large regional health center that was among the first to administer the shots.
Blood samples from 10 of 11 individuals with suspected allergic reactions reacted to polyethylene glycol (PEG), a component of both the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, according to a report in JAMA Network Open.
In total, only 22 individuals had suspected allergic reactions out of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered, the investigators reported, noting that the reactions were generally mild and all fully resolved.
Those findings should be reassuring to individuals who are reticent to sign up for a COVID-19 vaccine because of fear of an allergic reaction, said study senior author Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“We’re hoping that this word will get out and then that the companies could also think about making vaccines that have other products in them that don’t include polyethylene glycol,” Dr. Nadeau said in an interview.
PEG is a compound used in many products, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. In the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, PEG serves to stabilize the lipid nanoparticles that help protect and transport mRNA. However, its use in this setting has been linked to allergic reactions in this and previous studies.
No immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies to PEG were detected among the 22 individuals with suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, but PEG immunoglobulin G (IgG) was present. That suggests non-IgE mediated allergic reactions to PEG may be implicated for the majority of cases, Dr. Nadeau said.
This case series provides interesting new evidence to confirm previous reports that a mechanism other than the classic IgE-mediated allergic response is behind the suspected allergic reactions that are occurring after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, said Aleena Banerji, MD, associate professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and clinical director of the Drug Allergy Program at Massachusetts General Hospital.
“We need to further understand the mechanism of these reactions, but what we know is that IGE mediated allergy to excipients like PEG is probably not the main cause,” Dr. Banerji, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
In a recent research letter published in JAMA Internal Medicine, Dr. Banerji and coauthors reported that all individuals with immediate suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine went on to tolerate the second dose, with mild symptoms reported in the minority of patients (32 out of 159, or about 20%).
“Again, that is very consistent with not having an IgE-mediated allergy, so it seems to all be fitting with that picture,” Dr. Banerji said.
The case series by Dr. Nadeau and coauthors was based on review of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered between December 18, 2020 and January 26, 2021. Most mRNA vaccine recipients were Stanford-affiliated health care workers, according to the report.
Among recipients of those doses, they identified 148 individuals who had anaphylaxis-related ICD-10 codes recorded over the same time period. In a review of medical records, investigators pinpointed 22 individuals as having suspected allergy and invited them to participate in follow-up allergy testing.
A total of 11 individuals underwent skin prick testing, but none of them tested positive to PEG or to polysorbate 80, another excipient that has been linked to vaccine-related allergic reactions. One of the patients tested positive to the same mRNA vaccine they had previously received, according to the report.
Those same 11 individuals also underwent basophil activation testing (BAT). In contrast to the skin testing results, BAT results were positive for PEG in 10 of 11 cases (or 91%) and positive for their administered vaccine in all 11 cases, the report shows.
High levels of IgG to PEG were identified in blood samples of individuals with an allergy to the vaccine. Investigators said it’s possible that the BAT results were activated due to IgG via complement activation–related pseudoallergy, or CARPA, as has been hypothesized by some other investigators.
The negative skin prick testing results for PEG, which contrast with the positive BAT results to PEG, suggest that the former may not be appropriate for use as a predictive marker of potential vaccine allergy, according to Dr. Nadeau.
“The take-home message for doctors is to be careful,” she said. “Don’t assume that just because the person skin-tests negative to PEG or to the vaccine itself that you’re out of the woods, because the skin test would be often negative in those scenarios.”
The study was supported by a grants from the Asthma and Allergic Diseases Cooperative Research Centers, a grant from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease SARS Vaccine study, the Parker Foundation, the Crown Foundation, and the Sunshine Foundation. Dr. Nadeau reports numerous conflicts with various sources in the industry. Dr. Banerji has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A common inert ingredient may be the culprit behind the rare allergic reactions reported among individuals who have received mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, according to investigators at a large regional health center that was among the first to administer the shots.
Blood samples from 10 of 11 individuals with suspected allergic reactions reacted to polyethylene glycol (PEG), a component of both the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, according to a report in JAMA Network Open.
In total, only 22 individuals had suspected allergic reactions out of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered, the investigators reported, noting that the reactions were generally mild and all fully resolved.
Those findings should be reassuring to individuals who are reticent to sign up for a COVID-19 vaccine because of fear of an allergic reaction, said study senior author Kari Nadeau, MD, PhD, director of the Parker Center for Allergy and Asthma Research at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“We’re hoping that this word will get out and then that the companies could also think about making vaccines that have other products in them that don’t include polyethylene glycol,” Dr. Nadeau said in an interview.
PEG is a compound used in many products, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. In the mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, PEG serves to stabilize the lipid nanoparticles that help protect and transport mRNA. However, its use in this setting has been linked to allergic reactions in this and previous studies.
No immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies to PEG were detected among the 22 individuals with suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, but PEG immunoglobulin G (IgG) was present. That suggests non-IgE mediated allergic reactions to PEG may be implicated for the majority of cases, Dr. Nadeau said.
This case series provides interesting new evidence to confirm previous reports that a mechanism other than the classic IgE-mediated allergic response is behind the suspected allergic reactions that are occurring after mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, said Aleena Banerji, MD, associate professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and clinical director of the Drug Allergy Program at Massachusetts General Hospital.
“We need to further understand the mechanism of these reactions, but what we know is that IGE mediated allergy to excipients like PEG is probably not the main cause,” Dr. Banerji, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
In a recent research letter published in JAMA Internal Medicine, Dr. Banerji and coauthors reported that all individuals with immediate suspected allergic reactions to mRNA COVID-19 vaccine went on to tolerate the second dose, with mild symptoms reported in the minority of patients (32 out of 159, or about 20%).
“Again, that is very consistent with not having an IgE-mediated allergy, so it seems to all be fitting with that picture,” Dr. Banerji said.
The case series by Dr. Nadeau and coauthors was based on review of nearly 39,000 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine doses administered between December 18, 2020 and January 26, 2021. Most mRNA vaccine recipients were Stanford-affiliated health care workers, according to the report.
Among recipients of those doses, they identified 148 individuals who had anaphylaxis-related ICD-10 codes recorded over the same time period. In a review of medical records, investigators pinpointed 22 individuals as having suspected allergy and invited them to participate in follow-up allergy testing.
A total of 11 individuals underwent skin prick testing, but none of them tested positive to PEG or to polysorbate 80, another excipient that has been linked to vaccine-related allergic reactions. One of the patients tested positive to the same mRNA vaccine they had previously received, according to the report.
Those same 11 individuals also underwent basophil activation testing (BAT). In contrast to the skin testing results, BAT results were positive for PEG in 10 of 11 cases (or 91%) and positive for their administered vaccine in all 11 cases, the report shows.
High levels of IgG to PEG were identified in blood samples of individuals with an allergy to the vaccine. Investigators said it’s possible that the BAT results were activated due to IgG via complement activation–related pseudoallergy, or CARPA, as has been hypothesized by some other investigators.
The negative skin prick testing results for PEG, which contrast with the positive BAT results to PEG, suggest that the former may not be appropriate for use as a predictive marker of potential vaccine allergy, according to Dr. Nadeau.
“The take-home message for doctors is to be careful,” she said. “Don’t assume that just because the person skin-tests negative to PEG or to the vaccine itself that you’re out of the woods, because the skin test would be often negative in those scenarios.”
The study was supported by a grants from the Asthma and Allergic Diseases Cooperative Research Centers, a grant from the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease SARS Vaccine study, the Parker Foundation, the Crown Foundation, and the Sunshine Foundation. Dr. Nadeau reports numerous conflicts with various sources in the industry. Dr. Banerji has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Alarming’ increase in fake pills laced with fentanyl, methamphetamine, DEA warns
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Top questions answered about COVID-19 boosters for your patients
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Confusion continues to circulate in the wake of decisions on booster doses of the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, all announced within 1 week. Many people – including those now eligible and those who officially have to wait for their shot at a third dose – have questions.
Multiple agencies are involved in the booster decisions, and they have put out multiple – and sometimes conflicting – messages about booster doses, leaving more questions than answers for many people.
On Sept. 22, the Food and Drug Administration granted an emergency use authorization (EUA) for a booster dose of the Pfizer mRNA COVID-19 vaccine for those 65 and older and those at high risk for severe illness from the coronavirus, including essential workers whose jobs increase their risk for infection – such as frontline health care workers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, then overruled advice from the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) to recommend boosters for essential workers such as those working on the front lines during the pandemic.
As it stands now, the CDC recommends that the following groups should get a third dose of the Pfizer vaccine:
- People aged 65 years and older.
- People aged 18 years and older in long-term care settings.
- People aged 50-64 years with underlying medical conditions.
The CDC also recommends that the following groups may receive a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine, based on their individual benefits and risks:
- People aged 18-49 years with underlying medical conditions.
- People aged 18-64 years at increased risk for COVID-19 exposure and transmission because of occupational or institutional setting.
The CDC currently considers the following groups at increased risk for COVID-19:
- First responders (health care workers, firefighters, police, congregate care staff).
- Education staff (teachers, support staff, day care workers).
- Food and agriculture workers.
- Manufacturing workers.
- Corrections workers.
- U.S. Postal Service workers.
- Public transit workers.
- Grocery store workers.
Health care professionals, among the most trusted sources of COVID-19 information, are likely to encounter a number of patients wondering how all this will work.
“It’s fantastic that boosters will be available for those who the data supports need [them],” Rachael Piltch-Loeb, PhD, said during a media briefing on Sept. 23, held between the FDA and CDC decisions.
“But we’re really in a place where we have a lot more questions and answers about what the next phase of the vaccine availability and updates are going to be in the United States,” added Dr. Piltch-Loeb, preparedness fellow in the division of policy translation and leadership development and a research associate in the department of biostatistics at the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
1. What is the biggest concern you are hearing from patients about getting a booster?
“The biggest concerns are that everyone wants it and they don’t know where to get it. In health care’s defense, the CDC just figured out what to do,” said Janet Englund, MD, professor of pediatric infectious diseases and an infectious disease and virology expert at Seattle Children’s Hospital in Washington.
“Everyone thinks they should be eligible for a booster ... people in their 50s who are not yet 65+, people with young grandchildren, etc.,” she added. “I’m at Seattle Children’s Hospital, so people are asking about booster shots and about getting their children vaccinated.”
Boosters for all COVID-19 vaccines are completely free.
“All COVID-19 vaccines, including booster doses, will be provided free of charge to the U.S. population,” the CDC has said.
2. Will patients need to prove they meet eligibility criteria for a booster shot or will it be the honor system?
“No, patients will only need to attest that they fall into one of the high-risk groups for whom a booster vaccine is authorized,” said Robert Atmar, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston.
Dr. Piltch-Loeb agreed. “It is likely to be an honor system. It is very unlikely that there will be punishments or other ramifications ... if doses are administered, beyond the approved usage.”
3. If a patient who had the Moderna or the Johnson and Johnson vaccination requests a booster, can health care workers give them Pfizer?
The short answer is no. “This only applies to individuals who have received the Pfizer vaccine,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said.
More data will be needed before other vaccine boosters are authorized, she added.
“My understanding is the Moderna people have just recently submitted their information, all of their data to the FDA and J&J is in line to do that very shortly,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. “I would hope that within the next month to 6 weeks, we will get information about both of those vaccines,” Dr. Schaffner said.
4. When are the “mix-and-match” vaccine study results expected to come out?
“We expect that data from the study will be available in the coming weeks,” said Dr. Atmar, who is the national co-principal investigator of a mix-and-match booster trial launched in June 2021.
5. Are side effects of a booster vaccine expected to be about the same as what people experienced during their first or second immunization?
“I’m expecting the side effects will be similar to the second dose,” Dr. Englund said.
“The data presented ... at ACIP suggests that the side effects from the third shot are either the same or actually less than the first two shots,” said Carlos del Rio, MD, distinguished professor of medicine, epidemiology, and global health, and executive associate dean of Emory University School of Medicine at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
”Everyone reacts very differently to vaccines, regardless of vaccine type,” said Eric Ascher, MD, a family medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City. “I have had patients (as well as personal experience) where there were none to minimal symptoms, and others who felt they had a mild flu for 24 hours.”
“I expect no side effects greater than what was felt with you prior doses,” he said. “The vaccine is very safe and the benefit of vaccination outweighs the risks of any mild side effects.”
6. Is it unethical to give a booster to someone outside the approved groups if there are doses remaining at the end of the day in an open vial?
“Offering a booster shot to someone outside of approved groups if remaining doses will go to waste at the end of the day seems like a prudent decision, and relatively harmless action,” said Faith Fletcher, PhD, assistant professor at the Center for Medical Ethics and Health Policy at Baylor College of Medicine.
“However, if doses continue to fall in the laps of unapproved groups, we must evaluate the vaccine systems and structures that advantage some groups and disadvantage others,” she added. “We know that the distribution of COVID-19 vaccines has not been equitable – and some groups have been left behind.”
“I am not an ethicist and there are many competing concerns that this question addresses,” Dr. Atmar said. For example, “there is not a limitation of vaccine supply in the U.S., so that using leftover vaccine to prevent waste is no longer a major concern in the U.S.”
It could be more of a legal than ethical question, Dr. Atmar said. For an individual outside the authorized groups, legally, the FDA’s EUA for boosting does not allow the vaccine to be administered to this person, he said.
“The rationale for the restricted use in the EUA is that at this time the safety and risks associated with such administration are not known, and the benefits also have not been determined,” Dr. Atmar said. “Members of the ACIP raised concerns about other individuals who may potentially benefit from a booster but are not eligible and the importance of making boosters available to them, but from a legal standpoint – I am also not a lawyer, so this is my understanding – administration of the vaccine is limited to those identified in the EUA.”
7. What is the likelihood that one shot will combine COVID and flu protection in the near future?
It is not likely, Dr. Englund said. “The reason is that the flu vaccine changes so much, and it already has four different antigens. This is assuming we keep the same method of making the flu vaccine – the answer could be different if the flu vaccine becomes an mRNA vaccine in the future.”
Companies such as Moderna and Novavax are testing single-dose shots for COVID-19 and influenza, but they are still far from having anything ready for this flu season in the United States.
8. Is there any chance a booster shot distributed now will need to be redesigned for a future variant?
“Absolutely,” Dr. Englund said. “And a booster dose is the time we may want to consider re-engineering a vaccine.”
9. Do you think the FDA/CDC limitations on who is eligible for a booster was in any way influenced by the World Health Organization call for prioritizing shots for the unvaccinated in lower-resource countries?
“This is absolutely still a global problem,” Dr. Piltch-Loeb said. “We need to get more vaccine to more countries and more people as soon as possible, because if there’s anything we’ve seen about the variants it is that ... they can come from all different places.”
“That being said, I think that it is unlikely to change the course of action in the U.S.,” she added, when it comes to comparing the global need with the domestic policy priorities of the administration.
Dr. Atmar was more direct. “No,” he said. “The WHO recommends against boosting of anyone. The U.S. decisions about boosting those in this country who are eligible are aimed toward addressing perceived needs domestically at the same time that vaccines are being provided to other countries.
“The philosophy is to address both ‘needs’ at the same time,” Dr. Atmar said.
10. What does the future hold for booster shots?
“Predicting the future is really hard, especially when it involves COVID,” Dr. del Rio said.
“Having said that, COVID is not the flu, so I doubt there will be need for annual boosters. I think the population eligible for boosters will be expanded ... and the major population not addressed at this point is the people that received either Moderna or J&J [vaccines].”
Kelly Davis contributed to this feature. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.











