User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Maternal Immunization to Prevent Serious Respiratory Illness
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.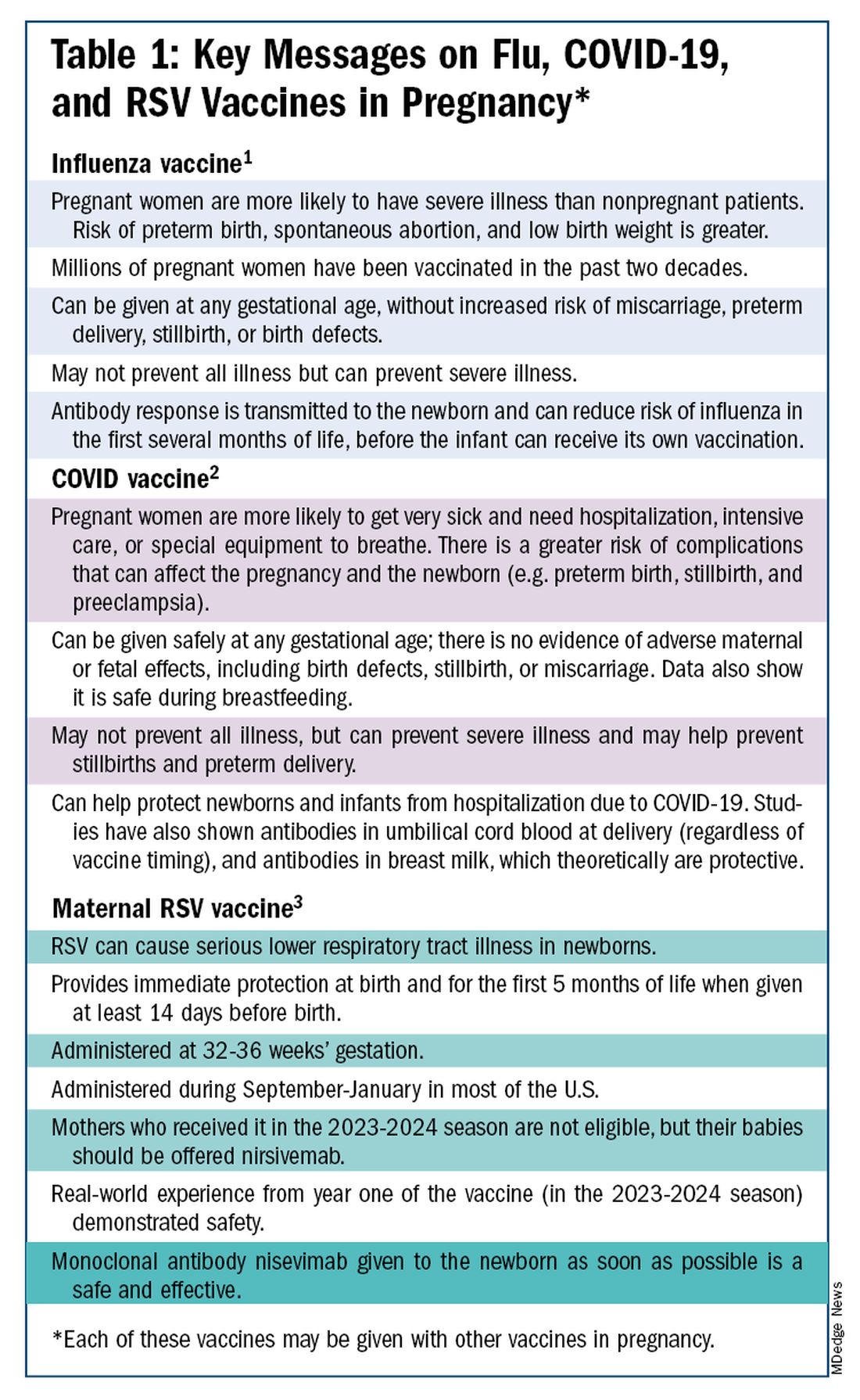
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Lawsuit Targets Publishers: Is Peer Review Flawed?
The peer-review process, which is used by scientific journals to validate legitimate research, is now under legal scrutiny. The US District Court for the Southern District of New York will soon rule on whether scientific publishers have compromised this system for profit. In mid-September, University of California, Los Angeles neuroscientist Lucina Uddin filed a class action lawsuit against six leading academic publishers — Elsevier, Wolters Kluwer, Wiley, Sage Publications, Taylor & Francis, and Springer Nature — accusing them of violating antitrust laws and obstructing academic research.
The lawsuit targets several long-standing practices in scientific publishing, including the lack of compensation for peer reviewers, restrictions that require submitting to only one journal at a time, and bans on sharing manuscripts under review. Uddin’s complaint argues that these practices contribute to inefficiencies in the review process, thus delaying the publication of critical discoveries, which could hinder research, clinical advancements, and the development of new medical treatments.
The suit also noted that these publishers generated $10 billion in revenue in 2023 in peer-reviewed journals. However, the complaint seemingly overlooks the widespread practice of preprint repositories, where many manuscripts are shared while awaiting peer review.
Flawed Reviews
A growing number of studies have highlighted subpar or unethical behaviors among reviewers, who are supposed to adhere to the highest standards of methodological rigor, both in conducting research and reviewing work for journals. One recent study published in Scientometrics in August examined 263 reviews from 37 journals across various disciplines and found alarming patterns of duplication. Many of the reviews contained identical or highly similar language. Some reviewers were found to be suggesting that the authors expand their bibliographies to include the reviewers’ own work, thus inflating their citation counts.
As María Ángeles Oviedo-García from the University of Seville in Spain, pointed out: “The analysis of 263 review reports shows a pattern of vague, repetitive statements — often identical or very similar — along with coercive citations, ultimately resulting in misleading reviews.”
Experts in research integrity and ethics argue that while issues persist, the integrity of scientific research is improving. Increasing research and public disclosure reflect a heightened awareness of problems long overlooked.
Speaking to this news organization, Fanelli, who has been studying scientific misconduct for about 20 years, noted that while his early work left him disillusioned, further research has replaced his cynicism with what he describes as healthy skepticism and a more optimistic outlook. Fanelli also collaborates with the Luxembourg Agency for Research Integrity and the Advisory Committee on Research Ethics and Bioethics at the Italian National Research Council (CNR), where he helped develop the first research integrity guidelines.
Lack of Awareness
A recurring challenge is the difficulty in distinguishing between honest mistakes and intentional misconduct. “This is why greater investment in education is essential,” said Daniel Pizzolato, European Network of Research Ethics Committees, Bonn, Germany, and the Centre for Biomedical Ethics and Law, KU Leuven in Belgium.
While Pizzolato acknowledged that institutions such as the CNR in Italy provide a positive example, awareness of research integrity is generally still lacking across much of Europe, and there are few offices dedicated to promoting research integrity. However, he pointed to promising developments in other countries. “In France and Denmark, researchers are required to be familiar with integrity norms because codes of conduct have legal standing. Some major international funding bodies like the European Molecular Biology Organization are making participation in research integrity courses a condition for receiving grants.”
Pizzolato remains optimistic. “There is a growing willingness to move past this impasse,” he said.
A recent study published in The Journal of Clinical Epidemiology reveals troubling gaps in how retracted biomedical articles are flagged and cited. Led by Caitlin Bakkera, Department of Epidemiology, Maastricht University, Maastricht, the Netherlands, the research sought to determine whether articles retracted because of errors or fraud were properly flagged across various databases.
The results were concerning: Less than 5% of retracted articles had consistent retraction notices across all databases that hosted them, and less than 50% of citations referenced the retraction. None of the 414 retraction notices analyzed met best-practice guidelines for completeness. Bakkera and colleagues warned that these shortcomings threaten the integrity of public health research.
Fanelli’s Perspective
Despite the concerns, Fanelli remains calm. “Science is based on debate and a perspective called organized skepticism, which helps reveal the truth,” he explained. “While there is often excessive skepticism today, the overall quality of clinical trials is improving.
“It’s important to remember that reliable results take time and shouldn’t depend on the outcome of a single study. It’s essential to consider the broader context, the history of the research field, and potential conflicts of interest, both financial and otherwise. Biomedical research requires constant updates,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The peer-review process, which is used by scientific journals to validate legitimate research, is now under legal scrutiny. The US District Court for the Southern District of New York will soon rule on whether scientific publishers have compromised this system for profit. In mid-September, University of California, Los Angeles neuroscientist Lucina Uddin filed a class action lawsuit against six leading academic publishers — Elsevier, Wolters Kluwer, Wiley, Sage Publications, Taylor & Francis, and Springer Nature — accusing them of violating antitrust laws and obstructing academic research.
The lawsuit targets several long-standing practices in scientific publishing, including the lack of compensation for peer reviewers, restrictions that require submitting to only one journal at a time, and bans on sharing manuscripts under review. Uddin’s complaint argues that these practices contribute to inefficiencies in the review process, thus delaying the publication of critical discoveries, which could hinder research, clinical advancements, and the development of new medical treatments.
The suit also noted that these publishers generated $10 billion in revenue in 2023 in peer-reviewed journals. However, the complaint seemingly overlooks the widespread practice of preprint repositories, where many manuscripts are shared while awaiting peer review.
Flawed Reviews
A growing number of studies have highlighted subpar or unethical behaviors among reviewers, who are supposed to adhere to the highest standards of methodological rigor, both in conducting research and reviewing work for journals. One recent study published in Scientometrics in August examined 263 reviews from 37 journals across various disciplines and found alarming patterns of duplication. Many of the reviews contained identical or highly similar language. Some reviewers were found to be suggesting that the authors expand their bibliographies to include the reviewers’ own work, thus inflating their citation counts.
As María Ángeles Oviedo-García from the University of Seville in Spain, pointed out: “The analysis of 263 review reports shows a pattern of vague, repetitive statements — often identical or very similar — along with coercive citations, ultimately resulting in misleading reviews.”
Experts in research integrity and ethics argue that while issues persist, the integrity of scientific research is improving. Increasing research and public disclosure reflect a heightened awareness of problems long overlooked.
Speaking to this news organization, Fanelli, who has been studying scientific misconduct for about 20 years, noted that while his early work left him disillusioned, further research has replaced his cynicism with what he describes as healthy skepticism and a more optimistic outlook. Fanelli also collaborates with the Luxembourg Agency for Research Integrity and the Advisory Committee on Research Ethics and Bioethics at the Italian National Research Council (CNR), where he helped develop the first research integrity guidelines.
Lack of Awareness
A recurring challenge is the difficulty in distinguishing between honest mistakes and intentional misconduct. “This is why greater investment in education is essential,” said Daniel Pizzolato, European Network of Research Ethics Committees, Bonn, Germany, and the Centre for Biomedical Ethics and Law, KU Leuven in Belgium.
While Pizzolato acknowledged that institutions such as the CNR in Italy provide a positive example, awareness of research integrity is generally still lacking across much of Europe, and there are few offices dedicated to promoting research integrity. However, he pointed to promising developments in other countries. “In France and Denmark, researchers are required to be familiar with integrity norms because codes of conduct have legal standing. Some major international funding bodies like the European Molecular Biology Organization are making participation in research integrity courses a condition for receiving grants.”
Pizzolato remains optimistic. “There is a growing willingness to move past this impasse,” he said.
A recent study published in The Journal of Clinical Epidemiology reveals troubling gaps in how retracted biomedical articles are flagged and cited. Led by Caitlin Bakkera, Department of Epidemiology, Maastricht University, Maastricht, the Netherlands, the research sought to determine whether articles retracted because of errors or fraud were properly flagged across various databases.
The results were concerning: Less than 5% of retracted articles had consistent retraction notices across all databases that hosted them, and less than 50% of citations referenced the retraction. None of the 414 retraction notices analyzed met best-practice guidelines for completeness. Bakkera and colleagues warned that these shortcomings threaten the integrity of public health research.
Fanelli’s Perspective
Despite the concerns, Fanelli remains calm. “Science is based on debate and a perspective called organized skepticism, which helps reveal the truth,” he explained. “While there is often excessive skepticism today, the overall quality of clinical trials is improving.
“It’s important to remember that reliable results take time and shouldn’t depend on the outcome of a single study. It’s essential to consider the broader context, the history of the research field, and potential conflicts of interest, both financial and otherwise. Biomedical research requires constant updates,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The peer-review process, which is used by scientific journals to validate legitimate research, is now under legal scrutiny. The US District Court for the Southern District of New York will soon rule on whether scientific publishers have compromised this system for profit. In mid-September, University of California, Los Angeles neuroscientist Lucina Uddin filed a class action lawsuit against six leading academic publishers — Elsevier, Wolters Kluwer, Wiley, Sage Publications, Taylor & Francis, and Springer Nature — accusing them of violating antitrust laws and obstructing academic research.
The lawsuit targets several long-standing practices in scientific publishing, including the lack of compensation for peer reviewers, restrictions that require submitting to only one journal at a time, and bans on sharing manuscripts under review. Uddin’s complaint argues that these practices contribute to inefficiencies in the review process, thus delaying the publication of critical discoveries, which could hinder research, clinical advancements, and the development of new medical treatments.
The suit also noted that these publishers generated $10 billion in revenue in 2023 in peer-reviewed journals. However, the complaint seemingly overlooks the widespread practice of preprint repositories, where many manuscripts are shared while awaiting peer review.
Flawed Reviews
A growing number of studies have highlighted subpar or unethical behaviors among reviewers, who are supposed to adhere to the highest standards of methodological rigor, both in conducting research and reviewing work for journals. One recent study published in Scientometrics in August examined 263 reviews from 37 journals across various disciplines and found alarming patterns of duplication. Many of the reviews contained identical or highly similar language. Some reviewers were found to be suggesting that the authors expand their bibliographies to include the reviewers’ own work, thus inflating their citation counts.
As María Ángeles Oviedo-García from the University of Seville in Spain, pointed out: “The analysis of 263 review reports shows a pattern of vague, repetitive statements — often identical or very similar — along with coercive citations, ultimately resulting in misleading reviews.”
Experts in research integrity and ethics argue that while issues persist, the integrity of scientific research is improving. Increasing research and public disclosure reflect a heightened awareness of problems long overlooked.
Speaking to this news organization, Fanelli, who has been studying scientific misconduct for about 20 years, noted that while his early work left him disillusioned, further research has replaced his cynicism with what he describes as healthy skepticism and a more optimistic outlook. Fanelli also collaborates with the Luxembourg Agency for Research Integrity and the Advisory Committee on Research Ethics and Bioethics at the Italian National Research Council (CNR), where he helped develop the first research integrity guidelines.
Lack of Awareness
A recurring challenge is the difficulty in distinguishing between honest mistakes and intentional misconduct. “This is why greater investment in education is essential,” said Daniel Pizzolato, European Network of Research Ethics Committees, Bonn, Germany, and the Centre for Biomedical Ethics and Law, KU Leuven in Belgium.
While Pizzolato acknowledged that institutions such as the CNR in Italy provide a positive example, awareness of research integrity is generally still lacking across much of Europe, and there are few offices dedicated to promoting research integrity. However, he pointed to promising developments in other countries. “In France and Denmark, researchers are required to be familiar with integrity norms because codes of conduct have legal standing. Some major international funding bodies like the European Molecular Biology Organization are making participation in research integrity courses a condition for receiving grants.”
Pizzolato remains optimistic. “There is a growing willingness to move past this impasse,” he said.
A recent study published in The Journal of Clinical Epidemiology reveals troubling gaps in how retracted biomedical articles are flagged and cited. Led by Caitlin Bakkera, Department of Epidemiology, Maastricht University, Maastricht, the Netherlands, the research sought to determine whether articles retracted because of errors or fraud were properly flagged across various databases.
The results were concerning: Less than 5% of retracted articles had consistent retraction notices across all databases that hosted them, and less than 50% of citations referenced the retraction. None of the 414 retraction notices analyzed met best-practice guidelines for completeness. Bakkera and colleagues warned that these shortcomings threaten the integrity of public health research.
Fanelli’s Perspective
Despite the concerns, Fanelli remains calm. “Science is based on debate and a perspective called organized skepticism, which helps reveal the truth,” he explained. “While there is often excessive skepticism today, the overall quality of clinical trials is improving.
“It’s important to remember that reliable results take time and shouldn’t depend on the outcome of a single study. It’s essential to consider the broader context, the history of the research field, and potential conflicts of interest, both financial and otherwise. Biomedical research requires constant updates,” he concluded.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Is Metformin An Unexpected Ally Against Long COVID?
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Previous studies have shown that metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection reduces severe COVID-19 and postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, in adults.
- A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between metformin use before and during SARS-CoV-2 infection and the subsequent incidence of PASC.
- Researchers used data from the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) and National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet) electronic health record (EHR) databases to identify adults (age, ≥ 21 years) with T2D prescribed a diabetes medication within the past 12 months.
- Participants were categorized into those using metformin (metformin group) and those using other noninsulin diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, or thiazolidinediones (the comparator group); those who used glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors were excluded.
- The primary outcome was the incidence of PASC or death within 180 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined using International Classification of Diseases U09.9 diagnosis code and/or computable phenotype defined by a predicted probability of > 75% for PASC using a machine learning model trained on patients diagnosed using U09.9 (PASC computable phenotype).
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers identified 51,385 and 37,947 participants from the N3C and PCORnet datasets, respectively.
- Metformin use was associated with a 21% lower risk for death or PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P < .001) and a 15% lower risk using the PASC computable phenotype (P < .001) in the N3C dataset than non-metformin use.
- In the PCORnet dataset, the risk for death or PASC was 13% lower using the U09.9 diagnosis code (P = .08) with metformin use vs non-metformin use, whereas the risk did not differ significantly between the groups when using the PASC computable phenotype (P = .58).
- The incidence of PASC using the U09.9 diagnosis code for the metformin and comparator groups was similar between the two datasets (1.6% and 2.0% in N3C and 2.2 and 2.6% in PCORnet, respectively).
- However, when using the computable phenotype, the incidence rates of PASC for the metformin and comparator groups were 4.8% and 5.2% in N3C and 25.2% and 24.2% in PCORnet, respectively.
IN PRACTICE:
“The incidence of PASC was lower when defined by [International Classification of Diseases] code, compared with a computable phenotype in both databases,” the authors wrote. “This may reflect the challenges of clinical care for adults needing chronic medication management and the likelihood of those adults receiving a formal PASC diagnosis.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Steven G. Johnson, PhD, Institute for Health Informatics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data had several limitations, including the inability to examine a dose-dependent relationship and the lack of information on whether medications were taken before, during, or after the acute infection. The outcome definition involved the need for a medical encounter and, thus, may not capture data on all patients experiencing symptoms of PASC. The analysis focused on the prevalent use of chronic medications, limiting the assessment of initiating metformin in those diagnosed with COVID-19.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Agreement as part of the RECOVER research program. One author reported receiving salary support from the Center for Pharmacoepidemiology and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies. Another author reported receiving grant support and consulting contracts, being involved in expert witness engagement, and owning stock options in various pharmaceutical, biopharmaceutical, diabetes management, and medical device companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Residents Are Joining Unions in Droves
Before the 350 residents finalized their union contract at the University of Vermont (UVM) Medical Center, Burlington, in 2022, Jesse Mostoller, DO, now a third-year pathology resident, recalls hearing about another resident at the hospital who resorted to moonlighting as an Uber driver to make ends meet.
“In Vermont, rent and childcare are expensive,” said Dr. Mostoller, adding that, thanks to union bargaining, first-year residents at UVM are now paid $71,000 per year instead of $61,000. In addition, residents now receive $1800 per year for food (up from $200-$300 annually) and a $1800 annual fund to help pay for board exams that can be carried over for 2 years. “When we were negotiating, the biggest item on our list of demands was to help alleviate the financial pressure residents have been facing for years.”
The UVM residents’ collective bargaining also includes a cap on working hours so that residents don’t work 80 hours a week, paid parental leave, affordable housing, and funds for education and wellness.
These are some of the most common challenges that are faced by residents all over the country, said A. Taylor Walker, MD, MPH, family medicine chief physician at Tufts University School of Medicine/Cambridge Health Alliance in Boston, Massachusetts, and national president of the Committee of Interns and Residents (CIR), which is part of the Service Employees International Union.
For these reasons, residents at Montefiore Medical Center, Stanford Health Care, George Washington University, and the University of Pennsylvania have recently voted to unionize, according to Dr. Walker.
And while there are several small local unions that have picked up residents at local hospitals, CIR is the largest union of physicians in the United States, with a total of 33,000 residents and fellows across the country (15% of the staff at more than 60 hospitals nationwide).
“We’ve doubled in size in the last 4 years,” said Dr. Walker. “The reason is that we’re in a national reckoning on the corporatization of American medicine and the way in which graduate medical education is rooted in a cycle of exploitation that doesn’t center on the health, well-being, or safety of our doctors and ultimately negatively affects our patients.”
Here’s what residents are fighting for — right now.
Adequate Parental Leave
Christopher Domanski, MD, a first-year resident in psychiatry at California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) in San Francisco, is also a new dad to a 5-month-old son and is currently in the sixth week of parental leave. One goal of CPMC’s union, started a year and a half ago, is to expand parental leave to 8 weeks.
“I started as a resident here in mid-June, but the fight with CPMC leaders has been going on for a year and a half,” Dr. Domanski said. “It can feel very frustrating because many times there’s no budge in the conversations we want to have.”
Contract negotiations here continue to be slow — and arduous.
“It goes back and forth,” said Dr. Domanski, who makes about $75,000 a year. “Sometimes they listen to our proposals, but they deny the vast majority or make a paltry increase in salary or time off. It goes like this: We’ll have a negotiation; we’ll talk about it, and then they say, ‘we’re not comfortable doing this’ and it stalls again.”
If a resident hasn’t started a family yet, access to fertility benefits and reproductive healthcare is paramount because most residents are in their 20s and 30s, Dr. Walker said.
“Our reproductive futures are really hindered by what care we have access to and what care is covered,” she added. “We don’t make enough money to pay for reproductive care out of pocket.”
Fair Pay
In Boston, the residents at Mass General Brigham certified their union in June 2023, but they still don’t have a contract.
“When I applied for a residency in September 2023, I spoke to the folks here, and I was basically under the impression that we would have a contract by the time I matched,” said Madison Masters, MD, a resident in internal medicine. “We are not there.”
This timeline isn’t unusual — the 1400 Penn Medicine residents who unionized in 2023 only recently secured a tentative union contract at the end of September, and at Stanford, the process to ratify their first contract took 13 months.
Still, the salary issue remains frustrating as resident compensation doesn’t line up with the cost of living or the amount of work residents do, said Dr. Masters, who says starting salaries at Mass General Brigham are $78,500 plus a $10,000 stipend for housing.
“There’s been a long tradition of underpaying residents — we’re treated like trainees, but we’re also a primary labor force,” Dr. Masters said, adding that nurse practitioners and physician assistants are paid almost twice as much as residents — some make $120,000 per year or more, while the salary range for residents nationwide is $49,000-$65,000 per year.
“Every time we discuss the contract and talk about a financial package, they offer a 1.5% raise for the next 3 years while we had asked for closer to 8%,” Dr. Masters said. “Then, when they come back for the next bargaining session, they go up a quarter of a percent each time. Recently, they said we will need to go to a mediator to try and resolve this.”
Adequate Healthcare
The biggest — and perhaps the most shocking — ask is for robust health insurance coverage.
“At my hospital, they’re telling us to get Amazon One Medical for health insurance,” Dr. Masters said. “They’re saying it’s hard for anyone to get primary care coverage here.”
Inadequate health insurance is a big issue, as burnout among residents and fellows remains a problem. At UVM, a $10,000 annual wellness stipend has helped address some of these issues. Even so, union members at UVM are planning to return to the table within 18 months to continue their collective bargaining.
The ability to access mental health services anywhere you want is also critical for residents, Dr. Walker said.
“If you can only go to a therapist at your own institution, there is a hesitation to utilize that specialist if that’s even offered,” Dr. Walker said. “Do you want to go to therapy with a colleague? Probably not.”
Ultimately, the residents we spoke to are committed to fighting for their workplace rights — no matter how time-consuming or difficult this has been.
“No administration wants us to have to have a union, but it’s necessary,” Dr. Mostoller said. “As an individual, you don’t have leverage to get a seat at the table, but now we have a seat at the table. We have a wonderful contract, but we’re going to keep fighting to make it even better.”
Paving the way for future residents is a key motivator, too.
“There’s this idea of leaving the campsite cleaner than you found it,” Dr. Mostoller told this news organization. “It’s the same thing here — we’re trying to fix this so that the next generation of residents won’t have to.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before the 350 residents finalized their union contract at the University of Vermont (UVM) Medical Center, Burlington, in 2022, Jesse Mostoller, DO, now a third-year pathology resident, recalls hearing about another resident at the hospital who resorted to moonlighting as an Uber driver to make ends meet.
“In Vermont, rent and childcare are expensive,” said Dr. Mostoller, adding that, thanks to union bargaining, first-year residents at UVM are now paid $71,000 per year instead of $61,000. In addition, residents now receive $1800 per year for food (up from $200-$300 annually) and a $1800 annual fund to help pay for board exams that can be carried over for 2 years. “When we were negotiating, the biggest item on our list of demands was to help alleviate the financial pressure residents have been facing for years.”
The UVM residents’ collective bargaining also includes a cap on working hours so that residents don’t work 80 hours a week, paid parental leave, affordable housing, and funds for education and wellness.
These are some of the most common challenges that are faced by residents all over the country, said A. Taylor Walker, MD, MPH, family medicine chief physician at Tufts University School of Medicine/Cambridge Health Alliance in Boston, Massachusetts, and national president of the Committee of Interns and Residents (CIR), which is part of the Service Employees International Union.
For these reasons, residents at Montefiore Medical Center, Stanford Health Care, George Washington University, and the University of Pennsylvania have recently voted to unionize, according to Dr. Walker.
And while there are several small local unions that have picked up residents at local hospitals, CIR is the largest union of physicians in the United States, with a total of 33,000 residents and fellows across the country (15% of the staff at more than 60 hospitals nationwide).
“We’ve doubled in size in the last 4 years,” said Dr. Walker. “The reason is that we’re in a national reckoning on the corporatization of American medicine and the way in which graduate medical education is rooted in a cycle of exploitation that doesn’t center on the health, well-being, or safety of our doctors and ultimately negatively affects our patients.”
Here’s what residents are fighting for — right now.
Adequate Parental Leave
Christopher Domanski, MD, a first-year resident in psychiatry at California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) in San Francisco, is also a new dad to a 5-month-old son and is currently in the sixth week of parental leave. One goal of CPMC’s union, started a year and a half ago, is to expand parental leave to 8 weeks.
“I started as a resident here in mid-June, but the fight with CPMC leaders has been going on for a year and a half,” Dr. Domanski said. “It can feel very frustrating because many times there’s no budge in the conversations we want to have.”
Contract negotiations here continue to be slow — and arduous.
“It goes back and forth,” said Dr. Domanski, who makes about $75,000 a year. “Sometimes they listen to our proposals, but they deny the vast majority or make a paltry increase in salary or time off. It goes like this: We’ll have a negotiation; we’ll talk about it, and then they say, ‘we’re not comfortable doing this’ and it stalls again.”
If a resident hasn’t started a family yet, access to fertility benefits and reproductive healthcare is paramount because most residents are in their 20s and 30s, Dr. Walker said.
“Our reproductive futures are really hindered by what care we have access to and what care is covered,” she added. “We don’t make enough money to pay for reproductive care out of pocket.”
Fair Pay
In Boston, the residents at Mass General Brigham certified their union in June 2023, but they still don’t have a contract.
“When I applied for a residency in September 2023, I spoke to the folks here, and I was basically under the impression that we would have a contract by the time I matched,” said Madison Masters, MD, a resident in internal medicine. “We are not there.”
This timeline isn’t unusual — the 1400 Penn Medicine residents who unionized in 2023 only recently secured a tentative union contract at the end of September, and at Stanford, the process to ratify their first contract took 13 months.
Still, the salary issue remains frustrating as resident compensation doesn’t line up with the cost of living or the amount of work residents do, said Dr. Masters, who says starting salaries at Mass General Brigham are $78,500 plus a $10,000 stipend for housing.
“There’s been a long tradition of underpaying residents — we’re treated like trainees, but we’re also a primary labor force,” Dr. Masters said, adding that nurse practitioners and physician assistants are paid almost twice as much as residents — some make $120,000 per year or more, while the salary range for residents nationwide is $49,000-$65,000 per year.
“Every time we discuss the contract and talk about a financial package, they offer a 1.5% raise for the next 3 years while we had asked for closer to 8%,” Dr. Masters said. “Then, when they come back for the next bargaining session, they go up a quarter of a percent each time. Recently, they said we will need to go to a mediator to try and resolve this.”
Adequate Healthcare
The biggest — and perhaps the most shocking — ask is for robust health insurance coverage.
“At my hospital, they’re telling us to get Amazon One Medical for health insurance,” Dr. Masters said. “They’re saying it’s hard for anyone to get primary care coverage here.”
Inadequate health insurance is a big issue, as burnout among residents and fellows remains a problem. At UVM, a $10,000 annual wellness stipend has helped address some of these issues. Even so, union members at UVM are planning to return to the table within 18 months to continue their collective bargaining.
The ability to access mental health services anywhere you want is also critical for residents, Dr. Walker said.
“If you can only go to a therapist at your own institution, there is a hesitation to utilize that specialist if that’s even offered,” Dr. Walker said. “Do you want to go to therapy with a colleague? Probably not.”
Ultimately, the residents we spoke to are committed to fighting for their workplace rights — no matter how time-consuming or difficult this has been.
“No administration wants us to have to have a union, but it’s necessary,” Dr. Mostoller said. “As an individual, you don’t have leverage to get a seat at the table, but now we have a seat at the table. We have a wonderful contract, but we’re going to keep fighting to make it even better.”
Paving the way for future residents is a key motivator, too.
“There’s this idea of leaving the campsite cleaner than you found it,” Dr. Mostoller told this news organization. “It’s the same thing here — we’re trying to fix this so that the next generation of residents won’t have to.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Before the 350 residents finalized their union contract at the University of Vermont (UVM) Medical Center, Burlington, in 2022, Jesse Mostoller, DO, now a third-year pathology resident, recalls hearing about another resident at the hospital who resorted to moonlighting as an Uber driver to make ends meet.
“In Vermont, rent and childcare are expensive,” said Dr. Mostoller, adding that, thanks to union bargaining, first-year residents at UVM are now paid $71,000 per year instead of $61,000. In addition, residents now receive $1800 per year for food (up from $200-$300 annually) and a $1800 annual fund to help pay for board exams that can be carried over for 2 years. “When we were negotiating, the biggest item on our list of demands was to help alleviate the financial pressure residents have been facing for years.”
The UVM residents’ collective bargaining also includes a cap on working hours so that residents don’t work 80 hours a week, paid parental leave, affordable housing, and funds for education and wellness.
These are some of the most common challenges that are faced by residents all over the country, said A. Taylor Walker, MD, MPH, family medicine chief physician at Tufts University School of Medicine/Cambridge Health Alliance in Boston, Massachusetts, and national president of the Committee of Interns and Residents (CIR), which is part of the Service Employees International Union.
For these reasons, residents at Montefiore Medical Center, Stanford Health Care, George Washington University, and the University of Pennsylvania have recently voted to unionize, according to Dr. Walker.
And while there are several small local unions that have picked up residents at local hospitals, CIR is the largest union of physicians in the United States, with a total of 33,000 residents and fellows across the country (15% of the staff at more than 60 hospitals nationwide).
“We’ve doubled in size in the last 4 years,” said Dr. Walker. “The reason is that we’re in a national reckoning on the corporatization of American medicine and the way in which graduate medical education is rooted in a cycle of exploitation that doesn’t center on the health, well-being, or safety of our doctors and ultimately negatively affects our patients.”
Here’s what residents are fighting for — right now.
Adequate Parental Leave
Christopher Domanski, MD, a first-year resident in psychiatry at California Pacific Medical Center (CPMC) in San Francisco, is also a new dad to a 5-month-old son and is currently in the sixth week of parental leave. One goal of CPMC’s union, started a year and a half ago, is to expand parental leave to 8 weeks.
“I started as a resident here in mid-June, but the fight with CPMC leaders has been going on for a year and a half,” Dr. Domanski said. “It can feel very frustrating because many times there’s no budge in the conversations we want to have.”
Contract negotiations here continue to be slow — and arduous.
“It goes back and forth,” said Dr. Domanski, who makes about $75,000 a year. “Sometimes they listen to our proposals, but they deny the vast majority or make a paltry increase in salary or time off. It goes like this: We’ll have a negotiation; we’ll talk about it, and then they say, ‘we’re not comfortable doing this’ and it stalls again.”
If a resident hasn’t started a family yet, access to fertility benefits and reproductive healthcare is paramount because most residents are in their 20s and 30s, Dr. Walker said.
“Our reproductive futures are really hindered by what care we have access to and what care is covered,” she added. “We don’t make enough money to pay for reproductive care out of pocket.”
Fair Pay
In Boston, the residents at Mass General Brigham certified their union in June 2023, but they still don’t have a contract.
“When I applied for a residency in September 2023, I spoke to the folks here, and I was basically under the impression that we would have a contract by the time I matched,” said Madison Masters, MD, a resident in internal medicine. “We are not there.”
This timeline isn’t unusual — the 1400 Penn Medicine residents who unionized in 2023 only recently secured a tentative union contract at the end of September, and at Stanford, the process to ratify their first contract took 13 months.
Still, the salary issue remains frustrating as resident compensation doesn’t line up with the cost of living or the amount of work residents do, said Dr. Masters, who says starting salaries at Mass General Brigham are $78,500 plus a $10,000 stipend for housing.
“There’s been a long tradition of underpaying residents — we’re treated like trainees, but we’re also a primary labor force,” Dr. Masters said, adding that nurse practitioners and physician assistants are paid almost twice as much as residents — some make $120,000 per year or more, while the salary range for residents nationwide is $49,000-$65,000 per year.
“Every time we discuss the contract and talk about a financial package, they offer a 1.5% raise for the next 3 years while we had asked for closer to 8%,” Dr. Masters said. “Then, when they come back for the next bargaining session, they go up a quarter of a percent each time. Recently, they said we will need to go to a mediator to try and resolve this.”
Adequate Healthcare
The biggest — and perhaps the most shocking — ask is for robust health insurance coverage.
“At my hospital, they’re telling us to get Amazon One Medical for health insurance,” Dr. Masters said. “They’re saying it’s hard for anyone to get primary care coverage here.”
Inadequate health insurance is a big issue, as burnout among residents and fellows remains a problem. At UVM, a $10,000 annual wellness stipend has helped address some of these issues. Even so, union members at UVM are planning to return to the table within 18 months to continue their collective bargaining.
The ability to access mental health services anywhere you want is also critical for residents, Dr. Walker said.
“If you can only go to a therapist at your own institution, there is a hesitation to utilize that specialist if that’s even offered,” Dr. Walker said. “Do you want to go to therapy with a colleague? Probably not.”
Ultimately, the residents we spoke to are committed to fighting for their workplace rights — no matter how time-consuming or difficult this has been.
“No administration wants us to have to have a union, but it’s necessary,” Dr. Mostoller said. “As an individual, you don’t have leverage to get a seat at the table, but now we have a seat at the table. We have a wonderful contract, but we’re going to keep fighting to make it even better.”
Paving the way for future residents is a key motivator, too.
“There’s this idea of leaving the campsite cleaner than you found it,” Dr. Mostoller told this news organization. “It’s the same thing here — we’re trying to fix this so that the next generation of residents won’t have to.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clozapine and Respiratory Infection Risk: What to Know
Clozapine is considered the drug of choice for treatment-resistant schizophrenia in guidelines globally, but it remains significantly underutilized. This is largely due to its range of side effects, particularly its increased infection risk which prompted the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to mandate regular blood testing to monitor neutrophil counts.
The COVID-19 pandemic raised new concerns about the care of clozapine-treated patients, leading clinicians and patients to urge the FDA to relax prescription requirements for the drug under the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program.
As the FDA prepares for a public hearing in November on proposed adjustments to the drug’s REMS criteria, a growing body of research is challenging the previous understanding of clozapine and infection risk.
Clarifying the Risk
Research on the link between clozapine and respiratory infections has produced conflicting results. Some studies indicate little to no increased risk for mild COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses, while others have shown a higher likelihood of severe infection.
A recent nationwide Danish registry study of respiratory infections in people with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder could bring some clarity, Maxime Taquet, MD, a clinical lecturer at the University of Oxford, Warneford Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
By tracking periods when patients were on and off clozapine and other antipsychotics, the study offers more precise risk estimates, distinguishing the risks associated with the antipsychotic from those related to underlying schizophrenia, said Dr. Taquet, who authored an accompanying editorial on the study.
“It’s very important to try to disentangle the effects of schizophrenia, its severity, from the medication,” Dr. Taquet said. “I think that the Danish study is the first to try and really do that with as much precision as possible.”
After adjusting for key confounders including economic status and COVID-19 vaccination status, the researchers found that individuals taking antipsychotics had lower odds of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 and similar rates of filled anti-infective prescriptions as those not taking the drugs.
Although antipsychotic use was not linked to higher rates of mild infection, it was linked to an increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization in individuals older than 70 years, as well as hospitalization and death from other respiratory infections, mainly pneumonia, in those older than 40 years.
Notably, there was no excess risk for any outcome with clozapine vs other antipsychotics.
Strong Link to Pneumonia Risk
Results from a longitudinal Finnish study, just published in The American Journal of Psychiatry, also show an increased risk for severe outcomes from ileus and pneumonia among more than 2600 patients with schizophrenia taking clozapine.
Twenty years after initiating clozapine, the cumulative incidence estimate for ileus was 5.3% — more than sixfold higher than previously reported. The incidence of pneumonia was also high, at 29.5%.
Both illnesses were significantly associated with mortality, with odds ratios of 4.5 and 2.8, respectively.
These findings align with previous pharmacovigilance studies, with reported mortality rates for gastrointestinal hypomotility and pneumonia that were 4-10 times higher than those for agranulocytosis, the researchers said.
The study “really adds to a growing body of research suggesting a connection between clozapine use and a higher risk of developing pneumonia,” Robert O. Cotes, MD, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in the use of clozapine, told this news organization.
“Additionally, when people on clozapine do contract pneumonia, there’s concern the condition may be more dangerous,” he added.
A Closer Look at Neutropenia Risk
Neutropenia receives the lion’s share of attention among clozapine’s potential side effects, but this focus may need to be re-evaluated, Dr. Cotes said.
He pointed out that recent data suggest the risk for severe neutropenia, 2-3 years after initiating clozapine, is comparable to that of other antipsychotics.
A study of 26,630 clozapine users in Australia and New Zealand showed that most cases of severe neutropenia leading to clozapine cessation peaked within 18 weeks and was negligible after 2 years. This suggests weekly hematologic monitoring could potentially be discontinued after the 2-year mark.
Another study reported earlier this year by this news organization showed a low risk for mild or moderate neutropenia and no severe cases in nearly 1000 people taking clozapine.
“I worry that we may be missing the forest for the trees by hyperfocusing on neutropenia and not considering clozapine’s other potential serious side effects like pneumonia, myocarditis, and gastrointestinal hypermotility,” Dr. Cotes said.
Importance of Vaccines
The findings of these studies highlight the importance of vaccines in this at-risk group, said Dr. Taquet, a point emphasized by investigators of the Danish study he reviewed.
“Inspired by the experience of COVID-19 vaccine prioritization in severe mental illness and based on our findings, there is momentum for preventive action,” the authors wrote. “Our findings do not suggest the avoidance of specific antipsychotics but rather a call for increased vigilance regarding this at-risk group.”
This includes recommending pneumococcal, influenza, COVID-19, and other anti-infective vaccines in those older than 40 years treated with, or due to start, an antipsychotic.
“It’s not mandatory, but we do recommend that patients on clozapine get the regular vaccines,” Dr. Taquet said.
Pointing to the recent study on pneumonia risk, Dr. Cotes said addressing underlying risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, and possibly sedation and excessive salivation caused by clozapine, is key.
“And to make sure that vaccinations are up to date, particularly heading into this fall,” he added.
Rethinking Clozapine REMS
One of the most challenging issues facing clinicians and researchers is how to help people understand the safety profile of clozapine and to use it with more confidence, Dr. Cotes said.
“A lot of people hear about clozapine and they think about neutropenia, they think about side effects, the REMS system, and all of these factors really drive down clozapine utilization,” he said.
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia affects about a quarter of those with schizophrenia, yet only 4% of these patients receive clozapine in the United States, Dr. Cotes said. That number may be even lower for its other indication of reducing suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
The clozapine REMS is viewed as a major barrier to utilization and requires certification of pharmacists and physicians and use of a central system to monitor absolute neutrophil counts for neutropenia in patients.
As previously reported by this news organization in November 2022, the FDA opted to temporarily exercise enforcement discretion for certain aspects of the drug safety program to ensure continuity of care for patients after concerns were raised by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) along with other professional organizations.
Even with that temporary enforcement discretion, “reports have shown that over half of those prescribed clozapine have trouble accessing the medication because of the REMS program,” a spokesperson for the APA told this news organization.
“Not only are patients having trouble accessing the medication, many have trouble finding a prescriber in their geographic locations and others because of the monitoring requirements have their treatment discontinued leading to negative outcomes,” the spokesperson said.
The FDA is currently reviewing the clozapine REMS and is holding a joint advisory committee meeting on November 19 to discuss the review and “possible changes to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of clozapine.”
The APA plans to submit written and oral comments to the advisory committees.
“We are hopeful that the re-evaluation meeting in November will remove barriers and increase access to clozapine, which is currently highly underutilized, especially in marginalized communities,” the spokesperson said.
Dr. Cotes reported serving as a speaker and consultant for Saladax Biomedical and as a consultant for Syneos Health. Dr. Taquet reported having no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clozapine is considered the drug of choice for treatment-resistant schizophrenia in guidelines globally, but it remains significantly underutilized. This is largely due to its range of side effects, particularly its increased infection risk which prompted the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to mandate regular blood testing to monitor neutrophil counts.
The COVID-19 pandemic raised new concerns about the care of clozapine-treated patients, leading clinicians and patients to urge the FDA to relax prescription requirements for the drug under the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program.
As the FDA prepares for a public hearing in November on proposed adjustments to the drug’s REMS criteria, a growing body of research is challenging the previous understanding of clozapine and infection risk.
Clarifying the Risk
Research on the link between clozapine and respiratory infections has produced conflicting results. Some studies indicate little to no increased risk for mild COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses, while others have shown a higher likelihood of severe infection.
A recent nationwide Danish registry study of respiratory infections in people with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder could bring some clarity, Maxime Taquet, MD, a clinical lecturer at the University of Oxford, Warneford Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
By tracking periods when patients were on and off clozapine and other antipsychotics, the study offers more precise risk estimates, distinguishing the risks associated with the antipsychotic from those related to underlying schizophrenia, said Dr. Taquet, who authored an accompanying editorial on the study.
“It’s very important to try to disentangle the effects of schizophrenia, its severity, from the medication,” Dr. Taquet said. “I think that the Danish study is the first to try and really do that with as much precision as possible.”
After adjusting for key confounders including economic status and COVID-19 vaccination status, the researchers found that individuals taking antipsychotics had lower odds of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 and similar rates of filled anti-infective prescriptions as those not taking the drugs.
Although antipsychotic use was not linked to higher rates of mild infection, it was linked to an increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization in individuals older than 70 years, as well as hospitalization and death from other respiratory infections, mainly pneumonia, in those older than 40 years.
Notably, there was no excess risk for any outcome with clozapine vs other antipsychotics.
Strong Link to Pneumonia Risk
Results from a longitudinal Finnish study, just published in The American Journal of Psychiatry, also show an increased risk for severe outcomes from ileus and pneumonia among more than 2600 patients with schizophrenia taking clozapine.
Twenty years after initiating clozapine, the cumulative incidence estimate for ileus was 5.3% — more than sixfold higher than previously reported. The incidence of pneumonia was also high, at 29.5%.
Both illnesses were significantly associated with mortality, with odds ratios of 4.5 and 2.8, respectively.
These findings align with previous pharmacovigilance studies, with reported mortality rates for gastrointestinal hypomotility and pneumonia that were 4-10 times higher than those for agranulocytosis, the researchers said.
The study “really adds to a growing body of research suggesting a connection between clozapine use and a higher risk of developing pneumonia,” Robert O. Cotes, MD, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in the use of clozapine, told this news organization.
“Additionally, when people on clozapine do contract pneumonia, there’s concern the condition may be more dangerous,” he added.
A Closer Look at Neutropenia Risk
Neutropenia receives the lion’s share of attention among clozapine’s potential side effects, but this focus may need to be re-evaluated, Dr. Cotes said.
He pointed out that recent data suggest the risk for severe neutropenia, 2-3 years after initiating clozapine, is comparable to that of other antipsychotics.
A study of 26,630 clozapine users in Australia and New Zealand showed that most cases of severe neutropenia leading to clozapine cessation peaked within 18 weeks and was negligible after 2 years. This suggests weekly hematologic monitoring could potentially be discontinued after the 2-year mark.
Another study reported earlier this year by this news organization showed a low risk for mild or moderate neutropenia and no severe cases in nearly 1000 people taking clozapine.
“I worry that we may be missing the forest for the trees by hyperfocusing on neutropenia and not considering clozapine’s other potential serious side effects like pneumonia, myocarditis, and gastrointestinal hypermotility,” Dr. Cotes said.
Importance of Vaccines
The findings of these studies highlight the importance of vaccines in this at-risk group, said Dr. Taquet, a point emphasized by investigators of the Danish study he reviewed.
“Inspired by the experience of COVID-19 vaccine prioritization in severe mental illness and based on our findings, there is momentum for preventive action,” the authors wrote. “Our findings do not suggest the avoidance of specific antipsychotics but rather a call for increased vigilance regarding this at-risk group.”
This includes recommending pneumococcal, influenza, COVID-19, and other anti-infective vaccines in those older than 40 years treated with, or due to start, an antipsychotic.
“It’s not mandatory, but we do recommend that patients on clozapine get the regular vaccines,” Dr. Taquet said.
Pointing to the recent study on pneumonia risk, Dr. Cotes said addressing underlying risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, and possibly sedation and excessive salivation caused by clozapine, is key.
“And to make sure that vaccinations are up to date, particularly heading into this fall,” he added.
Rethinking Clozapine REMS
One of the most challenging issues facing clinicians and researchers is how to help people understand the safety profile of clozapine and to use it with more confidence, Dr. Cotes said.
“A lot of people hear about clozapine and they think about neutropenia, they think about side effects, the REMS system, and all of these factors really drive down clozapine utilization,” he said.
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia affects about a quarter of those with schizophrenia, yet only 4% of these patients receive clozapine in the United States, Dr. Cotes said. That number may be even lower for its other indication of reducing suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
The clozapine REMS is viewed as a major barrier to utilization and requires certification of pharmacists and physicians and use of a central system to monitor absolute neutrophil counts for neutropenia in patients.
As previously reported by this news organization in November 2022, the FDA opted to temporarily exercise enforcement discretion for certain aspects of the drug safety program to ensure continuity of care for patients after concerns were raised by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) along with other professional organizations.
Even with that temporary enforcement discretion, “reports have shown that over half of those prescribed clozapine have trouble accessing the medication because of the REMS program,” a spokesperson for the APA told this news organization.
“Not only are patients having trouble accessing the medication, many have trouble finding a prescriber in their geographic locations and others because of the monitoring requirements have their treatment discontinued leading to negative outcomes,” the spokesperson said.
The FDA is currently reviewing the clozapine REMS and is holding a joint advisory committee meeting on November 19 to discuss the review and “possible changes to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of clozapine.”
The APA plans to submit written and oral comments to the advisory committees.
“We are hopeful that the re-evaluation meeting in November will remove barriers and increase access to clozapine, which is currently highly underutilized, especially in marginalized communities,” the spokesperson said.
Dr. Cotes reported serving as a speaker and consultant for Saladax Biomedical and as a consultant for Syneos Health. Dr. Taquet reported having no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clozapine is considered the drug of choice for treatment-resistant schizophrenia in guidelines globally, but it remains significantly underutilized. This is largely due to its range of side effects, particularly its increased infection risk which prompted the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to mandate regular blood testing to monitor neutrophil counts.
The COVID-19 pandemic raised new concerns about the care of clozapine-treated patients, leading clinicians and patients to urge the FDA to relax prescription requirements for the drug under the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program.
As the FDA prepares for a public hearing in November on proposed adjustments to the drug’s REMS criteria, a growing body of research is challenging the previous understanding of clozapine and infection risk.
Clarifying the Risk
Research on the link between clozapine and respiratory infections has produced conflicting results. Some studies indicate little to no increased risk for mild COVID-19 and other respiratory illnesses, while others have shown a higher likelihood of severe infection.
A recent nationwide Danish registry study of respiratory infections in people with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder could bring some clarity, Maxime Taquet, MD, a clinical lecturer at the University of Oxford, Warneford Hospital, Oxford, England, told this news organization.
By tracking periods when patients were on and off clozapine and other antipsychotics, the study offers more precise risk estimates, distinguishing the risks associated with the antipsychotic from those related to underlying schizophrenia, said Dr. Taquet, who authored an accompanying editorial on the study.
“It’s very important to try to disentangle the effects of schizophrenia, its severity, from the medication,” Dr. Taquet said. “I think that the Danish study is the first to try and really do that with as much precision as possible.”
After adjusting for key confounders including economic status and COVID-19 vaccination status, the researchers found that individuals taking antipsychotics had lower odds of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 and similar rates of filled anti-infective prescriptions as those not taking the drugs.
Although antipsychotic use was not linked to higher rates of mild infection, it was linked to an increased risk for COVID-19 hospitalization in individuals older than 70 years, as well as hospitalization and death from other respiratory infections, mainly pneumonia, in those older than 40 years.
Notably, there was no excess risk for any outcome with clozapine vs other antipsychotics.
Strong Link to Pneumonia Risk
Results from a longitudinal Finnish study, just published in The American Journal of Psychiatry, also show an increased risk for severe outcomes from ileus and pneumonia among more than 2600 patients with schizophrenia taking clozapine.
Twenty years after initiating clozapine, the cumulative incidence estimate for ileus was 5.3% — more than sixfold higher than previously reported. The incidence of pneumonia was also high, at 29.5%.
Both illnesses were significantly associated with mortality, with odds ratios of 4.5 and 2.8, respectively.
These findings align with previous pharmacovigilance studies, with reported mortality rates for gastrointestinal hypomotility and pneumonia that were 4-10 times higher than those for agranulocytosis, the researchers said.
The study “really adds to a growing body of research suggesting a connection between clozapine use and a higher risk of developing pneumonia,” Robert O. Cotes, MD, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Emory University, Atlanta, who specializes in the use of clozapine, told this news organization.
“Additionally, when people on clozapine do contract pneumonia, there’s concern the condition may be more dangerous,” he added.
A Closer Look at Neutropenia Risk
Neutropenia receives the lion’s share of attention among clozapine’s potential side effects, but this focus may need to be re-evaluated, Dr. Cotes said.
He pointed out that recent data suggest the risk for severe neutropenia, 2-3 years after initiating clozapine, is comparable to that of other antipsychotics.
A study of 26,630 clozapine users in Australia and New Zealand showed that most cases of severe neutropenia leading to clozapine cessation peaked within 18 weeks and was negligible after 2 years. This suggests weekly hematologic monitoring could potentially be discontinued after the 2-year mark.
Another study reported earlier this year by this news organization showed a low risk for mild or moderate neutropenia and no severe cases in nearly 1000 people taking clozapine.
“I worry that we may be missing the forest for the trees by hyperfocusing on neutropenia and not considering clozapine’s other potential serious side effects like pneumonia, myocarditis, and gastrointestinal hypermotility,” Dr. Cotes said.
Importance of Vaccines
The findings of these studies highlight the importance of vaccines in this at-risk group, said Dr. Taquet, a point emphasized by investigators of the Danish study he reviewed.
“Inspired by the experience of COVID-19 vaccine prioritization in severe mental illness and based on our findings, there is momentum for preventive action,” the authors wrote. “Our findings do not suggest the avoidance of specific antipsychotics but rather a call for increased vigilance regarding this at-risk group.”
This includes recommending pneumococcal, influenza, COVID-19, and other anti-infective vaccines in those older than 40 years treated with, or due to start, an antipsychotic.
“It’s not mandatory, but we do recommend that patients on clozapine get the regular vaccines,” Dr. Taquet said.
Pointing to the recent study on pneumonia risk, Dr. Cotes said addressing underlying risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, and possibly sedation and excessive salivation caused by clozapine, is key.
“And to make sure that vaccinations are up to date, particularly heading into this fall,” he added.
Rethinking Clozapine REMS
One of the most challenging issues facing clinicians and researchers is how to help people understand the safety profile of clozapine and to use it with more confidence, Dr. Cotes said.
“A lot of people hear about clozapine and they think about neutropenia, they think about side effects, the REMS system, and all of these factors really drive down clozapine utilization,” he said.
Treatment-resistant schizophrenia affects about a quarter of those with schizophrenia, yet only 4% of these patients receive clozapine in the United States, Dr. Cotes said. That number may be even lower for its other indication of reducing suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder.
The clozapine REMS is viewed as a major barrier to utilization and requires certification of pharmacists and physicians and use of a central system to monitor absolute neutrophil counts for neutropenia in patients.
As previously reported by this news organization in November 2022, the FDA opted to temporarily exercise enforcement discretion for certain aspects of the drug safety program to ensure continuity of care for patients after concerns were raised by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) along with other professional organizations.
Even with that temporary enforcement discretion, “reports have shown that over half of those prescribed clozapine have trouble accessing the medication because of the REMS program,” a spokesperson for the APA told this news organization.
“Not only are patients having trouble accessing the medication, many have trouble finding a prescriber in their geographic locations and others because of the monitoring requirements have their treatment discontinued leading to negative outcomes,” the spokesperson said.
The FDA is currently reviewing the clozapine REMS and is holding a joint advisory committee meeting on November 19 to discuss the review and “possible changes to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of clozapine.”
The APA plans to submit written and oral comments to the advisory committees.
“We are hopeful that the re-evaluation meeting in November will remove barriers and increase access to clozapine, which is currently highly underutilized, especially in marginalized communities,” the spokesperson said.
Dr. Cotes reported serving as a speaker and consultant for Saladax Biomedical and as a consultant for Syneos Health. Dr. Taquet reported having no competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Anticipated Effects of Pneumococcal Vaccines on Otitis
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).
Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).

Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Acute otitis media (AOM) is caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Since the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) shifts in the proportion of these three bacteria as causes of AOM and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles and strain diversity have occurred due to multiple factors including the PCVs and antibiotic selection pressure.
The 7-valent PCV (PCV7) was introduced in 2000 and was proven to be efficacious in preventing AOM, but no subsequent PCV has received an indication for prevention of AOM because the FDA required a tympanocentesis study to prove efficacy and that approval was not achieved for PCV13, PCV15, or PCV20. This is a little known fact. After introduction of PCV7, replacement pneumococcal strains expressing serotypes not in PCV7 emerged and antibiotic non-susceptible strains became predominant causes of AOM, especially antibiotic-resistant serotype 19A. To address the phenomena of pneumococcal serotype replacement, PCV13 was introduced in 2010. But serotype replacement continued to occur under PCV13 pressure, replacement serotypes increasingly caused AOM, and antibiotic-resistant serotype 35B emerged. Now we have two new higher valency PCVs: PCV15 (Merck) where serotypes 22F and 33F were added to the PCV13 serotypes and PCV20 (Pfizer) where 22F, 33F, 8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B were added to PCV13. Note that neither PCV15 nor PCV20 includes the most common serotype causing AOM – serotype 35B.1
While PCV15 and PCV20 should provide protection against more pneumococcal serotypes, increasing serotypes in both vaccines decreased immunogenicity of certain shared serotypes, more so with the addition of seven more in PCV20 than two more in PCV15, compared with PCV13. Whether lower antibody concentrations will make a difference clinically in terms of vaccine failure to prevent nasopharyngeal colonization, AOM, and/or invasive pneumococcal infections is currently unknown.
Our group from greater Rochester, New York, is the only one in the United States performing tympanocentesis to determine the etiology of AOM infections. Children between ages 6 and 36 months are studied. We recently reported our results for the time span September 2021 to September 2023, the immediate 2 years prior to recommendations for use of PCV15 and PCV20 in young children.2 Tympanocentesis was performed in 139 (78%) of 179 episodes of AOM, yielding 216 middle ear fluid samples (the higher number of middle ear fluids was due to bilateral tympanocentesis in some children). H. influenzae (40%) was the most common bacterial isolate, followed by S. pneumonia (19%) and M. catarrhalis (17%), with the remainder no growth. Polymerase chain reactions (PCR) was positive in many of those culture negative samples, suggesting prior use of antibiotics before tympanocentesis was performed. Among the pneumococcal isolates, 46% were oxacillin non-susceptible. Among the H. influenzae isolates, 27% were beta-lactamase producing and all M. catarrhalis were beta-lactamase-producing.
As we previously reported,1 we once again found that serotype 35B was the most frequent non-PCV15, non-PCV20, serotype. Other frequently detected non-PCV20 pneumococcal serotypes were 23A, 23B, 35D, 35F and 15C.2
Projected Pneumococcal Serotype Coverage by PCV15 and PCV20
PCV13 serotypes were identified in 9% of middle ear fluids, consistent with vaccine failure. Assuming 100% vaccine-type effectiveness, PCV15 will provide about 11% coverage of pneumococci causing AOM, the same PCV13 and PCV20 will provide 30% coverage, leaving 70% of pneumococci causing AOM in young children uncovered (Figure).

Thus, the high proportion of pneumococcal serotype 35B and other non-PCV15 or non-PCV20 serotypes will result in a relatively small incremental benefit over PCV13 in young children for AOM.
AOM is the most common cause of pediatric outpatient visits and antibiotic prescriptions in the United States that contributes to selection of antibiotic-resistant microbes.3 The economic burden of AOM is high, estimated at about $3 billion annually in the United States, when direct and indirect costs are calculated,4 thereby making AOM a major factor in calculations of cost effectiveness analyses of PCV immunizations in children.
While PCV15 and PCV20 include common serotypes associated with invasive pneumococcal diseases, their effectiveness in preventing AOM, acute sinusitis, and non-bacteremic community-acquired pneumonia is currently unknown because these vaccines were licensed based on safety and immunogenicity data, not proven efficacy.
The data on antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci and H. influenza and M. catarrhalis isolated in the late post PCV13 era from young children in a pediatric primary-care setting raise a question about empiric antibiotic choice for AOM today. For penicillin non-susceptible pneumococcal strains, higher dosages of amoxicillin can improve eradication. However, higher dosages of amoxicillin cannot overcome beta-lactamase production by H. influenza and M. catarrhalis. Based on the mix of pathogens causing AOM and the antibiotic susceptibility of those bacteria, high-dose amoxicillin/clavulanate or alternative cephalosporin drugs active against pneumococci and beta-lactamase producing H. influenza and M. catarrhalis would be a better empiric choice over high-dose amoxicillin.
Limitations of our study include that it occurred in one center in New York, although we have previously shown results of tympanocentesis at our center are similar to those in Virginia and Pennsylvania5 and our study population was composed of children living in urban, suburban, and rural households of all economic levels. Because this study was conducted during a relatively short time frame (2021-2023), the numbers of subjects and samples were sometimes insufficient to identify statistically significant differences in some comparisons. Some children were lost to follow-up, and not every participant was consented for tympanocentesis. Some participants received antibiotics prior to middle ear fluid specimen collection.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute, at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
1. Kaur R et al. Dynamic Changes in Otopathogens Colonizing the Nasopharynx and Causing Acute Otitis Media in Children After 13-Valent (PCV13) Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination During 2015-2019. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Jan;41(1):37-44. doi: 10.1007/s10096-021-04324-0.
2. Kaur R et al. Anticipated Effects of Higher-valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines on Colonization and Acute Otitis Media. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2024 Oct 1;43(10):1004-1010. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000004413.
3. King LM et al. Pediatric Outpatient Visits and Antibiotic Use Attributable to Higher Valency Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine Serotypes. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 25:2023.08.24.23294570. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.24.23294570.
4. Ahmed S et al. Incremental Health Care Utilization and Costs for Acute Otitis Media in Children. Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):301-5. doi: 10.1002/lary.24190.
5. Pichichero ME et al. Pathogens Causing Recurrent and Difficult-to-Treat Acute Otitis Media, 2003-2006. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2008 Nov;47(9):901-6. doi: 10.1177/0009922808319966.
Reduced Vaccination Rates Contribute to Rising Pertussis Numbers
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Public Health, Not Politics, Should Drive Mask Policies, Says Ethicist
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently saw a ban that has me very worried, concerned, and strongly in opposition.
Basically, the standard kind of medical mask would be captured, although I think their aim in doing this was to try to discourage people at political protests from being able to wear masks and hide their identity. They’re basically trying to discourage that. This is particularly triggered by, I think, protests about the invasion of Israel, the war that resulted in Gaza, and the demonstrations that have gone on around the country, with many people masked.
There may be issues about what is acceptable to wear when you go to a demonstration. I don’t claim to know about the civil rights of that.
In a time at which COVID-19 is flourishing, really on the rebound, expanding fast, and still causing 600 deaths a week; the flu season is going to be upon us soon enough; and there are also concerns about the possibility of avian flu jumping into the human population, it is absolutely the wrong time to single out those who are trying to mask for health reasons.
Basically, there are two strong reasons. One, there are people out there who wear a medical mask or mask for a medical reason because they have an underlying disease. They may have had a transplant or they may feel they’re immunocompromised for some reason. They worry that, if they don’t wear a mask, they’re going to get an infection from something like COVID-19 or flu, which could really be super-dangerous for them.
The other reason people mask is to protect their family members. They may have someone who’s immunocompromised in the family, or they’re doing it kindly and altruistically to protect the rest of us and to stop viruses from circulating.
These bans are not taking into account public health. They’re being brought forward in the midst of political heat about demonstrations and political issues. I think they should be opposed. I do not think they should be enacted.
I think the medical rights of people with disabilities and immunologic disorders, and those who want to mask to prevent getting sick at a time at which infectious diseases are still circulating and killing people, ought to take priority. Public health, in this case, should drive our policies about masks.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, NY, served on Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position), and is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently saw a ban that has me very worried, concerned, and strongly in opposition.
Basically, the standard kind of medical mask would be captured, although I think their aim in doing this was to try to discourage people at political protests from being able to wear masks and hide their identity. They’re basically trying to discourage that. This is particularly triggered by, I think, protests about the invasion of Israel, the war that resulted in Gaza, and the demonstrations that have gone on around the country, with many people masked.
There may be issues about what is acceptable to wear when you go to a demonstration. I don’t claim to know about the civil rights of that.
In a time at which COVID-19 is flourishing, really on the rebound, expanding fast, and still causing 600 deaths a week; the flu season is going to be upon us soon enough; and there are also concerns about the possibility of avian flu jumping into the human population, it is absolutely the wrong time to single out those who are trying to mask for health reasons.
Basically, there are two strong reasons. One, there are people out there who wear a medical mask or mask for a medical reason because they have an underlying disease. They may have had a transplant or they may feel they’re immunocompromised for some reason. They worry that, if they don’t wear a mask, they’re going to get an infection from something like COVID-19 or flu, which could really be super-dangerous for them.
The other reason people mask is to protect their family members. They may have someone who’s immunocompromised in the family, or they’re doing it kindly and altruistically to protect the rest of us and to stop viruses from circulating.
These bans are not taking into account public health. They’re being brought forward in the midst of political heat about demonstrations and political issues. I think they should be opposed. I do not think they should be enacted.
I think the medical rights of people with disabilities and immunologic disorders, and those who want to mask to prevent getting sick at a time at which infectious diseases are still circulating and killing people, ought to take priority. Public health, in this case, should drive our policies about masks.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, NY, served on Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position), and is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I recently saw a ban that has me very worried, concerned, and strongly in opposition.
Basically, the standard kind of medical mask would be captured, although I think their aim in doing this was to try to discourage people at political protests from being able to wear masks and hide their identity. They’re basically trying to discourage that. This is particularly triggered by, I think, protests about the invasion of Israel, the war that resulted in Gaza, and the demonstrations that have gone on around the country, with many people masked.
There may be issues about what is acceptable to wear when you go to a demonstration. I don’t claim to know about the civil rights of that.
In a time at which COVID-19 is flourishing, really on the rebound, expanding fast, and still causing 600 deaths a week; the flu season is going to be upon us soon enough; and there are also concerns about the possibility of avian flu jumping into the human population, it is absolutely the wrong time to single out those who are trying to mask for health reasons.
Basically, there are two strong reasons. One, there are people out there who wear a medical mask or mask for a medical reason because they have an underlying disease. They may have had a transplant or they may feel they’re immunocompromised for some reason. They worry that, if they don’t wear a mask, they’re going to get an infection from something like COVID-19 or flu, which could really be super-dangerous for them.
The other reason people mask is to protect their family members. They may have someone who’s immunocompromised in the family, or they’re doing it kindly and altruistically to protect the rest of us and to stop viruses from circulating.
These bans are not taking into account public health. They’re being brought forward in the midst of political heat about demonstrations and political issues. I think they should be opposed. I do not think they should be enacted.
I think the medical rights of people with disabilities and immunologic disorders, and those who want to mask to prevent getting sick at a time at which infectious diseases are still circulating and killing people, ought to take priority. Public health, in this case, should drive our policies about masks.
Dr. Caplan, director, Division of Medical Ethics, New York University Langone Medical Center, New York, NY, served on Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position), and is a contributing author and adviser for Medscape.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Six Tips on Coronavirus Testing for Doctors and Patients
according to the Robert Koch Institute, Germany. If a patient has a fever and cough and feels exhausted, it could be COVID-19. What significance do rapid tests have? And when should doctors advise their patients about them?
When to Test
People at a higher risk for severe COVID-19 benefit from tests. This population includes the following groups:
- Older patients
- Immunocompromised patients
- Patients with respiratory diseases
- Patients with cardiovascular diseases
- Patients with liver and kidney diseases
- Patients with neurological diseases
- Patients with obesity
If doctors detect SARS-CoV-2 infection early, they can prescribe Paxlovid, for example, to reduce morbidity and mortality risks. Conversely, people without specific risks should test themselves if they plan to visit vulnerable individuals.
Detecting New Variants
A comprehensive study from the fall of 2022 provides evidence that antigen tests targeting the nucleocapsid (N) protein of SARS-CoV-2 also detect new variants.
The researchers built a library of various versions of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Their collection included nearly 8000 individual amino acid substitutions, representing more than 99.5% of all statistically possible mutations of the N protein.
They then examined how these N proteins interacted with 17 antibodies used in 11 commercially available antigen rapid tests.
All antibodies were able to recognize altered N proteins. Since the researchers successfully investigated diagnostic antibodies against nearly all possible N-protein mutations, rapid tests should be able to detect future virus variants. However, sensitivity and specificity may still change.
Test Timing
Uncertainty about what time of day to test can be mitigated by performing multiple COVID-19 rapid tests over time. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and similar organizations make this recommendation. Studies of symptomatic individuals show that serial tests increase accuracy.
In the early stages of infection, swabs may contain too little virus material because of widespread immunity against SARS-CoV-2. That is, they may contain inadequate levels of the relevant antigen. Especially in asymptomatic individuals or patients in the incubation phase, a single test may therefore yield a false-negative result. Therefore, the FDA recommends conducting at least two additional tests 48 hours apart in case of a negative test result.
Costs of Rapid Tests
The days of free tests are long gone. In Germany, the distribution of free preventive coronavirus tests was discontinued on March 1, 2023.
Test kits are still available in pharmacies or drugstores. In packages with 5-10 tests, the individual test costs between €0.90 and €1.50, depending on the provider. If a patient still has old rapid coronavirus tests in his or her medicine cabinet, are they still suitable?
Expired Tests
Properly stored tests that have not passed their expiration dates can still be used. But microbiologist and pathologist Daniel Rhoads, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio warns against expired rapid tests.
The chemicals may have decomposed, the solvent may have evaporated, or antibodies may have lost their effectiveness, thus making false negative results more likely. “These are proteins that can decompose over time,” said Dr. Rhoads.
Ordering PCR Tests
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test remains the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19. It is still available within statutory health insurance coverage. As Germany’s National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians observes, form Muster 10 is used to order the test in that country.
The fee for the swab is included in the insured patient’s basic flat rate. Laboratories bill the PCR test using fee schedule position (GOP) 32816, according to the Uniform Value Scale (EBM).
There is no possibility for billing rapid tests for SARS-CoV-2 in medical practices within the EBM. A laboratory-based SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test (GOP 32779) can be requested via the Muster 10 form.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the Robert Koch Institute, Germany. If a patient has a fever and cough and feels exhausted, it could be COVID-19. What significance do rapid tests have? And when should doctors advise their patients about them?
When to Test
People at a higher risk for severe COVID-19 benefit from tests. This population includes the following groups:
- Older patients
- Immunocompromised patients
- Patients with respiratory diseases
- Patients with cardiovascular diseases
- Patients with liver and kidney diseases
- Patients with neurological diseases
- Patients with obesity
If doctors detect SARS-CoV-2 infection early, they can prescribe Paxlovid, for example, to reduce morbidity and mortality risks. Conversely, people without specific risks should test themselves if they plan to visit vulnerable individuals.
Detecting New Variants
A comprehensive study from the fall of 2022 provides evidence that antigen tests targeting the nucleocapsid (N) protein of SARS-CoV-2 also detect new variants.
The researchers built a library of various versions of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Their collection included nearly 8000 individual amino acid substitutions, representing more than 99.5% of all statistically possible mutations of the N protein.
They then examined how these N proteins interacted with 17 antibodies used in 11 commercially available antigen rapid tests.
All antibodies were able to recognize altered N proteins. Since the researchers successfully investigated diagnostic antibodies against nearly all possible N-protein mutations, rapid tests should be able to detect future virus variants. However, sensitivity and specificity may still change.
Test Timing
Uncertainty about what time of day to test can be mitigated by performing multiple COVID-19 rapid tests over time. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and similar organizations make this recommendation. Studies of symptomatic individuals show that serial tests increase accuracy.
In the early stages of infection, swabs may contain too little virus material because of widespread immunity against SARS-CoV-2. That is, they may contain inadequate levels of the relevant antigen. Especially in asymptomatic individuals or patients in the incubation phase, a single test may therefore yield a false-negative result. Therefore, the FDA recommends conducting at least two additional tests 48 hours apart in case of a negative test result.
Costs of Rapid Tests
The days of free tests are long gone. In Germany, the distribution of free preventive coronavirus tests was discontinued on March 1, 2023.
Test kits are still available in pharmacies or drugstores. In packages with 5-10 tests, the individual test costs between €0.90 and €1.50, depending on the provider. If a patient still has old rapid coronavirus tests in his or her medicine cabinet, are they still suitable?
Expired Tests
Properly stored tests that have not passed their expiration dates can still be used. But microbiologist and pathologist Daniel Rhoads, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio warns against expired rapid tests.
The chemicals may have decomposed, the solvent may have evaporated, or antibodies may have lost their effectiveness, thus making false negative results more likely. “These are proteins that can decompose over time,” said Dr. Rhoads.
Ordering PCR Tests
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test remains the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19. It is still available within statutory health insurance coverage. As Germany’s National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians observes, form Muster 10 is used to order the test in that country.
The fee for the swab is included in the insured patient’s basic flat rate. Laboratories bill the PCR test using fee schedule position (GOP) 32816, according to the Uniform Value Scale (EBM).
There is no possibility for billing rapid tests for SARS-CoV-2 in medical practices within the EBM. A laboratory-based SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test (GOP 32779) can be requested via the Muster 10 form.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the Robert Koch Institute, Germany. If a patient has a fever and cough and feels exhausted, it could be COVID-19. What significance do rapid tests have? And when should doctors advise their patients about them?
When to Test
People at a higher risk for severe COVID-19 benefit from tests. This population includes the following groups:
- Older patients
- Immunocompromised patients
- Patients with respiratory diseases
- Patients with cardiovascular diseases
- Patients with liver and kidney diseases
- Patients with neurological diseases
- Patients with obesity
If doctors detect SARS-CoV-2 infection early, they can prescribe Paxlovid, for example, to reduce morbidity and mortality risks. Conversely, people without specific risks should test themselves if they plan to visit vulnerable individuals.
Detecting New Variants
A comprehensive study from the fall of 2022 provides evidence that antigen tests targeting the nucleocapsid (N) protein of SARS-CoV-2 also detect new variants.
The researchers built a library of various versions of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. Their collection included nearly 8000 individual amino acid substitutions, representing more than 99.5% of all statistically possible mutations of the N protein.
They then examined how these N proteins interacted with 17 antibodies used in 11 commercially available antigen rapid tests.
All antibodies were able to recognize altered N proteins. Since the researchers successfully investigated diagnostic antibodies against nearly all possible N-protein mutations, rapid tests should be able to detect future virus variants. However, sensitivity and specificity may still change.
Test Timing
Uncertainty about what time of day to test can be mitigated by performing multiple COVID-19 rapid tests over time. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and similar organizations make this recommendation. Studies of symptomatic individuals show that serial tests increase accuracy.
In the early stages of infection, swabs may contain too little virus material because of widespread immunity against SARS-CoV-2. That is, they may contain inadequate levels of the relevant antigen. Especially in asymptomatic individuals or patients in the incubation phase, a single test may therefore yield a false-negative result. Therefore, the FDA recommends conducting at least two additional tests 48 hours apart in case of a negative test result.
Costs of Rapid Tests
The days of free tests are long gone. In Germany, the distribution of free preventive coronavirus tests was discontinued on March 1, 2023.
Test kits are still available in pharmacies or drugstores. In packages with 5-10 tests, the individual test costs between €0.90 and €1.50, depending on the provider. If a patient still has old rapid coronavirus tests in his or her medicine cabinet, are they still suitable?
Expired Tests
Properly stored tests that have not passed their expiration dates can still be used. But microbiologist and pathologist Daniel Rhoads, MD, from the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio warns against expired rapid tests.
The chemicals may have decomposed, the solvent may have evaporated, or antibodies may have lost their effectiveness, thus making false negative results more likely. “These are proteins that can decompose over time,” said Dr. Rhoads.
Ordering PCR Tests
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test remains the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19. It is still available within statutory health insurance coverage. As Germany’s National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Physicians observes, form Muster 10 is used to order the test in that country.
The fee for the swab is included in the insured patient’s basic flat rate. Laboratories bill the PCR test using fee schedule position (GOP) 32816, according to the Uniform Value Scale (EBM).
There is no possibility for billing rapid tests for SARS-CoV-2 in medical practices within the EBM. A laboratory-based SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection test (GOP 32779) can be requested via the Muster 10 form.
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID Levels Start to Dip, New Variant Emerges
A new COVID-19 variant called XEC is on the rise, and it has experts who track variants on alert.
Each time a new variant makes a grand entrance onto tracker lists, health officials take notice because it may mean there’s an important change in behavior of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID.
Countries reporting rising detections of XEC include Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands, Australian data scientist Mike Honey posted on the platform X this past week.
XEC’s “characteristic mutations” have been detected in at least 25 states, CBS News reported, with New Jersey, California, and Virginia labs reporting 10 or more cases each. New Jersey detections at least in part stem from the CDC’s testing program for international travelers at Newark Liberty International Airport.
Still, XEC hasn’t gained enough traction in Europe, the United States, or any other part of the world for it to be listed as a standalone variant on official watchlists maintained by the CDC, European Union, or World Health Organization.
However, Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-at-large for Medscape, believes XEC is the next variant “to get legs.”
The rate at which a new variant takes the stage doesn’t always predict how severe it will be. Around this time last year, health officials sounded alarms about another Omicron variant called BA.2.86, dubbed Pirola, that ultimately didn’t make major waves.
“CDC is not aware of any specific symptoms associated with XEC or any other co-circulating SARS-CoV-2 lineage,” a CDC spokesperson said in a statement to CBS News.
Its parent lineages are KP.2 and KP.3, and all of these belong to the Omicron family. The SARS-CoV-2 virus mutates over time, and scientists use the names and labels to identify groups of viral variants based on their similarities and on which strains a mutated descendant came from.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
A new COVID-19 variant called XEC is on the rise, and it has experts who track variants on alert.
Each time a new variant makes a grand entrance onto tracker lists, health officials take notice because it may mean there’s an important change in behavior of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID.
Countries reporting rising detections of XEC include Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands, Australian data scientist Mike Honey posted on the platform X this past week.
XEC’s “characteristic mutations” have been detected in at least 25 states, CBS News reported, with New Jersey, California, and Virginia labs reporting 10 or more cases each. New Jersey detections at least in part stem from the CDC’s testing program for international travelers at Newark Liberty International Airport.
Still, XEC hasn’t gained enough traction in Europe, the United States, or any other part of the world for it to be listed as a standalone variant on official watchlists maintained by the CDC, European Union, or World Health Organization.
However, Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-at-large for Medscape, believes XEC is the next variant “to get legs.”
The rate at which a new variant takes the stage doesn’t always predict how severe it will be. Around this time last year, health officials sounded alarms about another Omicron variant called BA.2.86, dubbed Pirola, that ultimately didn’t make major waves.
“CDC is not aware of any specific symptoms associated with XEC or any other co-circulating SARS-CoV-2 lineage,” a CDC spokesperson said in a statement to CBS News.
Its parent lineages are KP.2 and KP.3, and all of these belong to the Omicron family. The SARS-CoV-2 virus mutates over time, and scientists use the names and labels to identify groups of viral variants based on their similarities and on which strains a mutated descendant came from.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
A new COVID-19 variant called XEC is on the rise, and it has experts who track variants on alert.
Each time a new variant makes a grand entrance onto tracker lists, health officials take notice because it may mean there’s an important change in behavior of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID.
Countries reporting rising detections of XEC include Germany, the United Kingdom, and the Netherlands, Australian data scientist Mike Honey posted on the platform X this past week.
XEC’s “characteristic mutations” have been detected in at least 25 states, CBS News reported, with New Jersey, California, and Virginia labs reporting 10 or more cases each. New Jersey detections at least in part stem from the CDC’s testing program for international travelers at Newark Liberty International Airport.
Still, XEC hasn’t gained enough traction in Europe, the United States, or any other part of the world for it to be listed as a standalone variant on official watchlists maintained by the CDC, European Union, or World Health Organization.
However, Eric Topol, MD, executive vice president of Scripps Research and editor-at-large for Medscape, believes XEC is the next variant “to get legs.”
The rate at which a new variant takes the stage doesn’t always predict how severe it will be. Around this time last year, health officials sounded alarms about another Omicron variant called BA.2.86, dubbed Pirola, that ultimately didn’t make major waves.
“CDC is not aware of any specific symptoms associated with XEC or any other co-circulating SARS-CoV-2 lineage,” a CDC spokesperson said in a statement to CBS News.
Its parent lineages are KP.2 and KP.3, and all of these belong to the Omicron family. The SARS-CoV-2 virus mutates over time, and scientists use the names and labels to identify groups of viral variants based on their similarities and on which strains a mutated descendant came from.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.



