User login
Special CRC prevention efforts may focus on population with higher serum uric acid levels
Key clinical point: A significant positive association exists between elevated levels of serum uric acid (SUA) and the risk for incident colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: SUA levels and the risk for CRC showed a positive dose-response and linear association (P = .004), with the risk for incident CRC being 1.55-fold higher among participants in the highest vs lowest tertile of SUA levels (adjusted hazard ratio 1.55; P = .019).
Study details: Findings are from an ongoing prospective cohort study including 93,356 cancer-free participants.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Li W et al. The relationship between serum uric acid and colorectal cancer: A prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16677 (Oct 6). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20357-7
Key clinical point: A significant positive association exists between elevated levels of serum uric acid (SUA) and the risk for incident colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: SUA levels and the risk for CRC showed a positive dose-response and linear association (P = .004), with the risk for incident CRC being 1.55-fold higher among participants in the highest vs lowest tertile of SUA levels (adjusted hazard ratio 1.55; P = .019).
Study details: Findings are from an ongoing prospective cohort study including 93,356 cancer-free participants.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Li W et al. The relationship between serum uric acid and colorectal cancer: A prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16677 (Oct 6). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20357-7
Key clinical point: A significant positive association exists between elevated levels of serum uric acid (SUA) and the risk for incident colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: SUA levels and the risk for CRC showed a positive dose-response and linear association (P = .004), with the risk for incident CRC being 1.55-fold higher among participants in the highest vs lowest tertile of SUA levels (adjusted hazard ratio 1.55; P = .019).
Study details: Findings are from an ongoing prospective cohort study including 93,356 cancer-free participants.
Disclosures: This study did not report any source of funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Li W et al. The relationship between serum uric acid and colorectal cancer: A prospective cohort study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:16677 (Oct 6). Doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20357-7
Capecitabine consolidation chemotherapy after NCRT improves CR in LARC
Key clinical point: Consolidation chemotherapy (CC) with 1-2 cycles of capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) without extending the interval between NCRT and surgery was safe and improved the complete response (CR) rate without improving long-term outcomes in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).
Major finding: After propensity matching, the CR rate was significantly higher in the group receiving vs not receiving CC after NCRT (27.6% vs 16.2%; P = .045); however, the 3-year non-regrowth disease-free survival (P = .865), overall survival (P = .612), and grade ≥2 acute toxicity (P = .492) did not differ significantly between the groups.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 265 high-risk patients with LARC who either received (n = 136) or did not receive (n = 129) CC after NCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research, and National Natural Science Foundation, China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sheng XQ et al. Consolidation chemotherapy with capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: Propensity score study. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(9):1711-1726 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1711
Key clinical point: Consolidation chemotherapy (CC) with 1-2 cycles of capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) without extending the interval between NCRT and surgery was safe and improved the complete response (CR) rate without improving long-term outcomes in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).
Major finding: After propensity matching, the CR rate was significantly higher in the group receiving vs not receiving CC after NCRT (27.6% vs 16.2%; P = .045); however, the 3-year non-regrowth disease-free survival (P = .865), overall survival (P = .612), and grade ≥2 acute toxicity (P = .492) did not differ significantly between the groups.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 265 high-risk patients with LARC who either received (n = 136) or did not receive (n = 129) CC after NCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research, and National Natural Science Foundation, China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sheng XQ et al. Consolidation chemotherapy with capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: Propensity score study. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(9):1711-1726 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1711
Key clinical point: Consolidation chemotherapy (CC) with 1-2 cycles of capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (NCRT) without extending the interval between NCRT and surgery was safe and improved the complete response (CR) rate without improving long-term outcomes in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC).
Major finding: After propensity matching, the CR rate was significantly higher in the group receiving vs not receiving CC after NCRT (27.6% vs 16.2%; P = .045); however, the 3-year non-regrowth disease-free survival (P = .865), overall survival (P = .612), and grade ≥2 acute toxicity (P = .492) did not differ significantly between the groups.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study of 265 high-risk patients with LARC who either received (n = 136) or did not receive (n = 129) CC after NCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research, and National Natural Science Foundation, China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Sheng XQ et al. Consolidation chemotherapy with capecitabine after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in high-risk patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: Propensity score study. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(9):1711-1726 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i9.1711
Longer interval between nCRT and surgery increases tumor regression in LARC
Key clinical point: A >8-week interval between neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) and subsequent surgery improved tumor regression grade (TRG) compared with a 6-8-week interval in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), while pathological complete response (pCR) and survival outcomes were similar between the groups.
Major finding: The pCR rate (P = .836), 5-year relapse-free survival (P = .569), and 5-year overall survival (P = .956) were not significantly different between the 6-8-week and >8-week groups; however, TRG was significantly better in the >8-week group (P = .004).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 770 patients with LARC who had undergone total mesorectal excision either 6-8 weeks (n = 502) or >8 weeks (n = 268) after long‐course nCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants donated to Seoul National University Hospital under the name of Jung‐Ok Hwang. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Khamzina S et al. Standard versus longer interval of radical resection after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: A 20‐year single‐center experience & propensity‐score matching. J Surg Oncol. 2022 (Sep 28). Doi: 10.1002/jso.27105
Key clinical point: A >8-week interval between neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) and subsequent surgery improved tumor regression grade (TRG) compared with a 6-8-week interval in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), while pathological complete response (pCR) and survival outcomes were similar between the groups.
Major finding: The pCR rate (P = .836), 5-year relapse-free survival (P = .569), and 5-year overall survival (P = .956) were not significantly different between the 6-8-week and >8-week groups; however, TRG was significantly better in the >8-week group (P = .004).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 770 patients with LARC who had undergone total mesorectal excision either 6-8 weeks (n = 502) or >8 weeks (n = 268) after long‐course nCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants donated to Seoul National University Hospital under the name of Jung‐Ok Hwang. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Khamzina S et al. Standard versus longer interval of radical resection after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: A 20‐year single‐center experience & propensity‐score matching. J Surg Oncol. 2022 (Sep 28). Doi: 10.1002/jso.27105
Key clinical point: A >8-week interval between neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) and subsequent surgery improved tumor regression grade (TRG) compared with a 6-8-week interval in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC), while pathological complete response (pCR) and survival outcomes were similar between the groups.
Major finding: The pCR rate (P = .836), 5-year relapse-free survival (P = .569), and 5-year overall survival (P = .956) were not significantly different between the 6-8-week and >8-week groups; however, TRG was significantly better in the >8-week group (P = .004).
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective study including 770 patients with LARC who had undergone total mesorectal excision either 6-8 weeks (n = 502) or >8 weeks (n = 268) after long‐course nCRT.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants donated to Seoul National University Hospital under the name of Jung‐Ok Hwang. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Khamzina S et al. Standard versus longer interval of radical resection after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: A 20‐year single‐center experience & propensity‐score matching. J Surg Oncol. 2022 (Sep 28). Doi: 10.1002/jso.27105
Long-term use of antihypertensive drugs and CRC risk: Is there a link?
Key clinical point: Long-term use of major classes of antihypertensive drugs was unlikely to be associated with an increased risk for colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: Compared with never use, ≥11-year use of beta-blockers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.38; 95% CI 0.90-2.11), calcium channel blockers (aHR 0.92; 95% CI 0.57-1.46), thiazide diuretics (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.47-1.51), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (aHR 0.57; 95% CI 0.23-1.39), or other antihypertensive drugs (aHR 1.12; 95% CI 0.59-2.12) was not associated with an increased risk for CRC.
Study details: This was a prospective cohort study of eligible participants from the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study who were followed-up for 28 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the American Cancer Society Mentored Research Scholar Grant, US National Institutes of Health, World Cancer Research Fund, and others. Dr. Meyerhardt and Dr. Chan declared receiving institutional research funding from and consulting for various sources.
Source: Zhang Y et al. Long-term use of antihypertensive medications, hypertension and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: A prospective cohort study. Br J Cancer. 2022 (Sep 22). Doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01975-4
Key clinical point: Long-term use of major classes of antihypertensive drugs was unlikely to be associated with an increased risk for colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: Compared with never use, ≥11-year use of beta-blockers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.38; 95% CI 0.90-2.11), calcium channel blockers (aHR 0.92; 95% CI 0.57-1.46), thiazide diuretics (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.47-1.51), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (aHR 0.57; 95% CI 0.23-1.39), or other antihypertensive drugs (aHR 1.12; 95% CI 0.59-2.12) was not associated with an increased risk for CRC.
Study details: This was a prospective cohort study of eligible participants from the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study who were followed-up for 28 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the American Cancer Society Mentored Research Scholar Grant, US National Institutes of Health, World Cancer Research Fund, and others. Dr. Meyerhardt and Dr. Chan declared receiving institutional research funding from and consulting for various sources.
Source: Zhang Y et al. Long-term use of antihypertensive medications, hypertension and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: A prospective cohort study. Br J Cancer. 2022 (Sep 22). Doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01975-4
Key clinical point: Long-term use of major classes of antihypertensive drugs was unlikely to be associated with an increased risk for colorectal cancer (CRC).
Major finding: Compared with never use, ≥11-year use of beta-blockers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.38; 95% CI 0.90-2.11), calcium channel blockers (aHR 0.92; 95% CI 0.57-1.46), thiazide diuretics (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.47-1.51), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (aHR 0.57; 95% CI 0.23-1.39), or other antihypertensive drugs (aHR 1.12; 95% CI 0.59-2.12) was not associated with an increased risk for CRC.
Study details: This was a prospective cohort study of eligible participants from the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals Follow-up Study who were followed-up for 28 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the American Cancer Society Mentored Research Scholar Grant, US National Institutes of Health, World Cancer Research Fund, and others. Dr. Meyerhardt and Dr. Chan declared receiving institutional research funding from and consulting for various sources.
Source: Zhang Y et al. Long-term use of antihypertensive medications, hypertension and colorectal cancer risk and mortality: A prospective cohort study. Br J Cancer. 2022 (Sep 22). Doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01975-4
Benefits of simultaneous resection of liver metastasis restricted to patients with KRAS wild-type tumors
Key clinical point: Simultaneous vs delayed resection of synchronous liver metastasis (SLM) was associated with longer survival rates in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) with KRAS wild-type tumors but not in those with KRAS sequence variation.
Major finding: Perioperative complications within 60 days of surgery were not significantly different in the simultaneous vs delayed resection group (P = .89), but simultaneous vs delayed resection was associated with better 5-year overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 1.61; P < .001) and cancer-specific survival (HR 1.62; P = .003) in patients with KRAS wild-type tumors, but not in those with overall KRAS sequence variation.
Study details: This retrospective study included 1569 patients with CRC with or without KRAS sequence variation who underwent simultaneous (n = 512) or delayed (n = 1057) resection of SLM.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from Shanghai Shenkang Clinical Science and Technology Innovation Project, China. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Wu Y et al. Association of simultaneous vs delayed resection of liver metastasis with complications and survival among adults with colorectal cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(9):e2231956 (Sep 19). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31956
Key clinical point: Simultaneous vs delayed resection of synchronous liver metastasis (SLM) was associated with longer survival rates in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) with KRAS wild-type tumors but not in those with KRAS sequence variation.
Major finding: Perioperative complications within 60 days of surgery were not significantly different in the simultaneous vs delayed resection group (P = .89), but simultaneous vs delayed resection was associated with better 5-year overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 1.61; P < .001) and cancer-specific survival (HR 1.62; P = .003) in patients with KRAS wild-type tumors, but not in those with overall KRAS sequence variation.
Study details: This retrospective study included 1569 patients with CRC with or without KRAS sequence variation who underwent simultaneous (n = 512) or delayed (n = 1057) resection of SLM.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from Shanghai Shenkang Clinical Science and Technology Innovation Project, China. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Wu Y et al. Association of simultaneous vs delayed resection of liver metastasis with complications and survival among adults with colorectal cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(9):e2231956 (Sep 19). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31956
Key clinical point: Simultaneous vs delayed resection of synchronous liver metastasis (SLM) was associated with longer survival rates in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) with KRAS wild-type tumors but not in those with KRAS sequence variation.
Major finding: Perioperative complications within 60 days of surgery were not significantly different in the simultaneous vs delayed resection group (P = .89), but simultaneous vs delayed resection was associated with better 5-year overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] 1.61; P < .001) and cancer-specific survival (HR 1.62; P = .003) in patients with KRAS wild-type tumors, but not in those with overall KRAS sequence variation.
Study details: This retrospective study included 1569 patients with CRC with or without KRAS sequence variation who underwent simultaneous (n = 512) or delayed (n = 1057) resection of SLM.
Disclosures: This study was supported by a grant from Shanghai Shenkang Clinical Science and Technology Innovation Project, China. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Wu Y et al. Association of simultaneous vs delayed resection of liver metastasis with complications and survival among adults with colorectal cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(9):e2231956 (Sep 19). Doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31956
Low rectal cancer: Laparoscopic-assisted surgery safe in terms of short-term oncological outcomes
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic surgery for low rectal cancer when performed by experienced surgeons yielded short-term pathological outcomes, comparable to open surgery, along with a higher rate of sphincter preservation and a shorter duration of hospitalization.
Major finding: Laparoscopic vs open surgery was associated with similar rates of mesorectal excision (P = .78), negative circumferential resection margin (P = .09), negative distal resection margin (P = .36), postoperative complications (P = .07), and median number of retrieved lymph nodes (P = .39), along with a higher sphincter preservation rate (P = .03) and shorter hospitalization duration (P = .008).
Study details: Findings are from LASRE, a noninferiority randomized clinical trial, including 1039 patients scheduled for curative-intent resection of low rectal cancer who were randomly assigned to undergo laparoscopic (n = 712) or open (n = 358) surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of the National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Jiang WZ et al. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopy-assisted vs open surgery for patients with low rectal cancer: The LASRE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4079
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic surgery for low rectal cancer when performed by experienced surgeons yielded short-term pathological outcomes, comparable to open surgery, along with a higher rate of sphincter preservation and a shorter duration of hospitalization.
Major finding: Laparoscopic vs open surgery was associated with similar rates of mesorectal excision (P = .78), negative circumferential resection margin (P = .09), negative distal resection margin (P = .36), postoperative complications (P = .07), and median number of retrieved lymph nodes (P = .39), along with a higher sphincter preservation rate (P = .03) and shorter hospitalization duration (P = .008).
Study details: Findings are from LASRE, a noninferiority randomized clinical trial, including 1039 patients scheduled for curative-intent resection of low rectal cancer who were randomly assigned to undergo laparoscopic (n = 712) or open (n = 358) surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of the National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Jiang WZ et al. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopy-assisted vs open surgery for patients with low rectal cancer: The LASRE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4079
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic surgery for low rectal cancer when performed by experienced surgeons yielded short-term pathological outcomes, comparable to open surgery, along with a higher rate of sphincter preservation and a shorter duration of hospitalization.
Major finding: Laparoscopic vs open surgery was associated with similar rates of mesorectal excision (P = .78), negative circumferential resection margin (P = .09), negative distal resection margin (P = .36), postoperative complications (P = .07), and median number of retrieved lymph nodes (P = .39), along with a higher sphincter preservation rate (P = .03) and shorter hospitalization duration (P = .008).
Study details: Findings are from LASRE, a noninferiority randomized clinical trial, including 1039 patients scheduled for curative-intent resection of low rectal cancer who were randomly assigned to undergo laparoscopic (n = 712) or open (n = 358) surgery.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of the National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Jiang WZ et al. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopy-assisted vs open surgery for patients with low rectal cancer: The LASRE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022 (Sep 15). Doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4079
FDA panel recommends withdrawal of Makena for preterm birth
A federal advisory panel recommended the United States withdraw from the market an injection given to women at risk for giving birth prematurely. Many of its members argued this step is needed to allow further testing to see if this drug actually works.
The Food and Drug Administration has been seeking to pull the approval of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (17P) injection (Makena, Covis) since 2020, after the drug failed to show a benefit in the PROLONG study. This study was meant as a confirmatory trial for the accelerated approval the FDA granted Makena in 2011 based on promising results from an earlier small study, known as the Meis trial. The manufacturer, Covis, contends that the flaws in the PROLONG study made Makena appear ineffective.
The FDA asked its Obstetrics, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee to review the evidence gathered to date on Makena at a hearing that ran from Oct. 17 to Oct. 19. At the conclusion, the FDA asked the committee to vote on whether the agency should allow Makena to remain on the market while an appropriate confirmatory study is designed and conducted.
The vote was 14-1 against this plan.
There needs to be another study as a “tiebreaker” to determine which of the previous Makena trials was correct, said FDA panelist Michael K. Lindsay, MD, MPH, who is also director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine for Grady and Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta.
“I think there needs to be another trial,” Dr. Lindsay said. “If you can do the trial without the medication being FDA approved, then I am supportive of that.”
Members of the FDA panel noted the difficulties that would ensue if Covis attempted further study of Makena with the drug still approved, including difficulties in recruiting patients. Indeed, there were delays in recruiting patients for the PROLONG trial in part because Makena was perceived as the standard of care for pregnant women who had a prior spontaneous preterm birth. That led to efforts to enroll patients outside of the United States, particularly in Eastern European countries.
Panelist Cassandra E. Henderson, MD, of the New York-based Garden OB/GYN practice, was the dissenter in the 14-1 vote.
Withdrawing the approval of Makena may lead to increased use of pharmacy-compounded versions of this medicine, as women look for options to try to extend their pregnancies, she said.
“They may seek it in other ways and get something that we don’t have any control over, and we don’t know what the fetus may be exposed to,” Dr. Henderson said.
Dr. Henderson also said there should be greater discussion with patients about questions of potential “intergenerational risk” because of fetal exposure to the medicine. Covis could add a registry similar to the University of Chicago’s DES Program to its research program for Makena, she said.
Race-based argument
Covis has been fighting to keep the Makena approval by offering theories for why the PROLONG study failed to show a benefit for the drug.
Covis emphasizes the different racial make-up of patients in the two trials. Black women composed 59% of the Meis study population, compared with only 6.7% for the PROLONG study, Covis said in its briefing document for the hearing. The Luxembourg-based company also says that there may have been unreliable estimates of the gestational age in the PROLONG trial, which enrolled many subjects in Ukraine and Russia.
During deliberations among panelists on Oct. 19, Dr. Henderson emphasized a need to consider other factors that may have been involved and encouraged continued study of the drug in Black women. She dismissed the idea of a race-based difference being the explanation for the difference between the two trials, but instead stressed that race serves as a marker for inequities, which are known to increase risk for preterm birth.
“Targeting a population that is at risk, particularly Black women in the United States, may show something that would be beneficial” from Makena, Dr. Henderson said.
Other physicians have argued that this approach would actually put Black women and children at greater risk of an ineffective drug with potential side effects.
“The drug is not proven to work so keeping it on the market to be injected into Black women to see what subgroups it might work in essentially amounts to experimentation,” said Adam Urato, MD, chief of maternal-fetal medicine at MetroWest Medical Center in Framingham, Mass., during the public comment session of the hearing.
The vote marks the second time that the FDA’s advisers on reproductive health have told the agency that the evidence gathered on the drug does not support its use. An advisory committee also cast votes against the drug at a 2019 meeting.
The rate of preterm birth in Black women in 2020 was 14.4%, significantly higher than the rate of preterm birth in White or Hispanic women, 9.1% and 9.8%, respectively, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The potential for harm to children from premature birth led the FDA to clear Makena through the accelerated approval pathway, said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in the opening session of the hearing.
“We once thought Makena was likely to be part of the answer to that problem,” Dr. Cavazzoni said. “Unfortunately we no longer do, based on the evidence available.”
A federal advisory panel recommended the United States withdraw from the market an injection given to women at risk for giving birth prematurely. Many of its members argued this step is needed to allow further testing to see if this drug actually works.
The Food and Drug Administration has been seeking to pull the approval of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (17P) injection (Makena, Covis) since 2020, after the drug failed to show a benefit in the PROLONG study. This study was meant as a confirmatory trial for the accelerated approval the FDA granted Makena in 2011 based on promising results from an earlier small study, known as the Meis trial. The manufacturer, Covis, contends that the flaws in the PROLONG study made Makena appear ineffective.
The FDA asked its Obstetrics, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee to review the evidence gathered to date on Makena at a hearing that ran from Oct. 17 to Oct. 19. At the conclusion, the FDA asked the committee to vote on whether the agency should allow Makena to remain on the market while an appropriate confirmatory study is designed and conducted.
The vote was 14-1 against this plan.
There needs to be another study as a “tiebreaker” to determine which of the previous Makena trials was correct, said FDA panelist Michael K. Lindsay, MD, MPH, who is also director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine for Grady and Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta.
“I think there needs to be another trial,” Dr. Lindsay said. “If you can do the trial without the medication being FDA approved, then I am supportive of that.”
Members of the FDA panel noted the difficulties that would ensue if Covis attempted further study of Makena with the drug still approved, including difficulties in recruiting patients. Indeed, there were delays in recruiting patients for the PROLONG trial in part because Makena was perceived as the standard of care for pregnant women who had a prior spontaneous preterm birth. That led to efforts to enroll patients outside of the United States, particularly in Eastern European countries.
Panelist Cassandra E. Henderson, MD, of the New York-based Garden OB/GYN practice, was the dissenter in the 14-1 vote.
Withdrawing the approval of Makena may lead to increased use of pharmacy-compounded versions of this medicine, as women look for options to try to extend their pregnancies, she said.
“They may seek it in other ways and get something that we don’t have any control over, and we don’t know what the fetus may be exposed to,” Dr. Henderson said.
Dr. Henderson also said there should be greater discussion with patients about questions of potential “intergenerational risk” because of fetal exposure to the medicine. Covis could add a registry similar to the University of Chicago’s DES Program to its research program for Makena, she said.
Race-based argument
Covis has been fighting to keep the Makena approval by offering theories for why the PROLONG study failed to show a benefit for the drug.
Covis emphasizes the different racial make-up of patients in the two trials. Black women composed 59% of the Meis study population, compared with only 6.7% for the PROLONG study, Covis said in its briefing document for the hearing. The Luxembourg-based company also says that there may have been unreliable estimates of the gestational age in the PROLONG trial, which enrolled many subjects in Ukraine and Russia.
During deliberations among panelists on Oct. 19, Dr. Henderson emphasized a need to consider other factors that may have been involved and encouraged continued study of the drug in Black women. She dismissed the idea of a race-based difference being the explanation for the difference between the two trials, but instead stressed that race serves as a marker for inequities, which are known to increase risk for preterm birth.
“Targeting a population that is at risk, particularly Black women in the United States, may show something that would be beneficial” from Makena, Dr. Henderson said.
Other physicians have argued that this approach would actually put Black women and children at greater risk of an ineffective drug with potential side effects.
“The drug is not proven to work so keeping it on the market to be injected into Black women to see what subgroups it might work in essentially amounts to experimentation,” said Adam Urato, MD, chief of maternal-fetal medicine at MetroWest Medical Center in Framingham, Mass., during the public comment session of the hearing.
The vote marks the second time that the FDA’s advisers on reproductive health have told the agency that the evidence gathered on the drug does not support its use. An advisory committee also cast votes against the drug at a 2019 meeting.
The rate of preterm birth in Black women in 2020 was 14.4%, significantly higher than the rate of preterm birth in White or Hispanic women, 9.1% and 9.8%, respectively, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The potential for harm to children from premature birth led the FDA to clear Makena through the accelerated approval pathway, said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in the opening session of the hearing.
“We once thought Makena was likely to be part of the answer to that problem,” Dr. Cavazzoni said. “Unfortunately we no longer do, based on the evidence available.”
A federal advisory panel recommended the United States withdraw from the market an injection given to women at risk for giving birth prematurely. Many of its members argued this step is needed to allow further testing to see if this drug actually works.
The Food and Drug Administration has been seeking to pull the approval of hydroxyprogesterone caproate (17P) injection (Makena, Covis) since 2020, after the drug failed to show a benefit in the PROLONG study. This study was meant as a confirmatory trial for the accelerated approval the FDA granted Makena in 2011 based on promising results from an earlier small study, known as the Meis trial. The manufacturer, Covis, contends that the flaws in the PROLONG study made Makena appear ineffective.
The FDA asked its Obstetrics, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee to review the evidence gathered to date on Makena at a hearing that ran from Oct. 17 to Oct. 19. At the conclusion, the FDA asked the committee to vote on whether the agency should allow Makena to remain on the market while an appropriate confirmatory study is designed and conducted.
The vote was 14-1 against this plan.
There needs to be another study as a “tiebreaker” to determine which of the previous Makena trials was correct, said FDA panelist Michael K. Lindsay, MD, MPH, who is also director of the division of maternal-fetal medicine for Grady and Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta.
“I think there needs to be another trial,” Dr. Lindsay said. “If you can do the trial without the medication being FDA approved, then I am supportive of that.”
Members of the FDA panel noted the difficulties that would ensue if Covis attempted further study of Makena with the drug still approved, including difficulties in recruiting patients. Indeed, there were delays in recruiting patients for the PROLONG trial in part because Makena was perceived as the standard of care for pregnant women who had a prior spontaneous preterm birth. That led to efforts to enroll patients outside of the United States, particularly in Eastern European countries.
Panelist Cassandra E. Henderson, MD, of the New York-based Garden OB/GYN practice, was the dissenter in the 14-1 vote.
Withdrawing the approval of Makena may lead to increased use of pharmacy-compounded versions of this medicine, as women look for options to try to extend their pregnancies, she said.
“They may seek it in other ways and get something that we don’t have any control over, and we don’t know what the fetus may be exposed to,” Dr. Henderson said.
Dr. Henderson also said there should be greater discussion with patients about questions of potential “intergenerational risk” because of fetal exposure to the medicine. Covis could add a registry similar to the University of Chicago’s DES Program to its research program for Makena, she said.
Race-based argument
Covis has been fighting to keep the Makena approval by offering theories for why the PROLONG study failed to show a benefit for the drug.
Covis emphasizes the different racial make-up of patients in the two trials. Black women composed 59% of the Meis study population, compared with only 6.7% for the PROLONG study, Covis said in its briefing document for the hearing. The Luxembourg-based company also says that there may have been unreliable estimates of the gestational age in the PROLONG trial, which enrolled many subjects in Ukraine and Russia.
During deliberations among panelists on Oct. 19, Dr. Henderson emphasized a need to consider other factors that may have been involved and encouraged continued study of the drug in Black women. She dismissed the idea of a race-based difference being the explanation for the difference between the two trials, but instead stressed that race serves as a marker for inequities, which are known to increase risk for preterm birth.
“Targeting a population that is at risk, particularly Black women in the United States, may show something that would be beneficial” from Makena, Dr. Henderson said.
Other physicians have argued that this approach would actually put Black women and children at greater risk of an ineffective drug with potential side effects.
“The drug is not proven to work so keeping it on the market to be injected into Black women to see what subgroups it might work in essentially amounts to experimentation,” said Adam Urato, MD, chief of maternal-fetal medicine at MetroWest Medical Center in Framingham, Mass., during the public comment session of the hearing.
The vote marks the second time that the FDA’s advisers on reproductive health have told the agency that the evidence gathered on the drug does not support its use. An advisory committee also cast votes against the drug at a 2019 meeting.
The rate of preterm birth in Black women in 2020 was 14.4%, significantly higher than the rate of preterm birth in White or Hispanic women, 9.1% and 9.8%, respectively, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The potential for harm to children from premature birth led the FDA to clear Makena through the accelerated approval pathway, said Patrizia Cavazzoni, MD, the director of FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, in the opening session of the hearing.
“We once thought Makena was likely to be part of the answer to that problem,” Dr. Cavazzoni said. “Unfortunately we no longer do, based on the evidence available.”
First RCT evaluating benefits of colonoscopy screening rocks GI: NordICC
VIENNA – the 10-year follow-up of the large, multicenter, randomized Northern-European Initiative on Colorectal Cancer (NordICC) trial shows.
In effect, this means the number needed to invite to undergo screening to prevent one case of colorectal cancer is 455 (95% confidence interval, 270-1,429), the researchers determined.
The results were presented at the United European Gastroenterology Week 2022 meeting and were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The results of the study, which was designed to be truly population based and to mimic national colorectal cancer screening programs, provide an estimate of the effect of screening colonoscopy in the general population.
The primary outcome was determined on an intention-to-screen basis. All persons who were invited to undergo colonoscopy screening were compared with people who received usual care (that is, received no invitation or screening). At UEG 2022, the researchers presented the interim 10-year colorectal cancer risk, which was found to be 0.98%, compared to 1.20%. This represents a risk reduction of 18% among colonoscopy invitees (risk ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.70-0.93). During the study period, 259 cases of colorectal cancer were diagnosed in the invited group versus622 in the usual-care group.
The risk of death from colorectal cancer was 0.28% in the invited group and 0.31% in the usual-care group (RR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.64-1.16). The risk of death from any cause was similar in both the invited group and the usual-care group, at 11.03% and 11.04%, respectively (RR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.96-1.04).
The authors noted that the benefit would have been greater had more people undergone screening; only 42% of those who were invited actually underwent colonoscopy. In an adjusted analysis, had all those who had been invited to undergo screening undergone colonoscopy, the 10-year risk of colorectal cancer would have decreased from 1.22% to 0.84%, and the risk of colorectal cancer–related death would have fallen from 0.30% to 0.15%.
The researchers, led by gastroenterologist Michael Bretthauer, MD, from the department of medicine, gastrointestinal endoscopy, University of Oslo, who presented the data at UEG 2022 on behalf of the NordICC study group, acknowledged that, despite the “observed appreciable reductions in relative risks, the absolute risks of the risk of colorectal cancer and even more so of colorectal cancer–related death were lower than those in previous screening trials and lower than what we anticipated when the trial was planned.”
However, they add that “optimism related to the effects of screening on colorectal cancer–related death may be warranted in light of the 50% decrease observed in adjusted per-protocol analyses.”
With his coauthors, Dr. Bretthauer wrote that even their adjusted findings “probably underestimated the benefit because, as in most other large-scale trials of colorectal cancer screening, we could not adjust for all important confounders in all countries.”
Dr. Bretthauer also noted that results were similar to those achieved through sigmoidoscopy screening. By close comparison, sigmoidoscopy studies show the risk of colorectal cancer is reduced between 33% and 40%, according to per protocol analyses. “These results suggest that colonoscopy screening might not be substantially better in reducing the risk of colorectal cancer than sigmoidoscopy.”
Real-world, population-based study
NordICC is an ongoing, pragmatic study and is the first randomized trial to quantify the possible benefit of colonoscopy screening on risk of colorectal cancer and related death.
Researchers recruited healthy men and women from registries in Poland, Norway, Sweden, and the Netherlands between 2009 and 2014. Most participants came from Poland (54,258), followed by Norway (26,411) and Sweden (3,646). Data from the Netherlands could not be included owing to data protection law.
At baseline, 84,585 participants aged 55-64 years were randomly assigned in a 1:2 ratio either to receive an invitation to undergo a single screening colonoscopy (28,220; invited) or to undergo usual care in each participant country (56,365; no invitation or screening).
Any colorectal cancer lesions detected were removed, whenever possible. The primary endpoints were the risks of colorectal cancer and colorectal cancer–related death. The secondary endpoint was death from any cause.
‘Modest effectiveness,’ but longer follow-up to give fuller picture
In an editorial that accompanied publication of the study, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, from the division of gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle, and Douglas J. Robertson, MD, from White River Junction (Vt.) Veterans Affairs Medical Center, commented on the possible reasons for the low reduction in incident cancer and deaths seen in NordICC.
They pointed out that cohort studies suggest a 40%-69% decrease in the incidence of colorectal cancer and a 29%-88% decrease in the risk of death with colonoscopy. However, they noted that “cohort studies probably overestimate the real-world effectiveness of colonoscopy because of the inability to adjust for important factors such as incomplete adherence to testing and the tendency of healthier persons to seek preventive care.”
Referring to Dr. Bretthauer’s point about attendance to screening, Dr. Dominitz and Dr. Robertson added that, in the United States, colonoscopy is the predominant form of screening for colorectal cancer and that in countries where colonoscopy is less established, participation may be very different.
“The actual effectiveness of colonoscopy in populations that are more accepting of colonoscopy could more closely resemble the effectiveness shown in the per-protocol analysis in this trial,” they wrote.
The editorialists also pointed out that the benefits of screening colonoscopy take time to be realized “because the incidence of colorectal cancer is initially increased when presymptomatic cancers are identified.” A repeat and final analysis of the NordICC data is due at 15 years’ follow-up.
In addition, they noted that “colonoscopy is highly operator dependent” and that the adenoma detection rate is variable and affects cancer risk and related mortality.
Given the “modest effectiveness” of screening colonoscopy in the trial, they asserted that, “if the trial truly represents the real-world performance of population-based screening colonoscopy, it might be hard to justify the risk and expense of this form of screening when simpler, less-invasive strategies (e.g., sigmoidoscopy and FIT [fecal immunochemical test]) are available.”
However, they also noted that “additional analyses, including longer follow up and results from other ongoing comparative effectiveness trials, will help us to fully understand the benefits of this test.”
Also commenting on the study was Michiel Maas, MD, from the department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Radboud UMC, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, told this news organization that he agreed that the absolute effect on colorectal cancer risk or colorectal cancer–related death was not as high as expected and may be disappointing.
But Dr. Maas said that “around half of the patients in the study did not undergo colonoscopy, which may have negatively impacted the results.
“An additional factor, which can be influential in colonoscopy studies, is the potential variability in detection rates between operators/endoscopists,” he said.
Looking to the future, Dr. Maas noted that “AI [artificial intelligence] or computer-aided detection can level this playing field in detection rates.
“Nevertheless, this is a very interesting study, which sheds a new light on the efficacy on screening colonoscopies,” he said.
Dr. Bretthauer has relationships with Paion, Cybernet, and the Norwegian Council of Research. Dr. Dominitz is cochair of VA Cooperative Studies Program #577: “Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer” (the CONFIRM Study), which is funded by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. Robertson is national cochair (with Dr. Dominitz) of the CONFIRM trial and has received personal fees from Freenome outside of the submitted work. Dr. Maas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This study’s data show that colonoscopy is effective – if it is completed. Only 42% of patients randomized to colonoscopy completed the test; among patients who actually got a colonoscopy, results are much more impressive in colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention (31% decrease) and mortality (50% decrease). In this study, many endoscopists had ADRs below the 25% benchmark, and low ADRs are associated with a higher risk of postcolonoscopy CRC. Differences between the two groups may increase with longer follow-up, which is planned, because detection and removal of polyps via colonoscopy prevents future cancers.
Remind your patients that they shouldn’t let media headlines guide your health care decisions. You should also explain how colonoscopy can detect and remove polyps, which prevents those polyps from developing into cancer. Most of the patients in the Norway study skipped their colonoscopy, but the test can’t prevent cancers if it isn’t performed! Lastly, colonoscopy is effective in a U.S. population and can cut their risk of dying from CRC.
David Lieberman, MD, is a professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. He disclosed being a consultant for Freenome and Check-Cap.
This study’s data show that colonoscopy is effective – if it is completed. Only 42% of patients randomized to colonoscopy completed the test; among patients who actually got a colonoscopy, results are much more impressive in colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention (31% decrease) and mortality (50% decrease). In this study, many endoscopists had ADRs below the 25% benchmark, and low ADRs are associated with a higher risk of postcolonoscopy CRC. Differences between the two groups may increase with longer follow-up, which is planned, because detection and removal of polyps via colonoscopy prevents future cancers.
Remind your patients that they shouldn’t let media headlines guide your health care decisions. You should also explain how colonoscopy can detect and remove polyps, which prevents those polyps from developing into cancer. Most of the patients in the Norway study skipped their colonoscopy, but the test can’t prevent cancers if it isn’t performed! Lastly, colonoscopy is effective in a U.S. population and can cut their risk of dying from CRC.
David Lieberman, MD, is a professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. He disclosed being a consultant for Freenome and Check-Cap.
This study’s data show that colonoscopy is effective – if it is completed. Only 42% of patients randomized to colonoscopy completed the test; among patients who actually got a colonoscopy, results are much more impressive in colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention (31% decrease) and mortality (50% decrease). In this study, many endoscopists had ADRs below the 25% benchmark, and low ADRs are associated with a higher risk of postcolonoscopy CRC. Differences between the two groups may increase with longer follow-up, which is planned, because detection and removal of polyps via colonoscopy prevents future cancers.
Remind your patients that they shouldn’t let media headlines guide your health care decisions. You should also explain how colonoscopy can detect and remove polyps, which prevents those polyps from developing into cancer. Most of the patients in the Norway study skipped their colonoscopy, but the test can’t prevent cancers if it isn’t performed! Lastly, colonoscopy is effective in a U.S. population and can cut their risk of dying from CRC.
David Lieberman, MD, is a professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. He disclosed being a consultant for Freenome and Check-Cap.
VIENNA – the 10-year follow-up of the large, multicenter, randomized Northern-European Initiative on Colorectal Cancer (NordICC) trial shows.
In effect, this means the number needed to invite to undergo screening to prevent one case of colorectal cancer is 455 (95% confidence interval, 270-1,429), the researchers determined.
The results were presented at the United European Gastroenterology Week 2022 meeting and were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The results of the study, which was designed to be truly population based and to mimic national colorectal cancer screening programs, provide an estimate of the effect of screening colonoscopy in the general population.
The primary outcome was determined on an intention-to-screen basis. All persons who were invited to undergo colonoscopy screening were compared with people who received usual care (that is, received no invitation or screening). At UEG 2022, the researchers presented the interim 10-year colorectal cancer risk, which was found to be 0.98%, compared to 1.20%. This represents a risk reduction of 18% among colonoscopy invitees (risk ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.70-0.93). During the study period, 259 cases of colorectal cancer were diagnosed in the invited group versus622 in the usual-care group.
The risk of death from colorectal cancer was 0.28% in the invited group and 0.31% in the usual-care group (RR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.64-1.16). The risk of death from any cause was similar in both the invited group and the usual-care group, at 11.03% and 11.04%, respectively (RR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.96-1.04).
The authors noted that the benefit would have been greater had more people undergone screening; only 42% of those who were invited actually underwent colonoscopy. In an adjusted analysis, had all those who had been invited to undergo screening undergone colonoscopy, the 10-year risk of colorectal cancer would have decreased from 1.22% to 0.84%, and the risk of colorectal cancer–related death would have fallen from 0.30% to 0.15%.
The researchers, led by gastroenterologist Michael Bretthauer, MD, from the department of medicine, gastrointestinal endoscopy, University of Oslo, who presented the data at UEG 2022 on behalf of the NordICC study group, acknowledged that, despite the “observed appreciable reductions in relative risks, the absolute risks of the risk of colorectal cancer and even more so of colorectal cancer–related death were lower than those in previous screening trials and lower than what we anticipated when the trial was planned.”
However, they add that “optimism related to the effects of screening on colorectal cancer–related death may be warranted in light of the 50% decrease observed in adjusted per-protocol analyses.”
With his coauthors, Dr. Bretthauer wrote that even their adjusted findings “probably underestimated the benefit because, as in most other large-scale trials of colorectal cancer screening, we could not adjust for all important confounders in all countries.”
Dr. Bretthauer also noted that results were similar to those achieved through sigmoidoscopy screening. By close comparison, sigmoidoscopy studies show the risk of colorectal cancer is reduced between 33% and 40%, according to per protocol analyses. “These results suggest that colonoscopy screening might not be substantially better in reducing the risk of colorectal cancer than sigmoidoscopy.”
Real-world, population-based study
NordICC is an ongoing, pragmatic study and is the first randomized trial to quantify the possible benefit of colonoscopy screening on risk of colorectal cancer and related death.
Researchers recruited healthy men and women from registries in Poland, Norway, Sweden, and the Netherlands between 2009 and 2014. Most participants came from Poland (54,258), followed by Norway (26,411) and Sweden (3,646). Data from the Netherlands could not be included owing to data protection law.
At baseline, 84,585 participants aged 55-64 years were randomly assigned in a 1:2 ratio either to receive an invitation to undergo a single screening colonoscopy (28,220; invited) or to undergo usual care in each participant country (56,365; no invitation or screening).
Any colorectal cancer lesions detected were removed, whenever possible. The primary endpoints were the risks of colorectal cancer and colorectal cancer–related death. The secondary endpoint was death from any cause.
‘Modest effectiveness,’ but longer follow-up to give fuller picture
In an editorial that accompanied publication of the study, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, from the division of gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle, and Douglas J. Robertson, MD, from White River Junction (Vt.) Veterans Affairs Medical Center, commented on the possible reasons for the low reduction in incident cancer and deaths seen in NordICC.
They pointed out that cohort studies suggest a 40%-69% decrease in the incidence of colorectal cancer and a 29%-88% decrease in the risk of death with colonoscopy. However, they noted that “cohort studies probably overestimate the real-world effectiveness of colonoscopy because of the inability to adjust for important factors such as incomplete adherence to testing and the tendency of healthier persons to seek preventive care.”
Referring to Dr. Bretthauer’s point about attendance to screening, Dr. Dominitz and Dr. Robertson added that, in the United States, colonoscopy is the predominant form of screening for colorectal cancer and that in countries where colonoscopy is less established, participation may be very different.
“The actual effectiveness of colonoscopy in populations that are more accepting of colonoscopy could more closely resemble the effectiveness shown in the per-protocol analysis in this trial,” they wrote.
The editorialists also pointed out that the benefits of screening colonoscopy take time to be realized “because the incidence of colorectal cancer is initially increased when presymptomatic cancers are identified.” A repeat and final analysis of the NordICC data is due at 15 years’ follow-up.
In addition, they noted that “colonoscopy is highly operator dependent” and that the adenoma detection rate is variable and affects cancer risk and related mortality.
Given the “modest effectiveness” of screening colonoscopy in the trial, they asserted that, “if the trial truly represents the real-world performance of population-based screening colonoscopy, it might be hard to justify the risk and expense of this form of screening when simpler, less-invasive strategies (e.g., sigmoidoscopy and FIT [fecal immunochemical test]) are available.”
However, they also noted that “additional analyses, including longer follow up and results from other ongoing comparative effectiveness trials, will help us to fully understand the benefits of this test.”
Also commenting on the study was Michiel Maas, MD, from the department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Radboud UMC, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, told this news organization that he agreed that the absolute effect on colorectal cancer risk or colorectal cancer–related death was not as high as expected and may be disappointing.
But Dr. Maas said that “around half of the patients in the study did not undergo colonoscopy, which may have negatively impacted the results.
“An additional factor, which can be influential in colonoscopy studies, is the potential variability in detection rates between operators/endoscopists,” he said.
Looking to the future, Dr. Maas noted that “AI [artificial intelligence] or computer-aided detection can level this playing field in detection rates.
“Nevertheless, this is a very interesting study, which sheds a new light on the efficacy on screening colonoscopies,” he said.
Dr. Bretthauer has relationships with Paion, Cybernet, and the Norwegian Council of Research. Dr. Dominitz is cochair of VA Cooperative Studies Program #577: “Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer” (the CONFIRM Study), which is funded by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. Robertson is national cochair (with Dr. Dominitz) of the CONFIRM trial and has received personal fees from Freenome outside of the submitted work. Dr. Maas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
VIENNA – the 10-year follow-up of the large, multicenter, randomized Northern-European Initiative on Colorectal Cancer (NordICC) trial shows.
In effect, this means the number needed to invite to undergo screening to prevent one case of colorectal cancer is 455 (95% confidence interval, 270-1,429), the researchers determined.
The results were presented at the United European Gastroenterology Week 2022 meeting and were published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine.
The results of the study, which was designed to be truly population based and to mimic national colorectal cancer screening programs, provide an estimate of the effect of screening colonoscopy in the general population.
The primary outcome was determined on an intention-to-screen basis. All persons who were invited to undergo colonoscopy screening were compared with people who received usual care (that is, received no invitation or screening). At UEG 2022, the researchers presented the interim 10-year colorectal cancer risk, which was found to be 0.98%, compared to 1.20%. This represents a risk reduction of 18% among colonoscopy invitees (risk ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.70-0.93). During the study period, 259 cases of colorectal cancer were diagnosed in the invited group versus622 in the usual-care group.
The risk of death from colorectal cancer was 0.28% in the invited group and 0.31% in the usual-care group (RR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.64-1.16). The risk of death from any cause was similar in both the invited group and the usual-care group, at 11.03% and 11.04%, respectively (RR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.96-1.04).
The authors noted that the benefit would have been greater had more people undergone screening; only 42% of those who were invited actually underwent colonoscopy. In an adjusted analysis, had all those who had been invited to undergo screening undergone colonoscopy, the 10-year risk of colorectal cancer would have decreased from 1.22% to 0.84%, and the risk of colorectal cancer–related death would have fallen from 0.30% to 0.15%.
The researchers, led by gastroenterologist Michael Bretthauer, MD, from the department of medicine, gastrointestinal endoscopy, University of Oslo, who presented the data at UEG 2022 on behalf of the NordICC study group, acknowledged that, despite the “observed appreciable reductions in relative risks, the absolute risks of the risk of colorectal cancer and even more so of colorectal cancer–related death were lower than those in previous screening trials and lower than what we anticipated when the trial was planned.”
However, they add that “optimism related to the effects of screening on colorectal cancer–related death may be warranted in light of the 50% decrease observed in adjusted per-protocol analyses.”
With his coauthors, Dr. Bretthauer wrote that even their adjusted findings “probably underestimated the benefit because, as in most other large-scale trials of colorectal cancer screening, we could not adjust for all important confounders in all countries.”
Dr. Bretthauer also noted that results were similar to those achieved through sigmoidoscopy screening. By close comparison, sigmoidoscopy studies show the risk of colorectal cancer is reduced between 33% and 40%, according to per protocol analyses. “These results suggest that colonoscopy screening might not be substantially better in reducing the risk of colorectal cancer than sigmoidoscopy.”
Real-world, population-based study
NordICC is an ongoing, pragmatic study and is the first randomized trial to quantify the possible benefit of colonoscopy screening on risk of colorectal cancer and related death.
Researchers recruited healthy men and women from registries in Poland, Norway, Sweden, and the Netherlands between 2009 and 2014. Most participants came from Poland (54,258), followed by Norway (26,411) and Sweden (3,646). Data from the Netherlands could not be included owing to data protection law.
At baseline, 84,585 participants aged 55-64 years were randomly assigned in a 1:2 ratio either to receive an invitation to undergo a single screening colonoscopy (28,220; invited) or to undergo usual care in each participant country (56,365; no invitation or screening).
Any colorectal cancer lesions detected were removed, whenever possible. The primary endpoints were the risks of colorectal cancer and colorectal cancer–related death. The secondary endpoint was death from any cause.
‘Modest effectiveness,’ but longer follow-up to give fuller picture
In an editorial that accompanied publication of the study, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, from the division of gastroenterology, University of Washington, Seattle, and Douglas J. Robertson, MD, from White River Junction (Vt.) Veterans Affairs Medical Center, commented on the possible reasons for the low reduction in incident cancer and deaths seen in NordICC.
They pointed out that cohort studies suggest a 40%-69% decrease in the incidence of colorectal cancer and a 29%-88% decrease in the risk of death with colonoscopy. However, they noted that “cohort studies probably overestimate the real-world effectiveness of colonoscopy because of the inability to adjust for important factors such as incomplete adherence to testing and the tendency of healthier persons to seek preventive care.”
Referring to Dr. Bretthauer’s point about attendance to screening, Dr. Dominitz and Dr. Robertson added that, in the United States, colonoscopy is the predominant form of screening for colorectal cancer and that in countries where colonoscopy is less established, participation may be very different.
“The actual effectiveness of colonoscopy in populations that are more accepting of colonoscopy could more closely resemble the effectiveness shown in the per-protocol analysis in this trial,” they wrote.
The editorialists also pointed out that the benefits of screening colonoscopy take time to be realized “because the incidence of colorectal cancer is initially increased when presymptomatic cancers are identified.” A repeat and final analysis of the NordICC data is due at 15 years’ follow-up.
In addition, they noted that “colonoscopy is highly operator dependent” and that the adenoma detection rate is variable and affects cancer risk and related mortality.
Given the “modest effectiveness” of screening colonoscopy in the trial, they asserted that, “if the trial truly represents the real-world performance of population-based screening colonoscopy, it might be hard to justify the risk and expense of this form of screening when simpler, less-invasive strategies (e.g., sigmoidoscopy and FIT [fecal immunochemical test]) are available.”
However, they also noted that “additional analyses, including longer follow up and results from other ongoing comparative effectiveness trials, will help us to fully understand the benefits of this test.”
Also commenting on the study was Michiel Maas, MD, from the department of gastroenterology and hepatology, Radboud UMC, Nijmegen, the Netherlands, told this news organization that he agreed that the absolute effect on colorectal cancer risk or colorectal cancer–related death was not as high as expected and may be disappointing.
But Dr. Maas said that “around half of the patients in the study did not undergo colonoscopy, which may have negatively impacted the results.
“An additional factor, which can be influential in colonoscopy studies, is the potential variability in detection rates between operators/endoscopists,” he said.
Looking to the future, Dr. Maas noted that “AI [artificial intelligence] or computer-aided detection can level this playing field in detection rates.
“Nevertheless, this is a very interesting study, which sheds a new light on the efficacy on screening colonoscopies,” he said.
Dr. Bretthauer has relationships with Paion, Cybernet, and the Norwegian Council of Research. Dr. Dominitz is cochair of VA Cooperative Studies Program #577: “Colonoscopy vs. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) in Reducing Mortality from Colorectal Cancer” (the CONFIRM Study), which is funded by the Department of Veterans Affairs. Dr. Robertson is national cochair (with Dr. Dominitz) of the CONFIRM trial and has received personal fees from Freenome outside of the submitted work. Dr. Maas reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM UEG 2022
People of color more likely to be hospitalized for influenza, CDC report finds
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Black Americans are 80% more likely to be hospitalized for the flu, compared with White Americans, according to new federal data.
Black, Hispanic, and American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) adults in the United States also have had lower influenza vaccination rates, compared with their White counterparts, since 2010, researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed in a report.
The inequalities are the result of barriers to care, distrust of the medical system, and misinformation, the report said.
“We have many of the tools we need to address inequities and flu vaccination coverage and outcomes,” said CDC Acting Principal Deputy Director Debra Houry, MD, MPH, in a press call; “however, we must acknowledge that inequities in access to care continue to exist. To improve vaccine uptake, we must address the root causes of these ongoing disparities.”
The CDC has already reported early increases in flu activity in the United States, with the highest activity in the southeastern and south-central parts of the country. Experts also warn of a potentially more severe influenza season than in the previous 2 years. CDC officials emphasized that vaccination is the best protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death from the flu. “Everyone should get vaccinated against flu today and encourage others and their community to get a flu vaccine for the best protection against flu this fall and winter,” Dr. Houry said.
In the recent report on disparities by community published October 18 in CDC Vital Signs, researchers looked at hospitalization rates from 2009 to 2022 and vaccination rates from 2010 to 2022 based on race and ethnicity using two national databases, the Influenza-Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System. All individuals included in the analysis were aged 18 years or older, and the 2020-2021 flu season was excluded from the analysis because of insufficient data.
Compared with those for White adults, hospitalization rates were 80% higher for Black adults, 30% higher for Hispanic adults, and 20% higher for AI/AN adults. While flu vaccination rates were similar in White and Asian adults (about 54%), coverage was lower in Black (42%), Hispanic (38%), AI/AN (41%), and other/multiracial (43%) adults. This disparity persisted even among individuals who had medical insurance, a personal health care provider, and a routine checkup within the last year.
Carla Black, PhD, MPH, an epidemiologist at the CDC’s Immunization Services Division, said during the press call. While flu vaccines may not always prevent infection, people who do get sick after being vaccinated tend to have better outcomes, she added. The report noted that building trust, increasing access to vaccination services, and combating misinformation are important steps to increasing vaccine coverage in minority groups.
While social distancing measures such as masking have made it difficult for the flu to spread, the relaxation of these safety measures could also lead to higher case counts. “We’ve had two mild flu seasons, and this means we might be ripe for a severe season,” Dr. Black said. “People haven’t had natural disease in 2 years, so there’s less natural immunity out there. People are going back to work. People are traveling again. All of these factors could contribute to us having a more severe flu season.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
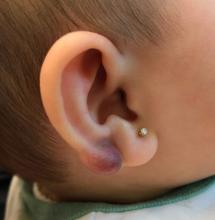
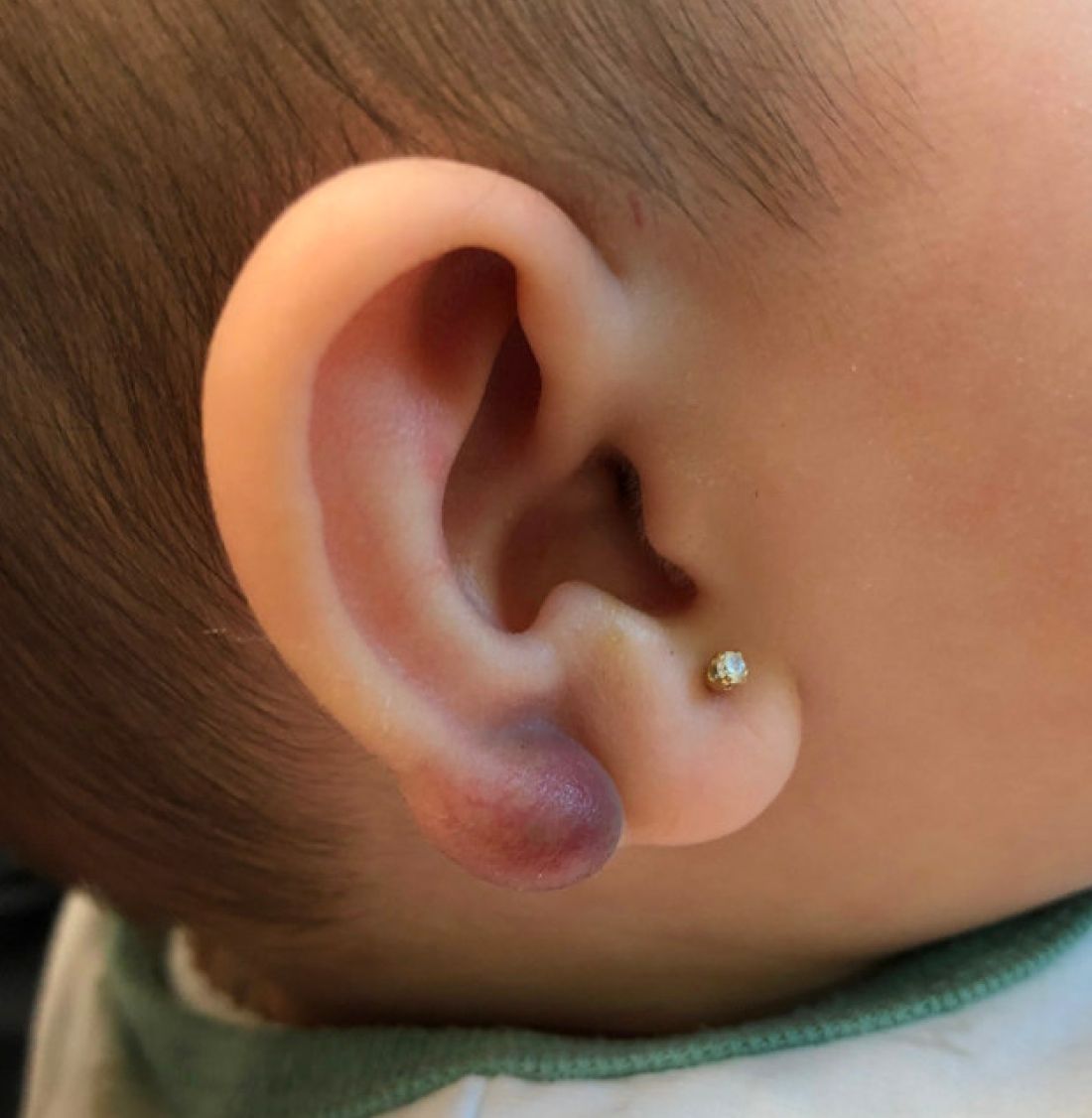
An infant with a tender bump on her ear
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A 4-month-old female was referred to our clinic for evaluation of a bump on the right ear. The lesion was first noted at 2 months of age as a little pimple. She was evaluated by her pediatrician and was treated with topical and oral antibiotics without resolution of the lesion. The bump continued to grow and seemed tender to palpation, so she was referred to dermatology for evaluation.
She was born via normal vaginal delivery at 40 weeks. Her mother has no medical conditions and the pregnancy was uneventful. She has been growing and developing well. She takes vitamin D and is currently breast fed.
There have been no other family members with similar lesions. She had her ears pierced at a month of age without any complications.
On skin examination she has a firm red nodule on the right ear that appears slightly tender to touch. She has no other skin lesions of concern. She has normal muscle tone and there are no other abnormalities noted on the physical exam. She has no hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or lymphadenopathy.