User login
Pemphigus Vulgaris Aggravated: Rifampicin Found at the Scene of the Crime
Case Report
A 60-year-old man presented with eroded areas in the mouth and blistering eruptions on the scalp, face, trunk, arms, and legs. He initially presented to an outside hospital 4 years prior and was treated with oral prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the eruptions responded rapidly; however, following a nearly 5-mg reduction of the dose per week by the patient and irregular oral administration, he experienced several episodes of recurrence, but he could not remember the exact dosage of prednisone he had taken during that period. Subsequently, he was admitted to our hospital because of large areas of erythema and erosions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.
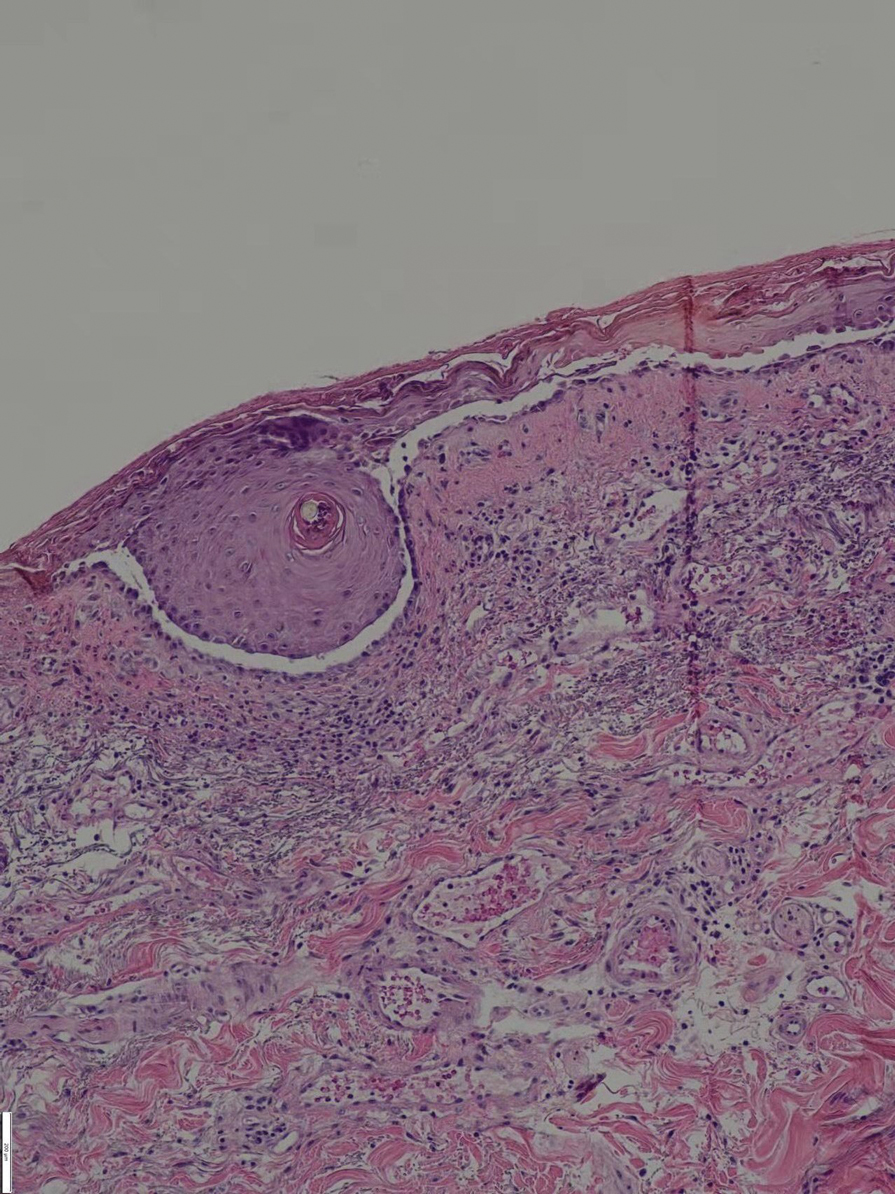
Since starting the prednisone regimen 4 years prior, the patient had experienced onset of hypertension, diabetes, glaucoma, cataracts, optic nerve atrophy, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, and osteoporosis. Biopsy of a new skin lesion
The patient initially was started again prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the skin eruptions responded, and 2 weeks later, the disease was considered controlled. The prednisone dosage was tapered to 20 mg daily 3 months later with no new blister formation. However, 2 weeks later, the patient was diagnosed by a tuberculosis specialist with pulmonary tuberculosis, and a daily regimen of isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and levofloxacin was instituted.
Ten days after starting antituberculosis therapy, the patient developed new erythematous blisters that could not be controlled and self-adjusted the prednisone dose to 50 mg daily. Two months later, blister formation continued.
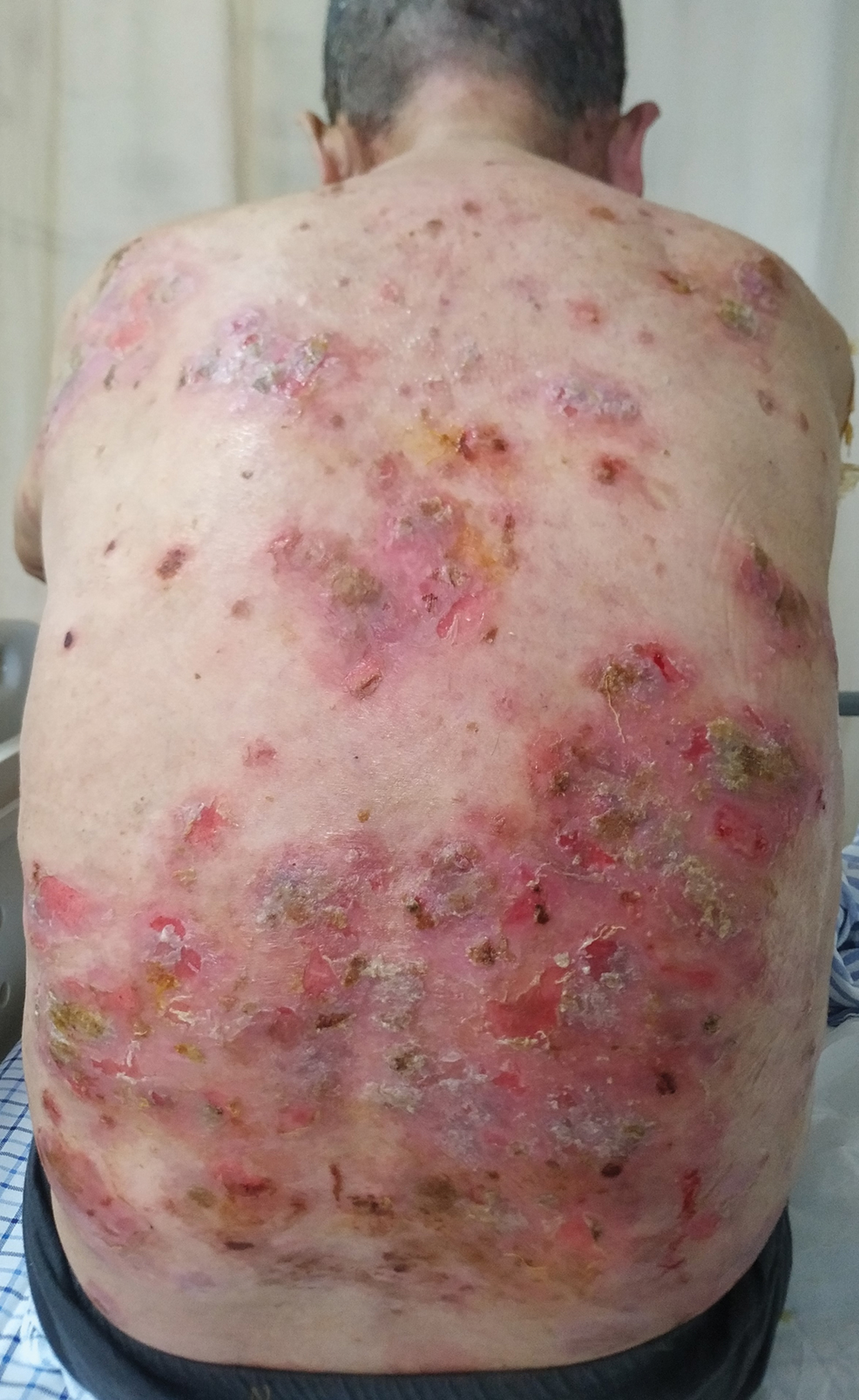
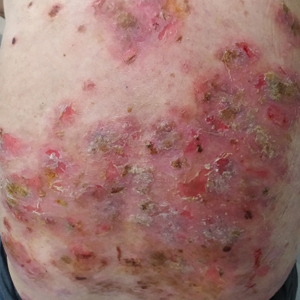
Six months after the initial presentation, the patient returned to our hospital because of uncontrollable rashes (Figure 2). On admission, he had a Pemphigus Disease Area Index (PDAI) score of 32 with disease involving 30% of the body surface area. Laboratory testing showed a desmoglein 1 level of 233 U/mL and desmoglein 3 level of 228 U/mL. A tuberculosis specialist from an outside hospital was consulted to evaluate the patient’s condition and assist in treatment. Based on findings from a pulmonary computed tomography scan, which showed the inflammation was considerably absorbed, treatment was adjusted to stop using ethambutol and levofloxacin and continue rifampicin and isoniazid. For the PV, prednisone was titrated upward to 75 mg daily, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1 g twice daily was added, and IVIG 400 mg/kg daily was administered for 7 days. After 3 weeks, the rash still expanded.
In considering possible interactions between the drugs, we consulted the literature and found reports1-3 that rifampicin accelerated glucocorticoid metabolism, of which the tuberculosis specialist that we consulted was not aware. Therefore, rifampicin was stopped, and the antituberculosis therapy was adjusted to levofloxacin and isoniazid. Meanwhile, the steroid was changed to methylprednisolone 120 mg daily for 3 days, then to 80 mg daily for 2 days.
After 5 days, the rash was controlled with no new development and the patient was discharged. He continued on prednisone 80 mg daily and MMF 1 g twice daily.
At 2-month follow-up, no new rash had developed. The patient had already self-discontinued the MMF for 1 month because it was difficult to obtain at local hospitals. The prednisone was reduced to 40 mg daily. Pulmonary computed tomography showed no signs of reactivation of tuberculosis.
Comment
Drugs that depend on these enzymes for their metabolism are prone to
Rifampicin causes a marked reduction in dose-corrected mycophenolic acid exposure when administered simultaneously with MMF through induction of glucuronidation activity and inhibition of enterohepatic recirculation.5,10In in vitro studies, rifampin and other cytochrome P450 inducers have been identified as potentially useful for increasing the rate of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide (an isomeric analogue of cyclophosphamide) 4-hydroxylation in the human liver in a manner that could have a favorable impact on the clinical pharmacokinetics of these anticancer prodrugs.11 However, clinical analysis of 16 patients indicated that co-administration of ifosfamide with rifampin did not result in changes in the pharmacokinetics of the parent drug or its metabolites.12
The steroids and
Conclusion
In our patient, the use of rifapentine resulted in a recurrence of previously controlled PV and resistance to treatment. The patient’s disease was quickly controlled after discontinuation of rifampicin and with a short-term course of high-dose methylprednisolone and remained stable when the dosages of MMF and prednisone were reduced.
- Miyagawa S, Yamashina Y, Okuchi T, et al. Exacerbation of pemphigus by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1986;114:729-732. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb04882.x
- Gange RW, Rhodes EL, Edwards CO, et al. Pemphigus induced by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95:445-448. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb00849.x
- Bergrem H, Refvem OK. Altered prednisolone pharmacokinetics in patients treated with rifampicin. Acta Med Scand. 1983;213:339-343. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1983.tb03748.x
- McAllister WA, Thompson PJ, Al-Habet SM, et al. Rifampicin reduces effectiveness and bioavailability of prednisolone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;286:923-925. doi:10.1136/bmj.286.6369.923
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106. doi:10.1007/s00403-017-1790-8
- Barman H, Dass R, Duwarah SG. Use of high-dose prednisolone to overcome rifampicin-induced corticosteroid non-responsiveness in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016;27:157-160. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.174198
- Okey AB, Roberts EA, Harper PA, et al. Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms and consequences. Clin Biochem. 1986;19:132-141. doi:10.1016/s0009-9120(86)80060-1
- Venkatesan K. Pharmacokinetic interactions with rifampicin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22:47-65. doi:10.2165/00003088-199222010-00005
- Naesens M, Kuypers DRJ, Streit F, et al. Rifampin induces alterations in mycophenolic acid glucuronidation and elimination: implications for drug exposure in renal allograft recipients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80:509-521. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.08.002
- Kuypers DRJ, Verleden G, Naesens M, et al. Drug interaction between mycophenolate mofetil and rifampin: possible induction of uridine diphosphate–glucuronosyltransferase. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:81-88. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.03.004
- Chenhsu RY, Loong CC, Chou MH, et al. Renal allograft dysfunction associated with rifampin–tacrolimus interaction. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:27-31. doi:10.1345/aph.19069
- Douglas JG, McLeod MJ. Pharmacokinetic factors in the modern drug treatment of tuberculosis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;37:127-146. doi:10.2165/00003088-199937020-00003
Case Report
A 60-year-old man presented with eroded areas in the mouth and blistering eruptions on the scalp, face, trunk, arms, and legs. He initially presented to an outside hospital 4 years prior and was treated with oral prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the eruptions responded rapidly; however, following a nearly 5-mg reduction of the dose per week by the patient and irregular oral administration, he experienced several episodes of recurrence, but he could not remember the exact dosage of prednisone he had taken during that period. Subsequently, he was admitted to our hospital because of large areas of erythema and erosions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.
Since starting the prednisone regimen 4 years prior, the patient had experienced onset of hypertension, diabetes, glaucoma, cataracts, optic nerve atrophy, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, and osteoporosis. Biopsy of a new skin lesion
The patient initially was started again prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the skin eruptions responded, and 2 weeks later, the disease was considered controlled. The prednisone dosage was tapered to 20 mg daily 3 months later with no new blister formation. However, 2 weeks later, the patient was diagnosed by a tuberculosis specialist with pulmonary tuberculosis, and a daily regimen of isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and levofloxacin was instituted.
Ten days after starting antituberculosis therapy, the patient developed new erythematous blisters that could not be controlled and self-adjusted the prednisone dose to 50 mg daily. Two months later, blister formation continued.
Six months after the initial presentation, the patient returned to our hospital because of uncontrollable rashes (Figure 2). On admission, he had a Pemphigus Disease Area Index (PDAI) score of 32 with disease involving 30% of the body surface area. Laboratory testing showed a desmoglein 1 level of 233 U/mL and desmoglein 3 level of 228 U/mL. A tuberculosis specialist from an outside hospital was consulted to evaluate the patient’s condition and assist in treatment. Based on findings from a pulmonary computed tomography scan, which showed the inflammation was considerably absorbed, treatment was adjusted to stop using ethambutol and levofloxacin and continue rifampicin and isoniazid. For the PV, prednisone was titrated upward to 75 mg daily, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1 g twice daily was added, and IVIG 400 mg/kg daily was administered for 7 days. After 3 weeks, the rash still expanded.
In considering possible interactions between the drugs, we consulted the literature and found reports1-3 that rifampicin accelerated glucocorticoid metabolism, of which the tuberculosis specialist that we consulted was not aware. Therefore, rifampicin was stopped, and the antituberculosis therapy was adjusted to levofloxacin and isoniazid. Meanwhile, the steroid was changed to methylprednisolone 120 mg daily for 3 days, then to 80 mg daily for 2 days.
After 5 days, the rash was controlled with no new development and the patient was discharged. He continued on prednisone 80 mg daily and MMF 1 g twice daily.
At 2-month follow-up, no new rash had developed. The patient had already self-discontinued the MMF for 1 month because it was difficult to obtain at local hospitals. The prednisone was reduced to 40 mg daily. Pulmonary computed tomography showed no signs of reactivation of tuberculosis.
Comment
Drugs that depend on these enzymes for their metabolism are prone to
Rifampicin causes a marked reduction in dose-corrected mycophenolic acid exposure when administered simultaneously with MMF through induction of glucuronidation activity and inhibition of enterohepatic recirculation.5,10In in vitro studies, rifampin and other cytochrome P450 inducers have been identified as potentially useful for increasing the rate of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide (an isomeric analogue of cyclophosphamide) 4-hydroxylation in the human liver in a manner that could have a favorable impact on the clinical pharmacokinetics of these anticancer prodrugs.11 However, clinical analysis of 16 patients indicated that co-administration of ifosfamide with rifampin did not result in changes in the pharmacokinetics of the parent drug or its metabolites.12
The steroids and
Conclusion
In our patient, the use of rifapentine resulted in a recurrence of previously controlled PV and resistance to treatment. The patient’s disease was quickly controlled after discontinuation of rifampicin and with a short-term course of high-dose methylprednisolone and remained stable when the dosages of MMF and prednisone were reduced.
Case Report
A 60-year-old man presented with eroded areas in the mouth and blistering eruptions on the scalp, face, trunk, arms, and legs. He initially presented to an outside hospital 4 years prior and was treated with oral prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the eruptions responded rapidly; however, following a nearly 5-mg reduction of the dose per week by the patient and irregular oral administration, he experienced several episodes of recurrence, but he could not remember the exact dosage of prednisone he had taken during that period. Subsequently, he was admitted to our hospital because of large areas of erythema and erosions on the scalp, trunk, arms, and legs.
Since starting the prednisone regimen 4 years prior, the patient had experienced onset of hypertension, diabetes, glaucoma, cataracts, optic nerve atrophy, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, and osteoporosis. Biopsy of a new skin lesion
The patient initially was started again prednisone 50 mg daily, to which the skin eruptions responded, and 2 weeks later, the disease was considered controlled. The prednisone dosage was tapered to 20 mg daily 3 months later with no new blister formation. However, 2 weeks later, the patient was diagnosed by a tuberculosis specialist with pulmonary tuberculosis, and a daily regimen of isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and levofloxacin was instituted.
Ten days after starting antituberculosis therapy, the patient developed new erythematous blisters that could not be controlled and self-adjusted the prednisone dose to 50 mg daily. Two months later, blister formation continued.
Six months after the initial presentation, the patient returned to our hospital because of uncontrollable rashes (Figure 2). On admission, he had a Pemphigus Disease Area Index (PDAI) score of 32 with disease involving 30% of the body surface area. Laboratory testing showed a desmoglein 1 level of 233 U/mL and desmoglein 3 level of 228 U/mL. A tuberculosis specialist from an outside hospital was consulted to evaluate the patient’s condition and assist in treatment. Based on findings from a pulmonary computed tomography scan, which showed the inflammation was considerably absorbed, treatment was adjusted to stop using ethambutol and levofloxacin and continue rifampicin and isoniazid. For the PV, prednisone was titrated upward to 75 mg daily, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) 1 g twice daily was added, and IVIG 400 mg/kg daily was administered for 7 days. After 3 weeks, the rash still expanded.
In considering possible interactions between the drugs, we consulted the literature and found reports1-3 that rifampicin accelerated glucocorticoid metabolism, of which the tuberculosis specialist that we consulted was not aware. Therefore, rifampicin was stopped, and the antituberculosis therapy was adjusted to levofloxacin and isoniazid. Meanwhile, the steroid was changed to methylprednisolone 120 mg daily for 3 days, then to 80 mg daily for 2 days.
After 5 days, the rash was controlled with no new development and the patient was discharged. He continued on prednisone 80 mg daily and MMF 1 g twice daily.
At 2-month follow-up, no new rash had developed. The patient had already self-discontinued the MMF for 1 month because it was difficult to obtain at local hospitals. The prednisone was reduced to 40 mg daily. Pulmonary computed tomography showed no signs of reactivation of tuberculosis.
Comment
Drugs that depend on these enzymes for their metabolism are prone to
Rifampicin causes a marked reduction in dose-corrected mycophenolic acid exposure when administered simultaneously with MMF through induction of glucuronidation activity and inhibition of enterohepatic recirculation.5,10In in vitro studies, rifampin and other cytochrome P450 inducers have been identified as potentially useful for increasing the rate of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide (an isomeric analogue of cyclophosphamide) 4-hydroxylation in the human liver in a manner that could have a favorable impact on the clinical pharmacokinetics of these anticancer prodrugs.11 However, clinical analysis of 16 patients indicated that co-administration of ifosfamide with rifampin did not result in changes in the pharmacokinetics of the parent drug or its metabolites.12
The steroids and
Conclusion
In our patient, the use of rifapentine resulted in a recurrence of previously controlled PV and resistance to treatment. The patient’s disease was quickly controlled after discontinuation of rifampicin and with a short-term course of high-dose methylprednisolone and remained stable when the dosages of MMF and prednisone were reduced.
- Miyagawa S, Yamashina Y, Okuchi T, et al. Exacerbation of pemphigus by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1986;114:729-732. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb04882.x
- Gange RW, Rhodes EL, Edwards CO, et al. Pemphigus induced by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95:445-448. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb00849.x
- Bergrem H, Refvem OK. Altered prednisolone pharmacokinetics in patients treated with rifampicin. Acta Med Scand. 1983;213:339-343. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1983.tb03748.x
- McAllister WA, Thompson PJ, Al-Habet SM, et al. Rifampicin reduces effectiveness and bioavailability of prednisolone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;286:923-925. doi:10.1136/bmj.286.6369.923
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106. doi:10.1007/s00403-017-1790-8
- Barman H, Dass R, Duwarah SG. Use of high-dose prednisolone to overcome rifampicin-induced corticosteroid non-responsiveness in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016;27:157-160. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.174198
- Okey AB, Roberts EA, Harper PA, et al. Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms and consequences. Clin Biochem. 1986;19:132-141. doi:10.1016/s0009-9120(86)80060-1
- Venkatesan K. Pharmacokinetic interactions with rifampicin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22:47-65. doi:10.2165/00003088-199222010-00005
- Naesens M, Kuypers DRJ, Streit F, et al. Rifampin induces alterations in mycophenolic acid glucuronidation and elimination: implications for drug exposure in renal allograft recipients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80:509-521. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.08.002
- Kuypers DRJ, Verleden G, Naesens M, et al. Drug interaction between mycophenolate mofetil and rifampin: possible induction of uridine diphosphate–glucuronosyltransferase. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:81-88. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.03.004
- Chenhsu RY, Loong CC, Chou MH, et al. Renal allograft dysfunction associated with rifampin–tacrolimus interaction. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:27-31. doi:10.1345/aph.19069
- Douglas JG, McLeod MJ. Pharmacokinetic factors in the modern drug treatment of tuberculosis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;37:127-146. doi:10.2165/00003088-199937020-00003
- Miyagawa S, Yamashina Y, Okuchi T, et al. Exacerbation of pemphigus by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1986;114:729-732. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1986.tb04882.x
- Gange RW, Rhodes EL, Edwards CO, et al. Pemphigus induced by rifampicin. Br J Dermatol. 1976;95:445-448. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb00849.x
- Bergrem H, Refvem OK. Altered prednisolone pharmacokinetics in patients treated with rifampicin. Acta Med Scand. 1983;213:339-343. doi:10.1111/j.0954-6820.1983.tb03748.x
- McAllister WA, Thompson PJ, Al-Habet SM, et al. Rifampicin reduces effectiveness and bioavailability of prednisolone. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1983;286:923-925. doi:10.1136/bmj.286.6369.923
- Tavakolpour S. Pemphigus trigger factors: special focus on pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus. Arch Dermatol Res. 2018;310:95-106. doi:10.1007/s00403-017-1790-8
- Barman H, Dass R, Duwarah SG. Use of high-dose prednisolone to overcome rifampicin-induced corticosteroid non-responsiveness in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016;27:157-160. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.174198
- Okey AB, Roberts EA, Harper PA, et al. Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes: mechanisms and consequences. Clin Biochem. 1986;19:132-141. doi:10.1016/s0009-9120(86)80060-1
- Venkatesan K. Pharmacokinetic interactions with rifampicin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22:47-65. doi:10.2165/00003088-199222010-00005
- Naesens M, Kuypers DRJ, Streit F, et al. Rifampin induces alterations in mycophenolic acid glucuronidation and elimination: implications for drug exposure in renal allograft recipients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80:509-521. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.08.002
- Kuypers DRJ, Verleden G, Naesens M, et al. Drug interaction between mycophenolate mofetil and rifampin: possible induction of uridine diphosphate–glucuronosyltransferase. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:81-88. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2005.03.004
- Chenhsu RY, Loong CC, Chou MH, et al. Renal allograft dysfunction associated with rifampin–tacrolimus interaction. Ann Pharmacother. 2000;34:27-31. doi:10.1345/aph.19069
- Douglas JG, McLeod MJ. Pharmacokinetic factors in the modern drug treatment of tuberculosis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1999;37:127-146. doi:10.2165/00003088-199937020-00003
Practice Points
- Long-term use of immunosuppressants requires constant attention for infections, especially latent infections in the body.
- Clinicians should carefully inquire with patients about concomitant diseases and medications used, and be vigilant about drug interactions.
Fidaxomicin favored over vancomycin in real-world C. diff study
Fidaxomicin (Fificid) emerged favorable to vancomycin for the treatment of both initial and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections in a Medicare population, according to a new retrospective study.
Although fidaxomicin was about 14% more effective than vancomycin in treating the initial infection, a larger difference of 30% was found among people with recurrent C. diff. infections.
Lead investigator Erik Dubberke, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, St. Louis, and colleagues noted that this real-world evidence of the two agents used to treat C. diff. was “strikingly similar” to clinical trial data.
They said that their findings support the 2021 change in clinical guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommending fidaxomicin over vancomycin.
The study was presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2022, which was held virtually and in San Diego.
Evaluating a high-risk population
Because few real-world data exist that compare these two agents for C. diff., “particularly in a high-risk, high-prevalence population like Medicare,” the researchers evaluated Medicare Parts A, B, and D claims from 2016 to 2018 and included patients who had received fidaxomicin or vancomycin for an initial episode of C. diff. and for any recurrent episodes.
The researchers compared sustained response and recurrence of C. diff. within 4 weeks and 8 weeks after initial treatment with fidaxomicin or vancomycin. Treatment was considered successful if clinical resolution occurred 1 day after finishing therapy and there was no evidence of C. diff. recurrence.
Recurrence of C. diff. was defined as any evidence of new treatment or hospitalization for the infection within 4 or 8 weeks of when a patient filled the prescription for fidaxomicin or vancomycin.
The treatment groups were similar in age and race. However, the fidaxomicin group was at higher risk for recurrence, owing to risk factors such as history of C. diff. infection and compromised immunity. To reduce bias in comparing the groups, Dr. Dubberke and colleagues used propensity score matching. This approach yielded 190 matched pairs in the initial C. diff. episode sample and 67 matched pairs in the recurrent episode sample.
Among patients with their first C. diff. infection, fidaxomicin had a 13.5% higher rate of 4-week sustained response, compared with vancomycin (71.7% vs. 58.2%; P = .0058). There was also a 13.2% higher rate for 8-week sustained response with fidaxomicin (63.2% vs. 50.0%; P = .0114).
Sustained response at 4 weeks and 8 weeks among the patients who experienced a recurrent episode of C. diff. favored fidaxomicin over vancomycin by 30.1% (P = .0002) and 27.6% (P = .0012), respectively.
The rates of C. diff. recurrence in patients who experienced their first C. diff. infection or who experienced a recurrent bout were lower with fidaxomicin than vancomycin, but the differences were not statistically significant.
A costly edge
When asked to comment, Colleen Kelly, MD, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said that the study was “worthwhile” and added that “Eric Dubberke has done a lot of work in this area.”
The study “gives more evidence that fidaxomicin does have a bit of an edge in people who have already had a bout of C. diff.,” she said.
Dr. Kelly added that the cost needs to be considered. Fidaxomicin “is about 30 times more expensive than vancomycin,” she said.
In part because of the cost difference, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2021 guidelines, which Dr. Kelly helped create, recommend that fidaxomicin be held as a second-line agent. The ACG guidance reserved fidaxomicin for people with C. diff. for whom initial treatment with vancomycin failed.
“The fidaxomicin question is going to get a lot easier once the cost of the drug comes down,” Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Dubberke is a consultant for Merck. Dr. Kelly reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fidaxomicin (Fificid) emerged favorable to vancomycin for the treatment of both initial and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections in a Medicare population, according to a new retrospective study.
Although fidaxomicin was about 14% more effective than vancomycin in treating the initial infection, a larger difference of 30% was found among people with recurrent C. diff. infections.
Lead investigator Erik Dubberke, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, St. Louis, and colleagues noted that this real-world evidence of the two agents used to treat C. diff. was “strikingly similar” to clinical trial data.
They said that their findings support the 2021 change in clinical guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommending fidaxomicin over vancomycin.
The study was presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2022, which was held virtually and in San Diego.
Evaluating a high-risk population
Because few real-world data exist that compare these two agents for C. diff., “particularly in a high-risk, high-prevalence population like Medicare,” the researchers evaluated Medicare Parts A, B, and D claims from 2016 to 2018 and included patients who had received fidaxomicin or vancomycin for an initial episode of C. diff. and for any recurrent episodes.
The researchers compared sustained response and recurrence of C. diff. within 4 weeks and 8 weeks after initial treatment with fidaxomicin or vancomycin. Treatment was considered successful if clinical resolution occurred 1 day after finishing therapy and there was no evidence of C. diff. recurrence.
Recurrence of C. diff. was defined as any evidence of new treatment or hospitalization for the infection within 4 or 8 weeks of when a patient filled the prescription for fidaxomicin or vancomycin.
The treatment groups were similar in age and race. However, the fidaxomicin group was at higher risk for recurrence, owing to risk factors such as history of C. diff. infection and compromised immunity. To reduce bias in comparing the groups, Dr. Dubberke and colleagues used propensity score matching. This approach yielded 190 matched pairs in the initial C. diff. episode sample and 67 matched pairs in the recurrent episode sample.
Among patients with their first C. diff. infection, fidaxomicin had a 13.5% higher rate of 4-week sustained response, compared with vancomycin (71.7% vs. 58.2%; P = .0058). There was also a 13.2% higher rate for 8-week sustained response with fidaxomicin (63.2% vs. 50.0%; P = .0114).
Sustained response at 4 weeks and 8 weeks among the patients who experienced a recurrent episode of C. diff. favored fidaxomicin over vancomycin by 30.1% (P = .0002) and 27.6% (P = .0012), respectively.
The rates of C. diff. recurrence in patients who experienced their first C. diff. infection or who experienced a recurrent bout were lower with fidaxomicin than vancomycin, but the differences were not statistically significant.
A costly edge
When asked to comment, Colleen Kelly, MD, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said that the study was “worthwhile” and added that “Eric Dubberke has done a lot of work in this area.”
The study “gives more evidence that fidaxomicin does have a bit of an edge in people who have already had a bout of C. diff.,” she said.
Dr. Kelly added that the cost needs to be considered. Fidaxomicin “is about 30 times more expensive than vancomycin,” she said.
In part because of the cost difference, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2021 guidelines, which Dr. Kelly helped create, recommend that fidaxomicin be held as a second-line agent. The ACG guidance reserved fidaxomicin for people with C. diff. for whom initial treatment with vancomycin failed.
“The fidaxomicin question is going to get a lot easier once the cost of the drug comes down,” Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Dubberke is a consultant for Merck. Dr. Kelly reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fidaxomicin (Fificid) emerged favorable to vancomycin for the treatment of both initial and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections in a Medicare population, according to a new retrospective study.
Although fidaxomicin was about 14% more effective than vancomycin in treating the initial infection, a larger difference of 30% was found among people with recurrent C. diff. infections.
Lead investigator Erik Dubberke, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, St. Louis, and colleagues noted that this real-world evidence of the two agents used to treat C. diff. was “strikingly similar” to clinical trial data.
They said that their findings support the 2021 change in clinical guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommending fidaxomicin over vancomycin.
The study was presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2022, which was held virtually and in San Diego.
Evaluating a high-risk population
Because few real-world data exist that compare these two agents for C. diff., “particularly in a high-risk, high-prevalence population like Medicare,” the researchers evaluated Medicare Parts A, B, and D claims from 2016 to 2018 and included patients who had received fidaxomicin or vancomycin for an initial episode of C. diff. and for any recurrent episodes.
The researchers compared sustained response and recurrence of C. diff. within 4 weeks and 8 weeks after initial treatment with fidaxomicin or vancomycin. Treatment was considered successful if clinical resolution occurred 1 day after finishing therapy and there was no evidence of C. diff. recurrence.
Recurrence of C. diff. was defined as any evidence of new treatment or hospitalization for the infection within 4 or 8 weeks of when a patient filled the prescription for fidaxomicin or vancomycin.
The treatment groups were similar in age and race. However, the fidaxomicin group was at higher risk for recurrence, owing to risk factors such as history of C. diff. infection and compromised immunity. To reduce bias in comparing the groups, Dr. Dubberke and colleagues used propensity score matching. This approach yielded 190 matched pairs in the initial C. diff. episode sample and 67 matched pairs in the recurrent episode sample.
Among patients with their first C. diff. infection, fidaxomicin had a 13.5% higher rate of 4-week sustained response, compared with vancomycin (71.7% vs. 58.2%; P = .0058). There was also a 13.2% higher rate for 8-week sustained response with fidaxomicin (63.2% vs. 50.0%; P = .0114).
Sustained response at 4 weeks and 8 weeks among the patients who experienced a recurrent episode of C. diff. favored fidaxomicin over vancomycin by 30.1% (P = .0002) and 27.6% (P = .0012), respectively.
The rates of C. diff. recurrence in patients who experienced their first C. diff. infection or who experienced a recurrent bout were lower with fidaxomicin than vancomycin, but the differences were not statistically significant.
A costly edge
When asked to comment, Colleen Kelly, MD, a gastroenterologist and associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I., said that the study was “worthwhile” and added that “Eric Dubberke has done a lot of work in this area.”
The study “gives more evidence that fidaxomicin does have a bit of an edge in people who have already had a bout of C. diff.,” she said.
Dr. Kelly added that the cost needs to be considered. Fidaxomicin “is about 30 times more expensive than vancomycin,” she said.
In part because of the cost difference, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2021 guidelines, which Dr. Kelly helped create, recommend that fidaxomicin be held as a second-line agent. The ACG guidance reserved fidaxomicin for people with C. diff. for whom initial treatment with vancomycin failed.
“The fidaxomicin question is going to get a lot easier once the cost of the drug comes down,” Dr. Kelly said.
The study was funded by Merck. Dr. Dubberke is a consultant for Merck. Dr. Kelly reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT DDW 2022
$7,000 for ‘flowers’: KY doc accused in murder plot against ex
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A Kentucky pediatrician accused of hiring a hitman to kill her ex-husband – and type a fake suicide text on his cell phone to disguise the plot – initially hatched the scheme 4 years ago during a custody dispute, according to court documents.
On May 19, agents with the Federal Bureau of Investigation arrested Stephanie Russell, MD, on a charge of using interstate commerce facilities in the commission of murder-for-hire, which carries a maximum 10-year sentence in federal prison.
Dr. Russell, who prosecutors said is 52, vehemently denied the plot when it was first relayed to investigators in 2020. She also dismissed suspicion from a court-appointed guardian at the time that the doctor harmed her own son, then 2, in a way “to make it appear” as if his father had hurt the child.
According to an FBI agent’s affidavit, Dr. Russell tried to recruit a killer through employees and ex-employees of Kidz Life Pediatrics, in Prospect, an upscale suburb of Louisville, Ky. She allegedly planned to time the murder during a 2-hour visitation period with her two children on the last day of the school year.
On May 24, Magistrate Judge Regina Edwards, of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Kentucky, ordered Dr. Russell to remain in custody. A future date for the next hearing has not been set.
‘No red flags’
The case has upended the Norton Commons development in Prospect, one of Kentucky’s wealthiest communities.
“There were no red flags,” said Lance Dooley, whose two daughters had been under Dr. Russell’s care at Kidz Life. “This neighborhood was like, ‘What the hell?’ Everybody went to her and trusted and respected her judgment.”
According to prosecutors, on May 15 – after having failed to have her ex-husband murdered during the holidays – Dr. Russell contacted a person she thought she had hired to murder her ex-husband in exchange for $7,000.
On May 18, Dr. Russell placed a $3,500 down payment in a specimen drop box outside her medical office. She agreed to pay the remaining half after the murder was done, according to prosecutors. The purported hit man was an undercover FBI agent.
While making plans, Dr. Russell used several burner phones and used the word “flowers” as a code word for killing her ex-husband, Ricky Crabtree, whom she had accused of sexually abusing their children. Mr. Crabtree, a financial planner, did not return phone messages left at his office.
Family Court Judge Denise Brown had earlier appointed a guardian to represent the children and an evaluator to monitor the couple’s custodial issues.
Dr. Russell sued the judge, saying Ms. Brown acted because of allegations that Dr. Russell was “coaching” her children and inflicting “emotional harm.” Dr. Russell also objected to what she called “a vague suggestion” that previously she “‘may’ have injured the older male child in a way to make it appear that [Mr.] Crabtree had done so.”
“There wasn’t any proof of it,” said David Mour, an attorney who represented Dr. Russell in that action. The state gave custody to the father in what Mr. Mour called a “Star Chamber” action based on unsubstantiated allegations. “I don’t believe a damned thing,” he said.
In her suit against Ms. Brown, which was dismissed in 2021, Dr. Russell criticized as “preposterous” allegations that, in May 2018, she “‘attempted to hire’ a ‘hitman’ to kill [Mr.] Crabtree.”
The FBI affidavit, however, displayed numerous text messages between Dr. Russell and a former nurse, whom she thought knew a hit man, and an FBI agent posing as the purported killer. When one witness initially agreed to find an assassin who would do the job over the 2021 holiday season, Dr. Russell texted, “I am hysterically crying tears of relief.”
The witness quit Kidz Life Pediatrics and ended contact with Dr. Russell when they realized Dr. Russell was “serious” about the plot, the affidavit stated. And when Dr. Russell found a willing contractor in May, she told the hitman to write a suicide text. The killer would have to unlock Mr. Crabtree’s cell phone by having the device recognize the face of his dead body.
Mr. Dooley said Kidz Life Pediatrics was closed during business hours when he tried to retrieve his children’s medical records. He has since found another pediatrician. Dr. Russell had cared for his children for more than 4 years, he said, betraying no clue of any darkness underneath. Kidz Life Pediatrics did not return phone calls seeking comment.
“It’s very close to home,” said Mr. Dooley, who runs an advertising agency with his wife. “Dr. Russell was really good.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Takotsubo syndrome more deadly in men
Takotsubo syndrome occurs much more frequently in women than it does in men, but men are much more likely to die from it, according to the results of a new study.
In an analysis of almost 2,500 patients with Takotsubo syndrome (TSS) who were enrolled in an international registry, men, who made up just 11% of the sample, had significantly higher rates of cardiogenic shock and were more than twice as likely to die in the hospital than their female counterparts.
The authors concluded that TSS in males requires close in-hospital monitoring and long-term follow-up. Their study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Takotsubo syndrome is a condition characterized by acute heart failure and transient ventricular contractile dysfunction that can be precipitated by acute emotional or physical stress. It affects mostly women, particularly postmenopausal women, although the reasons for this are still not fully clear, Luca Arcari, MD, from the Institute of Cardiology, Madre Giuseppina Vannini Hospital, Rome, and colleagues wrote.
The syndrome also affects men, and recent data have identified that male sex is associated with worse outcomes. But, because it occurs relatively uncommonly in men, information about outcomes in men is limited.
To shed more light on the influence of gender on TTS, the investigators looked at 2,492 TTS patients (286 men, 2,206 women) who were participants in the GEIST (German Italian Spanish Takotsubo) registry and compared the clinical features and short- and long-term outcomes between the two.
Male patients were significantly younger (69 years) than women (71 years; P = .005) and had a higher prevalence of comorbid conditions, including diabetes (25% vs. 19%; P = .01); pulmonary diseases (21% vs. 15%; P = .006); malignancies (25% vs. 13%; P < .001).
In addition, TTS in men was more likely to be caused by physical triggers (55% vs. 32%; P < .01), whereas emotional triggers were more common in females (39% vs. 19%; P < 0.001).
The investigators then performed a propensity score analysis by matching men and women 1:1; this yielded 207 patients from each group.
After propensity matching, male patients had higher rates of cardiogenic shock (16% vs 6%), and in-hospital mortality (8% vs. 3%; both P < .05).
Men also had a higher mortality rate during the acute and long-term follow up. Male sex remained independently associated with both in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 2.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.16-4.40) and long-term mortality (hazard ratio, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.32-2.52).
The study by Dr. Arcari and colleagues “shows convincingly that although men are far less likely to develop TTS than women, they have more serious complications and are more likely to die than women presenting with the syndrome, Ilan S. Wittstein, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
In an interview, Dr. Wittstein said one of the strengths of the study was its size.
“Over the years, there have been a lot of smaller, single center studies. This large registry had over 2,000 patients. So when the researchers say the rate of TTS is 10% in men and 90% in women, this is not necessarily surprising because that’s about the breakdown we’ve had since the very beginning, but it certainly validates that in a cohort that is large,” he said.
“I think what was novel about the paper is that the size of the cohort allowed the researchers to do propensity matching, so they were able not only to compare men versus women, they could do a 1:1 comparison. And they found even when you match men and women for various comorbidities, the men were much sicker
“What makes this a fascinating syndrome and different from most types of heart muscle problems is that, in the majority of patients, the condition is precipitated by an acute stressor,” said Dr. Wittstein.
“It can either be an emotional trigger, so for instance, getting some bad news that a loved one just died. That’s why we nicknamed the syndrome ‘broken heart syndrome’ many years ago. Or it can be a physical trigger, which can be a wide variety of things, such infection, a stroke, bad pneumonia, anything that stresses the body and causes a stress response. Regular heart attacks are not triggered in this way,” he said.
Dr. Arcari and Dr. Wittstein reported no relevant financial relationships.
Takotsubo syndrome occurs much more frequently in women than it does in men, but men are much more likely to die from it, according to the results of a new study.
In an analysis of almost 2,500 patients with Takotsubo syndrome (TSS) who were enrolled in an international registry, men, who made up just 11% of the sample, had significantly higher rates of cardiogenic shock and were more than twice as likely to die in the hospital than their female counterparts.
The authors concluded that TSS in males requires close in-hospital monitoring and long-term follow-up. Their study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Takotsubo syndrome is a condition characterized by acute heart failure and transient ventricular contractile dysfunction that can be precipitated by acute emotional or physical stress. It affects mostly women, particularly postmenopausal women, although the reasons for this are still not fully clear, Luca Arcari, MD, from the Institute of Cardiology, Madre Giuseppina Vannini Hospital, Rome, and colleagues wrote.
The syndrome also affects men, and recent data have identified that male sex is associated with worse outcomes. But, because it occurs relatively uncommonly in men, information about outcomes in men is limited.
To shed more light on the influence of gender on TTS, the investigators looked at 2,492 TTS patients (286 men, 2,206 women) who were participants in the GEIST (German Italian Spanish Takotsubo) registry and compared the clinical features and short- and long-term outcomes between the two.
Male patients were significantly younger (69 years) than women (71 years; P = .005) and had a higher prevalence of comorbid conditions, including diabetes (25% vs. 19%; P = .01); pulmonary diseases (21% vs. 15%; P = .006); malignancies (25% vs. 13%; P < .001).
In addition, TTS in men was more likely to be caused by physical triggers (55% vs. 32%; P < .01), whereas emotional triggers were more common in females (39% vs. 19%; P < 0.001).
The investigators then performed a propensity score analysis by matching men and women 1:1; this yielded 207 patients from each group.
After propensity matching, male patients had higher rates of cardiogenic shock (16% vs 6%), and in-hospital mortality (8% vs. 3%; both P < .05).
Men also had a higher mortality rate during the acute and long-term follow up. Male sex remained independently associated with both in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 2.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.16-4.40) and long-term mortality (hazard ratio, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.32-2.52).
The study by Dr. Arcari and colleagues “shows convincingly that although men are far less likely to develop TTS than women, they have more serious complications and are more likely to die than women presenting with the syndrome, Ilan S. Wittstein, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
In an interview, Dr. Wittstein said one of the strengths of the study was its size.
“Over the years, there have been a lot of smaller, single center studies. This large registry had over 2,000 patients. So when the researchers say the rate of TTS is 10% in men and 90% in women, this is not necessarily surprising because that’s about the breakdown we’ve had since the very beginning, but it certainly validates that in a cohort that is large,” he said.
“I think what was novel about the paper is that the size of the cohort allowed the researchers to do propensity matching, so they were able not only to compare men versus women, they could do a 1:1 comparison. And they found even when you match men and women for various comorbidities, the men were much sicker
“What makes this a fascinating syndrome and different from most types of heart muscle problems is that, in the majority of patients, the condition is precipitated by an acute stressor,” said Dr. Wittstein.
“It can either be an emotional trigger, so for instance, getting some bad news that a loved one just died. That’s why we nicknamed the syndrome ‘broken heart syndrome’ many years ago. Or it can be a physical trigger, which can be a wide variety of things, such infection, a stroke, bad pneumonia, anything that stresses the body and causes a stress response. Regular heart attacks are not triggered in this way,” he said.
Dr. Arcari and Dr. Wittstein reported no relevant financial relationships.
Takotsubo syndrome occurs much more frequently in women than it does in men, but men are much more likely to die from it, according to the results of a new study.
In an analysis of almost 2,500 patients with Takotsubo syndrome (TSS) who were enrolled in an international registry, men, who made up just 11% of the sample, had significantly higher rates of cardiogenic shock and were more than twice as likely to die in the hospital than their female counterparts.
The authors concluded that TSS in males requires close in-hospital monitoring and long-term follow-up. Their study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Takotsubo syndrome is a condition characterized by acute heart failure and transient ventricular contractile dysfunction that can be precipitated by acute emotional or physical stress. It affects mostly women, particularly postmenopausal women, although the reasons for this are still not fully clear, Luca Arcari, MD, from the Institute of Cardiology, Madre Giuseppina Vannini Hospital, Rome, and colleagues wrote.
The syndrome also affects men, and recent data have identified that male sex is associated with worse outcomes. But, because it occurs relatively uncommonly in men, information about outcomes in men is limited.
To shed more light on the influence of gender on TTS, the investigators looked at 2,492 TTS patients (286 men, 2,206 women) who were participants in the GEIST (German Italian Spanish Takotsubo) registry and compared the clinical features and short- and long-term outcomes between the two.
Male patients were significantly younger (69 years) than women (71 years; P = .005) and had a higher prevalence of comorbid conditions, including diabetes (25% vs. 19%; P = .01); pulmonary diseases (21% vs. 15%; P = .006); malignancies (25% vs. 13%; P < .001).
In addition, TTS in men was more likely to be caused by physical triggers (55% vs. 32%; P < .01), whereas emotional triggers were more common in females (39% vs. 19%; P < 0.001).
The investigators then performed a propensity score analysis by matching men and women 1:1; this yielded 207 patients from each group.
After propensity matching, male patients had higher rates of cardiogenic shock (16% vs 6%), and in-hospital mortality (8% vs. 3%; both P < .05).
Men also had a higher mortality rate during the acute and long-term follow up. Male sex remained independently associated with both in-hospital mortality (odds ratio, 2.26; 95% confidence interval, 1.16-4.40) and long-term mortality (hazard ratio, 1.83; 95% CI, 1.32-2.52).
The study by Dr. Arcari and colleagues “shows convincingly that although men are far less likely to develop TTS than women, they have more serious complications and are more likely to die than women presenting with the syndrome, Ilan S. Wittstein, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
In an interview, Dr. Wittstein said one of the strengths of the study was its size.
“Over the years, there have been a lot of smaller, single center studies. This large registry had over 2,000 patients. So when the researchers say the rate of TTS is 10% in men and 90% in women, this is not necessarily surprising because that’s about the breakdown we’ve had since the very beginning, but it certainly validates that in a cohort that is large,” he said.
“I think what was novel about the paper is that the size of the cohort allowed the researchers to do propensity matching, so they were able not only to compare men versus women, they could do a 1:1 comparison. And they found even when you match men and women for various comorbidities, the men were much sicker
“What makes this a fascinating syndrome and different from most types of heart muscle problems is that, in the majority of patients, the condition is precipitated by an acute stressor,” said Dr. Wittstein.
“It can either be an emotional trigger, so for instance, getting some bad news that a loved one just died. That’s why we nicknamed the syndrome ‘broken heart syndrome’ many years ago. Or it can be a physical trigger, which can be a wide variety of things, such infection, a stroke, bad pneumonia, anything that stresses the body and causes a stress response. Regular heart attacks are not triggered in this way,” he said.
Dr. Arcari and Dr. Wittstein reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Forceps for Milia Extraction
To the Editor:
Several techniques can be used to destroy milia including electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy. Manual extraction of milia uses a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet followed by the application of pressure to the lesion with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Many of these techniques fail to stabilize milia, particularly in sensitive areas such as around the eyes or mouth, which can make extraction challenging, inefficient, and painful for the patient. We report a novel technique that quickly and effectively removes milia with equipment commonly used in the practice of clinical dermatology.
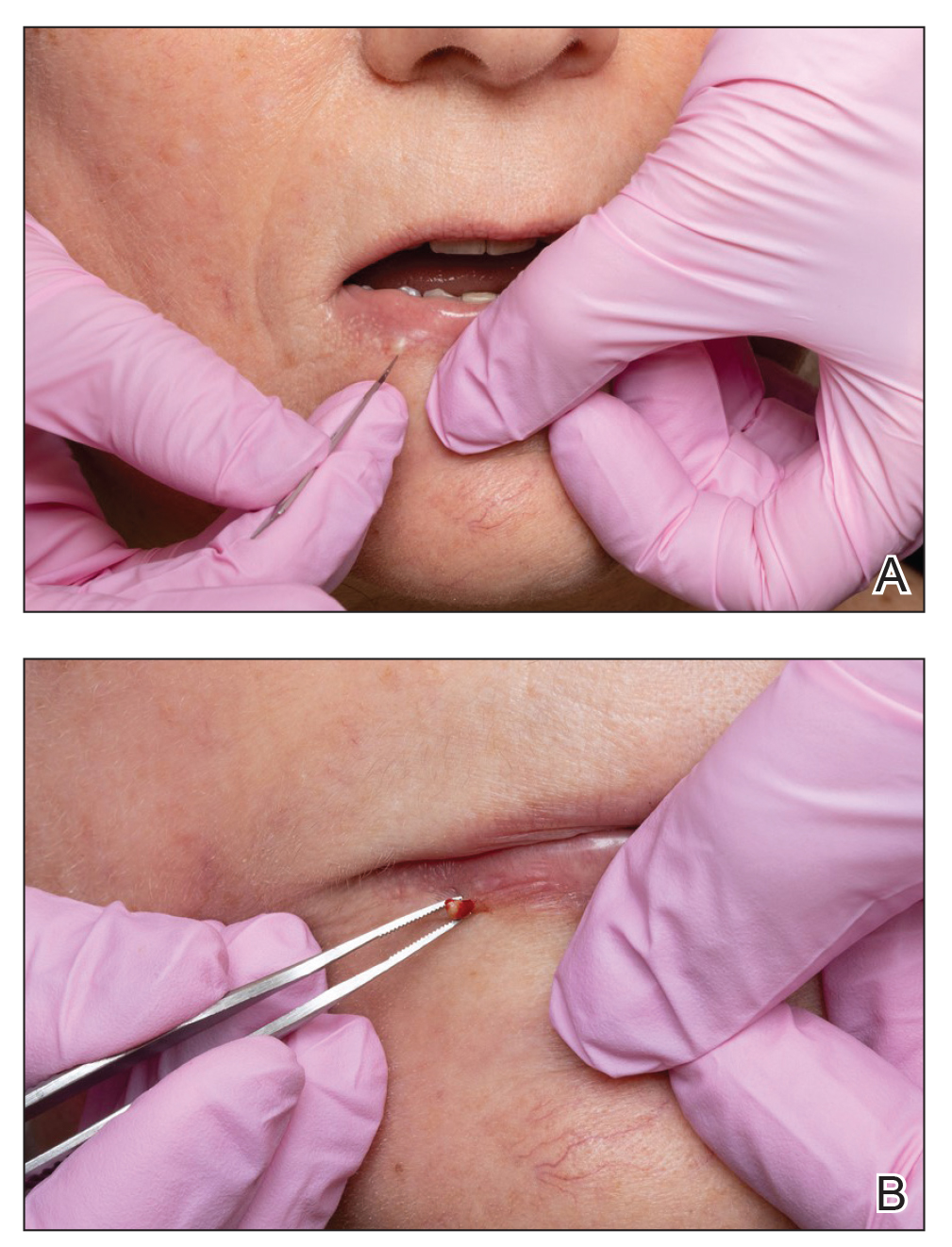
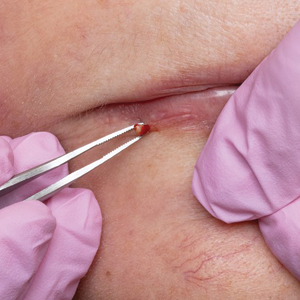
A 74-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic papule on the right lower vermilion border of several years' duration. Physical examination of the lesion revealed a 3-mm, firm, white, dome-shaped papule. Clinical features were most consistent with a benign acquired milium. The patient desired removal for cosmesis. The area was cleaned with an alcohol swab, the surface of the milium was nicked with a No. 11 blade (Figure, A), and then tips of nontoothed Adson forceps were used to gently secure and pinch the base of the papule (Figure, B). The intact cyst was quickly and effortlessly expressed through the epidermal nick. The patient tolerated the procedure well, experiencing minimal pain and bleeding.
Histologically, milia represent infundibular keratin-filled cysts lined with stratified squamous epithelial tissue that contains a granular cell layer. These lesions are classified as primary or secondary; the former represent spontaneous occurrence, and the latter are associated with medications, trauma, or genodermatoses.2 Multiple milia are associated with conditions such as Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, oro-facial-digital syndrome type I, atrichia with papular lesions, pachyonychia congenita type 2, basal cell nevus syndrome, basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome, and hereditary vitamin D–dependent rickets type 2.5-9 The most common subtype seen in clinical practice includes benign primary milia, which tends to favor the cheeks and eyelids.2
Although these lesions are benign, many patients seek extraction for cosmesis. Milia extraction is a common procedure performed in dermatology clinical practice. Proposed extraction techniques using destructive methods include electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy, and manual methods include nicking the surface of the lesion with a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet and then applying tangential pressure with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Topical retinoids have been proposed as treatment of multiple milia.10 Many of these techniques do not use equipment common to clinical practice, or they fail to stabilize milia in sensitive areas, which makes extraction challenging. We describe a case with a new manual technique that successfully extracts milia in an efficient and safe manner.
- Parlette HL III. Management of cutaneous cysts. In: Wheeland RG, ed. Cutaneous Surgery. WB Saunders; 1994:651-652.
- Berk DR, Bayliss SJ. Milia: a review and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:1050-1063.
- George DE, Wasko CA, Hsu S. Surgical pearl: evacuation of milia with a paper clip. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:326.
- Thami GP, Kaur S, Kanwar AJ. Surgical pearl: enucleation of milia with a disposable hypodermic needle. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:602-603.
- Goeteyn M, Geerts ML, Kint A, et al. The Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:337-342.
- Michaëlsson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome: a familial disorder with vermiculate atrophoderma, milia, hypotrichosis, trichoepitheliomas, basal cell carcinomas and peripheral vasodilation with cyanosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Gurrieri F, Franco B, Toriello H, et al. Oral-facial-digital syndromes: review and diagnostic guidelines. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A:3314-3323.
- Zlotogorski A, Panteleyev AA, Aita VM, et al. Clinical and molecular diagnostic criteria of congenital atrichia with papular lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1662-1665.
- Paller AS, Moore JA, Scher R. Pachyonychia congenita tarda. alate-onset form of pachyonychia congenita. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:701-703.
- Connelly T. Eruptive milia and rapid response to topical tretinoin. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:816-817.
To the Editor:
Several techniques can be used to destroy milia including electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy. Manual extraction of milia uses a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet followed by the application of pressure to the lesion with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Many of these techniques fail to stabilize milia, particularly in sensitive areas such as around the eyes or mouth, which can make extraction challenging, inefficient, and painful for the patient. We report a novel technique that quickly and effectively removes milia with equipment commonly used in the practice of clinical dermatology.
A 74-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic papule on the right lower vermilion border of several years' duration. Physical examination of the lesion revealed a 3-mm, firm, white, dome-shaped papule. Clinical features were most consistent with a benign acquired milium. The patient desired removal for cosmesis. The area was cleaned with an alcohol swab, the surface of the milium was nicked with a No. 11 blade (Figure, A), and then tips of nontoothed Adson forceps were used to gently secure and pinch the base of the papule (Figure, B). The intact cyst was quickly and effortlessly expressed through the epidermal nick. The patient tolerated the procedure well, experiencing minimal pain and bleeding.
Histologically, milia represent infundibular keratin-filled cysts lined with stratified squamous epithelial tissue that contains a granular cell layer. These lesions are classified as primary or secondary; the former represent spontaneous occurrence, and the latter are associated with medications, trauma, or genodermatoses.2 Multiple milia are associated with conditions such as Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, oro-facial-digital syndrome type I, atrichia with papular lesions, pachyonychia congenita type 2, basal cell nevus syndrome, basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome, and hereditary vitamin D–dependent rickets type 2.5-9 The most common subtype seen in clinical practice includes benign primary milia, which tends to favor the cheeks and eyelids.2
Although these lesions are benign, many patients seek extraction for cosmesis. Milia extraction is a common procedure performed in dermatology clinical practice. Proposed extraction techniques using destructive methods include electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy, and manual methods include nicking the surface of the lesion with a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet and then applying tangential pressure with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Topical retinoids have been proposed as treatment of multiple milia.10 Many of these techniques do not use equipment common to clinical practice, or they fail to stabilize milia in sensitive areas, which makes extraction challenging. We describe a case with a new manual technique that successfully extracts milia in an efficient and safe manner.
To the Editor:
Several techniques can be used to destroy milia including electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy. Manual extraction of milia uses a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet followed by the application of pressure to the lesion with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Many of these techniques fail to stabilize milia, particularly in sensitive areas such as around the eyes or mouth, which can make extraction challenging, inefficient, and painful for the patient. We report a novel technique that quickly and effectively removes milia with equipment commonly used in the practice of clinical dermatology.
A 74-year-old woman presented with an asymptomatic papule on the right lower vermilion border of several years' duration. Physical examination of the lesion revealed a 3-mm, firm, white, dome-shaped papule. Clinical features were most consistent with a benign acquired milium. The patient desired removal for cosmesis. The area was cleaned with an alcohol swab, the surface of the milium was nicked with a No. 11 blade (Figure, A), and then tips of nontoothed Adson forceps were used to gently secure and pinch the base of the papule (Figure, B). The intact cyst was quickly and effortlessly expressed through the epidermal nick. The patient tolerated the procedure well, experiencing minimal pain and bleeding.
Histologically, milia represent infundibular keratin-filled cysts lined with stratified squamous epithelial tissue that contains a granular cell layer. These lesions are classified as primary or secondary; the former represent spontaneous occurrence, and the latter are associated with medications, trauma, or genodermatoses.2 Multiple milia are associated with conditions such as Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Brooke-Spiegler syndrome, oro-facial-digital syndrome type I, atrichia with papular lesions, pachyonychia congenita type 2, basal cell nevus syndrome, basaloid follicular hamartoma syndrome, and hereditary vitamin D–dependent rickets type 2.5-9 The most common subtype seen in clinical practice includes benign primary milia, which tends to favor the cheeks and eyelids.2
Although these lesions are benign, many patients seek extraction for cosmesis. Milia extraction is a common procedure performed in dermatology clinical practice. Proposed extraction techniques using destructive methods include electrocautery, electrodesiccation, and laser therapy, and manual methods include nicking the surface of the lesion with a scalpel blade, needle, or stylet and then applying tangential pressure with a curette, comedone extractor, paper clip, cotton-tipped applicator, tongue blade, or hypodermic needle.1-4 Topical retinoids have been proposed as treatment of multiple milia.10 Many of these techniques do not use equipment common to clinical practice, or they fail to stabilize milia in sensitive areas, which makes extraction challenging. We describe a case with a new manual technique that successfully extracts milia in an efficient and safe manner.
- Parlette HL III. Management of cutaneous cysts. In: Wheeland RG, ed. Cutaneous Surgery. WB Saunders; 1994:651-652.
- Berk DR, Bayliss SJ. Milia: a review and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:1050-1063.
- George DE, Wasko CA, Hsu S. Surgical pearl: evacuation of milia with a paper clip. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:326.
- Thami GP, Kaur S, Kanwar AJ. Surgical pearl: enucleation of milia with a disposable hypodermic needle. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:602-603.
- Goeteyn M, Geerts ML, Kint A, et al. The Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:337-342.
- Michaëlsson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome: a familial disorder with vermiculate atrophoderma, milia, hypotrichosis, trichoepitheliomas, basal cell carcinomas and peripheral vasodilation with cyanosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Gurrieri F, Franco B, Toriello H, et al. Oral-facial-digital syndromes: review and diagnostic guidelines. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A:3314-3323.
- Zlotogorski A, Panteleyev AA, Aita VM, et al. Clinical and molecular diagnostic criteria of congenital atrichia with papular lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1662-1665.
- Paller AS, Moore JA, Scher R. Pachyonychia congenita tarda. alate-onset form of pachyonychia congenita. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:701-703.
- Connelly T. Eruptive milia and rapid response to topical tretinoin. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:816-817.
- Parlette HL III. Management of cutaneous cysts. In: Wheeland RG, ed. Cutaneous Surgery. WB Saunders; 1994:651-652.
- Berk DR, Bayliss SJ. Milia: a review and classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;59:1050-1063.
- George DE, Wasko CA, Hsu S. Surgical pearl: evacuation of milia with a paper clip. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:326.
- Thami GP, Kaur S, Kanwar AJ. Surgical pearl: enucleation of milia with a disposable hypodermic needle. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:602-603.
- Goeteyn M, Geerts ML, Kint A, et al. The Bazex-Dupré-Christol syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:337-342.
- Michaëlsson G, Olsson E, Westermark P. The Rombo syndrome: a familial disorder with vermiculate atrophoderma, milia, hypotrichosis, trichoepitheliomas, basal cell carcinomas and peripheral vasodilation with cyanosis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61:497-503.
- Gurrieri F, Franco B, Toriello H, et al. Oral-facial-digital syndromes: review and diagnostic guidelines. Am J Med Genet A. 2007;143A:3314-3323.
- Zlotogorski A, Panteleyev AA, Aita VM, et al. Clinical and molecular diagnostic criteria of congenital atrichia with papular lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117:1662-1665.
- Paller AS, Moore JA, Scher R. Pachyonychia congenita tarda. alate-onset form of pachyonychia congenita. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:701-703.
- Connelly T. Eruptive milia and rapid response to topical tretinoin. Arch Dermatol. 2008;144:816-817.
Practice Points
- Milia are common benign lesions that are cosmetically undesirable to some patients.
- Although some methods of milia removal can be painful, removal with forceps is quick and effective.
Navigating Motherhood and Dermatology Residency
Motherhood and dermatology residency are both full-time jobs. The thought that a woman must either be superhuman to succeed at both or that success at one must come at the expense of the other is antiquated. With careful navigation and sufficient support, these two roles can complement and heighten one another. The most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) report showed that nearly 60% of dermatology residents are women,1 with most women in training being of childbearing age. One study showed that female dermatologists were most likely to have children during residency (51% of those surveyed), despite residents reporting more barriers to childbearing at this career stage.2 Trainees thinking of starting a family have many considerations to navigate: timing of pregnancy, maternity leave scheduling, breastfeeding while working, and planning for childcare. For the first time in the history of the specialty, most active dermatologists in practice are women.3 Thus, the future of dermatology requires supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of these issues by today’s trainees.
Timing of Pregnancy
Timing of pregnancy can be a source of stress to the female dermatology resident. Barriers to childbearing during residency include the perception that women who have children during residency training are less committed to their jobs; concerns of overburdening fellow residents; and fear that residency may need to be extended, thereby delaying the ability to sit for the board examination.2 However, the potential increased risk for infertility in delaying pregnancy adds to the stress of pregnancy planning. A 2016 survey of female physicians (N=327) showed that 24.1% of respondents who had attempted conception were diagnosed with infertility, with an average age at diagnosis of 33.7 years.4 This is higher than the national average, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that approximately 19% of women aged 15 to 49 years with no prior births experience infertility.5 In a 1992 survey of female physician residents (N=373) who gave birth during residency, 32% indicated that they would not recommend the experience to others; of the 68% who would recommend the experience, one-third encouraged timing delivery to occur in the last 2 months of residency due to benefits of continued insurance coverage, a decrease in clinic responsibilities, and the potential for extended maternity leave during hiatus between jobs.6 Although this may be a good strategy, studying and sitting for board examinations while caring for a newborn right after graduation may be overly difficult for some. The first year of residency was perceived as the most stressful time to be pregnant, with each subsequent year being less problematic.6 Planning pregnancy for delivery near the end of the second year and beginning of the third year of dermatology residency may be a reasonable choice.
Maternity Leave
The Family and Medical Leave Act entitles eligible employees of covered employers to take unpaid, job-protected leave, with 12 workweeks of leave in a 12-month period for the birth of a child and to care for the newborn child within 1 year of birth.7 The actual length of maternity leave taken by most surveyed female dermatologists (n=96) is shorter: 25% (24/96) took less than 4 weeks, 42.7% (41/96) took 4 to 8 weeks, 25% (24/96) took 9 to 12 weeks, and 7.3% (7/96) were able to take more than 12 weeks of maternity leave.2
The American Board of Dermatology implemented a new Resident Leave policy that went into effect July 1, 2021, stipulating that, within certain parameters, time spent away from training for family and parental leave would not exhaust vacation time or require an extension in training. Under this policy, absence from training exceeding 8 weeks (6 weeks leave, plus 2 weeks of vacation) in a given year should be approved only under exceptional circumstances and may necessitate additional training time to ensure that competency requirements are met.8 Although this policy is a step in the right direction, institutional policies still may vary. Dermatology residents planning to start a family during training should consider their plans for fellowship, as taking an extended maternity leave beyond 8 weeks may jeopardize a July fellowship start date.
Lactation and Residency
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends exclusive breastfeeding for approximately 6 months, with continuation of breastfeeding for 1 year or longer as mutually desired by the mother and infant.9 Successful lactation and achieving breastfeeding goals can be difficult during medical training. A national cross-sectional survey of female residents (N=312) showed that the median total time of breastfeeding and pumping was 9 months, with 74% continuing after 6 months and 13% continuing past 12 months. Of those surveyed, 73% reported residency limited their ability to lactate, and 37% stopped prior to their desired goal.10 As of July 1, 2020, the ACGME requires that residency programs and sponsoring institutions provide clean and private facilities for lactation that have refrigeration capabilities, with proximity appropriate for safe patient care.11 There has been a call to dermatology program leadership to support breastfeeding residents by providing sufficient time and space to pump; a breastfeeding resident will need a 20- to 30-minute break to express milk approximately every 3 hours during the work day.12 One innovative initiative to meet the ACGME lactation requirement reported by the Kansas University Medical Center Graduate Medical Education program (Kansas City, Kansas) was the purchase of wearable breast pumps to loan to residents. The benefits of wearable breast pumps are that they are discreet and can allow mothers to express milk inconspicuously while working, can increase milk supply, require less set up and expression time than traditional pumps, and can allow the mother to manage time more efficiently.13 Breastfeeding plans and goals should be discussed with program leadership before return from leave to strategize and anticipate gaps in clinic scheduling to accommodate the lactating resident.
Planning for Childcare
Resident hours can be long and erratic, making choices for childcare difficult. In one survey of female residents, 61% of married or partnered respondents (n=447) were delaying childbearing, and 46% cited lack of access to childcare as a reason.14 Not all dermatology residents are fortunate enough to match to a program near family, but close family support can be an undeniable asset during childrearing and should be weighed heavily when ranking programs. Options for childcare include relying on a stay-at-home spouse or other family member, a live-in or live-out nanny, part-time babysitters, and daycare. It is crucial to have multiple layers and back-up options for childcare available at any given time when working as a resident. Even with a child enrolled in a full-time daycare and a live-in nanny, a daycare closure due to a COVID-19 exposure or sudden medical emergency in the nanny can still leave unpredicted holes in your childcare plan, leaving the resident to potentially miss work to fill the gap. A survey of residents at one institution showed that the most common backup childcare plan for situations in which either the child or the regular caregiver is ill is for the nontrainee parent or spouse to stay home (45%; n=101), with 25% of respondents staying home to care for a sick child themselves, which clearly has an impact on the hospital. The article proposed implementation of on-site or near-site childcare for residents with extended hours or a 24-hour emergency drop-in availability.15 One institution reported success with the development of a departmentally funded childcare supplementation stipend offered to residents to support daycare costs during the first 6 months of a baby’s life.16
Final Thoughts
Due to the competitiveness of the field, dermatology residents are by nature high performing and academically successful. For a high achiever, the idea of potentially disappointing faculty and colleagues by starting a family during residency can be guilt inducing. Concerns about one’s ability to adequately study the breadth of dermatology while simultaneously raising a child can be distressing; however, there are many ways in which motherhood can hone skills to become a better dermatology resident. Through motherhood one can enhance time management skills, increase efficiency, and improve rapport with pediatric patients and trust with their parents/guardians. A dermatology resident may be her own harshest critic, but it is time that the future generation of dermatologists become their own greatest advocates for establishing supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of motherhood and dermatology residency.
- ACGME residents and fellows by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/interactive-data/acgme-residents-and-fellows-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Mattessich S, Shea K, Whitaker-Worth D. Parenting and female dermatologists’ perceptions of work-life balance. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:127-130. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.04.001
- Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/interactive-data/active-physicians-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Stentz NC, Griffith KA, Perkins E, et al. Fertility and childbearing among American female physicians. J Womens Health. 2016;25:1059-1065. doi:10.1089/jwh.2015.5638
- Infertility. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated March 1, 2022. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Phelan ST. Sources of stress and support for the pregnant resident. Acad Med. 1992;67:408-410. doi:10.1097/00001888-199206000-00014
- Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla
- American Board of Dermatology. Effective July 2021: new family leave policy. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.abderm.org/public/announcements/effective-july-2021-new-family-leave-policy.aspx
- Eidelman AI, Schanler RJ, Johnston M, et al. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E827-E841. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3552
- Peters GW, Kuczmarska-Haas A, Holliday EB, et al. Lactation challenges of resident physicians: results of a national survey. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:762. doi:10.1186/s12884-020-03436-3
- Common program requirements (residency) sections I-V table of implementation dates. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/CPRResidencyImplementationTable.pdf
- Gracey LE, Mathes EF, Shinkai K. Supporting breastfeeding mothers during dermatology residency—challenges and best practices. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:117-118. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3759
- McMillin A, Behravesh B, Byrne P, et al. A GME wearable breast pump program: an innovative method to meet ACGME requirements and federal law. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13:422-423. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-20-01275.1
- Stack SW, Jagsi R, Biermann JS, et al. Childbearing decisions in residency: a multicenter survey of female residents. Acad Med. 2020;95:1550-1557. doi:10.1097/acm.0000000000003549
- Snyder RA, Tarpley MJ, Phillips SE, et al. The case for on-site child care in residency training and afterward. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5:365-367. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-12-00294.1
- Key LL. Child care supplementation: aid for residents and advantages for residency programs. J Pediatr. 2008;153:449-450. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.05.028
Motherhood and dermatology residency are both full-time jobs. The thought that a woman must either be superhuman to succeed at both or that success at one must come at the expense of the other is antiquated. With careful navigation and sufficient support, these two roles can complement and heighten one another. The most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) report showed that nearly 60% of dermatology residents are women,1 with most women in training being of childbearing age. One study showed that female dermatologists were most likely to have children during residency (51% of those surveyed), despite residents reporting more barriers to childbearing at this career stage.2 Trainees thinking of starting a family have many considerations to navigate: timing of pregnancy, maternity leave scheduling, breastfeeding while working, and planning for childcare. For the first time in the history of the specialty, most active dermatologists in practice are women.3 Thus, the future of dermatology requires supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of these issues by today’s trainees.
Timing of Pregnancy
Timing of pregnancy can be a source of stress to the female dermatology resident. Barriers to childbearing during residency include the perception that women who have children during residency training are less committed to their jobs; concerns of overburdening fellow residents; and fear that residency may need to be extended, thereby delaying the ability to sit for the board examination.2 However, the potential increased risk for infertility in delaying pregnancy adds to the stress of pregnancy planning. A 2016 survey of female physicians (N=327) showed that 24.1% of respondents who had attempted conception were diagnosed with infertility, with an average age at diagnosis of 33.7 years.4 This is higher than the national average, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that approximately 19% of women aged 15 to 49 years with no prior births experience infertility.5 In a 1992 survey of female physician residents (N=373) who gave birth during residency, 32% indicated that they would not recommend the experience to others; of the 68% who would recommend the experience, one-third encouraged timing delivery to occur in the last 2 months of residency due to benefits of continued insurance coverage, a decrease in clinic responsibilities, and the potential for extended maternity leave during hiatus between jobs.6 Although this may be a good strategy, studying and sitting for board examinations while caring for a newborn right after graduation may be overly difficult for some. The first year of residency was perceived as the most stressful time to be pregnant, with each subsequent year being less problematic.6 Planning pregnancy for delivery near the end of the second year and beginning of the third year of dermatology residency may be a reasonable choice.
Maternity Leave
The Family and Medical Leave Act entitles eligible employees of covered employers to take unpaid, job-protected leave, with 12 workweeks of leave in a 12-month period for the birth of a child and to care for the newborn child within 1 year of birth.7 The actual length of maternity leave taken by most surveyed female dermatologists (n=96) is shorter: 25% (24/96) took less than 4 weeks, 42.7% (41/96) took 4 to 8 weeks, 25% (24/96) took 9 to 12 weeks, and 7.3% (7/96) were able to take more than 12 weeks of maternity leave.2
The American Board of Dermatology implemented a new Resident Leave policy that went into effect July 1, 2021, stipulating that, within certain parameters, time spent away from training for family and parental leave would not exhaust vacation time or require an extension in training. Under this policy, absence from training exceeding 8 weeks (6 weeks leave, plus 2 weeks of vacation) in a given year should be approved only under exceptional circumstances and may necessitate additional training time to ensure that competency requirements are met.8 Although this policy is a step in the right direction, institutional policies still may vary. Dermatology residents planning to start a family during training should consider their plans for fellowship, as taking an extended maternity leave beyond 8 weeks may jeopardize a July fellowship start date.
Lactation and Residency
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends exclusive breastfeeding for approximately 6 months, with continuation of breastfeeding for 1 year or longer as mutually desired by the mother and infant.9 Successful lactation and achieving breastfeeding goals can be difficult during medical training. A national cross-sectional survey of female residents (N=312) showed that the median total time of breastfeeding and pumping was 9 months, with 74% continuing after 6 months and 13% continuing past 12 months. Of those surveyed, 73% reported residency limited their ability to lactate, and 37% stopped prior to their desired goal.10 As of July 1, 2020, the ACGME requires that residency programs and sponsoring institutions provide clean and private facilities for lactation that have refrigeration capabilities, with proximity appropriate for safe patient care.11 There has been a call to dermatology program leadership to support breastfeeding residents by providing sufficient time and space to pump; a breastfeeding resident will need a 20- to 30-minute break to express milk approximately every 3 hours during the work day.12 One innovative initiative to meet the ACGME lactation requirement reported by the Kansas University Medical Center Graduate Medical Education program (Kansas City, Kansas) was the purchase of wearable breast pumps to loan to residents. The benefits of wearable breast pumps are that they are discreet and can allow mothers to express milk inconspicuously while working, can increase milk supply, require less set up and expression time than traditional pumps, and can allow the mother to manage time more efficiently.13 Breastfeeding plans and goals should be discussed with program leadership before return from leave to strategize and anticipate gaps in clinic scheduling to accommodate the lactating resident.
Planning for Childcare
Resident hours can be long and erratic, making choices for childcare difficult. In one survey of female residents, 61% of married or partnered respondents (n=447) were delaying childbearing, and 46% cited lack of access to childcare as a reason.14 Not all dermatology residents are fortunate enough to match to a program near family, but close family support can be an undeniable asset during childrearing and should be weighed heavily when ranking programs. Options for childcare include relying on a stay-at-home spouse or other family member, a live-in or live-out nanny, part-time babysitters, and daycare. It is crucial to have multiple layers and back-up options for childcare available at any given time when working as a resident. Even with a child enrolled in a full-time daycare and a live-in nanny, a daycare closure due to a COVID-19 exposure or sudden medical emergency in the nanny can still leave unpredicted holes in your childcare plan, leaving the resident to potentially miss work to fill the gap. A survey of residents at one institution showed that the most common backup childcare plan for situations in which either the child or the regular caregiver is ill is for the nontrainee parent or spouse to stay home (45%; n=101), with 25% of respondents staying home to care for a sick child themselves, which clearly has an impact on the hospital. The article proposed implementation of on-site or near-site childcare for residents with extended hours or a 24-hour emergency drop-in availability.15 One institution reported success with the development of a departmentally funded childcare supplementation stipend offered to residents to support daycare costs during the first 6 months of a baby’s life.16
Final Thoughts
Due to the competitiveness of the field, dermatology residents are by nature high performing and academically successful. For a high achiever, the idea of potentially disappointing faculty and colleagues by starting a family during residency can be guilt inducing. Concerns about one’s ability to adequately study the breadth of dermatology while simultaneously raising a child can be distressing; however, there are many ways in which motherhood can hone skills to become a better dermatology resident. Through motherhood one can enhance time management skills, increase efficiency, and improve rapport with pediatric patients and trust with their parents/guardians. A dermatology resident may be her own harshest critic, but it is time that the future generation of dermatologists become their own greatest advocates for establishing supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of motherhood and dermatology residency.
Motherhood and dermatology residency are both full-time jobs. The thought that a woman must either be superhuman to succeed at both or that success at one must come at the expense of the other is antiquated. With careful navigation and sufficient support, these two roles can complement and heighten one another. The most recent Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) report showed that nearly 60% of dermatology residents are women,1 with most women in training being of childbearing age. One study showed that female dermatologists were most likely to have children during residency (51% of those surveyed), despite residents reporting more barriers to childbearing at this career stage.2 Trainees thinking of starting a family have many considerations to navigate: timing of pregnancy, maternity leave scheduling, breastfeeding while working, and planning for childcare. For the first time in the history of the specialty, most active dermatologists in practice are women.3 Thus, the future of dermatology requires supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of these issues by today’s trainees.
Timing of Pregnancy
Timing of pregnancy can be a source of stress to the female dermatology resident. Barriers to childbearing during residency include the perception that women who have children during residency training are less committed to their jobs; concerns of overburdening fellow residents; and fear that residency may need to be extended, thereby delaying the ability to sit for the board examination.2 However, the potential increased risk for infertility in delaying pregnancy adds to the stress of pregnancy planning. A 2016 survey of female physicians (N=327) showed that 24.1% of respondents who had attempted conception were diagnosed with infertility, with an average age at diagnosis of 33.7 years.4 This is higher than the national average, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reporting that approximately 19% of women aged 15 to 49 years with no prior births experience infertility.5 In a 1992 survey of female physician residents (N=373) who gave birth during residency, 32% indicated that they would not recommend the experience to others; of the 68% who would recommend the experience, one-third encouraged timing delivery to occur in the last 2 months of residency due to benefits of continued insurance coverage, a decrease in clinic responsibilities, and the potential for extended maternity leave during hiatus between jobs.6 Although this may be a good strategy, studying and sitting for board examinations while caring for a newborn right after graduation may be overly difficult for some. The first year of residency was perceived as the most stressful time to be pregnant, with each subsequent year being less problematic.6 Planning pregnancy for delivery near the end of the second year and beginning of the third year of dermatology residency may be a reasonable choice.
Maternity Leave
The Family and Medical Leave Act entitles eligible employees of covered employers to take unpaid, job-protected leave, with 12 workweeks of leave in a 12-month period for the birth of a child and to care for the newborn child within 1 year of birth.7 The actual length of maternity leave taken by most surveyed female dermatologists (n=96) is shorter: 25% (24/96) took less than 4 weeks, 42.7% (41/96) took 4 to 8 weeks, 25% (24/96) took 9 to 12 weeks, and 7.3% (7/96) were able to take more than 12 weeks of maternity leave.2
The American Board of Dermatology implemented a new Resident Leave policy that went into effect July 1, 2021, stipulating that, within certain parameters, time spent away from training for family and parental leave would not exhaust vacation time or require an extension in training. Under this policy, absence from training exceeding 8 weeks (6 weeks leave, plus 2 weeks of vacation) in a given year should be approved only under exceptional circumstances and may necessitate additional training time to ensure that competency requirements are met.8 Although this policy is a step in the right direction, institutional policies still may vary. Dermatology residents planning to start a family during training should consider their plans for fellowship, as taking an extended maternity leave beyond 8 weeks may jeopardize a July fellowship start date.
Lactation and Residency
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends exclusive breastfeeding for approximately 6 months, with continuation of breastfeeding for 1 year or longer as mutually desired by the mother and infant.9 Successful lactation and achieving breastfeeding goals can be difficult during medical training. A national cross-sectional survey of female residents (N=312) showed that the median total time of breastfeeding and pumping was 9 months, with 74% continuing after 6 months and 13% continuing past 12 months. Of those surveyed, 73% reported residency limited their ability to lactate, and 37% stopped prior to their desired goal.10 As of July 1, 2020, the ACGME requires that residency programs and sponsoring institutions provide clean and private facilities for lactation that have refrigeration capabilities, with proximity appropriate for safe patient care.11 There has been a call to dermatology program leadership to support breastfeeding residents by providing sufficient time and space to pump; a breastfeeding resident will need a 20- to 30-minute break to express milk approximately every 3 hours during the work day.12 One innovative initiative to meet the ACGME lactation requirement reported by the Kansas University Medical Center Graduate Medical Education program (Kansas City, Kansas) was the purchase of wearable breast pumps to loan to residents. The benefits of wearable breast pumps are that they are discreet and can allow mothers to express milk inconspicuously while working, can increase milk supply, require less set up and expression time than traditional pumps, and can allow the mother to manage time more efficiently.13 Breastfeeding plans and goals should be discussed with program leadership before return from leave to strategize and anticipate gaps in clinic scheduling to accommodate the lactating resident.
Planning for Childcare
Resident hours can be long and erratic, making choices for childcare difficult. In one survey of female residents, 61% of married or partnered respondents (n=447) were delaying childbearing, and 46% cited lack of access to childcare as a reason.14 Not all dermatology residents are fortunate enough to match to a program near family, but close family support can be an undeniable asset during childrearing and should be weighed heavily when ranking programs. Options for childcare include relying on a stay-at-home spouse or other family member, a live-in or live-out nanny, part-time babysitters, and daycare. It is crucial to have multiple layers and back-up options for childcare available at any given time when working as a resident. Even with a child enrolled in a full-time daycare and a live-in nanny, a daycare closure due to a COVID-19 exposure or sudden medical emergency in the nanny can still leave unpredicted holes in your childcare plan, leaving the resident to potentially miss work to fill the gap. A survey of residents at one institution showed that the most common backup childcare plan for situations in which either the child or the regular caregiver is ill is for the nontrainee parent or spouse to stay home (45%; n=101), with 25% of respondents staying home to care for a sick child themselves, which clearly has an impact on the hospital. The article proposed implementation of on-site or near-site childcare for residents with extended hours or a 24-hour emergency drop-in availability.15 One institution reported success with the development of a departmentally funded childcare supplementation stipend offered to residents to support daycare costs during the first 6 months of a baby’s life.16
Final Thoughts
Due to the competitiveness of the field, dermatology residents are by nature high performing and academically successful. For a high achiever, the idea of potentially disappointing faculty and colleagues by starting a family during residency can be guilt inducing. Concerns about one’s ability to adequately study the breadth of dermatology while simultaneously raising a child can be distressing; however, there are many ways in which motherhood can hone skills to become a better dermatology resident. Through motherhood one can enhance time management skills, increase efficiency, and improve rapport with pediatric patients and trust with their parents/guardians. A dermatology resident may be her own harshest critic, but it is time that the future generation of dermatologists become their own greatest advocates for establishing supportive policies and resources for the successful navigation of motherhood and dermatology residency.
- ACGME residents and fellows by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/interactive-data/acgme-residents-and-fellows-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Mattessich S, Shea K, Whitaker-Worth D. Parenting and female dermatologists’ perceptions of work-life balance. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:127-130. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.04.001
- Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/interactive-data/active-physicians-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Stentz NC, Griffith KA, Perkins E, et al. Fertility and childbearing among American female physicians. J Womens Health. 2016;25:1059-1065. doi:10.1089/jwh.2015.5638
- Infertility. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated March 1, 2022. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Phelan ST. Sources of stress and support for the pregnant resident. Acad Med. 1992;67:408-410. doi:10.1097/00001888-199206000-00014
- Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla
- American Board of Dermatology. Effective July 2021: new family leave policy. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.abderm.org/public/announcements/effective-july-2021-new-family-leave-policy.aspx
- Eidelman AI, Schanler RJ, Johnston M, et al. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E827-E841. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3552
- Peters GW, Kuczmarska-Haas A, Holliday EB, et al. Lactation challenges of resident physicians: results of a national survey. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:762. doi:10.1186/s12884-020-03436-3
- Common program requirements (residency) sections I-V table of implementation dates. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/CPRResidencyImplementationTable.pdf
- Gracey LE, Mathes EF, Shinkai K. Supporting breastfeeding mothers during dermatology residency—challenges and best practices. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:117-118. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3759
- McMillin A, Behravesh B, Byrne P, et al. A GME wearable breast pump program: an innovative method to meet ACGME requirements and federal law. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13:422-423. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-20-01275.1
- Stack SW, Jagsi R, Biermann JS, et al. Childbearing decisions in residency: a multicenter survey of female residents. Acad Med. 2020;95:1550-1557. doi:10.1097/acm.0000000000003549
- Snyder RA, Tarpley MJ, Phillips SE, et al. The case for on-site child care in residency training and afterward. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5:365-367. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-12-00294.1
- Key LL. Child care supplementation: aid for residents and advantages for residency programs. J Pediatr. 2008;153:449-450. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.05.028
- ACGME residents and fellows by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/interactive-data/acgme-residents-and-fellows-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Mattessich S, Shea K, Whitaker-Worth D. Parenting and female dermatologists’ perceptions of work-life balance. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2017;3:127-130. doi:10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.04.001
- Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2019. Association of American Medical Colleges website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/interactive-data/active-physicians-sex-and-specialty-2019
- Stentz NC, Griffith KA, Perkins E, et al. Fertility and childbearing among American female physicians. J Womens Health. 2016;25:1059-1065. doi:10.1089/jwh.2015.5638
- Infertility. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Updated March 1, 2022. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/infertility/
- Phelan ST. Sources of stress and support for the pregnant resident. Acad Med. 1992;67:408-410. doi:10.1097/00001888-199206000-00014
- Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla
- American Board of Dermatology. Effective July 2021: new family leave policy. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.abderm.org/public/announcements/effective-july-2021-new-family-leave-policy.aspx
- Eidelman AI, Schanler RJ, Johnston M, et al. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129:E827-E841. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3552
- Peters GW, Kuczmarska-Haas A, Holliday EB, et al. Lactation challenges of resident physicians: results of a national survey. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20:762. doi:10.1186/s12884-020-03436-3
- Common program requirements (residency) sections I-V table of implementation dates. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education website. Accessed April 21, 2022. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/CPRResidencyImplementationTable.pdf
- Gracey LE, Mathes EF, Shinkai K. Supporting breastfeeding mothers during dermatology residency—challenges and best practices. JAMA Dermatol. 2020;156:117-118. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.3759
- McMillin A, Behravesh B, Byrne P, et al. A GME wearable breast pump program: an innovative method to meet ACGME requirements and federal law. J Grad Med Educ. 2021;13:422-423. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-20-01275.1
- Stack SW, Jagsi R, Biermann JS, et al. Childbearing decisions in residency: a multicenter survey of female residents. Acad Med. 2020;95:1550-1557. doi:10.1097/acm.0000000000003549
- Snyder RA, Tarpley MJ, Phillips SE, et al. The case for on-site child care in residency training and afterward. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5:365-367. doi:10.4300/jgme-d-12-00294.1
- Key LL. Child care supplementation: aid for residents and advantages for residency programs. J Pediatr. 2008;153:449-450. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2008.05.028
Resident Pearl
- Female dermatology residents seeking motherhood during training have many obstacles to navigate, including the timing of pregnancy, maternity leave scheduling, planning for breastfeeding while working, and arranging for childcare. With supportive policies and resources, motherhood and dermatology training can be rewarding complements to one another.
Commentary: Immunotherapy Improves Outcomes in Hepatocellular Cancer, June 2022
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Commentary: Immunotherapy Improves Outcomes in Hepatocellular Cancer, June 2022
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Verset and colleagues reported results from cohort 2 of the phase 2 KEYNOTE-224 trial, which investigated first-line pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable HCC. Fifty-one patients were included in cohort 2. The overall response rate (ORR) was 16% [95% CI 7-29] and was similar across key subgroups. Median duration of response was 16 months (range 3-24+), and disease control rate was 57%. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4 months (95% CI 2-8), and median time to progression was 4 months (95% CI 3-9). Median overall survival (OS) was 17 months (95% CI 8-23). Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 16% of patients. The authors concluded that pembrolizumab is an effective treatment for patients with unresectable HCC and should be studied further in this setting.
Immunotherapy combinations are frequently used in the first-line setting for patients with unresectable HCC. In the past, many patients received immunotherapy in the second- or third-line settings. Sharma and coworkers reported patient outcomes following immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI). This retrospective, multicenter study examined anticancer treatment received after ICI treatment and assessed the impact of systemic treatment on post-ICI survival. A total of 420 patients with HCC were included. Most patients (n = 371; 88.3%) had received at least one prior treatment for HCC before ICI, including at least one line of systemic therapy (n = 289; 68.8%), with most receiving sorafenib (n = 237; 56.4%). Following immunotherapy, 31 (8.8%) died, 152 (36.2%) received best supportive care, and 163 patients (38.8%) received subsequent anticancer therapy. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI; n = 132; 80.9%), mostly sorafenib (n = 49; 30.0%), were the most common post-ICI therapy, followed by external beam radiotherapy (n = 28; 17.2%), further immunotherapy (n = 21; 12.9%), locoregional therapy (n = 23; 14.1%), chemotherapy (n = 9; 5.5%), and surgery (n = 6; 3.6%). Post-ICI therapy was associated with longer median OS compared with best supportive care (12.1 vs 3.3 months; hazard ratio [HR] 0.4; 95% CI 2.7-5.0). No difference in OS was noted if TKI were administered before or after ICI. The authors concluded that post-ICI therapy is associated with OS greater than 12 months, suggesting a role for therapeutic sequencing. OS from TKI therapy was similar to that reported in registration studies, suggesting preserved efficacy following ICI.
Finally, Ahn and colleagues looked at racial disparities in patients with HCC. In this report, 3248 (81.4%) patients received chemotherapy and 742 (18.6%) patients received immunotherapy as a first-line treatment. Immunotherapy was associated with improved OS compared with chemotherapy (adjusted HR 0.76; 95% CI 0.65-0.88). There were racial and ethnic disparities in access to immunotherapy, with Hispanic (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 0.63; 95% CI 0.46-0.83) and Black (aOR 0.71; 95% CI 0.54-0.89) patients less likely to receive immunotherapy compared with White patients.
Become a highly effective endoscopy teacher, from start to finish
When I first became an attending, I was struck by how difficult it was to teach endoscopy effectively. As a fellow, I saw the various teaching styles of my attendings, and it was easy to pick out the best teachers from the group. But when the roles switched, and suddenly I was the supervising faculty member, it was hard to recall exactly what those teachers were doing to create an optimal learning environment in the endoscopy suite. Not only did I lack a framework on how to teach endoscopy, I also was still building confidence in my own endoscopic skills while feeling the pressure to keep my room running on time. All in all, although I loved the opportunity to teach, I found the experience to be quite stressful.
Hoping to find some guidance, I turned to the literature and was fortunate to find some great pieces on how to teach endoscopy effectively. I learned of cognitive load theory – the idea that short-term or “working memory” can manage only a few pieces of information at a time – and how excess feedback or other external distractions (e.g., pagers) during a procedure can overwhelm a learner and lead to declining performance.1 I also read about the pursuit of “conscious competence,” where an endoscopist can verbalize the steps of a maneuver so that a trainee can remain on the scope and maximize hands-on participation.2
Motivated to bring these key concepts together in an evidence-based framework, I helped lead a Delphi study of GI fellowship program directors and endoscopy education experts to reach consensus on the best practices of teaching endoscopy.3 After two rounds of surveys, the participants identified 10 essential endoscopy teaching practices, which I will summarize in the next sections. What I found most helpful was how these practices were distributed throughout the endoscopy learning experience. By breaking down the complicated task of teaching endoscopy to three discrete parts – prior to the procedure, during the procedure, and after the procedure – I now had a framework to take back to the endoscopy suite.
Prior to the procedure
With a busy endoscopy schedule and increasing clinical demands, it is tempting to use the time between cases to complete documentation, address patient messages, and review emails. While this is great for efficiency, make sure to also reserve time to set the stage for your fellow. One of the key practices during this phase is to assess your fellow’s current procedural competency. I start open-ended by asking my fellows how they have been doing with colonoscopy and then ask if they are working on a specific skill. With this information, I have a sense of how much hands-on assistance they will need, what realistic goals to set for them (e.g., navigate out of the sigmoid colon for an early learner vs. efficiently and independently completing the entire case for a later learner), and the areas to focus my observation to provide feedback after the procedure.
During this preparatory time, faculty should also discuss the patient history and indications for the procedure. Reviewing information such as prior sedation requirements and confirming plans for the procedure (e.g., random colon biopsies in a patient with chronic diarrhea and concern for microscopic colitis) helps ensure a proper plan is in place for the patient while also presenting opportunities for learning. Faculty can take this time to review the steps of a more complicated procedure (e.g., PEG placement) and establish ground rules such as when the attending will take the scope from the trainee. Lastly, make sure that the patient understands the role of the fellow and the supervision you will be providing throughout the case.
During the procedure
Once the procedure starts, your most important task is to maintain attention throughout the case – if you do, the other best practices generally fall into place. I am most attentive when I am gowned and positioned next to the fellow. From this vantage point, I can see the patient, the fellow’s hands, and the endoscopy screen, which allows me to readily assist if needed while directly observing the fellow’s performance.
If I need to provide feedback in the moment, I often ask the fellows to pause what they are doing and first listen to my feedback. Taking this “timeout” helps manage their cognitive load such that they can actually hear the feedback. As a general rule, however, I try to reserve the bulk of my feedback for when the procedure is complete (see next section). Another way to manage your fellow’s cognitive load is by using standardized endoscopic language throughout the procedure. For example, rather than say “go to the left” during a colonoscopy, try saying “tip left” or “torque counterclockwise” to provide more clear instructions to the fellow. Holding your fellow’s pager during the procedure is a kind gesture that also helps minimize extraneous cognitive load so that the fellow can focus on the procedure.
If your fellows get to a point where they cannot complete the task despite your giving appropriate feedback, or if patient safety concerns arise, then it is time for you to take hands-on control of the scope. In my experience, most fellows welcome the hands-on assistance as they are overloaded by the difficulty of the procedure. Setting this expectation ahead of time, as noted above, makes for a smoother transition. While assuming control of the scope, try to narrate what you are doing differently so that the fellow can still learn while watching. Once you complete the difficult portion of the procedure (e.g., reducing a loop to reach the cecum), return the scope to the fellow to maximize the hands-on participation (if time permits).
After the procedure
In the third and final stage of the endoscopy teaching experience, faculty should take the time to confirm the findings of the procedure with the fellow and discuss next steps in management for the patient. Finding these teachable moments helps solidify the cognitive learning for the fellow while also ensuring the patient receives the appropriate postprocedure recommendations. As part of this process, make sure to review the procedure note drafted by the fellow, and if you need to make any substantive edits, review the changes with the fellow so that he or she can learn for future cases.
To wrap up the session, provide feedback to the fellow on performance based on your direct observation. Make sure to name this process aloud – “Let’s do some feedback” – and start by asking how the fellow felt about the performance, both in terms of what went well and what the fellow would like to improve. Then provide your feedback on the performance and be specific, such as, “I really like how you identified a loop and then reduced around the hepatic flexure.” Conclude by having the fellow set a plan for improvement and make sure to ask for feedback on your own teaching performance.
In conclusion, teaching endoscopy is hard – especially as a junior attending. By breaking down the endoscopy teaching experience into its three components, however, and committing to teaching from start to finish, you can provide high-quality endoscopy education to your fellows while ensuring the best care for your patients.
Dr. Kumar is associate medicine clerkship director at Harvard Medical School, and associate physician in the division of gastroenterology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest. He is on Twitter @NavinKumarMD.
References
1. Dilly CK and Sewell JL. 2017 Sep;153(3):632-36.
2. Waschke KA et al. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun;30(3):409-19.
3. Kumar NL et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar;18(3):574-79.
When I first became an attending, I was struck by how difficult it was to teach endoscopy effectively. As a fellow, I saw the various teaching styles of my attendings, and it was easy to pick out the best teachers from the group. But when the roles switched, and suddenly I was the supervising faculty member, it was hard to recall exactly what those teachers were doing to create an optimal learning environment in the endoscopy suite. Not only did I lack a framework on how to teach endoscopy, I also was still building confidence in my own endoscopic skills while feeling the pressure to keep my room running on time. All in all, although I loved the opportunity to teach, I found the experience to be quite stressful.
Hoping to find some guidance, I turned to the literature and was fortunate to find some great pieces on how to teach endoscopy effectively. I learned of cognitive load theory – the idea that short-term or “working memory” can manage only a few pieces of information at a time – and how excess feedback or other external distractions (e.g., pagers) during a procedure can overwhelm a learner and lead to declining performance.1 I also read about the pursuit of “conscious competence,” where an endoscopist can verbalize the steps of a maneuver so that a trainee can remain on the scope and maximize hands-on participation.2
Motivated to bring these key concepts together in an evidence-based framework, I helped lead a Delphi study of GI fellowship program directors and endoscopy education experts to reach consensus on the best practices of teaching endoscopy.3 After two rounds of surveys, the participants identified 10 essential endoscopy teaching practices, which I will summarize in the next sections. What I found most helpful was how these practices were distributed throughout the endoscopy learning experience. By breaking down the complicated task of teaching endoscopy to three discrete parts – prior to the procedure, during the procedure, and after the procedure – I now had a framework to take back to the endoscopy suite.
Prior to the procedure
With a busy endoscopy schedule and increasing clinical demands, it is tempting to use the time between cases to complete documentation, address patient messages, and review emails. While this is great for efficiency, make sure to also reserve time to set the stage for your fellow. One of the key practices during this phase is to assess your fellow’s current procedural competency. I start open-ended by asking my fellows how they have been doing with colonoscopy and then ask if they are working on a specific skill. With this information, I have a sense of how much hands-on assistance they will need, what realistic goals to set for them (e.g., navigate out of the sigmoid colon for an early learner vs. efficiently and independently completing the entire case for a later learner), and the areas to focus my observation to provide feedback after the procedure.
During this preparatory time, faculty should also discuss the patient history and indications for the procedure. Reviewing information such as prior sedation requirements and confirming plans for the procedure (e.g., random colon biopsies in a patient with chronic diarrhea and concern for microscopic colitis) helps ensure a proper plan is in place for the patient while also presenting opportunities for learning. Faculty can take this time to review the steps of a more complicated procedure (e.g., PEG placement) and establish ground rules such as when the attending will take the scope from the trainee. Lastly, make sure that the patient understands the role of the fellow and the supervision you will be providing throughout the case.
During the procedure
Once the procedure starts, your most important task is to maintain attention throughout the case – if you do, the other best practices generally fall into place. I am most attentive when I am gowned and positioned next to the fellow. From this vantage point, I can see the patient, the fellow’s hands, and the endoscopy screen, which allows me to readily assist if needed while directly observing the fellow’s performance.
If I need to provide feedback in the moment, I often ask the fellows to pause what they are doing and first listen to my feedback. Taking this “timeout” helps manage their cognitive load such that they can actually hear the feedback. As a general rule, however, I try to reserve the bulk of my feedback for when the procedure is complete (see next section). Another way to manage your fellow’s cognitive load is by using standardized endoscopic language throughout the procedure. For example, rather than say “go to the left” during a colonoscopy, try saying “tip left” or “torque counterclockwise” to provide more clear instructions to the fellow. Holding your fellow’s pager during the procedure is a kind gesture that also helps minimize extraneous cognitive load so that the fellow can focus on the procedure.
If your fellows get to a point where they cannot complete the task despite your giving appropriate feedback, or if patient safety concerns arise, then it is time for you to take hands-on control of the scope. In my experience, most fellows welcome the hands-on assistance as they are overloaded by the difficulty of the procedure. Setting this expectation ahead of time, as noted above, makes for a smoother transition. While assuming control of the scope, try to narrate what you are doing differently so that the fellow can still learn while watching. Once you complete the difficult portion of the procedure (e.g., reducing a loop to reach the cecum), return the scope to the fellow to maximize the hands-on participation (if time permits).
After the procedure
In the third and final stage of the endoscopy teaching experience, faculty should take the time to confirm the findings of the procedure with the fellow and discuss next steps in management for the patient. Finding these teachable moments helps solidify the cognitive learning for the fellow while also ensuring the patient receives the appropriate postprocedure recommendations. As part of this process, make sure to review the procedure note drafted by the fellow, and if you need to make any substantive edits, review the changes with the fellow so that he or she can learn for future cases.
To wrap up the session, provide feedback to the fellow on performance based on your direct observation. Make sure to name this process aloud – “Let’s do some feedback” – and start by asking how the fellow felt about the performance, both in terms of what went well and what the fellow would like to improve. Then provide your feedback on the performance and be specific, such as, “I really like how you identified a loop and then reduced around the hepatic flexure.” Conclude by having the fellow set a plan for improvement and make sure to ask for feedback on your own teaching performance.
In conclusion, teaching endoscopy is hard – especially as a junior attending. By breaking down the endoscopy teaching experience into its three components, however, and committing to teaching from start to finish, you can provide high-quality endoscopy education to your fellows while ensuring the best care for your patients.
Dr. Kumar is associate medicine clerkship director at Harvard Medical School, and associate physician in the division of gastroenterology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest. He is on Twitter @NavinKumarMD.
References
1. Dilly CK and Sewell JL. 2017 Sep;153(3):632-36.
2. Waschke KA et al. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun;30(3):409-19.
3. Kumar NL et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar;18(3):574-79.
When I first became an attending, I was struck by how difficult it was to teach endoscopy effectively. As a fellow, I saw the various teaching styles of my attendings, and it was easy to pick out the best teachers from the group. But when the roles switched, and suddenly I was the supervising faculty member, it was hard to recall exactly what those teachers were doing to create an optimal learning environment in the endoscopy suite. Not only did I lack a framework on how to teach endoscopy, I also was still building confidence in my own endoscopic skills while feeling the pressure to keep my room running on time. All in all, although I loved the opportunity to teach, I found the experience to be quite stressful.
Hoping to find some guidance, I turned to the literature and was fortunate to find some great pieces on how to teach endoscopy effectively. I learned of cognitive load theory – the idea that short-term or “working memory” can manage only a few pieces of information at a time – and how excess feedback or other external distractions (e.g., pagers) during a procedure can overwhelm a learner and lead to declining performance.1 I also read about the pursuit of “conscious competence,” where an endoscopist can verbalize the steps of a maneuver so that a trainee can remain on the scope and maximize hands-on participation.2
Motivated to bring these key concepts together in an evidence-based framework, I helped lead a Delphi study of GI fellowship program directors and endoscopy education experts to reach consensus on the best practices of teaching endoscopy.3 After two rounds of surveys, the participants identified 10 essential endoscopy teaching practices, which I will summarize in the next sections. What I found most helpful was how these practices were distributed throughout the endoscopy learning experience. By breaking down the complicated task of teaching endoscopy to three discrete parts – prior to the procedure, during the procedure, and after the procedure – I now had a framework to take back to the endoscopy suite.
Prior to the procedure
With a busy endoscopy schedule and increasing clinical demands, it is tempting to use the time between cases to complete documentation, address patient messages, and review emails. While this is great for efficiency, make sure to also reserve time to set the stage for your fellow. One of the key practices during this phase is to assess your fellow’s current procedural competency. I start open-ended by asking my fellows how they have been doing with colonoscopy and then ask if they are working on a specific skill. With this information, I have a sense of how much hands-on assistance they will need, what realistic goals to set for them (e.g., navigate out of the sigmoid colon for an early learner vs. efficiently and independently completing the entire case for a later learner), and the areas to focus my observation to provide feedback after the procedure.
During this preparatory time, faculty should also discuss the patient history and indications for the procedure. Reviewing information such as prior sedation requirements and confirming plans for the procedure (e.g., random colon biopsies in a patient with chronic diarrhea and concern for microscopic colitis) helps ensure a proper plan is in place for the patient while also presenting opportunities for learning. Faculty can take this time to review the steps of a more complicated procedure (e.g., PEG placement) and establish ground rules such as when the attending will take the scope from the trainee. Lastly, make sure that the patient understands the role of the fellow and the supervision you will be providing throughout the case.
During the procedure
Once the procedure starts, your most important task is to maintain attention throughout the case – if you do, the other best practices generally fall into place. I am most attentive when I am gowned and positioned next to the fellow. From this vantage point, I can see the patient, the fellow’s hands, and the endoscopy screen, which allows me to readily assist if needed while directly observing the fellow’s performance.
If I need to provide feedback in the moment, I often ask the fellows to pause what they are doing and first listen to my feedback. Taking this “timeout” helps manage their cognitive load such that they can actually hear the feedback. As a general rule, however, I try to reserve the bulk of my feedback for when the procedure is complete (see next section). Another way to manage your fellow’s cognitive load is by using standardized endoscopic language throughout the procedure. For example, rather than say “go to the left” during a colonoscopy, try saying “tip left” or “torque counterclockwise” to provide more clear instructions to the fellow. Holding your fellow’s pager during the procedure is a kind gesture that also helps minimize extraneous cognitive load so that the fellow can focus on the procedure.
If your fellows get to a point where they cannot complete the task despite your giving appropriate feedback, or if patient safety concerns arise, then it is time for you to take hands-on control of the scope. In my experience, most fellows welcome the hands-on assistance as they are overloaded by the difficulty of the procedure. Setting this expectation ahead of time, as noted above, makes for a smoother transition. While assuming control of the scope, try to narrate what you are doing differently so that the fellow can still learn while watching. Once you complete the difficult portion of the procedure (e.g., reducing a loop to reach the cecum), return the scope to the fellow to maximize the hands-on participation (if time permits).
After the procedure
In the third and final stage of the endoscopy teaching experience, faculty should take the time to confirm the findings of the procedure with the fellow and discuss next steps in management for the patient. Finding these teachable moments helps solidify the cognitive learning for the fellow while also ensuring the patient receives the appropriate postprocedure recommendations. As part of this process, make sure to review the procedure note drafted by the fellow, and if you need to make any substantive edits, review the changes with the fellow so that he or she can learn for future cases.
To wrap up the session, provide feedback to the fellow on performance based on your direct observation. Make sure to name this process aloud – “Let’s do some feedback” – and start by asking how the fellow felt about the performance, both in terms of what went well and what the fellow would like to improve. Then provide your feedback on the performance and be specific, such as, “I really like how you identified a loop and then reduced around the hepatic flexure.” Conclude by having the fellow set a plan for improvement and make sure to ask for feedback on your own teaching performance.
In conclusion, teaching endoscopy is hard – especially as a junior attending. By breaking down the endoscopy teaching experience into its three components, however, and committing to teaching from start to finish, you can provide high-quality endoscopy education to your fellows while ensuring the best care for your patients.
Dr. Kumar is associate medicine clerkship director at Harvard Medical School, and associate physician in the division of gastroenterology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest. He is on Twitter @NavinKumarMD.
References
1. Dilly CK and Sewell JL. 2017 Sep;153(3):632-36.
2. Waschke KA et al. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun;30(3):409-19.
3. Kumar NL et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar;18(3):574-79.
Lithium lowers osteoporosis risk in bipolar patients…and orthopedists take notice
NEW ORLEANS –
“Our findings emphasize that bone health should be a priority in the clinical management of bipolar disorder, and that the potential bone-protective effects of lithium should be subjected to further study – both in the context of osteoporosis and bipolar disorder,” said Soren D. Ostergaard, MD, PhD, the study’s first author and a professor in the psychosis research unit, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital – Psychiatry.
For the retrospective cohort study, presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, and also published recently in JAMA Psychiatry, the authors reviewed data on 22,912 patients treated for bipolar disorder in Denmark between 1996 and 2019, and compared each patient with 5 age- and sex-matched controls, amounting to 114,560 individuals in the general population.
Of the patients with bipolar disorder, 38.2% were treated with lithium, while 73.6% received an antipsychotic drug; 16.8% received valproate and 33.1% received lamotrigine.
With a median follow-up of 7.7 years, the incidence of osteoporosis per 1,000 person-years was 8.70 among patients with bipolar disorder, compared with an incidence of 7.84 among controls, (hazard rate ratio, 1.15).
The association of bipolar disorder with osteoporosis was notably more pronounced among males (HRR, 1.42) compared with females (HRR, 1.07).
Notably, those with bipolar disorder treated with lithium showed a significantly reduced risk of osteoporosis compared with patients not receiving lithium (HRR, 0.62), after adjustment for factors including age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, use of systemic corticosteroids, use of sedative medication, and eating disorder diagnosis. No similar reductions in osteoporosis risk were observed among those treated with antipsychotics, valproate or lamotrigine.
Of note, the reduced risk of osteoporosis with lithium appeared after about year 2 of treatment (HR, 0.77) and remained steady at more than 4 years (HR, 0.76). A higher cumulative lithium dose was meanwhile associated with a greater decrease in the risk of osteoporosis (P < .001).
Results confirm prior research
The results are consistent with previous smaller studies indicating that people with bipolar disorders shown an increased risk of low bone density, osteopenia, and even fracture.
The higher risk of osteoporosis in bipolar disorder may be explained by lifestyle factors, Dr. Ostergaard noted in an interview.
“It could be the depressive and manic phases in bipolar disorder, but generally speaking, both phases can lead to an unhealthy lifestyle and that’s likely what drives the association between bipolar disorder and osteoporosis,” he said. “Increases in behaviors such as smoking and alcohol consumption may be factors as well. Similar findings are seen with depression.”
While more needs to be understood, Dr. Ostergaard speculated that higher rates of such behaviors in men with bipolar disorder may explain the higher osteoporosis risk observed in men.
In general, however, the increased risk underscores the importance of raising awareness of bone health among patients with bipolar disorder, the authors concluded.
“Specifically, guiding patients toward a lifestyle supporting bone health (no smoking, reduced alcohol consumption, healthy diet, and exercising) and monitoring bone density via dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scans among those with additional risk factors seems warranted,” they wrote.
The implications of the lithium findings are trickier to determine, Dr. Ostergaard said.
“The evidence for lithium in bipolar disorder are well established, and our findings don’t really add to that,” he said. “The main thing is it suggests there might be some advantages of lithium that we’re not really aware of.”
Findings important for orthopedists
The unique properties observed with lithium have caught the attention of some in orthopedics, and researchers with the University of Toronto – having found intriguing bone healing with lithium in preclinical rodent studies – are currently conducting a first-of-its-kind multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial evaluating the potential effects of lithium in the healing of bone fractures.
Diane Nam, MD, of the division of orthopedic surgery, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, and lead investigator on the study, said in an interview that “I’m not surprised by [Dr. Ostergaard’s] paper because it’s consistent with what we have observed about the positive effects on bone healing.”
Dr. Nam and associates have already established administration parameters for their clinical study, determining that optimal effects in fracture healing appear to require that lithium treatment not begin at the time of fracture, but 2 weeks afterward, when new bone is ready to be laid down at the fracture site. In their trial, low daily doses of lithium (at 300 mg) are given only for a duration of 2 weeks.
“While our current trial is intended for a healthy, nonosteoporotic adult population, we have also demonstrated in our preclinical studies that lithium is just as effective in improving fracture healing in an osteoporotic model when the timing of administration is slightly delayed,” she said. “How this is relevant and translatable in patients with bipolar disorder requires further study.”
Dr. Nam said her research team thinks that “not only will the fracture heal faster, but it will heal reliably as delayed or impaired fracture healing remains a significant orthopedic problem.”
While details are not yet available, a preliminary analysis has shown results “going in a positive direction,” enough for the team to be granted funding for the multicenter trial.
Dr. Ostergaard and Dr. Nam reported no disclosures or conflicts.
NEW ORLEANS –
“Our findings emphasize that bone health should be a priority in the clinical management of bipolar disorder, and that the potential bone-protective effects of lithium should be subjected to further study – both in the context of osteoporosis and bipolar disorder,” said Soren D. Ostergaard, MD, PhD, the study’s first author and a professor in the psychosis research unit, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital – Psychiatry.
For the retrospective cohort study, presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, and also published recently in JAMA Psychiatry, the authors reviewed data on 22,912 patients treated for bipolar disorder in Denmark between 1996 and 2019, and compared each patient with 5 age- and sex-matched controls, amounting to 114,560 individuals in the general population.
Of the patients with bipolar disorder, 38.2% were treated with lithium, while 73.6% received an antipsychotic drug; 16.8% received valproate and 33.1% received lamotrigine.
With a median follow-up of 7.7 years, the incidence of osteoporosis per 1,000 person-years was 8.70 among patients with bipolar disorder, compared with an incidence of 7.84 among controls, (hazard rate ratio, 1.15).
The association of bipolar disorder with osteoporosis was notably more pronounced among males (HRR, 1.42) compared with females (HRR, 1.07).
Notably, those with bipolar disorder treated with lithium showed a significantly reduced risk of osteoporosis compared with patients not receiving lithium (HRR, 0.62), after adjustment for factors including age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, use of systemic corticosteroids, use of sedative medication, and eating disorder diagnosis. No similar reductions in osteoporosis risk were observed among those treated with antipsychotics, valproate or lamotrigine.
Of note, the reduced risk of osteoporosis with lithium appeared after about year 2 of treatment (HR, 0.77) and remained steady at more than 4 years (HR, 0.76). A higher cumulative lithium dose was meanwhile associated with a greater decrease in the risk of osteoporosis (P < .001).
Results confirm prior research
The results are consistent with previous smaller studies indicating that people with bipolar disorders shown an increased risk of low bone density, osteopenia, and even fracture.
The higher risk of osteoporosis in bipolar disorder may be explained by lifestyle factors, Dr. Ostergaard noted in an interview.
“It could be the depressive and manic phases in bipolar disorder, but generally speaking, both phases can lead to an unhealthy lifestyle and that’s likely what drives the association between bipolar disorder and osteoporosis,” he said. “Increases in behaviors such as smoking and alcohol consumption may be factors as well. Similar findings are seen with depression.”
While more needs to be understood, Dr. Ostergaard speculated that higher rates of such behaviors in men with bipolar disorder may explain the higher osteoporosis risk observed in men.
In general, however, the increased risk underscores the importance of raising awareness of bone health among patients with bipolar disorder, the authors concluded.
“Specifically, guiding patients toward a lifestyle supporting bone health (no smoking, reduced alcohol consumption, healthy diet, and exercising) and monitoring bone density via dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scans among those with additional risk factors seems warranted,” they wrote.
The implications of the lithium findings are trickier to determine, Dr. Ostergaard said.
“The evidence for lithium in bipolar disorder are well established, and our findings don’t really add to that,” he said. “The main thing is it suggests there might be some advantages of lithium that we’re not really aware of.”
Findings important for orthopedists
The unique properties observed with lithium have caught the attention of some in orthopedics, and researchers with the University of Toronto – having found intriguing bone healing with lithium in preclinical rodent studies – are currently conducting a first-of-its-kind multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial evaluating the potential effects of lithium in the healing of bone fractures.
Diane Nam, MD, of the division of orthopedic surgery, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, and lead investigator on the study, said in an interview that “I’m not surprised by [Dr. Ostergaard’s] paper because it’s consistent with what we have observed about the positive effects on bone healing.”
Dr. Nam and associates have already established administration parameters for their clinical study, determining that optimal effects in fracture healing appear to require that lithium treatment not begin at the time of fracture, but 2 weeks afterward, when new bone is ready to be laid down at the fracture site. In their trial, low daily doses of lithium (at 300 mg) are given only for a duration of 2 weeks.
“While our current trial is intended for a healthy, nonosteoporotic adult population, we have also demonstrated in our preclinical studies that lithium is just as effective in improving fracture healing in an osteoporotic model when the timing of administration is slightly delayed,” she said. “How this is relevant and translatable in patients with bipolar disorder requires further study.”
Dr. Nam said her research team thinks that “not only will the fracture heal faster, but it will heal reliably as delayed or impaired fracture healing remains a significant orthopedic problem.”
While details are not yet available, a preliminary analysis has shown results “going in a positive direction,” enough for the team to be granted funding for the multicenter trial.
Dr. Ostergaard and Dr. Nam reported no disclosures or conflicts.
NEW ORLEANS –
“Our findings emphasize that bone health should be a priority in the clinical management of bipolar disorder, and that the potential bone-protective effects of lithium should be subjected to further study – both in the context of osteoporosis and bipolar disorder,” said Soren D. Ostergaard, MD, PhD, the study’s first author and a professor in the psychosis research unit, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital – Psychiatry.
For the retrospective cohort study, presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, and also published recently in JAMA Psychiatry, the authors reviewed data on 22,912 patients treated for bipolar disorder in Denmark between 1996 and 2019, and compared each patient with 5 age- and sex-matched controls, amounting to 114,560 individuals in the general population.
Of the patients with bipolar disorder, 38.2% were treated with lithium, while 73.6% received an antipsychotic drug; 16.8% received valproate and 33.1% received lamotrigine.
With a median follow-up of 7.7 years, the incidence of osteoporosis per 1,000 person-years was 8.70 among patients with bipolar disorder, compared with an incidence of 7.84 among controls, (hazard rate ratio, 1.15).
The association of bipolar disorder with osteoporosis was notably more pronounced among males (HRR, 1.42) compared with females (HRR, 1.07).
Notably, those with bipolar disorder treated with lithium showed a significantly reduced risk of osteoporosis compared with patients not receiving lithium (HRR, 0.62), after adjustment for factors including age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, use of systemic corticosteroids, use of sedative medication, and eating disorder diagnosis. No similar reductions in osteoporosis risk were observed among those treated with antipsychotics, valproate or lamotrigine.
Of note, the reduced risk of osteoporosis with lithium appeared after about year 2 of treatment (HR, 0.77) and remained steady at more than 4 years (HR, 0.76). A higher cumulative lithium dose was meanwhile associated with a greater decrease in the risk of osteoporosis (P < .001).
Results confirm prior research
The results are consistent with previous smaller studies indicating that people with bipolar disorders shown an increased risk of low bone density, osteopenia, and even fracture.
The higher risk of osteoporosis in bipolar disorder may be explained by lifestyle factors, Dr. Ostergaard noted in an interview.
“It could be the depressive and manic phases in bipolar disorder, but generally speaking, both phases can lead to an unhealthy lifestyle and that’s likely what drives the association between bipolar disorder and osteoporosis,” he said. “Increases in behaviors such as smoking and alcohol consumption may be factors as well. Similar findings are seen with depression.”
While more needs to be understood, Dr. Ostergaard speculated that higher rates of such behaviors in men with bipolar disorder may explain the higher osteoporosis risk observed in men.
In general, however, the increased risk underscores the importance of raising awareness of bone health among patients with bipolar disorder, the authors concluded.
“Specifically, guiding patients toward a lifestyle supporting bone health (no smoking, reduced alcohol consumption, healthy diet, and exercising) and monitoring bone density via dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scans among those with additional risk factors seems warranted,” they wrote.
The implications of the lithium findings are trickier to determine, Dr. Ostergaard said.
“The evidence for lithium in bipolar disorder are well established, and our findings don’t really add to that,” he said. “The main thing is it suggests there might be some advantages of lithium that we’re not really aware of.”
Findings important for orthopedists
The unique properties observed with lithium have caught the attention of some in orthopedics, and researchers with the University of Toronto – having found intriguing bone healing with lithium in preclinical rodent studies – are currently conducting a first-of-its-kind multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial evaluating the potential effects of lithium in the healing of bone fractures.
Diane Nam, MD, of the division of orthopedic surgery, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, and lead investigator on the study, said in an interview that “I’m not surprised by [Dr. Ostergaard’s] paper because it’s consistent with what we have observed about the positive effects on bone healing.”
Dr. Nam and associates have already established administration parameters for their clinical study, determining that optimal effects in fracture healing appear to require that lithium treatment not begin at the time of fracture, but 2 weeks afterward, when new bone is ready to be laid down at the fracture site. In their trial, low daily doses of lithium (at 300 mg) are given only for a duration of 2 weeks.
“While our current trial is intended for a healthy, nonosteoporotic adult population, we have also demonstrated in our preclinical studies that lithium is just as effective in improving fracture healing in an osteoporotic model when the timing of administration is slightly delayed,” she said. “How this is relevant and translatable in patients with bipolar disorder requires further study.”
Dr. Nam said her research team thinks that “not only will the fracture heal faster, but it will heal reliably as delayed or impaired fracture healing remains a significant orthopedic problem.”
While details are not yet available, a preliminary analysis has shown results “going in a positive direction,” enough for the team to be granted funding for the multicenter trial.
Dr. Ostergaard and Dr. Nam reported no disclosures or conflicts.
AT APA 2022