User login
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Left-handed cardiology trainees face unique challenges when it comes to learning how to perform common procedures, according to a new report.
About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, and rates of left-handedness among medical students and practicing physicians is believed to be similar.
“Extrapolating this to 3,017 active general cardiovascular fellowship positions and 339 interventional cardiology fellowship positions for the year 2018-2019, it is estimated there are more than 300 LH [left-handed] trainees in U.S. cardiovascular fellowship programs at any given time. Despite this, any standard clinical setting is designed to be convenient for RH [right-handed] providers, thereby creating a variable amount of impediment for LH trainees,” wrote Prashant Patel, MD, and Mandira Patel, DO, from University of California, Riverside.
“With about 10% prevalence, left-handedness is far more common, including among cardiology trainees, than most people realize. Most of the procedural set-up is designed for the right-hand majority, and it may cause a variable amount of impediment for the left-handed trainees. It is very important for the academic cardiology community to recognize this,” Dr. Prashant Patel said in an interview.
The findings were published in the Jan.5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Dr. Prashant Patel, who is left-handed, said he was prompted to look into the issue because of his own experience.
“In my first procedural rotation several years ago, I noticed that I was positioning myself somewhat differently than my attendings due to my preference for using my left hand for fine motor control,” he said. “I started looking up existing literature to see what other left-handed cardiologists have done in the past, but realized that nothing along this line was published.
“I started discussions with my colleagues and superiors and found that our small cardiology fellowship program contains about 20%-40% of left-handed trainees at any given time, and we felt it was important to elaborate on this,” he added.
Practice makes perfect, and repeated practice eventually leads to automation of motor procedures, but the learning curve may be more protracted for left-handed trainees. “Acquisition of procedural skills is a function of time and repetition. Eventually, most practicing left-handed cardiologists see that as a nonissue and do not even realize they may have gone through a differential learning curve based on their hand dominance,” Dr. Prashant Patel noted.
“South-paw” cardiology trainees face their first challenge in the examination room.
Physicians typically examine patients from the right-hand side of the bed. The majority of clinic offices are set up for the right-handed provider, with the examining table placed with the head of the bed distal from the door and the left side of the bed aligned in close proximity to the wall, leaving examination on the right side of the patient as the only option. In the hospital setting, monitors and intravenous poles are usually placed on the patient’s left-hand side of the bed.
“This practice, more than anything else, is born out of tradition. The same clinical examination can potentially be performed with the same accuracy and efficacy from the left-hand side,” said Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the echocardiography lab, some facilities perform transthoracic echocardiography from the right side of the patient, thereby requiring the operator to get the right scanning hand over and across the patient.
“This is ergonomically disadvantageous, as one has to sit on the table, reach over the patient, and twist the torso. Scanning from the left side of the patient is ergonomically superior in preventing back injuries and may be advantageous for the left-handed person as the probe is held in the dominant hand,” noted Dr. Prashant Patel.
In the cath lab, the difficulty for left-handed cardiologists starts with establishing arterial or venous access.
“The two most frequently used arterial-access sites are right radial and right femoral. Both of them pose unique challenges in terms of positioning for most left-handed trainees in the early part of their training. The right arm is kept adducted and externally rotated in a standard setup, which is difficult to access for a left-handed operator, and would require the operator to use their nondominant right hand awkwardly to gain access,” he said.
A solution could be to reposition the patient’s arm using a radial board into abduction of the arm at about 45 degrees, with external rotation.
“This creates room for the left-handed operator to stand caudal to the patient’s arm and approach the radial access site conveniently using their dominant hand,” Dr. Prashant Patel suggested.
For the femoral approach, the left-handed operator could stand left of the patient and either get left femoral access or reach out across to the right groin of the patient and obtain access in this manner, or alternatively, the operator could resort to using their right hand to gain right femoral access.
“The large size of the femoral vessels allows even the strongly left-handed operators to get accustomed to using their nondominant hand with practice. This may be preferable to switching to the left side,” he said.
There are also some advantages to being left-handed, Dr. Prashant Patel said.
This is true “especially in the cath lab, for example, establishing antegrade right femoral access for peripheral interventions,” he noted. “Having a left-handed operator can also come in handy when two operators need to simultaneously and quickly work on both groins, as is often the case in complex coronary or structural interventions. Left-handed operators are also at ease obtaining left radial access, which has been shown to have certain advantages over right radial access.”
“We hope to raise awareness among the academic cardiology community about left-handedness,” Dr. Prashant Patel added. “We hope that acknowledgment, support, and minor modifications in work flow will allow a lot of young trainees in the early part of their career to stay on course and realize their full potential in this procedural specialty.”
An insightful paper
“This paper by Dr. Prashant Patel and Dr. Mandira Patel is most insightful about the unique challenges and occasional opportunities for the left-handed cardiologist,” wrote Simon Kendall, MBBS, president of the Society for Cardiothoracic Surgery Great Britain and Ireland, London, in an accompanying response.
“As a left-handed cardiac surgeon, I am embarrassed not to have considered such significant issues for my cardiology colleagues: the edict of examining a patient from the right side, performing echocardiography with the right hand, and the complex arena of catheter laboratory that is designed around the right-handed majority. Before reading this paper, I had not appreciated that for my whole career I have had to use my less-favored right hand when inserting a balloon pump,” Dr. Kendall wrote.
“Dr. Patel and Dr. Patel have written very sensible conclusions, such as that left-handedness should be acknowledged and adapted for and the training environment has to help access the specific tips and tricks from others, as shared in cardiac surgery, for instance. They rightly describe this as not a binary phenomenon and that there is a spectrum of laterality, so that some left-handers will adapt with ease and others will need more time and patience to learn the necessary skills,” he wrote. “We are fortunate to live in an era of increasing awareness and tolerance. Left-handedness is one small example of such progress.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Liver disease associated with worse COVID-19 outcomes
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
For the latest clinical guidance, education, research and physician resources about coronavirus, visit the AGA COVID-19 Resource Center at www.gastro.org/COVID.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
RSClin: A new tool for ‘TAILOR-ing’ treatment in early breast cancer
When results of the TAILORx trial were presented at ASCO 2018, many oncologists thought it seemed too simple that a single number from a genomic assay could separate patients who would and would not benefit from adjuvant postoperative chemotherapy.
Those oncologists were right to be skeptical. Subsequent data indicated that better predictive tools were needed.
A new tool called “RSClin” may fit the bill. RSClin integrates the prognostic and predictive value of the 21-gene Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS) with the additional prognostic information conveyed by patient age, tumor grade, and tumor size.
RSClin provides individualized estimates of distant relapse risk for women with node-negative, endocrine sensitive, HER2/neu oncogene-negative early breast cancer – and a quantification of the additive freedom from distant relapse if that patient receives adjuvant chemotherapy. The tool is now available via a tab on the professional portal at https://online.genomichealth.com/.
Details on RSClin, including how the tool was developed and validated, were presented at the 2020 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium by Joseph A. Sparano, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Beyond the initial publication of TAILORx
Results from the TAILORx trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2018 offered the potential for genomic risk assessment to guide the choice of postoperative therapy for many women with the most common type of primary breast cancer. The relative risk reduction with chemotherapy increased with increasing RS result.
Subsequent analyses of the TAILORx dataset, published in The New England Journal of Medicine and JAMA Oncology in 2019, examined the added effect of parameters of clinical risk (tumor size and grade) and patient age for patients with known genomic risk.
In these analyses, clinical risk was prognostic for recurrence but did not predict the absolute magnitude of chemotherapy benefit, regardless of age. There was a trend toward chemotherapy benefit in women who were younger than 50 years of age who had RS 21-15, but it was irrespective of clinical risk.
The development of RSClin
RSClin was derived from a patient-specific meta-analysis of 10,004 women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative, node-negative breast cancer, of whom 9,427 participated in the TAILORx trial.
In TAILORx, which ran from 2006 to 2015, women with RS 0-11 received contemporary hormone therapy alone. Women with RS 12-25 were randomized to receive hormone therapy alone or with conventional combination chemotherapy. Women with RS above 26 received chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy.
The other patients in the meta-analysis participated in NSABP studies B-14 (tamoxifen versus placebo) and B-20 (tamoxifen versus chemotherapy plus tamoxifen).
Cox regression models were fit separately to each study with covariates of the continuous variables of RS result, tumor size, and patient age and the discrete variable of histologic tumor grade (assessed centrally in B-14 and in local laboratories in TAILORx). The prespecified endpoint was time to first distant recurrence.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence risk were generated using baseline risk with TAILORx event rates to reflect current medical practice.
Model estimates were calculated for specified endocrine therapy with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors utilizing the treatment effect hazard ratio from an Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group meta-analysis.
Patient-specific absolute benefit of chemotherapy was estimated by combining patient-specific meta-analysis risk estimates for distant recurrence and for relative chemotherapy benefit using the B-20 and TAILORx trials.
RSClin results and external validation
Among all patients in the meta-analysis cohort, RSClin provided a significantly more accurate prediction of distant recurrence events, in comparison with RS alone or clinical-pathologic factors alone.
External validation was performed using data from real-world outcomes from the 1,098 evaluable node-negative patients in the Clalit Health Services registry, of whom 876 received endocrine therapy alone and 222 received endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence closely approximated the observed risk in the registry (standardized hazard ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.40-2.15; P < .001). Within each RSClin risk quintile, the average 10-year risk estimate approached the observed Kaplan-Meier estimates in the cohort (Lin concordance correlation = 0.962).
Shared decision-making
For many years, the dilemma of whether to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy to a patient with early breast cancer has prompted the generation of tools to quantify a patient’s risk of recurrence and the magnitude of benefit for endocrine therapy and/or chemotherapy.
When the original Adjuvant! Online program was developed, genomic risk profiling was in its infancy. Genomic tools such as the 21-gene RS have subsequently demonstrated that they can help optimize the adjuvant treatment we recommend.
The RSClin tool provides more precise, individualized information than does clinical-pathological or genomic data alone. It prognosticates the risk of distant recurrence of breast cancer, which patients and providers fervently wish to minimize.
RSClin estimates the incremental benefit of contemporary adjuvant chemotherapy over modern endocrine therapy alone, in absolute values, for individual patients. This transparent, discrete, easily explained information is vital for counseling patients.
However, as highlighted in an editorial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, RSClin is not without its potential drawbacks. These include:
- Tumor heterogeneity leading to misleading results.
- Variable patient adherence to endocrine therapy or chemotherapy.
- The influence of comorbid conditions on the risk/benefit ratio.
- The potential of ovarian function suppression in young women to approach the magnitude of benefit associated with chemotherapy.
Accordingly, RSClin may be the latest and best available tool, but it will not be the last.
For patients with RS above 26, for older women with intermediate RS, and for younger women with a low RS and low clinical-pathologic features, RSClin may not influence treatment recommendations.
However, for the common scenario of an intermediate-risk RS and a mix of pathologic features, the accurate prognostication for distant recurrence risk and estimate of absolute benefit from chemotherapy will be terrifically helpful to oncology caregivers.
Dr. Sparano disclosed funding from the National Cancer Institute and travel support from Rhenium.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
When results of the TAILORx trial were presented at ASCO 2018, many oncologists thought it seemed too simple that a single number from a genomic assay could separate patients who would and would not benefit from adjuvant postoperative chemotherapy.
Those oncologists were right to be skeptical. Subsequent data indicated that better predictive tools were needed.
A new tool called “RSClin” may fit the bill. RSClin integrates the prognostic and predictive value of the 21-gene Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS) with the additional prognostic information conveyed by patient age, tumor grade, and tumor size.
RSClin provides individualized estimates of distant relapse risk for women with node-negative, endocrine sensitive, HER2/neu oncogene-negative early breast cancer – and a quantification of the additive freedom from distant relapse if that patient receives adjuvant chemotherapy. The tool is now available via a tab on the professional portal at https://online.genomichealth.com/.
Details on RSClin, including how the tool was developed and validated, were presented at the 2020 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium by Joseph A. Sparano, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Beyond the initial publication of TAILORx
Results from the TAILORx trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2018 offered the potential for genomic risk assessment to guide the choice of postoperative therapy for many women with the most common type of primary breast cancer. The relative risk reduction with chemotherapy increased with increasing RS result.
Subsequent analyses of the TAILORx dataset, published in The New England Journal of Medicine and JAMA Oncology in 2019, examined the added effect of parameters of clinical risk (tumor size and grade) and patient age for patients with known genomic risk.
In these analyses, clinical risk was prognostic for recurrence but did not predict the absolute magnitude of chemotherapy benefit, regardless of age. There was a trend toward chemotherapy benefit in women who were younger than 50 years of age who had RS 21-15, but it was irrespective of clinical risk.
The development of RSClin
RSClin was derived from a patient-specific meta-analysis of 10,004 women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative, node-negative breast cancer, of whom 9,427 participated in the TAILORx trial.
In TAILORx, which ran from 2006 to 2015, women with RS 0-11 received contemporary hormone therapy alone. Women with RS 12-25 were randomized to receive hormone therapy alone or with conventional combination chemotherapy. Women with RS above 26 received chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy.
The other patients in the meta-analysis participated in NSABP studies B-14 (tamoxifen versus placebo) and B-20 (tamoxifen versus chemotherapy plus tamoxifen).
Cox regression models were fit separately to each study with covariates of the continuous variables of RS result, tumor size, and patient age and the discrete variable of histologic tumor grade (assessed centrally in B-14 and in local laboratories in TAILORx). The prespecified endpoint was time to first distant recurrence.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence risk were generated using baseline risk with TAILORx event rates to reflect current medical practice.
Model estimates were calculated for specified endocrine therapy with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors utilizing the treatment effect hazard ratio from an Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group meta-analysis.
Patient-specific absolute benefit of chemotherapy was estimated by combining patient-specific meta-analysis risk estimates for distant recurrence and for relative chemotherapy benefit using the B-20 and TAILORx trials.
RSClin results and external validation
Among all patients in the meta-analysis cohort, RSClin provided a significantly more accurate prediction of distant recurrence events, in comparison with RS alone or clinical-pathologic factors alone.
External validation was performed using data from real-world outcomes from the 1,098 evaluable node-negative patients in the Clalit Health Services registry, of whom 876 received endocrine therapy alone and 222 received endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence closely approximated the observed risk in the registry (standardized hazard ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.40-2.15; P < .001). Within each RSClin risk quintile, the average 10-year risk estimate approached the observed Kaplan-Meier estimates in the cohort (Lin concordance correlation = 0.962).
Shared decision-making
For many years, the dilemma of whether to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy to a patient with early breast cancer has prompted the generation of tools to quantify a patient’s risk of recurrence and the magnitude of benefit for endocrine therapy and/or chemotherapy.
When the original Adjuvant! Online program was developed, genomic risk profiling was in its infancy. Genomic tools such as the 21-gene RS have subsequently demonstrated that they can help optimize the adjuvant treatment we recommend.
The RSClin tool provides more precise, individualized information than does clinical-pathological or genomic data alone. It prognosticates the risk of distant recurrence of breast cancer, which patients and providers fervently wish to minimize.
RSClin estimates the incremental benefit of contemporary adjuvant chemotherapy over modern endocrine therapy alone, in absolute values, for individual patients. This transparent, discrete, easily explained information is vital for counseling patients.
However, as highlighted in an editorial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, RSClin is not without its potential drawbacks. These include:
- Tumor heterogeneity leading to misleading results.
- Variable patient adherence to endocrine therapy or chemotherapy.
- The influence of comorbid conditions on the risk/benefit ratio.
- The potential of ovarian function suppression in young women to approach the magnitude of benefit associated with chemotherapy.
Accordingly, RSClin may be the latest and best available tool, but it will not be the last.
For patients with RS above 26, for older women with intermediate RS, and for younger women with a low RS and low clinical-pathologic features, RSClin may not influence treatment recommendations.
However, for the common scenario of an intermediate-risk RS and a mix of pathologic features, the accurate prognostication for distant recurrence risk and estimate of absolute benefit from chemotherapy will be terrifically helpful to oncology caregivers.
Dr. Sparano disclosed funding from the National Cancer Institute and travel support from Rhenium.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
When results of the TAILORx trial were presented at ASCO 2018, many oncologists thought it seemed too simple that a single number from a genomic assay could separate patients who would and would not benefit from adjuvant postoperative chemotherapy.
Those oncologists were right to be skeptical. Subsequent data indicated that better predictive tools were needed.
A new tool called “RSClin” may fit the bill. RSClin integrates the prognostic and predictive value of the 21-gene Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS) with the additional prognostic information conveyed by patient age, tumor grade, and tumor size.
RSClin provides individualized estimates of distant relapse risk for women with node-negative, endocrine sensitive, HER2/neu oncogene-negative early breast cancer – and a quantification of the additive freedom from distant relapse if that patient receives adjuvant chemotherapy. The tool is now available via a tab on the professional portal at https://online.genomichealth.com/.
Details on RSClin, including how the tool was developed and validated, were presented at the 2020 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium by Joseph A. Sparano, MD, of Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York.
Beyond the initial publication of TAILORx
Results from the TAILORx trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine in 2018 offered the potential for genomic risk assessment to guide the choice of postoperative therapy for many women with the most common type of primary breast cancer. The relative risk reduction with chemotherapy increased with increasing RS result.
Subsequent analyses of the TAILORx dataset, published in The New England Journal of Medicine and JAMA Oncology in 2019, examined the added effect of parameters of clinical risk (tumor size and grade) and patient age for patients with known genomic risk.
In these analyses, clinical risk was prognostic for recurrence but did not predict the absolute magnitude of chemotherapy benefit, regardless of age. There was a trend toward chemotherapy benefit in women who were younger than 50 years of age who had RS 21-15, but it was irrespective of clinical risk.
The development of RSClin
RSClin was derived from a patient-specific meta-analysis of 10,004 women with hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative, node-negative breast cancer, of whom 9,427 participated in the TAILORx trial.
In TAILORx, which ran from 2006 to 2015, women with RS 0-11 received contemporary hormone therapy alone. Women with RS 12-25 were randomized to receive hormone therapy alone or with conventional combination chemotherapy. Women with RS above 26 received chemotherapy plus endocrine therapy.
The other patients in the meta-analysis participated in NSABP studies B-14 (tamoxifen versus placebo) and B-20 (tamoxifen versus chemotherapy plus tamoxifen).
Cox regression models were fit separately to each study with covariates of the continuous variables of RS result, tumor size, and patient age and the discrete variable of histologic tumor grade (assessed centrally in B-14 and in local laboratories in TAILORx). The prespecified endpoint was time to first distant recurrence.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence risk were generated using baseline risk with TAILORx event rates to reflect current medical practice.
Model estimates were calculated for specified endocrine therapy with tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors utilizing the treatment effect hazard ratio from an Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group meta-analysis.
Patient-specific absolute benefit of chemotherapy was estimated by combining patient-specific meta-analysis risk estimates for distant recurrence and for relative chemotherapy benefit using the B-20 and TAILORx trials.
RSClin results and external validation
Among all patients in the meta-analysis cohort, RSClin provided a significantly more accurate prediction of distant recurrence events, in comparison with RS alone or clinical-pathologic factors alone.
External validation was performed using data from real-world outcomes from the 1,098 evaluable node-negative patients in the Clalit Health Services registry, of whom 876 received endocrine therapy alone and 222 received endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy.
RSClin estimates of distant recurrence closely approximated the observed risk in the registry (standardized hazard ratio, 1.73; 95% confidence interval, 1.40-2.15; P < .001). Within each RSClin risk quintile, the average 10-year risk estimate approached the observed Kaplan-Meier estimates in the cohort (Lin concordance correlation = 0.962).
Shared decision-making
For many years, the dilemma of whether to recommend adjuvant chemotherapy to a patient with early breast cancer has prompted the generation of tools to quantify a patient’s risk of recurrence and the magnitude of benefit for endocrine therapy and/or chemotherapy.
When the original Adjuvant! Online program was developed, genomic risk profiling was in its infancy. Genomic tools such as the 21-gene RS have subsequently demonstrated that they can help optimize the adjuvant treatment we recommend.
The RSClin tool provides more precise, individualized information than does clinical-pathological or genomic data alone. It prognosticates the risk of distant recurrence of breast cancer, which patients and providers fervently wish to minimize.
RSClin estimates the incremental benefit of contemporary adjuvant chemotherapy over modern endocrine therapy alone, in absolute values, for individual patients. This transparent, discrete, easily explained information is vital for counseling patients.
However, as highlighted in an editorial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, RSClin is not without its potential drawbacks. These include:
- Tumor heterogeneity leading to misleading results.
- Variable patient adherence to endocrine therapy or chemotherapy.
- The influence of comorbid conditions on the risk/benefit ratio.
- The potential of ovarian function suppression in young women to approach the magnitude of benefit associated with chemotherapy.
Accordingly, RSClin may be the latest and best available tool, but it will not be the last.
For patients with RS above 26, for older women with intermediate RS, and for younger women with a low RS and low clinical-pathologic features, RSClin may not influence treatment recommendations.
However, for the common scenario of an intermediate-risk RS and a mix of pathologic features, the accurate prognostication for distant recurrence risk and estimate of absolute benefit from chemotherapy will be terrifically helpful to oncology caregivers.
Dr. Sparano disclosed funding from the National Cancer Institute and travel support from Rhenium.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
FROM SABCS 2020
Sticking His Neck Out Leads to Diagnosis
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
ANSWER
The correct answer is all of the above (choice “d”).
DISCUSSION
For this patient, there could have been even more items in the differential, including melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma, or even metastatic (from lung, colon, etc) origin. Dermatofibroma sarcoma protuberans is another possibility because it is rarely aggressive, though it is seldom as exophytic as this lesion. However, the prolonged, indolent course of the patient’s lesion was more consistent with the 3 choices listed. The overarching point is this: Why guess when the diagnosis is easily obtained by biopsy?
Biopsy of the lesion was ordered at the patient's first visit to dermatology. It revealed an invasive basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which almost never metastasizes. BCC requires extensive surgical removal and closure.
TREATMENT
The patient’s lesion needed a total excision with margins. Its size, location, and longevity called for the Mohs technique to assure clear margins and optimal closure.
Because of the findings and the patient’s history, he would also need to see dermatology every 6 months because he is a prime candidate for developing other skin cancers.
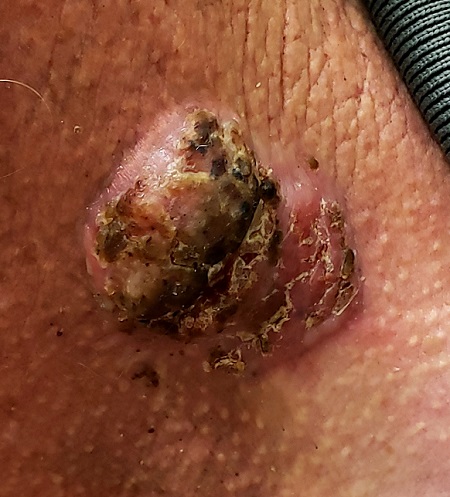
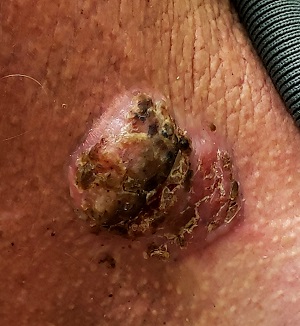
For 5 years, a lesion has been slowly growing on this 50-year-old man’s neck. He has seen several primary care providers who had provided different diagnoses, including wart, seborrheic keratosis, and keratoacanthoma. Throughout these visits, the only treatment he was offered was cryotherapy, but this was not effective at clearing the lesion. One family member convinced him it was time to try a dermatology provider.
In his lifetime, the patient has been exposed to a great deal of UV light. He has had several basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas removed from his face and arms.
He claims to be in otherwise good health, but further questioning reveals a > 40 pack-year history of smoking. He also has a recent diagnosis of early chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Physical examination of the lesion reveals a 4-x-3.5-cm sessile mass located on the left lateral neck. Its surface is rough and irregular, but there is no break in the skin.
On palpation, the lesion is quite firm and only partially mobile. No tenderness is detected. There are no palpable nodes in the region. There is evidence of advanced chronic sun damage on all sun-exposed areas, but especially on the head and neck. The rest of skin has no lesions.
COVID protections suppressed flu season in U.S.
Last fall, health experts said it was possible the United States could experience an easy 2020-21 flu season because health measures to fight COVID-19 would also thwart the spread of influenza.
It looks like that happened – and then some. Numbers are strikingly low for cases of the flu and other common respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses, health experts told the Washington Post.
“It’s crazy,” Lynnette Brammer, MPH, who leads the domestic influenza surveillance team at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, told the Washington Post. “This is my 30th flu season. I never would have expected to see flu activity this low.”
Influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, norovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, and the bacteria that cause whooping cough and pneumonia are circulating at near-record-low levels.
As an example, the Washington Post said in the third week of December 2019, the CDC’s network of clinical labs reported 16.2% of almost 30,000 samples tested positive for influenza A. During the same period in 2020, only 0.3% tested positive.
But there’s a possible downside to this suppression of viruses, because flu and other viruses may rebound once the coronavirus is brought under control.
“The best analogy is to a forest fire,” Bryan Grenfell, PhD, an epidemiologist and population biologist at Princeton (N.J.) University, told the Washington Post. “For the fire to spread, it needs to have unburned wood. For epidemics to spread, they require people who haven’t previously been infected. So if people don’t get infected this year by these viruses, they likely will at some point later on.”
American health experts like Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said last fall that they noticed Australia and other nations in the southern hemisphere had easy flu seasons, apparently because of COVID protection measures. The flu season there runs March through August.
COVID-19 now has a very low presence in Australia, but in recent months the flu has been making a comeback. Flu cases among children aged 5 and younger rose sixfold by December, when such cases are usually at their lowest, the Washington Post said.
“That’s an important cautionary tale for us,” said Kevin Messacar, MD, an infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Just because we get through the winter and don’t see much RSV or influenza doesn’t mean we’ll be out of the woods.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Last fall, health experts said it was possible the United States could experience an easy 2020-21 flu season because health measures to fight COVID-19 would also thwart the spread of influenza.
It looks like that happened – and then some. Numbers are strikingly low for cases of the flu and other common respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses, health experts told the Washington Post.
“It’s crazy,” Lynnette Brammer, MPH, who leads the domestic influenza surveillance team at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, told the Washington Post. “This is my 30th flu season. I never would have expected to see flu activity this low.”
Influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, norovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, and the bacteria that cause whooping cough and pneumonia are circulating at near-record-low levels.
As an example, the Washington Post said in the third week of December 2019, the CDC’s network of clinical labs reported 16.2% of almost 30,000 samples tested positive for influenza A. During the same period in 2020, only 0.3% tested positive.
But there’s a possible downside to this suppression of viruses, because flu and other viruses may rebound once the coronavirus is brought under control.
“The best analogy is to a forest fire,” Bryan Grenfell, PhD, an epidemiologist and population biologist at Princeton (N.J.) University, told the Washington Post. “For the fire to spread, it needs to have unburned wood. For epidemics to spread, they require people who haven’t previously been infected. So if people don’t get infected this year by these viruses, they likely will at some point later on.”
American health experts like Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said last fall that they noticed Australia and other nations in the southern hemisphere had easy flu seasons, apparently because of COVID protection measures. The flu season there runs March through August.
COVID-19 now has a very low presence in Australia, but in recent months the flu has been making a comeback. Flu cases among children aged 5 and younger rose sixfold by December, when such cases are usually at their lowest, the Washington Post said.
“That’s an important cautionary tale for us,” said Kevin Messacar, MD, an infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Just because we get through the winter and don’t see much RSV or influenza doesn’t mean we’ll be out of the woods.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Last fall, health experts said it was possible the United States could experience an easy 2020-21 flu season because health measures to fight COVID-19 would also thwart the spread of influenza.
It looks like that happened – and then some. Numbers are strikingly low for cases of the flu and other common respiratory and gastrointestinal viruses, health experts told the Washington Post.
“It’s crazy,” Lynnette Brammer, MPH, who leads the domestic influenza surveillance team at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, told the Washington Post. “This is my 30th flu season. I never would have expected to see flu activity this low.”
Influenza A, influenza B, parainfluenza, norovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, and the bacteria that cause whooping cough and pneumonia are circulating at near-record-low levels.
As an example, the Washington Post said in the third week of December 2019, the CDC’s network of clinical labs reported 16.2% of almost 30,000 samples tested positive for influenza A. During the same period in 2020, only 0.3% tested positive.
But there’s a possible downside to this suppression of viruses, because flu and other viruses may rebound once the coronavirus is brought under control.
“The best analogy is to a forest fire,” Bryan Grenfell, PhD, an epidemiologist and population biologist at Princeton (N.J.) University, told the Washington Post. “For the fire to spread, it needs to have unburned wood. For epidemics to spread, they require people who haven’t previously been infected. So if people don’t get infected this year by these viruses, they likely will at some point later on.”
American health experts like Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, said last fall that they noticed Australia and other nations in the southern hemisphere had easy flu seasons, apparently because of COVID protection measures. The flu season there runs March through August.
COVID-19 now has a very low presence in Australia, but in recent months the flu has been making a comeback. Flu cases among children aged 5 and younger rose sixfold by December, when such cases are usually at their lowest, the Washington Post said.
“That’s an important cautionary tale for us,” said Kevin Messacar, MD, an infectious disease doctor at Children’s Hospital Colorado, Aurora. “Just because we get through the winter and don’t see much RSV or influenza doesn’t mean we’ll be out of the woods.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Differences in right vs. left colon in Black vs. White individuals
The right colon appears to age faster in Black people than in White people, perhaps explaining the higher prevalence of right-side colon cancer among Black Americans, according to results from a biopsy study.
The findings were published online Dec. 30 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
For the study, investigators analyzed colon biopsy specimens from 128 individuals who underwent routine colorectal screening.
The researchers compared DNA methylation levels in right and left colon biopsy samples from the same patient. They then assigned epigenetic ages to the tissue samples using the Hovarth clock, which estimates tissue age on the basis of DNA methylation.
DNA methylation is influenced by age and environmental exposures. Aberrant DNA methylation is a hallmark of colorectal cancer, the researchers explained.
The epigenetic age of the right colon of the 88 Black patients was 1.51 years ahead of their left colon; the right colon of the 44 White patients was epigenetically 1.93 years younger than their left colon.
The right colon was epigenetically older than the left colon in 60.2% of Black patients; it was younger in more than 70% of White patients.
A unique pattern of DNA hypermethylation was found in the right colon of Black patients.
“Our results provide biological plausibility for the observed relative preponderance of right colon cancer and younger age of onset in African Americans as compared to European Americans,” wrote the investigators, led by Matthew Devall, PhD, a research associate at the Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Side-specific colonic epigenetic aging may be a promising marker to guide interventions to reduce CRC [colorectal cancer] burden,” they suggested.
If these findings are “corroborated in African Americans in future studies, these results could potentially explain racial differences in the site predilection of colorectal cancers,” Amit Joshi, MBBS, PhD, and Andrew Chan, MD, gastrointestinal molecular epidemiologists at Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, “it is not clear if the higher epigenetic aging measured using the Horvath clock ... directly translates to a higher risk of colorectal cancer,” they noted.
Some differences between the Black patients and the White patients in the study could explain the methylation differences, they pointed out. A higher proportion of Black patients smoked (37.5% vs. 15%), and Black patients were younger (median age, 55.5 years, vs. 61.7 years). In addition, the study included more Black women than White women (67% vs. 58%), and body mass indexes were higher for Black patients than White patients (31.36 kg/m2 vs 28.29 kg/m2).
“One or more of these factors, or others that were not measured, may be linked to differential methylation in the right compared with left colon,” the editorialists wrote.
Even so, among the Black patients, almost 70% of differentially methylated positions in the right colon were hypermethylated, compared to less than half in the left colon. These included positions previously associated with colorectal cancer, aging, and ancestry, “suggesting a role for genetic variation in contributing to DNA methylation differences in AA right colon,” the investigators said.
"This study’s observations are interesting and important. One additional limitation to consider is how race of the patient was determined, e.g. self-identified or ancestry history. If it was the former, than this study is limited by the fact that individuals who identify as African American may also have European ancestry, similarly European Americans may have African ancestry. As we advance in health disparities research, our work must acknowledge that there is a broad range of degree of European ancestry among Black Americans,” added Byron Cryer, MD, and Sandra Quezada, MD, the cochairs of the AGA Equity Project Advisory Board.
The work was supported the National Cancer Institute Cancer, the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, and the University of Virginia Cancer Center. The authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AGA applauds researchers who are working to raise our awareness of health disparities in digestive diseases. AGA is committed to addressing this important societal issue head on. Learn more about AGA’s commitment through the AGA Equity Project.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The right colon appears to age faster in Black people than in White people, perhaps explaining the higher prevalence of right-side colon cancer among Black Americans, according to results from a biopsy study.
The findings were published online Dec. 30 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
For the study, investigators analyzed colon biopsy specimens from 128 individuals who underwent routine colorectal screening.
The researchers compared DNA methylation levels in right and left colon biopsy samples from the same patient. They then assigned epigenetic ages to the tissue samples using the Hovarth clock, which estimates tissue age on the basis of DNA methylation.
DNA methylation is influenced by age and environmental exposures. Aberrant DNA methylation is a hallmark of colorectal cancer, the researchers explained.
The epigenetic age of the right colon of the 88 Black patients was 1.51 years ahead of their left colon; the right colon of the 44 White patients was epigenetically 1.93 years younger than their left colon.
The right colon was epigenetically older than the left colon in 60.2% of Black patients; it was younger in more than 70% of White patients.
A unique pattern of DNA hypermethylation was found in the right colon of Black patients.
“Our results provide biological plausibility for the observed relative preponderance of right colon cancer and younger age of onset in African Americans as compared to European Americans,” wrote the investigators, led by Matthew Devall, PhD, a research associate at the Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Side-specific colonic epigenetic aging may be a promising marker to guide interventions to reduce CRC [colorectal cancer] burden,” they suggested.
If these findings are “corroborated in African Americans in future studies, these results could potentially explain racial differences in the site predilection of colorectal cancers,” Amit Joshi, MBBS, PhD, and Andrew Chan, MD, gastrointestinal molecular epidemiologists at Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, “it is not clear if the higher epigenetic aging measured using the Horvath clock ... directly translates to a higher risk of colorectal cancer,” they noted.
Some differences between the Black patients and the White patients in the study could explain the methylation differences, they pointed out. A higher proportion of Black patients smoked (37.5% vs. 15%), and Black patients were younger (median age, 55.5 years, vs. 61.7 years). In addition, the study included more Black women than White women (67% vs. 58%), and body mass indexes were higher for Black patients than White patients (31.36 kg/m2 vs 28.29 kg/m2).
“One or more of these factors, or others that were not measured, may be linked to differential methylation in the right compared with left colon,” the editorialists wrote.
Even so, among the Black patients, almost 70% of differentially methylated positions in the right colon were hypermethylated, compared to less than half in the left colon. These included positions previously associated with colorectal cancer, aging, and ancestry, “suggesting a role for genetic variation in contributing to DNA methylation differences in AA right colon,” the investigators said.
"This study’s observations are interesting and important. One additional limitation to consider is how race of the patient was determined, e.g. self-identified or ancestry history. If it was the former, than this study is limited by the fact that individuals who identify as African American may also have European ancestry, similarly European Americans may have African ancestry. As we advance in health disparities research, our work must acknowledge that there is a broad range of degree of European ancestry among Black Americans,” added Byron Cryer, MD, and Sandra Quezada, MD, the cochairs of the AGA Equity Project Advisory Board.
The work was supported the National Cancer Institute Cancer, the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, and the University of Virginia Cancer Center. The authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AGA applauds researchers who are working to raise our awareness of health disparities in digestive diseases. AGA is committed to addressing this important societal issue head on. Learn more about AGA’s commitment through the AGA Equity Project.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The right colon appears to age faster in Black people than in White people, perhaps explaining the higher prevalence of right-side colon cancer among Black Americans, according to results from a biopsy study.
The findings were published online Dec. 30 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
For the study, investigators analyzed colon biopsy specimens from 128 individuals who underwent routine colorectal screening.
The researchers compared DNA methylation levels in right and left colon biopsy samples from the same patient. They then assigned epigenetic ages to the tissue samples using the Hovarth clock, which estimates tissue age on the basis of DNA methylation.
DNA methylation is influenced by age and environmental exposures. Aberrant DNA methylation is a hallmark of colorectal cancer, the researchers explained.
The epigenetic age of the right colon of the 88 Black patients was 1.51 years ahead of their left colon; the right colon of the 44 White patients was epigenetically 1.93 years younger than their left colon.
The right colon was epigenetically older than the left colon in 60.2% of Black patients; it was younger in more than 70% of White patients.
A unique pattern of DNA hypermethylation was found in the right colon of Black patients.
“Our results provide biological plausibility for the observed relative preponderance of right colon cancer and younger age of onset in African Americans as compared to European Americans,” wrote the investigators, led by Matthew Devall, PhD, a research associate at the Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“Side-specific colonic epigenetic aging may be a promising marker to guide interventions to reduce CRC [colorectal cancer] burden,” they suggested.
If these findings are “corroborated in African Americans in future studies, these results could potentially explain racial differences in the site predilection of colorectal cancers,” Amit Joshi, MBBS, PhD, and Andrew Chan, MD, gastrointestinal molecular epidemiologists at Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
However, “it is not clear if the higher epigenetic aging measured using the Horvath clock ... directly translates to a higher risk of colorectal cancer,” they noted.
Some differences between the Black patients and the White patients in the study could explain the methylation differences, they pointed out. A higher proportion of Black patients smoked (37.5% vs. 15%), and Black patients were younger (median age, 55.5 years, vs. 61.7 years). In addition, the study included more Black women than White women (67% vs. 58%), and body mass indexes were higher for Black patients than White patients (31.36 kg/m2 vs 28.29 kg/m2).
“One or more of these factors, or others that were not measured, may be linked to differential methylation in the right compared with left colon,” the editorialists wrote.
Even so, among the Black patients, almost 70% of differentially methylated positions in the right colon were hypermethylated, compared to less than half in the left colon. These included positions previously associated with colorectal cancer, aging, and ancestry, “suggesting a role for genetic variation in contributing to DNA methylation differences in AA right colon,” the investigators said.
"This study’s observations are interesting and important. One additional limitation to consider is how race of the patient was determined, e.g. self-identified or ancestry history. If it was the former, than this study is limited by the fact that individuals who identify as African American may also have European ancestry, similarly European Americans may have African ancestry. As we advance in health disparities research, our work must acknowledge that there is a broad range of degree of European ancestry among Black Americans,” added Byron Cryer, MD, and Sandra Quezada, MD, the cochairs of the AGA Equity Project Advisory Board.
The work was supported the National Cancer Institute Cancer, the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, and the University of Virginia Cancer Center. The authors and editorialists have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AGA applauds researchers who are working to raise our awareness of health disparities in digestive diseases. AGA is committed to addressing this important societal issue head on. Learn more about AGA’s commitment through the AGA Equity Project.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Liver disease associated with worse COVID-19 outcomes
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
A growing body of evidence suggests that patients with COVID-19 and preexisting liver disease face increased risks of decompensation and mortality, according to a review of recent literature.
The review aimed to bring together the best approaches for caring for patients with preexisting liver conditions based on recommendations from three major hepatology societies. Findings in included studies could guide clinical decision-making, but a reliable framework for patient management has yet to be established, most likely because of limited research, according to lead author Abdul Mohammed, MD, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and colleagues.
The relationship between chronic liver diseases and “COVID-19 is not well documented in the literature,” Dr. Mohammed and colleagues wrote in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology. “The intricate interplay between immune dysfunction in preexisting liver diseases and the immune dysregulation triggered by the SARS-CoV-2 virus needs further evaluation.”
Such knowledge gaps likely explain the inconsistencies in recommendations between major hepatology societies, including clinical guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease, the European Association for the Study of the Liver, and the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver.
Both the literature review and the societal guidance address nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), cirrhosis, and liver transplantation.
Dr. Mohammed and colleagues first offered an update of the relationship between COVID-19 and liver pathology. While it is clear that SARS-CoV-2 gains hepatic access through binding to ACE2 receptors in bile duct epithelial cells, it remains unclear whether this results in direct hepatic injury or indirect damage from virus-mediated cytokine release. Regardless, more than 90% of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 may develop increased levels of ALT and AST, and these elevations “appear to mirror disease severity,” the investigators wrote.
They noted that severity of COVID-19 appears to correlate with type of preexisting liver disease. For example, one study in the review associated NAFLD with a significantly increased risk of progressive COVID-19 (odds ratio, 6.4; 95% confidence interval, 1.5-31.2), and it also found that patients with NAFLD had longer duration of viral shedding than those without (17 vs. 12 days). Although the AASLD and APASL give no specific recommendations, the EASL recommends prioritizing COVID-19 patients with NAFLD.
Cirrhosis has been associated with a fourfold increased risk of mortality (relative risk, 4.6; 95% CI, 2.6-8.3) According to data from two international self-reporting registries, COVIDHep.net and COVIDCirrhosis.org, likelihood of death appears to move in tandem with Child-Turcotte-Pugh scores. Decompensated cirrhosis appears to predispose patients to having pulmonary complications, but more studies exploring this correlation need to be performed, according to the review authors. One study found that acute-on-chronic liver failure or acute decompensation occurred in 20% of patients who had COVID-19 and cirrhosis. It’s little surprise, then, that both the AASLD and the EASL recommend prioritizing in person evaluation for patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
Chronic HBV infection has also been associated with a higher COVID-19 mortality rate, although Dr. Mohammed and colleagues suggested that “larger studies are needed.” The review notes that the three societies recommend initiating HBV treatment only if there is clinical suspicion of hepatitis flare.
Findings are also cloudy among patients with autoimmune hepatitis and liver transplant recipients; however, the investigators noted that COVID-19 causes tissue damage primarily through cytokine release, and suggested that “immunosuppression can potentially curb this response.” Even so, recommendations from leading hepatology societies allude to a safe middle ground of immunosuppression, albeit with indistinct borders. All three caution against withdrawing immunosuppression, but the societies each describe tailoring regimens in different ways and for different patients, emphasizing continued corticosteroid treatments, according to the review.
Guidance also varies for management of HCC. “Since the tumor doubling time is 4-8 months and current guidelines recommend screening every 6 months, in patients at lower risk for developing HCC, a 2-month delay in ultrasound surveillance has been suggested by the AASLD,” the review authors noted. “In patients with a high risk of developing HCC, 6-month interval screening should be continued.” The AASLD recommends proceeding with treatment with newly diagnosed HCC, the EASL suggests that checkpoint inhibitors should be withheld and locoregional therapies should be postponed, and the APASL calls for a less frequent schedule of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy.
“COVID-19 patients with the preexisting liver disease face a higher risk of decompensation and mortality,” the review authors concluded. “We presented the most up-to-date literature on preexisting liver disease and its interaction with COVID-19.”
While such discrepancies may remain unresolved until further data are available, Wajahat Mehal, MD, PhD, director of the fatty liver disease program at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., suggested that clinicians remain vigilant for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is common among overweight and obese individuals, an overrepresented group among those hospitalized for COVID-19.
“This is of great significance because patients with various forms of liver disease have a worse outcome with COVID-19,” Dr. Mehal said. “When seeing a patient with COVID-19 it is therefore important to ask if they have underlying liver disease, with attention paid to NASH. This can be approached by seeing if they have any evidence of abnormal liver function tests before the onset of COVID and any evidence of abnormal liver imaging. The Fib-4 test is a good screening tool for the presence of advanced liver fibrosis and a positive result should lead to more specific tests of liver fibrosis status such as fibroscan.”
The investigators reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Mehal reported having nothing to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY
Childhood smoking and depression contribute to young adult opioid use
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
Depression and tobacco use in childhood significantly increased the risk for opioid use in young adults, according to data from a prospective study of approximately 1,000 individuals.
Previous research, including the annual Monitoring the Future study, documents opioid use among adolescents in the United States, but childhood risk factors for opioid use in young adults have not been well studied, wrote Lilly Shanahan, PhD, of the University of Zürich, and colleagues.
In a prospective cohort study published in JAMA Pediatrics, the researchers identified 1,252 non-Hispanic White and American Indian opioid-naive individuals aged 9-16 years in rural North Carolina. They interviewed participants and parents up to 7 times between January 1993 and December 2000, and interviewed participants only at ages 19, 21, 25, and 30 years between January 1999 and December 2015.
Overall, 24.2% of study participants had used a nonheroin opioid by age 30 years, and both chronic depression and dysthymia were significantly associated with this use (odds ratios 5.43 and 7.13, respectively).
In addition, 155 participants (8.8%) reported weekly use of a nonheroin opioid, and 95 (6.6%) reported weekly heroin use by age 30 years. Chronic depression and dysthymia also were strongly associated with weekly nonheroin opioid use (OR 8.89 and 11.51, respectively).
In a multivariate analysis, depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use at ages 9-16 years were strongly associated with overall opioid use at ages 19-30 years.
“One possible reason childhood chronic depression increases the risk of later opioid use is self-medication, including the use of psychoactive substances, to alleviate depression,” the researchers noted. In addition, the mood-altering properties of opioids may increase their appeal to depressed youth as a way to relieve impaired reward system function, they said.
Potential mechanisms for the association between early tobacco use and later opioid use include the alterations to neurodevelopment caused by nicotine exposure in adolescence, as well as increased risk for depression, reduced pain thresholds, and use of nicotine as a gateway to harder drugs, the researchers added.
Several childhood risk factors were not associated with young adult opioid use in multivariate analysis in this study, including alcohol use, sociodemographic status, maltreatment, family dysfunction, and anxiety, the researchers wrote. “Previous studies typically measured these risk factors retrospectively or in late adolescence and young adulthood, and most did not consider depressive disorders, which may mediate associations between select childhood risk factors and later opioid use,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to distinguish between medical and nonmedical opioid use, the incomplete list of available opioids, and the exclusion of Black participants because of low sample size, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the longitudinal, community-representative design and the inclusion of up to 11 assessments of opioid use, they said.
“Our findings suggest strong opportunities for early prevention and intervention, including in primary care settings,” using known evidence-based strategies, they concluded.
More screening is needed
“Children in the United States are at high risk of serious adult health issues as a result of childhood factors such as ACEs (adverse childhood experiences),” said Suzanne C. Boulter, MD, of the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H. “This study looks prospectively at other factors in childhood over a long period of time leading to opioid usage, with its serious risks and health consequences including overdose death,” she said. “It is unclear what the effects of COVID-19 will be on the population of children growing up now and how opioid usage might change as a result,” she noted.
“Some of the links to adult usage are predictable, such as depression, tobacco use, and cannabis use in early adolescence,” said Dr. Boulter. “Surprising was the lack of correlation between anxiety, early alcohol use, child mistreatment, and sociodemographic factors with future opioid use,” she said.
The take-home message for clinicians is to screen children and adolescents for factors leading to opioid usage in young adults “with preventive strategies including avoidance of pain medication prescriptions and early referral and treatment for depression and use of cannabis and tobacco products using tools like SBIRT (Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment),” Dr. Boulter emphasized.
As for additional research, “It would be interesting to study e-cigarette usage and see if the correlation with future opioid usage is similar to older tobacco products,” she said. “Also helpful would be to delve deeper into connections between medical or dental diagnoses when opioids were first prescribed and later usage of those products,” Dr. Boulter noted.
The study was supported in part by the by the National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Boulter had no disclosures but serves on the Pediatric News Editorial Advisory Board.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
Endocrine Society calls for action to reduce insulin costs
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Endocrine Society has issued a new position statement calling on all stakeholders, including clinicians, to play a role in reducing the cost of insulin for patients with diabetes in the United States.
“Addressing Insulin Access and Affordability: An Endocrine Society Position Statement,” was published online Jan. 12 in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
“The society believes all stakeholders across the supply chain have a role to play in addressing the high price of insulin,” said the 11 authors, who are all members of the society’s advocacy and public outreach core committee.
This is the first such statement from a major professional organization in 2021, which is the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin.
And the call for action was issued just a week prior to the inauguration of incoming U.S. President Joe Biden, who has pledged to “build on the Affordable Care Act by giving Americans more choice, reducing health care costs, and making our health care system less complex to navigate.”
The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years in the United States, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
The high cost of insulin has made access particularly difficult for people with diabetes with a low income, who have high-deductible health plans, are Medicare beneficiaries using Part B to cover insulin delivered via pump, or are in the Medicare Part D “donut hole,” as well as young adults once they reach their 26th birthday and can no longer be covered under their parents’ insurance.
“Inventors Frederick Banting and Charles Best sold the insulin patent for a mere $1 in the 1920s because they wanted their discovery to save lives and for insulin to be affordable and accessible to everyone who needed it,” said Endocrine Society President-elect Carol Wysham, MD, of the Rockwood/MultiCare Health Systems, Spokane, Wash.
“People with diabetes without full insurance are often paying increasing out-of-pocket costs for insulin resulting in many rationing their medication or skipping lifesaving doses altogether,” she said.
The society’s statement called for allowing government negotiation of drug prices and greater transparency across the supply chain to elucidate the reasons for rising insulin costs.
For physicians in particular, they advised training in use of lower-cost human NPH and regular insulin for appropriate patients with type 2 diabetes, and considering patients’ individual financial and coverage status when prescribing insulin.
Pharmacists are advised to learn about and share information with patients about lower-cost options offered by manufacturers.
Other policy recommendations for relevant stakeholders include:
- Limit future insulin list price increases to the rate of inflation.
- Limit out-of-pocket costs without increasing premiums or deductibles by limiting cost sharing to copays of no more than $35, providing first-dollar coverage, or capping costs at no more than $100 per month.
- Eliminate rebates or pass savings from rebates along to consumers without increasing premiums or deductibles.
- Expedite approval of insulin biosimilars to create market competition.
- Include real-time benefit information in electronic medical records.
- Develop a payment model for Medicare Part B beneficiaries, as well as Part D, to lower out-of-pocket copays.
For manufacturers, the society also recommended improving patient assistance programs to be less restrictive and more accountable. And employers, they said, should limit copays without increasing premiums or deductibles, and seek plan options that benefit people with diabetes and provide education about these options during open enrollment.
Of the 11 writing panel members, 4 have pharmaceutical industry disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Helping interracial couples navigate racism
Joe and Esi were in the therapist’s office wanting help with their relationship. The therapist had just asked the BIG question: How does race impact your lives?”
Esi began with her story about her ethics class, a story that was at sufficient distance from her life. Depending on her husband’s response, she would move in closer. His somewhat patronizing response made her feel both angry and that he lacked any real understanding.
“Me and a mulatto girl were in ethics class,” said Esi, who grew in Kenya. We had a White professor. He seemed to think I had no education. If you are a woman of color, you are automatically thought to have no education and that you don’t know what you are talking about. He tried to shut me up. When I persisted, I know he thought from the tone of my voice that I was an angry Black woman, even although I am not Black and I am not angry! In this country, if you have any color to your skin, you are called Black and relegated to a certain place: The bottom. I was excited about what he was teaching us, but when everyone looked at me with a certain gaze, like something bad was going to happen, all those White people, just looking, I tightened up inside and sat back down.”
Esi looked down at her folded hands. Her husband, who was White, reached over and reassuringly patted her hands.
“Yes, Esi, they are wrong. They shouldn’t have treated you that way. White people can be insensitive.”
Then, she continued, “Joe, you do the same to me!”
“What do you mean, Esi?” responded Joe, with an innocent and anxious look scanning back and forth between her and the White male therapist.
“Well, Joe, do you really want to hear how I felt last week after we came back from that party at your sister’s house?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“But do you really? Are you sure you want to hear this?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“Remember when we went over, me and the kids sat with the other people of color and you sat with your sister and her side of the family?
“Yes, I remember. What is wrong with that?”
“Well, me and my colored friends got loud and excited, and you shot me a look, like ‘pipe down over there.’ THEN, after we got home, the next day, your sister called you and said that you had better control your wife; she is too loud. Do you remember all that?
“Yes, well you do get loud – especially when you are around your people.”
“So why is it I have to fit in with your relatives and not the other way round? Why do I have to conform to the whiteness in your sister’s world, not the other way round?”
“Well, we were in her house.”
“So if they came to our house and were too quiet, how would you feel if I called them up and said they needed to participate with more enthusiasm?”
“Esi, that’s not fair, and you know it isn’t.”
Esi stops and looks at the therapist.
“So I check myself. It is the same all over, White people imposing their values and beliefs on me, on us. I am not an angry Black woman. I am just frustrated. People, White people, always want an explanation for what they think is my loss of control. You can see when their demeanor changes, they pull back, sit up, back away, fidget, and won’t look you in the eye. All these little tics that show that they are trying to get out of the situation.”
Esi took a breath and saw that her husband and the therapist were listening.
“These signs are ingrained in your brain ... these signs ... I saw it when I first came here to this country. The first time I had a good dose of it ... was in that ethics class in college. You can’t use words that you are accustomed to, ’cause they mean something else here, something bad.”
“Oh, Esi, I am so sorry,” said Joe, looking concerned.
“You may be sorry but you are not willing to stand up for me against your sister and her White values. You want me to conform.”
“What do you want me to do?”
“I want you to call your sister out.”
“But she may not ever speak to me again!”
“OK, don’t then,” and Esi looked down at her hands. She was finished talking. Joe looked at the therapist, waiting for something.
The therapist resisted intervening on the issue. “Keep talking this through,” he instructed them.
Joe could see that Esi had done talking and that it was his move.
“Do you really want me to call my sister out, even if it means that she will not talk to me again?”
“Yes.”
“I don’t know if I can do that.”
The therapist now intervened: “What does that mean to you, Esi, that he doesn’t know if he can do that.”
“It means he doesn’t really love me or value me or even value our mulatto children. What do think our daughter is learning?”
“That’s not true, Esi.”
The therapist, Dr. Swarthmore, watched Esi, who has very a dark, blue-black skin tone, with a flawless complexion and a shapely body. She wears her hair cropped and she looks like that Black model, what’s her name. Joe was short, a little plump with ultra White skin and freckles on his nose. He had been brought up in the Midwest and had had little exposure to Africans before his internship abroad in Kenya. Dr. S. thought he had probably not really thought much about Esi’s dilemma.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged Esi to talk about her immigration experience.
“Esi, can you talk more about what it is like to be an immigrant from Africa?”
“Well, I just have to check myself so that I can fit in with this White culture. If you want to see how I feel about it, you will have to see an angry Black woman and I have learned not to give you that satisfaction. You will just dismiss me. Please Dr. Swarthmore, can we move on?”
Dr. Swarthmore was caught between his desire to accept her wish to move on and his wish to have her express herself fully. He realized that it was not his desire that mattered; that the couple had to work this out between them if they were going to move forward. So he punted it back to them.
“Esi and Joe, you are both caught in an important dilemma. Esi, you want more respect from your husband and his family. Joe, you do not want to upset your family by confronting them. Is that right? You are both dammed if you do and dammed if you don’t.”
“I agree,” Joe and Esi both said, nodding.
“Do you want to work on this issue?”
They both agreed with equal enthusiasm.
“Ok, can you spend the next 10 minutes to work on this?”
They agreed.
“Ok, let’s start. What skills do you have that can help you resolve this important issue?”
Dr. Swarthmore framed the issue as one to be solved by the couple. The couple discussed that they are usually good at communication and solving problems. This problem is about whether or not Joe is more aligned with his White family than with Esi and their children.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged them to think about this more deeply and over time; that this is such an important issue that it requires time and deep conversation.
“How do you think you can educate yourselves about the issues at hand?”
Esi’s reading list
1. “Why I’m No Longer Talking to White People About Race” by Reni Eddo-Lodge (London: Bloomsbury, 2018).
2. “Americanah” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2013).
3. “How to be an Antiracist” by Ibram X. Kendi (New York: Random House, 2019).
Joe suggests that Esi think about what it might mean if his sister and their children were no longer part of their lives. She agrees to do this.
Dr. Swarthmore asks if they can each do their homework before they come back. They agree and thought they could manage that and the book for 2 weeks out.
Dr. Swarthmore decides that he will read one of the books Esi suggested, as he does not know much about racism and White privilege and he wants to learn more. Dr. Swarthmore demonstrates his desire to become more racially sensitive. The following steps can be taken by therapists who want to become more racially sensitive, according to TA Laszloffy and KV Hardy (Fam Process. 2000 Spring;39[1]:35-50):
1. Read and watch movies that address the experience of other cultural groups.
2. Go to and participate in cross-cultural events.
3. Engage in a racial self-exploration process. The following questions can begin the racial identity exploration process:
- How do I define myself racially?
- When did I first become aware of race/skin color in general, and mine in particular?
- What messages did I learn about race/skin color based on that first experience?
- What direct and indirect messages did I receive about race/skin color?
- How did the messages that I received about race/skin color affect how I thought and felt about myself racially?
- What benefits did I gain because of my race/skin color?
- What did I lose because of my race/skin?
- Have I ever dated cross-racially? Why or why not?
- How many friends of a different race do I have?
4. Internal commitment. This means committing to addressing racism in therapeutic encounters.
Lessons learned for psychiatrists
1. Therapeutic space is allocated to discuss the issue.
2. The time is strictly limited to 10 minutes, so the couple won’t feel that their emotions will overwhelm them.
3. The space is to focus on the strengths that they can bring to resolving the issue.
4. Give patients the impression that they can solve this and that it is an important issue.
5. Do not put yourself in the patients’ argument; take neither side.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Heru wrote the article in collaboration with Lynette Ramsingh Barros, artist and social commentator.
Joe and Esi were in the therapist’s office wanting help with their relationship. The therapist had just asked the BIG question: How does race impact your lives?”
Esi began with her story about her ethics class, a story that was at sufficient distance from her life. Depending on her husband’s response, she would move in closer. His somewhat patronizing response made her feel both angry and that he lacked any real understanding.
“Me and a mulatto girl were in ethics class,” said Esi, who grew in Kenya. We had a White professor. He seemed to think I had no education. If you are a woman of color, you are automatically thought to have no education and that you don’t know what you are talking about. He tried to shut me up. When I persisted, I know he thought from the tone of my voice that I was an angry Black woman, even although I am not Black and I am not angry! In this country, if you have any color to your skin, you are called Black and relegated to a certain place: The bottom. I was excited about what he was teaching us, but when everyone looked at me with a certain gaze, like something bad was going to happen, all those White people, just looking, I tightened up inside and sat back down.”
Esi looked down at her folded hands. Her husband, who was White, reached over and reassuringly patted her hands.
“Yes, Esi, they are wrong. They shouldn’t have treated you that way. White people can be insensitive.”
Then, she continued, “Joe, you do the same to me!”
“What do you mean, Esi?” responded Joe, with an innocent and anxious look scanning back and forth between her and the White male therapist.
“Well, Joe, do you really want to hear how I felt last week after we came back from that party at your sister’s house?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“But do you really? Are you sure you want to hear this?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“Remember when we went over, me and the kids sat with the other people of color and you sat with your sister and her side of the family?
“Yes, I remember. What is wrong with that?”
“Well, me and my colored friends got loud and excited, and you shot me a look, like ‘pipe down over there.’ THEN, after we got home, the next day, your sister called you and said that you had better control your wife; she is too loud. Do you remember all that?
“Yes, well you do get loud – especially when you are around your people.”
“So why is it I have to fit in with your relatives and not the other way round? Why do I have to conform to the whiteness in your sister’s world, not the other way round?”
“Well, we were in her house.”
“So if they came to our house and were too quiet, how would you feel if I called them up and said they needed to participate with more enthusiasm?”
“Esi, that’s not fair, and you know it isn’t.”
Esi stops and looks at the therapist.
“So I check myself. It is the same all over, White people imposing their values and beliefs on me, on us. I am not an angry Black woman. I am just frustrated. People, White people, always want an explanation for what they think is my loss of control. You can see when their demeanor changes, they pull back, sit up, back away, fidget, and won’t look you in the eye. All these little tics that show that they are trying to get out of the situation.”
Esi took a breath and saw that her husband and the therapist were listening.
“These signs are ingrained in your brain ... these signs ... I saw it when I first came here to this country. The first time I had a good dose of it ... was in that ethics class in college. You can’t use words that you are accustomed to, ’cause they mean something else here, something bad.”
“Oh, Esi, I am so sorry,” said Joe, looking concerned.
“You may be sorry but you are not willing to stand up for me against your sister and her White values. You want me to conform.”
“What do you want me to do?”
“I want you to call your sister out.”
“But she may not ever speak to me again!”
“OK, don’t then,” and Esi looked down at her hands. She was finished talking. Joe looked at the therapist, waiting for something.
The therapist resisted intervening on the issue. “Keep talking this through,” he instructed them.
Joe could see that Esi had done talking and that it was his move.
“Do you really want me to call my sister out, even if it means that she will not talk to me again?”
“Yes.”
“I don’t know if I can do that.”
The therapist now intervened: “What does that mean to you, Esi, that he doesn’t know if he can do that.”
“It means he doesn’t really love me or value me or even value our mulatto children. What do think our daughter is learning?”
“That’s not true, Esi.”
The therapist, Dr. Swarthmore, watched Esi, who has very a dark, blue-black skin tone, with a flawless complexion and a shapely body. She wears her hair cropped and she looks like that Black model, what’s her name. Joe was short, a little plump with ultra White skin and freckles on his nose. He had been brought up in the Midwest and had had little exposure to Africans before his internship abroad in Kenya. Dr. S. thought he had probably not really thought much about Esi’s dilemma.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged Esi to talk about her immigration experience.
“Esi, can you talk more about what it is like to be an immigrant from Africa?”
“Well, I just have to check myself so that I can fit in with this White culture. If you want to see how I feel about it, you will have to see an angry Black woman and I have learned not to give you that satisfaction. You will just dismiss me. Please Dr. Swarthmore, can we move on?”
Dr. Swarthmore was caught between his desire to accept her wish to move on and his wish to have her express herself fully. He realized that it was not his desire that mattered; that the couple had to work this out between them if they were going to move forward. So he punted it back to them.
“Esi and Joe, you are both caught in an important dilemma. Esi, you want more respect from your husband and his family. Joe, you do not want to upset your family by confronting them. Is that right? You are both dammed if you do and dammed if you don’t.”
“I agree,” Joe and Esi both said, nodding.
“Do you want to work on this issue?”
They both agreed with equal enthusiasm.
“Ok, can you spend the next 10 minutes to work on this?”
They agreed.
“Ok, let’s start. What skills do you have that can help you resolve this important issue?”
Dr. Swarthmore framed the issue as one to be solved by the couple. The couple discussed that they are usually good at communication and solving problems. This problem is about whether or not Joe is more aligned with his White family than with Esi and their children.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged them to think about this more deeply and over time; that this is such an important issue that it requires time and deep conversation.
“How do you think you can educate yourselves about the issues at hand?”
Esi’s reading list
1. “Why I’m No Longer Talking to White People About Race” by Reni Eddo-Lodge (London: Bloomsbury, 2018).
2. “Americanah” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2013).
3. “How to be an Antiracist” by Ibram X. Kendi (New York: Random House, 2019).
Joe suggests that Esi think about what it might mean if his sister and their children were no longer part of their lives. She agrees to do this.
Dr. Swarthmore asks if they can each do their homework before they come back. They agree and thought they could manage that and the book for 2 weeks out.
Dr. Swarthmore decides that he will read one of the books Esi suggested, as he does not know much about racism and White privilege and he wants to learn more. Dr. Swarthmore demonstrates his desire to become more racially sensitive. The following steps can be taken by therapists who want to become more racially sensitive, according to TA Laszloffy and KV Hardy (Fam Process. 2000 Spring;39[1]:35-50):
1. Read and watch movies that address the experience of other cultural groups.
2. Go to and participate in cross-cultural events.
3. Engage in a racial self-exploration process. The following questions can begin the racial identity exploration process:
- How do I define myself racially?
- When did I first become aware of race/skin color in general, and mine in particular?
- What messages did I learn about race/skin color based on that first experience?
- What direct and indirect messages did I receive about race/skin color?
- How did the messages that I received about race/skin color affect how I thought and felt about myself racially?
- What benefits did I gain because of my race/skin color?
- What did I lose because of my race/skin?
- Have I ever dated cross-racially? Why or why not?
- How many friends of a different race do I have?
4. Internal commitment. This means committing to addressing racism in therapeutic encounters.
Lessons learned for psychiatrists
1. Therapeutic space is allocated to discuss the issue.
2. The time is strictly limited to 10 minutes, so the couple won’t feel that their emotions will overwhelm them.
3. The space is to focus on the strengths that they can bring to resolving the issue.
4. Give patients the impression that they can solve this and that it is an important issue.
5. Do not put yourself in the patients’ argument; take neither side.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Heru wrote the article in collaboration with Lynette Ramsingh Barros, artist and social commentator.
Joe and Esi were in the therapist’s office wanting help with their relationship. The therapist had just asked the BIG question: How does race impact your lives?”
Esi began with her story about her ethics class, a story that was at sufficient distance from her life. Depending on her husband’s response, she would move in closer. His somewhat patronizing response made her feel both angry and that he lacked any real understanding.
“Me and a mulatto girl were in ethics class,” said Esi, who grew in Kenya. We had a White professor. He seemed to think I had no education. If you are a woman of color, you are automatically thought to have no education and that you don’t know what you are talking about. He tried to shut me up. When I persisted, I know he thought from the tone of my voice that I was an angry Black woman, even although I am not Black and I am not angry! In this country, if you have any color to your skin, you are called Black and relegated to a certain place: The bottom. I was excited about what he was teaching us, but when everyone looked at me with a certain gaze, like something bad was going to happen, all those White people, just looking, I tightened up inside and sat back down.”
Esi looked down at her folded hands. Her husband, who was White, reached over and reassuringly patted her hands.
“Yes, Esi, they are wrong. They shouldn’t have treated you that way. White people can be insensitive.”
Then, she continued, “Joe, you do the same to me!”
“What do you mean, Esi?” responded Joe, with an innocent and anxious look scanning back and forth between her and the White male therapist.
“Well, Joe, do you really want to hear how I felt last week after we came back from that party at your sister’s house?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“But do you really? Are you sure you want to hear this?”
“Yes, Esi.”
“Remember when we went over, me and the kids sat with the other people of color and you sat with your sister and her side of the family?
“Yes, I remember. What is wrong with that?”
“Well, me and my colored friends got loud and excited, and you shot me a look, like ‘pipe down over there.’ THEN, after we got home, the next day, your sister called you and said that you had better control your wife; she is too loud. Do you remember all that?
“Yes, well you do get loud – especially when you are around your people.”
“So why is it I have to fit in with your relatives and not the other way round? Why do I have to conform to the whiteness in your sister’s world, not the other way round?”
“Well, we were in her house.”
“So if they came to our house and were too quiet, how would you feel if I called them up and said they needed to participate with more enthusiasm?”
“Esi, that’s not fair, and you know it isn’t.”
Esi stops and looks at the therapist.
“So I check myself. It is the same all over, White people imposing their values and beliefs on me, on us. I am not an angry Black woman. I am just frustrated. People, White people, always want an explanation for what they think is my loss of control. You can see when their demeanor changes, they pull back, sit up, back away, fidget, and won’t look you in the eye. All these little tics that show that they are trying to get out of the situation.”
Esi took a breath and saw that her husband and the therapist were listening.
“These signs are ingrained in your brain ... these signs ... I saw it when I first came here to this country. The first time I had a good dose of it ... was in that ethics class in college. You can’t use words that you are accustomed to, ’cause they mean something else here, something bad.”
“Oh, Esi, I am so sorry,” said Joe, looking concerned.
“You may be sorry but you are not willing to stand up for me against your sister and her White values. You want me to conform.”
“What do you want me to do?”
“I want you to call your sister out.”
“But she may not ever speak to me again!”
“OK, don’t then,” and Esi looked down at her hands. She was finished talking. Joe looked at the therapist, waiting for something.
The therapist resisted intervening on the issue. “Keep talking this through,” he instructed them.
Joe could see that Esi had done talking and that it was his move.
“Do you really want me to call my sister out, even if it means that she will not talk to me again?”
“Yes.”
“I don’t know if I can do that.”
The therapist now intervened: “What does that mean to you, Esi, that he doesn’t know if he can do that.”
“It means he doesn’t really love me or value me or even value our mulatto children. What do think our daughter is learning?”
“That’s not true, Esi.”
The therapist, Dr. Swarthmore, watched Esi, who has very a dark, blue-black skin tone, with a flawless complexion and a shapely body. She wears her hair cropped and she looks like that Black model, what’s her name. Joe was short, a little plump with ultra White skin and freckles on his nose. He had been brought up in the Midwest and had had little exposure to Africans before his internship abroad in Kenya. Dr. S. thought he had probably not really thought much about Esi’s dilemma.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged Esi to talk about her immigration experience.
“Esi, can you talk more about what it is like to be an immigrant from Africa?”
“Well, I just have to check myself so that I can fit in with this White culture. If you want to see how I feel about it, you will have to see an angry Black woman and I have learned not to give you that satisfaction. You will just dismiss me. Please Dr. Swarthmore, can we move on?”
Dr. Swarthmore was caught between his desire to accept her wish to move on and his wish to have her express herself fully. He realized that it was not his desire that mattered; that the couple had to work this out between them if they were going to move forward. So he punted it back to them.
“Esi and Joe, you are both caught in an important dilemma. Esi, you want more respect from your husband and his family. Joe, you do not want to upset your family by confronting them. Is that right? You are both dammed if you do and dammed if you don’t.”
“I agree,” Joe and Esi both said, nodding.
“Do you want to work on this issue?”
They both agreed with equal enthusiasm.
“Ok, can you spend the next 10 minutes to work on this?”
They agreed.
“Ok, let’s start. What skills do you have that can help you resolve this important issue?”
Dr. Swarthmore framed the issue as one to be solved by the couple. The couple discussed that they are usually good at communication and solving problems. This problem is about whether or not Joe is more aligned with his White family than with Esi and their children.
Dr. Swarthmore encouraged them to think about this more deeply and over time; that this is such an important issue that it requires time and deep conversation.
“How do you think you can educate yourselves about the issues at hand?”
Esi’s reading list
1. “Why I’m No Longer Talking to White People About Race” by Reni Eddo-Lodge (London: Bloomsbury, 2018).
2. “Americanah” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 2013).
3. “How to be an Antiracist” by Ibram X. Kendi (New York: Random House, 2019).
Joe suggests that Esi think about what it might mean if his sister and their children were no longer part of their lives. She agrees to do this.
Dr. Swarthmore asks if they can each do their homework before they come back. They agree and thought they could manage that and the book for 2 weeks out.
Dr. Swarthmore decides that he will read one of the books Esi suggested, as he does not know much about racism and White privilege and he wants to learn more. Dr. Swarthmore demonstrates his desire to become more racially sensitive. The following steps can be taken by therapists who want to become more racially sensitive, according to TA Laszloffy and KV Hardy (Fam Process. 2000 Spring;39[1]:35-50):
1. Read and watch movies that address the experience of other cultural groups.
2. Go to and participate in cross-cultural events.
3. Engage in a racial self-exploration process. The following questions can begin the racial identity exploration process:
- How do I define myself racially?
- When did I first become aware of race/skin color in general, and mine in particular?
- What messages did I learn about race/skin color based on that first experience?
- What direct and indirect messages did I receive about race/skin color?
- How did the messages that I received about race/skin color affect how I thought and felt about myself racially?
- What benefits did I gain because of my race/skin color?
- What did I lose because of my race/skin?
- Have I ever dated cross-racially? Why or why not?
- How many friends of a different race do I have?
4. Internal commitment. This means committing to addressing racism in therapeutic encounters.
Lessons learned for psychiatrists
1. Therapeutic space is allocated to discuss the issue.
2. The time is strictly limited to 10 minutes, so the couple won’t feel that their emotions will overwhelm them.
3. The space is to focus on the strengths that they can bring to resolving the issue.
4. Give patients the impression that they can solve this and that it is an important issue.
5. Do not put yourself in the patients’ argument; take neither side.
Dr. Heru is professor of psychiatry at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. She is editor of “Working With Families in Medical Settings: A Multidisciplinary Guide for Psychiatrists and Other Health Professionals” (New York: Routledge, 2013). She has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Heru wrote the article in collaboration with Lynette Ramsingh Barros, artist and social commentator.