User login
COVID-19 ranks as a leading cause of death in United States
Adults over age 45 were more likely to die from COVID-19 than car crashes, respiratory diseases, drug overdoses, and suicide. And those over age 55 faced even higher rates of dying because of the coronavirus.
“The current exponential increase in COVID-19 is reaching a calamitous scale in the U.S.,” the authors wrote. “Putting these numbers in perspective may be difficult.”
Population health researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University put COVID-19 deaths into context by comparing this year’s numbers to the leading causes of death for March through October 2018, sorting by age.
By October 2020, COVID-19 had become the third leading cause of death overall for those between the ages of 45 and 84 years, following after heart disease and cancer. For those over age 85, COVID-19 was the second leading cause of death, surpassing cancer and following behind heart disease.
For people aged 35-44 years, COVID-19 surpassed car crashes and respiratory diseases and was slightly lower than suicide, heart disease, and cancer. For those under age 35, drug overdoses, suicide, and car crashes remained the leading causes of death.
Importantly, the authors wrote, death rates for the two leading causes – heart disease and cancer – are about 1,700 and 1,600 per day, respectively. COVID-19 deaths have surpassed these numbers individually throughout December and, on Wednesday, beat them combined. More than 3,400 deaths were reported, according to the COVID Tracking Project, marking an all-time high that continues to increase. Hospitalizations were also at a new high, with more than 113,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, and another 232,000 new cases were reported.
“With COVID-19 mortality rates now exceeding these thresholds, this infectious disease has become deadlier than heart disease and cancer,” the authors wrote. “Its lethality may increase further as transmission increases with holiday travel and gatherings and with the intensified indoor exposure that winter brings.”
The reported number of COVID-19 deaths is likely a 20% underestimate, they wrote, attributable to delays in reporting and an increase in non–COVID-19 deaths that were undetected and untreated because of pandemic-related disruptions. Since the coronavirus is communicable and spreads easily, COVID-19 deaths are particularly unique and worrying, they said.
“Individuals who die from homicide or cancer do not transmit the risk of morbidity and mortality to those nearby,” they wrote. “Every COVID-19 death signals the possibility of more deaths among close contacts.”
The fall surge in cases and deaths is widespread nationally, as compared to the spring, with hot spots on both coasts and in rural areas, according to an accompanying editorial in JAMA from public health researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. People of color have faced twice the death rate as well, with one in 875 Black people and one in 925 Indigenous people dying from COVID-19, as compared with one in 1,625 White people.
“The year 2020 ends with COVID-19 massively surging, as it was in the spring, to be the leading cause of death,” they wrote. “The accelerating numbers of deaths fall far short of fully capturing each devastating human story: Every death represents untold loss for countless families.”
Vaccines offer hope, they said, but won’t prevent the upcoming increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths this winter. In 2021, containing the pandemic will require national coordination, resources to help overwhelmed health care workers, new support for state and local public health officials, a stimulus package for schools and businesses, and financial aid for people on the brink of eviction. The country needs federal coordination of testing, contact tracing, personal protective equipment, travel precautions, and a face mask mandate, they wrote.
“Ending this crisis will require not only further advances in treatment but also unprecedented commitment to all aspects of prevention, vaccination, and public health,” they wrote. “Only by doing so can future years see this illness revert back to the unfamiliar and unknown condition it once was.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Adults over age 45 were more likely to die from COVID-19 than car crashes, respiratory diseases, drug overdoses, and suicide. And those over age 55 faced even higher rates of dying because of the coronavirus.
“The current exponential increase in COVID-19 is reaching a calamitous scale in the U.S.,” the authors wrote. “Putting these numbers in perspective may be difficult.”
Population health researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University put COVID-19 deaths into context by comparing this year’s numbers to the leading causes of death for March through October 2018, sorting by age.
By October 2020, COVID-19 had become the third leading cause of death overall for those between the ages of 45 and 84 years, following after heart disease and cancer. For those over age 85, COVID-19 was the second leading cause of death, surpassing cancer and following behind heart disease.
For people aged 35-44 years, COVID-19 surpassed car crashes and respiratory diseases and was slightly lower than suicide, heart disease, and cancer. For those under age 35, drug overdoses, suicide, and car crashes remained the leading causes of death.
Importantly, the authors wrote, death rates for the two leading causes – heart disease and cancer – are about 1,700 and 1,600 per day, respectively. COVID-19 deaths have surpassed these numbers individually throughout December and, on Wednesday, beat them combined. More than 3,400 deaths were reported, according to the COVID Tracking Project, marking an all-time high that continues to increase. Hospitalizations were also at a new high, with more than 113,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, and another 232,000 new cases were reported.
“With COVID-19 mortality rates now exceeding these thresholds, this infectious disease has become deadlier than heart disease and cancer,” the authors wrote. “Its lethality may increase further as transmission increases with holiday travel and gatherings and with the intensified indoor exposure that winter brings.”
The reported number of COVID-19 deaths is likely a 20% underestimate, they wrote, attributable to delays in reporting and an increase in non–COVID-19 deaths that were undetected and untreated because of pandemic-related disruptions. Since the coronavirus is communicable and spreads easily, COVID-19 deaths are particularly unique and worrying, they said.
“Individuals who die from homicide or cancer do not transmit the risk of morbidity and mortality to those nearby,” they wrote. “Every COVID-19 death signals the possibility of more deaths among close contacts.”
The fall surge in cases and deaths is widespread nationally, as compared to the spring, with hot spots on both coasts and in rural areas, according to an accompanying editorial in JAMA from public health researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. People of color have faced twice the death rate as well, with one in 875 Black people and one in 925 Indigenous people dying from COVID-19, as compared with one in 1,625 White people.
“The year 2020 ends with COVID-19 massively surging, as it was in the spring, to be the leading cause of death,” they wrote. “The accelerating numbers of deaths fall far short of fully capturing each devastating human story: Every death represents untold loss for countless families.”
Vaccines offer hope, they said, but won’t prevent the upcoming increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths this winter. In 2021, containing the pandemic will require national coordination, resources to help overwhelmed health care workers, new support for state and local public health officials, a stimulus package for schools and businesses, and financial aid for people on the brink of eviction. The country needs federal coordination of testing, contact tracing, personal protective equipment, travel precautions, and a face mask mandate, they wrote.
“Ending this crisis will require not only further advances in treatment but also unprecedented commitment to all aspects of prevention, vaccination, and public health,” they wrote. “Only by doing so can future years see this illness revert back to the unfamiliar and unknown condition it once was.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Adults over age 45 were more likely to die from COVID-19 than car crashes, respiratory diseases, drug overdoses, and suicide. And those over age 55 faced even higher rates of dying because of the coronavirus.
“The current exponential increase in COVID-19 is reaching a calamitous scale in the U.S.,” the authors wrote. “Putting these numbers in perspective may be difficult.”
Population health researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University put COVID-19 deaths into context by comparing this year’s numbers to the leading causes of death for March through October 2018, sorting by age.
By October 2020, COVID-19 had become the third leading cause of death overall for those between the ages of 45 and 84 years, following after heart disease and cancer. For those over age 85, COVID-19 was the second leading cause of death, surpassing cancer and following behind heart disease.
For people aged 35-44 years, COVID-19 surpassed car crashes and respiratory diseases and was slightly lower than suicide, heart disease, and cancer. For those under age 35, drug overdoses, suicide, and car crashes remained the leading causes of death.
Importantly, the authors wrote, death rates for the two leading causes – heart disease and cancer – are about 1,700 and 1,600 per day, respectively. COVID-19 deaths have surpassed these numbers individually throughout December and, on Wednesday, beat them combined. More than 3,400 deaths were reported, according to the COVID Tracking Project, marking an all-time high that continues to increase. Hospitalizations were also at a new high, with more than 113,000 COVID-19 patients in hospitals across the country, and another 232,000 new cases were reported.
“With COVID-19 mortality rates now exceeding these thresholds, this infectious disease has become deadlier than heart disease and cancer,” the authors wrote. “Its lethality may increase further as transmission increases with holiday travel and gatherings and with the intensified indoor exposure that winter brings.”
The reported number of COVID-19 deaths is likely a 20% underestimate, they wrote, attributable to delays in reporting and an increase in non–COVID-19 deaths that were undetected and untreated because of pandemic-related disruptions. Since the coronavirus is communicable and spreads easily, COVID-19 deaths are particularly unique and worrying, they said.
“Individuals who die from homicide or cancer do not transmit the risk of morbidity and mortality to those nearby,” they wrote. “Every COVID-19 death signals the possibility of more deaths among close contacts.”
The fall surge in cases and deaths is widespread nationally, as compared to the spring, with hot spots on both coasts and in rural areas, according to an accompanying editorial in JAMA from public health researchers at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. People of color have faced twice the death rate as well, with one in 875 Black people and one in 925 Indigenous people dying from COVID-19, as compared with one in 1,625 White people.
“The year 2020 ends with COVID-19 massively surging, as it was in the spring, to be the leading cause of death,” they wrote. “The accelerating numbers of deaths fall far short of fully capturing each devastating human story: Every death represents untold loss for countless families.”
Vaccines offer hope, they said, but won’t prevent the upcoming increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths this winter. In 2021, containing the pandemic will require national coordination, resources to help overwhelmed health care workers, new support for state and local public health officials, a stimulus package for schools and businesses, and financial aid for people on the brink of eviction. The country needs federal coordination of testing, contact tracing, personal protective equipment, travel precautions, and a face mask mandate, they wrote.
“Ending this crisis will require not only further advances in treatment but also unprecedented commitment to all aspects of prevention, vaccination, and public health,” they wrote. “Only by doing so can future years see this illness revert back to the unfamiliar and unknown condition it once was.”
This article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA clears first OTC rapid at-home COVID diagnostic test
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization (EUA) for the first COVID-19 diagnostic test that can be completed at home without a prescription.
Authorization of the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is “a major milestone in diagnostic testing for COVID-19,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
“By authorizing a test for over-the-counter use, the FDA allows it to be sold in places like drug stores, where a patient can buy it, swab their nose, run the test, and find out their results in as little as 20 minutes,” said Dr. Hahn.
The Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is a rapid antigen test that detects fragments of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from a nasal swab sample taken from anyone aged 2 years and older, including those not showing any symptoms.
In testing, the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test correctly identified 96% of positive samples and 100% of negative samples in individuals with symptoms.
In people without symptoms, the test correctly identified 91% of positive samples and 96% of negative samples, the FDA said.
The test includes a sterile nasal swab, a dropper, processing fluid, and a Bluetooth-connected analyzer for use with an app on the user’s smartphone. The sample is analyzed and results are automatically transmitted to the user’s smartphone.
“The Ellume COVID-19 home test’s core technology combines ultra-sensitive optics, electronics, and proprietary software to leverage best-in-class digital immunoassay technology with next-generation multi-quantum dot fluorescence technology,” the company said in a news release.
The mobile app requires individuals to input their ZIP code and date of birth, with optional fields including name and email address. The app automatically reports the results as appropriate to public health authorities to monitor disease prevalence.
Ellume expects to produce more than 3 million tests in January 2021. The company said the test will cost around $30.
FDA authorization of this first fully at-home nonprescription COVID-19 diagnostic test follows last month’s EUA for the first prescription COVID-19 test for home use, as reported this news organization.
Since the start of the pandemic, the FDA has authorized more than 225 diagnostic tests for COVID-19, including more than 25 tests that allow for home collection of samples, which are then sent to a lab for testing.
“As we continue to authorize additional tests for home use, we are helping expand Americans’ access to testing, reducing the burden on laboratories and test supplies, and giving Americans more testing options from the comfort and safety of their own homes,” Dr. Hahn said.
“This test, like other antigen tests, is less sensitive and less specific than typical molecular tests run in a lab,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in the release. “However, the fact that it can be used completely at home and return results quickly means that it can play an important role in response to the pandemic.”
As with other antigen tests, a small percentage of positive and negative results from the Ellume test may be false. In patients without symptoms, positive results should be treated as presumptively positive until confirmed by another test as soon as possible, the FDA advised.
This is especially true if there are fewer infections in a particular community, as false-positive results can be more common when antigen tests are used in populations where there is a low prevalence of COVID-19, the agency said.
Because all tests can give false-negative and false-positive results, individuals with positive results should self-isolate and seek additional care from their health care provider.
Individuals who test negative and have symptoms of COVID-19 should follow up with their health care provider, as negative results don’t preclude an individual from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization (EUA) for the first COVID-19 diagnostic test that can be completed at home without a prescription.
Authorization of the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is “a major milestone in diagnostic testing for COVID-19,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
“By authorizing a test for over-the-counter use, the FDA allows it to be sold in places like drug stores, where a patient can buy it, swab their nose, run the test, and find out their results in as little as 20 minutes,” said Dr. Hahn.
The Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is a rapid antigen test that detects fragments of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from a nasal swab sample taken from anyone aged 2 years and older, including those not showing any symptoms.
In testing, the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test correctly identified 96% of positive samples and 100% of negative samples in individuals with symptoms.
In people without symptoms, the test correctly identified 91% of positive samples and 96% of negative samples, the FDA said.
The test includes a sterile nasal swab, a dropper, processing fluid, and a Bluetooth-connected analyzer for use with an app on the user’s smartphone. The sample is analyzed and results are automatically transmitted to the user’s smartphone.
“The Ellume COVID-19 home test’s core technology combines ultra-sensitive optics, electronics, and proprietary software to leverage best-in-class digital immunoassay technology with next-generation multi-quantum dot fluorescence technology,” the company said in a news release.
The mobile app requires individuals to input their ZIP code and date of birth, with optional fields including name and email address. The app automatically reports the results as appropriate to public health authorities to monitor disease prevalence.
Ellume expects to produce more than 3 million tests in January 2021. The company said the test will cost around $30.
FDA authorization of this first fully at-home nonprescription COVID-19 diagnostic test follows last month’s EUA for the first prescription COVID-19 test for home use, as reported this news organization.
Since the start of the pandemic, the FDA has authorized more than 225 diagnostic tests for COVID-19, including more than 25 tests that allow for home collection of samples, which are then sent to a lab for testing.
“As we continue to authorize additional tests for home use, we are helping expand Americans’ access to testing, reducing the burden on laboratories and test supplies, and giving Americans more testing options from the comfort and safety of their own homes,” Dr. Hahn said.
“This test, like other antigen tests, is less sensitive and less specific than typical molecular tests run in a lab,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in the release. “However, the fact that it can be used completely at home and return results quickly means that it can play an important role in response to the pandemic.”
As with other antigen tests, a small percentage of positive and negative results from the Ellume test may be false. In patients without symptoms, positive results should be treated as presumptively positive until confirmed by another test as soon as possible, the FDA advised.
This is especially true if there are fewer infections in a particular community, as false-positive results can be more common when antigen tests are used in populations where there is a low prevalence of COVID-19, the agency said.
Because all tests can give false-negative and false-positive results, individuals with positive results should self-isolate and seek additional care from their health care provider.
Individuals who test negative and have symptoms of COVID-19 should follow up with their health care provider, as negative results don’t preclude an individual from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an emergency-use authorization (EUA) for the first COVID-19 diagnostic test that can be completed at home without a prescription.
Authorization of the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is “a major milestone in diagnostic testing for COVID-19,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said in a news release.
“By authorizing a test for over-the-counter use, the FDA allows it to be sold in places like drug stores, where a patient can buy it, swab their nose, run the test, and find out their results in as little as 20 minutes,” said Dr. Hahn.
The Ellume COVID-19 Home Test is a rapid antigen test that detects fragments of the SARS-CoV-2 virus from a nasal swab sample taken from anyone aged 2 years and older, including those not showing any symptoms.
In testing, the Ellume COVID-19 Home Test correctly identified 96% of positive samples and 100% of negative samples in individuals with symptoms.
In people without symptoms, the test correctly identified 91% of positive samples and 96% of negative samples, the FDA said.
The test includes a sterile nasal swab, a dropper, processing fluid, and a Bluetooth-connected analyzer for use with an app on the user’s smartphone. The sample is analyzed and results are automatically transmitted to the user’s smartphone.
“The Ellume COVID-19 home test’s core technology combines ultra-sensitive optics, electronics, and proprietary software to leverage best-in-class digital immunoassay technology with next-generation multi-quantum dot fluorescence technology,” the company said in a news release.
The mobile app requires individuals to input their ZIP code and date of birth, with optional fields including name and email address. The app automatically reports the results as appropriate to public health authorities to monitor disease prevalence.
Ellume expects to produce more than 3 million tests in January 2021. The company said the test will cost around $30.
FDA authorization of this first fully at-home nonprescription COVID-19 diagnostic test follows last month’s EUA for the first prescription COVID-19 test for home use, as reported this news organization.
Since the start of the pandemic, the FDA has authorized more than 225 diagnostic tests for COVID-19, including more than 25 tests that allow for home collection of samples, which are then sent to a lab for testing.
“As we continue to authorize additional tests for home use, we are helping expand Americans’ access to testing, reducing the burden on laboratories and test supplies, and giving Americans more testing options from the comfort and safety of their own homes,” Dr. Hahn said.
“This test, like other antigen tests, is less sensitive and less specific than typical molecular tests run in a lab,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, in the release. “However, the fact that it can be used completely at home and return results quickly means that it can play an important role in response to the pandemic.”
As with other antigen tests, a small percentage of positive and negative results from the Ellume test may be false. In patients without symptoms, positive results should be treated as presumptively positive until confirmed by another test as soon as possible, the FDA advised.
This is especially true if there are fewer infections in a particular community, as false-positive results can be more common when antigen tests are used in populations where there is a low prevalence of COVID-19, the agency said.
Because all tests can give false-negative and false-positive results, individuals with positive results should self-isolate and seek additional care from their health care provider.
Individuals who test negative and have symptoms of COVID-19 should follow up with their health care provider, as negative results don’t preclude an individual from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronavirus has infected over 2% of U.S. children
After last week’s ever-so-slightly positive news, the COVID-19 numbers in children have gone back to their old ways.
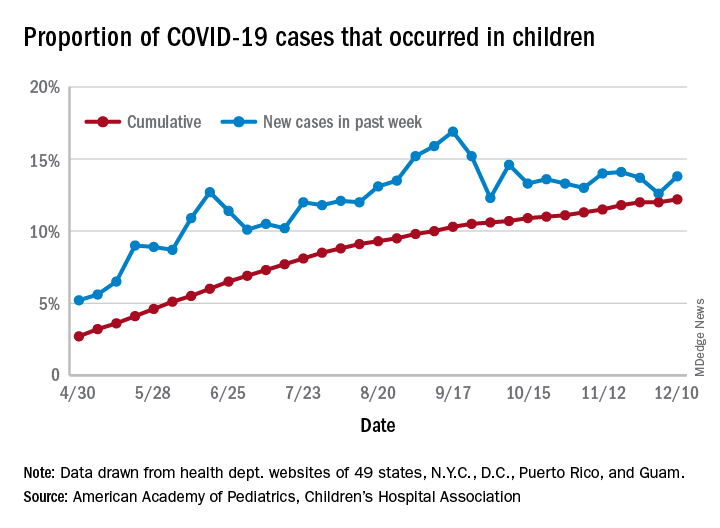
For the week ending Dec. 10, there were 178,823 new COVID-19 cases reported in U.S. children, the highest weekly total yet during the pandemic. The number of new cases had dropped the week before after setting a new high of almost 154,000 during the last full week of November, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
A new weekly high has been seen in 9 of the last 10 weeks, during which time the weekly total of child cases has gone from just over 40,000 (week ending Oct. 8) to almost 179,000, the two organizations said.
and that 2.1% of all children (2,179 per 100,000) in the United States have been infected with the coronavirus, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report, which includes health department data from 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative proportion of 12.2% has been exceeded in 27 states, as well as Puerto Rico and Guam, with the highest coming in Wyoming (21.3%), South Carolina (18.1%), and Tennessee (18.1%) and the lowest in Florida (6.7%, but the state uses an age range of 0-14 years) and New Jersey (7.6%), the AAP/CHA data show.
In a separate statement, AAP president Sally Goza, MD, welcomed the approval of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine but noted that the “virus is at unprecedented levels in nearly every community in the U.S., and in many areas, our health care system is terribly overburdened. The vaccine will not solve this overnight. I urge everyone to continue to practice social distancing, and wear masks or cloth face coverings, and get a flu shot, so we can protect the people we care about.”
Dr. Goza continued: “We applaud Pfizer-BioNTech for including children ages 12 through 17 in their clinical trials and we look forward to learning more about the data from children aged 12-15. We also want to acknowledge the discussion during the committee meeting on including 16- to 17-year-olds in the EUA [emergency-use authorization]. We believe that discussion underscores the need to keep expanding these trials to the pediatric population so we can collect robust data on this age group.”
rfranki@mdedge.com
After last week’s ever-so-slightly positive news, the COVID-19 numbers in children have gone back to their old ways.

For the week ending Dec. 10, there were 178,823 new COVID-19 cases reported in U.S. children, the highest weekly total yet during the pandemic. The number of new cases had dropped the week before after setting a new high of almost 154,000 during the last full week of November, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
A new weekly high has been seen in 9 of the last 10 weeks, during which time the weekly total of child cases has gone from just over 40,000 (week ending Oct. 8) to almost 179,000, the two organizations said.
and that 2.1% of all children (2,179 per 100,000) in the United States have been infected with the coronavirus, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report, which includes health department data from 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative proportion of 12.2% has been exceeded in 27 states, as well as Puerto Rico and Guam, with the highest coming in Wyoming (21.3%), South Carolina (18.1%), and Tennessee (18.1%) and the lowest in Florida (6.7%, but the state uses an age range of 0-14 years) and New Jersey (7.6%), the AAP/CHA data show.
In a separate statement, AAP president Sally Goza, MD, welcomed the approval of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine but noted that the “virus is at unprecedented levels in nearly every community in the U.S., and in many areas, our health care system is terribly overburdened. The vaccine will not solve this overnight. I urge everyone to continue to practice social distancing, and wear masks or cloth face coverings, and get a flu shot, so we can protect the people we care about.”
Dr. Goza continued: “We applaud Pfizer-BioNTech for including children ages 12 through 17 in their clinical trials and we look forward to learning more about the data from children aged 12-15. We also want to acknowledge the discussion during the committee meeting on including 16- to 17-year-olds in the EUA [emergency-use authorization]. We believe that discussion underscores the need to keep expanding these trials to the pediatric population so we can collect robust data on this age group.”
rfranki@mdedge.com
After last week’s ever-so-slightly positive news, the COVID-19 numbers in children have gone back to their old ways.

For the week ending Dec. 10, there were 178,823 new COVID-19 cases reported in U.S. children, the highest weekly total yet during the pandemic. The number of new cases had dropped the week before after setting a new high of almost 154,000 during the last full week of November, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
A new weekly high has been seen in 9 of the last 10 weeks, during which time the weekly total of child cases has gone from just over 40,000 (week ending Oct. 8) to almost 179,000, the two organizations said.
and that 2.1% of all children (2,179 per 100,000) in the United States have been infected with the coronavirus, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly report, which includes health department data from 49 states (New York does not report age distribution), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The cumulative proportion of 12.2% has been exceeded in 27 states, as well as Puerto Rico and Guam, with the highest coming in Wyoming (21.3%), South Carolina (18.1%), and Tennessee (18.1%) and the lowest in Florida (6.7%, but the state uses an age range of 0-14 years) and New Jersey (7.6%), the AAP/CHA data show.
In a separate statement, AAP president Sally Goza, MD, welcomed the approval of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine but noted that the “virus is at unprecedented levels in nearly every community in the U.S., and in many areas, our health care system is terribly overburdened. The vaccine will not solve this overnight. I urge everyone to continue to practice social distancing, and wear masks or cloth face coverings, and get a flu shot, so we can protect the people we care about.”
Dr. Goza continued: “We applaud Pfizer-BioNTech for including children ages 12 through 17 in their clinical trials and we look forward to learning more about the data from children aged 12-15. We also want to acknowledge the discussion during the committee meeting on including 16- to 17-year-olds in the EUA [emergency-use authorization]. We believe that discussion underscores the need to keep expanding these trials to the pediatric population so we can collect robust data on this age group.”
rfranki@mdedge.com
COVID-19 neurologic fallout not limited to the severely ill
Serious neurologic complications in patients with COVID-19 are not limited to the severely ill, new research confirms.
“We found a range of neurologic diagnoses, including stroke and seizures, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and the majority were not critically ill, suggesting that these complications are not limited just to those patients who require ICU care or a ventilator,” study investigator Pria Anand, MD, division of neuro-infectious diseases, Boston University, said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 9 in Neurology Clinical Practice.
‘Moderately severe’ disability
For the study, the investigators reviewed the medical records of 74 adults (mean age, 64 years) who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and evaluated for neurologic conditions at Boston Medical Center, a safety-net hospital caring primarily for underserved, low-income, racial and ethnic minority populations.
The most common COVID-19 symptoms on arrival to the hospital were cough (39%), dyspnea (36%), and fever (34%). Eleven patients required intubation (15%) and 28 required some form of supplemental oxygen (38%). Thirty-four patients required intensive care (46%).
The most common neurologic COVID-19 symptoms at presentation were altered mental status (53%), myalgia (24%), fatigue (24%), and headache (18%).
After neurologic assessment, the most common final neurologic diagnosis was multifactorial or toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (35%), followed by seizure (20%), ischemic stroke (20%), primary movement disorder (9%), peripheral neuropathy (8%), and hemorrhagic stroke (4%).
Three patients (4%) suffered traumatic brain injuries after falling in their homes after developing COVID-19.
Ten (14%) patients died in the hospital. Survivors had “moderately severe” disability at discharge (median modified Rankin Scale score of 4 from a preadmission mRS score of 2) and many were discharged to nursing facilities or rehabilitation hospitals.
“Although we do not have data on their posthospital course, this suggests that patients with neurologic complications of COVID-19 are likely to require ongoing rehabilitation, even after they leave the hospital,” Dr. Anand, a member of the American Academy of Neurology, said in an interview.
“There are a diverse range of mechanisms by which COVID-19 can cause neurologic complications,” Dr. Anand said.
“These complications can result from the body’s immunological response to the virus (e.g., Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disorder affecting the nerves), from having a systemic severe illness (e.g., brain injury as a result of insufficient oxygenation), from the increased tendency to form blood clots (e.g., stroke), from worsening of preexisting neurologic disorders, and possibly from involvement of the nervous system by the virus itself,” she explained.
The researchers said more study is needed to characterize the infectious and postinfectious neurologic complications of COVID-19 in diverse patient populations.
Lingering issues
In an interview, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, chair of neurology, University of Colorado, Denver, noted that this is one of the larger series published to date of the neurologic complications associated with COVID-19, and the first to come from a U.S. safety-net hospital in a large metropolitan area.
“Overall, the types and categories of neurological complications reported including encephalopathy (35%) and acute cerebrovascular events (~20%) are similar to those reported elsewhere,” said Dr. Tyler.
However, the frequency of stroke (~20%) is higher than in some other reports, “likely reflecting the comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, limited access to care [that are] present in this population,” he said.
Dr. Tyler also noted that the “relatively high frequency” of primary movement disorders, notably myoclonus, “hasn’t been particularly well recognized or described, although one of the authors has written on this in COVID-19, so perhaps there is a bit of an ‘ascertainment bias’ – as they were looking harder for it?”
Finally, he noted, it’s important to understand that all the published studies “vary tremendously in the populations they examine, so direct comparisons can be difficult.”
Also weighing in on the report in an interview, Richard Temes, MD, director, Northwell Health’s Center for Neurocritical Care in Manhasset, N.Y., said neurologic problems have been noted since the start of COVID-19 and have been well described.
“It’s common for patients to present with very nonspecific neurological complaints like confusion, disorientation, altered mental status, lethargy, but also neurological disease such as strokes, brain hemorrhages, and seizures are quite common as well,” said Dr. Temes.
He also noted that a number of patients with COVID-19 will have “lingering effects, especially patients who are hospitalized, that can range from memory deficit, cognitive slowing, and trouble with activities of daily living and depression.
“These effects can occur with any patient who is hospitalized for a [significant] period of time, especially in the intensive care unit, so it’s hard to tease out whether or not this is truly from COVID itself or if it’s just being a survivor from a very severe, critical illness. We don’t know yet. We need more data on that,” he cautioned.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Serious neurologic complications in patients with COVID-19 are not limited to the severely ill, new research confirms.
“We found a range of neurologic diagnoses, including stroke and seizures, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and the majority were not critically ill, suggesting that these complications are not limited just to those patients who require ICU care or a ventilator,” study investigator Pria Anand, MD, division of neuro-infectious diseases, Boston University, said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 9 in Neurology Clinical Practice.
‘Moderately severe’ disability
For the study, the investigators reviewed the medical records of 74 adults (mean age, 64 years) who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and evaluated for neurologic conditions at Boston Medical Center, a safety-net hospital caring primarily for underserved, low-income, racial and ethnic minority populations.
The most common COVID-19 symptoms on arrival to the hospital were cough (39%), dyspnea (36%), and fever (34%). Eleven patients required intubation (15%) and 28 required some form of supplemental oxygen (38%). Thirty-four patients required intensive care (46%).
The most common neurologic COVID-19 symptoms at presentation were altered mental status (53%), myalgia (24%), fatigue (24%), and headache (18%).
After neurologic assessment, the most common final neurologic diagnosis was multifactorial or toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (35%), followed by seizure (20%), ischemic stroke (20%), primary movement disorder (9%), peripheral neuropathy (8%), and hemorrhagic stroke (4%).
Three patients (4%) suffered traumatic brain injuries after falling in their homes after developing COVID-19.
Ten (14%) patients died in the hospital. Survivors had “moderately severe” disability at discharge (median modified Rankin Scale score of 4 from a preadmission mRS score of 2) and many were discharged to nursing facilities or rehabilitation hospitals.
“Although we do not have data on their posthospital course, this suggests that patients with neurologic complications of COVID-19 are likely to require ongoing rehabilitation, even after they leave the hospital,” Dr. Anand, a member of the American Academy of Neurology, said in an interview.
“There are a diverse range of mechanisms by which COVID-19 can cause neurologic complications,” Dr. Anand said.
“These complications can result from the body’s immunological response to the virus (e.g., Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disorder affecting the nerves), from having a systemic severe illness (e.g., brain injury as a result of insufficient oxygenation), from the increased tendency to form blood clots (e.g., stroke), from worsening of preexisting neurologic disorders, and possibly from involvement of the nervous system by the virus itself,” she explained.
The researchers said more study is needed to characterize the infectious and postinfectious neurologic complications of COVID-19 in diverse patient populations.
Lingering issues
In an interview, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, chair of neurology, University of Colorado, Denver, noted that this is one of the larger series published to date of the neurologic complications associated with COVID-19, and the first to come from a U.S. safety-net hospital in a large metropolitan area.
“Overall, the types and categories of neurological complications reported including encephalopathy (35%) and acute cerebrovascular events (~20%) are similar to those reported elsewhere,” said Dr. Tyler.
However, the frequency of stroke (~20%) is higher than in some other reports, “likely reflecting the comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, limited access to care [that are] present in this population,” he said.
Dr. Tyler also noted that the “relatively high frequency” of primary movement disorders, notably myoclonus, “hasn’t been particularly well recognized or described, although one of the authors has written on this in COVID-19, so perhaps there is a bit of an ‘ascertainment bias’ – as they were looking harder for it?”
Finally, he noted, it’s important to understand that all the published studies “vary tremendously in the populations they examine, so direct comparisons can be difficult.”
Also weighing in on the report in an interview, Richard Temes, MD, director, Northwell Health’s Center for Neurocritical Care in Manhasset, N.Y., said neurologic problems have been noted since the start of COVID-19 and have been well described.
“It’s common for patients to present with very nonspecific neurological complaints like confusion, disorientation, altered mental status, lethargy, but also neurological disease such as strokes, brain hemorrhages, and seizures are quite common as well,” said Dr. Temes.
He also noted that a number of patients with COVID-19 will have “lingering effects, especially patients who are hospitalized, that can range from memory deficit, cognitive slowing, and trouble with activities of daily living and depression.
“These effects can occur with any patient who is hospitalized for a [significant] period of time, especially in the intensive care unit, so it’s hard to tease out whether or not this is truly from COVID itself or if it’s just being a survivor from a very severe, critical illness. We don’t know yet. We need more data on that,” he cautioned.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Serious neurologic complications in patients with COVID-19 are not limited to the severely ill, new research confirms.
“We found a range of neurologic diagnoses, including stroke and seizures, among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and the majority were not critically ill, suggesting that these complications are not limited just to those patients who require ICU care or a ventilator,” study investigator Pria Anand, MD, division of neuro-infectious diseases, Boston University, said in an interview.
The study was published online Dec. 9 in Neurology Clinical Practice.
‘Moderately severe’ disability
For the study, the investigators reviewed the medical records of 74 adults (mean age, 64 years) who were hospitalized with COVID-19 and evaluated for neurologic conditions at Boston Medical Center, a safety-net hospital caring primarily for underserved, low-income, racial and ethnic minority populations.
The most common COVID-19 symptoms on arrival to the hospital were cough (39%), dyspnea (36%), and fever (34%). Eleven patients required intubation (15%) and 28 required some form of supplemental oxygen (38%). Thirty-four patients required intensive care (46%).
The most common neurologic COVID-19 symptoms at presentation were altered mental status (53%), myalgia (24%), fatigue (24%), and headache (18%).
After neurologic assessment, the most common final neurologic diagnosis was multifactorial or toxic-metabolic encephalopathy (35%), followed by seizure (20%), ischemic stroke (20%), primary movement disorder (9%), peripheral neuropathy (8%), and hemorrhagic stroke (4%).
Three patients (4%) suffered traumatic brain injuries after falling in their homes after developing COVID-19.
Ten (14%) patients died in the hospital. Survivors had “moderately severe” disability at discharge (median modified Rankin Scale score of 4 from a preadmission mRS score of 2) and many were discharged to nursing facilities or rehabilitation hospitals.
“Although we do not have data on their posthospital course, this suggests that patients with neurologic complications of COVID-19 are likely to require ongoing rehabilitation, even after they leave the hospital,” Dr. Anand, a member of the American Academy of Neurology, said in an interview.
“There are a diverse range of mechanisms by which COVID-19 can cause neurologic complications,” Dr. Anand said.
“These complications can result from the body’s immunological response to the virus (e.g., Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune disorder affecting the nerves), from having a systemic severe illness (e.g., brain injury as a result of insufficient oxygenation), from the increased tendency to form blood clots (e.g., stroke), from worsening of preexisting neurologic disorders, and possibly from involvement of the nervous system by the virus itself,” she explained.
The researchers said more study is needed to characterize the infectious and postinfectious neurologic complications of COVID-19 in diverse patient populations.
Lingering issues
In an interview, Kenneth L. Tyler, MD, chair of neurology, University of Colorado, Denver, noted that this is one of the larger series published to date of the neurologic complications associated with COVID-19, and the first to come from a U.S. safety-net hospital in a large metropolitan area.
“Overall, the types and categories of neurological complications reported including encephalopathy (35%) and acute cerebrovascular events (~20%) are similar to those reported elsewhere,” said Dr. Tyler.
However, the frequency of stroke (~20%) is higher than in some other reports, “likely reflecting the comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, limited access to care [that are] present in this population,” he said.
Dr. Tyler also noted that the “relatively high frequency” of primary movement disorders, notably myoclonus, “hasn’t been particularly well recognized or described, although one of the authors has written on this in COVID-19, so perhaps there is a bit of an ‘ascertainment bias’ – as they were looking harder for it?”
Finally, he noted, it’s important to understand that all the published studies “vary tremendously in the populations they examine, so direct comparisons can be difficult.”
Also weighing in on the report in an interview, Richard Temes, MD, director, Northwell Health’s Center for Neurocritical Care in Manhasset, N.Y., said neurologic problems have been noted since the start of COVID-19 and have been well described.
“It’s common for patients to present with very nonspecific neurological complaints like confusion, disorientation, altered mental status, lethargy, but also neurological disease such as strokes, brain hemorrhages, and seizures are quite common as well,” said Dr. Temes.
He also noted that a number of patients with COVID-19 will have “lingering effects, especially patients who are hospitalized, that can range from memory deficit, cognitive slowing, and trouble with activities of daily living and depression.
“These effects can occur with any patient who is hospitalized for a [significant] period of time, especially in the intensive care unit, so it’s hard to tease out whether or not this is truly from COVID itself or if it’s just being a survivor from a very severe, critical illness. We don’t know yet. We need more data on that,” he cautioned.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Baricitinib combo for COVID-19 accelerates recovery, study shows
according to trial results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Median time to recovery was 7 days for patients who received baricitinib versus 8 days for patients who received placebo.
The difference was greater in patients who required high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation during their hospitalization. In this group, baricitinib shortened median time to recovery from 18 days to 10 days.
“Baricitinib plus remdesivir was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time and accelerating improvement in clinical status, notably among patients receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive mechanical ventilation,” reported Andre C. Kalil, MD, MPH, from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues. In addition, the combination was associated with fewer adverse events.
The study details data from the ACTT-2 trial that the Food and Drug Administration used to issue an emergency-use authorization for baricitinib in combination with remdesivir on Nov. 19.
Under the emergency-use authorization, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly), a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, may be used in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead), an antiviral, for treating hospitalized adults and children aged at least 2 years with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination is intended for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Combo treatment favored
It is unclear how baricitinib compares with dexamethasone, which improved survival and led to a 1-day shorter hospital stay in another trial. There are differences between the drugs and trial designs, and only a “head-to-head comparison ... will allow the efficacy and safety differences between these two approaches to be fully understood,” Dr. Kalil and coauthors wrote.
“Dexamethasone has a long half-life, acts on glucocorticoid receptors, and reduces inflammation through a broad-pathway approach that has been associated with immunosuppression, hospital-acquired infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, hyperglycemia, and neuromuscular weakness, even with short courses,” they wrote. “Baricitinib has a short half-life, acts on targeted critical pathways to reduce inflammation while minimizing biologic redundancy with less immunosuppression, and may have antiviral activity.”
The ACTT-2 trial started in May and enrolled 1,033 patients in eight countries. Participants were randomly assigned to receive oral baricitinib tablets plus intravenous remdesivir or oral placebo tablets plus remdesivir.
Participants who received both drugs had significantly improved clinical status at day 15. Patients who received both treatments also had fewer serious adverse events.
“Although ACTT-2 was not powered to detect a difference in mortality between the two groups, both the survival rate and the time-to-death analyses favored combination treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The trial was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Some of the authors disclosed funding from government grants and financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gilead, and other companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to trial results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Median time to recovery was 7 days for patients who received baricitinib versus 8 days for patients who received placebo.
The difference was greater in patients who required high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation during their hospitalization. In this group, baricitinib shortened median time to recovery from 18 days to 10 days.
“Baricitinib plus remdesivir was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time and accelerating improvement in clinical status, notably among patients receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive mechanical ventilation,” reported Andre C. Kalil, MD, MPH, from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues. In addition, the combination was associated with fewer adverse events.
The study details data from the ACTT-2 trial that the Food and Drug Administration used to issue an emergency-use authorization for baricitinib in combination with remdesivir on Nov. 19.
Under the emergency-use authorization, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly), a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, may be used in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead), an antiviral, for treating hospitalized adults and children aged at least 2 years with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination is intended for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Combo treatment favored
It is unclear how baricitinib compares with dexamethasone, which improved survival and led to a 1-day shorter hospital stay in another trial. There are differences between the drugs and trial designs, and only a “head-to-head comparison ... will allow the efficacy and safety differences between these two approaches to be fully understood,” Dr. Kalil and coauthors wrote.
“Dexamethasone has a long half-life, acts on glucocorticoid receptors, and reduces inflammation through a broad-pathway approach that has been associated with immunosuppression, hospital-acquired infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, hyperglycemia, and neuromuscular weakness, even with short courses,” they wrote. “Baricitinib has a short half-life, acts on targeted critical pathways to reduce inflammation while minimizing biologic redundancy with less immunosuppression, and may have antiviral activity.”
The ACTT-2 trial started in May and enrolled 1,033 patients in eight countries. Participants were randomly assigned to receive oral baricitinib tablets plus intravenous remdesivir or oral placebo tablets plus remdesivir.
Participants who received both drugs had significantly improved clinical status at day 15. Patients who received both treatments also had fewer serious adverse events.
“Although ACTT-2 was not powered to detect a difference in mortality between the two groups, both the survival rate and the time-to-death analyses favored combination treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The trial was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Some of the authors disclosed funding from government grants and financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gilead, and other companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
according to trial results published Dec. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Median time to recovery was 7 days for patients who received baricitinib versus 8 days for patients who received placebo.
The difference was greater in patients who required high-flow oxygen or noninvasive ventilation during their hospitalization. In this group, baricitinib shortened median time to recovery from 18 days to 10 days.
“Baricitinib plus remdesivir was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time and accelerating improvement in clinical status, notably among patients receiving high-flow oxygen or noninvasive mechanical ventilation,” reported Andre C. Kalil, MD, MPH, from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and colleagues. In addition, the combination was associated with fewer adverse events.
The study details data from the ACTT-2 trial that the Food and Drug Administration used to issue an emergency-use authorization for baricitinib in combination with remdesivir on Nov. 19.
Under the emergency-use authorization, baricitinib (Olumiant, Eli Lilly), a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, may be used in combination with remdesivir (Veklury, Gilead), an antiviral, for treating hospitalized adults and children aged at least 2 years with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.
The combination is intended for patients who need supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
Combo treatment favored
It is unclear how baricitinib compares with dexamethasone, which improved survival and led to a 1-day shorter hospital stay in another trial. There are differences between the drugs and trial designs, and only a “head-to-head comparison ... will allow the efficacy and safety differences between these two approaches to be fully understood,” Dr. Kalil and coauthors wrote.
“Dexamethasone has a long half-life, acts on glucocorticoid receptors, and reduces inflammation through a broad-pathway approach that has been associated with immunosuppression, hospital-acquired infections, gastrointestinal bleeding, hyperglycemia, and neuromuscular weakness, even with short courses,” they wrote. “Baricitinib has a short half-life, acts on targeted critical pathways to reduce inflammation while minimizing biologic redundancy with less immunosuppression, and may have antiviral activity.”
The ACTT-2 trial started in May and enrolled 1,033 patients in eight countries. Participants were randomly assigned to receive oral baricitinib tablets plus intravenous remdesivir or oral placebo tablets plus remdesivir.
Participants who received both drugs had significantly improved clinical status at day 15. Patients who received both treatments also had fewer serious adverse events.
“Although ACTT-2 was not powered to detect a difference in mortality between the two groups, both the survival rate and the time-to-death analyses favored combination treatment,” the researchers wrote.
The trial was sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Some of the authors disclosed funding from government grants and financial ties to Eli Lilly, Gilead, and other companies.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ACC/AHA update two atrial fibrillation performance measures
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association Task Force on Performance Measures have made two changes to performance measures for adults with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
The 2020 Update to the 2016 ACC/AHA Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter was published online Dec. 7 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes. It was developed in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society.
Both performance measure changes were prompted by, and are in accordance with, the 2019 ACC/AHA/Heart Rhythm Society atrial fibrillation guideline focused update issued in January 2019, and reported by this news organization at that time.
The first change is the clarification that valvular atrial fibrillation is atrial fibrillation with either moderate or severe mitral stenosis or a mechanical heart valve. This change is incorporated into all the performance measures.
The second change, which only applies to the performance measure of anticoagulation prescribed, is the separation of a male and female threshold for the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
This threshold is now a score higher than 1 for men and higher than 2 for women, further demonstrating that the risk for stroke differs for men and women with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, the ACC/AHA noted in a press release.
“Successful implementation of these updated performance measures by clinicians and healthcare organizations will lead to quality improvement for adult patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter,” they said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC panel recommends Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine for people 16 and over
stating they found it was safe and effective.
The agency said it will quickly issue guidance to clinicians so they can determine when and when not to give the vaccine, and to help them communicate the risks and benefits to patients.
CDC staff gave a preview of those clinical considerations at the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) meeting on December 12 and said it would be holding calls with clinicians on December 13 and 14.
The CDC will also issue guidance December 13 on how organizations can handle the workforce problems that might arise as health care workers experience side effects from vaccination.
ACIP voted 11-0, with three recusals, to recommend use of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine in individuals 16 years or older according to the guidelines of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) emergency use authorization issued December 11.
The panel also voted unanimously to include the vaccine in 2021 immunization schedules. All panel members said the recommendation should go hand-in-hand with ACIP’s previous recommendation on December 1 that allocation of the vaccine be phased-in, with health care workers and residents and staff of long-term care facilities in phase 1a.
Allergies, pregnant women?
ACIP panelists said clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies.
The FDA health care provider information sheet said there is not enough data to recommend vaccinating those women or the immunocompromised, and also advises against giving the vaccine to individuals who have a history of serious allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologic Evaluation and Research (CBER) clarified this in a briefing on December 12, noting that women who are pregnant or lactating can make the decision in consultation with their physician. And, he said, patients with any other history of allergy should be able to safely get the vaccine.
The CDC — in its soon-to-be-released guidance — will make the same recommendations. For any woman considering vaccination, she should consider the level of COVID-19 in the community, her personal risk of contracting the virus, the risks to her or her fetus of developing the disease, and the vaccine’s known side effects, Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, a medical officer at the agency, said during the panel meeting December 12.
She added that the CDC will also urge physicians to advise women to take acetaminophen if they develop a fever after vaccination — to protect the developing fetus from fever.
Sandra Fryhofer, MD, representing the American Medical Association, commended the CDC for these recommendations. But she also called on Pfizer, the FDA, and the CDC to make data from the developmental and reproductive toxicity (DART) studies public as soon as possible.
“We really need to put those results on warp speed and get them out there to give our physicians and pregnant women more information,” said Fryhofer, an adjunct associate professor of medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) will also soon release guidance for vaccinating pregnant and breastfeeding women, said Linda Eckert, MD, FACOG, an ACOG representative on the panel.
ACOG and the CDC met the morning of December 12 to discuss risks and benefits with experts in immunology, placental pathology, and vaccine kinetics, she said.
“The overall complete consensus was that we don’t see biological plausibility at this time for placental transfer of the mRNA and that we see that direct fetal exposure or the possibility of fetal inflammatory response is extremely unlikely,” said Eckert, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. “Clearly we are waiting on the data.”
A Pfizer official told the ACIP panel that preliminary data “show no indication of either developmental or reproductive toxicity,” and that the company plans to send the final DART data to the FDA at the end of December.
On the potential for allergic reactions, the CDC concurred with the FDA that the vaccine should not be given to people with a history of serious reactions. The agency added that the category should include anyone who has had a reaction to any vaccine or injectable drug product because injectables may contain the same ingredients as the Pfizer vaccine, said Mbaeyi.
The CDC will also urge clinicians to observe patients with a history of anaphylaxis for 30 minutes after vaccination and all patients for at least 15 minutes afterward.
Should teens be a special population?
At least one ACIP panel member — Henry Bernstein, DO, MHCM, FAAP — said he was concerned that backing use of the vaccine in 16- and 17-year-olds was a leap of faith, given that Pfizer had extremely limited data on this cohort.
Bernstein, professor of pediatrics at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, also said that systemic reactions were more common in that age group.
He argued for making the 16- and 17-year-olds a “special population” that would get specific attention and guidance for vaccination from the federal agencies and professional societies.
Bernstein said he did not want to sow any more doubts in parents’ minds about vaccination, noting that hesitancy was a growing concern. “A successful pediatric vaccination program depends on creating and sustaining parental confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of this vaccine,” he said.
Many panelists, however, noted that there has been no evidence to suggest that the vaccine is not safe or less effective in that younger age group.
Yvonne Maldonado, MD, the American Academy of Pediatrics representative on the panel, said that this age group should not be denied the vaccine as they often have essential or front-line jobs that put them at higher risk for infection.
“I am very concerned about this message being sent out that this vaccine will not be safe in children,” said Maldonado, professor of pediatrics and health research and policy at Stanford University School of Medicine in California.
“We currently have no evidence that that is the case,” she said, adding there is also no indication younger children are biologically or physiologically different in their response or safety risk than 18-year-olds.
Vaccine = hope
Committee members breathed a sigh of relief at the end of the 2-day meeting, saying that although the Pfizer vaccine is not perfect, it represents a scientific milestone and a significant advance against the continuing march of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
“This vaccine and future vaccines do provide a promise for a lot of progress in the future,” said panelist Beth P. Bell, MD, MPH, clinical professor of global health at the University of Washington School of Public Health in Seattle.
Peter Szilagyi, MD, MPH, executive vice-chair and vice-chair for research at the University of California, Los Angeles pediatrics department, said, “I’m really hopeful that this is the beginning of the end of the coronavirus pandemic.”
“The need for this vaccine is profound,” said Veronica McNally, president and CEO of the Franny Strong Foundation in West Bloomfield, Michigan.
The ACIP panel also made the argument that while the at least $10 billion spent on vaccine development by the federal government’s Operation Warp Speed alone has been a good investment, more spending is needed to actually get Americans vaccinated.
The imbalance between the two is “shocking and needs to be corrected,” said Bell. “We are not going to be able to protect the American public if we don’t have a way to deliver the vaccine to them.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
stating they found it was safe and effective.
The agency said it will quickly issue guidance to clinicians so they can determine when and when not to give the vaccine, and to help them communicate the risks and benefits to patients.
CDC staff gave a preview of those clinical considerations at the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) meeting on December 12 and said it would be holding calls with clinicians on December 13 and 14.
The CDC will also issue guidance December 13 on how organizations can handle the workforce problems that might arise as health care workers experience side effects from vaccination.
ACIP voted 11-0, with three recusals, to recommend use of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine in individuals 16 years or older according to the guidelines of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) emergency use authorization issued December 11.
The panel also voted unanimously to include the vaccine in 2021 immunization schedules. All panel members said the recommendation should go hand-in-hand with ACIP’s previous recommendation on December 1 that allocation of the vaccine be phased-in, with health care workers and residents and staff of long-term care facilities in phase 1a.
Allergies, pregnant women?
ACIP panelists said clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies.
The FDA health care provider information sheet said there is not enough data to recommend vaccinating those women or the immunocompromised, and also advises against giving the vaccine to individuals who have a history of serious allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologic Evaluation and Research (CBER) clarified this in a briefing on December 12, noting that women who are pregnant or lactating can make the decision in consultation with their physician. And, he said, patients with any other history of allergy should be able to safely get the vaccine.
The CDC — in its soon-to-be-released guidance — will make the same recommendations. For any woman considering vaccination, she should consider the level of COVID-19 in the community, her personal risk of contracting the virus, the risks to her or her fetus of developing the disease, and the vaccine’s known side effects, Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, a medical officer at the agency, said during the panel meeting December 12.
She added that the CDC will also urge physicians to advise women to take acetaminophen if they develop a fever after vaccination — to protect the developing fetus from fever.
Sandra Fryhofer, MD, representing the American Medical Association, commended the CDC for these recommendations. But she also called on Pfizer, the FDA, and the CDC to make data from the developmental and reproductive toxicity (DART) studies public as soon as possible.
“We really need to put those results on warp speed and get them out there to give our physicians and pregnant women more information,” said Fryhofer, an adjunct associate professor of medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) will also soon release guidance for vaccinating pregnant and breastfeeding women, said Linda Eckert, MD, FACOG, an ACOG representative on the panel.
ACOG and the CDC met the morning of December 12 to discuss risks and benefits with experts in immunology, placental pathology, and vaccine kinetics, she said.
“The overall complete consensus was that we don’t see biological plausibility at this time for placental transfer of the mRNA and that we see that direct fetal exposure or the possibility of fetal inflammatory response is extremely unlikely,” said Eckert, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. “Clearly we are waiting on the data.”
A Pfizer official told the ACIP panel that preliminary data “show no indication of either developmental or reproductive toxicity,” and that the company plans to send the final DART data to the FDA at the end of December.
On the potential for allergic reactions, the CDC concurred with the FDA that the vaccine should not be given to people with a history of serious reactions. The agency added that the category should include anyone who has had a reaction to any vaccine or injectable drug product because injectables may contain the same ingredients as the Pfizer vaccine, said Mbaeyi.
The CDC will also urge clinicians to observe patients with a history of anaphylaxis for 30 minutes after vaccination and all patients for at least 15 minutes afterward.
Should teens be a special population?
At least one ACIP panel member — Henry Bernstein, DO, MHCM, FAAP — said he was concerned that backing use of the vaccine in 16- and 17-year-olds was a leap of faith, given that Pfizer had extremely limited data on this cohort.
Bernstein, professor of pediatrics at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, also said that systemic reactions were more common in that age group.
He argued for making the 16- and 17-year-olds a “special population” that would get specific attention and guidance for vaccination from the federal agencies and professional societies.
Bernstein said he did not want to sow any more doubts in parents’ minds about vaccination, noting that hesitancy was a growing concern. “A successful pediatric vaccination program depends on creating and sustaining parental confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of this vaccine,” he said.
Many panelists, however, noted that there has been no evidence to suggest that the vaccine is not safe or less effective in that younger age group.
Yvonne Maldonado, MD, the American Academy of Pediatrics representative on the panel, said that this age group should not be denied the vaccine as they often have essential or front-line jobs that put them at higher risk for infection.
“I am very concerned about this message being sent out that this vaccine will not be safe in children,” said Maldonado, professor of pediatrics and health research and policy at Stanford University School of Medicine in California.
“We currently have no evidence that that is the case,” she said, adding there is also no indication younger children are biologically or physiologically different in their response or safety risk than 18-year-olds.
Vaccine = hope
Committee members breathed a sigh of relief at the end of the 2-day meeting, saying that although the Pfizer vaccine is not perfect, it represents a scientific milestone and a significant advance against the continuing march of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
“This vaccine and future vaccines do provide a promise for a lot of progress in the future,” said panelist Beth P. Bell, MD, MPH, clinical professor of global health at the University of Washington School of Public Health in Seattle.
Peter Szilagyi, MD, MPH, executive vice-chair and vice-chair for research at the University of California, Los Angeles pediatrics department, said, “I’m really hopeful that this is the beginning of the end of the coronavirus pandemic.”
“The need for this vaccine is profound,” said Veronica McNally, president and CEO of the Franny Strong Foundation in West Bloomfield, Michigan.
The ACIP panel also made the argument that while the at least $10 billion spent on vaccine development by the federal government’s Operation Warp Speed alone has been a good investment, more spending is needed to actually get Americans vaccinated.
The imbalance between the two is “shocking and needs to be corrected,” said Bell. “We are not going to be able to protect the American public if we don’t have a way to deliver the vaccine to them.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
stating they found it was safe and effective.
The agency said it will quickly issue guidance to clinicians so they can determine when and when not to give the vaccine, and to help them communicate the risks and benefits to patients.
CDC staff gave a preview of those clinical considerations at the agency’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) meeting on December 12 and said it would be holding calls with clinicians on December 13 and 14.
The CDC will also issue guidance December 13 on how organizations can handle the workforce problems that might arise as health care workers experience side effects from vaccination.
ACIP voted 11-0, with three recusals, to recommend use of the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA vaccine in individuals 16 years or older according to the guidelines of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) emergency use authorization issued December 11.
The panel also voted unanimously to include the vaccine in 2021 immunization schedules. All panel members said the recommendation should go hand-in-hand with ACIP’s previous recommendation on December 1 that allocation of the vaccine be phased-in, with health care workers and residents and staff of long-term care facilities in phase 1a.
Allergies, pregnant women?
ACIP panelists said clinicians need more guidance on whether to use the vaccine in pregnant or breastfeeding women, the immunocompromised, or those who have a history of allergies.
The FDA health care provider information sheet said there is not enough data to recommend vaccinating those women or the immunocompromised, and also advises against giving the vaccine to individuals who have a history of serious allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologic Evaluation and Research (CBER) clarified this in a briefing on December 12, noting that women who are pregnant or lactating can make the decision in consultation with their physician. And, he said, patients with any other history of allergy should be able to safely get the vaccine.
The CDC — in its soon-to-be-released guidance — will make the same recommendations. For any woman considering vaccination, she should consider the level of COVID-19 in the community, her personal risk of contracting the virus, the risks to her or her fetus of developing the disease, and the vaccine’s known side effects, Sarah Mbaeyi, MD, MPH, a medical officer at the agency, said during the panel meeting December 12.
She added that the CDC will also urge physicians to advise women to take acetaminophen if they develop a fever after vaccination — to protect the developing fetus from fever.
Sandra Fryhofer, MD, representing the American Medical Association, commended the CDC for these recommendations. But she also called on Pfizer, the FDA, and the CDC to make data from the developmental and reproductive toxicity (DART) studies public as soon as possible.
“We really need to put those results on warp speed and get them out there to give our physicians and pregnant women more information,” said Fryhofer, an adjunct associate professor of medicine at Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) will also soon release guidance for vaccinating pregnant and breastfeeding women, said Linda Eckert, MD, FACOG, an ACOG representative on the panel.
ACOG and the CDC met the morning of December 12 to discuss risks and benefits with experts in immunology, placental pathology, and vaccine kinetics, she said.
“The overall complete consensus was that we don’t see biological plausibility at this time for placental transfer of the mRNA and that we see that direct fetal exposure or the possibility of fetal inflammatory response is extremely unlikely,” said Eckert, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle. “Clearly we are waiting on the data.”
A Pfizer official told the ACIP panel that preliminary data “show no indication of either developmental or reproductive toxicity,” and that the company plans to send the final DART data to the FDA at the end of December.
On the potential for allergic reactions, the CDC concurred with the FDA that the vaccine should not be given to people with a history of serious reactions. The agency added that the category should include anyone who has had a reaction to any vaccine or injectable drug product because injectables may contain the same ingredients as the Pfizer vaccine, said Mbaeyi.
The CDC will also urge clinicians to observe patients with a history of anaphylaxis for 30 minutes after vaccination and all patients for at least 15 minutes afterward.
Should teens be a special population?
At least one ACIP panel member — Henry Bernstein, DO, MHCM, FAAP — said he was concerned that backing use of the vaccine in 16- and 17-year-olds was a leap of faith, given that Pfizer had extremely limited data on this cohort.
Bernstein, professor of pediatrics at the Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, New York, also said that systemic reactions were more common in that age group.
He argued for making the 16- and 17-year-olds a “special population” that would get specific attention and guidance for vaccination from the federal agencies and professional societies.
Bernstein said he did not want to sow any more doubts in parents’ minds about vaccination, noting that hesitancy was a growing concern. “A successful pediatric vaccination program depends on creating and sustaining parental confidence in both the safety and effectiveness of this vaccine,” he said.
Many panelists, however, noted that there has been no evidence to suggest that the vaccine is not safe or less effective in that younger age group.
Yvonne Maldonado, MD, the American Academy of Pediatrics representative on the panel, said that this age group should not be denied the vaccine as they often have essential or front-line jobs that put them at higher risk for infection.
“I am very concerned about this message being sent out that this vaccine will not be safe in children,” said Maldonado, professor of pediatrics and health research and policy at Stanford University School of Medicine in California.
“We currently have no evidence that that is the case,” she said, adding there is also no indication younger children are biologically or physiologically different in their response or safety risk than 18-year-olds.
Vaccine = hope
Committee members breathed a sigh of relief at the end of the 2-day meeting, saying that although the Pfizer vaccine is not perfect, it represents a scientific milestone and a significant advance against the continuing march of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
“This vaccine and future vaccines do provide a promise for a lot of progress in the future,” said panelist Beth P. Bell, MD, MPH, clinical professor of global health at the University of Washington School of Public Health in Seattle.
Peter Szilagyi, MD, MPH, executive vice-chair and vice-chair for research at the University of California, Los Angeles pediatrics department, said, “I’m really hopeful that this is the beginning of the end of the coronavirus pandemic.”
“The need for this vaccine is profound,” said Veronica McNally, president and CEO of the Franny Strong Foundation in West Bloomfield, Michigan.
The ACIP panel also made the argument that while the at least $10 billion spent on vaccine development by the federal government’s Operation Warp Speed alone has been a good investment, more spending is needed to actually get Americans vaccinated.
The imbalance between the two is “shocking and needs to be corrected,” said Bell. “We are not going to be able to protect the American public if we don’t have a way to deliver the vaccine to them.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs emergency use of Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
The much-anticipated emergency use authorization (EUA) of this vaccine — the first such approval in the United States — was greeted with optimism by infectious disease and pulmonary experts, although unanswered questions remain regarding use in people with allergic hypersensitivity, safety in pregnant women, and how smooth distribution will be.
“I am delighted. This is a first, firm step on a long path to getting this COVID pandemic under control,” William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The FDA gave the green light after the December 10 recommendation from the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) meeting. The committee voted 17-4 in favor of the emergency authorization.
The COVID-19 vaccine is “going to have a major impact here in the US. I’m very optimistic about it,” Dial Hewlett, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of American (IDSA), told this news organization.
Daniel Culver, DO, chair of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, is likewise hopeful. “My understanding is that supplies of the vaccine are already in place in hubs and will be shipped relatively quickly. The hope would be we can start vaccinating people as early as next week.”
Allergic reactions reported in the UK
After vaccinations with the Pfizer vaccine began in the UK on December 8, reports surfaced of two healthcare workers who experienced allergic reactions. They have since recovered, but officials warned that people with a history of severe allergic reactions should not receive the Pfizer vaccine at this time.
“For the moment, they are asking people who have had notable allergic reactions to step aside while this is investigated. It shows you that the system is working,” Schaffner said.
Both vaccine recipients who experienced anaphylaxis carried EpiPens, as they were at high risk for allergic reactions, Hewlett said. Also, if other COVID-19 vaccines are approved for use in the future, people allergic to the Pfizer vaccine might have another option, he added.
Reassuring role models
Schaffner supports the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) decision to start vaccinations with healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities.
“Vaccinating healthcare workers, in particular, will be a model for the general public,” said Schaffner, who is also a former member of the IDSA board of directors. “If they see those of us in white coats and blue scrubs lining up for the vaccine, that will provide confidence.”
To further increase acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine, public health officials need to provide information and reassure the general public, Schaffner said.
Hewlett agreed. “I know there are a lot of people in the population who are very hesitant about vaccines. As infection disease specialists and people in public health, we are trying to allay a lot of concerns people have.”
Reassurance will be especially important in minority communities. “They have been disproportionately affected by the virus, and they have a traditional history of not being optimally vaccinated,” Schaffner said. “We need to reach them in particular with good information and reassurance…so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families.”
No vaccine is 100% effective or completely free of side effects. “There is always a chance there can be adverse reactions, but we think for the most part this is going to be a safe and effective vaccine,” said Hewlett, medical director at the Division of Disease Control and deputy to commissioner of health at the Westchester County Department of Health in White Plains, New York.
Distribution: Smooth or full of strife?
In addition to the concern that some people will not take advantage of vaccination against COVID-19, there could be vaccine supply issues down the road, Schaffner said.
Culver agreed. “In the early phases, I expect that there will be some kinks to work out, but because the numbers are relatively small, this should be okay,” he said.
“I think when we start to get into larger-scale vaccination programs — the supply chain, transport, and storage will be a Herculean undertaking,” Culver added. “It will take careful coordination between healthcare providers, distributors, suppliers, and public health officials to pull this off.”
Planning and distribution also should focus beyond US borders. Any issues in vaccine distribution or administration in the United States “will only be multiplied in several other parts of the world,” Culver said. Because COVID-19 is a pandemic, “we need to think about vaccinating globally.”
Investigating adverse events
Adverse events common to vaccinations in general — injection site pain, headaches, and fever — would not be unexpected with the COVID-19 vaccines. However, experts remain concerned that other, unrelated adverse events might be erroneously attributed to vaccination. For example, if a fall, heart attack, or death occurs within days of immunization, some might immediately blame the vaccine product.
“It’s important to remember that any new, highly touted medical therapy like this will receive a lot of scrutiny, so it would be unusual not to hear about something happening to somebody,” Culver said. Vaccine companies and health agencies will be carefully evaluating any reported adverse events to ensure no safety signal was missed in the trials.
“Fortunately, there are systems in place to investigate these events immediately,” Schaffner said.
Pregnancy recommendations pending
One question still looms: Is the COVID-19 vaccination safe for pregnant women? This isn’t just a question for the general public, either, Schaffner said. He estimated that about 70 percent of healthcare workers are women, and data suggests about 300,000 of these healthcare workers are pregnant.
“The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will speak to that just as soon as the EUA is issued,” he added.
Patients are asking Culver about the priority order for vaccination. He said it’s difficult to provide firm guidance at this point.
People also have “lingering skepticism” about whether vaccine development was done in a prudent way, Culver said. Some people question whether the Pfizer vaccine and others were rushed to market. “So we try to spend time with the patients, reassuring them that all the usual safety evaluations were carefully done,” he said.
Another concern is whether mRNA vaccines can interact with human DNA. “The quick, short, and definitive answer is no,” Schaffner said. The m stands for messenger — the vaccines transmit information. "Once it gets into a cell, the mRNA does not go anywhere near the DNA, and once it transmits its information to the cell appropriately, it gets metabolized, and we excrete all the remnants."
Hewlett pointed out that investigations and surveillance will continue. Because this is an EUA and not full approval, “that essentially means they will still be obligated to collect a lot more data than they would ordinarily,” he said.
How long immunoprotection will last also remains an unknown. “The big question left on the table now is the durability,” Culver said. “Of course, we won’t know the answer to that for quite some time.”
Schaffner and Culver have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hewlett was an employee of Pfizer until mid-2019. His previous work as Pfizer’s senior medical director of global medical product evaluation was not associated with development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The much-anticipated emergency use authorization (EUA) of this vaccine — the first such approval in the United States — was greeted with optimism by infectious disease and pulmonary experts, although unanswered questions remain regarding use in people with allergic hypersensitivity, safety in pregnant women, and how smooth distribution will be.
“I am delighted. This is a first, firm step on a long path to getting this COVID pandemic under control,” William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The FDA gave the green light after the December 10 recommendation from the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) meeting. The committee voted 17-4 in favor of the emergency authorization.
The COVID-19 vaccine is “going to have a major impact here in the US. I’m very optimistic about it,” Dial Hewlett, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of American (IDSA), told this news organization.
Daniel Culver, DO, chair of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, is likewise hopeful. “My understanding is that supplies of the vaccine are already in place in hubs and will be shipped relatively quickly. The hope would be we can start vaccinating people as early as next week.”
Allergic reactions reported in the UK
After vaccinations with the Pfizer vaccine began in the UK on December 8, reports surfaced of two healthcare workers who experienced allergic reactions. They have since recovered, but officials warned that people with a history of severe allergic reactions should not receive the Pfizer vaccine at this time.
“For the moment, they are asking people who have had notable allergic reactions to step aside while this is investigated. It shows you that the system is working,” Schaffner said.
Both vaccine recipients who experienced anaphylaxis carried EpiPens, as they were at high risk for allergic reactions, Hewlett said. Also, if other COVID-19 vaccines are approved for use in the future, people allergic to the Pfizer vaccine might have another option, he added.
Reassuring role models
Schaffner supports the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) decision to start vaccinations with healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities.
“Vaccinating healthcare workers, in particular, will be a model for the general public,” said Schaffner, who is also a former member of the IDSA board of directors. “If they see those of us in white coats and blue scrubs lining up for the vaccine, that will provide confidence.”
To further increase acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine, public health officials need to provide information and reassure the general public, Schaffner said.
Hewlett agreed. “I know there are a lot of people in the population who are very hesitant about vaccines. As infection disease specialists and people in public health, we are trying to allay a lot of concerns people have.”
Reassurance will be especially important in minority communities. “They have been disproportionately affected by the virus, and they have a traditional history of not being optimally vaccinated,” Schaffner said. “We need to reach them in particular with good information and reassurance…so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families.”
No vaccine is 100% effective or completely free of side effects. “There is always a chance there can be adverse reactions, but we think for the most part this is going to be a safe and effective vaccine,” said Hewlett, medical director at the Division of Disease Control and deputy to commissioner of health at the Westchester County Department of Health in White Plains, New York.
Distribution: Smooth or full of strife?
In addition to the concern that some people will not take advantage of vaccination against COVID-19, there could be vaccine supply issues down the road, Schaffner said.
Culver agreed. “In the early phases, I expect that there will be some kinks to work out, but because the numbers are relatively small, this should be okay,” he said.
“I think when we start to get into larger-scale vaccination programs — the supply chain, transport, and storage will be a Herculean undertaking,” Culver added. “It will take careful coordination between healthcare providers, distributors, suppliers, and public health officials to pull this off.”
Planning and distribution also should focus beyond US borders. Any issues in vaccine distribution or administration in the United States “will only be multiplied in several other parts of the world,” Culver said. Because COVID-19 is a pandemic, “we need to think about vaccinating globally.”
Investigating adverse events
Adverse events common to vaccinations in general — injection site pain, headaches, and fever — would not be unexpected with the COVID-19 vaccines. However, experts remain concerned that other, unrelated adverse events might be erroneously attributed to vaccination. For example, if a fall, heart attack, or death occurs within days of immunization, some might immediately blame the vaccine product.
“It’s important to remember that any new, highly touted medical therapy like this will receive a lot of scrutiny, so it would be unusual not to hear about something happening to somebody,” Culver said. Vaccine companies and health agencies will be carefully evaluating any reported adverse events to ensure no safety signal was missed in the trials.
“Fortunately, there are systems in place to investigate these events immediately,” Schaffner said.
Pregnancy recommendations pending
One question still looms: Is the COVID-19 vaccination safe for pregnant women? This isn’t just a question for the general public, either, Schaffner said. He estimated that about 70 percent of healthcare workers are women, and data suggests about 300,000 of these healthcare workers are pregnant.
“The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will speak to that just as soon as the EUA is issued,” he added.
Patients are asking Culver about the priority order for vaccination. He said it’s difficult to provide firm guidance at this point.
People also have “lingering skepticism” about whether vaccine development was done in a prudent way, Culver said. Some people question whether the Pfizer vaccine and others were rushed to market. “So we try to spend time with the patients, reassuring them that all the usual safety evaluations were carefully done,” he said.
Another concern is whether mRNA vaccines can interact with human DNA. “The quick, short, and definitive answer is no,” Schaffner said. The m stands for messenger — the vaccines transmit information. "Once it gets into a cell, the mRNA does not go anywhere near the DNA, and once it transmits its information to the cell appropriately, it gets metabolized, and we excrete all the remnants."
Hewlett pointed out that investigations and surveillance will continue. Because this is an EUA and not full approval, “that essentially means they will still be obligated to collect a lot more data than they would ordinarily,” he said.
How long immunoprotection will last also remains an unknown. “The big question left on the table now is the durability,” Culver said. “Of course, we won’t know the answer to that for quite some time.”
Schaffner and Culver have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hewlett was an employee of Pfizer until mid-2019. His previous work as Pfizer’s senior medical director of global medical product evaluation was not associated with development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The much-anticipated emergency use authorization (EUA) of this vaccine — the first such approval in the United States — was greeted with optimism by infectious disease and pulmonary experts, although unanswered questions remain regarding use in people with allergic hypersensitivity, safety in pregnant women, and how smooth distribution will be.
“I am delighted. This is a first, firm step on a long path to getting this COVID pandemic under control,” William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine in Nashville, Tennessee, said in an interview.
The FDA gave the green light after the December 10 recommendation from the agency’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) meeting. The committee voted 17-4 in favor of the emergency authorization.
The COVID-19 vaccine is “going to have a major impact here in the US. I’m very optimistic about it,” Dial Hewlett, MD, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of American (IDSA), told this news organization.
Daniel Culver, DO, chair of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, is likewise hopeful. “My understanding is that supplies of the vaccine are already in place in hubs and will be shipped relatively quickly. The hope would be we can start vaccinating people as early as next week.”
Allergic reactions reported in the UK
After vaccinations with the Pfizer vaccine began in the UK on December 8, reports surfaced of two healthcare workers who experienced allergic reactions. They have since recovered, but officials warned that people with a history of severe allergic reactions should not receive the Pfizer vaccine at this time.
“For the moment, they are asking people who have had notable allergic reactions to step aside while this is investigated. It shows you that the system is working,” Schaffner said.
Both vaccine recipients who experienced anaphylaxis carried EpiPens, as they were at high risk for allergic reactions, Hewlett said. Also, if other COVID-19 vaccines are approved for use in the future, people allergic to the Pfizer vaccine might have another option, he added.
Reassuring role models
Schaffner supports the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) decision to start vaccinations with healthcare workers and residents of long-term care facilities.
“Vaccinating healthcare workers, in particular, will be a model for the general public,” said Schaffner, who is also a former member of the IDSA board of directors. “If they see those of us in white coats and blue scrubs lining up for the vaccine, that will provide confidence.”
To further increase acceptance of the COVID-19 vaccine, public health officials need to provide information and reassure the general public, Schaffner said.
Hewlett agreed. “I know there are a lot of people in the population who are very hesitant about vaccines. As infection disease specialists and people in public health, we are trying to allay a lot of concerns people have.”
Reassurance will be especially important in minority communities. “They have been disproportionately affected by the virus, and they have a traditional history of not being optimally vaccinated,” Schaffner said. “We need to reach them in particular with good information and reassurance…so they can make good decisions for themselves and their families.”
No vaccine is 100% effective or completely free of side effects. “There is always a chance there can be adverse reactions, but we think for the most part this is going to be a safe and effective vaccine,” said Hewlett, medical director at the Division of Disease Control and deputy to commissioner of health at the Westchester County Department of Health in White Plains, New York.
Distribution: Smooth or full of strife?
In addition to the concern that some people will not take advantage of vaccination against COVID-19, there could be vaccine supply issues down the road, Schaffner said.
Culver agreed. “In the early phases, I expect that there will be some kinks to work out, but because the numbers are relatively small, this should be okay,” he said.
“I think when we start to get into larger-scale vaccination programs — the supply chain, transport, and storage will be a Herculean undertaking,” Culver added. “It will take careful coordination between healthcare providers, distributors, suppliers, and public health officials to pull this off.”
Planning and distribution also should focus beyond US borders. Any issues in vaccine distribution or administration in the United States “will only be multiplied in several other parts of the world,” Culver said. Because COVID-19 is a pandemic, “we need to think about vaccinating globally.”
Investigating adverse events
Adverse events common to vaccinations in general — injection site pain, headaches, and fever — would not be unexpected with the COVID-19 vaccines. However, experts remain concerned that other, unrelated adverse events might be erroneously attributed to vaccination. For example, if a fall, heart attack, or death occurs within days of immunization, some might immediately blame the vaccine product.
“It’s important to remember that any new, highly touted medical therapy like this will receive a lot of scrutiny, so it would be unusual not to hear about something happening to somebody,” Culver said. Vaccine companies and health agencies will be carefully evaluating any reported adverse events to ensure no safety signal was missed in the trials.
“Fortunately, there are systems in place to investigate these events immediately,” Schaffner said.
Pregnancy recommendations pending
One question still looms: Is the COVID-19 vaccination safe for pregnant women? This isn’t just a question for the general public, either, Schaffner said. He estimated that about 70 percent of healthcare workers are women, and data suggests about 300,000 of these healthcare workers are pregnant.
“The CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will speak to that just as soon as the EUA is issued,” he added.
Patients are asking Culver about the priority order for vaccination. He said it’s difficult to provide firm guidance at this point.
People also have “lingering skepticism” about whether vaccine development was done in a prudent way, Culver said. Some people question whether the Pfizer vaccine and others were rushed to market. “So we try to spend time with the patients, reassuring them that all the usual safety evaluations were carefully done,” he said.
Another concern is whether mRNA vaccines can interact with human DNA. “The quick, short, and definitive answer is no,” Schaffner said. The m stands for messenger — the vaccines transmit information. "Once it gets into a cell, the mRNA does not go anywhere near the DNA, and once it transmits its information to the cell appropriately, it gets metabolized, and we excrete all the remnants."
Hewlett pointed out that investigations and surveillance will continue. Because this is an EUA and not full approval, “that essentially means they will still be obligated to collect a lot more data than they would ordinarily,” he said.
How long immunoprotection will last also remains an unknown. “The big question left on the table now is the durability,” Culver said. “Of course, we won’t know the answer to that for quite some time.”
Schaffner and Culver have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hewlett was an employee of Pfizer until mid-2019. His previous work as Pfizer’s senior medical director of global medical product evaluation was not associated with development of the COVID-19 vaccine.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccines: Preparing for patient questions
With U.S. approval of one coronavirus vaccine likely imminent and approval of a second one expected soon after, physicians will likely be deluged with questions. Public attitudes about the vaccines vary by demographics, with a recent poll showing that men and older adults are more likely to choose vaccination, and women and people of color evincing more wariness.
Although the reasons for reluctance may vary, questions from patient will likely be similar. Some are related to the “warp speed” language about the vaccines. Other concerns arise from the fact that the platform – mRNA – has not been used in human vaccines before. And as with any vaccine, there are rumors and false claims making the rounds on social media.
In anticipation of the most common questions physicians may encounter, two experts, Krutika Kuppalli, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Angela Rasmussen, PhD, virologist and nonresident affiliate at Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, talked in an interview about what clinicians can expect and what evidence-based – as well as compassionate – answers might look like.
Q: Will this vaccine give me COVID-19?
“There is not an intact virus in there,” Dr. Rasmussen said. The mRNA-based vaccines cannot cause COVID-19 because they don’t use any part of the coronavirus itself. Instead, the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines contain manufactured mRNA molecules that carry the instructions for building the virus’ spike protein. After vaccine administration, the recipient’s own cells take up this mRNA, use it to build this bit of protein, and display it on their surfaces. The foreign protein flag triggers the immune system response.
The mRNA does not enter the cell nucleus or interact with the recipient’s DNA. And because it’s so fragile, it degrades quite quickly. To keep that from happening before cell entry, the mRNAs are cushioned in protective fats.
Q: Was this vaccine made too quickly?
“People have been working on this platform for 30 years, so it’s not that this is brand new,” Dr. Kuppalli said.
Researchers began working on mRNA vaccines in the 1990s. Technological developments in the last decade have meant that their use has become feasible, and they have been tested in animals against many viral diseases. The mRNA vaccines are attractive because they’re expected to be safe and easily manufactured from common materials. That’s what we’ve seen in the COVID-19 pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says on its website. Design of the spike protein mRNA component began as soon as the viral genome became available in January.
Usually, rolling out a vaccine takes years, so less than a year under a program called Operation Warp Speed can seem like moving too fast, Dr. Rasmussen acknowledged. “The name has given people the impression that by going at warp speed, we’re cutting all the corners. [But] the reality is that Operation Warp Speed is mostly for manufacturing and distribution.”
What underlies the speed is a restructuring of the normal vaccine development process, Dr. Kuppalli said. The same phases of development – animal testing, a small initial human phase, a second for safety testing, a third large phase for efficacy – were all conducted as for any vaccine. But in this case, some phases were completed in parallel, rather than sequentially. This approach has proved so successful that there is already talk about making it the model for developing future vaccines.
Two other factors contributed to the speed, said Dr. Kuppalli and Dr. Rasmussen. First, gearing up production can slow a rollout, but with these vaccines, companies ramped up production even before anyone knew if the vaccines would work – the “warp speed” part. The second factor has been the large number of cases, making exposures more likely and thus accelerating the results of the efficacy trials. “There is so much COVID being transmitted everywhere in the United States that it did not take long to hit the threshold of events to read out phase 3,” Dr. Rasmussen said.
Q: This vaccine has never been used in humans. How do we know it’s safe?
The Pfizer phase 3 trial included more than 43,000 people, and Moderna’s had more than 30,000. The first humans received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines in March. The most common adverse events emerge right after a vaccination, Dr. Kuppalli said.
As with any vaccine that gains approval, monitoring will continue.
UK health officials have reported that two health care workers vaccinated in the initial rollout of the Pfizer vaccine had what seems to have been a severe allergic response. Both recipients had a history of anaphylactic allergic responses and carried EpiPens, and both recovered. During the trial, allergic reaction rates were 0.63% in the vaccine group and 0.51% in the placebo group.
As a result of the two reactions, UK regulators are now recommending that patients with a history of severe allergies not receive the vaccine at the current time.
Q: What are the likely side effects?
So far, the most common side effects are pain at the injection site and an achy, flu-like feeling, Dr. Kuppalli said. More severe reactions have been reported, but were not common in the trials.
Dr. Rasmussen noted that the common side effects are a good sign, and signal that the recipient is generating “a robust immune response.”
“Everybody I’ve talked to who’s had the response has said they would go through it again,” Dr. Kruppalli said. “I definitely plan on lining up and being one of the first people to get the vaccine.”
Q: I already had COVID-19 or had a positive antibody test. Do I still need to get the vaccine?
Dr. Rasmussen said that there are “too many unknowns” to say if a history of COVID-19 would make a difference. “We don’t know how long neutralizing antibodies last” after infection, she said. “What we know is that the vaccine tends to produce antibody titers towards the higher end of the spectrum,” suggesting better immunity with vaccination than after natural infection.
Q: Can patients of color feel safe getting the vaccine?
“People of color might be understandably reluctant to take a vaccine that was developed in a way that appears to be faster [than past development],” said Dr. Rasmussen. She said physicians should acknowledge and understand the history that has led them to feel that way, “everything from Tuskegee to Henrietta Lacks to today.”
Empathy is key, and “providers should meet patients where they are and not condescend to them.”
Dr. Kuppalli agreed. “Clinicians really need to work on trying to strip away their biases.”
Thus far there are no safety signals that differ by race or ethnicity, according to the companies. The Pfizer phase 3 trial enrolled just over 9% Black participants, 0.5% Native American/Alaska Native, 0.2% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 2.3% multiracial participants, and 28% Hispanic/Latinx. For its part, Moderna says that approximately 37% of participants in its phase 3 trial come from communities of color.
Q: What about children and pregnant women?
Although the trials included participants from many different age groups and backgrounds, children and pregnant or lactating women were not among them. Pfizer gained approval in October to include participants as young as age 12 years, and a Moderna spokesperson said in an interview that the company planned pediatric inclusion at the end of 2020, pending approval.
“Unfortunately, we don’t have data on pregnant and lactating women,” Dr. Kuppalli said. She said she hopes that public health organizations such as the CDC will address that in the coming weeks. Dr. Rasmussen called the lack of data in pregnant women and children “a big oversight.”
Dr. Rasmussen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuppalli is a consultant with GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
With U.S. approval of one coronavirus vaccine likely imminent and approval of a second one expected soon after, physicians will likely be deluged with questions. Public attitudes about the vaccines vary by demographics, with a recent poll showing that men and older adults are more likely to choose vaccination, and women and people of color evincing more wariness.
Although the reasons for reluctance may vary, questions from patient will likely be similar. Some are related to the “warp speed” language about the vaccines. Other concerns arise from the fact that the platform – mRNA – has not been used in human vaccines before. And as with any vaccine, there are rumors and false claims making the rounds on social media.
In anticipation of the most common questions physicians may encounter, two experts, Krutika Kuppalli, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Angela Rasmussen, PhD, virologist and nonresident affiliate at Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, talked in an interview about what clinicians can expect and what evidence-based – as well as compassionate – answers might look like.
Q: Will this vaccine give me COVID-19?
“There is not an intact virus in there,” Dr. Rasmussen said. The mRNA-based vaccines cannot cause COVID-19 because they don’t use any part of the coronavirus itself. Instead, the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines contain manufactured mRNA molecules that carry the instructions for building the virus’ spike protein. After vaccine administration, the recipient’s own cells take up this mRNA, use it to build this bit of protein, and display it on their surfaces. The foreign protein flag triggers the immune system response.
The mRNA does not enter the cell nucleus or interact with the recipient’s DNA. And because it’s so fragile, it degrades quite quickly. To keep that from happening before cell entry, the mRNAs are cushioned in protective fats.
Q: Was this vaccine made too quickly?
“People have been working on this platform for 30 years, so it’s not that this is brand new,” Dr. Kuppalli said.
Researchers began working on mRNA vaccines in the 1990s. Technological developments in the last decade have meant that their use has become feasible, and they have been tested in animals against many viral diseases. The mRNA vaccines are attractive because they’re expected to be safe and easily manufactured from common materials. That’s what we’ve seen in the COVID-19 pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says on its website. Design of the spike protein mRNA component began as soon as the viral genome became available in January.
Usually, rolling out a vaccine takes years, so less than a year under a program called Operation Warp Speed can seem like moving too fast, Dr. Rasmussen acknowledged. “The name has given people the impression that by going at warp speed, we’re cutting all the corners. [But] the reality is that Operation Warp Speed is mostly for manufacturing and distribution.”
What underlies the speed is a restructuring of the normal vaccine development process, Dr. Kuppalli said. The same phases of development – animal testing, a small initial human phase, a second for safety testing, a third large phase for efficacy – were all conducted as for any vaccine. But in this case, some phases were completed in parallel, rather than sequentially. This approach has proved so successful that there is already talk about making it the model for developing future vaccines.
Two other factors contributed to the speed, said Dr. Kuppalli and Dr. Rasmussen. First, gearing up production can slow a rollout, but with these vaccines, companies ramped up production even before anyone knew if the vaccines would work – the “warp speed” part. The second factor has been the large number of cases, making exposures more likely and thus accelerating the results of the efficacy trials. “There is so much COVID being transmitted everywhere in the United States that it did not take long to hit the threshold of events to read out phase 3,” Dr. Rasmussen said.
Q: This vaccine has never been used in humans. How do we know it’s safe?
The Pfizer phase 3 trial included more than 43,000 people, and Moderna’s had more than 30,000. The first humans received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines in March. The most common adverse events emerge right after a vaccination, Dr. Kuppalli said.
As with any vaccine that gains approval, monitoring will continue.
UK health officials have reported that two health care workers vaccinated in the initial rollout of the Pfizer vaccine had what seems to have been a severe allergic response. Both recipients had a history of anaphylactic allergic responses and carried EpiPens, and both recovered. During the trial, allergic reaction rates were 0.63% in the vaccine group and 0.51% in the placebo group.
As a result of the two reactions, UK regulators are now recommending that patients with a history of severe allergies not receive the vaccine at the current time.
Q: What are the likely side effects?
So far, the most common side effects are pain at the injection site and an achy, flu-like feeling, Dr. Kuppalli said. More severe reactions have been reported, but were not common in the trials.
Dr. Rasmussen noted that the common side effects are a good sign, and signal that the recipient is generating “a robust immune response.”
“Everybody I’ve talked to who’s had the response has said they would go through it again,” Dr. Kruppalli said. “I definitely plan on lining up and being one of the first people to get the vaccine.”
Q: I already had COVID-19 or had a positive antibody test. Do I still need to get the vaccine?
Dr. Rasmussen said that there are “too many unknowns” to say if a history of COVID-19 would make a difference. “We don’t know how long neutralizing antibodies last” after infection, she said. “What we know is that the vaccine tends to produce antibody titers towards the higher end of the spectrum,” suggesting better immunity with vaccination than after natural infection.
Q: Can patients of color feel safe getting the vaccine?
“People of color might be understandably reluctant to take a vaccine that was developed in a way that appears to be faster [than past development],” said Dr. Rasmussen. She said physicians should acknowledge and understand the history that has led them to feel that way, “everything from Tuskegee to Henrietta Lacks to today.”
Empathy is key, and “providers should meet patients where they are and not condescend to them.”
Dr. Kuppalli agreed. “Clinicians really need to work on trying to strip away their biases.”
Thus far there are no safety signals that differ by race or ethnicity, according to the companies. The Pfizer phase 3 trial enrolled just over 9% Black participants, 0.5% Native American/Alaska Native, 0.2% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 2.3% multiracial participants, and 28% Hispanic/Latinx. For its part, Moderna says that approximately 37% of participants in its phase 3 trial come from communities of color.
Q: What about children and pregnant women?
Although the trials included participants from many different age groups and backgrounds, children and pregnant or lactating women were not among them. Pfizer gained approval in October to include participants as young as age 12 years, and a Moderna spokesperson said in an interview that the company planned pediatric inclusion at the end of 2020, pending approval.
“Unfortunately, we don’t have data on pregnant and lactating women,” Dr. Kuppalli said. She said she hopes that public health organizations such as the CDC will address that in the coming weeks. Dr. Rasmussen called the lack of data in pregnant women and children “a big oversight.”
Dr. Rasmussen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuppalli is a consultant with GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
With U.S. approval of one coronavirus vaccine likely imminent and approval of a second one expected soon after, physicians will likely be deluged with questions. Public attitudes about the vaccines vary by demographics, with a recent poll showing that men and older adults are more likely to choose vaccination, and women and people of color evincing more wariness.
Although the reasons for reluctance may vary, questions from patient will likely be similar. Some are related to the “warp speed” language about the vaccines. Other concerns arise from the fact that the platform – mRNA – has not been used in human vaccines before. And as with any vaccine, there are rumors and false claims making the rounds on social media.
In anticipation of the most common questions physicians may encounter, two experts, Krutika Kuppalli, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of infectious diseases at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Angela Rasmussen, PhD, virologist and nonresident affiliate at Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Science and Security, Washington, talked in an interview about what clinicians can expect and what evidence-based – as well as compassionate – answers might look like.
Q: Will this vaccine give me COVID-19?
“There is not an intact virus in there,” Dr. Rasmussen said. The mRNA-based vaccines cannot cause COVID-19 because they don’t use any part of the coronavirus itself. Instead, the Moderna and Pfizer vaccines contain manufactured mRNA molecules that carry the instructions for building the virus’ spike protein. After vaccine administration, the recipient’s own cells take up this mRNA, use it to build this bit of protein, and display it on their surfaces. The foreign protein flag triggers the immune system response.
The mRNA does not enter the cell nucleus or interact with the recipient’s DNA. And because it’s so fragile, it degrades quite quickly. To keep that from happening before cell entry, the mRNAs are cushioned in protective fats.
Q: Was this vaccine made too quickly?
“People have been working on this platform for 30 years, so it’s not that this is brand new,” Dr. Kuppalli said.
Researchers began working on mRNA vaccines in the 1990s. Technological developments in the last decade have meant that their use has become feasible, and they have been tested in animals against many viral diseases. The mRNA vaccines are attractive because they’re expected to be safe and easily manufactured from common materials. That’s what we’ve seen in the COVID-19 pandemic, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says on its website. Design of the spike protein mRNA component began as soon as the viral genome became available in January.
Usually, rolling out a vaccine takes years, so less than a year under a program called Operation Warp Speed can seem like moving too fast, Dr. Rasmussen acknowledged. “The name has given people the impression that by going at warp speed, we’re cutting all the corners. [But] the reality is that Operation Warp Speed is mostly for manufacturing and distribution.”
What underlies the speed is a restructuring of the normal vaccine development process, Dr. Kuppalli said. The same phases of development – animal testing, a small initial human phase, a second for safety testing, a third large phase for efficacy – were all conducted as for any vaccine. But in this case, some phases were completed in parallel, rather than sequentially. This approach has proved so successful that there is already talk about making it the model for developing future vaccines.
Two other factors contributed to the speed, said Dr. Kuppalli and Dr. Rasmussen. First, gearing up production can slow a rollout, but with these vaccines, companies ramped up production even before anyone knew if the vaccines would work – the “warp speed” part. The second factor has been the large number of cases, making exposures more likely and thus accelerating the results of the efficacy trials. “There is so much COVID being transmitted everywhere in the United States that it did not take long to hit the threshold of events to read out phase 3,” Dr. Rasmussen said.
Q: This vaccine has never been used in humans. How do we know it’s safe?
The Pfizer phase 3 trial included more than 43,000 people, and Moderna’s had more than 30,000. The first humans received mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines in March. The most common adverse events emerge right after a vaccination, Dr. Kuppalli said.
As with any vaccine that gains approval, monitoring will continue.
UK health officials have reported that two health care workers vaccinated in the initial rollout of the Pfizer vaccine had what seems to have been a severe allergic response. Both recipients had a history of anaphylactic allergic responses and carried EpiPens, and both recovered. During the trial, allergic reaction rates were 0.63% in the vaccine group and 0.51% in the placebo group.
As a result of the two reactions, UK regulators are now recommending that patients with a history of severe allergies not receive the vaccine at the current time.
Q: What are the likely side effects?
So far, the most common side effects are pain at the injection site and an achy, flu-like feeling, Dr. Kuppalli said. More severe reactions have been reported, but were not common in the trials.
Dr. Rasmussen noted that the common side effects are a good sign, and signal that the recipient is generating “a robust immune response.”
“Everybody I’ve talked to who’s had the response has said they would go through it again,” Dr. Kruppalli said. “I definitely plan on lining up and being one of the first people to get the vaccine.”
Q: I already had COVID-19 or had a positive antibody test. Do I still need to get the vaccine?
Dr. Rasmussen said that there are “too many unknowns” to say if a history of COVID-19 would make a difference. “We don’t know how long neutralizing antibodies last” after infection, she said. “What we know is that the vaccine tends to produce antibody titers towards the higher end of the spectrum,” suggesting better immunity with vaccination than after natural infection.
Q: Can patients of color feel safe getting the vaccine?
“People of color might be understandably reluctant to take a vaccine that was developed in a way that appears to be faster [than past development],” said Dr. Rasmussen. She said physicians should acknowledge and understand the history that has led them to feel that way, “everything from Tuskegee to Henrietta Lacks to today.”
Empathy is key, and “providers should meet patients where they are and not condescend to them.”
Dr. Kuppalli agreed. “Clinicians really need to work on trying to strip away their biases.”
Thus far there are no safety signals that differ by race or ethnicity, according to the companies. The Pfizer phase 3 trial enrolled just over 9% Black participants, 0.5% Native American/Alaska Native, 0.2% Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, 2.3% multiracial participants, and 28% Hispanic/Latinx. For its part, Moderna says that approximately 37% of participants in its phase 3 trial come from communities of color.
Q: What about children and pregnant women?
Although the trials included participants from many different age groups and backgrounds, children and pregnant or lactating women were not among them. Pfizer gained approval in October to include participants as young as age 12 years, and a Moderna spokesperson said in an interview that the company planned pediatric inclusion at the end of 2020, pending approval.
“Unfortunately, we don’t have data on pregnant and lactating women,” Dr. Kuppalli said. She said she hopes that public health organizations such as the CDC will address that in the coming weeks. Dr. Rasmussen called the lack of data in pregnant women and children “a big oversight.”
Dr. Rasmussen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kuppalli is a consultant with GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D deficiency in COVID-19 quadrupled death rate
Vitamin D deficiency on admission to hospital was associated with a 3.7-fold increase in the odds of dying from COVID-19, according to an observational study looking back at data from the first wave of the pandemic.
Nearly 60% of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient upon hospitalization, with men in the advanced stages of COVID-19 pneumonia showing the greatest deficit.
Importantly, the results were independent of comorbidities known to be affected by vitamin D deficiency, wrote the authors, led by Dieter De Smet, MD, from AZ Delta General Hospital, Roeselare, Belgium.
“[The findings] highlight the need for randomized, controlled trials specifically targeting vitamin D–deficient patients at intake, and make a call for general avoidance of vitamin D deficiency as a safe and inexpensive possible mitigation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic,” Dr. De Smet and colleagues wrote in their article, published online Nov. 25 in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
A search of ClinicalTrials.gov reveals there are currently close to 40 ongoing intervention trials with vitamin D in COVID-19 around the world for varying purposes, including prevention, and varying forms of treatment.
Consider vitamin D to prevent COVID-19 infection
With regard to the potential role in prevention, “Numerous observational studies have shown that low vitamin D levels are a major predictor for poor COVID outcomes,” noted Jacob Teitelbaum, MD, an internist who specializes in treating chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia who also has an interest in COVID-19.
“This study shows how severe a problem this is,” Dr. Teitelbaum said in an interview. “A 3.7-fold increase in death rate if someone’s vitamin D level was below 20 [ng/mL] is staggering. It is arguably one of the most important risk factors to consider.”
“What is not clear is whether vitamin D levels are acting as an acute-phase reactant, dropping because of the infection, with larger drops indicating more severe disease, or whether vitamin D deficiency is causing worse outcomes,” added Dr. Teitelbaum, who is director of the Center for Effective CFIDS/Fibromyalgia Therapies, Kailua-Kona, Hawaii.
Also asked to comment, Andrea Giustina, MD, president of the European Society of Endocrinology, said: “The paper by De Smet et al confirms what we already hypothesized in BMJ last March: that patients with low vitamin D levels are at high risk of hospitalization for COVID-19 and developing severe and lethal disease. This is likely due to the loss in the protective action of vitamin D on the immune system and against the SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm.”
He said it is particularly interesting that the authors of the new study had reported more prevalent vitamin D deficiency among men than women, most likely because women are more often treated with vitamin D for osteoporosis.
The new study should prompt all clinicians and health authorities to seriously consider vitamin D supplementation as an additional tool in the fight against COVID-19, particularly for the prevention of infection in those at high risk of both COVID-19 and hypovitaminosis D, such the elderly, urged Dr. Giustina, of San Raffaele Vita-Salute University, Milan.
Results adjusted for multiple confounders
Dr. De Smet and colleagues looked at serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in 186 patients hospitalized for severe COVID-19 infection as a function of radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia as well as the association between vitamin D status on admission and COVID-19 mortality.
Cognizant of the potential for confounding by multiple factors, they adjusted for age, sex, and known vitamin D–affected comorbidities such as diabetes, chronic lung disease, and coronary artery disease.
Patients were hospitalized from March 1 to April 7, 2020 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic) at their institution, AZ Delta General Hospital, a tertiary network hospital.
The mean age of patients was 69 years, 41% were women, and 59% had coronary artery disease. Upon admission to hospital, median vitamin D level was 18 ng/mL (women, 20.7 ng/mL; men, 17.6 ng/mL).
A remarkably high percentage (59%, 109/186) of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient (25[OH]D <20 ng/mL) when admitted (47% of women and 67% of men), wrote the authors.
“What surprises me,” said Dr. Teitelbaum, is that almost 60% “of these patients had 25(OH)D under 20 ng/mL but most clinicians consider under 50 to be low.”
All patients had a chest CT scan to determine the radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia and serum vitamin D measurement on admission. Radiologic stage of pneumonia was used as a proxy for immunologic phase of COVID-19.
Vitamin D deficiency correlated with worsening pneumonia
Among men, rates of vitamin D deficiency increased with advancing disease, with rates of 55% in stage 1, 67% in stage 2, and up to 74% in stage 3 pneumonia.
There is therefore “a clear correlation between 25(OH)D level and temporal stages of viral pneumonia, particularly in male patients,” the authors wrote.
“Vitamin D dampens excessive inflammation,” said Dr. Teitelbaum. “In these patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, the immune system has gone wild.”
“The study was carried out in Belgium, so there’s less sunlight there than some other places, but even here in Hawaii, with plenty of sunshine, we have vitamin D deficiency,” he added.
“More studies are needed, but I think there are enough data to suggest a multivitamin should be used to aid prophylaxis, and this is reflected in [some] infectious disease recommendations,” he noted.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D deficiency on admission to hospital was associated with a 3.7-fold increase in the odds of dying from COVID-19, according to an observational study looking back at data from the first wave of the pandemic.
Nearly 60% of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient upon hospitalization, with men in the advanced stages of COVID-19 pneumonia showing the greatest deficit.
Importantly, the results were independent of comorbidities known to be affected by vitamin D deficiency, wrote the authors, led by Dieter De Smet, MD, from AZ Delta General Hospital, Roeselare, Belgium.
“[The findings] highlight the need for randomized, controlled trials specifically targeting vitamin D–deficient patients at intake, and make a call for general avoidance of vitamin D deficiency as a safe and inexpensive possible mitigation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic,” Dr. De Smet and colleagues wrote in their article, published online Nov. 25 in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
A search of ClinicalTrials.gov reveals there are currently close to 40 ongoing intervention trials with vitamin D in COVID-19 around the world for varying purposes, including prevention, and varying forms of treatment.
Consider vitamin D to prevent COVID-19 infection
With regard to the potential role in prevention, “Numerous observational studies have shown that low vitamin D levels are a major predictor for poor COVID outcomes,” noted Jacob Teitelbaum, MD, an internist who specializes in treating chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia who also has an interest in COVID-19.
“This study shows how severe a problem this is,” Dr. Teitelbaum said in an interview. “A 3.7-fold increase in death rate if someone’s vitamin D level was below 20 [ng/mL] is staggering. It is arguably one of the most important risk factors to consider.”
“What is not clear is whether vitamin D levels are acting as an acute-phase reactant, dropping because of the infection, with larger drops indicating more severe disease, or whether vitamin D deficiency is causing worse outcomes,” added Dr. Teitelbaum, who is director of the Center for Effective CFIDS/Fibromyalgia Therapies, Kailua-Kona, Hawaii.
Also asked to comment, Andrea Giustina, MD, president of the European Society of Endocrinology, said: “The paper by De Smet et al confirms what we already hypothesized in BMJ last March: that patients with low vitamin D levels are at high risk of hospitalization for COVID-19 and developing severe and lethal disease. This is likely due to the loss in the protective action of vitamin D on the immune system and against the SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm.”
He said it is particularly interesting that the authors of the new study had reported more prevalent vitamin D deficiency among men than women, most likely because women are more often treated with vitamin D for osteoporosis.
The new study should prompt all clinicians and health authorities to seriously consider vitamin D supplementation as an additional tool in the fight against COVID-19, particularly for the prevention of infection in those at high risk of both COVID-19 and hypovitaminosis D, such the elderly, urged Dr. Giustina, of San Raffaele Vita-Salute University, Milan.
Results adjusted for multiple confounders
Dr. De Smet and colleagues looked at serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in 186 patients hospitalized for severe COVID-19 infection as a function of radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia as well as the association between vitamin D status on admission and COVID-19 mortality.
Cognizant of the potential for confounding by multiple factors, they adjusted for age, sex, and known vitamin D–affected comorbidities such as diabetes, chronic lung disease, and coronary artery disease.
Patients were hospitalized from March 1 to April 7, 2020 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic) at their institution, AZ Delta General Hospital, a tertiary network hospital.
The mean age of patients was 69 years, 41% were women, and 59% had coronary artery disease. Upon admission to hospital, median vitamin D level was 18 ng/mL (women, 20.7 ng/mL; men, 17.6 ng/mL).
A remarkably high percentage (59%, 109/186) of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient (25[OH]D <20 ng/mL) when admitted (47% of women and 67% of men), wrote the authors.
“What surprises me,” said Dr. Teitelbaum, is that almost 60% “of these patients had 25(OH)D under 20 ng/mL but most clinicians consider under 50 to be low.”
All patients had a chest CT scan to determine the radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia and serum vitamin D measurement on admission. Radiologic stage of pneumonia was used as a proxy for immunologic phase of COVID-19.
Vitamin D deficiency correlated with worsening pneumonia
Among men, rates of vitamin D deficiency increased with advancing disease, with rates of 55% in stage 1, 67% in stage 2, and up to 74% in stage 3 pneumonia.
There is therefore “a clear correlation between 25(OH)D level and temporal stages of viral pneumonia, particularly in male patients,” the authors wrote.
“Vitamin D dampens excessive inflammation,” said Dr. Teitelbaum. “In these patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, the immune system has gone wild.”
“The study was carried out in Belgium, so there’s less sunlight there than some other places, but even here in Hawaii, with plenty of sunshine, we have vitamin D deficiency,” he added.
“More studies are needed, but I think there are enough data to suggest a multivitamin should be used to aid prophylaxis, and this is reflected in [some] infectious disease recommendations,” he noted.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Vitamin D deficiency on admission to hospital was associated with a 3.7-fold increase in the odds of dying from COVID-19, according to an observational study looking back at data from the first wave of the pandemic.
Nearly 60% of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient upon hospitalization, with men in the advanced stages of COVID-19 pneumonia showing the greatest deficit.
Importantly, the results were independent of comorbidities known to be affected by vitamin D deficiency, wrote the authors, led by Dieter De Smet, MD, from AZ Delta General Hospital, Roeselare, Belgium.
“[The findings] highlight the need for randomized, controlled trials specifically targeting vitamin D–deficient patients at intake, and make a call for general avoidance of vitamin D deficiency as a safe and inexpensive possible mitigation of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic,” Dr. De Smet and colleagues wrote in their article, published online Nov. 25 in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
A search of ClinicalTrials.gov reveals there are currently close to 40 ongoing intervention trials with vitamin D in COVID-19 around the world for varying purposes, including prevention, and varying forms of treatment.
Consider vitamin D to prevent COVID-19 infection
With regard to the potential role in prevention, “Numerous observational studies have shown that low vitamin D levels are a major predictor for poor COVID outcomes,” noted Jacob Teitelbaum, MD, an internist who specializes in treating chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia who also has an interest in COVID-19.
“This study shows how severe a problem this is,” Dr. Teitelbaum said in an interview. “A 3.7-fold increase in death rate if someone’s vitamin D level was below 20 [ng/mL] is staggering. It is arguably one of the most important risk factors to consider.”
“What is not clear is whether vitamin D levels are acting as an acute-phase reactant, dropping because of the infection, with larger drops indicating more severe disease, or whether vitamin D deficiency is causing worse outcomes,” added Dr. Teitelbaum, who is director of the Center for Effective CFIDS/Fibromyalgia Therapies, Kailua-Kona, Hawaii.
Also asked to comment, Andrea Giustina, MD, president of the European Society of Endocrinology, said: “The paper by De Smet et al confirms what we already hypothesized in BMJ last March: that patients with low vitamin D levels are at high risk of hospitalization for COVID-19 and developing severe and lethal disease. This is likely due to the loss in the protective action of vitamin D on the immune system and against the SARS-CoV-2–induced cytokine storm.”
He said it is particularly interesting that the authors of the new study had reported more prevalent vitamin D deficiency among men than women, most likely because women are more often treated with vitamin D for osteoporosis.
The new study should prompt all clinicians and health authorities to seriously consider vitamin D supplementation as an additional tool in the fight against COVID-19, particularly for the prevention of infection in those at high risk of both COVID-19 and hypovitaminosis D, such the elderly, urged Dr. Giustina, of San Raffaele Vita-Salute University, Milan.
Results adjusted for multiple confounders
Dr. De Smet and colleagues looked at serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in 186 patients hospitalized for severe COVID-19 infection as a function of radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia as well as the association between vitamin D status on admission and COVID-19 mortality.
Cognizant of the potential for confounding by multiple factors, they adjusted for age, sex, and known vitamin D–affected comorbidities such as diabetes, chronic lung disease, and coronary artery disease.
Patients were hospitalized from March 1 to April 7, 2020 (the peak of the first wave of the pandemic) at their institution, AZ Delta General Hospital, a tertiary network hospital.
The mean age of patients was 69 years, 41% were women, and 59% had coronary artery disease. Upon admission to hospital, median vitamin D level was 18 ng/mL (women, 20.7 ng/mL; men, 17.6 ng/mL).
A remarkably high percentage (59%, 109/186) of patients with COVID-19 were vitamin D deficient (25[OH]D <20 ng/mL) when admitted (47% of women and 67% of men), wrote the authors.
“What surprises me,” said Dr. Teitelbaum, is that almost 60% “of these patients had 25(OH)D under 20 ng/mL but most clinicians consider under 50 to be low.”
All patients had a chest CT scan to determine the radiologic stage of COVID-19 pneumonia and serum vitamin D measurement on admission. Radiologic stage of pneumonia was used as a proxy for immunologic phase of COVID-19.
Vitamin D deficiency correlated with worsening pneumonia
Among men, rates of vitamin D deficiency increased with advancing disease, with rates of 55% in stage 1, 67% in stage 2, and up to 74% in stage 3 pneumonia.
There is therefore “a clear correlation between 25(OH)D level and temporal stages of viral pneumonia, particularly in male patients,” the authors wrote.
“Vitamin D dampens excessive inflammation,” said Dr. Teitelbaum. “In these patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, the immune system has gone wild.”
“The study was carried out in Belgium, so there’s less sunlight there than some other places, but even here in Hawaii, with plenty of sunshine, we have vitamin D deficiency,” he added.
“More studies are needed, but I think there are enough data to suggest a multivitamin should be used to aid prophylaxis, and this is reflected in [some] infectious disease recommendations,” he noted.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.

