User login
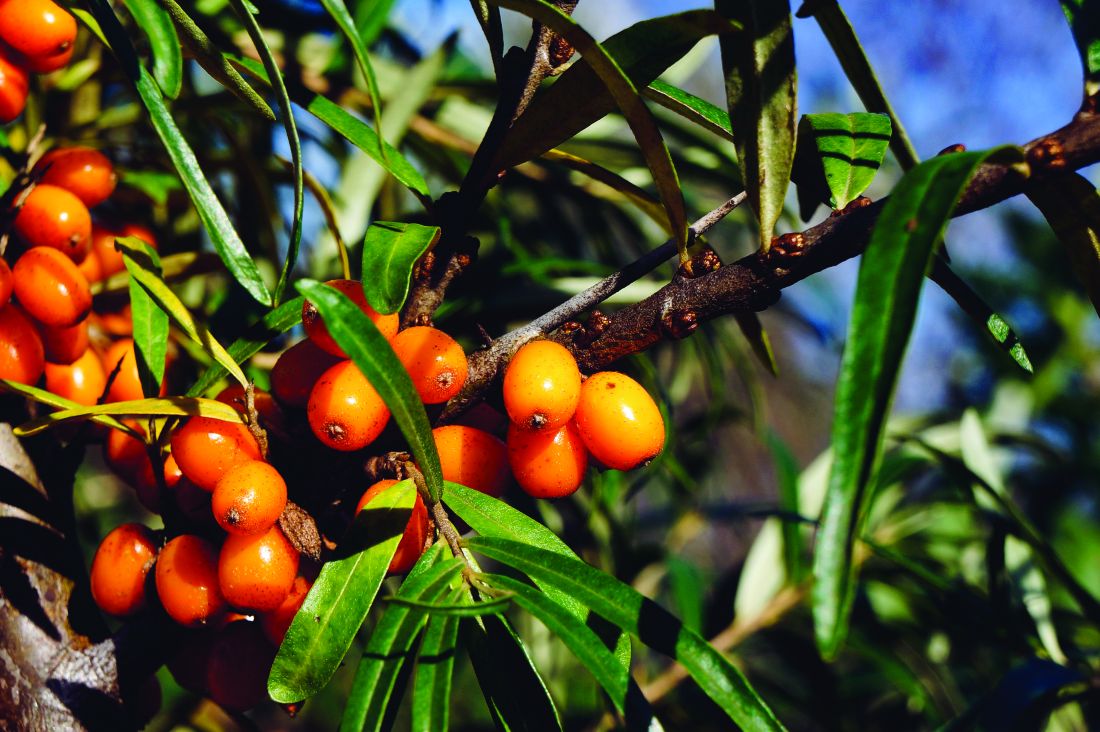
Sea Buckthorn
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
A member of the Elaeagnaceae family, Hippophae rhamnoides, better known as sea buckthorn, is a high-altitude wild shrub endemic to Europe and Asia with edible fruits and a lengthy record of use in traditional Chinese medicine.1-6 Used as a health supplement and consumed in the diet throughout the world,5 sea buckthorn berries, seeds, and leaves have been used in traditional medicine to treat burns/injuries, edema, hypertension, inflammation, skin grafts, ulcers, and wounds.4,7
This hardy plant is associated with a wide range of biologic activities, including anti-atherogenic, anti-atopic dermatitis, antibacterial, anticancer, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-psoriasis, anti-sebum, anti-stress, anti-tumor, cytoprotective, hepatoprotective, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, radioprotective, and tissue regenerative functions.4,5,8-11
Key Constituents
Functional constituents identified in sea buckthorn include alkaloids, carotenoids, flavonoids, lignans, organic acids, phenolic acids, proanthocyanidins, polyunsaturated acids (including omega-3, -6, -7, and -9), steroids, tannins, terpenoids, and volatile oils, as well as nutritional compounds such as minerals, proteins, and vitamins.4,5,11 Sea buckthorn pericarp oil contains copious amounts of saturated palmitic acid (29%-36%) and omega-7 unsaturated palmitoleic acid (36%-48%), which fosters cutaneous and mucosal epithelialization, as well as linoleic (10%-12%) and oleic (4%-6%) acids.12,6 Significant amounts of carotenoids as well as alpha‐linolenic fatty acid (38%), linoleic (36%), oleic (13%), and palmitic (7%) acids are present in sea buckthorn seed oil.6
Polysaccharides
In an expansive review on the pharmacological activities of sea buckthorn polysaccharides, Teng and colleagues reported in April 2024 that 20 diverse polysaccharides have been culled from sea buckthorn and exhibited various healthy activities, including antioxidant, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, and immunoregulation, and regulation of intestinal flora activities.1
Proanthocyanidins and Anti-Aging
In 2023, Liu and colleagues investigated the anti–skin aging impact of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins in D-galactose-induced aging in mice given the known free radical scavenging activity of these compounds. They found the proanthocyanidins mitigated D-galactose-induced aging and can augment the total antioxidant capacity of the body. Sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can further attenuate the effects of skin aging by regulating the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and MMPs/TIMP system, thus amplifying collagen I and tropoelastin content.13
A year earlier, many of the same investigators assessed the possible protective activity of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins against cutaneous aging engendered by oxidative stress from hydrogen peroxide. The compounds amplified superoxide dismutase and glutathione antioxidant functions. The extracts also fostered collagen I production in aging human skin fibroblasts via the TGF-beta1/Smads pathway and hindered collagen I degradation by regulating the MMPs/TIMPs system, which maintained extracellular matrix integrity. Senescent cell migration was also promoted with 100 mcg/mL of sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins. The researchers concluded that this sets the stage for investigating how sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can be incorporated in cosmetic formulations.14 In a separate study, Liu and colleagues demonstrated that sea buckthorn proanthocyanidins can attenuate oxidative damage and protect mitochondrial function.9
Acne and Barrier Functions
The extracts of H rhamnoides and Cassia fistula in a combined formulation were found to be effective in lowering skin sebum content in humans with grade I and grade II acne vulgaris in a 2014 single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, split-face study with two groups of 25 patients each (aged 18-37 years).15 Khan and colleagues have also reported that a sea buckthorn oil-in-water emulsion improved barrier function in human skin as tested by a tewameter and corneometer (noninvasive probes) in 13 healthy males with a mean age of 27 ± 4.8 years.16
Anti-Aging, Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Skin-Whitening Activity
Zaman and colleagues reported in 2011 that results from an in vivo study of the effects of a sea buckthorn fruit extract topical cream on stratum corneum water content and transepidermal water loss indicated that the formulation enhanced cell surface integrin expression thus facilitating collagen contraction.17
In 2012, Khan and colleagues reported amelioration in skin elasticity, thus achieving an anti-aging result, from the use of a water-in-oil–based hydroalcoholic cream loaded with fruit extract of H rhamnoides, as measured with a Cutometer.18 The previous year, some of the same researchers reported that the antioxidants and flavonoids found in a topical sea buckthorn formulation could decrease cutaneous melanin and erythema levels.
More recently, Gęgotek and colleagues found that sea buckthorn seed oil prevented redox balance and lipid metabolism disturbances in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes caused by UVA or UVB. They suggested that such findings point to the potential of this natural agent to confer anti-inflammatory properties and photoprotection to the skin.19
In 2020, Ivanišová and colleagues investigated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of H rhamnoides 100% oil, 100% juice, dry berries, and tea (dry berries, leaves, and twigs). They found that all of the studied sea buckthorn products displayed high antioxidant activity (identified through DPPH radical scavenging and molybdenum reducing antioxidant power tests). Sea buckthorn juice contained the highest total content of polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids. All of the tested products also exhibited substantial antibacterial activity against the tested microbes.20
Burns and Wound Healing
In a preclinical study of the effects of sea buckthorn leaf extracts on wound healing in albino rats using an excision-punch wound model in 2005, Gupta and colleagues found that twice daily topical application of the aqueous leaf extract fostered wound healing. This was indicated by higher hydroxyproline and protein levels, a diminished wound area, and lower lipid peroxide levels. The investigators suggested that sea buckthorn may facilitate wound healing at least in part because of elevated antioxidant activity in the granulation tissue.3
A year later, Wang and colleagues reported on observations of using H rhamnoides oil, a traditional Chinese herbal medicine derived from sea buckthorn fruit, as a burn treatment. In the study, 151 burn patients received an H rhamnoides oil dressing (changed every other day until wound healing) that was covered with a disinfecting dressing. The dressing reduced swelling and effusion, and alleviated pain, with patients receiving the sea buckthorn dressing experiencing greater apparent exudation reduction, pain reduction, and more rapid epithelial cell growth and wound healing than controls (treated only with Vaseline gauze). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant.21
Conclusion
Sea buckthorn has been used for hundreds if not thousands of years in traditional medical applications, including for dermatologic purposes. Emerging data appear to support the use of this dynamic plant for consideration in dermatologic applications. As is often the case, much more work is necessary in the form of randomized controlled trials to determine the effectiveness of sea buckthorn formulations as well as the most appropriate avenues of research or uses for dermatologic application of this traditionally used botanical agent.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a e-commerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Teng H et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117809. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117809.
2. Wang Z et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130206.
3. Gupta A et al. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2005 Jun;4(2):88-92. doi: 10.1177/1534734605277401.
4. Pundir S et al. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Feb 10;266:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113434.
5. Ma QG et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Mar 29;71(12):4769-4788. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06916.
6. Poljšak N et al. Phytother Res. 2020 Feb;34(2):254-269. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6524.
7. Upadhyay NK et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:659705. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep189.
8. Suryakumar G, Gupta A. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.024.
9. Liu K et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:914146. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.914146.
10. Akhtar N et al. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2010 Jan;2(1):13-7. doi: 10.4103/0975-7406.62698.
11. Ren R et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Dec 17;10(73):44654-44671. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06488b.
12. Ito H et al. Burns. 2014 May;40(3):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.011.
13. Liu X et al. Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 7;12(2):1082-1094. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3823.
14. Liu X at al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1900. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101900.
15. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2014 Aug;31(4):229-234. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2014.40934.
16. Khan BA, Akhtar N. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;27(6):1919-22.
17. Khan AB et al. African J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;5(8):1092-5.
18. Khan BA, Akhtar N, Braga VA. Trop J Pharm Res. 2012;11(6):955-62.
19. Gęgotek A et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Aug 23;7(9):110. doi: 10.3390/antiox7090110.
20. Ivanišová E et al. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2020 Apr-Jun;19(2):195-205. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.0809.
21. Wang ZY, Luo XL, He CP. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Jan;26(1):124-5.
Study Evaluates Safety of Benzoyl Peroxide Products for Acne
according to results from an analysis that used gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and other methods.
The analysis, which was published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and expands on a similar study released more than 6 months ago, also found that encapsulated BPO products break down into benzene at room temperature but that refrigerating them may mitigate this effect.
“Our research provides the first experimental evidence that cold storage can help reduce the rate of benzoyl peroxide breakdown into benzene,” said one of the study authors, Christopher G. Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. “Therefore, cold storage throughout the entire supply chain — from manufacturing to patient use — is a reasonable and proportional measure at this time for those continuing to use benzoyl peroxide medicine.” One acne product, the newer prescription triple-combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-BPO) “already has a cold shipping process in place; the patient just needs to continue that at home,” he noted.
For the study — which was funded by an independent lab, Valisure — researchers led by Valisure CEO and founder David Light, used gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to detect benzene levels in 111 BPO drug products from major US retailers and selected ion flow tube mass-spectrometry to quantify the release of benzene in real time. Benzene levels ranged from 0.16 ppm to 35.30 ppm, and 38 of the products (34%) had levels above the FDA limit of 2 ppm for drug products. “The results of the products sampled in this study suggest that formulation is likely the strongest contributor to benzene concentrations in BPO drug products that are commercially available, since the magnitude of benzene detected correlates most closely with specific brands or product types within certain brands,” the study authors wrote.
When the researchers tested the stability of a prescription encapsulated BPO drug product at cold (2 °C) and elevated temperature (50 °C), no apparent benzene formation was observed at 2 °C, whereas high levels of benzene formed at 50 °C, “suggesting that encapsulation technology may not stabilize BPO drug products, but cold storage may greatly reduce benzene formation,” they wrote.
In another component of the study, researchers exposed a BP drug product to a UVA/UVB lamp for 2 hours and found detectable benzene through evaporation and substantial benzene formation when exposed to UV light at levels below peak sunlight. The experiment “strongly justifies the package label warnings to avoid sun exposure when using BPO drug products,” the authors wrote. “Further evaluation to determine the influence of sun exposure on BPO drug product degradation and benzene formation is warranted.”
In an interview, John Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts characterized the findings as “an important issue that we should take seriously.” However, “we also must not overreact.”
BPO is a foundational acne treatment without any clear alternative, he said, pointing out that no evidence currently exists “to support that routine use of benzoyl peroxide–containing products for acne is associated with a meaningful risk of benzene in the blood or an increased risk of cancer.”
And although it is prudent to minimize benzene exposure as much as possible, Barbieri continued, “it is not clear that these levels are a clinically meaningful incremental risk in the setting of an acne cream or wash. There is minimal cutaneous absorption of benzene, and it is uncertain how much benzene aerosolizes with routine use, particularly for washes which are not left on the skin.”
Bunick said that the combined data from this and the study published in March 2024 affected which BPO products he recommends for patients with acne. “I am using exclusively the triple combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-benzoyl peroxide) because I know it has the necessary cold supply chain in place to protect the product’s stability. I further encourage patients to place all their benzoyl peroxide–containing products in the refrigerator at home to reduce benzene formation and exposure.”
Bunick reported having served as an investigator and/or a consultant/speaker for many pharmaceutical companies, including as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics; but none related to this study. Barbieri reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results from an analysis that used gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and other methods.
The analysis, which was published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and expands on a similar study released more than 6 months ago, also found that encapsulated BPO products break down into benzene at room temperature but that refrigerating them may mitigate this effect.
“Our research provides the first experimental evidence that cold storage can help reduce the rate of benzoyl peroxide breakdown into benzene,” said one of the study authors, Christopher G. Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. “Therefore, cold storage throughout the entire supply chain — from manufacturing to patient use — is a reasonable and proportional measure at this time for those continuing to use benzoyl peroxide medicine.” One acne product, the newer prescription triple-combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-BPO) “already has a cold shipping process in place; the patient just needs to continue that at home,” he noted.
For the study — which was funded by an independent lab, Valisure — researchers led by Valisure CEO and founder David Light, used gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to detect benzene levels in 111 BPO drug products from major US retailers and selected ion flow tube mass-spectrometry to quantify the release of benzene in real time. Benzene levels ranged from 0.16 ppm to 35.30 ppm, and 38 of the products (34%) had levels above the FDA limit of 2 ppm for drug products. “The results of the products sampled in this study suggest that formulation is likely the strongest contributor to benzene concentrations in BPO drug products that are commercially available, since the magnitude of benzene detected correlates most closely with specific brands or product types within certain brands,” the study authors wrote.
When the researchers tested the stability of a prescription encapsulated BPO drug product at cold (2 °C) and elevated temperature (50 °C), no apparent benzene formation was observed at 2 °C, whereas high levels of benzene formed at 50 °C, “suggesting that encapsulation technology may not stabilize BPO drug products, but cold storage may greatly reduce benzene formation,” they wrote.
In another component of the study, researchers exposed a BP drug product to a UVA/UVB lamp for 2 hours and found detectable benzene through evaporation and substantial benzene formation when exposed to UV light at levels below peak sunlight. The experiment “strongly justifies the package label warnings to avoid sun exposure when using BPO drug products,” the authors wrote. “Further evaluation to determine the influence of sun exposure on BPO drug product degradation and benzene formation is warranted.”
In an interview, John Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts characterized the findings as “an important issue that we should take seriously.” However, “we also must not overreact.”
BPO is a foundational acne treatment without any clear alternative, he said, pointing out that no evidence currently exists “to support that routine use of benzoyl peroxide–containing products for acne is associated with a meaningful risk of benzene in the blood or an increased risk of cancer.”
And although it is prudent to minimize benzene exposure as much as possible, Barbieri continued, “it is not clear that these levels are a clinically meaningful incremental risk in the setting of an acne cream or wash. There is minimal cutaneous absorption of benzene, and it is uncertain how much benzene aerosolizes with routine use, particularly for washes which are not left on the skin.”
Bunick said that the combined data from this and the study published in March 2024 affected which BPO products he recommends for patients with acne. “I am using exclusively the triple combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-benzoyl peroxide) because I know it has the necessary cold supply chain in place to protect the product’s stability. I further encourage patients to place all their benzoyl peroxide–containing products in the refrigerator at home to reduce benzene formation and exposure.”
Bunick reported having served as an investigator and/or a consultant/speaker for many pharmaceutical companies, including as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics; but none related to this study. Barbieri reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to results from an analysis that used gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and other methods.
The analysis, which was published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology and expands on a similar study released more than 6 months ago, also found that encapsulated BPO products break down into benzene at room temperature but that refrigerating them may mitigate this effect.
“Our research provides the first experimental evidence that cold storage can help reduce the rate of benzoyl peroxide breakdown into benzene,” said one of the study authors, Christopher G. Bunick, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut. “Therefore, cold storage throughout the entire supply chain — from manufacturing to patient use — is a reasonable and proportional measure at this time for those continuing to use benzoyl peroxide medicine.” One acne product, the newer prescription triple-combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-BPO) “already has a cold shipping process in place; the patient just needs to continue that at home,” he noted.
For the study — which was funded by an independent lab, Valisure — researchers led by Valisure CEO and founder David Light, used gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to detect benzene levels in 111 BPO drug products from major US retailers and selected ion flow tube mass-spectrometry to quantify the release of benzene in real time. Benzene levels ranged from 0.16 ppm to 35.30 ppm, and 38 of the products (34%) had levels above the FDA limit of 2 ppm for drug products. “The results of the products sampled in this study suggest that formulation is likely the strongest contributor to benzene concentrations in BPO drug products that are commercially available, since the magnitude of benzene detected correlates most closely with specific brands or product types within certain brands,” the study authors wrote.
When the researchers tested the stability of a prescription encapsulated BPO drug product at cold (2 °C) and elevated temperature (50 °C), no apparent benzene formation was observed at 2 °C, whereas high levels of benzene formed at 50 °C, “suggesting that encapsulation technology may not stabilize BPO drug products, but cold storage may greatly reduce benzene formation,” they wrote.
In another component of the study, researchers exposed a BP drug product to a UVA/UVB lamp for 2 hours and found detectable benzene through evaporation and substantial benzene formation when exposed to UV light at levels below peak sunlight. The experiment “strongly justifies the package label warnings to avoid sun exposure when using BPO drug products,” the authors wrote. “Further evaluation to determine the influence of sun exposure on BPO drug product degradation and benzene formation is warranted.”
In an interview, John Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts characterized the findings as “an important issue that we should take seriously.” However, “we also must not overreact.”
BPO is a foundational acne treatment without any clear alternative, he said, pointing out that no evidence currently exists “to support that routine use of benzoyl peroxide–containing products for acne is associated with a meaningful risk of benzene in the blood or an increased risk of cancer.”
And although it is prudent to minimize benzene exposure as much as possible, Barbieri continued, “it is not clear that these levels are a clinically meaningful incremental risk in the setting of an acne cream or wash. There is minimal cutaneous absorption of benzene, and it is uncertain how much benzene aerosolizes with routine use, particularly for washes which are not left on the skin.”
Bunick said that the combined data from this and the study published in March 2024 affected which BPO products he recommends for patients with acne. “I am using exclusively the triple combination therapy (adapalene-clindamycin-benzoyl peroxide) because I know it has the necessary cold supply chain in place to protect the product’s stability. I further encourage patients to place all their benzoyl peroxide–containing products in the refrigerator at home to reduce benzene formation and exposure.”
Bunick reported having served as an investigator and/or a consultant/speaker for many pharmaceutical companies, including as a consultant for Ortho-Dermatologics; but none related to this study. Barbieri reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY
Pulsed Dye Laser a “Go-To Device” Option for Acne Treatment When Access to 1726-nm Lasers Is Limited
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — Lasers and energy-based treatments alone or in combination with medical therapy may improve outcomes for patients with moderate to severe acne, according to Arielle Kauvar, MD.
At the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium, Kauvar, director of New York Laser & Skin Care, New York City, highlighted several reasons why using lasers for acne is beneficial. “First, we know that topical therapy alone is often ineffective, and antibiotic treatment does not address the cause of acne and can alter the skin and gut microbiome,” she said. “Isotretinoin is highly effective, but there’s an increasing reluctance to use it. Lasers and energy devices are effective in treating acne and may also treat the post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and scarring associated with it.”
The pathogenesis of acne is multifactorial, she continued, including a disruption of sebaceous gland activity, with overproduction and alteration of sebum and abnormal follicular keratinization. Acne also causes an imbalance of the skin microbiome, local inflammation, and activation of both innate and adaptive immunity.
“Many studies point to the fact that inflammation and immune system activation may actually be the primary event” of acne formation, said Kauvar, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at New York University, New York City. “This persistent immune activation is also associated with scarring,” she noted. “So, are we off the mark in terms of trying to kill sebaceous glands? Should we be concentrating on anti-inflammatory approaches?”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris in 2022, followed a few months later with the FDA clearance of another 1726-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System in November 2022. These lasers cause selective photothermolysis of sebaceous glands, but according to Kauvar, “access to these devices is somewhat limited at this time.”
What is available includes her go-to device, the pulsed dye laser (PDL), which has been widely studied and shown in a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies to be effective for acne. The PDL “targets dermal blood vessels facilitating inflammation, upregulates TGF-beta, and inhibits CD4+ T cell-mediated inflammation,” she said. “It can also treat PIH [post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation] and may be helpful in scar prevention.”
In an abstract presented at The American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) 2024 annual meeting, Kauvar and colleagues conducted a real-world study of PDL therapy in 15 adult women with recalcitrant acne who were maintained on their medical treatment regimen. Their mean age was 27 years, and they had skin types II-IV; they underwent four monthly PDL treatments with follow-up at 1 and 3 months. At each visit, the researchers took digital photographs and counted inflammatory acne lesions, non-inflammatory acne lesions, and post-inflammatory pigment alteration (PIPA) lesions.
The main outcomes of interest were the investigator global assessment (IGA) scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits. Kauvar and colleagues observed a significant improvement in IGA scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits (P < .05), with an average decrease of 1.8 and 1.6 points in the acne severity scale, respectively, from a baseline score of 3.4. By the 3-month follow-up visits, counts of inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions decreased significantly (P < .05), and 61% of study participants showed a decrease in the PIPA count. No adverse events occurred.
Kauvar disclosed that she has conducted research for Candela, Lumenis, and Sofwave, and is an adviser to Acclaro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — Lasers and energy-based treatments alone or in combination with medical therapy may improve outcomes for patients with moderate to severe acne, according to Arielle Kauvar, MD.
At the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium, Kauvar, director of New York Laser & Skin Care, New York City, highlighted several reasons why using lasers for acne is beneficial. “First, we know that topical therapy alone is often ineffective, and antibiotic treatment does not address the cause of acne and can alter the skin and gut microbiome,” she said. “Isotretinoin is highly effective, but there’s an increasing reluctance to use it. Lasers and energy devices are effective in treating acne and may also treat the post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and scarring associated with it.”
The pathogenesis of acne is multifactorial, she continued, including a disruption of sebaceous gland activity, with overproduction and alteration of sebum and abnormal follicular keratinization. Acne also causes an imbalance of the skin microbiome, local inflammation, and activation of both innate and adaptive immunity.
“Many studies point to the fact that inflammation and immune system activation may actually be the primary event” of acne formation, said Kauvar, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at New York University, New York City. “This persistent immune activation is also associated with scarring,” she noted. “So, are we off the mark in terms of trying to kill sebaceous glands? Should we be concentrating on anti-inflammatory approaches?”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris in 2022, followed a few months later with the FDA clearance of another 1726-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System in November 2022. These lasers cause selective photothermolysis of sebaceous glands, but according to Kauvar, “access to these devices is somewhat limited at this time.”
What is available includes her go-to device, the pulsed dye laser (PDL), which has been widely studied and shown in a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies to be effective for acne. The PDL “targets dermal blood vessels facilitating inflammation, upregulates TGF-beta, and inhibits CD4+ T cell-mediated inflammation,” she said. “It can also treat PIH [post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation] and may be helpful in scar prevention.”
In an abstract presented at The American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) 2024 annual meeting, Kauvar and colleagues conducted a real-world study of PDL therapy in 15 adult women with recalcitrant acne who were maintained on their medical treatment regimen. Their mean age was 27 years, and they had skin types II-IV; they underwent four monthly PDL treatments with follow-up at 1 and 3 months. At each visit, the researchers took digital photographs and counted inflammatory acne lesions, non-inflammatory acne lesions, and post-inflammatory pigment alteration (PIPA) lesions.
The main outcomes of interest were the investigator global assessment (IGA) scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits. Kauvar and colleagues observed a significant improvement in IGA scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits (P < .05), with an average decrease of 1.8 and 1.6 points in the acne severity scale, respectively, from a baseline score of 3.4. By the 3-month follow-up visits, counts of inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions decreased significantly (P < .05), and 61% of study participants showed a decrease in the PIPA count. No adverse events occurred.
Kauvar disclosed that she has conducted research for Candela, Lumenis, and Sofwave, and is an adviser to Acclaro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — Lasers and energy-based treatments alone or in combination with medical therapy may improve outcomes for patients with moderate to severe acne, according to Arielle Kauvar, MD.
At the Controversies and Conversations in Laser and Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium, Kauvar, director of New York Laser & Skin Care, New York City, highlighted several reasons why using lasers for acne is beneficial. “First, we know that topical therapy alone is often ineffective, and antibiotic treatment does not address the cause of acne and can alter the skin and gut microbiome,” she said. “Isotretinoin is highly effective, but there’s an increasing reluctance to use it. Lasers and energy devices are effective in treating acne and may also treat the post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and scarring associated with it.”
The pathogenesis of acne is multifactorial, she continued, including a disruption of sebaceous gland activity, with overproduction and alteration of sebum and abnormal follicular keratinization. Acne also causes an imbalance of the skin microbiome, local inflammation, and activation of both innate and adaptive immunity.
“Many studies point to the fact that inflammation and immune system activation may actually be the primary event” of acne formation, said Kauvar, who is also a clinical professor of dermatology at New York University, New York City. “This persistent immune activation is also associated with scarring,” she noted. “So, are we off the mark in terms of trying to kill sebaceous glands? Should we be concentrating on anti-inflammatory approaches?”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris in 2022, followed a few months later with the FDA clearance of another 1726-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System in November 2022. These lasers cause selective photothermolysis of sebaceous glands, but according to Kauvar, “access to these devices is somewhat limited at this time.”
What is available includes her go-to device, the pulsed dye laser (PDL), which has been widely studied and shown in a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies to be effective for acne. The PDL “targets dermal blood vessels facilitating inflammation, upregulates TGF-beta, and inhibits CD4+ T cell-mediated inflammation,” she said. “It can also treat PIH [post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation] and may be helpful in scar prevention.”
In an abstract presented at The American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) 2024 annual meeting, Kauvar and colleagues conducted a real-world study of PDL therapy in 15 adult women with recalcitrant acne who were maintained on their medical treatment regimen. Their mean age was 27 years, and they had skin types II-IV; they underwent four monthly PDL treatments with follow-up at 1 and 3 months. At each visit, the researchers took digital photographs and counted inflammatory acne lesions, non-inflammatory acne lesions, and post-inflammatory pigment alteration (PIPA) lesions.
The main outcomes of interest were the investigator global assessment (IGA) scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits. Kauvar and colleagues observed a significant improvement in IGA scores at the 1- and 3-month follow-up visits (P < .05), with an average decrease of 1.8 and 1.6 points in the acne severity scale, respectively, from a baseline score of 3.4. By the 3-month follow-up visits, counts of inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions decreased significantly (P < .05), and 61% of study participants showed a decrease in the PIPA count. No adverse events occurred.
Kauvar disclosed that she has conducted research for Candela, Lumenis, and Sofwave, and is an adviser to Acclaro.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Identifying Drug-Induced Rashes in Skin of Color: Heightened Awareness Can Accelerate Diagnosis
NEW YORK — Because of their heterogeneity in appearance, to speed the diagnosis.
This risk for a delayed or missed diagnosis in patients with darker skin is shared across skin rashes, but drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) is a telling example, according to Joanna Harp, MD, director of the Inpatient Dermatology Consult Service, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital, New York City.
DIHS, also known as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, Dr. Harp explained. While the fact that this disorder does not always include eosinophilia prompted the DIHS acronym, the maculopapular rash often serves as a critical clue of the underlying etiology.
In patients with darker skin, DIHS skin manifestations “can look different, can be more severe, and can have worse outcomes,” Dr. Harp said. As with other skin rashes that are primarily erythematous, the DIHS rash is often more subtle in Black-skinned patients, typically appearing gray or violaceous rather than red.
“The high amount of scale can be a clue,” said Dr. Harp, speaking at the 2024 Skin of Color Update. Scale is particularly prominent among Black patients, she said, because of the greater relative transepidermal water loss than lighter skin, increasing dryness and susceptibility to scale.
The maculopapular rash is “similar to a simple drug eruption, although it is usually more impressive,” she said. Emphasizing that DIHS is a systemic disease, she noted that the characteristic rash is typically accompanied by inflammation in multiple organs that not only includes the mucous membranes but can include major organs such as the lungs, kidneys, and heart.
In patients with DIHS and many of the even more serious types of rashes traced to drug exposures, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or erythema multiforme, the delay to appearance of the rash from the time of exposure can be the most confusing element.
“It can be months for some drugs such as allopurinol,” said Dr. Harp, pointing out that Black and Asian patients are more likely to carry the HLA-B*5801 genotype, a known risk factor for allopurinol hypersensitivity.
Signs of AGEP Can Be Subtle in Black Patients
Some of the same principles for diagnosing drug-induced rash in darker skin can also be applied to acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), another type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Like all drug-induced rashes, the earlier AGEP is recognized and treated, the better the outcome, but in Black patients, the signs can be subtle.
“The onset is usually fast and occurs in 1-2 days after [the causative drug] exposure,” said Dr. Harp, adding that antibiotics, such as cephalosporins or penicillin, and calcium channel blockers are among the prominent causes of AGEP.
One of the hallmark signs of early-onset AGEP are tiny erythematous pustules in flexural areas, such as the neck or the armpits. The issue of detecting erythema in darker skin is also relevant to this area, but there is an additional problem, according to Dr. Harp. The pustules often dry up quickly, leaving a neutrophilic scale that further complicates the effort to see the characteristic erythema.
“If you see a lot of scale, look for erythema underneath. Think of inflammation,” Dr. Harp said, explaining that the clinical appearance evolves quickly. “If you do not see the pustules, it does not mean they were not there; you just missed them.”
In addition to the flexural areas, “AGEP loves the ears, the face, and the geographic tongue,” she said, offering several pearls to help with the diagnosis. These include side lighting to make papules easier to see, pressing on the skin to highlight the difference between erythematous skin and blanched skin, and checking less pigmented skin, such as on the hands and feet, which makes erythema easier to see.
Steroids are often the first-line treatment for drug-induced skin rashes, but Dr. Harp moves to etanercept or cyclosporine for the most serious drug reactions, such as SJS and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Etanercept is typically her first choice because patients with systemic hypersensitivity reactions with major organ involvement are often quite ill, making cyclosporine harder to use. In her experience, etanercept has been well tolerated.
Conversely, she cautioned against the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Although this has been used traditionally for severe drug hypersensitivity reactions, “the data are not there,” she said. The data are stronger for a combination of high-dose steroids and IVIG, but she thinks even these data are inconsistent and not as strong as the data supporting etanercept or cyclosporine. She encouraged centers still using IVIG to consider alternatives.
After drug sensitivity reactions are controlled, follow-up care is particularly important for Black patients who face greater risks for sequelae, such as hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, or keloids. She recommended aggressive use of emollients and sunscreens for an extended period after lesions resolve to lessen these risks.
Differences in the manifestations of drug-induced skin rashes by race and ethnicity are important and perhaps underappreciated, agreed Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chairman of the Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Asked to comment at the meeting, Dr. Kwatra said that he appreciated Dr. Harp’s effort to translate published data and her experience into an overview that increases awareness of the risk for missed or delayed diagnoses of drug-induced rashes in skin of color. He noted that the strategies to identify erythema and pustules, such as increased suspicion in skin of color and the extra steps to rule them out, such as the use of side lighting in the case of pustules for AGEP, are simple and practical.
Dr. Harp and Dr. Kwatra had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Because of their heterogeneity in appearance, to speed the diagnosis.
This risk for a delayed or missed diagnosis in patients with darker skin is shared across skin rashes, but drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) is a telling example, according to Joanna Harp, MD, director of the Inpatient Dermatology Consult Service, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital, New York City.
DIHS, also known as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, Dr. Harp explained. While the fact that this disorder does not always include eosinophilia prompted the DIHS acronym, the maculopapular rash often serves as a critical clue of the underlying etiology.
In patients with darker skin, DIHS skin manifestations “can look different, can be more severe, and can have worse outcomes,” Dr. Harp said. As with other skin rashes that are primarily erythematous, the DIHS rash is often more subtle in Black-skinned patients, typically appearing gray or violaceous rather than red.
“The high amount of scale can be a clue,” said Dr. Harp, speaking at the 2024 Skin of Color Update. Scale is particularly prominent among Black patients, she said, because of the greater relative transepidermal water loss than lighter skin, increasing dryness and susceptibility to scale.
The maculopapular rash is “similar to a simple drug eruption, although it is usually more impressive,” she said. Emphasizing that DIHS is a systemic disease, she noted that the characteristic rash is typically accompanied by inflammation in multiple organs that not only includes the mucous membranes but can include major organs such as the lungs, kidneys, and heart.
In patients with DIHS and many of the even more serious types of rashes traced to drug exposures, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or erythema multiforme, the delay to appearance of the rash from the time of exposure can be the most confusing element.
“It can be months for some drugs such as allopurinol,” said Dr. Harp, pointing out that Black and Asian patients are more likely to carry the HLA-B*5801 genotype, a known risk factor for allopurinol hypersensitivity.
Signs of AGEP Can Be Subtle in Black Patients
Some of the same principles for diagnosing drug-induced rash in darker skin can also be applied to acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), another type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Like all drug-induced rashes, the earlier AGEP is recognized and treated, the better the outcome, but in Black patients, the signs can be subtle.
“The onset is usually fast and occurs in 1-2 days after [the causative drug] exposure,” said Dr. Harp, adding that antibiotics, such as cephalosporins or penicillin, and calcium channel blockers are among the prominent causes of AGEP.
One of the hallmark signs of early-onset AGEP are tiny erythematous pustules in flexural areas, such as the neck or the armpits. The issue of detecting erythema in darker skin is also relevant to this area, but there is an additional problem, according to Dr. Harp. The pustules often dry up quickly, leaving a neutrophilic scale that further complicates the effort to see the characteristic erythema.
“If you see a lot of scale, look for erythema underneath. Think of inflammation,” Dr. Harp said, explaining that the clinical appearance evolves quickly. “If you do not see the pustules, it does not mean they were not there; you just missed them.”
In addition to the flexural areas, “AGEP loves the ears, the face, and the geographic tongue,” she said, offering several pearls to help with the diagnosis. These include side lighting to make papules easier to see, pressing on the skin to highlight the difference between erythematous skin and blanched skin, and checking less pigmented skin, such as on the hands and feet, which makes erythema easier to see.
Steroids are often the first-line treatment for drug-induced skin rashes, but Dr. Harp moves to etanercept or cyclosporine for the most serious drug reactions, such as SJS and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Etanercept is typically her first choice because patients with systemic hypersensitivity reactions with major organ involvement are often quite ill, making cyclosporine harder to use. In her experience, etanercept has been well tolerated.
Conversely, she cautioned against the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Although this has been used traditionally for severe drug hypersensitivity reactions, “the data are not there,” she said. The data are stronger for a combination of high-dose steroids and IVIG, but she thinks even these data are inconsistent and not as strong as the data supporting etanercept or cyclosporine. She encouraged centers still using IVIG to consider alternatives.
After drug sensitivity reactions are controlled, follow-up care is particularly important for Black patients who face greater risks for sequelae, such as hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, or keloids. She recommended aggressive use of emollients and sunscreens for an extended period after lesions resolve to lessen these risks.
Differences in the manifestations of drug-induced skin rashes by race and ethnicity are important and perhaps underappreciated, agreed Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chairman of the Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Asked to comment at the meeting, Dr. Kwatra said that he appreciated Dr. Harp’s effort to translate published data and her experience into an overview that increases awareness of the risk for missed or delayed diagnoses of drug-induced rashes in skin of color. He noted that the strategies to identify erythema and pustules, such as increased suspicion in skin of color and the extra steps to rule them out, such as the use of side lighting in the case of pustules for AGEP, are simple and practical.
Dr. Harp and Dr. Kwatra had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW YORK — Because of their heterogeneity in appearance, to speed the diagnosis.
This risk for a delayed or missed diagnosis in patients with darker skin is shared across skin rashes, but drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DIHS) is a telling example, according to Joanna Harp, MD, director of the Inpatient Dermatology Consult Service, NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital, New York City.
DIHS, also known as a drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, is a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, Dr. Harp explained. While the fact that this disorder does not always include eosinophilia prompted the DIHS acronym, the maculopapular rash often serves as a critical clue of the underlying etiology.
In patients with darker skin, DIHS skin manifestations “can look different, can be more severe, and can have worse outcomes,” Dr. Harp said. As with other skin rashes that are primarily erythematous, the DIHS rash is often more subtle in Black-skinned patients, typically appearing gray or violaceous rather than red.
“The high amount of scale can be a clue,” said Dr. Harp, speaking at the 2024 Skin of Color Update. Scale is particularly prominent among Black patients, she said, because of the greater relative transepidermal water loss than lighter skin, increasing dryness and susceptibility to scale.
The maculopapular rash is “similar to a simple drug eruption, although it is usually more impressive,” she said. Emphasizing that DIHS is a systemic disease, she noted that the characteristic rash is typically accompanied by inflammation in multiple organs that not only includes the mucous membranes but can include major organs such as the lungs, kidneys, and heart.
In patients with DIHS and many of the even more serious types of rashes traced to drug exposures, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or erythema multiforme, the delay to appearance of the rash from the time of exposure can be the most confusing element.
“It can be months for some drugs such as allopurinol,” said Dr. Harp, pointing out that Black and Asian patients are more likely to carry the HLA-B*5801 genotype, a known risk factor for allopurinol hypersensitivity.
Signs of AGEP Can Be Subtle in Black Patients
Some of the same principles for diagnosing drug-induced rash in darker skin can also be applied to acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), another type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Like all drug-induced rashes, the earlier AGEP is recognized and treated, the better the outcome, but in Black patients, the signs can be subtle.
“The onset is usually fast and occurs in 1-2 days after [the causative drug] exposure,” said Dr. Harp, adding that antibiotics, such as cephalosporins or penicillin, and calcium channel blockers are among the prominent causes of AGEP.
One of the hallmark signs of early-onset AGEP are tiny erythematous pustules in flexural areas, such as the neck or the armpits. The issue of detecting erythema in darker skin is also relevant to this area, but there is an additional problem, according to Dr. Harp. The pustules often dry up quickly, leaving a neutrophilic scale that further complicates the effort to see the characteristic erythema.
“If you see a lot of scale, look for erythema underneath. Think of inflammation,” Dr. Harp said, explaining that the clinical appearance evolves quickly. “If you do not see the pustules, it does not mean they were not there; you just missed them.”
In addition to the flexural areas, “AGEP loves the ears, the face, and the geographic tongue,” she said, offering several pearls to help with the diagnosis. These include side lighting to make papules easier to see, pressing on the skin to highlight the difference between erythematous skin and blanched skin, and checking less pigmented skin, such as on the hands and feet, which makes erythema easier to see.
Steroids are often the first-line treatment for drug-induced skin rashes, but Dr. Harp moves to etanercept or cyclosporine for the most serious drug reactions, such as SJS and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Etanercept is typically her first choice because patients with systemic hypersensitivity reactions with major organ involvement are often quite ill, making cyclosporine harder to use. In her experience, etanercept has been well tolerated.
Conversely, she cautioned against the use of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG). Although this has been used traditionally for severe drug hypersensitivity reactions, “the data are not there,” she said. The data are stronger for a combination of high-dose steroids and IVIG, but she thinks even these data are inconsistent and not as strong as the data supporting etanercept or cyclosporine. She encouraged centers still using IVIG to consider alternatives.
After drug sensitivity reactions are controlled, follow-up care is particularly important for Black patients who face greater risks for sequelae, such as hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, or keloids. She recommended aggressive use of emollients and sunscreens for an extended period after lesions resolve to lessen these risks.
Differences in the manifestations of drug-induced skin rashes by race and ethnicity are important and perhaps underappreciated, agreed Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chairman of the Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland, Baltimore.
Asked to comment at the meeting, Dr. Kwatra said that he appreciated Dr. Harp’s effort to translate published data and her experience into an overview that increases awareness of the risk for missed or delayed diagnoses of drug-induced rashes in skin of color. He noted that the strategies to identify erythema and pustules, such as increased suspicion in skin of color and the extra steps to rule them out, such as the use of side lighting in the case of pustules for AGEP, are simple and practical.
Dr. Harp and Dr. Kwatra had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SOC 2024
Moving Beyond Traditional Methods for Treatment of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
The Comparison
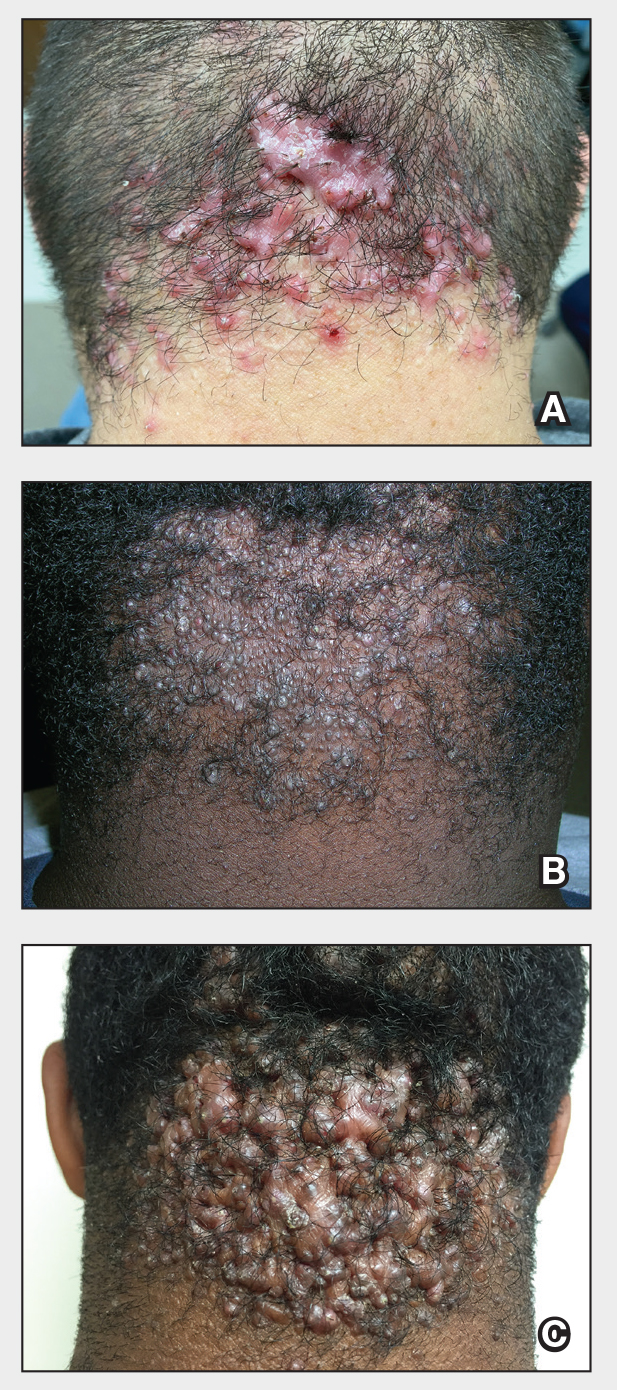
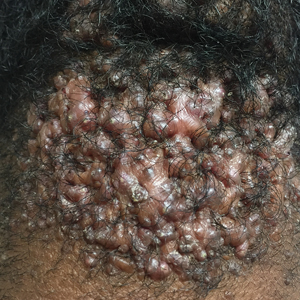
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
The Comparison

Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
The Comparison

Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a chronic inflammatory condition commonly affecting the occipital scalp and posterior neck. It causes discrete or extensive fibrosing papules that may coalesce to form pronounced tumorlike masses1,2 with scarring alopecia (Figure, A–C).3 Pustules, hair tufts, secondary bacterial infections, abscesses, and sinus tracts also may occur.1 The pathogenesis of AKN has been characterized as varying stages of follicular inflammation at the infundibular and isthmus levels followed by fibrotic occlusion of the follicular lumen.4 Pruritus, pain, bleeding, oozing, and a feeling of scalp tightness may occur.1,5
Umar et al6 performed a retrospective review of 108 men with AKN—58% of African descent, 37% Hispanic, 3% Asian, and 2% Middle Eastern—and proposed a 3-tier classification system for AKN. Tier 1 focused on the distribution and sagittal spread of AKN lesions between the clinical demarcation lines of the occipital notch and posterior hairline. Tier 2 focused on the type of lesions present—discrete papules or nodules, coalescing/abutting lesions, plaques (raised, atrophic, or indurated), or dome-shaped tumoral masses. Tier 3 focused on the presence or absence of co-existing dissecting cellulitis or folliculitis decalvans.6
Epidemiology
Acne keloidalis nuchae primarily manifests in adolescent and adult men of African or Afro-Caribbean descent.7 Among African American men, the prevalence of AKN ranges from 0.5% to 13.6%.8 Similar ranges have been reported among Nigerian, South African, and West African men.1 Acne keloidalis nuchae also affects Asian and Hispanic men but rarely is seen in non-Hispanic White men or in women of any ethnicity.9,10 The male to female ratio is 20:1.1,11 Hair texture, hairstyling practices such as closely shaved or faded haircuts, and genetics likely contribute to development of AKN. Sports and occupations that require the use of headgear or a tight collar may increase the risk for AKN.12
Key clinical features in people with darker skin tones
- The lesions of AKN range in color from pink to dark brown or black. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperchromia may be present around AKN lesions.
- Chronicity of AKN may lead to extended use of high-potency topical or intralesional corticosteroids, which causes transient or long-lasting hypopigmentation, especially in those with darker skin tones.
Worth noting
- Acne keloidalis nuchae can be disfiguring, which negatively impacts quality of life and self-esteem.12
- Some occupations (eg, military, police) have hair policies that may not be favorable to those with or at risk for AKN.
- Patients with AKN are 2 to 3 times more likely to present with metabolic syndrome, hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or obesity.13
Treatment
There are no treatments approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for AKN. Treatment approaches are based on the pathophysiology, secondary impacts on the skin, and disease severity. Growing out the hair may prevent worsening and/or decrease the risk for new lesions.6
- Options include but are not limited to topical and systemic therapies (eg, topical corticosteroids, oral or topical antibiotics, isotretinoin, topical retinoids, imiquimod, pimecrolimus), light devices (eg, phototherapy, laser), ablative therapies (eg, laser, cryotherapy, radiotherapy), and surgery (eg, excision, follicular unit excision), often in combination.6,14,15
- Intralesional triamcinolone injections are considered standard of care. Adotama et al16 found that injecting triamcinolone into the deep dermis in the area of flat or papular AKN yielded better control of inflammation and decreased appearance of lesions compared with injecting individual lesions.
- For extensive AKN lesions that do not respond to less-invasive therapies, consider surgical techniques,6,17 such as follicular unit excision18 and more extensive surgical excisions building on approaches from pioneers Drs. John Kenney and Harold Pierce.19 An innovative surgical approach for removal of large AKNs is the bat excision technique—wound shape resembles a bat in a spread-eagled position—with secondary intention healing with or without debridement and/or tension sutures. The resulting linear scar acts as a new posterior hair line.20
Health disparity highlights
Access to a dermatologic or plastic surgeon with expertise in the surgical treatment of large AKNs may be challenging but is needed to reduce risk for recurrence and adverse events.
Close-cropped haircuts on the occipital scalp, which are particularly popular among men of African descent, increase the risk for AKN.5 Although this grooming style may be a personal preference, other hairstyles commonly worn by those with tightly coiled hair may be deemed “unprofessional” in society or the workplace,21 which leads to hairstyling practices that may increase the risk for AKN.
Acne keloidalis nuchae remains an understudied entity that adversely affects patients with skin of color.
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
- Ogunbiyi A. Acne keloidalis nuchae: prevalence, impact, and management challenges. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2016;9:483-489. doi:10.2147/CCID.S99225
- Al Aboud DM, Badri T. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Updated July 31, 2023. Accessed August 2, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459135/ 3.
- Sperling LC, Homoky C, Pratt L, et al. Acne keloidalis is a form of primary scarring alopecia. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:479-484.
- Herzberg AJ, Dinehart SM, Kerns BJ, et al. Acne keloidalis: transverse microscopy, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy. Am J Dermatopathol. 1990;12:109-121. doi:10.1097/00000372-199004000-00001
- Saka B, Akakpo A-S, Téclessou JN, et al. Risk factors associated with acne keloidalis nuchae in black subjects: a case-control study. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2020;147:350-354. doi:10.1016/j.annder.2020.01.007
- Umar S, Lee DJ, Lullo JJ. A retrospective cohort study and clinical classification system of acne keloidalis nuchae. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021;14:E61-E67.
- Reja M, Silverberg NB. Acne keloidalis nuchae. In: Silverberg NB, Durán-McKinster C, Tay YK, eds. Pediatric Skin of Color. Springer; 2015:141-145. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6654-3_16 8.
- Knable AL Jr, Hanke CW, Gonin R. Prevalence of acne keloidalis nuchae in football players. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997;37:570-574. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70173-7
- Umar S, Ton D, Carter MJ, et al. Unveiling a shared precursor condition for acne keloidalis nuchae and primary cicatricial alopecias. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:2315-2327. doi:10.2147/CCID.S422310
- Na K, Oh SH, Kim SK. Acne keloidalis nuchae in Asian: a single institutional experience. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0189790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0189790
- Ogunbiyi A, George A. Acne keloidalis in females: case report and review of literature. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005;97:736-738.
- Alexis A, Heath CR, Halder RM. Folliculitis keloidalis nuchae and pseudofolliculitis barbae: are prevention and effective treatment within reach? Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:183-191. doi:10.1016/j.det.2013.12.001
- Kridin K, Solomon A, Tzur-Bitan D, et al. Acne keloidalis nuchae and the metabolic syndrome: a population-based study. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21:733-739. doi:10.1007/s40257-020-00541-z
- Smart K, Rodriguez I, Worswick S. Comorbidities and treatment options for acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Ther. Published online May 25, 2024. doi:10.1155/2024/8336926
- Callender VD, Young CM, Haverstock CL, et al. An open label study of clobetasol propionate 0.05% and betamethasone valerate 0.12% foams in the treatment of mild to moderate acne keloidalis. Cutis. 2005;75:317-321.
- Adotama P, Grullon K, Ali S, et al. How we do it: our method for triamcinolone injections of acne keloidalis nuchae. Dermatol Surg. 2023;49:713-714. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000003803
- Beckett N, Lawson C, Cohen G. Electrosurgical excision of acne keloidalis nuchae with secondary intention healing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2011;4:36-39.
- Esmat SM, Abdel Hay RM, Abu Zeid OM, et al. The efficacy of laser-assisted hair removal in the treatment of acne keloidalis nuchae; a pilot study. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:645-650. doi:10.1684/ejd.2012.1830
- Dillard AD, Quarles FN. African-American pioneers in dermatology. In: Taylor SC, Kelly AP, Lim HW, et al, eds. Dermatology for Skin of Color. 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill Education; 2016:717-730.
- Umar S, David CV, Castillo JR, et al. Innovative surgical approaches and selection criteria of large acne keloidalis nuchae lesions. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7:E2215. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000002215
- Lee MS, Nambudiri VE. The CROWN act and dermatology: taking a stand against race-based hair discrimination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84:1181-1182. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.11.065
Acne: Positive Outcomes Described With Laser Treatment
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CARLSBAD, CALIF. — at 1 year.
“Combining the AviClear with medical therapy and energy-based devices provides the best outcomes,” Dr. Moradzadeh, who practices facial and plastic surgery in Beverly Hills, California, said at the Controversies & Conversations in Laser & Cosmetic Surgery annual symposium. “You have to do all 300 pulses per treatment, and you do need to use settings of 19.5-21.5 J/cm2 to get a great result.”
AviClear became the first 1726-nm laser cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe acne vulgaris, followed a few months later by clearance of the 1926-nm laser, the Accure Acne Laser System. But few long-term “real-world” studies of these two devices exist, according to Dr. Moradzadeh.
The protocol for Dr. Moradzadeh’s study included three AviClear treatments spaced 3-4 weeks apart combined with medical therapy and other energy-based devices such as a near-infrared Nd:YAG laser (Laser Genesis) and a non-ablative fractional laser (LaseMD Ultra), with follow-up at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 1.5 years, and 2 years. Pain management options included acetaminophen, a numbing cream, and pre- and post-contact cooling.
Of the 100 patients, 90 were clear at 1 year, six patients were almost clear at 1 year, three patients were nonresponders, and one patient was lost to follow-up, Dr. Moradzadeh reported. “Two of the three nonresponders did not receive the full 300 pulses per treatment,” but all three cleared with isotretinoin treatment, he said. “What we now know from talking with other providers is that you really have to do all 300 pulses to get the best results.”
Of the 90 patients who achieved clearance, 80 remained clear at 1.5-2 years, and 10 are almost clear or have mild acne. “Of these, eight are adult females with hormonal acne and two are teenage males,” he said. “All 10 cleared with a fourth AviClear treatment and lifestyle modifications that included the elimination of whey, creatine, and skin care products containing vitamin E combined with vitamin C.”
During a question-and-answer session following the presentation, Jeffrey Dover, MD, director of SkinCare Physicians in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, said that general dermatologists have been slow to adopt the AviClear and Accure devices for treating patients with acne “because, for the most part, they are experts at treating acne with all the tools they have. They’re not used to using devices. They’re not used to having patients pay out of pocket for a treatment that is not covered by insurance. They don’t feel comfortable with that discussion.”
For example, the 14 dermatologists at SkinCare Physicians “almost never prescribe the 1726-nm devices for acne because it’s not in their sweet spot,” Dr. Dover continued, noting that one issue is that acne experts want more data.
In the experience of Nazanin Saedi, MD, clinical associate professor of dermatology at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, the 1726-nm laser devices for acne “fit nicely for women of childbearing age who have acne and don’t want to go on Accutane [isotretinoin], and also for teenagers who are either going to be noncompliant with Accutane or their parents are worried about side effects and the potential impacts on growth,” she said at the meeting. “That’s where we’ve found patients coming in wanting to do these treatments, and how it offers something that the medical treatments are lacking.”
Regarding concerns about out-of-pocket costs for AviClear or Accure treatments, Roy G. Geronemus, MD, who directs the Laser & Skin Surgery Center of New York, New York City, advised considering the long-term benefits. “If you calculate it out, it really is cost-effective to use the 1726-nm devices if you consider the copays, the cost of over-the-counter topicals, as well as the cost of prescription medications,” Dr. Geronemus said. “Over the long term, you are saving money for the patient.”
Dr. Dover acknowledged that was “a valid and important point,” but said that when the topic is discussed with general dermatologists who treat a lot of patients with acne, “they say patients are more willing to pay a copay [for a prescription] ... than write a check for $800 or $1000 per visit.”
The recently updated American Academy of Dermatology’s guidelines of care for the management of acne vulgaris, published in January 2024, characterized the available evidence as “insufficient” to develop a recommendation on the use of laser and light-based devices for the treatment of acne. Although the 1726-nm laser was cleared by the FDA for acne treatment in 2022, the authors of the guidelines wrote that “its evidence was not evaluated in the current guidelines due to lack of a randomized, controlled trial.”
Dr. Moradzadeh disclosed that he is a key opinion leader for Acclaro, Benev, Lutronic, Sofwave, and Cutera, the manufacturer for AviClear. Dr. Dover reported that he is a consultant for Cutera and performs research for the company. Dr. Saedi disclosed that she is a consultant to, a member of the advisory board for, and/or has received equipment and research support from many device and pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Geronemus disclosed that he is a member of the medical advisory board for and/or is an investigator for many device and pharmaceutical companies, including Accure. He also holds stock in the company.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Timing of iPLEDGE Updates Unclear
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
iPLEDGE, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–required Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) program launched in 2010, aims to manage the risks for the teratogenic acne drug isotretinoin and prevent fetal exposure. But it’s been dogged by issues and controversy, causing difficulties for patients and prescribers.
Late in 2023, there seemed to be a reason for optimism that improvements were coming. On November 30, 2023, the FDA informed isotretinoin manufacturers — known as the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturing Group (IPMG) — that they had 6 months to make five changes to the existing iPLEDGE REMS, addressing the controversies and potentially reducing glitches in the program and minimizing the burden of the program on patients, prescribers, and pharmacies — while maintaining safe use of the drug — and to submit their proposal by May 30, 2024.
The timeline for when an improved program might be in place remains unclear.
An FDA spokesperson, without confirming that the submission was submitted on time, recently said the review timeline once such a submission is received is generally 6 months.
‘Radio Silence’
No official FDA announcement has been made about the timeline, nor has information been forthcoming from the IPMG, and the silence has been frustrating for John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts. He chairs the American Academy of Dermatology Association’s IPLEDGE Work Group, which works with both the FDA and IPMG.
He began writing about issues with iPLEDGE about 4 years ago, when he and colleagues suggested, among other changes, simplifying the iPLEDGE contraception requirements in a paper published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In an interview, Dr. Barbieri expressed frustration about the lack of information on the status of the iPLEDGE changes. “We’ve been given no timeline [beyond the FDA’s May 30 deadline for the IPMG to respond] of what might happen when. We’ve asked what was submitted. No one will share it with us or tell us anything about it. It’s just radio silence.”
Dr. Barbieri is also frustrated at the lack of response from IPMG. Despite repeated requests to the group to include the dermatologists in the discussions, IPMG has repeatedly declined the help, he said.
IPMG appears to have no dedicated website. No response had been received to an email sent to an address attributed to the group asking if it would share the submission to the FDA.
Currently, isotretinoin, originally marketed as Accutane, is marketed under such brand names as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane.
Asked for specific information on the proposed changes, an FDA spokesperson said in an August 19 email that “the submission to the FDA from the isotretinoin manufacturers will be a major modification, and the review timeline is generally 6 months. Once approved, the isotretinoin manufacturers will need additional time to implement the changes.”
The spokesperson declined to provide additional information on the status of the IPMG proposal, to share the proposal itself, or to estimate the implementation period.
Reason for Hope?
In response to the comment that the review generally takes 6 months, Dr. Barbieri said it doesn’t give him much hope, adding that “any delay of implementing these reforms is a missed opportunity to improve the care of patients with acne.” He is also hopeful that the FDA will invite some public comment during the review period “so that stakeholders can share their feedback about the proposal to help guide FDA decision-making and ensure effective implementation.”
From Meeting to Mandate
The FDA order for the changes followed a joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee in March 2023 about the program requirements. It included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes, with a goal of reducing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers without compromising patient safety.
The Five Requested Changes
In the November 30 letter, the FDA requested the following from the IPMG:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests be performed in a specially certified lab (such as a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments lab). This would enable the tests to be done in a clinic setting rather than sending patients to a separate lab.
- Allow prescribers the option of letting patients use home pregnancy tests during and after treatment, with steps in place to minimize falsification.
- Remove the waiting period requirement, known as the “19-day lockout,” for patients if they don’t obtain the isotretinoin from the pharmacy within the first 7-day prescription window. Before initiation of isotretinoin, a repeat confirmatory test must be done in a medical setting without any required waiting period.
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement, removing the objective to document the outcome and associated collection of data for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling for those who can’t become pregnant from monthly counseling to counseling at enrollment only. Before each prescription is dispensed, the authorization must verify patient enrollment and prescriber certification. (In December 2021, a new, gender-neutral approach, approved by the FDA, was launched. It places potential patients into two risk categories — those who can become pregnant and those who cannot. Previously, there were three such categories: Females of reproductive potential, females not of reproductive potential, and males.)
Perspective on the Requested Changes
Of the requested changes, “really the most important is eliminating the request for monthly counseling for patients who cannot become pregnant,” Dr. Barbieri said. Because of that requirement, all patients need to have monthly visits with a dermatologist to get the medication refills, “and that creates a logistical barrier,” plus reducing time available for dermatologists to care for other patients with other dermatologic issues.
As for missing the 7-day prescription window, Dr. Barbieri said, in his experience, “it’s almost never the patient’s fault; it’s almost always an insurance problem.”
Dr. Barbieri reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do You Have Patients With JAKne — JAK Inhibitor–Associated Acne? Here’s What to Know
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Since the first Food and Drug Administration approval of a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor in 2011, the number of these medications available — and their treatment indications — have continued to grow. Prescribing physicians are familiar with the benefits and risks for these drugs, including higher risk for cardiac events and malignancy; however, one adverse effect may be overlooked, especially by specialties outside of dermatology: acne. Though less serious than some other side effects, JAK inhibitor–associated acne — JAKne, for short — can be a concern for patients.
“Your physical appearance and how you present yourself to the world is an important part of your self-confidence and living life on your own terms,” said Arash Mostaghimi, MD, the director of inpatient dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, Massachusetts. “I think letting people know about [JAKne] and then addressing it when it occurs should be a normal part of managing these medications.”
What Is JAKne?
JAKne generally looks like other kinds of acne, explained Janelle Nassim, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis. “It can affect the same areas that typical acne affects, including the face, chest, back, neck, and upper shoulders.”
Though it appears like typical forms of acne, it is not clear what drives these skin eruptions in patients taking JAK inhibitors.
“We don’t understand the underlying pathophysiology,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. “It looks like acne, but we don’t know if the exact underlying inflammatory process is the same or if it’s different.”
In a 2023 systematic review of clinical studies, Dr. Mostaghimi and colleagues found that patients on any JAK inhibitor were nearly four times more likely to experience acne than patients who received placebo, but risk varied between medications. Patients taking JAK inhibitors for skin conditions had higher risk for acne than those given the medications for other indications. However, Dr. Mostaghimi thinks this finding is the result of selection bias.
Participants may not mention side effects like acne in trials for rheumatologic or gastrointestinal conditions, he said, unlike in trials for skin conditions. “Clinically, I’ve seen it in patients across every indication.”
Patients with a history of acne seem to be more likely to develop this side effect, though formal studies looking into risk factors are lacking. In Dr. Mostaghimi’s own clinical experience, JAKne is also more common in younger patients, but it can happen to anyone. “I’ve seen 70-year-olds develop acne — patients who’ve never had an issue their whole life — when they’re taking a JAK inhibitor.”
This issue also appears to be more common earlier in treatment, he added, and may improve over time as a patient continues with the medication.
How Do You Treat It?
“I think in other specialties, you will often feel awkward addressing skin conditions or pointing out acne,” Dr. Mostaghimi said. The most important steps are being aware of this potential side effect, and if you see it practice, to bring it up.
“Say: I’m noticing there’s some changes in your skin. Some patients on JAK inhibitors develop more acne. Have you noticed this? And if so, is this bothering you?”
Generally, JAKne is mild to moderate, explained Dr. Nassim, and if non-dermatologists are comfortable, they can prescribe a first-line topical regimen for patients. Dr. Mostaghimi recommends prescribing a clindamycin 1% lotion or gel. In addition, patients can use a benzoyl peroxide wash (4% or 10%) combined with a gentle retinoid, such as adapalene. (Both of these treatments are now available over the counter.)
In patients with scalp or hairline involvement, he often prescribes a ketoconazole 2% shampoo, which patients can use to wash their scalp, face, chest, and back in the shower.
If they aren’t responding to these initial treatments, then refer to a dermatologist for further assessment.
“Ultimately, referring to a dermatologist is the best course of action,” Dr. Nassim said. “I have had patients on JAK inhibitors who improved with topical acne treatments, and some that required more aggressive treatment with oral medications.”
Dr. Mostaghimi reported consulting fees from AbbVie, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and 3Derm Systems; research funding from Incyte, Aclaris Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, and Concert Pharmaceuticals; personal fees from Equillium, ASLAN Pharmaceuticals, ACOM, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and advisory board fees from Fig.1 Beauty, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Hims & Hers Health. Dr. Nassim had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Identifies Oral Antibiotics Linked to Severe Cutaneous Reactions
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a large, population-based, nested case-control study of older adults, spanning two decades.
The findings, published online in JAMA, “underscore the importance of judicious prescribing, with preferential use of antibiotics associated with a lower risk when clinically appropriate,” noted senior author David Juurlink, MD, PhD, professor of medicine; pediatrics; and health policy, management and evaluation at the University of Toronto, and head of the Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology Division at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, also in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and coauthors.
“We hope our study raises awareness about the importance of drug allergy and gains support for future studies to improve drug allergy care,” lead author Erika Lee, MD, clinical immunology and allergy lecturer at the University of Toronto’s Drug Allergy Clinic, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, said in an interview. “It is important to recognize symptoms and signs of a severe drug rash and promptly stop culprit drugs to prevent worsening reaction.”
Serious cADRs are “a group of rare but potentially life-threatening drug hypersensitivity reactions involving the skin and, frequently, internal organs,” the authors wrote. “Typically delayed in onset, these reactions include drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) — the most severe cADR, which has a reported mortality of 20%-40%,” they noted.
Speculation Without Data
Although it has been speculated that some oral antibiotics are more likely than others to be associated with serious cADRs, there have been no population-based studies examining this, they added.
The study included adults aged 66 years or older and used administrative health databases in Ontario, spanning from April 1, 2002, to March 31, 2022. Data on antibiotic use were taken from the Ontario Drug Benefit database. The Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) National Ambulatory Care Reporting System was used to obtain data on emergency department (ED) visits for cADRs, while the CIHI Discharge Abstract Database was used to identify hospitalizations for cADRs. Finally, demographic information and outpatient healthcare utilization data were obtained from the Registered Persons Database and the Ontario Health Insurance Plan database, respectively.
A cohort of 21,758 older adults (median age, 75 years; 64.1% women) who had an ED visit or hospitalization for serious cADRs within 60 days of receiving antibiotic therapy was matched by age and sex with 87,025 antibiotic-treated controls who did not have a cutaneous reaction.
The median duration of antibiotic prescription was 7 days among cases and controls, and among the cases, the median latency period between antibiotic prescriptions and hospital visits for cADRs was 14 days. Most of the case patients went to the ED only (86.9%), and the rest were hospitalized.
The most commonly prescribed antibiotic class was penicillins (28.9%), followed by cephalosporins (18.2%), fluoroquinolones (16.5%), macrolides (14.8%), nitrofurantoin (8.6%), and sulfonamides (6.2%). Less commonly used antibiotics (“other” antibiotics) accounted for 6.9%.
Macrolide antibiotics were used as the reference because they are rarely associated with serious cADRs, noted the authors, and the multivariable analysis, adjusted for risk factors associated with serious cADRs, including malignancy, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, and HIV.
After multivariable adjustment, relative to macrolides, sulfonamides were most strongly associated with serious cADRs (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 2.9) but so were all other antibiotic classes, including cephalosporins (aOR, 2.6), “other” antibiotics (aOR, 2.3), nitrofurantoin (aOR, 2.2), penicillins (aOR, 1.4), and fluoroquinolones (aOR,1.3).
In the secondary analysis, the crude rate of ED visits or hospitalizations for cADRs was highest for cephalosporins (4.92 per 1000 prescriptions), followed by sulfonamides (3.22 per 1000 prescriptions). Among hospitalized patients, the median length of stay was 6 days, with 9.6% requiring transfer to a critical care unit and 5.3% dying in the hospital.
Hospitalizations, ED Visits Not Studied Previously
“Notably, the rate of antibiotic-associated serious cADRs leading to an ED visit or hospitalization has not been previously studied,” noted the authors. “We found that at least two hospital encounters for serious cADRs ensued for every 1000 antibiotic prescriptions. This rate is considerably higher than suggested by studies that examine only SJS/TEN and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms.”
Dr. Lee also emphasized the previously unreported findings about nitrofurantoin. “It is surprising to find that nitrofurantoin, a commonly prescribed antibiotic for urinary tract infection, is also associated with an increased risk of severe drug rash,” she said in an interview.
“This finding highlights a potential novel risk at a population-based level and should be further explored in other populations to verify this association,” the authors wrote.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in Baltimore, Maryland, and a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America, who was not involved in the study, agreed that the nitrofurantoin finding was surprising, but he was not surprised that sulfonamides were high on the list.
“The study reinforces that antibiotics are not benign medications to be dispensed injudiciously,” he said in an interview. “Antibiotics have risks, including serious skin reactions, as well as the fostering of antibiotic resistance. Clinicians should always first ask themselves if their patient actually merits an antibiotic and then assess what is the safest antibiotic for the purpose, bearing in mind that certain antibiotics are more likely to result in adverse reactions than others.”
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The study was conducted at ICES, which is funded in part by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. One coauthor reported receiving compensation from the British Journal of Dermatology as reviewer and section editor, the American Academy of Dermatology as guidelines writer, Canadian Dermatology Today as manuscript writer, and the National Eczema Association and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health as consultant; as well as receiving research grants to the coauthor’s institution from the National Eczema Association, Eczema Society of Canada, Canadian Dermatology Foundation, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, US National Institutes of Health, and PSI Foundation. Another coauthor reported receiving grants from AbbVie, Bausch Health, Celgene, Lilly, Incyte, Janssen, LEO Pharma, L’Oréal, Novartis, Organon, Pfizer, Sandoz, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; receiving payment or honoraria for speaking from Sanofi China; participating on advisory boards for LEO Pharma, Novartis, Sanofi, and Union Therapeutics; and receiving equipment donation from L’Oréal. Dr. Adalja reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Gluconolactone
This derivative of oxidized glucose lactone is present naturally in bread, cheese, fruit juices, honey, tofu, and wine, and is used as a food additive in Europe.1,2 In dermatology, it is most often used in chemical peels.
Polyhydroxy acids (PHAs) were discovered about 3 decades ago to exert similar functions as alpha hydroxy acids without provoking sensory irritation reactions. Gluconolactone along with lactobionic acid were the identified PHAs and further characterized as delivering more humectant and moisturizing activity than alpha hydroxy acids and effective in combination with retinoic acid to treat adult acne and with retinyl acetate to confer antiaging benefits.3 It is typically added to products for its skin-conditioning qualities, resulting in smoother, brighter, more toned skin.4 This column focuses on recent studies using this bioactive agent for dermatologic purposes.
Split-Face Studies Show Various Benefits
In 2023, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues conducted a split-face evaluation to assess the effects on various skin parameters (ie, hydration, pH, sebum, and transepidermal water loss [TEWL]) of gluconolactone and oxybrasion, compared with gluconolactone and microneedling. Twenty-one White women underwent a series of three split-face treatments at 1-week intervals. Chemical peels with 10% gluconolactone were performed on the whole face. The right side of the face was also treated with oxybrasion and the left with microneedle mesotherapy. Skin parameters were measured before the first and third treatments and 2 weeks following the final treatment. Photos were taken before and after the study. Both treatments resulted in improved hydration and reductions in sebum, pH, and TEWL. No statistically significant differences were noted between the treatment protocols. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone peels can be effectively combined with oxybrasion or microneedle mesotherapy to enhance skin hydration and to secure the hydrolipid barrier.5
Later that year, the same team evaluated pH, sebum levels, and TEWL before, during, and after several applications of 10% and 30% gluconolactone chemical peels in a split-face model in 16 female participants. The investigators conducted three procedures on both sides of the face, taking measurements on the forehead, periorbital area, on the cheek, and on the nose wing before, during, and 7 days after the final treatment. They found statistically significant improvements in sebum levels in the cheeks after the treatment series. Also, pH values were lower at each measurement site after each procedure. TEWL levels were significantly diminished around the eyes, as well as the left forehead and right cheek, with no significant discrepancy between gluconolactone concentrations. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone plays a major role in reducing cutaneous pH and TEWL and imparts a regulatory effect on sebum.1
Two years earlier, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues assessed skin moisture in a split-face model in 16 healthy women after the application of 10% and 30% gluconolactone. Investigators measured skin moisture before and after each of three treatments and a week after the final treatment from the forehead, periorbital area, and on the cheek. They observed no significant discrepancies between the 10% and 30% formulations, but a significant elevation in facial skin hydration was found to be promoted by gluconolactone. The investigators concluded that gluconolactone is an effective moisturizer for care of dry skin.6
Topical Formulation
In 2023, Zerbinati and colleagues determined that a gluconolactone-based lotion that they had begun testing 2 years earlier was safe and effective for dermatologic applications, with the noncomedogenic formulation found suitable as an antiaging agent, particularly as it treats aging-related pore dilatation.7,8
Acne Treatment
In 2019, Kantikosum and colleagues conducted a double-blind, within-person comparative study to assess the efficacy of various cosmeceutical ingredients, including gluconolactone, glycolic acid, licochalcone A, and salicylic acid, combined with the acne treatment adapalene vs adapalene monotherapy for mild to moderate acne. Each of 25 subjects over 28 days applied a product mixed with 0.1% adapalene on one side of the face, and 0.1% adapalene alone on the other side of the face once nightly. The VISIA camera system spot score pointed to a statistically significant improvement on the combination sides. Differences in lesion reduction and severity were within acceptable margins, the authors reported. They concluded that the cosmeceutical combinations yielded similar benefits as adapalene alone, with the combination formulations decreasing acne complications.9
Potential Use as an Antifibrotic Agent
In 2018, Jayamani and colleagues investigated the antifibrotic characteristics of glucono-delta-lactone, a known acidifier, to ascertain if it could directly suppress collagen fibrils or even cause them to disintegrate. The researchers noted that collagen fibrillation is pH dependent, and that glucono-delta-lactone was found to exert a concentration-dependent suppression of fibrils and disintegration of preformed collagen fibrils with the antifibrotic function of the compound ascribed to its capacity to decrease pH. Further, glucono-delta-lactone appeared to emerge as an ideal antifibrotic agent as it left intact the triple helical structure of collagen after treatment. The investigators concluded that glucono-delta-lactone provides the foundation for developing antifibrotic agents intended to treat disorders characterized by collagen deposition.10
Conclusion
Gluconolactone emerged in the 1990s as a PHA useful in skin peels as an alternative to alpha hydroxy acids because of its nonirritating qualities. Since then, its soothing, hydrating, and, in particular, antiacne and antiaging qualities have become established. Wider applications of this versatile agent for dermatologic purposes are likely to be further investigated.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Dec;22(12):3305-3312..
2. Qin X et al. Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 14;13:856699.
3. Grimes PE et al. Cutis. 2004 Feb;73(2 Suppl):3-13.
4. Glaser DA. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2003 May;11(2):219-227.
5. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2023 Jun;29(6):e13353.
6. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2021 Sep;27(5):925-930.
7. Zerbinati N et al. Molecules. 2021 Dec 15;26(24):7592.
8. Zerbinati Net al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;16(5):655.
9. Kantikosum K et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019 Feb 19;12:151-161.
10. Jayamani J et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt A):175-185.
This derivative of oxidized glucose lactone is present naturally in bread, cheese, fruit juices, honey, tofu, and wine, and is used as a food additive in Europe.1,2 In dermatology, it is most often used in chemical peels.
Polyhydroxy acids (PHAs) were discovered about 3 decades ago to exert similar functions as alpha hydroxy acids without provoking sensory irritation reactions. Gluconolactone along with lactobionic acid were the identified PHAs and further characterized as delivering more humectant and moisturizing activity than alpha hydroxy acids and effective in combination with retinoic acid to treat adult acne and with retinyl acetate to confer antiaging benefits.3 It is typically added to products for its skin-conditioning qualities, resulting in smoother, brighter, more toned skin.4 This column focuses on recent studies using this bioactive agent for dermatologic purposes.
Split-Face Studies Show Various Benefits
In 2023, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues conducted a split-face evaluation to assess the effects on various skin parameters (ie, hydration, pH, sebum, and transepidermal water loss [TEWL]) of gluconolactone and oxybrasion, compared with gluconolactone and microneedling. Twenty-one White women underwent a series of three split-face treatments at 1-week intervals. Chemical peels with 10% gluconolactone were performed on the whole face. The right side of the face was also treated with oxybrasion and the left with microneedle mesotherapy. Skin parameters were measured before the first and third treatments and 2 weeks following the final treatment. Photos were taken before and after the study. Both treatments resulted in improved hydration and reductions in sebum, pH, and TEWL. No statistically significant differences were noted between the treatment protocols. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone peels can be effectively combined with oxybrasion or microneedle mesotherapy to enhance skin hydration and to secure the hydrolipid barrier.5
Later that year, the same team evaluated pH, sebum levels, and TEWL before, during, and after several applications of 10% and 30% gluconolactone chemical peels in a split-face model in 16 female participants. The investigators conducted three procedures on both sides of the face, taking measurements on the forehead, periorbital area, on the cheek, and on the nose wing before, during, and 7 days after the final treatment. They found statistically significant improvements in sebum levels in the cheeks after the treatment series. Also, pH values were lower at each measurement site after each procedure. TEWL levels were significantly diminished around the eyes, as well as the left forehead and right cheek, with no significant discrepancy between gluconolactone concentrations. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone plays a major role in reducing cutaneous pH and TEWL and imparts a regulatory effect on sebum.1
Two years earlier, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues assessed skin moisture in a split-face model in 16 healthy women after the application of 10% and 30% gluconolactone. Investigators measured skin moisture before and after each of three treatments and a week after the final treatment from the forehead, periorbital area, and on the cheek. They observed no significant discrepancies between the 10% and 30% formulations, but a significant elevation in facial skin hydration was found to be promoted by gluconolactone. The investigators concluded that gluconolactone is an effective moisturizer for care of dry skin.6
Topical Formulation
In 2023, Zerbinati and colleagues determined that a gluconolactone-based lotion that they had begun testing 2 years earlier was safe and effective for dermatologic applications, with the noncomedogenic formulation found suitable as an antiaging agent, particularly as it treats aging-related pore dilatation.7,8
Acne Treatment
In 2019, Kantikosum and colleagues conducted a double-blind, within-person comparative study to assess the efficacy of various cosmeceutical ingredients, including gluconolactone, glycolic acid, licochalcone A, and salicylic acid, combined with the acne treatment adapalene vs adapalene monotherapy for mild to moderate acne. Each of 25 subjects over 28 days applied a product mixed with 0.1% adapalene on one side of the face, and 0.1% adapalene alone on the other side of the face once nightly. The VISIA camera system spot score pointed to a statistically significant improvement on the combination sides. Differences in lesion reduction and severity were within acceptable margins, the authors reported. They concluded that the cosmeceutical combinations yielded similar benefits as adapalene alone, with the combination formulations decreasing acne complications.9
Potential Use as an Antifibrotic Agent
In 2018, Jayamani and colleagues investigated the antifibrotic characteristics of glucono-delta-lactone, a known acidifier, to ascertain if it could directly suppress collagen fibrils or even cause them to disintegrate. The researchers noted that collagen fibrillation is pH dependent, and that glucono-delta-lactone was found to exert a concentration-dependent suppression of fibrils and disintegration of preformed collagen fibrils with the antifibrotic function of the compound ascribed to its capacity to decrease pH. Further, glucono-delta-lactone appeared to emerge as an ideal antifibrotic agent as it left intact the triple helical structure of collagen after treatment. The investigators concluded that glucono-delta-lactone provides the foundation for developing antifibrotic agents intended to treat disorders characterized by collagen deposition.10
Conclusion
Gluconolactone emerged in the 1990s as a PHA useful in skin peels as an alternative to alpha hydroxy acids because of its nonirritating qualities. Since then, its soothing, hydrating, and, in particular, antiacne and antiaging qualities have become established. Wider applications of this versatile agent for dermatologic purposes are likely to be further investigated.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Dec;22(12):3305-3312..
2. Qin X et al. Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 14;13:856699.
3. Grimes PE et al. Cutis. 2004 Feb;73(2 Suppl):3-13.
4. Glaser DA. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2003 May;11(2):219-227.
5. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2023 Jun;29(6):e13353.
6. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2021 Sep;27(5):925-930.
7. Zerbinati N et al. Molecules. 2021 Dec 15;26(24):7592.
8. Zerbinati Net al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;16(5):655.
9. Kantikosum K et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019 Feb 19;12:151-161.
10. Jayamani J et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt A):175-185.
This derivative of oxidized glucose lactone is present naturally in bread, cheese, fruit juices, honey, tofu, and wine, and is used as a food additive in Europe.1,2 In dermatology, it is most often used in chemical peels.
Polyhydroxy acids (PHAs) were discovered about 3 decades ago to exert similar functions as alpha hydroxy acids without provoking sensory irritation reactions. Gluconolactone along with lactobionic acid were the identified PHAs and further characterized as delivering more humectant and moisturizing activity than alpha hydroxy acids and effective in combination with retinoic acid to treat adult acne and with retinyl acetate to confer antiaging benefits.3 It is typically added to products for its skin-conditioning qualities, resulting in smoother, brighter, more toned skin.4 This column focuses on recent studies using this bioactive agent for dermatologic purposes.
Split-Face Studies Show Various Benefits
In 2023, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues conducted a split-face evaluation to assess the effects on various skin parameters (ie, hydration, pH, sebum, and transepidermal water loss [TEWL]) of gluconolactone and oxybrasion, compared with gluconolactone and microneedling. Twenty-one White women underwent a series of three split-face treatments at 1-week intervals. Chemical peels with 10% gluconolactone were performed on the whole face. The right side of the face was also treated with oxybrasion and the left with microneedle mesotherapy. Skin parameters were measured before the first and third treatments and 2 weeks following the final treatment. Photos were taken before and after the study. Both treatments resulted in improved hydration and reductions in sebum, pH, and TEWL. No statistically significant differences were noted between the treatment protocols. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone peels can be effectively combined with oxybrasion or microneedle mesotherapy to enhance skin hydration and to secure the hydrolipid barrier.5
Later that year, the same team evaluated pH, sebum levels, and TEWL before, during, and after several applications of 10% and 30% gluconolactone chemical peels in a split-face model in 16 female participants. The investigators conducted three procedures on both sides of the face, taking measurements on the forehead, periorbital area, on the cheek, and on the nose wing before, during, and 7 days after the final treatment. They found statistically significant improvements in sebum levels in the cheeks after the treatment series. Also, pH values were lower at each measurement site after each procedure. TEWL levels were significantly diminished around the eyes, as well as the left forehead and right cheek, with no significant discrepancy between gluconolactone concentrations. The researchers concluded that gluconolactone plays a major role in reducing cutaneous pH and TEWL and imparts a regulatory effect on sebum.1
Two years earlier, Jarząbek-Perz and colleagues assessed skin moisture in a split-face model in 16 healthy women after the application of 10% and 30% gluconolactone. Investigators measured skin moisture before and after each of three treatments and a week after the final treatment from the forehead, periorbital area, and on the cheek. They observed no significant discrepancies between the 10% and 30% formulations, but a significant elevation in facial skin hydration was found to be promoted by gluconolactone. The investigators concluded that gluconolactone is an effective moisturizer for care of dry skin.6
Topical Formulation
In 2023, Zerbinati and colleagues determined that a gluconolactone-based lotion that they had begun testing 2 years earlier was safe and effective for dermatologic applications, with the noncomedogenic formulation found suitable as an antiaging agent, particularly as it treats aging-related pore dilatation.7,8
Acne Treatment
In 2019, Kantikosum and colleagues conducted a double-blind, within-person comparative study to assess the efficacy of various cosmeceutical ingredients, including gluconolactone, glycolic acid, licochalcone A, and salicylic acid, combined with the acne treatment adapalene vs adapalene monotherapy for mild to moderate acne. Each of 25 subjects over 28 days applied a product mixed with 0.1% adapalene on one side of the face, and 0.1% adapalene alone on the other side of the face once nightly. The VISIA camera system spot score pointed to a statistically significant improvement on the combination sides. Differences in lesion reduction and severity were within acceptable margins, the authors reported. They concluded that the cosmeceutical combinations yielded similar benefits as adapalene alone, with the combination formulations decreasing acne complications.9
Potential Use as an Antifibrotic Agent
In 2018, Jayamani and colleagues investigated the antifibrotic characteristics of glucono-delta-lactone, a known acidifier, to ascertain if it could directly suppress collagen fibrils or even cause them to disintegrate. The researchers noted that collagen fibrillation is pH dependent, and that glucono-delta-lactone was found to exert a concentration-dependent suppression of fibrils and disintegration of preformed collagen fibrils with the antifibrotic function of the compound ascribed to its capacity to decrease pH. Further, glucono-delta-lactone appeared to emerge as an ideal antifibrotic agent as it left intact the triple helical structure of collagen after treatment. The investigators concluded that glucono-delta-lactone provides the foundation for developing antifibrotic agents intended to treat disorders characterized by collagen deposition.10
Conclusion
Gluconolactone emerged in the 1990s as a PHA useful in skin peels as an alternative to alpha hydroxy acids because of its nonirritating qualities. Since then, its soothing, hydrating, and, in particular, antiacne and antiaging qualities have become established. Wider applications of this versatile agent for dermatologic purposes are likely to be further investigated.
Dr. Baumann is a private practice dermatologist, researcher, author, and entrepreneur in Miami. She founded the division of cosmetic dermatology at the University of Miami in 1997. The third edition of her bestselling textbook, “Cosmetic Dermatology,” was published in 2022. Dr. Baumann has received funding for advisory boards and/or clinical research trials from Allergan, Galderma, Johnson & Johnson, and Burt’s Bees. She is the CEO of Skin Type Solutions, a SaaS company used to generate skin care routines in office and as a ecommerce solution. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Dec;22(12):3305-3312..
2. Qin X et al. Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 14;13:856699.
3. Grimes PE et al. Cutis. 2004 Feb;73(2 Suppl):3-13.
4. Glaser DA. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2003 May;11(2):219-227.
5. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2023 Jun;29(6):e13353.
6. Jarząbek-Perz S et al. Skin Res Technol. 2021 Sep;27(5):925-930.
7. Zerbinati N et al. Molecules. 2021 Dec 15;26(24):7592.
8. Zerbinati Net al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;16(5):655.
9. Kantikosum K et al. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2019 Feb 19;12:151-161.
10. Jayamani J et al. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt A):175-185.