User login
Bridging the Digital Divide in Teledermatology Usage: A Retrospective Review of Patient Visits
Teledermatology is an effective patient care model for the delivery of high-quality dermatologic care.1 Teledermatology can occur using synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid models of care. In asynchronous visits (AVs), patients or health professionals submit photographs and information for dermatologists to review and provide treatment recommendations. With synchronous visits (SVs), patients have a visit with a dermatology health professional in real time via live video conferencing software. Hybrid models incorporate asynchronous strategies for patient intake forms and skin photograph submissions as well as synchronous methods for live video consultation in a single visit.1 However, remarkable inequities in internet access limit telemedicine usage among medically marginalized patient populations, including racialized, elderly, and low socioeconomic status groups.2
Synchronous visits, a relatively newer teledermatology format, allow for communication with dermatology professionals from the convenience of a patient’s selected location. The live interaction of SVs allows dermatology professionals to answer questions, provide treatment recommendations, and build therapeutic relationships with patients. Concerns for dermatologist reimbursement, malpractice/liability, and technological challenges stalled large-scale uptake of teledermatology platforms.3 The COVID-19 pandemic led to a drastic increase in teledermatology usage of approximately 587.2%, largely due to public safety measures and Medicaid reimbursement parity between SV and in-office visits (IVs).3,4
With the implementation of SVs as a patient care model, we investigated the demographics of patients who utilized SVs, AVs, or IVs, and we propose strategies to promote equity in dermatologic care access.
Methods
This study was approved by the University of Pittsburgh institutional review board (STUDY20110043). We performed a retrospective electronic medical record review of deidentified data from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, a tertiary care center in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, with an established asynchronous teledermatology program. Hybrid SVs were integrated into the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center patient care visit options in March 2020. Patients were instructed to upload photographs of their skin conditions prior to SV appointments. The study included visits occurring between July and December 2020. Visit types included SVs, AVs, and IVs.
We analyzed the initial dermatology visits of 17,130 patients aged 17.5 years and older. Recorded data included diagnosis, age, sex, race, ethnicity, and insurance type for each visit type. Patients without a reported race (990 patients) or ethnicity (1712 patients) were excluded from analysis of race/ethnicity data. Patient zip codes were compared with the zip codes of Allegheny County municipalities as reported by the Allegheny County Elections Division.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated; frequency with percentage was used to report categorical variables, and the mean (SD) was used for normally distributed continuous variables. Univariate analysis was performed using the χ2 test for categorical variables. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare age among visit types. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24 (IBM Corp) was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
In our study population, 81.2% (13,916) of patients were residents of Allegheny County, where 51.6% of residents are female and 81.4% are older than 18 years according to data from 2020.5 The racial and ethnic demographics of Allegheny County were 13.4% African American/Black, 0.2% American Indian/Alaska Native, 4.2% Asian, 2.3% Hispanic/Latino, and 79.6% White. The percentage of residents who identified as Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander was reported to be greater than 0% but less than 0.5%.5
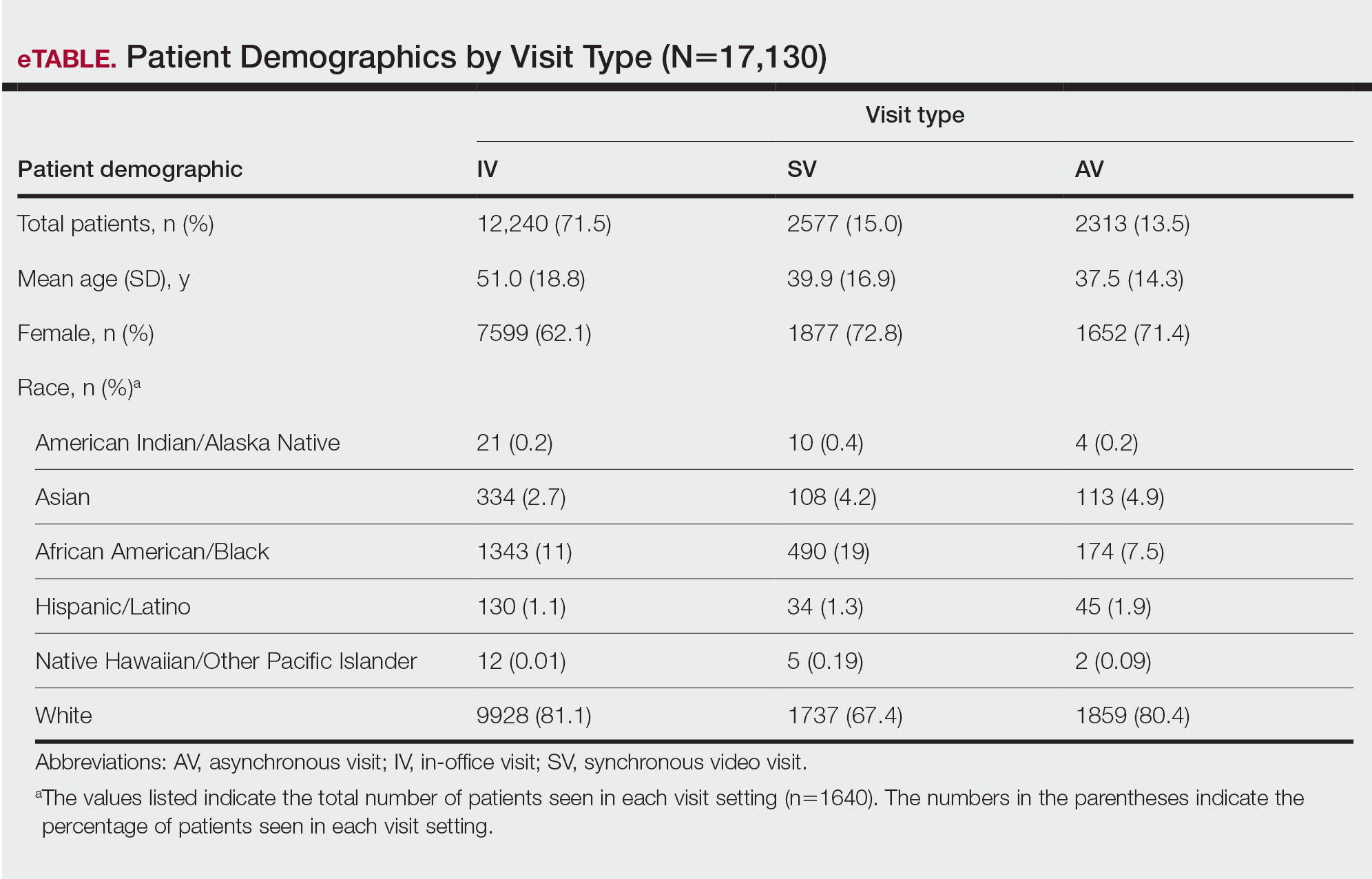
In our analysis, IVs were the most utilized visit type, accounting for 71.5% (12,240) of visits, followed by 15.0% (2577) for SVs and 13.5% (2313) for AVs. The mean age (SD) of IV patients was 51.0 (18.8) years compared with 39.9 (16.9) years for SV patients and 37.5 (14.3) years for AV patients (eTable). The majority of patients for all visits were female: 62.1% (7599) for IVs, 71.4% (1652) for AVs, and 72.8% (1877) for SVs. The largest racial or ethnic group for all visit types included White patients (83.8% [13,524] of all patients), followed by Black (12.4% [2007]), Hispanic/Latino (1.4% [209]), Asian (3.4% [555]), American Indian/Alaska Native (0.2% [35]), and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients (0.1% [19]).
Asian patients, who comprised 4.2% of Allegheny County residents,5 accounted for 2.7% (334) of IVs, 4.9% (113) of AVs, and 4.2% (108) of SVs. Black patients, who were reported as 13.4% of the Allegheny County population,5 were more likely to utilize SVs (19% [490])compared with AVs (7.5% [174]) and IVs (11% [1343]). Hispanic/Latino patients had a disproportionally lower utilization of dermatologic care in all settings, comprising 1.4% (209) of all patients in our study compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 White patients, who comprised 79.6% of Allegheny County residents, accounted for 81.1% (9928) of IVs, 67.4% (1737) of SVs, and 80.4% (1859) of AVs. There was no significant difference in the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients among visit types.
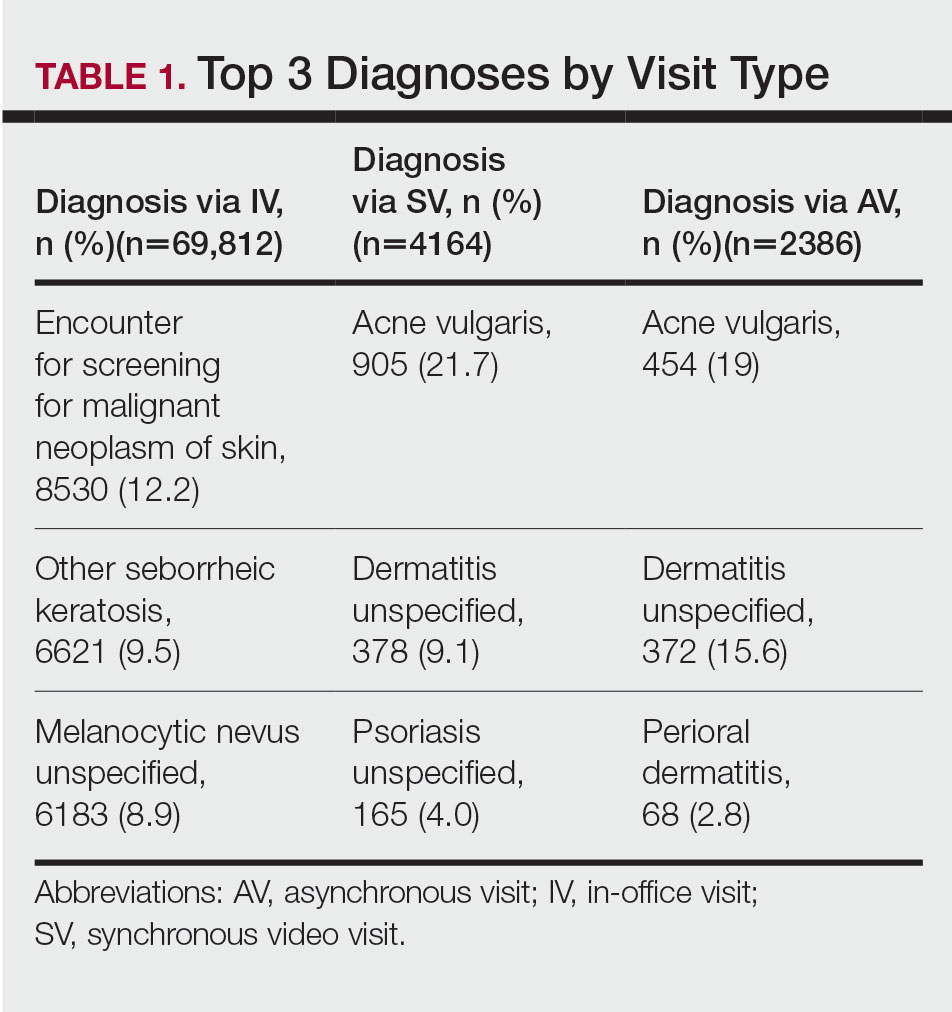
The 3 most common diagnoses for IVs were skin cancer screening, seborrheic keratosis, and melanocytic nevus (Table 1). Skin cancer screening was the most common diagnosis, accounting for 12.2% (8530) of 69,812 IVs. The 3 most common diagnoses for SVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and psoriasis. The 3 most common diagnoses for AVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and perioral dermatitis.
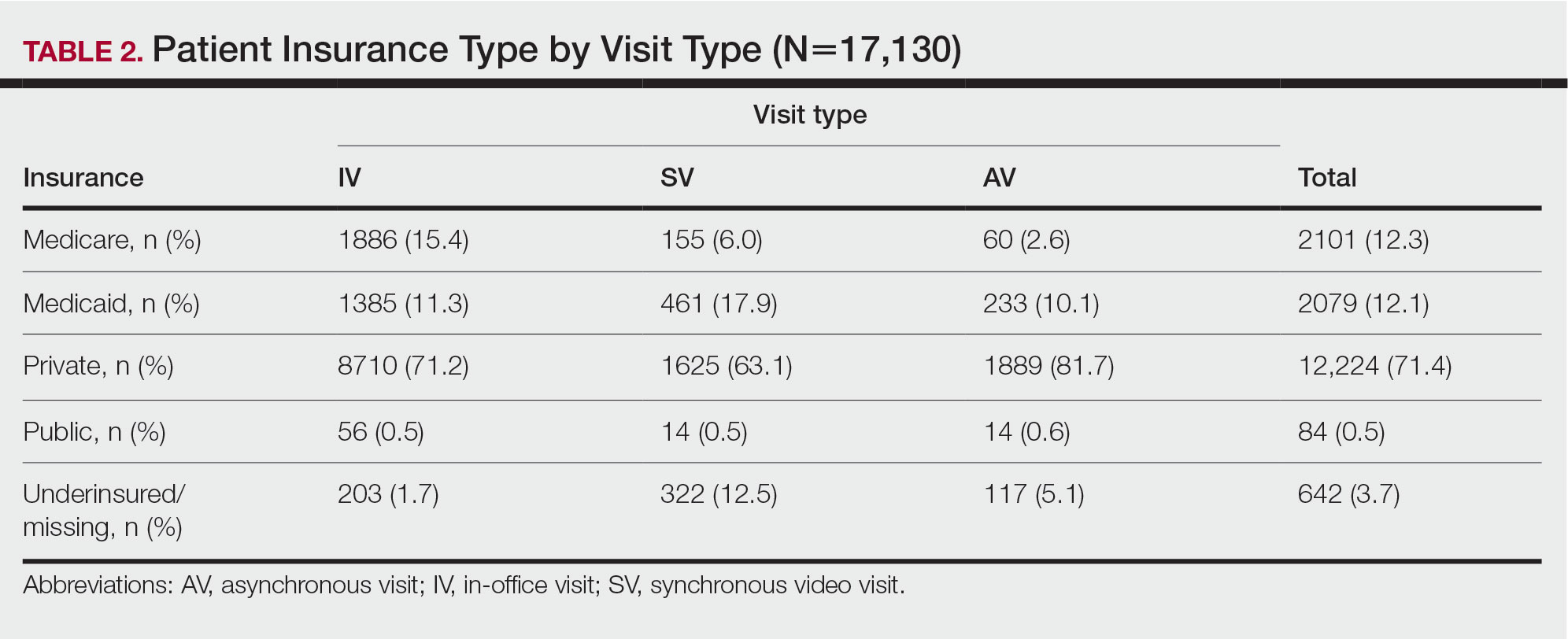
Private insurance was the most common insurance type among all patients (71.4% [12,224])(Table 2). A higher percentage of patients with Medicaid insurance (17.9% [461]) utilized SVs compared with AVs (10.1% [233]) and IVs (11.3% 1385]). Similarly, a higher percentage of patients with no insurance or no insurance listed were seen via SVs (12.5% [322]) compared with AVs (5.1% [117]) and IVs (1.7% [203]). Patients with Medicare insurance used IVs (15.4% [1886]) more than SVs (6.0% [155]) or AVs (2.6% [60]). There was no significant difference among visit type usage for patients with public insurance.
Comment
Teledermatology Benefits—In this retrospective review of medical records of patients who obtained dermatologic care after the implementation of SVs at our institution, we found a proportionally higher use of SVs among Black patients, patients with Medicaid, and patients who are underinsured. Benefits of teledermatology include decreases in patient transportation and associated costs, time away from work or home, and need for childcare.6 The SV format provides the additional advantage of direct live interaction and the development of a patient-physician or patient–physician assistant relationship. Although the prerequisite technology, internet, and broadband connectivity preclude use of teledermatology for many vulnerable patients,2 its convenience ultimately may reduce inequities in access.
Disparities in Dermatologic Care—Hispanic ethnicity and male sex are among described patient demographics associated with decreased rates of outpatient dermatologic care.7 We reported disparities in dermatologic care utilization across all visit types among Hispanic patients and males. Patients identifying as Hispanic/Latino composed only 1.4% (n=209) of our study population compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 During our study period, most patients seen were female, accounting for 62.1% to 72.8% of visits, compared with 51.6% of Allegheny County residents.5 These disparities in dermatologic care use may have implications for increased skin-associated morbidity and provide impetus for dermatologists to increase engagement with these patient groups.
Characteristics of Patients Using Teledermatology—Patients using SVs and AVs were significantly younger (mean age [SD], 39.9 [16.9] years and 37.5 [14.3] years, respectively) compared with those using IVs (51.0 [18.8] years). This finding reflects known digital knowledge barriers among older patients.8,9 The synchronous communication format of SVs simulates the traditional visit style of IVs, which may be preferable for some patients. Continued patient education and advocacy for broadband access may increase teledermatology use among older patients and patients with limited technology resources.8
Teledermatology visits were used most frequently for acne and dermatitis, while IVs were used for skin cancer screenings and examination of concerning lesions. This usage pattern is consistent with a previously described consensus among dermatologists on the conditions most amenable to teledermatology evaluation.3
Medicaid reimbursement parity for SVs is in effect nationally until the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration in the United States.10 As of February 2023, the public health emergency declaration has been renewed 12 times since January 2020, with the most recent renewal on January 11, 2023.11 As of January 2023, 21 states have enacted legislation providing permanent reimbursement parity for SV services. Six additional states have some payment parity in place, each with its own qualifying criteria, and 23 states have no payment parity.12 Only 25 Medicaid programs currently provide reimbursement for AV services.13
Study Limitations—Our study was limited by lack of data on patients who are multiracial and those who identify as nonbinary and transgender. Because of the low numbers of Hispanic patients associated with each race category and a high number of patients who did not report an ethnicity or race, race and ethnicity data were analyzed separately. For SVs, patients were instructed to upload photographs prior to their visit; however, the percentage of patients who uploaded photographs was not analyzed.
Conclusion
Expansion of teledermatology services, including SVs and AVs, patient outreach and education, advocacy for broadband access, and Medicaid payment parity, may improve dermatologic care access for medically marginalized groups. Teledermatology has the potential to serve as an effective health care option for patients who are racially minoritized, older, and underinsured. To further assess the effectiveness of teledermatology, we plan to analyze the number of SVs and AVs that were referred to IVs. Future studies also will investigate the impact of implementing patient education and patient-reported outcomes of teledermatology visits.
- Lee JJ, English JC. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Bakhtiar M, Elbuluk N, Lipoff JB. The digital divide: how COVID-19’s telemedicine expansion could exacerbate disparities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E345-E346.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. Accessed August 12, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/alleghenycountypennsylvania
- Moore HW. Teledermatology—access to specialized care via a different model. Dermatology Advisor. November 12, 2019. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.dermatologyadvisor.com/home/topics/practice-management/teledermatology-access-to-specialized-care-via-a-different-model/
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Nouri S, Khoong EC, Lyles CR, et al. Addressing equity in telemedicine for chronic disease management during the COVID-19 pandemic [published online May 4, 2020]. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. doi:10.1056/CAT.20.0123
- Swenson K, Ghertner R. People in low-income households have less access to internet services—2019 update. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation; US Department of Health and Human Services. March 2021. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/private/pdf/263601/internet-access-among-low-income-2019.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. COVID-19 frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) billing. Updated August 16, 2022. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03092020-covid-19-faqs-508.pdf
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Renewal of determination that a public health emergency exists. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 20, 2023. https://aspr.hhs.gov/legal/PHE/Pages/COVID19-9Feb2023.aspx?
- Augenstein J, Smith JM. Executive summary: tracking telehealth changes state-by-state in response to COVID-19. Updated January 27, 2023. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.manatt.com/insights/newsletters/covid-19-update/executive-summary-tracking-telehealth-changes-stat
- Center for Connected Health Policy. Policy trend maps: store and forward Medicaid reimbursement. Accessed June 23, 2022. https://www.cchpca.org/policy-trends/
Teledermatology is an effective patient care model for the delivery of high-quality dermatologic care.1 Teledermatology can occur using synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid models of care. In asynchronous visits (AVs), patients or health professionals submit photographs and information for dermatologists to review and provide treatment recommendations. With synchronous visits (SVs), patients have a visit with a dermatology health professional in real time via live video conferencing software. Hybrid models incorporate asynchronous strategies for patient intake forms and skin photograph submissions as well as synchronous methods for live video consultation in a single visit.1 However, remarkable inequities in internet access limit telemedicine usage among medically marginalized patient populations, including racialized, elderly, and low socioeconomic status groups.2
Synchronous visits, a relatively newer teledermatology format, allow for communication with dermatology professionals from the convenience of a patient’s selected location. The live interaction of SVs allows dermatology professionals to answer questions, provide treatment recommendations, and build therapeutic relationships with patients. Concerns for dermatologist reimbursement, malpractice/liability, and technological challenges stalled large-scale uptake of teledermatology platforms.3 The COVID-19 pandemic led to a drastic increase in teledermatology usage of approximately 587.2%, largely due to public safety measures and Medicaid reimbursement parity between SV and in-office visits (IVs).3,4
With the implementation of SVs as a patient care model, we investigated the demographics of patients who utilized SVs, AVs, or IVs, and we propose strategies to promote equity in dermatologic care access.
Methods
This study was approved by the University of Pittsburgh institutional review board (STUDY20110043). We performed a retrospective electronic medical record review of deidentified data from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, a tertiary care center in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, with an established asynchronous teledermatology program. Hybrid SVs were integrated into the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center patient care visit options in March 2020. Patients were instructed to upload photographs of their skin conditions prior to SV appointments. The study included visits occurring between July and December 2020. Visit types included SVs, AVs, and IVs.
We analyzed the initial dermatology visits of 17,130 patients aged 17.5 years and older. Recorded data included diagnosis, age, sex, race, ethnicity, and insurance type for each visit type. Patients without a reported race (990 patients) or ethnicity (1712 patients) were excluded from analysis of race/ethnicity data. Patient zip codes were compared with the zip codes of Allegheny County municipalities as reported by the Allegheny County Elections Division.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated; frequency with percentage was used to report categorical variables, and the mean (SD) was used for normally distributed continuous variables. Univariate analysis was performed using the χ2 test for categorical variables. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare age among visit types. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24 (IBM Corp) was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
In our study population, 81.2% (13,916) of patients were residents of Allegheny County, where 51.6% of residents are female and 81.4% are older than 18 years according to data from 2020.5 The racial and ethnic demographics of Allegheny County were 13.4% African American/Black, 0.2% American Indian/Alaska Native, 4.2% Asian, 2.3% Hispanic/Latino, and 79.6% White. The percentage of residents who identified as Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander was reported to be greater than 0% but less than 0.5%.5
In our analysis, IVs were the most utilized visit type, accounting for 71.5% (12,240) of visits, followed by 15.0% (2577) for SVs and 13.5% (2313) for AVs. The mean age (SD) of IV patients was 51.0 (18.8) years compared with 39.9 (16.9) years for SV patients and 37.5 (14.3) years for AV patients (eTable). The majority of patients for all visits were female: 62.1% (7599) for IVs, 71.4% (1652) for AVs, and 72.8% (1877) for SVs. The largest racial or ethnic group for all visit types included White patients (83.8% [13,524] of all patients), followed by Black (12.4% [2007]), Hispanic/Latino (1.4% [209]), Asian (3.4% [555]), American Indian/Alaska Native (0.2% [35]), and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients (0.1% [19]).

Asian patients, who comprised 4.2% of Allegheny County residents,5 accounted for 2.7% (334) of IVs, 4.9% (113) of AVs, and 4.2% (108) of SVs. Black patients, who were reported as 13.4% of the Allegheny County population,5 were more likely to utilize SVs (19% [490])compared with AVs (7.5% [174]) and IVs (11% [1343]). Hispanic/Latino patients had a disproportionally lower utilization of dermatologic care in all settings, comprising 1.4% (209) of all patients in our study compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 White patients, who comprised 79.6% of Allegheny County residents, accounted for 81.1% (9928) of IVs, 67.4% (1737) of SVs, and 80.4% (1859) of AVs. There was no significant difference in the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients among visit types.
The 3 most common diagnoses for IVs were skin cancer screening, seborrheic keratosis, and melanocytic nevus (Table 1). Skin cancer screening was the most common diagnosis, accounting for 12.2% (8530) of 69,812 IVs. The 3 most common diagnoses for SVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and psoriasis. The 3 most common diagnoses for AVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and perioral dermatitis.

Private insurance was the most common insurance type among all patients (71.4% [12,224])(Table 2). A higher percentage of patients with Medicaid insurance (17.9% [461]) utilized SVs compared with AVs (10.1% [233]) and IVs (11.3% 1385]). Similarly, a higher percentage of patients with no insurance or no insurance listed were seen via SVs (12.5% [322]) compared with AVs (5.1% [117]) and IVs (1.7% [203]). Patients with Medicare insurance used IVs (15.4% [1886]) more than SVs (6.0% [155]) or AVs (2.6% [60]). There was no significant difference among visit type usage for patients with public insurance.

Comment
Teledermatology Benefits—In this retrospective review of medical records of patients who obtained dermatologic care after the implementation of SVs at our institution, we found a proportionally higher use of SVs among Black patients, patients with Medicaid, and patients who are underinsured. Benefits of teledermatology include decreases in patient transportation and associated costs, time away from work or home, and need for childcare.6 The SV format provides the additional advantage of direct live interaction and the development of a patient-physician or patient–physician assistant relationship. Although the prerequisite technology, internet, and broadband connectivity preclude use of teledermatology for many vulnerable patients,2 its convenience ultimately may reduce inequities in access.
Disparities in Dermatologic Care—Hispanic ethnicity and male sex are among described patient demographics associated with decreased rates of outpatient dermatologic care.7 We reported disparities in dermatologic care utilization across all visit types among Hispanic patients and males. Patients identifying as Hispanic/Latino composed only 1.4% (n=209) of our study population compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 During our study period, most patients seen were female, accounting for 62.1% to 72.8% of visits, compared with 51.6% of Allegheny County residents.5 These disparities in dermatologic care use may have implications for increased skin-associated morbidity and provide impetus for dermatologists to increase engagement with these patient groups.
Characteristics of Patients Using Teledermatology—Patients using SVs and AVs were significantly younger (mean age [SD], 39.9 [16.9] years and 37.5 [14.3] years, respectively) compared with those using IVs (51.0 [18.8] years). This finding reflects known digital knowledge barriers among older patients.8,9 The synchronous communication format of SVs simulates the traditional visit style of IVs, which may be preferable for some patients. Continued patient education and advocacy for broadband access may increase teledermatology use among older patients and patients with limited technology resources.8
Teledermatology visits were used most frequently for acne and dermatitis, while IVs were used for skin cancer screenings and examination of concerning lesions. This usage pattern is consistent with a previously described consensus among dermatologists on the conditions most amenable to teledermatology evaluation.3
Medicaid reimbursement parity for SVs is in effect nationally until the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration in the United States.10 As of February 2023, the public health emergency declaration has been renewed 12 times since January 2020, with the most recent renewal on January 11, 2023.11 As of January 2023, 21 states have enacted legislation providing permanent reimbursement parity for SV services. Six additional states have some payment parity in place, each with its own qualifying criteria, and 23 states have no payment parity.12 Only 25 Medicaid programs currently provide reimbursement for AV services.13
Study Limitations—Our study was limited by lack of data on patients who are multiracial and those who identify as nonbinary and transgender. Because of the low numbers of Hispanic patients associated with each race category and a high number of patients who did not report an ethnicity or race, race and ethnicity data were analyzed separately. For SVs, patients were instructed to upload photographs prior to their visit; however, the percentage of patients who uploaded photographs was not analyzed.
Conclusion
Expansion of teledermatology services, including SVs and AVs, patient outreach and education, advocacy for broadband access, and Medicaid payment parity, may improve dermatologic care access for medically marginalized groups. Teledermatology has the potential to serve as an effective health care option for patients who are racially minoritized, older, and underinsured. To further assess the effectiveness of teledermatology, we plan to analyze the number of SVs and AVs that were referred to IVs. Future studies also will investigate the impact of implementing patient education and patient-reported outcomes of teledermatology visits.
Teledermatology is an effective patient care model for the delivery of high-quality dermatologic care.1 Teledermatology can occur using synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid models of care. In asynchronous visits (AVs), patients or health professionals submit photographs and information for dermatologists to review and provide treatment recommendations. With synchronous visits (SVs), patients have a visit with a dermatology health professional in real time via live video conferencing software. Hybrid models incorporate asynchronous strategies for patient intake forms and skin photograph submissions as well as synchronous methods for live video consultation in a single visit.1 However, remarkable inequities in internet access limit telemedicine usage among medically marginalized patient populations, including racialized, elderly, and low socioeconomic status groups.2
Synchronous visits, a relatively newer teledermatology format, allow for communication with dermatology professionals from the convenience of a patient’s selected location. The live interaction of SVs allows dermatology professionals to answer questions, provide treatment recommendations, and build therapeutic relationships with patients. Concerns for dermatologist reimbursement, malpractice/liability, and technological challenges stalled large-scale uptake of teledermatology platforms.3 The COVID-19 pandemic led to a drastic increase in teledermatology usage of approximately 587.2%, largely due to public safety measures and Medicaid reimbursement parity between SV and in-office visits (IVs).3,4
With the implementation of SVs as a patient care model, we investigated the demographics of patients who utilized SVs, AVs, or IVs, and we propose strategies to promote equity in dermatologic care access.
Methods
This study was approved by the University of Pittsburgh institutional review board (STUDY20110043). We performed a retrospective electronic medical record review of deidentified data from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, a tertiary care center in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, with an established asynchronous teledermatology program. Hybrid SVs were integrated into the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center patient care visit options in March 2020. Patients were instructed to upload photographs of their skin conditions prior to SV appointments. The study included visits occurring between July and December 2020. Visit types included SVs, AVs, and IVs.
We analyzed the initial dermatology visits of 17,130 patients aged 17.5 years and older. Recorded data included diagnosis, age, sex, race, ethnicity, and insurance type for each visit type. Patients without a reported race (990 patients) or ethnicity (1712 patients) were excluded from analysis of race/ethnicity data. Patient zip codes were compared with the zip codes of Allegheny County municipalities as reported by the Allegheny County Elections Division.
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were calculated; frequency with percentage was used to report categorical variables, and the mean (SD) was used for normally distributed continuous variables. Univariate analysis was performed using the χ2 test for categorical variables. One-way analysis of variance was used to compare age among visit types. Statistical significance was defined as P<.05. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 24 (IBM Corp) was used for all statistical analyses.
Results
In our study population, 81.2% (13,916) of patients were residents of Allegheny County, where 51.6% of residents are female and 81.4% are older than 18 years according to data from 2020.5 The racial and ethnic demographics of Allegheny County were 13.4% African American/Black, 0.2% American Indian/Alaska Native, 4.2% Asian, 2.3% Hispanic/Latino, and 79.6% White. The percentage of residents who identified as Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander was reported to be greater than 0% but less than 0.5%.5
In our analysis, IVs were the most utilized visit type, accounting for 71.5% (12,240) of visits, followed by 15.0% (2577) for SVs and 13.5% (2313) for AVs. The mean age (SD) of IV patients was 51.0 (18.8) years compared with 39.9 (16.9) years for SV patients and 37.5 (14.3) years for AV patients (eTable). The majority of patients for all visits were female: 62.1% (7599) for IVs, 71.4% (1652) for AVs, and 72.8% (1877) for SVs. The largest racial or ethnic group for all visit types included White patients (83.8% [13,524] of all patients), followed by Black (12.4% [2007]), Hispanic/Latino (1.4% [209]), Asian (3.4% [555]), American Indian/Alaska Native (0.2% [35]), and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients (0.1% [19]).

Asian patients, who comprised 4.2% of Allegheny County residents,5 accounted for 2.7% (334) of IVs, 4.9% (113) of AVs, and 4.2% (108) of SVs. Black patients, who were reported as 13.4% of the Allegheny County population,5 were more likely to utilize SVs (19% [490])compared with AVs (7.5% [174]) and IVs (11% [1343]). Hispanic/Latino patients had a disproportionally lower utilization of dermatologic care in all settings, comprising 1.4% (209) of all patients in our study compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 White patients, who comprised 79.6% of Allegheny County residents, accounted for 81.1% (9928) of IVs, 67.4% (1737) of SVs, and 80.4% (1859) of AVs. There was no significant difference in the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander patients among visit types.
The 3 most common diagnoses for IVs were skin cancer screening, seborrheic keratosis, and melanocytic nevus (Table 1). Skin cancer screening was the most common diagnosis, accounting for 12.2% (8530) of 69,812 IVs. The 3 most common diagnoses for SVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and psoriasis. The 3 most common diagnoses for AVs were acne vulgaris, dermatitis, and perioral dermatitis.

Private insurance was the most common insurance type among all patients (71.4% [12,224])(Table 2). A higher percentage of patients with Medicaid insurance (17.9% [461]) utilized SVs compared with AVs (10.1% [233]) and IVs (11.3% 1385]). Similarly, a higher percentage of patients with no insurance or no insurance listed were seen via SVs (12.5% [322]) compared with AVs (5.1% [117]) and IVs (1.7% [203]). Patients with Medicare insurance used IVs (15.4% [1886]) more than SVs (6.0% [155]) or AVs (2.6% [60]). There was no significant difference among visit type usage for patients with public insurance.

Comment
Teledermatology Benefits—In this retrospective review of medical records of patients who obtained dermatologic care after the implementation of SVs at our institution, we found a proportionally higher use of SVs among Black patients, patients with Medicaid, and patients who are underinsured. Benefits of teledermatology include decreases in patient transportation and associated costs, time away from work or home, and need for childcare.6 The SV format provides the additional advantage of direct live interaction and the development of a patient-physician or patient–physician assistant relationship. Although the prerequisite technology, internet, and broadband connectivity preclude use of teledermatology for many vulnerable patients,2 its convenience ultimately may reduce inequities in access.
Disparities in Dermatologic Care—Hispanic ethnicity and male sex are among described patient demographics associated with decreased rates of outpatient dermatologic care.7 We reported disparities in dermatologic care utilization across all visit types among Hispanic patients and males. Patients identifying as Hispanic/Latino composed only 1.4% (n=209) of our study population compared with 2.3% of Allegheny County residents.5 During our study period, most patients seen were female, accounting for 62.1% to 72.8% of visits, compared with 51.6% of Allegheny County residents.5 These disparities in dermatologic care use may have implications for increased skin-associated morbidity and provide impetus for dermatologists to increase engagement with these patient groups.
Characteristics of Patients Using Teledermatology—Patients using SVs and AVs were significantly younger (mean age [SD], 39.9 [16.9] years and 37.5 [14.3] years, respectively) compared with those using IVs (51.0 [18.8] years). This finding reflects known digital knowledge barriers among older patients.8,9 The synchronous communication format of SVs simulates the traditional visit style of IVs, which may be preferable for some patients. Continued patient education and advocacy for broadband access may increase teledermatology use among older patients and patients with limited technology resources.8
Teledermatology visits were used most frequently for acne and dermatitis, while IVs were used for skin cancer screenings and examination of concerning lesions. This usage pattern is consistent with a previously described consensus among dermatologists on the conditions most amenable to teledermatology evaluation.3
Medicaid reimbursement parity for SVs is in effect nationally until the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency declaration in the United States.10 As of February 2023, the public health emergency declaration has been renewed 12 times since January 2020, with the most recent renewal on January 11, 2023.11 As of January 2023, 21 states have enacted legislation providing permanent reimbursement parity for SV services. Six additional states have some payment parity in place, each with its own qualifying criteria, and 23 states have no payment parity.12 Only 25 Medicaid programs currently provide reimbursement for AV services.13
Study Limitations—Our study was limited by lack of data on patients who are multiracial and those who identify as nonbinary and transgender. Because of the low numbers of Hispanic patients associated with each race category and a high number of patients who did not report an ethnicity or race, race and ethnicity data were analyzed separately. For SVs, patients were instructed to upload photographs prior to their visit; however, the percentage of patients who uploaded photographs was not analyzed.
Conclusion
Expansion of teledermatology services, including SVs and AVs, patient outreach and education, advocacy for broadband access, and Medicaid payment parity, may improve dermatologic care access for medically marginalized groups. Teledermatology has the potential to serve as an effective health care option for patients who are racially minoritized, older, and underinsured. To further assess the effectiveness of teledermatology, we plan to analyze the number of SVs and AVs that were referred to IVs. Future studies also will investigate the impact of implementing patient education and patient-reported outcomes of teledermatology visits.
- Lee JJ, English JC. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Bakhtiar M, Elbuluk N, Lipoff JB. The digital divide: how COVID-19’s telemedicine expansion could exacerbate disparities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E345-E346.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. Accessed August 12, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/alleghenycountypennsylvania
- Moore HW. Teledermatology—access to specialized care via a different model. Dermatology Advisor. November 12, 2019. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.dermatologyadvisor.com/home/topics/practice-management/teledermatology-access-to-specialized-care-via-a-different-model/
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Nouri S, Khoong EC, Lyles CR, et al. Addressing equity in telemedicine for chronic disease management during the COVID-19 pandemic [published online May 4, 2020]. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. doi:10.1056/CAT.20.0123
- Swenson K, Ghertner R. People in low-income households have less access to internet services—2019 update. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation; US Department of Health and Human Services. March 2021. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/private/pdf/263601/internet-access-among-low-income-2019.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. COVID-19 frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) billing. Updated August 16, 2022. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03092020-covid-19-faqs-508.pdf
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Renewal of determination that a public health emergency exists. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 20, 2023. https://aspr.hhs.gov/legal/PHE/Pages/COVID19-9Feb2023.aspx?
- Augenstein J, Smith JM. Executive summary: tracking telehealth changes state-by-state in response to COVID-19. Updated January 27, 2023. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.manatt.com/insights/newsletters/covid-19-update/executive-summary-tracking-telehealth-changes-stat
- Center for Connected Health Policy. Policy trend maps: store and forward Medicaid reimbursement. Accessed June 23, 2022. https://www.cchpca.org/policy-trends/
- Lee JJ, English JC. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Bakhtiar M, Elbuluk N, Lipoff JB. The digital divide: how COVID-19’s telemedicine expansion could exacerbate disparities. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;83:E345-E346.
- Kennedy J, Arey S, Hopkins Z, et al. dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation and future use after COVID-19: demographics, barriers, and insights. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:595-597.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Using telehealth to expand access to essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Updated June 10, 2020. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/telehealth.html
- United States Census Bureau. QuickFacts: Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. Accessed August 12, 2021. https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/alleghenycountypennsylvania
- Moore HW. Teledermatology—access to specialized care via a different model. Dermatology Advisor. November 12, 2019. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.dermatologyadvisor.com/home/topics/practice-management/teledermatology-access-to-specialized-care-via-a-different-model/
- Tripathi R, Knusel KD, Ezaldein HH, et al. Association of demographic and socioeconomic characteristics with differences in use of outpatient dermatology services in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:1286-1291.
- Nouri S, Khoong EC, Lyles CR, et al. Addressing equity in telemedicine for chronic disease management during the COVID-19 pandemic [published online May 4, 2020]. NEJM Catal Innov Care Deliv. doi:10.1056/CAT.20.0123
- Swenson K, Ghertner R. People in low-income households have less access to internet services—2019 update. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation; US Department of Health and Human Services. March 2021. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/private/pdf/263601/internet-access-among-low-income-2019.pdf
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. COVID-19 frequently asked questions (FAQs) on Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) billing. Updated August 16, 2022. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/03092020-covid-19-faqs-508.pdf
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Renewal of determination that a public health emergency exists. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed February 20, 2023. https://aspr.hhs.gov/legal/PHE/Pages/COVID19-9Feb2023.aspx?
- Augenstein J, Smith JM. Executive summary: tracking telehealth changes state-by-state in response to COVID-19. Updated January 27, 2023. Accessed February 10, 2023. https://www.manatt.com/insights/newsletters/covid-19-update/executive-summary-tracking-telehealth-changes-stat
- Center for Connected Health Policy. Policy trend maps: store and forward Medicaid reimbursement. Accessed June 23, 2022. https://www.cchpca.org/policy-trends/
Practice Points
- There is increased use of synchronous video visits (SVs) among Black patients, patients with Medicaid, and patients who are underinsured.
- Synchronous video visits may increase dermatologic care utilization for medically marginalized groups.
- Efforts are needed to increase engagement with dermatologic care for Hispanic and male patients.
How to manage isotretinoin’s bothersome mucocutaneous side effects
HONOLULU –
“If they don’t have dry lips, you have to wonder if they’re even absorbing isotretinoin,” Dr. Barbieri, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “Everyone is going to get dry lips.”
According to a retrospective review of 1,743 patients started on isotretinoin, other common mucocutaneous side effects include eczema, nose bleeds, and eye problems. Emerging research suggests that there may be a role for oral omega-3 in decreasing such side effects of the drug. In a case control study, 118 patients were randomized to isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin plus 1 g/day of oral omega-3 for 16 weeks. At week 16, the rate of dry lips was 26% in the isoretinoin only group compared with 14% in the combination group; similar trends were seen with dry nose (11% vs. 0 %, respectively) and dry skin (11% vs. 2%).
“Omega-3 is a simple thing that we can think about recommending for patients,” Dr. Barbieri said. “It’s very safe, inexpensive, and it may help us manage these common sides effect we run into.”
Another potential side effect of isotretinoin that he characterized as underappreciated is chronic dry eye and other ocular changes. One retrospective cohort study of 14,682 adolescents and young adults in Israel found that use of the drug resulted in reduced tear production and reduced tear quality. In another study, a review and meta-analysis of 21 publications involving 1,105 eyes of 842 patients, isotretinoin use was associated with increased conjunctival fluorescein staining, decreased corneal thickness, and worse patient-reported ocular surface disease index scores.
“These changes may be mediated by meibomian gland dysfunction and atrophy,” Dr. Barbieri said. “Fortunately, many of these tear film changes appear to resolve after treatment. Those changes in corneal thickness do seem to get better. That’s reassuring.”
In a study of 54 patients treated with isotretinoin, tear production and quality returned to baseline within 6 months of treatment completion. “But some changes in the meibomian gland may be persistent,” Dr. Barbieri said. “At 6 and 12 months after the end of treatment, you can still see changes in the meibomian glands of patients who were treated with a standard course of 120 to 150 mg/kg isotretinoin,” he said, referring to the results of a study of 88 patients .
One study investigated the effects of omega-3 fatty acids and punctal plugs on tear film and ocular surface parameters in 90 patients receiving systemic isotretinoin therapy. They were divided into three groups: Those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug that was inserted in the inferior punctum of both eyes and received oral omega-3 fatty acid capsules twice daily for a total dose of 1,040 mg/day for 6 months; those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug and oral placebo, and those who received isotretinoin alone. At 6 months’ follow-up, those who were treated with omega-3 combined with the preloaded silicone plug had better meibomian gland function than did those who received isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin with the preloaded silicone plug.
Dr. Barbieri also noted that antihistamines may play a role in enhancing the effect of isotretinoin. In one study, 20 patients were treated with isotretinoin 0.4 mg/kg per day and 20 patients were also treated with an antihistamine, desloratadine 5 mg/day for 12 weeks. At week 12, patients in the group treated with isotretinoin and the antihistamine showed a more statistically significant decrease in acne lesion counts, compared with the isotretinoin-only group (reductions of 44.8% vs. 17.8%, respectively, in noninflammatory lesions; 55.8% vs. 22.9% in inflammatory lesions, and 45.6% vs. 18.7% in total lesions (P < .05 for all associations).
A subsequent larger study yielded similar findings. There were also lower rates of initial flaring and higher rates of patient satisfaction in the antihistamine groups in both studies.
In an interview at the meeting, Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, described Dr. Barbieri as “a leader in taking a comprehensive view on what the history and latest information is on isotretinoin. His fresh approach is something everyone should consider and figure out what they can use in their practice.”
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU –
“If they don’t have dry lips, you have to wonder if they’re even absorbing isotretinoin,” Dr. Barbieri, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “Everyone is going to get dry lips.”
According to a retrospective review of 1,743 patients started on isotretinoin, other common mucocutaneous side effects include eczema, nose bleeds, and eye problems. Emerging research suggests that there may be a role for oral omega-3 in decreasing such side effects of the drug. In a case control study, 118 patients were randomized to isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin plus 1 g/day of oral omega-3 for 16 weeks. At week 16, the rate of dry lips was 26% in the isoretinoin only group compared with 14% in the combination group; similar trends were seen with dry nose (11% vs. 0 %, respectively) and dry skin (11% vs. 2%).
“Omega-3 is a simple thing that we can think about recommending for patients,” Dr. Barbieri said. “It’s very safe, inexpensive, and it may help us manage these common sides effect we run into.”
Another potential side effect of isotretinoin that he characterized as underappreciated is chronic dry eye and other ocular changes. One retrospective cohort study of 14,682 adolescents and young adults in Israel found that use of the drug resulted in reduced tear production and reduced tear quality. In another study, a review and meta-analysis of 21 publications involving 1,105 eyes of 842 patients, isotretinoin use was associated with increased conjunctival fluorescein staining, decreased corneal thickness, and worse patient-reported ocular surface disease index scores.
“These changes may be mediated by meibomian gland dysfunction and atrophy,” Dr. Barbieri said. “Fortunately, many of these tear film changes appear to resolve after treatment. Those changes in corneal thickness do seem to get better. That’s reassuring.”
In a study of 54 patients treated with isotretinoin, tear production and quality returned to baseline within 6 months of treatment completion. “But some changes in the meibomian gland may be persistent,” Dr. Barbieri said. “At 6 and 12 months after the end of treatment, you can still see changes in the meibomian glands of patients who were treated with a standard course of 120 to 150 mg/kg isotretinoin,” he said, referring to the results of a study of 88 patients .
One study investigated the effects of omega-3 fatty acids and punctal plugs on tear film and ocular surface parameters in 90 patients receiving systemic isotretinoin therapy. They were divided into three groups: Those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug that was inserted in the inferior punctum of both eyes and received oral omega-3 fatty acid capsules twice daily for a total dose of 1,040 mg/day for 6 months; those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug and oral placebo, and those who received isotretinoin alone. At 6 months’ follow-up, those who were treated with omega-3 combined with the preloaded silicone plug had better meibomian gland function than did those who received isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin with the preloaded silicone plug.
Dr. Barbieri also noted that antihistamines may play a role in enhancing the effect of isotretinoin. In one study, 20 patients were treated with isotretinoin 0.4 mg/kg per day and 20 patients were also treated with an antihistamine, desloratadine 5 mg/day for 12 weeks. At week 12, patients in the group treated with isotretinoin and the antihistamine showed a more statistically significant decrease in acne lesion counts, compared with the isotretinoin-only group (reductions of 44.8% vs. 17.8%, respectively, in noninflammatory lesions; 55.8% vs. 22.9% in inflammatory lesions, and 45.6% vs. 18.7% in total lesions (P < .05 for all associations).
A subsequent larger study yielded similar findings. There were also lower rates of initial flaring and higher rates of patient satisfaction in the antihistamine groups in both studies.
In an interview at the meeting, Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, described Dr. Barbieri as “a leader in taking a comprehensive view on what the history and latest information is on isotretinoin. His fresh approach is something everyone should consider and figure out what they can use in their practice.”
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
HONOLULU –
“If they don’t have dry lips, you have to wonder if they’re even absorbing isotretinoin,” Dr. Barbieri, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by MedscapeLIVE! “Everyone is going to get dry lips.”
According to a retrospective review of 1,743 patients started on isotretinoin, other common mucocutaneous side effects include eczema, nose bleeds, and eye problems. Emerging research suggests that there may be a role for oral omega-3 in decreasing such side effects of the drug. In a case control study, 118 patients were randomized to isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin plus 1 g/day of oral omega-3 for 16 weeks. At week 16, the rate of dry lips was 26% in the isoretinoin only group compared with 14% in the combination group; similar trends were seen with dry nose (11% vs. 0 %, respectively) and dry skin (11% vs. 2%).
“Omega-3 is a simple thing that we can think about recommending for patients,” Dr. Barbieri said. “It’s very safe, inexpensive, and it may help us manage these common sides effect we run into.”
Another potential side effect of isotretinoin that he characterized as underappreciated is chronic dry eye and other ocular changes. One retrospective cohort study of 14,682 adolescents and young adults in Israel found that use of the drug resulted in reduced tear production and reduced tear quality. In another study, a review and meta-analysis of 21 publications involving 1,105 eyes of 842 patients, isotretinoin use was associated with increased conjunctival fluorescein staining, decreased corneal thickness, and worse patient-reported ocular surface disease index scores.
“These changes may be mediated by meibomian gland dysfunction and atrophy,” Dr. Barbieri said. “Fortunately, many of these tear film changes appear to resolve after treatment. Those changes in corneal thickness do seem to get better. That’s reassuring.”
In a study of 54 patients treated with isotretinoin, tear production and quality returned to baseline within 6 months of treatment completion. “But some changes in the meibomian gland may be persistent,” Dr. Barbieri said. “At 6 and 12 months after the end of treatment, you can still see changes in the meibomian glands of patients who were treated with a standard course of 120 to 150 mg/kg isotretinoin,” he said, referring to the results of a study of 88 patients .
One study investigated the effects of omega-3 fatty acids and punctal plugs on tear film and ocular surface parameters in 90 patients receiving systemic isotretinoin therapy. They were divided into three groups: Those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug that was inserted in the inferior punctum of both eyes and received oral omega-3 fatty acid capsules twice daily for a total dose of 1,040 mg/day for 6 months; those who received a soft preloaded silicone plug and oral placebo, and those who received isotretinoin alone. At 6 months’ follow-up, those who were treated with omega-3 combined with the preloaded silicone plug had better meibomian gland function than did those who received isotretinoin alone or isotretinoin with the preloaded silicone plug.
Dr. Barbieri also noted that antihistamines may play a role in enhancing the effect of isotretinoin. In one study, 20 patients were treated with isotretinoin 0.4 mg/kg per day and 20 patients were also treated with an antihistamine, desloratadine 5 mg/day for 12 weeks. At week 12, patients in the group treated with isotretinoin and the antihistamine showed a more statistically significant decrease in acne lesion counts, compared with the isotretinoin-only group (reductions of 44.8% vs. 17.8%, respectively, in noninflammatory lesions; 55.8% vs. 22.9% in inflammatory lesions, and 45.6% vs. 18.7% in total lesions (P < .05 for all associations).
A subsequent larger study yielded similar findings. There were also lower rates of initial flaring and higher rates of patient satisfaction in the antihistamine groups in both studies.
In an interview at the meeting, Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, described Dr. Barbieri as “a leader in taking a comprehensive view on what the history and latest information is on isotretinoin. His fresh approach is something everyone should consider and figure out what they can use in their practice.”
Dr. Barbieri disclosed that he receives consulting fees from Dexcel for work unrelated to his presentation. Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics. Medscape and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT THE MEDSCAPE LIVE! HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Embattled iPLEDGE program: Changes ahead?
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study documents link between preadolescent acne and elevated BMI
The that used age- and sex-matched controls.
The investigators also identified “a potential association” with precocious puberty that they said “should be considered, especially among those presenting [with acne] under 8 or 9 years old.” The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology .
Senior author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, and coauthors used resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project to identify all residents of Olmstead County, Minn., who were diagnosed with acne between the ages of 7 and 12 years during 2010-2018. They then randomly selected two age and sex-matched community controls in order to evaluate the relationship of preadolescent acne and BMI.
They confirmed 643 acne cases, and calculated an annual age- and sex-adjusted incidence rate for ages 7-12 of 58 per 10,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 53.5-62.5). The incidence rate was significantly higher in females than males (89.2 vs. 28.2 per 10,000 person-years; P < .001), and it significantly increased with age (incidence rates of 4.3, 24.4, and 144.3 per 10,000 person-years among those ages 7-8, 9-10, and 11-12 years, respectively).
The median BMI percentile among children with acne was significantly higher than those without an acne diagnosis (75.0 vs. 65.0; P <.001). They also were much more likely to be obese: 16.7% of the children with acne had a BMI in at least the 95th percentile, compared with 12.2% among controls with no acne diagnosis (P = .01). (The qualifying 581 acne cases for this analysis had BMIs recorded within 8 months of the index data, in addition to not having pre-existing acne-relevant endocrine disorders.)
“High BMI is a strong risk factor for acne development and severity in adults, but until now pediatric studies have revealed mixed information ... [and have been] largely retrospective reviews without controls,” Dr. Tollefson, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote.
‘Valuable’ data
Leah Lalor, MD, a pediatric dermatologist not involved with the research, said she is happy to see it. “It’s really valuable,” she said in an interview. “It’s actually the first study that gives us incidence data for preadolescent acne. We all have [had our estimates], but this study quantifies it ... and it will set the stage for further studies of preadolescents in the future.”
The study also documents that “girls are more likely to present to the clinic with acne, and to do so at younger ages, which we’ve suspected and which makes physiologic sense since girls tend to go through puberty earlier than boys,” said Dr. Lalor, assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the Medical College of Wisconsin and the Children’s Wisconsin Clinics, both in Milwaukee. “And most interestingly, it really reveals that BMI is higher among preadolescents with acne than those without.”
The important caveat, she emphasized, is that the study population in Olmstead County, Minn. has a relatively higher level of education, wealth, and employment than the rest of the United States.
The investigators also found that use of systemic acne medications increased with increasing BMI (odds ratio, 1.43 per 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI; 95% CI, 1.07-1.92; P = .015). Approximately 5% of underweight or normal children were prescribed systemic acne medications, compared with 8.1% of overweight children, and 10.3% of those who were obese – data that suggest that most preadolescents with acne had mild to moderate disease and that more severe acne may be associated with increasing BMI percentiles, the authors wrote.
Approximately 4% of the 643 preadolescents with acne were diagnosed with an acne-relevant endocrine disorder prior to or at the time of acne diagnosis – most commonly precocious puberty. Of the 24 diagnoses of precocious puberty, 22 were in females, with a mean age at diagnosis of 7.3 years.
Puberty before age 8 in girls and 9 in boys is classified as precocious puberty. “Thus, a thorough review of systems and exam should be done in this population [with acne] to look for precocious puberty with a low threshold for systemic evaluation if indicated,” the authors wrote, also noting that 19 or the 482 female patients with acne were subsequently diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Dr. Lalor said she “automatically” refers children with acne who are younger than 7 for an endocrine workup, but not necessarily children ages 7, 8, or 9 because “that’s considered within the normal realm of starting to get some acne.” Acne in the context of other symptoms such as body odor, hair, or thelarche may prompt referral in these ages, however, she said.
Future research
Obesity may influence preadolescent acne development through its effect on puberty, as overweight and obese girls achieve puberty earlier than those with normal BMI. And “insulin resistance, which may be related to obesity, has been implicated with inducing or worsening acne potentially related to shifts in IGF-1 [insulin-like growth factor 1] signaling and hyperandrogenemia,” Dr. Tollefson and colleagues wrote. Nutrition is also a possible confounder in the study.
“Patients and families have long felt that certain foods or practices contribute to acne, though this has been difficult to prove,” Dr. Lalor said. “We know that excess skim milk seems to contribute ... and there’s a correlation between high glycemic load diets [and acne].”
Assessing dietary habits in conjunction with BMI, and acne incidence and severity, would be valuable. So would research to determine “if decreasing the BMI percentile [in children with acne] would improve or prevent acne, without doing any acne treatments,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the Rochester Epidemiology Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lalor also reported no conflicts of interest.
The that used age- and sex-matched controls.
The investigators also identified “a potential association” with precocious puberty that they said “should be considered, especially among those presenting [with acne] under 8 or 9 years old.” The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology .
Senior author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, and coauthors used resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project to identify all residents of Olmstead County, Minn., who were diagnosed with acne between the ages of 7 and 12 years during 2010-2018. They then randomly selected two age and sex-matched community controls in order to evaluate the relationship of preadolescent acne and BMI.
They confirmed 643 acne cases, and calculated an annual age- and sex-adjusted incidence rate for ages 7-12 of 58 per 10,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 53.5-62.5). The incidence rate was significantly higher in females than males (89.2 vs. 28.2 per 10,000 person-years; P < .001), and it significantly increased with age (incidence rates of 4.3, 24.4, and 144.3 per 10,000 person-years among those ages 7-8, 9-10, and 11-12 years, respectively).
The median BMI percentile among children with acne was significantly higher than those without an acne diagnosis (75.0 vs. 65.0; P <.001). They also were much more likely to be obese: 16.7% of the children with acne had a BMI in at least the 95th percentile, compared with 12.2% among controls with no acne diagnosis (P = .01). (The qualifying 581 acne cases for this analysis had BMIs recorded within 8 months of the index data, in addition to not having pre-existing acne-relevant endocrine disorders.)
“High BMI is a strong risk factor for acne development and severity in adults, but until now pediatric studies have revealed mixed information ... [and have been] largely retrospective reviews without controls,” Dr. Tollefson, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote.
‘Valuable’ data
Leah Lalor, MD, a pediatric dermatologist not involved with the research, said she is happy to see it. “It’s really valuable,” she said in an interview. “It’s actually the first study that gives us incidence data for preadolescent acne. We all have [had our estimates], but this study quantifies it ... and it will set the stage for further studies of preadolescents in the future.”
The study also documents that “girls are more likely to present to the clinic with acne, and to do so at younger ages, which we’ve suspected and which makes physiologic sense since girls tend to go through puberty earlier than boys,” said Dr. Lalor, assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the Medical College of Wisconsin and the Children’s Wisconsin Clinics, both in Milwaukee. “And most interestingly, it really reveals that BMI is higher among preadolescents with acne than those without.”
The important caveat, she emphasized, is that the study population in Olmstead County, Minn. has a relatively higher level of education, wealth, and employment than the rest of the United States.
The investigators also found that use of systemic acne medications increased with increasing BMI (odds ratio, 1.43 per 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI; 95% CI, 1.07-1.92; P = .015). Approximately 5% of underweight or normal children were prescribed systemic acne medications, compared with 8.1% of overweight children, and 10.3% of those who were obese – data that suggest that most preadolescents with acne had mild to moderate disease and that more severe acne may be associated with increasing BMI percentiles, the authors wrote.
Approximately 4% of the 643 preadolescents with acne were diagnosed with an acne-relevant endocrine disorder prior to or at the time of acne diagnosis – most commonly precocious puberty. Of the 24 diagnoses of precocious puberty, 22 were in females, with a mean age at diagnosis of 7.3 years.
Puberty before age 8 in girls and 9 in boys is classified as precocious puberty. “Thus, a thorough review of systems and exam should be done in this population [with acne] to look for precocious puberty with a low threshold for systemic evaluation if indicated,” the authors wrote, also noting that 19 or the 482 female patients with acne were subsequently diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Dr. Lalor said she “automatically” refers children with acne who are younger than 7 for an endocrine workup, but not necessarily children ages 7, 8, or 9 because “that’s considered within the normal realm of starting to get some acne.” Acne in the context of other symptoms such as body odor, hair, or thelarche may prompt referral in these ages, however, she said.
Future research
Obesity may influence preadolescent acne development through its effect on puberty, as overweight and obese girls achieve puberty earlier than those with normal BMI. And “insulin resistance, which may be related to obesity, has been implicated with inducing or worsening acne potentially related to shifts in IGF-1 [insulin-like growth factor 1] signaling and hyperandrogenemia,” Dr. Tollefson and colleagues wrote. Nutrition is also a possible confounder in the study.
“Patients and families have long felt that certain foods or practices contribute to acne, though this has been difficult to prove,” Dr. Lalor said. “We know that excess skim milk seems to contribute ... and there’s a correlation between high glycemic load diets [and acne].”
Assessing dietary habits in conjunction with BMI, and acne incidence and severity, would be valuable. So would research to determine “if decreasing the BMI percentile [in children with acne] would improve or prevent acne, without doing any acne treatments,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the Rochester Epidemiology Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lalor also reported no conflicts of interest.
The that used age- and sex-matched controls.
The investigators also identified “a potential association” with precocious puberty that they said “should be considered, especially among those presenting [with acne] under 8 or 9 years old.” The study was published in Pediatric Dermatology .
Senior author Megha M. Tollefson, MD, and coauthors used resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project to identify all residents of Olmstead County, Minn., who were diagnosed with acne between the ages of 7 and 12 years during 2010-2018. They then randomly selected two age and sex-matched community controls in order to evaluate the relationship of preadolescent acne and BMI.
They confirmed 643 acne cases, and calculated an annual age- and sex-adjusted incidence rate for ages 7-12 of 58 per 10,000 person-years (95% confidence interval, 53.5-62.5). The incidence rate was significantly higher in females than males (89.2 vs. 28.2 per 10,000 person-years; P < .001), and it significantly increased with age (incidence rates of 4.3, 24.4, and 144.3 per 10,000 person-years among those ages 7-8, 9-10, and 11-12 years, respectively).
The median BMI percentile among children with acne was significantly higher than those without an acne diagnosis (75.0 vs. 65.0; P <.001). They also were much more likely to be obese: 16.7% of the children with acne had a BMI in at least the 95th percentile, compared with 12.2% among controls with no acne diagnosis (P = .01). (The qualifying 581 acne cases for this analysis had BMIs recorded within 8 months of the index data, in addition to not having pre-existing acne-relevant endocrine disorders.)
“High BMI is a strong risk factor for acne development and severity in adults, but until now pediatric studies have revealed mixed information ... [and have been] largely retrospective reviews without controls,” Dr. Tollefson, professor of pediatrics and dermatology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote.
‘Valuable’ data
Leah Lalor, MD, a pediatric dermatologist not involved with the research, said she is happy to see it. “It’s really valuable,” she said in an interview. “It’s actually the first study that gives us incidence data for preadolescent acne. We all have [had our estimates], but this study quantifies it ... and it will set the stage for further studies of preadolescents in the future.”
The study also documents that “girls are more likely to present to the clinic with acne, and to do so at younger ages, which we’ve suspected and which makes physiologic sense since girls tend to go through puberty earlier than boys,” said Dr. Lalor, assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the Medical College of Wisconsin and the Children’s Wisconsin Clinics, both in Milwaukee. “And most interestingly, it really reveals that BMI is higher among preadolescents with acne than those without.”
The important caveat, she emphasized, is that the study population in Olmstead County, Minn. has a relatively higher level of education, wealth, and employment than the rest of the United States.
The investigators also found that use of systemic acne medications increased with increasing BMI (odds ratio, 1.43 per 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI; 95% CI, 1.07-1.92; P = .015). Approximately 5% of underweight or normal children were prescribed systemic acne medications, compared with 8.1% of overweight children, and 10.3% of those who were obese – data that suggest that most preadolescents with acne had mild to moderate disease and that more severe acne may be associated with increasing BMI percentiles, the authors wrote.
Approximately 4% of the 643 preadolescents with acne were diagnosed with an acne-relevant endocrine disorder prior to or at the time of acne diagnosis – most commonly precocious puberty. Of the 24 diagnoses of precocious puberty, 22 were in females, with a mean age at diagnosis of 7.3 years.
Puberty before age 8 in girls and 9 in boys is classified as precocious puberty. “Thus, a thorough review of systems and exam should be done in this population [with acne] to look for precocious puberty with a low threshold for systemic evaluation if indicated,” the authors wrote, also noting that 19 or the 482 female patients with acne were subsequently diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Dr. Lalor said she “automatically” refers children with acne who are younger than 7 for an endocrine workup, but not necessarily children ages 7, 8, or 9 because “that’s considered within the normal realm of starting to get some acne.” Acne in the context of other symptoms such as body odor, hair, or thelarche may prompt referral in these ages, however, she said.
Future research
Obesity may influence preadolescent acne development through its effect on puberty, as overweight and obese girls achieve puberty earlier than those with normal BMI. And “insulin resistance, which may be related to obesity, has been implicated with inducing or worsening acne potentially related to shifts in IGF-1 [insulin-like growth factor 1] signaling and hyperandrogenemia,” Dr. Tollefson and colleagues wrote. Nutrition is also a possible confounder in the study.
“Patients and families have long felt that certain foods or practices contribute to acne, though this has been difficult to prove,” Dr. Lalor said. “We know that excess skim milk seems to contribute ... and there’s a correlation between high glycemic load diets [and acne].”
Assessing dietary habits in conjunction with BMI, and acne incidence and severity, would be valuable. So would research to determine “if decreasing the BMI percentile [in children with acne] would improve or prevent acne, without doing any acne treatments,” she said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging and the Rochester Epidemiology Project. The authors reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Lalor also reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Large cohort study finds isotretinoin not associated with IBD
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.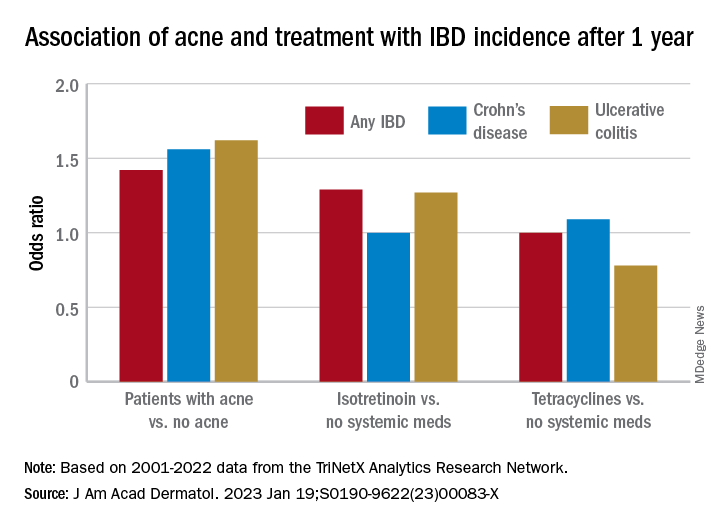
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
that also found no significant association of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics with IBD – and a small but statistically significant association of acne itself with the inflammatory disorders that make up IBD.
For the study, senior author John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, of the department of dermatology, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues used data from the TriNetX global research platform, which mines patient-level electronic medical record data from dozens of health care organizations, mainly in the United States. The network includes over 106 million patients. They looked at four cohorts: Patients without acne; those with acne but no current or prior use of systemic medications; those with acne managed with isotretinoin (and no prior use of oral tetracycline-class antibiotics); and those with acne managed with oral tetracycline-class antibiotics (and no exposure to isotretinoin).
For the acne cohorts, the investigators captured first encounters with a diagnosis of acne and first prescriptions of interest. And studywide, they used propensity score matching to balance cohorts for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and combined oral contraceptive use.
“These data should provide more reassurance to patients and prescribers that isotretinoin does not appear to result in a meaningfully increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease,” they wrote in the study, published online in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These are important findings as isotretinoin is a valuable treatment for acne that can result in a durable remission of disease activity, prevent acne scarring, and reduce our overreliance on oral antibiotics for acne,” they added.
Indeed, dermatologist Jonathan S. Weiss, MD, who was not involved in the research and was asked to comment on the study, said that the findings “are reassuring given the large numbers of patients evaluated and treated.” The smallest cohort – the isotretinoin group – had over 11,000 patients, and the other cohorts had over 100,000 patients each, he said in an interview.
“At this point, I’m not sure we need any other immediate information to feel comfortable using isotretinoin with respect to a potential to cause IBD, but it would be nice to see some longitudinal follow-up data for longer-term reassurance,” added Dr. Weiss, who practices in Snellville, Georgia, and is on the board of the directors of the American Acne and Rosacea Society.
The findings: Risk with acne
To assess the potential association between acne and IBD, the researchers identified more than 350,000 patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and propensity score matched them with patients who did not have acne. Altogether, their mean age was 22; 32.1% were male, and 59.6% were White.
Compared with the controls who did not have acne, they found a statistically significant association between acne and risk of incident IBD (odds ratio, 1.42; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-1.65) and an absolute risk difference of .04%. Separated into Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), ORs were 1.56 and 1.62, respectively.
Tetracyclines
To assess the association of oral tetracycline use and IBD, they compared more than 144,000 patients whose acne was managed with antibiotics with patients whose acne was managed without systemic medications. The patients had a mean age of 24.4; 34.7% were male, and 68.2% were White.
Compared with the patients who were not on systemic medications, there were no significant associations among those on oral tetracyclines, with an OR for incident IBD of 1 (95% CI, 0.82-1.22), an OR for incident CD of 1.09 (95% CI, 0.86-1.38), and an OR for UC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.61-1.00).
Isotretinoin
To evaluate the association of isotretinoin and IBD, the researchers compared more than 11,000 patients treated with isotretinoin with two matched groups: patients with acne managed without systemic medications, and patients with acne managed with oral tetracyclines. The latter comparison was made to minimize potential confounding by acne severity. These patients had a mean age of 21.1; 49.5% were male, and 75.3% were White.
In the first comparison, compared with patients not treated with systemic medications, the OR for 1-year incidence of IBD among patients treated with isotretinoin was 1.29 (95% CI, 0.64-2.59), with an absolute risk difference of .036%. The ORs for CD and UC were 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23) and 1.27 (95% CI, .58-2.80), respectively.
And compared with the antibiotic-managed group, the OR for incident IBD among those on isotretinoin was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.57-2.21), with an absolute risk difference of .018%. The OR for CD was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.45-2.23). The OR for UC could not be accurately estimated because of an insufficient number of events in the tetracycline-treated group.
‘Challenging’ area of research
Researching acne treatments and the potential risk of IBD has been a methodologically “challenging topic to study” because of possible confounding and surveillance bias depending on study designs, Dr. Barbieri, director of the Brigham and Women’s Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic, said in an interview.
Studies that have identified a potential association between isotretinoin and IBD often have not adequately controlled for prior antibiotic exposure, for instance. And other studies, including a retrospective cohort study also published recently in JAAD using the same TriNetX database, have found 6-month isotretinoin-related risks of IBD but no increased risk at 1 year or more of follow-up – a finding that suggests a role of surveillance bias, Dr. Barbieri said.
The follow-up period of 1 year in their new study was chosen to minimize the risk of such bias. “Since patients on isotretinoin are seen more often, and since there are historical concerns about isotretinoin and IBD, patients on isotretinoin may be more likely to be screened earlier and thus could be diagnosed sooner than those not on [the medication],” he said.
He and his coauthors considered similar potential bias in designing the no-acne cohort, choosing patients who had routine primary care visits without abnormal findings in order to “reduce potential for bias due to frequency of interaction with the health care system,” they noted in their paper. (Patients had no prior encounters for acne and no history of acne treatments.)
Antibiotics, acne itself
Research on antibiotic use for acne and risk of IBD is scant, and the few studies that have been published show conflicting findings, Dr. Barbieri noted. In the meantime, studies and meta-analyses in the general medical literature – not involving acne – have identified an association between lifetime oral antibiotic exposure and IBD, he said.
While the results of the new study “are reassuring that oral tetracycline-class exposure for acne may not be associated with a significant absolute risk of inflammatory bowel disease, given the potential for antibiotic resistance and other antibiotic-associated complications, it remains important to be judicious” with their use in acne management, he and his coauthors wrote in the study.
The potential association between antibiotics for acne and IBD needs further study, preferably with longer follow-up duration, Dr. Barbieri said in the interview, but researchers are challenged by the lack of datasets with high-quality longitudinal data “beyond a few years of follow-up.”
The extent to which acne itself is associated with IBD is another area ripe for more research. Thus far, it seems that IBD and acne – and other chronic inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis – involve similar pathogenic pathways. “We know that in IBD Th17 and TNF immunologic pathways are important, so it’s not surprising that there may be associations,” he said.
In their paper, Dr. Barbieri and his coauthors emphasize, however, that the absolute risk difference between acne and IBD is small. It’s “unlikely that population level screening is warranted among patients with acne,” they wrote.
A second new study
The other study, also published recently in JAAD, used the same TriNetX research platform to identify approximately 77,000 patients with acne starting isotretinoin and matched them with patients starting oral antibiotics.
The investigators, Khalaf Kridin MD, PhD, and Ralf J. Ludwig, MD, of the Lübeck Institute of Experimental Dermatology, University of Lübeck (Germany), found that the lifetime risks (greater than 6 months) for patients on isotretinoin were not significantly elevated, compared with those on oral antibiotics for either CD (hazard ratio 1.05; 95% CI, 0.89-1.24, P = .583) or UC (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.95-1.34; P = .162) They also looked at the risk of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and found a lower lifetime risk in the isotretinoin group.
In the short term, during the first 6 months after drug initiation, there was a significant, but slight increase in UC in the isotretinoin group. But this risk decreased to the level of the antibiotic group with longer follow up. “The absolute incidence rates [of IBD] and the risk difference of UC within the first 6 months are of limited clinical significance,” they wrote.
It may be, Dr. Weiss said in commenting on this study, “that isotretinoin unmasks an already-existing genetic tendency to UC early on in the course of treatment, but that it does not truly cause an increased incidence of any type of IBD.”
Both studies, said Dr. Barbieri, “add to an extensive body of literature that supports that isotretinoin is not associated with IBD.”
Dr. Barbieri had no disclosures for the study, for which Matthew T. Taylor served as first author. Coauthor Shawn Kwatra, MD, disclosed that he is an advisory board member/consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and has served as an investigator for several. Both are supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. The other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Kridin and Dr. Ludwig had no disclosures for their study. Dr. Weiss had no disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Berdazimer gel under review at FDA for treating molluscum contagiosum
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
, the manufacturer announced.
If the submission is accepted by the FDA, the topical product could be approved in the first quarter of 2024, according to a press release from Novan, the manufacturer. If approved, it would be the first-in-class topical treatment for MC, the common, contagious viral skin infection that affects approximately six million individuals in the United States each year, most of them children aged 1-14 years, the statement noted. No FDA-approved therapies currently exist for the condition, which causes unsightly lesions on the face, trunk, limbs, and axillae that may persist untreated for a period of years.
The active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3% is berdazimer sodium, a nitric oxide–releasing agent. A 3.4% formulation is in development for the topical treatment of acne, according to the company.
The submission for FDA approval is based on data from the B-SIMPLE4 study, a phase 3 randomized trial of nearly 900 individuals with MC aged 6 months and older (mean age, 6.6 years), with 3-70 raised lesions. Participants were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel 10.3% or a vehicle gel applied in a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. The results were published in JAMA Dermatology.
The primary outcome was complete clearance of all lesions. At 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved this outcome vs. 19.7% of those in the vehicle group (P < .001). Overall adverse event rates were low in both groups; 4.1% of patients on berdazimer and 0.7% of those on the vehicle experienced adverse events that led to discontinuation of treatment. The most common adverse events across both groups were application-site pain and erythema, and most of these were mild or moderate.
Topical treatment options for acne continue to expand
SAN DIEGO – , according to Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD.
The product, known as IDP-126 and being developed by Ortho Dermatologics, is a fixed dose triple combination of clindamycin 1.2% plus benzoyl peroxide 3.1% and adapalene 0.15% being evaluated in patients nine years of age and older. According to a 2021 press release from the company, results from a second 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial showed a treatment success of 50.5% and 20.5% for IDP-126 and its vehicle, respectively, along with significant changes from baseline in inflammatory lesion count and non-inflammatory lesion count.
More recently, researchers led by Linda Stein Gold, MD, conducted a 12-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind study of IDP-126 in 741 children, adolescents, and adults with moderate to severe acne. They reported 52.5% of patients treated with IDP-126 gel achieved treatment success by week 12, with over 70% reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
“This will be interesting to follow as it moves along,” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in a presentation on the newest topical acne treatments.
“If approved, we probably will be able to decrease our need for systemic therapies in some individuals,” he said. “It’s something that may become important in practices that mix and match between medical and procedural or surgical approaches to acne.”
Dr. Eichenfield highlighted other products for the topical treatment of acne:
- Trifarotene cream 0.005% (Aklief). In 2019, Food and Drug Administration approval made trifarotene cream the first new retinoid indicated for acne in several decades. It is indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older and has been studied in acne of the face, chest, and back.
- Tazarotene lotion 0.045% (Arazlo). The 0.1% formulation of tazarotene is commonly used for acne, but it can cause skin irritation, dryness, and erythema. The new 0.045% formulation was developed in a three-dimensional mesh matrix, with ingredients from an oil-in-water emulsion. “Many of the new acne products come with a background of vehicle delivery systems that minimize the concentration gradient, so it decreases irritation,” said Dr. Eichenfield, one of the authors of a 2021 review article on the management of acne vulgaris in JAMA. “This has very good efficacy without the traditional irritation of other tazarotene products,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Minocycline 4% topical foam (Amzeeq). The 2019 U.S. approval marked the first and so far only topical minocycline prescription treatment for acne. “Its hydrophobic composition allows for stable and efficient delivery of inherently unstable pharmaceutical ingredients,” he said. “It’s generally well tolerated.”
- Clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi). This first-in-class topical androgen receptor inhibitor is approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years and older. It competes with dihydrotestosterone and selectively targets androgen receptors in sebocytes and hair papilla cells. “It is safe for use in men, has been studied on the face and trunk, and has been shown to inhibit sebum production, reduce secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibit inflammatory pathways,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Micro-encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo). This is a once-daily fixed-dose combination of tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide indicated for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older. According to a press release from Sol-Gel, the manufacturer, silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures separate micro-encapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the two active ingredients in the cream.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD.
The product, known as IDP-126 and being developed by Ortho Dermatologics, is a fixed dose triple combination of clindamycin 1.2% plus benzoyl peroxide 3.1% and adapalene 0.15% being evaluated in patients nine years of age and older. According to a 2021 press release from the company, results from a second 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial showed a treatment success of 50.5% and 20.5% for IDP-126 and its vehicle, respectively, along with significant changes from baseline in inflammatory lesion count and non-inflammatory lesion count.
More recently, researchers led by Linda Stein Gold, MD, conducted a 12-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind study of IDP-126 in 741 children, adolescents, and adults with moderate to severe acne. They reported 52.5% of patients treated with IDP-126 gel achieved treatment success by week 12, with over 70% reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
“This will be interesting to follow as it moves along,” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in a presentation on the newest topical acne treatments.
“If approved, we probably will be able to decrease our need for systemic therapies in some individuals,” he said. “It’s something that may become important in practices that mix and match between medical and procedural or surgical approaches to acne.”
Dr. Eichenfield highlighted other products for the topical treatment of acne:
- Trifarotene cream 0.005% (Aklief). In 2019, Food and Drug Administration approval made trifarotene cream the first new retinoid indicated for acne in several decades. It is indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older and has been studied in acne of the face, chest, and back.
- Tazarotene lotion 0.045% (Arazlo). The 0.1% formulation of tazarotene is commonly used for acne, but it can cause skin irritation, dryness, and erythema. The new 0.045% formulation was developed in a three-dimensional mesh matrix, with ingredients from an oil-in-water emulsion. “Many of the new acne products come with a background of vehicle delivery systems that minimize the concentration gradient, so it decreases irritation,” said Dr. Eichenfield, one of the authors of a 2021 review article on the management of acne vulgaris in JAMA. “This has very good efficacy without the traditional irritation of other tazarotene products,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Minocycline 4% topical foam (Amzeeq). The 2019 U.S. approval marked the first and so far only topical minocycline prescription treatment for acne. “Its hydrophobic composition allows for stable and efficient delivery of inherently unstable pharmaceutical ingredients,” he said. “It’s generally well tolerated.”
- Clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi). This first-in-class topical androgen receptor inhibitor is approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years and older. It competes with dihydrotestosterone and selectively targets androgen receptors in sebocytes and hair papilla cells. “It is safe for use in men, has been studied on the face and trunk, and has been shown to inhibit sebum production, reduce secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibit inflammatory pathways,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Micro-encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo). This is a once-daily fixed-dose combination of tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide indicated for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older. According to a press release from Sol-Gel, the manufacturer, silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures separate micro-encapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the two active ingredients in the cream.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics.
SAN DIEGO – , according to Lawrence F. Eichenfield, MD.
The product, known as IDP-126 and being developed by Ortho Dermatologics, is a fixed dose triple combination of clindamycin 1.2% plus benzoyl peroxide 3.1% and adapalene 0.15% being evaluated in patients nine years of age and older. According to a 2021 press release from the company, results from a second 12-week pivotal phase 3 trial showed a treatment success of 50.5% and 20.5% for IDP-126 and its vehicle, respectively, along with significant changes from baseline in inflammatory lesion count and non-inflammatory lesion count.
More recently, researchers led by Linda Stein Gold, MD, conducted a 12-week multicenter, randomized, double-blind study of IDP-126 in 741 children, adolescents, and adults with moderate to severe acne. They reported 52.5% of patients treated with IDP-126 gel achieved treatment success by week 12, with over 70% reduction in inflammatory and noninflammatory lesions.
“This will be interesting to follow as it moves along,” Dr. Eichenfield, chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in a presentation on the newest topical acne treatments.
“If approved, we probably will be able to decrease our need for systemic therapies in some individuals,” he said. “It’s something that may become important in practices that mix and match between medical and procedural or surgical approaches to acne.”
Dr. Eichenfield highlighted other products for the topical treatment of acne:
- Trifarotene cream 0.005% (Aklief). In 2019, Food and Drug Administration approval made trifarotene cream the first new retinoid indicated for acne in several decades. It is indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older and has been studied in acne of the face, chest, and back.
- Tazarotene lotion 0.045% (Arazlo). The 0.1% formulation of tazarotene is commonly used for acne, but it can cause skin irritation, dryness, and erythema. The new 0.045% formulation was developed in a three-dimensional mesh matrix, with ingredients from an oil-in-water emulsion. “Many of the new acne products come with a background of vehicle delivery systems that minimize the concentration gradient, so it decreases irritation,” said Dr. Eichenfield, one of the authors of a 2021 review article on the management of acne vulgaris in JAMA. “This has very good efficacy without the traditional irritation of other tazarotene products,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Minocycline 4% topical foam (Amzeeq). The 2019 U.S. approval marked the first and so far only topical minocycline prescription treatment for acne. “Its hydrophobic composition allows for stable and efficient delivery of inherently unstable pharmaceutical ingredients,” he said. “It’s generally well tolerated.”
- Clascoterone cream 1% (Winlevi). This first-in-class topical androgen receptor inhibitor is approved for the treatment of acne in patients 12 years and older. It competes with dihydrotestosterone and selectively targets androgen receptors in sebocytes and hair papilla cells. “It is safe for use in men, has been studied on the face and trunk, and has been shown to inhibit sebum production, reduce secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and inhibit inflammatory pathways,” Dr. Eichenfield said.
- Micro-encapsulated benzoyl peroxide 3% and tretinoin 0.1% cream (Twyneo). This is a once-daily fixed-dose combination of tretinoin and benzoyl peroxide indicated for the treatment of acne vulgaris in patients age 9 and older. According to a press release from Sol-Gel, the manufacturer, silica (silicon dioxide) core shell structures separate micro-encapsulate tretinoin crystals and benzoyl peroxide crystals, enabling inclusion of the two active ingredients in the cream.
Dr. Eichenfield disclosed that he has been an investigator and/or consultant for Almirall, Cassiopea, Dermata, Galderma, and Ortho Dermatologics.
AT MOAS 2022
‘Slugging’: A TikTok skin trend that has some merit
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They’ve been around for a while and show no signs of going away: videos on TikTok of people, often teens, slathering their face with petroleum jelly and claiming that it’s transformed their skin, cured their acne, or given them an amazing “glow up.”
TikTok videos mentioning petrolatum increased by 46% and Instagram videos by 93% from 2021 to 2022, reported Gabriel Santos Malave, BA, of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and William D. James, MD, professor of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in a review of petroleum jelly’s uses recently published in Cutis.
The authors said that after application of a moisturizer.
In a typical demonstration, a dermatologist in the United Kingdom showed how she incorporates slugging into her routine in a TikTok video that’s had more than 1 million views.
Unlike many TikTok trends, slugging may not be entirely bad, say dermatologists.
“I think it’s a great way to keep your skin protected and moisturized, especially in those dry, cold winter months,” said dermatologist Mamina Turegano, MD, in a video posted in February 2022. That TikTok video has had more than 6 million views.
Dr. Turegano, who is in private practice in the New Orleans suburb of Metairie, La., told this news organization that she decided to post about slugging after she’d noticed that the topic was trending. Also, she had tried the technique herself when she was a resident in Washington more than a decade ago.
At the time, Dr. Turegano said that she was aware that “putting petroleum jelly on your face was not a normal thing.” But, given its history of being used in dermatology, she gave it a try and found that it worked well for her dry skin, she said.
Dr. Turegano is one among many dermatologists who have joined TikTok to dispel myths, educate, and inform. It’s important for them to be there “to engage and empower the public to become a better consumer of information out there and take ownership of their skin health,” said Jean McGee, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, and assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
Dr. McGee and colleagues studied TikTok content on slugging and found that by far, videos that were created by health care providers were more educational. Dermatologists who posted were more likely to discuss the risks and benefits, whereas so-called “influencers” rarely posted on the risks, according to the study, published in Clinics in Dermatology.
Slugging is generally safe and effective for those who have a compromised skin barrier or “for those who have sensitive skin and can’t tolerate other products but need some form of moisturization,” said Dr. Turegano.
“Its oil-based nature allows it to seal water in the skin by creating a hydrophobic barrier that decreases transepidermal water loss (TEWL),” write Mr. Malave and Dr. James in Cutis. They note that petrolatum reduces TEWL by 98%, compared with only 20% to 30% for other oil-based moisturizers.
Dermatologists have often recommended a “seal and trap” regimen for dry skin or eczema. It involves a short, lukewarm shower, followed by immediately moisturizing with a petrolatum-based ointment, said Dr. McGee.
This could be safe for the face, but “other variables need to be considered,” including use of other topical medications and other skin care practices, she added.
The concept of double-layering a moisturizer and an occlusive agent can be beneficial but more typically for the hands and feet, where the skin can be severely dry and cracked, said Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, George Washington University, Washington. “I would not recommend that on the face,” Dr. Friedman told this news organization.
He and other dermatologists warned about the potential for slugging – given petroleum jelly’s occlusive nature – to enhance the action of any topical steroid, retinol, or exfoliating agent.
Muneeb Shah, MD, who practices in Mooresville, N.C., is one of the most popular dermatologists on TikTok, with more than 17 million followers. He also warned in a February 2022 video about potential downsides. “Be careful after using retinol or exfoliating acids because it may actually irritate your skin more,” he says in the video.
“Slugging is awesome for some people but not for others, and not for every night,” said Whitney Bowe, MD, on a TikTok video she posted in July. She recommended it for eczema or really dry skin. Dr. Bowe, who practices with Advanced Dermatology in New York, advised those with acne-prone skin to “skip this trend.”
On a web page aimed at the general public, the American Academy of Dermatology similarly cautioned, “Avoid putting petroleum jelly on your face if you are acne-prone, as this may cause breakouts in some people.”
Acne cure or pore clogger?
And yet, plenty of TikTok users claim that it has improved their acne.
One such user posted a before and after video purporting to show that slugging had almost completely eliminated her acne and prior scarring. Not surprisingly, it has been viewed some 9 million times and got 1.5 million “likes.”
Dr. Friedman notes that it’s theoretically possible – but not likely – that acne could improve by slugging, given that acne basically is a disease of barrier disruption. “The idea here is you have disrupted skin barrier throughout the face regardless of whether you have a pimple in that spot or not, so you need to repair it,” he said. “That’s where I think slugging is somewhat on the right track, because by putting an occlusive agent on the skin, you are restoring the barrier element,” he said.
However, applying a thick, greasy ointment on the face could block pores and cause a backup of sebum and dead skin cells, and it could trap bacteria, he said. “Skin barrier protection and repair is central to acne management, but you need to do it in a safe way,” he said. He noted that that means applying an oil-free moisturizer to damp skin.
Dr. Turegano said she has seen slugging improve acne, but it’s hard to say which people with acne-prone skin would be the best candidates. Those who have used harsh products to treat acne and subsequently experienced worsening acne could potentially benefit, she said.
Even so, she said, “I’d be very cautious in anyone with acne.”
Dr. Friedman, Dr. McGee, and Dr. Turegano reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consider gaps in access and knowledge in diagnosis and treatment in skin of color
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
LAS VEGAS – and patients, Susan C. Taylor, MD, said in a presentation at MedscapeLive’s annual Las Vegas Dermatology Seminar.
Additionally, some disparities occur because of gaps in access to health care, said Dr. Taylor, vice chair, diversity, equity and inclusion, in the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who moderated an expert panel discussion of treatment tips for several common dermatologic conditions in skin of color patients.
Atopic dermatitis angles
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the fourth most common dermatologic complaint in Black patients, based on data from the United States National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Also, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey show that Black children are nearly twice as likely as White children to develop AD after controlling for socioeconomic factors, Dr. Taylor said.
When Black patients present with AD, “you may not see the erythema,” said Valerie D. Callender, MD, of Howard University, Washington, who presented on AD. Instead, “you may see more follicular and papular presentations.” Erythema and erythroderma can present as shades of violet, gray, or dark brown in patients with rich skin tones, added Dr. Callender, who practices in Glenn Dale, Md.
Consequently, disease severity can be misinterpreted, she said, noting that data suggest that scoring systems such as the Eczema Area and Severity Index and Scoring Atopic Dermatitis underestimate AD severity in dark skin.
As for treatment, skin of color patients with AD are often as bothered by postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) as by active lesions, so treatment should take these concerns into account, Dr. Callender said. Studies evaluating the effectiveness of AD treatments in diverse populations are limited by lack of representation of racial groups in clinical trials and lack of subset analyses by race.
Acne awareness
An important consideration of acne in skin of color patients is that the acne “might not be red, it might just be darker,” said Andrew F. Alexis, MD, vice-chair for diversity and inclusion in the department of dermatology, and professor of clinical dermatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. A study published in JAMA Dermatology of nearly 30,000 patients with acne from 2007 to 2017 found that non-Hispanic Black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic White patients to see a dermatologist for acne, but Black patients received fewer prescriptions for acne medications than White patients.
The study also showed that Black patients who received prescriptions for acne were more likely to receive topical retinoids and topical antibiotics, and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin, compared with White patients. Similarly, Asian patients were more likely to receive topical antibiotics and less likely to receive oral antibiotics, compared with White patients.
Other panelists shared some of their best practices for acne in patients with skin of color, including treatment with topical retinoids (for inflammation) and spironolactone, and therapies that address both inflammation and pigmentation, such as salicylic acid and azelaic acid. Dr. Callender also advised asking patients about makeup, as they may not know that many types of makeup used to cover acne are in fact comedogenic.
Melanoma misconceptions
One of the most common misperceptions about melanoma among skin of color patients is that they don’t think they can get it, Dr. Taylor said. Many health care providers don’t think about melanoma in skin of color patients because of the dramatically lower incidence in this population, but as a result, cases may go undiagnosed, and as studies have shown, the mortality rate from melanoma is higher in Black patients.
Consider the palms, soles, nails, and web spaces as possible melanoma sites, Dr. Taylor added.
Educating skin of color patients about melanoma is important, although the incidence is 20 to 30 times lower than in non-Hispanic Whites, said Nada Elbuluk, MD, the founder and director of the University of Southern California Skin of Color Center and Pigmentary Disorders Clinic, Los Angeles. A 2020 editorial published in Cancer Cytopathology pointed out that 1 in 3 Black men or women with a melanoma diagnosis in the United States dies of the disease, compared with 1 in 7 non-Hispanic White men and 1 in 11 non-Hispanic White women with melanoma.
Don’t skip the total body skin exam in these patients, Dr. Elbuluk emphasized. Many patients will only partially undress, and areas such as toes can be missed.
Rosacea review
For patients with skin of color, clinicians need to look for different signs of rosacea than those typically seen in White patients, Dr. Elbuluk said. “The most common presentation of rosacea in skin of color is papulopustular,” and the granulomatous variant.
“These patients will often give you a history of sensitivity to products,” Dr. Elbuluk noted. They may not always have the flushing, but they may report warmth or itching, in addition to product sensitivity.
When considering rosacea in skin of color patients, be sure to have good lighting for close examination, as skin thickening is another subtle sign of rosacea in these patients, she said. Skin thickening “is a very early sign that will present in skin of color with no erythema, so keep that in mind.”
Stinging and burning sensations may be reported by skin of color patients with rosacea. Use patient history to confirm the diagnosis of rosacea, which is often delayed in skin of color patients because of a low index of suspicion, she said.
Psoriasis pointers
Psoriasis in skin of color patients used to be considered rare, “but that is far from true,” Dr. Alexis said. In fact, many cases of psoriasis are undiagnosed or the diagnosis is delayed in these patients.
The panelists noted that current guidelines for psoriasis treatment are based on clinical trials composed mainly of White patients, and do not contain specific recommendations for skin of color patients.
Notably, the morphology, location, and color of psoriasis lesions may be different for patients with darker skin, such as thicker plaques and more scaling over larger areas, they said. Also, skin of color patients may experience long-lasting dyspigmentation from psoriasis lesions that have resolved.
When developing a strategy for psoriasis in skin of color patients, consider not only disease severity, but also comorbidities and medications, response (if any) to prior therapies, patient preferences, and quality of life, the panelists said.
Dr. Callender, Dr. Elbuluk, Dr. Taylor, and Dr. Alexis reported conflicts of interest from numerous sources in industry. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
AT INNOVATIONS IN DERMATOLOGY
Laser and light devices for acne treatment continue to advance
The calendar year
This was preceded by the FDA clearance of AviClear, marketed by Cutera, in March, and the commercial launch of TheraClearX, marketed by StrataSkin, in July.
“It’s an exciting time to be working with acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “We’ll see a lot of people using new devices. I’m looking forward to seeing results in the long term.”
AviClear and the Accure Laser System, marketed by Accure, are both powered by a 1,726-nm laser, but they work differently. AviClear, which was cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, has a maximum fluence of 30 J/cm2 in single-pulse mode and a maximum fluence of 20 J/cm2 in double-pulse mode. The treatment handpiece has an integrated scanner for delivering treatment spot(s) in an operator-selected pattern. “It’s a little bit lower powered than the Accure and has a maximum pulse energy of 5 joules and a pulse duration of up to 50 milliseconds,” Dr. Sakamoto said. In the treatment of acne, laser and light treatments target the sebaceous gland.
In pivotal data submitted to the FDA, 104 patients with acne who were enrolled at 7 U.S. sites received 304 treatments with AviClear spaced 2-5 weeks apart. Each treatment took about 30 minutes. Treatment success was defined as having at least 50% fewer inflammatory acne lesions 12 weeks after the final treatment visit, compared with baseline. At the week 4 follow-up visit, there were median and mean reductions of 42% and 37%, respectively, in the inflammatory lesion counts from baseline (P < .001). The researchers found that, at the week 4 follow-up visit, 36% of patients had achieved treatment success, which increased to 78% at the 12-week follow-up visit. Treatment was considered safe and tolerable, according to the manufacturer.
The other newcomer device with a 1,726-nm wavelength is the Accure Laser System, which features a smart laser handpiece for real-time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. The device received CE Mark approval in 2020 for the treatment of moderate acne, and on Nov. 22, 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had been cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe inflammatory acne vulgaris.
Dr. Sakamoto and her Wellman colleagues have been working with five dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, and Mitchel Goldman, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2022, more than 50 patients with mild to severe acne were enrolled in four studies and an additional 30 were enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment after four monthly treatment sessions. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean visual analog scale score immediately after treatment was 2.09 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device overall with no adverse events reported. At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histologic studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other skin structures.
Dr. Sakamoto emphasized that to date no direct clinical comparisons have been made between the AviClear and Accure devices. “Are all 1,726-nm lasers made equal? That is a question that we have to keep in our mind,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “They are using the same wavelength, but they are different types of lasers.”
For example, the Accure Laser treats to temperature, relies on air cooling, and is targeted to dermatologists and plastic surgeons, while the AviClear treats to fluence, relies on contact cooling, and includes med spas and other nonphysician providers as the target users. “Mathematically, the difference between the two devices is that the Accure can achieve deeper penetration in a single pulse, while the AviClear is a little more superficial,” she said. “Whether that is translated clinically is unknown at this point.”
Dr. Sakamoto also discussed the TheraClearX, which is FDA cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, including comedonal, pustular, and inflammatory acne vulgaris. The device, which is a new version of the Palomar Acleara, uses a vacuum technique with up to 3 psi pressure in conjunction with broadband light with a wavelength spectrum of 500 nm–1,200 nm delivered through a liquid-cooled, handheld delivery system. The predicate device was the Aesthera Isolaz System. The vacuum extracts buildup of sebaceous material. “At the same time, it takes the blood out of the competing chromophore,” she said. “By doing so, it potentially damages the sebaceous glands and reduces the inflammatory lesions.”
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she is the founder of and science advisor for Lightwater Bioscience. She is also a science advisor for Accure Acne and has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital.
The calendar year
This was preceded by the FDA clearance of AviClear, marketed by Cutera, in March, and the commercial launch of TheraClearX, marketed by StrataSkin, in July.
“It’s an exciting time to be working with acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “We’ll see a lot of people using new devices. I’m looking forward to seeing results in the long term.”
AviClear and the Accure Laser System, marketed by Accure, are both powered by a 1,726-nm laser, but they work differently. AviClear, which was cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, has a maximum fluence of 30 J/cm2 in single-pulse mode and a maximum fluence of 20 J/cm2 in double-pulse mode. The treatment handpiece has an integrated scanner for delivering treatment spot(s) in an operator-selected pattern. “It’s a little bit lower powered than the Accure and has a maximum pulse energy of 5 joules and a pulse duration of up to 50 milliseconds,” Dr. Sakamoto said. In the treatment of acne, laser and light treatments target the sebaceous gland.
In pivotal data submitted to the FDA, 104 patients with acne who were enrolled at 7 U.S. sites received 304 treatments with AviClear spaced 2-5 weeks apart. Each treatment took about 30 minutes. Treatment success was defined as having at least 50% fewer inflammatory acne lesions 12 weeks after the final treatment visit, compared with baseline. At the week 4 follow-up visit, there were median and mean reductions of 42% and 37%, respectively, in the inflammatory lesion counts from baseline (P < .001). The researchers found that, at the week 4 follow-up visit, 36% of patients had achieved treatment success, which increased to 78% at the 12-week follow-up visit. Treatment was considered safe and tolerable, according to the manufacturer.
The other newcomer device with a 1,726-nm wavelength is the Accure Laser System, which features a smart laser handpiece for real-time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. The device received CE Mark approval in 2020 for the treatment of moderate acne, and on Nov. 22, 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had been cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe inflammatory acne vulgaris.
Dr. Sakamoto and her Wellman colleagues have been working with five dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, and Mitchel Goldman, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2022, more than 50 patients with mild to severe acne were enrolled in four studies and an additional 30 were enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment after four monthly treatment sessions. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean visual analog scale score immediately after treatment was 2.09 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device overall with no adverse events reported. At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histologic studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other skin structures.
Dr. Sakamoto emphasized that to date no direct clinical comparisons have been made between the AviClear and Accure devices. “Are all 1,726-nm lasers made equal? That is a question that we have to keep in our mind,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “They are using the same wavelength, but they are different types of lasers.”
For example, the Accure Laser treats to temperature, relies on air cooling, and is targeted to dermatologists and plastic surgeons, while the AviClear treats to fluence, relies on contact cooling, and includes med spas and other nonphysician providers as the target users. “Mathematically, the difference between the two devices is that the Accure can achieve deeper penetration in a single pulse, while the AviClear is a little more superficial,” she said. “Whether that is translated clinically is unknown at this point.”
Dr. Sakamoto also discussed the TheraClearX, which is FDA cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, including comedonal, pustular, and inflammatory acne vulgaris. The device, which is a new version of the Palomar Acleara, uses a vacuum technique with up to 3 psi pressure in conjunction with broadband light with a wavelength spectrum of 500 nm–1,200 nm delivered through a liquid-cooled, handheld delivery system. The predicate device was the Aesthera Isolaz System. The vacuum extracts buildup of sebaceous material. “At the same time, it takes the blood out of the competing chromophore,” she said. “By doing so, it potentially damages the sebaceous glands and reduces the inflammatory lesions.”
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she is the founder of and science advisor for Lightwater Bioscience. She is also a science advisor for Accure Acne and has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital.
The calendar year
This was preceded by the FDA clearance of AviClear, marketed by Cutera, in March, and the commercial launch of TheraClearX, marketed by StrataSkin, in July.
“It’s an exciting time to be working with acne,” Fernanda H. Sakamoto, MD, PhD, a dermatologist at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. “We’ll see a lot of people using new devices. I’m looking forward to seeing results in the long term.”
AviClear and the Accure Laser System, marketed by Accure, are both powered by a 1,726-nm laser, but they work differently. AviClear, which was cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, has a maximum fluence of 30 J/cm2 in single-pulse mode and a maximum fluence of 20 J/cm2 in double-pulse mode. The treatment handpiece has an integrated scanner for delivering treatment spot(s) in an operator-selected pattern. “It’s a little bit lower powered than the Accure and has a maximum pulse energy of 5 joules and a pulse duration of up to 50 milliseconds,” Dr. Sakamoto said. In the treatment of acne, laser and light treatments target the sebaceous gland.
In pivotal data submitted to the FDA, 104 patients with acne who were enrolled at 7 U.S. sites received 304 treatments with AviClear spaced 2-5 weeks apart. Each treatment took about 30 minutes. Treatment success was defined as having at least 50% fewer inflammatory acne lesions 12 weeks after the final treatment visit, compared with baseline. At the week 4 follow-up visit, there were median and mean reductions of 42% and 37%, respectively, in the inflammatory lesion counts from baseline (P < .001). The researchers found that, at the week 4 follow-up visit, 36% of patients had achieved treatment success, which increased to 78% at the 12-week follow-up visit. Treatment was considered safe and tolerable, according to the manufacturer.
The other newcomer device with a 1,726-nm wavelength is the Accure Laser System, which features a smart laser handpiece for real-time thermal monitoring and precise delivery of laser emissions. The device received CE Mark approval in 2020 for the treatment of moderate acne, and on Nov. 22, 2022, the manufacturer announced that it had been cleared by the FDA for the treatment of mild to severe inflammatory acne vulgaris.
Dr. Sakamoto and her Wellman colleagues have been working with five dermatologists to conduct clinical trials of the device: Emil Tanghetti, MD, and Mitchel Goldman, MD, in California; Roy Geronemus, MD, in New York; Joel Cohen, MD, in Colorado; and Daniel Friedmann, MD, in Texas. As of Oct. 2, 2022, more than 50 patients with mild to severe acne were enrolled in four studies and an additional 30 were enrolled in a pilot facial acne trial, Dr. Sakamoto said. In the trials, patients are followed at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment.
Among patients enrolled in the facial acne trial, researchers have observed a 100% responder rate for patients with more than five acne lesions at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks post treatment after four monthly treatment sessions. The average lesion reduction at week 12 was 82% and the mean visual analog scale score immediately after treatment was 2.09 out of 10. Each patient received more than 12,000 trigger pulls of energy from the device overall with no adverse events reported. At 12 months, they observed a 90% inflammatory lesion count reduction from baseline and a rapid response to treatment: a 73% reduction achieved after the first two treatment sessions. Histologic studies revealed selective sebaceous gland destruction with no damage to the epidermis, surrounding dermis, or other skin structures.
Dr. Sakamoto emphasized that to date no direct clinical comparisons have been made between the AviClear and Accure devices. “Are all 1,726-nm lasers made equal? That is a question that we have to keep in our mind,” she said during the meeting, which was sponsored by Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine. “They are using the same wavelength, but they are different types of lasers.”
For example, the Accure Laser treats to temperature, relies on air cooling, and is targeted to dermatologists and plastic surgeons, while the AviClear treats to fluence, relies on contact cooling, and includes med spas and other nonphysician providers as the target users. “Mathematically, the difference between the two devices is that the Accure can achieve deeper penetration in a single pulse, while the AviClear is a little more superficial,” she said. “Whether that is translated clinically is unknown at this point.”
Dr. Sakamoto also discussed the TheraClearX, which is FDA cleared for the treatment of mild, moderate, and severe acne, including comedonal, pustular, and inflammatory acne vulgaris. The device, which is a new version of the Palomar Acleara, uses a vacuum technique with up to 3 psi pressure in conjunction with broadband light with a wavelength spectrum of 500 nm–1,200 nm delivered through a liquid-cooled, handheld delivery system. The predicate device was the Aesthera Isolaz System. The vacuum extracts buildup of sebaceous material. “At the same time, it takes the blood out of the competing chromophore,” she said. “By doing so, it potentially damages the sebaceous glands and reduces the inflammatory lesions.”
Dr. Sakamoto disclosed that she is the founder of and science advisor for Lightwater Bioscience. She is also a science advisor for Accure Acne and has received portions of patent royalties from Massachusetts General Hospital.
FROM A LASER & AESTHETIC SKIN THERAPY COURSE