User login
‘Bane of my existence:’ The burden of Medicare Advantage denials
, a recent analysis suggests.
The report from the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services found that 13% of prior authorization denials were for service requests, which included cancer care, that met Medicare coverage rules and 18% of payment denials were for claims that met Medicare coverage and MAO billing rules, delaying or halting payments for services that clinicians had provided.
MAO denials are the “bane of my existence,” said Michael Buckstein, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York.
“Working at a large hospital in a metropolitan city, we spend enormous and increasing amounts of time on prior approvals and we get denials quite frequently, which certainly can lead to delays in treatment,” said Dr. Buckstein, who reviewed the OIG report for this news organization.
According to Dr. Buckstein, once a claim is denied, staff must spend time filing and scheduling an appeal, and if the appeal is denied in a physician peer-to-peer review, staff could face secondary and tertiary appeals. “We have been living with this frustration for a long time,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Widespread and persistent problems
Medicare Advantage plans, which are approved by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services but run by private companies, continue to grow in popularity.
In 2021, 26.4 million Medicare beneficiaries (42%) were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan, and by 2030, about 51% of all Medicare beneficiaries will be enrolled, according to estimates from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
“Although MAOs approve the vast majority of prior authorization requests and provider payment requests, MAOs also deny millions of requests each year,” the OIG wrote. “CMS’s annual audits of MAOs have highlighted widespread and persistent problems related to inappropriate denials of services and payment.”
In the current report, the OIG reviewed case files for 247 denials of prior authorization requests and 183 payment denials issued by 15 of the largest MAOs during 1 week in June of 2019.
The authors found that 13% of prior authorization denials occurred for service requests that met Medicare coverage rules, meaning these services would likely have been approved had the patient been enrolled in traditional Medicare.
The most prominent service types among these denials included imaging services, stays in postacute facilities, and injections.
In one case, for example, the MAO stated that a beneficiary would need to wait at least 1 year for a follow-up MRI because the size of the patient’s adrenal lesion (< 2 cm) was too small to warrant follow-up before 1 year. However, this restriction is not included in Medicare coverage rules. And an OIG physician panel found that the documentation in the original request demonstrated that the MRI was medically necessary to determine whether the lesion seen on an earlier CT scan was malignant.
Upon appeal, the MAO reversed its original denial.
Among the payment requests that MAOs denied, almost one in five were for claims that met Medicare coverage and billing rules, which delayed or prevented payments for services already delivered. Most payment denials were caused by human error during manual claims-processing reviews and system processing errors, the OIG report found.
In one case, for example, a MAO denied payment for radiation treatment for a patient with a tumor on the pancreas, incorrectly claiming that no prior authorization had been submitted for the service. However, the physician subsequently provided a screenshot demonstrating that the MAO had granted prior authorization for the billed claim, and the MAO reversed the denial.
Most of these prior authorization denial reversals occurred because of an appeal filed by the beneficiary or the provider, which can take weeks.
In one case, an MAO denied a request for a CT scan of the chest and pelvis for a beneficiary with endometrial cancer. It took 5 weeks for the provider to get the denial reversed. The OIG panel determined that the original request included sufficient documentation to demonstrate the CT was needed to assess the stage of the cancer and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
These denials and reversals not only waste time but may also cause harm. In a 2021 American Medical Association survey, 34% of physicians reported that prior authorization led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care, including hospitalization, medical intervention to prevent permanent impairment, and even disability or death.
Almost 90% of the physicians surveyed described the burden associated with prior authorizations as ‘high’ or ‘extremely high.’ More specifically, physicians and their staff spend nearly 2 days a week on prior authorizations and 40% of physicians have staff who work exclusively on prior authorizations.
“It’s just not the way medicine should be practiced, especially for cancer patients who are very vulnerable and want rapid care,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Time for action
Weighing in on the OIG report, Robert E. Wailes, MD, president of the California Medical Association, noted that “it has become common practice for health insurance companies to create obstacles for patients in hopes of not having to pay for essential healthcare.”
The reason for these obstacles is simple, he said: “Fewer procedures performed translates to larger insurance company profits.”
America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) defended prior authorization, saying it is “an important patient safety, cost-saving, and waste-prevention tool.”
The group also called out the OIG review for its “extraordinarily small” sample of 247 prior authorization requests over 1 week.
“Drawing far-reaching conclusions based on a very small sample of data and misleading headlines is not a productive way to improve our healthcare system for patients,” the AHIP statement reads.
But, according to Anna Schwamlein Howard, who works on policy development at the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the recent OIG report is in line with previous OIG reports.
And, Ms. Howard emphasized, the current report and others like it “highlight the need for CMS to utilize its audit authority and ensure that beneficiaries have access to medically necessary treatments, particularly cancer treatments.”
Along those lines, the OIG report recommends that the CMS should issue new guidance on the appropriate use of MAO clinical criteria in medical necessity reviews, update its audit protocols to address issues identified in the report, and direct MAOs to take additional steps to identify and address vulnerabilities that can lead to manual review and system errors.
In a statement, the CMS said it is committed to oversight and enforcement of the requirements of the Medicare Advantage program and agreed with the OIG recommendations.
“Lawmakers must act now to place patient needs before corporate profits and simplify by streamlining prior authorization processes,” Dr. Wailes said.
The ACS recently released a paper on this topic entitled, “The Medicare Appeals Process: Reforms Needed to Ensure Beneficiary Access.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a recent analysis suggests.
The report from the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services found that 13% of prior authorization denials were for service requests, which included cancer care, that met Medicare coverage rules and 18% of payment denials were for claims that met Medicare coverage and MAO billing rules, delaying or halting payments for services that clinicians had provided.
MAO denials are the “bane of my existence,” said Michael Buckstein, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York.
“Working at a large hospital in a metropolitan city, we spend enormous and increasing amounts of time on prior approvals and we get denials quite frequently, which certainly can lead to delays in treatment,” said Dr. Buckstein, who reviewed the OIG report for this news organization.
According to Dr. Buckstein, once a claim is denied, staff must spend time filing and scheduling an appeal, and if the appeal is denied in a physician peer-to-peer review, staff could face secondary and tertiary appeals. “We have been living with this frustration for a long time,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Widespread and persistent problems
Medicare Advantage plans, which are approved by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services but run by private companies, continue to grow in popularity.
In 2021, 26.4 million Medicare beneficiaries (42%) were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan, and by 2030, about 51% of all Medicare beneficiaries will be enrolled, according to estimates from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
“Although MAOs approve the vast majority of prior authorization requests and provider payment requests, MAOs also deny millions of requests each year,” the OIG wrote. “CMS’s annual audits of MAOs have highlighted widespread and persistent problems related to inappropriate denials of services and payment.”
In the current report, the OIG reviewed case files for 247 denials of prior authorization requests and 183 payment denials issued by 15 of the largest MAOs during 1 week in June of 2019.
The authors found that 13% of prior authorization denials occurred for service requests that met Medicare coverage rules, meaning these services would likely have been approved had the patient been enrolled in traditional Medicare.
The most prominent service types among these denials included imaging services, stays in postacute facilities, and injections.
In one case, for example, the MAO stated that a beneficiary would need to wait at least 1 year for a follow-up MRI because the size of the patient’s adrenal lesion (< 2 cm) was too small to warrant follow-up before 1 year. However, this restriction is not included in Medicare coverage rules. And an OIG physician panel found that the documentation in the original request demonstrated that the MRI was medically necessary to determine whether the lesion seen on an earlier CT scan was malignant.
Upon appeal, the MAO reversed its original denial.
Among the payment requests that MAOs denied, almost one in five were for claims that met Medicare coverage and billing rules, which delayed or prevented payments for services already delivered. Most payment denials were caused by human error during manual claims-processing reviews and system processing errors, the OIG report found.
In one case, for example, a MAO denied payment for radiation treatment for a patient with a tumor on the pancreas, incorrectly claiming that no prior authorization had been submitted for the service. However, the physician subsequently provided a screenshot demonstrating that the MAO had granted prior authorization for the billed claim, and the MAO reversed the denial.
Most of these prior authorization denial reversals occurred because of an appeal filed by the beneficiary or the provider, which can take weeks.
In one case, an MAO denied a request for a CT scan of the chest and pelvis for a beneficiary with endometrial cancer. It took 5 weeks for the provider to get the denial reversed. The OIG panel determined that the original request included sufficient documentation to demonstrate the CT was needed to assess the stage of the cancer and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
These denials and reversals not only waste time but may also cause harm. In a 2021 American Medical Association survey, 34% of physicians reported that prior authorization led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care, including hospitalization, medical intervention to prevent permanent impairment, and even disability or death.
Almost 90% of the physicians surveyed described the burden associated with prior authorizations as ‘high’ or ‘extremely high.’ More specifically, physicians and their staff spend nearly 2 days a week on prior authorizations and 40% of physicians have staff who work exclusively on prior authorizations.
“It’s just not the way medicine should be practiced, especially for cancer patients who are very vulnerable and want rapid care,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Time for action
Weighing in on the OIG report, Robert E. Wailes, MD, president of the California Medical Association, noted that “it has become common practice for health insurance companies to create obstacles for patients in hopes of not having to pay for essential healthcare.”
The reason for these obstacles is simple, he said: “Fewer procedures performed translates to larger insurance company profits.”
America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) defended prior authorization, saying it is “an important patient safety, cost-saving, and waste-prevention tool.”
The group also called out the OIG review for its “extraordinarily small” sample of 247 prior authorization requests over 1 week.
“Drawing far-reaching conclusions based on a very small sample of data and misleading headlines is not a productive way to improve our healthcare system for patients,” the AHIP statement reads.
But, according to Anna Schwamlein Howard, who works on policy development at the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the recent OIG report is in line with previous OIG reports.
And, Ms. Howard emphasized, the current report and others like it “highlight the need for CMS to utilize its audit authority and ensure that beneficiaries have access to medically necessary treatments, particularly cancer treatments.”
Along those lines, the OIG report recommends that the CMS should issue new guidance on the appropriate use of MAO clinical criteria in medical necessity reviews, update its audit protocols to address issues identified in the report, and direct MAOs to take additional steps to identify and address vulnerabilities that can lead to manual review and system errors.
In a statement, the CMS said it is committed to oversight and enforcement of the requirements of the Medicare Advantage program and agreed with the OIG recommendations.
“Lawmakers must act now to place patient needs before corporate profits and simplify by streamlining prior authorization processes,” Dr. Wailes said.
The ACS recently released a paper on this topic entitled, “The Medicare Appeals Process: Reforms Needed to Ensure Beneficiary Access.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a recent analysis suggests.
The report from the Office of Inspector General (OIG) of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services found that 13% of prior authorization denials were for service requests, which included cancer care, that met Medicare coverage rules and 18% of payment denials were for claims that met Medicare coverage and MAO billing rules, delaying or halting payments for services that clinicians had provided.
MAO denials are the “bane of my existence,” said Michael Buckstein, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York.
“Working at a large hospital in a metropolitan city, we spend enormous and increasing amounts of time on prior approvals and we get denials quite frequently, which certainly can lead to delays in treatment,” said Dr. Buckstein, who reviewed the OIG report for this news organization.
According to Dr. Buckstein, once a claim is denied, staff must spend time filing and scheduling an appeal, and if the appeal is denied in a physician peer-to-peer review, staff could face secondary and tertiary appeals. “We have been living with this frustration for a long time,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Widespread and persistent problems
Medicare Advantage plans, which are approved by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services but run by private companies, continue to grow in popularity.
In 2021, 26.4 million Medicare beneficiaries (42%) were enrolled in a Medicare Advantage plan, and by 2030, about 51% of all Medicare beneficiaries will be enrolled, according to estimates from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
“Although MAOs approve the vast majority of prior authorization requests and provider payment requests, MAOs also deny millions of requests each year,” the OIG wrote. “CMS’s annual audits of MAOs have highlighted widespread and persistent problems related to inappropriate denials of services and payment.”
In the current report, the OIG reviewed case files for 247 denials of prior authorization requests and 183 payment denials issued by 15 of the largest MAOs during 1 week in June of 2019.
The authors found that 13% of prior authorization denials occurred for service requests that met Medicare coverage rules, meaning these services would likely have been approved had the patient been enrolled in traditional Medicare.
The most prominent service types among these denials included imaging services, stays in postacute facilities, and injections.
In one case, for example, the MAO stated that a beneficiary would need to wait at least 1 year for a follow-up MRI because the size of the patient’s adrenal lesion (< 2 cm) was too small to warrant follow-up before 1 year. However, this restriction is not included in Medicare coverage rules. And an OIG physician panel found that the documentation in the original request demonstrated that the MRI was medically necessary to determine whether the lesion seen on an earlier CT scan was malignant.
Upon appeal, the MAO reversed its original denial.
Among the payment requests that MAOs denied, almost one in five were for claims that met Medicare coverage and billing rules, which delayed or prevented payments for services already delivered. Most payment denials were caused by human error during manual claims-processing reviews and system processing errors, the OIG report found.
In one case, for example, a MAO denied payment for radiation treatment for a patient with a tumor on the pancreas, incorrectly claiming that no prior authorization had been submitted for the service. However, the physician subsequently provided a screenshot demonstrating that the MAO had granted prior authorization for the billed claim, and the MAO reversed the denial.
Most of these prior authorization denial reversals occurred because of an appeal filed by the beneficiary or the provider, which can take weeks.
In one case, an MAO denied a request for a CT scan of the chest and pelvis for a beneficiary with endometrial cancer. It took 5 weeks for the provider to get the denial reversed. The OIG panel determined that the original request included sufficient documentation to demonstrate the CT was needed to assess the stage of the cancer and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
These denials and reversals not only waste time but may also cause harm. In a 2021 American Medical Association survey, 34% of physicians reported that prior authorization led to a serious adverse event for a patient in their care, including hospitalization, medical intervention to prevent permanent impairment, and even disability or death.
Almost 90% of the physicians surveyed described the burden associated with prior authorizations as ‘high’ or ‘extremely high.’ More specifically, physicians and their staff spend nearly 2 days a week on prior authorizations and 40% of physicians have staff who work exclusively on prior authorizations.
“It’s just not the way medicine should be practiced, especially for cancer patients who are very vulnerable and want rapid care,” Dr. Buckstein said.
Time for action
Weighing in on the OIG report, Robert E. Wailes, MD, president of the California Medical Association, noted that “it has become common practice for health insurance companies to create obstacles for patients in hopes of not having to pay for essential healthcare.”
The reason for these obstacles is simple, he said: “Fewer procedures performed translates to larger insurance company profits.”
America’s Health Insurance Plans (AHIP) defended prior authorization, saying it is “an important patient safety, cost-saving, and waste-prevention tool.”
The group also called out the OIG review for its “extraordinarily small” sample of 247 prior authorization requests over 1 week.
“Drawing far-reaching conclusions based on a very small sample of data and misleading headlines is not a productive way to improve our healthcare system for patients,” the AHIP statement reads.
But, according to Anna Schwamlein Howard, who works on policy development at the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network, the recent OIG report is in line with previous OIG reports.
And, Ms. Howard emphasized, the current report and others like it “highlight the need for CMS to utilize its audit authority and ensure that beneficiaries have access to medically necessary treatments, particularly cancer treatments.”
Along those lines, the OIG report recommends that the CMS should issue new guidance on the appropriate use of MAO clinical criteria in medical necessity reviews, update its audit protocols to address issues identified in the report, and direct MAOs to take additional steps to identify and address vulnerabilities that can lead to manual review and system errors.
In a statement, the CMS said it is committed to oversight and enforcement of the requirements of the Medicare Advantage program and agreed with the OIG recommendations.
“Lawmakers must act now to place patient needs before corporate profits and simplify by streamlining prior authorization processes,” Dr. Wailes said.
The ACS recently released a paper on this topic entitled, “The Medicare Appeals Process: Reforms Needed to Ensure Beneficiary Access.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dermatology attracts more than its share of physician assistants
Dermatology added PAs at a mean rate of 11.6% annually over that 6-year period, compared with a mean of 7.8% for all other specialties (P <.001), as the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA) tallied 2,324 working in dermatology and 64,490 in all other specialties in 2013 and 3,938/94,616, respectively, in 2018, Justin D. Arnold, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.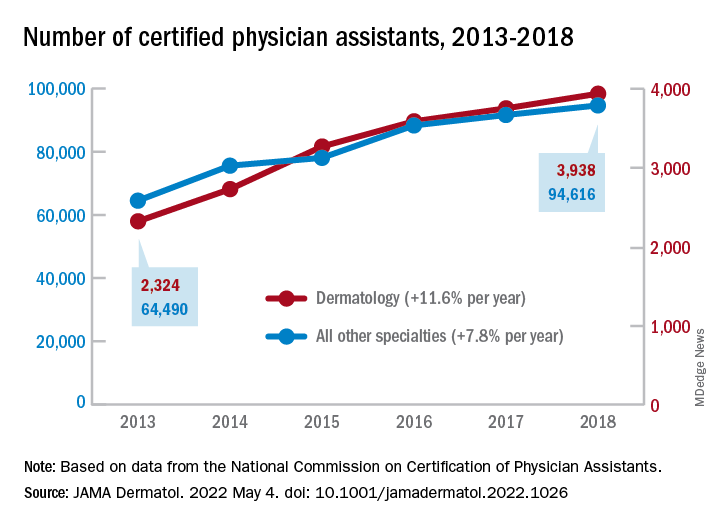
“There is, however, a lack of racial and ethnic diversity within the dermatology PA workforce,” they noted. A detailed comparison using the 2018 data showed that only 1.6% of dermatology PAs identified as Black, compared with 3.7% of those in all other specialties (P <.001), although “similar rates of Hispanic ethnicity were observed” in dermatology PAs (6.0%) and PAs in other fields (6.5%), the investigators added.
That was not the case for women in the profession, as 82% of PAs in dermatology were female in 2018, compared with 67% in the other specialties. Dermatology PAs also were significantly more likely to work in office-based practices than their nondermatology peers (93% vs. 37%, P < .001) and to reside in metropolitan areas (95% vs. 92%, P < .001), Dr. Arnold and associates said in the research letter.
The dermatology PAs also were more likely to work part time (30 or fewer hours per week) than those outside dermatology, 19.1% vs. 12.9% (P < .001). Despite that, the dermatology PAs reported seeing more patients per week (a mean of 119) than those in all of the other specialties (a mean of 71), the investigators said.
The total number of certified PAs was over 131,000 in 2018, but about 25% had not selected a principal specialty in their PA Professional Profiles and were not included in the study, they explained.
“Although this study did not assess the reasons for the substantial increase of dermatology PAs, numerous factors, such as a potential physician shortage or the expansion of private equity–owned practices, may contribute to the accelerating use of PAs within the field,” they wrote.
Dermatology added PAs at a mean rate of 11.6% annually over that 6-year period, compared with a mean of 7.8% for all other specialties (P <.001), as the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA) tallied 2,324 working in dermatology and 64,490 in all other specialties in 2013 and 3,938/94,616, respectively, in 2018, Justin D. Arnold, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
“There is, however, a lack of racial and ethnic diversity within the dermatology PA workforce,” they noted. A detailed comparison using the 2018 data showed that only 1.6% of dermatology PAs identified as Black, compared with 3.7% of those in all other specialties (P <.001), although “similar rates of Hispanic ethnicity were observed” in dermatology PAs (6.0%) and PAs in other fields (6.5%), the investigators added.
That was not the case for women in the profession, as 82% of PAs in dermatology were female in 2018, compared with 67% in the other specialties. Dermatology PAs also were significantly more likely to work in office-based practices than their nondermatology peers (93% vs. 37%, P < .001) and to reside in metropolitan areas (95% vs. 92%, P < .001), Dr. Arnold and associates said in the research letter.
The dermatology PAs also were more likely to work part time (30 or fewer hours per week) than those outside dermatology, 19.1% vs. 12.9% (P < .001). Despite that, the dermatology PAs reported seeing more patients per week (a mean of 119) than those in all of the other specialties (a mean of 71), the investigators said.
The total number of certified PAs was over 131,000 in 2018, but about 25% had not selected a principal specialty in their PA Professional Profiles and were not included in the study, they explained.
“Although this study did not assess the reasons for the substantial increase of dermatology PAs, numerous factors, such as a potential physician shortage or the expansion of private equity–owned practices, may contribute to the accelerating use of PAs within the field,” they wrote.
Dermatology added PAs at a mean rate of 11.6% annually over that 6-year period, compared with a mean of 7.8% for all other specialties (P <.001), as the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants (NCCPA) tallied 2,324 working in dermatology and 64,490 in all other specialties in 2013 and 3,938/94,616, respectively, in 2018, Justin D. Arnold, MD, of the University of California, Irvine, and associates reported in JAMA Dermatology.
“There is, however, a lack of racial and ethnic diversity within the dermatology PA workforce,” they noted. A detailed comparison using the 2018 data showed that only 1.6% of dermatology PAs identified as Black, compared with 3.7% of those in all other specialties (P <.001), although “similar rates of Hispanic ethnicity were observed” in dermatology PAs (6.0%) and PAs in other fields (6.5%), the investigators added.
That was not the case for women in the profession, as 82% of PAs in dermatology were female in 2018, compared with 67% in the other specialties. Dermatology PAs also were significantly more likely to work in office-based practices than their nondermatology peers (93% vs. 37%, P < .001) and to reside in metropolitan areas (95% vs. 92%, P < .001), Dr. Arnold and associates said in the research letter.
The dermatology PAs also were more likely to work part time (30 or fewer hours per week) than those outside dermatology, 19.1% vs. 12.9% (P < .001). Despite that, the dermatology PAs reported seeing more patients per week (a mean of 119) than those in all of the other specialties (a mean of 71), the investigators said.
The total number of certified PAs was over 131,000 in 2018, but about 25% had not selected a principal specialty in their PA Professional Profiles and were not included in the study, they explained.
“Although this study did not assess the reasons for the substantial increase of dermatology PAs, numerous factors, such as a potential physician shortage or the expansion of private equity–owned practices, may contribute to the accelerating use of PAs within the field,” they wrote.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
U.S. docs at double the risk of postpartum depression
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in four new mothers who are physicians report experiencing postpartum depression, a rate twice that of the general population, according to new survey findings presented at the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) 2022 Annual Meeting.
The survey results weren’t all grim. More than three-fourths (78%) of new mothers reported meeting their own breastfeeding goals. Still, Alison Stuebe, MD, director of maternal-fetal medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, said the high postpartum depression rates among physicians might be associated with worse patient care.
“Physicians who have had postpartum depression and provide clinical care for children and birthing people can bring their negative experiences to their clinical work, potentially impacting how they counsel and support their patients,” Dr. Stuebe, who was not involved in the study, told this news organization.
For the study, Emily Eischen, a fourth-year medical student at the University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, and her colleagues sought to learn how physicians and physician trainee mothers fared in the face of the unique stressors of their jobs, including “strenuous work hours, pressures to get back to work, and limited maternity leave.”
The researchers recruited 637 physicians and medical students with a singleton pregnancy to respond to a survey adapted largely from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Infant Feeding Practices Study and the CDC’s Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System.
Most of the respondents, who were enrolled through social media physician groups and email list-serves, were married non-Hispanic White persons; 71% were practicing or training in pediatrics, family medicine, or obstetrics/gynecology, and 2% were medical students.
Data showed that 25% of participants reported postpartum depression. The highest rates were seen among Hispanic/Latino respondents (31%), Black persons (30%), and non-Hispanic White persons (25%). The lowest rates of postpartum depression were for respondents identifying as Asian (15%).
Guilt a driver
Most respondents (80%) with symptoms of postpartum depression attributed their condition to sleep deprivation. Other frequently cited reasons were problems related to infant feeding (44%), lack of adequate maternity leave (41%), and lack of support at work (33%).
“Feeling guilty for not fulfilling work responsibilities, especially for residents, who are in the most difficult time in their careers and have to hand the workload off to others, can be very stressful,” Ms. Eischen said.
Despite the high rates of postpartum depression in the survey, the investigators found that 99% of respondents had initiated breastfeeding, 72% were exclusively breastfeeding, and 78% said they were meeting their personal breastfeeding goals. All of those rates are higher than what is seen in the general population.
Rates of self-reported postpartum depression were higher among those who did not meet their breastfeeding goals than among those who did (36% vs. 23%; P = .003), the researchers found.
Adetola Louis-Jacques, MD, an assistant professor of medicine, USF Health Obstetrics and Gynecology, and the senior author of the study, said the high breastfeeding rates can be attributed partly to an increased appreciation among physicians that lactation and breastfeeding have proven benefits for women and infant health.
“We still have work to do, but at least the journey has started in supporting birthing and lactating physicians,” she said.
However, Dr. Stuebe wondered whether the survey captured a group of respondents more likely to meet breastfeeding goals. She said she was surprised by the high proportion of respondents who did so.
“When surveys are distributed via social media, we don’t have a clear sense of who chooses to participate and who opts out,” she said in an interview. “If the survey was shared through social media groups that focus on supporting breastfeeding among physicians, it could have affected the results.”
No relevant financial relationships have been reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Innocent doc sued after 'secret' medical expert says claim has merit
When the hospital’s trauma team could not get an IV inserted into an accident victim, they called Illinois emergency physician William Sullivan, DO, JD, for help. Dr. Sullivan, who is based in the Chicago suburb of Frankfort, inserted a central line into the patient’s leg on his first attempt – a task that took about 20 minutes.
A year later, Dr. Sullivan was shocked and angry to learn he was being sued by the trauma patient’s family. Inserting the line was his only interaction with the woman, and he had no role in her care management, he said. Yet, the suit claimed he was negligent for failing to diagnose the patient with internal bleeding and for not performing surgery.
“The lawsuit put a lot of stress on our family,” Dr. Sullivan recalled. “At the time my wife was pregnant. I was in law school, and I was also working full time in the ER to support our family. I remember my wife crying on the couch after reading the complaint and asking how the plaintiff’s attorney could get away with making the allegations he made.”
Dr. Sullivan soon learned that 15 medical providers in the patient’s medical record were named as defendants. This included the director of the radiology department, whose name was on a radiology report as “director” but who was actually out of the country when the incident occurred.
Despite some of the accusations being impossible, a medical expert had claimed there was a “meritorious claim” against every health professional named in the suit. Illinois is among the 28 states that require plaintiffs’ attorneys to file an affidavit of merit for medical malpractice claims to move forward.
Dr. Sullivan wondered who would endorse such outlandish accusations, but the expert’s identity was a mystery. According to Illinois law, About one-third of states with merit requirements permit anonymous experts, according to research and attorneys familiar with the issue.
Because the expert’s identity remains hidden, physicians have no way of knowing whether they were qualified to render an opinion, Dr. Sullivan said. The loopholes can drag out frivolous claims and waste significant time and expense, say legal experts. Frequently, it takes a year or more before innocent physicians are dismissed from unfounded lawsuits by the court or dropped when plaintiffs can’t support the claim.
“It’s hugely frustrating,” said Bruce Montoya, JD, a Colorado medical liability defense attorney. “You have an expert who is not disclosed. Further down the road, when experts are being deposed, the plaintiff does not have to reveal whether any of those testifying experts is the same one who certified the case. You never get to determine whether they, in fact, had a certificate reviewer who was legitimate.”
The laws have led to a recent outcry among physicians and fueled a revised resolution by the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) denouncing anonymous affidavits of merit. (The revision has not yet been published online.)
“The minute experts are identified, they can be vetted,” said Rade B. Vukmir, MD, JD, chair of ACEP’s Medical Legal Committee. “There are reasons that you want to clarify the qualification and veracity of the witness. [Anonymous affidavits of merit] don’t allow that, and there’s something inherently wrong with that.”
Because the identities of consulting experts are unknown, it’s hard to know how many are unqualified. Expert witnesses who testify during trials, on the other hand, have long come under scrutiny for questionable qualifications. Some have come under fire for allegedly lying under oath about their experience, misrepresenting their credentials, and falsely representing their knowledge.
“Considering the known problem of potentially unethical expert witness testimony at trial, there’s is the potential likelihood that experts in anonymous affidavits of merit may sometimes lack the qualifications to give opinions,” said Dr. Vukmir, an emergency care physician in Pittsburgh.
Attorneys: Hidden experts increase costs, waste time
In Colorado, Mr. Montoya has seen firsthand how anonymous experts can prolong questionable claims and burden defendants.
Like Illinois, Colorado does not require attorneys to identify the medical experts used to fulfill its certificate of review statute. The expert consulted must have expertise in the same area of the alleged negligence, but does not have to practice in the same specialty, and the statute allows one expert to certify a lawsuit against multiple doctors.
In a recent case, Mr. Montoya represented a Denver neurosurgeon who was sued along with multiple other health care professionals. From the outset, Mr. Montoya argued the claim had no merit against the neurosurgeon, but the plaintiff’s attorney refused to dismiss the physician. Mr. Montoya asked whether the expert consulted for the certificate of merit was a neurosurgeon, but the attorney declined to disclose that information, he said.
The case progressed and Mr. Montoya eventually asked the judge to review the certificate of merit. By law, a judge can confidentially review the certificate of merit and decide whether it aligns with the state statute, but without disclosing the expert’s identity to the defense. The judge ruled the certificate appeared to conform with state law, and the case continued.
A year later, as both sides were getting ready to disclose their experts who would testify, Mr. Montoya again argued the neurosurgeon should be dropped from the suit. This time, he warned if the claim continued against the neurosurgeon, the defense would be filing a motion for summary judgment and pursuing attorney fees and costs. Colorado law allows for such fees if the filing or pursuit of an action is frivolous.
“Boom, my client was dismissed,” Mr. Montoya said. “This is a year later, after multiple conferences among the attorneys, multiple pleadings filed, expert witnesses retained to review the care, discovery exchanged, and records obtained. If we had [a stronger] certificate of review statute, it would have been a different ballgame. It’s never going to get a year down the road.”
In New York, physician defendants have experienced similar woes. The state’s law requires plaintiffs’ attorneys to certify that they consulted with a physician prior to filing the claim, and that they believe based on that discussion, there’s a reasonable basis for the claim to move forward. Attorneys are not required to disclose the expert’s identity.
The law also allows “an out,” explained Morris Auster, JD, senior vice president and chief legislative counsel for the Medical Society of the State of New York. If the attorney made three separate attempts to obtain a consultation, and all three experts would not agree to the consultation, the lawsuit can be filed anyway, he said.
“From our standpoint, it’s important to have an affidavit of merit requirement; it’s better than not having it,” Mr. Auster said. “But its effectiveness in providing control over the filing of lawsuits in New York has never been as strong as it could’ve been.”
Mr. Auster notes that New York has some of the highest liability costs in the country in addition to doctors paying some of the steepest medical liability insurance premiums.
“This really affects a lot of physicians and it’s driving physicians into employment arrangements, so they don’t have to deal with it on their own,” he said. “We support a number of measures to address these significantly high costs, and stronger certificate of merit requirements would certainly be one of those advocacy goals.”
Why are anonymous experts allowed?
Certificates of merit that shield the identity of consultants encourage a greater pool of physicians willing to review cases, said J. Matthew Dudley, JD, president of the Illinois Trial Lawyers Association. When the requirements first went into effect in Illinois, there was significant animosity among physicians toward doctors who testified in medical malpractice cases for patients, Mr. Dudley explained.
“Sometimes they would be ostracized from their professional societies, or it would hurt a referral relationship.” he said. “Over time, that animosity has lessened, but there was a concern that if the identity of physicians in certificates of merit weren’t protected, then doctors would not look at cases for patients.”
This would result in additional barriers for patients and their attorneys in pursuing their legal rights, Mr. Dudley said. He said Illinois’ certificate of merit statute is successful in fulfilling its intended purpose, and he has not seen any statistical evidence to suggest otherwise.
“It has proven effective at decreasing filings in medical malpractice and effectively screening medical malpractice cases,” he said. “Certificates of merit help to decrease filings by firms that aren’t that experienced in dealing with those kinds of cases.”
Kentucky is another state that does not require attorneys to identity the experts consulted for certificates of merit. Malpractice defense attorney Andrew DeSimone, JD, who practices in Kentucky, said this isn’t a problem since attorneys eventually must disclose the expert witnesses who will testify at trial.
“Knowing the name behind the certificate of merit is not that pertinent,” Mr. DeSimone said. “Physicians and their attorneys will ultimately have the chance to question and evaluate the expert witnesses used at trial. The certificate of merit is designed to weed out totally frivolous cases that do not have expert support. It’s not designed to be a trial on the merits.”
The belief that plaintiffs’ attorneys frequently bring weak cases and use unqualified experts to certify claims is not realistic or logical, added Sean Domnick, JD, a Florida medical malpractice attorney and vice president for the American Association for Justice. Medical malpractice cases are extremely challenging for plaintiffs – and they’re expensive, Mr. Domnick said.
“We can’t afford to take bad cases,” he said. “For me to take on a medical malpractice case, it’s not unusual for me to spend well over $100,000. Remember, if we lose, I don’t get that money back and I don’t get paid. Why in the world would a plaintiff take on that type of a burden for a case they didn’t believe in? The logic escapes me.”
In Florida, where Mr. Domnick practices, plaintiffs’ attorneys must send their certificates of merit to the defense with the expert identified. Domnick believes the requirement is a hindrance.
“It creates a delay that is unnecessary in a system that is already designed to wear our clients down,” he said. “It’s just another component that makes it harder on them.”
Hidden experts may insulate plaintiffs’ attorneys from liability
Dr. Sullivan, the Illinois emergency physician, was ultimately dismissed from the multiparty lawsuit, but not for roughly 18 months. After the dismissal, he fought back. He sued the plaintiff’s law firm for malicious prosecution, negligence in hiring, and relying on the opinion of an expert who was unqualified to render an opinion against an emergency physician.
The law firm, however, argued that it was immune from liability because it reasonably relied on the expert’s opinion as required by Illinois law. A trial court agreed with the plaintiffs’ firm. The judge denied Dr. Sullivan’s request to identify the expert, ruling there was no finding that the affidavit was untrue or made without reasonable cause. Dr. Sullivan appealed, and the appellate court upheld the trial’s court decision.
“As happened with my case, law firms can use the affidavit as a defense against countersuits or motions for sanctions,” Dr. Sullivan said. “Although the certificate of merit is intended to prevent attorneys from filing frivolous cases, it can also have the opposite effect of helping to insulate plaintiff attorneys from liability for filing a frivolous lawsuit.”
In Colorado, complaints about the state’s certificate of merit statute have gone before the Colorado Supreme Court. In one case, a lower court ruled that a certificate of merit was deficient because the consultants were not chiropractors. In another case, a nurse defendant argued the claim’s certificate of review was insufficient because the consulting expert was a physician.
In both instances, Colorado judges held the state’s statute does not require consultants to be in the same profession or the same specialty as the health professional defendant.
In New York, meanwhile, Mr. Auster said several bills to strengthen the state’s certificate of merit requirements have failed in recent years.
“It’s hard to say whether it will improve anytime soon,” he said. “The trial lawyers are a very powerful advocacy force in the state, and they tend to oppose even the slightest of changes in civil liability. [In addition], some of these issues have been put on a lower tier because of trying to manage the pandemic.”
Ultimately, Dr. Sullivan said that courts and legislatures need to strongly consider the ethics of allowing anonymous experts to provide testimony against defendant physicians.
“I also think we need to consider how the notion of a secret expert comports with a defendant physician’s due process,” he said. “If an expert’s opinion is appropriate, why would there be a need to shroud one’s identity in a veil of secrecy?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the hospital’s trauma team could not get an IV inserted into an accident victim, they called Illinois emergency physician William Sullivan, DO, JD, for help. Dr. Sullivan, who is based in the Chicago suburb of Frankfort, inserted a central line into the patient’s leg on his first attempt – a task that took about 20 minutes.
A year later, Dr. Sullivan was shocked and angry to learn he was being sued by the trauma patient’s family. Inserting the line was his only interaction with the woman, and he had no role in her care management, he said. Yet, the suit claimed he was negligent for failing to diagnose the patient with internal bleeding and for not performing surgery.
“The lawsuit put a lot of stress on our family,” Dr. Sullivan recalled. “At the time my wife was pregnant. I was in law school, and I was also working full time in the ER to support our family. I remember my wife crying on the couch after reading the complaint and asking how the plaintiff’s attorney could get away with making the allegations he made.”
Dr. Sullivan soon learned that 15 medical providers in the patient’s medical record were named as defendants. This included the director of the radiology department, whose name was on a radiology report as “director” but who was actually out of the country when the incident occurred.
Despite some of the accusations being impossible, a medical expert had claimed there was a “meritorious claim” against every health professional named in the suit. Illinois is among the 28 states that require plaintiffs’ attorneys to file an affidavit of merit for medical malpractice claims to move forward.
Dr. Sullivan wondered who would endorse such outlandish accusations, but the expert’s identity was a mystery. According to Illinois law, About one-third of states with merit requirements permit anonymous experts, according to research and attorneys familiar with the issue.
Because the expert’s identity remains hidden, physicians have no way of knowing whether they were qualified to render an opinion, Dr. Sullivan said. The loopholes can drag out frivolous claims and waste significant time and expense, say legal experts. Frequently, it takes a year or more before innocent physicians are dismissed from unfounded lawsuits by the court or dropped when plaintiffs can’t support the claim.
“It’s hugely frustrating,” said Bruce Montoya, JD, a Colorado medical liability defense attorney. “You have an expert who is not disclosed. Further down the road, when experts are being deposed, the plaintiff does not have to reveal whether any of those testifying experts is the same one who certified the case. You never get to determine whether they, in fact, had a certificate reviewer who was legitimate.”
The laws have led to a recent outcry among physicians and fueled a revised resolution by the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) denouncing anonymous affidavits of merit. (The revision has not yet been published online.)
“The minute experts are identified, they can be vetted,” said Rade B. Vukmir, MD, JD, chair of ACEP’s Medical Legal Committee. “There are reasons that you want to clarify the qualification and veracity of the witness. [Anonymous affidavits of merit] don’t allow that, and there’s something inherently wrong with that.”
Because the identities of consulting experts are unknown, it’s hard to know how many are unqualified. Expert witnesses who testify during trials, on the other hand, have long come under scrutiny for questionable qualifications. Some have come under fire for allegedly lying under oath about their experience, misrepresenting their credentials, and falsely representing their knowledge.
“Considering the known problem of potentially unethical expert witness testimony at trial, there’s is the potential likelihood that experts in anonymous affidavits of merit may sometimes lack the qualifications to give opinions,” said Dr. Vukmir, an emergency care physician in Pittsburgh.
Attorneys: Hidden experts increase costs, waste time
In Colorado, Mr. Montoya has seen firsthand how anonymous experts can prolong questionable claims and burden defendants.
Like Illinois, Colorado does not require attorneys to identify the medical experts used to fulfill its certificate of review statute. The expert consulted must have expertise in the same area of the alleged negligence, but does not have to practice in the same specialty, and the statute allows one expert to certify a lawsuit against multiple doctors.
In a recent case, Mr. Montoya represented a Denver neurosurgeon who was sued along with multiple other health care professionals. From the outset, Mr. Montoya argued the claim had no merit against the neurosurgeon, but the plaintiff’s attorney refused to dismiss the physician. Mr. Montoya asked whether the expert consulted for the certificate of merit was a neurosurgeon, but the attorney declined to disclose that information, he said.
The case progressed and Mr. Montoya eventually asked the judge to review the certificate of merit. By law, a judge can confidentially review the certificate of merit and decide whether it aligns with the state statute, but without disclosing the expert’s identity to the defense. The judge ruled the certificate appeared to conform with state law, and the case continued.
A year later, as both sides were getting ready to disclose their experts who would testify, Mr. Montoya again argued the neurosurgeon should be dropped from the suit. This time, he warned if the claim continued against the neurosurgeon, the defense would be filing a motion for summary judgment and pursuing attorney fees and costs. Colorado law allows for such fees if the filing or pursuit of an action is frivolous.
“Boom, my client was dismissed,” Mr. Montoya said. “This is a year later, after multiple conferences among the attorneys, multiple pleadings filed, expert witnesses retained to review the care, discovery exchanged, and records obtained. If we had [a stronger] certificate of review statute, it would have been a different ballgame. It’s never going to get a year down the road.”
In New York, physician defendants have experienced similar woes. The state’s law requires plaintiffs’ attorneys to certify that they consulted with a physician prior to filing the claim, and that they believe based on that discussion, there’s a reasonable basis for the claim to move forward. Attorneys are not required to disclose the expert’s identity.
The law also allows “an out,” explained Morris Auster, JD, senior vice president and chief legislative counsel for the Medical Society of the State of New York. If the attorney made three separate attempts to obtain a consultation, and all three experts would not agree to the consultation, the lawsuit can be filed anyway, he said.
“From our standpoint, it’s important to have an affidavit of merit requirement; it’s better than not having it,” Mr. Auster said. “But its effectiveness in providing control over the filing of lawsuits in New York has never been as strong as it could’ve been.”
Mr. Auster notes that New York has some of the highest liability costs in the country in addition to doctors paying some of the steepest medical liability insurance premiums.
“This really affects a lot of physicians and it’s driving physicians into employment arrangements, so they don’t have to deal with it on their own,” he said. “We support a number of measures to address these significantly high costs, and stronger certificate of merit requirements would certainly be one of those advocacy goals.”
Why are anonymous experts allowed?
Certificates of merit that shield the identity of consultants encourage a greater pool of physicians willing to review cases, said J. Matthew Dudley, JD, president of the Illinois Trial Lawyers Association. When the requirements first went into effect in Illinois, there was significant animosity among physicians toward doctors who testified in medical malpractice cases for patients, Mr. Dudley explained.
“Sometimes they would be ostracized from their professional societies, or it would hurt a referral relationship.” he said. “Over time, that animosity has lessened, but there was a concern that if the identity of physicians in certificates of merit weren’t protected, then doctors would not look at cases for patients.”
This would result in additional barriers for patients and their attorneys in pursuing their legal rights, Mr. Dudley said. He said Illinois’ certificate of merit statute is successful in fulfilling its intended purpose, and he has not seen any statistical evidence to suggest otherwise.
“It has proven effective at decreasing filings in medical malpractice and effectively screening medical malpractice cases,” he said. “Certificates of merit help to decrease filings by firms that aren’t that experienced in dealing with those kinds of cases.”
Kentucky is another state that does not require attorneys to identity the experts consulted for certificates of merit. Malpractice defense attorney Andrew DeSimone, JD, who practices in Kentucky, said this isn’t a problem since attorneys eventually must disclose the expert witnesses who will testify at trial.
“Knowing the name behind the certificate of merit is not that pertinent,” Mr. DeSimone said. “Physicians and their attorneys will ultimately have the chance to question and evaluate the expert witnesses used at trial. The certificate of merit is designed to weed out totally frivolous cases that do not have expert support. It’s not designed to be a trial on the merits.”
The belief that plaintiffs’ attorneys frequently bring weak cases and use unqualified experts to certify claims is not realistic or logical, added Sean Domnick, JD, a Florida medical malpractice attorney and vice president for the American Association for Justice. Medical malpractice cases are extremely challenging for plaintiffs – and they’re expensive, Mr. Domnick said.
“We can’t afford to take bad cases,” he said. “For me to take on a medical malpractice case, it’s not unusual for me to spend well over $100,000. Remember, if we lose, I don’t get that money back and I don’t get paid. Why in the world would a plaintiff take on that type of a burden for a case they didn’t believe in? The logic escapes me.”
In Florida, where Mr. Domnick practices, plaintiffs’ attorneys must send their certificates of merit to the defense with the expert identified. Domnick believes the requirement is a hindrance.
“It creates a delay that is unnecessary in a system that is already designed to wear our clients down,” he said. “It’s just another component that makes it harder on them.”
Hidden experts may insulate plaintiffs’ attorneys from liability
Dr. Sullivan, the Illinois emergency physician, was ultimately dismissed from the multiparty lawsuit, but not for roughly 18 months. After the dismissal, he fought back. He sued the plaintiff’s law firm for malicious prosecution, negligence in hiring, and relying on the opinion of an expert who was unqualified to render an opinion against an emergency physician.
The law firm, however, argued that it was immune from liability because it reasonably relied on the expert’s opinion as required by Illinois law. A trial court agreed with the plaintiffs’ firm. The judge denied Dr. Sullivan’s request to identify the expert, ruling there was no finding that the affidavit was untrue or made without reasonable cause. Dr. Sullivan appealed, and the appellate court upheld the trial’s court decision.
“As happened with my case, law firms can use the affidavit as a defense against countersuits or motions for sanctions,” Dr. Sullivan said. “Although the certificate of merit is intended to prevent attorneys from filing frivolous cases, it can also have the opposite effect of helping to insulate plaintiff attorneys from liability for filing a frivolous lawsuit.”
In Colorado, complaints about the state’s certificate of merit statute have gone before the Colorado Supreme Court. In one case, a lower court ruled that a certificate of merit was deficient because the consultants were not chiropractors. In another case, a nurse defendant argued the claim’s certificate of review was insufficient because the consulting expert was a physician.
In both instances, Colorado judges held the state’s statute does not require consultants to be in the same profession or the same specialty as the health professional defendant.
In New York, meanwhile, Mr. Auster said several bills to strengthen the state’s certificate of merit requirements have failed in recent years.
“It’s hard to say whether it will improve anytime soon,” he said. “The trial lawyers are a very powerful advocacy force in the state, and they tend to oppose even the slightest of changes in civil liability. [In addition], some of these issues have been put on a lower tier because of trying to manage the pandemic.”
Ultimately, Dr. Sullivan said that courts and legislatures need to strongly consider the ethics of allowing anonymous experts to provide testimony against defendant physicians.
“I also think we need to consider how the notion of a secret expert comports with a defendant physician’s due process,” he said. “If an expert’s opinion is appropriate, why would there be a need to shroud one’s identity in a veil of secrecy?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When the hospital’s trauma team could not get an IV inserted into an accident victim, they called Illinois emergency physician William Sullivan, DO, JD, for help. Dr. Sullivan, who is based in the Chicago suburb of Frankfort, inserted a central line into the patient’s leg on his first attempt – a task that took about 20 minutes.
A year later, Dr. Sullivan was shocked and angry to learn he was being sued by the trauma patient’s family. Inserting the line was his only interaction with the woman, and he had no role in her care management, he said. Yet, the suit claimed he was negligent for failing to diagnose the patient with internal bleeding and for not performing surgery.
“The lawsuit put a lot of stress on our family,” Dr. Sullivan recalled. “At the time my wife was pregnant. I was in law school, and I was also working full time in the ER to support our family. I remember my wife crying on the couch after reading the complaint and asking how the plaintiff’s attorney could get away with making the allegations he made.”
Dr. Sullivan soon learned that 15 medical providers in the patient’s medical record were named as defendants. This included the director of the radiology department, whose name was on a radiology report as “director” but who was actually out of the country when the incident occurred.
Despite some of the accusations being impossible, a medical expert had claimed there was a “meritorious claim” against every health professional named in the suit. Illinois is among the 28 states that require plaintiffs’ attorneys to file an affidavit of merit for medical malpractice claims to move forward.
Dr. Sullivan wondered who would endorse such outlandish accusations, but the expert’s identity was a mystery. According to Illinois law, About one-third of states with merit requirements permit anonymous experts, according to research and attorneys familiar with the issue.
Because the expert’s identity remains hidden, physicians have no way of knowing whether they were qualified to render an opinion, Dr. Sullivan said. The loopholes can drag out frivolous claims and waste significant time and expense, say legal experts. Frequently, it takes a year or more before innocent physicians are dismissed from unfounded lawsuits by the court or dropped when plaintiffs can’t support the claim.
“It’s hugely frustrating,” said Bruce Montoya, JD, a Colorado medical liability defense attorney. “You have an expert who is not disclosed. Further down the road, when experts are being deposed, the plaintiff does not have to reveal whether any of those testifying experts is the same one who certified the case. You never get to determine whether they, in fact, had a certificate reviewer who was legitimate.”
The laws have led to a recent outcry among physicians and fueled a revised resolution by the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) denouncing anonymous affidavits of merit. (The revision has not yet been published online.)
“The minute experts are identified, they can be vetted,” said Rade B. Vukmir, MD, JD, chair of ACEP’s Medical Legal Committee. “There are reasons that you want to clarify the qualification and veracity of the witness. [Anonymous affidavits of merit] don’t allow that, and there’s something inherently wrong with that.”
Because the identities of consulting experts are unknown, it’s hard to know how many are unqualified. Expert witnesses who testify during trials, on the other hand, have long come under scrutiny for questionable qualifications. Some have come under fire for allegedly lying under oath about their experience, misrepresenting their credentials, and falsely representing their knowledge.
“Considering the known problem of potentially unethical expert witness testimony at trial, there’s is the potential likelihood that experts in anonymous affidavits of merit may sometimes lack the qualifications to give opinions,” said Dr. Vukmir, an emergency care physician in Pittsburgh.
Attorneys: Hidden experts increase costs, waste time
In Colorado, Mr. Montoya has seen firsthand how anonymous experts can prolong questionable claims and burden defendants.
Like Illinois, Colorado does not require attorneys to identify the medical experts used to fulfill its certificate of review statute. The expert consulted must have expertise in the same area of the alleged negligence, but does not have to practice in the same specialty, and the statute allows one expert to certify a lawsuit against multiple doctors.
In a recent case, Mr. Montoya represented a Denver neurosurgeon who was sued along with multiple other health care professionals. From the outset, Mr. Montoya argued the claim had no merit against the neurosurgeon, but the plaintiff’s attorney refused to dismiss the physician. Mr. Montoya asked whether the expert consulted for the certificate of merit was a neurosurgeon, but the attorney declined to disclose that information, he said.
The case progressed and Mr. Montoya eventually asked the judge to review the certificate of merit. By law, a judge can confidentially review the certificate of merit and decide whether it aligns with the state statute, but without disclosing the expert’s identity to the defense. The judge ruled the certificate appeared to conform with state law, and the case continued.
A year later, as both sides were getting ready to disclose their experts who would testify, Mr. Montoya again argued the neurosurgeon should be dropped from the suit. This time, he warned if the claim continued against the neurosurgeon, the defense would be filing a motion for summary judgment and pursuing attorney fees and costs. Colorado law allows for such fees if the filing or pursuit of an action is frivolous.
“Boom, my client was dismissed,” Mr. Montoya said. “This is a year later, after multiple conferences among the attorneys, multiple pleadings filed, expert witnesses retained to review the care, discovery exchanged, and records obtained. If we had [a stronger] certificate of review statute, it would have been a different ballgame. It’s never going to get a year down the road.”
In New York, physician defendants have experienced similar woes. The state’s law requires plaintiffs’ attorneys to certify that they consulted with a physician prior to filing the claim, and that they believe based on that discussion, there’s a reasonable basis for the claim to move forward. Attorneys are not required to disclose the expert’s identity.
The law also allows “an out,” explained Morris Auster, JD, senior vice president and chief legislative counsel for the Medical Society of the State of New York. If the attorney made three separate attempts to obtain a consultation, and all three experts would not agree to the consultation, the lawsuit can be filed anyway, he said.
“From our standpoint, it’s important to have an affidavit of merit requirement; it’s better than not having it,” Mr. Auster said. “But its effectiveness in providing control over the filing of lawsuits in New York has never been as strong as it could’ve been.”
Mr. Auster notes that New York has some of the highest liability costs in the country in addition to doctors paying some of the steepest medical liability insurance premiums.
“This really affects a lot of physicians and it’s driving physicians into employment arrangements, so they don’t have to deal with it on their own,” he said. “We support a number of measures to address these significantly high costs, and stronger certificate of merit requirements would certainly be one of those advocacy goals.”
Why are anonymous experts allowed?
Certificates of merit that shield the identity of consultants encourage a greater pool of physicians willing to review cases, said J. Matthew Dudley, JD, president of the Illinois Trial Lawyers Association. When the requirements first went into effect in Illinois, there was significant animosity among physicians toward doctors who testified in medical malpractice cases for patients, Mr. Dudley explained.
“Sometimes they would be ostracized from their professional societies, or it would hurt a referral relationship.” he said. “Over time, that animosity has lessened, but there was a concern that if the identity of physicians in certificates of merit weren’t protected, then doctors would not look at cases for patients.”
This would result in additional barriers for patients and their attorneys in pursuing their legal rights, Mr. Dudley said. He said Illinois’ certificate of merit statute is successful in fulfilling its intended purpose, and he has not seen any statistical evidence to suggest otherwise.
“It has proven effective at decreasing filings in medical malpractice and effectively screening medical malpractice cases,” he said. “Certificates of merit help to decrease filings by firms that aren’t that experienced in dealing with those kinds of cases.”
Kentucky is another state that does not require attorneys to identity the experts consulted for certificates of merit. Malpractice defense attorney Andrew DeSimone, JD, who practices in Kentucky, said this isn’t a problem since attorneys eventually must disclose the expert witnesses who will testify at trial.
“Knowing the name behind the certificate of merit is not that pertinent,” Mr. DeSimone said. “Physicians and their attorneys will ultimately have the chance to question and evaluate the expert witnesses used at trial. The certificate of merit is designed to weed out totally frivolous cases that do not have expert support. It’s not designed to be a trial on the merits.”
The belief that plaintiffs’ attorneys frequently bring weak cases and use unqualified experts to certify claims is not realistic or logical, added Sean Domnick, JD, a Florida medical malpractice attorney and vice president for the American Association for Justice. Medical malpractice cases are extremely challenging for plaintiffs – and they’re expensive, Mr. Domnick said.
“We can’t afford to take bad cases,” he said. “For me to take on a medical malpractice case, it’s not unusual for me to spend well over $100,000. Remember, if we lose, I don’t get that money back and I don’t get paid. Why in the world would a plaintiff take on that type of a burden for a case they didn’t believe in? The logic escapes me.”
In Florida, where Mr. Domnick practices, plaintiffs’ attorneys must send their certificates of merit to the defense with the expert identified. Domnick believes the requirement is a hindrance.
“It creates a delay that is unnecessary in a system that is already designed to wear our clients down,” he said. “It’s just another component that makes it harder on them.”
Hidden experts may insulate plaintiffs’ attorneys from liability
Dr. Sullivan, the Illinois emergency physician, was ultimately dismissed from the multiparty lawsuit, but not for roughly 18 months. After the dismissal, he fought back. He sued the plaintiff’s law firm for malicious prosecution, negligence in hiring, and relying on the opinion of an expert who was unqualified to render an opinion against an emergency physician.
The law firm, however, argued that it was immune from liability because it reasonably relied on the expert’s opinion as required by Illinois law. A trial court agreed with the plaintiffs’ firm. The judge denied Dr. Sullivan’s request to identify the expert, ruling there was no finding that the affidavit was untrue or made without reasonable cause. Dr. Sullivan appealed, and the appellate court upheld the trial’s court decision.
“As happened with my case, law firms can use the affidavit as a defense against countersuits or motions for sanctions,” Dr. Sullivan said. “Although the certificate of merit is intended to prevent attorneys from filing frivolous cases, it can also have the opposite effect of helping to insulate plaintiff attorneys from liability for filing a frivolous lawsuit.”
In Colorado, complaints about the state’s certificate of merit statute have gone before the Colorado Supreme Court. In one case, a lower court ruled that a certificate of merit was deficient because the consultants were not chiropractors. In another case, a nurse defendant argued the claim’s certificate of review was insufficient because the consulting expert was a physician.
In both instances, Colorado judges held the state’s statute does not require consultants to be in the same profession or the same specialty as the health professional defendant.
In New York, meanwhile, Mr. Auster said several bills to strengthen the state’s certificate of merit requirements have failed in recent years.
“It’s hard to say whether it will improve anytime soon,” he said. “The trial lawyers are a very powerful advocacy force in the state, and they tend to oppose even the slightest of changes in civil liability. [In addition], some of these issues have been put on a lower tier because of trying to manage the pandemic.”
Ultimately, Dr. Sullivan said that courts and legislatures need to strongly consider the ethics of allowing anonymous experts to provide testimony against defendant physicians.
“I also think we need to consider how the notion of a secret expert comports with a defendant physician’s due process,” he said. “If an expert’s opinion is appropriate, why would there be a need to shroud one’s identity in a veil of secrecy?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Together, we can demand improvements’: Stanford Health Care’s residents vote to join union
More than 81% of the health system’s resident physicians voted to join the union; the decision garnered 835 yes votes and 214 no votes, according to a CIR-SEIU announcement. The largest housestaff union in the United States and a local of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU), CIR-SEIU represents more than 20,000 resident physicians and fellows.
“With its successful representation with the Committee of Interns and Residents, Stanford housestaff now join the strong community of allied unions and fellow health care workers such as the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement (CRONA), an independent union of Stanford nurses,” according to CIR-SEIU.
“We are organizing not only for a new economic contract that enables all potential housestaff and their families to afford living in the Bay Area but also for a new social contract that redefines how we are valued by the hospital system,” Ben Solomon, MD, PhD, a third-year resident physician in pediatrics at Stanford Medicine and a member of CIR-SEIU, said in an interview.
“This includes advocating for more humane working hours, reasonable parental leave, and childcare support, as well as resources to combat burnout in young physicians,” he added.
Lisa Kim, a spokesperson for Stanford Health Care, told this news organization that “a majority of residents and fellows at Stanford Health Care voted in favor of unionization. Of 1,478 total residents and fellows, 835 voted in favor. CIR/SEIU will be certified as the exclusive bargaining representative for all residents and fellows. Stanford Health Care does not plan to contest the election results.”
“As we begin the collective bargaining process, our goal remains unchanged: providing our residents and fellows with a world-class training experience. We will bring this same focus to negotiations as we strive to support their development as physician leaders,” she added.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) must certify the election results before they are considered final, per CIR-SEIU. An independent federal agency, the NLRB safeguards employees’ rights to organize and determines whether union participation is appropriate while also preventing and remedying unfair labor practices committed by private sector employers and unions.
Concerns date back to initial COVID-19 vaccine rollout
The residents delivered a formal demand to Stanford Health Care to recognize the union in February; their request was not accepted by the health system. The residents’ concerns date as far back as the availability of the COVID-19 vaccines at the end of 2020.
Of the health system’s 5,000 doses, only seven residents and fellows were included in the initial round.
Niraj Sehgal, MD, chief medical officer for Stanford Health Care, apologized in a letter to the graduate medical education community, posted by Palo Alto Weekly, which revealed the root causes to be an algorithm used by the hospital and the age of the residents.
The vote by Stanford Health Care’s residents comes a day after nurses at Stanford and Lucile Packard Children’s hospitals ratified a new contract with their union after a strike for better working conditions and higher pay stretched on for a week, reported Palo Alto Online.
Part of a growing trend
Dr. Solomon got involved in the unionization effort at Stanford Health Care “to have a say in working conditions for residents and fellows,” he said. “As individuals, it’s virtually impossible to make demands to our hospital without risking our careers, but together we can demand improvements on the job and in patient care.”
The health system’s inability to extend COVID-19 vaccines during the initial rollout, “despite our role working with COVID patients on the frontlines,” spurred his involvement in the union effort, said Dr. Solomon.
In the short term, the union will be involved in negotiating its first contract, he said. “However, in the long term, we are committed to supporting the unionization efforts of residents and fellows across the country, including partnering with many housestaff unions here in California.”
Stanford Health Care’s residents are participating in a growing trend. In Worcester, Mass., UMass Medical School’s 613 residents and fellow physicians, who are also represented by CIR-SEIU, had their union certified by the Massachusetts Department of Labor Relations in March 2021, reported the (Worcester) Telegram & Gazette.
Other unionization efforts across the country include a supermajority of 85 interns, residents, and fellows employed by Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California , who requested that Los Angeles County+USC Medical Center recognize their union, per an announcement. That’s in addition to residents at University of Vermont Medical Center, who announced their intention to unionize in March, reported VTDigger.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 81% of the health system’s resident physicians voted to join the union; the decision garnered 835 yes votes and 214 no votes, according to a CIR-SEIU announcement. The largest housestaff union in the United States and a local of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU), CIR-SEIU represents more than 20,000 resident physicians and fellows.
“With its successful representation with the Committee of Interns and Residents, Stanford housestaff now join the strong community of allied unions and fellow health care workers such as the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement (CRONA), an independent union of Stanford nurses,” according to CIR-SEIU.
“We are organizing not only for a new economic contract that enables all potential housestaff and their families to afford living in the Bay Area but also for a new social contract that redefines how we are valued by the hospital system,” Ben Solomon, MD, PhD, a third-year resident physician in pediatrics at Stanford Medicine and a member of CIR-SEIU, said in an interview.
“This includes advocating for more humane working hours, reasonable parental leave, and childcare support, as well as resources to combat burnout in young physicians,” he added.
Lisa Kim, a spokesperson for Stanford Health Care, told this news organization that “a majority of residents and fellows at Stanford Health Care voted in favor of unionization. Of 1,478 total residents and fellows, 835 voted in favor. CIR/SEIU will be certified as the exclusive bargaining representative for all residents and fellows. Stanford Health Care does not plan to contest the election results.”
“As we begin the collective bargaining process, our goal remains unchanged: providing our residents and fellows with a world-class training experience. We will bring this same focus to negotiations as we strive to support their development as physician leaders,” she added.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) must certify the election results before they are considered final, per CIR-SEIU. An independent federal agency, the NLRB safeguards employees’ rights to organize and determines whether union participation is appropriate while also preventing and remedying unfair labor practices committed by private sector employers and unions.
Concerns date back to initial COVID-19 vaccine rollout
The residents delivered a formal demand to Stanford Health Care to recognize the union in February; their request was not accepted by the health system. The residents’ concerns date as far back as the availability of the COVID-19 vaccines at the end of 2020.
Of the health system’s 5,000 doses, only seven residents and fellows were included in the initial round.
Niraj Sehgal, MD, chief medical officer for Stanford Health Care, apologized in a letter to the graduate medical education community, posted by Palo Alto Weekly, which revealed the root causes to be an algorithm used by the hospital and the age of the residents.
The vote by Stanford Health Care’s residents comes a day after nurses at Stanford and Lucile Packard Children’s hospitals ratified a new contract with their union after a strike for better working conditions and higher pay stretched on for a week, reported Palo Alto Online.
Part of a growing trend
Dr. Solomon got involved in the unionization effort at Stanford Health Care “to have a say in working conditions for residents and fellows,” he said. “As individuals, it’s virtually impossible to make demands to our hospital without risking our careers, but together we can demand improvements on the job and in patient care.”
The health system’s inability to extend COVID-19 vaccines during the initial rollout, “despite our role working with COVID patients on the frontlines,” spurred his involvement in the union effort, said Dr. Solomon.
In the short term, the union will be involved in negotiating its first contract, he said. “However, in the long term, we are committed to supporting the unionization efforts of residents and fellows across the country, including partnering with many housestaff unions here in California.”
Stanford Health Care’s residents are participating in a growing trend. In Worcester, Mass., UMass Medical School’s 613 residents and fellow physicians, who are also represented by CIR-SEIU, had their union certified by the Massachusetts Department of Labor Relations in March 2021, reported the (Worcester) Telegram & Gazette.
Other unionization efforts across the country include a supermajority of 85 interns, residents, and fellows employed by Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California , who requested that Los Angeles County+USC Medical Center recognize their union, per an announcement. That’s in addition to residents at University of Vermont Medical Center, who announced their intention to unionize in March, reported VTDigger.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than 81% of the health system’s resident physicians voted to join the union; the decision garnered 835 yes votes and 214 no votes, according to a CIR-SEIU announcement. The largest housestaff union in the United States and a local of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU), CIR-SEIU represents more than 20,000 resident physicians and fellows.
“With its successful representation with the Committee of Interns and Residents, Stanford housestaff now join the strong community of allied unions and fellow health care workers such as the Committee for Recognition of Nursing Achievement (CRONA), an independent union of Stanford nurses,” according to CIR-SEIU.
“We are organizing not only for a new economic contract that enables all potential housestaff and their families to afford living in the Bay Area but also for a new social contract that redefines how we are valued by the hospital system,” Ben Solomon, MD, PhD, a third-year resident physician in pediatrics at Stanford Medicine and a member of CIR-SEIU, said in an interview.
“This includes advocating for more humane working hours, reasonable parental leave, and childcare support, as well as resources to combat burnout in young physicians,” he added.
Lisa Kim, a spokesperson for Stanford Health Care, told this news organization that “a majority of residents and fellows at Stanford Health Care voted in favor of unionization. Of 1,478 total residents and fellows, 835 voted in favor. CIR/SEIU will be certified as the exclusive bargaining representative for all residents and fellows. Stanford Health Care does not plan to contest the election results.”
“As we begin the collective bargaining process, our goal remains unchanged: providing our residents and fellows with a world-class training experience. We will bring this same focus to negotiations as we strive to support their development as physician leaders,” she added.
The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) must certify the election results before they are considered final, per CIR-SEIU. An independent federal agency, the NLRB safeguards employees’ rights to organize and determines whether union participation is appropriate while also preventing and remedying unfair labor practices committed by private sector employers and unions.
Concerns date back to initial COVID-19 vaccine rollout
The residents delivered a formal demand to Stanford Health Care to recognize the union in February; their request was not accepted by the health system. The residents’ concerns date as far back as the availability of the COVID-19 vaccines at the end of 2020.
Of the health system’s 5,000 doses, only seven residents and fellows were included in the initial round.
Niraj Sehgal, MD, chief medical officer for Stanford Health Care, apologized in a letter to the graduate medical education community, posted by Palo Alto Weekly, which revealed the root causes to be an algorithm used by the hospital and the age of the residents.
The vote by Stanford Health Care’s residents comes a day after nurses at Stanford and Lucile Packard Children’s hospitals ratified a new contract with their union after a strike for better working conditions and higher pay stretched on for a week, reported Palo Alto Online.
Part of a growing trend
Dr. Solomon got involved in the unionization effort at Stanford Health Care “to have a say in working conditions for residents and fellows,” he said. “As individuals, it’s virtually impossible to make demands to our hospital without risking our careers, but together we can demand improvements on the job and in patient care.”
The health system’s inability to extend COVID-19 vaccines during the initial rollout, “despite our role working with COVID patients on the frontlines,” spurred his involvement in the union effort, said Dr. Solomon.
In the short term, the union will be involved in negotiating its first contract, he said. “However, in the long term, we are committed to supporting the unionization efforts of residents and fellows across the country, including partnering with many housestaff unions here in California.”
Stanford Health Care’s residents are participating in a growing trend. In Worcester, Mass., UMass Medical School’s 613 residents and fellow physicians, who are also represented by CIR-SEIU, had their union certified by the Massachusetts Department of Labor Relations in March 2021, reported the (Worcester) Telegram & Gazette.
Other unionization efforts across the country include a supermajority of 85 interns, residents, and fellows employed by Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California , who requested that Los Angeles County+USC Medical Center recognize their union, per an announcement. That’s in addition to residents at University of Vermont Medical Center, who announced their intention to unionize in March, reported VTDigger.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The puzzling thing about puzzles
A few weeks ago I talked about my evening practice of doing jigsaw puzzles to relax, as a pleasant alternative to surfing the Internet.
Last week my daughter moved home from college for the summer. It’s been several years since she and I last did puzzles together, and I’d forgotten how much she likes them.
So now each night we sit there, either side by side or across the table from each other, each quietly working on some little portion of the same jigsaw. Very little is said, but it’s still the same bonding time I’ve always cherished.
But I notice things I’d never thought of.
I always start a puzzle like I thought most people do: Pick out the flat edge pieces to build the outside frame, then work inward from there.
But she doesn’t. Once the box is opened and pieces dumped out, she starts sorting them by patterns and colors, and begins there. The edges don’t get her attention at all as she begins. She assembles like-pieces and gradually expands from there.
Why?
I mean, I’m a neurologist. Brains are my business. So why are our thought patterns on the same task so different?
I have no clue.
This is part of the mystery of the brain. Why different ones, although anatomically similar, can function so differently in how they approach and solve the same problem.
I can’t blame this on who she learned from. We’ve been doing puzzles together since she was little. Think about it – do you even remember someone teaching you to do jigsaw puzzles at some point? Neither do I. I assume a family member or schoolteacher showed me a basic one at some point, and how the pieces fit together, but that’s a guess.
So I sit there working on my section and watch her doing hers, and the neurologist turns the whole thing over. Does she have more neurons and/or glia in whatever the “puzzle solving” portion of her brain (I assume part of visual memory and spatial relationships) is? Or do I? Like so much of neurology this should have a structural answer – I think.
It reminds me of how little we still know. And it bugs me.
Has anyone done PET scans while people work on jigsaw puzzles? I checked PubMed and couldn’t find anything. I doubt it due to the logistics of having someone do one inside a scanner. Searching Google with the same question only gets me ads for customized jigsaws of pets.
So I made the leap to doing a jigsaw puzzle on an iPad while in a PET machine. But even then, how do I know I’d be testing the same functions? The touchscreen is similar, but not the same, as doing a real jigsaw. (In my opinion real puzzles are preferable to iPad ones, except when traveling).
At the end of the day , and realistically shouldn’t think too much about.
Because this summer the real meaning of the puzzle isn’t the jigsaw itself. It’s the young woman sitting next to me working on it.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A few weeks ago I talked about my evening practice of doing jigsaw puzzles to relax, as a pleasant alternative to surfing the Internet.
Last week my daughter moved home from college for the summer. It’s been several years since she and I last did puzzles together, and I’d forgotten how much she likes them.
So now each night we sit there, either side by side or across the table from each other, each quietly working on some little portion of the same jigsaw. Very little is said, but it’s still the same bonding time I’ve always cherished.
But I notice things I’d never thought of.
I always start a puzzle like I thought most people do: Pick out the flat edge pieces to build the outside frame, then work inward from there.
But she doesn’t. Once the box is opened and pieces dumped out, she starts sorting them by patterns and colors, and begins there. The edges don’t get her attention at all as she begins. She assembles like-pieces and gradually expands from there.
Why?
I mean, I’m a neurologist. Brains are my business. So why are our thought patterns on the same task so different?
I have no clue.
This is part of the mystery of the brain. Why different ones, although anatomically similar, can function so differently in how they approach and solve the same problem.
I can’t blame this on who she learned from. We’ve been doing puzzles together since she was little. Think about it – do you even remember someone teaching you to do jigsaw puzzles at some point? Neither do I. I assume a family member or schoolteacher showed me a basic one at some point, and how the pieces fit together, but that’s a guess.
So I sit there working on my section and watch her doing hers, and the neurologist turns the whole thing over. Does she have more neurons and/or glia in whatever the “puzzle solving” portion of her brain (I assume part of visual memory and spatial relationships) is? Or do I? Like so much of neurology this should have a structural answer – I think.
It reminds me of how little we still know. And it bugs me.
Has anyone done PET scans while people work on jigsaw puzzles? I checked PubMed and couldn’t find anything. I doubt it due to the logistics of having someone do one inside a scanner. Searching Google with the same question only gets me ads for customized jigsaws of pets.
So I made the leap to doing a jigsaw puzzle on an iPad while in a PET machine. But even then, how do I know I’d be testing the same functions? The touchscreen is similar, but not the same, as doing a real jigsaw. (In my opinion real puzzles are preferable to iPad ones, except when traveling).
At the end of the day , and realistically shouldn’t think too much about.
Because this summer the real meaning of the puzzle isn’t the jigsaw itself. It’s the young woman sitting next to me working on it.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
A few weeks ago I talked about my evening practice of doing jigsaw puzzles to relax, as a pleasant alternative to surfing the Internet.
Last week my daughter moved home from college for the summer. It’s been several years since she and I last did puzzles together, and I’d forgotten how much she likes them.
So now each night we sit there, either side by side or across the table from each other, each quietly working on some little portion of the same jigsaw. Very little is said, but it’s still the same bonding time I’ve always cherished.
But I notice things I’d never thought of.
I always start a puzzle like I thought most people do: Pick out the flat edge pieces to build the outside frame, then work inward from there.
But she doesn’t. Once the box is opened and pieces dumped out, she starts sorting them by patterns and colors, and begins there. The edges don’t get her attention at all as she begins. She assembles like-pieces and gradually expands from there.
Why?
I mean, I’m a neurologist. Brains are my business. So why are our thought patterns on the same task so different?
I have no clue.
This is part of the mystery of the brain. Why different ones, although anatomically similar, can function so differently in how they approach and solve the same problem.
I can’t blame this on who she learned from. We’ve been doing puzzles together since she was little. Think about it – do you even remember someone teaching you to do jigsaw puzzles at some point? Neither do I. I assume a family member or schoolteacher showed me a basic one at some point, and how the pieces fit together, but that’s a guess.
So I sit there working on my section and watch her doing hers, and the neurologist turns the whole thing over. Does she have more neurons and/or glia in whatever the “puzzle solving” portion of her brain (I assume part of visual memory and spatial relationships) is? Or do I? Like so much of neurology this should have a structural answer – I think.
It reminds me of how little we still know. And it bugs me.
Has anyone done PET scans while people work on jigsaw puzzles? I checked PubMed and couldn’t find anything. I doubt it due to the logistics of having someone do one inside a scanner. Searching Google with the same question only gets me ads for customized jigsaws of pets.
So I made the leap to doing a jigsaw puzzle on an iPad while in a PET machine. But even then, how do I know I’d be testing the same functions? The touchscreen is similar, but not the same, as doing a real jigsaw. (In my opinion real puzzles are preferable to iPad ones, except when traveling).
At the end of the day , and realistically shouldn’t think too much about.
Because this summer the real meaning of the puzzle isn’t the jigsaw itself. It’s the young woman sitting next to me working on it.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Telehealth continues to loom large, say experts
This physician, Brian Hasselfeld, MD, said his university’s health system did 50-80 telemedicine visits a month before COVID, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. This soared to close to 100,000 a month in the pandemic, and now the health system does close to 40,000 a month, he continued.
“Life is definitely different in how we engage with our patients on a day-to-day basis,” said Dr. Hasselfeld, who oversees the telehealth for six hospitals and 50 ambulatory-care locations in Maryland and three other states.
Attitudes gauged in Johns Hopkins surveys suggest that a lot of medical care will continue to be provided by telemedicine. Nine out of 10 patients said they would likely recommend telemedicine to friends and family, and 88% said it would be either moderately, very, or extremely important to have video visit options in the future, he said.
A survey of the Hopkins system’s 3,600 physicians, which generated about 1,300 responses, found that physicians would like to have a considerable chunk of time set aside for telemedicine visits – the median response was 30%.
Virtual care is in ‘early-adopter phase’
But Dr. Hasselfeld said virtual care is still in the “early-adopter phase.” While many physicians said they would like more than half of their time devoted to telehealth, a larger proportion was more likely to say they wanted very little time devoted to it, Dr. Hasselfeld said. Among those wanting to do it are some who want to do all of their visits virtually, he said.
Those who are eager to do it will be those guiding the change, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
“As we move forward – and thinking about how to optimize virtual-care options for your patients – it’s not going to be a forced issue,” he said.
Providing better access to certain patient groups continues to be a challenge. A dashboard developed at Hopkins to identify groups who are at a technological disadvantage and don’t have ready access to telemedicine found that those living in low-income zip codes, African-Americans, and those on Medicaid and Medicare tend to have higher percentages of “audio-only” visits, mainly because of lack of connectivity allowing video visits, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The lower share of video visits in the inner city suggests that access to telemedicine isn’t just a problem in remote rural areas, as the conventional wisdom has gone, he said.
“It doesn’t matter how many towers we have in downtown Baltimore, or how much fiber we have in the ground,” he said. “If you can’t have a data plan to access that high-speed Internet, or have a home with high-speed Internet, it doesn’t matter.”
Hopkins has developed a tool to assess how likely it is that someone will have trouble connecting for a telemedicine visit – if they’ve previously had an audio-only visit, for instance – and try to get in touch with those patients shortly before a visit so that it runs smoothly, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The explosion of telemedicine has led to the rise of companies providing care through apps on phones and tablets, he said.
“This is real care being provided to our patients through nontraditional routes, and this is a new force, one our patients see out in the marketplace,” he said. “We have to acknowledge and wrestle with the fact that convenience is a new part of what it means to [provide] access [to] care for patients.”
Heather Hirsch, MD, an internist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview after the session that telemedicine is poised to improve care.
“I think the good is definitely going to outweigh the bad so long as the infrastructure and the legislation will allow it,” said Dr. Hirsch, who does about half of her visits in person and half through telemedicine, which she performs while at the office. “It does allow for a lot of flexibility for both patients and providers.”
But health care at academic medical centers, she said, needs to adjust to the times.
“We need [academic medicine] for so many reasons,” she said, “but the reality is that it moves very slowly, and the old infrastructure and the slowness to catch up with technology is the worry.”
Dr. Hasselfeld reported financial relationships with Humana and TRUE-See Systems.
This physician, Brian Hasselfeld, MD, said his university’s health system did 50-80 telemedicine visits a month before COVID, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. This soared to close to 100,000 a month in the pandemic, and now the health system does close to 40,000 a month, he continued.
“Life is definitely different in how we engage with our patients on a day-to-day basis,” said Dr. Hasselfeld, who oversees the telehealth for six hospitals and 50 ambulatory-care locations in Maryland and three other states.
Attitudes gauged in Johns Hopkins surveys suggest that a lot of medical care will continue to be provided by telemedicine. Nine out of 10 patients said they would likely recommend telemedicine to friends and family, and 88% said it would be either moderately, very, or extremely important to have video visit options in the future, he said.
A survey of the Hopkins system’s 3,600 physicians, which generated about 1,300 responses, found that physicians would like to have a considerable chunk of time set aside for telemedicine visits – the median response was 30%.
Virtual care is in ‘early-adopter phase’
But Dr. Hasselfeld said virtual care is still in the “early-adopter phase.” While many physicians said they would like more than half of their time devoted to telehealth, a larger proportion was more likely to say they wanted very little time devoted to it, Dr. Hasselfeld said. Among those wanting to do it are some who want to do all of their visits virtually, he said.
Those who are eager to do it will be those guiding the change, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
“As we move forward – and thinking about how to optimize virtual-care options for your patients – it’s not going to be a forced issue,” he said.
Providing better access to certain patient groups continues to be a challenge. A dashboard developed at Hopkins to identify groups who are at a technological disadvantage and don’t have ready access to telemedicine found that those living in low-income zip codes, African-Americans, and those on Medicaid and Medicare tend to have higher percentages of “audio-only” visits, mainly because of lack of connectivity allowing video visits, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The lower share of video visits in the inner city suggests that access to telemedicine isn’t just a problem in remote rural areas, as the conventional wisdom has gone, he said.
“It doesn’t matter how many towers we have in downtown Baltimore, or how much fiber we have in the ground,” he said. “If you can’t have a data plan to access that high-speed Internet, or have a home with high-speed Internet, it doesn’t matter.”
Hopkins has developed a tool to assess how likely it is that someone will have trouble connecting for a telemedicine visit – if they’ve previously had an audio-only visit, for instance – and try to get in touch with those patients shortly before a visit so that it runs smoothly, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The explosion of telemedicine has led to the rise of companies providing care through apps on phones and tablets, he said.
“This is real care being provided to our patients through nontraditional routes, and this is a new force, one our patients see out in the marketplace,” he said. “We have to acknowledge and wrestle with the fact that convenience is a new part of what it means to [provide] access [to] care for patients.”
Heather Hirsch, MD, an internist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview after the session that telemedicine is poised to improve care.
“I think the good is definitely going to outweigh the bad so long as the infrastructure and the legislation will allow it,” said Dr. Hirsch, who does about half of her visits in person and half through telemedicine, which she performs while at the office. “It does allow for a lot of flexibility for both patients and providers.”
But health care at academic medical centers, she said, needs to adjust to the times.
“We need [academic medicine] for so many reasons,” she said, “but the reality is that it moves very slowly, and the old infrastructure and the slowness to catch up with technology is the worry.”
Dr. Hasselfeld reported financial relationships with Humana and TRUE-See Systems.
This physician, Brian Hasselfeld, MD, said his university’s health system did 50-80 telemedicine visits a month before COVID, during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Physicians. This soared to close to 100,000 a month in the pandemic, and now the health system does close to 40,000 a month, he continued.
“Life is definitely different in how we engage with our patients on a day-to-day basis,” said Dr. Hasselfeld, who oversees the telehealth for six hospitals and 50 ambulatory-care locations in Maryland and three other states.
Attitudes gauged in Johns Hopkins surveys suggest that a lot of medical care will continue to be provided by telemedicine. Nine out of 10 patients said they would likely recommend telemedicine to friends and family, and 88% said it would be either moderately, very, or extremely important to have video visit options in the future, he said.
A survey of the Hopkins system’s 3,600 physicians, which generated about 1,300 responses, found that physicians would like to have a considerable chunk of time set aside for telemedicine visits – the median response was 30%.
Virtual care is in ‘early-adopter phase’
But Dr. Hasselfeld said virtual care is still in the “early-adopter phase.” While many physicians said they would like more than half of their time devoted to telehealth, a larger proportion was more likely to say they wanted very little time devoted to it, Dr. Hasselfeld said. Among those wanting to do it are some who want to do all of their visits virtually, he said.
Those who are eager to do it will be those guiding the change, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
“As we move forward – and thinking about how to optimize virtual-care options for your patients – it’s not going to be a forced issue,” he said.
Providing better access to certain patient groups continues to be a challenge. A dashboard developed at Hopkins to identify groups who are at a technological disadvantage and don’t have ready access to telemedicine found that those living in low-income zip codes, African-Americans, and those on Medicaid and Medicare tend to have higher percentages of “audio-only” visits, mainly because of lack of connectivity allowing video visits, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The lower share of video visits in the inner city suggests that access to telemedicine isn’t just a problem in remote rural areas, as the conventional wisdom has gone, he said.
“It doesn’t matter how many towers we have in downtown Baltimore, or how much fiber we have in the ground,” he said. “If you can’t have a data plan to access that high-speed Internet, or have a home with high-speed Internet, it doesn’t matter.”
Hopkins has developed a tool to assess how likely it is that someone will have trouble connecting for a telemedicine visit – if they’ve previously had an audio-only visit, for instance – and try to get in touch with those patients shortly before a visit so that it runs smoothly, Dr. Hasselfeld said.
The explosion of telemedicine has led to the rise of companies providing care through apps on phones and tablets, he said.
“This is real care being provided to our patients through nontraditional routes, and this is a new force, one our patients see out in the marketplace,” he said. “We have to acknowledge and wrestle with the fact that convenience is a new part of what it means to [provide] access [to] care for patients.”
Heather Hirsch, MD, an internist with Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, said in an interview after the session that telemedicine is poised to improve care.
“I think the good is definitely going to outweigh the bad so long as the infrastructure and the legislation will allow it,” said Dr. Hirsch, who does about half of her visits in person and half through telemedicine, which she performs while at the office. “It does allow for a lot of flexibility for both patients and providers.”
But health care at academic medical centers, she said, needs to adjust to the times.
“We need [academic medicine] for so many reasons,” she said, “but the reality is that it moves very slowly, and the old infrastructure and the slowness to catch up with technology is the worry.”
Dr. Hasselfeld reported financial relationships with Humana and TRUE-See Systems.
AT INTERNAL MEDICINE 2022
Docs find new and better ways to cut EHR documentation time
About 60% of physicians cite documenting information in the electronic health record and other paperwork as major contributors to burnout. Physicians have been working with a variety of ways to reduce their documentation burdens; could one of them be right for you?
The first is widely used speech-to-text software, which requires the doctors to manually enter the text into the EHR; the second uses artificial intelligence (AI) to not only turn speech into text but to also automatically organize it and enter it into the EHR.
These AI solutions, which are only a few years old, are widely considered to be a work in progress – but many doctors who have used these products are impressed.
Other people do the documenting: On-site scribes
“It’s estimated that now one in five to one in eight doctors use scribes,” said Jeffrey A. Gold, MD, an internist who has studied the phenomenon. Utilization is already very high in emergency medicine and has been surging in specialties such as orthopedic surgery; it is also growing in primary care.
Scribes work with the doctor and enter information into the EHR. Their numbers have reportedly been rising in recent years, as more doctors look for ways to cut back on their documentation, according to Dr. Gold, vice chair for quality and safety at the department of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland.
The price tag of $33,000 a year or more for an on-site scribe is a major barrier. And because the typical scribe only works for 1-1.5 years, they must be constantly hired and trained, which is done by scribing services such as Scrivas in Miami.
However, Scrivas CEO Fernando G. Mendoza, MD, said scribes typically pay for themselves because they allow physicians to see more patients. Scribes can save doctors 2-3 hours of work per day, increase reimbursement by around 20% by producing more detailed notes, and improve satisfaction for both patients and doctors, according to several studies. In one study, physician documentation time significantly decreased, averaging 3 minutes per patient and 36 minutes per session.
Despite these possible savings, many health systems resisted hiring scribes for their employed physicians until the past few years, according to Kevin Brady, president of Physicians Angels, a scribing service based in Toledo, Ohio. “They figured they’d just spent millions on EHRs and didn’t want to spend any more,” he said. “They were also waiting for the EHR vendors to simplify documentation, but that never happened.”
Mr. Brady said what finally convinced many systems to invest in scribes was the need to reduce physician turnover and improve recruitment. Newly minted physicians often look for jobs that don’t interfere with their leisure time.
On-site scribes
On-site scribes accompany the doctor into the exam room and type the note during the encounter. Typically, the note is completed when the encounter is over, allowing for orders to be carried out immediately.
The traditional scribe is a premed student who wants to get acquainted with medicine and is thus willing to make a fairly low income. This career trajectory is the reason scribes have a high turnover. As demand surged, the scribe pool was supplemented with students aspiring to other health care professions like nursing, and even with people who want to make a career of scribing.
Since scribes have to set aside time for studying, scribe companies provide each physician-customer with one or two backup scribes. Dr. Mendoza bills his scribes as “personal assistants” who can do some nonclinical tasks beyond filling in the EHR, such as reminding doctors about the need to order a test or check in on another patient briefly before moving on to the next exam room.
Dr. Gold, however, warned against allowing “functional creep,” where scribes are asked to carry out tasks beyond their abilities, such as interpreting medical data. He added that doctors are expected to read through and sign all scribe-generated orders.
Some practices grow their own scribes, cross-training their medical assistants (MAs) to do the work. This addresses the turnover problem and could reduce costs. MAs already know clinical terms and how the doctor works, and they may be able to get special training at a local community college. However, some MAs do not want this extra work, and in any case, the work would take them away from other duties.
How often do physicians use their scribes? “Our doctors generally use them for all of their visits, but surgeons tend to limit use to their clinic days when they’re not in surgery,” said Tony Andrulonis, MD, president of ScribeAmerica in Fort Lauderdale, Fla.
Virtual scribes work off-site
Virtual scribes, who operate remotely from the doctor and can cost up to $10 less per hour than on-site scribes, got a boost during the COVID-19 pandemic because they fit well with telemedicine visits. Furthermore, the growing availability of virtual scribes from abroad has made scribes even more affordable.
“When doctors could no longer work on-site due to the pandemic, they replaced their on-site scribes with virtual scribes, and to some extent this trend is still going on,” Dr. Gold said.
One downside with virtual scribes is that they cannot do many of the extra tasks that on-site scribes can do. However, they are often a necessity in rural areas where on-site scribes are not available. In addition to having an audio-video connection, they may also just be on audio in areas where internet reception is poor or the patient wants privacy, Dr. Andrulonis said.
Mr. Brady said Physicians Angels uses offshore scribes from India. The company charges $16-$18 per hour, compared with $26-$28 per hour for U.S.-based virtual scribes. He said well over half of his clients are family physicians, who appreciate the lower cost.
Another advantage of offshore scribes is slower turnover and full-time availability. Mr. Brady said his scribes usually stay with the company for 5-6 years and are always available. “This is their full-time job,” Brady said.
Mr. Brady said when large organizations arrange with his company for scribes, often the goal is that the scribes pay for themselves. “They’ll tell their doctors: ‘We’ll let you have scribes as long as you see one or two more patients a day,’ ” he said. Mr. Brady then helps the organization reach that goal, which he said is easily achievable, except when doctors have no clear incentive to see more patients. He also works with clients on other goals, such as higher quality of life or time saved.
Speech-to-text software
For years, doctors have been using speech-to-text software to transform their speech into notes. They speak into the microphone, calling out punctuation and referring to prep-made templates for routine tasks. As they speak, the text appears on a screen. They can correct the text if necessary, and then they must put that information into the EHR.
Speech-to-text systems are used by more physicians than those using human scribes. Nuance’s Dragon Medical One system is the most popular, with more than 1000 large healthcare organizations signed up. Competitors include Dolbey, Entrada, and nVoq.
Prices are just a fraction of the cost of a human scribe. Dolbey’s Fusion Narrate system, for example, costs about $800-$850 a year per user. Doctors should shop around for these systems, because prices can vary by 30%-50%, said Wayne Kaniewski, MD, a retired family and urgent care physician and now owner and CEO of Twin Cities EMR Consulting in Minneapolis.
As a contracted reseller of the nVoq and Dolbey systems, Dr. Kaniewski provides training and support. During 13 years in business, he said machine dictation systems have become faster, more accurate, and, thanks to cloud-based technology, easier to set up.
Digital assistants
AI software, also known as digital assistants, takes speech-to-text software to the next logical step – organizing and automatically entering the information into the EHR. Using ambient technology, a smartphone captures the physician-patient conversation in the exam room, extracts the needed information, and distributes it in the EHR.
The cost is about one-sixth that of a human scribe, but higher than the cost for speech-to-text software because the technology still makes errors and requires a human at the software company to guide the process.
Currently about 10 companies sell digital scribes, including Nuance’s Dragon Medical One, NoteSwift, DeepScribe, and ScribeAmerica. These systems can be connected to the major EHR systems, and in some cases EHR systems have agreements with digital scribe vendors so that their systems can be seamlessly connected.
“DAX software can understand nonlinear conversations – the way normal conversations bounce from topic to topic,” said Kenneth Harper, general manager of Nuance’s Ambient Clinical Intelligence Division. “This level of technology was not possible 5 years ago.”
Mr. Harper said DAX saves doctors 6 minutes per patient on average, and 70% of doctors using it reported less burnout and fatigue. Kansas University Medical Center has been testing DAX with physicians there. Many of them no longer need to write up their notes after hours, said Denton Shanks, DO, the medical center’s digital health medical director.
One of the things Dr. Shanks likes about DAX is that it remembers all the details of a visit. As a family physician, “there are something like 15 different problems that come up in one typical visit. Before, I had to carry those problems in my head, and when I wrote up my notes at the end of the day, I might have forgotten a few of them. Not so with DAX.”
Dr. Shanks knows he has to speak clearly and unambiguously when using DAX. “DAX can only document what it hears, so I describe what I am looking at in a physical exam or I might further explain the patient’s account so DAX can pick up on it.”
Are digital assistants ready for doctors?
Since a human at the software company is needed to guide the system, it takes a few hours for the digital assistant to complete entries into the EHR, but vendors are looking for ways to eliminate human guidance.
“We’re definitely moving toward digital scribes, but we’re not there yet,” Dr. Gold said, pointing to a 2018 study that found a significantly higher error rate for speech recognition software than for human scribes.
Dr. Kaniewski added that digital scribes pick up a great deal of irrelevant information, making for a bloated note. “Clinicians must then edit the note down, which is more work than just dictating a concise note,” he said.
Many doctors, however, are happy with these new systems. Steven Y. Lin, MD, a family physician who has been testing a digital scribe system with 40 fellow clinicians at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care, said 95% of clinicians who stayed with the trial are continuing to use the system, but he concedes that there was a relatively high dropout rate. “These people felt that they had lost control of the process when using the software.”
Furthermore, Dr. Lin is concerned that using a digital scribe may eliminate doctors’ crucial step of sitting down and writing the clinical note. Here “doctors bring together everything they have heard and then come up with the diagnosis and treatment.” He recognized that doctors could still take this step when reviewing the digital note, but it would be easy to skip.
What is the future for documentation aids?
Increasingly more doctors are finding ways to expedite documentation tasks. Speech-to-text software is still the most popular solution, but more physicians are now using human scribes, driven by the decisions of some large organizations to start paying for them.
However, these physicians are often expected to work harder in order for the scribes to pay for themselves, which is a solution that could, ironically, add to burnout rather than alleviate it.
Digital assistants answer these concerns because they are more affordable and are supposed to do all the work of human scribes. This software parses the physician-patient conversation into a clinical note and other data and deposits them directly into the EHR.
Most experts think digital assistants will eventually meet their promise, but it is widely thought that they’re not ready yet. It will be up to vendors like Nuance to convince skeptics that their products are ready for doctors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 60% of physicians cite documenting information in the electronic health record and other paperwork as major contributors to burnout. Physicians have been working with a variety of ways to reduce their documentation burdens; could one of them be right for you?
The first is widely used speech-to-text software, which requires the doctors to manually enter the text into the EHR; the second uses artificial intelligence (AI) to not only turn speech into text but to also automatically organize it and enter it into the EHR.
These AI solutions, which are only a few years old, are widely considered to be a work in progress – but many doctors who have used these products are impressed.
Other people do the documenting: On-site scribes
“It’s estimated that now one in five to one in eight doctors use scribes,” said Jeffrey A. Gold, MD, an internist who has studied the phenomenon. Utilization is already very high in emergency medicine and has been surging in specialties such as orthopedic surgery; it is also growing in primary care.
Scribes work with the doctor and enter information into the EHR. Their numbers have reportedly been rising in recent years, as more doctors look for ways to cut back on their documentation, according to Dr. Gold, vice chair for quality and safety at the department of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland.
The price tag of $33,000 a year or more for an on-site scribe is a major barrier. And because the typical scribe only works for 1-1.5 years, they must be constantly hired and trained, which is done by scribing services such as Scrivas in Miami.
However, Scrivas CEO Fernando G. Mendoza, MD, said scribes typically pay for themselves because they allow physicians to see more patients. Scribes can save doctors 2-3 hours of work per day, increase reimbursement by around 20% by producing more detailed notes, and improve satisfaction for both patients and doctors, according to several studies. In one study, physician documentation time significantly decreased, averaging 3 minutes per patient and 36 minutes per session.
Despite these possible savings, many health systems resisted hiring scribes for their employed physicians until the past few years, according to Kevin Brady, president of Physicians Angels, a scribing service based in Toledo, Ohio. “They figured they’d just spent millions on EHRs and didn’t want to spend any more,” he said. “They were also waiting for the EHR vendors to simplify documentation, but that never happened.”
Mr. Brady said what finally convinced many systems to invest in scribes was the need to reduce physician turnover and improve recruitment. Newly minted physicians often look for jobs that don’t interfere with their leisure time.
On-site scribes
On-site scribes accompany the doctor into the exam room and type the note during the encounter. Typically, the note is completed when the encounter is over, allowing for orders to be carried out immediately.
The traditional scribe is a premed student who wants to get acquainted with medicine and is thus willing to make a fairly low income. This career trajectory is the reason scribes have a high turnover. As demand surged, the scribe pool was supplemented with students aspiring to other health care professions like nursing, and even with people who want to make a career of scribing.
Since scribes have to set aside time for studying, scribe companies provide each physician-customer with one or two backup scribes. Dr. Mendoza bills his scribes as “personal assistants” who can do some nonclinical tasks beyond filling in the EHR, such as reminding doctors about the need to order a test or check in on another patient briefly before moving on to the next exam room.
Dr. Gold, however, warned against allowing “functional creep,” where scribes are asked to carry out tasks beyond their abilities, such as interpreting medical data. He added that doctors are expected to read through and sign all scribe-generated orders.
Some practices grow their own scribes, cross-training their medical assistants (MAs) to do the work. This addresses the turnover problem and could reduce costs. MAs already know clinical terms and how the doctor works, and they may be able to get special training at a local community college. However, some MAs do not want this extra work, and in any case, the work would take them away from other duties.
How often do physicians use their scribes? “Our doctors generally use them for all of their visits, but surgeons tend to limit use to their clinic days when they’re not in surgery,” said Tony Andrulonis, MD, president of ScribeAmerica in Fort Lauderdale, Fla.
Virtual scribes work off-site
Virtual scribes, who operate remotely from the doctor and can cost up to $10 less per hour than on-site scribes, got a boost during the COVID-19 pandemic because they fit well with telemedicine visits. Furthermore, the growing availability of virtual scribes from abroad has made scribes even more affordable.
“When doctors could no longer work on-site due to the pandemic, they replaced their on-site scribes with virtual scribes, and to some extent this trend is still going on,” Dr. Gold said.
One downside with virtual scribes is that they cannot do many of the extra tasks that on-site scribes can do. However, they are often a necessity in rural areas where on-site scribes are not available. In addition to having an audio-video connection, they may also just be on audio in areas where internet reception is poor or the patient wants privacy, Dr. Andrulonis said.
Mr. Brady said Physicians Angels uses offshore scribes from India. The company charges $16-$18 per hour, compared with $26-$28 per hour for U.S.-based virtual scribes. He said well over half of his clients are family physicians, who appreciate the lower cost.
Another advantage of offshore scribes is slower turnover and full-time availability. Mr. Brady said his scribes usually stay with the company for 5-6 years and are always available. “This is their full-time job,” Brady said.
Mr. Brady said when large organizations arrange with his company for scribes, often the goal is that the scribes pay for themselves. “They’ll tell their doctors: ‘We’ll let you have scribes as long as you see one or two more patients a day,’ ” he said. Mr. Brady then helps the organization reach that goal, which he said is easily achievable, except when doctors have no clear incentive to see more patients. He also works with clients on other goals, such as higher quality of life or time saved.
Speech-to-text software
For years, doctors have been using speech-to-text software to transform their speech into notes. They speak into the microphone, calling out punctuation and referring to prep-made templates for routine tasks. As they speak, the text appears on a screen. They can correct the text if necessary, and then they must put that information into the EHR.
Speech-to-text systems are used by more physicians than those using human scribes. Nuance’s Dragon Medical One system is the most popular, with more than 1000 large healthcare organizations signed up. Competitors include Dolbey, Entrada, and nVoq.
Prices are just a fraction of the cost of a human scribe. Dolbey’s Fusion Narrate system, for example, costs about $800-$850 a year per user. Doctors should shop around for these systems, because prices can vary by 30%-50%, said Wayne Kaniewski, MD, a retired family and urgent care physician and now owner and CEO of Twin Cities EMR Consulting in Minneapolis.
As a contracted reseller of the nVoq and Dolbey systems, Dr. Kaniewski provides training and support. During 13 years in business, he said machine dictation systems have become faster, more accurate, and, thanks to cloud-based technology, easier to set up.
Digital assistants
AI software, also known as digital assistants, takes speech-to-text software to the next logical step – organizing and automatically entering the information into the EHR. Using ambient technology, a smartphone captures the physician-patient conversation in the exam room, extracts the needed information, and distributes it in the EHR.
The cost is about one-sixth that of a human scribe, but higher than the cost for speech-to-text software because the technology still makes errors and requires a human at the software company to guide the process.
Currently about 10 companies sell digital scribes, including Nuance’s Dragon Medical One, NoteSwift, DeepScribe, and ScribeAmerica. These systems can be connected to the major EHR systems, and in some cases EHR systems have agreements with digital scribe vendors so that their systems can be seamlessly connected.
“DAX software can understand nonlinear conversations – the way normal conversations bounce from topic to topic,” said Kenneth Harper, general manager of Nuance’s Ambient Clinical Intelligence Division. “This level of technology was not possible 5 years ago.”
Mr. Harper said DAX saves doctors 6 minutes per patient on average, and 70% of doctors using it reported less burnout and fatigue. Kansas University Medical Center has been testing DAX with physicians there. Many of them no longer need to write up their notes after hours, said Denton Shanks, DO, the medical center’s digital health medical director.
One of the things Dr. Shanks likes about DAX is that it remembers all the details of a visit. As a family physician, “there are something like 15 different problems that come up in one typical visit. Before, I had to carry those problems in my head, and when I wrote up my notes at the end of the day, I might have forgotten a few of them. Not so with DAX.”
Dr. Shanks knows he has to speak clearly and unambiguously when using DAX. “DAX can only document what it hears, so I describe what I am looking at in a physical exam or I might further explain the patient’s account so DAX can pick up on it.”
Are digital assistants ready for doctors?
Since a human at the software company is needed to guide the system, it takes a few hours for the digital assistant to complete entries into the EHR, but vendors are looking for ways to eliminate human guidance.
“We’re definitely moving toward digital scribes, but we’re not there yet,” Dr. Gold said, pointing to a 2018 study that found a significantly higher error rate for speech recognition software than for human scribes.
Dr. Kaniewski added that digital scribes pick up a great deal of irrelevant information, making for a bloated note. “Clinicians must then edit the note down, which is more work than just dictating a concise note,” he said.
Many doctors, however, are happy with these new systems. Steven Y. Lin, MD, a family physician who has been testing a digital scribe system with 40 fellow clinicians at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care, said 95% of clinicians who stayed with the trial are continuing to use the system, but he concedes that there was a relatively high dropout rate. “These people felt that they had lost control of the process when using the software.”
Furthermore, Dr. Lin is concerned that using a digital scribe may eliminate doctors’ crucial step of sitting down and writing the clinical note. Here “doctors bring together everything they have heard and then come up with the diagnosis and treatment.” He recognized that doctors could still take this step when reviewing the digital note, but it would be easy to skip.
What is the future for documentation aids?
Increasingly more doctors are finding ways to expedite documentation tasks. Speech-to-text software is still the most popular solution, but more physicians are now using human scribes, driven by the decisions of some large organizations to start paying for them.
However, these physicians are often expected to work harder in order for the scribes to pay for themselves, which is a solution that could, ironically, add to burnout rather than alleviate it.
Digital assistants answer these concerns because they are more affordable and are supposed to do all the work of human scribes. This software parses the physician-patient conversation into a clinical note and other data and deposits them directly into the EHR.
Most experts think digital assistants will eventually meet their promise, but it is widely thought that they’re not ready yet. It will be up to vendors like Nuance to convince skeptics that their products are ready for doctors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 60% of physicians cite documenting information in the electronic health record and other paperwork as major contributors to burnout. Physicians have been working with a variety of ways to reduce their documentation burdens; could one of them be right for you?
The first is widely used speech-to-text software, which requires the doctors to manually enter the text into the EHR; the second uses artificial intelligence (AI) to not only turn speech into text but to also automatically organize it and enter it into the EHR.
These AI solutions, which are only a few years old, are widely considered to be a work in progress – but many doctors who have used these products are impressed.
Other people do the documenting: On-site scribes
“It’s estimated that now one in five to one in eight doctors use scribes,” said Jeffrey A. Gold, MD, an internist who has studied the phenomenon. Utilization is already very high in emergency medicine and has been surging in specialties such as orthopedic surgery; it is also growing in primary care.
Scribes work with the doctor and enter information into the EHR. Their numbers have reportedly been rising in recent years, as more doctors look for ways to cut back on their documentation, according to Dr. Gold, vice chair for quality and safety at the department of medicine at Oregon Health and Science University, Portland.
The price tag of $33,000 a year or more for an on-site scribe is a major barrier. And because the typical scribe only works for 1-1.5 years, they must be constantly hired and trained, which is done by scribing services such as Scrivas in Miami.
However, Scrivas CEO Fernando G. Mendoza, MD, said scribes typically pay for themselves because they allow physicians to see more patients. Scribes can save doctors 2-3 hours of work per day, increase reimbursement by around 20% by producing more detailed notes, and improve satisfaction for both patients and doctors, according to several studies. In one study, physician documentation time significantly decreased, averaging 3 minutes per patient and 36 minutes per session.
Despite these possible savings, many health systems resisted hiring scribes for their employed physicians until the past few years, according to Kevin Brady, president of Physicians Angels, a scribing service based in Toledo, Ohio. “They figured they’d just spent millions on EHRs and didn’t want to spend any more,” he said. “They were also waiting for the EHR vendors to simplify documentation, but that never happened.”
Mr. Brady said what finally convinced many systems to invest in scribes was the need to reduce physician turnover and improve recruitment. Newly minted physicians often look for jobs that don’t interfere with their leisure time.
On-site scribes
On-site scribes accompany the doctor into the exam room and type the note during the encounter. Typically, the note is completed when the encounter is over, allowing for orders to be carried out immediately.
The traditional scribe is a premed student who wants to get acquainted with medicine and is thus willing to make a fairly low income. This career trajectory is the reason scribes have a high turnover. As demand surged, the scribe pool was supplemented with students aspiring to other health care professions like nursing, and even with people who want to make a career of scribing.
Since scribes have to set aside time for studying, scribe companies provide each physician-customer with one or two backup scribes. Dr. Mendoza bills his scribes as “personal assistants” who can do some nonclinical tasks beyond filling in the EHR, such as reminding doctors about the need to order a test or check in on another patient briefly before moving on to the next exam room.
Dr. Gold, however, warned against allowing “functional creep,” where scribes are asked to carry out tasks beyond their abilities, such as interpreting medical data. He added that doctors are expected to read through and sign all scribe-generated orders.
Some practices grow their own scribes, cross-training their medical assistants (MAs) to do the work. This addresses the turnover problem and could reduce costs. MAs already know clinical terms and how the doctor works, and they may be able to get special training at a local community college. However, some MAs do not want this extra work, and in any case, the work would take them away from other duties.
How often do physicians use their scribes? “Our doctors generally use them for all of their visits, but surgeons tend to limit use to their clinic days when they’re not in surgery,” said Tony Andrulonis, MD, president of ScribeAmerica in Fort Lauderdale, Fla.
Virtual scribes work off-site
Virtual scribes, who operate remotely from the doctor and can cost up to $10 less per hour than on-site scribes, got a boost during the COVID-19 pandemic because they fit well with telemedicine visits. Furthermore, the growing availability of virtual scribes from abroad has made scribes even more affordable.
“When doctors could no longer work on-site due to the pandemic, they replaced their on-site scribes with virtual scribes, and to some extent this trend is still going on,” Dr. Gold said.
One downside with virtual scribes is that they cannot do many of the extra tasks that on-site scribes can do. However, they are often a necessity in rural areas where on-site scribes are not available. In addition to having an audio-video connection, they may also just be on audio in areas where internet reception is poor or the patient wants privacy, Dr. Andrulonis said.
Mr. Brady said Physicians Angels uses offshore scribes from India. The company charges $16-$18 per hour, compared with $26-$28 per hour for U.S.-based virtual scribes. He said well over half of his clients are family physicians, who appreciate the lower cost.
Another advantage of offshore scribes is slower turnover and full-time availability. Mr. Brady said his scribes usually stay with the company for 5-6 years and are always available. “This is their full-time job,” Brady said.
Mr. Brady said when large organizations arrange with his company for scribes, often the goal is that the scribes pay for themselves. “They’ll tell their doctors: ‘We’ll let you have scribes as long as you see one or two more patients a day,’ ” he said. Mr. Brady then helps the organization reach that goal, which he said is easily achievable, except when doctors have no clear incentive to see more patients. He also works with clients on other goals, such as higher quality of life or time saved.
Speech-to-text software
For years, doctors have been using speech-to-text software to transform their speech into notes. They speak into the microphone, calling out punctuation and referring to prep-made templates for routine tasks. As they speak, the text appears on a screen. They can correct the text if necessary, and then they must put that information into the EHR.
Speech-to-text systems are used by more physicians than those using human scribes. Nuance’s Dragon Medical One system is the most popular, with more than 1000 large healthcare organizations signed up. Competitors include Dolbey, Entrada, and nVoq.
Prices are just a fraction of the cost of a human scribe. Dolbey’s Fusion Narrate system, for example, costs about $800-$850 a year per user. Doctors should shop around for these systems, because prices can vary by 30%-50%, said Wayne Kaniewski, MD, a retired family and urgent care physician and now owner and CEO of Twin Cities EMR Consulting in Minneapolis.
As a contracted reseller of the nVoq and Dolbey systems, Dr. Kaniewski provides training and support. During 13 years in business, he said machine dictation systems have become faster, more accurate, and, thanks to cloud-based technology, easier to set up.
Digital assistants
AI software, also known as digital assistants, takes speech-to-text software to the next logical step – organizing and automatically entering the information into the EHR. Using ambient technology, a smartphone captures the physician-patient conversation in the exam room, extracts the needed information, and distributes it in the EHR.
The cost is about one-sixth that of a human scribe, but higher than the cost for speech-to-text software because the technology still makes errors and requires a human at the software company to guide the process.
Currently about 10 companies sell digital scribes, including Nuance’s Dragon Medical One, NoteSwift, DeepScribe, and ScribeAmerica. These systems can be connected to the major EHR systems, and in some cases EHR systems have agreements with digital scribe vendors so that their systems can be seamlessly connected.
“DAX software can understand nonlinear conversations – the way normal conversations bounce from topic to topic,” said Kenneth Harper, general manager of Nuance’s Ambient Clinical Intelligence Division. “This level of technology was not possible 5 years ago.”
Mr. Harper said DAX saves doctors 6 minutes per patient on average, and 70% of doctors using it reported less burnout and fatigue. Kansas University Medical Center has been testing DAX with physicians there. Many of them no longer need to write up their notes after hours, said Denton Shanks, DO, the medical center’s digital health medical director.
One of the things Dr. Shanks likes about DAX is that it remembers all the details of a visit. As a family physician, “there are something like 15 different problems that come up in one typical visit. Before, I had to carry those problems in my head, and when I wrote up my notes at the end of the day, I might have forgotten a few of them. Not so with DAX.”
Dr. Shanks knows he has to speak clearly and unambiguously when using DAX. “DAX can only document what it hears, so I describe what I am looking at in a physical exam or I might further explain the patient’s account so DAX can pick up on it.”
Are digital assistants ready for doctors?
Since a human at the software company is needed to guide the system, it takes a few hours for the digital assistant to complete entries into the EHR, but vendors are looking for ways to eliminate human guidance.
“We’re definitely moving toward digital scribes, but we’re not there yet,” Dr. Gold said, pointing to a 2018 study that found a significantly higher error rate for speech recognition software than for human scribes.
Dr. Kaniewski added that digital scribes pick up a great deal of irrelevant information, making for a bloated note. “Clinicians must then edit the note down, which is more work than just dictating a concise note,” he said.
Many doctors, however, are happy with these new systems. Steven Y. Lin, MD, a family physician who has been testing a digital scribe system with 40 fellow clinicians at Stanford (Calif.) Health Care, said 95% of clinicians who stayed with the trial are continuing to use the system, but he concedes that there was a relatively high dropout rate. “These people felt that they had lost control of the process when using the software.”
Furthermore, Dr. Lin is concerned that using a digital scribe may eliminate doctors’ crucial step of sitting down and writing the clinical note. Here “doctors bring together everything they have heard and then come up with the diagnosis and treatment.” He recognized that doctors could still take this step when reviewing the digital note, but it would be easy to skip.
What is the future for documentation aids?
Increasingly more doctors are finding ways to expedite documentation tasks. Speech-to-text software is still the most popular solution, but more physicians are now using human scribes, driven by the decisions of some large organizations to start paying for them.
However, these physicians are often expected to work harder in order for the scribes to pay for themselves, which is a solution that could, ironically, add to burnout rather than alleviate it.
Digital assistants answer these concerns because they are more affordable and are supposed to do all the work of human scribes. This software parses the physician-patient conversation into a clinical note and other data and deposits them directly into the EHR.
Most experts think digital assistants will eventually meet their promise, but it is widely thought that they’re not ready yet. It will be up to vendors like Nuance to convince skeptics that their products are ready for doctors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Q&A with Hubert (Hugh) Greenway, MD
who was also recently selected as program director for cutaneous oncology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center in San Diego. He is also a former president of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
After earning his medical degree from the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, in 1974, Dr. Greenway was fellowship trained in Mohs skin cancer surgery by Frederic E. Mohs, MD, at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He completed his dermatology residency at the Naval Medical Center San Diego and joined Scripps Clinic in 1983, where he launched the institution’s first Mohs surgery program, as well as a popular annual intensive course in superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery that bears his name. He was also the first physician in the world to use interferon as a nonsurgical treatment of basal cell carcinoma.
To date, Dr. Greenway has performed more than 41,000 Mohs surgery cases and has trained 61 fellows who practice in academic and clinical settings. In 2017, he received the Frederic E. Mohs Award from the ACMS at the college’s annual meeting. He is also a past CEO of Scripps Clinic. In this Q&A, Dr. Greenway opens up about what it was like to train with Dr. Mohs, what makes a good Mohs surgeon, and why he’s excited about the future of dermatology.
I understand that you first became interested in a medical career after meeting Dr. Carl Jones, a friend of your father who was your Scoutmaster in the Boy Scouts in Georgia. What about Dr. Jones inspired you to pursue a career in medicine?
Dr. Jones was an internist/allergist in Atlanta, where I grew up. His three sons and I were friends. My dad had dealt with several medical problems being injured in World War II and subsequently undergoing a couple of kidney transplantations, so I developed an interest in medicine personally. Even though Dr. Jones was a specialist, he started out as a family doctor like I did, so he was interested in the whole person and all of his or her medical problems as opposed to those related to his specialty only. I traveled with the Boy Scouts to camp at places like Valley Forge in Pennsylvania, and Dr. Jones was involved with the medical set-ups of those large events. That also contributed to my interest in medicine.
As part of your 9-year service in the U.S. Navy, you spent 2 years as the flight surgeon at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base. What was your most memorable experience from that assignment?
Dobbins is a large facility with two Lockheed plants, and the Air Force had built the medical clinic, which was staffed by the Navy. Getting to know some of the active-duty members of the Air Force, the Navy, and the National Guard, and their commitment to our country, was memorable. Jimmy Carter was the president in those days. When he would fly in Dobbins, one of my jobs as the flight surgeon was to be on base when Air Force One landed or departed. One night, we had a DC-9 commercial aircraft coming from Huntsville, Ala., to Atlanta that got caught in a thunderstorm a little above 30,000 feet. Both engines went out and the aircraft essentially became a glider. The pilots tried to land on our runway but unfortunately, they ended up 4 miles short. We were heavily involved in responding to the crash, which was a tragic event. I also learned to fly (second seat) different types of aircraft during my assignment at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base, everything from the large C-5s to Navy fighter jets and helicopters. Coincidentally, Dr. Jones was involved with a couple of free health clinics in Atlanta when I was stationed there. Every Tuesday night, my wife (who is a nurse) and I would volunteer at a clinic in Cabbagetown, which was one of the poorer areas of Atlanta. It was a chance to give back to a group of people who didn’t have a whole lot.
In the middle your dermatology residency at Naval Medical Center San Diego, you were selected by Dr. Mohs for fellowship training in Mohs skin cancer surgery at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. What do you remember most about your training with Dr. Mohs?
Dr. Mohs was a kind, humble man who had this great idea about skin cancer. He was not a dermatologist; he was a general surgeon. The technique he developed was originally called chemosurgery because he put a chemical onto the skin. This was known as the fixed-tissue technique. Then we had a fresh-tissue technique, where we did not use the chemical, but we were able to use local anesthesia right away. That developed into the Mohs surgery we know today. Dr. Mohs did not name it that; he was very humble, but he was very proud of his technique. He was also a very hard worker. On the first day of my fellowship, I started at 7 in the morning and ended at 7 at night. It was the same for the last day of my fellowship. He also had an excellent office staff, many of whom had worked with him for many years. Patients with difficult skin cancers traveled to Madison from all over the world because there weren’t that many Mohs surgery clinics in those days. During the latter part of my fellowship, Michael McCall, MD, and I had the opportunity to remove a skin cancer from the nose of Dr. Mohs. We presented the case at a national conference, and I titled the talk “Mohs Surgery for Mohs’ Nose.”
Early in your career Dr. Mohs asked you to take over his practice, but you accepted an offer to establish the first Mohs surgery office at Scripps in San Diego instead. What convinced you to head West?
After my fellowship, I returned to San Diego to complete my residency with the Navy, where we opened a Mohs surgery clinic. Dr. Mohs came out for the ribbon cutting. During that time, I was taking care of several patients that he had treated in Wisconsin. Through that my wife and I ended up going to dinner with Cecil and Ida Green, philanthropists who made several financial gifts to Scripps Clinic – and for whom Scripps Green Hospital is named. Cecil cofounded Texas Instruments and was knighted by Queen Elizabeth. During dinner, he suggested that I stay in San Diego for a year and work at Scripps after my residency assignment with the Navy. I agreed and have been here ever since.
What do you find most interesting about Mohs surgery?
In Mohs surgery, you’re able to provide not only surgical care to eliminate the tumor, but also the pathology and the reconstruction. That was interesting to me. Dr. Mohs was not that interested in reconstruction. He was more focused on the tumor, in part because with the original fixed-tissue technique you could not do the reconstruction. You had to wait for an extra layer of tissue to separate. But with the fresh-tissue technique, you were able to provide the reconstruction that day. Mohs surgery deals with a subset of tumors that are challenging to treat. That also spiked my academic and clinical interest.
In your opinion, what’s been the most important advance in Mohs surgery to date?
In recent years, immunology has come into play, so now we have teams of clinicians in dermatology, medical oncology, surgery, and other subspecialties providing patients the best of care. In the arena of Mohs surgery itself, in the 1980s, the American College of Mohs Surgery developed a 1-year fellowship program, which enabled us to train many men and women to practice Mohs surgery. Most of them are dermatologists.
Please complete the sentence: “You can tell a good Mohs surgeon by the way he/she ...”
Treats patients, is willing to spend time with them, and shows an interest in them. One of the things we should strive for is to let patients know that they as a person are important; it’s not just the melanoma on their nose. We’re not only dealing with a skin cancer; we’re dealing with a patient who has skin cancer.
For the past 39 years, you have led Hugh Greenway’s Superficial Anatomy and Cutaneous Surgery course, which takes place every January in San Diego. What’s been key to sustaining this training course for nearly 4 decades?
There have been many people involved in its success, so it’s not just me. When I first started my practice, there really was not a focus on anatomy in the general dermatologic community. Dermatologic surgery textbooks contained very little content on surgical anatomy so I developed an interest a putting together a course that would cover some of this material. I met with Terence Davidson, MD, an otolaryngologist who was dean of continuing medical education at the University of California, San Diego. The course includes lectures from experts in many subspecialties and hands-on laboratories using cadavers to work on anatomy and surgical techniques. After about 16 years of doing the course Dr. Davidson told me: “When we started this course, as a group, the head and neck surgeons were the best to do the reconstructions on the face with skin flaps and grafts and layered closures. But now, as a group, the dermatologists are best at doing that.” That’s what we want to hear in medical education.
During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, what were your most significant challenges from both a clinical and a personal standpoint?
I’m fortunate to practice at a place like Scripps, where there are many resources to look at what was happening with COVID-19. Clinically, we had to put a lot of things on hold, but we tried our best to keep our cancer patients in particular in the forefront of care. It has been a challenge, but fortunately we have been able to take care of patients after a brief timeout. Many of us remember the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. Having worked overseas and at missionary hospital where we had children die of measles because they were not vaccinated gave me a larger appreciation for the importance of vaccines. I recommend all young physicians who work with me to read, “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History,” by John M. Barry, which recounts the 1918 flu epidemic.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
I don’t view what I do as work. Dr. Jones and Dr. Mohs continue to inspire me with what they accomplished during their careers. You have to love people and love patients. Every patient who comes to see me has a story, so I try to understand their story. One of the things I really enjoy is training the young fellows. We train three Mohs fellows per year at Scripps, and it’s a great challenge every day.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
Dermatology will continue to evolve just like all other medical specialties. We’re going to see a large growth in telemedicine, and immunotherapy is playing a key role in dermatologic oncology. What excites me the most in medicine is the young people who enter the field willing to contribute their lives to helping others.
who was also recently selected as program director for cutaneous oncology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center in San Diego. He is also a former president of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
After earning his medical degree from the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, in 1974, Dr. Greenway was fellowship trained in Mohs skin cancer surgery by Frederic E. Mohs, MD, at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He completed his dermatology residency at the Naval Medical Center San Diego and joined Scripps Clinic in 1983, where he launched the institution’s first Mohs surgery program, as well as a popular annual intensive course in superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery that bears his name. He was also the first physician in the world to use interferon as a nonsurgical treatment of basal cell carcinoma.
To date, Dr. Greenway has performed more than 41,000 Mohs surgery cases and has trained 61 fellows who practice in academic and clinical settings. In 2017, he received the Frederic E. Mohs Award from the ACMS at the college’s annual meeting. He is also a past CEO of Scripps Clinic. In this Q&A, Dr. Greenway opens up about what it was like to train with Dr. Mohs, what makes a good Mohs surgeon, and why he’s excited about the future of dermatology.
I understand that you first became interested in a medical career after meeting Dr. Carl Jones, a friend of your father who was your Scoutmaster in the Boy Scouts in Georgia. What about Dr. Jones inspired you to pursue a career in medicine?
Dr. Jones was an internist/allergist in Atlanta, where I grew up. His three sons and I were friends. My dad had dealt with several medical problems being injured in World War II and subsequently undergoing a couple of kidney transplantations, so I developed an interest in medicine personally. Even though Dr. Jones was a specialist, he started out as a family doctor like I did, so he was interested in the whole person and all of his or her medical problems as opposed to those related to his specialty only. I traveled with the Boy Scouts to camp at places like Valley Forge in Pennsylvania, and Dr. Jones was involved with the medical set-ups of those large events. That also contributed to my interest in medicine.
As part of your 9-year service in the U.S. Navy, you spent 2 years as the flight surgeon at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base. What was your most memorable experience from that assignment?
Dobbins is a large facility with two Lockheed plants, and the Air Force had built the medical clinic, which was staffed by the Navy. Getting to know some of the active-duty members of the Air Force, the Navy, and the National Guard, and their commitment to our country, was memorable. Jimmy Carter was the president in those days. When he would fly in Dobbins, one of my jobs as the flight surgeon was to be on base when Air Force One landed or departed. One night, we had a DC-9 commercial aircraft coming from Huntsville, Ala., to Atlanta that got caught in a thunderstorm a little above 30,000 feet. Both engines went out and the aircraft essentially became a glider. The pilots tried to land on our runway but unfortunately, they ended up 4 miles short. We were heavily involved in responding to the crash, which was a tragic event. I also learned to fly (second seat) different types of aircraft during my assignment at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base, everything from the large C-5s to Navy fighter jets and helicopters. Coincidentally, Dr. Jones was involved with a couple of free health clinics in Atlanta when I was stationed there. Every Tuesday night, my wife (who is a nurse) and I would volunteer at a clinic in Cabbagetown, which was one of the poorer areas of Atlanta. It was a chance to give back to a group of people who didn’t have a whole lot.
In the middle your dermatology residency at Naval Medical Center San Diego, you were selected by Dr. Mohs for fellowship training in Mohs skin cancer surgery at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. What do you remember most about your training with Dr. Mohs?
Dr. Mohs was a kind, humble man who had this great idea about skin cancer. He was not a dermatologist; he was a general surgeon. The technique he developed was originally called chemosurgery because he put a chemical onto the skin. This was known as the fixed-tissue technique. Then we had a fresh-tissue technique, where we did not use the chemical, but we were able to use local anesthesia right away. That developed into the Mohs surgery we know today. Dr. Mohs did not name it that; he was very humble, but he was very proud of his technique. He was also a very hard worker. On the first day of my fellowship, I started at 7 in the morning and ended at 7 at night. It was the same for the last day of my fellowship. He also had an excellent office staff, many of whom had worked with him for many years. Patients with difficult skin cancers traveled to Madison from all over the world because there weren’t that many Mohs surgery clinics in those days. During the latter part of my fellowship, Michael McCall, MD, and I had the opportunity to remove a skin cancer from the nose of Dr. Mohs. We presented the case at a national conference, and I titled the talk “Mohs Surgery for Mohs’ Nose.”
Early in your career Dr. Mohs asked you to take over his practice, but you accepted an offer to establish the first Mohs surgery office at Scripps in San Diego instead. What convinced you to head West?
After my fellowship, I returned to San Diego to complete my residency with the Navy, where we opened a Mohs surgery clinic. Dr. Mohs came out for the ribbon cutting. During that time, I was taking care of several patients that he had treated in Wisconsin. Through that my wife and I ended up going to dinner with Cecil and Ida Green, philanthropists who made several financial gifts to Scripps Clinic – and for whom Scripps Green Hospital is named. Cecil cofounded Texas Instruments and was knighted by Queen Elizabeth. During dinner, he suggested that I stay in San Diego for a year and work at Scripps after my residency assignment with the Navy. I agreed and have been here ever since.
What do you find most interesting about Mohs surgery?
In Mohs surgery, you’re able to provide not only surgical care to eliminate the tumor, but also the pathology and the reconstruction. That was interesting to me. Dr. Mohs was not that interested in reconstruction. He was more focused on the tumor, in part because with the original fixed-tissue technique you could not do the reconstruction. You had to wait for an extra layer of tissue to separate. But with the fresh-tissue technique, you were able to provide the reconstruction that day. Mohs surgery deals with a subset of tumors that are challenging to treat. That also spiked my academic and clinical interest.
In your opinion, what’s been the most important advance in Mohs surgery to date?
In recent years, immunology has come into play, so now we have teams of clinicians in dermatology, medical oncology, surgery, and other subspecialties providing patients the best of care. In the arena of Mohs surgery itself, in the 1980s, the American College of Mohs Surgery developed a 1-year fellowship program, which enabled us to train many men and women to practice Mohs surgery. Most of them are dermatologists.
Please complete the sentence: “You can tell a good Mohs surgeon by the way he/she ...”
Treats patients, is willing to spend time with them, and shows an interest in them. One of the things we should strive for is to let patients know that they as a person are important; it’s not just the melanoma on their nose. We’re not only dealing with a skin cancer; we’re dealing with a patient who has skin cancer.
For the past 39 years, you have led Hugh Greenway’s Superficial Anatomy and Cutaneous Surgery course, which takes place every January in San Diego. What’s been key to sustaining this training course for nearly 4 decades?
There have been many people involved in its success, so it’s not just me. When I first started my practice, there really was not a focus on anatomy in the general dermatologic community. Dermatologic surgery textbooks contained very little content on surgical anatomy so I developed an interest a putting together a course that would cover some of this material. I met with Terence Davidson, MD, an otolaryngologist who was dean of continuing medical education at the University of California, San Diego. The course includes lectures from experts in many subspecialties and hands-on laboratories using cadavers to work on anatomy and surgical techniques. After about 16 years of doing the course Dr. Davidson told me: “When we started this course, as a group, the head and neck surgeons were the best to do the reconstructions on the face with skin flaps and grafts and layered closures. But now, as a group, the dermatologists are best at doing that.” That’s what we want to hear in medical education.
During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, what were your most significant challenges from both a clinical and a personal standpoint?
I’m fortunate to practice at a place like Scripps, where there are many resources to look at what was happening with COVID-19. Clinically, we had to put a lot of things on hold, but we tried our best to keep our cancer patients in particular in the forefront of care. It has been a challenge, but fortunately we have been able to take care of patients after a brief timeout. Many of us remember the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. Having worked overseas and at missionary hospital where we had children die of measles because they were not vaccinated gave me a larger appreciation for the importance of vaccines. I recommend all young physicians who work with me to read, “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History,” by John M. Barry, which recounts the 1918 flu epidemic.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
I don’t view what I do as work. Dr. Jones and Dr. Mohs continue to inspire me with what they accomplished during their careers. You have to love people and love patients. Every patient who comes to see me has a story, so I try to understand their story. One of the things I really enjoy is training the young fellows. We train three Mohs fellows per year at Scripps, and it’s a great challenge every day.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
Dermatology will continue to evolve just like all other medical specialties. We’re going to see a large growth in telemedicine, and immunotherapy is playing a key role in dermatologic oncology. What excites me the most in medicine is the young people who enter the field willing to contribute their lives to helping others.
who was also recently selected as program director for cutaneous oncology at Scripps MD Anderson Cancer Center in San Diego. He is also a former president of the American College of Mohs Surgery.
After earning his medical degree from the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, in 1974, Dr. Greenway was fellowship trained in Mohs skin cancer surgery by Frederic E. Mohs, MD, at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He completed his dermatology residency at the Naval Medical Center San Diego and joined Scripps Clinic in 1983, where he launched the institution’s first Mohs surgery program, as well as a popular annual intensive course in superficial anatomy and cutaneous surgery that bears his name. He was also the first physician in the world to use interferon as a nonsurgical treatment of basal cell carcinoma.
To date, Dr. Greenway has performed more than 41,000 Mohs surgery cases and has trained 61 fellows who practice in academic and clinical settings. In 2017, he received the Frederic E. Mohs Award from the ACMS at the college’s annual meeting. He is also a past CEO of Scripps Clinic. In this Q&A, Dr. Greenway opens up about what it was like to train with Dr. Mohs, what makes a good Mohs surgeon, and why he’s excited about the future of dermatology.
I understand that you first became interested in a medical career after meeting Dr. Carl Jones, a friend of your father who was your Scoutmaster in the Boy Scouts in Georgia. What about Dr. Jones inspired you to pursue a career in medicine?
Dr. Jones was an internist/allergist in Atlanta, where I grew up. His three sons and I were friends. My dad had dealt with several medical problems being injured in World War II and subsequently undergoing a couple of kidney transplantations, so I developed an interest in medicine personally. Even though Dr. Jones was a specialist, he started out as a family doctor like I did, so he was interested in the whole person and all of his or her medical problems as opposed to those related to his specialty only. I traveled with the Boy Scouts to camp at places like Valley Forge in Pennsylvania, and Dr. Jones was involved with the medical set-ups of those large events. That also contributed to my interest in medicine.
As part of your 9-year service in the U.S. Navy, you spent 2 years as the flight surgeon at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base. What was your most memorable experience from that assignment?
Dobbins is a large facility with two Lockheed plants, and the Air Force had built the medical clinic, which was staffed by the Navy. Getting to know some of the active-duty members of the Air Force, the Navy, and the National Guard, and their commitment to our country, was memorable. Jimmy Carter was the president in those days. When he would fly in Dobbins, one of my jobs as the flight surgeon was to be on base when Air Force One landed or departed. One night, we had a DC-9 commercial aircraft coming from Huntsville, Ala., to Atlanta that got caught in a thunderstorm a little above 30,000 feet. Both engines went out and the aircraft essentially became a glider. The pilots tried to land on our runway but unfortunately, they ended up 4 miles short. We were heavily involved in responding to the crash, which was a tragic event. I also learned to fly (second seat) different types of aircraft during my assignment at NAS Atlanta/Dobbins Air Force Base, everything from the large C-5s to Navy fighter jets and helicopters. Coincidentally, Dr. Jones was involved with a couple of free health clinics in Atlanta when I was stationed there. Every Tuesday night, my wife (who is a nurse) and I would volunteer at a clinic in Cabbagetown, which was one of the poorer areas of Atlanta. It was a chance to give back to a group of people who didn’t have a whole lot.
In the middle your dermatology residency at Naval Medical Center San Diego, you were selected by Dr. Mohs for fellowship training in Mohs skin cancer surgery at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. What do you remember most about your training with Dr. Mohs?
Dr. Mohs was a kind, humble man who had this great idea about skin cancer. He was not a dermatologist; he was a general surgeon. The technique he developed was originally called chemosurgery because he put a chemical onto the skin. This was known as the fixed-tissue technique. Then we had a fresh-tissue technique, where we did not use the chemical, but we were able to use local anesthesia right away. That developed into the Mohs surgery we know today. Dr. Mohs did not name it that; he was very humble, but he was very proud of his technique. He was also a very hard worker. On the first day of my fellowship, I started at 7 in the morning and ended at 7 at night. It was the same for the last day of my fellowship. He also had an excellent office staff, many of whom had worked with him for many years. Patients with difficult skin cancers traveled to Madison from all over the world because there weren’t that many Mohs surgery clinics in those days. During the latter part of my fellowship, Michael McCall, MD, and I had the opportunity to remove a skin cancer from the nose of Dr. Mohs. We presented the case at a national conference, and I titled the talk “Mohs Surgery for Mohs’ Nose.”
Early in your career Dr. Mohs asked you to take over his practice, but you accepted an offer to establish the first Mohs surgery office at Scripps in San Diego instead. What convinced you to head West?
After my fellowship, I returned to San Diego to complete my residency with the Navy, where we opened a Mohs surgery clinic. Dr. Mohs came out for the ribbon cutting. During that time, I was taking care of several patients that he had treated in Wisconsin. Through that my wife and I ended up going to dinner with Cecil and Ida Green, philanthropists who made several financial gifts to Scripps Clinic – and for whom Scripps Green Hospital is named. Cecil cofounded Texas Instruments and was knighted by Queen Elizabeth. During dinner, he suggested that I stay in San Diego for a year and work at Scripps after my residency assignment with the Navy. I agreed and have been here ever since.
What do you find most interesting about Mohs surgery?
In Mohs surgery, you’re able to provide not only surgical care to eliminate the tumor, but also the pathology and the reconstruction. That was interesting to me. Dr. Mohs was not that interested in reconstruction. He was more focused on the tumor, in part because with the original fixed-tissue technique you could not do the reconstruction. You had to wait for an extra layer of tissue to separate. But with the fresh-tissue technique, you were able to provide the reconstruction that day. Mohs surgery deals with a subset of tumors that are challenging to treat. That also spiked my academic and clinical interest.
In your opinion, what’s been the most important advance in Mohs surgery to date?
In recent years, immunology has come into play, so now we have teams of clinicians in dermatology, medical oncology, surgery, and other subspecialties providing patients the best of care. In the arena of Mohs surgery itself, in the 1980s, the American College of Mohs Surgery developed a 1-year fellowship program, which enabled us to train many men and women to practice Mohs surgery. Most of them are dermatologists.
Please complete the sentence: “You can tell a good Mohs surgeon by the way he/she ...”
Treats patients, is willing to spend time with them, and shows an interest in them. One of the things we should strive for is to let patients know that they as a person are important; it’s not just the melanoma on their nose. We’re not only dealing with a skin cancer; we’re dealing with a patient who has skin cancer.
For the past 39 years, you have led Hugh Greenway’s Superficial Anatomy and Cutaneous Surgery course, which takes place every January in San Diego. What’s been key to sustaining this training course for nearly 4 decades?
There have been many people involved in its success, so it’s not just me. When I first started my practice, there really was not a focus on anatomy in the general dermatologic community. Dermatologic surgery textbooks contained very little content on surgical anatomy so I developed an interest a putting together a course that would cover some of this material. I met with Terence Davidson, MD, an otolaryngologist who was dean of continuing medical education at the University of California, San Diego. The course includes lectures from experts in many subspecialties and hands-on laboratories using cadavers to work on anatomy and surgical techniques. After about 16 years of doing the course Dr. Davidson told me: “When we started this course, as a group, the head and neck surgeons were the best to do the reconstructions on the face with skin flaps and grafts and layered closures. But now, as a group, the dermatologists are best at doing that.” That’s what we want to hear in medical education.
During the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, what were your most significant challenges from both a clinical and a personal standpoint?
I’m fortunate to practice at a place like Scripps, where there are many resources to look at what was happening with COVID-19. Clinically, we had to put a lot of things on hold, but we tried our best to keep our cancer patients in particular in the forefront of care. It has been a challenge, but fortunately we have been able to take care of patients after a brief timeout. Many of us remember the polio vaccine back in the 1950s. Having worked overseas and at missionary hospital where we had children die of measles because they were not vaccinated gave me a larger appreciation for the importance of vaccines. I recommend all young physicians who work with me to read, “The Great Influenza: The Story of the Deadliest Pandemic in History,” by John M. Barry, which recounts the 1918 flu epidemic.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
I don’t view what I do as work. Dr. Jones and Dr. Mohs continue to inspire me with what they accomplished during their careers. You have to love people and love patients. Every patient who comes to see me has a story, so I try to understand their story. One of the things I really enjoy is training the young fellows. We train three Mohs fellows per year at Scripps, and it’s a great challenge every day.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
Dermatology will continue to evolve just like all other medical specialties. We’re going to see a large growth in telemedicine, and immunotherapy is playing a key role in dermatologic oncology. What excites me the most in medicine is the young people who enter the field willing to contribute their lives to helping others.
Roe v. Wade reversal would rock ob.gyn. residencies
A decision by the U.S. Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade could have far-reaching impacts on residents in ob.gyn. medical programs across the country, from learning simple procedures like ultrasounds to how to manage miscarriages.
On Monday, Politico published a leaked initial draft majority opinion written by Justice Samuel Alito, which declares Roe unconstitutional. The actual opinion is due at the end of June. If all the justices keep their positions for that vote, the 1973 court case that legalized abortion rights in the United States would no longer keep states from banning the procedure before viability, which is defined as 24-26 weeks into a pregnancy.
Loss of federal protections provided by Roe would leave a patchwork of states where providers would have to change reproductive health practices. Medical schools in those states would also have to curtail any abortion care training, experts told this news organization.
Constance Bohon, MD, co-chair of the Legislative and Liability Committee of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), said: “As a profession, we are concerned about the possibility that there will be ob.gyn. residents who graduate without the experience and training needed to care for a patient who has complications from an abortion or a missed abortion. We are very concerned that without adequate training and access to care for these patients, the maternal mortality rate will rise.”
The loss of Roe “means that sadly, and realistically, many residents just won’t get the training, or we will need to think about mitigation strategies, like providing simulation training,” said Kavita Vinekar, MD, MPH, assistant clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “I can assure you that without access to abortion training, the quality of ob.gyn. training will absolutely suffer.”
Twenty-two states, including large swaths of the south and Midwest, already have laws that would go into effect immediately to ban abortion in the absence of Roe. Four states, including Florida, Montana, and Indiana, would likely ban abortion, according to an analysis from the Guttmacher Institute.
Almost 45% of ob.gyn. obstetrics and gynecology residency programs are in these states, totaling 2,638 residents as of 2022, according to a study published in April by researchers at the UCLA.
Most reproductive health care training lasts between 1-2 months during residency and includes instruction on ultrasounds, best practices in managing pregnancy complications, learning how to safely evacuate a uterus in the event of a stillbirth or miscarriage, and counseling for family planning options.
A glimpse at the future
The potential for a new reality is already playing out in Texas, where a law banning abortions after 6 weeks in pregnancy took effect last Sept. 1. The Ryan Program, a national initiative to teach abortion care to medical school residents, started a pilot to match resident physicians in Texas with hospital programs in other states without abortion restrictions.
The Ryan Program has matched over 40 residents since the law took effect, according to Jody Steinauer, MD, PhD, who oversees the Ryan Program at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco. Matching students is an arduous and timely process because students have hectic schedules, and state licensure and other regulatory issues must be worked out, she said.
“It will take a while to get systems in place to really support resident travel, and not every resident is going to be able to travel, so I’m just worried about the future impacts on patient care,” Dr. Steinauer told this news organization. “We have hundreds of residents who are not learning the skills they need, and they’re not going be able to provide evidence-based, patient-centered care.”
But Dr. Bohon expressed skepticism that the Ryan Program and other initiatives to provide training for travel residents would be sufficient. “Unfortunately, it is anticipated that this program will not be sufficient to provide training for all of the ob.gyn. residents who do not have access to abortion training because of the state where their residency is,” she said. “There are residency programs that have the capacity to have ob.gyns. get training at their programs, but there is a limited number of these positions available as well.”
She added that the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology is actively pursuing options to provide abortion training for residents for whom such training is not available.
Spillover effect
Health care professionals in states without restrictive abortion laws will also see an increase in patients seeking abortion-related care. This spike already is happening in New Mexico, which borders not only Texas, but Oklahoma and Arizona – states that have severely restricted abortion rights.
“It’s difficult in the states that will be overloaded with additional abortion care to then incorporate learners on top of that,” said Eve Espey, MD, MPH, distinguished professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Logistically, to fill that gap in care and train at the same time will be really challenging.”
Dr. Espey said the UNM Center for Reproductive Health has already seen patients from Texas who would likely fall under an exemption in that state’s law that allows abortions if a patient faces a medical emergency if the pregnancy continues.
“Providers are so afraid of these laws, and if they’re risk adverse, they’re always going to err on the side of not taking care of the patient if you think you can get in trouble,” Dr. Espey said, pointing to patients who presented with lethal fetal anomalies or ruptured fetal membranes early in pregnancy that might fall under the medical emergency exemption.
Dr. Steinauer with the Ryan Program said that many Texas residency program directors have told her they’ve heard from applicants who are giving low ranks to residency programs in the state.
“They’re saying, ‘if we want to be able to be trained as an ob.gyn., why would we want to go to a program with such significant restrictions?’” Dr. Steinauer said. “That is a real worry.”
Most ob.gyn. medical residency programs now provide built-in abortion training, which the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in 1995. A small majority do not. According to a 2020 research letter from the ACOG, about 11% of ob.gyn. residents said their programs hypothetically offer training without a clear process to obtain it, and 8% reported that their programs offered no such training at all.
Residents can also opt out of abortion training, although students increasingly are choosing to only opt out of certain parts, such as training for abortions provided later in pregnancies, according to Dr. Steinauer.
A looming ‘pipeline problem’
There were about 3,550 abortion service clinicians in 2020, 72% of whom were ob.gyns., followed by family medicine doctors and advanced practice registered nurses, according to research published in March in JAMA Internal Medicine. This number is likely not an accurate tally, however, because the authors queried a national medical claims database that did not include self-pay patients.
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a senior research scientist at The George Washington University Milken Institute School of Public Health, Washington, D.C., who led the study, said states could create policies to broaden access to abortion for patients and training for medical residents.
Those include expanding laws to allow advanced practice clinicians to provide abortion care, allowing state Medicaid programs to opt-in for abortion payment, and establishing abortion care continuing medical education requirements for state boards of medicine for both ob.gyn. and primary care.
“Providers that practice in those restricted states will not only stop providing care there but also won’t be able to train the next generation of workforce to be able to provide that care,” Dr. Strasser said. “It’s a pipeline problem.”
States also could encourage their medical residency programs to not hold slots open for students who want to opt out of abortion care training. The University of Washington, Seattle, in 2000 eliminated slots it had been holding open for opt-out students because the state does not have restrictions on abortion.
As abortion becomes increasingly restricted across the country, Dr. Strasser said, for medical schools in “a state that continues to make abortion available, it’s essentially their duty to make that training available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A decision by the U.S. Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade could have far-reaching impacts on residents in ob.gyn. medical programs across the country, from learning simple procedures like ultrasounds to how to manage miscarriages.
On Monday, Politico published a leaked initial draft majority opinion written by Justice Samuel Alito, which declares Roe unconstitutional. The actual opinion is due at the end of June. If all the justices keep their positions for that vote, the 1973 court case that legalized abortion rights in the United States would no longer keep states from banning the procedure before viability, which is defined as 24-26 weeks into a pregnancy.
Loss of federal protections provided by Roe would leave a patchwork of states where providers would have to change reproductive health practices. Medical schools in those states would also have to curtail any abortion care training, experts told this news organization.
Constance Bohon, MD, co-chair of the Legislative and Liability Committee of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), said: “As a profession, we are concerned about the possibility that there will be ob.gyn. residents who graduate without the experience and training needed to care for a patient who has complications from an abortion or a missed abortion. We are very concerned that without adequate training and access to care for these patients, the maternal mortality rate will rise.”
The loss of Roe “means that sadly, and realistically, many residents just won’t get the training, or we will need to think about mitigation strategies, like providing simulation training,” said Kavita Vinekar, MD, MPH, assistant clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “I can assure you that without access to abortion training, the quality of ob.gyn. training will absolutely suffer.”
Twenty-two states, including large swaths of the south and Midwest, already have laws that would go into effect immediately to ban abortion in the absence of Roe. Four states, including Florida, Montana, and Indiana, would likely ban abortion, according to an analysis from the Guttmacher Institute.
Almost 45% of ob.gyn. obstetrics and gynecology residency programs are in these states, totaling 2,638 residents as of 2022, according to a study published in April by researchers at the UCLA.
Most reproductive health care training lasts between 1-2 months during residency and includes instruction on ultrasounds, best practices in managing pregnancy complications, learning how to safely evacuate a uterus in the event of a stillbirth or miscarriage, and counseling for family planning options.
A glimpse at the future
The potential for a new reality is already playing out in Texas, where a law banning abortions after 6 weeks in pregnancy took effect last Sept. 1. The Ryan Program, a national initiative to teach abortion care to medical school residents, started a pilot to match resident physicians in Texas with hospital programs in other states without abortion restrictions.
The Ryan Program has matched over 40 residents since the law took effect, according to Jody Steinauer, MD, PhD, who oversees the Ryan Program at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco. Matching students is an arduous and timely process because students have hectic schedules, and state licensure and other regulatory issues must be worked out, she said.
“It will take a while to get systems in place to really support resident travel, and not every resident is going to be able to travel, so I’m just worried about the future impacts on patient care,” Dr. Steinauer told this news organization. “We have hundreds of residents who are not learning the skills they need, and they’re not going be able to provide evidence-based, patient-centered care.”
But Dr. Bohon expressed skepticism that the Ryan Program and other initiatives to provide training for travel residents would be sufficient. “Unfortunately, it is anticipated that this program will not be sufficient to provide training for all of the ob.gyn. residents who do not have access to abortion training because of the state where their residency is,” she said. “There are residency programs that have the capacity to have ob.gyns. get training at their programs, but there is a limited number of these positions available as well.”
She added that the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology is actively pursuing options to provide abortion training for residents for whom such training is not available.
Spillover effect
Health care professionals in states without restrictive abortion laws will also see an increase in patients seeking abortion-related care. This spike already is happening in New Mexico, which borders not only Texas, but Oklahoma and Arizona – states that have severely restricted abortion rights.
“It’s difficult in the states that will be overloaded with additional abortion care to then incorporate learners on top of that,” said Eve Espey, MD, MPH, distinguished professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Logistically, to fill that gap in care and train at the same time will be really challenging.”
Dr. Espey said the UNM Center for Reproductive Health has already seen patients from Texas who would likely fall under an exemption in that state’s law that allows abortions if a patient faces a medical emergency if the pregnancy continues.
“Providers are so afraid of these laws, and if they’re risk adverse, they’re always going to err on the side of not taking care of the patient if you think you can get in trouble,” Dr. Espey said, pointing to patients who presented with lethal fetal anomalies or ruptured fetal membranes early in pregnancy that might fall under the medical emergency exemption.
Dr. Steinauer with the Ryan Program said that many Texas residency program directors have told her they’ve heard from applicants who are giving low ranks to residency programs in the state.
“They’re saying, ‘if we want to be able to be trained as an ob.gyn., why would we want to go to a program with such significant restrictions?’” Dr. Steinauer said. “That is a real worry.”
Most ob.gyn. medical residency programs now provide built-in abortion training, which the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in 1995. A small majority do not. According to a 2020 research letter from the ACOG, about 11% of ob.gyn. residents said their programs hypothetically offer training without a clear process to obtain it, and 8% reported that their programs offered no such training at all.
Residents can also opt out of abortion training, although students increasingly are choosing to only opt out of certain parts, such as training for abortions provided later in pregnancies, according to Dr. Steinauer.
A looming ‘pipeline problem’
There were about 3,550 abortion service clinicians in 2020, 72% of whom were ob.gyns., followed by family medicine doctors and advanced practice registered nurses, according to research published in March in JAMA Internal Medicine. This number is likely not an accurate tally, however, because the authors queried a national medical claims database that did not include self-pay patients.
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a senior research scientist at The George Washington University Milken Institute School of Public Health, Washington, D.C., who led the study, said states could create policies to broaden access to abortion for patients and training for medical residents.
Those include expanding laws to allow advanced practice clinicians to provide abortion care, allowing state Medicaid programs to opt-in for abortion payment, and establishing abortion care continuing medical education requirements for state boards of medicine for both ob.gyn. and primary care.
“Providers that practice in those restricted states will not only stop providing care there but also won’t be able to train the next generation of workforce to be able to provide that care,” Dr. Strasser said. “It’s a pipeline problem.”
States also could encourage their medical residency programs to not hold slots open for students who want to opt out of abortion care training. The University of Washington, Seattle, in 2000 eliminated slots it had been holding open for opt-out students because the state does not have restrictions on abortion.
As abortion becomes increasingly restricted across the country, Dr. Strasser said, for medical schools in “a state that continues to make abortion available, it’s essentially their duty to make that training available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A decision by the U.S. Supreme Court to overturn Roe v. Wade could have far-reaching impacts on residents in ob.gyn. medical programs across the country, from learning simple procedures like ultrasounds to how to manage miscarriages.
On Monday, Politico published a leaked initial draft majority opinion written by Justice Samuel Alito, which declares Roe unconstitutional. The actual opinion is due at the end of June. If all the justices keep their positions for that vote, the 1973 court case that legalized abortion rights in the United States would no longer keep states from banning the procedure before viability, which is defined as 24-26 weeks into a pregnancy.
Loss of federal protections provided by Roe would leave a patchwork of states where providers would have to change reproductive health practices. Medical schools in those states would also have to curtail any abortion care training, experts told this news organization.
Constance Bohon, MD, co-chair of the Legislative and Liability Committee of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), said: “As a profession, we are concerned about the possibility that there will be ob.gyn. residents who graduate without the experience and training needed to care for a patient who has complications from an abortion or a missed abortion. We are very concerned that without adequate training and access to care for these patients, the maternal mortality rate will rise.”
The loss of Roe “means that sadly, and realistically, many residents just won’t get the training, or we will need to think about mitigation strategies, like providing simulation training,” said Kavita Vinekar, MD, MPH, assistant clinical professor in the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “I can assure you that without access to abortion training, the quality of ob.gyn. training will absolutely suffer.”
Twenty-two states, including large swaths of the south and Midwest, already have laws that would go into effect immediately to ban abortion in the absence of Roe. Four states, including Florida, Montana, and Indiana, would likely ban abortion, according to an analysis from the Guttmacher Institute.
Almost 45% of ob.gyn. obstetrics and gynecology residency programs are in these states, totaling 2,638 residents as of 2022, according to a study published in April by researchers at the UCLA.
Most reproductive health care training lasts between 1-2 months during residency and includes instruction on ultrasounds, best practices in managing pregnancy complications, learning how to safely evacuate a uterus in the event of a stillbirth or miscarriage, and counseling for family planning options.
A glimpse at the future
The potential for a new reality is already playing out in Texas, where a law banning abortions after 6 weeks in pregnancy took effect last Sept. 1. The Ryan Program, a national initiative to teach abortion care to medical school residents, started a pilot to match resident physicians in Texas with hospital programs in other states without abortion restrictions.
The Ryan Program has matched over 40 residents since the law took effect, according to Jody Steinauer, MD, PhD, who oversees the Ryan Program at the Bixby Center for Global Reproductive Health at the University of California, San Francisco. Matching students is an arduous and timely process because students have hectic schedules, and state licensure and other regulatory issues must be worked out, she said.
“It will take a while to get systems in place to really support resident travel, and not every resident is going to be able to travel, so I’m just worried about the future impacts on patient care,” Dr. Steinauer told this news organization. “We have hundreds of residents who are not learning the skills they need, and they’re not going be able to provide evidence-based, patient-centered care.”
But Dr. Bohon expressed skepticism that the Ryan Program and other initiatives to provide training for travel residents would be sufficient. “Unfortunately, it is anticipated that this program will not be sufficient to provide training for all of the ob.gyn. residents who do not have access to abortion training because of the state where their residency is,” she said. “There are residency programs that have the capacity to have ob.gyns. get training at their programs, but there is a limited number of these positions available as well.”
She added that the Council on Resident Education in Obstetrics and Gynecology is actively pursuing options to provide abortion training for residents for whom such training is not available.
Spillover effect
Health care professionals in states without restrictive abortion laws will also see an increase in patients seeking abortion-related care. This spike already is happening in New Mexico, which borders not only Texas, but Oklahoma and Arizona – states that have severely restricted abortion rights.
“It’s difficult in the states that will be overloaded with additional abortion care to then incorporate learners on top of that,” said Eve Espey, MD, MPH, distinguished professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “Logistically, to fill that gap in care and train at the same time will be really challenging.”
Dr. Espey said the UNM Center for Reproductive Health has already seen patients from Texas who would likely fall under an exemption in that state’s law that allows abortions if a patient faces a medical emergency if the pregnancy continues.
“Providers are so afraid of these laws, and if they’re risk adverse, they’re always going to err on the side of not taking care of the patient if you think you can get in trouble,” Dr. Espey said, pointing to patients who presented with lethal fetal anomalies or ruptured fetal membranes early in pregnancy that might fall under the medical emergency exemption.
Dr. Steinauer with the Ryan Program said that many Texas residency program directors have told her they’ve heard from applicants who are giving low ranks to residency programs in the state.
“They’re saying, ‘if we want to be able to be trained as an ob.gyn., why would we want to go to a program with such significant restrictions?’” Dr. Steinauer said. “That is a real worry.”
Most ob.gyn. medical residency programs now provide built-in abortion training, which the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education mandated in 1995. A small majority do not. According to a 2020 research letter from the ACOG, about 11% of ob.gyn. residents said their programs hypothetically offer training without a clear process to obtain it, and 8% reported that their programs offered no such training at all.
Residents can also opt out of abortion training, although students increasingly are choosing to only opt out of certain parts, such as training for abortions provided later in pregnancies, according to Dr. Steinauer.
A looming ‘pipeline problem’
There were about 3,550 abortion service clinicians in 2020, 72% of whom were ob.gyns., followed by family medicine doctors and advanced practice registered nurses, according to research published in March in JAMA Internal Medicine. This number is likely not an accurate tally, however, because the authors queried a national medical claims database that did not include self-pay patients.
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a senior research scientist at The George Washington University Milken Institute School of Public Health, Washington, D.C., who led the study, said states could create policies to broaden access to abortion for patients and training for medical residents.
Those include expanding laws to allow advanced practice clinicians to provide abortion care, allowing state Medicaid programs to opt-in for abortion payment, and establishing abortion care continuing medical education requirements for state boards of medicine for both ob.gyn. and primary care.
“Providers that practice in those restricted states will not only stop providing care there but also won’t be able to train the next generation of workforce to be able to provide that care,” Dr. Strasser said. “It’s a pipeline problem.”
States also could encourage their medical residency programs to not hold slots open for students who want to opt out of abortion care training. The University of Washington, Seattle, in 2000 eliminated slots it had been holding open for opt-out students because the state does not have restrictions on abortion.
As abortion becomes increasingly restricted across the country, Dr. Strasser said, for medical schools in “a state that continues to make abortion available, it’s essentially their duty to make that training available.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

