User login
Machine learning–derived risk score predicts heart failure risk in diabetes patients
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
PHILADELPHIA – For patients with high-risk diabetes, a novel, machine learning–derived risk score based on 10 common clinical variables can identify those facing a heart failure risk of up to nearly 20% over the ensuing 5 years, an investigator said at the annual meeting of the Heart Failure Society of America.
The risk score, dubbed WATCH-DM, has greater accuracy in predicting incident heart failure than traditional risk-based models, and requires no specific cardiovascular biomarkers or imaging, according to Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and faculty at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
The tool may help inform risk-based monitoring and introduction of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, which have been shown in multiple clinical trials to prevent heart failure in at-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), Dr. Vaduganathan said.
“Patients identified at high risk based on WATCH-DM should be strongly considered for initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical practice,” Dr. Vaduganathan said in an interview.
WATCH-DM is available online at cvriskscores.com. Work is underway to integrate the tool into electronic health record systems at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “I expect that to be launched in the next year,” he said.
The WATCH-DM score was developed based on data from the ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes) trial, including 8,756 T2DM patients with inadequate glycemic control at high cardiovascular risk and no heart failure at baseline.
Starting with 147 variables, the investigators used a decision-tree machine learning approach to identify predictors of heart failure.
“What machine learning does is automate the variable selection process, as a form of artificial intelligence,” Dr. Vaduganathan said.
The WATCH-DM risk score was based on the 10 best-performing predictors as selected by machine learning, including body mass index, age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, serum creatinine, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, QRS duration, prior myocardial infarction, and prior coronary artery bypass grafting.
The 5-year risk of heart failure was just 1.1% for patients with WATCH-DM scores in the lowest quintile, increasing in a graded fashion to nearly 20% (17.4%) in the highest quintile, study results show.
Findings of the study were simultaneously published in the journal Diabetes Care.
Dr. Vaduganathan said he is supported by an award from Harvard Catalyst. He provided disclosures related to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Baxter Healthcare, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim (advisory boards), and with Novartis and the National Institutes of Health (participation on clinical endpoint committees).
SOURCE: HFSA 2019; Segar MW, Vaduganathan M et al. Diabetes Care. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0587.
REPORTING FROM HFSA 2019
Hyponatremia almost as common with spironolactone as chlorthalidone
NEW ORLEANS – .
The investigators reviewed hypertension patients whose treatment regimens included one diuretic. Forty on chlorthalidone developed hyponatremia – defined as a serum sodium below 133 mEq/L – across 1,322 prescriptions, for an incidence of 3.03%. There were 31 cases across 1,159 spironolactone prescriptions, an incidence of 2.67%.
Among 14 patients in a substudy who discontinued chlorthalidone after developing hyponatremia at a mean of about 2 weeks, six (43%) subsequently developed hyponatremia on spironolactone, also at an average of about 2 weeks.
The findings suggest that spironolactone is more likely than generally thought to cause hyponatremia, a potentially severe complication of diuretics, and that hyponatremia on chlorthalidone increases the risk, said lead investigator Faris Matanes, MD, a hypertension researcher at the university.
“We used to think” that hyponatremia on spironolactone was “very unlikely, but actually it’s not; the incidence is really close to chlorthalidone,” a well-known cause, and “if a patient develops hyponatremia on chlorthalidone, we should be more careful about giving them spironolactone,” he said.
Almost half the spironolactone cases were on 25 mg/day or less, and over a quarter of the chlorthalidone cases were on 12.5 mg/day. Of the 154 hyponatremia cases across 10,660 hydrochlorothiazide prescriptions (1.44%), over a third were taking 12.5 mg/day or less.
Overall, hyponatremia was diagnosed at a mean of 40.4 days, but sometimes after 2 or more months of treatment.
The findings “mean that even if we start patients on a low dose, we can’t stop checking after one or two normal sodium levels.” Measurements need to be ongoing, Dr. Matanes said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
He and his team wanted to get around the limitations of previous diuretic hyponatremia studies, including use of more than one diuretic, markedly poor kidney function, and other confounders. To that end, the study was limited to outpatients on a single diuretic who had normal sodium levels both before and after their hyponatremic episode, and estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) of at least 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Exclusion criteria included heart failure, cirrhosis, and adrenal insufficiency.
Older white people with lower baseline sodium and eGFR values were most at risk. Contrary to previous reports, hyponatremia wasn’t more likely in men.
The mean sodium level during an episode was 130.2 mEq/L; the majority of patients eventually normalized and continued treatment.
Subjects in the main study were a mean of 66 years old, about two-thirds were white, and about 60% were women. The baseline eGFR was 77.2 mL/min/1.73 m2, and baseline sodium level 135.8 mEq/L.
All but one of the 14 substudy patients were women. Those who became hyponatremic when switched to spironolactone were older (mean 74.2 versus 65.8 years), had lower baseline eGFRs (63.7 versus 69.7 mL/min/1.73 m2), and were more likely to be white, but the differences were not statistically significant.
There was no external funding, and the investigators didn’t have any industry disclosures.
SOURCE: Matanes F et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstracts 187 and 174.
NEW ORLEANS – .
The investigators reviewed hypertension patients whose treatment regimens included one diuretic. Forty on chlorthalidone developed hyponatremia – defined as a serum sodium below 133 mEq/L – across 1,322 prescriptions, for an incidence of 3.03%. There were 31 cases across 1,159 spironolactone prescriptions, an incidence of 2.67%.
Among 14 patients in a substudy who discontinued chlorthalidone after developing hyponatremia at a mean of about 2 weeks, six (43%) subsequently developed hyponatremia on spironolactone, also at an average of about 2 weeks.
The findings suggest that spironolactone is more likely than generally thought to cause hyponatremia, a potentially severe complication of diuretics, and that hyponatremia on chlorthalidone increases the risk, said lead investigator Faris Matanes, MD, a hypertension researcher at the university.
“We used to think” that hyponatremia on spironolactone was “very unlikely, but actually it’s not; the incidence is really close to chlorthalidone,” a well-known cause, and “if a patient develops hyponatremia on chlorthalidone, we should be more careful about giving them spironolactone,” he said.
Almost half the spironolactone cases were on 25 mg/day or less, and over a quarter of the chlorthalidone cases were on 12.5 mg/day. Of the 154 hyponatremia cases across 10,660 hydrochlorothiazide prescriptions (1.44%), over a third were taking 12.5 mg/day or less.
Overall, hyponatremia was diagnosed at a mean of 40.4 days, but sometimes after 2 or more months of treatment.
The findings “mean that even if we start patients on a low dose, we can’t stop checking after one or two normal sodium levels.” Measurements need to be ongoing, Dr. Matanes said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
He and his team wanted to get around the limitations of previous diuretic hyponatremia studies, including use of more than one diuretic, markedly poor kidney function, and other confounders. To that end, the study was limited to outpatients on a single diuretic who had normal sodium levels both before and after their hyponatremic episode, and estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) of at least 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Exclusion criteria included heart failure, cirrhosis, and adrenal insufficiency.
Older white people with lower baseline sodium and eGFR values were most at risk. Contrary to previous reports, hyponatremia wasn’t more likely in men.
The mean sodium level during an episode was 130.2 mEq/L; the majority of patients eventually normalized and continued treatment.
Subjects in the main study were a mean of 66 years old, about two-thirds were white, and about 60% were women. The baseline eGFR was 77.2 mL/min/1.73 m2, and baseline sodium level 135.8 mEq/L.
All but one of the 14 substudy patients were women. Those who became hyponatremic when switched to spironolactone were older (mean 74.2 versus 65.8 years), had lower baseline eGFRs (63.7 versus 69.7 mL/min/1.73 m2), and were more likely to be white, but the differences were not statistically significant.
There was no external funding, and the investigators didn’t have any industry disclosures.
SOURCE: Matanes F et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstracts 187 and 174.
NEW ORLEANS – .
The investigators reviewed hypertension patients whose treatment regimens included one diuretic. Forty on chlorthalidone developed hyponatremia – defined as a serum sodium below 133 mEq/L – across 1,322 prescriptions, for an incidence of 3.03%. There were 31 cases across 1,159 spironolactone prescriptions, an incidence of 2.67%.
Among 14 patients in a substudy who discontinued chlorthalidone after developing hyponatremia at a mean of about 2 weeks, six (43%) subsequently developed hyponatremia on spironolactone, also at an average of about 2 weeks.
The findings suggest that spironolactone is more likely than generally thought to cause hyponatremia, a potentially severe complication of diuretics, and that hyponatremia on chlorthalidone increases the risk, said lead investigator Faris Matanes, MD, a hypertension researcher at the university.
“We used to think” that hyponatremia on spironolactone was “very unlikely, but actually it’s not; the incidence is really close to chlorthalidone,” a well-known cause, and “if a patient develops hyponatremia on chlorthalidone, we should be more careful about giving them spironolactone,” he said.
Almost half the spironolactone cases were on 25 mg/day or less, and over a quarter of the chlorthalidone cases were on 12.5 mg/day. Of the 154 hyponatremia cases across 10,660 hydrochlorothiazide prescriptions (1.44%), over a third were taking 12.5 mg/day or less.
Overall, hyponatremia was diagnosed at a mean of 40.4 days, but sometimes after 2 or more months of treatment.
The findings “mean that even if we start patients on a low dose, we can’t stop checking after one or two normal sodium levels.” Measurements need to be ongoing, Dr. Matanes said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
He and his team wanted to get around the limitations of previous diuretic hyponatremia studies, including use of more than one diuretic, markedly poor kidney function, and other confounders. To that end, the study was limited to outpatients on a single diuretic who had normal sodium levels both before and after their hyponatremic episode, and estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) of at least 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Exclusion criteria included heart failure, cirrhosis, and adrenal insufficiency.
Older white people with lower baseline sodium and eGFR values were most at risk. Contrary to previous reports, hyponatremia wasn’t more likely in men.
The mean sodium level during an episode was 130.2 mEq/L; the majority of patients eventually normalized and continued treatment.
Subjects in the main study were a mean of 66 years old, about two-thirds were white, and about 60% were women. The baseline eGFR was 77.2 mL/min/1.73 m2, and baseline sodium level 135.8 mEq/L.
All but one of the 14 substudy patients were women. Those who became hyponatremic when switched to spironolactone were older (mean 74.2 versus 65.8 years), had lower baseline eGFRs (63.7 versus 69.7 mL/min/1.73 m2), and were more likely to be white, but the differences were not statistically significant.
There was no external funding, and the investigators didn’t have any industry disclosures.
SOURCE: Matanes F et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstracts 187 and 174.
REPORTING FROM JOINT HYPERTENSION 2019
ABPM rarely used for hypertension management in United States
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a University of Florida, Gainesville, analysis of claims data for almost 4 million people.
“With each iteration, evidence-based guidelines have more strongly recommended out-of-office blood pressure measurement, but it’s basically had no impact. If we are going to continue to recommend this aggressively, we need to put some pressure on both payers and providers,” said lead investigator Steven M. Smith, PharmD, of the department of pharmacotherapy & translational research, associate director of the Center for Integrative Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases at the university.
“A number of studies show that ambulatory blood pressure monitoring [ABPM] is more strongly predictive of outcomes than office pressure.” It’s “considered the gold standard for hypertension,” he said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension
The reason is that ABPM gives a continual reading of blood pressure over 24 hours, not just an office snapshot, and can do things that office measurements cannot, including ruling out white coat hypertension, identifying masked hypertension, and checking nocturnal dipping and morning surge, both of which are related to cardiovascular risk.
Although common in Canada and Europe, it’s no secret that ABPM hasn’t caught on in the United States. The goal of Dr. Smith’s work was to help quantify the situation.
Using Truven Health Analytics commercial insurance claims data, he and his team identified 3,378,645 adults starting their first hypertension medication and 335,200 starting their fourth from 2008 to 2017. They looked for ABPM claims in the previous 6 months as well as the month after patients started their new medication. The idea was to assess ABPM use in both new and resistant hypertensive patients.
ABPM claims were submitted for 0.15% of patients starting their first drug in 2008, rising to 0.3% in 2017. ABPM was used mostly before treatment initiation.
ABPM use actually declined among resistant patients from about 0.27% in 2008 to about 0.12% in 2017. Use was split about evenly before and after they started their fourth medication.
About 80% of claims – generally for interpreting ABPM results, not the upfront cost of the machine – were paid. Claims submitted tended to come from more high-end plans. Reimbursement rates were similar for more bargain plans, but there were many fewer claims submitted, Dr. Smith said.
He thought plans would at least follow Medicare’s reimbursement policy, which, at the time of the study, covered ABPM to rule out white coat hypertension, “but they didn’t seem to,” he said. Medicare recently added coverage for suspected masked hypertension.
The study doesn’t address why uptake is so low in the United States, but outside the world of hypertension specialists, “physicians don’t see a value in it. They don’t recognize what they would get from ABPM and how that would change what they do,” in part because treatment is currently based on office measurements. There’s also probably uncertainty about how to interpret the results, Dr. Smith said.
Standardization across payers about what they’ll cover and for whom would probably help, he added.
Findings in the study were similar for home blood pressure monitoring, but probably not an accurate gauge of use. Patients mostly buy their own devices and report the results to their physician, without getting insurance involved, he said.
There was no industry funding, and the investigators didn’t have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith SM et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstract P2067.
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a University of Florida, Gainesville, analysis of claims data for almost 4 million people.
“With each iteration, evidence-based guidelines have more strongly recommended out-of-office blood pressure measurement, but it’s basically had no impact. If we are going to continue to recommend this aggressively, we need to put some pressure on both payers and providers,” said lead investigator Steven M. Smith, PharmD, of the department of pharmacotherapy & translational research, associate director of the Center for Integrative Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases at the university.
“A number of studies show that ambulatory blood pressure monitoring [ABPM] is more strongly predictive of outcomes than office pressure.” It’s “considered the gold standard for hypertension,” he said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension
The reason is that ABPM gives a continual reading of blood pressure over 24 hours, not just an office snapshot, and can do things that office measurements cannot, including ruling out white coat hypertension, identifying masked hypertension, and checking nocturnal dipping and morning surge, both of which are related to cardiovascular risk.
Although common in Canada and Europe, it’s no secret that ABPM hasn’t caught on in the United States. The goal of Dr. Smith’s work was to help quantify the situation.
Using Truven Health Analytics commercial insurance claims data, he and his team identified 3,378,645 adults starting their first hypertension medication and 335,200 starting their fourth from 2008 to 2017. They looked for ABPM claims in the previous 6 months as well as the month after patients started their new medication. The idea was to assess ABPM use in both new and resistant hypertensive patients.
ABPM claims were submitted for 0.15% of patients starting their first drug in 2008, rising to 0.3% in 2017. ABPM was used mostly before treatment initiation.
ABPM use actually declined among resistant patients from about 0.27% in 2008 to about 0.12% in 2017. Use was split about evenly before and after they started their fourth medication.
About 80% of claims – generally for interpreting ABPM results, not the upfront cost of the machine – were paid. Claims submitted tended to come from more high-end plans. Reimbursement rates were similar for more bargain plans, but there were many fewer claims submitted, Dr. Smith said.
He thought plans would at least follow Medicare’s reimbursement policy, which, at the time of the study, covered ABPM to rule out white coat hypertension, “but they didn’t seem to,” he said. Medicare recently added coverage for suspected masked hypertension.
The study doesn’t address why uptake is so low in the United States, but outside the world of hypertension specialists, “physicians don’t see a value in it. They don’t recognize what they would get from ABPM and how that would change what they do,” in part because treatment is currently based on office measurements. There’s also probably uncertainty about how to interpret the results, Dr. Smith said.
Standardization across payers about what they’ll cover and for whom would probably help, he added.
Findings in the study were similar for home blood pressure monitoring, but probably not an accurate gauge of use. Patients mostly buy their own devices and report the results to their physician, without getting insurance involved, he said.
There was no industry funding, and the investigators didn’t have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith SM et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstract P2067.
NEW ORLEANS – , according to a University of Florida, Gainesville, analysis of claims data for almost 4 million people.
“With each iteration, evidence-based guidelines have more strongly recommended out-of-office blood pressure measurement, but it’s basically had no impact. If we are going to continue to recommend this aggressively, we need to put some pressure on both payers and providers,” said lead investigator Steven M. Smith, PharmD, of the department of pharmacotherapy & translational research, associate director of the Center for Integrative Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases at the university.
“A number of studies show that ambulatory blood pressure monitoring [ABPM] is more strongly predictive of outcomes than office pressure.” It’s “considered the gold standard for hypertension,” he said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension
The reason is that ABPM gives a continual reading of blood pressure over 24 hours, not just an office snapshot, and can do things that office measurements cannot, including ruling out white coat hypertension, identifying masked hypertension, and checking nocturnal dipping and morning surge, both of which are related to cardiovascular risk.
Although common in Canada and Europe, it’s no secret that ABPM hasn’t caught on in the United States. The goal of Dr. Smith’s work was to help quantify the situation.
Using Truven Health Analytics commercial insurance claims data, he and his team identified 3,378,645 adults starting their first hypertension medication and 335,200 starting their fourth from 2008 to 2017. They looked for ABPM claims in the previous 6 months as well as the month after patients started their new medication. The idea was to assess ABPM use in both new and resistant hypertensive patients.
ABPM claims were submitted for 0.15% of patients starting their first drug in 2008, rising to 0.3% in 2017. ABPM was used mostly before treatment initiation.
ABPM use actually declined among resistant patients from about 0.27% in 2008 to about 0.12% in 2017. Use was split about evenly before and after they started their fourth medication.
About 80% of claims – generally for interpreting ABPM results, not the upfront cost of the machine – were paid. Claims submitted tended to come from more high-end plans. Reimbursement rates were similar for more bargain plans, but there were many fewer claims submitted, Dr. Smith said.
He thought plans would at least follow Medicare’s reimbursement policy, which, at the time of the study, covered ABPM to rule out white coat hypertension, “but they didn’t seem to,” he said. Medicare recently added coverage for suspected masked hypertension.
The study doesn’t address why uptake is so low in the United States, but outside the world of hypertension specialists, “physicians don’t see a value in it. They don’t recognize what they would get from ABPM and how that would change what they do,” in part because treatment is currently based on office measurements. There’s also probably uncertainty about how to interpret the results, Dr. Smith said.
Standardization across payers about what they’ll cover and for whom would probably help, he added.
Findings in the study were similar for home blood pressure monitoring, but probably not an accurate gauge of use. Patients mostly buy their own devices and report the results to their physician, without getting insurance involved, he said.
There was no industry funding, and the investigators didn’t have any disclosures.
SOURCE: Smith SM et al. Joint Hypertension 2019, Abstract P2067.
REPORTING FROM JOINT HYPERTENSION 2019
Reversal agents for direct-acting oral anticoagulants
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3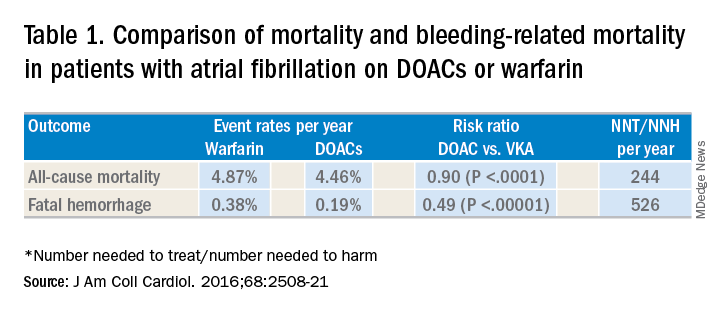
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4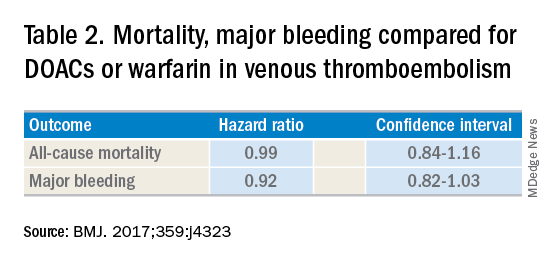
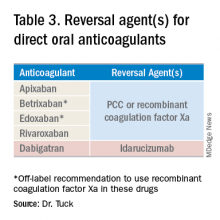
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
Summary of guidelines published in the Journal of Hospital Medicine
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
When on call for admissions, a hospitalist receives a request from a colleague to admit an octogenarian man with an acute uncomplicated deep vein thrombosis to start heparin, bridging to warfarin. The patient has no evidence of postphlebitic syndrome, pulmonary embolism, or right-sided heart strain. The hospitalist asks her colleague if he had considered treating the patient in the ambulatory setting using a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC). After all, this would save the patient an unnecessary hospitalization, weekly international normalized ratio checks, and other important lifestyle changes. In response, the colleague voices concern that the “new drugs don’t have antidotes.”
DOACs have several benefits over vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) and heparins. DOACs have quicker onset of action, can be taken by mouth, in general do not require dosage adjustment, and have fewer dietary and lifestyle modifications, compared with VKAs and heparins. In atrial fibrillation, DOACs have been shown to have lower all-cause and bleeding-related mortality than warfarin (see Table 1).1 Observational studies also suggest less risk of major bleeding with DOACs over warfarin but no difference in overall mortality when used to treat venous thromboembolism (see Table 2).2 Because of these combined advantages, DOACs are increasingly prescribed, accounting for approximately half of all oral anticoagulant prescriptions in 2014.3
Although DOACs have been shown to be as good if not superior to VKAs and heparins in these circumstances, there are situations where a DOAC should not be used. There is limited data on the safety of DOACs in patients with mechanical heart valves, liver failure, and chronic kidney disease with a creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min.4 Therefore, warfarin is still the preferred agent in these settings. There is some data that apixaban may be safe in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than 10 mL/min, but long-term safety studies have not been performed in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.5 Finally, in patients requiring concomitant inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein or cytochrome P450 enzymes like antiepileptics and protease inhibitors, VKAs and heparins are favored.4
Notwithstanding their advantages, when DOACs first hit the market there were concerns that reversal agents were not available. In the August issue of the Journal of Hospital Medicine’s Clinical Guideline Highlights for the Hospitalist, Emily Gottenborg, MD, and Gregory Misky, MD, summarized guideline recommendations for reversal of the newer agents.6 This includes use of idarucizumab for patients on dabigatran and use of prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC) or recombinant coagulation factor Xa (andexanet alfa) for patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding.
Idarucizumab is a monoclonal antibody developed to reverse the effects of dabigatran, the only DOAC that directly inhibits thrombin. In 2017, researchers reported on a cohort of subjects receiving idarucizumab for uncontrolled bleeding or who were on dabigatran and about to undergo an urgent procedure.7 Of those with uncontrolled bleeding, two-thirds had confirmed bleeding cessation within 24 hours. Periprocedural hemostasis was achieved in 93.4% of patients undergoing urgent procedures. However, it should be noted that use of idarucizumab conferred an increase risk (6.3%) of thrombosis within 90 days. Based on these findings, guidelines recommend use of idarucizumab in patients experiencing life-threatening bleeding, balanced against the risk of thrombosis.8
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding in patients on apixaban or rivaroxaban.9 The approval came after a study by the ANNEXA-4 investigators showed that recombinant coagulation factor Xa quickly and effectively achieved hemostasis.10 Full study results were published in April 2019, demonstrating 82% of patients receiving the drug attained clinical hemostasis.11 However, as with idarucizumab, up to 10% of patients had a thrombotic event in the follow-up period. Use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa for treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to betrixaban and edoxaban is considered off label but is recommended by guidelines.8 Studies on investigational reversal agents for betrixaban and edoxaban are ongoing.
Both unactivated and activated PCC contain clotting factor X. Their use to control bleeding related to DOAC use is based on observational studies. In a systematic review of the nonrandomized studies, the efficacy of PCC to stem major bleeding was 69% and the risk for thromboembolism was 4%.12 There are no head-to-head studies comparing use of recombinant coagulation factor Xa and PCC. Therefore, guidelines are to use either recombinant factor Xa or PCC for the treatment of life-threatening bleeding related to DOAC use.7
As thrombosis risk heightens after use of any reversal agent, the recommendations are to resume anticoagulation within 90 days if the patient is at moderate or high risk for recurrent thromboembolism.8
After discussion with the hospitalist about the new agents available to reverse anticoagulation, the colleague decided to place the patient on a DOAC and keep the patient in his nursing home. Thankfully, the patient did not thereafter experience sustained bleeding necessitating use of these reversal agents. More importantly for the patient, he was able to stay in the comfort of his home.
Dr. Tuck is associate section chief for hospital medicine at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Washington, D.C.
References
1. Gómez-Outes A et al. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508-21.
2. Jun M et al. Comparative safety of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin in venous thromboembolism: multicentre, population-based, observational study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4323.
3. Barnes GD et al. National trends in ambulatory oral anticoagulant use. Am J Med. 2015;128:(1300-5).e2.
4. Reddy P et al. Practical approach to VTE management in hospitalized patients. Am J Ther. 2017;24(4):e442-67.
5. Kimachi M et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for preventing stroke and systemic embolic events among atrial fibrillation patients with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 6;11:CD011373.
6. Gottenborg E et al. Clinical guideline highlights for the hospitalist: The management of anticoagulation in the hospitalized adult. J Hosp Med. 2019; 14(8):499-500.
7. Pollack CV Jr et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal – full cohort analysis. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(5):431-41.
8. Witt DM et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Optimal management of anticoagulation therapy. Blood Adv. 2018;2(22):3257-91.
9. Malarky M et al. FDA accelerated approval letter. Retrieved July 15, 2019. https://www.fda.gov/media/113285/download
10. Connolly SJ et al. Andexanet alfa for acute major bleeding associated with factor Xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(12):1131-41.
11. Connolly SJ et al. Full study report of andexanet alfa for bleeding associated with factor xa inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(14):1326-35.
12. Piran S et al. Management of direct factor Xa inhibitor–related major bleeding with prothrombin complex concentrate: A meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019;3(2):158-67.
Early infusion of mononuclear cells may benefit stroke patients
, results from a single-arm, phase I trial demonstrated. Unlike autologous mesenchymal stem cells, mononuclear cells (MNCs) do not require passage in culture, which allows for testing in the early poststroke time therapy window.
Bone marrow MNCs are attractive in regenerative medicine studies because they can be rapidly isolated; are enriched with hematopoietic, mesenchymal, and endothelial progenitor cells; and permit autologous applications. “The regenerative potential of bone marrow–derived MNCs is attributed to various mechanisms that impact stroke recovery,” researchers led by Sean I. Savitz, MD, wrote in a study published online Sept. 17 in Stem Cells. “These cells migrate to the site of injury, release cytokines and other trophic factors, decrease proinflammatory and upregulate anti-inflammatory pathways, and enhance angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis.”
For the trial, Dr. Savitz, MD, director of the Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease at UTHealth, Houston, and colleagues recruited 25 patients to receive an IV dose of their own bone marrow mononuclear cells within 72 hours after stroke onset, a time frame supported by previous preclinical studies. They followed the patients for 1 year and compared the results with a control group of 185 patients who received conventional poststroke treatment. Primary outcomes were study-related serious adverse events and the proportion of patients successfully completing study intervention.
The researchers reported results from 25 patients who received bone marrow MNCs. The mean age of patients in the MNC and control groups were 61 and 63 years, respectively, 53% were female, and 69% were white. No study-related adverse events were observed in the MNC group, but three (12%) had infarct expansion between enrollment and harvest and underwent elective hemicraniectomy after cell infusion.
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging revealed that the average mean fractional anisotropy (FA), a measure of structural integrity and directional coherence of axonal fibers, within the ipsilesional pons was decreased between 1 and 3 months after stroke, “which translated to a relative FA [rFA] comparable with prior reports at this time point,” the researchers wrote. “However, by 6 months, mean rFA began to increase and by 2 years it was significantly higher than at 1 month. This increasing trend in rFA may imply an increase in axonal and fiber coherence as well as thickness in myelin sheets, suggesting microstructural repair. However, without a comparable group of stroke patients not treated with MNCs, we cannot directly ascribe the white matter changes to MNC treatment.”
In light of the findings, the researchers concluded that MNCs “pose no additional harm in ischemic stroke patients when given during the acute phase, doses up to 10 million cells per kilogram are tolerated, and it is feasible to perform a bone marrow harvest and reinfusion of MNCs for a wide range of stroke patients. Well-designed RCTs are needed to further assess safety and efficacy of this novel investigational approach to enhance stroke recovery.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Savitz and many of his coauthors disclosed having numerous financial ties to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
, results from a single-arm, phase I trial demonstrated. Unlike autologous mesenchymal stem cells, mononuclear cells (MNCs) do not require passage in culture, which allows for testing in the early poststroke time therapy window.
Bone marrow MNCs are attractive in regenerative medicine studies because they can be rapidly isolated; are enriched with hematopoietic, mesenchymal, and endothelial progenitor cells; and permit autologous applications. “The regenerative potential of bone marrow–derived MNCs is attributed to various mechanisms that impact stroke recovery,” researchers led by Sean I. Savitz, MD, wrote in a study published online Sept. 17 in Stem Cells. “These cells migrate to the site of injury, release cytokines and other trophic factors, decrease proinflammatory and upregulate anti-inflammatory pathways, and enhance angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis.”
For the trial, Dr. Savitz, MD, director of the Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease at UTHealth, Houston, and colleagues recruited 25 patients to receive an IV dose of their own bone marrow mononuclear cells within 72 hours after stroke onset, a time frame supported by previous preclinical studies. They followed the patients for 1 year and compared the results with a control group of 185 patients who received conventional poststroke treatment. Primary outcomes were study-related serious adverse events and the proportion of patients successfully completing study intervention.
The researchers reported results from 25 patients who received bone marrow MNCs. The mean age of patients in the MNC and control groups were 61 and 63 years, respectively, 53% were female, and 69% were white. No study-related adverse events were observed in the MNC group, but three (12%) had infarct expansion between enrollment and harvest and underwent elective hemicraniectomy after cell infusion.
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging revealed that the average mean fractional anisotropy (FA), a measure of structural integrity and directional coherence of axonal fibers, within the ipsilesional pons was decreased between 1 and 3 months after stroke, “which translated to a relative FA [rFA] comparable with prior reports at this time point,” the researchers wrote. “However, by 6 months, mean rFA began to increase and by 2 years it was significantly higher than at 1 month. This increasing trend in rFA may imply an increase in axonal and fiber coherence as well as thickness in myelin sheets, suggesting microstructural repair. However, without a comparable group of stroke patients not treated with MNCs, we cannot directly ascribe the white matter changes to MNC treatment.”
In light of the findings, the researchers concluded that MNCs “pose no additional harm in ischemic stroke patients when given during the acute phase, doses up to 10 million cells per kilogram are tolerated, and it is feasible to perform a bone marrow harvest and reinfusion of MNCs for a wide range of stroke patients. Well-designed RCTs are needed to further assess safety and efficacy of this novel investigational approach to enhance stroke recovery.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Savitz and many of his coauthors disclosed having numerous financial ties to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
, results from a single-arm, phase I trial demonstrated. Unlike autologous mesenchymal stem cells, mononuclear cells (MNCs) do not require passage in culture, which allows for testing in the early poststroke time therapy window.
Bone marrow MNCs are attractive in regenerative medicine studies because they can be rapidly isolated; are enriched with hematopoietic, mesenchymal, and endothelial progenitor cells; and permit autologous applications. “The regenerative potential of bone marrow–derived MNCs is attributed to various mechanisms that impact stroke recovery,” researchers led by Sean I. Savitz, MD, wrote in a study published online Sept. 17 in Stem Cells. “These cells migrate to the site of injury, release cytokines and other trophic factors, decrease proinflammatory and upregulate anti-inflammatory pathways, and enhance angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and synaptogenesis.”
For the trial, Dr. Savitz, MD, director of the Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease at UTHealth, Houston, and colleagues recruited 25 patients to receive an IV dose of their own bone marrow mononuclear cells within 72 hours after stroke onset, a time frame supported by previous preclinical studies. They followed the patients for 1 year and compared the results with a control group of 185 patients who received conventional poststroke treatment. Primary outcomes were study-related serious adverse events and the proportion of patients successfully completing study intervention.
The researchers reported results from 25 patients who received bone marrow MNCs. The mean age of patients in the MNC and control groups were 61 and 63 years, respectively, 53% were female, and 69% were white. No study-related adverse events were observed in the MNC group, but three (12%) had infarct expansion between enrollment and harvest and underwent elective hemicraniectomy after cell infusion.
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging revealed that the average mean fractional anisotropy (FA), a measure of structural integrity and directional coherence of axonal fibers, within the ipsilesional pons was decreased between 1 and 3 months after stroke, “which translated to a relative FA [rFA] comparable with prior reports at this time point,” the researchers wrote. “However, by 6 months, mean rFA began to increase and by 2 years it was significantly higher than at 1 month. This increasing trend in rFA may imply an increase in axonal and fiber coherence as well as thickness in myelin sheets, suggesting microstructural repair. However, without a comparable group of stroke patients not treated with MNCs, we cannot directly ascribe the white matter changes to MNC treatment.”
In light of the findings, the researchers concluded that MNCs “pose no additional harm in ischemic stroke patients when given during the acute phase, doses up to 10 million cells per kilogram are tolerated, and it is feasible to perform a bone marrow harvest and reinfusion of MNCs for a wide range of stroke patients. Well-designed RCTs are needed to further assess safety and efficacy of this novel investigational approach to enhance stroke recovery.”
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Savitz and many of his coauthors disclosed having numerous financial ties to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
FROM STEM CELLS
Daily polypill lowers BP, cholesterol in underserved population
A daily polypill regimen improved cardiovascular risk factors in a socioeconomically vulnerable minority population, in a randomized controlled trial.
Patients at a federally qualified community health center in Alabama who received treatment with a combination pill for 1 year had greater reductions in systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol than did patients who received usual care, according to results published online on Sept. 19 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The simplicity and low cost of the polypill regimen make this approach attractive” when barriers such as lack of income, underinsurance, and difficulty attending clinic visits are common, said first author Daniel Muñoz, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and coinvestigators. The investigators obtained the pills at a cost of $26 per month per participant.
People with low socioeconomic status and those who are nonwhite have high cardiovascular mortality, and the southeastern United States and rural areas have disproportionately high levels of cardiovascular disease burden, according to the investigators. The rates at which people with low socioeconomic status receive treatment for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia – leading cardiovascular disease risk factors – “are strikingly low,” Dr. Muñoz and colleagues said.
To assess the effectiveness of a polypill-based strategy in an underserved population with low socioeconomic status, the researchers conducted the randomized trial.
They enrolled 303 adults without cardiovascular disease, and 148 of the patients were randomized to receive the polypill, which contained generic versions of atorvastatin (10 mg), amlodipine (2.5 mg), losartan (25 mg), and hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg). The remaining 155 patients received usual care. All participants scheduled 2-month and 12-month follow-up visits.
The participants had an average age of 56 years, 60% were women, and more than 95% were black. More than 70% had an annual household income of less than $15,000. Baseline characteristics of the treatment groups did not significantly differ.
At baseline, the average BP was 140/83 mm Hg, and the average LDL cholesterol level was 113 mg/dL.
In all, 91% of the participants completed the 12-month trial visit. Average systolic BP decreased by 9 mm Hg in the group that received the polypill, compared with 2 mm Hg in the group that received usual care. Average LDL cholesterol level decreased by 15 mg/dL in the polypill group, versus 4 mg/dL in the usual-care group.
Changes in other medications
Clinicians discontinued or reduced doses of other antihypertensive or lipid-lowering medications in 44% of the patients in the polypill group and none in the usual-care group. Clinicians escalated therapy in 2% of the participants in the polypill group and in 10% of the usual-care group.
Side effects in participants who received the polypill included a 1% incidence of myalgias and a 1% incidence of hypotension or light-headedness. Liver function test results were normal.
Five serious adverse events that occurred during the trial – two in the polypill group and three in the usual-care group – were judged to be unrelated to the trial by a data and safety monitoring board.
The authors noted that limitations of the trial include its open-label design and that it was conducted at a single center.
“It is important to emphasize that use of the polypill does not preclude individualized, add-on therapies for residual elevations in blood-pressure or cholesterol levels, as judged by a patient’s physician,” said Dr. Muñoz and colleagues. “We recognize that a ‘one size fits all’ approach to cardiovascular disease prevention runs counter to current trends in precision medicine, in which clinical, genomic, and lifestyle factors are used for the development of individualized treatment strategies. Although the precision approach has clear virtues, a broader approach may benefit patients who face barriers to accessing the full advantages of precision medicine.”
The study was supported by grants from the American Heart Association Strategically Focused Prevention Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed personal fees from Novartis outside the study.
SOURCE: Muñoz D et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 18;381(12):1114-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1815359.
A daily polypill regimen improved cardiovascular risk factors in a socioeconomically vulnerable minority population, in a randomized controlled trial.
Patients at a federally qualified community health center in Alabama who received treatment with a combination pill for 1 year had greater reductions in systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol than did patients who received usual care, according to results published online on Sept. 19 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The simplicity and low cost of the polypill regimen make this approach attractive” when barriers such as lack of income, underinsurance, and difficulty attending clinic visits are common, said first author Daniel Muñoz, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and coinvestigators. The investigators obtained the pills at a cost of $26 per month per participant.
People with low socioeconomic status and those who are nonwhite have high cardiovascular mortality, and the southeastern United States and rural areas have disproportionately high levels of cardiovascular disease burden, according to the investigators. The rates at which people with low socioeconomic status receive treatment for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia – leading cardiovascular disease risk factors – “are strikingly low,” Dr. Muñoz and colleagues said.
To assess the effectiveness of a polypill-based strategy in an underserved population with low socioeconomic status, the researchers conducted the randomized trial.
They enrolled 303 adults without cardiovascular disease, and 148 of the patients were randomized to receive the polypill, which contained generic versions of atorvastatin (10 mg), amlodipine (2.5 mg), losartan (25 mg), and hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg). The remaining 155 patients received usual care. All participants scheduled 2-month and 12-month follow-up visits.
The participants had an average age of 56 years, 60% were women, and more than 95% were black. More than 70% had an annual household income of less than $15,000. Baseline characteristics of the treatment groups did not significantly differ.
At baseline, the average BP was 140/83 mm Hg, and the average LDL cholesterol level was 113 mg/dL.
In all, 91% of the participants completed the 12-month trial visit. Average systolic BP decreased by 9 mm Hg in the group that received the polypill, compared with 2 mm Hg in the group that received usual care. Average LDL cholesterol level decreased by 15 mg/dL in the polypill group, versus 4 mg/dL in the usual-care group.
Changes in other medications
Clinicians discontinued or reduced doses of other antihypertensive or lipid-lowering medications in 44% of the patients in the polypill group and none in the usual-care group. Clinicians escalated therapy in 2% of the participants in the polypill group and in 10% of the usual-care group.
Side effects in participants who received the polypill included a 1% incidence of myalgias and a 1% incidence of hypotension or light-headedness. Liver function test results were normal.
Five serious adverse events that occurred during the trial – two in the polypill group and three in the usual-care group – were judged to be unrelated to the trial by a data and safety monitoring board.
The authors noted that limitations of the trial include its open-label design and that it was conducted at a single center.
“It is important to emphasize that use of the polypill does not preclude individualized, add-on therapies for residual elevations in blood-pressure or cholesterol levels, as judged by a patient’s physician,” said Dr. Muñoz and colleagues. “We recognize that a ‘one size fits all’ approach to cardiovascular disease prevention runs counter to current trends in precision medicine, in which clinical, genomic, and lifestyle factors are used for the development of individualized treatment strategies. Although the precision approach has clear virtues, a broader approach may benefit patients who face barriers to accessing the full advantages of precision medicine.”
The study was supported by grants from the American Heart Association Strategically Focused Prevention Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed personal fees from Novartis outside the study.
SOURCE: Muñoz D et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 18;381(12):1114-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1815359.
A daily polypill regimen improved cardiovascular risk factors in a socioeconomically vulnerable minority population, in a randomized controlled trial.
Patients at a federally qualified community health center in Alabama who received treatment with a combination pill for 1 year had greater reductions in systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol than did patients who received usual care, according to results published online on Sept. 19 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“The simplicity and low cost of the polypill regimen make this approach attractive” when barriers such as lack of income, underinsurance, and difficulty attending clinic visits are common, said first author Daniel Muñoz, MD, of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, and coinvestigators. The investigators obtained the pills at a cost of $26 per month per participant.
People with low socioeconomic status and those who are nonwhite have high cardiovascular mortality, and the southeastern United States and rural areas have disproportionately high levels of cardiovascular disease burden, according to the investigators. The rates at which people with low socioeconomic status receive treatment for hypertension and hypercholesterolemia – leading cardiovascular disease risk factors – “are strikingly low,” Dr. Muñoz and colleagues said.
To assess the effectiveness of a polypill-based strategy in an underserved population with low socioeconomic status, the researchers conducted the randomized trial.
They enrolled 303 adults without cardiovascular disease, and 148 of the patients were randomized to receive the polypill, which contained generic versions of atorvastatin (10 mg), amlodipine (2.5 mg), losartan (25 mg), and hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg). The remaining 155 patients received usual care. All participants scheduled 2-month and 12-month follow-up visits.
The participants had an average age of 56 years, 60% were women, and more than 95% were black. More than 70% had an annual household income of less than $15,000. Baseline characteristics of the treatment groups did not significantly differ.
At baseline, the average BP was 140/83 mm Hg, and the average LDL cholesterol level was 113 mg/dL.
In all, 91% of the participants completed the 12-month trial visit. Average systolic BP decreased by 9 mm Hg in the group that received the polypill, compared with 2 mm Hg in the group that received usual care. Average LDL cholesterol level decreased by 15 mg/dL in the polypill group, versus 4 mg/dL in the usual-care group.
Changes in other medications
Clinicians discontinued or reduced doses of other antihypertensive or lipid-lowering medications in 44% of the patients in the polypill group and none in the usual-care group. Clinicians escalated therapy in 2% of the participants in the polypill group and in 10% of the usual-care group.
Side effects in participants who received the polypill included a 1% incidence of myalgias and a 1% incidence of hypotension or light-headedness. Liver function test results were normal.
Five serious adverse events that occurred during the trial – two in the polypill group and three in the usual-care group – were judged to be unrelated to the trial by a data and safety monitoring board.
The authors noted that limitations of the trial include its open-label design and that it was conducted at a single center.
“It is important to emphasize that use of the polypill does not preclude individualized, add-on therapies for residual elevations in blood-pressure or cholesterol levels, as judged by a patient’s physician,” said Dr. Muñoz and colleagues. “We recognize that a ‘one size fits all’ approach to cardiovascular disease prevention runs counter to current trends in precision medicine, in which clinical, genomic, and lifestyle factors are used for the development of individualized treatment strategies. Although the precision approach has clear virtues, a broader approach may benefit patients who face barriers to accessing the full advantages of precision medicine.”
The study was supported by grants from the American Heart Association Strategically Focused Prevention Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed personal fees from Novartis outside the study.
SOURCE: Muñoz D et al. N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 18;381(12):1114-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1815359.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point: A daily polypill regimen may improve cardiovascular disease prevention in underserved populations.
Major finding: Mean LDL cholesterol levels decreased by 15 mg/dL in the polypill group, vs. 4 mg/dL in the usual-care group.
Study details: An open-label, randomized trial that enrolled 303 adults without cardiovascular disease at a federally qualified community health center in Alabama.
Disclosures: The study was supported by grants from the American Heart Association Strategically Focused Prevention Research Network and the National Institutes of Health. One author disclosed personal fees from Novartis outside the study.
Source: Muñoz D et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(12):1114-23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1815359.
Remember that preeclampsia has a ‘fourth trimester’
NEW ORLEANS – according to Natalie Bello, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University in New York.
In medical school, “they told me that you deliver the placenta, and the preeclampsia goes away. Not the case. Postpartum preeclampsia is a real thing. We are seeing a lot of it at our sites, which have a lot of underserved women who hadn’t had great prenatal care” elsewhere, she said.
Headache and visual changes in association with hypertension during what’s been dubbed “the fourth trimester” raise suspicions. Women can progress rapidly to eclampsia and HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count), but sometimes providers don’t recognize what’s going on because they don’t know women have recently given birth. “We can do better; we should be doing better. Please always ask women if they’ve delivered recently,” Dr. Bello said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
Hypertension should resolve within 6 weeks of delivery, and blood pressure should be back to baseline by 3 months. To make sure that happens, BP should be checked within a few days of birth and regularly thereafter. It can be tough to get busy and tired new moms back into the office, but “they’ll do whatever it takes” to get their baby to a pediatric appointment, so maybe having pediatricians involved in checking blood pressure would help, she said.
The cutoff point for hypertension in pregnancy is 140/90 mm Hg, and it’s considered severe when values hit 160/110 mm Hg or higher. Evidence is strong for treating severe hypertension to reduce strokes, placental abruptions, and other problems, but the data for treating nonsevere hypertension are less clear, Dr. Bello explained.
The Chronic Hypertension and Pregnancy (CHAP) trial is expected to fill the evidence gap in a few years; women are being randomized to start treatment at either 140/90 mm Hg or 160/105 mm Hg. Meanwhile, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recently suggested that treatment of nonsevere hypertension might be appropriate in the setting of comorbidities and renal dysfunction (Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jan;133[1]:e26-e50).
Dr. Bello prefers treating with extended-release calcium channel blocker nifedipine over the beta-blocker labetalol. “We think it is a little more effective,” and the once daily dosing, instead of two or three times a day, helps with compliance. Thiazide diuretics and hydralazine are also in her arsenal, but hydralazine shouldn’t be used in isolation because of its reflex tachycardia risk. The old standby, the antiadrenergic methyldopa, has fallen out of favor because of depression and other concerns. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, renin inhibitors, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists shouldn’t be used in pregnancy, she said.
Intravenous labetalol and short-acting oral nifedipine are the mainstays for urgent, severe hypertension, along with high-dose intravenous magnesium, especially for seizure control. IV hydralazine or nitroglycerin are other options, the latter particularly for pulmonary edema. “Be careful of synergistic hypotension with magnesium and nifedipine,” Dr. Bello said.
Dr. Bello didn’t have any industry disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – according to Natalie Bello, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University in New York.
In medical school, “they told me that you deliver the placenta, and the preeclampsia goes away. Not the case. Postpartum preeclampsia is a real thing. We are seeing a lot of it at our sites, which have a lot of underserved women who hadn’t had great prenatal care” elsewhere, she said.
Headache and visual changes in association with hypertension during what’s been dubbed “the fourth trimester” raise suspicions. Women can progress rapidly to eclampsia and HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count), but sometimes providers don’t recognize what’s going on because they don’t know women have recently given birth. “We can do better; we should be doing better. Please always ask women if they’ve delivered recently,” Dr. Bello said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
Hypertension should resolve within 6 weeks of delivery, and blood pressure should be back to baseline by 3 months. To make sure that happens, BP should be checked within a few days of birth and regularly thereafter. It can be tough to get busy and tired new moms back into the office, but “they’ll do whatever it takes” to get their baby to a pediatric appointment, so maybe having pediatricians involved in checking blood pressure would help, she said.
The cutoff point for hypertension in pregnancy is 140/90 mm Hg, and it’s considered severe when values hit 160/110 mm Hg or higher. Evidence is strong for treating severe hypertension to reduce strokes, placental abruptions, and other problems, but the data for treating nonsevere hypertension are less clear, Dr. Bello explained.
The Chronic Hypertension and Pregnancy (CHAP) trial is expected to fill the evidence gap in a few years; women are being randomized to start treatment at either 140/90 mm Hg or 160/105 mm Hg. Meanwhile, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recently suggested that treatment of nonsevere hypertension might be appropriate in the setting of comorbidities and renal dysfunction (Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jan;133[1]:e26-e50).
Dr. Bello prefers treating with extended-release calcium channel blocker nifedipine over the beta-blocker labetalol. “We think it is a little more effective,” and the once daily dosing, instead of two or three times a day, helps with compliance. Thiazide diuretics and hydralazine are also in her arsenal, but hydralazine shouldn’t be used in isolation because of its reflex tachycardia risk. The old standby, the antiadrenergic methyldopa, has fallen out of favor because of depression and other concerns. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, renin inhibitors, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists shouldn’t be used in pregnancy, she said.
Intravenous labetalol and short-acting oral nifedipine are the mainstays for urgent, severe hypertension, along with high-dose intravenous magnesium, especially for seizure control. IV hydralazine or nitroglycerin are other options, the latter particularly for pulmonary edema. “Be careful of synergistic hypotension with magnesium and nifedipine,” Dr. Bello said.
Dr. Bello didn’t have any industry disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – according to Natalie Bello, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University in New York.
In medical school, “they told me that you deliver the placenta, and the preeclampsia goes away. Not the case. Postpartum preeclampsia is a real thing. We are seeing a lot of it at our sites, which have a lot of underserved women who hadn’t had great prenatal care” elsewhere, she said.
Headache and visual changes in association with hypertension during what’s been dubbed “the fourth trimester” raise suspicions. Women can progress rapidly to eclampsia and HELLP syndrome (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count), but sometimes providers don’t recognize what’s going on because they don’t know women have recently given birth. “We can do better; we should be doing better. Please always ask women if they’ve delivered recently,” Dr. Bello said at the joint scientific sessions of the American Heart Association Council on Hypertension, AHA Council on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, and American Society of Hypertension.
Hypertension should resolve within 6 weeks of delivery, and blood pressure should be back to baseline by 3 months. To make sure that happens, BP should be checked within a few days of birth and regularly thereafter. It can be tough to get busy and tired new moms back into the office, but “they’ll do whatever it takes” to get their baby to a pediatric appointment, so maybe having pediatricians involved in checking blood pressure would help, she said.
The cutoff point for hypertension in pregnancy is 140/90 mm Hg, and it’s considered severe when values hit 160/110 mm Hg or higher. Evidence is strong for treating severe hypertension to reduce strokes, placental abruptions, and other problems, but the data for treating nonsevere hypertension are less clear, Dr. Bello explained.
The Chronic Hypertension and Pregnancy (CHAP) trial is expected to fill the evidence gap in a few years; women are being randomized to start treatment at either 140/90 mm Hg or 160/105 mm Hg. Meanwhile, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recently suggested that treatment of nonsevere hypertension might be appropriate in the setting of comorbidities and renal dysfunction (Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jan;133[1]:e26-e50).
Dr. Bello prefers treating with extended-release calcium channel blocker nifedipine over the beta-blocker labetalol. “We think it is a little more effective,” and the once daily dosing, instead of two or three times a day, helps with compliance. Thiazide diuretics and hydralazine are also in her arsenal, but hydralazine shouldn’t be used in isolation because of its reflex tachycardia risk. The old standby, the antiadrenergic methyldopa, has fallen out of favor because of depression and other concerns. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, renin inhibitors, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists shouldn’t be used in pregnancy, she said.
Intravenous labetalol and short-acting oral nifedipine are the mainstays for urgent, severe hypertension, along with high-dose intravenous magnesium, especially for seizure control. IV hydralazine or nitroglycerin are other options, the latter particularly for pulmonary edema. “Be careful of synergistic hypotension with magnesium and nifedipine,” Dr. Bello said.
Dr. Bello didn’t have any industry disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM JOINT HYPERTENSION 2019
Drug abuse–linked infective endocarditis spiking in U.S.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
Hospitalizations for infective endocarditis associated with drug abuse doubled in the United States from 2002 to 2016, in a trend investigators call “alarming,” and link to a concurrent rise in opioid abuse.
Patients tend to be younger, poorer white males, according to findings published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
For their research, Amer N. Kadri, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic and colleagues looked at records for nearly a million hospitalizations for infective endocarditis (IE) in the National Inpatient Sample registry. All U.S. regions saw increases in drug abuse–linked cases of IE as a share of IE hospitalizations. Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC rose from 48 cases/100,000 population in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016. The Midwest saw the highest rate of change, with an annual percent increase of 4.9%.
While most IE hospitalizations in the study cohort were of white men (including 68% for drug-linked cases), the drug abuse–related cases were younger (median age, 38 vs. 70 years for nondrug-related IE), and more likely male (55.5% vs. 50%). About 45% of the drug-related cases were in people receiving Medicaid, and 42% were in the lowest quartile of median household income.
The drug abuse cases had fewer renal and cardiovascular comorbidities, compared with the nondrug cases, but were significantly more likely to present with HIV, hepatitis C, alcohol abuse, and liver disease. Inpatient mortality was lower among the drug-linked cases – 6% vs. 9% – but the drug cases saw significantly more cardiac or valve surgeries, longer hospital stays, and higher costs.
“Hospitalizations for IE have been increasing side by side with the opioid epidemic,” the investigators wrote in their analysis. “The opioid crisis has reached epidemic levels, and now drug overdoses have been the leading cause of injury-related death in the U.S. Heroin deaths had remained relatively low from 1999 until 2010 whereas it then increased threefold from 2010-2015.” The analysis showed a rise in drug abuse–associated IE “that corresponds to this general period.” The findings argue, the investigators said, for better treatment for opioid addiction after hospitalization and greater efforts to make drug rehabilitation available after discharge. The researchers described as a limitation of their study the use of billing codes that changed late in the study period, increasing detection of drug abuse cases after 2015. They reported no outside funding or conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Incidence of drug abuse–associated IC increased from 48 cases/100,000 in 2002 to 79/100,000 in 2016.
Study details: A retrospective cohort study identifying about a more than 950,000 cases of IC from the National Inpatient Sample registry.
Disclosures: None.
Source: Kadri AN et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Sep 18.
FDA grants sirolimus-eluting balloon breakthrough device designation for PAD
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted the Breakthrough Device Designation to the Virtue sirolimus-eluting balloon (SEB) for below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease, according to a statement from Orchestra BioMed.
According to the FDA, this designation indicates that the Virtue SEB could provide a “more effective treatment option ... for a life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating disease”; as the release notes, below-the-knee atherosclerosis presents a high rate of amputation and poor survival outcomes but has limited treatment options. The designation leads to expedited development, assessment, and review.
Darren R. Sherman, president, CEO, and cofounder of Orchestra BioMed, noted that the Virtue SEB “has the potential to improve long-term outcomes and reduce periprocedural complications” that can “extend hospital stay and increase cost of treatment.” The system had previously received this designation for coronary in-stent restenosis based upon the 3-year results of the European SABRE trial.
ISAR-REACT 5: Prasugrel superior to ticagrelor in ACS
PARIS – Prasugrel proved superior to ticagrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in what was hailed as “a landmark study” presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The results of ISAR-REACT 5 (Intracoronary Stenting and Antithrombotic Regimen: Rapid Early Action for Coronary Treatment 5) were unequivocal: “In ACS patients with or without ST-segment elevation, treatment with prasugrel as compared with ticagrelor significantly reduced the composite rate of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke at 1 year without an increase in major bleeding,” declared first author Stephanie Schuepke, MD, a cardiologist at the German Heart Center in Munich.
The study outcome was totally unexpected. Indeed, the result didn’t merely turn heads, it no doubt caused numerous wrenched necks caused by strenuous double-takes on the part of interventional cardiologists at the congress. That’s because, even though both ticagrelor and prasugrel enjoy a class I recommendation for use in ACS in the ESC guidelines, it has been widely assumed – based on previous evidence plus the fact that ticagrelor is the more potent platelet inhibitor – that ticagrelor is the superior drug in this setting. It turns out, however, that those earlier studies weren’t germane to the issue directly addressed in ISAR-REACT 5, the first-ever direct head-to-head comparison of the two potent P2Y12 inhibitors in the setting of ACS with a planned invasive strategy.
“Obviously, very surprising results,” commented Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology research and clinical trials at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who cochaired a press conference where Dr. Schuepke shared the study findings.
“We were surprised as well,” confessed Dr. Schuepke. “We assumed that ticagrelor is superior to prasugrel in terms of clinical outcomes in patients with ACS with a planned invasive strategy. But the results show us that the opposite is true.”
ISAR-REACT 5 was an open-label, investigator-initiated randomized trial conducted at 23 centers in Germany and Italy. It included 4,018 participants with ST-elevation segment MI (STEMI), without STEMI, or with unstable angina, all with scheduled coronary angiography. Participants were randomized to ticagrelor or prasugrel and were expected to remain on their assigned potent antiplatelet agent plus aspirin for 1 year of dual-antiplatelet therapy.
The primary outcome was the composite of death, MI, or stroke at 1 year of follow-up. This endpoint occurred in 9.3% of the ticagrelor group and 6.9% of patients in the prasugrel group, for a highly significant 36% increased relative risk in the ticagrelor-treated patients. Prasugrel had a numeric advantage in each of the individual components of the endpoint: the 1-year rate of all-cause mortality was 4.5% with ticagrelor versus 3.7% with prasugrel; for MI, the incidence was 4.8% with ticagrelor and 3.0% with prasugrel, a statistically significant difference; and for stroke, 1.1% versus 1.0%.
Major bleeding as defined by the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium scale occurred in 5.4% of patients in the ticagrelor arm, and was similar at 4.8% in the prasugrel group, Dr. Schuepke continued.
Definite or probable stent thrombosis occurred in 1.3% of the ticagrelor group and 1.0% of patients assigned to prasugrel.
The mechanism for prasugrel’s superior results is unclear, she said. Possibilities include the fact that it’s a once-daily drug, compared with twice-daily ticagrelor, which could affect adherence; a differential profile in terms of drug interactions; and prasugrel’s reversibility of action and capacity for step-down dosing in patients at high bleeding risk.
Discussant Gilles Montalescot, MD, PhD, called ISAR-REACT 5 a “fascinating” study. He elaborated: “It is a pragmatic study to answer a pragmatic question. It’s not a drug trial; really, it’s more a strategy trial, with a comparison of two drugs and two strategies.”
In ISAR-REACT 5, ticagrelor was utilized in standard fashion: Patients, regardless of their ACS type, received a 180-mg loading dose as soon as possible after randomization, typically about 3 hours after presentation. That was also the protocol in the prasugrel arm, but only in patients with STEMI, who quickly got a 60-mg loading dose. In contrast, patients without STEMI or with unstable angina didn’t get a loading dose of prasugrel until they’d undergone coronary angiography and their coronary anatomy was known. That was the ISAR-REACT 5 strategy in light of an earlier study, which concluded that giving prasugrel prior to angiography in such patients led to increased bleeding without any improvement in clinical outcomes.
The essence of ISAR-REACT 5 lies in that difference in treatment strategies and the impact it had on outcomes. “The one-size-fits-all strategy – here, with ticagrelor – was inferior to an individualized strategy, here with prasugrel,” observed Dr. Montalescot, professor of cardiology at the University of Paris VI and director of the cardiac care unit at Paris-Salpetriere Hospital.
The study results were notably consistent, favoring prasugrel over ticagrelor numerically across the board regardless of whether a patient presented with STEMI, without STEMI, or with unstable angina. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that this was also true in terms of the individual components of the 1-year composite endpoint. Dr. Montalescot drew special attention to the large subset of patients who had presented with STEMI and thus received the same treatment strategy involving a loading dose of their assigned P2Y12 inhibitor prior to angiography. This allowed for a direct head-to-head comparison of the clinical efficacy of the two antiplatelet agents in STEMI patients. The clear winner here was prasugrel, as the composite event rate was 10.1% in the ticagrelor group, compared with 7.9% in the prasugrel group.
“ISAR-REACT 5 is a landmark study which is going to impact our practice and the next set of guidelines to come in 2020,” the interventional cardiologist predicted.
Dr. Schuepke reported having no financial conflicts regarding the ISAR-REACT 5 study, sponsored by the German Heart Center and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research.
Simultaneous with her presentation of ISAR-REACT 5, the study results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908973).
PARIS – Prasugrel proved superior to ticagrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in what was hailed as “a landmark study” presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The results of ISAR-REACT 5 (Intracoronary Stenting and Antithrombotic Regimen: Rapid Early Action for Coronary Treatment 5) were unequivocal: “In ACS patients with or without ST-segment elevation, treatment with prasugrel as compared with ticagrelor significantly reduced the composite rate of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke at 1 year without an increase in major bleeding,” declared first author Stephanie Schuepke, MD, a cardiologist at the German Heart Center in Munich.
The study outcome was totally unexpected. Indeed, the result didn’t merely turn heads, it no doubt caused numerous wrenched necks caused by strenuous double-takes on the part of interventional cardiologists at the congress. That’s because, even though both ticagrelor and prasugrel enjoy a class I recommendation for use in ACS in the ESC guidelines, it has been widely assumed – based on previous evidence plus the fact that ticagrelor is the more potent platelet inhibitor – that ticagrelor is the superior drug in this setting. It turns out, however, that those earlier studies weren’t germane to the issue directly addressed in ISAR-REACT 5, the first-ever direct head-to-head comparison of the two potent P2Y12 inhibitors in the setting of ACS with a planned invasive strategy.
“Obviously, very surprising results,” commented Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology research and clinical trials at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who cochaired a press conference where Dr. Schuepke shared the study findings.
“We were surprised as well,” confessed Dr. Schuepke. “We assumed that ticagrelor is superior to prasugrel in terms of clinical outcomes in patients with ACS with a planned invasive strategy. But the results show us that the opposite is true.”
ISAR-REACT 5 was an open-label, investigator-initiated randomized trial conducted at 23 centers in Germany and Italy. It included 4,018 participants with ST-elevation segment MI (STEMI), without STEMI, or with unstable angina, all with scheduled coronary angiography. Participants were randomized to ticagrelor or prasugrel and were expected to remain on their assigned potent antiplatelet agent plus aspirin for 1 year of dual-antiplatelet therapy.
The primary outcome was the composite of death, MI, or stroke at 1 year of follow-up. This endpoint occurred in 9.3% of the ticagrelor group and 6.9% of patients in the prasugrel group, for a highly significant 36% increased relative risk in the ticagrelor-treated patients. Prasugrel had a numeric advantage in each of the individual components of the endpoint: the 1-year rate of all-cause mortality was 4.5% with ticagrelor versus 3.7% with prasugrel; for MI, the incidence was 4.8% with ticagrelor and 3.0% with prasugrel, a statistically significant difference; and for stroke, 1.1% versus 1.0%.
Major bleeding as defined by the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium scale occurred in 5.4% of patients in the ticagrelor arm, and was similar at 4.8% in the prasugrel group, Dr. Schuepke continued.
Definite or probable stent thrombosis occurred in 1.3% of the ticagrelor group and 1.0% of patients assigned to prasugrel.
The mechanism for prasugrel’s superior results is unclear, she said. Possibilities include the fact that it’s a once-daily drug, compared with twice-daily ticagrelor, which could affect adherence; a differential profile in terms of drug interactions; and prasugrel’s reversibility of action and capacity for step-down dosing in patients at high bleeding risk.
Discussant Gilles Montalescot, MD, PhD, called ISAR-REACT 5 a “fascinating” study. He elaborated: “It is a pragmatic study to answer a pragmatic question. It’s not a drug trial; really, it’s more a strategy trial, with a comparison of two drugs and two strategies.”
In ISAR-REACT 5, ticagrelor was utilized in standard fashion: Patients, regardless of their ACS type, received a 180-mg loading dose as soon as possible after randomization, typically about 3 hours after presentation. That was also the protocol in the prasugrel arm, but only in patients with STEMI, who quickly got a 60-mg loading dose. In contrast, patients without STEMI or with unstable angina didn’t get a loading dose of prasugrel until they’d undergone coronary angiography and their coronary anatomy was known. That was the ISAR-REACT 5 strategy in light of an earlier study, which concluded that giving prasugrel prior to angiography in such patients led to increased bleeding without any improvement in clinical outcomes.
The essence of ISAR-REACT 5 lies in that difference in treatment strategies and the impact it had on outcomes. “The one-size-fits-all strategy – here, with ticagrelor – was inferior to an individualized strategy, here with prasugrel,” observed Dr. Montalescot, professor of cardiology at the University of Paris VI and director of the cardiac care unit at Paris-Salpetriere Hospital.
The study results were notably consistent, favoring prasugrel over ticagrelor numerically across the board regardless of whether a patient presented with STEMI, without STEMI, or with unstable angina. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that this was also true in terms of the individual components of the 1-year composite endpoint. Dr. Montalescot drew special attention to the large subset of patients who had presented with STEMI and thus received the same treatment strategy involving a loading dose of their assigned P2Y12 inhibitor prior to angiography. This allowed for a direct head-to-head comparison of the clinical efficacy of the two antiplatelet agents in STEMI patients. The clear winner here was prasugrel, as the composite event rate was 10.1% in the ticagrelor group, compared with 7.9% in the prasugrel group.
“ISAR-REACT 5 is a landmark study which is going to impact our practice and the next set of guidelines to come in 2020,” the interventional cardiologist predicted.
Dr. Schuepke reported having no financial conflicts regarding the ISAR-REACT 5 study, sponsored by the German Heart Center and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research.
Simultaneous with her presentation of ISAR-REACT 5, the study results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908973).
PARIS – Prasugrel proved superior to ticagrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in what was hailed as “a landmark study” presented at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The results of ISAR-REACT 5 (Intracoronary Stenting and Antithrombotic Regimen: Rapid Early Action for Coronary Treatment 5) were unequivocal: “In ACS patients with or without ST-segment elevation, treatment with prasugrel as compared with ticagrelor significantly reduced the composite rate of death, myocardial infarction, or stroke at 1 year without an increase in major bleeding,” declared first author Stephanie Schuepke, MD, a cardiologist at the German Heart Center in Munich.
The study outcome was totally unexpected. Indeed, the result didn’t merely turn heads, it no doubt caused numerous wrenched necks caused by strenuous double-takes on the part of interventional cardiologists at the congress. That’s because, even though both ticagrelor and prasugrel enjoy a class I recommendation for use in ACS in the ESC guidelines, it has been widely assumed – based on previous evidence plus the fact that ticagrelor is the more potent platelet inhibitor – that ticagrelor is the superior drug in this setting. It turns out, however, that those earlier studies weren’t germane to the issue directly addressed in ISAR-REACT 5, the first-ever direct head-to-head comparison of the two potent P2Y12 inhibitors in the setting of ACS with a planned invasive strategy.
“Obviously, very surprising results,” commented Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology research and clinical trials at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, who cochaired a press conference where Dr. Schuepke shared the study findings.
“We were surprised as well,” confessed Dr. Schuepke. “We assumed that ticagrelor is superior to prasugrel in terms of clinical outcomes in patients with ACS with a planned invasive strategy. But the results show us that the opposite is true.”
ISAR-REACT 5 was an open-label, investigator-initiated randomized trial conducted at 23 centers in Germany and Italy. It included 4,018 participants with ST-elevation segment MI (STEMI), without STEMI, or with unstable angina, all with scheduled coronary angiography. Participants were randomized to ticagrelor or prasugrel and were expected to remain on their assigned potent antiplatelet agent plus aspirin for 1 year of dual-antiplatelet therapy.
The primary outcome was the composite of death, MI, or stroke at 1 year of follow-up. This endpoint occurred in 9.3% of the ticagrelor group and 6.9% of patients in the prasugrel group, for a highly significant 36% increased relative risk in the ticagrelor-treated patients. Prasugrel had a numeric advantage in each of the individual components of the endpoint: the 1-year rate of all-cause mortality was 4.5% with ticagrelor versus 3.7% with prasugrel; for MI, the incidence was 4.8% with ticagrelor and 3.0% with prasugrel, a statistically significant difference; and for stroke, 1.1% versus 1.0%.
Major bleeding as defined by the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium scale occurred in 5.4% of patients in the ticagrelor arm, and was similar at 4.8% in the prasugrel group, Dr. Schuepke continued.
Definite or probable stent thrombosis occurred in 1.3% of the ticagrelor group and 1.0% of patients assigned to prasugrel.
The mechanism for prasugrel’s superior results is unclear, she said. Possibilities include the fact that it’s a once-daily drug, compared with twice-daily ticagrelor, which could affect adherence; a differential profile in terms of drug interactions; and prasugrel’s reversibility of action and capacity for step-down dosing in patients at high bleeding risk.
Discussant Gilles Montalescot, MD, PhD, called ISAR-REACT 5 a “fascinating” study. He elaborated: “It is a pragmatic study to answer a pragmatic question. It’s not a drug trial; really, it’s more a strategy trial, with a comparison of two drugs and two strategies.”
In ISAR-REACT 5, ticagrelor was utilized in standard fashion: Patients, regardless of their ACS type, received a 180-mg loading dose as soon as possible after randomization, typically about 3 hours after presentation. That was also the protocol in the prasugrel arm, but only in patients with STEMI, who quickly got a 60-mg loading dose. In contrast, patients without STEMI or with unstable angina didn’t get a loading dose of prasugrel until they’d undergone coronary angiography and their coronary anatomy was known. That was the ISAR-REACT 5 strategy in light of an earlier study, which concluded that giving prasugrel prior to angiography in such patients led to increased bleeding without any improvement in clinical outcomes.
The essence of ISAR-REACT 5 lies in that difference in treatment strategies and the impact it had on outcomes. “The one-size-fits-all strategy – here, with ticagrelor – was inferior to an individualized strategy, here with prasugrel,” observed Dr. Montalescot, professor of cardiology at the University of Paris VI and director of the cardiac care unit at Paris-Salpetriere Hospital.
The study results were notably consistent, favoring prasugrel over ticagrelor numerically across the board regardless of whether a patient presented with STEMI, without STEMI, or with unstable angina. Particularly noteworthy was the finding that this was also true in terms of the individual components of the 1-year composite endpoint. Dr. Montalescot drew special attention to the large subset of patients who had presented with STEMI and thus received the same treatment strategy involving a loading dose of their assigned P2Y12 inhibitor prior to angiography. This allowed for a direct head-to-head comparison of the clinical efficacy of the two antiplatelet agents in STEMI patients. The clear winner here was prasugrel, as the composite event rate was 10.1% in the ticagrelor group, compared with 7.9% in the prasugrel group.
“ISAR-REACT 5 is a landmark study which is going to impact our practice and the next set of guidelines to come in 2020,” the interventional cardiologist predicted.
Dr. Schuepke reported having no financial conflicts regarding the ISAR-REACT 5 study, sponsored by the German Heart Center and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research.
Simultaneous with her presentation of ISAR-REACT 5, the study results were published online (N Engl J Med. 2019 Sep 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1908973).
REPORTING FROM THE ESC CONGRESS 2019