User login
Shifting Demographics: A Temporal Analysis of the Alarming Rise in Rectal Adenocarcinoma Among Young Adults
Background
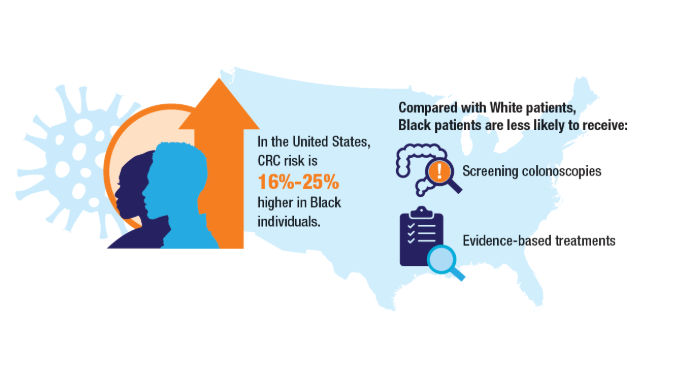
Rectal adenocarcinoma has long been associated with older adults, with routine screening typically beginning at age 45 or older. However, recent data reveal a concerning rise in rectal cancer incidence among adults under 40. These early-onset cases often present at later stages and may have distinct biological features. While some research attributes this trend to genetic or environmental factors, the contribution of socioeconomic disparities and healthcare access has not been fully explored. Identifying these influences is essential to shaping targeted prevention and early detection strategies for younger populations.
Objective
To evaluate temporal trends in rectal adenocarcinoma among young adults and assess demographic and socioeconomic predictors of early-onset diagnosis.
Methods
Data were drawn from the National Cancer Database (NCDB) for patients diagnosed with rectal adenocarcinoma from 2004 to 2022. Among 440,316 cases, 17,842 (4.1%) occurred in individuals under 40. Linear regression assessed temporal trends, while logistic regression evaluated associations between early-onset diagnosis and variables including sex, race, insurance status, income level, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score, and tumor stage. Statistical significance was defined as α = 0.05.
Results
The number of young adults diagnosed rose from 424 in 2004 to 937 in 2022—an increase of over 120%. Each year was associated with a 1.7% rise in odds of early diagnosis (OR = 1.017, p < 0.001). Male patients had 24.7% higher odds (OR = 1.247, p < 0.001), and Black patients had 59.3% higher odds compared to White patients (OR = 1.593, p < 0.001). Non-private insurance was linked to a 41.6% decrease in early diagnosis (OR = 0.584, p < 0.001). Income level was not significant (p = 0.426). Lower Charlson-Deyo scores and higher tumor stages were also associated with early-onset cases.
Conclusions
Rectal adenocarcinoma is increasingly affecting younger adults, with significant associations across demographic and insurance variables. These findings call for improved awareness, early diagnostic strategies, and further research into underlying causes to mitigate this growing public health concern.
Background
Rectal adenocarcinoma has long been associated with older adults, with routine screening typically beginning at age 45 or older. However, recent data reveal a concerning rise in rectal cancer incidence among adults under 40. These early-onset cases often present at later stages and may have distinct biological features. While some research attributes this trend to genetic or environmental factors, the contribution of socioeconomic disparities and healthcare access has not been fully explored. Identifying these influences is essential to shaping targeted prevention and early detection strategies for younger populations.
Objective
To evaluate temporal trends in rectal adenocarcinoma among young adults and assess demographic and socioeconomic predictors of early-onset diagnosis.
Methods
Data were drawn from the National Cancer Database (NCDB) for patients diagnosed with rectal adenocarcinoma from 2004 to 2022. Among 440,316 cases, 17,842 (4.1%) occurred in individuals under 40. Linear regression assessed temporal trends, while logistic regression evaluated associations between early-onset diagnosis and variables including sex, race, insurance status, income level, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score, and tumor stage. Statistical significance was defined as α = 0.05.
Results
The number of young adults diagnosed rose from 424 in 2004 to 937 in 2022—an increase of over 120%. Each year was associated with a 1.7% rise in odds of early diagnosis (OR = 1.017, p < 0.001). Male patients had 24.7% higher odds (OR = 1.247, p < 0.001), and Black patients had 59.3% higher odds compared to White patients (OR = 1.593, p < 0.001). Non-private insurance was linked to a 41.6% decrease in early diagnosis (OR = 0.584, p < 0.001). Income level was not significant (p = 0.426). Lower Charlson-Deyo scores and higher tumor stages were also associated with early-onset cases.
Conclusions
Rectal adenocarcinoma is increasingly affecting younger adults, with significant associations across demographic and insurance variables. These findings call for improved awareness, early diagnostic strategies, and further research into underlying causes to mitigate this growing public health concern.
Background
Rectal adenocarcinoma has long been associated with older adults, with routine screening typically beginning at age 45 or older. However, recent data reveal a concerning rise in rectal cancer incidence among adults under 40. These early-onset cases often present at later stages and may have distinct biological features. While some research attributes this trend to genetic or environmental factors, the contribution of socioeconomic disparities and healthcare access has not been fully explored. Identifying these influences is essential to shaping targeted prevention and early detection strategies for younger populations.
Objective
To evaluate temporal trends in rectal adenocarcinoma among young adults and assess demographic and socioeconomic predictors of early-onset diagnosis.
Methods
Data were drawn from the National Cancer Database (NCDB) for patients diagnosed with rectal adenocarcinoma from 2004 to 2022. Among 440,316 cases, 17,842 (4.1%) occurred in individuals under 40. Linear regression assessed temporal trends, while logistic regression evaluated associations between early-onset diagnosis and variables including sex, race, insurance status, income level, Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score, and tumor stage. Statistical significance was defined as α = 0.05.
Results
The number of young adults diagnosed rose from 424 in 2004 to 937 in 2022—an increase of over 120%. Each year was associated with a 1.7% rise in odds of early diagnosis (OR = 1.017, p < 0.001). Male patients had 24.7% higher odds (OR = 1.247, p < 0.001), and Black patients had 59.3% higher odds compared to White patients (OR = 1.593, p < 0.001). Non-private insurance was linked to a 41.6% decrease in early diagnosis (OR = 0.584, p < 0.001). Income level was not significant (p = 0.426). Lower Charlson-Deyo scores and higher tumor stages were also associated with early-onset cases.
Conclusions
Rectal adenocarcinoma is increasingly affecting younger adults, with significant associations across demographic and insurance variables. These findings call for improved awareness, early diagnostic strategies, and further research into underlying causes to mitigate this growing public health concern.
Expansion of an Intervention to Ensure Accuracy and Usefulness of a SQL Code Identifying Oncology Patients for VACCR
Purpose
The Veterans Affairs Central Cancer Registry (VACCR) is a data management system for cancer surveillance and epidemiologic-based efforts, seeking to reduce the overall cancer burden. In 2024, the local VACCR successfully implemented a Structured Query Language (SQL) code, created to identify documents in the electronic medical record (EMR) with associated ICD-10 codes matching reportable cancer cases in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) list. In 2025, code application expansion began at four additional VISN9 sites.
Outcomes Studied
Accuracy and usefulness of SQL code application in a significantly larger population and a diagnosis-specific population.
Methods
Local Cancer Program leadership collaborated with VISN9 leadership to expand the SQL code to the four sites’ EMR, identifying the Veteran’s name, social security number, location by city/state/county, and visit-associated data including location, ICD-10 code, and visit year. Data validation focused on ICD- 10-specific data and quality replication.
Results
After SQL code application to Mt Home TN VACCR data, 750 unique, randomized charts from 2015-2025 were selected for accuracy review. Data validation found that 90.5% (679) had a reportable cancer; 14.9% (112) were not entered into VACCR. 9.5% (71) were not reportable. The SQL code was applied to Lexington data to identify colorectal cancer (CRC) (ICD-10 codes C17-C21.9). 746 charts from 2015-2025 were identified. 88.9% (663) had a reportable CRC; 14.9% (111) of those were not entered into VACCR, and 11% (83) were not reportable. Most cases not entered into VACCR at both sites were cases in which the majority of care was provided through Care in the Community (CITC). Historically, identification of CITC-provided oncologic care has been manual and notoriously difficult.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of the SQL code in the identification of Veterans with diagnoses matching the SEER list in a large population and at a diagnosis-specific level. VISN-wide use of the report will increase efficiency and timeliness of data entry into VACCR, especially related to care provided through CITC. An improved understanding of oncologic care in the VISN would provide critical data to VISN executive leadership, enabling them to advocate for resources, targeted interventions, and access to care.
Purpose
The Veterans Affairs Central Cancer Registry (VACCR) is a data management system for cancer surveillance and epidemiologic-based efforts, seeking to reduce the overall cancer burden. In 2024, the local VACCR successfully implemented a Structured Query Language (SQL) code, created to identify documents in the electronic medical record (EMR) with associated ICD-10 codes matching reportable cancer cases in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) list. In 2025, code application expansion began at four additional VISN9 sites.
Outcomes Studied
Accuracy and usefulness of SQL code application in a significantly larger population and a diagnosis-specific population.
Methods
Local Cancer Program leadership collaborated with VISN9 leadership to expand the SQL code to the four sites’ EMR, identifying the Veteran’s name, social security number, location by city/state/county, and visit-associated data including location, ICD-10 code, and visit year. Data validation focused on ICD- 10-specific data and quality replication.
Results
After SQL code application to Mt Home TN VACCR data, 750 unique, randomized charts from 2015-2025 were selected for accuracy review. Data validation found that 90.5% (679) had a reportable cancer; 14.9% (112) were not entered into VACCR. 9.5% (71) were not reportable. The SQL code was applied to Lexington data to identify colorectal cancer (CRC) (ICD-10 codes C17-C21.9). 746 charts from 2015-2025 were identified. 88.9% (663) had a reportable CRC; 14.9% (111) of those were not entered into VACCR, and 11% (83) were not reportable. Most cases not entered into VACCR at both sites were cases in which the majority of care was provided through Care in the Community (CITC). Historically, identification of CITC-provided oncologic care has been manual and notoriously difficult.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of the SQL code in the identification of Veterans with diagnoses matching the SEER list in a large population and at a diagnosis-specific level. VISN-wide use of the report will increase efficiency and timeliness of data entry into VACCR, especially related to care provided through CITC. An improved understanding of oncologic care in the VISN would provide critical data to VISN executive leadership, enabling them to advocate for resources, targeted interventions, and access to care.
Purpose
The Veterans Affairs Central Cancer Registry (VACCR) is a data management system for cancer surveillance and epidemiologic-based efforts, seeking to reduce the overall cancer burden. In 2024, the local VACCR successfully implemented a Structured Query Language (SQL) code, created to identify documents in the electronic medical record (EMR) with associated ICD-10 codes matching reportable cancer cases in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) list. In 2025, code application expansion began at four additional VISN9 sites.
Outcomes Studied
Accuracy and usefulness of SQL code application in a significantly larger population and a diagnosis-specific population.
Methods
Local Cancer Program leadership collaborated with VISN9 leadership to expand the SQL code to the four sites’ EMR, identifying the Veteran’s name, social security number, location by city/state/county, and visit-associated data including location, ICD-10 code, and visit year. Data validation focused on ICD- 10-specific data and quality replication.
Results
After SQL code application to Mt Home TN VACCR data, 750 unique, randomized charts from 2015-2025 were selected for accuracy review. Data validation found that 90.5% (679) had a reportable cancer; 14.9% (112) were not entered into VACCR. 9.5% (71) were not reportable. The SQL code was applied to Lexington data to identify colorectal cancer (CRC) (ICD-10 codes C17-C21.9). 746 charts from 2015-2025 were identified. 88.9% (663) had a reportable CRC; 14.9% (111) of those were not entered into VACCR, and 11% (83) were not reportable. Most cases not entered into VACCR at both sites were cases in which the majority of care was provided through Care in the Community (CITC). Historically, identification of CITC-provided oncologic care has been manual and notoriously difficult.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of the SQL code in the identification of Veterans with diagnoses matching the SEER list in a large population and at a diagnosis-specific level. VISN-wide use of the report will increase efficiency and timeliness of data entry into VACCR, especially related to care provided through CITC. An improved understanding of oncologic care in the VISN would provide critical data to VISN executive leadership, enabling them to advocate for resources, targeted interventions, and access to care.
The Role of CDH1 Mutation in Colon Cancer Screening
Background
Genetic testing can reveal inherited or acquired genetic changes that can help with identifying diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and risk of the malignancy. CDH1 is a gene that prevents cancer by controlling cell growth. Mutated CDH1 gene can lead to specific malignancies including gastric and breast cancer.
Case Presentation
42 year old female with past medical history of ovarian cysts presented to the VA Emergency Department for right sided abdominal pain and red colored stool. Further workup showed ileocolonic intussusception with stranding. She underwent a colonoscopy which showed 4 centimeter mass at the ileocecal valve. Biopsy was done which showed invasive adenocarcinoma. She underwent laparoscopic hemicolectomy and was referred to oncology. Referral to genetic testing was positive for CDH1 gene mutation. She was advised that CDH1 mutation has a high risk of developing gastric and breast cancer with recommendations including possible total gastrectomy and bilateral mastectomies. The patient however, decided to decline gastrectomy and mastectomy and instead decided to be followed by frequent EGDs and mammograms.
Discussion
CDH1 mutations are found in only 3.8% of colorectal signet ring cell cancers, with limited data of their presence in typical adenocarcinomas. This case underscores the value of genetic testing in all colorectal adenocarcinomas for its prognostic significance and potential impact on other cancer screenings. CDH1 mutations can lead to an aggressive type of gastric cancer called hereditary diffuse gastric cancer in 56-70% of patients with the mutation. CDH1 mutations also have a 37-55% of having breast cancer compared to the 12% in the general population and patients tend to present with lobular breast cancer. Patients with positive CDH1 mutation should have regular screenings or in some cases, prophylactic surgery.
CDH1 mutation is an important tool in genetic testing because it allows physicians to tailor a treatment plan for their patients. It is important that patients who have a positive CDH1 mutation be advised of the risks of both gastric and breast cancer and should also be educated on treatment options including frequent screenings and prophylactic surgery.
Background
Genetic testing can reveal inherited or acquired genetic changes that can help with identifying diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and risk of the malignancy. CDH1 is a gene that prevents cancer by controlling cell growth. Mutated CDH1 gene can lead to specific malignancies including gastric and breast cancer.
Case Presentation
42 year old female with past medical history of ovarian cysts presented to the VA Emergency Department for right sided abdominal pain and red colored stool. Further workup showed ileocolonic intussusception with stranding. She underwent a colonoscopy which showed 4 centimeter mass at the ileocecal valve. Biopsy was done which showed invasive adenocarcinoma. She underwent laparoscopic hemicolectomy and was referred to oncology. Referral to genetic testing was positive for CDH1 gene mutation. She was advised that CDH1 mutation has a high risk of developing gastric and breast cancer with recommendations including possible total gastrectomy and bilateral mastectomies. The patient however, decided to decline gastrectomy and mastectomy and instead decided to be followed by frequent EGDs and mammograms.
Discussion
CDH1 mutations are found in only 3.8% of colorectal signet ring cell cancers, with limited data of their presence in typical adenocarcinomas. This case underscores the value of genetic testing in all colorectal adenocarcinomas for its prognostic significance and potential impact on other cancer screenings. CDH1 mutations can lead to an aggressive type of gastric cancer called hereditary diffuse gastric cancer in 56-70% of patients with the mutation. CDH1 mutations also have a 37-55% of having breast cancer compared to the 12% in the general population and patients tend to present with lobular breast cancer. Patients with positive CDH1 mutation should have regular screenings or in some cases, prophylactic surgery.
CDH1 mutation is an important tool in genetic testing because it allows physicians to tailor a treatment plan for their patients. It is important that patients who have a positive CDH1 mutation be advised of the risks of both gastric and breast cancer and should also be educated on treatment options including frequent screenings and prophylactic surgery.
Background
Genetic testing can reveal inherited or acquired genetic changes that can help with identifying diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and risk of the malignancy. CDH1 is a gene that prevents cancer by controlling cell growth. Mutated CDH1 gene can lead to specific malignancies including gastric and breast cancer.
Case Presentation
42 year old female with past medical history of ovarian cysts presented to the VA Emergency Department for right sided abdominal pain and red colored stool. Further workup showed ileocolonic intussusception with stranding. She underwent a colonoscopy which showed 4 centimeter mass at the ileocecal valve. Biopsy was done which showed invasive adenocarcinoma. She underwent laparoscopic hemicolectomy and was referred to oncology. Referral to genetic testing was positive for CDH1 gene mutation. She was advised that CDH1 mutation has a high risk of developing gastric and breast cancer with recommendations including possible total gastrectomy and bilateral mastectomies. The patient however, decided to decline gastrectomy and mastectomy and instead decided to be followed by frequent EGDs and mammograms.
Discussion
CDH1 mutations are found in only 3.8% of colorectal signet ring cell cancers, with limited data of their presence in typical adenocarcinomas. This case underscores the value of genetic testing in all colorectal adenocarcinomas for its prognostic significance and potential impact on other cancer screenings. CDH1 mutations can lead to an aggressive type of gastric cancer called hereditary diffuse gastric cancer in 56-70% of patients with the mutation. CDH1 mutations also have a 37-55% of having breast cancer compared to the 12% in the general population and patients tend to present with lobular breast cancer. Patients with positive CDH1 mutation should have regular screenings or in some cases, prophylactic surgery.
CDH1 mutation is an important tool in genetic testing because it allows physicians to tailor a treatment plan for their patients. It is important that patients who have a positive CDH1 mutation be advised of the risks of both gastric and breast cancer and should also be educated on treatment options including frequent screenings and prophylactic surgery.
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
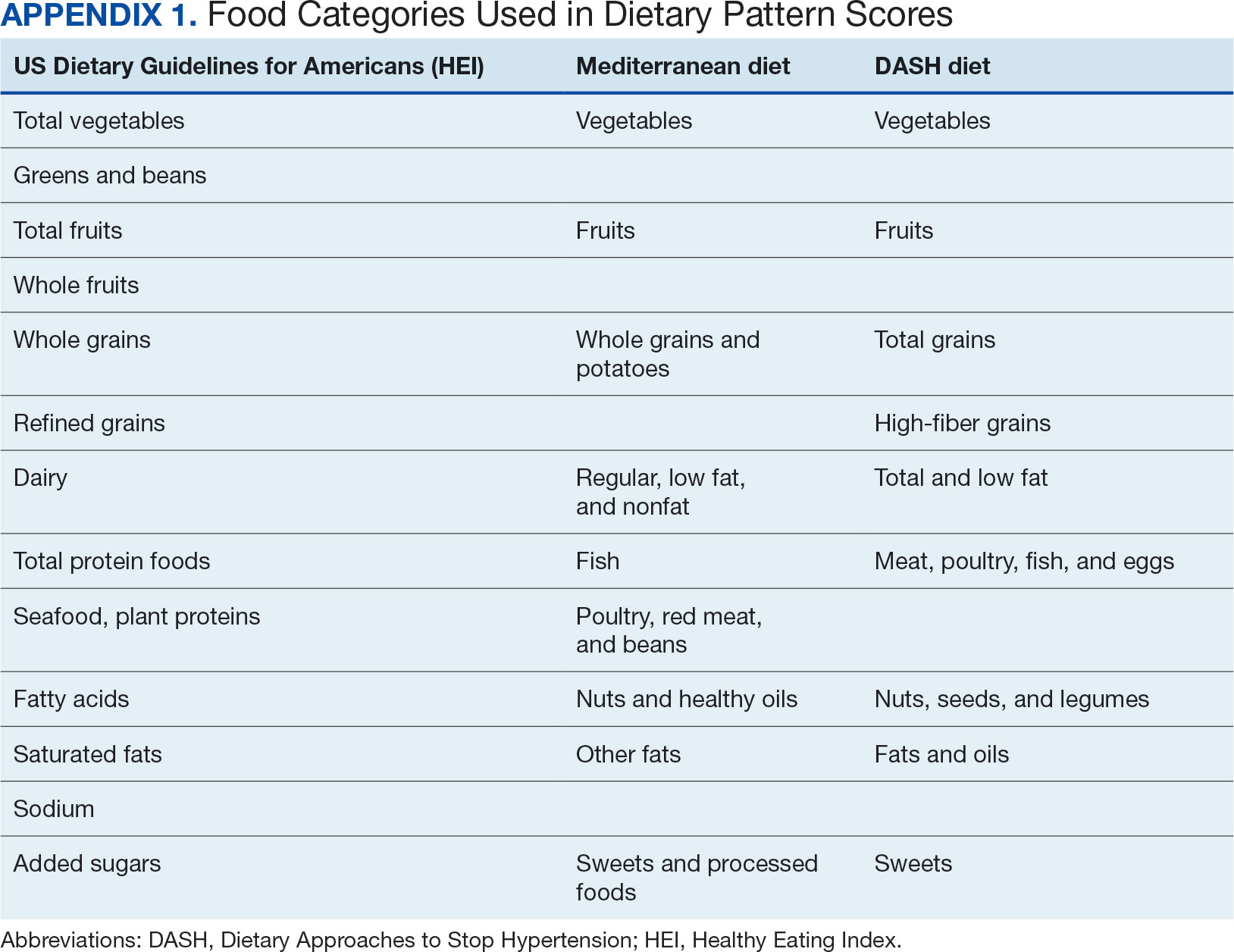
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
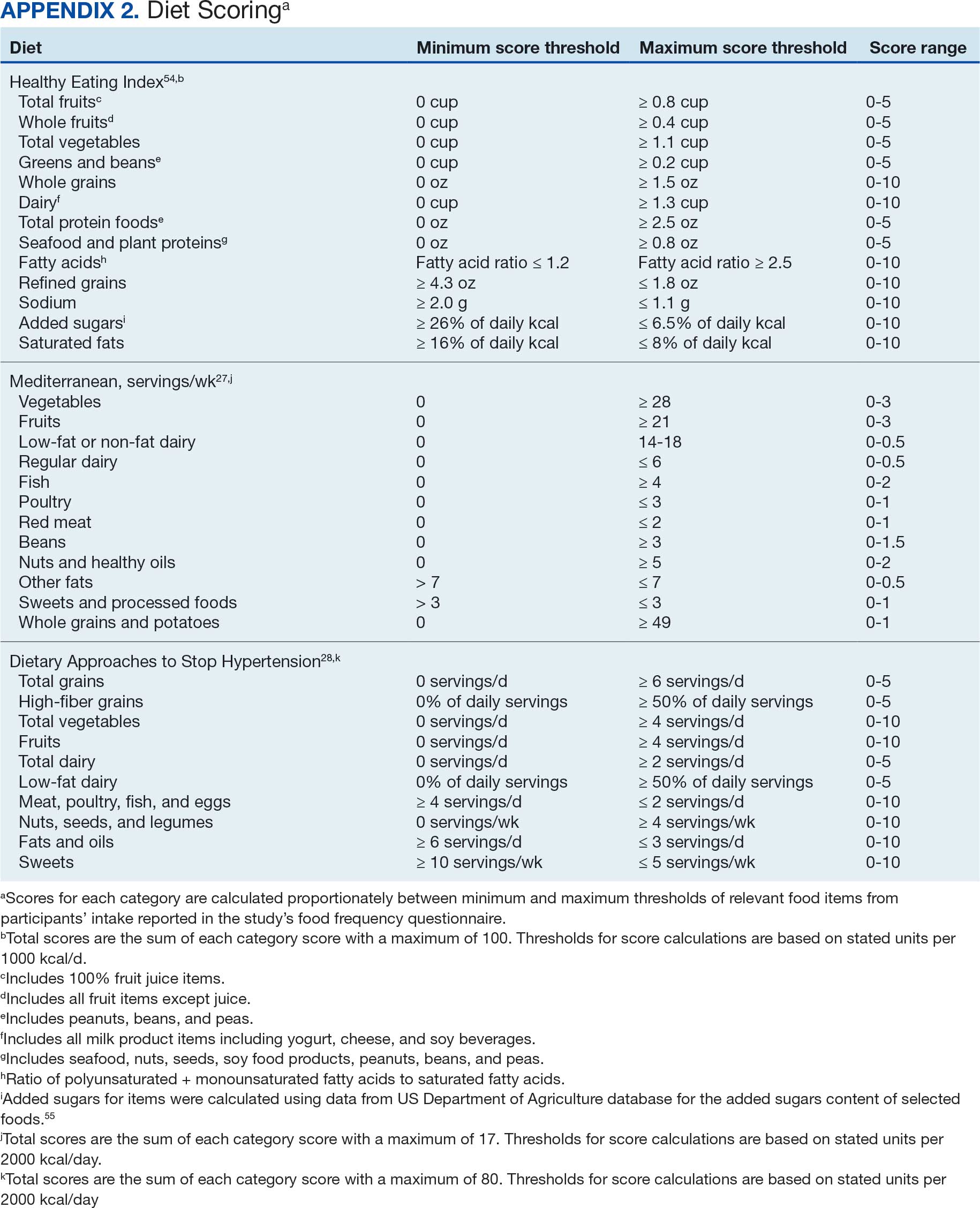
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.
Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
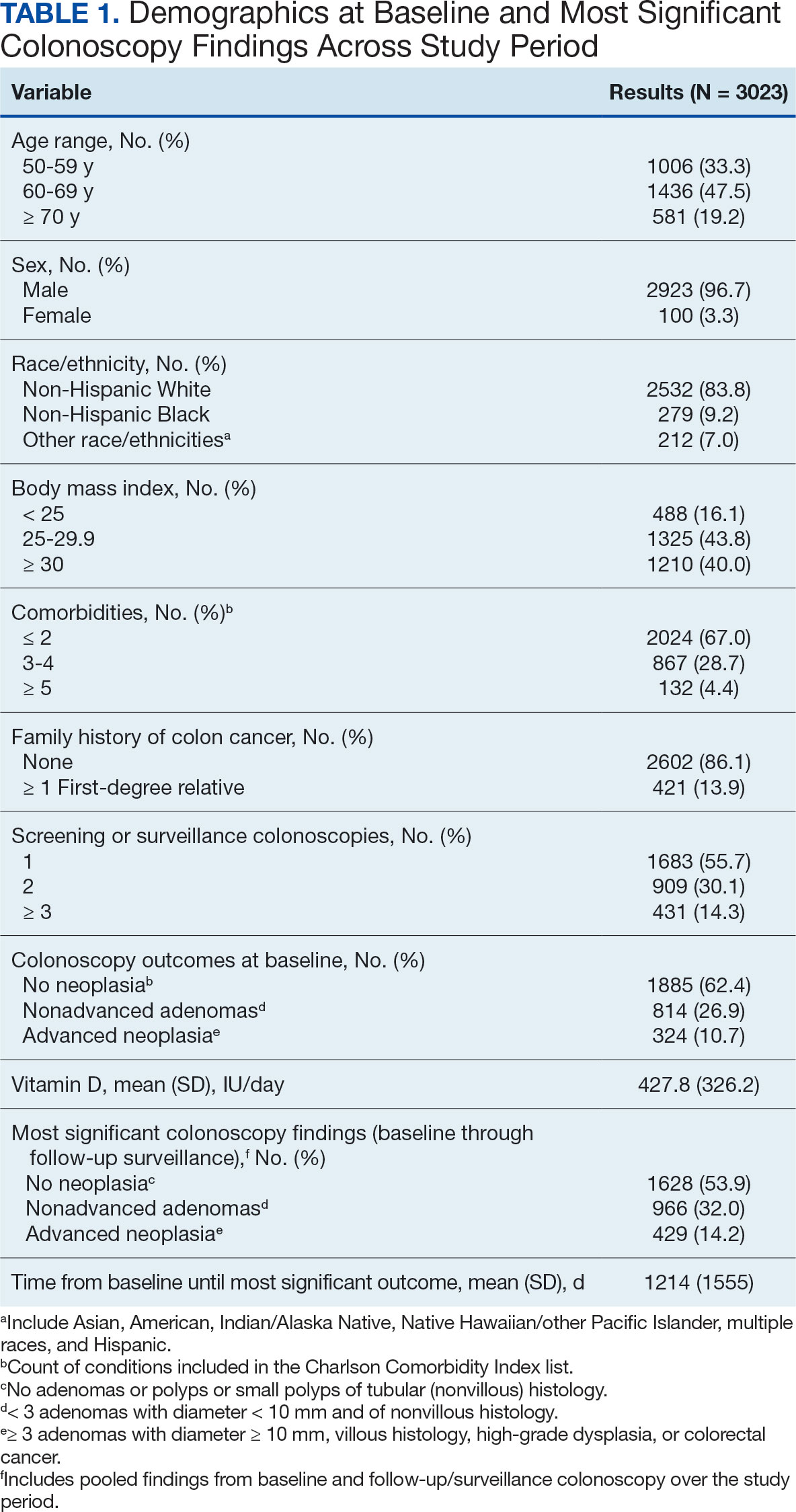
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.
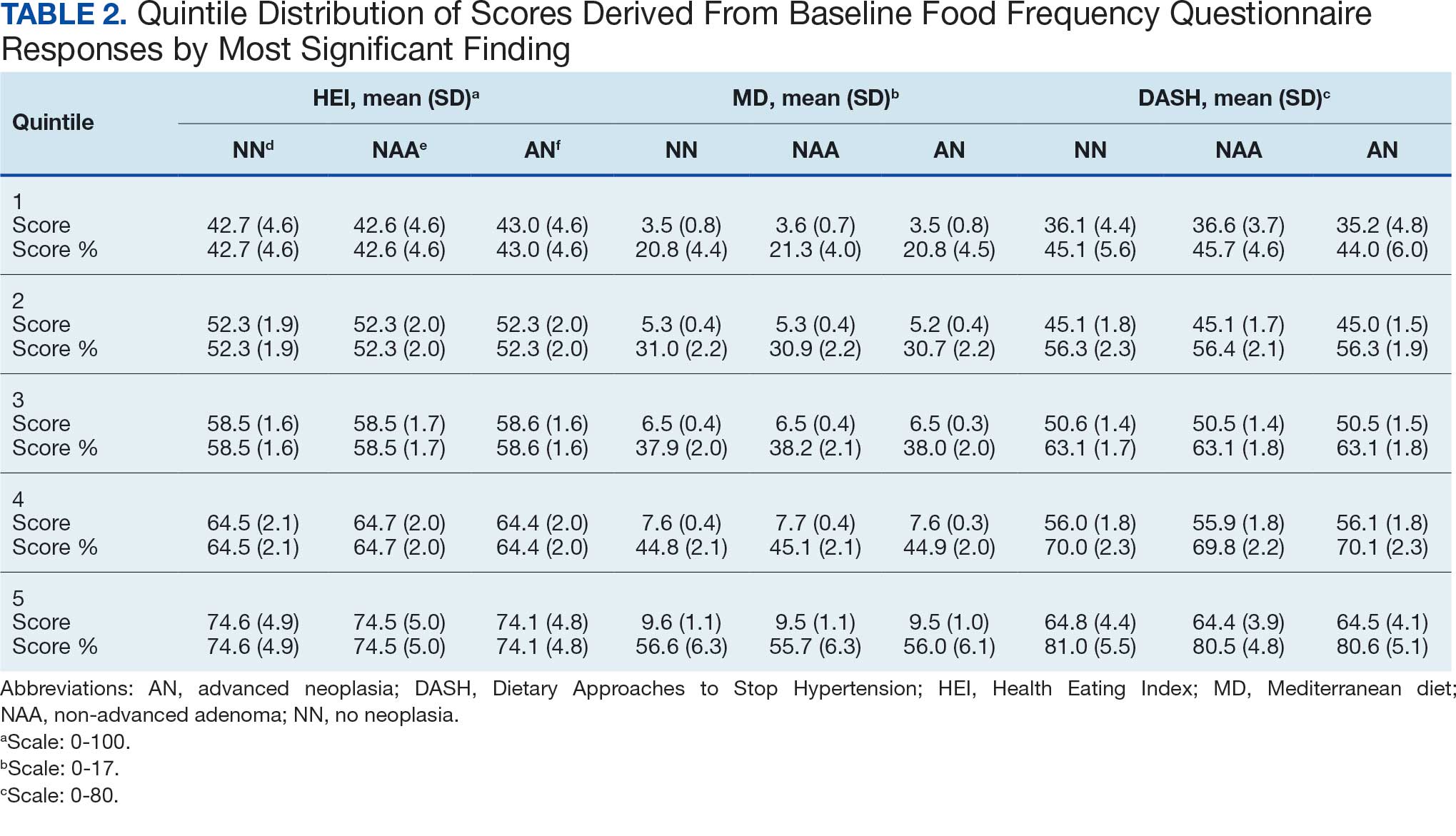
Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).
Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).
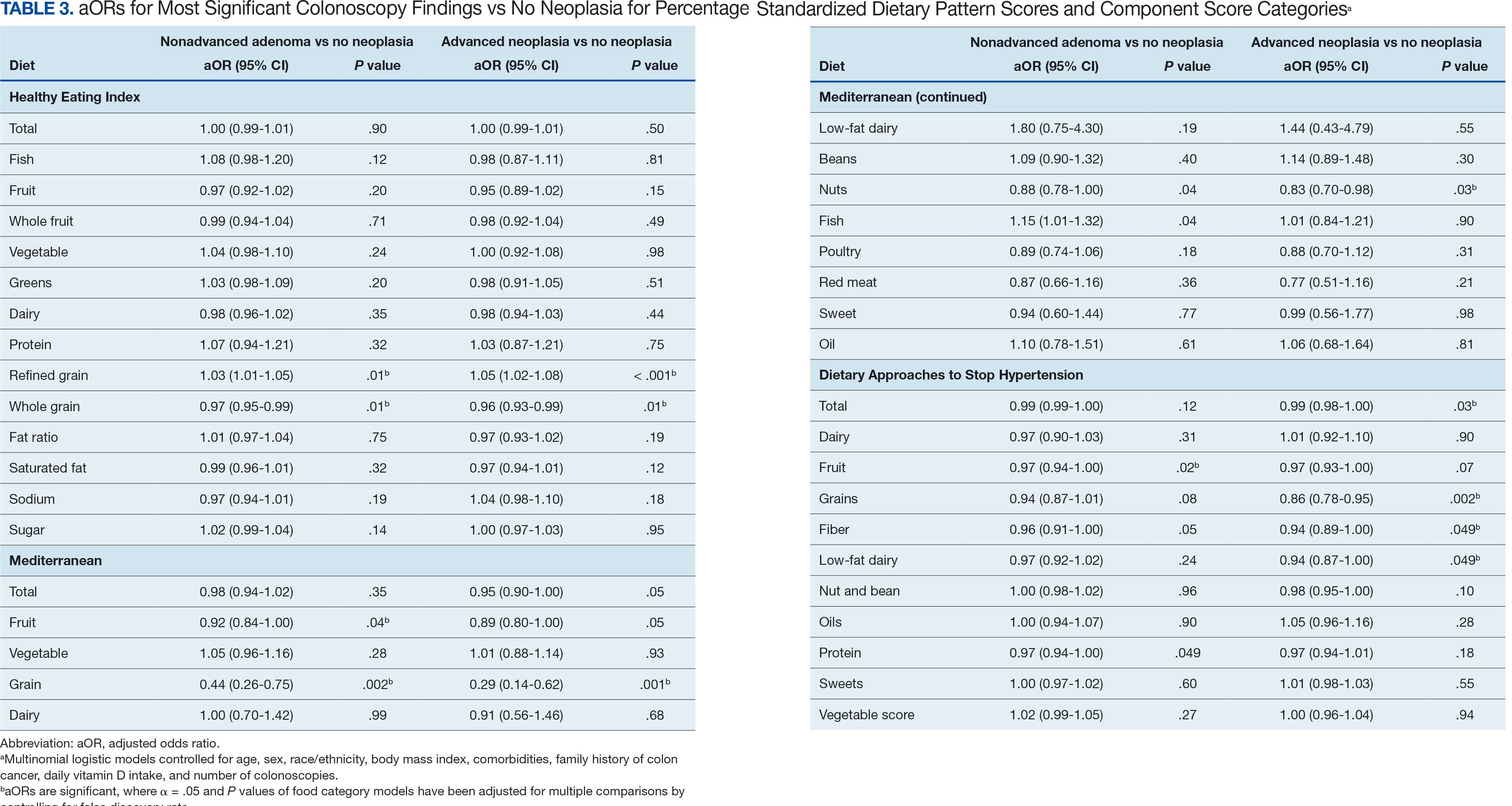
We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.


Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.

Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).

Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).

We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) with colonoscopy enables the identification and removal of CRC precursors (colonic adenomas) and has been associated with reduced risk of CRC incidence and mortality.1-3 Furthermore, there is consensus that diet and lifestyle may be associated with forestalling CRC pathogenesis at the intermediate adenoma stages.4-7 However, studies have shown that US veterans have poorer diet quality and a higher risk for neoplasia compared with nonveterans, reinforcing the need for tailored clinical approaches.8,9 Combining screening with conversations about modifiable environmental and lifestyle risk factors, such as poor diet, is a highly relevant and possibly easily leveraged prevention for those at high risk. However, there is limited evidence for any particular dietary patterns or dietary features that are most important over time.7
Several dietary components have been shown to be associated with CRC risk,10 either as potentially chemopreventive (fiber, fruits and vegetables,11 dairy,12 supplemental vitamin D,13 calcium,14 and multivitamins15) or carcinogenic (red meat16 and alcohol17). Previous studies of veterans have similarly shown that higher intake of fiber and vitamin D reduced risk, and red meat is associated with an increased risk for finding CRC precursors during colonoscopy.18 However, these dietary categories are often analyzed in isolation. Studying healthy dietary patterns in aggregate may be more clinically relevant and easier to implement for prevention of CRC and its precursors.19-21 Healthy dietary patterns, such as the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans represented by the Healthy Eating Index (HEI), the Mediterranean diet (MD), and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet, have been associated with lower risk for chronic disease.22-24 Despite the extant literature, no known studies have compared these dietary patterns for associations with risk of CRC precursor or CRC development among US veterans undergoing long-term screening and follow-up after a baseline colonoscopy.
The objective of this study was to test for associations between baseline scores of healthy dietary patterns and the most severe colonoscopy findings (MSCFs) over ≥ 10 years following a baseline screening colonoscopy in veterans.
Methods
Participants in the Cooperative Studies Program (CSP) #380 cohort study included 3121 asymptomatic veterans aged 50 to 75 years at baseline who had consented to initial screening colonoscopy between 1994 and 1997, with subsequent follow-up and surveillance.25 Prior to their colonoscopy, all participants completed a baseline study survey that included questions about cancer risk factors including family history of CRC, diet, physical activity, and medication use.
Included in this cross-sectional analysis were data from a sample of veteran participants of the CSP #380 cohort with 1 baseline colonoscopy, follow-up surveillance through 2009, a cancer risk factor survey collected at baseline, and complete demographic and clinical indicator data. Excluded from the analysis were 67 participants with insufficient responses to the dietary food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) and 31 participants with missing body mass index (BMI), 3023 veterans.
Measures
MSCF. The outcome of interest in this study was the MSCF recorded across all participant colonoscopies during the study period. MSCF was categorized as either (1) no neoplasia; (2) < 2 nonadvanced adenomas, including small adenomas (diameter < 10 mm) with tubular histology; or (3) advanced neoplasia (AN), which is characterized by adenomas > 10 mm in diameter, with villous histology, with high-grade dysplasia, or CRC.
Dietary patterns. Dietary pattern scores representing dietary quality and calculated based on recommendations of the US Dietary Guidelines for Americans using the HEI, MD, and DASH diets were independent variables.26-28 These 3 dietary patterns were chosen for their hypothesized relationship with CRC risk, but each weighs food categories differently (Appendix 1).22-24,29 Dietary pattern scores were calculated using the CSP #380 self-reported responses to 129 baseline survey questions adapted from a well-established and previously validated semiquantitative FFQ.30 The form was administered by mail twice to a sample of 127 participants at baseline and at 1 year. During this interval, men completed 1-week diet records twice, spaced about 6 months apart. Mean values for intake of most nutrients assessed by the 2 methods were similar. Intraclass correlation coefficients for the baseline and 1-year FFQ-assessed nutrient intakes that ranged from 0.47 for vitamin E (without supplements) to 0.80 for vitamin C (with supplements). Correlation coefficients between the energy-adjusted nutrient intakes were measured by diet records and the 1-year FFQ, which asked about diet during the year encompassing the diet records. Higher raw and percent scores indicated better alignment with recommendations from each respective dietary pattern. Percent scores were calculated as a standardizing method and used in analyses for ease of comparing the dietary patterns. Scoring can be found in Appendix 2.


Demographic characteristics and clinical indicators. Demographic characteristics included age categories, sex, and race/ethnicity. Clinical indicators included BMI, the number of comorbid conditions used to calculate the Charlson Comorbidity Index, family history of CRC in first-degree relatives, number of follow-up colonoscopies across the study period, and food-based vitamin D intake.31 These variables were chosen for their applicability found in previous CSP #380 cohort studies.18,32,33 Self-reported race and ethnicity were collapsed due to small numbers in some groups. The authors acknowledge these are distinct concepts and the variable has limited utility other than for controlling for systemic racism in the model.
Statistical Analyses
Descriptive statistics were used to describe distributional assumptions for all variables, including demographics, clinical indicators, colonoscopy results, and dietary patterns. Pairwise correlations between the total dietary pattern scores and food category scores were calculated with Pearson correlation (r).
Multinomial logistic regression models were created using SAS procedure LOGISTIC with the outcome of the categorical MSCF (no neoplasia, nonadvanced adenoma, or AN).34 A model was created for each independent predictor variable of interest (ie, the HEI, MD, or DASH percentage-standardized dietary pattern score and each food category comprising each dietary pattern score). All models were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, number of comorbidities, family history of CRC, number of follow-up colonoscopies, and estimated daily food-derived vitamin D intake. The demographic and clinical indicators were included in the models as they are known to be associated with CRC risk.18 The number of colonoscopies was included to control for surveillance intensity presuming risk for AN is reduced as polyps are removed. Because colonoscopy findings from an initial screening have unique clinical implications compared with follow- up and surveillance, MSCF was observed in 2 ways in sensitivity analyses: (1) baseline and (2) aggregate follow-up and surveillance only, excluding baseline findings.
Adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% CIs for each of the MSCF outcomes with a reference finding of no neoplasia for the models are presented. We chose not to adjust for multiple comparisons across the different dietary patterns given the correlation between dietary pattern total and category scores but did adjust for multiple comparisons for dietary categories within each dietary pattern. Tests for statistical significance used α= .05 for the dietary pattern total scores and P values for the dietary category scores for each dietary pattern controlled for false discovery rate using the MULTTEST SAS procedure.35 All data manipulations and analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4.
Results
The study included 3023 patients. All were aged 50 to 75 years, 2923 (96.7%) were male and 2532 (83.8%) were non-Hispanic White (Table 1). Most participants were overweight or obese (n = 2535 [83.8%]), 2024 (67.0%) had ≤ 2 comorbidities, and 2602 (86.1%) had no family history of CRC. The MSCF for 1628 patients (53.9%) was no neoplasia, 966 patients (32.0%) was nonadvanced adenoma, and 429 participants (14.2%) had AN.

Mean percent scores were 58.5% for HEI, 38.2% for MD, and 63.1% for the DASH diet, with higher percentages indicating greater alignment with the recommendations for each diet (Table 2). All 3 dietary patterns scores standardized to percentages were strongly and significantly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI:MD, r = 0.62 (P < .001); HEI:DASH, r = 0.60 (P < .001); and MD:DASH, r = 0.72 (P < .001). Likewise, food category scores were significantly correlated across dietary patterns. For example, whole grain and fiber values from each dietary score were strongly correlated in pairwise comparisons: HEI Whole Grain:MD Grain, r = 0.64 (P < .001); HEI Whole Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.71 (P < .001); and MD Grain:DASH Fiber, r = 0.70 (P < .001).

Associations between individual participants' dietary pattern scores and the outcome of their pooled MSCF from baseline screening and ≥ 10 years of surveillance are presented in Table 3. For each single-point increases in dietary pattern scores (reflecting better dietary quality), aORs for nonadvanced adenoma vs no neoplasia were slightly lower but not statistically significantly: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.98 (95% CI, 0.94-1.02); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00). aORs for AN vs no neoplasia were slightly lower for each dietary pattern assessed, and only the MD and DASH scores were significantly different from 1.00: HEI, aOR, 1.00 (95% CI, 0.99-1.01); MD, aOR, 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90-1.00); and DASH, aOR, 0.99 (95% CI, 0.98-1.00).

We observed lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma and AN among all these dietary patterns when there was greater alignment with the recommended intake of whole grains and fiber. In separate models conducted using food categories comprising the dietary patterns as independent variables and after correcting for multiple tests, higher scores for the HEI Refined Grain category were associated with higher odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 1.03 [95% CI, 1.01-1.05]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 1.05 [95% CI, 1.02-1.08]; P < .001). Higher scores for the HEI Whole Grain category were associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.97 [95% CI, 0.95-0.99]; P = .01) and AN (aOR, 0.96 [95% CI, 0.93-0.99]; P = .01). Higher scores for the MD Grain category were significantly associated with lower odds for nonadvanced adenoma (aOR, 0.44 [95% CI, 0.26-0.75]; P = .002) and AN (aOR, 0.29 [95% CI, 0.14-0.62]; P = .001). The DASH Grains category also was significantly associated with lower odds for AN (aOR, 0.86 [95% CI, 0.78-0.95]; P = .002).
Discussion
In this study of 3023 veterans undergoing first-time screening colonoscopy and ≥ 10 years of surveillance, we found that healthy dietary patterns, as assessed by the MD and DASH diet, were significantly associated with lower risk of AN. Additionally, we identified lower odds for AN and nonadvanced adenoma compared with no neoplasia for higher grain scores for all the dietary patterns studied. Other food categories that comprise the dietary pattern scores had mixed associations with the MSCF outcomes. Several other studies have examined associations between dietary patterns and risk for CRC but to our knowledge, no studies have explored these associations among US veterans.
These results also indicate study participants had better than average (based on a 50% threshold) dietary quality according to the HEI and DASH diet scoring methods we used, but poor dietary quality according to the MD scoring method. The mean HEI scores for the present study were higher than a US Department of Agriculture study by Dong et al that compared dietary quality between veterans and nonveterans using the HEI, for which veterans’ expected HEI score was 45.6 of 100.8 This could be explained by the fact that the participants needed to be healthy to be eligible and those with healthier behaviors overall may have self-selected into the study due to motivation for screening during a time when screening was not yet commonplace. 36 Similarly, participants of the present study had higher adherence to the DASH diet (63.1%) than adolescents with diabetes in a study by Günther et al. Conversely, firefighters who were coached to use a Mediterranean-style dietary pattern and dietary had higher adherence to MD than did participants in this study.27
A closer examination of specific food category component scores that comprise the 3 distinct dietary patterns revealed mixed results from the multinomial modeling, which may have to do with the guideline thresholds used to calculate the dietary scores. When analyzed separately in the logistic regression models for their associations with nonadvanced adenomas and AN compared with no neoplasia, higher MD and DASH fruit scores (but not HEI fruit scores) were found to be significant. Other studies have had mixed findings when attempting to test for associations of fruit intake with adenoma recurrence.10,37
This study had some unexpected findings. Vegetable intake was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN risk. Studies of food categories have consistently found vegetable (specifically cruciferous ones) intake to be linked with lower odds for cancers.38 Likewise, the red meat category, which was only a unique food category in the MD score, was not associated with nonadvanced adenomas or AN. Despite consistent literature suggesting higher intake of red meat and processed meats increases CRC risk, in 2019 the Nutritional Recommendations Consortium indicated that the evidence was weak.39,40 This study showed higher DASH diet scores for low-fat dairy, which were maximized when participants reported at least 50% of their dairy servings per day as being low-fat, had lower odds for AN. Yet, the MD scores for low-fat dairy had no association with either outcome; their calculation was based on total number of servings per week. This difference in findings suggests the fat intake ratio may be more relevant to CRC risk than intake quantity.
The literature is mixed regarding fatty acid intake and CRC risk, which may be relevant to both dairy and meat intake. One systematic review and meta-analysis found dietary fat and types of fatty acid intake had no association with CRC risk.41 However, a more recent meta-analysis that assessed both dietary intake and plasma levels of fatty acids did find some statistically significant differences for various types of fatty acids and CRC risk.42
The findings in the present study that grain intake is associated with lower odds for more severe colonoscopy findings among veterans are notable.43 Lieberman et al, using the CSP #380 data, found that cereal fiber intake was associated with a lower odds for AN compared with hyperplastic polyps (OR, 0.98 [95% CI, 0.96- 1.00]).18 Similarly, Hullings et al determined that older adults in the highest quintile of cereal fiber intake had significantly lower odds of CRC than those in lower odds for CRC when compared with lowest quintile (OR, 0.89 [95% CI, 0.83- 0.96]; P < .001).44 These findings support existing guidance that prioritizes whole grains as a key source of dietary fiber for CRC prevention.
A recent literature review on fiber, fat, and CRC risk suggested a consensus regarding one protective mechanism: dietary fiber from grains modulates the gut microbiota by promoting butyrate synthesis.45 Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid that supports energy production in colonocytes and has tumor-suppressing properties.46 Our findings suggest there could be more to learn about the relationship between butyrate production and reduction of CRC risk through metabolomic studies that use measurements of plasma butyrate. These studies may examine associations between not just a singular food or food category, but rather food patterns that include fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, and whole grains known to promote butyrate production and plasma butyrate.47
Improved understanding of mechanisms and risk-modifying lifestyle factors such as dietary patterns may enhance prevention strategies. Identifying the collective chemopreventive characteristics of a specific dietary pattern (eg, MD) will be helpful to clinicians and health care staff to promote healthy eating to reduce cancer risk. More studies are needed to understand whether such promotion is more clinically applicable and effective for patients, as compared with eating more or less of specific foods (eg, more whole grains, less red meat). Furthermore, considering important environmental factors collectively beyond dietary patterns may offer a way to better tailor screening and implement a variety of lifestyle interventions. In the literature, this is often referred to as a teachable moment when patients’ attentions are captured and may position them to be more receptive to guidance.48
Limitations
This study has several important limitations and leaves opportunities for future studies that explore the role of dietary patterns and AN or CRC risk. First, the FFQ data used to calculate dietary pattern scores used in analysis were only captured at baseline, and there are nearly 3 decades across the study period. However, it is widely assumed that the diets of older adults, like those included in this study, remain stable over time which is appropriate given our sample population was aged 50 to 75 years when the baseline FFQ data were collected.49-51 Additionally, while the HEI is a well-documented, standard scoring method for dietary quality, there are multitudes of dietary pattern scoring approaches for MD and DASH.23,52,53 Finally, findings from this study using the sample of veterans may not be generalizable to a broader population. Future longitudinal studies that test for a clinically significant change threshold are warranted.
Conclusion
Results of this study suggest future research should further explore the effects of dietary patterns, particularly intake of specific food groups in combination, as opposed to individual nutrients or food items, on AN and CRC risk. Possible studies might explore these dietary patterns for their mechanistic role in altering the microbiome metabolism, which may influence CRC outcomes or include diet in a more comprehensive, holistic risk score that could be used to predict colonic neoplasia risk or in intervention studies that assess the effects of dietary changes on long-term CRC prevention. We suggest there are differences in people’s dietary intake patterns that might be important to consider when implementing tailored approaches to CRC risk mitigation.
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
- Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O’Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectalcancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(8):687-696. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1100370
- Nishihara R, Wu K, Lochhead P, et al. Long-term colorectal-cancer incidence and mortality after lower endoscopy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1095-1105. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1301969
- Bretthauer M, Løberg M, Wieszczy P, et al. Effect of colonoscopy screening on risks of colorectal cancer and related death. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(17):1547-1556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2208375
- Cottet V, Bonithon-Kopp C, Kronborg O, et al. Dietary patterns and the risk of colorectal adenoma recurrence in a European intervention trial. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2005;14(1):21.
- Miller PE, Lesko SM, Muscat JE, Lazarus P, Hartman TJ. Dietary patterns and colorectal adenoma and cancer risk: a review of the epidemiological evidence. Nutr Cancer. 2010;62(4):413-424. doi:10.1080/01635580903407114
- Godos J, Bella F, Torrisi A, Sciacca S, Galvano F, Grosso G. Dietary patterns and risk of colorectal adenoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J Hum Nutr Diet Off J Br Diet Assoc. 2016;29(6):757-767. doi:10.1111/jhn.12395
- Haggar FA, Boushey RP. Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2009;22(4):191-197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
- Dong D, Stewart H, Carlson AC. An Examination of Veterans’ Diet Quality. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service; 2019:32.
- El-Halabi MM, Rex DK, Saito A, Eckert GJ, Kahi CJ. Defining adenoma detection rate benchmarks in average-risk male veterans. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89(1):137-143. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.08.021
- Alberts DS, Hess LM, eds. Fundamentals of Cancer Prevention. Springer International Publishing; 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-15935-1
- Dahm CC, Keogh RH, Spencer EA, et al. Dietary fiber and colorectal cancer risk: a nested case-control study using food diaries. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(9):614-626. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq092
- Aune D, Lau R, Chan DSM, et al. Dairy products and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and metaanalysis of cohort studies. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):37-45. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr269
- Lee JE, Li H, Chan AT, et al. Circulating levels of vitamin D and colon and rectal cancer: the Physicians’ Health Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Cancer Prev Res Phila Pa. 2011;4(5):735-743. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0289
- Carroll C, Cooper K, Papaioannou D, Hind D, Pilgrim H, Tappenden P. Supplemental calcium in the chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Ther. 2010;32(5):789-803. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.04.024
- Park Y, Spiegelman D, Hunter DJ, et al. Intakes of vitamins A, C, and E and use of multiple vitamin supplements and risk of colon cancer: a pooled analysis of prospective cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control CCC. 2010;21(11):1745- 1757. doi:10.1007/s10552-010-9549-y
- Alexander DD, Weed DL, Miller PE, Mohamed MA. Red meat and colorectal cancer: a quantitative update on the state of the epidemiologic science. J Am Coll Nutr. 2015;34(6):521-543. doi:10.1080/07315724.2014.992553
- Park SY, Wilkens LR, Setiawan VW, Monroe KR, Haiman CA, Le Marchand L. Alcohol intake and colorectal cancer risk in the multiethnic cohort study. Am J Epidemiol. 2019;188(1):67-76. doi:10.1093/aje/kwy208
- Lieberman DA. Risk Factors for advanced colonic neoplasia and hyperplastic polyps in asymptomatic individuals. JAMA. 2003;290(22):2959. doi:10.1001/jama.290.22.2959
- Archambault AN, Jeon J, Lin Y, et al. Risk stratification for early-onset colorectal cancer using a combination of genetic and environmental risk scores: an international multi-center study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2022;114(4):528-539. doi:10.1093/jnci/djac003
- Carr PR, Weigl K, Edelmann D, et al. Estimation of absolute risk of colorectal cancer based on healthy lifestyle, genetic risk, and colonoscopy status in a populationbased study. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(1):129-138.e9. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.016
- Sullivan BA, Qin X, Miller C, et al. Screening colonoscopy findings are associated with noncolorectal cancer mortality. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13(4):e00479. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000479
- Erben V, Carr PR, Holleczek B, Stegmaier C, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Dietary patterns and risk of advanced colorectal neoplasms: A large population based screening study in Germany. Prev Med. 2018;111:101-109. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2018.02.025
- Donovan MG, Selmin OI, Doetschman TC, Romagnolo DF. Mediterranean diet: prevention of colorectal cancer. Front Nutr. 2017;4:59. doi:10.3389/fnut.2017.00059
- Mohseni R, Mohseni F, Alizadeh S, Abbasi S. The Association of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet with the risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Nutr Cancer. 2020;72(5):778-790. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1651880
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Bond JH, Ahnen DJ, Garewal H, Chejfec G. Use of colonoscopy to screen asymptomatic adults for colorectal cancer. Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group 380. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(3):162-168. doi:10.1056/NEJM200007203430301
- Developing the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) | EGRP/ DCCPS/NCI/NIH. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/hei/developing.html#2015c
- Reeve E, Piccici F, Feairheller DL. Validation of a Mediterranean diet scoring system for intervention based research. J Nutr Med Diet Care. 2021;7(1):053. doi:10.23937/2572-3278/1510053
- Günther AL, Liese AD, Bell RA, et al. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE DIETARY APPROACHES TO HYPERTENSION (DASH) DIET AND HYPERTENSION IN YOUTH WITH DIABETES. Hypertens Dallas Tex 1979. 2009;53(1):6-12. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.116665
- Buckland G, Agudo A, Luján L, et al. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and risk of gastric adenocarcinoma within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(2):381- 390. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28209
- Rimm EB, Giovannucci EL, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Litin LB, Willett WC. Reproducibility and validity of an expanded self-administered semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire among male health professionals. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135(10):1114-1126. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116211
- Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-383. doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
- Lieberman DA, Weiss DG, Harford WV, et al. Fiveyear colon surveillance after screening colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(4):1077-1085. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.07.006
- Lieberman D, Sullivan BA, Hauser ER, et al. Baseline colonoscopy findings associated with 10-year outcomes in a screening cohort undergoing colonoscopy surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):862-874.e8. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.052
- PROC LOGISTIC: PROC LOGISTIC Statement : SAS/STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_logistic_sect004.htm
- PROC MULTTEST: PROC MULTTEST Statement : SAS/ STAT(R) 9.22 User’s Guide. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63347/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_multtest_sect005.htm
- Elston DM. Participation bias, self-selection bias, and response bias. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online June 18, 2021. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2021.06.025
- Sansbury LB, Wanke K, Albert PS, et al. The effect of strict adherence to a high-fiber, high-fruit and -vegetable, and low-fat eating pattern on adenoma recurrence. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(5):576-584. doi:10.1093/aje/kwp169
- Borgas P, Gonzalez G, Veselkov K, Mirnezami R. Phytochemically rich dietary components and the risk of colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. World J Clin Oncol. 2021;12(6):482- 499. doi:10.5306/wjco.v12.i6.482
- Papadimitriou N, Markozannes G, Kanellopoulou A, et al. An umbrella review of the evidence associating diet and cancer risk at 11 anatomical sites. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4579. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24861-8
- Johnston BC, Zeraatkar D, Han MA, et al. Unprocessed red meat and processed meat consumption: dietary guideline recommendations from the nutritional recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171(10):756-764. doi:10.7326/M19-1621
- Kim M, Park K. Dietary fat intake and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1963. doi:10.3390/nu10121963
- Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):730. doi:10.3390/nu15030730
- Gherasim A, Arhire LI, Ni.a O, Popa AD, Graur M, Mihalache L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79(3):311-323. doi:10.1017/S0029665120006898
- Hullings AG, Sinha R, Liao LM, Freedman ND, Graubard BI, Loftfield E. Whole grain and dietary fiber intake and risk of colorectal cancer in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(3):603- 612. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqaa161
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: new insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(11):62. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2
- O’Keefe SJD. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;13(12):691-706. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2016.165
- The health benefits and side effects of Butyrate Cleveland Clinic. July 11, 2022. Accessed July 22, 2025. https://health.clevelandclinic.org/butyrate-benefits/
- Knudsen MD, Wang L, Wang K, et al. Changes in lifestyle factors after endoscopic screening: a prospective study in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol Off ClinPract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc. 2022;20(6):e1240-e1249. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.014
- Thorpe MG, Milte CM, Crawford D, McNaughton SA. Education and lifestyle predict change in dietary patterns and diet quality of adults 55 years and over. Nutr J. 2019;18(1):67. doi:10.1186/s12937-019-0495-6
- Chapman K, Ogden J. How do people change their diet?: an exploration into mechanisms of dietary change. J Health Psychol. 2009;14(8):1229-1242. doi:10.1177/1359105309342289
- Djoussé L, Petrone AB, Weir NL, et al. Repeated versus single measurement of plasma omega-3 fatty acids and risk of heart failure. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(6):1403-1408. doi:10.1007/s00394-013-0642-3
- Bach-Faig A, Berry EM, Lairon D, et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011;14(12A):2274-2284. doi:10.1017/S1368980011002515
- Miller PE, Cross AJ, Subar AF, et al. Comparison of 4 established DASH diet indexes: examining associations of index scores and colorectal cancer123. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):794-803. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.063602
- Krebs-Smith SM, Pannucci TE, Subar AF, et al. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018;118(9):1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
- P.R. Pehrsson, Cutrufelli RL, Gebhardt SE, et al. USDA Database for the Added Sugars Content of Selected Foods. USDA; 2005. www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Associations Between Prescreening Dietary Patterns and Longitudinal Colonoscopy Outcomes in Veterans
Access, Race, and "Colon Age": Improving CRC Screening
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820.
2. Riviere P, Morgan KM, Deshler LN, et al. Racial disparities in colorectal cancer outcomes and access to care: a multi-cohort analysis. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1414361. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1414361
3. Imperiale TF, Myers LJ, Barker BC, Stump TE, Daggy JK. Colon Age: A metric for whether and how to screen male veterans for early-onset colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res. 2024:17:377-384. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-23-0544
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820.
2. Riviere P, Morgan KM, Deshler LN, et al. Racial disparities in colorectal cancer outcomes and access to care: a multi-cohort analysis. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1414361. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1414361
3. Imperiale TF, Myers LJ, Barker BC, Stump TE, Daggy JK. Colon Age: A metric for whether and how to screen male veterans for early-onset colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res. 2024:17:377-384. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-23-0544
1. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12-49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820.
2. Riviere P, Morgan KM, Deshler LN, et al. Racial disparities in colorectal cancer outcomes and access to care: a multi-cohort analysis. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1414361. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1414361
3. Imperiale TF, Myers LJ, Barker BC, Stump TE, Daggy JK. Colon Age: A metric for whether and how to screen male veterans for early-onset colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev Res. 2024:17:377-384. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-23-0544
AI-Aided Colonoscopy’s ‘Intelligent’ Module Ups Polyp Detection
Colin J. Rees, a professor of gastroenterology in the Faculty of Medical Sciences at Newcastle University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and colleagues compared the real-world clinical effectiveness of computer-aided detection (CADe)–assisted colonoscopy using an “intelligent” module with that of standard colonoscopy in a study in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
They found the GI Genius Intelligent Endoscopy Module (Medtronic) increased the mean number of adenomas detected per procedure and the adenoma detection rate, especially for small, flat (type 0-IIa) polyps, and sessile serrated lesions, which are more likely to be missed.
“Missed sessile serrated lesions disproportionately increase the risk of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer, thus the adoption of GI Genius into routine colonoscopy practice could not only increase polyp detection but also reduce the incidence of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer,” the investigators wrote.
“AI is going to have a major impact upon most aspects of healthcare. Some areas of medical practice are now well established, and some are still in evolution,” Rees, who is also president of the British Society of Gastroenterology, said in an interview. “Within gastroenterology, the role of AI in endoscopic diagnostics is also evolving. The COLO-DETECT trial demonstrates that AI increases detection of lesions, and work is ongoing to see how AI might help with characterization and other elements of endoscopic practice.”
Study Details
The multicenter, open-label, parallel-arm, pragmatic randomized controlled trial was conducted at 12 National Health Service hospitals in England. The study cohort consisted of adults ≥ 18 years undergoing colorectal cancer (CRC) screening or colonoscopy for gastrointestinal symptom surveillance owing to personal or family history.
Recruiting staff, participants, and colonoscopists were unmasked to allocation, whereas histopathologists, cochief investigators, and trial statisticians were masked.
CADe-assisted colonoscopy consisted of standard colonoscopy plus the GI Genius module active for at least the entire inspection phase of colonoscope withdrawal.
The primary outcome was mean adenomas per procedure (total number of adenomas detected divided by total number of procedures). The key secondary outcome was adenoma detection rate (proportion of colonoscopies with at least one adenoma).
From March 2021 to April 2023, the investigators recruited 2032 participants, 55.7% men, with a mean cohort age of 62.4 years and randomly assigned them to CADe-assisted colonoscopy (n = 1015) or to standard colonoscopy (n = 1017). Of these, 60.6% were undergoing screening and 39.4% had symptomatic indications.
Mean adenomas per procedure were 1.56 (SD, 2.82; n = 1001 participants with data) in the CADe-assisted group vs 1.21 (n = 1009) in the standard group, for an adjusted mean difference of 0.36 (95% CI, 0.14-0.57; adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.15-1.47; P < .0001).
Adenomas were detected in 555 (56.6%) of 980 participants in the CADe-assisted group vs 477 (48.4%) of 986 in the standard group, representing a proportion difference of 8.3% (95% CI, 3.9-12.7; adjusted odds ratio, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.21-1.78; P < .0001).
As to safety, adverse events were numerically comparable in both the intervention and control groups, with overall events 25 vs 19 and serious events 4 vs 6. On independent review, no adverse events in the CADe-assisted colonoscopy group were related to GI Genius.
Offering a US perspective on the study, Nabil M. Mansour, MD, an associate professor and director of the McNair General GI Clinic at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said GI Genius and other CADe systems represent a significant advance over standard colonoscopy for identifying premalignant polyps. “While the data have been mixed, most studies, particularly randomized controlled trials have shown significant improvements with CADe in detection both terms of in adenomas per colonoscopy and reductions in adenoma miss rate,” he said in an interview.
He added that the main utility of CADe is for asymptomatic patients undergoing average-risk screening and surveillance colonoscopy for CRC screening and prevention, as well as for those with positive stool-based screening tests, “though there is no downside to using it in symptomatic patients as well.” Though AI colonoscopy likely still stands at < 50% of endoscopy centers overall, and is used mainly at academic centers, his clinic has been using it for the past year.
The main question, Mansour cautioned, is whether increased detection of small polyps will actually reduce CRC incidence or mortality, and it will likely be several years before clear, concrete data can answer that.
“Most studies have shown the improvement in adenoma detection is mainly for diminutive polyps < 5 mm in diameter, but whether that will actually translate to substantive improvements in hard outcomes is as yet unknown,” he said. “But if gastroenterologists are interested in doing everything they can today to help improve detection rates and lower miss rates of premalignant polyps, serious consideration should be given to adopting the use of CADe in practice.”
This study was supported by Medtronic. Rees reported receiving grant funding from ARC Medical, Norgine, Medtronic, 3-D Matrix, and Olympus Medical, and has been an expert witness for ARC Medical. Other authors disclosed receiving research funding, honoraria, or travel expenses from Medtronic or other private companies. Mansour had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Colin J. Rees, a professor of gastroenterology in the Faculty of Medical Sciences at Newcastle University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and colleagues compared the real-world clinical effectiveness of computer-aided detection (CADe)–assisted colonoscopy using an “intelligent” module with that of standard colonoscopy in a study in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
They found the GI Genius Intelligent Endoscopy Module (Medtronic) increased the mean number of adenomas detected per procedure and the adenoma detection rate, especially for small, flat (type 0-IIa) polyps, and sessile serrated lesions, which are more likely to be missed.
“Missed sessile serrated lesions disproportionately increase the risk of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer, thus the adoption of GI Genius into routine colonoscopy practice could not only increase polyp detection but also reduce the incidence of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer,” the investigators wrote.
“AI is going to have a major impact upon most aspects of healthcare. Some areas of medical practice are now well established, and some are still in evolution,” Rees, who is also president of the British Society of Gastroenterology, said in an interview. “Within gastroenterology, the role of AI in endoscopic diagnostics is also evolving. The COLO-DETECT trial demonstrates that AI increases detection of lesions, and work is ongoing to see how AI might help with characterization and other elements of endoscopic practice.”
Study Details
The multicenter, open-label, parallel-arm, pragmatic randomized controlled trial was conducted at 12 National Health Service hospitals in England. The study cohort consisted of adults ≥ 18 years undergoing colorectal cancer (CRC) screening or colonoscopy for gastrointestinal symptom surveillance owing to personal or family history.
Recruiting staff, participants, and colonoscopists were unmasked to allocation, whereas histopathologists, cochief investigators, and trial statisticians were masked.
CADe-assisted colonoscopy consisted of standard colonoscopy plus the GI Genius module active for at least the entire inspection phase of colonoscope withdrawal.
The primary outcome was mean adenomas per procedure (total number of adenomas detected divided by total number of procedures). The key secondary outcome was adenoma detection rate (proportion of colonoscopies with at least one adenoma).
From March 2021 to April 2023, the investigators recruited 2032 participants, 55.7% men, with a mean cohort age of 62.4 years and randomly assigned them to CADe-assisted colonoscopy (n = 1015) or to standard colonoscopy (n = 1017). Of these, 60.6% were undergoing screening and 39.4% had symptomatic indications.
Mean adenomas per procedure were 1.56 (SD, 2.82; n = 1001 participants with data) in the CADe-assisted group vs 1.21 (n = 1009) in the standard group, for an adjusted mean difference of 0.36 (95% CI, 0.14-0.57; adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.15-1.47; P < .0001).
Adenomas were detected in 555 (56.6%) of 980 participants in the CADe-assisted group vs 477 (48.4%) of 986 in the standard group, representing a proportion difference of 8.3% (95% CI, 3.9-12.7; adjusted odds ratio, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.21-1.78; P < .0001).
As to safety, adverse events were numerically comparable in both the intervention and control groups, with overall events 25 vs 19 and serious events 4 vs 6. On independent review, no adverse events in the CADe-assisted colonoscopy group were related to GI Genius.
Offering a US perspective on the study, Nabil M. Mansour, MD, an associate professor and director of the McNair General GI Clinic at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said GI Genius and other CADe systems represent a significant advance over standard colonoscopy for identifying premalignant polyps. “While the data have been mixed, most studies, particularly randomized controlled trials have shown significant improvements with CADe in detection both terms of in adenomas per colonoscopy and reductions in adenoma miss rate,” he said in an interview.
He added that the main utility of CADe is for asymptomatic patients undergoing average-risk screening and surveillance colonoscopy for CRC screening and prevention, as well as for those with positive stool-based screening tests, “though there is no downside to using it in symptomatic patients as well.” Though AI colonoscopy likely still stands at < 50% of endoscopy centers overall, and is used mainly at academic centers, his clinic has been using it for the past year.
The main question, Mansour cautioned, is whether increased detection of small polyps will actually reduce CRC incidence or mortality, and it will likely be several years before clear, concrete data can answer that.
“Most studies have shown the improvement in adenoma detection is mainly for diminutive polyps < 5 mm in diameter, but whether that will actually translate to substantive improvements in hard outcomes is as yet unknown,” he said. “But if gastroenterologists are interested in doing everything they can today to help improve detection rates and lower miss rates of premalignant polyps, serious consideration should be given to adopting the use of CADe in practice.”
This study was supported by Medtronic. Rees reported receiving grant funding from ARC Medical, Norgine, Medtronic, 3-D Matrix, and Olympus Medical, and has been an expert witness for ARC Medical. Other authors disclosed receiving research funding, honoraria, or travel expenses from Medtronic or other private companies. Mansour had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Colin J. Rees, a professor of gastroenterology in the Faculty of Medical Sciences at Newcastle University in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and colleagues compared the real-world clinical effectiveness of computer-aided detection (CADe)–assisted colonoscopy using an “intelligent” module with that of standard colonoscopy in a study in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
They found the GI Genius Intelligent Endoscopy Module (Medtronic) increased the mean number of adenomas detected per procedure and the adenoma detection rate, especially for small, flat (type 0-IIa) polyps, and sessile serrated lesions, which are more likely to be missed.
“Missed sessile serrated lesions disproportionately increase the risk of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer, thus the adoption of GI Genius into routine colonoscopy practice could not only increase polyp detection but also reduce the incidence of post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer,” the investigators wrote.
“AI is going to have a major impact upon most aspects of healthcare. Some areas of medical practice are now well established, and some are still in evolution,” Rees, who is also president of the British Society of Gastroenterology, said in an interview. “Within gastroenterology, the role of AI in endoscopic diagnostics is also evolving. The COLO-DETECT trial demonstrates that AI increases detection of lesions, and work is ongoing to see how AI might help with characterization and other elements of endoscopic practice.”
Study Details
The multicenter, open-label, parallel-arm, pragmatic randomized controlled trial was conducted at 12 National Health Service hospitals in England. The study cohort consisted of adults ≥ 18 years undergoing colorectal cancer (CRC) screening or colonoscopy for gastrointestinal symptom surveillance owing to personal or family history.
Recruiting staff, participants, and colonoscopists were unmasked to allocation, whereas histopathologists, cochief investigators, and trial statisticians were masked.
CADe-assisted colonoscopy consisted of standard colonoscopy plus the GI Genius module active for at least the entire inspection phase of colonoscope withdrawal.
The primary outcome was mean adenomas per procedure (total number of adenomas detected divided by total number of procedures). The key secondary outcome was adenoma detection rate (proportion of colonoscopies with at least one adenoma).
From March 2021 to April 2023, the investigators recruited 2032 participants, 55.7% men, with a mean cohort age of 62.4 years and randomly assigned them to CADe-assisted colonoscopy (n = 1015) or to standard colonoscopy (n = 1017). Of these, 60.6% were undergoing screening and 39.4% had symptomatic indications.
Mean adenomas per procedure were 1.56 (SD, 2.82; n = 1001 participants with data) in the CADe-assisted group vs 1.21 (n = 1009) in the standard group, for an adjusted mean difference of 0.36 (95% CI, 0.14-0.57; adjusted incidence rate ratio, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.15-1.47; P < .0001).
Adenomas were detected in 555 (56.6%) of 980 participants in the CADe-assisted group vs 477 (48.4%) of 986 in the standard group, representing a proportion difference of 8.3% (95% CI, 3.9-12.7; adjusted odds ratio, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.21-1.78; P < .0001).
As to safety, adverse events were numerically comparable in both the intervention and control groups, with overall events 25 vs 19 and serious events 4 vs 6. On independent review, no adverse events in the CADe-assisted colonoscopy group were related to GI Genius.
Offering a US perspective on the study, Nabil M. Mansour, MD, an associate professor and director of the McNair General GI Clinic at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said GI Genius and other CADe systems represent a significant advance over standard colonoscopy for identifying premalignant polyps. “While the data have been mixed, most studies, particularly randomized controlled trials have shown significant improvements with CADe in detection both terms of in adenomas per colonoscopy and reductions in adenoma miss rate,” he said in an interview.
He added that the main utility of CADe is for asymptomatic patients undergoing average-risk screening and surveillance colonoscopy for CRC screening and prevention, as well as for those with positive stool-based screening tests, “though there is no downside to using it in symptomatic patients as well.” Though AI colonoscopy likely still stands at < 50% of endoscopy centers overall, and is used mainly at academic centers, his clinic has been using it for the past year.
The main question, Mansour cautioned, is whether increased detection of small polyps will actually reduce CRC incidence or mortality, and it will likely be several years before clear, concrete data can answer that.
“Most studies have shown the improvement in adenoma detection is mainly for diminutive polyps < 5 mm in diameter, but whether that will actually translate to substantive improvements in hard outcomes is as yet unknown,” he said. “But if gastroenterologists are interested in doing everything they can today to help improve detection rates and lower miss rates of premalignant polyps, serious consideration should be given to adopting the use of CADe in practice.”
This study was supported by Medtronic. Rees reported receiving grant funding from ARC Medical, Norgine, Medtronic, 3-D Matrix, and Olympus Medical, and has been an expert witness for ARC Medical. Other authors disclosed receiving research funding, honoraria, or travel expenses from Medtronic or other private companies. Mansour had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY
Does Intensive Follow-Up Testing Improve Survival in CRC?
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a secondary analysis.
METHODOLOGY:
- After curative surgery for CRC, intensive patient follow-up is common in clinical practice. However, there’s limited evidence to suggest that more frequent testing provides a long-term survival benefit.
- In the COLOFOL trial, patients with stage II or III CRC who had undergone curative resection were randomly assigned to either high-frequency follow-up (CT scans and CEA screening at 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months) or low-frequency follow-up (testing at 12 and 36 months) after surgery.
- This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL trial included 2456 patients (median age, 65 years), 1227 of whom received high-frequency follow-up and 1229 of whom received low-frequency follow-up.
- The main outcome of the secondary analysis was 10-year overall mortality and CRC–specific mortality rates.
- The analysis included both intention-to-treat and per-protocol approaches, with outcomes measured through December 2020.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the intention-to-treat analysis, the 10-year overall mortality rates were similar between the high- and low-frequency follow-up groups — 27.1% and 28.4%, respectively (risk difference, 1.3%; P = .46).
- A per-protocol analysis confirmed these findings: The 10-year overall mortality risk was 26.4% in the high-frequency group and 27.8% in the low-frequency group.
- The 10-year CRC–specific mortality rate was also similar between the high-frequency and low-frequency groups — 15.6% and 16.0%, respectively — (risk difference, 0.4%; P = .72). The same pattern was seen in the per-protocol analysis, which found a 10-year CRC–specific mortality risk of 15.6% in the high-frequency group and 15.9% in the low-frequency group.
- Subgroup analyses by cancer stage and location (rectal and colon) also revealed no significant differences in mortality outcomes between the two follow-up groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL randomized clinical trial found that, among patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer, more frequent follow-up testing with CT scan and CEA screening, compared with less frequent follow-up, did not result in a significant rate reduction in 10-year overall mortality or colorectal cancer-specific mortality,” the authors concluded. “The results of this trial should be considered as the evidence base for updating clinical guidelines.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Henrik Toft Sørensen, MD, PhD, DMSc, DSc, Aarhus University Hospital and Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The staff turnover at recruitment centers potentially affected protocol adherence. The inability to blind patients and physicians to the follow-up frequency was another limitation. The low-frequency follow-up protocol was less intensive than that recommended in the current guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Society of Clinical Oncology, potentially limiting comparisons to current standard practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The initial trial received unrestricted grants from multiple organizations including the Nordic Cancer Union, A.P. Møller Foundation, Beckett Foundation, Danish Cancer Society, and Swedish Cancer Foundation project. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a secondary analysis.
METHODOLOGY:
- After curative surgery for CRC, intensive patient follow-up is common in clinical practice. However, there’s limited evidence to suggest that more frequent testing provides a long-term survival benefit.
- In the COLOFOL trial, patients with stage II or III CRC who had undergone curative resection were randomly assigned to either high-frequency follow-up (CT scans and CEA screening at 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months) or low-frequency follow-up (testing at 12 and 36 months) after surgery.
- This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL trial included 2456 patients (median age, 65 years), 1227 of whom received high-frequency follow-up and 1229 of whom received low-frequency follow-up.
- The main outcome of the secondary analysis was 10-year overall mortality and CRC–specific mortality rates.
- The analysis included both intention-to-treat and per-protocol approaches, with outcomes measured through December 2020.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the intention-to-treat analysis, the 10-year overall mortality rates were similar between the high- and low-frequency follow-up groups — 27.1% and 28.4%, respectively (risk difference, 1.3%; P = .46).
- A per-protocol analysis confirmed these findings: The 10-year overall mortality risk was 26.4% in the high-frequency group and 27.8% in the low-frequency group.
- The 10-year CRC–specific mortality rate was also similar between the high-frequency and low-frequency groups — 15.6% and 16.0%, respectively — (risk difference, 0.4%; P = .72). The same pattern was seen in the per-protocol analysis, which found a 10-year CRC–specific mortality risk of 15.6% in the high-frequency group and 15.9% in the low-frequency group.
- Subgroup analyses by cancer stage and location (rectal and colon) also revealed no significant differences in mortality outcomes between the two follow-up groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL randomized clinical trial found that, among patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer, more frequent follow-up testing with CT scan and CEA screening, compared with less frequent follow-up, did not result in a significant rate reduction in 10-year overall mortality or colorectal cancer-specific mortality,” the authors concluded. “The results of this trial should be considered as the evidence base for updating clinical guidelines.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Henrik Toft Sørensen, MD, PhD, DMSc, DSc, Aarhus University Hospital and Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The staff turnover at recruitment centers potentially affected protocol adherence. The inability to blind patients and physicians to the follow-up frequency was another limitation. The low-frequency follow-up protocol was less intensive than that recommended in the current guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Society of Clinical Oncology, potentially limiting comparisons to current standard practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The initial trial received unrestricted grants from multiple organizations including the Nordic Cancer Union, A.P. Møller Foundation, Beckett Foundation, Danish Cancer Society, and Swedish Cancer Foundation project. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to findings from a secondary analysis.
METHODOLOGY:
- After curative surgery for CRC, intensive patient follow-up is common in clinical practice. However, there’s limited evidence to suggest that more frequent testing provides a long-term survival benefit.
- In the COLOFOL trial, patients with stage II or III CRC who had undergone curative resection were randomly assigned to either high-frequency follow-up (CT scans and CEA screening at 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months) or low-frequency follow-up (testing at 12 and 36 months) after surgery.
- This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL trial included 2456 patients (median age, 65 years), 1227 of whom received high-frequency follow-up and 1229 of whom received low-frequency follow-up.
- The main outcome of the secondary analysis was 10-year overall mortality and CRC–specific mortality rates.
- The analysis included both intention-to-treat and per-protocol approaches, with outcomes measured through December 2020.
TAKEAWAY:
- In the intention-to-treat analysis, the 10-year overall mortality rates were similar between the high- and low-frequency follow-up groups — 27.1% and 28.4%, respectively (risk difference, 1.3%; P = .46).
- A per-protocol analysis confirmed these findings: The 10-year overall mortality risk was 26.4% in the high-frequency group and 27.8% in the low-frequency group.
- The 10-year CRC–specific mortality rate was also similar between the high-frequency and low-frequency groups — 15.6% and 16.0%, respectively — (risk difference, 0.4%; P = .72). The same pattern was seen in the per-protocol analysis, which found a 10-year CRC–specific mortality risk of 15.6% in the high-frequency group and 15.9% in the low-frequency group.
- Subgroup analyses by cancer stage and location (rectal and colon) also revealed no significant differences in mortality outcomes between the two follow-up groups.
IN PRACTICE:
“This secondary analysis of the COLOFOL randomized clinical trial found that, among patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer, more frequent follow-up testing with CT scan and CEA screening, compared with less frequent follow-up, did not result in a significant rate reduction in 10-year overall mortality or colorectal cancer-specific mortality,” the authors concluded. “The results of this trial should be considered as the evidence base for updating clinical guidelines.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Henrik Toft Sørensen, MD, PhD, DMSc, DSc, Aarhus University Hospital and Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The staff turnover at recruitment centers potentially affected protocol adherence. The inability to blind patients and physicians to the follow-up frequency was another limitation. The low-frequency follow-up protocol was less intensive than that recommended in the current guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and the American Society of Clinical Oncology, potentially limiting comparisons to current standard practices.
DISCLOSURES:
The initial trial received unrestricted grants from multiple organizations including the Nordic Cancer Union, A.P. Møller Foundation, Beckett Foundation, Danish Cancer Society, and Swedish Cancer Foundation project. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could Diet and Gut Bacteria Be Fueling Early CRC?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’d like to reflect a little on the ever-rising incidence of early-onset colorectal cancer. I saw two patients in the clinic on Friday, both in their early thirties, presenting with stage IV disease. Both had young families — a disaster.
This is an issue that we must address, I think, epidemiologically. We know that and currently, around 200,000 such cases are diagnosed every year, but it is said to increase unquestionably.
The epidemiologists, I think, correctly have identified that this sharp, rapid increase does imply that there is a new environmental change that is underpinning or underscoring this rise in early-onset disease.
There’s a fantastic team that has been put together by Paul Brennan, Mike Stratton, and colleagues, a collaborative group of epidemiologists, geneticists, and bioinformaticians, who are looking at a global study to try to understand the basis of early-onset colorectal cancer. Their approach is to combine conventional epidemiology, genomics, and fantastic computational support to try to unpick the mutational signatures involved.
The dominant hypothesis is that, over the past 20-25 years or so, there has been a change in diet that has allowed an alteration in the gut microbiome such that we now harbor, in some cases, more bacteria capable of manufacturing, synthesizing, and releasing mutagenic chemicals. There’s a subtype of Escherichia coli which manufactures one such mutagen called colibactin.
Again, through some of the painstaking, extraordinary work that Mike Stratton and colleagues have done at the Sanger Institute, they have managed to, using a variety of different techniques — in vitro, observational, and so on — relate exposure to the mutagen colibactin to a particular mutational signature.
They plan to do a large global study — one of the strengths — involving many different countries around the globe, collect material from older colorectal cancer patients and early-onset colorectal cancer patients, and undertake a staggeringly large mutational study to see if the mutational signature associated with colibactin is more highly represented in these early-onset cases. The hypothesis is that, if you’re exposed to this mutagen in childhood, then it increases the tumor mutational burden and therefore the likelihood of developing cancer at an earlier age.
All of us believe that converting a normal cell into a tumor cell usually requires five or six or seven separate mutational events occurring at random. The earlier these occur, the greater the tumor, the greater the normal single-cellular mutational burden, and the more likely it is to develop cancer sooner rather than later.
This is a fantastically interesting study, and it’s the way ahead with modern genetic epidemiology, one would say. We wish them well. This will be a 3- to 5-year truly international effort, bringing together a genuinely internationally outstanding research team. We hope that they are able to shed more light on the epidemiology of this early-onset disease, because only by understanding can we deflect and deal with it.
Knowledge is power, as I’ve said many times before. If we understand the underlying epidemiology, that will allow us to intervene, one would hope, and avoid the chaotic disaster of my clinic on Friday, with these two young patients with an extremely limited lifespan and large families who will be left bereft in having lost a parent.
More power to the team. We wish them well with the study, but again, this is a pointer to the future, one would hope, of modern genetic computational epidemiology.
I’d be really interested in any ideas or comments that you might have. Are you in the field? Are you seeing more young patients? Do you have any ideas or hypotheses of your own around the microbiome and what bugs might be involved and so on?
Dr. Kerr, Professor, Nuffield Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, University of Oxford, England; Professor of Cancer Medicine, Oxford Cancer Centre, Oxford, United Kingdom, has disclosed relevant financial relationships with Celleron Therapeutics, Oxford Cancer Biomarkers, Afrox, GlaxoSmithKline, Bayer, Genomic Health, Merck Serono, and Roche.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AI-Assisted Colonoscopy Linked to Higher Rate of Benign Lesion Removal
PHILADELPHIA — according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
In particular, AIAC led to a statistically and clinically significant increase in the proportion of exams that detected lesions that after resection were all found to be benign, compared with unassisted colonoscopy.
“The potential implications include increased procedural risks, as well as costs, such as pathology costs and other healthcare expenditures, without any additional colorectal cancer prevention benefit,” said lead author Tessa Herman, MD, chief resident of internal medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System.
In a previous implementation trial at the Minneapolis VA Medical Center, Herman and colleagues compared ADR between a group of patients undergoing AIAC and a historical cohort of patients who had non–AI-assisted colonoscopy.
In this subsequent study, the research team conducted an ad hoc analysis of data from the previous trial to determine the proportion of colonoscopies for screening, surveillance, and positive fecal immunochemical tests which detect lesions that after resection are all found to be benign. They excluded colonoscopies conducted for diagnostic indications or inflammatory bowel disease, as well as incomplete colonoscopies, and for those with inadequate bowel preparation.
Overall, they studied 441 non-AIAC colonoscopies (between November 2022 and April 2023) and 599 AIAC colonoscopies (between May 2023 and October 2023). The groups were balanced, and there were no significant differences in patient demographics, endoscopists, AI technology, procedure time, or average number of polyps detected.
In the non-AIAC cohort, 37 cases (8.4%) had polypectomies that revealed only benign lesions, as compared with 74 cases (12.4%) in the AIAC cohort. The most common resected lesions were benign colonic mucosa, lymphoid aggregates, and hyperplastic polyps.
Applied to the 15 million colonoscopies conducted in the United States per year, the findings indicate that full adoption of AIAC could result in about 600,000 more colonoscopies in which only benign, nonadenomatous lesions are removed, compared with traditional colonoscopy, Herman said.
More study of AIAC is needed, said Daniel Pambianco, MD, managing partner of GastroHealth-Charlottesville in Virginia and the 2023 ACG president. “This technology is in a fledging stage, and the more data we have, the more helpful it’ll be to know if we’re removing the right lesions at a better rate.”
“There’s a hope that assistance will improve detection, removal of polyps, and ultimately, colon cancer,” added Pambianco, who comoderated the session on colorectal cancer prevention.
Future longitudinal studies should monitor both ADR and benign lesion resection rates with AIAC, and modeling studies could determine the benefits and costs of the technology, Herman said. In addition, development of hybrid CADe and computer-aided diagnosis systems could mitigate concerns about excessive benign lesion resection with AI tools.
Clinicians already are able to find colon mucosa that are polypoid or lymphoid aggregates during colonoscopy without AI assistance, said the session’s comoderator, Sita Chokhavatia, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Valley Medical Group in Ridgewood, New Jersey.
“Instead, we need a tool that can help us to not remove these polyps that are not neoplastic,” she said. “With future developments, we may be able to take it to the next step where the algorithm tells us that it’s benign and not to touch it.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Herman, Pambianco, and Chokhavatia reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
In particular, AIAC led to a statistically and clinically significant increase in the proportion of exams that detected lesions that after resection were all found to be benign, compared with unassisted colonoscopy.
“The potential implications include increased procedural risks, as well as costs, such as pathology costs and other healthcare expenditures, without any additional colorectal cancer prevention benefit,” said lead author Tessa Herman, MD, chief resident of internal medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System.
In a previous implementation trial at the Minneapolis VA Medical Center, Herman and colleagues compared ADR between a group of patients undergoing AIAC and a historical cohort of patients who had non–AI-assisted colonoscopy.
In this subsequent study, the research team conducted an ad hoc analysis of data from the previous trial to determine the proportion of colonoscopies for screening, surveillance, and positive fecal immunochemical tests which detect lesions that after resection are all found to be benign. They excluded colonoscopies conducted for diagnostic indications or inflammatory bowel disease, as well as incomplete colonoscopies, and for those with inadequate bowel preparation.
Overall, they studied 441 non-AIAC colonoscopies (between November 2022 and April 2023) and 599 AIAC colonoscopies (between May 2023 and October 2023). The groups were balanced, and there were no significant differences in patient demographics, endoscopists, AI technology, procedure time, or average number of polyps detected.
In the non-AIAC cohort, 37 cases (8.4%) had polypectomies that revealed only benign lesions, as compared with 74 cases (12.4%) in the AIAC cohort. The most common resected lesions were benign colonic mucosa, lymphoid aggregates, and hyperplastic polyps.
Applied to the 15 million colonoscopies conducted in the United States per year, the findings indicate that full adoption of AIAC could result in about 600,000 more colonoscopies in which only benign, nonadenomatous lesions are removed, compared with traditional colonoscopy, Herman said.
More study of AIAC is needed, said Daniel Pambianco, MD, managing partner of GastroHealth-Charlottesville in Virginia and the 2023 ACG president. “This technology is in a fledging stage, and the more data we have, the more helpful it’ll be to know if we’re removing the right lesions at a better rate.”
“There’s a hope that assistance will improve detection, removal of polyps, and ultimately, colon cancer,” added Pambianco, who comoderated the session on colorectal cancer prevention.
Future longitudinal studies should monitor both ADR and benign lesion resection rates with AIAC, and modeling studies could determine the benefits and costs of the technology, Herman said. In addition, development of hybrid CADe and computer-aided diagnosis systems could mitigate concerns about excessive benign lesion resection with AI tools.
Clinicians already are able to find colon mucosa that are polypoid or lymphoid aggregates during colonoscopy without AI assistance, said the session’s comoderator, Sita Chokhavatia, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Valley Medical Group in Ridgewood, New Jersey.
“Instead, we need a tool that can help us to not remove these polyps that are not neoplastic,” she said. “With future developments, we may be able to take it to the next step where the algorithm tells us that it’s benign and not to touch it.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Herman, Pambianco, and Chokhavatia reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG).
In particular, AIAC led to a statistically and clinically significant increase in the proportion of exams that detected lesions that after resection were all found to be benign, compared with unassisted colonoscopy.
“The potential implications include increased procedural risks, as well as costs, such as pathology costs and other healthcare expenditures, without any additional colorectal cancer prevention benefit,” said lead author Tessa Herman, MD, chief resident of internal medicine at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, and Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System.
In a previous implementation trial at the Minneapolis VA Medical Center, Herman and colleagues compared ADR between a group of patients undergoing AIAC and a historical cohort of patients who had non–AI-assisted colonoscopy.
In this subsequent study, the research team conducted an ad hoc analysis of data from the previous trial to determine the proportion of colonoscopies for screening, surveillance, and positive fecal immunochemical tests which detect lesions that after resection are all found to be benign. They excluded colonoscopies conducted for diagnostic indications or inflammatory bowel disease, as well as incomplete colonoscopies, and for those with inadequate bowel preparation.
Overall, they studied 441 non-AIAC colonoscopies (between November 2022 and April 2023) and 599 AIAC colonoscopies (between May 2023 and October 2023). The groups were balanced, and there were no significant differences in patient demographics, endoscopists, AI technology, procedure time, or average number of polyps detected.
In the non-AIAC cohort, 37 cases (8.4%) had polypectomies that revealed only benign lesions, as compared with 74 cases (12.4%) in the AIAC cohort. The most common resected lesions were benign colonic mucosa, lymphoid aggregates, and hyperplastic polyps.
Applied to the 15 million colonoscopies conducted in the United States per year, the findings indicate that full adoption of AIAC could result in about 600,000 more colonoscopies in which only benign, nonadenomatous lesions are removed, compared with traditional colonoscopy, Herman said.
More study of AIAC is needed, said Daniel Pambianco, MD, managing partner of GastroHealth-Charlottesville in Virginia and the 2023 ACG president. “This technology is in a fledging stage, and the more data we have, the more helpful it’ll be to know if we’re removing the right lesions at a better rate.”
“There’s a hope that assistance will improve detection, removal of polyps, and ultimately, colon cancer,” added Pambianco, who comoderated the session on colorectal cancer prevention.
Future longitudinal studies should monitor both ADR and benign lesion resection rates with AIAC, and modeling studies could determine the benefits and costs of the technology, Herman said. In addition, development of hybrid CADe and computer-aided diagnosis systems could mitigate concerns about excessive benign lesion resection with AI tools.
Clinicians already are able to find colon mucosa that are polypoid or lymphoid aggregates during colonoscopy without AI assistance, said the session’s comoderator, Sita Chokhavatia, MD, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Valley Medical Group in Ridgewood, New Jersey.
“Instead, we need a tool that can help us to not remove these polyps that are not neoplastic,” she said. “With future developments, we may be able to take it to the next step where the algorithm tells us that it’s benign and not to touch it.”
The study was named an ACG Newsworthy Abstract. Herman, Pambianco, and Chokhavatia reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
GLP-1 RAs Reduce Early-Onset CRC Risk in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
PHILADELPHIA — according to the results of a retrospective study.
“This is the first large study to investigate the impact of GLP-1 RA use on EO-CRC risk,” principal investigator Temitope Olasehinde, MD, resident physician at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
The results indicate the GLP-1 RAs have a potentially protective role to play in combating EO-CRC, the incidence of which is notably rising in younger adults, with a corresponding increase in associated mortality.
Previous studies investigating the link between GLP-1 RAs and CRC did not capture patients aged younger than 50 years; thus, it was unknown if these results could be extrapolated to a younger age group, said Olasehinde.
The researcher presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Retrospective Database Analysis
Olasehinde and colleagues analyzed data from TriNetX, a large federated deidentified health research network, to identify patients (age ≤ 49 years) with diagnosed T2D subsequently prescribed antidiabetic medications who had not received a prior diagnosis of CRC. Additionally, patients were stratified on the basis of first-time GLP-1 RA use.
They identified 2,025,034 drug-naive patients with T2D; of these, 284,685 were subsequently prescribed GLP-1 RAs, and 1,740,349 remained in the non–GLP-1 RA cohort. Following propensity score matching, there were 86,186 patients in each cohort.
Patients who received GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than those who received non–GLP-1 RAs (0.6% vs 0.9%; P < .001; odds ratio [OR], 0.61; 95% CI, 0.54-068).
Furthermore, a sub-analysis revealed that patients who were obese and taking GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than patients who were obese but not taking GLP-1 RAs (0.7% vs 1.1%; P < .001; OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.50-067).
A Proposed Protective Effect
Although GLP-1 RAs are indicated for the treatment of T2D and obesity, recent evidence suggests that they may play a role in reducing the risk for CRC as well. This protective effect may be produced not only by addressing T2D and obesity — both important risk factors for CRC — but also via cellular mechanisms, Olasehinde noted.
“GLP-1 receptors are widely expressed throughout the gastrointestinal tract, with various effects on tissues in the stomach, small intestine, and colon,” she explained. Specifically, activation of these receptors in the proximal and distal colon promotes the release of “important factors that protect and facilitate healing of the intestinal epithelium” and “regulate the gut microbiome.”
This is particularly relevant in EO-CRC, she added, given its greater association with T2D and obesity, both factors that “have been shown to create dysbiosis in the gut microbiome and low-grade inflammation via release of free radicals/inflammatory cytokines.”
These results provide more evidence that EO-CRC “is clinically and molecularly distinct from late-onset colorectal cancer,” which is important for both clinicians and patients to understand, said Olasehinde.
“It is imperative that we are all aware of the specific signs and symptoms this population presents with and the implications of this diagnosis in younger age groups,” she added. “Patients should continue making informed dietary and lifestyle modifications/choices to help reduce the burden of EO-CRC.”
Hypothesis-Generating Results
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the research, called the results promising but — at this stage — primarily useful for stimulating future research.
"We do need more studies such as this to generate hypotheses that can be studied prospectively," Shaukat, professor of medicine and population health, and director of GI Outcomes Research at NYU Langone Health in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
She referred to another study, published in JAMA Oncology, that also used the TriNetX research network, which showed that GLP-1 RAs were associated with reduced CRC risk in drug-naive patients with T2D.
Shaukat also noted that the current analysis has limitations that should be considered. "The study is retrospective, and confounding is a possibility,” she said.
“How the groups that did and did not receive GLP-1 RAs differ in other risk factors that could be the drivers of the cancers is not known. Whether cancers were detected through screening or symptoms, stage, and other features that may differ are not known. Finally, since we don’t know who did or did not have colonoscopy, undiagnosed cancers are not known," she explained.
Shaukat, who was the lead author of the ACG 2021 Colorectal Cancer Screening Guidelines, added that the field would benefit from studies providing "biological plausibility information, such as animal studies to understand how GLP-1 RAs may modulate risk of colon cancer; other population-based cohort studies on the incidence of colon cancer among GLP-1 RA users and non-users; and prospective trials on chemoprevention."
The study had no specific funding. Olasehinde reported no relevant financial relationships. Shaukat reported serving as a consultant for Freenome, Medtronic, and Motus GI, as well as an advisory board member for Iterative Scopes Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to the results of a retrospective study.
“This is the first large study to investigate the impact of GLP-1 RA use on EO-CRC risk,” principal investigator Temitope Olasehinde, MD, resident physician at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
The results indicate the GLP-1 RAs have a potentially protective role to play in combating EO-CRC, the incidence of which is notably rising in younger adults, with a corresponding increase in associated mortality.
Previous studies investigating the link between GLP-1 RAs and CRC did not capture patients aged younger than 50 years; thus, it was unknown if these results could be extrapolated to a younger age group, said Olasehinde.
The researcher presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Retrospective Database Analysis
Olasehinde and colleagues analyzed data from TriNetX, a large federated deidentified health research network, to identify patients (age ≤ 49 years) with diagnosed T2D subsequently prescribed antidiabetic medications who had not received a prior diagnosis of CRC. Additionally, patients were stratified on the basis of first-time GLP-1 RA use.
They identified 2,025,034 drug-naive patients with T2D; of these, 284,685 were subsequently prescribed GLP-1 RAs, and 1,740,349 remained in the non–GLP-1 RA cohort. Following propensity score matching, there were 86,186 patients in each cohort.
Patients who received GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than those who received non–GLP-1 RAs (0.6% vs 0.9%; P < .001; odds ratio [OR], 0.61; 95% CI, 0.54-068).
Furthermore, a sub-analysis revealed that patients who were obese and taking GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than patients who were obese but not taking GLP-1 RAs (0.7% vs 1.1%; P < .001; OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.50-067).
A Proposed Protective Effect
Although GLP-1 RAs are indicated for the treatment of T2D and obesity, recent evidence suggests that they may play a role in reducing the risk for CRC as well. This protective effect may be produced not only by addressing T2D and obesity — both important risk factors for CRC — but also via cellular mechanisms, Olasehinde noted.
“GLP-1 receptors are widely expressed throughout the gastrointestinal tract, with various effects on tissues in the stomach, small intestine, and colon,” she explained. Specifically, activation of these receptors in the proximal and distal colon promotes the release of “important factors that protect and facilitate healing of the intestinal epithelium” and “regulate the gut microbiome.”
This is particularly relevant in EO-CRC, she added, given its greater association with T2D and obesity, both factors that “have been shown to create dysbiosis in the gut microbiome and low-grade inflammation via release of free radicals/inflammatory cytokines.”
These results provide more evidence that EO-CRC “is clinically and molecularly distinct from late-onset colorectal cancer,” which is important for both clinicians and patients to understand, said Olasehinde.
“It is imperative that we are all aware of the specific signs and symptoms this population presents with and the implications of this diagnosis in younger age groups,” she added. “Patients should continue making informed dietary and lifestyle modifications/choices to help reduce the burden of EO-CRC.”
Hypothesis-Generating Results
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the research, called the results promising but — at this stage — primarily useful for stimulating future research.
"We do need more studies such as this to generate hypotheses that can be studied prospectively," Shaukat, professor of medicine and population health, and director of GI Outcomes Research at NYU Langone Health in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
She referred to another study, published in JAMA Oncology, that also used the TriNetX research network, which showed that GLP-1 RAs were associated with reduced CRC risk in drug-naive patients with T2D.
Shaukat also noted that the current analysis has limitations that should be considered. "The study is retrospective, and confounding is a possibility,” she said.
“How the groups that did and did not receive GLP-1 RAs differ in other risk factors that could be the drivers of the cancers is not known. Whether cancers were detected through screening or symptoms, stage, and other features that may differ are not known. Finally, since we don’t know who did or did not have colonoscopy, undiagnosed cancers are not known," she explained.
Shaukat, who was the lead author of the ACG 2021 Colorectal Cancer Screening Guidelines, added that the field would benefit from studies providing "biological plausibility information, such as animal studies to understand how GLP-1 RAs may modulate risk of colon cancer; other population-based cohort studies on the incidence of colon cancer among GLP-1 RA users and non-users; and prospective trials on chemoprevention."
The study had no specific funding. Olasehinde reported no relevant financial relationships. Shaukat reported serving as a consultant for Freenome, Medtronic, and Motus GI, as well as an advisory board member for Iterative Scopes Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA — according to the results of a retrospective study.
“This is the first large study to investigate the impact of GLP-1 RA use on EO-CRC risk,” principal investigator Temitope Olasehinde, MD, resident physician at the University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview.
The results indicate the GLP-1 RAs have a potentially protective role to play in combating EO-CRC, the incidence of which is notably rising in younger adults, with a corresponding increase in associated mortality.
Previous studies investigating the link between GLP-1 RAs and CRC did not capture patients aged younger than 50 years; thus, it was unknown if these results could be extrapolated to a younger age group, said Olasehinde.
The researcher presented the findings at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Retrospective Database Analysis
Olasehinde and colleagues analyzed data from TriNetX, a large federated deidentified health research network, to identify patients (age ≤ 49 years) with diagnosed T2D subsequently prescribed antidiabetic medications who had not received a prior diagnosis of CRC. Additionally, patients were stratified on the basis of first-time GLP-1 RA use.
They identified 2,025,034 drug-naive patients with T2D; of these, 284,685 were subsequently prescribed GLP-1 RAs, and 1,740,349 remained in the non–GLP-1 RA cohort. Following propensity score matching, there were 86,186 patients in each cohort.
Patients who received GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than those who received non–GLP-1 RAs (0.6% vs 0.9%; P < .001; odds ratio [OR], 0.61; 95% CI, 0.54-068).
Furthermore, a sub-analysis revealed that patients who were obese and taking GLP-1 RAs had significantly lower odds of developing EO-CRC than patients who were obese but not taking GLP-1 RAs (0.7% vs 1.1%; P < .001; OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.50-067).
A Proposed Protective Effect
Although GLP-1 RAs are indicated for the treatment of T2D and obesity, recent evidence suggests that they may play a role in reducing the risk for CRC as well. This protective effect may be produced not only by addressing T2D and obesity — both important risk factors for CRC — but also via cellular mechanisms, Olasehinde noted.
“GLP-1 receptors are widely expressed throughout the gastrointestinal tract, with various effects on tissues in the stomach, small intestine, and colon,” she explained. Specifically, activation of these receptors in the proximal and distal colon promotes the release of “important factors that protect and facilitate healing of the intestinal epithelium” and “regulate the gut microbiome.”
This is particularly relevant in EO-CRC, she added, given its greater association with T2D and obesity, both factors that “have been shown to create dysbiosis in the gut microbiome and low-grade inflammation via release of free radicals/inflammatory cytokines.”
These results provide more evidence that EO-CRC “is clinically and molecularly distinct from late-onset colorectal cancer,” which is important for both clinicians and patients to understand, said Olasehinde.
“It is imperative that we are all aware of the specific signs and symptoms this population presents with and the implications of this diagnosis in younger age groups,” she added. “Patients should continue making informed dietary and lifestyle modifications/choices to help reduce the burden of EO-CRC.”
Hypothesis-Generating Results
Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH, who was not affiliated with the research, called the results promising but — at this stage — primarily useful for stimulating future research.
"We do need more studies such as this to generate hypotheses that can be studied prospectively," Shaukat, professor of medicine and population health, and director of GI Outcomes Research at NYU Langone Health in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
She referred to another study, published in JAMA Oncology, that also used the TriNetX research network, which showed that GLP-1 RAs were associated with reduced CRC risk in drug-naive patients with T2D.
Shaukat also noted that the current analysis has limitations that should be considered. "The study is retrospective, and confounding is a possibility,” she said.
“How the groups that did and did not receive GLP-1 RAs differ in other risk factors that could be the drivers of the cancers is not known. Whether cancers were detected through screening or symptoms, stage, and other features that may differ are not known. Finally, since we don’t know who did or did not have colonoscopy, undiagnosed cancers are not known," she explained.
Shaukat, who was the lead author of the ACG 2021 Colorectal Cancer Screening Guidelines, added that the field would benefit from studies providing "biological plausibility information, such as animal studies to understand how GLP-1 RAs may modulate risk of colon cancer; other population-based cohort studies on the incidence of colon cancer among GLP-1 RA users and non-users; and prospective trials on chemoprevention."
The study had no specific funding. Olasehinde reported no relevant financial relationships. Shaukat reported serving as a consultant for Freenome, Medtronic, and Motus GI, as well as an advisory board member for Iterative Scopes Inc.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024