User login
Increase in Troublesome Fungal Infections Requires All-Out Approach
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
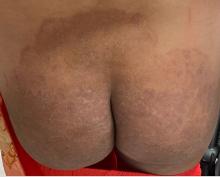
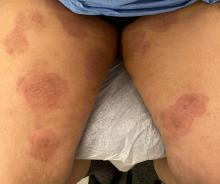
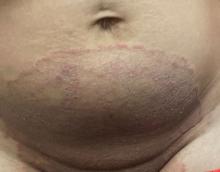
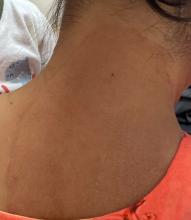
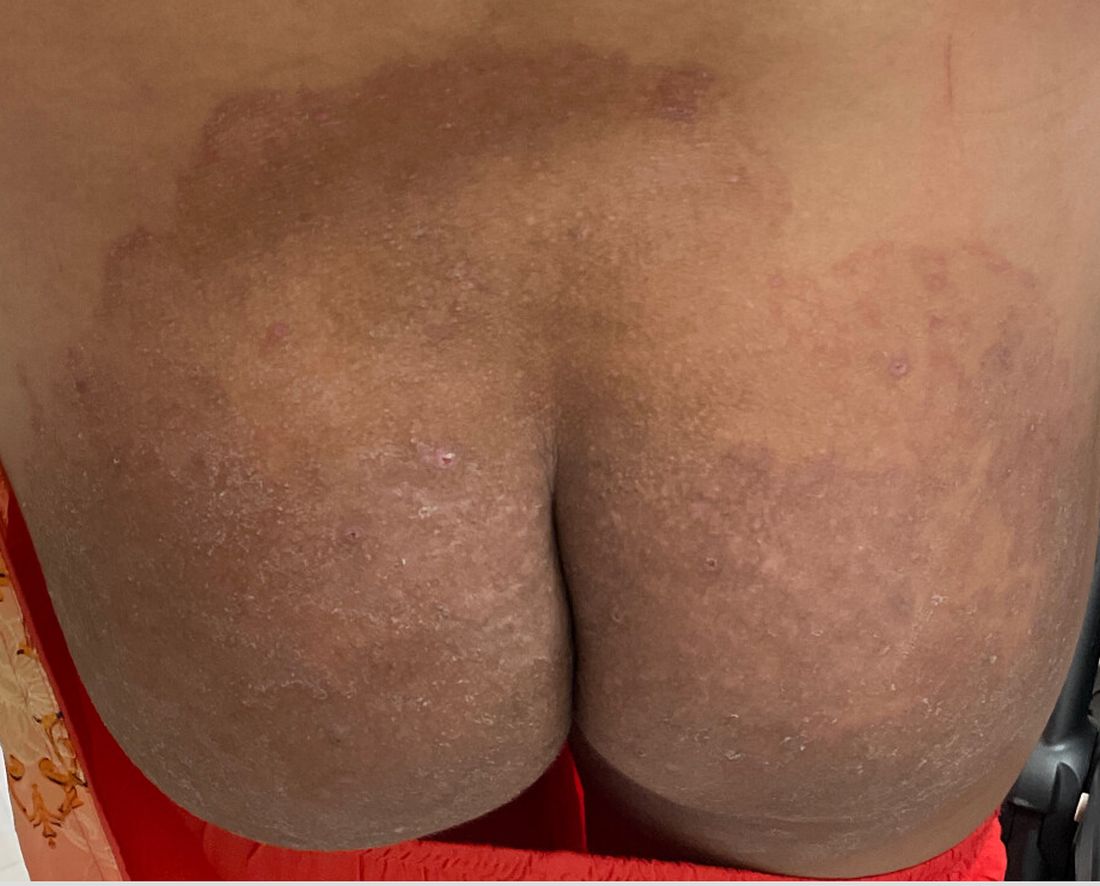
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.
Resistant T rubrum
“The biggest difference with T rubrum resistance is you may not see that widespread infection that we see with T indotineae,” said Caplan. T rubrum is probably the most common dermatophyte that dermatologists see, added Elewski, who encounters a resistant case at least monthly. One such patient, featured in a January 2021 British Journal of Dermatology research letter, cleared on itraconazole and ciclopirox cream but subsequently returned with itraconazole-resistant T rubrum because he had been doctor-shopping for the drug intermittently for years, she said. He cleared on posaconazole 300 mg daily, then was lost to follow-up.
TMVII
A 2023 Emerging Infectious Diseases report highlighted the potential for this dermatophyte to spread among men who have sex with men (MSM), presenting as an itchy, scaly rash affecting the pubic, genital, and buttocks skin. “People don’t generally think of a fungal infection as something that could behave like a sexually transmitted infection (STI),” said Gold.
Caplan and coauthors recently reported the first confirmed US TMVII case in JAMA Dermatology. Many experts suspect that unreported US cases existed previously, he said. “When it circulates in Europe and there’s so much travel, it’s probably here too.”
The fact that T indotineae was formerly called TMVIII has created confusion, added Caplan. “I’ve had patients say, ‘I’m worried I have that resistant ringworm that’s spreading among MSM.’ Whenever we talk about STIs and introduce the word ‘resistant,’ that comes with the potential for stigma, anxiety, and concern.” Fortunately, he said, TMVII has shown no resistance to first-line antifungals.
Why the Rise
Gold said, “We don’t know for sure why we’re seeing these different drug-resistant species popping up.” One possibility, he said, is the common misuse and overuse of topical antifungals — especially those available overseas in combination with high-potency steroids, such as clobetasol. Consumers use these products for a few weeks until symptoms resolve, then reapply them off and on over years, fueling resistance, said Gold.
“We are worried that with warming temperatures, there’s potential to see expansion of the geographic range of epidemic fungi,” he added. “That could be part of what has fueled recent increases in resistant dermatophytes. But it’s hard to prove.”
Climate change may be behind the emergence of Candida auris, according to a 2022 article in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This potentially fatal multidrug-resistant infection spreads easily among sick patients in healthcare facilities, according to a CDC information page on C auris.
Confirming Dermatophyte Infection
“A biopsy will only confirm the presence of fungus,” said Elewski. “Here you will need a lab that knows how to do a fungal culture.” Most state laboratories can do this, she said, as can some hospitals and special labs such as CMM in Cleveland.
It takes a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments–certified lab to perform KOH prep in-house, added Caplan, plus up-to-date gear and knowledge of where and how to scrape and what to look for microscopically. Moreover, identifying T indotineae requires molecular testing available at only a handful of laboratories — listed on the AAD Emerging Dermatophytes webpage — nationwide.
Nevertheless, said Caplan, nailing down a diagnosis can guide treatment, often supplanting empirically prescribed antifungal steroid creams. “Those are probably not going to help. And people may be using those on areas of the body they shouldn’t. Both the clinical clues and the steps to make the diagnosis need to come together. But that’s often easier said than done, especially in a busy practice.”
Identifying resistance requires antifungal sensitivity testing, he added, which few labs perform. “Practically speaking,” said Elewski, “if the patient failed terbinafine, I would try itraconazole. You don’t necessarily need proof” of resistance. But if a patient does not respond to itraconazole and terbinafine clinically, she said that she might consider fungal susceptibility testing.
Treatment Tips
To address any resistant dermatophyte, Elewski recommended getting comfortable with itraconazole. For decades, she said, dermatologists have avoided itraconazole because terbinafine typically costs patients $10 for 3 months. “Itraconazole could be $200 per month,” said Elewski. Because of potential drug-drug interactions and absorption issues — and a boxed warning regarding congestive heart failure — physicians historically reserved itraconazole for severe fungal infections.
Itraconazole labeled dosing for onychomycosis is 200 mg daily for 12 weeks. Elewski favors a two-pronged attack, often combining an -azole antifungal with topical ciclopirox.
Another element that emerging tinea pathogens share is slower response to treatment. For T indotineae, reports appearing in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2022 and 2024 suggest duration from 6-8 weeks up to 20 weeks.
To avoid recurrences of resistant T rubrum, Elewski treats for a year. However, she has problems getting itraconazole approved, when often it is the only agent that works. “I’ve written more letters than I like to insurance companies” to document terbinafine failure, she said.
Rarely, said Gold, dermatophyte infections resist both terbinafine and itraconazole. Next-line agents such as voriconazole, which some dermatologists have used for resistant T indotineae, can be much harder to tolerate, with more drug interactions, he said.
And because itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole are all triazoles, added Elewski, the latter two might not work better than the former. But because these drugs might outperform itraconazole in selected cases, she said, “that’s when you want to do fungal susceptibility testing.”
TMVII is so new, said Caplan, that optimal therapy duration remains unclear. “One of the challenges with TMVII is when it gets into the genital skin, it’s a hair-bearing area. And based on various grooming practices, there’s an opportunity for the tinea to get deeper into the hair follicle and dermis. That may also be true of T indotineae.”
Anemic Arsenal
Unfortunately, said Gold, the arsenal of antifungals available in the United States remains limited. “Depending on how you count, there are only three to four classes of antifungal drugs designed to treat severe or invasive infections. So whenever we hear about a new fungal pathogen that’s causing resistant infections, it causes public health concern.”
Promising drugs in development include olorofim (F2G) and fosmanogepix (Basilea), according to Gold. However, he said, the development of these drugs to date has targeted invasive fungal infections such as aspergillosis. In June 2023, the Food and Drug Administration rejected the new drug application for olorofim, requesting additional data and analyses. Regarding fosmanogepix, a double-blinded noninferiority phase 3 trial in invasive yeast infections was recently launched, according to a September 24 press release.
Gold, Caplan, and Elewski reported no relevant financial disclosures. Freeman is a COVID-19 co-author for UpToDate and chair of the AAD Emerging Diseases Task Force.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A Dermatologist’s Tips for Supporting LGBTQ Youth
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
HUNTINGTON BEACH, CALIFORNIA —
“Sometimes in dermatology we might say, ‘This gender care stuff, that’s really for pediatricians and primary care doctors,’ ” Boos, a pediatric dermatologist at Seattle Children’s Hospital, Seattle, said at the annual meeting of the Pacific Dermatologic Association. However, he added, “gender-affirming care happens not only with medications but with communication, curiosity, and respect.” For instance, an LGBTQ patient who is being treated with isotretinoin for acne is seen once a month by a dermatologist, which is probably more frequent than seeing their primary care physician, he said. “Every time you see that child, you can make them feel seen. You can respect them. You can let them know that you care about them. Hopefully then they understand what it feels like to get good care from a provider and then will not settle for poor care from someone else.”
According to Gallup polling, the proportion of people in the United States who identify as non-cisgender or nonheterosexual increased from 3.5% in 2012 to 7% in 2021. “The estimation is that 2.5%-3.5% of all teenagers identify as gay or bisexual, and another 1% identify as transgender, though some studies estimate the percentage of gender diverse youth to be as high as 9.2%,” said Boos.
He discussed several barriers to dermatologic care for LGBTQ youth, including availability. “There are only about 400 practicing pediatric dermatologists in the US, so there’s not a lot of pediatric dermatology care to go around for any child,” Boos said. “My plea to general dermatologists who see adolescents and teenagers: You can care for LGBTQ adolescents; they need your help.”
Accessibility is also an issue. For example, his clinic is in a wealthy and somewhat isolated area of Seattle, “which makes it hard for some patients to access our services because they may have to drive from far away or take multiple modes of public transportation to see us,” explained Boos, who came out as gay about 10 years ago after beginning his practice in Seattle. “Time matters, too. Children are in school. They don’t necessarily want to take time off to go to the doctor’s office. We want to make sure we have services at different times of day, including evenings or weekends if possible.”
Another potential barrier to care for this patient population is acceptability. “I can say that I welcome any patient to my practice, but if I’m not humble and informed about their concerns, especially queer or trans kids, if they feel that I’m not respecting them, that’s going to be a huge problem,” Boos said. “They won’t view that care as acceptable, and they’re not going to come back if they feel like I’m not looking out for their best interests.”
In a large cross-sectional study of patients with chronic inflammatory skin diseases published in 2023, sexual and gender minority (SGM) individuals were significantly more likely than non-SGM individuals to delay specialist care including dermatologic care (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 1.23), mental health care (AOR, 1.62), and filing a prescription (AOR, 1.30) because of cost. The barriers for SGM patients were transportation issues, not having a healthcare practitioner (HCP) from the same racial or ethnic background, “and they were more likely to report not always being treated with respect by HCPs,” said Boos, who was not involved with the study. “SGM patients of minoritized racial identities such as Black, Hispanic, and Latino were also more likely to experience barriers to care.”
Boos offered several tips for improving the dermatologic care of LGBTQ youth:
Use inclusive language and follow your patient’s lead. “There are many ways that people identify, both with respect to their sexual orientation and their gender identity,” he said. “We often think that a person is either gay or straight, or cisgender or transgender. There are many folks who reject these binaries and may view their gender identity or sexual orientation outside of these descriptors. You can be bisexual. You can be asexual.” He also emphasized that sexual orientation is different from sexual behavior.
Be deliberate about your phrasing. Boos said he strives to make new patients feel comfortable by asking them such questions as what pronouns they use, how he should address them, and whether they have a partner or are in a relationship. “Then, in general, just follow your patient’s lead,” Boos said. “If they’re referring to their partner in a certain way or to themselves with certain pronouns, go along with it. When in doubt, just ask. And if you make a mistake like using the wrong pronouns or name of a patient, the best thing to do is immediately apologize and try your best not to repeat that error.”
When asking about sexual practices, don’t make assumptions. Boos recommends a 2019 article on dermatologic care of LGBT persons, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, which includes specific examples of how to elicit a sexual history from adults and teens. One of the recommendations is “to be very direct, say, ‘This may feel uncomfortable, but I have to ask you these direct questions about what you’re doing sexually because I need to understand if you’re at risk for things like sexually transmitted infections,’ ” Boos said. “It’s also important to use terminology that our patients know. If I ask someone if they’ve had sex before, they usually understand that as penile-vaginal intercourse, but it’s also important to understand if they have oral or anal sex. But if you ask, ‘Have you had insertive anal sex?’ they may not know what that means as opposed to receptive anal sex. Instead, you might ask, ‘Are you a top or a bottom?’ which are more commonly used and understood terms in the queer community. It may feel really uncomfortable to use that kind of language, but we want to make sure patients understand what we’re asking them so we can take the best possible care of them.”
Pay attention to the details. One way to demonstrate inclusivity in your practice includes collecting pronoun and sexual orientation information for the electronic medical record so your entire staff can use proper pronouns for the patient. “Also, acknowledge that for queer folks, family can mean more than just biological family,” Boos added. “I do not buy into the stereotype that all queer kids are ostracized from their families and not loved by their families, but it is true that they are at risk for those experiences. So, sometimes a member of the patient’s ‘chosen family’ accompanies them on their visit.”
Privacy is also key. “You never know who else is in the room when you’re on a telehealth call, so you need to address that before you ask about personal things,” Boos said. “One sticking point that can also come up is that parents often fill out their child’s patient demographic form, which may not tell the real story. I typically start to have confidential time without parents and may take a sexual history as early as 12 or 13 years of age if it’s a patient that I’m seeing for an extended period or if I’m worried about a skin finding that might suggest an STI.”
He highlighted the unique opportunity dermatologists have to transform the healthcare landscape for LGBTQ children and adolescents. “It’s about extending yourself to nurture the growth of another person,” Boos said. “This can feel challenging, but you want to see each person for who they are and help get them to where they want to go. That’s what we went into medicine for, right? We want to care about people.”
Boos had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PDA 2024
Responses Sustained with Ritlecitinib in Patients with Alopecia Through 48 Weeks
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, and up to one third of nonresponders at week 24 also achieved responses by week 48.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of an international, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b/3 trial (ALLEGRO) and included 718 adults and adolescents aged 12 or older with severe AA (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score ≥ 50).
- Patients received various doses of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor ritlecitinib, with or without a 4-week loading dose, including 200/50 mg, 200/30 mg, 50 mg, or 30 mg, with or without a 4-week loading dose for up to 24 weeks and continued to receive their assigned maintenance dose.
- Researchers assessed sustained clinical responses at week 48 for those who had achieved SALT scores ≤ 20 and ≤ 10 at 24 weeks, and nonresponders at week 24 were assessed for responses through week 48.
- Adverse events were also evaluated.
TAKEAWAY:
- Among patients on ritlecitinib who had responded at week 24, SALT responses ≤ 20 were sustained in 85.2%-100% of patients through week 48. Similar results were seen among patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 (68.8%-91.7%) and improvements in eyebrow (70.4%-96.9%) or eyelash (52.4%-94.1%) assessment scores.
- Among those who were nonresponders at week 24, 22.2%-33.7% achieved a SALT score ≤ 20 and 19.8%-25.5% achieved a SALT score ≤ 10 by week 48. Similarly, among those with no eyebrow or eyelash responses at week 24, 19.7%-32.8% and 16.7%-30.2% had improved eyebrow or eyelash assessment scores, respectively, at week 48.
- Between weeks 24 and 48, adverse events were reported in 74%-93% of patients who achieved a SALT score ≤ 20, most were mild or moderate; two serious events were reported but deemed unrelated to treatment. The safety profile was similar across all subgroups.
- No deaths, malignancies, major cardiovascular events, opportunistic infections, or herpes zoster infections were observed.
IN PRACTICE:
“The majority of ritlecitinib-treated patients with AA who met target clinical response based on scalp, eyebrow, or eyelash regrowth at week 24 sustained their response through week 48 with continued treatment,” the authors wrote. “Some patients, including those with more extensive hair loss, may require ritlecitinib treatment beyond 6 months to achieve target clinical response,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Melissa Piliang, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Cleveland Clinic, and was published online on October 17 in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The analysis was limited by its post hoc nature, small sample size in each treatment group, and a follow-up period of only 48 weeks.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Pfizer. Piliang disclosed being a consultant or investigator for Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Procter & Gamble. Six authors were employees or shareholders of or received salary from Pfizer. Other authors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies outside this work, including Pfizer.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
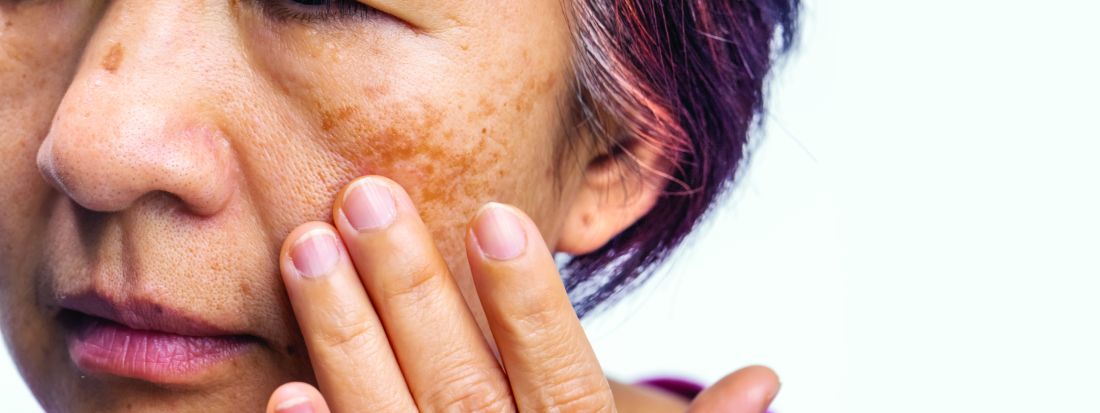
New Cosmeceutical as Effective as Cysteamine for Facial Melasma
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Phase 2 Data on New Drug Class for Prurigo Nodularis Promising
AMSTERDAM — presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress are further validated.
“We now have a pipeline of clinical studies in PN. Who would have even thought that a few years ago,” said Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chair, Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. That is a remarkable turn of events for a difficult disease, he added.
Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13, was the first treatment approved for PN by the Food and Drug Administration 2 years ago. Approval of nemolizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-31, a cytokine strongly implicated in the itch response, followed in August 2024. Povorcitinib, which targets Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), is on track to be the third.
New data on both nemolizumab and povorcitinib were presented in late breaking news sessions at EADV.
For povorcitinib, a JAK inhibitor, Dr. Kwatra presented extended phase 2 results through 40 weeks at a late-breaker session at the EADV meeting. They follow 16-week data from a randomized study presented earlier this year.
Of the 146 patients followed in the original 16-week randomized trial, which compared 15, 45, and 75 mg of oral povorcitinib once daily against placebo, 126 entered an extension in which all patients were treated with active therapy. In this single-blind phase, those who were responders at 16 weeks received 45 mg povorcitinib, and those who were nonresponders received 75 mg povorcitinib.
At 16 weeks, all doses were superior to placebo in achieving at least a 4-point reduction on the Itch Numerical Rating Scale (NRS4) and the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear), as well as in a composite endpoint of both. However, even though the lowest dose of povorcitinib was active, there was a “very clear dose response” demonstrated in speed of response and proportion of responders, according to Dr. Kwatra.
On the 75-mg dose, the time to improvement was a median of 19 days, while the median times to improvement were 35 days on the 45-mg dose and 58 days on the 15-mg dose.
Among povorcitinib responders, 96% had met the NRS4 response at the time they entered the extension study. During the extension study, the proportion of responders who maintained this level of itch control hovered around 90% for the duration. The proportion was 89% at week 40.
The proportion of responders at 16 weeks achieving IGA 0/1, signifying clear or almost clear, was 93%. Again, the rate hovered around 90% for the full 40 weeks. At week 40, the proportion at this outcome was also 89%. The composite outcome among responders persisted at about 80% for most of the follow-up but fell to 63% at the last follow-up.
Among nonresponders who transitioned to 75 mg povorcitinib for the extension period, the NSR4 response rates climbed within 4 weeks to approximately 60% and reached 70% at week 40. For the endpoint of IGA 0/1, rates rose incrementally among the nonresponders over time, reaching 51% at week 40. The composite endpoint was reached at 40 weeks by 41% of nonresponders switched to 75 mg during the 24-week extension.
The results at 40 weeks were highly encouraging, according to Dr. Kwatra, who reported there were no surprises in regard to safety during the extension period. He reported some transient reductions in hemoglobin and infections that resolved, but there were no cardiac events or other more serious events that have been previously associated with JAK inhibitors during the 40-week study period.
When asked if there might be an advantage for povorcitinib relative to the monoclonal antibodies in regard to speed of onset, Dr. Kwatra said that there are no comparative data. Like previous experience with dupilumab, some patients responded rapidly with povorcitinib, but others took longer to achieve benefit.
This variability in response is consistent with the growing evidence that PN is a heterogeneous disease, according to Dr. Kwatra. With multiple up-regulated cytokines implicated in the pathogenesis of PN, he suggested that more treatment options would be useful. When it comes to the multiple molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of PN, he said, “patients can be at a different edge of a spectrum.”
In other evidence suggesting that more options are needed, another late-breaking news study at the 2024 EADV congress underlined the fact that PN is a chronic disease. Presented by Franz J. Legat, MD, professor of dermatology at the Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, the data involved a withdrawal evaluation nested in a long-term extension (LTE) of the OLYMPIA pivotal trials with nemolizumab.
After 52 weeks in the LTE, 34 patients entered the OLYMPIA DURABILITY study, in which they were randomized to withdrawal or to continue on nemolizumab on an every 4-week dosing schedule.
The relapse rate over 24 weeks was 16.7% (3 of 18 patients) in the continuous nemolizumab arm and 75% (12 of 16 patients) in the withdrawal arm. The median time to relapse was 112.5 days for those in the withdrawal arm and was not reached during follow-up in the nemolizumab arm.
Praising the patients who were willing to risk PN relapse by entering this randomized trial, Dr. Legat said that the study shows a relatively high risk for relapse within months of treatment withdrawal even after good PN control over a period of 52 weeks.
“These data clearly support continuous nemolizumab beyond 52 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biotherapeutics, Aslan, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Incyte, which is developing povorcitinib for PN. Dr. Legat reported financial relationships with Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Trevi, Vifor, and Galderma, which provided funding for the nemolizumab studies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress are further validated.
“We now have a pipeline of clinical studies in PN. Who would have even thought that a few years ago,” said Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chair, Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. That is a remarkable turn of events for a difficult disease, he added.
Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13, was the first treatment approved for PN by the Food and Drug Administration 2 years ago. Approval of nemolizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-31, a cytokine strongly implicated in the itch response, followed in August 2024. Povorcitinib, which targets Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), is on track to be the third.
New data on both nemolizumab and povorcitinib were presented in late breaking news sessions at EADV.
For povorcitinib, a JAK inhibitor, Dr. Kwatra presented extended phase 2 results through 40 weeks at a late-breaker session at the EADV meeting. They follow 16-week data from a randomized study presented earlier this year.
Of the 146 patients followed in the original 16-week randomized trial, which compared 15, 45, and 75 mg of oral povorcitinib once daily against placebo, 126 entered an extension in which all patients were treated with active therapy. In this single-blind phase, those who were responders at 16 weeks received 45 mg povorcitinib, and those who were nonresponders received 75 mg povorcitinib.
At 16 weeks, all doses were superior to placebo in achieving at least a 4-point reduction on the Itch Numerical Rating Scale (NRS4) and the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear), as well as in a composite endpoint of both. However, even though the lowest dose of povorcitinib was active, there was a “very clear dose response” demonstrated in speed of response and proportion of responders, according to Dr. Kwatra.
On the 75-mg dose, the time to improvement was a median of 19 days, while the median times to improvement were 35 days on the 45-mg dose and 58 days on the 15-mg dose.
Among povorcitinib responders, 96% had met the NRS4 response at the time they entered the extension study. During the extension study, the proportion of responders who maintained this level of itch control hovered around 90% for the duration. The proportion was 89% at week 40.
The proportion of responders at 16 weeks achieving IGA 0/1, signifying clear or almost clear, was 93%. Again, the rate hovered around 90% for the full 40 weeks. At week 40, the proportion at this outcome was also 89%. The composite outcome among responders persisted at about 80% for most of the follow-up but fell to 63% at the last follow-up.
Among nonresponders who transitioned to 75 mg povorcitinib for the extension period, the NSR4 response rates climbed within 4 weeks to approximately 60% and reached 70% at week 40. For the endpoint of IGA 0/1, rates rose incrementally among the nonresponders over time, reaching 51% at week 40. The composite endpoint was reached at 40 weeks by 41% of nonresponders switched to 75 mg during the 24-week extension.
The results at 40 weeks were highly encouraging, according to Dr. Kwatra, who reported there were no surprises in regard to safety during the extension period. He reported some transient reductions in hemoglobin and infections that resolved, but there were no cardiac events or other more serious events that have been previously associated with JAK inhibitors during the 40-week study period.
When asked if there might be an advantage for povorcitinib relative to the monoclonal antibodies in regard to speed of onset, Dr. Kwatra said that there are no comparative data. Like previous experience with dupilumab, some patients responded rapidly with povorcitinib, but others took longer to achieve benefit.
This variability in response is consistent with the growing evidence that PN is a heterogeneous disease, according to Dr. Kwatra. With multiple up-regulated cytokines implicated in the pathogenesis of PN, he suggested that more treatment options would be useful. When it comes to the multiple molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of PN, he said, “patients can be at a different edge of a spectrum.”
In other evidence suggesting that more options are needed, another late-breaking news study at the 2024 EADV congress underlined the fact that PN is a chronic disease. Presented by Franz J. Legat, MD, professor of dermatology at the Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, the data involved a withdrawal evaluation nested in a long-term extension (LTE) of the OLYMPIA pivotal trials with nemolizumab.
After 52 weeks in the LTE, 34 patients entered the OLYMPIA DURABILITY study, in which they were randomized to withdrawal or to continue on nemolizumab on an every 4-week dosing schedule.
The relapse rate over 24 weeks was 16.7% (3 of 18 patients) in the continuous nemolizumab arm and 75% (12 of 16 patients) in the withdrawal arm. The median time to relapse was 112.5 days for those in the withdrawal arm and was not reached during follow-up in the nemolizumab arm.
Praising the patients who were willing to risk PN relapse by entering this randomized trial, Dr. Legat said that the study shows a relatively high risk for relapse within months of treatment withdrawal even after good PN control over a period of 52 weeks.
“These data clearly support continuous nemolizumab beyond 52 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biotherapeutics, Aslan, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Incyte, which is developing povorcitinib for PN. Dr. Legat reported financial relationships with Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Trevi, Vifor, and Galderma, which provided funding for the nemolizumab studies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress are further validated.
“We now have a pipeline of clinical studies in PN. Who would have even thought that a few years ago,” said Shawn Kwatra, MD, professor and chair, Department of Dermatology, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. That is a remarkable turn of events for a difficult disease, he added.
Dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of interleukin (IL)–4 and IL-13, was the first treatment approved for PN by the Food and Drug Administration 2 years ago. Approval of nemolizumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets IL-31, a cytokine strongly implicated in the itch response, followed in August 2024. Povorcitinib, which targets Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), is on track to be the third.
New data on both nemolizumab and povorcitinib were presented in late breaking news sessions at EADV.
For povorcitinib, a JAK inhibitor, Dr. Kwatra presented extended phase 2 results through 40 weeks at a late-breaker session at the EADV meeting. They follow 16-week data from a randomized study presented earlier this year.
Of the 146 patients followed in the original 16-week randomized trial, which compared 15, 45, and 75 mg of oral povorcitinib once daily against placebo, 126 entered an extension in which all patients were treated with active therapy. In this single-blind phase, those who were responders at 16 weeks received 45 mg povorcitinib, and those who were nonresponders received 75 mg povorcitinib.
At 16 weeks, all doses were superior to placebo in achieving at least a 4-point reduction on the Itch Numerical Rating Scale (NRS4) and the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score 0 or 1 (clear or almost clear), as well as in a composite endpoint of both. However, even though the lowest dose of povorcitinib was active, there was a “very clear dose response” demonstrated in speed of response and proportion of responders, according to Dr. Kwatra.
On the 75-mg dose, the time to improvement was a median of 19 days, while the median times to improvement were 35 days on the 45-mg dose and 58 days on the 15-mg dose.
Among povorcitinib responders, 96% had met the NRS4 response at the time they entered the extension study. During the extension study, the proportion of responders who maintained this level of itch control hovered around 90% for the duration. The proportion was 89% at week 40.
The proportion of responders at 16 weeks achieving IGA 0/1, signifying clear or almost clear, was 93%. Again, the rate hovered around 90% for the full 40 weeks. At week 40, the proportion at this outcome was also 89%. The composite outcome among responders persisted at about 80% for most of the follow-up but fell to 63% at the last follow-up.
Among nonresponders who transitioned to 75 mg povorcitinib for the extension period, the NSR4 response rates climbed within 4 weeks to approximately 60% and reached 70% at week 40. For the endpoint of IGA 0/1, rates rose incrementally among the nonresponders over time, reaching 51% at week 40. The composite endpoint was reached at 40 weeks by 41% of nonresponders switched to 75 mg during the 24-week extension.
The results at 40 weeks were highly encouraging, according to Dr. Kwatra, who reported there were no surprises in regard to safety during the extension period. He reported some transient reductions in hemoglobin and infections that resolved, but there were no cardiac events or other more serious events that have been previously associated with JAK inhibitors during the 40-week study period.
When asked if there might be an advantage for povorcitinib relative to the monoclonal antibodies in regard to speed of onset, Dr. Kwatra said that there are no comparative data. Like previous experience with dupilumab, some patients responded rapidly with povorcitinib, but others took longer to achieve benefit.
This variability in response is consistent with the growing evidence that PN is a heterogeneous disease, according to Dr. Kwatra. With multiple up-regulated cytokines implicated in the pathogenesis of PN, he suggested that more treatment options would be useful. When it comes to the multiple molecular pathways involved in the pathogenesis of PN, he said, “patients can be at a different edge of a spectrum.”
In other evidence suggesting that more options are needed, another late-breaking news study at the 2024 EADV congress underlined the fact that PN is a chronic disease. Presented by Franz J. Legat, MD, professor of dermatology at the Medical University of Graz, Graz, Austria, the data involved a withdrawal evaluation nested in a long-term extension (LTE) of the OLYMPIA pivotal trials with nemolizumab.
After 52 weeks in the LTE, 34 patients entered the OLYMPIA DURABILITY study, in which they were randomized to withdrawal or to continue on nemolizumab on an every 4-week dosing schedule.
The relapse rate over 24 weeks was 16.7% (3 of 18 patients) in the continuous nemolizumab arm and 75% (12 of 16 patients) in the withdrawal arm. The median time to relapse was 112.5 days for those in the withdrawal arm and was not reached during follow-up in the nemolizumab arm.
Praising the patients who were willing to risk PN relapse by entering this randomized trial, Dr. Legat said that the study shows a relatively high risk for relapse within months of treatment withdrawal even after good PN control over a period of 52 weeks.
“These data clearly support continuous nemolizumab beyond 52 weeks,” he said.
Dr. Kwatra reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Biotherapeutics, Aslan, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Incyte, which is developing povorcitinib for PN. Dr. Legat reported financial relationships with Almirall, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Menlo Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Trevi, Vifor, and Galderma, which provided funding for the nemolizumab studies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Over 3 Years, Atopic Dermatitis Well-Controlled with Lebrikizumab
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — among those followed up for an additional 2 years, according to the latest data from an extension study.
At the end of the maintenance phase of the pivotal trials at 12 months, 84% of the patients enrolled into the extension had clear or almost clear skin, as per the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA). This overall figure as well as the proportion with even better responses have persisted unchanged, reported Diamant Thaçi, MD, PhD, professor and head of the Comprehensive Center for Inflammatory Medicine, University of Lübeck in Germany.
Responses at 3 Years Maintained
“This is really quite remarkable,” Dr. Thaçi said. “Roughly all the patients maintained their response.” These results became even more remarkable when patients were assessed for their use of adjunctive therapy to control flares.
“Over the whole follow-up, 90% had no need for topical corticosteroids or any other rescue therapy,” Dr. Thaçi reported, providing data from the ADjoin lebrikizumab extension study during a late-breaking news session at the annual meeting of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
The patients in ADjoin were enrolled from the pivotal phase 3 ADvocate 1 and 2 trials completed almost 2 years ago and published together in March 2023. Lebrikizumab was approved in the United States in September 2024 for moderate to severe AD in patients aged ≥ 12 years, following previous approvals in Europe in 2023 and in Japan in January 2024.
In these two identical trials with a total of 564 patients, the primary endpoint was an IGA of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin. At nearly 40%, the proportion of patients reaching this outcome at 16 weeks was about threefold greater (P < .001) on lebrikizumab than on placebo. The benefit was similar on secondary endpoints, such as 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI75) score.
At the end of the double-blind, placebo-controlled 16-week phase of the ADvocate 1 and 2 trials, which enrolled adults and adolescents aged ≥ 12 years, responders were enrolled into a maintenance phase in which they were rerandomized to 250 mg lebrikizumab every 2 weeks (Q2W) or every 4 weeks (Q4W). The latter is the approved maintenance dose.
At the end of the maintenance phase, which lasted another 32 weeks (total exposure of 52 weeks for those initially randomized to lebrikizumab), patients were invited into the ADjoin extension. The only exclusions from the extension were serious adverse events related to lebrikizumab and noncompliance.
Response Curves Appear as Straight Lines
Over the next 2 years of ADjoin, response curves appeared as straight lines not only for the overall response but when patients were stratified for different levels of response at the extension study entry. Specifically, 81.5% and 83.3% had an IGA score of 0 or 1 in the Q2W and Q4W arms at completion of the ADvocate 16-week double-blind phase. At 3 years, the rates were 84.0% and 82.9%, respectively.
For the subgroup who entered ADjoin with an EASI75 or an EASI90 response, the persistence of this level of response over 2 years was similar, although there was some gain observed among those who entered the trial with an EASI75 response.
“Not only did these patients maintain their response, but the response on average slowly improved, so that there were more patients with an EASI90 response at the 3-year timepoint,” Dr. Thaçi said.
Of the 181 patients in the ADjoin extension, 82 patients were maintained on Q2W dosing and 99 were maintained on Q4W lebrikizumab. Their mean age was about 35 years, more than half were women, and nearly 40% had severe AD at the time they enrolled in the ADvocate trials. There was essentially no difference in response rates among those in the Q2W and Q4W arms over time in ADjoin.
Side Effect Profile Essentially Unchanged
The side effect and tolerability profiles, which were favorable in the original 16-week placebo-controlled study, have remained unchanged over the subsequent maintenance phase and through the additional 2 years of the ADjoin extension.
“There continued to be reports of conjunctivitis, which is very specific for anti–IL-13 therapies,” Dr. Thaçi said. However, he said that the incidence did not increase over time, and because it was easy to treat, “most patients do not discontinue lebrikizumab for this reason.” Moreover, he said the impression was that “the number of patients experiencing adverse effects has been decreasing over time.”
Calling these long-term results “very exciting,” Dr. Thaçi called lebrikizumab “a very valuable option for long-term AD care.”
Asked for his perspective on the results, Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, Director of Clinical Research, Department of Dermatology, George Washington University, Washington, DC, said that it is important to study long-term efficacy, and these results are positive. Without direct comparisons to other biologics available for AD, nothing can be implied about the relative efficacy of monoclonal antibodies approved for AD.
“These data are important both from an efficacy and safety perspective” for those advising patients who need chronic AD treatment, said Dr. Silverberg, who was the principal investigator of the ADvocate trials.
Earlier this year, 5-year follow-up data were published for dupilumab. Of 326 patients who remained on therapy this long, 220 (67%) maintained an IGA of 0 or 1 at the end of the study. There were no unexpected adverse events, which were generally stable or declined throughout the study.
Dr. Thaçi has financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Galderma, Leo Pharma, L’Oreal, Janssen-Cilag, New Bridge, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, UCB, and Vichy. Dr. Silverberg reported financial relationships with more than 40 pharmaceutical companies including those that make drugs for AD.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Topical JAK Inhibitor Shows Benefits in Small Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Study
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Different Biomarker Profiles Identified in Study of Late Dupilumab Responders
AMSTERDAM — A proteomics study designed to determine why some patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) respond quickly to dupilumab, others respond more slowly, and the remainder do not respond at all demonstrated that molecular responses in these three groups are very different.
A discovery that could lead to personalizing therapies, the data identified “distinct systemic biomarker profiles,” according to Ester Del Duca, MD, an instructor in the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
The study was conducted with 67 patients with AD and 16 healthy controls. Serum was collected at two timepoints: An average of 20 weeks after starting dupilumab, then at a mean interval of about 9 months later. At these timepoints, called follow-up 1 and 2, a panel of more than 600 proteins, including unique markers for immunologic, cardiovascular, and neurologic activity, were evaluated.
The criterion for differentiating the three response groups was an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin (or at least a 2-point IGA reduction from baseline). Early responders were those who met the criterion at both follow-ups, late responders were those who met this criterion only at the second follow-up, and nonresponders never met the criterion.
“There were no significant differences at baseline in clinical severity, past medical history, or patient characteristics,” said Del Duca, who presented these data in a late breaking news session at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
For early responders, there was an early normalization of the proteome, reported Del Duca, illustrating the differences in the proteome of the three groups with a color-coded chart of protein up-regulation and down-regulation relative to healthy controls. The normalization of the proteome persisted in early responders when assessed at the second follow-up.
In the late responders, the proteome dysregulation was substantial relative to healthy controls at the first follow-up, but there was considerable improvement by the second follow-up. Although the change at the second follow-up was still not as robust as that seen in the early responders at either follow-up, Del Duca described the proteomic profile as a 45% improvement from the first follow-up.
In contrast, nonresponders showed worsening in their blood proteome from follow-up 1 to 2. Nonresponders at first follow-up showed up-regulation relative to healthy controls for many proteins associated with the Th1 response, such as interferon gamma, CXCL9, and CXCL10, and Th2 response, such as interleukin-4 and Th17/22, and these did not normalize or worsen by the second follow-up.
“Uniquely to nonresponders, key Th1 biomarkers remained significantly up-regulated relative to controls at both follow-up 1 and 2,” with a P value < .05, Del Duca reported.
To achieve normalization of the proteome as defined by healthy controls, both up-regulation and down-regulation of protein activity were required, although more up-regulations than down-regulations were observed.
When evaluating the proteome changes most implicated in immunoregulation, the investigators were able to show a correlation between worsening in the proteome and greater severity of AD as defined by IGA, Eczema Area and Severity Index, and body surface area involvement.
“Spearman analysis revealed strong and positive correlations between improvements in biomarkers at follow-up 1 and 2 with improvements in clinical markers,” Del Duca said. As examples, she noted favorable changes in biomarkers specifically associated with T cells, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells as clinical outcomes improved.
Conversely, the worsening in T-cell activation among nonresponders, particularly Th1 biomarkers, also tracked with increasing AD symptoms over time.
The implications of the research are broad, and most importantly, it shows that therapeutic targets are likely to differ between patients with AD, according to Del Duca. Although proteomic studies have not yet been conducted with other treatments, these might provide further insight about how patients with AD differ in response across other drugs.
This is important work, according to Brigitte Dréno, MD, PhD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Nantes University Hospital in France. As moderator of the late-breaking news session, she suggested that there are many potential messages from these data, not least that treatment of AD likely involves targeting cytokines beyond those affected by dupilumab in at least some patients.
When Dréno asked Del Duca about what could be surmised about changes from baseline before treatment to the first follow-up, Del Duca said that the study was retrospective, so baseline data were not available.
This is an important missing piece of this investigation, according to Dréno.
“As you move this work forward,” she said that it would be “very important” to determine “if there are predictive markers for evaluating which patients will respond.”
This is a small study with many additional variables to consider in order to develop a clinically useful tool, Del Duca noted. However, this work not only has the potential to guide treatment selection but the biomarkers up-regulated in nonresponders are already “suggesting potential targets for refining therapeutic strategies,” she said.
The study received funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Del Duca reported no financial relationships with industry. Dréno reported financial relationships with La Roche–Posay, Pierre Fabré, and Galderma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — A proteomics study designed to determine why some patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) respond quickly to dupilumab, others respond more slowly, and the remainder do not respond at all demonstrated that molecular responses in these three groups are very different.
A discovery that could lead to personalizing therapies, the data identified “distinct systemic biomarker profiles,” according to Ester Del Duca, MD, an instructor in the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
The study was conducted with 67 patients with AD and 16 healthy controls. Serum was collected at two timepoints: An average of 20 weeks after starting dupilumab, then at a mean interval of about 9 months later. At these timepoints, called follow-up 1 and 2, a panel of more than 600 proteins, including unique markers for immunologic, cardiovascular, and neurologic activity, were evaluated.
The criterion for differentiating the three response groups was an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin (or at least a 2-point IGA reduction from baseline). Early responders were those who met the criterion at both follow-ups, late responders were those who met this criterion only at the second follow-up, and nonresponders never met the criterion.
“There were no significant differences at baseline in clinical severity, past medical history, or patient characteristics,” said Del Duca, who presented these data in a late breaking news session at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
For early responders, there was an early normalization of the proteome, reported Del Duca, illustrating the differences in the proteome of the three groups with a color-coded chart of protein up-regulation and down-regulation relative to healthy controls. The normalization of the proteome persisted in early responders when assessed at the second follow-up.
In the late responders, the proteome dysregulation was substantial relative to healthy controls at the first follow-up, but there was considerable improvement by the second follow-up. Although the change at the second follow-up was still not as robust as that seen in the early responders at either follow-up, Del Duca described the proteomic profile as a 45% improvement from the first follow-up.
In contrast, nonresponders showed worsening in their blood proteome from follow-up 1 to 2. Nonresponders at first follow-up showed up-regulation relative to healthy controls for many proteins associated with the Th1 response, such as interferon gamma, CXCL9, and CXCL10, and Th2 response, such as interleukin-4 and Th17/22, and these did not normalize or worsen by the second follow-up.
“Uniquely to nonresponders, key Th1 biomarkers remained significantly up-regulated relative to controls at both follow-up 1 and 2,” with a P value < .05, Del Duca reported.
To achieve normalization of the proteome as defined by healthy controls, both up-regulation and down-regulation of protein activity were required, although more up-regulations than down-regulations were observed.
When evaluating the proteome changes most implicated in immunoregulation, the investigators were able to show a correlation between worsening in the proteome and greater severity of AD as defined by IGA, Eczema Area and Severity Index, and body surface area involvement.
“Spearman analysis revealed strong and positive correlations between improvements in biomarkers at follow-up 1 and 2 with improvements in clinical markers,” Del Duca said. As examples, she noted favorable changes in biomarkers specifically associated with T cells, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells as clinical outcomes improved.
Conversely, the worsening in T-cell activation among nonresponders, particularly Th1 biomarkers, also tracked with increasing AD symptoms over time.
The implications of the research are broad, and most importantly, it shows that therapeutic targets are likely to differ between patients with AD, according to Del Duca. Although proteomic studies have not yet been conducted with other treatments, these might provide further insight about how patients with AD differ in response across other drugs.
This is important work, according to Brigitte Dréno, MD, PhD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Nantes University Hospital in France. As moderator of the late-breaking news session, she suggested that there are many potential messages from these data, not least that treatment of AD likely involves targeting cytokines beyond those affected by dupilumab in at least some patients.
When Dréno asked Del Duca about what could be surmised about changes from baseline before treatment to the first follow-up, Del Duca said that the study was retrospective, so baseline data were not available.
This is an important missing piece of this investigation, according to Dréno.
“As you move this work forward,” she said that it would be “very important” to determine “if there are predictive markers for evaluating which patients will respond.”
This is a small study with many additional variables to consider in order to develop a clinically useful tool, Del Duca noted. However, this work not only has the potential to guide treatment selection but the biomarkers up-regulated in nonresponders are already “suggesting potential targets for refining therapeutic strategies,” she said.
The study received funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Del Duca reported no financial relationships with industry. Dréno reported financial relationships with La Roche–Posay, Pierre Fabré, and Galderma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — A proteomics study designed to determine why some patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) respond quickly to dupilumab, others respond more slowly, and the remainder do not respond at all demonstrated that molecular responses in these three groups are very different.
A discovery that could lead to personalizing therapies, the data identified “distinct systemic biomarker profiles,” according to Ester Del Duca, MD, an instructor in the Laboratory of Inflammatory Skin Diseases at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City.
The study was conducted with 67 patients with AD and 16 healthy controls. Serum was collected at two timepoints: An average of 20 weeks after starting dupilumab, then at a mean interval of about 9 months later. At these timepoints, called follow-up 1 and 2, a panel of more than 600 proteins, including unique markers for immunologic, cardiovascular, and neurologic activity, were evaluated.
The criterion for differentiating the three response groups was an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 or 1, signifying clear or almost clear skin (or at least a 2-point IGA reduction from baseline). Early responders were those who met the criterion at both follow-ups, late responders were those who met this criterion only at the second follow-up, and nonresponders never met the criterion.
“There were no significant differences at baseline in clinical severity, past medical history, or patient characteristics,” said Del Duca, who presented these data in a late breaking news session at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
For early responders, there was an early normalization of the proteome, reported Del Duca, illustrating the differences in the proteome of the three groups with a color-coded chart of protein up-regulation and down-regulation relative to healthy controls. The normalization of the proteome persisted in early responders when assessed at the second follow-up.
In the late responders, the proteome dysregulation was substantial relative to healthy controls at the first follow-up, but there was considerable improvement by the second follow-up. Although the change at the second follow-up was still not as robust as that seen in the early responders at either follow-up, Del Duca described the proteomic profile as a 45% improvement from the first follow-up.
In contrast, nonresponders showed worsening in their blood proteome from follow-up 1 to 2. Nonresponders at first follow-up showed up-regulation relative to healthy controls for many proteins associated with the Th1 response, such as interferon gamma, CXCL9, and CXCL10, and Th2 response, such as interleukin-4 and Th17/22, and these did not normalize or worsen by the second follow-up.
“Uniquely to nonresponders, key Th1 biomarkers remained significantly up-regulated relative to controls at both follow-up 1 and 2,” with a P value < .05, Del Duca reported.
To achieve normalization of the proteome as defined by healthy controls, both up-regulation and down-regulation of protein activity were required, although more up-regulations than down-regulations were observed.
When evaluating the proteome changes most implicated in immunoregulation, the investigators were able to show a correlation between worsening in the proteome and greater severity of AD as defined by IGA, Eczema Area and Severity Index, and body surface area involvement.
“Spearman analysis revealed strong and positive correlations between improvements in biomarkers at follow-up 1 and 2 with improvements in clinical markers,” Del Duca said. As examples, she noted favorable changes in biomarkers specifically associated with T cells, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells as clinical outcomes improved.
Conversely, the worsening in T-cell activation among nonresponders, particularly Th1 biomarkers, also tracked with increasing AD symptoms over time.
The implications of the research are broad, and most importantly, it shows that therapeutic targets are likely to differ between patients with AD, according to Del Duca. Although proteomic studies have not yet been conducted with other treatments, these might provide further insight about how patients with AD differ in response across other drugs.
This is important work, according to Brigitte Dréno, MD, PhD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Nantes University Hospital in France. As moderator of the late-breaking news session, she suggested that there are many potential messages from these data, not least that treatment of AD likely involves targeting cytokines beyond those affected by dupilumab in at least some patients.
When Dréno asked Del Duca about what could be surmised about changes from baseline before treatment to the first follow-up, Del Duca said that the study was retrospective, so baseline data were not available.
This is an important missing piece of this investigation, according to Dréno.
“As you move this work forward,” she said that it would be “very important” to determine “if there are predictive markers for evaluating which patients will respond.”
This is a small study with many additional variables to consider in order to develop a clinically useful tool, Del Duca noted. However, this work not only has the potential to guide treatment selection but the biomarkers up-regulated in nonresponders are already “suggesting potential targets for refining therapeutic strategies,” she said.
The study received funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Del Duca reported no financial relationships with industry. Dréno reported financial relationships with La Roche–Posay, Pierre Fabré, and Galderma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Nodules Respond to As Needed Topical JAK Inhibitor
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
PCPs Play a Key Role in Managing and Preventing the Atopic March in Children
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Primary care physicians (PCPs) play a key role in treating young patients as they progress through the “atopic march” from atopic dermatitis through food allergy, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. They can also help prevent the process from starting.
“The PCP is usually the first clinician a family with concerns about atopic conditions sees, unless they first visit urgent care or an emergency department after an allergic reaction to food. Either way, families rely on their PCP for ongoing guidance,” said Terri F. Brown-Whitehorn, MD, attending physician in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at the Center for Pediatric Eosinophilic Disorders and the Integrative Health Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia.
“The most important thing PCPs can do is know that the atopic march exists, how it progresses over time, and what signs and symptoms to look for,” she told this news organization.
The Atopic March
The atopic march describes the progression of allergic diseases in a child over time, with atopic dermatitis and food allergy in infancy tending to be followed by allergic rhinitis and asthma into later childhood and adulthood.
Although the pathophysiology of the inflammation that precedes atopic dermatitis is unclear, two main hypotheses have been proposed. The first suggests a primary immune dysfunction leads to immunoglobulin E (IgE) sensitization, allergic inflammation, and a secondary disturbance of the epithelial barrier; the second starts with a primary defect in the epithelial barrier that leads to secondary immunologic dysregulation and results in inflammation.
Genetics, infection, hygiene, extreme climate, food allergens, probiotics, aeroallergens, and tobacco smoke are thought to play roles in atopic dermatitis. An estimated 10%-12% of children and 1% of adults in the United States have been reported to have the condition, and the prevalence appears to be increasing. An estimated 85% of cases occur during the first year of life and 95% before the age of 5 years.
“Atopy often, though not always, runs in families, so PCPs should inquire about the history of atopic dermatitis, IgE-mediated food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and asthma in the patient’s siblings, parents, and grandparents,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Key Educators
PCPs treat the full gamut of atopic conditions and are key educators on ways families can help mitigate their children’s atopic march or stop it before it begins, said Gerald Bell Lee, MD, an allergist and immunologist at Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta and an associate professor in the Division of Allergy and Immunology at Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta.
“Most parents who bring their infants with eczema to the PCP assume their child ate something that caused their rash. But the relationship between atopic dermatitis, a type of eczema, and food allergy is more complicated,” he added.
Lee said PCPs should explain to their patients what atopic dermatitis is, how it starts and progresses, and how families can help prevent the condition by, for example, introducing allergenic foods to infants at around 4-6 months of age.
Atopic Dermatitis
PCPs should inform parents and other caregivers to wash their hands before moisturizing their child, take care not to contaminate the moisturizer, and bathe their child only when the child is dirty.
“Soap removes protective natural skin oils and increases moisture loss, and exposure to soap and bathing is a main contributor to eczema,” said Lee. “Dry skin loses its protective barrier, allowing outside agents to penetrate and be identified by the immune system.”
“According to one hypothesis, parents may eat food, not wash their hands afterwards, then moisturize their baby. This unhygienic practice spreads food proteins from the adult’s meal, and possibly from contaminants present in the moisturizer, all over the baby’s body,” he added.
Lee said he and his colleagues discourage overbathing babies to minimize the risk for skin injury that begins the atopic march: “New parents are inundated with infant skincare messaging and products. But we need to weigh societal pressures against practicality and ask, ‘Is the child’s skin actually dirty?’ ”
Atopic dermatitis tends to appear on the extensor surfaces, face, and scalp in infants and around arm and leg creases in toddlers and older children. Severe forms of the condition can be more widely distributed on the body, said Aarti P. Pandya, MD, medical director of the Food Allergy Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, Missouri.
Avoid Triggers, Minimize Flares
Triggers of eczema are varied and common. To help minimize flares, PCPs can encourage caregivers to avoid products with fragrances or dyes, minimize the use of soaps, and completely rinse laundry detergent from clothing and household items. “Advise them to keep fingernails short and control dander, pollen, mold, household chemicals, and tobacco smoke, as well as the child’s stress and anxiety, which can also be a trigger,” Lee said.
“Skin infections from organisms such as staph, herpes, or coxsackie can also exacerbate symptoms,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “PCPs can educate caregivers to avoid all known triggers and give them an ‘action plan’ to carry out when skin flares.”
Food Allergies
Parents may be unaware food allergens can travel far beyond the plate, Lee said. Researchers vacuuming household bedding, carpets, furniture, and other surfaces have detected unnoticeably tiny quantities of allergenic food proteins in ordinary house dust. Touching this dust appears to provide the main exposure to those allergens.
“According to the dual exposure to allergen hypothesis, an infant’s tolerance to antigens occurs through high-dose exposure by mouth, and allergic sensitization occurs through low-dose exposure through the skin,” he said. “As young as four to six months of age, even before eating solid food, a child develops eczema, has a leaky skin barrier, comes in contact with food, and develops a food allergy.”
IgE-mediated food allergies can begin at any age. “Symptoms occur when a food is ingested and the patient develops symptoms including but not limited to urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, flushing, vomiting, diarrhea, coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, presyncope, or syncope,” Pandya noted.
In the case of eosinophilic esophagitis, which may also be part of the atopic march, infants and toddlers often have challenging-to-treat symptoms of reflux, while school-age children have reflux and abdominal pain, and adolescents and adults may experience difficulty swallowing and impactions of food or pills, Brown-Whitehorn said.
To differentiate between food allergy and contact dermatitis, Lee suggested providers ask, “ ’Is the rash hives? If yes, is the rash generalized or in a limited area?’ Then consider the statistical probabilities. Skin problems after milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, or sesame are likely due to IgE-mediated food allergy, but after ketchup or strawberry are probably from skin contact.”
Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma
“For asthma, ask about frequency of night cough and symptoms with exercise, laughing, or crying. For allergic rhinitis, look for runny nose, itchy eyes, or sneezing,” Brown-Whitehorn said.
Testing and Monitoring
Assessing the extent of eczema with the Eczema Area and Severity Index or the SCORing Atopic Dermatitis index takes time but may be necessary to obtain insurance coverage for treatments such as biologics.
Avoid ordering IgE food panels, which can result in false positives that can lead to loss of tolerance and nutritional deficiencies; psychological harm from bullying, anxiety, and decreased quality of life; and higher food and healthcare costs, Pandya said.
Treatments
Caregivers may be wary about treatments, and all the three experts this news organization spoke with stressed the importance of educating caregivers about how treatments work and what to expect from them.
“Early and aggressive atopic dermatitis treatment could prevent sensitization to food or aeroallergens, which could help prevent additional atopic diseases, including those on the atopic march,” Pandya said. “Topical steroids are considered first line at any age. Topical phosphodiesterase inhibitors are approved at 3 months of age and above. Topical calcineurin inhibitors are approved at 2 years of age and above. Wet wrap therapy and bleach baths can be effective. Other options include biologic therapy, allergen immunotherapy, and UV therapy.”
“Epinephrine auto-injectors can counteract food reactions. For allergic rhinitis, non-sedating antihistamines, steroidal nasal sprays, and nasal antihistamines help. Asthma treatments include various inhaled medications,” Brown-Whitehorn added.
When to Refer to Specialists
Involving an allergist, dermatologist, pulmonologist, or ear nose throat specialist to the patient’s care team is advisable in more challenging cases.
If a child is younger than 3 months and has moderate to severe atopic dermatitis, an underlying immune defect may be to blame, so an allergy and immunology assessment is warranted, Brown-Whitehorn said. “An allergist can help any child who has recurrent coughing or wheezing avoid the emergency room or hospitalization.”
“In pediatrics, we always try to find the medication, regimen, and avoidance strategies that use the least treatment to provide the best care for each patient,” Brown-Whitehorn added. “Children eat, play, learn, and sleep, and every stage of the atopic march affects each of these activities. As clinicians, we need to be sure that we are helping children make the best of all these activities.”
Brown-Whitehorn reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. Lee reported financial relationships with Novartis. Pandya reported financial relationships with DBV Technologies, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.