User login
Antipsychotic cuts Alzheimer’s-related agitation
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
results of a phase 3 study suggest.
“In this phase 3 trial of patients with agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia, treatment with brexpiprazole 2 or 3 mg/day resulted in statistically significantly greater improvements in agitation versus placebo on the primary and key secondary endpoints,” said study investigator George Grossberg, MD, professor and director of the division of geriatric psychiatry, department of psychiatry & behavioral neuroscience, Saint Louis University.
Dr. Grossberg presented the findings as part of the annual meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry.
Agitation common, distressing
With two previous studies also showing efficacy of brexpiprazole in AD-related agitation, Dr. Grossberg speculated that brexpiprazole will become the first drug to be approved for agitation in AD.
Agitation is one of the most common AD symptoms and is arguably the most distressing for patients and caregivers alike, Dr. Grossberg noted.
The drug was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 as an adjunctive therapy to antidepressants for adults with major depressive disorder and for adults with schizophrenia.
To investigate the drug at effective doses for AD-related agitation, the researchers conducted a phase 3 multicenter trial that included 345 patients with AD who met criteria for agitation and aggression.
Study participants had a mean Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score between 5 and 22 at screening and baseline and a mean Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) total score of about 79. A score above 45 is considered clinically significant agitation. Use of AD medications were permitted.
Patients had a mean age of 74 years and were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive treatment with brexpiprazole 2 mg (n = 75) or 3 mg (n = 153) per day, or placebo (n = 117).
The study’s primary endpoint was improvement as assessed by the CMAI. Over 12 weeks, participants in the brexpiprazole group experienced greater improvement in agitation, with a mean change of –22.6 with brexpiprazole vs. –17.3 with placebo (P = .0026).
Brexpiprazole was also associated with significantly greater improvement in the secondary outcome of change from baseline to week 12 in agitation severity, as assessed using the Clinical Global Impression-Severity of Illness (CGI-S) score (mean change, –1.20 with brexpiprazole vs. –0.93 with placebo; P = .0078).
Specifically, treatment with the drug resulted in improvements in three key subscales of agitation, including aggressive behavior, such as physically striking out (P < .01 vs. placebo); physically nonaggressive; and verbally agitated, such as screaming or cursing (both P < .05).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) associated with brexpiprazole vs. placebo included somnolence (3.5% vs. 0.9%), nasopharyngitis (3.1% vs. 1.7%), dizziness (2.7% vs. 1.7%), diarrhea (2.2% vs. 0.9%), urinary tract infection (2.2% vs. 0.9%), and asthenia (2.2% vs. 0.0%).
“Aside from headache, no other TEAEs had an incidence of more than 5% in the brexpiprazole (2 or 3 mg) group, or in either dose group,” Dr. Grossberg said. “Cognition also remained stable,” he added.
Boxed warnings
Adverse events commonly associated with brexpiprazole include weight change, extrapyramidal events, falls, cardiovascular events, and sedation. In the study, all occurred at an incidence of less than 2% in both study groups, he noted.
Compared with the antipsychotic aripiprazole, brexpiprazole is associated with lower weight gain and akathisia, or motor restlessness.
One death occurred in the brexpiprazole 3 mg group in a patient who had heart failure, pneumonia, and cachexia. At autopsy, it was found the patient had cerebral and coronary atherosclerosis. The death was considered to be unrelated to brexpiprazole, said Dr. Grossberg.
This finding is notable because a caveat is that brexpiprazole, like aripiprazole and other typical and atypical antipsychotics, carries an FDA boxed warning related to an increased risk for death in older patients when used for dementia-related psychosis.
Noting that a black box warning about mortality risk is not a minor issue, Dr. Grossberg added that the risks are relatively low, whereas the risks associated with agitation in dementia can be high.
“If it’s an emergency situation, you have to treat the patient because otherwise they may harm someone else, or harm the staff, or harm their loved ones or themselves, and in those cases, we want to treat the patient first, get them under control, and then we worry about the black box,” he said.
In addition, “the No. 1 reason for getting kicked out of a nursing home is agitation or severe behaviors in the context of a dementia or a major neurocognitive disorder that the facility cannot control,” Dr. Grossberg added.
In such cases, patients may wind up in an emergency department and may not be welcome back at the nursing home.
“There’s always a risk/benefit ratio, and I have that discussion with patients and their families, but I can tell you that I’ve never had a family ask me not to use a medication because of the black box warning, because they see how miserable and how out of control their loved one is and they’re miserable because they see the suffering and will ask that we do anything that we can to get this behavior under control,” Dr. Grossberg said.
Caution still warranted
Commenting on the study, Rajesh R. Tampi, MD, professor and chairman of the department of psychiatry and the Bhatia Family Endowed Chair in Psychiatry at Creighton University, Omaha, Neb., underscored that, owing to the concerns behind the FDA warnings, “nonpharmacologic management is the cornerstone of treating agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia.”
He noted that the lack of an FDA-approved drug for agitation with AD is the result of “the overall benefits of any of the drug classes or drugs trialed to treat agitation in Alzheimer’s dementia vs. their adverse effect profile,” he said.
Therefore, he continued, “any medication or medication class should be used with caution among these individuals who often have polymorbidity.”
Dr. Tampi agreed that “the use of each drug for agitation in AD should be on a case-by-case basis with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with the patient and their families.”
“These medications should only be used for refractory symptoms or emergency situations where the agitation is not managed adequately with nonpharmacologic techniques and with a clear and documented risk/benefit discussion with patients and their families,” Dr. Tampi said.
The study was supported by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization and H. Lundbeck. Dr. Grossberg has received consulting fees from Acadia, Avanir, Biogen, BioXcel, Genentech, Karuna, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, and Takeda. Dr. Tampi had no disclosures to report.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 3/14/23.
AT AAGP 2023
Childhood nightmares a prelude to cognitive problems, Parkinson’s?
new research shows.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams between ages 7 and 11 years, those who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment and roughly seven times more likely to develop PD by age 50 years.
It’s been shown previously that sleep problems in adulthood, including distressing dreams, can precede the onset of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or PD by several years, and in some cases decades, study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham (England), told this news organization.
However, no studies have investigated whether distressing dreams during childhood might also be associated with increased risk for cognitive decline or PD.
“As such, these findings provide evidence for the first time that certain sleep problems in childhood (having regular distressing dreams) could be an early indicator of increased dementia and PD risk,” Dr. Otaiku said.
He noted that the findings build on previous studies which showed that regular nightmares in childhood could be an early indicator for psychiatric problems in adolescence, such as borderline personality disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and psychosis.
The study was published online February 26 in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine.
Statistically significant
The prospective, longitudinal analysis used data from the 1958 British Birth Cohort Study, a prospective birth cohort which included all people born in Britain during a single week in 1958.
At age 7 years (in 1965) and 11 years (in 1969), mothers were asked to report whether their child experienced “bad dreams or night terrors” in the past 3 months, and cognitive impairment and PD were determined at age 50 (2008).
Among a total of 6,991 children (51% girls), 78.2% never had distressing dreams, 17.9% had transient distressing dreams (either at ages 7 or 11 years), and 3.8% had persistent distressing dreams (at both ages 7 and 11 years).
By age 50, 262 participants had developed cognitive impairment, and five had been diagnosed with PD.
After adjusting for all covariates, having more regular distressing dreams during childhood was “linearly and statistically significantly” associated with higher risk of developing cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 years (P = .037). This was the case in both boys and girls.
Compared with children who never had bad dreams, peers who had persistent distressing dreams (at ages 7 and 11 years) had an 85% increased risk for cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-3.11; P = .019).
The associations remained when incident cognitive impairment and incident PD were analyzed separately.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams, children who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment by age 50 years (aOR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.03-2.99; P = .037), and were about seven times more likely to be diagnosed with PD by age 50 years (aOR, 7.35; 95% CI, 1.03-52.73; P = .047).
The linear association was statistically significant for PD (P = .050) and had a trend toward statistical significance for cognitive impairment (P = .074).
Mechanism unclear
“Early-life nightmares might be causally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, noncausally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, or both. At this stage it remains unclear which of the three options is correct. Therefore, further research on mechanisms is needed,” Dr. Otaiku told this news organization.
“One plausible noncausal explanation is that there are shared genetic factors which predispose individuals to having frequent nightmares in childhood, and to developing neurodegenerative diseases such as AD or PD in adulthood,” he added.
It’s also plausible that having regular nightmares throughout childhood could be a causal risk factor for cognitive impairment and PD by causing chronic sleep disruption, he noted.
“Chronic sleep disruption due to nightmares might lead to impaired glymphatic clearance during sleep – and thus greater accumulation of pathological proteins in the brain, such as amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Disrupted sleep throughout childhood might also impair normal brain development, which could make children’s brains less resilient to neuropathologic damage, he said.
Clinical implications?
There are established treatments for childhood nightmares, including nonpharmacologic approaches.
“For children who have regular nightmares that lead to impaired daytime functioning, it may well be a good idea for them to see a sleep physician to discuss whether treatment may be needed,” Dr. Otaiku said.
But should doctors treat children with persistent nightmares for the purpose of preventing neurodegenerative diseases in adulthood or psychiatric problems in adolescence?
“It’s an interesting possibility. However, more research is needed to confirm these epidemiological associations and to determine whether or not nightmares are a causal risk factor for these conditions,” Dr. Otaiku concluded.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku reports no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams between ages 7 and 11 years, those who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment and roughly seven times more likely to develop PD by age 50 years.
It’s been shown previously that sleep problems in adulthood, including distressing dreams, can precede the onset of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or PD by several years, and in some cases decades, study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham (England), told this news organization.
However, no studies have investigated whether distressing dreams during childhood might also be associated with increased risk for cognitive decline or PD.
“As such, these findings provide evidence for the first time that certain sleep problems in childhood (having regular distressing dreams) could be an early indicator of increased dementia and PD risk,” Dr. Otaiku said.
He noted that the findings build on previous studies which showed that regular nightmares in childhood could be an early indicator for psychiatric problems in adolescence, such as borderline personality disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and psychosis.
The study was published online February 26 in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine.
Statistically significant
The prospective, longitudinal analysis used data from the 1958 British Birth Cohort Study, a prospective birth cohort which included all people born in Britain during a single week in 1958.
At age 7 years (in 1965) and 11 years (in 1969), mothers were asked to report whether their child experienced “bad dreams or night terrors” in the past 3 months, and cognitive impairment and PD were determined at age 50 (2008).
Among a total of 6,991 children (51% girls), 78.2% never had distressing dreams, 17.9% had transient distressing dreams (either at ages 7 or 11 years), and 3.8% had persistent distressing dreams (at both ages 7 and 11 years).
By age 50, 262 participants had developed cognitive impairment, and five had been diagnosed with PD.
After adjusting for all covariates, having more regular distressing dreams during childhood was “linearly and statistically significantly” associated with higher risk of developing cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 years (P = .037). This was the case in both boys and girls.
Compared with children who never had bad dreams, peers who had persistent distressing dreams (at ages 7 and 11 years) had an 85% increased risk for cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-3.11; P = .019).
The associations remained when incident cognitive impairment and incident PD were analyzed separately.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams, children who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment by age 50 years (aOR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.03-2.99; P = .037), and were about seven times more likely to be diagnosed with PD by age 50 years (aOR, 7.35; 95% CI, 1.03-52.73; P = .047).
The linear association was statistically significant for PD (P = .050) and had a trend toward statistical significance for cognitive impairment (P = .074).
Mechanism unclear
“Early-life nightmares might be causally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, noncausally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, or both. At this stage it remains unclear which of the three options is correct. Therefore, further research on mechanisms is needed,” Dr. Otaiku told this news organization.
“One plausible noncausal explanation is that there are shared genetic factors which predispose individuals to having frequent nightmares in childhood, and to developing neurodegenerative diseases such as AD or PD in adulthood,” he added.
It’s also plausible that having regular nightmares throughout childhood could be a causal risk factor for cognitive impairment and PD by causing chronic sleep disruption, he noted.
“Chronic sleep disruption due to nightmares might lead to impaired glymphatic clearance during sleep – and thus greater accumulation of pathological proteins in the brain, such as amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Disrupted sleep throughout childhood might also impair normal brain development, which could make children’s brains less resilient to neuropathologic damage, he said.
Clinical implications?
There are established treatments for childhood nightmares, including nonpharmacologic approaches.
“For children who have regular nightmares that lead to impaired daytime functioning, it may well be a good idea for them to see a sleep physician to discuss whether treatment may be needed,” Dr. Otaiku said.
But should doctors treat children with persistent nightmares for the purpose of preventing neurodegenerative diseases in adulthood or psychiatric problems in adolescence?
“It’s an interesting possibility. However, more research is needed to confirm these epidemiological associations and to determine whether or not nightmares are a causal risk factor for these conditions,” Dr. Otaiku concluded.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku reports no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams between ages 7 and 11 years, those who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment and roughly seven times more likely to develop PD by age 50 years.
It’s been shown previously that sleep problems in adulthood, including distressing dreams, can precede the onset of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) or PD by several years, and in some cases decades, study investigator Abidemi Otaiku, BMBS, University of Birmingham (England), told this news organization.
However, no studies have investigated whether distressing dreams during childhood might also be associated with increased risk for cognitive decline or PD.
“As such, these findings provide evidence for the first time that certain sleep problems in childhood (having regular distressing dreams) could be an early indicator of increased dementia and PD risk,” Dr. Otaiku said.
He noted that the findings build on previous studies which showed that regular nightmares in childhood could be an early indicator for psychiatric problems in adolescence, such as borderline personality disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and psychosis.
The study was published online February 26 in The Lancet journal eClinicalMedicine.
Statistically significant
The prospective, longitudinal analysis used data from the 1958 British Birth Cohort Study, a prospective birth cohort which included all people born in Britain during a single week in 1958.
At age 7 years (in 1965) and 11 years (in 1969), mothers were asked to report whether their child experienced “bad dreams or night terrors” in the past 3 months, and cognitive impairment and PD were determined at age 50 (2008).
Among a total of 6,991 children (51% girls), 78.2% never had distressing dreams, 17.9% had transient distressing dreams (either at ages 7 or 11 years), and 3.8% had persistent distressing dreams (at both ages 7 and 11 years).
By age 50, 262 participants had developed cognitive impairment, and five had been diagnosed with PD.
After adjusting for all covariates, having more regular distressing dreams during childhood was “linearly and statistically significantly” associated with higher risk of developing cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 years (P = .037). This was the case in both boys and girls.
Compared with children who never had bad dreams, peers who had persistent distressing dreams (at ages 7 and 11 years) had an 85% increased risk for cognitive impairment or PD by age 50 (adjusted odds ratio, 1.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.10-3.11; P = .019).
The associations remained when incident cognitive impairment and incident PD were analyzed separately.
Compared with children who never had distressing dreams, children who had persistent distressing dreams were 76% more likely to develop cognitive impairment by age 50 years (aOR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.03-2.99; P = .037), and were about seven times more likely to be diagnosed with PD by age 50 years (aOR, 7.35; 95% CI, 1.03-52.73; P = .047).
The linear association was statistically significant for PD (P = .050) and had a trend toward statistical significance for cognitive impairment (P = .074).
Mechanism unclear
“Early-life nightmares might be causally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, noncausally associated with cognitive impairment and PD, or both. At this stage it remains unclear which of the three options is correct. Therefore, further research on mechanisms is needed,” Dr. Otaiku told this news organization.
“One plausible noncausal explanation is that there are shared genetic factors which predispose individuals to having frequent nightmares in childhood, and to developing neurodegenerative diseases such as AD or PD in adulthood,” he added.
It’s also plausible that having regular nightmares throughout childhood could be a causal risk factor for cognitive impairment and PD by causing chronic sleep disruption, he noted.
“Chronic sleep disruption due to nightmares might lead to impaired glymphatic clearance during sleep – and thus greater accumulation of pathological proteins in the brain, such as amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein,” Dr. Otaiku said.
Disrupted sleep throughout childhood might also impair normal brain development, which could make children’s brains less resilient to neuropathologic damage, he said.
Clinical implications?
There are established treatments for childhood nightmares, including nonpharmacologic approaches.
“For children who have regular nightmares that lead to impaired daytime functioning, it may well be a good idea for them to see a sleep physician to discuss whether treatment may be needed,” Dr. Otaiku said.
But should doctors treat children with persistent nightmares for the purpose of preventing neurodegenerative diseases in adulthood or psychiatric problems in adolescence?
“It’s an interesting possibility. However, more research is needed to confirm these epidemiological associations and to determine whether or not nightmares are a causal risk factor for these conditions,” Dr. Otaiku concluded.
The study received no external funding. Dr. Otaiku reports no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECLINICALMEDICINE
Daily socialization may extend lifespan in elderly
Sometimes more is more.
Correlations between socializing and survival were detected regardless of baseline health status, suggesting that physicians should be recommending daily socialization for all elderly patients, lead author Ziqiong Wang, MD, of Sichuan University West China Hospital, Chengdu, China, and colleagues reported.
These findings align with an array of prior studies reporting physical and mental health benefits from socialization, and negative impacts from isolation, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. Not all studies have yielded the same picture, however, and most research has been conducted in Western countries, leading to uncertainty about whether different outcomes would be seen in populations in other parts of the world. Furthermore, the authors added that few studies have explored the amount of socialization needed to derive a positive benefit.
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed survival data from 28,563 participants in the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey with a median age of 89 years at baseline.
“[This analysis] is from a highly respected ongoing longitudinal study of aging in China, which includes a large number of subjects and employs very strong research design and statistical analytical methods, so it has credibility,” John W. Rowe, MD, Julius B. Richmond Professor of Health Policy and Aging at Columbia University, New York, said in a written comment.
The investigators stratified frequency of socialization into five tiers: never, not monthly but sometimes, not weekly but at least once per month, not daily but at least once per week, and almost every day.
Survival proportions were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method after accounting for a range of individual characteristics, including age, sex, household income, smoking status, diabetes, self-rated health, and others. Comparative findings were described in terms of time ratios using multivariable parametric accelerated failure time (AFT) models.
“The AFT model estimates the time ratio (TR), which is interpreted as the expected time to events in one category relative to the reference group,” the investigators wrote. “Unlike the interpretation of proportional hazard model results where hazard ratios larger than 1 are equal to higher risk, a TR of greater than 1 is considered to have a longer time to events, compared with the reference group.”
From baseline to 5 years, each socialization tier was significantly associated with prolonged survival, suggesting a general benefit. Compared with no socialization, socializing sometimes but not monthly was associated with 42% longer survival, at least monthly socialization was associated with 48% longer survival, at least weekly was associated with 110% longer survival, and socializing almost every day was associated with 87% longer survival.
The outsized benefit of daily socialization became clear in a long-term survival analysis, which spanned 5 years through the end of follow-up. Compared with no socialization, daily socialization tripled survival (TR, 3.04; P < .001), compared with prolongations ranging from 5% to 64% for less socialization, with just one of these lower tiers achieving statistical significance (P = .046).
Of note, the benefit of daily socialization was detected regardless of a person’s health status at baseline.
“No matter if elderly participants had chronic diseases or not, [and] no matter if older people had good self-rated health or not, the survival benefits of frequently participating in social activity were the same,” said principal author Sen He, MD, of Sichuan University, in a written comment.
“Socializing almost every day seems to be the most beneficial for a long life,” Dr. Sen added, noting that more research is needed to determine if there is an optimal type of social activity.
Dr. Rowe pointed out two key findings from the study. The first was that it confirmed “prior studies that have identified a beneficial effect of social activity on life expectancy.
“We have known that engagement is essential for successful aging and that isolation is toxic. While this finding is not novel, it is nice to see this confirmation of what we thought we knew,” he wrote.
Secondly, the study has identified “a threshold effect”, which is that “the long-term benefit on life expectancy was only seen in the presence of fairly intense social interactions, essentially daily,” he said.
According to Preeti Malani, MD, professor of medicine and geriatrician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the findings are also helpful because they offer data from another part of the world, adding confidence in findings from Western countries.
“This [study] happens to focus on older adults in China, which is helpful since aging is not the same everywhere in the world,” Dr. Malani said. “While the numbers here may not be precise, it’s fair to say that socialization is good for your health – for everyone but especially for older adults.”
Considering the body of evidence now spanning a range of populations, Dr. Malani said physicians should be screening for, and recommending, socialization for all elderly patients, particularly because many aren’t getting enough of it.
“Work that my colleagues and I have done (with the National Poll on Healthy Aging) suggests that there is a portion of older adults that have very little to no social contact,” Dr. Malani said. “A physician may not know this unless they are asking routinely about socialization the way we might ask about diet and exercise. How much is enough? No one knows, but anything is better than nothing and likely more is better.”
She also suggested that personalization is key.
“Physical and emotional health may limit the ability to socialize, so not everyone can engage all the time,” Dr. Malani said. “Also, socialization can look different for different people. Technology allows for socialization even if an individual has trouble leaving their home. I especially worry about this issue for older adults that are also caregivers. Those individuals also need time for themselves” and on way to fulfill that need is by socializing with others.
The study was supported by Sichuan (China) Science and Technology Program, the National Key R&D Program of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The investigators, Dr. Rowe, and Dr. Malani disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Sometimes more is more.
Correlations between socializing and survival were detected regardless of baseline health status, suggesting that physicians should be recommending daily socialization for all elderly patients, lead author Ziqiong Wang, MD, of Sichuan University West China Hospital, Chengdu, China, and colleagues reported.
These findings align with an array of prior studies reporting physical and mental health benefits from socialization, and negative impacts from isolation, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. Not all studies have yielded the same picture, however, and most research has been conducted in Western countries, leading to uncertainty about whether different outcomes would be seen in populations in other parts of the world. Furthermore, the authors added that few studies have explored the amount of socialization needed to derive a positive benefit.
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed survival data from 28,563 participants in the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey with a median age of 89 years at baseline.
“[This analysis] is from a highly respected ongoing longitudinal study of aging in China, which includes a large number of subjects and employs very strong research design and statistical analytical methods, so it has credibility,” John W. Rowe, MD, Julius B. Richmond Professor of Health Policy and Aging at Columbia University, New York, said in a written comment.
The investigators stratified frequency of socialization into five tiers: never, not monthly but sometimes, not weekly but at least once per month, not daily but at least once per week, and almost every day.
Survival proportions were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method after accounting for a range of individual characteristics, including age, sex, household income, smoking status, diabetes, self-rated health, and others. Comparative findings were described in terms of time ratios using multivariable parametric accelerated failure time (AFT) models.
“The AFT model estimates the time ratio (TR), which is interpreted as the expected time to events in one category relative to the reference group,” the investigators wrote. “Unlike the interpretation of proportional hazard model results where hazard ratios larger than 1 are equal to higher risk, a TR of greater than 1 is considered to have a longer time to events, compared with the reference group.”
From baseline to 5 years, each socialization tier was significantly associated with prolonged survival, suggesting a general benefit. Compared with no socialization, socializing sometimes but not monthly was associated with 42% longer survival, at least monthly socialization was associated with 48% longer survival, at least weekly was associated with 110% longer survival, and socializing almost every day was associated with 87% longer survival.
The outsized benefit of daily socialization became clear in a long-term survival analysis, which spanned 5 years through the end of follow-up. Compared with no socialization, daily socialization tripled survival (TR, 3.04; P < .001), compared with prolongations ranging from 5% to 64% for less socialization, with just one of these lower tiers achieving statistical significance (P = .046).
Of note, the benefit of daily socialization was detected regardless of a person’s health status at baseline.
“No matter if elderly participants had chronic diseases or not, [and] no matter if older people had good self-rated health or not, the survival benefits of frequently participating in social activity were the same,” said principal author Sen He, MD, of Sichuan University, in a written comment.
“Socializing almost every day seems to be the most beneficial for a long life,” Dr. Sen added, noting that more research is needed to determine if there is an optimal type of social activity.
Dr. Rowe pointed out two key findings from the study. The first was that it confirmed “prior studies that have identified a beneficial effect of social activity on life expectancy.
“We have known that engagement is essential for successful aging and that isolation is toxic. While this finding is not novel, it is nice to see this confirmation of what we thought we knew,” he wrote.
Secondly, the study has identified “a threshold effect”, which is that “the long-term benefit on life expectancy was only seen in the presence of fairly intense social interactions, essentially daily,” he said.
According to Preeti Malani, MD, professor of medicine and geriatrician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the findings are also helpful because they offer data from another part of the world, adding confidence in findings from Western countries.
“This [study] happens to focus on older adults in China, which is helpful since aging is not the same everywhere in the world,” Dr. Malani said. “While the numbers here may not be precise, it’s fair to say that socialization is good for your health – for everyone but especially for older adults.”
Considering the body of evidence now spanning a range of populations, Dr. Malani said physicians should be screening for, and recommending, socialization for all elderly patients, particularly because many aren’t getting enough of it.
“Work that my colleagues and I have done (with the National Poll on Healthy Aging) suggests that there is a portion of older adults that have very little to no social contact,” Dr. Malani said. “A physician may not know this unless they are asking routinely about socialization the way we might ask about diet and exercise. How much is enough? No one knows, but anything is better than nothing and likely more is better.”
She also suggested that personalization is key.
“Physical and emotional health may limit the ability to socialize, so not everyone can engage all the time,” Dr. Malani said. “Also, socialization can look different for different people. Technology allows for socialization even if an individual has trouble leaving their home. I especially worry about this issue for older adults that are also caregivers. Those individuals also need time for themselves” and on way to fulfill that need is by socializing with others.
The study was supported by Sichuan (China) Science and Technology Program, the National Key R&D Program of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The investigators, Dr. Rowe, and Dr. Malani disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
Sometimes more is more.
Correlations between socializing and survival were detected regardless of baseline health status, suggesting that physicians should be recommending daily socialization for all elderly patients, lead author Ziqiong Wang, MD, of Sichuan University West China Hospital, Chengdu, China, and colleagues reported.
These findings align with an array of prior studies reporting physical and mental health benefits from socialization, and negative impacts from isolation, the investigators wrote in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health. Not all studies have yielded the same picture, however, and most research has been conducted in Western countries, leading to uncertainty about whether different outcomes would be seen in populations in other parts of the world. Furthermore, the authors added that few studies have explored the amount of socialization needed to derive a positive benefit.
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed survival data from 28,563 participants in the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey with a median age of 89 years at baseline.
“[This analysis] is from a highly respected ongoing longitudinal study of aging in China, which includes a large number of subjects and employs very strong research design and statistical analytical methods, so it has credibility,” John W. Rowe, MD, Julius B. Richmond Professor of Health Policy and Aging at Columbia University, New York, said in a written comment.
The investigators stratified frequency of socialization into five tiers: never, not monthly but sometimes, not weekly but at least once per month, not daily but at least once per week, and almost every day.
Survival proportions were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method after accounting for a range of individual characteristics, including age, sex, household income, smoking status, diabetes, self-rated health, and others. Comparative findings were described in terms of time ratios using multivariable parametric accelerated failure time (AFT) models.
“The AFT model estimates the time ratio (TR), which is interpreted as the expected time to events in one category relative to the reference group,” the investigators wrote. “Unlike the interpretation of proportional hazard model results where hazard ratios larger than 1 are equal to higher risk, a TR of greater than 1 is considered to have a longer time to events, compared with the reference group.”
From baseline to 5 years, each socialization tier was significantly associated with prolonged survival, suggesting a general benefit. Compared with no socialization, socializing sometimes but not monthly was associated with 42% longer survival, at least monthly socialization was associated with 48% longer survival, at least weekly was associated with 110% longer survival, and socializing almost every day was associated with 87% longer survival.
The outsized benefit of daily socialization became clear in a long-term survival analysis, which spanned 5 years through the end of follow-up. Compared with no socialization, daily socialization tripled survival (TR, 3.04; P < .001), compared with prolongations ranging from 5% to 64% for less socialization, with just one of these lower tiers achieving statistical significance (P = .046).
Of note, the benefit of daily socialization was detected regardless of a person’s health status at baseline.
“No matter if elderly participants had chronic diseases or not, [and] no matter if older people had good self-rated health or not, the survival benefits of frequently participating in social activity were the same,” said principal author Sen He, MD, of Sichuan University, in a written comment.
“Socializing almost every day seems to be the most beneficial for a long life,” Dr. Sen added, noting that more research is needed to determine if there is an optimal type of social activity.
Dr. Rowe pointed out two key findings from the study. The first was that it confirmed “prior studies that have identified a beneficial effect of social activity on life expectancy.
“We have known that engagement is essential for successful aging and that isolation is toxic. While this finding is not novel, it is nice to see this confirmation of what we thought we knew,” he wrote.
Secondly, the study has identified “a threshold effect”, which is that “the long-term benefit on life expectancy was only seen in the presence of fairly intense social interactions, essentially daily,” he said.
According to Preeti Malani, MD, professor of medicine and geriatrician at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the findings are also helpful because they offer data from another part of the world, adding confidence in findings from Western countries.
“This [study] happens to focus on older adults in China, which is helpful since aging is not the same everywhere in the world,” Dr. Malani said. “While the numbers here may not be precise, it’s fair to say that socialization is good for your health – for everyone but especially for older adults.”
Considering the body of evidence now spanning a range of populations, Dr. Malani said physicians should be screening for, and recommending, socialization for all elderly patients, particularly because many aren’t getting enough of it.
“Work that my colleagues and I have done (with the National Poll on Healthy Aging) suggests that there is a portion of older adults that have very little to no social contact,” Dr. Malani said. “A physician may not know this unless they are asking routinely about socialization the way we might ask about diet and exercise. How much is enough? No one knows, but anything is better than nothing and likely more is better.”
She also suggested that personalization is key.
“Physical and emotional health may limit the ability to socialize, so not everyone can engage all the time,” Dr. Malani said. “Also, socialization can look different for different people. Technology allows for socialization even if an individual has trouble leaving their home. I especially worry about this issue for older adults that are also caregivers. Those individuals also need time for themselves” and on way to fulfill that need is by socializing with others.
The study was supported by Sichuan (China) Science and Technology Program, the National Key R&D Program of China, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The investigators, Dr. Rowe, and Dr. Malani disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY & COMMUNITY HEALTH
Distinct suicidal thought patterns flag those at highest risk
Long-term assessment of suicide risk and ideation in older adults may help identify distinct ideation patterns and predict potential future suicidal behavior, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 300 older adults, assessing suicidal ideation and behavior for up to 14 years at least once annually. They then identified four suicidal ideation profiles.
They found that In turn, fast-remitting ideators were at higher risk in comparison to low/nonideators with no attempts or suicide.
Chronic severe ideators also showed the most severe levels of dysfunction across personality, social characteristics, and impulsivity measures, while highly variable and fast-remitting ideators displayed more specific deficits.
“We identified longitudinal ideation profiles that convey differential risk of future suicidal behavior to help clinicians recognize high suicide risk patients for preventing suicide,” said lead author Hanga Galfalvy, PhD, associate professor, department of psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Clinicians should repeatedly assess suicidal ideation and ask not only about current ideation but also about the worst ideation since the last visit [because] similar levels of ideation during a single assessment can belong to very different risk profiles,” said Dr. Galfalvy, also a professor of biostatistics and a coinvestigator in the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention at Columbia University.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Vulnerable population
“Older adults in most countries, including the U.S., are at the highest risk of dying of suicide out of all age groups,” said Dr. Galfalvy. “A significant number of depressed older adults experience thoughts of killing themselves, but fortunately, only a few transition from suicidal thoughts to behavior.”
Senior author Katalin Szanto, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview that currently established clinical and psychosocial suicide risk factors have “low predictive value and provide little insight into the high suicide rate in the elderly.”
These traditional risk factors “poorly distinguish between suicide ideators and suicide attempters and do not take into consideration the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” said Dr. Szanto, principal investigator at the University of Pittsburgh’s Longitudinal research Program in Late-Life Suicide, where the study was conducted.
“Suicidal ideation measured at one time point – current or lifetime – may not be enough to accurately predict suicide risk,” the investigators wrote.
The current study, a collaboration between investigators from the Longitudinal Research Program in Late-Life Suicide and the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention, investigates “profiles of suicidal thoughts and behavior in patients with late-life depression over a longer period of time,” Dr. Galfalvy said.
The researchers used latent profile analysis (LPA) in a cohort of adults with nonpsychotic unipolar depression (aged 50-93 years; n = 337; mean age, 65.12 years) to “identify distinct ideation profiles and their clinical correlates” and to “test the profiles’ association with the risk of suicidal behavior before and during follow-up.”
LPA is “a data-driven method of grouping individuals into subgroups, based on quantitative characteristics,” Dr. Galfalvy explained.
The LPA yielded four profiles of ideation.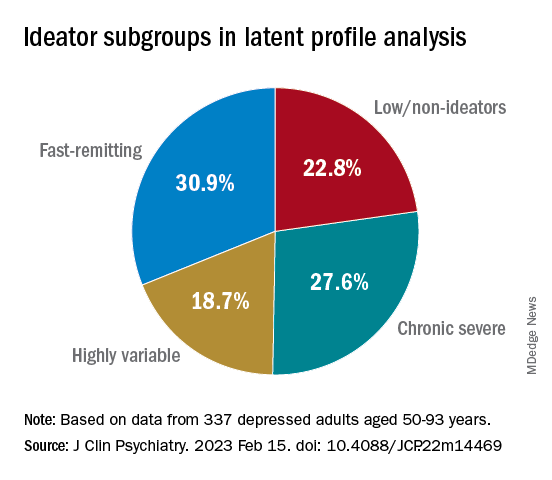
At baseline, the researchers assessed the presence or absence of suicidal behavior history and the number and lethality of attempts. They prospectively assessed suicidal ideation and attempts at least once annually thereafter over a period ranging from 3 months to 14 years (median, 3 years; IQR, 1.6-4 years).
At baseline and at follow-ups, they assessed ideation severity.
They also assessed depression severity, impulsivity, and personality measures, as well as perception of social support, social problem solving, cognitive performance, and physical comorbidities.
Personalized prevention
Of the original cohort, 92 patients died during the follow-up period, with 13 dying of suicide (or suspected suicide).
Over half (60%) of the chronic severe as well as the highly variable groups and almost half (48%) of the fast-remitting group had a history of past suicide attempt – all significantly higher than the low-nonideators (0%).
Despite comparable current ideation severity at baseline, the risk of suicide attempt/death was greater for chronic severe ideators versus fast-remitting ideators, but not greater than for highly variable ideators. On the other hand, highly variable ideators were at greater risk, compared with fast-remitting ideators.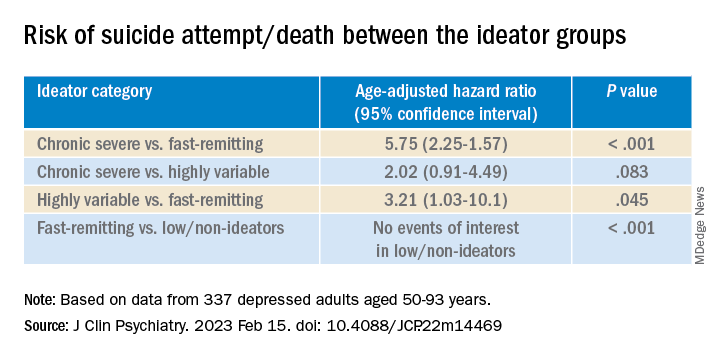
Cognitive factors “did not significantly discriminate between the ideation profiles, although ... lower global cognitive performance predicted suicidal behavior during follow-up,” the authors wrote.
This finding “aligns with prior studies indicating that late-life suicidal behavior but not ideation may be related to cognition ... and instead, ideation and cognition may act as independent risk factors for suicidal behavior,” they added.
“Patients in the fluctuating ideator group generally had moderate or high levels of worst suicidal ideation between visits, but not when asked about current ideation levels at the time of the follow-up assessment,” Dr. Galfalvy noted. “For them, the time frame of the question made a difference as to the level of ideation reported.”
The study “identified several clinical differences among these subgroups which could lead to more personalized suicide prevention efforts and further research into the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” she suggested.
New insight
Commenting on the study, Ari Cuperfain, MD, of the University of Toronto said the study “adds to the nuanced understanding of how changes in suicidal ideation over time can lead to suicidal actions and behavior.”
The study “sheds light on the notion of how older adults who die by suicide can demonstrate a greater degree of premeditated intent relative to younger cohorts, with chronic severe ideators portending the highest risk for suicide in this sample,” added Dr. Cuperfain, who was not involved with the current research.
“Overall, the paper highlights the importance of both screening for current levels of suicidal ideation in addition to the evolution of suicidal ideation in developing a risk assessment and in finding interventions to reduce this risk when it is most prominent,” he stated.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Cuperfain disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term assessment of suicide risk and ideation in older adults may help identify distinct ideation patterns and predict potential future suicidal behavior, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 300 older adults, assessing suicidal ideation and behavior for up to 14 years at least once annually. They then identified four suicidal ideation profiles.
They found that In turn, fast-remitting ideators were at higher risk in comparison to low/nonideators with no attempts or suicide.
Chronic severe ideators also showed the most severe levels of dysfunction across personality, social characteristics, and impulsivity measures, while highly variable and fast-remitting ideators displayed more specific deficits.
“We identified longitudinal ideation profiles that convey differential risk of future suicidal behavior to help clinicians recognize high suicide risk patients for preventing suicide,” said lead author Hanga Galfalvy, PhD, associate professor, department of psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Clinicians should repeatedly assess suicidal ideation and ask not only about current ideation but also about the worst ideation since the last visit [because] similar levels of ideation during a single assessment can belong to very different risk profiles,” said Dr. Galfalvy, also a professor of biostatistics and a coinvestigator in the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention at Columbia University.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Vulnerable population
“Older adults in most countries, including the U.S., are at the highest risk of dying of suicide out of all age groups,” said Dr. Galfalvy. “A significant number of depressed older adults experience thoughts of killing themselves, but fortunately, only a few transition from suicidal thoughts to behavior.”
Senior author Katalin Szanto, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview that currently established clinical and psychosocial suicide risk factors have “low predictive value and provide little insight into the high suicide rate in the elderly.”
These traditional risk factors “poorly distinguish between suicide ideators and suicide attempters and do not take into consideration the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” said Dr. Szanto, principal investigator at the University of Pittsburgh’s Longitudinal research Program in Late-Life Suicide, where the study was conducted.
“Suicidal ideation measured at one time point – current or lifetime – may not be enough to accurately predict suicide risk,” the investigators wrote.
The current study, a collaboration between investigators from the Longitudinal Research Program in Late-Life Suicide and the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention, investigates “profiles of suicidal thoughts and behavior in patients with late-life depression over a longer period of time,” Dr. Galfalvy said.
The researchers used latent profile analysis (LPA) in a cohort of adults with nonpsychotic unipolar depression (aged 50-93 years; n = 337; mean age, 65.12 years) to “identify distinct ideation profiles and their clinical correlates” and to “test the profiles’ association with the risk of suicidal behavior before and during follow-up.”
LPA is “a data-driven method of grouping individuals into subgroups, based on quantitative characteristics,” Dr. Galfalvy explained.
The LPA yielded four profiles of ideation.
At baseline, the researchers assessed the presence or absence of suicidal behavior history and the number and lethality of attempts. They prospectively assessed suicidal ideation and attempts at least once annually thereafter over a period ranging from 3 months to 14 years (median, 3 years; IQR, 1.6-4 years).
At baseline and at follow-ups, they assessed ideation severity.
They also assessed depression severity, impulsivity, and personality measures, as well as perception of social support, social problem solving, cognitive performance, and physical comorbidities.
Personalized prevention
Of the original cohort, 92 patients died during the follow-up period, with 13 dying of suicide (or suspected suicide).
Over half (60%) of the chronic severe as well as the highly variable groups and almost half (48%) of the fast-remitting group had a history of past suicide attempt – all significantly higher than the low-nonideators (0%).
Despite comparable current ideation severity at baseline, the risk of suicide attempt/death was greater for chronic severe ideators versus fast-remitting ideators, but not greater than for highly variable ideators. On the other hand, highly variable ideators were at greater risk, compared with fast-remitting ideators.
Cognitive factors “did not significantly discriminate between the ideation profiles, although ... lower global cognitive performance predicted suicidal behavior during follow-up,” the authors wrote.
This finding “aligns with prior studies indicating that late-life suicidal behavior but not ideation may be related to cognition ... and instead, ideation and cognition may act as independent risk factors for suicidal behavior,” they added.
“Patients in the fluctuating ideator group generally had moderate or high levels of worst suicidal ideation between visits, but not when asked about current ideation levels at the time of the follow-up assessment,” Dr. Galfalvy noted. “For them, the time frame of the question made a difference as to the level of ideation reported.”
The study “identified several clinical differences among these subgroups which could lead to more personalized suicide prevention efforts and further research into the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” she suggested.
New insight
Commenting on the study, Ari Cuperfain, MD, of the University of Toronto said the study “adds to the nuanced understanding of how changes in suicidal ideation over time can lead to suicidal actions and behavior.”
The study “sheds light on the notion of how older adults who die by suicide can demonstrate a greater degree of premeditated intent relative to younger cohorts, with chronic severe ideators portending the highest risk for suicide in this sample,” added Dr. Cuperfain, who was not involved with the current research.
“Overall, the paper highlights the importance of both screening for current levels of suicidal ideation in addition to the evolution of suicidal ideation in developing a risk assessment and in finding interventions to reduce this risk when it is most prominent,” he stated.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Cuperfain disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Long-term assessment of suicide risk and ideation in older adults may help identify distinct ideation patterns and predict potential future suicidal behavior, new research suggests.
Investigators studied over 300 older adults, assessing suicidal ideation and behavior for up to 14 years at least once annually. They then identified four suicidal ideation profiles.
They found that In turn, fast-remitting ideators were at higher risk in comparison to low/nonideators with no attempts or suicide.
Chronic severe ideators also showed the most severe levels of dysfunction across personality, social characteristics, and impulsivity measures, while highly variable and fast-remitting ideators displayed more specific deficits.
“We identified longitudinal ideation profiles that convey differential risk of future suicidal behavior to help clinicians recognize high suicide risk patients for preventing suicide,” said lead author Hanga Galfalvy, PhD, associate professor, department of psychiatry, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York.
“Clinicians should repeatedly assess suicidal ideation and ask not only about current ideation but also about the worst ideation since the last visit [because] similar levels of ideation during a single assessment can belong to very different risk profiles,” said Dr. Galfalvy, also a professor of biostatistics and a coinvestigator in the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention at Columbia University.
The study was published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Vulnerable population
“Older adults in most countries, including the U.S., are at the highest risk of dying of suicide out of all age groups,” said Dr. Galfalvy. “A significant number of depressed older adults experience thoughts of killing themselves, but fortunately, only a few transition from suicidal thoughts to behavior.”
Senior author Katalin Szanto, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh, said in an interview that currently established clinical and psychosocial suicide risk factors have “low predictive value and provide little insight into the high suicide rate in the elderly.”
These traditional risk factors “poorly distinguish between suicide ideators and suicide attempters and do not take into consideration the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” said Dr. Szanto, principal investigator at the University of Pittsburgh’s Longitudinal research Program in Late-Life Suicide, where the study was conducted.
“Suicidal ideation measured at one time point – current or lifetime – may not be enough to accurately predict suicide risk,” the investigators wrote.
The current study, a collaboration between investigators from the Longitudinal Research Program in Late-Life Suicide and the Conte Center for Suicide Prevention, investigates “profiles of suicidal thoughts and behavior in patients with late-life depression over a longer period of time,” Dr. Galfalvy said.
The researchers used latent profile analysis (LPA) in a cohort of adults with nonpsychotic unipolar depression (aged 50-93 years; n = 337; mean age, 65.12 years) to “identify distinct ideation profiles and their clinical correlates” and to “test the profiles’ association with the risk of suicidal behavior before and during follow-up.”
LPA is “a data-driven method of grouping individuals into subgroups, based on quantitative characteristics,” Dr. Galfalvy explained.
The LPA yielded four profiles of ideation.
At baseline, the researchers assessed the presence or absence of suicidal behavior history and the number and lethality of attempts. They prospectively assessed suicidal ideation and attempts at least once annually thereafter over a period ranging from 3 months to 14 years (median, 3 years; IQR, 1.6-4 years).
At baseline and at follow-ups, they assessed ideation severity.
They also assessed depression severity, impulsivity, and personality measures, as well as perception of social support, social problem solving, cognitive performance, and physical comorbidities.
Personalized prevention
Of the original cohort, 92 patients died during the follow-up period, with 13 dying of suicide (or suspected suicide).
Over half (60%) of the chronic severe as well as the highly variable groups and almost half (48%) of the fast-remitting group had a history of past suicide attempt – all significantly higher than the low-nonideators (0%).
Despite comparable current ideation severity at baseline, the risk of suicide attempt/death was greater for chronic severe ideators versus fast-remitting ideators, but not greater than for highly variable ideators. On the other hand, highly variable ideators were at greater risk, compared with fast-remitting ideators.
Cognitive factors “did not significantly discriminate between the ideation profiles, although ... lower global cognitive performance predicted suicidal behavior during follow-up,” the authors wrote.
This finding “aligns with prior studies indicating that late-life suicidal behavior but not ideation may be related to cognition ... and instead, ideation and cognition may act as independent risk factors for suicidal behavior,” they added.
“Patients in the fluctuating ideator group generally had moderate or high levels of worst suicidal ideation between visits, but not when asked about current ideation levels at the time of the follow-up assessment,” Dr. Galfalvy noted. “For them, the time frame of the question made a difference as to the level of ideation reported.”
The study “identified several clinical differences among these subgroups which could lead to more personalized suicide prevention efforts and further research into the heterogeneity of suicidal behavior,” she suggested.
New insight
Commenting on the study, Ari Cuperfain, MD, of the University of Toronto said the study “adds to the nuanced understanding of how changes in suicidal ideation over time can lead to suicidal actions and behavior.”
The study “sheds light on the notion of how older adults who die by suicide can demonstrate a greater degree of premeditated intent relative to younger cohorts, with chronic severe ideators portending the highest risk for suicide in this sample,” added Dr. Cuperfain, who was not involved with the current research.
“Overall, the paper highlights the importance of both screening for current levels of suicidal ideation in addition to the evolution of suicidal ideation in developing a risk assessment and in finding interventions to reduce this risk when it is most prominent,” he stated.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors and Dr. Cuperfain disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Childhood trauma tied to increased Parkinson’s disease severity
new research shows.
Results of the first study to evaluate the relationship between childhood trauma and PD investigators found that the relationship appears to be dose dependent. Patients with PD who reported more than one ACE all experienced a statistically significant decrease in QOL, and for each additional ACE, there was significant worsening of motor symptoms.
This study supports a recent-call to-action paper in JAMA Neurology encouraging adoption of “trauma-informed neurology,” study investigator Indu Subramanian, MD, clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We need to start asking about ACEs in everyone. It should be part of our medical intake,” said Dr. Subramanian, who is also the director of the Southwest Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center, West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
The study was published online in Neurology: Clinical Practice.
Hard on the mind and body
A robust body of literature has clearly established a connection between ACEs, which include physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction, and negative physical health outcomes across the lifespan. These include stroke, dementia, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, hypertension, and premature death as well as psychosocial health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, substance use, and suicide.
However, until now, the effects of childhood trauma have not been evaluated in a PD population.
As part of the MVP study, 712 adults with PD responded to an online survey asking about childhood trauma.
As anticipated, patients with the least reported childhood trauma reported the highest current QOL and lowest patient-reported motor and nonmotor symptom burden compared with peers with higher reported childhood trauma, the researchers reported.
PD symptom burden increased and QOL decreased as the number of ACEs increased.
Patients with ACE scores of 4 or higher reported greater PD symptom severity for 45% of the variables assessed, including apathy, muscle pain, daytime sleepiness, restless leg syndrome, depression, fatigue, comprehension, and anxiety (P < .05), compared with peers with trauma scores of 0.
Limitations of the study included the cross-sectional nature, which prevents making any causal determinations. Also, the ACE questionnaire, because it is self-reported and a retrospective collection of data, introduces the risk for recall bias. In addition, 65% of respondents were women, and racial and ethnic minority groups were not well represented.
Looking ahead, Dr. Subramanian and coauthors believe future research should “attempt to include more diverse populations, attempt improve the response rate of these sensitive questions and, most importantly, determine whether the adverse outcomes associated with childhood trauma can be mitigated with lifestyle modification, psychosocial support, and intervention in adulthood.”
“As a trauma-informed approach, something sorely lacking yet needed in the field of movement disorders, clinicians can proactively screen for ACEs while being mindful to avoid retraumatization,” they suggested. “They can begin to identify how ACEs may physiologically contribute to PD symptom and focus on targeting appropriate interventions that may improve outcomes.”
Life experiences matter
In a comment, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor, Parkinson’s Foundation, and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said that “the idea that childhood trauma could be associated with a mild increase in severity of Parkinson’s symptoms such as apathy, pain, sleepiness and depression is fascinating.”
“We should however temper our enthusiasm for the results of this study because they were obtained through a direct patient survey, and not collected from large well characterized medical database,” Dr. Okun said.
He added” “If the data on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s can be replicated, we must ask why this could be?
“For Parkinson clinicians this as a reminder of how important obtaining a complete life history can be when strategizing on a plan to reduce motor and nonmotor Parkinson symptoms. Life experiences matter and can impact symptoms,” Dr. Okun said.
The MVP study was initiated with support of the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. The ongoing data collection has been supported by a donation from Sondra and Bill Fondren. Dr. Subramanian and Dr. Okun disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Results of the first study to evaluate the relationship between childhood trauma and PD investigators found that the relationship appears to be dose dependent. Patients with PD who reported more than one ACE all experienced a statistically significant decrease in QOL, and for each additional ACE, there was significant worsening of motor symptoms.
This study supports a recent-call to-action paper in JAMA Neurology encouraging adoption of “trauma-informed neurology,” study investigator Indu Subramanian, MD, clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We need to start asking about ACEs in everyone. It should be part of our medical intake,” said Dr. Subramanian, who is also the director of the Southwest Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center, West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
The study was published online in Neurology: Clinical Practice.
Hard on the mind and body
A robust body of literature has clearly established a connection between ACEs, which include physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction, and negative physical health outcomes across the lifespan. These include stroke, dementia, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, hypertension, and premature death as well as psychosocial health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, substance use, and suicide.
However, until now, the effects of childhood trauma have not been evaluated in a PD population.
As part of the MVP study, 712 adults with PD responded to an online survey asking about childhood trauma.
As anticipated, patients with the least reported childhood trauma reported the highest current QOL and lowest patient-reported motor and nonmotor symptom burden compared with peers with higher reported childhood trauma, the researchers reported.
PD symptom burden increased and QOL decreased as the number of ACEs increased.
Patients with ACE scores of 4 or higher reported greater PD symptom severity for 45% of the variables assessed, including apathy, muscle pain, daytime sleepiness, restless leg syndrome, depression, fatigue, comprehension, and anxiety (P < .05), compared with peers with trauma scores of 0.
Limitations of the study included the cross-sectional nature, which prevents making any causal determinations. Also, the ACE questionnaire, because it is self-reported and a retrospective collection of data, introduces the risk for recall bias. In addition, 65% of respondents were women, and racial and ethnic minority groups were not well represented.
Looking ahead, Dr. Subramanian and coauthors believe future research should “attempt to include more diverse populations, attempt improve the response rate of these sensitive questions and, most importantly, determine whether the adverse outcomes associated with childhood trauma can be mitigated with lifestyle modification, psychosocial support, and intervention in adulthood.”
“As a trauma-informed approach, something sorely lacking yet needed in the field of movement disorders, clinicians can proactively screen for ACEs while being mindful to avoid retraumatization,” they suggested. “They can begin to identify how ACEs may physiologically contribute to PD symptom and focus on targeting appropriate interventions that may improve outcomes.”
Life experiences matter
In a comment, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor, Parkinson’s Foundation, and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said that “the idea that childhood trauma could be associated with a mild increase in severity of Parkinson’s symptoms such as apathy, pain, sleepiness and depression is fascinating.”
“We should however temper our enthusiasm for the results of this study because they were obtained through a direct patient survey, and not collected from large well characterized medical database,” Dr. Okun said.
He added” “If the data on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s can be replicated, we must ask why this could be?
“For Parkinson clinicians this as a reminder of how important obtaining a complete life history can be when strategizing on a plan to reduce motor and nonmotor Parkinson symptoms. Life experiences matter and can impact symptoms,” Dr. Okun said.
The MVP study was initiated with support of the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. The ongoing data collection has been supported by a donation from Sondra and Bill Fondren. Dr. Subramanian and Dr. Okun disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Results of the first study to evaluate the relationship between childhood trauma and PD investigators found that the relationship appears to be dose dependent. Patients with PD who reported more than one ACE all experienced a statistically significant decrease in QOL, and for each additional ACE, there was significant worsening of motor symptoms.
This study supports a recent-call to-action paper in JAMA Neurology encouraging adoption of “trauma-informed neurology,” study investigator Indu Subramanian, MD, clinical professor, department of neurology, University of California, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We need to start asking about ACEs in everyone. It should be part of our medical intake,” said Dr. Subramanian, who is also the director of the Southwest Parkinson’s Disease Research, Education, and Clinical Center, West Los Angeles Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
The study was published online in Neurology: Clinical Practice.
Hard on the mind and body
A robust body of literature has clearly established a connection between ACEs, which include physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction, and negative physical health outcomes across the lifespan. These include stroke, dementia, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, hypertension, and premature death as well as psychosocial health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, substance use, and suicide.
However, until now, the effects of childhood trauma have not been evaluated in a PD population.
As part of the MVP study, 712 adults with PD responded to an online survey asking about childhood trauma.
As anticipated, patients with the least reported childhood trauma reported the highest current QOL and lowest patient-reported motor and nonmotor symptom burden compared with peers with higher reported childhood trauma, the researchers reported.
PD symptom burden increased and QOL decreased as the number of ACEs increased.
Patients with ACE scores of 4 or higher reported greater PD symptom severity for 45% of the variables assessed, including apathy, muscle pain, daytime sleepiness, restless leg syndrome, depression, fatigue, comprehension, and anxiety (P < .05), compared with peers with trauma scores of 0.
Limitations of the study included the cross-sectional nature, which prevents making any causal determinations. Also, the ACE questionnaire, because it is self-reported and a retrospective collection of data, introduces the risk for recall bias. In addition, 65% of respondents were women, and racial and ethnic minority groups were not well represented.
Looking ahead, Dr. Subramanian and coauthors believe future research should “attempt to include more diverse populations, attempt improve the response rate of these sensitive questions and, most importantly, determine whether the adverse outcomes associated with childhood trauma can be mitigated with lifestyle modification, psychosocial support, and intervention in adulthood.”
“As a trauma-informed approach, something sorely lacking yet needed in the field of movement disorders, clinicians can proactively screen for ACEs while being mindful to avoid retraumatization,” they suggested. “They can begin to identify how ACEs may physiologically contribute to PD symptom and focus on targeting appropriate interventions that may improve outcomes.”
Life experiences matter
In a comment, Michael S. Okun, MD, medical advisor, Parkinson’s Foundation, and director of the Norman Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases, University of Florida Health, Gainesville, said that “the idea that childhood trauma could be associated with a mild increase in severity of Parkinson’s symptoms such as apathy, pain, sleepiness and depression is fascinating.”
“We should however temper our enthusiasm for the results of this study because they were obtained through a direct patient survey, and not collected from large well characterized medical database,” Dr. Okun said.
He added” “If the data on childhood trauma and Parkinson’s can be replicated, we must ask why this could be?
“For Parkinson clinicians this as a reminder of how important obtaining a complete life history can be when strategizing on a plan to reduce motor and nonmotor Parkinson symptoms. Life experiences matter and can impact symptoms,” Dr. Okun said.
The MVP study was initiated with support of the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. The ongoing data collection has been supported by a donation from Sondra and Bill Fondren. Dr. Subramanian and Dr. Okun disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY: CLINICAL PRACTICE
Any level of physical activity tied to better later-life memory
new research suggests.
A prospective study of 1,400 participants showed that those who exercised to any extent in adulthood had significantly better cognitive scores later in life, compared with their peers who were physically inactive.
Maintaining an exercise routine throughout adulthood showed the strongest link to subsequent mental acuity.
Although these associations lessened when investigators controlled for childhood cognitive ability, socioeconomic background, and education, they remained statistically significant.
“Our findings support recommendations for greater participation in physical activity across adulthood,” lead investigator Sarah-Naomi James, PhD, research fellow at the Medical Research Council Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing at the University College London, told this news organization.
“We provide evidence to encourage inactive adults to be active even to a small extent … at any point during adulthood,” which can improve cognition and memory later in life, Dr. James said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Exercise timing
Previous studies have established a link between fitness training and cognitive benefit later in life, but the researchers wanted to explore whether the timing or type of exercise influenced cognitive outcomes in later life.
The investigators asked more than 1,400 participants in the 1946 British birth cohort how much they had exercised at ages 36, 43, 60, and 69 years.
The questions changed slightly for each assessment period, but in general, participants were asked whether in the past month they had exercised or participated in such activities as badminton, swimming, fitness exercises, yoga, dancing, football, mountain climbing, jogging, or brisk walks for 30 minutes or more; and if so, how many times they participated per month.
Prior research showed that when the participants were aged 60 years, the most commonly reported activities were walking (71%), swimming (33%), floor exercises (24%), and cycling (15%).
When they turned 69, researchers tested participants’ cognitive performance using the Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination–III, which measures attention and orientation, verbal fluency, memory, language, and visuospatial function. In this study sample, 53% were women, and all were White.
Physical activity levels were classified as inactive, moderately active (one to four times per month), and most active (five or more times per month). In addition, they were summed across all five assessments to create a total score ranging from 0 (inactive at all ages) to 5 (active at all ages).
Overall, 11% of participants were physically inactive at all five time points; 17% were active at one time point; 20% were active at two and three time points; 17% were active at four time points; and 15% were active at all five time points.
‘Cradle to grave’ study?
Results showed that being physically active at all study time points was significantly associated with higher cognitive performance, verbal memory, and processing speed when participants were aged 69 (P < .01).
Those who exercised to any extent in adulthood – even just once a month during one of the time periods, fared better cognitively in later life, compared with physically inactive participants. (P < .01).
Study limitations cited include a lack of diversity among participants and a disproportionately high attrition rate among those who were socially disadvantaged.
“Our findings show that being active during every decade from their 30s on was associated with better cognition at around 70. Indeed, those who were active for longer had the highest cognitive function,” Dr. James said.
“However, it is also never too late to start. People in our study who only started being active in their 50s or 60s still had higher cognitive scores at age 70, compared to people of the same age who had never been active,” she added.
Dr. James intends to continue following the study sample to determine whether physical activity is linked to preserved cognitive aging “and buffers the effects of cognitive deterioration in the presence of disease markers that cause dementia, ultimately delaying dementia onset.
“We hope the cohort we study will be the first ‘cradle to grave’ study in the world, where we have followed people for their entire lives,” she said.
Encouraging finding
In a comment, Joel Hughes, PhD, professor of psychology and director of clinical training at Kent (Ohio) State University, said the study contributes to the idea that “accumulation of physical activity over one’s lifetime fits the data better than a ‘sensitive period’ – which suggests that it’s never too late to start exercising.”
Dr. Hughes, who was not involved in the research, noted that “exercise can improve cerebral blood flow and hemodynamic function, as well as greater activation of relevant brain regions such as the frontal lobes.”
While observing that the effects of exercise on cognition are likely complex from a mechanistic point of view, the finding that “exercise preserves or improves cognition later in life is encouraging,” he said.
The study received funding from the UK Medical Research Council and Alzheimer’s Research UK. The investigators and Dr. Hughes report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
A prospective study of 1,400 participants showed that those who exercised to any extent in adulthood had significantly better cognitive scores later in life, compared with their peers who were physically inactive.
Maintaining an exercise routine throughout adulthood showed the strongest link to subsequent mental acuity.
Although these associations lessened when investigators controlled for childhood cognitive ability, socioeconomic background, and education, they remained statistically significant.
“Our findings support recommendations for greater participation in physical activity across adulthood,” lead investigator Sarah-Naomi James, PhD, research fellow at the Medical Research Council Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing at the University College London, told this news organization.
“We provide evidence to encourage inactive adults to be active even to a small extent … at any point during adulthood,” which can improve cognition and memory later in life, Dr. James said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Exercise timing
Previous studies have established a link between fitness training and cognitive benefit later in life, but the researchers wanted to explore whether the timing or type of exercise influenced cognitive outcomes in later life.
The investigators asked more than 1,400 participants in the 1946 British birth cohort how much they had exercised at ages 36, 43, 60, and 69 years.
The questions changed slightly for each assessment period, but in general, participants were asked whether in the past month they had exercised or participated in such activities as badminton, swimming, fitness exercises, yoga, dancing, football, mountain climbing, jogging, or brisk walks for 30 minutes or more; and if so, how many times they participated per month.
Prior research showed that when the participants were aged 60 years, the most commonly reported activities were walking (71%), swimming (33%), floor exercises (24%), and cycling (15%).
When they turned 69, researchers tested participants’ cognitive performance using the Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination–III, which measures attention and orientation, verbal fluency, memory, language, and visuospatial function. In this study sample, 53% were women, and all were White.
Physical activity levels were classified as inactive, moderately active (one to four times per month), and most active (five or more times per month). In addition, they were summed across all five assessments to create a total score ranging from 0 (inactive at all ages) to 5 (active at all ages).
Overall, 11% of participants were physically inactive at all five time points; 17% were active at one time point; 20% were active at two and three time points; 17% were active at four time points; and 15% were active at all five time points.
‘Cradle to grave’ study?
Results showed that being physically active at all study time points was significantly associated with higher cognitive performance, verbal memory, and processing speed when participants were aged 69 (P < .01).
Those who exercised to any extent in adulthood – even just once a month during one of the time periods, fared better cognitively in later life, compared with physically inactive participants. (P < .01).
Study limitations cited include a lack of diversity among participants and a disproportionately high attrition rate among those who were socially disadvantaged.
“Our findings show that being active during every decade from their 30s on was associated with better cognition at around 70. Indeed, those who were active for longer had the highest cognitive function,” Dr. James said.
“However, it is also never too late to start. People in our study who only started being active in their 50s or 60s still had higher cognitive scores at age 70, compared to people of the same age who had never been active,” she added.
Dr. James intends to continue following the study sample to determine whether physical activity is linked to preserved cognitive aging “and buffers the effects of cognitive deterioration in the presence of disease markers that cause dementia, ultimately delaying dementia onset.
“We hope the cohort we study will be the first ‘cradle to grave’ study in the world, where we have followed people for their entire lives,” she said.
Encouraging finding
In a comment, Joel Hughes, PhD, professor of psychology and director of clinical training at Kent (Ohio) State University, said the study contributes to the idea that “accumulation of physical activity over one’s lifetime fits the data better than a ‘sensitive period’ – which suggests that it’s never too late to start exercising.”
Dr. Hughes, who was not involved in the research, noted that “exercise can improve cerebral blood flow and hemodynamic function, as well as greater activation of relevant brain regions such as the frontal lobes.”
While observing that the effects of exercise on cognition are likely complex from a mechanistic point of view, the finding that “exercise preserves or improves cognition later in life is encouraging,” he said.
The study received funding from the UK Medical Research Council and Alzheimer’s Research UK. The investigators and Dr. Hughes report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
A prospective study of 1,400 participants showed that those who exercised to any extent in adulthood had significantly better cognitive scores later in life, compared with their peers who were physically inactive.
Maintaining an exercise routine throughout adulthood showed the strongest link to subsequent mental acuity.
Although these associations lessened when investigators controlled for childhood cognitive ability, socioeconomic background, and education, they remained statistically significant.
“Our findings support recommendations for greater participation in physical activity across adulthood,” lead investigator Sarah-Naomi James, PhD, research fellow at the Medical Research Council Unit for Lifelong Health and Ageing at the University College London, told this news organization.
“We provide evidence to encourage inactive adults to be active even to a small extent … at any point during adulthood,” which can improve cognition and memory later in life, Dr. James said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Exercise timing
Previous studies have established a link between fitness training and cognitive benefit later in life, but the researchers wanted to explore whether the timing or type of exercise influenced cognitive outcomes in later life.
The investigators asked more than 1,400 participants in the 1946 British birth cohort how much they had exercised at ages 36, 43, 60, and 69 years.
The questions changed slightly for each assessment period, but in general, participants were asked whether in the past month they had exercised or participated in such activities as badminton, swimming, fitness exercises, yoga, dancing, football, mountain climbing, jogging, or brisk walks for 30 minutes or more; and if so, how many times they participated per month.
Prior research showed that when the participants were aged 60 years, the most commonly reported activities were walking (71%), swimming (33%), floor exercises (24%), and cycling (15%).
When they turned 69, researchers tested participants’ cognitive performance using the Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination–III, which measures attention and orientation, verbal fluency, memory, language, and visuospatial function. In this study sample, 53% were women, and all were White.
Physical activity levels were classified as inactive, moderately active (one to four times per month), and most active (five or more times per month). In addition, they were summed across all five assessments to create a total score ranging from 0 (inactive at all ages) to 5 (active at all ages).
Overall, 11% of participants were physically inactive at all five time points; 17% were active at one time point; 20% were active at two and three time points; 17% were active at four time points; and 15% were active at all five time points.
‘Cradle to grave’ study?
Results showed that being physically active at all study time points was significantly associated with higher cognitive performance, verbal memory, and processing speed when participants were aged 69 (P < .01).
Those who exercised to any extent in adulthood – even just once a month during one of the time periods, fared better cognitively in later life, compared with physically inactive participants. (P < .01).
Study limitations cited include a lack of diversity among participants and a disproportionately high attrition rate among those who were socially disadvantaged.
“Our findings show that being active during every decade from their 30s on was associated with better cognition at around 70. Indeed, those who were active for longer had the highest cognitive function,” Dr. James said.
“However, it is also never too late to start. People in our study who only started being active in their 50s or 60s still had higher cognitive scores at age 70, compared to people of the same age who had never been active,” she added.
Dr. James intends to continue following the study sample to determine whether physical activity is linked to preserved cognitive aging “and buffers the effects of cognitive deterioration in the presence of disease markers that cause dementia, ultimately delaying dementia onset.
“We hope the cohort we study will be the first ‘cradle to grave’ study in the world, where we have followed people for their entire lives,” she said.
Encouraging finding
In a comment, Joel Hughes, PhD, professor of psychology and director of clinical training at Kent (Ohio) State University, said the study contributes to the idea that “accumulation of physical activity over one’s lifetime fits the data better than a ‘sensitive period’ – which suggests that it’s never too late to start exercising.”
Dr. Hughes, who was not involved in the research, noted that “exercise can improve cerebral blood flow and hemodynamic function, as well as greater activation of relevant brain regions such as the frontal lobes.”
While observing that the effects of exercise on cognition are likely complex from a mechanistic point of view, the finding that “exercise preserves or improves cognition later in life is encouraging,” he said.
The study received funding from the UK Medical Research Council and Alzheimer’s Research UK. The investigators and Dr. Hughes report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY, NEUROSURGERY & PSYCHIATRY
500 more steps a day tied to 14% lower CVD risk in older adults
Older adults who added a quarter mile of steps to their day showed a reduction in risk of cardiovascular events by 14% within 4 years, according to a study in more than 400 individuals.
“Aging is such a dynamic process, but most studies of daily steps and step goals are conducted on younger populations,” lead author Erin E. Dooley, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The impact of more modest step goals in older adults has not been well studied, Dr. Dooley said.
The population in the current study ranged from 71 to 92 years, with an average age of 78 years. The older age and relatively short follow-up period show the importance of steps and physical activity in older adults, she said.
Dr. Dooley presented the study at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting.
She and her colleagues analyzed a subsample of participants in Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, an ongoing study conducted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The study population included 452 adults for whom step data were available at visit 6 of the ARIC study between 2016 and 2017. Participants wore an accelerometer on the waist for at least 10 hours a day for at least 3 days. The mean age of the participants was 78.4 years, 59% were women, and 20% were Black.
Outcomes were measured through December 2019 and included fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) events of coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
Overall, each additional 500 steps per day was linked to a 14% reduction in risk of a CVD event (hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98). The mean step count was 3,447 steps per day, and 34 participants (7.5%) experienced a CVD event over 1,269 person-years of follow-up.
The cumulative risk of CVD was significantly higher (11.5%) in the quartile of adults with the lowest step count (defined as fewer than 2,077 steps per day), compared with 3.5% in those with the highest step count (defined as at least 4,453 steps per day).
In addition, adults in the highest quartile of steps had a 77% reduced risk of a proximal CVD (within 3.5 years) event over the study period (HR, 0.23).
Additional research is needed to explore whether increased steps prevent or delay CVD and whether low step counts may be a biomarker for underlying disease, the researchers noted in their abstract.
However, the results support the value of even a modest increase in activity to reduce CVD risk in older adults.
Small steps may get patients started
Dr. Dooley said she was surprised at the degree of benefits on heart health from 500 steps, and noted that the findings have clinical implications.
“Steps may be a more understandable metric for physical activity for patients than talking about moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity,” she said in an interview. “While we do not want to diminish the importance of higher intensity physical activity, encouraging small increases in the number of daily steps can also have great benefits for heart health.
“Steps are counted using a variety of devices and phones, so it may be helpful for patients to show clinicians their activity during well visits,” Dr. Dooley said. “Walking may also be more manageable for people as it is low impact. Achievable goals are also important. This study suggests that, for older adults, around 3,000 steps or more was associated with reduced CVD risk,” although the greatest benefits were seen with the most active group who averaged 4,500 or more steps per day.
More research is needed to show how steps may change over time, and how this relates to CVD and heart health,” she said. “At this time, we only had a single measure of physical activity.”
Study fills research gap for older adults
“Currently, the majority of the literature exploring a relationship between physical activity and the risk for developing cardiovascular disease has evaluated all adults together, not only those who are 70 year of age and older,” Monica C. Serra, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, said in an interview. “This study allows us to start to target specific cardiovascular recommendations for older adults.”.
“It is always exciting to see results from physical activity studies that continue to support prior evidence that even small amounts of physical activity are beneficial to cardiovascular health,” said Dr. Serra, who is also vice chair of the program committee for the meeting. “These results suggest that even if only small additions in physical activity are achievable, they may have cumulative benefits in reducing cardiovascular disease risk.” For clinicians, the results also provide targets that are easy for patients to understand, said Dr. Serra. Daily step counts allow clinicians to provide specific and measurable goals to help their older patients increase physical activity.
“Small additions in total daily step counts may have clinically meaningful benefits to heart health, so promoting their patients to make any slight changes that are able to be consistently incorporated into their schedule should be encouraged. This may be best monitored by encouraging the use of an activity tracker,” she said.
Although the current study adds to the literature with objective measures of physical activity utilizing accelerometers, these devices are not as sensitive at picking up activities such as bicycling or swimming, which may be more appropriate for some older adults with mobility limitations and chronic conditions, Dr. Serra said. Additional research is needed to assess the impact of other activities on CVD in the older population.
The meeting was sponsored by the American Heart Association. The study received no outside funding. Dr. Dooley and Dr. Serra had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Older adults who added a quarter mile of steps to their day showed a reduction in risk of cardiovascular events by 14% within 4 years, according to a study in more than 400 individuals.
“Aging is such a dynamic process, but most studies of daily steps and step goals are conducted on younger populations,” lead author Erin E. Dooley, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The impact of more modest step goals in older adults has not been well studied, Dr. Dooley said.
The population in the current study ranged from 71 to 92 years, with an average age of 78 years. The older age and relatively short follow-up period show the importance of steps and physical activity in older adults, she said.
Dr. Dooley presented the study at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting.
She and her colleagues analyzed a subsample of participants in Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, an ongoing study conducted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The study population included 452 adults for whom step data were available at visit 6 of the ARIC study between 2016 and 2017. Participants wore an accelerometer on the waist for at least 10 hours a day for at least 3 days. The mean age of the participants was 78.4 years, 59% were women, and 20% were Black.
Outcomes were measured through December 2019 and included fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) events of coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
Overall, each additional 500 steps per day was linked to a 14% reduction in risk of a CVD event (hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98). The mean step count was 3,447 steps per day, and 34 participants (7.5%) experienced a CVD event over 1,269 person-years of follow-up.
The cumulative risk of CVD was significantly higher (11.5%) in the quartile of adults with the lowest step count (defined as fewer than 2,077 steps per day), compared with 3.5% in those with the highest step count (defined as at least 4,453 steps per day).
In addition, adults in the highest quartile of steps had a 77% reduced risk of a proximal CVD (within 3.5 years) event over the study period (HR, 0.23).
Additional research is needed to explore whether increased steps prevent or delay CVD and whether low step counts may be a biomarker for underlying disease, the researchers noted in their abstract.
However, the results support the value of even a modest increase in activity to reduce CVD risk in older adults.
Small steps may get patients started
Dr. Dooley said she was surprised at the degree of benefits on heart health from 500 steps, and noted that the findings have clinical implications.
“Steps may be a more understandable metric for physical activity for patients than talking about moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity,” she said in an interview. “While we do not want to diminish the importance of higher intensity physical activity, encouraging small increases in the number of daily steps can also have great benefits for heart health.
“Steps are counted using a variety of devices and phones, so it may be helpful for patients to show clinicians their activity during well visits,” Dr. Dooley said. “Walking may also be more manageable for people as it is low impact. Achievable goals are also important. This study suggests that, for older adults, around 3,000 steps or more was associated with reduced CVD risk,” although the greatest benefits were seen with the most active group who averaged 4,500 or more steps per day.
More research is needed to show how steps may change over time, and how this relates to CVD and heart health,” she said. “At this time, we only had a single measure of physical activity.”
Study fills research gap for older adults
“Currently, the majority of the literature exploring a relationship between physical activity and the risk for developing cardiovascular disease has evaluated all adults together, not only those who are 70 year of age and older,” Monica C. Serra, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, said in an interview. “This study allows us to start to target specific cardiovascular recommendations for older adults.”.
“It is always exciting to see results from physical activity studies that continue to support prior evidence that even small amounts of physical activity are beneficial to cardiovascular health,” said Dr. Serra, who is also vice chair of the program committee for the meeting. “These results suggest that even if only small additions in physical activity are achievable, they may have cumulative benefits in reducing cardiovascular disease risk.” For clinicians, the results also provide targets that are easy for patients to understand, said Dr. Serra. Daily step counts allow clinicians to provide specific and measurable goals to help their older patients increase physical activity.
“Small additions in total daily step counts may have clinically meaningful benefits to heart health, so promoting their patients to make any slight changes that are able to be consistently incorporated into their schedule should be encouraged. This may be best monitored by encouraging the use of an activity tracker,” she said.
Although the current study adds to the literature with objective measures of physical activity utilizing accelerometers, these devices are not as sensitive at picking up activities such as bicycling or swimming, which may be more appropriate for some older adults with mobility limitations and chronic conditions, Dr. Serra said. Additional research is needed to assess the impact of other activities on CVD in the older population.
The meeting was sponsored by the American Heart Association. The study received no outside funding. Dr. Dooley and Dr. Serra had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Older adults who added a quarter mile of steps to their day showed a reduction in risk of cardiovascular events by 14% within 4 years, according to a study in more than 400 individuals.
“Aging is such a dynamic process, but most studies of daily steps and step goals are conducted on younger populations,” lead author Erin E. Dooley, PhD, an epidemiologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
The impact of more modest step goals in older adults has not been well studied, Dr. Dooley said.
The population in the current study ranged from 71 to 92 years, with an average age of 78 years. The older age and relatively short follow-up period show the importance of steps and physical activity in older adults, she said.
Dr. Dooley presented the study at the Epidemiology and Prevention/Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health meeting.
She and her colleagues analyzed a subsample of participants in Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, an ongoing study conducted by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The study population included 452 adults for whom step data were available at visit 6 of the ARIC study between 2016 and 2017. Participants wore an accelerometer on the waist for at least 10 hours a day for at least 3 days. The mean age of the participants was 78.4 years, 59% were women, and 20% were Black.
Outcomes were measured through December 2019 and included fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) events of coronary heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
Overall, each additional 500 steps per day was linked to a 14% reduction in risk of a CVD event (hazard ratio, 0.86; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.98). The mean step count was 3,447 steps per day, and 34 participants (7.5%) experienced a CVD event over 1,269 person-years of follow-up.
The cumulative risk of CVD was significantly higher (11.5%) in the quartile of adults with the lowest step count (defined as fewer than 2,077 steps per day), compared with 3.5% in those with the highest step count (defined as at least 4,453 steps per day).
In addition, adults in the highest quartile of steps had a 77% reduced risk of a proximal CVD (within 3.5 years) event over the study period (HR, 0.23).
Additional research is needed to explore whether increased steps prevent or delay CVD and whether low step counts may be a biomarker for underlying disease, the researchers noted in their abstract.
However, the results support the value of even a modest increase in activity to reduce CVD risk in older adults.
Small steps may get patients started
Dr. Dooley said she was surprised at the degree of benefits on heart health from 500 steps, and noted that the findings have clinical implications.
“Steps may be a more understandable metric for physical activity for patients than talking about moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity,” she said in an interview. “While we do not want to diminish the importance of higher intensity physical activity, encouraging small increases in the number of daily steps can also have great benefits for heart health.
“Steps are counted using a variety of devices and phones, so it may be helpful for patients to show clinicians their activity during well visits,” Dr. Dooley said. “Walking may also be more manageable for people as it is low impact. Achievable goals are also important. This study suggests that, for older adults, around 3,000 steps or more was associated with reduced CVD risk,” although the greatest benefits were seen with the most active group who averaged 4,500 or more steps per day.
More research is needed to show how steps may change over time, and how this relates to CVD and heart health,” she said. “At this time, we only had a single measure of physical activity.”
Study fills research gap for older adults
“Currently, the majority of the literature exploring a relationship between physical activity and the risk for developing cardiovascular disease has evaluated all adults together, not only those who are 70 year of age and older,” Monica C. Serra, PhD, of the University of Texas, San Antonio, said in an interview. “This study allows us to start to target specific cardiovascular recommendations for older adults.”.
“It is always exciting to see results from physical activity studies that continue to support prior evidence that even small amounts of physical activity are beneficial to cardiovascular health,” said Dr. Serra, who is also vice chair of the program committee for the meeting. “These results suggest that even if only small additions in physical activity are achievable, they may have cumulative benefits in reducing cardiovascular disease risk.” For clinicians, the results also provide targets that are easy for patients to understand, said Dr. Serra. Daily step counts allow clinicians to provide specific and measurable goals to help their older patients increase physical activity.
“Small additions in total daily step counts may have clinically meaningful benefits to heart health, so promoting their patients to make any slight changes that are able to be consistently incorporated into their schedule should be encouraged. This may be best monitored by encouraging the use of an activity tracker,” she said.
Although the current study adds to the literature with objective measures of physical activity utilizing accelerometers, these devices are not as sensitive at picking up activities such as bicycling or swimming, which may be more appropriate for some older adults with mobility limitations and chronic conditions, Dr. Serra said. Additional research is needed to assess the impact of other activities on CVD in the older population.
The meeting was sponsored by the American Heart Association. The study received no outside funding. Dr. Dooley and Dr. Serra had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM EPI/LIFESTYLE 2023
U.S. vs. French guidelines for osteoporosis treatment
Lille, France – Bernard Cortet, MD, PhD, chairperson of the Osteoporosis Research and Information Group and head of the rheumatology department at Lille (France) University Hospital, has agreed to compare the new U.S. guidelines to the 2018 French recommendations written under the aegis of the French Society for Rheumatology and GRIO. Dr. Cortet participated in drafting the French recommendations.
Question: The ACP “strongly” recommends initial pharmacologic treatment with bisphosphonate antiresorptive drugs (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, zoledronate) in postmenopausal females diagnosed with primary osteoporosis. Isn’t this what the SFR–GRIO have been recommending for many years?
Answer: The ACP reinforces its stance by arguing that in postmenopausal females with primary osteoporosis, bisphosphonates have the most favorable balance between benefits, harms, patient values and preferences, and cost among the drug classes that were evaluated. In addition to net clinical benefits, bisphosphonates are much cheaper than other pharmacologic treatments and are available in generic oral and injectable formulations.
Our French recommendations specify the choice of drug based on the type of fracture in women and on their bone mineral density (BMD). However, bisphosphonates are definitely given pride of place. When treatment for osteoporosis needs to be started, most of the time, a bisphosphonate is the treatment of choice.
Nevertheless, as also highlighted by the ACP, a more “aggressive” approach must be considered for more severe cases.
In the case of a severe fracture, the French recommendations indicate that all treatments can be prescribed. However, zoledronic acid should be favored as first-line treatment for a hip fracture. In other cases – with or without a nonsevere fracture – the therapeutic indication depends on the BMD values, and in difficult cases, on tools such as FRAX [the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool].
Our guidance strongly recommends opting for an injection in other contexts, such as significant decrease in bone density, presence of comorbidities, poor treatment compliance, brain function disorders, and polymedication.
Q. But it’s not really as simple as prescribing a bisphosphonate, is it?
A. You’re right, many people find the idea of taking bisphosphonates worrying because of associated jaw problems – osteonecrosis of the jaw – or atypical femoral fractures, based on what they’ve read on the Internet, where these serious adverse events are on display front and center with no mention of how often they actually happen and, often, failing to mention how effective bisphosphonates truly are.
These complications are real, but fortunately rare, especially during the first 5 years of treatment. To put this into context, for bisphosphonates, there’s one case of osteonecrosis of the jaw for every 10,000. And for denosumab, there are five cases for every 10,000. For atypical fractures, there’s one case for every 30,000 to 50,000.
Q. The U.S. guidelines also recommend that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab, also an antiresorptive drug – as second-line medical treatment. This is to reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women diagnosed with primary osteoporosis and presenting with contraindications or side effects of bisphosphonates. Do you support the use of denosumab as second-line treatment?
A. French legislation classifies it as a second-line treatment, after bisphosphonates. However, there are arguments in favor of prescribing it as first-line treatment in some contexts. If denosumab is to be prescribed – via a twice-yearly subcutaneous injection – full compliance must be observed. If a patient is to stop taking denosumab, an opinion from a medical professional is required before treatment can be discontinued, and then treatment with bisphosphonates must be prescribed.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use either a sclerostin inhibitor – romosozumab – or recombinant human parathyroid hormone – teriparatide – two anabolic agents, followed by a bisphosphonate, with the aim of reducing the risk of fractures. This is only used in women with primary osteoporosis who are at a very high risk of fracture. As romosozumab is not available in France, it’s not really worth discussing its use. Does this strategy seem advisable to you, though?
A. The main issue is what is understood by “women at a very high risk of fracture.” There’s no consensus on the definition of what constitutes a woman at a very high risk of fracture, but we can assume that it involves the combination of low BMD and at least one severe fracture.
The role of anabolic bone treatment, as [the ACP] has defined it, seems logical to me, because in cases of severe osteoporosis with fracture, the risk of recurrence is very high in the next 2-3 years. In a study comparing risedronate and teriparatide in cases of severe osteoporosis, teriparatide was more effective in reducing the recurrence of vertebral fractures.
The favorable opinion of the French National Authority for Health in relation to medical coverage for romosozumab in the treatment of severe postmenopausal osteoporosis in women under the age of 75 years with a history of severe fractures, a T-score less than –2.5, and no previous history of coronary artery disease dates to 2021. This is because medical coverage for this specific group was not listed in the marketing authorization (MA) description for this drug.
But the review by the Economic Committee for Health Products failed to reach a consensus regarding the price. Today, in theory, romosozumab can be dispensed in France by hospital pharmacies, because it is approved for use in public hospitals. Romosozumab is a very interesting drug for relatively young women, especially those with multiple vertebral fractures. This injectable treatment is more effective than teriparatide in increasing BMD values and more effective than alendronate in preventing the recurrence of fractures.
Regarding medical coverage, as it stands, in cases where patients have a T-score less than or equal to –3, the 2018 SFR–GRIO recommends starting treatment even if the patient has no fractures. In cases with severe fractures combined with very low BMD (T-score ≤ –3), injectable treatments may be used to reach a bone density target (T-score > –2.5 to –2 for the hip) at the end of the treatment plan. [These treatments include] zoledronic acid, denosumab (in case of bisphosphonate failure or intolerance), or a treatment plan with teriparatide (covered by medical insurance if the patient has at least two vertebral fractures) followed by an antiresorptive drug (bisphosphonate or denosumab).
Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG2) that binds to sclerostin and acts as an inhibitor. This increases bone formation because of the activation of [bone lining cells], the production of bone matrix by osteoblasts, and the recruitment of osteochondroprogenitor cells. Moreover, romosozumab causes changes in the expression of osteoclast mediators, which decreases bone resorption. Together, these two effects that increase bone formation and decrease bone resorption lead to the rapid increase of trabecular and cortical bone mass, as well as improvements in bone structure and strength.
Women treated with a bone anabolic agent must take an antiresorptive agent at the end of their treatment so that the benefits from the treatment remain in the long term. The French and U.S. guidelines line up on this point.
In patients with two prevalent vertebral fractures, the U.S. guidelines state that teriparatide can be prescribed as first-line treatment at diagnosis in the absence of any contraindications. We agree on this point as well.
Moreover, in women under the age of 70 years with osteoporosis requiring treatment, French experts recommend prescribing raloxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator. This is if the risk of nonvertebral fracture is low, as defined by the absence of the following criteria: low hip T-score, risk of falling, and history of nonvertebral fracture. Opportunities for its use are limited, and it doesn’t even figure among the U.S. recommendations.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians adopt an individualized approach regarding whether to start medical treatment with a bisphosphonate in women over age 65 years with low bone mass (osteopenia) to reduce the risk of fractures. If treatment is started, they›re of the opinion that a bisphosphonate must be used. What are the recommendations in France?
A. It should be noted that this recommendation by the ACP is conditional because of the low-certainty evidence.
Here’s a brief reminder of important things to note: a T-score between –2.5 and –1 indicates osteopenia; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 indicates osteoporosis; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 with one or several fractures indicates severe osteoporosis. The French recommendations state that treatment is not justified if a patient’s T-score is higher than –2 and there’s no presence of fractures, even with risk factors (and/or multiple falls). For T-scores less than or equal to –2 and higher than –3, the decision to prescribe depends on the specialist.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use bisphosphonates for the initial medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis.
A. The ACP recommends that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab – as second-line medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis who present with contraindications or who are experiencing side effects of bisphosphonates. This treatment is not covered by health insurance for men in France.
Between 20% and 25% of clinical osteoporotic fractures occur in men. After age 50 years, men are roughly 20% more likely to experience an osteoporotic fracture in their lifetime. The French recommendations regarding the management and treatment of osteoporosis in men were published in 2021.
In the case of severe fractures (vertebrae, pelvis, upper end of the femur, distal femur, proximal humerus) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –1.
In the case of nonsevere fractures (particularly wrist and ankle) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –2. If there are no fractures, osteoporosis treatment is recommended in men at risk of bone fragility or of falling and if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –3. In patients who had a fracture of the upper end of the femur attributable to bone fragility, zoledronic acid is recommended as first-line treatment.
For men with a severe nonvertebral fracture, single vertebral fracture, or nonsevere fracture, two treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: zoledronic acid and risedronate. In men with at least two vertebral fractures, the following treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: teriparatide and risedronate. In this case, teriparatide is prescribed for a period of 18 months. It must be followed by a prescription of oral or intravenous bisphosphonates.
Q. What is your take on the HAS update to the proper use of osteoporosis medication that’s just been published?
A. Like in the 2018 SFR–GRIO guidelines, no update has been made to the section on postmenopausal osteoporosis, except for the HAS introduction to the proper use of romosozumab, even though it’s not covered by health insurance in France.
In accordance with the MA, it doesn’t make sense to include this drug on the list of treatment options available for women with and without fractures, as it’s not included in the HAS-selected list of drugs covered by health insurance in France.
But I’m glad that the HAS has adopted the GRIO and SFR recommendations regarding corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Preventive treatment for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis must be considered as soon as the daily dose of corticosteroids reaches or exceeds the equivalent of 7.5 mg of prednisone and when the estimated duration of corticosteroid therapy exceeds 3 months.
In summary, in women and men over the age of 50 years, the intake of the equivalent of 7.5 mg/day or more of prednisone or a history of a low-trauma fracture or being age 70 years or older, even with a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 for one of the two sites, indicates prescribing a bisphosphonate. Teriparatide is indicated if the patient has two vertebral fractures.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lille, France – Bernard Cortet, MD, PhD, chairperson of the Osteoporosis Research and Information Group and head of the rheumatology department at Lille (France) University Hospital, has agreed to compare the new U.S. guidelines to the 2018 French recommendations written under the aegis of the French Society for Rheumatology and GRIO. Dr. Cortet participated in drafting the French recommendations.
Question: The ACP “strongly” recommends initial pharmacologic treatment with bisphosphonate antiresorptive drugs (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, zoledronate) in postmenopausal females diagnosed with primary osteoporosis. Isn’t this what the SFR–GRIO have been recommending for many years?
Answer: The ACP reinforces its stance by arguing that in postmenopausal females with primary osteoporosis, bisphosphonates have the most favorable balance between benefits, harms, patient values and preferences, and cost among the drug classes that were evaluated. In addition to net clinical benefits, bisphosphonates are much cheaper than other pharmacologic treatments and are available in generic oral and injectable formulations.
Our French recommendations specify the choice of drug based on the type of fracture in women and on their bone mineral density (BMD). However, bisphosphonates are definitely given pride of place. When treatment for osteoporosis needs to be started, most of the time, a bisphosphonate is the treatment of choice.
Nevertheless, as also highlighted by the ACP, a more “aggressive” approach must be considered for more severe cases.
In the case of a severe fracture, the French recommendations indicate that all treatments can be prescribed. However, zoledronic acid should be favored as first-line treatment for a hip fracture. In other cases – with or without a nonsevere fracture – the therapeutic indication depends on the BMD values, and in difficult cases, on tools such as FRAX [the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool].
Our guidance strongly recommends opting for an injection in other contexts, such as significant decrease in bone density, presence of comorbidities, poor treatment compliance, brain function disorders, and polymedication.
Q. But it’s not really as simple as prescribing a bisphosphonate, is it?
A. You’re right, many people find the idea of taking bisphosphonates worrying because of associated jaw problems – osteonecrosis of the jaw – or atypical femoral fractures, based on what they’ve read on the Internet, where these serious adverse events are on display front and center with no mention of how often they actually happen and, often, failing to mention how effective bisphosphonates truly are.
These complications are real, but fortunately rare, especially during the first 5 years of treatment. To put this into context, for bisphosphonates, there’s one case of osteonecrosis of the jaw for every 10,000. And for denosumab, there are five cases for every 10,000. For atypical fractures, there’s one case for every 30,000 to 50,000.
Q. The U.S. guidelines also recommend that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab, also an antiresorptive drug – as second-line medical treatment. This is to reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women diagnosed with primary osteoporosis and presenting with contraindications or side effects of bisphosphonates. Do you support the use of denosumab as second-line treatment?
A. French legislation classifies it as a second-line treatment, after bisphosphonates. However, there are arguments in favor of prescribing it as first-line treatment in some contexts. If denosumab is to be prescribed – via a twice-yearly subcutaneous injection – full compliance must be observed. If a patient is to stop taking denosumab, an opinion from a medical professional is required before treatment can be discontinued, and then treatment with bisphosphonates must be prescribed.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use either a sclerostin inhibitor – romosozumab – or recombinant human parathyroid hormone – teriparatide – two anabolic agents, followed by a bisphosphonate, with the aim of reducing the risk of fractures. This is only used in women with primary osteoporosis who are at a very high risk of fracture. As romosozumab is not available in France, it’s not really worth discussing its use. Does this strategy seem advisable to you, though?
A. The main issue is what is understood by “women at a very high risk of fracture.” There’s no consensus on the definition of what constitutes a woman at a very high risk of fracture, but we can assume that it involves the combination of low BMD and at least one severe fracture.
The role of anabolic bone treatment, as [the ACP] has defined it, seems logical to me, because in cases of severe osteoporosis with fracture, the risk of recurrence is very high in the next 2-3 years. In a study comparing risedronate and teriparatide in cases of severe osteoporosis, teriparatide was more effective in reducing the recurrence of vertebral fractures.
The favorable opinion of the French National Authority for Health in relation to medical coverage for romosozumab in the treatment of severe postmenopausal osteoporosis in women under the age of 75 years with a history of severe fractures, a T-score less than –2.5, and no previous history of coronary artery disease dates to 2021. This is because medical coverage for this specific group was not listed in the marketing authorization (MA) description for this drug.
But the review by the Economic Committee for Health Products failed to reach a consensus regarding the price. Today, in theory, romosozumab can be dispensed in France by hospital pharmacies, because it is approved for use in public hospitals. Romosozumab is a very interesting drug for relatively young women, especially those with multiple vertebral fractures. This injectable treatment is more effective than teriparatide in increasing BMD values and more effective than alendronate in preventing the recurrence of fractures.
Regarding medical coverage, as it stands, in cases where patients have a T-score less than or equal to –3, the 2018 SFR–GRIO recommends starting treatment even if the patient has no fractures. In cases with severe fractures combined with very low BMD (T-score ≤ –3), injectable treatments may be used to reach a bone density target (T-score > –2.5 to –2 for the hip) at the end of the treatment plan. [These treatments include] zoledronic acid, denosumab (in case of bisphosphonate failure or intolerance), or a treatment plan with teriparatide (covered by medical insurance if the patient has at least two vertebral fractures) followed by an antiresorptive drug (bisphosphonate or denosumab).
Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG2) that binds to sclerostin and acts as an inhibitor. This increases bone formation because of the activation of [bone lining cells], the production of bone matrix by osteoblasts, and the recruitment of osteochondroprogenitor cells. Moreover, romosozumab causes changes in the expression of osteoclast mediators, which decreases bone resorption. Together, these two effects that increase bone formation and decrease bone resorption lead to the rapid increase of trabecular and cortical bone mass, as well as improvements in bone structure and strength.
Women treated with a bone anabolic agent must take an antiresorptive agent at the end of their treatment so that the benefits from the treatment remain in the long term. The French and U.S. guidelines line up on this point.
In patients with two prevalent vertebral fractures, the U.S. guidelines state that teriparatide can be prescribed as first-line treatment at diagnosis in the absence of any contraindications. We agree on this point as well.
Moreover, in women under the age of 70 years with osteoporosis requiring treatment, French experts recommend prescribing raloxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator. This is if the risk of nonvertebral fracture is low, as defined by the absence of the following criteria: low hip T-score, risk of falling, and history of nonvertebral fracture. Opportunities for its use are limited, and it doesn’t even figure among the U.S. recommendations.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians adopt an individualized approach regarding whether to start medical treatment with a bisphosphonate in women over age 65 years with low bone mass (osteopenia) to reduce the risk of fractures. If treatment is started, they›re of the opinion that a bisphosphonate must be used. What are the recommendations in France?
A. It should be noted that this recommendation by the ACP is conditional because of the low-certainty evidence.
Here’s a brief reminder of important things to note: a T-score between –2.5 and –1 indicates osteopenia; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 indicates osteoporosis; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 with one or several fractures indicates severe osteoporosis. The French recommendations state that treatment is not justified if a patient’s T-score is higher than –2 and there’s no presence of fractures, even with risk factors (and/or multiple falls). For T-scores less than or equal to –2 and higher than –3, the decision to prescribe depends on the specialist.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use bisphosphonates for the initial medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis.
A. The ACP recommends that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab – as second-line medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis who present with contraindications or who are experiencing side effects of bisphosphonates. This treatment is not covered by health insurance for men in France.
Between 20% and 25% of clinical osteoporotic fractures occur in men. After age 50 years, men are roughly 20% more likely to experience an osteoporotic fracture in their lifetime. The French recommendations regarding the management and treatment of osteoporosis in men were published in 2021.
In the case of severe fractures (vertebrae, pelvis, upper end of the femur, distal femur, proximal humerus) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –1.
In the case of nonsevere fractures (particularly wrist and ankle) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –2. If there are no fractures, osteoporosis treatment is recommended in men at risk of bone fragility or of falling and if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –3. In patients who had a fracture of the upper end of the femur attributable to bone fragility, zoledronic acid is recommended as first-line treatment.
For men with a severe nonvertebral fracture, single vertebral fracture, or nonsevere fracture, two treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: zoledronic acid and risedronate. In men with at least two vertebral fractures, the following treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: teriparatide and risedronate. In this case, teriparatide is prescribed for a period of 18 months. It must be followed by a prescription of oral or intravenous bisphosphonates.
Q. What is your take on the HAS update to the proper use of osteoporosis medication that’s just been published?
A. Like in the 2018 SFR–GRIO guidelines, no update has been made to the section on postmenopausal osteoporosis, except for the HAS introduction to the proper use of romosozumab, even though it’s not covered by health insurance in France.
In accordance with the MA, it doesn’t make sense to include this drug on the list of treatment options available for women with and without fractures, as it’s not included in the HAS-selected list of drugs covered by health insurance in France.
But I’m glad that the HAS has adopted the GRIO and SFR recommendations regarding corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Preventive treatment for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis must be considered as soon as the daily dose of corticosteroids reaches or exceeds the equivalent of 7.5 mg of prednisone and when the estimated duration of corticosteroid therapy exceeds 3 months.
In summary, in women and men over the age of 50 years, the intake of the equivalent of 7.5 mg/day or more of prednisone or a history of a low-trauma fracture or being age 70 years or older, even with a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 for one of the two sites, indicates prescribing a bisphosphonate. Teriparatide is indicated if the patient has two vertebral fractures.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lille, France – Bernard Cortet, MD, PhD, chairperson of the Osteoporosis Research and Information Group and head of the rheumatology department at Lille (France) University Hospital, has agreed to compare the new U.S. guidelines to the 2018 French recommendations written under the aegis of the French Society for Rheumatology and GRIO. Dr. Cortet participated in drafting the French recommendations.
Question: The ACP “strongly” recommends initial pharmacologic treatment with bisphosphonate antiresorptive drugs (alendronate, ibandronate, risedronate, zoledronate) in postmenopausal females diagnosed with primary osteoporosis. Isn’t this what the SFR–GRIO have been recommending for many years?
Answer: The ACP reinforces its stance by arguing that in postmenopausal females with primary osteoporosis, bisphosphonates have the most favorable balance between benefits, harms, patient values and preferences, and cost among the drug classes that were evaluated. In addition to net clinical benefits, bisphosphonates are much cheaper than other pharmacologic treatments and are available in generic oral and injectable formulations.
Our French recommendations specify the choice of drug based on the type of fracture in women and on their bone mineral density (BMD). However, bisphosphonates are definitely given pride of place. When treatment for osteoporosis needs to be started, most of the time, a bisphosphonate is the treatment of choice.
Nevertheless, as also highlighted by the ACP, a more “aggressive” approach must be considered for more severe cases.
In the case of a severe fracture, the French recommendations indicate that all treatments can be prescribed. However, zoledronic acid should be favored as first-line treatment for a hip fracture. In other cases – with or without a nonsevere fracture – the therapeutic indication depends on the BMD values, and in difficult cases, on tools such as FRAX [the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool].
Our guidance strongly recommends opting for an injection in other contexts, such as significant decrease in bone density, presence of comorbidities, poor treatment compliance, brain function disorders, and polymedication.
Q. But it’s not really as simple as prescribing a bisphosphonate, is it?
A. You’re right, many people find the idea of taking bisphosphonates worrying because of associated jaw problems – osteonecrosis of the jaw – or atypical femoral fractures, based on what they’ve read on the Internet, where these serious adverse events are on display front and center with no mention of how often they actually happen and, often, failing to mention how effective bisphosphonates truly are.
These complications are real, but fortunately rare, especially during the first 5 years of treatment. To put this into context, for bisphosphonates, there’s one case of osteonecrosis of the jaw for every 10,000. And for denosumab, there are five cases for every 10,000. For atypical fractures, there’s one case for every 30,000 to 50,000.
Q. The U.S. guidelines also recommend that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab, also an antiresorptive drug – as second-line medical treatment. This is to reduce the risk of fractures in postmenopausal women diagnosed with primary osteoporosis and presenting with contraindications or side effects of bisphosphonates. Do you support the use of denosumab as second-line treatment?
A. French legislation classifies it as a second-line treatment, after bisphosphonates. However, there are arguments in favor of prescribing it as first-line treatment in some contexts. If denosumab is to be prescribed – via a twice-yearly subcutaneous injection – full compliance must be observed. If a patient is to stop taking denosumab, an opinion from a medical professional is required before treatment can be discontinued, and then treatment with bisphosphonates must be prescribed.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use either a sclerostin inhibitor – romosozumab – or recombinant human parathyroid hormone – teriparatide – two anabolic agents, followed by a bisphosphonate, with the aim of reducing the risk of fractures. This is only used in women with primary osteoporosis who are at a very high risk of fracture. As romosozumab is not available in France, it’s not really worth discussing its use. Does this strategy seem advisable to you, though?
A. The main issue is what is understood by “women at a very high risk of fracture.” There’s no consensus on the definition of what constitutes a woman at a very high risk of fracture, but we can assume that it involves the combination of low BMD and at least one severe fracture.
The role of anabolic bone treatment, as [the ACP] has defined it, seems logical to me, because in cases of severe osteoporosis with fracture, the risk of recurrence is very high in the next 2-3 years. In a study comparing risedronate and teriparatide in cases of severe osteoporosis, teriparatide was more effective in reducing the recurrence of vertebral fractures.
The favorable opinion of the French National Authority for Health in relation to medical coverage for romosozumab in the treatment of severe postmenopausal osteoporosis in women under the age of 75 years with a history of severe fractures, a T-score less than –2.5, and no previous history of coronary artery disease dates to 2021. This is because medical coverage for this specific group was not listed in the marketing authorization (MA) description for this drug.
But the review by the Economic Committee for Health Products failed to reach a consensus regarding the price. Today, in theory, romosozumab can be dispensed in France by hospital pharmacies, because it is approved for use in public hospitals. Romosozumab is a very interesting drug for relatively young women, especially those with multiple vertebral fractures. This injectable treatment is more effective than teriparatide in increasing BMD values and more effective than alendronate in preventing the recurrence of fractures.
Regarding medical coverage, as it stands, in cases where patients have a T-score less than or equal to –3, the 2018 SFR–GRIO recommends starting treatment even if the patient has no fractures. In cases with severe fractures combined with very low BMD (T-score ≤ –3), injectable treatments may be used to reach a bone density target (T-score > –2.5 to –2 for the hip) at the end of the treatment plan. [These treatments include] zoledronic acid, denosumab (in case of bisphosphonate failure or intolerance), or a treatment plan with teriparatide (covered by medical insurance if the patient has at least two vertebral fractures) followed by an antiresorptive drug (bisphosphonate or denosumab).
Romosozumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG2) that binds to sclerostin and acts as an inhibitor. This increases bone formation because of the activation of [bone lining cells], the production of bone matrix by osteoblasts, and the recruitment of osteochondroprogenitor cells. Moreover, romosozumab causes changes in the expression of osteoclast mediators, which decreases bone resorption. Together, these two effects that increase bone formation and decrease bone resorption lead to the rapid increase of trabecular and cortical bone mass, as well as improvements in bone structure and strength.
Women treated with a bone anabolic agent must take an antiresorptive agent at the end of their treatment so that the benefits from the treatment remain in the long term. The French and U.S. guidelines line up on this point.
In patients with two prevalent vertebral fractures, the U.S. guidelines state that teriparatide can be prescribed as first-line treatment at diagnosis in the absence of any contraindications. We agree on this point as well.
Moreover, in women under the age of 70 years with osteoporosis requiring treatment, French experts recommend prescribing raloxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator. This is if the risk of nonvertebral fracture is low, as defined by the absence of the following criteria: low hip T-score, risk of falling, and history of nonvertebral fracture. Opportunities for its use are limited, and it doesn’t even figure among the U.S. recommendations.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians adopt an individualized approach regarding whether to start medical treatment with a bisphosphonate in women over age 65 years with low bone mass (osteopenia) to reduce the risk of fractures. If treatment is started, they›re of the opinion that a bisphosphonate must be used. What are the recommendations in France?
A. It should be noted that this recommendation by the ACP is conditional because of the low-certainty evidence.
Here’s a brief reminder of important things to note: a T-score between –2.5 and –1 indicates osteopenia; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 indicates osteoporosis; a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 with one or several fractures indicates severe osteoporosis. The French recommendations state that treatment is not justified if a patient’s T-score is higher than –2 and there’s no presence of fractures, even with risk factors (and/or multiple falls). For T-scores less than or equal to –2 and higher than –3, the decision to prescribe depends on the specialist.
Q. The ACP recommends that clinicians use bisphosphonates for the initial medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis.
A. The ACP recommends that clinicians use a RANK ligand inhibitor – denosumab – as second-line medical treatment to reduce the risk of fractures in men diagnosed with primary osteoporosis who present with contraindications or who are experiencing side effects of bisphosphonates. This treatment is not covered by health insurance for men in France.
Between 20% and 25% of clinical osteoporotic fractures occur in men. After age 50 years, men are roughly 20% more likely to experience an osteoporotic fracture in their lifetime. The French recommendations regarding the management and treatment of osteoporosis in men were published in 2021.
In the case of severe fractures (vertebrae, pelvis, upper end of the femur, distal femur, proximal humerus) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –1.
In the case of nonsevere fractures (particularly wrist and ankle) attributable to bone fragility, osteoporosis treatment is recommended if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –2. If there are no fractures, osteoporosis treatment is recommended in men at risk of bone fragility or of falling and if one of the T-scores is less than or equal to –3. In patients who had a fracture of the upper end of the femur attributable to bone fragility, zoledronic acid is recommended as first-line treatment.
For men with a severe nonvertebral fracture, single vertebral fracture, or nonsevere fracture, two treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: zoledronic acid and risedronate. In men with at least two vertebral fractures, the following treatments are indicated and covered by health insurance in France: teriparatide and risedronate. In this case, teriparatide is prescribed for a period of 18 months. It must be followed by a prescription of oral or intravenous bisphosphonates.
Q. What is your take on the HAS update to the proper use of osteoporosis medication that’s just been published?
A. Like in the 2018 SFR–GRIO guidelines, no update has been made to the section on postmenopausal osteoporosis, except for the HAS introduction to the proper use of romosozumab, even though it’s not covered by health insurance in France.
In accordance with the MA, it doesn’t make sense to include this drug on the list of treatment options available for women with and without fractures, as it’s not included in the HAS-selected list of drugs covered by health insurance in France.
But I’m glad that the HAS has adopted the GRIO and SFR recommendations regarding corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis. Preventive treatment for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis must be considered as soon as the daily dose of corticosteroids reaches or exceeds the equivalent of 7.5 mg of prednisone and when the estimated duration of corticosteroid therapy exceeds 3 months.
In summary, in women and men over the age of 50 years, the intake of the equivalent of 7.5 mg/day or more of prednisone or a history of a low-trauma fracture or being age 70 years or older, even with a T-score less than or equal to –2.5 for one of the two sites, indicates prescribing a bisphosphonate. Teriparatide is indicated if the patient has two vertebral fractures.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Back pain: Red flags and when to image
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientific advances and dietary measures to slow down aging
These findings are closer than ever to being applied in older adults. Currently, diet is the most accessible form of intervention, but it is appropriate to clarify current myths and realities.
An article published in Cell in 2013 summarized for the first time the molecular indicators of aging in mammals. The article had a great impact and served as a knowledge map about aging. Now the authors have updated and extended this knowledge in the same journal.
A barometer of interest in the topic is that approximately 300,000 articles on aging have been published since 2013, which is as many as were published during the previous century. In addition, almost 80 experiments have been conducted with mammals, including humans, that confirm that interventions in the aging process can prevent, delay, and even avoid age-related diseases such as cancer.
María A. Blasco, MD, scientific director of the National Cancer Research Center, an international leader in telomere research and coauthor of the study, noted on the institution’s website, “The spectacular advances in recent years to increase the longevity of model organisms, including in mammals, indicate that it will be important to develop rational strategies to intervene in human aging.”
Eighty experimental interventions
The new article verifies the conclusions of the analysis carried out a decade ago. “Now there is much more investment, and we are closer to applying basic knowledge to new ways of treating diseases,” said Dr. Blasco. The researchers identified nine indicators of aging – molecular signatures that mark the progress of the process and on which it was possible to act to prolong life.
They also point to four primary causes of aging: genomic instability, shortening of telomeres, epigenetic alterations, and imbalance between protein synthesis and degradation. These are strongly interconnected processes. Aging results from their joint action, which is why there are multiple ways to act on the physiologic process of aging. The new study includes a table with almost 80 recent experimental interventions with mammals (mostly mice) that suggest that it is possible to prolong life or treat age-associated diseases. Some of those studies concern humans; others investigate how to delay aging through diet. “Acting on the diet is one of the most accessible ways to intervene in human aging,” according to the researchers.
Nutrient sensors
Dietary interventions are related to a key indicator of aging: the dysregulation of the nutrient sensing mechanism. This mechanism is the sophisticated network of molecular signals that alert all mammals that food is available.
“Nutrient sensors are therapeutic targets for potential anti-longevity drugs, but health benefits and lifespan extension could also be achieved through dietary interventions. However, the results obtained in this line in our species are still unclear: Clinical trials based on dietary restriction in humans become complicated due to poor compliance, although they suggest positive effects on immunity and inflammation,” wrote the researchers.
Diet and disease
Javier Gómez Pavón, MD, head of geriatrics at Red Cross Hospital in Madrid and member of the leadership team of the Spanish Society of Geriatrics and Gerontology, told this news organization, “Currently, the evidence we have indicates that certain types of diet in population cohort studies are associated with a lower incidence and prevalence of certain diseases.”
Dr. Gómez mentioned contrasting examples. “The Mediterranean diet has been shown in different studies to be associated with a lower cardiovascular risk (stroke, ischemic heart disease, dyslipidemia) and a lower risk of cognitive impairment, especially due to its vascular component.”
Eating nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts) is associated with a less dyslipidemia. A diet rich in fiber is also associated with less colonic digestive pathology, such as constipation and especially colon cancer. In addition, a diet low in fatty meats and rich in fruits and vegetables is associated with less prostate, breast, and colon disease. A diet with adequate protein intake is related to better muscle mass at all ages, and a diet rich in calcium products, such as nuts and dairy products, is linked to better bone mass and less osteoporosis and its consequences.
“At the moment, there is no study that links any type of diet with greater longevity, although in view of these data, it seems logical that a Mediterranean diet rich in fruits, vegetables, vegetables with proteins of animal origin, preferably fish or white meat, avoiding excess red meat and its calcium component in the form of nuts and dairy products would be associated with better disease-free aging,” said Dr. Gómez.
Aging indicators
The article expands the aging indicators from 9 to 12 (genomic instability, telomere wear, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, inactivated macroautophagy, dysregulation of nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells, alteration of intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and imbalances in the microbiome), which are measurable processes that change with the aging of the organism and which, when manipulated experimentally, induce an acceleration or, on the contrary, an interruption, even a regression, of aging.
“Each of these indicators should be considered an entry point for future exploration of the aging process, as well as for the development of new antiaging drugs,” the researchers concluded.
A decade ago, it was recognized that telomere shortening was at the origin of age-related diseases, said Dr. Blasco. “It is now emphasized that the generation of mouse models with short telomeres has shown that telomeric wasting is at the origin of prevalent age-associated diseases, such as pulmonary and renal fibrosis.”
The recent study reviews new interventions to delay aging and age-related diseases that act on telomeres. “For example, the activation of telomerase through a gene therapy strategy has shown therapeutic effects in mouse models of pulmonary fibrosis and aplastic anemia,” Dr. Blasco added.
Food fact and fiction
Since diet is currently the most easily accessible element to slow down aging, Dr. Gómez refutes the most widespread myths that are circulating about food and longevity. First, regarding dairy products, it is said that yogurt is not useful for the elderly, since the elderly do not have adequate enzymes to digest yogurt and that it is only for children or young people who are growing. “It is not true. Dairy products are not important for their proteins but for their calcium and vitamin D content. [These are] fundamental elements at all ages, but especially in aging, where there is bone loss secondary to aging itself and an increased risk of osteoporosis and associated fractures. Especially in the elderly, the tragic hip fracture is associated with high morbidity and mortality.”
Another myth is that it is not good to eat fruit with meals. “Due to its rich content in antioxidants and vitamins, it is a fundamental food of the Mediterranean diet. Antioxidants of any type (nuts, vegetables, fruits, etc.) are undoubtedly the most important components against pathological aging (stroke, myocardial infarction, dementia, etc.). It may be true that they can be more easily digested if they are eaten outside of meals, but the important thing is that they be eaten whenever.”
Sugars and meat
“Regarding the ‘fact’ that the sugars in legumes and bread are harmful, it is not true. In addition to sugar, legumes contain fiber and other very important antioxidants, just like bread. The difference is the amount, as in all food. On the contrary, refined sugars, such as pastries, sugary drinks, etc., should be avoided, since they are directly related to cardiovascular disease and obesity,” added Dr. Gómez.
“As for the popular saying, ‘Do not even try meat,’ it is not sound, since red meat and fish, including oily fish, are rich in protein and vitamin B as well as iron and, therefore, are necessary.
“As always, it is the amount that should be limited, especially red meat, not so much oily fish. I would recommend reducing red meat and replacing it with white meat, since the former are rich in saturated fats that produce more cholesterol,” added Dr. Gómez.
Another phrase that circulates around is that wine is food. “Careful. Wine in small quantities, a glass at lunch and dinner, is beneficial due to its antioxidant power, but at more than these amounts, the negative power of alcohol predominates over its benefits,” concluded Dr. Gómez.
Dr. Gómez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
These findings are closer than ever to being applied in older adults. Currently, diet is the most accessible form of intervention, but it is appropriate to clarify current myths and realities.
An article published in Cell in 2013 summarized for the first time the molecular indicators of aging in mammals. The article had a great impact and served as a knowledge map about aging. Now the authors have updated and extended this knowledge in the same journal.
A barometer of interest in the topic is that approximately 300,000 articles on aging have been published since 2013, which is as many as were published during the previous century. In addition, almost 80 experiments have been conducted with mammals, including humans, that confirm that interventions in the aging process can prevent, delay, and even avoid age-related diseases such as cancer.
María A. Blasco, MD, scientific director of the National Cancer Research Center, an international leader in telomere research and coauthor of the study, noted on the institution’s website, “The spectacular advances in recent years to increase the longevity of model organisms, including in mammals, indicate that it will be important to develop rational strategies to intervene in human aging.”
Eighty experimental interventions
The new article verifies the conclusions of the analysis carried out a decade ago. “Now there is much more investment, and we are closer to applying basic knowledge to new ways of treating diseases,” said Dr. Blasco. The researchers identified nine indicators of aging – molecular signatures that mark the progress of the process and on which it was possible to act to prolong life.
They also point to four primary causes of aging: genomic instability, shortening of telomeres, epigenetic alterations, and imbalance between protein synthesis and degradation. These are strongly interconnected processes. Aging results from their joint action, which is why there are multiple ways to act on the physiologic process of aging. The new study includes a table with almost 80 recent experimental interventions with mammals (mostly mice) that suggest that it is possible to prolong life or treat age-associated diseases. Some of those studies concern humans; others investigate how to delay aging through diet. “Acting on the diet is one of the most accessible ways to intervene in human aging,” according to the researchers.
Nutrient sensors
Dietary interventions are related to a key indicator of aging: the dysregulation of the nutrient sensing mechanism. This mechanism is the sophisticated network of molecular signals that alert all mammals that food is available.
“Nutrient sensors are therapeutic targets for potential anti-longevity drugs, but health benefits and lifespan extension could also be achieved through dietary interventions. However, the results obtained in this line in our species are still unclear: Clinical trials based on dietary restriction in humans become complicated due to poor compliance, although they suggest positive effects on immunity and inflammation,” wrote the researchers.
Diet and disease
Javier Gómez Pavón, MD, head of geriatrics at Red Cross Hospital in Madrid and member of the leadership team of the Spanish Society of Geriatrics and Gerontology, told this news organization, “Currently, the evidence we have indicates that certain types of diet in population cohort studies are associated with a lower incidence and prevalence of certain diseases.”
Dr. Gómez mentioned contrasting examples. “The Mediterranean diet has been shown in different studies to be associated with a lower cardiovascular risk (stroke, ischemic heart disease, dyslipidemia) and a lower risk of cognitive impairment, especially due to its vascular component.”
Eating nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts) is associated with a less dyslipidemia. A diet rich in fiber is also associated with less colonic digestive pathology, such as constipation and especially colon cancer. In addition, a diet low in fatty meats and rich in fruits and vegetables is associated with less prostate, breast, and colon disease. A diet with adequate protein intake is related to better muscle mass at all ages, and a diet rich in calcium products, such as nuts and dairy products, is linked to better bone mass and less osteoporosis and its consequences.
“At the moment, there is no study that links any type of diet with greater longevity, although in view of these data, it seems logical that a Mediterranean diet rich in fruits, vegetables, vegetables with proteins of animal origin, preferably fish or white meat, avoiding excess red meat and its calcium component in the form of nuts and dairy products would be associated with better disease-free aging,” said Dr. Gómez.
Aging indicators
The article expands the aging indicators from 9 to 12 (genomic instability, telomere wear, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, inactivated macroautophagy, dysregulation of nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells, alteration of intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and imbalances in the microbiome), which are measurable processes that change with the aging of the organism and which, when manipulated experimentally, induce an acceleration or, on the contrary, an interruption, even a regression, of aging.
“Each of these indicators should be considered an entry point for future exploration of the aging process, as well as for the development of new antiaging drugs,” the researchers concluded.
A decade ago, it was recognized that telomere shortening was at the origin of age-related diseases, said Dr. Blasco. “It is now emphasized that the generation of mouse models with short telomeres has shown that telomeric wasting is at the origin of prevalent age-associated diseases, such as pulmonary and renal fibrosis.”
The recent study reviews new interventions to delay aging and age-related diseases that act on telomeres. “For example, the activation of telomerase through a gene therapy strategy has shown therapeutic effects in mouse models of pulmonary fibrosis and aplastic anemia,” Dr. Blasco added.
Food fact and fiction
Since diet is currently the most easily accessible element to slow down aging, Dr. Gómez refutes the most widespread myths that are circulating about food and longevity. First, regarding dairy products, it is said that yogurt is not useful for the elderly, since the elderly do not have adequate enzymes to digest yogurt and that it is only for children or young people who are growing. “It is not true. Dairy products are not important for their proteins but for their calcium and vitamin D content. [These are] fundamental elements at all ages, but especially in aging, where there is bone loss secondary to aging itself and an increased risk of osteoporosis and associated fractures. Especially in the elderly, the tragic hip fracture is associated with high morbidity and mortality.”
Another myth is that it is not good to eat fruit with meals. “Due to its rich content in antioxidants and vitamins, it is a fundamental food of the Mediterranean diet. Antioxidants of any type (nuts, vegetables, fruits, etc.) are undoubtedly the most important components against pathological aging (stroke, myocardial infarction, dementia, etc.). It may be true that they can be more easily digested if they are eaten outside of meals, but the important thing is that they be eaten whenever.”
Sugars and meat
“Regarding the ‘fact’ that the sugars in legumes and bread are harmful, it is not true. In addition to sugar, legumes contain fiber and other very important antioxidants, just like bread. The difference is the amount, as in all food. On the contrary, refined sugars, such as pastries, sugary drinks, etc., should be avoided, since they are directly related to cardiovascular disease and obesity,” added Dr. Gómez.
“As for the popular saying, ‘Do not even try meat,’ it is not sound, since red meat and fish, including oily fish, are rich in protein and vitamin B as well as iron and, therefore, are necessary.
“As always, it is the amount that should be limited, especially red meat, not so much oily fish. I would recommend reducing red meat and replacing it with white meat, since the former are rich in saturated fats that produce more cholesterol,” added Dr. Gómez.
Another phrase that circulates around is that wine is food. “Careful. Wine in small quantities, a glass at lunch and dinner, is beneficial due to its antioxidant power, but at more than these amounts, the negative power of alcohol predominates over its benefits,” concluded Dr. Gómez.
Dr. Gómez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
These findings are closer than ever to being applied in older adults. Currently, diet is the most accessible form of intervention, but it is appropriate to clarify current myths and realities.
An article published in Cell in 2013 summarized for the first time the molecular indicators of aging in mammals. The article had a great impact and served as a knowledge map about aging. Now the authors have updated and extended this knowledge in the same journal.
A barometer of interest in the topic is that approximately 300,000 articles on aging have been published since 2013, which is as many as were published during the previous century. In addition, almost 80 experiments have been conducted with mammals, including humans, that confirm that interventions in the aging process can prevent, delay, and even avoid age-related diseases such as cancer.
María A. Blasco, MD, scientific director of the National Cancer Research Center, an international leader in telomere research and coauthor of the study, noted on the institution’s website, “The spectacular advances in recent years to increase the longevity of model organisms, including in mammals, indicate that it will be important to develop rational strategies to intervene in human aging.”
Eighty experimental interventions
The new article verifies the conclusions of the analysis carried out a decade ago. “Now there is much more investment, and we are closer to applying basic knowledge to new ways of treating diseases,” said Dr. Blasco. The researchers identified nine indicators of aging – molecular signatures that mark the progress of the process and on which it was possible to act to prolong life.
They also point to four primary causes of aging: genomic instability, shortening of telomeres, epigenetic alterations, and imbalance between protein synthesis and degradation. These are strongly interconnected processes. Aging results from their joint action, which is why there are multiple ways to act on the physiologic process of aging. The new study includes a table with almost 80 recent experimental interventions with mammals (mostly mice) that suggest that it is possible to prolong life or treat age-associated diseases. Some of those studies concern humans; others investigate how to delay aging through diet. “Acting on the diet is one of the most accessible ways to intervene in human aging,” according to the researchers.
Nutrient sensors
Dietary interventions are related to a key indicator of aging: the dysregulation of the nutrient sensing mechanism. This mechanism is the sophisticated network of molecular signals that alert all mammals that food is available.
“Nutrient sensors are therapeutic targets for potential anti-longevity drugs, but health benefits and lifespan extension could also be achieved through dietary interventions. However, the results obtained in this line in our species are still unclear: Clinical trials based on dietary restriction in humans become complicated due to poor compliance, although they suggest positive effects on immunity and inflammation,” wrote the researchers.
Diet and disease
Javier Gómez Pavón, MD, head of geriatrics at Red Cross Hospital in Madrid and member of the leadership team of the Spanish Society of Geriatrics and Gerontology, told this news organization, “Currently, the evidence we have indicates that certain types of diet in population cohort studies are associated with a lower incidence and prevalence of certain diseases.”
Dr. Gómez mentioned contrasting examples. “The Mediterranean diet has been shown in different studies to be associated with a lower cardiovascular risk (stroke, ischemic heart disease, dyslipidemia) and a lower risk of cognitive impairment, especially due to its vascular component.”
Eating nuts (e.g., almonds, walnuts) is associated with a less dyslipidemia. A diet rich in fiber is also associated with less colonic digestive pathology, such as constipation and especially colon cancer. In addition, a diet low in fatty meats and rich in fruits and vegetables is associated with less prostate, breast, and colon disease. A diet with adequate protein intake is related to better muscle mass at all ages, and a diet rich in calcium products, such as nuts and dairy products, is linked to better bone mass and less osteoporosis and its consequences.
“At the moment, there is no study that links any type of diet with greater longevity, although in view of these data, it seems logical that a Mediterranean diet rich in fruits, vegetables, vegetables with proteins of animal origin, preferably fish or white meat, avoiding excess red meat and its calcium component in the form of nuts and dairy products would be associated with better disease-free aging,” said Dr. Gómez.
Aging indicators
The article expands the aging indicators from 9 to 12 (genomic instability, telomere wear, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, inactivated macroautophagy, dysregulation of nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells, alteration of intercellular communication, chronic inflammation, and imbalances in the microbiome), which are measurable processes that change with the aging of the organism and which, when manipulated experimentally, induce an acceleration or, on the contrary, an interruption, even a regression, of aging.
“Each of these indicators should be considered an entry point for future exploration of the aging process, as well as for the development of new antiaging drugs,” the researchers concluded.
A decade ago, it was recognized that telomere shortening was at the origin of age-related diseases, said Dr. Blasco. “It is now emphasized that the generation of mouse models with short telomeres has shown that telomeric wasting is at the origin of prevalent age-associated diseases, such as pulmonary and renal fibrosis.”
The recent study reviews new interventions to delay aging and age-related diseases that act on telomeres. “For example, the activation of telomerase through a gene therapy strategy has shown therapeutic effects in mouse models of pulmonary fibrosis and aplastic anemia,” Dr. Blasco added.
Food fact and fiction
Since diet is currently the most easily accessible element to slow down aging, Dr. Gómez refutes the most widespread myths that are circulating about food and longevity. First, regarding dairy products, it is said that yogurt is not useful for the elderly, since the elderly do not have adequate enzymes to digest yogurt and that it is only for children or young people who are growing. “It is not true. Dairy products are not important for their proteins but for their calcium and vitamin D content. [These are] fundamental elements at all ages, but especially in aging, where there is bone loss secondary to aging itself and an increased risk of osteoporosis and associated fractures. Especially in the elderly, the tragic hip fracture is associated with high morbidity and mortality.”
Another myth is that it is not good to eat fruit with meals. “Due to its rich content in antioxidants and vitamins, it is a fundamental food of the Mediterranean diet. Antioxidants of any type (nuts, vegetables, fruits, etc.) are undoubtedly the most important components against pathological aging (stroke, myocardial infarction, dementia, etc.). It may be true that they can be more easily digested if they are eaten outside of meals, but the important thing is that they be eaten whenever.”
Sugars and meat
“Regarding the ‘fact’ that the sugars in legumes and bread are harmful, it is not true. In addition to sugar, legumes contain fiber and other very important antioxidants, just like bread. The difference is the amount, as in all food. On the contrary, refined sugars, such as pastries, sugary drinks, etc., should be avoided, since they are directly related to cardiovascular disease and obesity,” added Dr. Gómez.
“As for the popular saying, ‘Do not even try meat,’ it is not sound, since red meat and fish, including oily fish, are rich in protein and vitamin B as well as iron and, therefore, are necessary.
“As always, it is the amount that should be limited, especially red meat, not so much oily fish. I would recommend reducing red meat and replacing it with white meat, since the former are rich in saturated fats that produce more cholesterol,” added Dr. Gómez.
Another phrase that circulates around is that wine is food. “Careful. Wine in small quantities, a glass at lunch and dinner, is beneficial due to its antioxidant power, but at more than these amounts, the negative power of alcohol predominates over its benefits,” concluded Dr. Gómez.
Dr. Gómez has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL