User login
Two swings, two misses with colchicine, Vascepa in COVID-19
The anti-inflammatory agents colchicine and icosapent ethyl (Vascepa; Amarin) failed to provide substantial benefits in separate randomized COVID-19 trials.
Both were reported at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The open-label ECLA PHRI COLCOVID trial randomized 1,277 hospitalized adults (mean age 62 years) to usual care alone or with colchicine at a loading dose of 1.5 mg for 2 hours followed by 0.5 mg on day 1 and then 0.5 mg twice daily for 14 days or until discharge.
The investigators hypothesized that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, might modulate the hyperinflammatory syndrome, or cytokine storm, associated with COVID-19.
Results showed that the need for mechanical ventilation or death occurred in 25.0% of patients receiving colchicine and 28.8% with usual care (P = .08).
The coprimary endpoint of death at 28 days was also not significantly different between groups (20.5% vs. 22.2%), principal investigator Rafael Diaz, MD, said in a late-breaking COVID-19 trials session at the congress.
Among the secondary outcomes at 28 days, colchicine significantly reduced the incidence of new intubation or death from respiratory failure from 27.0% to 22.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99) but not mortality from respiratory failure (19.5% vs. 16.8%).
The only important adverse effect was severe diarrhea, which was reported in 11.3% of the colchicine group vs. 4.5% in the control group, said Dr. Diaz, director of Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica (ECLA), Rosario, Argentina.
The results are consistent with those from the massive RECOVERY trial, which earlier this year stopped enrollment in the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, and COLCORONA, which missed its primary endpoint using colchicine among nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.
Session chair and COLCORONA principal investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, pointed out that, as clinicians, it’s fairly uncommon to combine systemic steroids with colchicine, which was the case in 92% of patients in ECLA PHRI COLCOVID.
“I think it is an inherent limitation of testing colchicine on top of steroids,” said Dr. Tardif, of the Montreal Heart Institute.
Icosapent ethyl in PREPARE-IT
Dr. Diaz returned in the ESC session to present the results of the PREPARE-IT trial, which tested whether icosapent ethyl – at a loading dose of 8 grams (4 capsules) for the first 3 days and 4 g/d on days 4-60 – could reduce the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection in 2,041 health care and other public workers in Argentina at high risk for infection (mean age 40.5 years).
Vascepa was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012 for the reduction of elevated triglyceride levels, with an added indication in 2019 to reduce cardiovascular (CV) events in people with elevated triglycerides and established CV disease or diabetes with other CV risk factors.
The rationale for using the high-dose prescription eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) preparation includes its anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects, and that unsaturated fatty acids, especially EPA, might inactivate the enveloped virus, he explained.
Among 1,712 participants followed for up to 60 days, however, the SARS-CoV-2 infection rate was 7.9% with icosapent ethyl vs. 7.1% with a mineral oil placebo (P = .58).
There were also no significant changes from baseline in the icosapent ethyl and placebo groups for the secondary outcomes of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (0 vs. 0), triglycerides (median –2 mg/dL vs. 7 mg/dL), or Influenza Patient-Reported Outcome (FLU-PRO) questionnaire scores (median 0.01 vs. 0.03).
The use of a mineral oil placebo has been the subject of controversy in previous fish oil trials, but, Dr. Diaz noted, it did not have a significant proinflammatory effect or cause any excess adverse events.
Overall, adverse events were similar between the active and placebo groups, including atrial fibrillation (none), major bleeding (none), minor bleeding (7 events vs. 10 events), gastrointestinal symptoms (6.8% vs. 7.0%), and diarrhea (8.6% vs. 7.7%).
Although it missed the primary endpoint, Dr. Diaz said, “this is the first large, randomized blinded trial to demonstrate excellent safety and tolerability of an 8-gram-per-day loading dose of icosapent ethyl, opening up the potential for acute use in randomized trials of myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndromes, strokes, and revascularization.”
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Diaz said the Delta variant was not present at the time of the analysis and that the second half of the trial will report on whether icosapent ethyl can reduce the risk for hospitalization or death in participants diagnosed with COVID-19.
ECLA PHRI COLCOVID was supported by the Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica Population Health Research Institute. PREPARE-IT was supported by Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica with collaboration from Amarin. Dr. Diaz reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The anti-inflammatory agents colchicine and icosapent ethyl (Vascepa; Amarin) failed to provide substantial benefits in separate randomized COVID-19 trials.
Both were reported at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The open-label ECLA PHRI COLCOVID trial randomized 1,277 hospitalized adults (mean age 62 years) to usual care alone or with colchicine at a loading dose of 1.5 mg for 2 hours followed by 0.5 mg on day 1 and then 0.5 mg twice daily for 14 days or until discharge.
The investigators hypothesized that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, might modulate the hyperinflammatory syndrome, or cytokine storm, associated with COVID-19.
Results showed that the need for mechanical ventilation or death occurred in 25.0% of patients receiving colchicine and 28.8% with usual care (P = .08).
The coprimary endpoint of death at 28 days was also not significantly different between groups (20.5% vs. 22.2%), principal investigator Rafael Diaz, MD, said in a late-breaking COVID-19 trials session at the congress.
Among the secondary outcomes at 28 days, colchicine significantly reduced the incidence of new intubation or death from respiratory failure from 27.0% to 22.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99) but not mortality from respiratory failure (19.5% vs. 16.8%).
The only important adverse effect was severe diarrhea, which was reported in 11.3% of the colchicine group vs. 4.5% in the control group, said Dr. Diaz, director of Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica (ECLA), Rosario, Argentina.
The results are consistent with those from the massive RECOVERY trial, which earlier this year stopped enrollment in the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, and COLCORONA, which missed its primary endpoint using colchicine among nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.
Session chair and COLCORONA principal investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, pointed out that, as clinicians, it’s fairly uncommon to combine systemic steroids with colchicine, which was the case in 92% of patients in ECLA PHRI COLCOVID.
“I think it is an inherent limitation of testing colchicine on top of steroids,” said Dr. Tardif, of the Montreal Heart Institute.
Icosapent ethyl in PREPARE-IT
Dr. Diaz returned in the ESC session to present the results of the PREPARE-IT trial, which tested whether icosapent ethyl – at a loading dose of 8 grams (4 capsules) for the first 3 days and 4 g/d on days 4-60 – could reduce the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection in 2,041 health care and other public workers in Argentina at high risk for infection (mean age 40.5 years).
Vascepa was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012 for the reduction of elevated triglyceride levels, with an added indication in 2019 to reduce cardiovascular (CV) events in people with elevated triglycerides and established CV disease or diabetes with other CV risk factors.
The rationale for using the high-dose prescription eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) preparation includes its anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects, and that unsaturated fatty acids, especially EPA, might inactivate the enveloped virus, he explained.
Among 1,712 participants followed for up to 60 days, however, the SARS-CoV-2 infection rate was 7.9% with icosapent ethyl vs. 7.1% with a mineral oil placebo (P = .58).
There were also no significant changes from baseline in the icosapent ethyl and placebo groups for the secondary outcomes of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (0 vs. 0), triglycerides (median –2 mg/dL vs. 7 mg/dL), or Influenza Patient-Reported Outcome (FLU-PRO) questionnaire scores (median 0.01 vs. 0.03).
The use of a mineral oil placebo has been the subject of controversy in previous fish oil trials, but, Dr. Diaz noted, it did not have a significant proinflammatory effect or cause any excess adverse events.
Overall, adverse events were similar between the active and placebo groups, including atrial fibrillation (none), major bleeding (none), minor bleeding (7 events vs. 10 events), gastrointestinal symptoms (6.8% vs. 7.0%), and diarrhea (8.6% vs. 7.7%).
Although it missed the primary endpoint, Dr. Diaz said, “this is the first large, randomized blinded trial to demonstrate excellent safety and tolerability of an 8-gram-per-day loading dose of icosapent ethyl, opening up the potential for acute use in randomized trials of myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndromes, strokes, and revascularization.”
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Diaz said the Delta variant was not present at the time of the analysis and that the second half of the trial will report on whether icosapent ethyl can reduce the risk for hospitalization or death in participants diagnosed with COVID-19.
ECLA PHRI COLCOVID was supported by the Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica Population Health Research Institute. PREPARE-IT was supported by Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica with collaboration from Amarin. Dr. Diaz reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The anti-inflammatory agents colchicine and icosapent ethyl (Vascepa; Amarin) failed to provide substantial benefits in separate randomized COVID-19 trials.
Both were reported at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The open-label ECLA PHRI COLCOVID trial randomized 1,277 hospitalized adults (mean age 62 years) to usual care alone or with colchicine at a loading dose of 1.5 mg for 2 hours followed by 0.5 mg on day 1 and then 0.5 mg twice daily for 14 days or until discharge.
The investigators hypothesized that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, might modulate the hyperinflammatory syndrome, or cytokine storm, associated with COVID-19.
Results showed that the need for mechanical ventilation or death occurred in 25.0% of patients receiving colchicine and 28.8% with usual care (P = .08).
The coprimary endpoint of death at 28 days was also not significantly different between groups (20.5% vs. 22.2%), principal investigator Rafael Diaz, MD, said in a late-breaking COVID-19 trials session at the congress.
Among the secondary outcomes at 28 days, colchicine significantly reduced the incidence of new intubation or death from respiratory failure from 27.0% to 22.3% (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99) but not mortality from respiratory failure (19.5% vs. 16.8%).
The only important adverse effect was severe diarrhea, which was reported in 11.3% of the colchicine group vs. 4.5% in the control group, said Dr. Diaz, director of Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica (ECLA), Rosario, Argentina.
The results are consistent with those from the massive RECOVERY trial, which earlier this year stopped enrollment in the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, and COLCORONA, which missed its primary endpoint using colchicine among nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19.
Session chair and COLCORONA principal investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, pointed out that, as clinicians, it’s fairly uncommon to combine systemic steroids with colchicine, which was the case in 92% of patients in ECLA PHRI COLCOVID.
“I think it is an inherent limitation of testing colchicine on top of steroids,” said Dr. Tardif, of the Montreal Heart Institute.
Icosapent ethyl in PREPARE-IT
Dr. Diaz returned in the ESC session to present the results of the PREPARE-IT trial, which tested whether icosapent ethyl – at a loading dose of 8 grams (4 capsules) for the first 3 days and 4 g/d on days 4-60 – could reduce the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection in 2,041 health care and other public workers in Argentina at high risk for infection (mean age 40.5 years).
Vascepa was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012 for the reduction of elevated triglyceride levels, with an added indication in 2019 to reduce cardiovascular (CV) events in people with elevated triglycerides and established CV disease or diabetes with other CV risk factors.
The rationale for using the high-dose prescription eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) preparation includes its anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic effects, and that unsaturated fatty acids, especially EPA, might inactivate the enveloped virus, he explained.
Among 1,712 participants followed for up to 60 days, however, the SARS-CoV-2 infection rate was 7.9% with icosapent ethyl vs. 7.1% with a mineral oil placebo (P = .58).
There were also no significant changes from baseline in the icosapent ethyl and placebo groups for the secondary outcomes of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (0 vs. 0), triglycerides (median –2 mg/dL vs. 7 mg/dL), or Influenza Patient-Reported Outcome (FLU-PRO) questionnaire scores (median 0.01 vs. 0.03).
The use of a mineral oil placebo has been the subject of controversy in previous fish oil trials, but, Dr. Diaz noted, it did not have a significant proinflammatory effect or cause any excess adverse events.
Overall, adverse events were similar between the active and placebo groups, including atrial fibrillation (none), major bleeding (none), minor bleeding (7 events vs. 10 events), gastrointestinal symptoms (6.8% vs. 7.0%), and diarrhea (8.6% vs. 7.7%).
Although it missed the primary endpoint, Dr. Diaz said, “this is the first large, randomized blinded trial to demonstrate excellent safety and tolerability of an 8-gram-per-day loading dose of icosapent ethyl, opening up the potential for acute use in randomized trials of myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndromes, strokes, and revascularization.”
During a discussion of the results, Dr. Diaz said the Delta variant was not present at the time of the analysis and that the second half of the trial will report on whether icosapent ethyl can reduce the risk for hospitalization or death in participants diagnosed with COVID-19.
ECLA PHRI COLCOVID was supported by the Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica Population Health Research Institute. PREPARE-IT was supported by Estudios Clínicos Latinoamérica with collaboration from Amarin. Dr. Diaz reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Western and proinflammatory diets are important drivers of gout risk
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
Diets high in red meats, saturated fats, and sugars, relative to diets dominated by fruits, vegetables, and legumes, are associated with an increased risk of gout independent of an underlying genetic risk, according to independent sets of data presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
Only one of the two retrospective analyses evaluated diet in the context of a genetic risk score, but “no evidence of an additional or multiplicative interaction” was seen when genetic risk was evaluated on top of the risk already known to be associated with a Western diet, reported Chio Yokose, MD, a researcher and clinician in the division of rheumatology, allergy, and immunology at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
A parallel study presented at the EULAR Congress looked at the impact of a proinflammatory diet. Although genetic predisposition was not considered in this analysis, this diet, too, was associated with increased risk of gout independent of a long list of other variables. Each of the studies supports the potential for diet to be a target for risk reduction.
“Adhering to a diet with low inflammatory potential may mediate systemic and metabolic inflammation,” reported Natalie McCormick, PhD, a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the association of an inflammatory diet with gout is analogous to previous studies linking this type of diet to type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease because the inflammatory response is a pathogenic factor.
The two retrospective studies evaluated different but overlapping sets of data. Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick collaborated on both studies.
In the study of Western diet, which was restricted to women, the focus was on both diet and genes. Using food frequency questionnaires completed by 18,512 women participating in the Nurses’ Health Study (NHS), subjects were placed in quintiles for relative exposure to Western diets and for an interventional diet called DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) that is high in fruits and vegetables.
A genetic risk score (GRS) was developed for participants using 114 serum urate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study.
For the Western diet, there was a stepwise increased risk of gout per quintile associated with greater exposure. For the DASH diet, the same phenomenon was seen in reverse so that risk of gout was incrementally lower per quintile defining greater adherence.
When considered as a variable, GRS altered these basic relationships only for the DASH diet. After adjusting for multiple factors, such as age, menopause, use of hormone therapy, and hypertension, there was no significant interaction observed for genetic predisposition in relation to the Western diet.
For the DASH diet, there was an even greater reduction in the relative risk of gout among those with a high GRS if they were in the quintile defining greatest adherence to the DASH diet. Although this association fell just short of reaching statistical significance (P = .056), Dr. Yokose indicated that it was a strong trend.
Gout similarly associated with proinflammatory diet
The proinflammatory diet shares many food items with the Western diet, including refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, red meat, and fried foods. The study that evaluated its impact used dietary history collected from in 164,090 women in the NHS and 40,598 men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study. In both, participants completed dietary questionnaires every 4 years. Patients were assigned an Empirical Dietary Index of Inflammatory Potential (EDIP) score on the basis of these questionnaires.
When the 2,874 incident gout cases were evaluated by EDIP quintile, those in the highest had a 50% greater risk of gout than did those in the lowest when adjusted for multiple potential confounders. When stratified by intake of alcohol, the impact of being in the highest quintile of inflammatory diet was even greater, producing a 2.37-fold increased risk of gout.
Impact of weight on risk for gout
The impact of proinflammatory diet was detectable even after adjusting for adiposity, a gout risk factor reconfirmed in a third study presented at EULAR by this same team of investigators. In that study, presented by Dr. Yokose, a GRS above the mean was associated with a further increased likelihood of gout among those with elevated body mass index. However, obesity remained a risk factor for gout even among those with a low GRS.
The data from this study indicate “maintaining healthy weight is an important gout prevention strategy, regardless of underlying genetic risk,” Dr. Yokose reported.
All three studies reinforce diet as a modifiable risk factor for gout. According to both Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick, healthy diets should be considered as a gout prevention strategy.
Annelies Boonen, MD, PhD, professor of internal medicine (rheumatology) at the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands), did not challenge these conclusions. However, she cautioned that it is “very difficult to evaluate food questionnaires.” She further noted that retrospective analyses complicate efforts to control for the many potential confounders.
Ultimately, healthy diets can be recommended for many reasons, particularly in individuals with other risk factors for gout. For this reason, Dr. Boonen indicated that it will be difficult to prove definitively that gout can be prevented by avoiding Western diets and other diets high in proinflammatory foods. However, definitive proof of this benefit might not be essential for the purpose of a general recommendation to eat healthy foods.
Dr. Yokose and Dr. McCormick reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM THE EULAR 2021 CONGRESS
Rheumatology clinics find success with smoking cessation referral program
A new protocol designed to help patients in rheumatology clinics quit smoking proved both efficient and effective in referring willing participants to free tobacco quit lines.
“Rheumatology visits provide a unique opportunity to address smoking as a chronic modifiable risk factor in populations at high risk for cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, and rheumatic disease progression,” wrote Christie M. Bartels, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To assess the effectiveness of implementing a smoking cessation protocol for patients with rheumatic diseases, the researchers launched a quasi-experimental cohort study in which their Quit Connect protocol was tested at three rheumatology clinics. Adapting the Ask, Advise, Connect primary care protocol to a new setting, nurses and medical assistants were trained to use electronic health record (EHR) prompts that would check if patients who smoked were ready to quit within 30 days, advise them to do so, and then use electronic referrals to connect them to state-run tobacco quit lines. An extended baseline period – October 2012 to March 2016 – was compared to a 6-month intervention period from April to October 2016.
Across 54,090 pre- and postimplementation rheumatology clinic visits, 4,601 were with current smokers. Demographics were similar across both periods: The mean age of the patients was 51 years, about two-thirds were female, and 85% were White.
Clinicians’ assessment of tobacco use before and after implementation of the program stayed steady at 96% of patient visits, but the percentage of tobacco users’ visits that included checking for readiness to quit within the next 30 days rose from 3% (135 of 4,078) to 80% (421 of 523).
Before the implementation of the program, 0.6% of eligible visits with current smokers included a quit-line referral offer. After implementation, 93 (18%) of the 523 smokers who visited – 122 of whom said they were ready to quit – were offered referrals, a 26-fold increase. Of the 93 offered referrals, 66 (71%) accepted and 16 set a quit date or reported having quit; 11 accepted counseling services and nicotine replacement.
Although clinic staff reported encountering several obstacles, such as the need to craft nonthreatening language for challenging patients, they also contributed their own talking points that were included in the EHR tools and desktop brochures. On average, the protocol took less than 90 seconds to perform.
Rheumatologists can make headway on patients quitting smoking
“While smoking cessation programs require time and resources to implement, this study suggests a role for evidence-based protocols within rheumatology centers,” Medha Barbhaiya, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “Given that current smokers are at an increased risk of developing more severe rheumatic disease and cardiovascular disease, and patients often visit their rheumatologist multiple times yearly, rheumatologists may be well-positioned to address smoking cessation with patients.”
In regard to next steps, she noted that “while future large studies in diverse cohorts are needed to confirm these findings, implementing a formal smoking cessation protocol within rheumatology centers may provide a unique opportunity for rheumatologists to directly help patients modify their disease risk, leading to improved health outcomes.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the fact that it was a prepost design and not a randomized trial. They also recognized that many tobacco users require 8-10 attempts before permanently quitting, likely lessening the lasting impact of the short-term study. They did cite expert analysis, however, that says “connecting patients to evidence-based resources makes them more likely to permanently quit.”
The study was supported in part by Pfizer’s office of Independent Grants for Learning and Change and by a grant collaboration from the University of Wisconsin Clinical and Translational Science Award and the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health’s Wisconsin Partnership Program, through the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
A new protocol designed to help patients in rheumatology clinics quit smoking proved both efficient and effective in referring willing participants to free tobacco quit lines.
“Rheumatology visits provide a unique opportunity to address smoking as a chronic modifiable risk factor in populations at high risk for cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, and rheumatic disease progression,” wrote Christie M. Bartels, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To assess the effectiveness of implementing a smoking cessation protocol for patients with rheumatic diseases, the researchers launched a quasi-experimental cohort study in which their Quit Connect protocol was tested at three rheumatology clinics. Adapting the Ask, Advise, Connect primary care protocol to a new setting, nurses and medical assistants were trained to use electronic health record (EHR) prompts that would check if patients who smoked were ready to quit within 30 days, advise them to do so, and then use electronic referrals to connect them to state-run tobacco quit lines. An extended baseline period – October 2012 to March 2016 – was compared to a 6-month intervention period from April to October 2016.
Across 54,090 pre- and postimplementation rheumatology clinic visits, 4,601 were with current smokers. Demographics were similar across both periods: The mean age of the patients was 51 years, about two-thirds were female, and 85% were White.
Clinicians’ assessment of tobacco use before and after implementation of the program stayed steady at 96% of patient visits, but the percentage of tobacco users’ visits that included checking for readiness to quit within the next 30 days rose from 3% (135 of 4,078) to 80% (421 of 523).
Before the implementation of the program, 0.6% of eligible visits with current smokers included a quit-line referral offer. After implementation, 93 (18%) of the 523 smokers who visited – 122 of whom said they were ready to quit – were offered referrals, a 26-fold increase. Of the 93 offered referrals, 66 (71%) accepted and 16 set a quit date or reported having quit; 11 accepted counseling services and nicotine replacement.
Although clinic staff reported encountering several obstacles, such as the need to craft nonthreatening language for challenging patients, they also contributed their own talking points that were included in the EHR tools and desktop brochures. On average, the protocol took less than 90 seconds to perform.
Rheumatologists can make headway on patients quitting smoking
“While smoking cessation programs require time and resources to implement, this study suggests a role for evidence-based protocols within rheumatology centers,” Medha Barbhaiya, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “Given that current smokers are at an increased risk of developing more severe rheumatic disease and cardiovascular disease, and patients often visit their rheumatologist multiple times yearly, rheumatologists may be well-positioned to address smoking cessation with patients.”
In regard to next steps, she noted that “while future large studies in diverse cohorts are needed to confirm these findings, implementing a formal smoking cessation protocol within rheumatology centers may provide a unique opportunity for rheumatologists to directly help patients modify their disease risk, leading to improved health outcomes.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the fact that it was a prepost design and not a randomized trial. They also recognized that many tobacco users require 8-10 attempts before permanently quitting, likely lessening the lasting impact of the short-term study. They did cite expert analysis, however, that says “connecting patients to evidence-based resources makes them more likely to permanently quit.”
The study was supported in part by Pfizer’s office of Independent Grants for Learning and Change and by a grant collaboration from the University of Wisconsin Clinical and Translational Science Award and the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health’s Wisconsin Partnership Program, through the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
A new protocol designed to help patients in rheumatology clinics quit smoking proved both efficient and effective in referring willing participants to free tobacco quit lines.
“Rheumatology visits provide a unique opportunity to address smoking as a chronic modifiable risk factor in populations at high risk for cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, and rheumatic disease progression,” wrote Christie M. Bartels, MD, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and colleagues. The study was published in Arthritis Care & Research.
To assess the effectiveness of implementing a smoking cessation protocol for patients with rheumatic diseases, the researchers launched a quasi-experimental cohort study in which their Quit Connect protocol was tested at three rheumatology clinics. Adapting the Ask, Advise, Connect primary care protocol to a new setting, nurses and medical assistants were trained to use electronic health record (EHR) prompts that would check if patients who smoked were ready to quit within 30 days, advise them to do so, and then use electronic referrals to connect them to state-run tobacco quit lines. An extended baseline period – October 2012 to March 2016 – was compared to a 6-month intervention period from April to October 2016.
Across 54,090 pre- and postimplementation rheumatology clinic visits, 4,601 were with current smokers. Demographics were similar across both periods: The mean age of the patients was 51 years, about two-thirds were female, and 85% were White.
Clinicians’ assessment of tobacco use before and after implementation of the program stayed steady at 96% of patient visits, but the percentage of tobacco users’ visits that included checking for readiness to quit within the next 30 days rose from 3% (135 of 4,078) to 80% (421 of 523).
Before the implementation of the program, 0.6% of eligible visits with current smokers included a quit-line referral offer. After implementation, 93 (18%) of the 523 smokers who visited – 122 of whom said they were ready to quit – were offered referrals, a 26-fold increase. Of the 93 offered referrals, 66 (71%) accepted and 16 set a quit date or reported having quit; 11 accepted counseling services and nicotine replacement.
Although clinic staff reported encountering several obstacles, such as the need to craft nonthreatening language for challenging patients, they also contributed their own talking points that were included in the EHR tools and desktop brochures. On average, the protocol took less than 90 seconds to perform.
Rheumatologists can make headway on patients quitting smoking
“While smoking cessation programs require time and resources to implement, this study suggests a role for evidence-based protocols within rheumatology centers,” Medha Barbhaiya, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital for Special Surgery in New York, said in an interview. “Given that current smokers are at an increased risk of developing more severe rheumatic disease and cardiovascular disease, and patients often visit their rheumatologist multiple times yearly, rheumatologists may be well-positioned to address smoking cessation with patients.”
In regard to next steps, she noted that “while future large studies in diverse cohorts are needed to confirm these findings, implementing a formal smoking cessation protocol within rheumatology centers may provide a unique opportunity for rheumatologists to directly help patients modify their disease risk, leading to improved health outcomes.”
The authors acknowledged their study’s limitations, including the fact that it was a prepost design and not a randomized trial. They also recognized that many tobacco users require 8-10 attempts before permanently quitting, likely lessening the lasting impact of the short-term study. They did cite expert analysis, however, that says “connecting patients to evidence-based resources makes them more likely to permanently quit.”
The study was supported in part by Pfizer’s office of Independent Grants for Learning and Change and by a grant collaboration from the University of Wisconsin Clinical and Translational Science Award and the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health’s Wisconsin Partnership Program, through the NIH National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
FROM ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Febuxostat, allopurinol real-world cardiovascular risk appears equal
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
Febuxostat (Uloric) was not associated with increased cardiovascular risk in patients with gout when compared to those who used allopurinol, in an analysis of new users of the drugs in Medicare fee-for-service claims data from the period of 2008-2016.
The findings, published March 25 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, update and echo the results from a similar previous study by the same Brigham and Women’s Hospital research group that covered 2008-2013 Medicare claims data. That original claims data study from 2018 sought to confirm the findings of the postmarketing surveillance CARES (Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat and Allopurinol in Patients With Gout and Cardiovascular Morbidities) trial that led to a boxed warning for increased risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality vs. allopurinol. The trial, however, did not show a higher rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) overall with febuxostat.
The recency of the new data with more febuxostat-exposed patients overall provides greater reassurance on the safety of the drug, corresponding author Seoyoung C. Kim, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview. “We also were able to get data on cause of death, which we did not have before when we conducted our first paper.”
Dr. Kim said she was not surprised by any of the findings, which were consistent with the results of her earlier work. “Our result on CV death also was consistent and reassuring,” she noted.
The newest Medicare claims study also corroborates results from FAST (Febuxostat Versus Allopurinol Streamlined Trial), a separate postmarketing surveillance study that was ordered by the European Medicines Agency after febuxostat’s approval in 2009. It showed that the two drugs were noninferior to each other for the risk of all-cause mortality or a composite cardiovascular outcome (hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction, biomarker-positive acute coronary syndrome, nonfatal stroke, or cardiovascular death).
“While CARES showed higher CV death and all-cause death rates in febuxostat compared to allopurinol, FAST did not,” Dr. Kim noted. “Our study of more than 111,000 older gout patients treated with either febuxostat or allopurinol in real-world settings also did not find a difference in the risk of MACE, CV mortality, or all-cause mortality,” she added. “Taking these data all together, I think we can be more certain about the CV safety of febuxostat when its use is clinically indicated or needed,” she said.
Study details
Dr. Kim, first author Ajinkya Pawar, PhD, of Brigham and Women’s, and colleagues identified 467,461 people with gout aged 65 years and older who had been enrolled in Medicare for at least a year. They then used propensity-score matching to compare 27,881 first-time users of febuxostat with 83,643 first-time users of allopurinol on the primary outcome of the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), defined as the first occurrence of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular mortality.
In the updated study, the mean follow‐up periods for febuxostat and allopurinol were 284 days and 339 days, respectively. Overall, febuxostat was noninferior to allopurinol with regard to MACE (hazard ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.93-1.05), and the results were consistent among patients with baseline CVD (HR, 0.94). In addition, rates of secondary outcomes of MI, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality were not significantly different between febuxostat and allopurinol patients, except for all-cause mortality (HR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.87-0.98).
The study findings were limited mainly by the potential bias caused by nonadherence to medications, and potential for residual confounding and misclassification bias, the researchers noted.
However, the study was strengthened by its incident new-user design that allowed only patients with no use of either medication for a year before the first dispensing and its active comparator design, and the data are generalizable to the greater population of older gout patients, they said.
Consequently, the data from this large, real-world study support the safety of febuxostat with regard to cardiovascular risk in gout patients, including those with baseline cardiovascular disease, they concluded.
The study was supported by the division of pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacoeconomics at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Dr. Kim disclosed research grants to Brigham and Women’s Hospital from Roche, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Bristol‐Myers Squibb for unrelated studies. Another author reported serving as the principal investigator with research grants from Vertex, Bayer, and Novartis to Brigham and Women’s Hospital for unrelated projects.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
COVID-19 vaccination in RMD patients: Safety data “reassuring”
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Two reports support the safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) and represent the first available data on such patients.
In an observational cohort study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, Caoilfhionn M. Connolly, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues reviewed data from 325 adults with RMDs who received the first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine during the period of Dec. 17, 2020, to Feb. 11, 2021. Of these, 51% received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine and 49% received the Moderna vaccine.
The patients, who were invited to participate on social media, were aged 34-54 years, 96% were women, and 89% were White. Inflammatory arthritis was the most common RMD condition (38%), followed by systemic lupus erythematosus (28%) and overlap connective tissue disease (19%). The patients were using a range of immunomodulatory treatment regimens, including nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in 44%, biologics in 19%, and combination therapy in 37%.
Overall, 89% of patients reported localized symptoms of pain, swelling, and erythema, and 69% reported systemic symptoms. Fatigue was the most common systemic symptom, and 7.4% reported severe fatigue.
None of the patients experienced allergic reactions requiring epinephrine, and 3% reported new infections that required treatment.
“These early, reassuring results may ameliorate concern among patients and provide guidance for rheumatology providers in critical discussions regarding vaccine hesitancy or refusal,” they concluded.
Antibody responses
In another study published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases by the same group of researchers, antibody responses against the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were seen in 74% of 123 adults with an RMD at 18-26 days after receiving a first dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine (52% Pfizer vaccine and 48% Moderna) between Jan. 8, 2021, and Feb. 12, 2021.
The most common diagnoses in these patients were inflammatory arthritis (28%), systemic lupus erythematosus (20%), and Sjögren’s syndrome (13%). A total of 28% of participants reported taking no immunomodulatory agents, 19% reported nonbiologic DMARDs, 14% reported biologic DMARDs, and 19% reported combination therapy.
Although no differences appeared based on disease groups or overall categories of immunomodulatory therapies, patients whose treatment included mycophenolate or rituximab were significantly less likely to develop antibody responses than were patients not taking these medications (P = .001 and P = .04, respectively). Although rituximab and methotrexate have been associated with reduced responses to vaccines such as the flu vaccine, methotrexate was not associated with reduced vaccine response in this study. A total of 94% of patients taking a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor had detectable antibodies.
The studies’ findings were limited by several factors including a lack of longer-term safety data; the small, nonrandomized sample of mainly white women; limited information on immunomodulatory drug dosage and timing; lack of serial antibody measurements; use of an enzyme immunoassay designed to detect antibody response after natural infection; and the inclusion of data only on the first dose of a two-dose vaccine series, the researchers noted. However, the data should provide additional reassurance to RMD patients and their health care teams about vaccination against COVID-19, they said.
Both studies were supported by the Ben-Dov family. In addition, the studies were supported by grants to various study authors from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Transplantation and Immunology Research Network of the American Society of Transplantation. One author disclosed financial relationships with Sanofi, Novartis, CSL Behring, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Veloxis, Mallinckrodt, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. The other researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
RECOVERY trial of COVID-19 treatments stops colchicine arm
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
On the advice of its independent data monitoring committee (DMC), the RECOVERY trial has stopped recruitment to the colchicine arm for lack of efficacy in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
“The DMC saw no convincing evidence that further recruitment would provide conclusive proof of worthwhile mortality benefit either overall or in any prespecified subgroup,” the British investigators announced on March 5.
“The RECOVERY trial has already identified two anti-inflammatory drugs – dexamethasone and tocilizumab – that improve the chances of survival for patients with severe COVID-19. So, it is disappointing that colchicine, which is widely used to treat gout and other inflammatory conditions, has no effect in these patients,” cochief investigator Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, said in a statement.
“We do large, randomized trials to establish whether a drug that seems promising in theory has real benefits for patients in practice. Unfortunately, colchicine is not one of those,” said Dr. Landry, University of Oxford (England).
The RECOVERY trial is evaluating a range of potential treatments for COVID-19 at 180 hospitals in the United Kingdom, Indonesia, and Nepal, and was designed with the expectation that drugs would be added or dropped as the evidence changes. Since November 2020, the trial has included an arm comparing colchicine with usual care alone.
As part of a routine meeting March 4, the DMC reviewed data from a preliminary analysis based on 2,178 deaths among 11,162 patients, 94% of whom were being treated with a corticosteroid such as dexamethasone.
The results showed no significant difference in the primary endpoint of 28-day mortality in patients randomized to colchicine versus usual care alone (20% vs. 19%; risk ratio, 1.02; 95% confidence interval, 0.94-1.11; P = .63).
Follow-up is ongoing and final results will be published as soon as possible, the investigators said. Thus far, there has been no convincing evidence of an effect of colchicine on clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
Recruitment will continue to all other treatment arms – aspirin, baricitinib, Regeneron’s antibody cocktail, and, in select hospitals, dimethyl fumarate – the investigators said.
Cochief investigator Peter Hornby, MD, PhD, also from the University of Oxford, noted that this has been the largest trial ever of colchicine. “Whilst we are disappointed that the overall result is negative, it is still important information for the future care of patients in the U.K. and worldwide.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 vaccination recommended for rheumatology patients
People with rheumatic diseases should get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 as soon as possible, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) recommends.
“It may be that people with rheumatic diseases are at increased risk of developing COVID or serious COVID-related complications,” Jonathan Hausmann, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an ACR podcast. “So the need to prevent COVID-19 is incredibly important in this group of patients.”
The guidelines recommend a delay in vaccination only in rare circumstances, such as for patients with very severe illness or who have recently been administered rituximab, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, MPH, lead author of the guidelines, said in the podcast.
“Our members have been inundated with questions and concerns from their patients on whether they should receive the vaccine,” ACR President David Karp, MD, PhD, said in a press release.
So the ACR convened a panel of nine rheumatologists, two infectious disease specialists, and two public health experts. Over the course of 8 weeks, the task force reviewed the literature and agreed on recommendations. The organization posted a summary of the guidelines on its website after its board of directors approved it Feb. 8. The paper is pending journal peer review.
Some risks are real
The task force confined its research to the COVID-19 vaccines being offered by Pfizer and Moderna because they are currently the only ones approved by the Food and Drug Administration. It found no reason to distinguish between the two vaccines in its recommendations.
Because little research has directly addressed the question concerning COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic diseases, the task force extrapolated from data on other vaccinations in people with rheumatic disease and on the COVID-19 vaccinations in other populations.
It analyzed reports that other types of vaccination, such as for influenza, triggered flares of rheumatic conditions. “It is really individual case reports or small cohorts where there may be a somewhat higher incidence of flare, but it’s usually not very large in its magnitude nor duration,” said Dr. Curtis of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
The task force also considered the possibility that vaccinations could lead to a new autoimmune disorder, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or Bell palsy. The risk is real, the task force decided, but not significant enough to influence their recommendations.
Likewise, in immunocompromised people, vaccinations with live virus, such as those for shingles, might trigger the infection the vaccination is meant to prevent. But this can’t happen with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines because they contain messenger RNA instead of live viruses, Dr. Curtis said.
Although it might be optimal to administer the vaccines when rheumatic diseases are quiescent, the urgency of getting vaccinated overrides that consideration, Dr. Curtis said. “By and large, there was a general consensus to not want to delay vaccination until somebody was stable and doing great, because you don’t know how long that’s going to be,” he said.
How well does it work?
One unanswered question is whether the COVID-19 vaccines work as well for patients with rheumatic diseases. The task force was reassured by data showing efficacy across a range of subgroups, including some with immunosenescence, Dr. Curtis said. “But until we have data in rheumatology patients, we’re just not going to know,” he said.
The guidelines specify that some drug regimens be modified when patients are vaccinated.
For patients taking rituximab, vaccination should be delayed, but only for those who are able to maintain safe social distancing to reduce the risk for COVID-19 exposure, Dr. Curtis said. “If somebody has just gotten rituximab recently, it might be more ideal to complete the vaccine series about 2-4 weeks before the next rituximab dose,” he said. “So if you are giving that therapy, say, at 6-month intervals, if you could vaccinate them at around month 5 from the most recent rituximab cycle, that might be more ideal.”
The guidance calls for withholding JAK inhibitors for a week after each vaccine dose is administered.
It calls for holding SQ abatacept 1 week prior and 1 week after the first COVID-19 vaccine dose, with no interruption after the second dose.
For abatacept IV, clinicians should “time vaccine administration so that the first vaccination will occur 4 weeks after abatacept infusion (i.e., the entire dosing interval), and postpone the subsequent abatacept infusion by 1 week (i.e., a 5-week gap in total).” It recommends no medication adjustment for the second vaccine dose.
For cyclophosphamide, the guidance recommends timing administration to occur about a week after each vaccine dose, when feasible.
None of this advice should supersede clinical judgment, Dr. Curtis said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with rheumatic diseases should get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 as soon as possible, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) recommends.
“It may be that people with rheumatic diseases are at increased risk of developing COVID or serious COVID-related complications,” Jonathan Hausmann, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an ACR podcast. “So the need to prevent COVID-19 is incredibly important in this group of patients.”
The guidelines recommend a delay in vaccination only in rare circumstances, such as for patients with very severe illness or who have recently been administered rituximab, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, MPH, lead author of the guidelines, said in the podcast.
“Our members have been inundated with questions and concerns from their patients on whether they should receive the vaccine,” ACR President David Karp, MD, PhD, said in a press release.
So the ACR convened a panel of nine rheumatologists, two infectious disease specialists, and two public health experts. Over the course of 8 weeks, the task force reviewed the literature and agreed on recommendations. The organization posted a summary of the guidelines on its website after its board of directors approved it Feb. 8. The paper is pending journal peer review.
Some risks are real
The task force confined its research to the COVID-19 vaccines being offered by Pfizer and Moderna because they are currently the only ones approved by the Food and Drug Administration. It found no reason to distinguish between the two vaccines in its recommendations.
Because little research has directly addressed the question concerning COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic diseases, the task force extrapolated from data on other vaccinations in people with rheumatic disease and on the COVID-19 vaccinations in other populations.
It analyzed reports that other types of vaccination, such as for influenza, triggered flares of rheumatic conditions. “It is really individual case reports or small cohorts where there may be a somewhat higher incidence of flare, but it’s usually not very large in its magnitude nor duration,” said Dr. Curtis of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
The task force also considered the possibility that vaccinations could lead to a new autoimmune disorder, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or Bell palsy. The risk is real, the task force decided, but not significant enough to influence their recommendations.
Likewise, in immunocompromised people, vaccinations with live virus, such as those for shingles, might trigger the infection the vaccination is meant to prevent. But this can’t happen with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines because they contain messenger RNA instead of live viruses, Dr. Curtis said.
Although it might be optimal to administer the vaccines when rheumatic diseases are quiescent, the urgency of getting vaccinated overrides that consideration, Dr. Curtis said. “By and large, there was a general consensus to not want to delay vaccination until somebody was stable and doing great, because you don’t know how long that’s going to be,” he said.
How well does it work?
One unanswered question is whether the COVID-19 vaccines work as well for patients with rheumatic diseases. The task force was reassured by data showing efficacy across a range of subgroups, including some with immunosenescence, Dr. Curtis said. “But until we have data in rheumatology patients, we’re just not going to know,” he said.
The guidelines specify that some drug regimens be modified when patients are vaccinated.
For patients taking rituximab, vaccination should be delayed, but only for those who are able to maintain safe social distancing to reduce the risk for COVID-19 exposure, Dr. Curtis said. “If somebody has just gotten rituximab recently, it might be more ideal to complete the vaccine series about 2-4 weeks before the next rituximab dose,” he said. “So if you are giving that therapy, say, at 6-month intervals, if you could vaccinate them at around month 5 from the most recent rituximab cycle, that might be more ideal.”
The guidance calls for withholding JAK inhibitors for a week after each vaccine dose is administered.
It calls for holding SQ abatacept 1 week prior and 1 week after the first COVID-19 vaccine dose, with no interruption after the second dose.
For abatacept IV, clinicians should “time vaccine administration so that the first vaccination will occur 4 weeks after abatacept infusion (i.e., the entire dosing interval), and postpone the subsequent abatacept infusion by 1 week (i.e., a 5-week gap in total).” It recommends no medication adjustment for the second vaccine dose.
For cyclophosphamide, the guidance recommends timing administration to occur about a week after each vaccine dose, when feasible.
None of this advice should supersede clinical judgment, Dr. Curtis said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with rheumatic diseases should get vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 as soon as possible, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) recommends.
“It may be that people with rheumatic diseases are at increased risk of developing COVID or serious COVID-related complications,” Jonathan Hausmann, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an ACR podcast. “So the need to prevent COVID-19 is incredibly important in this group of patients.”
The guidelines recommend a delay in vaccination only in rare circumstances, such as for patients with very severe illness or who have recently been administered rituximab, Jeffrey R. Curtis, MD, MPH, lead author of the guidelines, said in the podcast.
“Our members have been inundated with questions and concerns from their patients on whether they should receive the vaccine,” ACR President David Karp, MD, PhD, said in a press release.
So the ACR convened a panel of nine rheumatologists, two infectious disease specialists, and two public health experts. Over the course of 8 weeks, the task force reviewed the literature and agreed on recommendations. The organization posted a summary of the guidelines on its website after its board of directors approved it Feb. 8. The paper is pending journal peer review.
Some risks are real
The task force confined its research to the COVID-19 vaccines being offered by Pfizer and Moderna because they are currently the only ones approved by the Food and Drug Administration. It found no reason to distinguish between the two vaccines in its recommendations.
Because little research has directly addressed the question concerning COVID-19 vaccination for patients with rheumatic diseases, the task force extrapolated from data on other vaccinations in people with rheumatic disease and on the COVID-19 vaccinations in other populations.
It analyzed reports that other types of vaccination, such as for influenza, triggered flares of rheumatic conditions. “It is really individual case reports or small cohorts where there may be a somewhat higher incidence of flare, but it’s usually not very large in its magnitude nor duration,” said Dr. Curtis of the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
The task force also considered the possibility that vaccinations could lead to a new autoimmune disorder, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or Bell palsy. The risk is real, the task force decided, but not significant enough to influence their recommendations.
Likewise, in immunocompromised people, vaccinations with live virus, such as those for shingles, might trigger the infection the vaccination is meant to prevent. But this can’t happen with the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines because they contain messenger RNA instead of live viruses, Dr. Curtis said.
Although it might be optimal to administer the vaccines when rheumatic diseases are quiescent, the urgency of getting vaccinated overrides that consideration, Dr. Curtis said. “By and large, there was a general consensus to not want to delay vaccination until somebody was stable and doing great, because you don’t know how long that’s going to be,” he said.
How well does it work?
One unanswered question is whether the COVID-19 vaccines work as well for patients with rheumatic diseases. The task force was reassured by data showing efficacy across a range of subgroups, including some with immunosenescence, Dr. Curtis said. “But until we have data in rheumatology patients, we’re just not going to know,” he said.
The guidelines specify that some drug regimens be modified when patients are vaccinated.
For patients taking rituximab, vaccination should be delayed, but only for those who are able to maintain safe social distancing to reduce the risk for COVID-19 exposure, Dr. Curtis said. “If somebody has just gotten rituximab recently, it might be more ideal to complete the vaccine series about 2-4 weeks before the next rituximab dose,” he said. “So if you are giving that therapy, say, at 6-month intervals, if you could vaccinate them at around month 5 from the most recent rituximab cycle, that might be more ideal.”
The guidance calls for withholding JAK inhibitors for a week after each vaccine dose is administered.
It calls for holding SQ abatacept 1 week prior and 1 week after the first COVID-19 vaccine dose, with no interruption after the second dose.
For abatacept IV, clinicians should “time vaccine administration so that the first vaccination will occur 4 weeks after abatacept infusion (i.e., the entire dosing interval), and postpone the subsequent abatacept infusion by 1 week (i.e., a 5-week gap in total).” It recommends no medication adjustment for the second vaccine dose.
For cyclophosphamide, the guidance recommends timing administration to occur about a week after each vaccine dose, when feasible.
None of this advice should supersede clinical judgment, Dr. Curtis said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ColCORONA: More questions than answers for colchicine in COVID-19
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.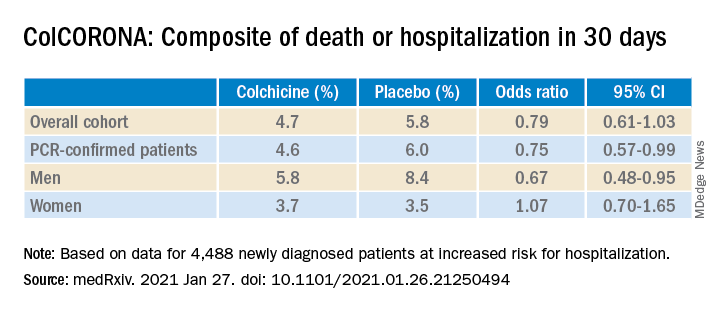
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Science by press release and preprint has cooled clinician enthusiasm for the use of colchicine in nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19, despite a pressing need for early treatments.
As previously reported by this news organization, a Jan. 22 press release announced that the massive ColCORONA study missed its primary endpoint of hospitalization or death among 4,488 newly diagnosed patients at increased risk for hospitalization.
But it also touted that use of the anti-inflammatory drug significantly reduced the primary endpoint in 4,159 of those patients with polymerase chain reaction–confirmed COVID and led to reductions of 25%, 50%, and 44%, respectively, for hospitalizations, ventilations, and death.
Lead investigator Jean-Claude Tardif, MD, director of the Montreal Heart Institute Research Centre, deemed the findings a “medical breakthrough.”
When the preprint released a few days later, however, newly revealed confidence intervals showed colchicine did not meaningfully reduce the need for mechanical ventilation (odds ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-1.07) or death alone (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.19-1.66).
Further, the significant benefit on the primary outcome came at the cost of a fivefold increase in pulmonary embolism (11 vs. 2; P = .01), which was not mentioned in the press release.
“Whether this represents a real phenomenon or simply the play of chance is not known,” Dr. Tardif and colleagues noted later in the preprint.
“I read the preprint on colchicine and I have so many questions,” Aaron E. Glatt, MD, spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and chief of infectious diseases, Mount Sinai South Nassau, Hewlett, N.Y., said in an interview. “I’ve been burned too many times with COVID and prefer to see better data.
“People sometimes say if you wait for perfect data, people are going to die,” he said. “Yeah, but we have no idea if people are going to die from getting this drug more than not getting it. That’s what concerns me. How many pulmonary emboli are going to be fatal versus the slight benefit that the study showed?”
The pushback to the non–peer-reviewed data on social media and via emails was so strong that Dr. Tardif posted a nearly 2,000-word letter responding to the many questions at play.
Chief among them was why the trial, originally planned for 6,000 patients, was stopped early by the investigators without consultation with the data safety monitoring board (DSMB).
The explanation in the letter that logistical issues like running the study call center, budget constraints, and a perceived need to quickly communicate the results left some calling foul that the study wasn’t allowed to finish and come to a more definitive conclusion.
“I can be a little bit sympathetic to their cause but at the same time the DSMB should have said no,” said David Boulware, MD, MPH, who led a recent hydroxychloroquine trial in COVID-19. “The problem is we’re sort of left in limbo, where some people kind of believe it and some say it’s not really a thing. So it’s not really moving the needle, as far as guidelines go.”
Indeed, a Twitter poll by cardiologist James Januzzi Jr., MD, captured the uncertainty, with 28% of respondents saying the trial was “neutral,” 58% saying “maybe but meh,” and 14% saying “colchicine for all.”
Another poll cheekily asked whether ColCORONA was the Gamestop/Reddit equivalent of COVID.
“The press release really didn’t help things because it very much oversold the effect. That, I think, poisoned the well,” said Dr. Boulware, professor of medicine in infectious diseases at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
“The question I’m left with is not whether colchicine works, but who does it work in,” he said. “That’s really the fundamental question because it does seem that there are probably high-risk groups in their trial and others where they benefit, whereas other groups don’t benefit. In the subgroup analysis, there was absolutely no beneficial effect in women.”
According to the authors, the number needed to treat to prevent one death or hospitalization was 71 overall, but 29 for patients with diabetes, 31 for those aged 70 years and older, 53 for patients with respiratory disease, and 25 for those with coronary disease or heart failure.
Men are at higher risk overall for poor outcomes. But “the authors didn’t present a multivariable analysis, so it is unclear if another factor, such as a differential prevalence of smoking or cardiovascular risk factors, contributed to the differential benefit,” Rachel Bender Ignacio, MD, MPH, infectious disease specialist, University of Washington, Seattle, said in an interview.
Importantly, in this pragmatic study, duration and severity of symptoms were not reported, observed Dr. Bender Ignacio, who is also a STOP-COVID-2 investigator. “We don’t yet have data as to whether colchicine shortens duration or severity of symptoms or prevents long COVID, so we need more data on that.”
The overall risk for serious adverse events was lower in the colchicine group, but the difference in pulmonary embolism (PE) was striking, she said. This could be caused by a real biologic effect, or it’s possible that persons with shortness of breath and hypoxia, without evident viral pneumonia on chest x-ray after a positive COVID-19 test, were more likely to receive a CT-PE study.
The press release also failed to include information, later noted in the preprint, that the MHI has submitted two patents related to colchicine: “Methods of treating a coronavirus infection using colchicine” and “Early administration of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction.”
Reached for clarification, MHI communications adviser Camille Turbide said in an interview that the first patent “simply refers to the novel concept of preventing complications of COVID-19, such as admission to the hospital, with colchicine as tested in the ColCORONA study.”
The second patent, she said, refers to the “novel concept that administering colchicine early after a major adverse cardiovascular event is better than waiting several days,” as supported by the COLCOT study, which Dr. Tardif also led.
The patents are being reviewed by authorities and “Dr. Tardif has waived his rights in these patents and does not stand to benefit financially at all if colchicine becomes used as a treatment for COVID-19,” Ms. Turbide said.
Dr. Tardif did not respond to interview requests for this story. Dr. Glatt said conflicts of interest must be assessed and are “something that is of great concern in any scientific study.”
Cardiologist Steve Nissen, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic said in an interview that, “despite the negative results, the study does suggest that colchicine might have a benefit and should be studied in future trials. These findings are not sufficient evidence to suggest use of the drug in patients infected with COVID-19.”
He noted that adverse effects like diarrhea were expected but that the excess PE was unexpected and needs greater clarification.
“Stopping the trial for administrative reasons is puzzling and undermined the ability of the trial to give a reliable answer,” Dr. Nissen said. “This is a reasonable pilot study that should be viewed as hypothesis generating but inconclusive.”
Several sources said a new trial is unlikely, particularly given the cost and 28 trials already evaluating colchicine. Among these are RECOVERY and COLCOVID, testing whether colchicine can reduce the duration of hospitalization or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Because there are so many trials ongoing right now, including for antivirals and other immunomodulators, it’s important that, if colchicine comes to routine clinical use, it provides access to treatment for those not able or willing to access clinical trials, rather than impeding clinical trial enrollment, Dr. Bender Ignacio suggested.
“We have already learned the lesson in the pandemic that early adoption of potentially promising therapies can negatively impact our ability to study and develop other promising treatments,” she said.
The trial was coordinated by the Montreal Heart Institute and funded by the government of Quebec; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; Montreal philanthropist Sophie Desmarais, and the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard. CGI, Dacima, and Pharmascience of Montreal were also collaborators. Dr. Glatt reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Boulware reported receiving $18 in food and beverages from Gilead Sciences in 2018.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Rheumatologic disease activity an important influencer of COVID-19 death risk
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
People with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) who contract the SARS-CoV-2 virus appear more likely to die from COVID-19 if their rheumatologic condition is not being well controlled at the time of their infection.
New data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance (GRA) physician registry reported in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases have found that the odds of dying from COVID-19 were 87% higher in individuals recorded as having moderate to high disease activity versus those reported to be in remission or having low disease activity.
“I think this really highlights the importance of continuing to appropriately, and actively, treat our patients, and the importance of controlling their disease,” Pedro Machado, MD, PhD, said in an interview. Dr. Machado, an associate professor in rheumatology and muscle diseases at University College London and a consultant rheumatologist at several U.K. hospitals, has been involved in the GRA physician registry from the start, and sits on the GRA steering committee.
Alongside higher disease activity, several other important factors were found to be associated with increased odds of dying from COVID-19 – older age, male gender, and the presence of one or more comorbidities, such as hypertension combined with cardiovascular disease or chronic lung disease.
These demographic and disease-based factors have been linked to an increased risk for COVID-19–related hospitalization before, both in people with RMDs and in the general population, but the latest GRA physician registry data now take that a step further, and link them also to an increased risk for death, together with several other factors more specific to RMDs.
Logging COVID-19 rheumatologic cases
Since the start of the global pandemic, the potential effects that SARS-CoV-2 infection might have on people with RMDs in particular has concerned the rheumatology community. The main worries being that, either because of the underlying RMD itself or to its treatment, there may be immunoregulatory deficits or other risk factors that would make individuals more susceptible to not only infection but also to developing more severe COVID-19 than the general population.
These concerns led to the rapid formation of the GRA and the COVID-19 GRA physician registry in March 2020 to collect and analyze data on adults with rheumatic disease and confirmed or presumptive COVID-19. Entries into the registry are made by or under the direction of rheumatologists, and this is a voluntary process.
“This population cannot ever be entirely representative of the population of patients with rheumatic diseases,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. There will be selection and other biases that affect the reported data. That said, it’s the largest database of reported COVID-19 cases in adult rheumatology patients across the world, with more than 9,000 cases so far included from multiple registries, including those based in Europe and North and South America. Data from one of these – the French RMD cohort – have also recently been published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, showing much the same findings but on a national level.
Hospitalization was the focus of a previous report because “you need large sample sizes” to look at endpoints that occur less frequently. When the first analysis was done, there were around 600 cases from 40 countries in the registry with sufficient data that could be used. Now, with a greater number of recorded cases, factors influencing the risk for death could be examined.
Death rate and risk factors found
Data on 3,729 COVID-19 cases in people with RMDs were included in the current analysis, all recorded in the first few months of the registry being open and up until July 1, 2020. In all, 390 (10.5%) of people died. While this is “clearly higher” than reported in the general population in most countries, the analysis was not designed to calculate a precise estimate.
“It should not be taken as an estimate of the overall death rate among patients with rheumatic diseases and COVID-19,” Dr. Machado and coauthors have been keen to point out.
“Age is always the biggest risk factor,” Dr. Machado explained. “There’s always a gradient: the older the patient, the worse the outcome.”
Indeed, there was a threefold increased risk for death among those aged 66-75 years versus those who were 65 years or younger (odds ratio, 3.00), and a sixfold increased risk for patients older than 75, compared with the younger age group (OR, 6.18).
Having both hypertension and cardiovascular disease was associated with an OR of 1.89, and coexisting chronic lung disease also significantly increased the chances of dying from COVID-19 (OR, 1.68).
Being of male sex was associated with a 46% increased risk for death from COVID-19 versus being of female sex.
The risk for COVID-19 death also rose with the use of corticosteroids. Compared with no steroid use, there was a 69% increased risk for with death at doses of 10 mg or more prednisolone equivalent per day.
“The finding about moderate to high doses of steroids being associated with a worse outcome is consistent with the first report; it was the same for hospitalization,” Dr. Machado observed.
The general consensus on steroid use in the COVID-19 setting is that they should be continued as needed, but at the lowest possible dose, as outlined in provisional recommendations set out by the recently renamed European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology.
The GRA physician registry findings provide further support for this, suggesting that disease control should be optimized with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, ideally without increasing the dose of steroids.
Surprise over sulfasalazine risk
“Taking all medications into account – such as methotrexate, leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, [tumor necrosis factor] blockers, interleukin-6 blockers, and [Janus kinase] inhibitors – it is quite reassuring because we did not see an association with worse outcome with those drugs overall,” Dr. Machado said.
However, treatment with rituximab (OR, 4.0), sulfasalazine (OR, 3.6), and immunosuppressive agents such as azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, mycophenolate, or tacrolimus (OR, 2.2), were associated with higher odds of dying from COVID-19 when compared with treatment with methotrexate alone.
The findings for rituximab and immunosuppressant use were perhaps not unexpected, but the possible association between sulfasalazine and COVID-19 death was “a bit intriguing,” Dr. Machado observed. “Sulfasalazine is believed to have low immunosuppressive effect.”
This warrants further investigation, but there are likely a range of confounding factors at play. One could be that people considered to be at higher risk may have been more often prescribed sulfasalazine because it was thought to be less immunosuppressive. Another might be because people taking sulfasalazine were more likely to be smokers, and they were also not advised to protect themselves from exposure to the virus (shielding) during the first wave of the pandemic, at least not in the United Kingdom.
Rituximab caution and vaccination
“Rituximab is a concern,” Dr. Machado acknowledged. “It is a concern that rheumatologists are now aware of and they are addressing, but then it’s a concern for a very specific subgroup of patients.”
While rheumatologists are, and will continue to prescribe it, there will be even more careful consideration over when, in whom, and how to use it during, and possibly even after, the pandemic.
“COVID is here to stay, it will become endemic, and it’s going to be part of our lives like the flu virus is,” Dr. Machado predicted.
Then there is the issue on vaccinating people against COVID-19, should those on rituximab still receive it? The answer is a yes, but, as with other vaccinations it’s all about the timing of when the vaccination is given.
Societies such as the British Society for Rheumatology have already begun to include guidance on this, recommending one of the available COVID-19 vaccines is given at least a month before the next or first dose of rituximab is due. As rituximab is given every few months, with doses sometimes spaced as much as 9 months or even a year apart, this should not be too much of a problem, but it is “better to have the vaccine first,” Dr. Machado said.
Has COVID-19 care improved in RMDs?
In separate research published in The Lancet Rheumatology, April Jorge, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and associates found that the risks of severe COVID-19 outcomes have improved over time, although they still “remain substantial.”
Dr. Jorge and colleagues looked at temporal trends in COVID-19 outcomes in patients with RMDs over the course of the first 6 months of the pandemic in 2020, using data from a large, multicenter, electronic health record network (TriNetX).
They formed two patient cohorts – a late (diagnosed from April 20 to July 20) and an early (diagnosed from January 20 to April 20) cohort – to see if outcomes had improved and discovered lower relative risks among patients in the late cohort for hospitalization (0.67), admission to the ICU (0.56), mechanical ventilation (0.39), acute kidney injury (0.66), renal replacement (0.53), and death (0.39).
“These results are encouraging,” but it’s difficult to match these different populations of patients, Dr. Machado said. “There are always factors that you cannot match for” and were not included in the U.S. analysis.
While there are important caveats in how the analysis was performed and thus in interpreting these data, they do “suggest that one of the reasons why outcomes have improved is because we have become better at treating these patients,” Dr. Machado added.
“Our treatment has improved, and our capacity to treat the complications has improved. We understand better how the disease behaves – we know that they can have thromboembolic complications that we can manage, and we are now able to manage ventilation issues better.”
Moreover, Dr. Machado said that, not only were clinicians more aware of what they should or should not do, there were treatments that were being used routinely or in some cases based on recent clinical trial results. “I think we are indeed treating these patients better.”
The COVID-19 GRA physician registry is financially supported by the American College of Rheumatology and EULAR. Dr. Machado had no relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
COVID-19: Another study links colchicine to better results
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
The gout drug colchicine appears to lower the severity of COVID-19, a small new Brazilian study finds, adding to evidence that the familiar medication holds promise as a treatment for hospitalized patients.
Patients who received colchicine in this randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial presented better evolution in terms of the need for supplemental oxygen and the length of hospitalisation. ... Colchicine was safe and well tolerated,” the study authors wrote in RMD Open. However, deaths were rare in the trial, they added, and it is impossible to “evaluate the capacity of colchicine to avoid admission to ICU and reduce mortality.”
The oral anti-inflammatory colchicine, widely used as treatment in rheumatic disease, was first approved in the United States 60 years ago. Researchers began to explore its potential as a COVID-19 treatment in the early months of the pandemic.
On Jan. 25, an international team of researchers reported in a press release – but not yet a published paper – that the drug seemed to reduce hospitalizations, mechanical ventilation, and deaths in the ColCORONA trial. Earlier, a much-smaller, randomized, open-label, Greek trial linked the drug to reduced time to clinical deterioration and hospital stay.
The Brazilian authors of the new study, led by Maria Isabel Lopes of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School, randomly assigned 75 hospitalized patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 to colchicine or placebo. A total of 72 subjects completed the April-August 2020 trial: 36 received colchicine (typically 0.5 mg three times for 5 days, then 0.5 mg twice daily for 5 days; doses were adjusted in low-weight patients and those with chronic kidney disease). The other 36 received the placebo.
(In the United States, 0.6-mg tablets of generic colchicine cost as little as $1.90 each with free coupons, according to goodrx.com.)
The median age in the groups was similar (55 years); and the placebo group had more women (61% vs. 47% in the colchicine group, P = .34). All 72 patients received the same COVID-19 treatment at the time of the trial: azithromycin, hydroxychloroquine, and unfractionated heparin. Most patients, about two-thirds in both groups, also received methylprednisolone because they needed higher amounts of supplemental oxygen.
Patients in the colchicine group needed supplemental oxygen for less time: Their median time of need was 4.0 days (interquartile range [IQR], 2.0-6.0) vs. 6.5 days (IQR, 4.0-9.0) for the placebo group (P < .001). The median time for hospitalization was also lower at 7.0 days (IQR, 5.0–9.0) for the colchicine group vs. 9.0 (IQR, 7.0–12.0) for the placebo group (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001).
The researchers also reported the percentage of patients who needed supplemental oxygen at day 2 as 67% with colchicine vs. 86% with placebo, and at day 7 as 9% vs. 42% (log rank test, 10.6; P = .001). Two patients in the placebo group died, both from ventilator-associated pneumonia.
As for side effects, new or worsened diarrhea was reported more often in the colchicine group (17% vs. 6% with placebo), but the difference was not statistically significant (P = .26), and diarrhea was controlled via medication.
The researchers reported that limitations include the exclusion criteria and their inability to link colchicine to rates of ICU admissions and death.
The drug appears to help patients with COVID-19, the study authors wrote, by “inhibiting inflammasome, reducing neutrophil migration and activation, or preventing endothelial damage.”
A “well-conceived and well-designed” study
In an interview, NYU Langone Health rheumatologist Michael H. Pillinger, MD – an investigator with the ColCORONA trial – praised the Brazilian study. It “appears well-conceived and well-designed, and was enrolled at a rate that was greater than the sample size that was estimated to be needed based on power analysis,” he said.
The Brazilian study is small, he noted. (In contrast, the ColCORONA trial had 4,488 outpatient participants.) “This study differs from ColCORONA in several ways – the most important being that it is a study of inpatients with moderate to severe COVID (really mostly moderate),” he added. “ColCORONA is looking at a target audience that is much larger – outpatients with mild to moderate COVID with risk factors for hospitalization. Both questions are really important and certainly not mutually exclusive, since our care remains inadequate in both venues. This study also adds value in that several other studies have been conducted in hospital patients with enrollment criteria relatively similar to this one, and all showed benefit, but those were open-label or retrospective, and this is blinded and placebo-controlled.”
Using colchicine in patients with COVID-19
Should physicians turn to colchicine in patients with COVID-19? “I would rather that it still be used in the context of research until formal recommendations can be made by bodies like the NIH and CDC,” Dr. Pillinger said. “But certainly, there may be times when physicians feel compelled to treat patients off label.”
He cautioned, however, that colchicine should never be used with some other drugs. Its interaction with the antibiotic clarithromycin can be fatal, he noted. And, he said, the drug must be monitored in general since it can cause rare, severe problems.
“Overall, colchicine probably works on the overabundant inflammatory response to COVID, and it may be that it can be combined with other drugs that affect viral replication or promote immunity – e.g. vaccines,” Dr. Pillinger said. “So far, it seems as if there is no safety problem with combining colchicine with other approaches, but this has not been studied in a rigorous manner.”
Moving forward, he said, the drug’s very low price outside of the United States “could provide resource-poor countries with a way to help keep patients out of precious hospital beds – or help them go home sooner once admitted.” For now, however, “we need a large-scale inpatient study, and one is currently going on in Great Britain. We also need validation of the outpatient ColCORONA study, and studies to look at whether colchicine can work in conjunction with other strategies.”
The study was funded by grants from the São Paulo Research Foundation, Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, and CAPES Foundation. No disclosures are reported. Dr. Pillinger reports serving as an investigator for the ColCORONA trial and receiving a unrelated investigator-initiated grant from Hikma, a colchicine manufacturer.
FROM RMD OPEN