User login
Modern surgical techniques for gastrointestinal endometriosis
About 10% of all reproductive-aged women and 35% to 50% of women with pelvic pain and infertility are affected by endometriosis.1,2 The disease typically involves the reproductive tract organs, anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and uterosacral ligaments. However, disease outside of the reproductive tract occurs frequently and has been found on all organs except the spleen.3
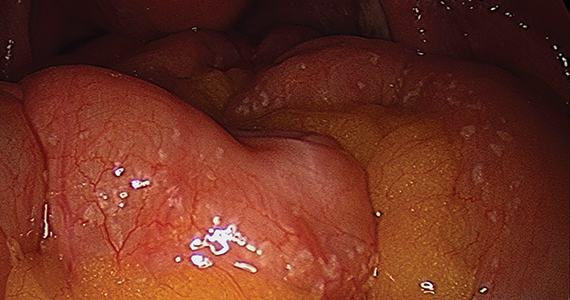
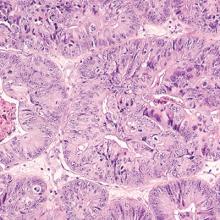
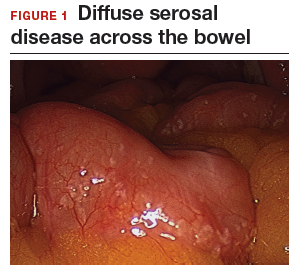
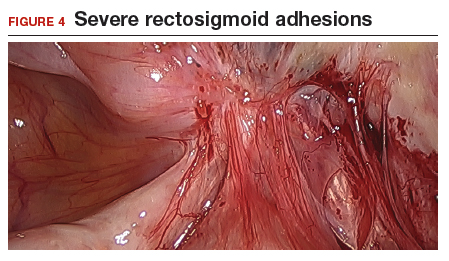
The bowel is the most common site for extragenital endometriosis, affected in an estimated 3.8% to 37% of patients with known endometriosis.4-7 Implants may be superficial, involving the bowel serosa and subserosa (FIGURE 1), or they can manifest as deeply infiltrating lesions involving the muscularis and mucosa (FIGURE 2). The rectosigmoid colon is the most common location for bowel endometriosis, followed by the rectum, ileum, appendix, and cecum4,8 (FIGURES 3, 4, and 5). Case reports also have described endometrial implants on the stomach and transverse colon.9 Although isolated bowel involvement has been recognized, most patients with bowel endometriosis have concurrent disease elsewhere.2,4
Historically, segmental resection was performed regardless of the anatomical location of the lesion.10 Even today, many surgeons continue to routinely perform segmental bowel resection as a first-line surgical approach.11 Unnecessary segmental resection, however, places patients at risk for short- and long-term postoperative morbidity, including the possibility of permanent ostomy. Modern surgical techniques, such as shaving excision and disc resection, have been performed to successfully treat bowel endometriosis with excellent long-term outcomes and fewer complications when compared with traditional segmental resection.2,12-16
In this article, we focus on the clinical indications and surgical techniques for video-laparoscopic management, but first we describe the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis of bowel endometriosis.


Pathophysiology of bowel endometriosis
The pathogenesis of endometriosis remains unknown, as no single mechanism explains all clinical cases of the disease. The most popular proposed theory describes retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes.17 Once inside the peritoneal cavity, endometrial cells attach to and invade healthy peritoneum, establishing a blood supply necessary for growth and survival.
In the case of bowel endometriosis, deposition of effluxed endometrial cells may lead to an inflammatory response that increases the risk of adhesion formation, leading to potential cul-de-sac obliteration. Lesions may originate as Allen-Masters peritoneal defects, developing into deeply infiltrative rectovaginal septum lesions. The anatomical shelter theory contributes to lesions within the pelvis, with the rectosigmoid colon blocking the cephalad flow of effluxed menstrual blood from the pelvis, thus leading to a preponderance of lesions in the pelvis and along the rectosigmoid colon.2
Continue to: Clinical presentation and diagnosis...
Clinical presentation and diagnosis
Women presenting with endometriosis of the bowel are typically of reproductive age and commonly report symptoms of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, and dyschezia. Some women also experience catamenial diarrhea, constipation, hematochezia, and bloating.2 The differential diagnosis of these symptoms is broad and includes irritable bowel disease, ischemic colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and malignancy.
Because of its nonspecific symptoms, bowel endometriosis is often misdiagnosed and the disease goes untreated for years.18 Therefore, it is imperative that clinicians maintain a high index of suspicion when evaluating reproductive-aged women with gastrointestinal symptoms and pelvic pain.
Physical examination can be helpful in making the diagnosis of endometriosis. During bimanual examination, findings such as a fixed, tender, or retroverted uterus, uterosacral ligament nodularity, or an enlarged adnexal mass representing an ovarian endometrioma may be appreciated. Rectovaginal exam can identify areas of tenderness and nodularity along the rectovaginal septum. Speculum exam may reveal a laterally displaced cervix or blue powder-burn lesions along the cervix or posterior fornix.19 Rarely, endometriosis is found on the perineum within an episiotomy scar.20
Imaging studies can be used in conjunction with physical examination findings to aid in the diagnosis of endometriosis. Images also guide preoperative planning by characterizing lesions based on their size, location, and depth of invasion. Hudelist and colleagues found transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to have an overall sensitivity of 71% to 98% and a specificity of 92% to 100%.21 However, it was noted that the accuracy of the diagnosis was directly related to the experience of the sonographer, and lesions above the sigmoid colon were generally unable to be diagnosed. Other imaging modalities that have been reported to have high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing bowel endometriosis include rectal water contrast TVUS,22,23 rectal endoscopic sonography,22 magnetic resonance imaging,22 and barium enema.24
Medical management
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis is utilized with the goal of suppressing ovulation, lowering circulating hormone levels, and inducing endometrial atrophy. Medications commonly employed include gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists, anabolic steriods such as danazol, combined oral contraceptive pills, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Continue to: To date, no optimal hormonal regimen...
To date, no optimal hormonal regimen has been established for the treatment of bowel endometriosis. Vercellini and colleagues demonstrated that progestins with and without low-dose estrogen improved symptoms of dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia.25 Ferrero and colleagues reported that 2.5 mg of norethindrone daily resulted in 53% of women with colorectal endometriosis reporting improved gastrointestinal symptoms.26 However, by 12 months of follow-up, 33% of these patients had elected to undergo surgical management.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, such as leuprolide acetate, also can be used to mitigate symptoms of bowel endometriosis or to decrease disease burden at the time of surgery, and they can be used with add-back norethindrone acetate. The use of these medications is limited by adverse effects, such as vasomotor symptoms and decreased bone mineral density when used for longer than 6 months.2
Medical therapy is commonly used for patients with mild to moderate symptoms and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgical intervention. Medical therapy is especially useful when employed postoperatively to suppress the regrowth of microscopic ectopic endometrial tissue.
Patients must be counseled, however, that even with medical management, they may still require surgery in the future to control their symptoms and/or to preserve organ function.2
Surgical management
Surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis depends on the disease location, the size and depth of the lesion, the presence or absence of stricture, and the surgeon’s level of expertise.2,12,27-30
In our group, we advocate for video-laparoscopy, with or without robotic as sistance. Minimally invasive surgery offers reduced blood loss, shorter recovery time, and fewer postoperative complications compared with laparotomy.2,16,27,31-33 The conversion rate to laparotomy has been reported to be about 3% when performed by an experienced surgeon.12
Darai and colleagues conducted a randomized trial of 52 patients undergoing surgery for colorectal endometriosis via either laparoscopic or open colon resection.33 Blood loss was significantly lower in the laparoscopy group (1.6 vs 2.7 mg/L, P <.05). No difference was noted in long-term outcomes. In a retrospective study of 436 cases, Ruffo and colleagues showed that those who underwent laparoscopic colorectal resection had higher postoperative pregnancy rates compared with those who had laparotomy (57.6% vs 23.1%, P <.035).32
The goal of surgical management of bowel endometriosis is to remove as many of the endometriotic lesions as possible while minimizing short- and long-term complications. Three surgical approaches have been described: shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection.2
Some surgeons prefer traditional segmental resection of the bowel regardless of the anatomical site, citing reduced disease recurrence with this approach; however, traditional segmental resection confers increased risk of complications. Increasingly, in an effort to reduce morbidity, more surgeons are advocating for the less aggressive methods of shaving excision and disc resection.
Aggressive resection at the level of the low rectum requires extensive surgical dissection of the retrorectal space, with the potential for inadvertent injury to surrounding neurovascular structures, such as the pelvic splanchnic nerves and superior and inferior hypogastric plexus.29 Injury to these structures can lead to significant complications, including bowel stenosis, fistula formation, constipation, and urinary retention. Complete resection of other areas, such as the small bowel, do not carry the same risks and may have more significant benefit to the patient than less aggressive techniques.
Our group recommends carefully balancing the risks and benefits of aggressive surgical treatment for each individual and treating the patient with the appropriate technique. Regardless of technique, surgical treatment of bowel endometriosis can lead to long-term improvements in pain and infertility.29,30,34,35
- The clinical presentation of bowel endometriosis is often nonspecific, with a broad differential diagnosis. Maintain a high index of suspicion when reproductive-aged women present for evaluation of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, bloating, dyschezia, or hematochezia.
- Symptomatic patients not desiring fertility, poor surgical candidates, and those declining surgical intervention may benefit from medical management. Patients who fail medical therapy, have severe symptoms, or experience infertility are candidates for surgical intervention.
- Surgical management involves shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection. Some surgeons advocate for aggressive segmental resection regardless of the endometriotic lesion's location. Based on our extensive experience, we prefer shaving excision for lesions below the sigmoid to avoid dissection into the retrorectal space and inadvertent injury to nerve tissue controlling bowel and bladder function.
- Following shaving excision, patients experience low complication rates29,39,40 and favorable long-term outcomes.15,40,56 For lesions above the sigmoid colon, including the small bowel, segmental resection or disc resection for smaller lesions are reasonable surgical approaches.
Continue to: Shaving excision...
Shaving excision
The most conservative approach to resection of bowel endometriosis is shaving excision; this involves removing endometriotic tissue layer-by-layer until healthy, underlying tissue is encountered.2 With bowel endometriosis, the goal of shaving excision is to remove as much of the diseased tissue as possible while leaving behind the mucosal layer and a portion of the muscularis.2,15,16,36-38 This is the most conservative of the 3 surgical techniques and is associated with the lowest complication rate.2,14,15,36,37
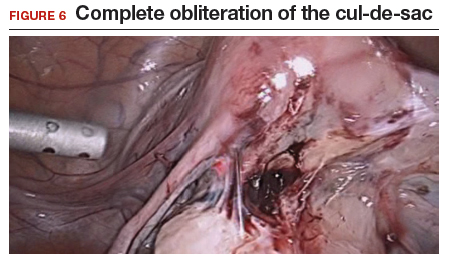
Our group reported on 185 women who underwent shaving excision for bowel endometriosis. At the time of surgery, 80 women had complete obliteration of the cul-de-sac (FIGURE 6). Of the study patients, 174 patients were available for follow-up, with 93% reporting moderate to complete pain relief.15
In a retrospective analysis of 3,298 surgeries for rectovaginal endometriosis in which shaving excision was used on all but 1% of patients, Donnez and colleagues reported a very low complication rate, with 1 case of rectal perforation, 1 case of fecal peritonitis, and 3 cases of ureteral injury.39
Roman and colleagues described the use of shaving excision for rectal endometriosis using plasma energy (n = 54) and laparoscopic scissors (n = 68).40 Only 4% of patients reported experiencing symptom recurrence, and the pregnancy rate was 65.4%, with 59% of those patients spontaneously conceiving. Two cases of rectal fistula were noted.
Disc resection
Laparoscopic disc excision has been described in the literature since the 1980s, and the technique involves the full-thickness removal of the diseased portion of the bowel, followed by closure of the remaining defect.2,12-14,28,29,31,41-45 To be appropriate for this technique, a lesion should involve only a portion of the bowel wall and, preferably, less than one-half of the bowel circumference.2,42 Disc excision results in excellent outcomes with fewer postoperative complications than segmental resection, but with more complications when compared to shaving excision.2,12,13,29,45,46
We reported on a series of 141 women with bowel endometriosis who underwent disc excision.2 At 1-month follow-up, 87% of patients experienced an improvement in their symptoms. No cases required conversion to laparotomy or were complicated by rectovaginal fistula formation, ureteral injury, bowel perforation, or pelvic abscess.2
Continue to: Segmental resection...
Segmental resection
The most aggressive surgical approach, segmental resection involves complete removal of a diseased portion of bowel, followed by side-to-side or end-to-end reanastomosis of the adjacent segments.2 For this procedure, a multidisciplinary approach is recommended, with involvement of a colorectal surgeon or gynecologic oncologist trained in performing bowel resections. Segmental resection is indicated for lesions that are larger than 3 cm, circumferential, obstructive, or multifocal.
Given the higher complication rate associated with this procedure and the good outcomes associated with less invasive techniques, we avoid segmental resection whenever possible, especially for lesions near the anal verge.2
Complications associated with surgical approach
In 2005, our group reported on a cohort of 178 women who underwent laparoscopic treatment of deeply infiltrative bowel endometriosis with shaving excision (n = 93), disc excision (n = 38), and segmental resection (n = 47).34 The major complication rate was significantly higher for those undergoing segmental resection (12.5%, P <.001); only 7.7% of those who underwent disc resection experienced a major complication; and none were observed in the group treated with shaving excision.
In 2011, De Cicco and colleagues conducted a systematic review of 1,889 patients who underwent segmental bowel resection.35 The major complication rate was 11%, with a leakage rate of 2.7%, fistula rate of 1.8%, major obstruction rate of 2.7%, and hemorrhage rate of 2.5%. Many of these complications, however, occurred in patients who had low rectal resections.
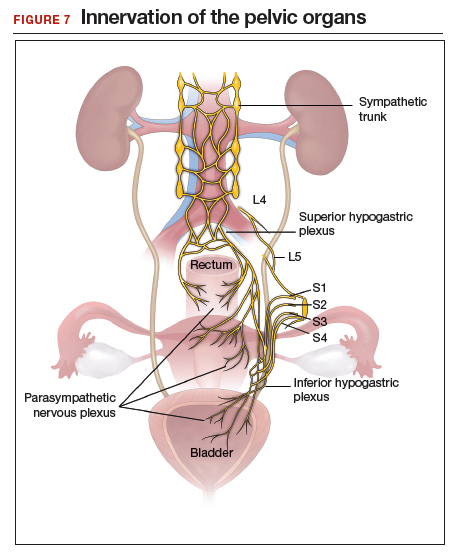
Regardless of surgical approach, the complication rate is related to the surgeon’s ability to preserve the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses and the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve bundles (FIGURE 7). Nerve-sparing techniques should be used to decrease the incidence of postoperative bowel, bladder, and sexual function complications.2
Our group’s preferences
In our practice, we emphasize that the choice of surgical technique depends on the location, size, and depth of the lesion, as well as the extent of bowel wall circumferential invasion.2
We categorize lesions by their anatomic location: those above the sigmoid colon, on the sigmoid colon, on the rectosigmoid colon, and on the rectum. For lesions above the sigmoid colon, segmental or disc resection is appropriate.2 We recommend segmental resection for multifocal lesions, lesions larger than 3 cm, or for lesions involving more than one-third of the bowel lumen.37,44,45,47 Disc resection is appropriate for lesions smaller than 3 cm even if the bowel lumen is involved.44,45,48 If endometriosis is encountered in any location along the bowel, appendectomy can be performed even without visible disease, due to a high incidence of occult disease of the appendix.49,50
When lesions involve the sigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible to limit dissection of the retrorectal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.2 Segmental resection at or below the sigmoid colon has been associated with postoperative surgical site leakage51 and long-term bowel and bladder dysfunction with risk of permanent colostomy.52,53 For lesions smaller than 3 cm or involving less than one-third of the bowel lumen, disc resection can be performed. Segmental resection is required if multifocal disease or obstruction are present, if lesions are larger than 3 cm, or if more than one-third of the bowel lumen is involved.
For lesions along the rectosigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible.2 Disc excision can be performed utilizing a transanal approach, being mindful to minimize dissection of the retroperitoneal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.48 Segmental resection is avoided even with lesions larger than 3 cm, unless prior surgery has failed. Approaches for segmental resection can utilize laparoscopy or the natural orifices of the rectum or vagina.31,51
For lesions on the rectum, we strongly advise shaving excision.2 Evidence fails to show that the benefits of segmental resection outweigh the risks when compared to conservative techniques at the rectum.30,39,54 There is evidence indicating that aggressive surgery 5 to 8 cm from the anal verge is predictive of postoperative complications.55 In our group, we use shaving excision to remove as much disease as possible without compromising the integrity of the bowel wall or surrounding neurovascular structures. We err on the side of caution, leaving some of the disease on the rectum to avoid rectal perforation, and plan for postoperative hormonal suppression in these patients.
For patients desiring fertility, successful pregnancy is often achieved using the shaving technique.41
- Giudice LC. Clinical practice. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2389-2398.
- Nezhat C, Li A, Falik R, et al. Bowel endometriosis: diagnosis and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:549-562.
- Markham SM, Carpenter SE, Rock JA. Extrapelvic endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1989;16:193-219.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Redwine DB. Ovarian endometriosis: a marker for more extensive pelvic and intestinal disease. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:310-315.
- Weed JC, Ray JE. Endometriosis of the bowel. Obstet Gynecol. 1987;69:727-730.
- Wheeler JM. Epidemiology of endometriosis-associated infertility. J Reprod Med. 1989;34:41-46.
- Redwine DB. Intestinal endometriosis. In: Redwine DB. Surgical Management of Endometriosis. New York, NY: Martin Dunitz; 2004:196.
- Hartmann D, Schilling D, Roth SU, et al. [Endometriosis of the transverse colon--a rare localization]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2002;127:2317-2320.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Macafee CH, Greer HL. Intestinal endometriosis. A report of 29 cases and a survey of the literature. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1960;67:539-555.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Ambroze W, et al. Laparoscopic repair of small bowel and colon. A report of 26 cases. Surg Endosc. 1993;7:88-89.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E, et al. Laparoscopic disk excision and primary repair of the anterior rectal wall for the treatment of full-thickness bowel endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1994;8:682-685.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Evaluation of safety of videolaseroscopic treatment of bowel endometriosis. Presented at: 44th Annual Meeting of the American Fertility Society; October, 1988; Atlanta, GA.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E. Laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative rectosigmoid colon and rectovaginal septum endometriosis by the technique of videolaparoscopy and the CO2 laser. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992;99:664-667.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Skoog SM, Foxx-Orenstein AE, Levy MJ, et al. Intestinal endometriosis: the great masquerader. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:405-409.
- Alabiso G, Alio L, Arena S, et al. How to manage bowel endometriosis: the ETIC approach. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:517-529.
- Heller DS, Lespinasse P, Mirani N. Endometriosis of the perineum: a rare diagnosis usually associated with episiotomy. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:e48-e49.
- Hudelist G, English J, Thomas AE, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound for non-invasive diagnosis of bowel endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:257-263.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Menada MV, Remorgida V, Abbamonte LH, et al. Transvaginal ultrasonography combined with water-contrast in the rectum in the diagnosis of rectovaginal endometriosis infiltrating the bowel. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:699-700.
- Gordon RL, Evers K, Kressel HY, et al. Double-contrast enema in pelvic endometriosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;138:549-552.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, et al. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84:1375-1387.
- Ferrero S, Camerini G, Ragni N, et al. Norethisterone acetate in the treatment of colorectal endometriosis: a pilot study. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:94-100.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Laparoscopic management of bowel endometriosis: predictors of severe disease and recurrence. JSLS. 2011;15:431-438.
- Roman H, Milles M, Vassilieff M, et al. Long-term functional outcomes following colorectal resection versus shaving for rectal endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:762.e1-762.e9.
- Kent A, Shakir F, Rockall T, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for severe rectovaginal endometriosis compromising the bowel: a prospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:526-534.
- Nezhat F, Nezhat C, Pennington E. Laparoscopic proctectomy for infiltrating endometriosis of the rectum. Fertil Steril. 1992;57:1129-1132.
- Ruffo G, Scopelliti F, Scioscia M, et al. Laparoscopic colorectal resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: analysis of 436 cases. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:63-67.
- Darai E, Dubernard G, Coutant C, et al. Randomized trial of laparoscopically assisted versus open colorectal resection for endometriosis: morbidity, symptoms, quality of life, and fertility. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1018-1023.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- De Cicco C, Corona R, Schonman R, et al. Bowel resection for deep endometriosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2011;118:285-291.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Donnez J, Squifflet J. Complications, pregnancy and recurrence in a prospective series of 500 patients operated on by the shaving technique for deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:1949-1958.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy and videolaseroscopy. Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 1987;16:303-312.
- Donnez J, Jadoul P, Colette S, et al. Deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules: perioperative complications from a series of 3,298 patients operated on by the shaving technique. Gynecol Surg. 2013;10:31-40.
- Roman H, Moatassim-Drissa S, Marty N, et al. Rectal shaving for deep endometriosis infiltrating the rectum: a 5-year continuous retrospective series. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:1438-1445.e2.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- Jerby BL, Kessler H, Falcone T, et al. Laparoscopic management of colorectal endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1999;13:1125-1128.
- Coronado C, Franklin RR, Lotze EC, et al. Surgical treatment of symptomatic colorectal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1990;53:411-416.
- Fanfani F, Fagotti A, Gagliardi ML, et al. Discoid or segmental rectosigmoid resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: a case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:444-449.
- Landi S, Pontrelli G, Surico D, et al. Laparoscopic disk resection for bowel endometriosis using a circular stapler and a new endoscopic method to control postoperative bleeding from the stapler line. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:205-209.
- Slack A, Child T, Lindsey I, et al. Urological and colorectal complications following surgery for rectovaginal endometriosis. BJOG. 2007;114:1278-1282.
- Ceccaroni M, Clarizia R, Bruni F, et al. Nerve-sparing laparoscopic eradication of deep endometriosis with segmental rectal and parametrial resection: the Negrar method. A single-center, prospective, clinical trial. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:2029-2045.
- Roman H, Abo C, Huet E, et al. Deep shaving and transanal disc excision in large endometriosis of mid and lower rectum: the Rouen technique. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:2626-2627.
- Gustofson RL, Kim N, Liu S, et al. Endometriosis and the appendix: a case series and comprehensive review of the literature. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:298-303.
- Berker B, Lashay N, Davarpanah R, et al. Laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2005;12:206-209.
- Ret Dávalos ML, De Cicco C, D'Hoore A, et al. Outcome after rectum or sigmoid resection: a review for gynecologists. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2007;14:33-38.
- Alves A, Panis Y, Mathieu P, et al; Association Française de Chirurgie (AFC). Mortality and morbidity after surgery of mid and low rectal cancer. Results of a French prospective multicentric study. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005;29:509-514.
- Camilleri-Brennan J, Steele RJ. Objective assessment of morbidity and quality of life after surgery for low rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2002;4:61-66.
- Acien P, Núñez C, Quereda F, et al. Is a bowel resection necessary for deep endometriosis with rectovaginal or colorectal involvement? Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:449-455.
- Abrão MS, Petraglia F, Falcone T, et al. Deep endometriosis infiltrating the recto-sigmoid: critical factors to consider before management. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21:329-339.
- Donnez J, Nisolle M, Gillerot S, et al. Rectovaginal septum adenomyotic nodules: a series of 500 cases. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:1014-1018.
About 10% of all reproductive-aged women and 35% to 50% of women with pelvic pain and infertility are affected by endometriosis.1,2 The disease typically involves the reproductive tract organs, anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and uterosacral ligaments. However, disease outside of the reproductive tract occurs frequently and has been found on all organs except the spleen.3
The bowel is the most common site for extragenital endometriosis, affected in an estimated 3.8% to 37% of patients with known endometriosis.4-7 Implants may be superficial, involving the bowel serosa and subserosa (FIGURE 1), or they can manifest as deeply infiltrating lesions involving the muscularis and mucosa (FIGURE 2). The rectosigmoid colon is the most common location for bowel endometriosis, followed by the rectum, ileum, appendix, and cecum4,8 (FIGURES 3, 4, and 5). Case reports also have described endometrial implants on the stomach and transverse colon.9 Although isolated bowel involvement has been recognized, most patients with bowel endometriosis have concurrent disease elsewhere.2,4
Historically, segmental resection was performed regardless of the anatomical location of the lesion.10 Even today, many surgeons continue to routinely perform segmental bowel resection as a first-line surgical approach.11 Unnecessary segmental resection, however, places patients at risk for short- and long-term postoperative morbidity, including the possibility of permanent ostomy. Modern surgical techniques, such as shaving excision and disc resection, have been performed to successfully treat bowel endometriosis with excellent long-term outcomes and fewer complications when compared with traditional segmental resection.2,12-16
In this article, we focus on the clinical indications and surgical techniques for video-laparoscopic management, but first we describe the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis of bowel endometriosis.





Pathophysiology of bowel endometriosis
The pathogenesis of endometriosis remains unknown, as no single mechanism explains all clinical cases of the disease. The most popular proposed theory describes retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes.17 Once inside the peritoneal cavity, endometrial cells attach to and invade healthy peritoneum, establishing a blood supply necessary for growth and survival.
In the case of bowel endometriosis, deposition of effluxed endometrial cells may lead to an inflammatory response that increases the risk of adhesion formation, leading to potential cul-de-sac obliteration. Lesions may originate as Allen-Masters peritoneal defects, developing into deeply infiltrative rectovaginal septum lesions. The anatomical shelter theory contributes to lesions within the pelvis, with the rectosigmoid colon blocking the cephalad flow of effluxed menstrual blood from the pelvis, thus leading to a preponderance of lesions in the pelvis and along the rectosigmoid colon.2
Continue to: Clinical presentation and diagnosis...
Clinical presentation and diagnosis
Women presenting with endometriosis of the bowel are typically of reproductive age and commonly report symptoms of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, and dyschezia. Some women also experience catamenial diarrhea, constipation, hematochezia, and bloating.2 The differential diagnosis of these symptoms is broad and includes irritable bowel disease, ischemic colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and malignancy.
Because of its nonspecific symptoms, bowel endometriosis is often misdiagnosed and the disease goes untreated for years.18 Therefore, it is imperative that clinicians maintain a high index of suspicion when evaluating reproductive-aged women with gastrointestinal symptoms and pelvic pain.
Physical examination can be helpful in making the diagnosis of endometriosis. During bimanual examination, findings such as a fixed, tender, or retroverted uterus, uterosacral ligament nodularity, or an enlarged adnexal mass representing an ovarian endometrioma may be appreciated. Rectovaginal exam can identify areas of tenderness and nodularity along the rectovaginal septum. Speculum exam may reveal a laterally displaced cervix or blue powder-burn lesions along the cervix or posterior fornix.19 Rarely, endometriosis is found on the perineum within an episiotomy scar.20
Imaging studies can be used in conjunction with physical examination findings to aid in the diagnosis of endometriosis. Images also guide preoperative planning by characterizing lesions based on their size, location, and depth of invasion. Hudelist and colleagues found transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to have an overall sensitivity of 71% to 98% and a specificity of 92% to 100%.21 However, it was noted that the accuracy of the diagnosis was directly related to the experience of the sonographer, and lesions above the sigmoid colon were generally unable to be diagnosed. Other imaging modalities that have been reported to have high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing bowel endometriosis include rectal water contrast TVUS,22,23 rectal endoscopic sonography,22 magnetic resonance imaging,22 and barium enema.24
Medical management
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis is utilized with the goal of suppressing ovulation, lowering circulating hormone levels, and inducing endometrial atrophy. Medications commonly employed include gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists, anabolic steriods such as danazol, combined oral contraceptive pills, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Continue to: To date, no optimal hormonal regimen...
To date, no optimal hormonal regimen has been established for the treatment of bowel endometriosis. Vercellini and colleagues demonstrated that progestins with and without low-dose estrogen improved symptoms of dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia.25 Ferrero and colleagues reported that 2.5 mg of norethindrone daily resulted in 53% of women with colorectal endometriosis reporting improved gastrointestinal symptoms.26 However, by 12 months of follow-up, 33% of these patients had elected to undergo surgical management.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, such as leuprolide acetate, also can be used to mitigate symptoms of bowel endometriosis or to decrease disease burden at the time of surgery, and they can be used with add-back norethindrone acetate. The use of these medications is limited by adverse effects, such as vasomotor symptoms and decreased bone mineral density when used for longer than 6 months.2
Medical therapy is commonly used for patients with mild to moderate symptoms and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgical intervention. Medical therapy is especially useful when employed postoperatively to suppress the regrowth of microscopic ectopic endometrial tissue.
Patients must be counseled, however, that even with medical management, they may still require surgery in the future to control their symptoms and/or to preserve organ function.2
Surgical management
Surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis depends on the disease location, the size and depth of the lesion, the presence or absence of stricture, and the surgeon’s level of expertise.2,12,27-30
In our group, we advocate for video-laparoscopy, with or without robotic as sistance. Minimally invasive surgery offers reduced blood loss, shorter recovery time, and fewer postoperative complications compared with laparotomy.2,16,27,31-33 The conversion rate to laparotomy has been reported to be about 3% when performed by an experienced surgeon.12
Darai and colleagues conducted a randomized trial of 52 patients undergoing surgery for colorectal endometriosis via either laparoscopic or open colon resection.33 Blood loss was significantly lower in the laparoscopy group (1.6 vs 2.7 mg/L, P <.05). No difference was noted in long-term outcomes. In a retrospective study of 436 cases, Ruffo and colleagues showed that those who underwent laparoscopic colorectal resection had higher postoperative pregnancy rates compared with those who had laparotomy (57.6% vs 23.1%, P <.035).32
The goal of surgical management of bowel endometriosis is to remove as many of the endometriotic lesions as possible while minimizing short- and long-term complications. Three surgical approaches have been described: shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection.2
Some surgeons prefer traditional segmental resection of the bowel regardless of the anatomical site, citing reduced disease recurrence with this approach; however, traditional segmental resection confers increased risk of complications. Increasingly, in an effort to reduce morbidity, more surgeons are advocating for the less aggressive methods of shaving excision and disc resection.
Aggressive resection at the level of the low rectum requires extensive surgical dissection of the retrorectal space, with the potential for inadvertent injury to surrounding neurovascular structures, such as the pelvic splanchnic nerves and superior and inferior hypogastric plexus.29 Injury to these structures can lead to significant complications, including bowel stenosis, fistula formation, constipation, and urinary retention. Complete resection of other areas, such as the small bowel, do not carry the same risks and may have more significant benefit to the patient than less aggressive techniques.
Our group recommends carefully balancing the risks and benefits of aggressive surgical treatment for each individual and treating the patient with the appropriate technique. Regardless of technique, surgical treatment of bowel endometriosis can lead to long-term improvements in pain and infertility.29,30,34,35
- The clinical presentation of bowel endometriosis is often nonspecific, with a broad differential diagnosis. Maintain a high index of suspicion when reproductive-aged women present for evaluation of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, bloating, dyschezia, or hematochezia.
- Symptomatic patients not desiring fertility, poor surgical candidates, and those declining surgical intervention may benefit from medical management. Patients who fail medical therapy, have severe symptoms, or experience infertility are candidates for surgical intervention.
- Surgical management involves shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection. Some surgeons advocate for aggressive segmental resection regardless of the endometriotic lesion's location. Based on our extensive experience, we prefer shaving excision for lesions below the sigmoid to avoid dissection into the retrorectal space and inadvertent injury to nerve tissue controlling bowel and bladder function.
- Following shaving excision, patients experience low complication rates29,39,40 and favorable long-term outcomes.15,40,56 For lesions above the sigmoid colon, including the small bowel, segmental resection or disc resection for smaller lesions are reasonable surgical approaches.
Continue to: Shaving excision...
Shaving excision
The most conservative approach to resection of bowel endometriosis is shaving excision; this involves removing endometriotic tissue layer-by-layer until healthy, underlying tissue is encountered.2 With bowel endometriosis, the goal of shaving excision is to remove as much of the diseased tissue as possible while leaving behind the mucosal layer and a portion of the muscularis.2,15,16,36-38 This is the most conservative of the 3 surgical techniques and is associated with the lowest complication rate.2,14,15,36,37
Our group reported on 185 women who underwent shaving excision for bowel endometriosis. At the time of surgery, 80 women had complete obliteration of the cul-de-sac (FIGURE 6). Of the study patients, 174 patients were available for follow-up, with 93% reporting moderate to complete pain relief.15
In a retrospective analysis of 3,298 surgeries for rectovaginal endometriosis in which shaving excision was used on all but 1% of patients, Donnez and colleagues reported a very low complication rate, with 1 case of rectal perforation, 1 case of fecal peritonitis, and 3 cases of ureteral injury.39
Roman and colleagues described the use of shaving excision for rectal endometriosis using plasma energy (n = 54) and laparoscopic scissors (n = 68).40 Only 4% of patients reported experiencing symptom recurrence, and the pregnancy rate was 65.4%, with 59% of those patients spontaneously conceiving. Two cases of rectal fistula were noted.

Disc resection
Laparoscopic disc excision has been described in the literature since the 1980s, and the technique involves the full-thickness removal of the diseased portion of the bowel, followed by closure of the remaining defect.2,12-14,28,29,31,41-45 To be appropriate for this technique, a lesion should involve only a portion of the bowel wall and, preferably, less than one-half of the bowel circumference.2,42 Disc excision results in excellent outcomes with fewer postoperative complications than segmental resection, but with more complications when compared to shaving excision.2,12,13,29,45,46
We reported on a series of 141 women with bowel endometriosis who underwent disc excision.2 At 1-month follow-up, 87% of patients experienced an improvement in their symptoms. No cases required conversion to laparotomy or were complicated by rectovaginal fistula formation, ureteral injury, bowel perforation, or pelvic abscess.2
Continue to: Segmental resection...
Segmental resection
The most aggressive surgical approach, segmental resection involves complete removal of a diseased portion of bowel, followed by side-to-side or end-to-end reanastomosis of the adjacent segments.2 For this procedure, a multidisciplinary approach is recommended, with involvement of a colorectal surgeon or gynecologic oncologist trained in performing bowel resections. Segmental resection is indicated for lesions that are larger than 3 cm, circumferential, obstructive, or multifocal.
Given the higher complication rate associated with this procedure and the good outcomes associated with less invasive techniques, we avoid segmental resection whenever possible, especially for lesions near the anal verge.2
Complications associated with surgical approach
In 2005, our group reported on a cohort of 178 women who underwent laparoscopic treatment of deeply infiltrative bowel endometriosis with shaving excision (n = 93), disc excision (n = 38), and segmental resection (n = 47).34 The major complication rate was significantly higher for those undergoing segmental resection (12.5%, P <.001); only 7.7% of those who underwent disc resection experienced a major complication; and none were observed in the group treated with shaving excision.
In 2011, De Cicco and colleagues conducted a systematic review of 1,889 patients who underwent segmental bowel resection.35 The major complication rate was 11%, with a leakage rate of 2.7%, fistula rate of 1.8%, major obstruction rate of 2.7%, and hemorrhage rate of 2.5%. Many of these complications, however, occurred in patients who had low rectal resections.
Regardless of surgical approach, the complication rate is related to the surgeon’s ability to preserve the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses and the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve bundles (FIGURE 7). Nerve-sparing techniques should be used to decrease the incidence of postoperative bowel, bladder, and sexual function complications.2

Our group’s preferences
In our practice, we emphasize that the choice of surgical technique depends on the location, size, and depth of the lesion, as well as the extent of bowel wall circumferential invasion.2
We categorize lesions by their anatomic location: those above the sigmoid colon, on the sigmoid colon, on the rectosigmoid colon, and on the rectum. For lesions above the sigmoid colon, segmental or disc resection is appropriate.2 We recommend segmental resection for multifocal lesions, lesions larger than 3 cm, or for lesions involving more than one-third of the bowel lumen.37,44,45,47 Disc resection is appropriate for lesions smaller than 3 cm even if the bowel lumen is involved.44,45,48 If endometriosis is encountered in any location along the bowel, appendectomy can be performed even without visible disease, due to a high incidence of occult disease of the appendix.49,50
When lesions involve the sigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible to limit dissection of the retrorectal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.2 Segmental resection at or below the sigmoid colon has been associated with postoperative surgical site leakage51 and long-term bowel and bladder dysfunction with risk of permanent colostomy.52,53 For lesions smaller than 3 cm or involving less than one-third of the bowel lumen, disc resection can be performed. Segmental resection is required if multifocal disease or obstruction are present, if lesions are larger than 3 cm, or if more than one-third of the bowel lumen is involved.
For lesions along the rectosigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible.2 Disc excision can be performed utilizing a transanal approach, being mindful to minimize dissection of the retroperitoneal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.48 Segmental resection is avoided even with lesions larger than 3 cm, unless prior surgery has failed. Approaches for segmental resection can utilize laparoscopy or the natural orifices of the rectum or vagina.31,51
For lesions on the rectum, we strongly advise shaving excision.2 Evidence fails to show that the benefits of segmental resection outweigh the risks when compared to conservative techniques at the rectum.30,39,54 There is evidence indicating that aggressive surgery 5 to 8 cm from the anal verge is predictive of postoperative complications.55 In our group, we use shaving excision to remove as much disease as possible without compromising the integrity of the bowel wall or surrounding neurovascular structures. We err on the side of caution, leaving some of the disease on the rectum to avoid rectal perforation, and plan for postoperative hormonal suppression in these patients.
For patients desiring fertility, successful pregnancy is often achieved using the shaving technique.41
About 10% of all reproductive-aged women and 35% to 50% of women with pelvic pain and infertility are affected by endometriosis.1,2 The disease typically involves the reproductive tract organs, anterior and posterior cul-de-sacs, and uterosacral ligaments. However, disease outside of the reproductive tract occurs frequently and has been found on all organs except the spleen.3
The bowel is the most common site for extragenital endometriosis, affected in an estimated 3.8% to 37% of patients with known endometriosis.4-7 Implants may be superficial, involving the bowel serosa and subserosa (FIGURE 1), or they can manifest as deeply infiltrating lesions involving the muscularis and mucosa (FIGURE 2). The rectosigmoid colon is the most common location for bowel endometriosis, followed by the rectum, ileum, appendix, and cecum4,8 (FIGURES 3, 4, and 5). Case reports also have described endometrial implants on the stomach and transverse colon.9 Although isolated bowel involvement has been recognized, most patients with bowel endometriosis have concurrent disease elsewhere.2,4
Historically, segmental resection was performed regardless of the anatomical location of the lesion.10 Even today, many surgeons continue to routinely perform segmental bowel resection as a first-line surgical approach.11 Unnecessary segmental resection, however, places patients at risk for short- and long-term postoperative morbidity, including the possibility of permanent ostomy. Modern surgical techniques, such as shaving excision and disc resection, have been performed to successfully treat bowel endometriosis with excellent long-term outcomes and fewer complications when compared with traditional segmental resection.2,12-16
In this article, we focus on the clinical indications and surgical techniques for video-laparoscopic management, but first we describe the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis of bowel endometriosis.





Pathophysiology of bowel endometriosis
The pathogenesis of endometriosis remains unknown, as no single mechanism explains all clinical cases of the disease. The most popular proposed theory describes retrograde menstruation through the fallopian tubes.17 Once inside the peritoneal cavity, endometrial cells attach to and invade healthy peritoneum, establishing a blood supply necessary for growth and survival.
In the case of bowel endometriosis, deposition of effluxed endometrial cells may lead to an inflammatory response that increases the risk of adhesion formation, leading to potential cul-de-sac obliteration. Lesions may originate as Allen-Masters peritoneal defects, developing into deeply infiltrative rectovaginal septum lesions. The anatomical shelter theory contributes to lesions within the pelvis, with the rectosigmoid colon blocking the cephalad flow of effluxed menstrual blood from the pelvis, thus leading to a preponderance of lesions in the pelvis and along the rectosigmoid colon.2
Continue to: Clinical presentation and diagnosis...
Clinical presentation and diagnosis
Women presenting with endometriosis of the bowel are typically of reproductive age and commonly report symptoms of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, and dyschezia. Some women also experience catamenial diarrhea, constipation, hematochezia, and bloating.2 The differential diagnosis of these symptoms is broad and includes irritable bowel disease, ischemic colitis, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and malignancy.
Because of its nonspecific symptoms, bowel endometriosis is often misdiagnosed and the disease goes untreated for years.18 Therefore, it is imperative that clinicians maintain a high index of suspicion when evaluating reproductive-aged women with gastrointestinal symptoms and pelvic pain.
Physical examination can be helpful in making the diagnosis of endometriosis. During bimanual examination, findings such as a fixed, tender, or retroverted uterus, uterosacral ligament nodularity, or an enlarged adnexal mass representing an ovarian endometrioma may be appreciated. Rectovaginal exam can identify areas of tenderness and nodularity along the rectovaginal septum. Speculum exam may reveal a laterally displaced cervix or blue powder-burn lesions along the cervix or posterior fornix.19 Rarely, endometriosis is found on the perineum within an episiotomy scar.20
Imaging studies can be used in conjunction with physical examination findings to aid in the diagnosis of endometriosis. Images also guide preoperative planning by characterizing lesions based on their size, location, and depth of invasion. Hudelist and colleagues found transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) to have an overall sensitivity of 71% to 98% and a specificity of 92% to 100%.21 However, it was noted that the accuracy of the diagnosis was directly related to the experience of the sonographer, and lesions above the sigmoid colon were generally unable to be diagnosed. Other imaging modalities that have been reported to have high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing bowel endometriosis include rectal water contrast TVUS,22,23 rectal endoscopic sonography,22 magnetic resonance imaging,22 and barium enema.24
Medical management
Medical therapy for patients with endometriosis is utilized with the goal of suppressing ovulation, lowering circulating hormone levels, and inducing endometrial atrophy. Medications commonly employed include gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists and antagonists, anabolic steriods such as danazol, combined oral contraceptive pills, progestins, and aromatase inhibitors.
Continue to: To date, no optimal hormonal regimen...
To date, no optimal hormonal regimen has been established for the treatment of bowel endometriosis. Vercellini and colleagues demonstrated that progestins with and without low-dose estrogen improved symptoms of dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia.25 Ferrero and colleagues reported that 2.5 mg of norethindrone daily resulted in 53% of women with colorectal endometriosis reporting improved gastrointestinal symptoms.26 However, by 12 months of follow-up, 33% of these patients had elected to undergo surgical management.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, such as leuprolide acetate, also can be used to mitigate symptoms of bowel endometriosis or to decrease disease burden at the time of surgery, and they can be used with add-back norethindrone acetate. The use of these medications is limited by adverse effects, such as vasomotor symptoms and decreased bone mineral density when used for longer than 6 months.2
Medical therapy is commonly used for patients with mild to moderate symptoms and in those who are poor surgical candidates or decline surgical intervention. Medical therapy is especially useful when employed postoperatively to suppress the regrowth of microscopic ectopic endometrial tissue.
Patients must be counseled, however, that even with medical management, they may still require surgery in the future to control their symptoms and/or to preserve organ function.2
Surgical management
Surgical treatment for bowel endometriosis depends on the disease location, the size and depth of the lesion, the presence or absence of stricture, and the surgeon’s level of expertise.2,12,27-30
In our group, we advocate for video-laparoscopy, with or without robotic as sistance. Minimally invasive surgery offers reduced blood loss, shorter recovery time, and fewer postoperative complications compared with laparotomy.2,16,27,31-33 The conversion rate to laparotomy has been reported to be about 3% when performed by an experienced surgeon.12
Darai and colleagues conducted a randomized trial of 52 patients undergoing surgery for colorectal endometriosis via either laparoscopic or open colon resection.33 Blood loss was significantly lower in the laparoscopy group (1.6 vs 2.7 mg/L, P <.05). No difference was noted in long-term outcomes. In a retrospective study of 436 cases, Ruffo and colleagues showed that those who underwent laparoscopic colorectal resection had higher postoperative pregnancy rates compared with those who had laparotomy (57.6% vs 23.1%, P <.035).32
The goal of surgical management of bowel endometriosis is to remove as many of the endometriotic lesions as possible while minimizing short- and long-term complications. Three surgical approaches have been described: shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection.2
Some surgeons prefer traditional segmental resection of the bowel regardless of the anatomical site, citing reduced disease recurrence with this approach; however, traditional segmental resection confers increased risk of complications. Increasingly, in an effort to reduce morbidity, more surgeons are advocating for the less aggressive methods of shaving excision and disc resection.
Aggressive resection at the level of the low rectum requires extensive surgical dissection of the retrorectal space, with the potential for inadvertent injury to surrounding neurovascular structures, such as the pelvic splanchnic nerves and superior and inferior hypogastric plexus.29 Injury to these structures can lead to significant complications, including bowel stenosis, fistula formation, constipation, and urinary retention. Complete resection of other areas, such as the small bowel, do not carry the same risks and may have more significant benefit to the patient than less aggressive techniques.
Our group recommends carefully balancing the risks and benefits of aggressive surgical treatment for each individual and treating the patient with the appropriate technique. Regardless of technique, surgical treatment of bowel endometriosis can lead to long-term improvements in pain and infertility.29,30,34,35
- The clinical presentation of bowel endometriosis is often nonspecific, with a broad differential diagnosis. Maintain a high index of suspicion when reproductive-aged women present for evaluation of dysmenorrhea, chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, bloating, dyschezia, or hematochezia.
- Symptomatic patients not desiring fertility, poor surgical candidates, and those declining surgical intervention may benefit from medical management. Patients who fail medical therapy, have severe symptoms, or experience infertility are candidates for surgical intervention.
- Surgical management involves shaving excision, disc resection, and segmental resection. Some surgeons advocate for aggressive segmental resection regardless of the endometriotic lesion's location. Based on our extensive experience, we prefer shaving excision for lesions below the sigmoid to avoid dissection into the retrorectal space and inadvertent injury to nerve tissue controlling bowel and bladder function.
- Following shaving excision, patients experience low complication rates29,39,40 and favorable long-term outcomes.15,40,56 For lesions above the sigmoid colon, including the small bowel, segmental resection or disc resection for smaller lesions are reasonable surgical approaches.
Continue to: Shaving excision...
Shaving excision
The most conservative approach to resection of bowel endometriosis is shaving excision; this involves removing endometriotic tissue layer-by-layer until healthy, underlying tissue is encountered.2 With bowel endometriosis, the goal of shaving excision is to remove as much of the diseased tissue as possible while leaving behind the mucosal layer and a portion of the muscularis.2,15,16,36-38 This is the most conservative of the 3 surgical techniques and is associated with the lowest complication rate.2,14,15,36,37
Our group reported on 185 women who underwent shaving excision for bowel endometriosis. At the time of surgery, 80 women had complete obliteration of the cul-de-sac (FIGURE 6). Of the study patients, 174 patients were available for follow-up, with 93% reporting moderate to complete pain relief.15
In a retrospective analysis of 3,298 surgeries for rectovaginal endometriosis in which shaving excision was used on all but 1% of patients, Donnez and colleagues reported a very low complication rate, with 1 case of rectal perforation, 1 case of fecal peritonitis, and 3 cases of ureteral injury.39
Roman and colleagues described the use of shaving excision for rectal endometriosis using plasma energy (n = 54) and laparoscopic scissors (n = 68).40 Only 4% of patients reported experiencing symptom recurrence, and the pregnancy rate was 65.4%, with 59% of those patients spontaneously conceiving. Two cases of rectal fistula were noted.

Disc resection
Laparoscopic disc excision has been described in the literature since the 1980s, and the technique involves the full-thickness removal of the diseased portion of the bowel, followed by closure of the remaining defect.2,12-14,28,29,31,41-45 To be appropriate for this technique, a lesion should involve only a portion of the bowel wall and, preferably, less than one-half of the bowel circumference.2,42 Disc excision results in excellent outcomes with fewer postoperative complications than segmental resection, but with more complications when compared to shaving excision.2,12,13,29,45,46
We reported on a series of 141 women with bowel endometriosis who underwent disc excision.2 At 1-month follow-up, 87% of patients experienced an improvement in their symptoms. No cases required conversion to laparotomy or were complicated by rectovaginal fistula formation, ureteral injury, bowel perforation, or pelvic abscess.2
Continue to: Segmental resection...
Segmental resection
The most aggressive surgical approach, segmental resection involves complete removal of a diseased portion of bowel, followed by side-to-side or end-to-end reanastomosis of the adjacent segments.2 For this procedure, a multidisciplinary approach is recommended, with involvement of a colorectal surgeon or gynecologic oncologist trained in performing bowel resections. Segmental resection is indicated for lesions that are larger than 3 cm, circumferential, obstructive, or multifocal.
Given the higher complication rate associated with this procedure and the good outcomes associated with less invasive techniques, we avoid segmental resection whenever possible, especially for lesions near the anal verge.2
Complications associated with surgical approach
In 2005, our group reported on a cohort of 178 women who underwent laparoscopic treatment of deeply infiltrative bowel endometriosis with shaving excision (n = 93), disc excision (n = 38), and segmental resection (n = 47).34 The major complication rate was significantly higher for those undergoing segmental resection (12.5%, P <.001); only 7.7% of those who underwent disc resection experienced a major complication; and none were observed in the group treated with shaving excision.
In 2011, De Cicco and colleagues conducted a systematic review of 1,889 patients who underwent segmental bowel resection.35 The major complication rate was 11%, with a leakage rate of 2.7%, fistula rate of 1.8%, major obstruction rate of 2.7%, and hemorrhage rate of 2.5%. Many of these complications, however, occurred in patients who had low rectal resections.
Regardless of surgical approach, the complication rate is related to the surgeon’s ability to preserve the superior and inferior hypogastric plexuses and the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve bundles (FIGURE 7). Nerve-sparing techniques should be used to decrease the incidence of postoperative bowel, bladder, and sexual function complications.2

Our group’s preferences
In our practice, we emphasize that the choice of surgical technique depends on the location, size, and depth of the lesion, as well as the extent of bowel wall circumferential invasion.2
We categorize lesions by their anatomic location: those above the sigmoid colon, on the sigmoid colon, on the rectosigmoid colon, and on the rectum. For lesions above the sigmoid colon, segmental or disc resection is appropriate.2 We recommend segmental resection for multifocal lesions, lesions larger than 3 cm, or for lesions involving more than one-third of the bowel lumen.37,44,45,47 Disc resection is appropriate for lesions smaller than 3 cm even if the bowel lumen is involved.44,45,48 If endometriosis is encountered in any location along the bowel, appendectomy can be performed even without visible disease, due to a high incidence of occult disease of the appendix.49,50
When lesions involve the sigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible to limit dissection of the retrorectal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.2 Segmental resection at or below the sigmoid colon has been associated with postoperative surgical site leakage51 and long-term bowel and bladder dysfunction with risk of permanent colostomy.52,53 For lesions smaller than 3 cm or involving less than one-third of the bowel lumen, disc resection can be performed. Segmental resection is required if multifocal disease or obstruction are present, if lesions are larger than 3 cm, or if more than one-third of the bowel lumen is involved.
For lesions along the rectosigmoid colon, we prefer utilizing shaving excision when possible.2 Disc excision can be performed utilizing a transanal approach, being mindful to minimize dissection of the retroperitoneal space and pelvic sidewall nerves.48 Segmental resection is avoided even with lesions larger than 3 cm, unless prior surgery has failed. Approaches for segmental resection can utilize laparoscopy or the natural orifices of the rectum or vagina.31,51
For lesions on the rectum, we strongly advise shaving excision.2 Evidence fails to show that the benefits of segmental resection outweigh the risks when compared to conservative techniques at the rectum.30,39,54 There is evidence indicating that aggressive surgery 5 to 8 cm from the anal verge is predictive of postoperative complications.55 In our group, we use shaving excision to remove as much disease as possible without compromising the integrity of the bowel wall or surrounding neurovascular structures. We err on the side of caution, leaving some of the disease on the rectum to avoid rectal perforation, and plan for postoperative hormonal suppression in these patients.
For patients desiring fertility, successful pregnancy is often achieved using the shaving technique.41
- Giudice LC. Clinical practice. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2389-2398.
- Nezhat C, Li A, Falik R, et al. Bowel endometriosis: diagnosis and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:549-562.
- Markham SM, Carpenter SE, Rock JA. Extrapelvic endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1989;16:193-219.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Redwine DB. Ovarian endometriosis: a marker for more extensive pelvic and intestinal disease. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:310-315.
- Weed JC, Ray JE. Endometriosis of the bowel. Obstet Gynecol. 1987;69:727-730.
- Wheeler JM. Epidemiology of endometriosis-associated infertility. J Reprod Med. 1989;34:41-46.
- Redwine DB. Intestinal endometriosis. In: Redwine DB. Surgical Management of Endometriosis. New York, NY: Martin Dunitz; 2004:196.
- Hartmann D, Schilling D, Roth SU, et al. [Endometriosis of the transverse colon--a rare localization]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2002;127:2317-2320.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Macafee CH, Greer HL. Intestinal endometriosis. A report of 29 cases and a survey of the literature. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1960;67:539-555.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Ambroze W, et al. Laparoscopic repair of small bowel and colon. A report of 26 cases. Surg Endosc. 1993;7:88-89.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E, et al. Laparoscopic disk excision and primary repair of the anterior rectal wall for the treatment of full-thickness bowel endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1994;8:682-685.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Evaluation of safety of videolaseroscopic treatment of bowel endometriosis. Presented at: 44th Annual Meeting of the American Fertility Society; October, 1988; Atlanta, GA.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E. Laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative rectosigmoid colon and rectovaginal septum endometriosis by the technique of videolaparoscopy and the CO2 laser. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992;99:664-667.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Skoog SM, Foxx-Orenstein AE, Levy MJ, et al. Intestinal endometriosis: the great masquerader. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:405-409.
- Alabiso G, Alio L, Arena S, et al. How to manage bowel endometriosis: the ETIC approach. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:517-529.
- Heller DS, Lespinasse P, Mirani N. Endometriosis of the perineum: a rare diagnosis usually associated with episiotomy. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:e48-e49.
- Hudelist G, English J, Thomas AE, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound for non-invasive diagnosis of bowel endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:257-263.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Menada MV, Remorgida V, Abbamonte LH, et al. Transvaginal ultrasonography combined with water-contrast in the rectum in the diagnosis of rectovaginal endometriosis infiltrating the bowel. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:699-700.
- Gordon RL, Evers K, Kressel HY, et al. Double-contrast enema in pelvic endometriosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;138:549-552.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, et al. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84:1375-1387.
- Ferrero S, Camerini G, Ragni N, et al. Norethisterone acetate in the treatment of colorectal endometriosis: a pilot study. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:94-100.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Laparoscopic management of bowel endometriosis: predictors of severe disease and recurrence. JSLS. 2011;15:431-438.
- Roman H, Milles M, Vassilieff M, et al. Long-term functional outcomes following colorectal resection versus shaving for rectal endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:762.e1-762.e9.
- Kent A, Shakir F, Rockall T, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for severe rectovaginal endometriosis compromising the bowel: a prospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:526-534.
- Nezhat F, Nezhat C, Pennington E. Laparoscopic proctectomy for infiltrating endometriosis of the rectum. Fertil Steril. 1992;57:1129-1132.
- Ruffo G, Scopelliti F, Scioscia M, et al. Laparoscopic colorectal resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: analysis of 436 cases. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:63-67.
- Darai E, Dubernard G, Coutant C, et al. Randomized trial of laparoscopically assisted versus open colorectal resection for endometriosis: morbidity, symptoms, quality of life, and fertility. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1018-1023.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- De Cicco C, Corona R, Schonman R, et al. Bowel resection for deep endometriosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2011;118:285-291.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Donnez J, Squifflet J. Complications, pregnancy and recurrence in a prospective series of 500 patients operated on by the shaving technique for deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:1949-1958.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy and videolaseroscopy. Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 1987;16:303-312.
- Donnez J, Jadoul P, Colette S, et al. Deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules: perioperative complications from a series of 3,298 patients operated on by the shaving technique. Gynecol Surg. 2013;10:31-40.
- Roman H, Moatassim-Drissa S, Marty N, et al. Rectal shaving for deep endometriosis infiltrating the rectum: a 5-year continuous retrospective series. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:1438-1445.e2.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- Jerby BL, Kessler H, Falcone T, et al. Laparoscopic management of colorectal endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1999;13:1125-1128.
- Coronado C, Franklin RR, Lotze EC, et al. Surgical treatment of symptomatic colorectal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1990;53:411-416.
- Fanfani F, Fagotti A, Gagliardi ML, et al. Discoid or segmental rectosigmoid resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: a case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:444-449.
- Landi S, Pontrelli G, Surico D, et al. Laparoscopic disk resection for bowel endometriosis using a circular stapler and a new endoscopic method to control postoperative bleeding from the stapler line. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:205-209.
- Slack A, Child T, Lindsey I, et al. Urological and colorectal complications following surgery for rectovaginal endometriosis. BJOG. 2007;114:1278-1282.
- Ceccaroni M, Clarizia R, Bruni F, et al. Nerve-sparing laparoscopic eradication of deep endometriosis with segmental rectal and parametrial resection: the Negrar method. A single-center, prospective, clinical trial. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:2029-2045.
- Roman H, Abo C, Huet E, et al. Deep shaving and transanal disc excision in large endometriosis of mid and lower rectum: the Rouen technique. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:2626-2627.
- Gustofson RL, Kim N, Liu S, et al. Endometriosis and the appendix: a case series and comprehensive review of the literature. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:298-303.
- Berker B, Lashay N, Davarpanah R, et al. Laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2005;12:206-209.
- Ret Dávalos ML, De Cicco C, D'Hoore A, et al. Outcome after rectum or sigmoid resection: a review for gynecologists. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2007;14:33-38.
- Alves A, Panis Y, Mathieu P, et al; Association Française de Chirurgie (AFC). Mortality and morbidity after surgery of mid and low rectal cancer. Results of a French prospective multicentric study. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005;29:509-514.
- Camilleri-Brennan J, Steele RJ. Objective assessment of morbidity and quality of life after surgery for low rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2002;4:61-66.
- Acien P, Núñez C, Quereda F, et al. Is a bowel resection necessary for deep endometriosis with rectovaginal or colorectal involvement? Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:449-455.
- Abrão MS, Petraglia F, Falcone T, et al. Deep endometriosis infiltrating the recto-sigmoid: critical factors to consider before management. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21:329-339.
- Donnez J, Nisolle M, Gillerot S, et al. Rectovaginal septum adenomyotic nodules: a series of 500 cases. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:1014-1018.
- Giudice LC. Clinical practice. Endometriosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2389-2398.
- Nezhat C, Li A, Falik R, et al. Bowel endometriosis: diagnosis and management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:549-562.
- Markham SM, Carpenter SE, Rock JA. Extrapelvic endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1989;16:193-219.
- Veeraswamy A, Lewis M, Mann A, et al. Extragenital endometriosis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;53:449-466.
- Redwine DB. Ovarian endometriosis: a marker for more extensive pelvic and intestinal disease. Fertil Steril. 1999;72:310-315.
- Weed JC, Ray JE. Endometriosis of the bowel. Obstet Gynecol. 1987;69:727-730.
- Wheeler JM. Epidemiology of endometriosis-associated infertility. J Reprod Med. 1989;34:41-46.
- Redwine DB. Intestinal endometriosis. In: Redwine DB. Surgical Management of Endometriosis. New York, NY: Martin Dunitz; 2004:196.
- Hartmann D, Schilling D, Roth SU, et al. [Endometriosis of the transverse colon--a rare localization]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2002;127:2317-2320.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Nezhat C. Endometriosis: ancient disease, ancient treatments. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(6 suppl):S1-62.
- Macafee CH, Greer HL. Intestinal endometriosis. A report of 29 cases and a survey of the literature. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1960;67:539-555.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Ambroze W, et al. Laparoscopic repair of small bowel and colon. A report of 26 cases. Surg Endosc. 1993;7:88-89.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E, et al. Laparoscopic disk excision and primary repair of the anterior rectal wall for the treatment of full-thickness bowel endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1994;8:682-685.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F. Evaluation of safety of videolaseroscopic treatment of bowel endometriosis. Presented at: 44th Annual Meeting of the American Fertility Society; October, 1988; Atlanta, GA.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat F, Pennington E. Laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative rectosigmoid colon and rectovaginal septum endometriosis by the technique of videolaparoscopy and the CO2 laser. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1992;99:664-667.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy. Fertil Steril. 1986;45:778-783.
- Sourial S, Tempest N, Hapangama DK. Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med. 2014;2014:179515.
- Skoog SM, Foxx-Orenstein AE, Levy MJ, et al. Intestinal endometriosis: the great masquerader. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:405-409.
- Alabiso G, Alio L, Arena S, et al. How to manage bowel endometriosis: the ETIC approach. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:517-529.
- Heller DS, Lespinasse P, Mirani N. Endometriosis of the perineum: a rare diagnosis usually associated with episiotomy. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2016;20:e48-e49.
- Hudelist G, English J, Thomas AE, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound for non-invasive diagnosis of bowel endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:257-263.
- Nisenblat V, Bossuyt PM, Farquhar C, et al. Imaging modalities for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2:CD009591.
- Menada MV, Remorgida V, Abbamonte LH, et al. Transvaginal ultrasonography combined with water-contrast in the rectum in the diagnosis of rectovaginal endometriosis infiltrating the bowel. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:699-700.
- Gordon RL, Evers K, Kressel HY, et al. Double-contrast enema in pelvic endometriosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;138:549-552.
- Vercellini P, Pietropaolo G, De Giorgi O, et al. Treatment of symptomatic rectovaginal endometriosis with an estrogen-progestogen combination versus low-dose norethindrone acetate. Fertil Steril. 2005;84:1375-1387.
- Ferrero S, Camerini G, Ragni N, et al. Norethisterone acetate in the treatment of colorectal endometriosis: a pilot study. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:94-100.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic treatment of bowel, bladder, and ureteral endometriosis. JSLS. 2011;15:387-392.
- Nezhat C, Hajhosseini B, King LP. Laparoscopic management of bowel endometriosis: predictors of severe disease and recurrence. JSLS. 2011;15:431-438.
- Roman H, Milles M, Vassilieff M, et al. Long-term functional outcomes following colorectal resection versus shaving for rectal endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215:762.e1-762.e9.
- Kent A, Shakir F, Rockall T, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for severe rectovaginal endometriosis compromising the bowel: a prospective cohort study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016;23:526-534.
- Nezhat F, Nezhat C, Pennington E. Laparoscopic proctectomy for infiltrating endometriosis of the rectum. Fertil Steril. 1992;57:1129-1132.
- Ruffo G, Scopelliti F, Scioscia M, et al. Laparoscopic colorectal resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: analysis of 436 cases. Surg Endosc. 2010;24:63-67.
- Darai E, Dubernard G, Coutant C, et al. Randomized trial of laparoscopically assisted versus open colorectal resection for endometriosis: morbidity, symptoms, quality of life, and fertility. Ann Surg. 2010;251:1018-1023.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- De Cicco C, Corona R, Schonman R, et al. Bowel resection for deep endometriosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2011;118:285-291.
- Nezhat C, Nezhat FR. Safe laser endoscopic excision or vaporization of peritoneal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1989;52:149-151.
- Donnez J, Squifflet J. Complications, pregnancy and recurrence in a prospective series of 500 patients operated on by the shaving technique for deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules. Hum Reprod. 2010;25:1949-1958.
- Nezhat C, Crowgey SR, Garrison CP. Surgical treatment of endometriosis via laser laparoscopy and videolaseroscopy. Contrib Gynecol Obstet. 1987;16:303-312.
- Donnez J, Jadoul P, Colette S, et al. Deep rectovaginal endometriotic nodules: perioperative complications from a series of 3,298 patients operated on by the shaving technique. Gynecol Surg. 2013;10:31-40.
- Roman H, Moatassim-Drissa S, Marty N, et al. Rectal shaving for deep endometriosis infiltrating the rectum: a 5-year continuous retrospective series. Fertil Steril. 2016;106:1438-1445.e2.
- Mohr C, Nezhat FR, Nezhat CH, et al. Fertility considerations in laparoscopic treatment of infiltrative bowel endometriosis. JSLS. 2005;9:16-24.
- Jerby BL, Kessler H, Falcone T, et al. Laparoscopic management of colorectal endometriosis. Surg Endosc. 1999;13:1125-1128.
- Coronado C, Franklin RR, Lotze EC, et al. Surgical treatment of symptomatic colorectal endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1990;53:411-416.
- Fanfani F, Fagotti A, Gagliardi ML, et al. Discoid or segmental rectosigmoid resection for deep infiltrating endometriosis: a case-control study. Fertil Steril. 2010;94:444-449.
- Landi S, Pontrelli G, Surico D, et al. Laparoscopic disk resection for bowel endometriosis using a circular stapler and a new endoscopic method to control postoperative bleeding from the stapler line. J Am Coll Surg. 2008;207:205-209.
- Slack A, Child T, Lindsey I, et al. Urological and colorectal complications following surgery for rectovaginal endometriosis. BJOG. 2007;114:1278-1282.
- Ceccaroni M, Clarizia R, Bruni F, et al. Nerve-sparing laparoscopic eradication of deep endometriosis with segmental rectal and parametrial resection: the Negrar method. A single-center, prospective, clinical trial. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:2029-2045.
- Roman H, Abo C, Huet E, et al. Deep shaving and transanal disc excision in large endometriosis of mid and lower rectum: the Rouen technique. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:2626-2627.
- Gustofson RL, Kim N, Liu S, et al. Endometriosis and the appendix: a case series and comprehensive review of the literature. Fertil Steril. 2006;86:298-303.
- Berker B, Lashay N, Davarpanah R, et al. Laparoscopic appendectomy in patients with endometriosis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2005;12:206-209.
- Ret Dávalos ML, De Cicco C, D'Hoore A, et al. Outcome after rectum or sigmoid resection: a review for gynecologists. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2007;14:33-38.
- Alves A, Panis Y, Mathieu P, et al; Association Française de Chirurgie (AFC). Mortality and morbidity after surgery of mid and low rectal cancer. Results of a French prospective multicentric study. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2005;29:509-514.
- Camilleri-Brennan J, Steele RJ. Objective assessment of morbidity and quality of life after surgery for low rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2002;4:61-66.
- Acien P, Núñez C, Quereda F, et al. Is a bowel resection necessary for deep endometriosis with rectovaginal or colorectal involvement? Int J Womens Health. 2013;5:449-455.
- Abrão MS, Petraglia F, Falcone T, et al. Deep endometriosis infiltrating the recto-sigmoid: critical factors to consider before management. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21:329-339.
- Donnez J, Nisolle M, Gillerot S, et al. Rectovaginal septum adenomyotic nodules: a series of 500 cases. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:1014-1018.
Younger men and women show similar rates of osteopenia
according to findings from a cross-sectional study.
The high prevalence of osteopenia – once viewed as restricted largely to older women – in the study’s younger, cross-sex population should spur physicians to ask all patients about calcium intake and exercise as well as to screen for osteoporosis in all patients, Martha A. Bass, PhD,`wrote in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association.
“It is important that early detection of the precursors for osteoporosis become part of the annual physical for people in this age range, as well as in older patients,” noted Dr Bass of the University of Mississippi School of Applied Sciences in Oxford, and coauthors. “Primary care physicians should begin educating patients as early as adolescence or young adulthood so the consequences of osteoporosis can be prevented. The result would be the prevention of future bone fractures and the morbidity and mortality associated with bone fractures, thus leading to improved quality of life.”
The researchers set out to examine the likelihood of low bone mineral density (BMD) and related risk factors in 173 adults aged 35-50 years. All of the participants completed a questionnaire assessing calcium intake, weekly exercise, smoking, and body mass index, and all underwent screening for BMD. The study’s primary outcome was BMD at the femoral neck, trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine.
Among the 81 men in the sample, 25 (30%) had a normal body mass index, and the remainder were either overweight (47.5%) or obese (22.5%). One of the women was underweight, 48.9% were normal weight, 28.3% were overweight, and 21.7% were obese.
Most of the sample, regardless of gender, reported consuming fewer than three dairy items per day. Exercise frequency was better, with 68% of men and 56.4% of women saying they exercised at least 20 times per month.
There were no total femur osteoporosis findings in either sex. However, osteopenia at the femoral neck was present in 28.4% of the men and 26.1% of the women. Osteopenia at the lumbar spine occurred in 21% of men and 15.2% of women, with 6.2% of men and 2.2% of women showing osteoporosis at this site.
An adjusted analysis determined that exercise correlated significantly and negatively with femoral neck BMD in men. But in women, there was a significant and positive correlation with BMD at the lumbar spine and at all femoral measurements.
Body mass index also played into the risk picture. Among men, almost all BMD measurements (trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine) were positively associated with higher BMI. For women, higher BMI was associated with better BMD at the all the femoral sites, but not at the lumbar spine.
The negative correlation between femoral neck BMD and exercise in men seemed to contradict findings from previous studies. The authors said that could be a result of reporting bias, with men overestimating their amount of exercise, and could suggest that higher BMI confers some protection against bone loss in men.
The study found no significant correlations between dairy intake and BMD at any site in either sex. The finding suggests that both sexes need to improve both vitamin D and calcium intake.
None of the authors reported any financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bass MA et al. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119(6):357-63.
according to findings from a cross-sectional study.
The high prevalence of osteopenia – once viewed as restricted largely to older women – in the study’s younger, cross-sex population should spur physicians to ask all patients about calcium intake and exercise as well as to screen for osteoporosis in all patients, Martha A. Bass, PhD,`wrote in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association.
“It is important that early detection of the precursors for osteoporosis become part of the annual physical for people in this age range, as well as in older patients,” noted Dr Bass of the University of Mississippi School of Applied Sciences in Oxford, and coauthors. “Primary care physicians should begin educating patients as early as adolescence or young adulthood so the consequences of osteoporosis can be prevented. The result would be the prevention of future bone fractures and the morbidity and mortality associated with bone fractures, thus leading to improved quality of life.”
The researchers set out to examine the likelihood of low bone mineral density (BMD) and related risk factors in 173 adults aged 35-50 years. All of the participants completed a questionnaire assessing calcium intake, weekly exercise, smoking, and body mass index, and all underwent screening for BMD. The study’s primary outcome was BMD at the femoral neck, trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine.
Among the 81 men in the sample, 25 (30%) had a normal body mass index, and the remainder were either overweight (47.5%) or obese (22.5%). One of the women was underweight, 48.9% were normal weight, 28.3% were overweight, and 21.7% were obese.
Most of the sample, regardless of gender, reported consuming fewer than three dairy items per day. Exercise frequency was better, with 68% of men and 56.4% of women saying they exercised at least 20 times per month.
There were no total femur osteoporosis findings in either sex. However, osteopenia at the femoral neck was present in 28.4% of the men and 26.1% of the women. Osteopenia at the lumbar spine occurred in 21% of men and 15.2% of women, with 6.2% of men and 2.2% of women showing osteoporosis at this site.
An adjusted analysis determined that exercise correlated significantly and negatively with femoral neck BMD in men. But in women, there was a significant and positive correlation with BMD at the lumbar spine and at all femoral measurements.
Body mass index also played into the risk picture. Among men, almost all BMD measurements (trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine) were positively associated with higher BMI. For women, higher BMI was associated with better BMD at the all the femoral sites, but not at the lumbar spine.
The negative correlation between femoral neck BMD and exercise in men seemed to contradict findings from previous studies. The authors said that could be a result of reporting bias, with men overestimating their amount of exercise, and could suggest that higher BMI confers some protection against bone loss in men.
The study found no significant correlations between dairy intake and BMD at any site in either sex. The finding suggests that both sexes need to improve both vitamin D and calcium intake.
None of the authors reported any financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bass MA et al. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119(6):357-63.
according to findings from a cross-sectional study.
The high prevalence of osteopenia – once viewed as restricted largely to older women – in the study’s younger, cross-sex population should spur physicians to ask all patients about calcium intake and exercise as well as to screen for osteoporosis in all patients, Martha A. Bass, PhD,`wrote in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association.
“It is important that early detection of the precursors for osteoporosis become part of the annual physical for people in this age range, as well as in older patients,” noted Dr Bass of the University of Mississippi School of Applied Sciences in Oxford, and coauthors. “Primary care physicians should begin educating patients as early as adolescence or young adulthood so the consequences of osteoporosis can be prevented. The result would be the prevention of future bone fractures and the morbidity and mortality associated with bone fractures, thus leading to improved quality of life.”
The researchers set out to examine the likelihood of low bone mineral density (BMD) and related risk factors in 173 adults aged 35-50 years. All of the participants completed a questionnaire assessing calcium intake, weekly exercise, smoking, and body mass index, and all underwent screening for BMD. The study’s primary outcome was BMD at the femoral neck, trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine.
Among the 81 men in the sample, 25 (30%) had a normal body mass index, and the remainder were either overweight (47.5%) or obese (22.5%). One of the women was underweight, 48.9% were normal weight, 28.3% were overweight, and 21.7% were obese.
Most of the sample, regardless of gender, reported consuming fewer than three dairy items per day. Exercise frequency was better, with 68% of men and 56.4% of women saying they exercised at least 20 times per month.
There were no total femur osteoporosis findings in either sex. However, osteopenia at the femoral neck was present in 28.4% of the men and 26.1% of the women. Osteopenia at the lumbar spine occurred in 21% of men and 15.2% of women, with 6.2% of men and 2.2% of women showing osteoporosis at this site.
An adjusted analysis determined that exercise correlated significantly and negatively with femoral neck BMD in men. But in women, there was a significant and positive correlation with BMD at the lumbar spine and at all femoral measurements.
Body mass index also played into the risk picture. Among men, almost all BMD measurements (trochanter, intertrochanteric crest, total femur, and lumbar spine) were positively associated with higher BMI. For women, higher BMI was associated with better BMD at the all the femoral sites, but not at the lumbar spine.
The negative correlation between femoral neck BMD and exercise in men seemed to contradict findings from previous studies. The authors said that could be a result of reporting bias, with men overestimating their amount of exercise, and could suggest that higher BMI confers some protection against bone loss in men.
The study found no significant correlations between dairy intake and BMD at any site in either sex. The finding suggests that both sexes need to improve both vitamin D and calcium intake.
None of the authors reported any financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Bass MA et al. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119(6):357-63.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN OSTEOPATHIC ASSOCIATION
2019 Update on menopause
Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

Among peri- and postmenopausal women, abnormal bleeding, breast cancer, and mood disorders represent prevalent conditions. In this Update, we discuss data from a review that provides quantitative information on the likelihood of finding endometrial cancer among women with postmenopausal bleeding (PMB). We also summarize 2 recent consensus recommendations: One addresses the clinically important but controversial issue of the treatment of genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) in breast cancer survivors, and the other provides guidance on the management of depression in perimenopausal women.
Endometrial cancer is associated with a high prevalence of PMB
Clarke MA, Long BJ, Del Mar Morillo A, et al. Association of endometrial cancer risk with postmenopausal bleeding in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1210-1222.
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic malignancy and the fourth most common cancer among US women. In recent years, the incidence of and mortality from endometrial cancer have increased.1 Despite the high prevalence of endometrial cancer, population-based screening currently is not recommended.
PMB affects up to 10% of women and can be caused by endometrial atrophy, endometrial polyps, uterine leiomyoma, and malignancy. While it is well known that PMB is a common presenting symptom of endometrial cancer, we do not have good data to guide counseling patients with PMB on the likelihood that endometrial cancer is present. Similarly, estimates are lacking regarding what proportion of women with endometrial cancer will present with PMB.
To address these 2 issues, Clarke and colleagues conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of PMB among women with endometrial cancer (sensitivity) and the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB (positive predictive value). The authors included 129 studies--with 34,432 women with PMB and 6,358 with endometrial cancer--in their report.
Cancer prevalence varied with HT use, geographic location
The study findings demonstrated that the prevalence of PMB in women with endometrial cancer was 90% (95% confidence interval [CI], 84%-94%), and there was no significant difference in the occurrence of PMB by cancer stage. The risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB ranged from 0% to 48%, yielding an overall pooled estimate of 9% (95% CI, 8%-11%). As an editorialist pointed out, the risk of endometrial cancer in women with PMB is similar to that of colorectal cancer in individuals with rectal bleeding (8%) and breast cancer in women with a palpable mass (10%), supporting current guidance that recommends evaluation of women with PMB.2 Evaluating 100 women with PMB to diagnose 9 endometrial cancers does not seem excessive.
Interestingly, among women with PMB, the prevalence of endometrial cancer was significantly higher among women not using hormone therapy (HT) than among users of HT (12% and 7%, respectively). In 7 studies restricted to women with PMB and polyps (n = 2,801), the pooled risk of endometrial cancer was 3% (95% CI, 3%-4%). In an analysis stratified by geographic region, a striking difference was noted in the risk of endometrial cancer among women with PMB in North America (5%), Northern Europe (7%), and in Western Europe (13%). This finding may be explained by regional differences in the approach to evaluating PMB, cultural perceptions of PMB that can affect thresholds to present for care, and differences in risk factors between these populations.
The study had several limitations, including an inability to evaluate the number of years since menopause and the effects of body mass index. Additionally, the study did not address endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia.
PMB accounts for two-thirds of all gynecologic visits among perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.3 This study revealed a 9% risk of endometrial cancer in patients experiencing PMB, which supports current practice guidelines to further evaluate and rule out endometrial cancer among all women presenting with PMB4; it also provides reassurance that targeting this high-risk group of women for early detection and prevention strategies will capture most cases of endometrial cancers. However, the relatively low positive predictive value of PMB emphasizes the need for additional triage tests with high specificity to improve management of PMB and minimize unnecessary biopsies in low-risk women.
Treating GSM in breast cancer survivors: New guidance targets QoL and sexuality
Faubion SS, Larkin LC, Stuenkel CA, et al. Management of genitourinary syndrome of menopause in women with or at high risk for breast cancer: consensus recommendations from The North American Menopause Society and The International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health. Menopause. 2018;25:596-608.
Given that there is little evidence addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen, other hormonal therapies, and nonprescription treatments for GSM in breast cancer survivors, many survivors with bothersome GSM symptoms are not appropriately treated.
Continue to: Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance...
Expert panel creates evidence-based guidance
Against this backdrop, The North American Menopause Society and the International Society for the Study of Women's Sexual Health convened a group comprised of menopause specialists (ObGyns, internists, and nurse practitioners), specialists in sexuality, medical oncologists specializing in breast cancer, and a psychologist to create evidence-based interdisciplinary consensus guidelines for enhancing quality of life and sexuality for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Measures to help enhance quality of life and sexuality
The group's key recommendations for clinicians include:
- Sexual function and quality of life (QoL) should be assessed in all women with or at high risk for breast cancer.
- Management of GSM should be individualized based on shared decision-making involving the patient and her oncologist.
- Initial treatment options include:
—over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers used several times weekly on a regular basis
—lubricants used with intercourse
—vaginal dilator therapy
—pelvic floor physical therapy.
- Low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy may be appropriate for select women who have been treated for breast cancer:
—With use of vaginal estrogen, serum estradiol levels remain in the postmenopausal range.
—Based on limited data, use of vaginal estrogen is associated with a minimal risk for recurrence of breast cancer.
—Because their use is associated with the lowest serum estradiol levels, vaginal tablets, rings, or inserts may be preferable to creams.
—Decisions regarding use of vaginal estrogen in breast cancer survivors should involve the woman's oncologist. Appropriate candidates for off-label use of vaginal estrogen may be survivors:
–who are at relatively low risk for recurrence
–with hormone receptor-negative disease
–using tamoxifen rather than an AI
–who are particularly concerned about quality of life.
—Given that AIs prevent recurrence by lowering estrogen levels, oncologists may be reluctant to consider use of vaginal estrogen in survivors using adjuvant agents.
—With respect to use of vaginal estrogen, oncologists may be more comfortable with use in patients taking tamoxifen.
- Neither intravaginal dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; prasterone) nor the oral selective estrogen receptor modulator ospemifene has been studied in breast cancer survivors.
In women with metastatic disease, QoL, comfort, and sexual intimacy are key considerations when weighing potential therapies; optimal choices will vary with probability of long-term survival.
Although more data addressing the safety of vaginal estrogen as well as prasterone and ospemifene in breast cancer survivors clearly are needed, these guidelines should help clinicians who care for breast cancer survivors with GSM.
Framework provided for managing depressive disorders in perimenopausal women
Maki PM, Kornstein SG, Joffe H, et al; Board of Trustees for The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) and the Women and Mood Disorders Task Force of the National Network of Depression Centers. Guidelines for the evaluation and treatment of perimenopausal depression: summary and recommendations. Menopause. 2018;25:1069-1085.
Although perimenopausal women are more susceptible to the development of depressive symptoms and major depressive episodes (MDE), there is a lack of consensus regarding how to evaluate and treat depression in women during the menopausal transition and postmenopausal period.
Recently, an expert panel comprised of representatives from The North American Menopause Society and the National Network of Depression Centers Women and Mood Disorders Task Group developed clinical guidelines addressing epidemiology, clinical presentation, therapeutic effects of antidepressants, effects of HT, and efficacy of other therapies. Here we provide a summary of the expert panel's findings and guidelines.
Continue to: Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression...
Certain factors are associated with higher risk for depression
The perimenopause represents a time of increased risk for depressive symptoms and major depressive disorder (MDD), even in women with no prior history of depression. Several characteristics and health factors are associated with the increased risk during the menopause transition. These include a prior history of MDD, current antidepressant use, anxiety, premenstrual depressive symptoms, African American race, high body mass index, younger age, social isolation, upsetting life events, and menopausal sleep disturbances.
Although data are inconclusive on whether surgical menopause increases or decreases the risk for developing depression compared with women who transition through menopause naturally, recent studies show an elevated risk of depression in women following hysterectomy with and without oophorectomy.6,7
Menopausal and depressive symptoms can overlap
Midlife depression presents with classic depressive symptoms that commonly occur in combination with menopausal symptoms, including vasomotor symptoms, sleep and sexual disturbances, and weight and energy changes. These menopausal symptoms can complicate, co-occur, and overlap with the clinical presentation of depression.
Conversely, depression may affect an individual's judgment of the degree of bother from menopausal somatic symptoms, thereby further magnifying the effect of symptoms on quality of life. The interrelationship between depressive symptoms and menopausal symptoms may pose a challenge when attempting to parse out contributing etiologies, relative contributions of each etiology, and the potential additive effects.
Diagnosis and treatment options
Diagnosis involves identifying the menopausal stage, assessing for co-existing psychiatric and menopause symptoms, appreciating the psychosocial factors common in midlife, and considering the differential diagnosis. Validated screening instruments can be helpful. Although a menopause-specific mood disorder scale does not yet exist, several general validated screening measures, such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, or PHQ-9, can be used for categorical determination of mood disorder diagnoses during the menopause transition.
Antidepressants, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other psychotherapies are considered first-line treatments for perimenopausal major depressive episodes. Only desvenlafaxine has been studied in large randomized placebo-controlled trials and has proven efficacious for the treatment of MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.
A number of small open-label studies of other selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and mirtazapine to treat MDD in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women have demonstrated a positive effect on mood, and several SSRIs and SNRIs also have the added benefit of improving menopause-related symptoms.
In women with a history of MDD, a prior adequate response to a particular antidepressant should guide treatment selection when MDD recurs during the midlife years.
Although estrogen is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration specifically for the treatment of mood disturbances, some evidence suggests that unopposed estrogen therapy has efficacy similar to that of antidepressant medications in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women,8-11 but it is ineffective in treating depressive disorders in postmenopausal women. Estrogen therapy also may augment the clinical response to antidepressants in midlife and older women.12,13 The data on combined HT (estrogen plus progestogen) or for different progestogens in treating depressive disorders in perimenopausal women are lacking and inconclusive.
The findings from this expert review panel demonstrate that women in the perimenopausal transition are at increased risk for depressive symptoms, major depressive episodes, and major depressive disorder. The interrelationship between symptoms of depression and menopause can complicate, co-occur, overlap, and magnify one another. Clinicians treating perimenopausal women with depression that is unresponsive to conventional antidepressant therapy should consider concurrent use of estrogen-based hormone therapy or referring the patient to a clinician comfortable doing so.

- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7-30.
- Matteson KA, Robison K, Jacoby VL. Opportunities for early detection of endometrial cancer in women with postmenopausal bleeding. JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:1222-1223.
- van Hanegem N, Breijer MC, Khan KS, et al. Diagnostic evaluation of the endometrium in postmenopausal bleeding: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas. 2011;68:155-164.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 734 summary. The role of transvaginal ultrasonography in evaluating the endometrium of women with postmenopausal bleeding. Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 131:945-946.
- Baumgart J, Nilsson K, Evers AS, et al. Sexual dysfunction in women on adjuvant endocrine therapy after breast cancer. Menopause. 2013;20:162-168.
- Chou PH, Lin CH, Cheng C, et al. Risk of depressive disorders in women undergoing hysterectomy: a population-based follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:186-191.
- Wilson L, Pandeya N, Byles J, et al. Hysterectomy and incidence of depressive symptoms in midlife women: the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2018;27:381-392.
- Schmidt PJ, Nieman L, Danaceau MA, et al. Estrogen replacement in perimenopause-related depression: a preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:414-420.
- Rasgon NL, Altshuler LL, Fairbanks L. Estrogen-replacement therapy for depression. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1738.
- Soares CN, Almeida OP, Joffe H, et al. Efficacy of estradiol for the treatment of major depressive disorders in perimenopausal women: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58:529-534.
- Cohen LS, Soares CN, Poitras JR, et al. Short-term use of estradiol for depression in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: a preliminary report. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1519-1522.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Hamilton SH, et al. Estrogen replacement and response to fluoxetine in a multicenter geriatric depression trial. Fluoxetine Collaborative Study Group. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1997;5:97-106.
- Schneider LS, Small GW, Clary CM. Estrogen replacement therapy and antidepressant response to sertraline in older depressed women. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2001;9:393-399.
What’s in store for ObGyn reimbursement in the EHR age and beyond
In an effort to reduce burden on physicians and qualified health care professionals, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services ( CMS) has made changes to Evaluation and Management (E/M) documentation requirements and payment policies. Get ready for fairly extensive changes planned for CY 2021. Here we outline already-implemented and future changes and describe the commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to ObGyn payment in its collaborations with CMS and the American Medical Association (AMA).

E/M services: CMS reduced documentation
Effective January 2019, the CMS made changes to the documentation requirements for E/M services to provide some common-sense relief for physicians facing excessive documentation requirements in their practices. Most physicians agree that modern medical practice, with the use of electronic health records (EHRs), is different now than in the mid-1990s, when the current E/M structures were developed and implemented. Streamlining documentation requirements reduces paperwork burden and some of the time-consuming duplicative work involved in medical practice today.
For instance, when relevant information is already contained in the medical record, it is not necessary to re-document a full medical history. Physicians will now be able to focus their documentation on the interval since the previous visit. Physicians should still review prior data, update as necessary, and indicate in the medical record that they have done so.
Also, for E/M office and outpatient visits for both new and established patients, physicians are no longer required to re-document information that has already been entered in the patient’s record by practice staff or by the patient. If the patient’s chief complaint and history already has been entered by ancillary staff or the beneficiary, the physician should simply indicate in the medical record that the information has been reviewed and verified.
For E/M visits furnished by teaching physicians, CMS has removed the requirement for potentially duplicative notations that may have been made previously in the medical records by residents or other members of the medical team.
Finally, CMS eliminated the requirement to document the medical necessity of a home visit in lieu of an office visit.
Continue to: Outpatient coding changes for 2021...
Outpatient coding changes for 2021
Outpatient coding for E/M will continue in its current form for the remainder of 2019 and 2020. However, in 2021, expect substantial changes to take effect. If the CMS rule is instituted, payment for E/M office and outpatient visits will be drastically “simplified.” The current CMS plan for 2021 is to collapse payment for existing E/M Levels 2 through 4 to one payment level for new patients and one payment level for established patients, with optional add-on codes. Level 5 visits will continue at a separate payment level and with continuation of current documentation requirements.
In addition to collapsing the payment in E/M Levels 2, 3, and 4, CMS also will allow flexibility in how those E/M office and outpatient visits are documented. Specifically, documentation may be based on any of the following:
- current framework (1995 or 1997 guidelines)
- medical decision making (MDM)
- time.
When using MDM or the current 1995/1997 framework to document an office visit, Medicare will only require documentation to support a Level 2 E/M outpatient visit code for history, exam, and/or MDM. When time is used as the basis for coding the visit, physicians will document the medical necessity of the visit and that the billing practitioner personally spent the required amount of time face-to-face with the beneficiary.
CMS also has finalized the creation of new add-on codes that describe the additional resources inherent in visits for primary care and particular kinds of nonprocedural specialized medical care (and will not be restricted by physician specialty). These codes would only be reportable with E/M office and outpatient level 2 through 4 visits, and their use generally would not impose new documentation requirements. It is not clear which types of visits would support the use of these add-on codes at this time.
Finally, a new “extended visit” add-on code will be available for use only with E/M Level 2 through 4 visits to account for the additional resources required when spending extended time with a patient.
CMS believes these policies will allow physicians, and all who bill E/M codes, greater flexibility to exercise clinical judgment in their documentation, so that they can focus on what is clinically relevant and medically necessary for the beneficiary.
ACOG’s voice in the process
ACOG strongly opposed several proposals that CMS made during the rule-making process that the agency decided not to finalize. These aspects of the proposal would have:
1. reduced payment by 50% for the least expensive procedure or visit when an E/M office or outpatient visit is furnished on the same day as a procedure by the same physician. These are separately identifiable E/M visits that normally would be reported with a modifier 25.
2. established separate coding and payment for podiatric E/M visits, or
3. standardized the allocation of practice expense relative value units (RVUs) for the codes that describe these services.
CMS has stated that they intend to engage in further discussions with the public and stakeholders to potentially further refine the policies for CY 2021.
Continue to: AMA-CPT and RUC initiative...
AMA-CPT and RUC initiative
Although the AMA, ACOG, and physicians in general applauded the CMS initiative to reduce the administrative and documentation burden on providers, there was concern about the unintended consequences of the payment changes that are currently scheduled to take effect in 2021. To address these concerns, the AMA convened a work group of physician experts who are knowledgeable in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code development and valuation processes. The charge to the E/M work group is to collaborate across the provider, payer, and coding communities to establish or revise the coding structure and guidelines for outpatient E/M services. The members formed a multispecialty work group representing primary care and surgical specialties and have experience in developing, defining, and valuing codes.
Dr. Barbara Levy, ACOG’s Vice President of Health Policy, co-chaired this expert panel with geriatrician Dr. Peter Hollmann to develop comprehensive consensus-led changes to revise and modernize E/M codes. The work group followed 4 guiding principles to inform their E/M work:
- to decrease the administrative burden of documentation and coding
- to decrease the need for audits
- to decrease unnecessary and redundant documentation in the medical record that is not needed for patient care
- to ensure that payment for E/M services is resource based. There is no direct goal for payment redistribution among specialties.
A primary concern expressed by physicians about the CMS proposal was that the collapse of payment for E/M visit across levels 2–4 might lead to a lack of appropriate care for more complex patients since the CMS rule does not provide payment based on the resources required to perform the work of the visit. No one believes that the work needed to care for someone with a sore throat or pink eye is equivalent to the work involved in diagnosing and managing depression, for example.
Beginning in August 2018, the work group met regularly to build consensus. The work group worked at an accelerated pace to develop and value codes that better fit the current medical workflows and meet patient needs.
The work group submitted a code change proposal for E/M codes to the CPT Editorial Panel for consideration during the February 2019 meeting. The next step was the code valuation process through the AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) process.
CMS has stated that the 2-year delay to 2021 in implementation of their original proposed changes is to allow time for the E/M code change proposals to move through the development and valuation process and subsequent review by the agency. To date, commercial payers and coders have been supportive of the AMA E/M work group proposals. Dr. Levy, Dr. Hollmann, and AMA staff are meeting with CMS and Department of Health and Human Services staff to provide clarity as they review the CPT proposals. ACOG supports the changes, which would simplify documentation for outpatient E/M codes while retaining differential payments. CMS is closely following the progress of the code changes through the CPT process and RUC code valuation process. We await further rulemaking by CMS in defining and valuing this important code set.
- CPT code 99201 to be deleted
- Revision of codes 99202-99215 as follows:
- removing history and examination as key components
(A) for selecting the level of service but requiring a medically appropriate history and or examination be performed in order to report codes 99202-99215
(B) making the basis for code selection on either the level of medical decision making (MDM) performed or the total time spent performing the service on the day of the encounter
(C) changing the definition of the time element associated with codes 99202-99215 from typical face-to-face time to total time spent on the day of the encounter and changing the amount of time associated with each code.
- Revision of the MDM elements associated with codes 99202-99215 as follows:
(i) revising "Number of Diagnoses or Management Options" to "Number and Complexity of Problems Addressed";
(ii) revising "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed" to "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed"; and
(iii) revising "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality" to "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality of Patient Management."
- Revision of the E/M guidelines by:
(A) restructuring the guidelines into three sections: "Guidelines Common to All E/M Services," "Guidelines for Hospital Observation, Hospital Inpatient, Consultations, Emergency Department, Nursing Facility, Domiciliary, Rest Home or Custodial Care and Home E/M Services," and "Guidelines for Office or Other Outpatient E/M Services" to distinguish the new reporting guidelines for the Office or Other Outpatient Services codes 99202-99215
(B) adding new guidelines that are applicable only to Office or Other Outpatient codes (99202-99215); adding a Summary of Guideline Differences table of the differences between the sets of guidelines
(C) revised existing E/M guidelines to ensure there is no conflicting information between the different sets of guidelines
(D) adding definitions of terms associated with the elements of MDM applicable to codes 99202-99215
(E) adding an MDM table that is applicable to codes 99202-99215
(F) defining total time associated with codes 99202-99215
(G) adding guidelines for reporting time when more than one individual performs distinct parts of an E/M service; revision of the MDM table in the Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed column:
(1) inserted a dash (-) after the asterisk in the asterisk definition, "* - Each unique test, order, or document may be summed if multiple," to clarify this is the meaning of the asterisk and not an asterisked item itself
(2) for limited amount of data to be reviewed and analyzed (codes 99203/99213), the parenthetical regarding the number of categories for which requirements must be met was revised to state, "¬categories of tests and documents, or independent historian(s)" rather than "categories within tests, documents, or independent historian(s)"
(3) removing the word "or" after each of the bulleted items for limited, moderate (codes 99202/99214), and high (99205/99215) amount and/or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed.
Continue to: ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye...
ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye
This is a challenging undertaking because E/M codes are used across specialties for office visits and outpatient care. The potential for unintended consequences for all services that include E/M, such as the global obstetrical services or 90-day global surgical services, is substantial. ACOG is intimately involved in this undertaking, watching the developments carefully to ensure that the interests of ObGyns and their patients are protected.
In an effort to reduce burden on physicians and qualified health care professionals, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services ( CMS) has made changes to Evaluation and Management (E/M) documentation requirements and payment policies. Get ready for fairly extensive changes planned for CY 2021. Here we outline already-implemented and future changes and describe the commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to ObGyn payment in its collaborations with CMS and the American Medical Association (AMA).

E/M services: CMS reduced documentation
Effective January 2019, the CMS made changes to the documentation requirements for E/M services to provide some common-sense relief for physicians facing excessive documentation requirements in their practices. Most physicians agree that modern medical practice, with the use of electronic health records (EHRs), is different now than in the mid-1990s, when the current E/M structures were developed and implemented. Streamlining documentation requirements reduces paperwork burden and some of the time-consuming duplicative work involved in medical practice today.
For instance, when relevant information is already contained in the medical record, it is not necessary to re-document a full medical history. Physicians will now be able to focus their documentation on the interval since the previous visit. Physicians should still review prior data, update as necessary, and indicate in the medical record that they have done so.
Also, for E/M office and outpatient visits for both new and established patients, physicians are no longer required to re-document information that has already been entered in the patient’s record by practice staff or by the patient. If the patient’s chief complaint and history already has been entered by ancillary staff or the beneficiary, the physician should simply indicate in the medical record that the information has been reviewed and verified.
For E/M visits furnished by teaching physicians, CMS has removed the requirement for potentially duplicative notations that may have been made previously in the medical records by residents or other members of the medical team.
Finally, CMS eliminated the requirement to document the medical necessity of a home visit in lieu of an office visit.
Continue to: Outpatient coding changes for 2021...
Outpatient coding changes for 2021
Outpatient coding for E/M will continue in its current form for the remainder of 2019 and 2020. However, in 2021, expect substantial changes to take effect. If the CMS rule is instituted, payment for E/M office and outpatient visits will be drastically “simplified.” The current CMS plan for 2021 is to collapse payment for existing E/M Levels 2 through 4 to one payment level for new patients and one payment level for established patients, with optional add-on codes. Level 5 visits will continue at a separate payment level and with continuation of current documentation requirements.
In addition to collapsing the payment in E/M Levels 2, 3, and 4, CMS also will allow flexibility in how those E/M office and outpatient visits are documented. Specifically, documentation may be based on any of the following:
- current framework (1995 or 1997 guidelines)
- medical decision making (MDM)
- time.
When using MDM or the current 1995/1997 framework to document an office visit, Medicare will only require documentation to support a Level 2 E/M outpatient visit code for history, exam, and/or MDM. When time is used as the basis for coding the visit, physicians will document the medical necessity of the visit and that the billing practitioner personally spent the required amount of time face-to-face with the beneficiary.
CMS also has finalized the creation of new add-on codes that describe the additional resources inherent in visits for primary care and particular kinds of nonprocedural specialized medical care (and will not be restricted by physician specialty). These codes would only be reportable with E/M office and outpatient level 2 through 4 visits, and their use generally would not impose new documentation requirements. It is not clear which types of visits would support the use of these add-on codes at this time.
Finally, a new “extended visit” add-on code will be available for use only with E/M Level 2 through 4 visits to account for the additional resources required when spending extended time with a patient.
CMS believes these policies will allow physicians, and all who bill E/M codes, greater flexibility to exercise clinical judgment in their documentation, so that they can focus on what is clinically relevant and medically necessary for the beneficiary.
ACOG’s voice in the process
ACOG strongly opposed several proposals that CMS made during the rule-making process that the agency decided not to finalize. These aspects of the proposal would have:
1. reduced payment by 50% for the least expensive procedure or visit when an E/M office or outpatient visit is furnished on the same day as a procedure by the same physician. These are separately identifiable E/M visits that normally would be reported with a modifier 25.
2. established separate coding and payment for podiatric E/M visits, or
3. standardized the allocation of practice expense relative value units (RVUs) for the codes that describe these services.
CMS has stated that they intend to engage in further discussions with the public and stakeholders to potentially further refine the policies for CY 2021.
Continue to: AMA-CPT and RUC initiative...
AMA-CPT and RUC initiative
Although the AMA, ACOG, and physicians in general applauded the CMS initiative to reduce the administrative and documentation burden on providers, there was concern about the unintended consequences of the payment changes that are currently scheduled to take effect in 2021. To address these concerns, the AMA convened a work group of physician experts who are knowledgeable in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code development and valuation processes. The charge to the E/M work group is to collaborate across the provider, payer, and coding communities to establish or revise the coding structure and guidelines for outpatient E/M services. The members formed a multispecialty work group representing primary care and surgical specialties and have experience in developing, defining, and valuing codes.
Dr. Barbara Levy, ACOG’s Vice President of Health Policy, co-chaired this expert panel with geriatrician Dr. Peter Hollmann to develop comprehensive consensus-led changes to revise and modernize E/M codes. The work group followed 4 guiding principles to inform their E/M work:
- to decrease the administrative burden of documentation and coding
- to decrease the need for audits
- to decrease unnecessary and redundant documentation in the medical record that is not needed for patient care
- to ensure that payment for E/M services is resource based. There is no direct goal for payment redistribution among specialties.
A primary concern expressed by physicians about the CMS proposal was that the collapse of payment for E/M visit across levels 2–4 might lead to a lack of appropriate care for more complex patients since the CMS rule does not provide payment based on the resources required to perform the work of the visit. No one believes that the work needed to care for someone with a sore throat or pink eye is equivalent to the work involved in diagnosing and managing depression, for example.
Beginning in August 2018, the work group met regularly to build consensus. The work group worked at an accelerated pace to develop and value codes that better fit the current medical workflows and meet patient needs.
The work group submitted a code change proposal for E/M codes to the CPT Editorial Panel for consideration during the February 2019 meeting. The next step was the code valuation process through the AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) process.
CMS has stated that the 2-year delay to 2021 in implementation of their original proposed changes is to allow time for the E/M code change proposals to move through the development and valuation process and subsequent review by the agency. To date, commercial payers and coders have been supportive of the AMA E/M work group proposals. Dr. Levy, Dr. Hollmann, and AMA staff are meeting with CMS and Department of Health and Human Services staff to provide clarity as they review the CPT proposals. ACOG supports the changes, which would simplify documentation for outpatient E/M codes while retaining differential payments. CMS is closely following the progress of the code changes through the CPT process and RUC code valuation process. We await further rulemaking by CMS in defining and valuing this important code set.
- CPT code 99201 to be deleted
- Revision of codes 99202-99215 as follows:
- removing history and examination as key components
(A) for selecting the level of service but requiring a medically appropriate history and or examination be performed in order to report codes 99202-99215
(B) making the basis for code selection on either the level of medical decision making (MDM) performed or the total time spent performing the service on the day of the encounter
(C) changing the definition of the time element associated with codes 99202-99215 from typical face-to-face time to total time spent on the day of the encounter and changing the amount of time associated with each code.
- Revision of the MDM elements associated with codes 99202-99215 as follows:
(i) revising "Number of Diagnoses or Management Options" to "Number and Complexity of Problems Addressed";
(ii) revising "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed" to "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed"; and
(iii) revising "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality" to "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality of Patient Management."
- Revision of the E/M guidelines by:
(A) restructuring the guidelines into three sections: "Guidelines Common to All E/M Services," "Guidelines for Hospital Observation, Hospital Inpatient, Consultations, Emergency Department, Nursing Facility, Domiciliary, Rest Home or Custodial Care and Home E/M Services," and "Guidelines for Office or Other Outpatient E/M Services" to distinguish the new reporting guidelines for the Office or Other Outpatient Services codes 99202-99215
(B) adding new guidelines that are applicable only to Office or Other Outpatient codes (99202-99215); adding a Summary of Guideline Differences table of the differences between the sets of guidelines
(C) revised existing E/M guidelines to ensure there is no conflicting information between the different sets of guidelines
(D) adding definitions of terms associated with the elements of MDM applicable to codes 99202-99215
(E) adding an MDM table that is applicable to codes 99202-99215
(F) defining total time associated with codes 99202-99215
(G) adding guidelines for reporting time when more than one individual performs distinct parts of an E/M service; revision of the MDM table in the Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed column:
(1) inserted a dash (-) after the asterisk in the asterisk definition, "* - Each unique test, order, or document may be summed if multiple," to clarify this is the meaning of the asterisk and not an asterisked item itself
(2) for limited amount of data to be reviewed and analyzed (codes 99203/99213), the parenthetical regarding the number of categories for which requirements must be met was revised to state, "¬categories of tests and documents, or independent historian(s)" rather than "categories within tests, documents, or independent historian(s)"
(3) removing the word "or" after each of the bulleted items for limited, moderate (codes 99202/99214), and high (99205/99215) amount and/or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed.
Continue to: ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye...
ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye
This is a challenging undertaking because E/M codes are used across specialties for office visits and outpatient care. The potential for unintended consequences for all services that include E/M, such as the global obstetrical services or 90-day global surgical services, is substantial. ACOG is intimately involved in this undertaking, watching the developments carefully to ensure that the interests of ObGyns and their patients are protected.
In an effort to reduce burden on physicians and qualified health care professionals, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services ( CMS) has made changes to Evaluation and Management (E/M) documentation requirements and payment policies. Get ready for fairly extensive changes planned for CY 2021. Here we outline already-implemented and future changes and describe the commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to ObGyn payment in its collaborations with CMS and the American Medical Association (AMA).

E/M services: CMS reduced documentation
Effective January 2019, the CMS made changes to the documentation requirements for E/M services to provide some common-sense relief for physicians facing excessive documentation requirements in their practices. Most physicians agree that modern medical practice, with the use of electronic health records (EHRs), is different now than in the mid-1990s, when the current E/M structures were developed and implemented. Streamlining documentation requirements reduces paperwork burden and some of the time-consuming duplicative work involved in medical practice today.
For instance, when relevant information is already contained in the medical record, it is not necessary to re-document a full medical history. Physicians will now be able to focus their documentation on the interval since the previous visit. Physicians should still review prior data, update as necessary, and indicate in the medical record that they have done so.
Also, for E/M office and outpatient visits for both new and established patients, physicians are no longer required to re-document information that has already been entered in the patient’s record by practice staff or by the patient. If the patient’s chief complaint and history already has been entered by ancillary staff or the beneficiary, the physician should simply indicate in the medical record that the information has been reviewed and verified.
For E/M visits furnished by teaching physicians, CMS has removed the requirement for potentially duplicative notations that may have been made previously in the medical records by residents or other members of the medical team.
Finally, CMS eliminated the requirement to document the medical necessity of a home visit in lieu of an office visit.
Continue to: Outpatient coding changes for 2021...
Outpatient coding changes for 2021
Outpatient coding for E/M will continue in its current form for the remainder of 2019 and 2020. However, in 2021, expect substantial changes to take effect. If the CMS rule is instituted, payment for E/M office and outpatient visits will be drastically “simplified.” The current CMS plan for 2021 is to collapse payment for existing E/M Levels 2 through 4 to one payment level for new patients and one payment level for established patients, with optional add-on codes. Level 5 visits will continue at a separate payment level and with continuation of current documentation requirements.
In addition to collapsing the payment in E/M Levels 2, 3, and 4, CMS also will allow flexibility in how those E/M office and outpatient visits are documented. Specifically, documentation may be based on any of the following:
- current framework (1995 or 1997 guidelines)
- medical decision making (MDM)
- time.
When using MDM or the current 1995/1997 framework to document an office visit, Medicare will only require documentation to support a Level 2 E/M outpatient visit code for history, exam, and/or MDM. When time is used as the basis for coding the visit, physicians will document the medical necessity of the visit and that the billing practitioner personally spent the required amount of time face-to-face with the beneficiary.
CMS also has finalized the creation of new add-on codes that describe the additional resources inherent in visits for primary care and particular kinds of nonprocedural specialized medical care (and will not be restricted by physician specialty). These codes would only be reportable with E/M office and outpatient level 2 through 4 visits, and their use generally would not impose new documentation requirements. It is not clear which types of visits would support the use of these add-on codes at this time.
Finally, a new “extended visit” add-on code will be available for use only with E/M Level 2 through 4 visits to account for the additional resources required when spending extended time with a patient.
CMS believes these policies will allow physicians, and all who bill E/M codes, greater flexibility to exercise clinical judgment in their documentation, so that they can focus on what is clinically relevant and medically necessary for the beneficiary.
ACOG’s voice in the process
ACOG strongly opposed several proposals that CMS made during the rule-making process that the agency decided not to finalize. These aspects of the proposal would have:
1. reduced payment by 50% for the least expensive procedure or visit when an E/M office or outpatient visit is furnished on the same day as a procedure by the same physician. These are separately identifiable E/M visits that normally would be reported with a modifier 25.
2. established separate coding and payment for podiatric E/M visits, or
3. standardized the allocation of practice expense relative value units (RVUs) for the codes that describe these services.
CMS has stated that they intend to engage in further discussions with the public and stakeholders to potentially further refine the policies for CY 2021.
Continue to: AMA-CPT and RUC initiative...
AMA-CPT and RUC initiative
Although the AMA, ACOG, and physicians in general applauded the CMS initiative to reduce the administrative and documentation burden on providers, there was concern about the unintended consequences of the payment changes that are currently scheduled to take effect in 2021. To address these concerns, the AMA convened a work group of physician experts who are knowledgeable in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code development and valuation processes. The charge to the E/M work group is to collaborate across the provider, payer, and coding communities to establish or revise the coding structure and guidelines for outpatient E/M services. The members formed a multispecialty work group representing primary care and surgical specialties and have experience in developing, defining, and valuing codes.
Dr. Barbara Levy, ACOG’s Vice President of Health Policy, co-chaired this expert panel with geriatrician Dr. Peter Hollmann to develop comprehensive consensus-led changes to revise and modernize E/M codes. The work group followed 4 guiding principles to inform their E/M work:
- to decrease the administrative burden of documentation and coding
- to decrease the need for audits
- to decrease unnecessary and redundant documentation in the medical record that is not needed for patient care
- to ensure that payment for E/M services is resource based. There is no direct goal for payment redistribution among specialties.
A primary concern expressed by physicians about the CMS proposal was that the collapse of payment for E/M visit across levels 2–4 might lead to a lack of appropriate care for more complex patients since the CMS rule does not provide payment based on the resources required to perform the work of the visit. No one believes that the work needed to care for someone with a sore throat or pink eye is equivalent to the work involved in diagnosing and managing depression, for example.
Beginning in August 2018, the work group met regularly to build consensus. The work group worked at an accelerated pace to develop and value codes that better fit the current medical workflows and meet patient needs.
The work group submitted a code change proposal for E/M codes to the CPT Editorial Panel for consideration during the February 2019 meeting. The next step was the code valuation process through the AMA/Specialty Society RVS Update Committee (RUC) process.
CMS has stated that the 2-year delay to 2021 in implementation of their original proposed changes is to allow time for the E/M code change proposals to move through the development and valuation process and subsequent review by the agency. To date, commercial payers and coders have been supportive of the AMA E/M work group proposals. Dr. Levy, Dr. Hollmann, and AMA staff are meeting with CMS and Department of Health and Human Services staff to provide clarity as they review the CPT proposals. ACOG supports the changes, which would simplify documentation for outpatient E/M codes while retaining differential payments. CMS is closely following the progress of the code changes through the CPT process and RUC code valuation process. We await further rulemaking by CMS in defining and valuing this important code set.
- CPT code 99201 to be deleted
- Revision of codes 99202-99215 as follows:
- removing history and examination as key components
(A) for selecting the level of service but requiring a medically appropriate history and or examination be performed in order to report codes 99202-99215
(B) making the basis for code selection on either the level of medical decision making (MDM) performed or the total time spent performing the service on the day of the encounter
(C) changing the definition of the time element associated with codes 99202-99215 from typical face-to-face time to total time spent on the day of the encounter and changing the amount of time associated with each code.
- Revision of the MDM elements associated with codes 99202-99215 as follows:
(i) revising "Number of Diagnoses or Management Options" to "Number and Complexity of Problems Addressed";
(ii) revising "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed" to "Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed"; and
(iii) revising "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality" to "Risk of Complications and/or Morbidity or Mortality of Patient Management."
- Revision of the E/M guidelines by:
(A) restructuring the guidelines into three sections: "Guidelines Common to All E/M Services," "Guidelines for Hospital Observation, Hospital Inpatient, Consultations, Emergency Department, Nursing Facility, Domiciliary, Rest Home or Custodial Care and Home E/M Services," and "Guidelines for Office or Other Outpatient E/M Services" to distinguish the new reporting guidelines for the Office or Other Outpatient Services codes 99202-99215
(B) adding new guidelines that are applicable only to Office or Other Outpatient codes (99202-99215); adding a Summary of Guideline Differences table of the differences between the sets of guidelines
(C) revised existing E/M guidelines to ensure there is no conflicting information between the different sets of guidelines
(D) adding definitions of terms associated with the elements of MDM applicable to codes 99202-99215
(E) adding an MDM table that is applicable to codes 99202-99215
(F) defining total time associated with codes 99202-99215
(G) adding guidelines for reporting time when more than one individual performs distinct parts of an E/M service; revision of the MDM table in the Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed and Analyzed column:
(1) inserted a dash (-) after the asterisk in the asterisk definition, "* - Each unique test, order, or document may be summed if multiple," to clarify this is the meaning of the asterisk and not an asterisked item itself
(2) for limited amount of data to be reviewed and analyzed (codes 99203/99213), the parenthetical regarding the number of categories for which requirements must be met was revised to state, "¬categories of tests and documents, or independent historian(s)" rather than "categories within tests, documents, or independent historian(s)"
(3) removing the word "or" after each of the bulleted items for limited, moderate (codes 99202/99214), and high (99205/99215) amount and/or complexity of data to be reviewed and analyzed.
Continue to: ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye...
ACOG is at the helm, with a watchful eye
This is a challenging undertaking because E/M codes are used across specialties for office visits and outpatient care. The potential for unintended consequences for all services that include E/M, such as the global obstetrical services or 90-day global surgical services, is substantial. ACOG is intimately involved in this undertaking, watching the developments carefully to ensure that the interests of ObGyns and their patients are protected.
What to do when a patient presents with breast pain
Breast pain is one of the most common breast-related patient complaints and is found to affect at least 50% of the female population.1 Most cases are self-limiting and are related to hormonal and normal fibrocystic changes. The median age of onset of symptoms is 36 years, with most women experiencing pain for 5 to 12 years.2 Because the cause of breast pain is not always clear, its presence can produce anxiety in patients and physicians over the possibility of underlying malignancy. Although breast cancer is not associated with breast pain, many patients presenting with pain are referred for diagnostic imaging (usually with negative results). The majority of women with mastalgia and normal clinical examination findings can be reassured with education about the many benign causes of breast pain.
What are causes of breast pain without an imaging abnormality?
Hormones. Mastalgia can be focal or generalized and is mostly due to hormonal changes. Elevated estrogen can stimulate the growth of breast tissue, which is known as epithelial hyperplasia.3 Fluctuations in hormone levels can occur in perimenopausal women in their forties and can result in new symptoms of breast pain.4 Sometimes starting a new contraceptive medication or hormone replacement therapy can exacerbate the pain. Switching brands or medications may help. Another cause of mastalgia may be elevated prolactin levels, with hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction.5,6
Diet. There is evidence to link a high-fat diet with breast pain. The pain has been shown to improve when lipid intake is reduced and high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are normalized. As estrogen is a steroid hormone that can be synthesized from lipids and fatty acids, elevated lipid metabolism can increase estrogen levels and exacerbate breast pain symptoms.7,8 Essential fatty acids, such as evening primrose oil and vitamin E, have been used to treat mastalgia because they reduce inflammation in fatty breast tissue through the prostaglandin pathway.9,10
Caffeine. Methylxanthines can be found in coffee, tea, and chocolate and can aggravate mastalgia by enhancing the cyclin adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. This pathway stimulates cellular proliferation and fibrocystic changes which in turn can exacerbate breast pain.11
Smoking. In my clinical practice I have clearly noted a higher incidence of breast pain in patients who smoke. The pain tends to improve significantly when the patient quits or even cuts back on smoking. The exact reasons for smoking’s effects on breast pain are not well known; however, they are thought to be related to acceleration of the cAMP pathway.
Large breast size. Very large breasts will strain and weaken the suspensory ligaments, leading to pain and discomfort. It has been shown that wearing a supportive sports bra during episodes of breast pain is effective.
Types of breast pain
Cyclical
Women with fibrocystic breasts tend to experience more breast pain. Breast sensitivity can be localized to the upper outer quadrants or to the nipple and sub-areolar area. It also can be generalized. The pain tends to peak with ovulation, improve with menses, and to recur every few weeks. Patients who have had partial hysterectomy (with ovaries in situ) or endometrial ablation will be unable to correlate their symptoms to menstruation. Therefore, women are encouraged to keep a diary or calendar of their symptoms to detect any correlation with their ovarian cycle. Such correlation is reassuring.
Continue to: Noncyclical...
Noncyclical
Noncyclical breast pain is not associated with the menstrual cycle and can be unilateral or bilateral. Providers should perform a good history of patients presenting with noncyclicalbreast pain, to include character, onset, duration, location, radiation, alleviating, and aggravating factors. A physical examination may elicit point tenderness at the chest by pushing the breast tissue off of the chest wall while the patient is in supine position and pressing directly over the ribs. Lack of tenderness on palpation of the breast parenchyma, but pain on the chest wall, points to a musculoskeletal etiology. Chest wall pain may be related to muscle spasm or muscle strain, trauma, rib fracture, or costochondritis (Tietze syndrome). Finally, based on history of review of systems and physical examination, referred pain from biliary or cardiac etiology should be considered.
When breast pain occurs with skin changes
Skin changes usually have an underlying pathology. Infectious processes, such as infected epidermal inclusion cyst, hidradenitis of the cleavage and inframammary crease, or breast abscess will present with pain and induration with an acute onset of 5 to 10 days. Large pendulous breasts may develop yeast infection at the inframammary crease. Chronic infectious irritation can lead to hyperpigmentation of that area. Eczema or contact dermatitis frequently can affect the areola and become confused with Paget disease (ductal carcinoma in situ of the nipple). With Paget, the excoriation always starts at the nipple and can then spread to the areola. However, with dermatitis, the rash begins on the peri-areolar skin, without affecting the nipple itself.
When breast pain occurs with nipple discharge
Breast pain with nipple discharge usually is bilateral and more common in patients with significant fibrocystic changes who smoke. If the nipple discharge is bilateral, serous and non-bloody, and multiduct, it is considered benign and physiologic. Physiologic nipple discharge can be multifactorial and hormonal. It may be related to thyroid disorders or medications such as antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics. The only nipple discharge that is considered pathologic is unilateral spontaneous bloody discharge for which diagnostic imaging and breast surgeon referral is indicated. Women should be discouraged from self-expressing their nipples, as 80% will experience serous nipple discharge upon manual self-expression.
Breast pain is not associated with breast cancer. Most breast cancers do not hurt; they present as firm, painless masses. However, when a woman notices pain in her breast, her first concern is breast cancer. This concern is re-enforced by the medical provider whose first impulse is to order diagnostic imaging. Yet less than 3% of breast cancers are associated with breast pain.
There have been multiple published retrospective and prospective radiologic studies about the utility of breast imaging in women with breast pain without a palpable mass. All of the studies have demonstrated that breast imaging with mammography and ultrasonography in these patients yields mostly negative or benign findings. The incidence of breast cancer during imaging work-up in women with breast pain and no clinical abnormality is only 0.4% to 1.8%.1-3 Some patients may develop future subsequent breast cancer in the symptomatic breast. But this is considered incidental and possibly related to increased cell turnover related to fibrocystic changes. Breast imaging for evaluation of breast pain only provides reassurance to the physician. The patient's reassurance will come from a medical explanation for the symptoms and advice on symptom management from the provider.
Researchers from MD Anderson Cancer Center reported imaging findings and cost analysis for 799 patients presenting with breast pain from 3 large network community-based breast imaging centers in 2014. Breast ultrasound was the initial imaging modality for women younger than age 30. Digital mammography (sometimes with tomosynthesis) was used for those older than age 30 that had not had a mammogram in the last 6 months. Breast magnetic resonance imaging was performed only when ordered by the referring physician. Most of the patients presented for diagnostic imaging, and 95% had negative findings and 5% had a benign finding. Only 1 patient was found to have an incidental cancer in the contralateral breast, which was detected by tomosynthesis. The cost of breast imaging was $87,322 in younger women and $152,732 in women older than age 40, representing overutilization of health care resources and no association between breast pain and breast cancer.4
References
- Chetlan AL, Kapoor MM, Watts MR. Mastalgia: imaging work-up appropriateness. Acad Radiol. 2017;24:345-349.
- Arslan M, Kücükerdem HS, Can H, et al. Retrospective analysis of women with only mastalgia. J Breast Health. 2016;12:151-154.
- Noroozian M, Stein LF, Gaetke-Udager K, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in women with breast pain in the absence of additional clinical findings: Mammography remains indicated. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;149:417-424.
- Kushwaha AC, Shin K, Kalambo M, et al. Overutilization of health care resources for breast pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 211:217-223.
Management of mastalgia
Appropriate breast pain management begins with a good history and physical examination. The decision to perform imaging should depend on clinical exam findings and not on symptoms of breast pain. If there is a palpable mass, then breast imaging and possible biopsy is appropriate. However, if clinical exam is normal, there is no indication for breast imaging in low-risk women under the age of 40 whose only symptom is breast pain. Women older than age 40 can undergo diagnostic imaging, if they have not had a negative screening mammogram in the past year.
Breast pain with abnormal clinical exam
In the patient who is younger than age 30 with a palpable mass. For this patient order targeted breast ultrasound (US) (FIGURE 1). If results are negative, repeat the clinical examination 1 week after menses. If the mass is persistent, refer the patient to a breast surgeon. If diagnostic imaging results are negative, consider breast MRI, especially if there is a strong family history of breast cancer.
In the patient who is aged 30 and older with a palpable mass. For this patient, bilateral diagnostic mammogram and US are in order. The testing is best performed 1 week after menses to reduce false-positive findings. If imaging is negative and the patient still has a clinically suspicious finding or mass, refer her to a breast surgeon and consider breast MRI. At this point if there is a persistent firm dominant mass, a biopsy is indicated as part of the triple test. If the mass resolves with menses, the patient can be reassured that the cause is most likely benign, with clinical examination repeated in 3 months.
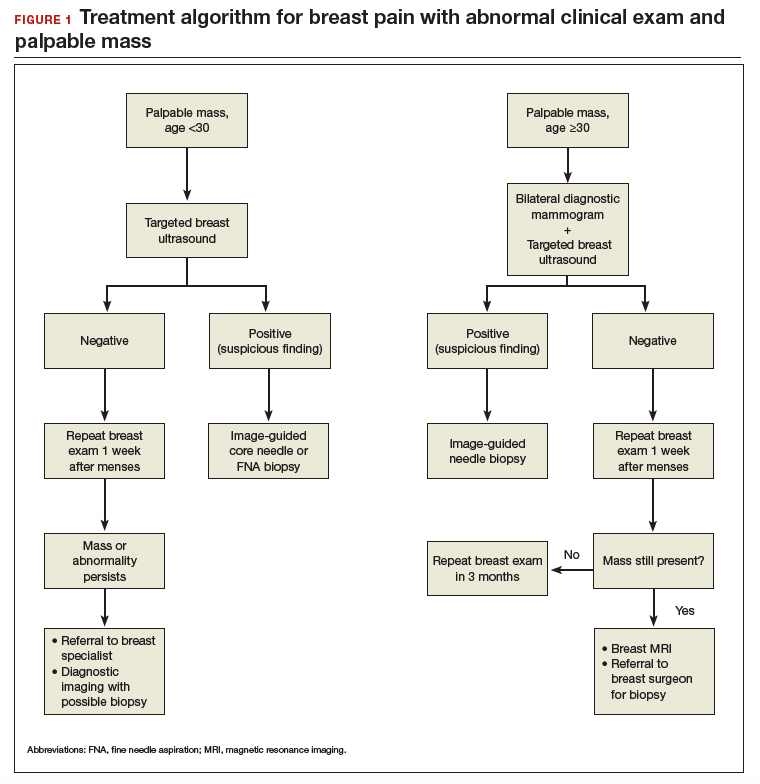
Continue to: Breast pain and normal clinical exam...
Breast pain and normal clinical exam
When women who report breast pain have normal clinical examination findings (and have a negative screening mammogram in the past 12 months if older than age 40), there are several management strategies you can offer (FIGURE 2).
Reassurance and education. The majority of women with breast pain can be managed with reassurance and education, which are often sufficient to reduce their anxieties.
Supportive bra. The most effective intervention is to wear and sleep in a well-fitted supportive sports bra for 4 to 12 weeks. In a nonrandomized single-center trial of danazol versus sports bra, 85% of women reported relief of their breast pain with bra alone (vs 58% with danazol).12 A supportive bra is the first-line management of mastalgia (Level II evidence).
Symptom diary/calendar. Many women do not know whether or not their symptoms correspond to their ovarian cycle or are related to hormonal fluctuations. Therefore, it is reassuring and informative for them to keep a calendar or a diary of their symptoms to determine whether their symptoms occur or are exacerbated in a cyclical pattern.
Diet and lifestyle modification. Women should avoid caffeine (especially when having pain). Studies on methylxanthines have demonstrated some symptom relief with reducing caffeine intake.11,13 One cup of coffee or tea per day most likely will not make a difference. However, if a woman is drinking large quantities of caffeinated beverages throughout the day, it will very likely improve her breast pain if she cuts back. This is especially true during the times of exacerbated pain prior to her menses.
In addition, recommend reduced dietary fat (overall good health). This is good advice for any patient. There were 2 small studies that showed improvement in breast pain with a 15% reduction in dietary fat.7,8
Finally, advise that patients stop smoking. Smoking aggravates and exacerbates fibrocystic changes, and these will lead to more breast pain.
Medical management. Over-the-counter medications that are found in the vitamin section of a local drug store are vitamin E and evening primrose oil. There are no significant adverse effects with these treatments. Their efficacy is theoretical, however; 3 randomized controlled trials demonstrated no significant clinical benefit with evening primrose oil versus placebo for treatment of mastalgia.14
Topical or oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; Voltaren gel, topical compound pain creams) are useful as second-line management after using a supportive bra. Three randomized controlled trials have demonstrated up to 90% improvement of mastalgia with topical NSAIDs.15-17
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM), which is an antagonist to the estrogen receptor (ER) in the breast and an agonist to the ER in the endometrium. Tamoxifen has been found to reduce symptoms of mastalgia by 70% even at a lower dosage of 10-mg per day (for 6 months), or as a topical gel (afimoxifene). The oral form can have some adverse effects, including hot flashes, and has a low risk for thromboembolic events and endometrial neoplasia.18-20
Danazol is very effective in reducing breast pain symptoms (by 80%), with a higher relapse after stopping the medication. Danazol is less tolerated due to its androgenic effects, such as hirsutism, acne, menorrhagia, and voice changes. Both danazol and tamoxifen can be teratogenic and should be used with caution in women of child-bearing age.21
Finally, bromocriptine inhibits serum prolactin and has been reported to provide 65% improvement in breast pain. Its use for breast pain is not US Food and Drug Administration–approved and adverse effects include nausea, dizziness, and hypotension.22
Tamoxifen, danazol, and bromocriptine can be considered as third-line management options for severe treatment-resistant mastalgia.
Continue to: FIGURE 2 Treatment algorithm for breast pain...
In summary
Evaluation and counseling for breast pain should be managed by women’s health care providers in a primary care setting. Most patients need reassurance and medical explanation of their symptoms. They should be educated that more than 95% of the time breast pain is not caused by an underlying malignancy but rather due to hormonal and fibrocystic changes, which can be managed conservatively. If the clinical breast examination and recent screening mammogram (in women over age 40) results are negative, patients should be educated that their pain is benign and undergo a trial of conservative measures: wear and sleep in a supporting bra; keep a calendar of symptoms to determine any relation to cyclical changes; and avoid nicotine, caffeine, and fatty food. Topical pain creams with diclofenac and evening primrose oil also can be effective in ameliorating the symptoms. Breast pain is not a surgical disease; referral to a surgical specialist and diagnostic imaging can be unnecessary and expensive.
- Scurr J, Hedger W, Morris P, et al. The prevalence, severity, and impact of breast pain in the general population. Breast J. 2014;20:508-513.
- Davies EL, Gateley CA, Miers M, et al. The long-term course of mastalgia. J R Soc Med. 1998;91:462-464.
- Singletary SE, Robb GL, Hortobagy GN. Advanced Therapy of Breast Disease. 2nd ed. Ontario, Canada: BC Decker Inc.; 2004.
- Gong C, Song E, Jia W, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of toremifen therapy for mastaglia. Arch Surg. 2006;141:43-47.
- Kumar S, Mansel RE, Scanlon MF, et al. Altered responses of prolactin, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone secretion to thyrotrophin releasing hormone/gonadotrophin releasing hormone stimulation in cyclical mastalgia. Br J Surg. 1984;71:870-873.
- Mansel RE, Dogliotti L. European multicentre trial of bromocriptine in cyclical mastalgia. Lancet. 1990;335:190-193.
- Rose DP, Boyar AP, Cohen C, et al. Effect of a low-fat diet on hormone levels in women with cystic breast disease. I. Serum steroids and gonadotropins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:623-626.
- Goodwin JP, Miller A, Del Giudice ME, et al. Elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and dietary fat intake in women with cyclic mastopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:430-437.
- Goyal A, Mansel RE. Efamast Study Group. A randomized multicenter study of gamolenic acid (Efamast) with and without antioxidant vitamins and minerals in the management of mastalgia. Breast J. 2005;11(1):41-47.
- Parsay S, Olfati F, Nahidi S. Therapeutic effects of vitamin E on cyclic mastalgia. Breast J. 2009;15:510-514.
- Allen SS, Froberg DG. The effect of decreased caffeine consumption on benign proliferative breast disease: a randomized clinical trial. Surgery. 1987;101:720-730.
- Hadi MS. Sports brassiere: is it a solution for mastalgia? Breast J. 2000;6:407-409.
- Russell LC. Caffeine restriction as initial treatment for breast pain. Nurse Pract. 1989; 14(2): 36-7.
- Srivastava A, Mansel RE, Arvind N, et al. Evidence-based management of mastalgia: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Breast. 2007;16:503-512.
- Irving AD, Morrison SL. Effectiveness of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the management of breast pain. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1998;43:158-159.
- Colak T, Ipek T, Kanik A, et al. Efficiency of topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in mastalgia treatment. J Am Coll Surg. 2003;196(4):525-530.
- Kaviani A, Mehrdad N, Najafi M, et al. Comparison of naproxen with placebo for the management of noncyclical breast pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. World J Surg. 2008;32:2464-2470.
- Fentiman IS, Caleffi M, Brame K, et al. Double-blind controlled trial of tamoxifen therapy for mastalgia. Lancet. 1986;1:287-288.
- Jain BK, Bansal A, Choudhary D, et al. Centchroman vs tamoxifen for regression of mastalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Intl J Surg. 2015;15:11-16.
- Mansel R, Goyal A, Le Nestour EL, et al; Afimoxifene (4-OHT) Breast Pain Research group. A phase II trial of Afimoxifene (4-hydroxyamoxifen gel) for cyclical mastalgia in premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106:389-397.
- O'Brien PM, Abukhalil IE. Randomized controlled trial of the management of premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual mastalgia using luteal phase-only danazol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:18-23.
- Blichert-Toft M, Andersen AN, Henriksen OB, et al. Treatment of mastalgia with bromocriptine: a double-blind cross-over study. Br Med J. 1979;1:237.
Breast pain is one of the most common breast-related patient complaints and is found to affect at least 50% of the female population.1 Most cases are self-limiting and are related to hormonal and normal fibrocystic changes. The median age of onset of symptoms is 36 years, with most women experiencing pain for 5 to 12 years.2 Because the cause of breast pain is not always clear, its presence can produce anxiety in patients and physicians over the possibility of underlying malignancy. Although breast cancer is not associated with breast pain, many patients presenting with pain are referred for diagnostic imaging (usually with negative results). The majority of women with mastalgia and normal clinical examination findings can be reassured with education about the many benign causes of breast pain.
What are causes of breast pain without an imaging abnormality?
Hormones. Mastalgia can be focal or generalized and is mostly due to hormonal changes. Elevated estrogen can stimulate the growth of breast tissue, which is known as epithelial hyperplasia.3 Fluctuations in hormone levels can occur in perimenopausal women in their forties and can result in new symptoms of breast pain.4 Sometimes starting a new contraceptive medication or hormone replacement therapy can exacerbate the pain. Switching brands or medications may help. Another cause of mastalgia may be elevated prolactin levels, with hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction.5,6
Diet. There is evidence to link a high-fat diet with breast pain. The pain has been shown to improve when lipid intake is reduced and high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are normalized. As estrogen is a steroid hormone that can be synthesized from lipids and fatty acids, elevated lipid metabolism can increase estrogen levels and exacerbate breast pain symptoms.7,8 Essential fatty acids, such as evening primrose oil and vitamin E, have been used to treat mastalgia because they reduce inflammation in fatty breast tissue through the prostaglandin pathway.9,10
Caffeine. Methylxanthines can be found in coffee, tea, and chocolate and can aggravate mastalgia by enhancing the cyclin adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. This pathway stimulates cellular proliferation and fibrocystic changes which in turn can exacerbate breast pain.11
Smoking. In my clinical practice I have clearly noted a higher incidence of breast pain in patients who smoke. The pain tends to improve significantly when the patient quits or even cuts back on smoking. The exact reasons for smoking’s effects on breast pain are not well known; however, they are thought to be related to acceleration of the cAMP pathway.
Large breast size. Very large breasts will strain and weaken the suspensory ligaments, leading to pain and discomfort. It has been shown that wearing a supportive sports bra during episodes of breast pain is effective.
Types of breast pain
Cyclical
Women with fibrocystic breasts tend to experience more breast pain. Breast sensitivity can be localized to the upper outer quadrants or to the nipple and sub-areolar area. It also can be generalized. The pain tends to peak with ovulation, improve with menses, and to recur every few weeks. Patients who have had partial hysterectomy (with ovaries in situ) or endometrial ablation will be unable to correlate their symptoms to menstruation. Therefore, women are encouraged to keep a diary or calendar of their symptoms to detect any correlation with their ovarian cycle. Such correlation is reassuring.

Continue to: Noncyclical...
Noncyclical
Noncyclical breast pain is not associated with the menstrual cycle and can be unilateral or bilateral. Providers should perform a good history of patients presenting with noncyclicalbreast pain, to include character, onset, duration, location, radiation, alleviating, and aggravating factors. A physical examination may elicit point tenderness at the chest by pushing the breast tissue off of the chest wall while the patient is in supine position and pressing directly over the ribs. Lack of tenderness on palpation of the breast parenchyma, but pain on the chest wall, points to a musculoskeletal etiology. Chest wall pain may be related to muscle spasm or muscle strain, trauma, rib fracture, or costochondritis (Tietze syndrome). Finally, based on history of review of systems and physical examination, referred pain from biliary or cardiac etiology should be considered.
When breast pain occurs with skin changes
Skin changes usually have an underlying pathology. Infectious processes, such as infected epidermal inclusion cyst, hidradenitis of the cleavage and inframammary crease, or breast abscess will present with pain and induration with an acute onset of 5 to 10 days. Large pendulous breasts may develop yeast infection at the inframammary crease. Chronic infectious irritation can lead to hyperpigmentation of that area. Eczema or contact dermatitis frequently can affect the areola and become confused with Paget disease (ductal carcinoma in situ of the nipple). With Paget, the excoriation always starts at the nipple and can then spread to the areola. However, with dermatitis, the rash begins on the peri-areolar skin, without affecting the nipple itself.
When breast pain occurs with nipple discharge
Breast pain with nipple discharge usually is bilateral and more common in patients with significant fibrocystic changes who smoke. If the nipple discharge is bilateral, serous and non-bloody, and multiduct, it is considered benign and physiologic. Physiologic nipple discharge can be multifactorial and hormonal. It may be related to thyroid disorders or medications such as antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics. The only nipple discharge that is considered pathologic is unilateral spontaneous bloody discharge for which diagnostic imaging and breast surgeon referral is indicated. Women should be discouraged from self-expressing their nipples, as 80% will experience serous nipple discharge upon manual self-expression.
Breast pain is not associated with breast cancer. Most breast cancers do not hurt; they present as firm, painless masses. However, when a woman notices pain in her breast, her first concern is breast cancer. This concern is re-enforced by the medical provider whose first impulse is to order diagnostic imaging. Yet less than 3% of breast cancers are associated with breast pain.
There have been multiple published retrospective and prospective radiologic studies about the utility of breast imaging in women with breast pain without a palpable mass. All of the studies have demonstrated that breast imaging with mammography and ultrasonography in these patients yields mostly negative or benign findings. The incidence of breast cancer during imaging work-up in women with breast pain and no clinical abnormality is only 0.4% to 1.8%.1-3 Some patients may develop future subsequent breast cancer in the symptomatic breast. But this is considered incidental and possibly related to increased cell turnover related to fibrocystic changes. Breast imaging for evaluation of breast pain only provides reassurance to the physician. The patient's reassurance will come from a medical explanation for the symptoms and advice on symptom management from the provider.
Researchers from MD Anderson Cancer Center reported imaging findings and cost analysis for 799 patients presenting with breast pain from 3 large network community-based breast imaging centers in 2014. Breast ultrasound was the initial imaging modality for women younger than age 30. Digital mammography (sometimes with tomosynthesis) was used for those older than age 30 that had not had a mammogram in the last 6 months. Breast magnetic resonance imaging was performed only when ordered by the referring physician. Most of the patients presented for diagnostic imaging, and 95% had negative findings and 5% had a benign finding. Only 1 patient was found to have an incidental cancer in the contralateral breast, which was detected by tomosynthesis. The cost of breast imaging was $87,322 in younger women and $152,732 in women older than age 40, representing overutilization of health care resources and no association between breast pain and breast cancer.4
References
- Chetlan AL, Kapoor MM, Watts MR. Mastalgia: imaging work-up appropriateness. Acad Radiol. 2017;24:345-349.
- Arslan M, Kücükerdem HS, Can H, et al. Retrospective analysis of women with only mastalgia. J Breast Health. 2016;12:151-154.
- Noroozian M, Stein LF, Gaetke-Udager K, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in women with breast pain in the absence of additional clinical findings: Mammography remains indicated. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;149:417-424.
- Kushwaha AC, Shin K, Kalambo M, et al. Overutilization of health care resources for breast pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 211:217-223.
Management of mastalgia
Appropriate breast pain management begins with a good history and physical examination. The decision to perform imaging should depend on clinical exam findings and not on symptoms of breast pain. If there is a palpable mass, then breast imaging and possible biopsy is appropriate. However, if clinical exam is normal, there is no indication for breast imaging in low-risk women under the age of 40 whose only symptom is breast pain. Women older than age 40 can undergo diagnostic imaging, if they have not had a negative screening mammogram in the past year.
Breast pain with abnormal clinical exam
In the patient who is younger than age 30 with a palpable mass. For this patient order targeted breast ultrasound (US) (FIGURE 1). If results are negative, repeat the clinical examination 1 week after menses. If the mass is persistent, refer the patient to a breast surgeon. If diagnostic imaging results are negative, consider breast MRI, especially if there is a strong family history of breast cancer.
In the patient who is aged 30 and older with a palpable mass. For this patient, bilateral diagnostic mammogram and US are in order. The testing is best performed 1 week after menses to reduce false-positive findings. If imaging is negative and the patient still has a clinically suspicious finding or mass, refer her to a breast surgeon and consider breast MRI. At this point if there is a persistent firm dominant mass, a biopsy is indicated as part of the triple test. If the mass resolves with menses, the patient can be reassured that the cause is most likely benign, with clinical examination repeated in 3 months.

Continue to: Breast pain and normal clinical exam...
Breast pain and normal clinical exam
When women who report breast pain have normal clinical examination findings (and have a negative screening mammogram in the past 12 months if older than age 40), there are several management strategies you can offer (FIGURE 2).
Reassurance and education. The majority of women with breast pain can be managed with reassurance and education, which are often sufficient to reduce their anxieties.
Supportive bra. The most effective intervention is to wear and sleep in a well-fitted supportive sports bra for 4 to 12 weeks. In a nonrandomized single-center trial of danazol versus sports bra, 85% of women reported relief of their breast pain with bra alone (vs 58% with danazol).12 A supportive bra is the first-line management of mastalgia (Level II evidence).
Symptom diary/calendar. Many women do not know whether or not their symptoms correspond to their ovarian cycle or are related to hormonal fluctuations. Therefore, it is reassuring and informative for them to keep a calendar or a diary of their symptoms to determine whether their symptoms occur or are exacerbated in a cyclical pattern.
Diet and lifestyle modification. Women should avoid caffeine (especially when having pain). Studies on methylxanthines have demonstrated some symptom relief with reducing caffeine intake.11,13 One cup of coffee or tea per day most likely will not make a difference. However, if a woman is drinking large quantities of caffeinated beverages throughout the day, it will very likely improve her breast pain if she cuts back. This is especially true during the times of exacerbated pain prior to her menses.
In addition, recommend reduced dietary fat (overall good health). This is good advice for any patient. There were 2 small studies that showed improvement in breast pain with a 15% reduction in dietary fat.7,8
Finally, advise that patients stop smoking. Smoking aggravates and exacerbates fibrocystic changes, and these will lead to more breast pain.
Medical management. Over-the-counter medications that are found in the vitamin section of a local drug store are vitamin E and evening primrose oil. There are no significant adverse effects with these treatments. Their efficacy is theoretical, however; 3 randomized controlled trials demonstrated no significant clinical benefit with evening primrose oil versus placebo for treatment of mastalgia.14
Topical or oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; Voltaren gel, topical compound pain creams) are useful as second-line management after using a supportive bra. Three randomized controlled trials have demonstrated up to 90% improvement of mastalgia with topical NSAIDs.15-17
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM), which is an antagonist to the estrogen receptor (ER) in the breast and an agonist to the ER in the endometrium. Tamoxifen has been found to reduce symptoms of mastalgia by 70% even at a lower dosage of 10-mg per day (for 6 months), or as a topical gel (afimoxifene). The oral form can have some adverse effects, including hot flashes, and has a low risk for thromboembolic events and endometrial neoplasia.18-20
Danazol is very effective in reducing breast pain symptoms (by 80%), with a higher relapse after stopping the medication. Danazol is less tolerated due to its androgenic effects, such as hirsutism, acne, menorrhagia, and voice changes. Both danazol and tamoxifen can be teratogenic and should be used with caution in women of child-bearing age.21
Finally, bromocriptine inhibits serum prolactin and has been reported to provide 65% improvement in breast pain. Its use for breast pain is not US Food and Drug Administration–approved and adverse effects include nausea, dizziness, and hypotension.22
Tamoxifen, danazol, and bromocriptine can be considered as third-line management options for severe treatment-resistant mastalgia.
Continue to: FIGURE 2 Treatment algorithm for breast pain...

In summary
Evaluation and counseling for breast pain should be managed by women’s health care providers in a primary care setting. Most patients need reassurance and medical explanation of their symptoms. They should be educated that more than 95% of the time breast pain is not caused by an underlying malignancy but rather due to hormonal and fibrocystic changes, which can be managed conservatively. If the clinical breast examination and recent screening mammogram (in women over age 40) results are negative, patients should be educated that their pain is benign and undergo a trial of conservative measures: wear and sleep in a supporting bra; keep a calendar of symptoms to determine any relation to cyclical changes; and avoid nicotine, caffeine, and fatty food. Topical pain creams with diclofenac and evening primrose oil also can be effective in ameliorating the symptoms. Breast pain is not a surgical disease; referral to a surgical specialist and diagnostic imaging can be unnecessary and expensive.
Breast pain is one of the most common breast-related patient complaints and is found to affect at least 50% of the female population.1 Most cases are self-limiting and are related to hormonal and normal fibrocystic changes. The median age of onset of symptoms is 36 years, with most women experiencing pain for 5 to 12 years.2 Because the cause of breast pain is not always clear, its presence can produce anxiety in patients and physicians over the possibility of underlying malignancy. Although breast cancer is not associated with breast pain, many patients presenting with pain are referred for diagnostic imaging (usually with negative results). The majority of women with mastalgia and normal clinical examination findings can be reassured with education about the many benign causes of breast pain.
What are causes of breast pain without an imaging abnormality?
Hormones. Mastalgia can be focal or generalized and is mostly due to hormonal changes. Elevated estrogen can stimulate the growth of breast tissue, which is known as epithelial hyperplasia.3 Fluctuations in hormone levels can occur in perimenopausal women in their forties and can result in new symptoms of breast pain.4 Sometimes starting a new contraceptive medication or hormone replacement therapy can exacerbate the pain. Switching brands or medications may help. Another cause of mastalgia may be elevated prolactin levels, with hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction.5,6
Diet. There is evidence to link a high-fat diet with breast pain. The pain has been shown to improve when lipid intake is reduced and high- and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels are normalized. As estrogen is a steroid hormone that can be synthesized from lipids and fatty acids, elevated lipid metabolism can increase estrogen levels and exacerbate breast pain symptoms.7,8 Essential fatty acids, such as evening primrose oil and vitamin E, have been used to treat mastalgia because they reduce inflammation in fatty breast tissue through the prostaglandin pathway.9,10
Caffeine. Methylxanthines can be found in coffee, tea, and chocolate and can aggravate mastalgia by enhancing the cyclin adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway. This pathway stimulates cellular proliferation and fibrocystic changes which in turn can exacerbate breast pain.11
Smoking. In my clinical practice I have clearly noted a higher incidence of breast pain in patients who smoke. The pain tends to improve significantly when the patient quits or even cuts back on smoking. The exact reasons for smoking’s effects on breast pain are not well known; however, they are thought to be related to acceleration of the cAMP pathway.
Large breast size. Very large breasts will strain and weaken the suspensory ligaments, leading to pain and discomfort. It has been shown that wearing a supportive sports bra during episodes of breast pain is effective.
Types of breast pain
Cyclical
Women with fibrocystic breasts tend to experience more breast pain. Breast sensitivity can be localized to the upper outer quadrants or to the nipple and sub-areolar area. It also can be generalized. The pain tends to peak with ovulation, improve with menses, and to recur every few weeks. Patients who have had partial hysterectomy (with ovaries in situ) or endometrial ablation will be unable to correlate their symptoms to menstruation. Therefore, women are encouraged to keep a diary or calendar of their symptoms to detect any correlation with their ovarian cycle. Such correlation is reassuring.

Continue to: Noncyclical...
Noncyclical
Noncyclical breast pain is not associated with the menstrual cycle and can be unilateral or bilateral. Providers should perform a good history of patients presenting with noncyclicalbreast pain, to include character, onset, duration, location, radiation, alleviating, and aggravating factors. A physical examination may elicit point tenderness at the chest by pushing the breast tissue off of the chest wall while the patient is in supine position and pressing directly over the ribs. Lack of tenderness on palpation of the breast parenchyma, but pain on the chest wall, points to a musculoskeletal etiology. Chest wall pain may be related to muscle spasm or muscle strain, trauma, rib fracture, or costochondritis (Tietze syndrome). Finally, based on history of review of systems and physical examination, referred pain from biliary or cardiac etiology should be considered.
When breast pain occurs with skin changes
Skin changes usually have an underlying pathology. Infectious processes, such as infected epidermal inclusion cyst, hidradenitis of the cleavage and inframammary crease, or breast abscess will present with pain and induration with an acute onset of 5 to 10 days. Large pendulous breasts may develop yeast infection at the inframammary crease. Chronic infectious irritation can lead to hyperpigmentation of that area. Eczema or contact dermatitis frequently can affect the areola and become confused with Paget disease (ductal carcinoma in situ of the nipple). With Paget, the excoriation always starts at the nipple and can then spread to the areola. However, with dermatitis, the rash begins on the peri-areolar skin, without affecting the nipple itself.
When breast pain occurs with nipple discharge
Breast pain with nipple discharge usually is bilateral and more common in patients with significant fibrocystic changes who smoke. If the nipple discharge is bilateral, serous and non-bloody, and multiduct, it is considered benign and physiologic. Physiologic nipple discharge can be multifactorial and hormonal. It may be related to thyroid disorders or medications such as antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), mood stabilizers, or antipsychotics. The only nipple discharge that is considered pathologic is unilateral spontaneous bloody discharge for which diagnostic imaging and breast surgeon referral is indicated. Women should be discouraged from self-expressing their nipples, as 80% will experience serous nipple discharge upon manual self-expression.
Breast pain is not associated with breast cancer. Most breast cancers do not hurt; they present as firm, painless masses. However, when a woman notices pain in her breast, her first concern is breast cancer. This concern is re-enforced by the medical provider whose first impulse is to order diagnostic imaging. Yet less than 3% of breast cancers are associated with breast pain.
There have been multiple published retrospective and prospective radiologic studies about the utility of breast imaging in women with breast pain without a palpable mass. All of the studies have demonstrated that breast imaging with mammography and ultrasonography in these patients yields mostly negative or benign findings. The incidence of breast cancer during imaging work-up in women with breast pain and no clinical abnormality is only 0.4% to 1.8%.1-3 Some patients may develop future subsequent breast cancer in the symptomatic breast. But this is considered incidental and possibly related to increased cell turnover related to fibrocystic changes. Breast imaging for evaluation of breast pain only provides reassurance to the physician. The patient's reassurance will come from a medical explanation for the symptoms and advice on symptom management from the provider.
Researchers from MD Anderson Cancer Center reported imaging findings and cost analysis for 799 patients presenting with breast pain from 3 large network community-based breast imaging centers in 2014. Breast ultrasound was the initial imaging modality for women younger than age 30. Digital mammography (sometimes with tomosynthesis) was used for those older than age 30 that had not had a mammogram in the last 6 months. Breast magnetic resonance imaging was performed only when ordered by the referring physician. Most of the patients presented for diagnostic imaging, and 95% had negative findings and 5% had a benign finding. Only 1 patient was found to have an incidental cancer in the contralateral breast, which was detected by tomosynthesis. The cost of breast imaging was $87,322 in younger women and $152,732 in women older than age 40, representing overutilization of health care resources and no association between breast pain and breast cancer.4
References
- Chetlan AL, Kapoor MM, Watts MR. Mastalgia: imaging work-up appropriateness. Acad Radiol. 2017;24:345-349.
- Arslan M, Kücükerdem HS, Can H, et al. Retrospective analysis of women with only mastalgia. J Breast Health. 2016;12:151-154.
- Noroozian M, Stein LF, Gaetke-Udager K, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in women with breast pain in the absence of additional clinical findings: Mammography remains indicated. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015;149:417-424.
- Kushwaha AC, Shin K, Kalambo M, et al. Overutilization of health care resources for breast pain. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 211:217-223.
Management of mastalgia
Appropriate breast pain management begins with a good history and physical examination. The decision to perform imaging should depend on clinical exam findings and not on symptoms of breast pain. If there is a palpable mass, then breast imaging and possible biopsy is appropriate. However, if clinical exam is normal, there is no indication for breast imaging in low-risk women under the age of 40 whose only symptom is breast pain. Women older than age 40 can undergo diagnostic imaging, if they have not had a negative screening mammogram in the past year.
Breast pain with abnormal clinical exam
In the patient who is younger than age 30 with a palpable mass. For this patient order targeted breast ultrasound (US) (FIGURE 1). If results are negative, repeat the clinical examination 1 week after menses. If the mass is persistent, refer the patient to a breast surgeon. If diagnostic imaging results are negative, consider breast MRI, especially if there is a strong family history of breast cancer.
In the patient who is aged 30 and older with a palpable mass. For this patient, bilateral diagnostic mammogram and US are in order. The testing is best performed 1 week after menses to reduce false-positive findings. If imaging is negative and the patient still has a clinically suspicious finding or mass, refer her to a breast surgeon and consider breast MRI. At this point if there is a persistent firm dominant mass, a biopsy is indicated as part of the triple test. If the mass resolves with menses, the patient can be reassured that the cause is most likely benign, with clinical examination repeated in 3 months.

Continue to: Breast pain and normal clinical exam...
Breast pain and normal clinical exam
When women who report breast pain have normal clinical examination findings (and have a negative screening mammogram in the past 12 months if older than age 40), there are several management strategies you can offer (FIGURE 2).
Reassurance and education. The majority of women with breast pain can be managed with reassurance and education, which are often sufficient to reduce their anxieties.
Supportive bra. The most effective intervention is to wear and sleep in a well-fitted supportive sports bra for 4 to 12 weeks. In a nonrandomized single-center trial of danazol versus sports bra, 85% of women reported relief of their breast pain with bra alone (vs 58% with danazol).12 A supportive bra is the first-line management of mastalgia (Level II evidence).
Symptom diary/calendar. Many women do not know whether or not their symptoms correspond to their ovarian cycle or are related to hormonal fluctuations. Therefore, it is reassuring and informative for them to keep a calendar or a diary of their symptoms to determine whether their symptoms occur or are exacerbated in a cyclical pattern.
Diet and lifestyle modification. Women should avoid caffeine (especially when having pain). Studies on methylxanthines have demonstrated some symptom relief with reducing caffeine intake.11,13 One cup of coffee or tea per day most likely will not make a difference. However, if a woman is drinking large quantities of caffeinated beverages throughout the day, it will very likely improve her breast pain if she cuts back. This is especially true during the times of exacerbated pain prior to her menses.
In addition, recommend reduced dietary fat (overall good health). This is good advice for any patient. There were 2 small studies that showed improvement in breast pain with a 15% reduction in dietary fat.7,8
Finally, advise that patients stop smoking. Smoking aggravates and exacerbates fibrocystic changes, and these will lead to more breast pain.
Medical management. Over-the-counter medications that are found in the vitamin section of a local drug store are vitamin E and evening primrose oil. There are no significant adverse effects with these treatments. Their efficacy is theoretical, however; 3 randomized controlled trials demonstrated no significant clinical benefit with evening primrose oil versus placebo for treatment of mastalgia.14
Topical or oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs; Voltaren gel, topical compound pain creams) are useful as second-line management after using a supportive bra. Three randomized controlled trials have demonstrated up to 90% improvement of mastalgia with topical NSAIDs.15-17
Tamoxifen is a selective estrogen-receptor modulator (SERM), which is an antagonist to the estrogen receptor (ER) in the breast and an agonist to the ER in the endometrium. Tamoxifen has been found to reduce symptoms of mastalgia by 70% even at a lower dosage of 10-mg per day (for 6 months), or as a topical gel (afimoxifene). The oral form can have some adverse effects, including hot flashes, and has a low risk for thromboembolic events and endometrial neoplasia.18-20
Danazol is very effective in reducing breast pain symptoms (by 80%), with a higher relapse after stopping the medication. Danazol is less tolerated due to its androgenic effects, such as hirsutism, acne, menorrhagia, and voice changes. Both danazol and tamoxifen can be teratogenic and should be used with caution in women of child-bearing age.21
Finally, bromocriptine inhibits serum prolactin and has been reported to provide 65% improvement in breast pain. Its use for breast pain is not US Food and Drug Administration–approved and adverse effects include nausea, dizziness, and hypotension.22
Tamoxifen, danazol, and bromocriptine can be considered as third-line management options for severe treatment-resistant mastalgia.
Continue to: FIGURE 2 Treatment algorithm for breast pain...

In summary
Evaluation and counseling for breast pain should be managed by women’s health care providers in a primary care setting. Most patients need reassurance and medical explanation of their symptoms. They should be educated that more than 95% of the time breast pain is not caused by an underlying malignancy but rather due to hormonal and fibrocystic changes, which can be managed conservatively. If the clinical breast examination and recent screening mammogram (in women over age 40) results are negative, patients should be educated that their pain is benign and undergo a trial of conservative measures: wear and sleep in a supporting bra; keep a calendar of symptoms to determine any relation to cyclical changes; and avoid nicotine, caffeine, and fatty food. Topical pain creams with diclofenac and evening primrose oil also can be effective in ameliorating the symptoms. Breast pain is not a surgical disease; referral to a surgical specialist and diagnostic imaging can be unnecessary and expensive.
- Scurr J, Hedger W, Morris P, et al. The prevalence, severity, and impact of breast pain in the general population. Breast J. 2014;20:508-513.
- Davies EL, Gateley CA, Miers M, et al. The long-term course of mastalgia. J R Soc Med. 1998;91:462-464.
- Singletary SE, Robb GL, Hortobagy GN. Advanced Therapy of Breast Disease. 2nd ed. Ontario, Canada: BC Decker Inc.; 2004.
- Gong C, Song E, Jia W, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of toremifen therapy for mastaglia. Arch Surg. 2006;141:43-47.
- Kumar S, Mansel RE, Scanlon MF, et al. Altered responses of prolactin, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone secretion to thyrotrophin releasing hormone/gonadotrophin releasing hormone stimulation in cyclical mastalgia. Br J Surg. 1984;71:870-873.
- Mansel RE, Dogliotti L. European multicentre trial of bromocriptine in cyclical mastalgia. Lancet. 1990;335:190-193.
- Rose DP, Boyar AP, Cohen C, et al. Effect of a low-fat diet on hormone levels in women with cystic breast disease. I. Serum steroids and gonadotropins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:623-626.
- Goodwin JP, Miller A, Del Giudice ME, et al. Elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and dietary fat intake in women with cyclic mastopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:430-437.
- Goyal A, Mansel RE. Efamast Study Group. A randomized multicenter study of gamolenic acid (Efamast) with and without antioxidant vitamins and minerals in the management of mastalgia. Breast J. 2005;11(1):41-47.
- Parsay S, Olfati F, Nahidi S. Therapeutic effects of vitamin E on cyclic mastalgia. Breast J. 2009;15:510-514.
- Allen SS, Froberg DG. The effect of decreased caffeine consumption on benign proliferative breast disease: a randomized clinical trial. Surgery. 1987;101:720-730.
- Hadi MS. Sports brassiere: is it a solution for mastalgia? Breast J. 2000;6:407-409.
- Russell LC. Caffeine restriction as initial treatment for breast pain. Nurse Pract. 1989; 14(2): 36-7.
- Srivastava A, Mansel RE, Arvind N, et al. Evidence-based management of mastalgia: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Breast. 2007;16:503-512.
- Irving AD, Morrison SL. Effectiveness of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the management of breast pain. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1998;43:158-159.
- Colak T, Ipek T, Kanik A, et al. Efficiency of topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in mastalgia treatment. J Am Coll Surg. 2003;196(4):525-530.
- Kaviani A, Mehrdad N, Najafi M, et al. Comparison of naproxen with placebo for the management of noncyclical breast pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. World J Surg. 2008;32:2464-2470.
- Fentiman IS, Caleffi M, Brame K, et al. Double-blind controlled trial of tamoxifen therapy for mastalgia. Lancet. 1986;1:287-288.
- Jain BK, Bansal A, Choudhary D, et al. Centchroman vs tamoxifen for regression of mastalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Intl J Surg. 2015;15:11-16.
- Mansel R, Goyal A, Le Nestour EL, et al; Afimoxifene (4-OHT) Breast Pain Research group. A phase II trial of Afimoxifene (4-hydroxyamoxifen gel) for cyclical mastalgia in premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106:389-397.
- O'Brien PM, Abukhalil IE. Randomized controlled trial of the management of premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual mastalgia using luteal phase-only danazol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:18-23.
- Blichert-Toft M, Andersen AN, Henriksen OB, et al. Treatment of mastalgia with bromocriptine: a double-blind cross-over study. Br Med J. 1979;1:237.
- Scurr J, Hedger W, Morris P, et al. The prevalence, severity, and impact of breast pain in the general population. Breast J. 2014;20:508-513.
- Davies EL, Gateley CA, Miers M, et al. The long-term course of mastalgia. J R Soc Med. 1998;91:462-464.
- Singletary SE, Robb GL, Hortobagy GN. Advanced Therapy of Breast Disease. 2nd ed. Ontario, Canada: BC Decker Inc.; 2004.
- Gong C, Song E, Jia W, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial of toremifen therapy for mastaglia. Arch Surg. 2006;141:43-47.
- Kumar S, Mansel RE, Scanlon MF, et al. Altered responses of prolactin, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone secretion to thyrotrophin releasing hormone/gonadotrophin releasing hormone stimulation in cyclical mastalgia. Br J Surg. 1984;71:870-873.
- Mansel RE, Dogliotti L. European multicentre trial of bromocriptine in cyclical mastalgia. Lancet. 1990;335:190-193.
- Rose DP, Boyar AP, Cohen C, et al. Effect of a low-fat diet on hormone levels in women with cystic breast disease. I. Serum steroids and gonadotropins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:623-626.
- Goodwin JP, Miller A, Del Giudice ME, et al. Elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and dietary fat intake in women with cyclic mastopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:430-437.
- Goyal A, Mansel RE. Efamast Study Group. A randomized multicenter study of gamolenic acid (Efamast) with and without antioxidant vitamins and minerals in the management of mastalgia. Breast J. 2005;11(1):41-47.
- Parsay S, Olfati F, Nahidi S. Therapeutic effects of vitamin E on cyclic mastalgia. Breast J. 2009;15:510-514.
- Allen SS, Froberg DG. The effect of decreased caffeine consumption on benign proliferative breast disease: a randomized clinical trial. Surgery. 1987;101:720-730.
- Hadi MS. Sports brassiere: is it a solution for mastalgia? Breast J. 2000;6:407-409.
- Russell LC. Caffeine restriction as initial treatment for breast pain. Nurse Pract. 1989; 14(2): 36-7.
- Srivastava A, Mansel RE, Arvind N, et al. Evidence-based management of mastalgia: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Breast. 2007;16:503-512.
- Irving AD, Morrison SL. Effectiveness of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the management of breast pain. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1998;43:158-159.
- Colak T, Ipek T, Kanik A, et al. Efficiency of topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in mastalgia treatment. J Am Coll Surg. 2003;196(4):525-530.
- Kaviani A, Mehrdad N, Najafi M, et al. Comparison of naproxen with placebo for the management of noncyclical breast pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. World J Surg. 2008;32:2464-2470.
- Fentiman IS, Caleffi M, Brame K, et al. Double-blind controlled trial of tamoxifen therapy for mastalgia. Lancet. 1986;1:287-288.
- Jain BK, Bansal A, Choudhary D, et al. Centchroman vs tamoxifen for regression of mastalgia: a randomized controlled trial. Intl J Surg. 2015;15:11-16.
- Mansel R, Goyal A, Le Nestour EL, et al; Afimoxifene (4-OHT) Breast Pain Research group. A phase II trial of Afimoxifene (4-hydroxyamoxifen gel) for cyclical mastalgia in premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;106:389-397.
- O'Brien PM, Abukhalil IE. Randomized controlled trial of the management of premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual mastalgia using luteal phase-only danazol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:18-23.
- Blichert-Toft M, Andersen AN, Henriksen OB, et al. Treatment of mastalgia with bromocriptine: a double-blind cross-over study. Br Med J. 1979;1:237.
Pharmacist-prescribed hormonal contraception safe, effective
Pharmacists in Oregon with the authority to prescribe hormonal contraceptive therapy have improved access to and continuation of contraceptive therapy, based on two retrospective studies of Medicaid patients published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Additionally, the safety profile associated with pharmacist prescribing of hormonal contraceptive therapy was on par with that of other prescribing clinicians.
“In the first 2 years of program implementation, we found evidence that pharmacists were safely reaching new contraceptive users and [helping to meet national goals in reducing unwanted pregnancy],” Lorinda Anderson, PharmD, and colleagues, the authors of one of the studies, wrote.
In 2016, Oregon became the first state to grant pharmacists authority to prescribe hormonal contraception without requiring consultation. The findings suggest that expanding prescribing authority for contraceptive therapy to pharmacists in other states could limit barriers to access, as 90% of United States residents live within 5 miles of a pharmacy.
In one of the two studies, Maria I. Rodriguez, MD, MPH, and colleagues conducted a claims-based review of the primary outcomes of pharmacist-initiated and non-pharmacist-initiated prescriptions on unintended pregnancies in Oregon’s Medicaid program. They also evaluated secondary outcomes, such as costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
In the first 2 years after the Oregon law went into effect, 248 pharmacists wrote 1,313, or 10%, of all hormonal contraception prescriptions for women who were Medicaid recipients and were prescribed hormonal contraception by any legally allowed healthcare provider. Pharmacists prescribed hormonal contraception for 367 of the 3,614 women studied.
Based on an economic model, pharmacist-initiated hormonal contraceptive therapy prevented an estimated 51 unintended pregnancies and saved $1.6 million in the first two years following the program’s inception in Oregon. Quality of life improved with 158 QALYs per 198,100 women.
Additionally, pharmacist-provided services cost less per patient than non pharmacist health care provider-services, $28 vs. $81.
“We believe our findings to be conservative given that our model was based on use 24 months after implementation. We expect over time that knowledge of and use of contraceptive access from pharmacists will increase,” Dr. Rodriguez, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues wrote.
In the second study, Dr. Anderson, of the Oregon State University, Corvallis, and colleagues pooled Oregon Medicaid pharmacy claims, eligibility, medical, diagnostic, and demographic data over the 2-year period for the 3,614 patients who received new prescriptions for transdermal and oral contraception, and the 1,313 claims filed for 367 women prescribed contraception by 162 pharmacists.
Within the first 4 months following the program’s inception in Oregon, pharmacists averaged 40 contraceptive claims per month. Over the next 7 months, claims increased to 61 and peaked at 80 claims after 18 months. Chain community pharmacies accounted for 94% of the claims; 71% of claims were in metropolitan areas.
Based on demographics, 73.8% of the women who were prescribed contraception by a pharmacist were first-time recipients. Combined oral contraception was prescribed for 90.5% of the women, and 82% of the women were 18-35 years of age. In the 180-day period prior to receiving pharmacist-prescribed contraception, 61.5% of patients were not using contraception but were attempting to engage in pharmacy-provided hormonal contraceptive care.
The researchers also examined contraceptive safety by looking at whether patients with medical contraindications (Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4) were receiving contraindicated methods. “We found that overall adherence to the clinical algorithm for prescribing pharmacists was high. Only 12 (5%) patients were identified as having Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4 medical conditions, and two (less than 1%) patients with medications contraindicating OC use received a prescription,” Dr. Anderson and her colleagues wrote.
They noted that the initial legislation passed in Oregon only included oral and transdermal hormonal contraception as methods pharmacists could prescribe. In 2017, with implementation in 2018, this was amended to include the vaginal ring and injection. “As the program matures, and contracts with additional insurers are implemented at pharmacies, we expect the number of pharmacist prescriptions to increase,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Rodriguez reported financial compensation from Merck, the World Health Organization, CooperSurgical, and a previous relationship with Merck. Dr. Anderson reports no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Rodriguez M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1238-46; Anderson A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1231-7.
Pharmacists in Oregon with the authority to prescribe hormonal contraceptive therapy have improved access to and continuation of contraceptive therapy, based on two retrospective studies of Medicaid patients published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Additionally, the safety profile associated with pharmacist prescribing of hormonal contraceptive therapy was on par with that of other prescribing clinicians.
“In the first 2 years of program implementation, we found evidence that pharmacists were safely reaching new contraceptive users and [helping to meet national goals in reducing unwanted pregnancy],” Lorinda Anderson, PharmD, and colleagues, the authors of one of the studies, wrote.
In 2016, Oregon became the first state to grant pharmacists authority to prescribe hormonal contraception without requiring consultation. The findings suggest that expanding prescribing authority for contraceptive therapy to pharmacists in other states could limit barriers to access, as 90% of United States residents live within 5 miles of a pharmacy.
In one of the two studies, Maria I. Rodriguez, MD, MPH, and colleagues conducted a claims-based review of the primary outcomes of pharmacist-initiated and non-pharmacist-initiated prescriptions on unintended pregnancies in Oregon’s Medicaid program. They also evaluated secondary outcomes, such as costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
In the first 2 years after the Oregon law went into effect, 248 pharmacists wrote 1,313, or 10%, of all hormonal contraception prescriptions for women who were Medicaid recipients and were prescribed hormonal contraception by any legally allowed healthcare provider. Pharmacists prescribed hormonal contraception for 367 of the 3,614 women studied.
Based on an economic model, pharmacist-initiated hormonal contraceptive therapy prevented an estimated 51 unintended pregnancies and saved $1.6 million in the first two years following the program’s inception in Oregon. Quality of life improved with 158 QALYs per 198,100 women.
Additionally, pharmacist-provided services cost less per patient than non pharmacist health care provider-services, $28 vs. $81.
“We believe our findings to be conservative given that our model was based on use 24 months after implementation. We expect over time that knowledge of and use of contraceptive access from pharmacists will increase,” Dr. Rodriguez, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues wrote.
In the second study, Dr. Anderson, of the Oregon State University, Corvallis, and colleagues pooled Oregon Medicaid pharmacy claims, eligibility, medical, diagnostic, and demographic data over the 2-year period for the 3,614 patients who received new prescriptions for transdermal and oral contraception, and the 1,313 claims filed for 367 women prescribed contraception by 162 pharmacists.
Within the first 4 months following the program’s inception in Oregon, pharmacists averaged 40 contraceptive claims per month. Over the next 7 months, claims increased to 61 and peaked at 80 claims after 18 months. Chain community pharmacies accounted for 94% of the claims; 71% of claims were in metropolitan areas.
Based on demographics, 73.8% of the women who were prescribed contraception by a pharmacist were first-time recipients. Combined oral contraception was prescribed for 90.5% of the women, and 82% of the women were 18-35 years of age. In the 180-day period prior to receiving pharmacist-prescribed contraception, 61.5% of patients were not using contraception but were attempting to engage in pharmacy-provided hormonal contraceptive care.
The researchers also examined contraceptive safety by looking at whether patients with medical contraindications (Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4) were receiving contraindicated methods. “We found that overall adherence to the clinical algorithm for prescribing pharmacists was high. Only 12 (5%) patients were identified as having Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4 medical conditions, and two (less than 1%) patients with medications contraindicating OC use received a prescription,” Dr. Anderson and her colleagues wrote.
They noted that the initial legislation passed in Oregon only included oral and transdermal hormonal contraception as methods pharmacists could prescribe. In 2017, with implementation in 2018, this was amended to include the vaginal ring and injection. “As the program matures, and contracts with additional insurers are implemented at pharmacies, we expect the number of pharmacist prescriptions to increase,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Rodriguez reported financial compensation from Merck, the World Health Organization, CooperSurgical, and a previous relationship with Merck. Dr. Anderson reports no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Rodriguez M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1238-46; Anderson A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1231-7.
Pharmacists in Oregon with the authority to prescribe hormonal contraceptive therapy have improved access to and continuation of contraceptive therapy, based on two retrospective studies of Medicaid patients published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Additionally, the safety profile associated with pharmacist prescribing of hormonal contraceptive therapy was on par with that of other prescribing clinicians.
“In the first 2 years of program implementation, we found evidence that pharmacists were safely reaching new contraceptive users and [helping to meet national goals in reducing unwanted pregnancy],” Lorinda Anderson, PharmD, and colleagues, the authors of one of the studies, wrote.
In 2016, Oregon became the first state to grant pharmacists authority to prescribe hormonal contraception without requiring consultation. The findings suggest that expanding prescribing authority for contraceptive therapy to pharmacists in other states could limit barriers to access, as 90% of United States residents live within 5 miles of a pharmacy.
In one of the two studies, Maria I. Rodriguez, MD, MPH, and colleagues conducted a claims-based review of the primary outcomes of pharmacist-initiated and non-pharmacist-initiated prescriptions on unintended pregnancies in Oregon’s Medicaid program. They also evaluated secondary outcomes, such as costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
In the first 2 years after the Oregon law went into effect, 248 pharmacists wrote 1,313, or 10%, of all hormonal contraception prescriptions for women who were Medicaid recipients and were prescribed hormonal contraception by any legally allowed healthcare provider. Pharmacists prescribed hormonal contraception for 367 of the 3,614 women studied.
Based on an economic model, pharmacist-initiated hormonal contraceptive therapy prevented an estimated 51 unintended pregnancies and saved $1.6 million in the first two years following the program’s inception in Oregon. Quality of life improved with 158 QALYs per 198,100 women.
Additionally, pharmacist-provided services cost less per patient than non pharmacist health care provider-services, $28 vs. $81.
“We believe our findings to be conservative given that our model was based on use 24 months after implementation. We expect over time that knowledge of and use of contraceptive access from pharmacists will increase,” Dr. Rodriguez, of Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, and colleagues wrote.
In the second study, Dr. Anderson, of the Oregon State University, Corvallis, and colleagues pooled Oregon Medicaid pharmacy claims, eligibility, medical, diagnostic, and demographic data over the 2-year period for the 3,614 patients who received new prescriptions for transdermal and oral contraception, and the 1,313 claims filed for 367 women prescribed contraception by 162 pharmacists.
Within the first 4 months following the program’s inception in Oregon, pharmacists averaged 40 contraceptive claims per month. Over the next 7 months, claims increased to 61 and peaked at 80 claims after 18 months. Chain community pharmacies accounted for 94% of the claims; 71% of claims were in metropolitan areas.
Based on demographics, 73.8% of the women who were prescribed contraception by a pharmacist were first-time recipients. Combined oral contraception was prescribed for 90.5% of the women, and 82% of the women were 18-35 years of age. In the 180-day period prior to receiving pharmacist-prescribed contraception, 61.5% of patients were not using contraception but were attempting to engage in pharmacy-provided hormonal contraceptive care.
The researchers also examined contraceptive safety by looking at whether patients with medical contraindications (Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4) were receiving contraindicated methods. “We found that overall adherence to the clinical algorithm for prescribing pharmacists was high. Only 12 (5%) patients were identified as having Medical Eligibility Criteria Category 3 or 4 medical conditions, and two (less than 1%) patients with medications contraindicating OC use received a prescription,” Dr. Anderson and her colleagues wrote.
They noted that the initial legislation passed in Oregon only included oral and transdermal hormonal contraception as methods pharmacists could prescribe. In 2017, with implementation in 2018, this was amended to include the vaginal ring and injection. “As the program matures, and contracts with additional insurers are implemented at pharmacies, we expect the number of pharmacist prescriptions to increase,” the authors wrote.
Dr. Rodriguez reported financial compensation from Merck, the World Health Organization, CooperSurgical, and a previous relationship with Merck. Dr. Anderson reports no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Rodriguez M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1238-46; Anderson A et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1231-7.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
HPV vaccine: Is one dose enough?
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – There is good news and bad news about human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination as a means of preventing cervical cancer.
The bad news is the HPV vaccines are projected to be in short supply, unable to meet global demand until at least 2024. The good news is that – in one study, for 11 years and counting – which would effectively double the existing supply, Aimee R. Kreimer, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
These data come from post hoc analyses of major phase 3 randomized controlled trials of bivalent HPV vaccine in Costa Rica and quadrivalent vaccine in India. However, these secondary analyses aren’t considered rock solid evidence because the subjects who got a single dose weren’t randomized to that strategy, they simply for one reason or another didn’t receive the recommended additional dose or doses.
“I don’t know if these studies are enough, so several studies have been launched over the past couple of years with an eye toward generating the quality of data that would be sufficient to motivate policy change, if in fact one dose is proven to be effective,” said Dr. Kreimer, a senior scientist at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
The first of these formal randomized, controlled trials – a delayed second-dose study in 9- to 11-year-old U.S. boys and girls – is due to be completed next year. Four other trials ongoing in Africa and Costa Rica, all in females, are expected to report findings in 2022-2025.
Dr. Kreimer is first author of a soon-to-be-published 11-year update from the phase 3 Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which was launched prior to licensure of the GlaxoSmithKline bivalent HPV vaccine. Previous analyses showed that at both 4 and 7 years of follow-up, a single dose of the vaccine was as effective as two or three in preventing infection with HPV types 16 and 18, which are covered by the vaccine.
“Now the research question has transitioned to, ‘Will one dose be sufficiently durable?’ she explained.
The answer from this study is yes. At 11 years since receipt of the bivalent HPV vaccine, there was no difference in terms of prevalent HPV 16/18 infection between the one-, two-, and three-dose groups. To address the issue of possible selection bias in this post hoc nonrandomized comparison, Dr. Kreimer and her coinvestigators looked at rates of infection with HPV 31 and 45, which aren’t covered by the vaccine. The rates were similar regardless of the number of vaccine doses received 11 years earlier, indicating women in all three dosing groups are at similar risk for acquiring HPV infection, thus bolstering the legitimacy of the conclusion that one dose provides effective long-term protection.
Intriguingly, HPV serum antibody levels in the single-dose group have remained stable for 11 years at a level that’s only about one-quarter of that associated with three doses of the vaccine, albeit an order of magnitude greater than the level induced by natural immunity.
“This really challenges the dogma of the HPV vaccine,” according to Dr. Kreimer. “It suggests that inferior [HPV] antibodies do not necessarily mean inferior protection.”
The explanation for this phenomenon appears to be that HPV subunit vaccine mimics the shell of authentic virions so well that the immune system sees it as dangerous and mounts long-term antibody production. Also, cervical infection by HPV is a relatively slow process, allowing time for vaccine-induced antibodies to interrupt it, she said.
In contrast to the encouraging findings from this post hoc analysis and another from a phase 3 trial of quadrivalent vaccine in India, numerous phase 4 vaccine effectiveness monitoring studies have shown markedly lower vaccine effectiveness for one dose of HPV vaccine. Dr. Kreimer cautioned that this is a flawed conclusion attributable to a methodologic artifact whereby the investigators have lumped together single-dose recipients who were 17 years old or more at the time with those who were younger.
“The problem is that many people who are aged 17-18 years already have HPV infection, so when they are vaccinated it shows up as a vaccine failure. That’s not correct. These are prophylactic HPV vaccines. They’re not meant to help clear an infection,” she noted.
Stepping back, Dr. Kreimer observed that cervical cancer “is really a story of inequality.” Indeed, 90% of cervical cancers occur in low-income countries, where HPV vaccination uptake remains very low even more than a decade after licensure. When modelers project out in the future, they estimate that at current HPV vaccination levels in Sub-Saharan Africa, which has the highest cervical cancer rates in the world, it would take more than 100 years to achieve the World Health Organization goal of eliminating the malignancy.
Asked by an audience member how low a single-dose vaccine effectiveness level she considers acceptable to help reach the goal of eliminating cervical cancer in developing countries, Dr. Kreimer cautioned against the tendency to let ‘perfect’ become the enemy of ‘good.’
“I’ll remind everyone that, in this moment, very few of the target girls in the lower– and upper-lower–income countries are getting any vaccination. So I don’t think it’s a question of whether we should be going from two to one dose, I think it’s really a question of, for those who are at zero doses, how do we get them one dose? And with the HPV vaccine, we’ve even seen suggestions of herd immunity if we have 50% uptake,” she replied.
Dr. Kreimer reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – There is good news and bad news about human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination as a means of preventing cervical cancer.
The bad news is the HPV vaccines are projected to be in short supply, unable to meet global demand until at least 2024. The good news is that – in one study, for 11 years and counting – which would effectively double the existing supply, Aimee R. Kreimer, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
These data come from post hoc analyses of major phase 3 randomized controlled trials of bivalent HPV vaccine in Costa Rica and quadrivalent vaccine in India. However, these secondary analyses aren’t considered rock solid evidence because the subjects who got a single dose weren’t randomized to that strategy, they simply for one reason or another didn’t receive the recommended additional dose or doses.
“I don’t know if these studies are enough, so several studies have been launched over the past couple of years with an eye toward generating the quality of data that would be sufficient to motivate policy change, if in fact one dose is proven to be effective,” said Dr. Kreimer, a senior scientist at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
The first of these formal randomized, controlled trials – a delayed second-dose study in 9- to 11-year-old U.S. boys and girls – is due to be completed next year. Four other trials ongoing in Africa and Costa Rica, all in females, are expected to report findings in 2022-2025.
Dr. Kreimer is first author of a soon-to-be-published 11-year update from the phase 3 Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which was launched prior to licensure of the GlaxoSmithKline bivalent HPV vaccine. Previous analyses showed that at both 4 and 7 years of follow-up, a single dose of the vaccine was as effective as two or three in preventing infection with HPV types 16 and 18, which are covered by the vaccine.
“Now the research question has transitioned to, ‘Will one dose be sufficiently durable?’ she explained.
The answer from this study is yes. At 11 years since receipt of the bivalent HPV vaccine, there was no difference in terms of prevalent HPV 16/18 infection between the one-, two-, and three-dose groups. To address the issue of possible selection bias in this post hoc nonrandomized comparison, Dr. Kreimer and her coinvestigators looked at rates of infection with HPV 31 and 45, which aren’t covered by the vaccine. The rates were similar regardless of the number of vaccine doses received 11 years earlier, indicating women in all three dosing groups are at similar risk for acquiring HPV infection, thus bolstering the legitimacy of the conclusion that one dose provides effective long-term protection.
Intriguingly, HPV serum antibody levels in the single-dose group have remained stable for 11 years at a level that’s only about one-quarter of that associated with three doses of the vaccine, albeit an order of magnitude greater than the level induced by natural immunity.
“This really challenges the dogma of the HPV vaccine,” according to Dr. Kreimer. “It suggests that inferior [HPV] antibodies do not necessarily mean inferior protection.”
The explanation for this phenomenon appears to be that HPV subunit vaccine mimics the shell of authentic virions so well that the immune system sees it as dangerous and mounts long-term antibody production. Also, cervical infection by HPV is a relatively slow process, allowing time for vaccine-induced antibodies to interrupt it, she said.
In contrast to the encouraging findings from this post hoc analysis and another from a phase 3 trial of quadrivalent vaccine in India, numerous phase 4 vaccine effectiveness monitoring studies have shown markedly lower vaccine effectiveness for one dose of HPV vaccine. Dr. Kreimer cautioned that this is a flawed conclusion attributable to a methodologic artifact whereby the investigators have lumped together single-dose recipients who were 17 years old or more at the time with those who were younger.
“The problem is that many people who are aged 17-18 years already have HPV infection, so when they are vaccinated it shows up as a vaccine failure. That’s not correct. These are prophylactic HPV vaccines. They’re not meant to help clear an infection,” she noted.
Stepping back, Dr. Kreimer observed that cervical cancer “is really a story of inequality.” Indeed, 90% of cervical cancers occur in low-income countries, where HPV vaccination uptake remains very low even more than a decade after licensure. When modelers project out in the future, they estimate that at current HPV vaccination levels in Sub-Saharan Africa, which has the highest cervical cancer rates in the world, it would take more than 100 years to achieve the World Health Organization goal of eliminating the malignancy.
Asked by an audience member how low a single-dose vaccine effectiveness level she considers acceptable to help reach the goal of eliminating cervical cancer in developing countries, Dr. Kreimer cautioned against the tendency to let ‘perfect’ become the enemy of ‘good.’
“I’ll remind everyone that, in this moment, very few of the target girls in the lower– and upper-lower–income countries are getting any vaccination. So I don’t think it’s a question of whether we should be going from two to one dose, I think it’s really a question of, for those who are at zero doses, how do we get them one dose? And with the HPV vaccine, we’ve even seen suggestions of herd immunity if we have 50% uptake,” she replied.
Dr. Kreimer reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – There is good news and bad news about human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination as a means of preventing cervical cancer.
The bad news is the HPV vaccines are projected to be in short supply, unable to meet global demand until at least 2024. The good news is that – in one study, for 11 years and counting – which would effectively double the existing supply, Aimee R. Kreimer, PhD, said at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
These data come from post hoc analyses of major phase 3 randomized controlled trials of bivalent HPV vaccine in Costa Rica and quadrivalent vaccine in India. However, these secondary analyses aren’t considered rock solid evidence because the subjects who got a single dose weren’t randomized to that strategy, they simply for one reason or another didn’t receive the recommended additional dose or doses.
“I don’t know if these studies are enough, so several studies have been launched over the past couple of years with an eye toward generating the quality of data that would be sufficient to motivate policy change, if in fact one dose is proven to be effective,” said Dr. Kreimer, a senior scientist at the National Cancer Institute in Bethesda, Md.
The first of these formal randomized, controlled trials – a delayed second-dose study in 9- to 11-year-old U.S. boys and girls – is due to be completed next year. Four other trials ongoing in Africa and Costa Rica, all in females, are expected to report findings in 2022-2025.
Dr. Kreimer is first author of a soon-to-be-published 11-year update from the phase 3 Costa Rica HPV Vaccine Trial, which was launched prior to licensure of the GlaxoSmithKline bivalent HPV vaccine. Previous analyses showed that at both 4 and 7 years of follow-up, a single dose of the vaccine was as effective as two or three in preventing infection with HPV types 16 and 18, which are covered by the vaccine.
“Now the research question has transitioned to, ‘Will one dose be sufficiently durable?’ she explained.
The answer from this study is yes. At 11 years since receipt of the bivalent HPV vaccine, there was no difference in terms of prevalent HPV 16/18 infection between the one-, two-, and three-dose groups. To address the issue of possible selection bias in this post hoc nonrandomized comparison, Dr. Kreimer and her coinvestigators looked at rates of infection with HPV 31 and 45, which aren’t covered by the vaccine. The rates were similar regardless of the number of vaccine doses received 11 years earlier, indicating women in all three dosing groups are at similar risk for acquiring HPV infection, thus bolstering the legitimacy of the conclusion that one dose provides effective long-term protection.
Intriguingly, HPV serum antibody levels in the single-dose group have remained stable for 11 years at a level that’s only about one-quarter of that associated with three doses of the vaccine, albeit an order of magnitude greater than the level induced by natural immunity.
“This really challenges the dogma of the HPV vaccine,” according to Dr. Kreimer. “It suggests that inferior [HPV] antibodies do not necessarily mean inferior protection.”
The explanation for this phenomenon appears to be that HPV subunit vaccine mimics the shell of authentic virions so well that the immune system sees it as dangerous and mounts long-term antibody production. Also, cervical infection by HPV is a relatively slow process, allowing time for vaccine-induced antibodies to interrupt it, she said.
In contrast to the encouraging findings from this post hoc analysis and another from a phase 3 trial of quadrivalent vaccine in India, numerous phase 4 vaccine effectiveness monitoring studies have shown markedly lower vaccine effectiveness for one dose of HPV vaccine. Dr. Kreimer cautioned that this is a flawed conclusion attributable to a methodologic artifact whereby the investigators have lumped together single-dose recipients who were 17 years old or more at the time with those who were younger.
“The problem is that many people who are aged 17-18 years already have HPV infection, so when they are vaccinated it shows up as a vaccine failure. That’s not correct. These are prophylactic HPV vaccines. They’re not meant to help clear an infection,” she noted.
Stepping back, Dr. Kreimer observed that cervical cancer “is really a story of inequality.” Indeed, 90% of cervical cancers occur in low-income countries, where HPV vaccination uptake remains very low even more than a decade after licensure. When modelers project out in the future, they estimate that at current HPV vaccination levels in Sub-Saharan Africa, which has the highest cervical cancer rates in the world, it would take more than 100 years to achieve the World Health Organization goal of eliminating the malignancy.
Asked by an audience member how low a single-dose vaccine effectiveness level she considers acceptable to help reach the goal of eliminating cervical cancer in developing countries, Dr. Kreimer cautioned against the tendency to let ‘perfect’ become the enemy of ‘good.’
“I’ll remind everyone that, in this moment, very few of the target girls in the lower– and upper-lower–income countries are getting any vaccination. So I don’t think it’s a question of whether we should be going from two to one dose, I think it’s really a question of, for those who are at zero doses, how do we get them one dose? And with the HPV vaccine, we’ve even seen suggestions of herd immunity if we have 50% uptake,” she replied.
Dr. Kreimer reported having no financial conflicts regarding her presentation.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ESPID 2019
Preventing delayed genitourinary tract injury during benign hysterectomy
and the circumstances under which it should be performed. Procedures directed at prolapse and incontinence have rates of genitourinary injury as high as 11%-38%, and national guidelines affirm the importance of cystoscopy in these patients.1 However, for patients undergoing hysterectomy in the absence of these procedures, the optimal strategy is debated. One approach that has been advanced is a policy of universal cystoscopy at the time of hysterectomy. This policy, by which all women undergoing hysterectomy would undergo cystoscopy, aims to prevent the occurrence of an unrecognized genitourinary injury by diagnosing and treating the injury intraoperatively. However, cystoscopy is not the only method that can be used to evaluate the urinary tract. Retroperitoneal dissection also can be used to visually identify the pertinent structures and has been performed with high fidelity by generations of experienced and skilled pelvic surgeons.
Injuries that are not identified intraoperatively at the time of surgery, so-called delayed genitourinary tract injuries, are associated with serious postoperative consequences for patients and high costs for institutions. As surgeons strive to decrease complications and improve the quality of gynecologic surgery, the question of whether cystoscopy should routinely be performed at the time of hysterectomy for benign indications remains unanswered. Proponents argue that cystoscopy is a low-cost assessment and that 75% of genitourinary injuries occur in women without identifiable risk factors.2 Opponents point out that cystoscopy is not an entirely benign intervention; it is associated with increased rates of urinary tract infection, bladder and ureteral trauma, and additional operating room time. Furthermore, it is unclear that the use of cystoscopy will reduce the incidence of delayed genitourinary tract injury in clinical practice.
Ultimately, cystoscopy after hysterectomy is being used as a screening test for genitourinary injury, and this lens can be applied to provide more information about its usefulness. For screening tests, the sensitivity and false negative rate are of paramount importance. High sensitivity and resultant few false negatives are the characteristics of a robust screening test which has a low likelihood of missing a diagnosis. Unfortunately, the sensitivity of cystoscopy is not 100% for genitourinary tract injury; it ranges from 60% to 85% and can be as low as 43% for ureteral injury.3,4 This means that cystoscopy will falsely reassure the surgeon with normal results in greater than 50% of the cases in which the patient actually has a ureteral injury.
Some larger series call into question the usefulness of cystoscopy as a screening tool, finding that this evaluation is not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary injury. A recent publication by our group of a series of 39,529 women who underwent benign hysterectomy without procedures directed at incontinence and prolapse recorded in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database between 2015 and 2017 found no difference in the rate of delayed genitourinary injury among women exposed to diagnostic cystoscopy and those who were not.5 These results are consistent with those of the largest systematic review and meta-analysis of 79 studies capturing 41,482 hysterectomies which found universal cystoscopy was not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary tract injury.6
Another consideration with the use of universal cystoscopy is cost. Although cystoscopy is typically a short procedure, the false positive rate is approximately 2%,2 often leading to additional interventions to evaluate the urinary tract which can be time consuming. In the limited available data regarding operative time, patients who underwent cystoscopy had a median operative time that was 17 minutes longer than it was among patients who did not.5 Moreover, there may be risks associated with this additional bladder instrumentation, evidenced by an increased incidence of urinary tract infection among women undergoing cystoscopy. In a recent cost-effectiveness analysis of cystoscopy at the time of benign hysterectomy, universal cystoscopy was found to add $51.39-$57.86 per case, and the risk of bladder injury would need to exceed 21%-47% and ureteral injury 27%-38% to be cost saving, compared with selective cystoscopy.7 A prior cost-effectiveness analysis concluded that universal cystoscopy is cost effective when the incidence of ureteral injury at the time of hysterectomy exceeds 1.5%-2.0%.8 Given these high thresholds, with a contemporary composite lower–genitourinary tract injury incidence of 0.24%-0.27%, it is unlikely that universal cystoscopy could be considered a cost-saving strategy in the majority of clinical settings.
Potential explanations for these results are many. Intraoperative cystoscopy is likely to be normal in the setting of nonobstructive and thermal injuries, which in the current era of minimally invasive surgery may be more prevalent mechanisms of injury. False positives can occur leading to unnecessary interventions, as well as overdiagnosis of asymptomatic urinary tract injuries that may have resolved spontaneously.9 It has been observed that cystoscopy is performed less frequently when hysterectomy is completed by a high-volume surgeon, which suggests that surgeon skill and experience play a significant role in the usefulness of this evaluation.9
Given these data, what is the best way forward regarding evaluation of the urinary tract at the time of benign hysterectomy? Ultimately, this is a clinical question that should be individualized, taking into account patient and surgical complexity, as well as surgeon training and individual rates of genitourinary injuries.9 Given its low sensitivity, caution should be exercised regarding the routine use of cystoscopy alone for evaluation of the urinary tract because false negatives occur with significant frequency. Benefits of cystoscopy in a given clinical scenario should be weighed against the risks of longer operative time, increased costs, and increased rate of urinary tract infection. In the absence of clinical scenarios with high rates of genitourinary injury (greater than 5%), selective rather than universal cystoscopy is the preferred strategy.7 Cystoscopy is fundamentally a form of secondary prevention that aims to mitigate damage that has already been done, and is no substitute for primary prevention of genitourinary tract injury itself through thorough knowledge of pelvic anatomy, comfort with retroperitoneal dissection, and awareness of the ureter and bladder at all times.
Dr. Polan is a resident in obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Barber is an assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology, specializing in gynecologic oncology, at the university. Neither of them have relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Polan and Dr. Barber at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;219(1):75-7.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2009 Jan;113(1):6-10.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;127(2):369-75.
4. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015 Nov-Dec;22(7):1278-86.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):888-95.
6. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Dec;126(6):1161-9.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Apr;220(4):369.e1-7.
8. Obstet Gynecol. 2001 May;97(5 Pt 1):685-92.
9. Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Dec;120(6):1363-70.
and the circumstances under which it should be performed. Procedures directed at prolapse and incontinence have rates of genitourinary injury as high as 11%-38%, and national guidelines affirm the importance of cystoscopy in these patients.1 However, for patients undergoing hysterectomy in the absence of these procedures, the optimal strategy is debated. One approach that has been advanced is a policy of universal cystoscopy at the time of hysterectomy. This policy, by which all women undergoing hysterectomy would undergo cystoscopy, aims to prevent the occurrence of an unrecognized genitourinary injury by diagnosing and treating the injury intraoperatively. However, cystoscopy is not the only method that can be used to evaluate the urinary tract. Retroperitoneal dissection also can be used to visually identify the pertinent structures and has been performed with high fidelity by generations of experienced and skilled pelvic surgeons.
Injuries that are not identified intraoperatively at the time of surgery, so-called delayed genitourinary tract injuries, are associated with serious postoperative consequences for patients and high costs for institutions. As surgeons strive to decrease complications and improve the quality of gynecologic surgery, the question of whether cystoscopy should routinely be performed at the time of hysterectomy for benign indications remains unanswered. Proponents argue that cystoscopy is a low-cost assessment and that 75% of genitourinary injuries occur in women without identifiable risk factors.2 Opponents point out that cystoscopy is not an entirely benign intervention; it is associated with increased rates of urinary tract infection, bladder and ureteral trauma, and additional operating room time. Furthermore, it is unclear that the use of cystoscopy will reduce the incidence of delayed genitourinary tract injury in clinical practice.
Ultimately, cystoscopy after hysterectomy is being used as a screening test for genitourinary injury, and this lens can be applied to provide more information about its usefulness. For screening tests, the sensitivity and false negative rate are of paramount importance. High sensitivity and resultant few false negatives are the characteristics of a robust screening test which has a low likelihood of missing a diagnosis. Unfortunately, the sensitivity of cystoscopy is not 100% for genitourinary tract injury; it ranges from 60% to 85% and can be as low as 43% for ureteral injury.3,4 This means that cystoscopy will falsely reassure the surgeon with normal results in greater than 50% of the cases in which the patient actually has a ureteral injury.
Some larger series call into question the usefulness of cystoscopy as a screening tool, finding that this evaluation is not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary injury. A recent publication by our group of a series of 39,529 women who underwent benign hysterectomy without procedures directed at incontinence and prolapse recorded in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database between 2015 and 2017 found no difference in the rate of delayed genitourinary injury among women exposed to diagnostic cystoscopy and those who were not.5 These results are consistent with those of the largest systematic review and meta-analysis of 79 studies capturing 41,482 hysterectomies which found universal cystoscopy was not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary tract injury.6
Another consideration with the use of universal cystoscopy is cost. Although cystoscopy is typically a short procedure, the false positive rate is approximately 2%,2 often leading to additional interventions to evaluate the urinary tract which can be time consuming. In the limited available data regarding operative time, patients who underwent cystoscopy had a median operative time that was 17 minutes longer than it was among patients who did not.5 Moreover, there may be risks associated with this additional bladder instrumentation, evidenced by an increased incidence of urinary tract infection among women undergoing cystoscopy. In a recent cost-effectiveness analysis of cystoscopy at the time of benign hysterectomy, universal cystoscopy was found to add $51.39-$57.86 per case, and the risk of bladder injury would need to exceed 21%-47% and ureteral injury 27%-38% to be cost saving, compared with selective cystoscopy.7 A prior cost-effectiveness analysis concluded that universal cystoscopy is cost effective when the incidence of ureteral injury at the time of hysterectomy exceeds 1.5%-2.0%.8 Given these high thresholds, with a contemporary composite lower–genitourinary tract injury incidence of 0.24%-0.27%, it is unlikely that universal cystoscopy could be considered a cost-saving strategy in the majority of clinical settings.
Potential explanations for these results are many. Intraoperative cystoscopy is likely to be normal in the setting of nonobstructive and thermal injuries, which in the current era of minimally invasive surgery may be more prevalent mechanisms of injury. False positives can occur leading to unnecessary interventions, as well as overdiagnosis of asymptomatic urinary tract injuries that may have resolved spontaneously.9 It has been observed that cystoscopy is performed less frequently when hysterectomy is completed by a high-volume surgeon, which suggests that surgeon skill and experience play a significant role in the usefulness of this evaluation.9
Given these data, what is the best way forward regarding evaluation of the urinary tract at the time of benign hysterectomy? Ultimately, this is a clinical question that should be individualized, taking into account patient and surgical complexity, as well as surgeon training and individual rates of genitourinary injuries.9 Given its low sensitivity, caution should be exercised regarding the routine use of cystoscopy alone for evaluation of the urinary tract because false negatives occur with significant frequency. Benefits of cystoscopy in a given clinical scenario should be weighed against the risks of longer operative time, increased costs, and increased rate of urinary tract infection. In the absence of clinical scenarios with high rates of genitourinary injury (greater than 5%), selective rather than universal cystoscopy is the preferred strategy.7 Cystoscopy is fundamentally a form of secondary prevention that aims to mitigate damage that has already been done, and is no substitute for primary prevention of genitourinary tract injury itself through thorough knowledge of pelvic anatomy, comfort with retroperitoneal dissection, and awareness of the ureter and bladder at all times.
Dr. Polan is a resident in obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Barber is an assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology, specializing in gynecologic oncology, at the university. Neither of them have relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Polan and Dr. Barber at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;219(1):75-7.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2009 Jan;113(1):6-10.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;127(2):369-75.
4. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015 Nov-Dec;22(7):1278-86.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):888-95.
6. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Dec;126(6):1161-9.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Apr;220(4):369.e1-7.
8. Obstet Gynecol. 2001 May;97(5 Pt 1):685-92.
9. Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Dec;120(6):1363-70.
and the circumstances under which it should be performed. Procedures directed at prolapse and incontinence have rates of genitourinary injury as high as 11%-38%, and national guidelines affirm the importance of cystoscopy in these patients.1 However, for patients undergoing hysterectomy in the absence of these procedures, the optimal strategy is debated. One approach that has been advanced is a policy of universal cystoscopy at the time of hysterectomy. This policy, by which all women undergoing hysterectomy would undergo cystoscopy, aims to prevent the occurrence of an unrecognized genitourinary injury by diagnosing and treating the injury intraoperatively. However, cystoscopy is not the only method that can be used to evaluate the urinary tract. Retroperitoneal dissection also can be used to visually identify the pertinent structures and has been performed with high fidelity by generations of experienced and skilled pelvic surgeons.
Injuries that are not identified intraoperatively at the time of surgery, so-called delayed genitourinary tract injuries, are associated with serious postoperative consequences for patients and high costs for institutions. As surgeons strive to decrease complications and improve the quality of gynecologic surgery, the question of whether cystoscopy should routinely be performed at the time of hysterectomy for benign indications remains unanswered. Proponents argue that cystoscopy is a low-cost assessment and that 75% of genitourinary injuries occur in women without identifiable risk factors.2 Opponents point out that cystoscopy is not an entirely benign intervention; it is associated with increased rates of urinary tract infection, bladder and ureteral trauma, and additional operating room time. Furthermore, it is unclear that the use of cystoscopy will reduce the incidence of delayed genitourinary tract injury in clinical practice.
Ultimately, cystoscopy after hysterectomy is being used as a screening test for genitourinary injury, and this lens can be applied to provide more information about its usefulness. For screening tests, the sensitivity and false negative rate are of paramount importance. High sensitivity and resultant few false negatives are the characteristics of a robust screening test which has a low likelihood of missing a diagnosis. Unfortunately, the sensitivity of cystoscopy is not 100% for genitourinary tract injury; it ranges from 60% to 85% and can be as low as 43% for ureteral injury.3,4 This means that cystoscopy will falsely reassure the surgeon with normal results in greater than 50% of the cases in which the patient actually has a ureteral injury.
Some larger series call into question the usefulness of cystoscopy as a screening tool, finding that this evaluation is not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary injury. A recent publication by our group of a series of 39,529 women who underwent benign hysterectomy without procedures directed at incontinence and prolapse recorded in the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) database between 2015 and 2017 found no difference in the rate of delayed genitourinary injury among women exposed to diagnostic cystoscopy and those who were not.5 These results are consistent with those of the largest systematic review and meta-analysis of 79 studies capturing 41,482 hysterectomies which found universal cystoscopy was not associated with a decreased rate of delayed genitourinary tract injury.6
Another consideration with the use of universal cystoscopy is cost. Although cystoscopy is typically a short procedure, the false positive rate is approximately 2%,2 often leading to additional interventions to evaluate the urinary tract which can be time consuming. In the limited available data regarding operative time, patients who underwent cystoscopy had a median operative time that was 17 minutes longer than it was among patients who did not.5 Moreover, there may be risks associated with this additional bladder instrumentation, evidenced by an increased incidence of urinary tract infection among women undergoing cystoscopy. In a recent cost-effectiveness analysis of cystoscopy at the time of benign hysterectomy, universal cystoscopy was found to add $51.39-$57.86 per case, and the risk of bladder injury would need to exceed 21%-47% and ureteral injury 27%-38% to be cost saving, compared with selective cystoscopy.7 A prior cost-effectiveness analysis concluded that universal cystoscopy is cost effective when the incidence of ureteral injury at the time of hysterectomy exceeds 1.5%-2.0%.8 Given these high thresholds, with a contemporary composite lower–genitourinary tract injury incidence of 0.24%-0.27%, it is unlikely that universal cystoscopy could be considered a cost-saving strategy in the majority of clinical settings.
Potential explanations for these results are many. Intraoperative cystoscopy is likely to be normal in the setting of nonobstructive and thermal injuries, which in the current era of minimally invasive surgery may be more prevalent mechanisms of injury. False positives can occur leading to unnecessary interventions, as well as overdiagnosis of asymptomatic urinary tract injuries that may have resolved spontaneously.9 It has been observed that cystoscopy is performed less frequently when hysterectomy is completed by a high-volume surgeon, which suggests that surgeon skill and experience play a significant role in the usefulness of this evaluation.9
Given these data, what is the best way forward regarding evaluation of the urinary tract at the time of benign hysterectomy? Ultimately, this is a clinical question that should be individualized, taking into account patient and surgical complexity, as well as surgeon training and individual rates of genitourinary injuries.9 Given its low sensitivity, caution should be exercised regarding the routine use of cystoscopy alone for evaluation of the urinary tract because false negatives occur with significant frequency. Benefits of cystoscopy in a given clinical scenario should be weighed against the risks of longer operative time, increased costs, and increased rate of urinary tract infection. In the absence of clinical scenarios with high rates of genitourinary injury (greater than 5%), selective rather than universal cystoscopy is the preferred strategy.7 Cystoscopy is fundamentally a form of secondary prevention that aims to mitigate damage that has already been done, and is no substitute for primary prevention of genitourinary tract injury itself through thorough knowledge of pelvic anatomy, comfort with retroperitoneal dissection, and awareness of the ureter and bladder at all times.
Dr. Polan is a resident in obstetrics and gynecology at Northwestern University, Chicago. Dr. Barber is an assistant professor of obstetrics and gynecology, specializing in gynecologic oncology, at the university. Neither of them have relevant financial disclosures. Email Dr. Polan and Dr. Barber at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jul;219(1):75-7.
2. Obstet Gynecol. 2009 Jan;113(1):6-10.
3. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Feb;127(2):369-75.
4. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015 Nov-Dec;22(7):1278-86.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):888-95.
6. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Dec;126(6):1161-9.
7. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Apr;220(4):369.e1-7.
8. Obstet Gynecol. 2001 May;97(5 Pt 1):685-92.
9. Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Dec;120(6):1363-70.
Addressing the sexual and reproductive health needs of trans and gender nonconforming patients
Separating gender identity from sexual identity to allow for more comprehensive history-taking
Grouping the term “transgender” in the abbreviation LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender) has historically been empowering for trans and gender nonconforming (GNC) persons. However, it also has contributed to the misunderstanding that gender identity is interchangeable with sexual identity. This common misconception can be a barrier to trans and GNC patients seeking care from ob.gyns. for their reproductive health needs.
By definition, gender identity refers to an internal experience of one’s gender, of one’s self.1 While gender identity has social implications, it ultimately is something that a person experiences independently of interactions with others. By contrast, sexual orientation has an explicitly relational underpinning because sexual orientation involves attraction to others. The distinction between gender identity and sexual orientation is similar to an internal-versus-external, or a self-versus-other dichotomy. A further nuance to add is that sexual behavior does not always reflect sexual orientation, and sexual behavior can vary along a wide spectrum when gender identity is added to the equation.
Overall, When approaching a sexual history with any patient, but especially a transgender or GNC patient, providers should think deeply about what information is medically relevant.2 The purpose of a sexual history is to identify behaviors that contribute to health risk, including pregnancy, sexually transmitted infection, and social problems such as sex-trafficking or intimate partner violence. The health care provider’s job is to ask questions that will uncover these risk factors.
With the advent of a more inclusive attitude toward gay and lesbian partnership, many providers already have learned to collect the sexual history without assuming the gender of a person’s sexual contacts. Still, when a provider is taking the sexual history, gender often is inappropriately used as proxy for the type of sex that a patient may be having. For example, a provider asking a cisgender woman about her sexual activity may ask, “how many sexual partners have you had in the last year?” But then, the provider may follow-up her response of “three sexual partners in the last year” by asking “men, women, or both?” By asking a patient if the patient’s sexual partners are “men, women, or both,” providers fail to accurately elucidate the risk factors that they are actually seeking when taking a sexual history. The cisgender woman from the above scenario may reply that she has been sleeping only with women for the last year, but if the sexual partners are transgender women, aka a woman who was assigned male at birth and therefore still may use her penis/testes for sexual purposes, then the patient actually may be at risk for pregnancy and may also have a different risk factor profile for sexually transmitted infections than if the patient were sexually active with cisgender women.
A different approach to using gender in taking the sexual history is to speak plainly about which sex organs come into contact during sexual activity. When patients identify as transgender or GNC, a provider first should start by asking them what language they would like providers to use when discussing sex organs.3 One example is that many trans men, both those who have undergone mastectomy as well as those who have not, may not use the word “breasts” to describe their “chests.” This distinction may make the difference between gaining and losing the trust of a trans/GNC patient in your clinic. After identifying how a patient would like to refer to sex organs, a provider can continue by asking which of the patient’s sex partners’ organs come into contact with the patient’s organs during sexual activity. Alternatively, starting with an even more broad line of questioning may be best for some patients, such as “how do you like to have sex?”
Carefully identifying the type of sex and what sex organs are involved has concrete medical implications. Patients assigned female at birth who are on hormone therapy with testosterone may need supportive care if they continue to use their vaginas in sexual encounters because testosterone can lead to a relatively hypoestrogenic state. Patients assigned male at birth who have undergone vaginoplasty procedures may need counseling about how to use and support their neovaginas as well as adjusted testing for dysplasia. Patients assigned female at birth who want to avoid pregnancy may need a nuanced consultation regarding contraception. These are just a few examples of how obstetrician-gynecologists can better support the sexual health of their trans/GNC patients by having an accurate understanding of how a trans/GNC person has sex.
Dr. Joyner is an assistant professor at Emory University, Atlanta, and is the director of gynecologic services in the Gender Center at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. Dr. Joyner identifies as a cisgender female and uses she/hers/her as her personal pronouns. Dr. Joey Bahng is a PGY-1 resident physician in Emory University’s gynecology & obstetrics residency program. Dr. Bahng identifies as nonbinary and uses they/them/their as their personal pronouns. Dr. Bahng and Dr. Joyner reported no relevant financial disclosures
References
1. Sexual orientation and gender identity definitions. Human Rights Campaign.
2. Taking a sexual history from transgender people. Transforming Health at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Sexual health history: Talking sex with gender non-conforming and trans patients. National LGBT Health Education Center at The Fenway Institute.
Separating gender identity from sexual identity to allow for more comprehensive history-taking
Separating gender identity from sexual identity to allow for more comprehensive history-taking
Grouping the term “transgender” in the abbreviation LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender) has historically been empowering for trans and gender nonconforming (GNC) persons. However, it also has contributed to the misunderstanding that gender identity is interchangeable with sexual identity. This common misconception can be a barrier to trans and GNC patients seeking care from ob.gyns. for their reproductive health needs.
By definition, gender identity refers to an internal experience of one’s gender, of one’s self.1 While gender identity has social implications, it ultimately is something that a person experiences independently of interactions with others. By contrast, sexual orientation has an explicitly relational underpinning because sexual orientation involves attraction to others. The distinction between gender identity and sexual orientation is similar to an internal-versus-external, or a self-versus-other dichotomy. A further nuance to add is that sexual behavior does not always reflect sexual orientation, and sexual behavior can vary along a wide spectrum when gender identity is added to the equation.
Overall, When approaching a sexual history with any patient, but especially a transgender or GNC patient, providers should think deeply about what information is medically relevant.2 The purpose of a sexual history is to identify behaviors that contribute to health risk, including pregnancy, sexually transmitted infection, and social problems such as sex-trafficking or intimate partner violence. The health care provider’s job is to ask questions that will uncover these risk factors.
With the advent of a more inclusive attitude toward gay and lesbian partnership, many providers already have learned to collect the sexual history without assuming the gender of a person’s sexual contacts. Still, when a provider is taking the sexual history, gender often is inappropriately used as proxy for the type of sex that a patient may be having. For example, a provider asking a cisgender woman about her sexual activity may ask, “how many sexual partners have you had in the last year?” But then, the provider may follow-up her response of “three sexual partners in the last year” by asking “men, women, or both?” By asking a patient if the patient’s sexual partners are “men, women, or both,” providers fail to accurately elucidate the risk factors that they are actually seeking when taking a sexual history. The cisgender woman from the above scenario may reply that she has been sleeping only with women for the last year, but if the sexual partners are transgender women, aka a woman who was assigned male at birth and therefore still may use her penis/testes for sexual purposes, then the patient actually may be at risk for pregnancy and may also have a different risk factor profile for sexually transmitted infections than if the patient were sexually active with cisgender women.
A different approach to using gender in taking the sexual history is to speak plainly about which sex organs come into contact during sexual activity. When patients identify as transgender or GNC, a provider first should start by asking them what language they would like providers to use when discussing sex organs.3 One example is that many trans men, both those who have undergone mastectomy as well as those who have not, may not use the word “breasts” to describe their “chests.” This distinction may make the difference between gaining and losing the trust of a trans/GNC patient in your clinic. After identifying how a patient would like to refer to sex organs, a provider can continue by asking which of the patient’s sex partners’ organs come into contact with the patient’s organs during sexual activity. Alternatively, starting with an even more broad line of questioning may be best for some patients, such as “how do you like to have sex?”
Carefully identifying the type of sex and what sex organs are involved has concrete medical implications. Patients assigned female at birth who are on hormone therapy with testosterone may need supportive care if they continue to use their vaginas in sexual encounters because testosterone can lead to a relatively hypoestrogenic state. Patients assigned male at birth who have undergone vaginoplasty procedures may need counseling about how to use and support their neovaginas as well as adjusted testing for dysplasia. Patients assigned female at birth who want to avoid pregnancy may need a nuanced consultation regarding contraception. These are just a few examples of how obstetrician-gynecologists can better support the sexual health of their trans/GNC patients by having an accurate understanding of how a trans/GNC person has sex.
Dr. Joyner is an assistant professor at Emory University, Atlanta, and is the director of gynecologic services in the Gender Center at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. Dr. Joyner identifies as a cisgender female and uses she/hers/her as her personal pronouns. Dr. Joey Bahng is a PGY-1 resident physician in Emory University’s gynecology & obstetrics residency program. Dr. Bahng identifies as nonbinary and uses they/them/their as their personal pronouns. Dr. Bahng and Dr. Joyner reported no relevant financial disclosures
References
1. Sexual orientation and gender identity definitions. Human Rights Campaign.
2. Taking a sexual history from transgender people. Transforming Health at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Sexual health history: Talking sex with gender non-conforming and trans patients. National LGBT Health Education Center at The Fenway Institute.
Grouping the term “transgender” in the abbreviation LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender) has historically been empowering for trans and gender nonconforming (GNC) persons. However, it also has contributed to the misunderstanding that gender identity is interchangeable with sexual identity. This common misconception can be a barrier to trans and GNC patients seeking care from ob.gyns. for their reproductive health needs.
By definition, gender identity refers to an internal experience of one’s gender, of one’s self.1 While gender identity has social implications, it ultimately is something that a person experiences independently of interactions with others. By contrast, sexual orientation has an explicitly relational underpinning because sexual orientation involves attraction to others. The distinction between gender identity and sexual orientation is similar to an internal-versus-external, or a self-versus-other dichotomy. A further nuance to add is that sexual behavior does not always reflect sexual orientation, and sexual behavior can vary along a wide spectrum when gender identity is added to the equation.
Overall, When approaching a sexual history with any patient, but especially a transgender or GNC patient, providers should think deeply about what information is medically relevant.2 The purpose of a sexual history is to identify behaviors that contribute to health risk, including pregnancy, sexually transmitted infection, and social problems such as sex-trafficking or intimate partner violence. The health care provider’s job is to ask questions that will uncover these risk factors.
With the advent of a more inclusive attitude toward gay and lesbian partnership, many providers already have learned to collect the sexual history without assuming the gender of a person’s sexual contacts. Still, when a provider is taking the sexual history, gender often is inappropriately used as proxy for the type of sex that a patient may be having. For example, a provider asking a cisgender woman about her sexual activity may ask, “how many sexual partners have you had in the last year?” But then, the provider may follow-up her response of “three sexual partners in the last year” by asking “men, women, or both?” By asking a patient if the patient’s sexual partners are “men, women, or both,” providers fail to accurately elucidate the risk factors that they are actually seeking when taking a sexual history. The cisgender woman from the above scenario may reply that she has been sleeping only with women for the last year, but if the sexual partners are transgender women, aka a woman who was assigned male at birth and therefore still may use her penis/testes for sexual purposes, then the patient actually may be at risk for pregnancy and may also have a different risk factor profile for sexually transmitted infections than if the patient were sexually active with cisgender women.
A different approach to using gender in taking the sexual history is to speak plainly about which sex organs come into contact during sexual activity. When patients identify as transgender or GNC, a provider first should start by asking them what language they would like providers to use when discussing sex organs.3 One example is that many trans men, both those who have undergone mastectomy as well as those who have not, may not use the word “breasts” to describe their “chests.” This distinction may make the difference between gaining and losing the trust of a trans/GNC patient in your clinic. After identifying how a patient would like to refer to sex organs, a provider can continue by asking which of the patient’s sex partners’ organs come into contact with the patient’s organs during sexual activity. Alternatively, starting with an even more broad line of questioning may be best for some patients, such as “how do you like to have sex?”
Carefully identifying the type of sex and what sex organs are involved has concrete medical implications. Patients assigned female at birth who are on hormone therapy with testosterone may need supportive care if they continue to use their vaginas in sexual encounters because testosterone can lead to a relatively hypoestrogenic state. Patients assigned male at birth who have undergone vaginoplasty procedures may need counseling about how to use and support their neovaginas as well as adjusted testing for dysplasia. Patients assigned female at birth who want to avoid pregnancy may need a nuanced consultation regarding contraception. These are just a few examples of how obstetrician-gynecologists can better support the sexual health of their trans/GNC patients by having an accurate understanding of how a trans/GNC person has sex.
Dr. Joyner is an assistant professor at Emory University, Atlanta, and is the director of gynecologic services in the Gender Center at Grady Memorial Hospital in Atlanta. Dr. Joyner identifies as a cisgender female and uses she/hers/her as her personal pronouns. Dr. Joey Bahng is a PGY-1 resident physician in Emory University’s gynecology & obstetrics residency program. Dr. Bahng identifies as nonbinary and uses they/them/their as their personal pronouns. Dr. Bahng and Dr. Joyner reported no relevant financial disclosures
References
1. Sexual orientation and gender identity definitions. Human Rights Campaign.
2. Taking a sexual history from transgender people. Transforming Health at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Sexual health history: Talking sex with gender non-conforming and trans patients. National LGBT Health Education Center at The Fenway Institute.
Targeted sequencing panel IDs Lynch syndrome in women with/at risk for endometrial cancer
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , according to findings in a prospective patient cohort.
The findings, which also suggest that the incidence of Lynch syndrome among endometrial cancer patients is higher than previously recognized, have “immediate and major implications for the individual patient with endometrial cancer ... and implications for related family members,” Maria Mercedes M. Padron, MD, reported during an e-poster session at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Of 71 patients included in the study, 67 were undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 7 (3 among those undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 4 who did not have endometrial cancer) were known to have Lynch syndrome.
Of the 67 undergoing treatment, 22 (33%) were identified by the direct sequencing panel as having Lynch syndrome mutations, and of those, 7 (10%) had mutations classified as high confidence inactivating mutations in either MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, or MSH2 genes, said Dr. Padron, a research scholar at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. The remaining 15 patients had rare mutations and met previously defined phenotypic criteria for Lynch syndrome pathogenicity, she reported.
The sequencing panel–based results were compared with commercially available gene tests, including immunohistochemistry (IHC) and microsatellite instability testing (MSI); 10 patients were identified by IHC to have loss of nuclear mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression, and 8 of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive. In addition, two patients were MSI-high, and both of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive.
Thus, two Lynch syndrome patients were missed by direct sequencing, noted Dr. Padron.
However, an additional 10 patients who were not identified as having Lynch syndrome by IHC and MSI testing were potentially identified as such using the sequencing panel, Dr. Padron said, noting that “the pathogenicity of these additional variants needs to be defined.”
Lynch syndrome is a hereditary cancer syndrome caused by germline mutations in DNA MMR genes; it is the third most common malignancy in women and it confers an increased risk of several types of cancer, including colorectal, ovarian, gastric, and endometrial cancer, among others.
“It is estimated that 3% to 5% of endometrial cancers will arise from Lynch syndrome,” Dr. Padron explained during the poster session.
Because the presence of Lynch syndrome directly affects immediate clinical management and future risk-reducing and surveillance strategies for patients and at-risk family members, screening is recommended in all women with endometrial cancer, she added, noting, however, that “the optimum screening method has yet to be established.”
The sequencing panel evaluated in this study – Swift’s Accel-Amplicon Plus Lynch Syndrome Panel – requires only low input amounts of DNA, and in an earlier test using 10 control samples, it exhibited greater than 90% on-target and coverage uniformity. The work flow allowed for data analysis within 2 days, Dr. Padron noted.
The panel then was tested in the current cohort of patients who were referred to a gynecology oncology clinic for either treatment of endometrial cancer or for evaluation of risk for endometrial cancer.
Germline/tumor DNA was isolated and 10 ng DNA was used for targeted exon-level hotspot coverage of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The findings suggest that the prevalence of Lynch syndrome may be six to seven times greater than previously estimated, Dr. Padron said during the poster presentation.
“If confirmed, this would have huge implications for our patients and health care system,” she said, adding that the ability to perform and analyze the sequencing within 48 hours of sample collection using a very low DNA input also was of note.
Taken together, “the findings of this study support future larger studies that can be performed concurrently with current standard of care technologies,” she and her colleagues concluded, noting that such studies would better determine more robust estimates of the prevalence of Lynch syndrome in women with endometrial cancer, help define improved standard-of-care guidelines, and provide future guidance for possible universal/targeted screening programs – all with the goal of improving the clinical care of women.
Dr. Padron reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , according to findings in a prospective patient cohort.
The findings, which also suggest that the incidence of Lynch syndrome among endometrial cancer patients is higher than previously recognized, have “immediate and major implications for the individual patient with endometrial cancer ... and implications for related family members,” Maria Mercedes M. Padron, MD, reported during an e-poster session at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Of 71 patients included in the study, 67 were undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 7 (3 among those undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 4 who did not have endometrial cancer) were known to have Lynch syndrome.
Of the 67 undergoing treatment, 22 (33%) were identified by the direct sequencing panel as having Lynch syndrome mutations, and of those, 7 (10%) had mutations classified as high confidence inactivating mutations in either MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, or MSH2 genes, said Dr. Padron, a research scholar at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. The remaining 15 patients had rare mutations and met previously defined phenotypic criteria for Lynch syndrome pathogenicity, she reported.
The sequencing panel–based results were compared with commercially available gene tests, including immunohistochemistry (IHC) and microsatellite instability testing (MSI); 10 patients were identified by IHC to have loss of nuclear mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression, and 8 of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive. In addition, two patients were MSI-high, and both of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive.
Thus, two Lynch syndrome patients were missed by direct sequencing, noted Dr. Padron.
However, an additional 10 patients who were not identified as having Lynch syndrome by IHC and MSI testing were potentially identified as such using the sequencing panel, Dr. Padron said, noting that “the pathogenicity of these additional variants needs to be defined.”
Lynch syndrome is a hereditary cancer syndrome caused by germline mutations in DNA MMR genes; it is the third most common malignancy in women and it confers an increased risk of several types of cancer, including colorectal, ovarian, gastric, and endometrial cancer, among others.
“It is estimated that 3% to 5% of endometrial cancers will arise from Lynch syndrome,” Dr. Padron explained during the poster session.
Because the presence of Lynch syndrome directly affects immediate clinical management and future risk-reducing and surveillance strategies for patients and at-risk family members, screening is recommended in all women with endometrial cancer, she added, noting, however, that “the optimum screening method has yet to be established.”
The sequencing panel evaluated in this study – Swift’s Accel-Amplicon Plus Lynch Syndrome Panel – requires only low input amounts of DNA, and in an earlier test using 10 control samples, it exhibited greater than 90% on-target and coverage uniformity. The work flow allowed for data analysis within 2 days, Dr. Padron noted.
The panel then was tested in the current cohort of patients who were referred to a gynecology oncology clinic for either treatment of endometrial cancer or for evaluation of risk for endometrial cancer.
Germline/tumor DNA was isolated and 10 ng DNA was used for targeted exon-level hotspot coverage of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The findings suggest that the prevalence of Lynch syndrome may be six to seven times greater than previously estimated, Dr. Padron said during the poster presentation.
“If confirmed, this would have huge implications for our patients and health care system,” she said, adding that the ability to perform and analyze the sequencing within 48 hours of sample collection using a very low DNA input also was of note.
Taken together, “the findings of this study support future larger studies that can be performed concurrently with current standard of care technologies,” she and her colleagues concluded, noting that such studies would better determine more robust estimates of the prevalence of Lynch syndrome in women with endometrial cancer, help define improved standard-of-care guidelines, and provide future guidance for possible universal/targeted screening programs – all with the goal of improving the clinical care of women.
Dr. Padron reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – , according to findings in a prospective patient cohort.
The findings, which also suggest that the incidence of Lynch syndrome among endometrial cancer patients is higher than previously recognized, have “immediate and major implications for the individual patient with endometrial cancer ... and implications for related family members,” Maria Mercedes M. Padron, MD, reported during an e-poster session at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Of 71 patients included in the study, 67 were undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 7 (3 among those undergoing endometrial cancer treatment and 4 who did not have endometrial cancer) were known to have Lynch syndrome.
Of the 67 undergoing treatment, 22 (33%) were identified by the direct sequencing panel as having Lynch syndrome mutations, and of those, 7 (10%) had mutations classified as high confidence inactivating mutations in either MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, or MSH2 genes, said Dr. Padron, a research scholar at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. The remaining 15 patients had rare mutations and met previously defined phenotypic criteria for Lynch syndrome pathogenicity, she reported.
The sequencing panel–based results were compared with commercially available gene tests, including immunohistochemistry (IHC) and microsatellite instability testing (MSI); 10 patients were identified by IHC to have loss of nuclear mismatch repair (MMR) protein expression, and 8 of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive. In addition, two patients were MSI-high, and both of those were Lynch syndrome mutation positive.
Thus, two Lynch syndrome patients were missed by direct sequencing, noted Dr. Padron.
However, an additional 10 patients who were not identified as having Lynch syndrome by IHC and MSI testing were potentially identified as such using the sequencing panel, Dr. Padron said, noting that “the pathogenicity of these additional variants needs to be defined.”
Lynch syndrome is a hereditary cancer syndrome caused by germline mutations in DNA MMR genes; it is the third most common malignancy in women and it confers an increased risk of several types of cancer, including colorectal, ovarian, gastric, and endometrial cancer, among others.
“It is estimated that 3% to 5% of endometrial cancers will arise from Lynch syndrome,” Dr. Padron explained during the poster session.
Because the presence of Lynch syndrome directly affects immediate clinical management and future risk-reducing and surveillance strategies for patients and at-risk family members, screening is recommended in all women with endometrial cancer, she added, noting, however, that “the optimum screening method has yet to be established.”
The sequencing panel evaluated in this study – Swift’s Accel-Amplicon Plus Lynch Syndrome Panel – requires only low input amounts of DNA, and in an earlier test using 10 control samples, it exhibited greater than 90% on-target and coverage uniformity. The work flow allowed for data analysis within 2 days, Dr. Padron noted.
The panel then was tested in the current cohort of patients who were referred to a gynecology oncology clinic for either treatment of endometrial cancer or for evaluation of risk for endometrial cancer.
Germline/tumor DNA was isolated and 10 ng DNA was used for targeted exon-level hotspot coverage of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2.
The findings suggest that the prevalence of Lynch syndrome may be six to seven times greater than previously estimated, Dr. Padron said during the poster presentation.
“If confirmed, this would have huge implications for our patients and health care system,” she said, adding that the ability to perform and analyze the sequencing within 48 hours of sample collection using a very low DNA input also was of note.
Taken together, “the findings of this study support future larger studies that can be performed concurrently with current standard of care technologies,” she and her colleagues concluded, noting that such studies would better determine more robust estimates of the prevalence of Lynch syndrome in women with endometrial cancer, help define improved standard-of-care guidelines, and provide future guidance for possible universal/targeted screening programs – all with the goal of improving the clinical care of women.
Dr. Padron reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2019