User login
Prediabetes is linked independently to myocardial infarction
Prediabetes is not only a predictor of diabetes and the cardiovascular complications that ensue, but it is also a risk factor by itself for myocardial infarction, according to data drawn from almost 1.8 million patients hospitalized for MI.
“Our study serves as a wakeup call for clinicians and patients to shift the focus to preventing prediabetes, and not just diabetes, said Geethika Thota, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
There are plenty of data suggesting that prediabetes places patients on a trajectory toward cardiovascular disease. In a meta-analysis of 129 studies published 2 years ago, prediabetes was not only associated with a statistically significant 16% increase in coronary heart disease, but also a 13% increased risk of all-cause mortality relative to those with normoglycemia.
Data drawn from 1.8 million patients
In this study, 1,794,149 weighted patient hospitalizations for MI were drawn from the National Inpatient Sample database. Excluding patients who eventually developed diabetes, roughly 1% of these patients had a history of prediabetes in the past, according to a search of ICD-10 codes.
Before adjustment for other risk factors, prediabetes was linked to a greater than 40% increased odds of MI (odds ratio, 1.41; P < .01). After adjustment for a large array of known MI risk factors – including prior history of MI, dyslipidemia, hypertension, nicotine dependence, and obesity – prediabetes remained an independent risk factor, corresponding with a 25% increased risk of MI (OR, 1.25; P < .01).
A history of prediabetes was also an independent risk factor for percutaneous intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting, with increased risk of 45% and 95%, respectively.
As a retrospective study looking at prediabetes as a risk factor in those who already had a MI, it is possible that not all patients with prediabetes were properly coded, but Dr. Thota said that was unlikely to have been an issue of sufficient magnitude to have affected the major conclusions.
Relevance seen for community care
Although the study was drawn from hospitalized patients, its relevance is for the community setting, where screening and intervention for prediabetes has the potential to alter the risk, according to Dr. Thota.
Most clinicians are likely aware of the value of screening for prediabetes, which was defined in this study as a hemoglobin A1c of 5.7%-6.4%, but Dr. Thota suggested that many might not fully grasp the full scope of goals. Early detection and prevention will prevent diabetes and, by extension, cardiovascular disease, but her data suggest that control of prediabetes with lower cardiovascular risk by a more direct route.
“Despite mounting evidence, many clinicians are unaware that prediabetes is also a major risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Thota, an internal medicine resident at Saint Peter’s University Hospital, New Brunswick, N.J.
Like diabetes, the prevalence of prediabetes is growing rapidly, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control that Dr. Thota cited. In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 38% of the adult population have prediabetes. By 2030, one model predicts a further 25% growth.
Screening for hyperglycemia is part of routine patient evaluations at Dr. Thota’s center. In an interview, she said that once a diagnosis of prediabetes is entered in the electronic medical record, the history is carried forward so that changes in status are continually monitored.
Worsening prediabetes should be addressed
“Prediabetes is not treated with medication, at least initially,” Dr. Thota explained. Rather, patients are educated about important lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, that can reverse the diagnosis. However, patients who remain on a path of worsening hyperglycemia are candidates for more intensive lifestyle intervention and might be considered selectively for metformin.
“Early recognition of prediabetes through screening is important,” Dr. Thota emphasized. The benefit for preventing patients from progressing to diabetes is well recognized, but these data provide the basis for incentivizing lifestyle changes in patients with prediabetes by telling them that it can reduce their risk for MI.
These data have an important message, but they are not surprising, according to Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director, interventional cardiovascular programs, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston.
“In fact, in daily practice we see a substantial percentage of patients with MI who have prediabetes that had not been previously recognized or formally diagnosed,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
“Identifying these patients – preferably prior to coming in with cardiovascular complications – is important both to reduce cardiovascular risk but also to try and prevent progression at diabetes,” he added.
Dr. Bhatt went on to say that this large analysis, confirming that prediabetes is independently associated with MI, should prompt clinicians to screen patients rigorously for this condition.
“At a minimum, such patients would be candidates for intensive lifestyle modification aimed at weight loss and treatment of frequent coexistent conditions, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Dr. Thota reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhatt has financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, many of which make products relevant to the management of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Prediabetes is not only a predictor of diabetes and the cardiovascular complications that ensue, but it is also a risk factor by itself for myocardial infarction, according to data drawn from almost 1.8 million patients hospitalized for MI.
“Our study serves as a wakeup call for clinicians and patients to shift the focus to preventing prediabetes, and not just diabetes, said Geethika Thota, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
There are plenty of data suggesting that prediabetes places patients on a trajectory toward cardiovascular disease. In a meta-analysis of 129 studies published 2 years ago, prediabetes was not only associated with a statistically significant 16% increase in coronary heart disease, but also a 13% increased risk of all-cause mortality relative to those with normoglycemia.
Data drawn from 1.8 million patients
In this study, 1,794,149 weighted patient hospitalizations for MI were drawn from the National Inpatient Sample database. Excluding patients who eventually developed diabetes, roughly 1% of these patients had a history of prediabetes in the past, according to a search of ICD-10 codes.
Before adjustment for other risk factors, prediabetes was linked to a greater than 40% increased odds of MI (odds ratio, 1.41; P < .01). After adjustment for a large array of known MI risk factors – including prior history of MI, dyslipidemia, hypertension, nicotine dependence, and obesity – prediabetes remained an independent risk factor, corresponding with a 25% increased risk of MI (OR, 1.25; P < .01).
A history of prediabetes was also an independent risk factor for percutaneous intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting, with increased risk of 45% and 95%, respectively.
As a retrospective study looking at prediabetes as a risk factor in those who already had a MI, it is possible that not all patients with prediabetes were properly coded, but Dr. Thota said that was unlikely to have been an issue of sufficient magnitude to have affected the major conclusions.
Relevance seen for community care
Although the study was drawn from hospitalized patients, its relevance is for the community setting, where screening and intervention for prediabetes has the potential to alter the risk, according to Dr. Thota.
Most clinicians are likely aware of the value of screening for prediabetes, which was defined in this study as a hemoglobin A1c of 5.7%-6.4%, but Dr. Thota suggested that many might not fully grasp the full scope of goals. Early detection and prevention will prevent diabetes and, by extension, cardiovascular disease, but her data suggest that control of prediabetes with lower cardiovascular risk by a more direct route.
“Despite mounting evidence, many clinicians are unaware that prediabetes is also a major risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Thota, an internal medicine resident at Saint Peter’s University Hospital, New Brunswick, N.J.
Like diabetes, the prevalence of prediabetes is growing rapidly, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control that Dr. Thota cited. In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 38% of the adult population have prediabetes. By 2030, one model predicts a further 25% growth.
Screening for hyperglycemia is part of routine patient evaluations at Dr. Thota’s center. In an interview, she said that once a diagnosis of prediabetes is entered in the electronic medical record, the history is carried forward so that changes in status are continually monitored.
Worsening prediabetes should be addressed
“Prediabetes is not treated with medication, at least initially,” Dr. Thota explained. Rather, patients are educated about important lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, that can reverse the diagnosis. However, patients who remain on a path of worsening hyperglycemia are candidates for more intensive lifestyle intervention and might be considered selectively for metformin.
“Early recognition of prediabetes through screening is important,” Dr. Thota emphasized. The benefit for preventing patients from progressing to diabetes is well recognized, but these data provide the basis for incentivizing lifestyle changes in patients with prediabetes by telling them that it can reduce their risk for MI.
These data have an important message, but they are not surprising, according to Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director, interventional cardiovascular programs, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston.
“In fact, in daily practice we see a substantial percentage of patients with MI who have prediabetes that had not been previously recognized or formally diagnosed,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
“Identifying these patients – preferably prior to coming in with cardiovascular complications – is important both to reduce cardiovascular risk but also to try and prevent progression at diabetes,” he added.
Dr. Bhatt went on to say that this large analysis, confirming that prediabetes is independently associated with MI, should prompt clinicians to screen patients rigorously for this condition.
“At a minimum, such patients would be candidates for intensive lifestyle modification aimed at weight loss and treatment of frequent coexistent conditions, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Dr. Thota reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhatt has financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, many of which make products relevant to the management of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Prediabetes is not only a predictor of diabetes and the cardiovascular complications that ensue, but it is also a risk factor by itself for myocardial infarction, according to data drawn from almost 1.8 million patients hospitalized for MI.
“Our study serves as a wakeup call for clinicians and patients to shift the focus to preventing prediabetes, and not just diabetes, said Geethika Thota, MD, at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
There are plenty of data suggesting that prediabetes places patients on a trajectory toward cardiovascular disease. In a meta-analysis of 129 studies published 2 years ago, prediabetes was not only associated with a statistically significant 16% increase in coronary heart disease, but also a 13% increased risk of all-cause mortality relative to those with normoglycemia.
Data drawn from 1.8 million patients
In this study, 1,794,149 weighted patient hospitalizations for MI were drawn from the National Inpatient Sample database. Excluding patients who eventually developed diabetes, roughly 1% of these patients had a history of prediabetes in the past, according to a search of ICD-10 codes.
Before adjustment for other risk factors, prediabetes was linked to a greater than 40% increased odds of MI (odds ratio, 1.41; P < .01). After adjustment for a large array of known MI risk factors – including prior history of MI, dyslipidemia, hypertension, nicotine dependence, and obesity – prediabetes remained an independent risk factor, corresponding with a 25% increased risk of MI (OR, 1.25; P < .01).
A history of prediabetes was also an independent risk factor for percutaneous intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting, with increased risk of 45% and 95%, respectively.
As a retrospective study looking at prediabetes as a risk factor in those who already had a MI, it is possible that not all patients with prediabetes were properly coded, but Dr. Thota said that was unlikely to have been an issue of sufficient magnitude to have affected the major conclusions.
Relevance seen for community care
Although the study was drawn from hospitalized patients, its relevance is for the community setting, where screening and intervention for prediabetes has the potential to alter the risk, according to Dr. Thota.
Most clinicians are likely aware of the value of screening for prediabetes, which was defined in this study as a hemoglobin A1c of 5.7%-6.4%, but Dr. Thota suggested that many might not fully grasp the full scope of goals. Early detection and prevention will prevent diabetes and, by extension, cardiovascular disease, but her data suggest that control of prediabetes with lower cardiovascular risk by a more direct route.
“Despite mounting evidence, many clinicians are unaware that prediabetes is also a major risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said Dr. Thota, an internal medicine resident at Saint Peter’s University Hospital, New Brunswick, N.J.
Like diabetes, the prevalence of prediabetes is growing rapidly, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control that Dr. Thota cited. In 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 38% of the adult population have prediabetes. By 2030, one model predicts a further 25% growth.
Screening for hyperglycemia is part of routine patient evaluations at Dr. Thota’s center. In an interview, she said that once a diagnosis of prediabetes is entered in the electronic medical record, the history is carried forward so that changes in status are continually monitored.
Worsening prediabetes should be addressed
“Prediabetes is not treated with medication, at least initially,” Dr. Thota explained. Rather, patients are educated about important lifestyle changes, such as diet and physical activity, that can reverse the diagnosis. However, patients who remain on a path of worsening hyperglycemia are candidates for more intensive lifestyle intervention and might be considered selectively for metformin.
“Early recognition of prediabetes through screening is important,” Dr. Thota emphasized. The benefit for preventing patients from progressing to diabetes is well recognized, but these data provide the basis for incentivizing lifestyle changes in patients with prediabetes by telling them that it can reduce their risk for MI.
These data have an important message, but they are not surprising, according to Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, executive director, interventional cardiovascular programs, Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Boston.
“In fact, in daily practice we see a substantial percentage of patients with MI who have prediabetes that had not been previously recognized or formally diagnosed,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
“Identifying these patients – preferably prior to coming in with cardiovascular complications – is important both to reduce cardiovascular risk but also to try and prevent progression at diabetes,” he added.
Dr. Bhatt went on to say that this large analysis, confirming that prediabetes is independently associated with MI, should prompt clinicians to screen patients rigorously for this condition.
“At a minimum, such patients would be candidates for intensive lifestyle modification aimed at weight loss and treatment of frequent coexistent conditions, such as hypertension and dyslipidemia,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Dr. Thota reports no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bhatt has financial relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies, many of which make products relevant to the management of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
FROM ENDO 2022
Avexitide promising for hypoglycemia after weight-loss surgery
Avexitide (Eiger Biopharmaceuticals), a first-in-class glucagonlike peptide (GLP)–1 receptor blocker, significantly reduced hypoglycemia in patients with refractory postbariatric hypoglycemia, new research finds.
Postbariatric hypoglycemia is a complication of bariatric surgery that is estimated to occur in about 29%-34% of people who undergo Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and in 11%-23% of those who undergo vertical sleeve gastrectomy. It typically manifests about 1-3 hours after meals and can lead to severe neuroglycopenic symptoms including blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, and incoordination.
In addition, more than one-third (37%) with the condition have hypoglycemic unawareness. This can lead to seizures in about 59%, loss of consciousness and hospitalization in 50%, motor vehicle accidents, and even death. More than 90% with the condition consider themselves disabled, and 41% report being unable to work.
There are no currently approved medical treatments for postbariatric hypoglycemia. The standard of care is medical nutrition therapy involving a low-carbohydrate diet with carb restriction and small, frequent mixed meals. If this doesn’t work, off-label stepped pharmacotherapy has been tried, including acarbose (Precose), octreotide (Sandostatin), and diazoxide (Proglycem).
But “these are limited by efficacy and tolerability,” said Marilyn Tan, MD, who presented the findings from the phase 2 trial of avexitide at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
In very severe cases, gastrostomy tubes or bypass reversal are options but those lead to weight regain and incomplete efficacy. “Safe, effective, and targeted therapies are needed urgently for postbariatric hypoglycemia,” said Dr. Tan, of the department of endocrinology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The pathophysiology isn’t fully understood, but there appears to be an exaggerated GLP-1 response that leads to abnormal insulin secretion and symptomatic hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Avexitide (formerly exendin 9-39), blocks the GLP-1 receptor and mitigates the excessive GLP-1 response, she explained.
Asked to comment, session moderator Michelle Van Name, MD, told this news organization, “This is a problem and it’s important for us to understand more about it and to identify different treatment options so these patients can continue to live their full, healthy lives post bariatric surgery.”
And, avexitide also holds potential for treating congenital hyperinsulinism, “which is a very challenging disease to treat in babies,” noted Dr. Van Name, a pediatric endocrinologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Drug reduced all levels of hypoglycemia, across surgery types
The study enrolled 14 women and 2 men with severe refractory postbariatric surgery hypoglycemia despite medical nutrition therapy. A majority (9) had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, 4 had vertical sleeve gastrectomy, 2 gastrectomy, and 1 had Nissen fundoplication. Seven patients (43.7%) had experienced loss of consciousness from hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. None had diabetes.
They were randomly assigned to either subcutaneous 45 mg of avexitide twice daily or 90 mg once daily for 14 days each, with a 2-day washout period followed by a switch to the other dose.
Both doses resulted in significant reductions in hypoglycemia as measured by self–blood glucose monitoring. The once-daily dose reduced level 1 hypoglycemia (glucose < 70 mg/dL) by 67.5% and it reduced level 2 (< 54 mg/dL) by 53.3% (P = .0043).
Even greater reductions were seen in severe hypoglycemia (that is, altered mental status/requiring assistance) – by 67.5% for the twice-daily dose (P = .0003) and by 66.1% with the once-daily dose (P = .0003).
“This is consistent with what we’ve seen in prior avexitide trials,” Dr. Tan noted.
More hypoglycemic events were captured using blinded continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), since it picked up episodes of which the patient was unaware. There were significant reductions in percentage time spent in level 1 and level 2 hypoglycemia, as well as in absolute number of hypoglycemic events over 14 days.
Here, the effect was greater with the once-daily 90 mg dose, with reductions of up to 65% in time spent and number of events, but results for the twice-daily dose were also significant, Dr. Tan said.
The drug was effective across all surgical subtypes. Patients who underwent vertical sleeve gastrectomy/gastrectomy had greater rates of hypoglycemia at baseline and “robust responses to avexitide subcutaneous injections. This supports the critical role of GLP-1,” Dr. Tan said.
There were no severe adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse events were diarrhea, headache, bloating, and injection-site reaction/bruising. All were mild and self-limited and resolved without treatment. No participants withdrew from the study.
Eiger Biopharmaceuticals is currently working with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency to design a phase 3 trial.
The study is an investor-initiated trial with funding from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Tan receives research support from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals as a site investigator. Dr. Van Name is an investigator for a trial sponsored by Provention Bio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Avexitide (Eiger Biopharmaceuticals), a first-in-class glucagonlike peptide (GLP)–1 receptor blocker, significantly reduced hypoglycemia in patients with refractory postbariatric hypoglycemia, new research finds.
Postbariatric hypoglycemia is a complication of bariatric surgery that is estimated to occur in about 29%-34% of people who undergo Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and in 11%-23% of those who undergo vertical sleeve gastrectomy. It typically manifests about 1-3 hours after meals and can lead to severe neuroglycopenic symptoms including blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, and incoordination.
In addition, more than one-third (37%) with the condition have hypoglycemic unawareness. This can lead to seizures in about 59%, loss of consciousness and hospitalization in 50%, motor vehicle accidents, and even death. More than 90% with the condition consider themselves disabled, and 41% report being unable to work.
There are no currently approved medical treatments for postbariatric hypoglycemia. The standard of care is medical nutrition therapy involving a low-carbohydrate diet with carb restriction and small, frequent mixed meals. If this doesn’t work, off-label stepped pharmacotherapy has been tried, including acarbose (Precose), octreotide (Sandostatin), and diazoxide (Proglycem).
But “these are limited by efficacy and tolerability,” said Marilyn Tan, MD, who presented the findings from the phase 2 trial of avexitide at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
In very severe cases, gastrostomy tubes or bypass reversal are options but those lead to weight regain and incomplete efficacy. “Safe, effective, and targeted therapies are needed urgently for postbariatric hypoglycemia,” said Dr. Tan, of the department of endocrinology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The pathophysiology isn’t fully understood, but there appears to be an exaggerated GLP-1 response that leads to abnormal insulin secretion and symptomatic hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Avexitide (formerly exendin 9-39), blocks the GLP-1 receptor and mitigates the excessive GLP-1 response, she explained.
Asked to comment, session moderator Michelle Van Name, MD, told this news organization, “This is a problem and it’s important for us to understand more about it and to identify different treatment options so these patients can continue to live their full, healthy lives post bariatric surgery.”
And, avexitide also holds potential for treating congenital hyperinsulinism, “which is a very challenging disease to treat in babies,” noted Dr. Van Name, a pediatric endocrinologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Drug reduced all levels of hypoglycemia, across surgery types
The study enrolled 14 women and 2 men with severe refractory postbariatric surgery hypoglycemia despite medical nutrition therapy. A majority (9) had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, 4 had vertical sleeve gastrectomy, 2 gastrectomy, and 1 had Nissen fundoplication. Seven patients (43.7%) had experienced loss of consciousness from hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. None had diabetes.
They were randomly assigned to either subcutaneous 45 mg of avexitide twice daily or 90 mg once daily for 14 days each, with a 2-day washout period followed by a switch to the other dose.
Both doses resulted in significant reductions in hypoglycemia as measured by self–blood glucose monitoring. The once-daily dose reduced level 1 hypoglycemia (glucose < 70 mg/dL) by 67.5% and it reduced level 2 (< 54 mg/dL) by 53.3% (P = .0043).
Even greater reductions were seen in severe hypoglycemia (that is, altered mental status/requiring assistance) – by 67.5% for the twice-daily dose (P = .0003) and by 66.1% with the once-daily dose (P = .0003).
“This is consistent with what we’ve seen in prior avexitide trials,” Dr. Tan noted.
More hypoglycemic events were captured using blinded continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), since it picked up episodes of which the patient was unaware. There were significant reductions in percentage time spent in level 1 and level 2 hypoglycemia, as well as in absolute number of hypoglycemic events over 14 days.
Here, the effect was greater with the once-daily 90 mg dose, with reductions of up to 65% in time spent and number of events, but results for the twice-daily dose were also significant, Dr. Tan said.
The drug was effective across all surgical subtypes. Patients who underwent vertical sleeve gastrectomy/gastrectomy had greater rates of hypoglycemia at baseline and “robust responses to avexitide subcutaneous injections. This supports the critical role of GLP-1,” Dr. Tan said.
There were no severe adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse events were diarrhea, headache, bloating, and injection-site reaction/bruising. All were mild and self-limited and resolved without treatment. No participants withdrew from the study.
Eiger Biopharmaceuticals is currently working with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency to design a phase 3 trial.
The study is an investor-initiated trial with funding from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Tan receives research support from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals as a site investigator. Dr. Van Name is an investigator for a trial sponsored by Provention Bio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Avexitide (Eiger Biopharmaceuticals), a first-in-class glucagonlike peptide (GLP)–1 receptor blocker, significantly reduced hypoglycemia in patients with refractory postbariatric hypoglycemia, new research finds.
Postbariatric hypoglycemia is a complication of bariatric surgery that is estimated to occur in about 29%-34% of people who undergo Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and in 11%-23% of those who undergo vertical sleeve gastrectomy. It typically manifests about 1-3 hours after meals and can lead to severe neuroglycopenic symptoms including blurred vision, confusion, drowsiness, and incoordination.
In addition, more than one-third (37%) with the condition have hypoglycemic unawareness. This can lead to seizures in about 59%, loss of consciousness and hospitalization in 50%, motor vehicle accidents, and even death. More than 90% with the condition consider themselves disabled, and 41% report being unable to work.
There are no currently approved medical treatments for postbariatric hypoglycemia. The standard of care is medical nutrition therapy involving a low-carbohydrate diet with carb restriction and small, frequent mixed meals. If this doesn’t work, off-label stepped pharmacotherapy has been tried, including acarbose (Precose), octreotide (Sandostatin), and diazoxide (Proglycem).
But “these are limited by efficacy and tolerability,” said Marilyn Tan, MD, who presented the findings from the phase 2 trial of avexitide at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
In very severe cases, gastrostomy tubes or bypass reversal are options but those lead to weight regain and incomplete efficacy. “Safe, effective, and targeted therapies are needed urgently for postbariatric hypoglycemia,” said Dr. Tan, of the department of endocrinology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
The pathophysiology isn’t fully understood, but there appears to be an exaggerated GLP-1 response that leads to abnormal insulin secretion and symptomatic hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Avexitide (formerly exendin 9-39), blocks the GLP-1 receptor and mitigates the excessive GLP-1 response, she explained.
Asked to comment, session moderator Michelle Van Name, MD, told this news organization, “This is a problem and it’s important for us to understand more about it and to identify different treatment options so these patients can continue to live their full, healthy lives post bariatric surgery.”
And, avexitide also holds potential for treating congenital hyperinsulinism, “which is a very challenging disease to treat in babies,” noted Dr. Van Name, a pediatric endocrinologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Drug reduced all levels of hypoglycemia, across surgery types
The study enrolled 14 women and 2 men with severe refractory postbariatric surgery hypoglycemia despite medical nutrition therapy. A majority (9) had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, 4 had vertical sleeve gastrectomy, 2 gastrectomy, and 1 had Nissen fundoplication. Seven patients (43.7%) had experienced loss of consciousness from hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. None had diabetes.
They were randomly assigned to either subcutaneous 45 mg of avexitide twice daily or 90 mg once daily for 14 days each, with a 2-day washout period followed by a switch to the other dose.
Both doses resulted in significant reductions in hypoglycemia as measured by self–blood glucose monitoring. The once-daily dose reduced level 1 hypoglycemia (glucose < 70 mg/dL) by 67.5% and it reduced level 2 (< 54 mg/dL) by 53.3% (P = .0043).
Even greater reductions were seen in severe hypoglycemia (that is, altered mental status/requiring assistance) – by 67.5% for the twice-daily dose (P = .0003) and by 66.1% with the once-daily dose (P = .0003).
“This is consistent with what we’ve seen in prior avexitide trials,” Dr. Tan noted.
More hypoglycemic events were captured using blinded continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), since it picked up episodes of which the patient was unaware. There were significant reductions in percentage time spent in level 1 and level 2 hypoglycemia, as well as in absolute number of hypoglycemic events over 14 days.
Here, the effect was greater with the once-daily 90 mg dose, with reductions of up to 65% in time spent and number of events, but results for the twice-daily dose were also significant, Dr. Tan said.
The drug was effective across all surgical subtypes. Patients who underwent vertical sleeve gastrectomy/gastrectomy had greater rates of hypoglycemia at baseline and “robust responses to avexitide subcutaneous injections. This supports the critical role of GLP-1,” Dr. Tan said.
There were no severe adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse events were diarrhea, headache, bloating, and injection-site reaction/bruising. All were mild and self-limited and resolved without treatment. No participants withdrew from the study.
Eiger Biopharmaceuticals is currently working with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency to design a phase 3 trial.
The study is an investor-initiated trial with funding from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals. Dr. Tan receives research support from Eiger Biopharmaceuticals as a site investigator. Dr. Van Name is an investigator for a trial sponsored by Provention Bio.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2022
Post-hoc analysis offers hope for novel cholesterol drug
MILAN, Italy – The antisense oligonucleotide vupanorsen substantially reduces very-low-density-lipoprotein (VLDL) and remnant cholesterol levels in patients with raised lipids despite statin therapy, suggests a subanalysis of TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 that appears to offer more hope than the primary study findings.
Vupanorsen targets hepatic angiopoietin-like protein 3 (ANGPTL3), which inhibits enzymes involved in triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism.
Earlier this year, headline data from TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 suggested that the drug reduced triglycerides and non–high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol to a degree that was significant but not clinically meaningful for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Moreover, as reported by this news organization, there were safety concerns over increases in liver enzymes among patients taking the drug, as well as dose-related increases in hepatic fat.
As a result, Pfizer announced that it would discontinue its clinical development program for vupanorsen and return the development rights to Ionis, following the signing of a worldwide exclusive agreement in November 2019.
Now, Nicholas A. Marston, MD, MPH, cardiovascular medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, has presented a post-hoc analysis of the phase 2b study, showing that the drug reduces VLDL and remnant cholesterol levels by up to 60%.
These were closely tied to reductions in ANGPTL3 levels, although substantial reductions in cholesterol levels were achieved even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL3, where the impact on safety outcomes was reduced.
Dr. Marston said that lower doses of vupanorsen, where the safety effects would be less, or other drugs that inhibit ANGPTL3, “may have an important role in patients with residual dyslipidemia despite current therapy.”
The results were presented at the 90th European Atherosclerosis Society Congress on May 23.
Dr. Marston told this news organization that some of the reductions they saw with the lower doses of vupanorsen were “just as good as any other therapy, and the safety profile was … much better than at the highest dose.”
They wanted to pursue the subgroup analysis, despite Pfizer’s announcement, partly to “learn something in terms of the potential efficacy of the ANGPTL3 pathway in general.”
Dr. Marston said that Ionis is now focused on ANGPTL3, and the current results suggest that it “works very well,” so if other drugs are able to achieve the same efficacy as vupanorsen “but without the effects,” then it may “get elbowed out.”
Børge G. Nordestgaard, MD, PhD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen, who was not involved in the study, called the findings “very encouraging.”
He told this news organization that being able to reduce LDL cholesterol as well as VLDL and remnant cholesterol is “exactly what I would be dreaming about” with a drug like vupanorsen.
Dr. Nordestgaard nevertheless underlined that “one would have to look carefully” at the safety of the drug.
“If it was my money, I would certainly try to look into if this was some sort of transient thing. Even when they started talking about statins, there was also this transient increase in alanine transaminase that seems to go away after a while,” he said.
“But of course, if this was persistent and triglycerides in the liver kept accumulating, then it’s a problem,” Dr. Nordestgaard added, “and then you would need to have some sort of thinking about whether you could couple it with something that got rid of the liver fat.”
He also agreed with Dr. Marston that, even if vupanorsen does not clear all hurdles before making it to market, the approach is promising.
“The target,” Dr. Nordestgaard said, seems “fantastic, from my point of view anyway.”
Dr. Marston explained that VLDL cholesterol, remnant cholesterol, and triglycerides are “surrogates for triglyceride-rich” lipoproteins, and that they are “increasingly recognized” as cardiovascular risk factors.
He highlighted that currently available therapies achieve reductions of these compounds of between 30% and 50%.
TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 included adults on stable statin therapy who had a triglyceride level of 150 mg/dL to 500 mg/dL and a non-HDL cholesterol level of 100 mg/dL or higher.
The participants were randomly assigned to one of six 2- or 4-week dosing schedules of vupanorsen or placebo and followed up over 24 weeks for a series of primary and additional endpoints, as well as safety outcomes.
The team recruited 286 individuals, who had a median age of 64 years; 44% were female. The majority (87%) were white.
The mean body mass index was 32 kg/m2, 50% had diabetes, 13% had experienced a prior myocardial infarction, and 51% were receiving high-intensity statins.
As previously reported, vupanorsen was associated with a reduction in non-HDL cholesterol vs. placebo of 22%-28%, alongside a 6%-15% reduction in apolipoprotein B levels and an 8%-16% reduction in LDL cholesterol.
In contrast, Dr. Marston showed that the various dosing schedules of the drug were associated with reductions in levels of VLDL cholesterol of 52%-66% vs. placebo at 24 weeks.
Over the same period, remnant cholesterol levels were lowered by 42%-59% vs. placebo, and triglycerides were reduced by 44%-57% in patients given vupanorsen.
There were also reductions in ANGPTL3 levels of 70%-95%.
Subgroup analysis indicated that the effect of vupanorsen was seen regardless of age, sex, body mass index, presence of diabetes, baseline triglycerides, and intensity of statin therapy.
Dr. Marston highlighted that the reductions in triglycerides, VLDL cholesterol, and remnant cholesterol levels were directly related to those for ANGPTL3 levels, but that the reductions remained meaningful even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL.
For example, even when ANGPTL3 levels were reduced by 70%, there were 50% reductions in triglyceride levels, 70% reductions in VLDL cholesterol levels, and a 50% drop in remnant cholesterol levels.
This, he noted, is important given that safety signals such as increases in alanine transaminase and hepatic fat occurred in a dose-dependent manner with ANGPTL3 reductions and were “most pronounced” only at the highest level of ANGPTL3 reduction.
The TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Marston disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, Ionis, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Nordestgaard disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Ionis, Amgen, Kowa, Denka, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN, Italy – The antisense oligonucleotide vupanorsen substantially reduces very-low-density-lipoprotein (VLDL) and remnant cholesterol levels in patients with raised lipids despite statin therapy, suggests a subanalysis of TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 that appears to offer more hope than the primary study findings.
Vupanorsen targets hepatic angiopoietin-like protein 3 (ANGPTL3), which inhibits enzymes involved in triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism.
Earlier this year, headline data from TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 suggested that the drug reduced triglycerides and non–high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol to a degree that was significant but not clinically meaningful for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Moreover, as reported by this news organization, there were safety concerns over increases in liver enzymes among patients taking the drug, as well as dose-related increases in hepatic fat.
As a result, Pfizer announced that it would discontinue its clinical development program for vupanorsen and return the development rights to Ionis, following the signing of a worldwide exclusive agreement in November 2019.
Now, Nicholas A. Marston, MD, MPH, cardiovascular medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, has presented a post-hoc analysis of the phase 2b study, showing that the drug reduces VLDL and remnant cholesterol levels by up to 60%.
These were closely tied to reductions in ANGPTL3 levels, although substantial reductions in cholesterol levels were achieved even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL3, where the impact on safety outcomes was reduced.
Dr. Marston said that lower doses of vupanorsen, where the safety effects would be less, or other drugs that inhibit ANGPTL3, “may have an important role in patients with residual dyslipidemia despite current therapy.”
The results were presented at the 90th European Atherosclerosis Society Congress on May 23.
Dr. Marston told this news organization that some of the reductions they saw with the lower doses of vupanorsen were “just as good as any other therapy, and the safety profile was … much better than at the highest dose.”
They wanted to pursue the subgroup analysis, despite Pfizer’s announcement, partly to “learn something in terms of the potential efficacy of the ANGPTL3 pathway in general.”
Dr. Marston said that Ionis is now focused on ANGPTL3, and the current results suggest that it “works very well,” so if other drugs are able to achieve the same efficacy as vupanorsen “but without the effects,” then it may “get elbowed out.”
Børge G. Nordestgaard, MD, PhD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen, who was not involved in the study, called the findings “very encouraging.”
He told this news organization that being able to reduce LDL cholesterol as well as VLDL and remnant cholesterol is “exactly what I would be dreaming about” with a drug like vupanorsen.
Dr. Nordestgaard nevertheless underlined that “one would have to look carefully” at the safety of the drug.
“If it was my money, I would certainly try to look into if this was some sort of transient thing. Even when they started talking about statins, there was also this transient increase in alanine transaminase that seems to go away after a while,” he said.
“But of course, if this was persistent and triglycerides in the liver kept accumulating, then it’s a problem,” Dr. Nordestgaard added, “and then you would need to have some sort of thinking about whether you could couple it with something that got rid of the liver fat.”
He also agreed with Dr. Marston that, even if vupanorsen does not clear all hurdles before making it to market, the approach is promising.
“The target,” Dr. Nordestgaard said, seems “fantastic, from my point of view anyway.”
Dr. Marston explained that VLDL cholesterol, remnant cholesterol, and triglycerides are “surrogates for triglyceride-rich” lipoproteins, and that they are “increasingly recognized” as cardiovascular risk factors.
He highlighted that currently available therapies achieve reductions of these compounds of between 30% and 50%.
TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 included adults on stable statin therapy who had a triglyceride level of 150 mg/dL to 500 mg/dL and a non-HDL cholesterol level of 100 mg/dL or higher.
The participants were randomly assigned to one of six 2- or 4-week dosing schedules of vupanorsen or placebo and followed up over 24 weeks for a series of primary and additional endpoints, as well as safety outcomes.
The team recruited 286 individuals, who had a median age of 64 years; 44% were female. The majority (87%) were white.
The mean body mass index was 32 kg/m2, 50% had diabetes, 13% had experienced a prior myocardial infarction, and 51% were receiving high-intensity statins.
As previously reported, vupanorsen was associated with a reduction in non-HDL cholesterol vs. placebo of 22%-28%, alongside a 6%-15% reduction in apolipoprotein B levels and an 8%-16% reduction in LDL cholesterol.
In contrast, Dr. Marston showed that the various dosing schedules of the drug were associated with reductions in levels of VLDL cholesterol of 52%-66% vs. placebo at 24 weeks.
Over the same period, remnant cholesterol levels were lowered by 42%-59% vs. placebo, and triglycerides were reduced by 44%-57% in patients given vupanorsen.
There were also reductions in ANGPTL3 levels of 70%-95%.
Subgroup analysis indicated that the effect of vupanorsen was seen regardless of age, sex, body mass index, presence of diabetes, baseline triglycerides, and intensity of statin therapy.
Dr. Marston highlighted that the reductions in triglycerides, VLDL cholesterol, and remnant cholesterol levels were directly related to those for ANGPTL3 levels, but that the reductions remained meaningful even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL.
For example, even when ANGPTL3 levels were reduced by 70%, there were 50% reductions in triglyceride levels, 70% reductions in VLDL cholesterol levels, and a 50% drop in remnant cholesterol levels.
This, he noted, is important given that safety signals such as increases in alanine transaminase and hepatic fat occurred in a dose-dependent manner with ANGPTL3 reductions and were “most pronounced” only at the highest level of ANGPTL3 reduction.
The TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Marston disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, Ionis, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Nordestgaard disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Ionis, Amgen, Kowa, Denka, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN, Italy – The antisense oligonucleotide vupanorsen substantially reduces very-low-density-lipoprotein (VLDL) and remnant cholesterol levels in patients with raised lipids despite statin therapy, suggests a subanalysis of TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 that appears to offer more hope than the primary study findings.
Vupanorsen targets hepatic angiopoietin-like protein 3 (ANGPTL3), which inhibits enzymes involved in triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism.
Earlier this year, headline data from TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 suggested that the drug reduced triglycerides and non–high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol to a degree that was significant but not clinically meaningful for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Moreover, as reported by this news organization, there were safety concerns over increases in liver enzymes among patients taking the drug, as well as dose-related increases in hepatic fat.
As a result, Pfizer announced that it would discontinue its clinical development program for vupanorsen and return the development rights to Ionis, following the signing of a worldwide exclusive agreement in November 2019.
Now, Nicholas A. Marston, MD, MPH, cardiovascular medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, has presented a post-hoc analysis of the phase 2b study, showing that the drug reduces VLDL and remnant cholesterol levels by up to 60%.
These were closely tied to reductions in ANGPTL3 levels, although substantial reductions in cholesterol levels were achieved even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL3, where the impact on safety outcomes was reduced.
Dr. Marston said that lower doses of vupanorsen, where the safety effects would be less, or other drugs that inhibit ANGPTL3, “may have an important role in patients with residual dyslipidemia despite current therapy.”
The results were presented at the 90th European Atherosclerosis Society Congress on May 23.
Dr. Marston told this news organization that some of the reductions they saw with the lower doses of vupanorsen were “just as good as any other therapy, and the safety profile was … much better than at the highest dose.”
They wanted to pursue the subgroup analysis, despite Pfizer’s announcement, partly to “learn something in terms of the potential efficacy of the ANGPTL3 pathway in general.”
Dr. Marston said that Ionis is now focused on ANGPTL3, and the current results suggest that it “works very well,” so if other drugs are able to achieve the same efficacy as vupanorsen “but without the effects,” then it may “get elbowed out.”
Børge G. Nordestgaard, MD, PhD, of Herlev and Gentofte Hospital, Copenhagen, who was not involved in the study, called the findings “very encouraging.”
He told this news organization that being able to reduce LDL cholesterol as well as VLDL and remnant cholesterol is “exactly what I would be dreaming about” with a drug like vupanorsen.
Dr. Nordestgaard nevertheless underlined that “one would have to look carefully” at the safety of the drug.
“If it was my money, I would certainly try to look into if this was some sort of transient thing. Even when they started talking about statins, there was also this transient increase in alanine transaminase that seems to go away after a while,” he said.
“But of course, if this was persistent and triglycerides in the liver kept accumulating, then it’s a problem,” Dr. Nordestgaard added, “and then you would need to have some sort of thinking about whether you could couple it with something that got rid of the liver fat.”
He also agreed with Dr. Marston that, even if vupanorsen does not clear all hurdles before making it to market, the approach is promising.
“The target,” Dr. Nordestgaard said, seems “fantastic, from my point of view anyway.”
Dr. Marston explained that VLDL cholesterol, remnant cholesterol, and triglycerides are “surrogates for triglyceride-rich” lipoproteins, and that they are “increasingly recognized” as cardiovascular risk factors.
He highlighted that currently available therapies achieve reductions of these compounds of between 30% and 50%.
TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 included adults on stable statin therapy who had a triglyceride level of 150 mg/dL to 500 mg/dL and a non-HDL cholesterol level of 100 mg/dL or higher.
The participants were randomly assigned to one of six 2- or 4-week dosing schedules of vupanorsen or placebo and followed up over 24 weeks for a series of primary and additional endpoints, as well as safety outcomes.
The team recruited 286 individuals, who had a median age of 64 years; 44% were female. The majority (87%) were white.
The mean body mass index was 32 kg/m2, 50% had diabetes, 13% had experienced a prior myocardial infarction, and 51% were receiving high-intensity statins.
As previously reported, vupanorsen was associated with a reduction in non-HDL cholesterol vs. placebo of 22%-28%, alongside a 6%-15% reduction in apolipoprotein B levels and an 8%-16% reduction in LDL cholesterol.
In contrast, Dr. Marston showed that the various dosing schedules of the drug were associated with reductions in levels of VLDL cholesterol of 52%-66% vs. placebo at 24 weeks.
Over the same period, remnant cholesterol levels were lowered by 42%-59% vs. placebo, and triglycerides were reduced by 44%-57% in patients given vupanorsen.
There were also reductions in ANGPTL3 levels of 70%-95%.
Subgroup analysis indicated that the effect of vupanorsen was seen regardless of age, sex, body mass index, presence of diabetes, baseline triglycerides, and intensity of statin therapy.
Dr. Marston highlighted that the reductions in triglycerides, VLDL cholesterol, and remnant cholesterol levels were directly related to those for ANGPTL3 levels, but that the reductions remained meaningful even at less than maximal reductions in ANGPTL.
For example, even when ANGPTL3 levels were reduced by 70%, there were 50% reductions in triglyceride levels, 70% reductions in VLDL cholesterol levels, and a 50% drop in remnant cholesterol levels.
This, he noted, is important given that safety signals such as increases in alanine transaminase and hepatic fat occurred in a dose-dependent manner with ANGPTL3 reductions and were “most pronounced” only at the highest level of ANGPTL3 reduction.
The TRANSLATE-TIMI 70 study was sponsored by Pfizer. Dr. Marston disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Amgen, Ionis, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. Dr. Nordestgaard disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Regeneron, Akcea, Ionis, Amgen, Kowa, Denka, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Esperion, and Silence Therapeutics.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EAS 2022
ADA updates on finerenone, SGLT2 inhibitors, and race-based eGFR
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As it gears up for the first in-person scientific sessions for 3 years, the American Diabetes Association has issued an addendum to its most recent annual clinical practice recommendations published in December 2021, the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes, based on recent trial evidence and consensus.
The update informs clinicians about:
- The effect of the nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (Kerendia) on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
- The effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor on heart failure and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The National Kidney Foundation and the American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation to remove race in the formula for calculating estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
“This is the fifth year that we are able to update the Standards of Care after it has been published through our Living Standards of Care updates, making it possible to give diabetes care providers the most important information and the latest evidence relevant to their practice,” Robert A. Gabbay, MD, PhD, ADA chief scientific and medical officer, said in a press release from the organization.
The addendum, entitled, “Living Standards of Care,” updates Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” and Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management” of the 2022 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
The amendments were approved by the ADA Professional Practice Committee, which is responsible for developing the Standards of Care. The American College of Cardiology reviewed and endorsed the section on CVD and risk management.
The Living Standards Update was published online in Diabetes Care.
CVD and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 10, “Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “For patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease treated with maximum tolerated doses of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers, addition of finerenone should be considered to improve cardiovascular outcomes and reduce the risk of chronic kidney disease progression. A”
- “Patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease should be considered for treatment with finerenone to reduce cardiovascular outcomes and the risk of chronic kidney disease progression.”
- “In patients with type 2 diabetes and established heart failure with either preserved or reduced ejection fraction, an SGLT2 inhibitor [with proven benefit in this patient population] is recommended to reduce risk of worsening heart failure, hospitalizations for heart failure, and cardiovascular death. ”
In the section “Statin Treatment,” the addendum no longer states that “a prospective trial of a newer fibrate ... is ongoing,” because that trial investigating pemafibrate (Kowa), a novel selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator (or fibrate), has been discontinued.
Chronic kidney disease and risk management
In the Addendum to Section 11, “Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk Management,” the committee writes:
- “Traditionally, eGFR is calculated from serum creatinine using a validated formula. The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation is preferred. ... Historically, a correction factor for muscle mass was included in a modified equation for African Americans; however, due to various issues with inequities, it was decided to the equation such that it applies to all. Hence, a committee was convened, resulting in the recommendation for immediate implementation of the CKD-EPI creatinine equation refit without the race variable in all laboratories in the U.S.” (This is based on an National Kidney Foundation and American Society of Nephrology Task Force recommendation.)
- “Additionally, increased use of cystatin C, especially to confirm estimated GFR in adults who are at risk for or have chronic kidney disease, because combining filtration markers (creatinine and cystatin C) is more accurate and would support better clinical decisions than either marker alone.”
Evidence from clinical trials
The update is based on findings from the following clinical trials:
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIDELIO-DKD)
- Efficacy and Safety of Finerenone in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Clinical Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney Disease (FIGARO-DKD)
- FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD
- Empagliflozin Outcome Trial in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction (EMPEROR-Preserved)
- Effects of Dapagliflozin on Biomarkers, Symptoms and Functional Status in Patients with PRESERVED Ejection Fraction Heart Failure (PRESERVED-HF)
- Pemafibrate to Reduce Cardiovascular Outcomes by Reducing Triglycerides in Patients with Diabetes (PROMINENT).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
Data concerns mount despite ISCHEMIA substudy correction
A long-standing request to clarify data irregularities in a 2021 ISCHEMIA substudy resulted in the publication of one correction, with a second correction in the works.
Further, the lone cardiac surgeon on the ISCHEMIA trial steering committee, T. Bruce Ferguson, MD, has resigned from the committee, citing a series of factors, including an inability to reconcile data in the substudy and two additional ISCHEMIA papers currently under review.
As previously reported, cardiac surgeons Faisal Bakaeen, MD, and Joseph Sabik III, MD, notified the journal Circulation in March that the Dr. Reynolds et al. substudy had inconsistencies between data in the main paper and supplemental tables detailing patients’ coronary artery disease (CAD) and ischemia severity.
The substudy found that CAD severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the landmark trial.
Circulation published a correction for the substudy on May 20, explaining that a “formatting error” resulted in data being incorrectly presented in two supplemental tables. It does not mention the surgeons’ letter to the editor, which can be found by clicking the “Q” icon below the paper.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, and Dr. Sabik, from University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told this news organization that they submitted a second letter to editor on May 23 stating that “significant discrepancies” persist.
For example, 7.2% of participants (179/2,475) had moderate stenosis in one coronary vessel in the corrected Reynolds paper (Supplemental Tables I and II) versus 23.3% (697/2,986) in the primary ISCHEMIA manuscript published in the New England Journal of Medicine (Table S5).
The number of patients with left main ≥ 50% stenosis is, surprisingly, identical in both manuscripts, at 40, they said, despite the denominator dropping from 3,845 participants in the primary study to 2,475 participants with an evaluable modified Duke Prognostic Index score in the substudy.
The number of participants with previous coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is also hard to reconcile between manuscripts and, importantly, the substudy doesn’t distinguish between lesions bypassed with patent grafts and unbypassed grafts or those with occluded grafts.
“The fact that the authors are working on a second correction is appreciated, but with such numerous inconsistencies, at some point you reach the conclusion that an independent review of the data is the right thing to do for such a high-profile study that received over $100 million of National Institutes of Health support,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “No one should be satisfied or happy if there is any shadow of doubt here regarding the accuracy of the data.”
Speaking to this news organization prior to the first correction, lead substudy author Harmony Reynolds, MD, NYU Langone Health, detailed in depth how the formatting glitch inadvertently upgraded the number of diseased vessels and lesion severity in two supplemental tables.
She noted, as does the correction, that the data were correctly reported in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement.
Dr. Reynolds also said they’re in the process of preparing the data for “public sharing soon,” including the Duke Prognostic score at all levels. Dr. Reynolds had not responded by the time of this publication to a request for further details or a timeline.
The surgeons’ first letter to the editor was rejected because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters and was posted as a public comment April 18 via the research platform, Remarq.
Dr. Bakaeen said they were told their second letter was rejected because of Circulation’s “long standing policy” not to publish letters to the editor regarding manuscript corrections but that a correction is being issued.
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said via email that the journal will update its online policies to more clearly state its requirements for publication and that it has been fully transparent with Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik regarding where it is in the current process.
He confirmed the surgeons were told June 1 that “after additional review, the authors have determined that whereas there are no errors, an additional minor correction is warranted to clarify the description of the study population and sample size. This correction will be published soon.”
Dr. Hill thanked Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik for bringing the matter to their attention and said, “It is also important to note that both updates to the Dr. Reynolds et al. paper are published as corrections. However, the results and conclusions of the paper remain unchanged.”
The bigger issue
Importantly, the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used ISCHEMIA data to support downgrading the CABG recommendation from class 1 to class 2B in 3-vessel CAD with normal left ventricular function and from class 1 to 2a in 3-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction.
The trial reported no significant benefit with an initial invasive strategy over medical therapy in stable patients with moderate or severe CAD. European guidelines, however, give CABG a class I recommendation for severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal left anterior descending (LAD) involvement.
Dr. Sabik and Dr. Bakaeen say patients with severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal LAD involvement were underrepresented in the randomized trials cited by the guidelines but are the typical CABG patients in modern-day practice.
“That is why it is important to determine the severity of CAD accurately and definitively in ISCHEMIA,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “But the more we look at the data, the more errors we encounter.”
Two U.S. surgical groups that were part of the writing process withdrew support for the revascularization guidelines, as did several international surgical societies, citing the data used to support the changes as well as the makeup of the writing committee.
Dr. Ferguson, now with the medical device manufacturer Perfusio, said he resigned from the ISCHEMIA steering committee on May 8 after being unable to accurately reconcile the ISCHEMIA surgical subset data with the Reynolds substudy and two other ISCHEMIA papers on the CABG subset. At least one of those papers, he noted, was being hurriedly pushed through the review process to counter concerns raised by surgeons regarding interpretation of ISCHEMIA.
“This is the first time in my lengthy career in medicine where a level of political agendaism was actually driving the truck,” he said. “It was appalling to me, and I would have said that if I was an interventional cardiologist looking at the results.”
ISCHEMIA results have also been touted as representing state-of-the-art care around the world, but that didn’t appear to be the case for the surgical subset where, for example, China and India performed most CABGs off pump, and globally there was considerable variation in how surgeons approached surgical revascularization strategies, Dr. Ferguson said. “Whether this variability might impact the guideline discussion and these papers coming out remains to be determined.”
He noted that the study protocol allowed for the ISCHEMIA investigators to evaluate whether the variability in the surgical subset influenced the results by comparing the data to that in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons registry, but this option was never acted upon despite being brought to their attention.
“Something political between 2020 and 2022 has crept into the ISCHEMIA trial mindset gestalt, and I don’t like it,” Dr. Ferguson said. “And this can have enormous consequences.”
Asked whether their letters to Circulation are being used to undermine confidence in the ISCHEMIA findings, Dr. Sabik replied, “It is not about undermining ISCHEMIA, but understanding how applicable ISCHEMIA is to patients having CABG today. Understanding the severity of the CAD in patients enrolled in ISCHEMIA is, therefore, necessary.”
“The authors and Circulation have admitted to errors,” he said. “We want to be sure we understand how severe the errors are.”
“This is just about accuracy in a manuscript that may affect patient treatment and therefore patient lives. We want to make sure it is correct,” Dr. Sabik added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A long-standing request to clarify data irregularities in a 2021 ISCHEMIA substudy resulted in the publication of one correction, with a second correction in the works.
Further, the lone cardiac surgeon on the ISCHEMIA trial steering committee, T. Bruce Ferguson, MD, has resigned from the committee, citing a series of factors, including an inability to reconcile data in the substudy and two additional ISCHEMIA papers currently under review.
As previously reported, cardiac surgeons Faisal Bakaeen, MD, and Joseph Sabik III, MD, notified the journal Circulation in March that the Dr. Reynolds et al. substudy had inconsistencies between data in the main paper and supplemental tables detailing patients’ coronary artery disease (CAD) and ischemia severity.
The substudy found that CAD severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the landmark trial.
Circulation published a correction for the substudy on May 20, explaining that a “formatting error” resulted in data being incorrectly presented in two supplemental tables. It does not mention the surgeons’ letter to the editor, which can be found by clicking the “Q” icon below the paper.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, and Dr. Sabik, from University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told this news organization that they submitted a second letter to editor on May 23 stating that “significant discrepancies” persist.
For example, 7.2% of participants (179/2,475) had moderate stenosis in one coronary vessel in the corrected Reynolds paper (Supplemental Tables I and II) versus 23.3% (697/2,986) in the primary ISCHEMIA manuscript published in the New England Journal of Medicine (Table S5).
The number of patients with left main ≥ 50% stenosis is, surprisingly, identical in both manuscripts, at 40, they said, despite the denominator dropping from 3,845 participants in the primary study to 2,475 participants with an evaluable modified Duke Prognostic Index score in the substudy.
The number of participants with previous coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is also hard to reconcile between manuscripts and, importantly, the substudy doesn’t distinguish between lesions bypassed with patent grafts and unbypassed grafts or those with occluded grafts.
“The fact that the authors are working on a second correction is appreciated, but with such numerous inconsistencies, at some point you reach the conclusion that an independent review of the data is the right thing to do for such a high-profile study that received over $100 million of National Institutes of Health support,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “No one should be satisfied or happy if there is any shadow of doubt here regarding the accuracy of the data.”
Speaking to this news organization prior to the first correction, lead substudy author Harmony Reynolds, MD, NYU Langone Health, detailed in depth how the formatting glitch inadvertently upgraded the number of diseased vessels and lesion severity in two supplemental tables.
She noted, as does the correction, that the data were correctly reported in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement.
Dr. Reynolds also said they’re in the process of preparing the data for “public sharing soon,” including the Duke Prognostic score at all levels. Dr. Reynolds had not responded by the time of this publication to a request for further details or a timeline.
The surgeons’ first letter to the editor was rejected because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters and was posted as a public comment April 18 via the research platform, Remarq.
Dr. Bakaeen said they were told their second letter was rejected because of Circulation’s “long standing policy” not to publish letters to the editor regarding manuscript corrections but that a correction is being issued.
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said via email that the journal will update its online policies to more clearly state its requirements for publication and that it has been fully transparent with Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik regarding where it is in the current process.
He confirmed the surgeons were told June 1 that “after additional review, the authors have determined that whereas there are no errors, an additional minor correction is warranted to clarify the description of the study population and sample size. This correction will be published soon.”
Dr. Hill thanked Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik for bringing the matter to their attention and said, “It is also important to note that both updates to the Dr. Reynolds et al. paper are published as corrections. However, the results and conclusions of the paper remain unchanged.”
The bigger issue
Importantly, the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used ISCHEMIA data to support downgrading the CABG recommendation from class 1 to class 2B in 3-vessel CAD with normal left ventricular function and from class 1 to 2a in 3-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction.
The trial reported no significant benefit with an initial invasive strategy over medical therapy in stable patients with moderate or severe CAD. European guidelines, however, give CABG a class I recommendation for severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal left anterior descending (LAD) involvement.
Dr. Sabik and Dr. Bakaeen say patients with severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal LAD involvement were underrepresented in the randomized trials cited by the guidelines but are the typical CABG patients in modern-day practice.
“That is why it is important to determine the severity of CAD accurately and definitively in ISCHEMIA,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “But the more we look at the data, the more errors we encounter.”
Two U.S. surgical groups that were part of the writing process withdrew support for the revascularization guidelines, as did several international surgical societies, citing the data used to support the changes as well as the makeup of the writing committee.
Dr. Ferguson, now with the medical device manufacturer Perfusio, said he resigned from the ISCHEMIA steering committee on May 8 after being unable to accurately reconcile the ISCHEMIA surgical subset data with the Reynolds substudy and two other ISCHEMIA papers on the CABG subset. At least one of those papers, he noted, was being hurriedly pushed through the review process to counter concerns raised by surgeons regarding interpretation of ISCHEMIA.
“This is the first time in my lengthy career in medicine where a level of political agendaism was actually driving the truck,” he said. “It was appalling to me, and I would have said that if I was an interventional cardiologist looking at the results.”
ISCHEMIA results have also been touted as representing state-of-the-art care around the world, but that didn’t appear to be the case for the surgical subset where, for example, China and India performed most CABGs off pump, and globally there was considerable variation in how surgeons approached surgical revascularization strategies, Dr. Ferguson said. “Whether this variability might impact the guideline discussion and these papers coming out remains to be determined.”
He noted that the study protocol allowed for the ISCHEMIA investigators to evaluate whether the variability in the surgical subset influenced the results by comparing the data to that in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons registry, but this option was never acted upon despite being brought to their attention.
“Something political between 2020 and 2022 has crept into the ISCHEMIA trial mindset gestalt, and I don’t like it,” Dr. Ferguson said. “And this can have enormous consequences.”
Asked whether their letters to Circulation are being used to undermine confidence in the ISCHEMIA findings, Dr. Sabik replied, “It is not about undermining ISCHEMIA, but understanding how applicable ISCHEMIA is to patients having CABG today. Understanding the severity of the CAD in patients enrolled in ISCHEMIA is, therefore, necessary.”
“The authors and Circulation have admitted to errors,” he said. “We want to be sure we understand how severe the errors are.”
“This is just about accuracy in a manuscript that may affect patient treatment and therefore patient lives. We want to make sure it is correct,” Dr. Sabik added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A long-standing request to clarify data irregularities in a 2021 ISCHEMIA substudy resulted in the publication of one correction, with a second correction in the works.
Further, the lone cardiac surgeon on the ISCHEMIA trial steering committee, T. Bruce Ferguson, MD, has resigned from the committee, citing a series of factors, including an inability to reconcile data in the substudy and two additional ISCHEMIA papers currently under review.
As previously reported, cardiac surgeons Faisal Bakaeen, MD, and Joseph Sabik III, MD, notified the journal Circulation in March that the Dr. Reynolds et al. substudy had inconsistencies between data in the main paper and supplemental tables detailing patients’ coronary artery disease (CAD) and ischemia severity.
The substudy found that CAD severity, classified using the modified Duke Prognostic Index score, predicted 4-year mortality and myocardial infarction in the landmark trial.
Circulation published a correction for the substudy on May 20, explaining that a “formatting error” resulted in data being incorrectly presented in two supplemental tables. It does not mention the surgeons’ letter to the editor, which can be found by clicking the “Q” icon below the paper.
Dr. Bakaeen, from the Cleveland Clinic, and Dr. Sabik, from University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, told this news organization that they submitted a second letter to editor on May 23 stating that “significant discrepancies” persist.
For example, 7.2% of participants (179/2,475) had moderate stenosis in one coronary vessel in the corrected Reynolds paper (Supplemental Tables I and II) versus 23.3% (697/2,986) in the primary ISCHEMIA manuscript published in the New England Journal of Medicine (Table S5).
The number of patients with left main ≥ 50% stenosis is, surprisingly, identical in both manuscripts, at 40, they said, despite the denominator dropping from 3,845 participants in the primary study to 2,475 participants with an evaluable modified Duke Prognostic Index score in the substudy.
The number of participants with previous coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is also hard to reconcile between manuscripts and, importantly, the substudy doesn’t distinguish between lesions bypassed with patent grafts and unbypassed grafts or those with occluded grafts.
“The fact that the authors are working on a second correction is appreciated, but with such numerous inconsistencies, at some point you reach the conclusion that an independent review of the data is the right thing to do for such a high-profile study that received over $100 million of National Institutes of Health support,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “No one should be satisfied or happy if there is any shadow of doubt here regarding the accuracy of the data.”
Speaking to this news organization prior to the first correction, lead substudy author Harmony Reynolds, MD, NYU Langone Health, detailed in depth how the formatting glitch inadvertently upgraded the number of diseased vessels and lesion severity in two supplemental tables.
She noted, as does the correction, that the data were correctly reported in the main manuscript tables and figures and in the remainder of the supplement.
Dr. Reynolds also said they’re in the process of preparing the data for “public sharing soon,” including the Duke Prognostic score at all levels. Dr. Reynolds had not responded by the time of this publication to a request for further details or a timeline.
The surgeons’ first letter to the editor was rejected because it was submitted outside the journal’s 6-week window for letters and was posted as a public comment April 18 via the research platform, Remarq.
Dr. Bakaeen said they were told their second letter was rejected because of Circulation’s “long standing policy” not to publish letters to the editor regarding manuscript corrections but that a correction is being issued.
Circulation editor-in-chief Joseph A. Hill, MD, PhD, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said via email that the journal will update its online policies to more clearly state its requirements for publication and that it has been fully transparent with Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik regarding where it is in the current process.
He confirmed the surgeons were told June 1 that “after additional review, the authors have determined that whereas there are no errors, an additional minor correction is warranted to clarify the description of the study population and sample size. This correction will be published soon.”
Dr. Hill thanked Dr. Bakaeen and Dr. Sabik for bringing the matter to their attention and said, “It is also important to note that both updates to the Dr. Reynolds et al. paper are published as corrections. However, the results and conclusions of the paper remain unchanged.”
The bigger issue
Importantly, the recent AHA/ACC/SCAI coronary revascularization guidelines used ISCHEMIA data to support downgrading the CABG recommendation from class 1 to class 2B in 3-vessel CAD with normal left ventricular function and from class 1 to 2a in 3-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction.
The trial reported no significant benefit with an initial invasive strategy over medical therapy in stable patients with moderate or severe CAD. European guidelines, however, give CABG a class I recommendation for severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal left anterior descending (LAD) involvement.
Dr. Sabik and Dr. Bakaeen say patients with severe three- or two-vessel disease with proximal LAD involvement were underrepresented in the randomized trials cited by the guidelines but are the typical CABG patients in modern-day practice.
“That is why it is important to determine the severity of CAD accurately and definitively in ISCHEMIA,” Dr. Bakaeen said. “But the more we look at the data, the more errors we encounter.”
Two U.S. surgical groups that were part of the writing process withdrew support for the revascularization guidelines, as did several international surgical societies, citing the data used to support the changes as well as the makeup of the writing committee.
Dr. Ferguson, now with the medical device manufacturer Perfusio, said he resigned from the ISCHEMIA steering committee on May 8 after being unable to accurately reconcile the ISCHEMIA surgical subset data with the Reynolds substudy and two other ISCHEMIA papers on the CABG subset. At least one of those papers, he noted, was being hurriedly pushed through the review process to counter concerns raised by surgeons regarding interpretation of ISCHEMIA.
“This is the first time in my lengthy career in medicine where a level of political agendaism was actually driving the truck,” he said. “It was appalling to me, and I would have said that if I was an interventional cardiologist looking at the results.”
ISCHEMIA results have also been touted as representing state-of-the-art care around the world, but that didn’t appear to be the case for the surgical subset where, for example, China and India performed most CABGs off pump, and globally there was considerable variation in how surgeons approached surgical revascularization strategies, Dr. Ferguson said. “Whether this variability might impact the guideline discussion and these papers coming out remains to be determined.”
He noted that the study protocol allowed for the ISCHEMIA investigators to evaluate whether the variability in the surgical subset influenced the results by comparing the data to that in the Society of Thoracic Surgeons registry, but this option was never acted upon despite being brought to their attention.
“Something political between 2020 and 2022 has crept into the ISCHEMIA trial mindset gestalt, and I don’t like it,” Dr. Ferguson said. “And this can have enormous consequences.”
Asked whether their letters to Circulation are being used to undermine confidence in the ISCHEMIA findings, Dr. Sabik replied, “It is not about undermining ISCHEMIA, but understanding how applicable ISCHEMIA is to patients having CABG today. Understanding the severity of the CAD in patients enrolled in ISCHEMIA is, therefore, necessary.”
“The authors and Circulation have admitted to errors,” he said. “We want to be sure we understand how severe the errors are.”
“This is just about accuracy in a manuscript that may affect patient treatment and therefore patient lives. We want to make sure it is correct,” Dr. Sabik added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CTO PCI success rates rising, with blip during COVID-19, registry shows
Technical and procedural success rates for chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention (CTO PCI) have increased steadily over the past 6 years, with rates of in-hospital major adverse cardiac events (MACE) declining to the 2%-or-lower range in that time.
“CTO PCI technical and procedural success rates are high and continue to increase over time,” Spyridon Kostantinis, MD said in presenting updated results from the international PROGRESS-CTO registry at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions annual scientific sessions.
“The overall success rate increased from 81.6% in 2018 to 88.1% in 2021,” he added. The overall incidence of in-hospital MACE in that time was “an acceptable” 2.1% without significant changes over that period.
The analysis examined clinical, angiographic and procedural outcomes of 10,249 CTO PCIs performed on 10,019 patients from 63 centers in nine countries during 2016-2021. PROGRESS-CTO stands for Prospective Global Registry for the Study of Chronic Total Occlusion Intervention.
The target CTOs were highly complex, he said, with an average J-CTO (multicenter CTO registry in Japan) score of 2.4 ± 1.3 and PROGRESS-CTO score of 1.3 ± 1. The most common CTO target vessel was the right coronary artery (53%), followed by the left anterior descending artery (26%) and the circumflex artery (19%).
The registry also tracked how characteristics of the CTO PCI procedures themselves changed over time. “The septal and the epicardial collaterals were the most common collaterals used for retrograde crossing, with a decreasing trend for epicardial collaterals over time,” said Dr. Kostantinis, a research fellow at the Minneapolis Heart Institute.
Septal collateral use varied between 64% and 69% of cases from 2016 to 2021, but the share of epicardial collaterals declined from 35% to 22% in that time.
“Over time, the range of antegrade wiring as the final successfully crossing strategy increased from 46% in 2016 to 61% in 2021, with a decrease in antegrade dissection and re-entry (ADR) and no change in the retrograde approach,” Dr. Kostantinis said. The percentage of procedures using ADR as the final crossing strategy declined from 18% in 2016 to 12% in 2021, with the rate of retrograde crossings peaking at 21% in 2016 but leveling off to 18% or 19% in the subsequent years.
“An increasing use in the efficiency of antegrade wiring may reflect an improvement in guidewire retrograde crossing as well as the increasing operator expertise,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
The study also found that contrast volume, air kerma radiation dose, fluoroscopy time, and procedure time declined steadily over time. “The potential explanations for these are using new x-ray systems as well as the use of intravascular imaging,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
In 2020, the rates of technical and procedural success, as well as the number of overall procedures, declined from 2019, while MACE rates ticked upward that year, probably because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Kostantinis said.
“It is true that we noticed a rise in MACE rate from 1.6% in 2019 to 2.7% in 2020, but in 2021 that decreased again to 1.7%,” he said in an interview. “Another potential explanation is the higher angiographic complexity of CTOs treated during that year (2020) that resulted in more adverse events.”
Previous results from the PROGRESS-CTO registry reported the difference in MACE between 2019 and 2020 was significant (P = .01). “So, yes, the difference between those 2 years is significant,” Dr. Kostantinis said. However, he noted, the overall trend was not significant, with a P value of .194.
The risk profile of CTO PCI has improved “slowly” over time, said Kirk N. Garratt, MD, but “it’s not yet were it needs to be.”
He added, “Undoubtedly we’ve learned that, without any question, one method for minimizing the risk is to concentrate these cases in the hands of those that do many of them.” As the number of procedures fell – an “embedded” pandemic impact –“I worry that it’s inevitable that complication rates will tick up a bit,” said Dr. Garratt, director of the Center for Heart and Vascular Health at Christiana Care in Newark, Del.
By the same token, he added, this situation with regard to CTOs “parallels what’s happening elsewhere in interventional medicine and medicine broadly; numbers are increasing and we’re busy again. In most domains we’re not as busy as we had been prepandemic, and time will allow us to catch up.”
PROGRESS-CTO has received funding from the Joseph F. and Mary M. Fleischhacker Foundation and the Abbott Northwestern Hospital Foundation Innovation Grant.
Dr. Kostantinis has no disclosures. Dr. Garratt is an advisory board member for Abbott.
Technical and procedural success rates for chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention (CTO PCI) have increased steadily over the past 6 years, with rates of in-hospital major adverse cardiac events (MACE) declining to the 2%-or-lower range in that time.
“CTO PCI technical and procedural success rates are high and continue to increase over time,” Spyridon Kostantinis, MD said in presenting updated results from the international PROGRESS-CTO registry at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions annual scientific sessions.
“The overall success rate increased from 81.6% in 2018 to 88.1% in 2021,” he added. The overall incidence of in-hospital MACE in that time was “an acceptable” 2.1% without significant changes over that period.
The analysis examined clinical, angiographic and procedural outcomes of 10,249 CTO PCIs performed on 10,019 patients from 63 centers in nine countries during 2016-2021. PROGRESS-CTO stands for Prospective Global Registry for the Study of Chronic Total Occlusion Intervention.
The target CTOs were highly complex, he said, with an average J-CTO (multicenter CTO registry in Japan) score of 2.4 ± 1.3 and PROGRESS-CTO score of 1.3 ± 1. The most common CTO target vessel was the right coronary artery (53%), followed by the left anterior descending artery (26%) and the circumflex artery (19%).
The registry also tracked how characteristics of the CTO PCI procedures themselves changed over time. “The septal and the epicardial collaterals were the most common collaterals used for retrograde crossing, with a decreasing trend for epicardial collaterals over time,” said Dr. Kostantinis, a research fellow at the Minneapolis Heart Institute.
Septal collateral use varied between 64% and 69% of cases from 2016 to 2021, but the share of epicardial collaterals declined from 35% to 22% in that time.
“Over time, the range of antegrade wiring as the final successfully crossing strategy increased from 46% in 2016 to 61% in 2021, with a decrease in antegrade dissection and re-entry (ADR) and no change in the retrograde approach,” Dr. Kostantinis said. The percentage of procedures using ADR as the final crossing strategy declined from 18% in 2016 to 12% in 2021, with the rate of retrograde crossings peaking at 21% in 2016 but leveling off to 18% or 19% in the subsequent years.
“An increasing use in the efficiency of antegrade wiring may reflect an improvement in guidewire retrograde crossing as well as the increasing operator expertise,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
The study also found that contrast volume, air kerma radiation dose, fluoroscopy time, and procedure time declined steadily over time. “The potential explanations for these are using new x-ray systems as well as the use of intravascular imaging,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
In 2020, the rates of technical and procedural success, as well as the number of overall procedures, declined from 2019, while MACE rates ticked upward that year, probably because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Kostantinis said.
“It is true that we noticed a rise in MACE rate from 1.6% in 2019 to 2.7% in 2020, but in 2021 that decreased again to 1.7%,” he said in an interview. “Another potential explanation is the higher angiographic complexity of CTOs treated during that year (2020) that resulted in more adverse events.”
Previous results from the PROGRESS-CTO registry reported the difference in MACE between 2019 and 2020 was significant (P = .01). “So, yes, the difference between those 2 years is significant,” Dr. Kostantinis said. However, he noted, the overall trend was not significant, with a P value of .194.
The risk profile of CTO PCI has improved “slowly” over time, said Kirk N. Garratt, MD, but “it’s not yet were it needs to be.”
He added, “Undoubtedly we’ve learned that, without any question, one method for minimizing the risk is to concentrate these cases in the hands of those that do many of them.” As the number of procedures fell – an “embedded” pandemic impact –“I worry that it’s inevitable that complication rates will tick up a bit,” said Dr. Garratt, director of the Center for Heart and Vascular Health at Christiana Care in Newark, Del.
By the same token, he added, this situation with regard to CTOs “parallels what’s happening elsewhere in interventional medicine and medicine broadly; numbers are increasing and we’re busy again. In most domains we’re not as busy as we had been prepandemic, and time will allow us to catch up.”
PROGRESS-CTO has received funding from the Joseph F. and Mary M. Fleischhacker Foundation and the Abbott Northwestern Hospital Foundation Innovation Grant.
Dr. Kostantinis has no disclosures. Dr. Garratt is an advisory board member for Abbott.
Technical and procedural success rates for chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention (CTO PCI) have increased steadily over the past 6 years, with rates of in-hospital major adverse cardiac events (MACE) declining to the 2%-or-lower range in that time.
“CTO PCI technical and procedural success rates are high and continue to increase over time,” Spyridon Kostantinis, MD said in presenting updated results from the international PROGRESS-CTO registry at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions annual scientific sessions.
“The overall success rate increased from 81.6% in 2018 to 88.1% in 2021,” he added. The overall incidence of in-hospital MACE in that time was “an acceptable” 2.1% without significant changes over that period.
The analysis examined clinical, angiographic and procedural outcomes of 10,249 CTO PCIs performed on 10,019 patients from 63 centers in nine countries during 2016-2021. PROGRESS-CTO stands for Prospective Global Registry for the Study of Chronic Total Occlusion Intervention.
The target CTOs were highly complex, he said, with an average J-CTO (multicenter CTO registry in Japan) score of 2.4 ± 1.3 and PROGRESS-CTO score of 1.3 ± 1. The most common CTO target vessel was the right coronary artery (53%), followed by the left anterior descending artery (26%) and the circumflex artery (19%).
The registry also tracked how characteristics of the CTO PCI procedures themselves changed over time. “The septal and the epicardial collaterals were the most common collaterals used for retrograde crossing, with a decreasing trend for epicardial collaterals over time,” said Dr. Kostantinis, a research fellow at the Minneapolis Heart Institute.
Septal collateral use varied between 64% and 69% of cases from 2016 to 2021, but the share of epicardial collaterals declined from 35% to 22% in that time.
“Over time, the range of antegrade wiring as the final successfully crossing strategy increased from 46% in 2016 to 61% in 2021, with a decrease in antegrade dissection and re-entry (ADR) and no change in the retrograde approach,” Dr. Kostantinis said. The percentage of procedures using ADR as the final crossing strategy declined from 18% in 2016 to 12% in 2021, with the rate of retrograde crossings peaking at 21% in 2016 but leveling off to 18% or 19% in the subsequent years.
“An increasing use in the efficiency of antegrade wiring may reflect an improvement in guidewire retrograde crossing as well as the increasing operator expertise,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
The study also found that contrast volume, air kerma radiation dose, fluoroscopy time, and procedure time declined steadily over time. “The potential explanations for these are using new x-ray systems as well as the use of intravascular imaging,” Dr. Kostantinis said.
In 2020, the rates of technical and procedural success, as well as the number of overall procedures, declined from 2019, while MACE rates ticked upward that year, probably because of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Kostantinis said.
“It is true that we noticed a rise in MACE rate from 1.6% in 2019 to 2.7% in 2020, but in 2021 that decreased again to 1.7%,” he said in an interview. “Another potential explanation is the higher angiographic complexity of CTOs treated during that year (2020) that resulted in more adverse events.”
Previous results from the PROGRESS-CTO registry reported the difference in MACE between 2019 and 2020 was significant (P = .01). “So, yes, the difference between those 2 years is significant,” Dr. Kostantinis said. However, he noted, the overall trend was not significant, with a P value of .194.
The risk profile of CTO PCI has improved “slowly” over time, said Kirk N. Garratt, MD, but “it’s not yet were it needs to be.”
He added, “Undoubtedly we’ve learned that, without any question, one method for minimizing the risk is to concentrate these cases in the hands of those that do many of them.” As the number of procedures fell – an “embedded” pandemic impact –“I worry that it’s inevitable that complication rates will tick up a bit,” said Dr. Garratt, director of the Center for Heart and Vascular Health at Christiana Care in Newark, Del.
By the same token, he added, this situation with regard to CTOs “parallels what’s happening elsewhere in interventional medicine and medicine broadly; numbers are increasing and we’re busy again. In most domains we’re not as busy as we had been prepandemic, and time will allow us to catch up.”
PROGRESS-CTO has received funding from the Joseph F. and Mary M. Fleischhacker Foundation and the Abbott Northwestern Hospital Foundation Innovation Grant.
Dr. Kostantinis has no disclosures. Dr. Garratt is an advisory board member for Abbott.
FROM SCAI 2022
Antipsychotic tied to dose-related weight gain, higher cholesterol
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.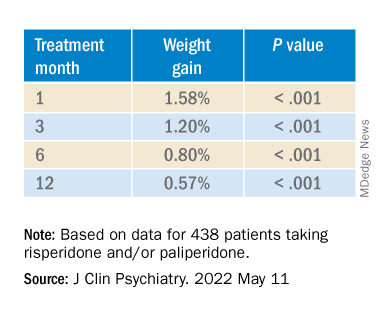
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.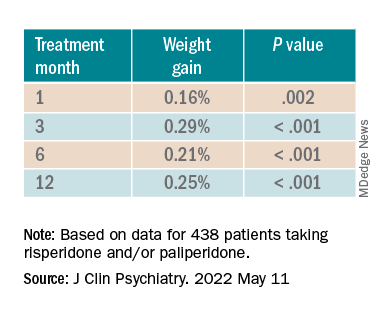
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.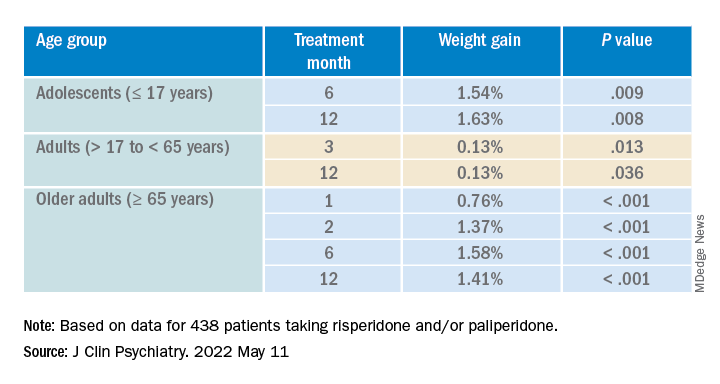
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Obesity in adolescence raises risk for adult type 1 diabetes
NEW ORLEANS – Obesity in adolescence is linked to an increased risk for type 1 diabetes onset in adulthood, new research suggests.
These new data, from Israeli military recruits followed for over a decade, suggest that obesity may be playing a causal role in type 1 as well as type 2 diabetes.
The incidence of type 1 diabetes has been increasing by about 2%-3% annually over recent decades, but the reasons aren’t clear. The study is the first to examine the role of obesity in adolescence and type 1 diabetes in young adulthood, and also the first to examine the question of using antibody status as part of the criteria for a type 1 diagnosis.
The findings were reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association by Gilad Twig, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Sheba Medical Center, Tel HaShomer, Israel. “For people who might have a high risk for developing type 1 diabetes, these results emphasize the importance of maintaining a normal weight,” he said in an interview. He noted that, although this recommendation applies to everyone, “here it’s becoming more precise for the population – more individualized in the sense that this might specifically help you.”
Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor and honorary consultant in cardiovascular and medical sciences at the University of Glasgow, said in an interview that carrying too much weight “will make the pancreas have to work harder to make insulin to keep the sugar normal. So, if you’re stressing the system and the pancreas is already likely to fail, it will fail faster.”
Clinically, Dr. Sattar said, “Lifestyle does matter to the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. The weighting may be different [from type 2]. The major factor in type 1 is still the genetics, but if you have a family history of type 1 and your genetic potential is greater, you will minimize your risk by staying leaner.”
Study highlights that type 1 is not always ‘juvenile’
In addition to countering the long-held belief that type 1 diabetes is primarily a condition of thin individuals and unrelated to obesity, the data also reinforce the emerging recognition that type 1 diabetes isn’t always “juvenile” and in fact often arises in adulthood.
“About half of all cases of type 1 diabetes develop after age 18. By reputation, people think it’s a disease of children. But it’s begun to grow so that now 50% of cases occur after late adolescence,” noted Dr. Twig.
Dr. Sattar pointed to a UK Biobank study showing that nearly half of all cases of type 1 diabetes arise after age 30 years. “You absolutely can get type 1 in adulthood. It’s not rare.”
Direct correlation seen in otherwise healthy young people
The retrospective nationwide cohort study included 1,426,362 17-year-olds (834,050 male and 592,312 female) who underwent medical evaluation prior to military conscription starting in January 1996 and followed them through 2016. At baseline, none had a history of dysglycemia.
The data were linked with information about adult-onset type 1 diabetes in the Israeli National Diabetes Registry. In all, 777 incident type 1 diabetes cases were recorded over the study period, with a rate of 4.9 cases per 100,000 person-years.
Over a median follow-up of 11.2 years, there was a graded incidence of type 1 diabetes across BMI groups from underweight to obesity, from 3.6 to 8.4 cases per 100,000 person-years.
After adjustment for sex, birth year, age at study entry, education, and cognitive performance with BMI 5th-49th percentiles as the reference, the hazard ratios were 1.05 for the 50th-74th BMI percentiles, 1.41 for 75th-84th, 1.54 for those who were overweight, and 2.05 for those with obesity.
Every 5-unit increment in BMI corresponded to a 35% greater incidence of type 1 diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35) and every one increment was associated with a 35% greater risk (1.25), both values significant.
Sensitivity analyses resulted in similar findings for those with no other chronic health conditions at baseline. The results also didn’t change in a separate analysis of 574,720 subjects in whom autoantibody data were available to confirm the type 1 diabetes diagnosis.
Hypotheses for mechanisms
The mechanism for the association isn’t clear, but in a simultaneously published article in Diabetologia, Dr. Twig and colleagues outline several hypotheses. One relates to the growing evidence of a link between various autoimmune conditions, which point to the possibility of elevated adipokines and cytokines in obesity diminishing self-tolerance by promoting proinflammatory processes.
The authors cite data from the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention study of relatives of people with type 1 diabetes in which participants who were overweight and obese had an increased risk of islet autoantibody expression. However, not all data have supported this finding.
“Obesity is related to several other autoimmune conditions, so it’s not a complete surprise it might be related to another,” Dr. Twig noted.
Other possibilities include vitamin D deficiency, a high-fat diet, and alterations in gut microbiota.
And then there’s the “accelerator hypothesis,” suggesting that both type 1 and type 2 diabetes result from insulin resistance and genetic background that affect the rate of beta cell loss and the disease phenotype. Dr. Sattar said that the accelerator hypotheses “makes complete sense to me. Because the population is so obese, we’re seeing it more now whereas we might not have seen it 40 years ago when the BMI differentials were far less in society.”
Dr. Twig has no disclosures. Dr. Sattar has consulted for or received lecture fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi, and received grant support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics through his institution.
NEW ORLEANS – Obesity in adolescence is linked to an increased risk for type 1 diabetes onset in adulthood, new research suggests.
These new data, from Israeli military recruits followed for over a decade, suggest that obesity may be playing a causal role in type 1 as well as type 2 diabetes.
The incidence of type 1 diabetes has been increasing by about 2%-3% annually over recent decades, but the reasons aren’t clear. The study is the first to examine the role of obesity in adolescence and type 1 diabetes in young adulthood, and also the first to examine the question of using antibody status as part of the criteria for a type 1 diagnosis.
The findings were reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association by Gilad Twig, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Sheba Medical Center, Tel HaShomer, Israel. “For people who might have a high risk for developing type 1 diabetes, these results emphasize the importance of maintaining a normal weight,” he said in an interview. He noted that, although this recommendation applies to everyone, “here it’s becoming more precise for the population – more individualized in the sense that this might specifically help you.”
Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor and honorary consultant in cardiovascular and medical sciences at the University of Glasgow, said in an interview that carrying too much weight “will make the pancreas have to work harder to make insulin to keep the sugar normal. So, if you’re stressing the system and the pancreas is already likely to fail, it will fail faster.”
Clinically, Dr. Sattar said, “Lifestyle does matter to the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. The weighting may be different [from type 2]. The major factor in type 1 is still the genetics, but if you have a family history of type 1 and your genetic potential is greater, you will minimize your risk by staying leaner.”
Study highlights that type 1 is not always ‘juvenile’
In addition to countering the long-held belief that type 1 diabetes is primarily a condition of thin individuals and unrelated to obesity, the data also reinforce the emerging recognition that type 1 diabetes isn’t always “juvenile” and in fact often arises in adulthood.
“About half of all cases of type 1 diabetes develop after age 18. By reputation, people think it’s a disease of children. But it’s begun to grow so that now 50% of cases occur after late adolescence,” noted Dr. Twig.
Dr. Sattar pointed to a UK Biobank study showing that nearly half of all cases of type 1 diabetes arise after age 30 years. “You absolutely can get type 1 in adulthood. It’s not rare.”
Direct correlation seen in otherwise healthy young people
The retrospective nationwide cohort study included 1,426,362 17-year-olds (834,050 male and 592,312 female) who underwent medical evaluation prior to military conscription starting in January 1996 and followed them through 2016. At baseline, none had a history of dysglycemia.
The data were linked with information about adult-onset type 1 diabetes in the Israeli National Diabetes Registry. In all, 777 incident type 1 diabetes cases were recorded over the study period, with a rate of 4.9 cases per 100,000 person-years.
Over a median follow-up of 11.2 years, there was a graded incidence of type 1 diabetes across BMI groups from underweight to obesity, from 3.6 to 8.4 cases per 100,000 person-years.
After adjustment for sex, birth year, age at study entry, education, and cognitive performance with BMI 5th-49th percentiles as the reference, the hazard ratios were 1.05 for the 50th-74th BMI percentiles, 1.41 for 75th-84th, 1.54 for those who were overweight, and 2.05 for those with obesity.
Every 5-unit increment in BMI corresponded to a 35% greater incidence of type 1 diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35) and every one increment was associated with a 35% greater risk (1.25), both values significant.
Sensitivity analyses resulted in similar findings for those with no other chronic health conditions at baseline. The results also didn’t change in a separate analysis of 574,720 subjects in whom autoantibody data were available to confirm the type 1 diabetes diagnosis.
Hypotheses for mechanisms
The mechanism for the association isn’t clear, but in a simultaneously published article in Diabetologia, Dr. Twig and colleagues outline several hypotheses. One relates to the growing evidence of a link between various autoimmune conditions, which point to the possibility of elevated adipokines and cytokines in obesity diminishing self-tolerance by promoting proinflammatory processes.
The authors cite data from the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention study of relatives of people with type 1 diabetes in which participants who were overweight and obese had an increased risk of islet autoantibody expression. However, not all data have supported this finding.
“Obesity is related to several other autoimmune conditions, so it’s not a complete surprise it might be related to another,” Dr. Twig noted.
Other possibilities include vitamin D deficiency, a high-fat diet, and alterations in gut microbiota.
And then there’s the “accelerator hypothesis,” suggesting that both type 1 and type 2 diabetes result from insulin resistance and genetic background that affect the rate of beta cell loss and the disease phenotype. Dr. Sattar said that the accelerator hypotheses “makes complete sense to me. Because the population is so obese, we’re seeing it more now whereas we might not have seen it 40 years ago when the BMI differentials were far less in society.”
Dr. Twig has no disclosures. Dr. Sattar has consulted for or received lecture fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi, and received grant support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics through his institution.
NEW ORLEANS – Obesity in adolescence is linked to an increased risk for type 1 diabetes onset in adulthood, new research suggests.
These new data, from Israeli military recruits followed for over a decade, suggest that obesity may be playing a causal role in type 1 as well as type 2 diabetes.
The incidence of type 1 diabetes has been increasing by about 2%-3% annually over recent decades, but the reasons aren’t clear. The study is the first to examine the role of obesity in adolescence and type 1 diabetes in young adulthood, and also the first to examine the question of using antibody status as part of the criteria for a type 1 diagnosis.
The findings were reported at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association by Gilad Twig, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Sheba Medical Center, Tel HaShomer, Israel. “For people who might have a high risk for developing type 1 diabetes, these results emphasize the importance of maintaining a normal weight,” he said in an interview. He noted that, although this recommendation applies to everyone, “here it’s becoming more precise for the population – more individualized in the sense that this might specifically help you.”
Naveed Sattar, PhD, professor and honorary consultant in cardiovascular and medical sciences at the University of Glasgow, said in an interview that carrying too much weight “will make the pancreas have to work harder to make insulin to keep the sugar normal. So, if you’re stressing the system and the pancreas is already likely to fail, it will fail faster.”
Clinically, Dr. Sattar said, “Lifestyle does matter to the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. The weighting may be different [from type 2]. The major factor in type 1 is still the genetics, but if you have a family history of type 1 and your genetic potential is greater, you will minimize your risk by staying leaner.”
Study highlights that type 1 is not always ‘juvenile’
In addition to countering the long-held belief that type 1 diabetes is primarily a condition of thin individuals and unrelated to obesity, the data also reinforce the emerging recognition that type 1 diabetes isn’t always “juvenile” and in fact often arises in adulthood.
“About half of all cases of type 1 diabetes develop after age 18. By reputation, people think it’s a disease of children. But it’s begun to grow so that now 50% of cases occur after late adolescence,” noted Dr. Twig.
Dr. Sattar pointed to a UK Biobank study showing that nearly half of all cases of type 1 diabetes arise after age 30 years. “You absolutely can get type 1 in adulthood. It’s not rare.”
Direct correlation seen in otherwise healthy young people
The retrospective nationwide cohort study included 1,426,362 17-year-olds (834,050 male and 592,312 female) who underwent medical evaluation prior to military conscription starting in January 1996 and followed them through 2016. At baseline, none had a history of dysglycemia.
The data were linked with information about adult-onset type 1 diabetes in the Israeli National Diabetes Registry. In all, 777 incident type 1 diabetes cases were recorded over the study period, with a rate of 4.9 cases per 100,000 person-years.
Over a median follow-up of 11.2 years, there was a graded incidence of type 1 diabetes across BMI groups from underweight to obesity, from 3.6 to 8.4 cases per 100,000 person-years.
After adjustment for sex, birth year, age at study entry, education, and cognitive performance with BMI 5th-49th percentiles as the reference, the hazard ratios were 1.05 for the 50th-74th BMI percentiles, 1.41 for 75th-84th, 1.54 for those who were overweight, and 2.05 for those with obesity.
Every 5-unit increment in BMI corresponded to a 35% greater incidence of type 1 diabetes (adjusted hazard ratio 1.35) and every one increment was associated with a 35% greater risk (1.25), both values significant.
Sensitivity analyses resulted in similar findings for those with no other chronic health conditions at baseline. The results also didn’t change in a separate analysis of 574,720 subjects in whom autoantibody data were available to confirm the type 1 diabetes diagnosis.
Hypotheses for mechanisms
The mechanism for the association isn’t clear, but in a simultaneously published article in Diabetologia, Dr. Twig and colleagues outline several hypotheses. One relates to the growing evidence of a link between various autoimmune conditions, which point to the possibility of elevated adipokines and cytokines in obesity diminishing self-tolerance by promoting proinflammatory processes.
The authors cite data from the TrialNet Pathway to Prevention study of relatives of people with type 1 diabetes in which participants who were overweight and obese had an increased risk of islet autoantibody expression. However, not all data have supported this finding.
“Obesity is related to several other autoimmune conditions, so it’s not a complete surprise it might be related to another,” Dr. Twig noted.
Other possibilities include vitamin D deficiency, a high-fat diet, and alterations in gut microbiota.
And then there’s the “accelerator hypothesis,” suggesting that both type 1 and type 2 diabetes result from insulin resistance and genetic background that affect the rate of beta cell loss and the disease phenotype. Dr. Sattar said that the accelerator hypotheses “makes complete sense to me. Because the population is so obese, we’re seeing it more now whereas we might not have seen it 40 years ago when the BMI differentials were far less in society.”
Dr. Twig has no disclosures. Dr. Sattar has consulted for or received lecture fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Sanofi, and received grant support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, and Roche Diagnostics through his institution.
AT ADA 2022
Tirzepatide powers ‘unprecedented’ weight loss in SURMOUNT-1
NEW ORLEANS – Treatment of people with obesity but no diabetes with the dual–incretin agonist tirzepatide safely produced “unprecedented” levels of weight loss in the vast majority of patients in SURMOUNT-1, a placebo-controlled trial with more than 2,500 people with obesity or overweight plus at least one weight-related complication.
Although the pivotal trial did not directly compare weekly subcutaneous injection with the twincretin tirzepatide (at 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) with either bariatric surgery or what has been the reigning champ of weight-loss agents, a 2.4-mg/week injection of semaglutide (Wegovy), the new findings are impressive because they eclipsed semaglutide’s past performance in at least three important ways, said Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, SURMOUNT-1’s lead investigator, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
First, the highest-tested dosage of tirzepatide, 15 mg/week, for 72 weeks, produced a 5% or greater loss in baseline weight in 91%-96% of patients, an effect “not previously seen” in any prior phase 3 trial of a weight-loss agent, noted Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and director of Weight Management & Obesity Prevention at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Second, the average level of weight loss among the 630 people who received 15 mg/week was 22.5% in the on-treatment analysis, and 20.9% in the intention-to-treat analysis, again a magnitude of effect never before seen with any other medical intervention.
And in an exploratory analysis, 40% of people who received the highest-tested tirzepatide dose of 15 mg/week had at least a 25% loss in baseline weight in the on-treatment analysis, another example of unprecedented weight-loss achievement, said Dr. Jastreboff.
Looking at the data another way, the average baseline weight of those in the trial was 104 kg (230 lb) at the start, and the average weight loss was between 35 and 52 lbs by 72 weeks on treatment, Dr. Jastreboff said in a press conference.
She noted, however, that not everyone will respond to tirzepatide, “but if you do respond to this medicine, you will feel full earlier, you won’t want to go back for seconds, and you may eat smaller amounts more often.”
Such weight-loss agents will need to be taken chronically, in the same way that medications are for hypertension or dyslipidemia, Dr. Jastreboff stressed. “If you stop the antiobesity medication then the body fat mass set point will go back up so this necessitates long-term treatment.”
A new era: Weight loss ‘in the range of bariatric surgery’
Tirzepatide, developed by Lilly, has recently been approved in the United States for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, under the brand name Mounjaro.
SURMOUNT-1 was designed to examine the effect of the agent in overweight/obesity, and the company will be filing for the additional indication of weight loss in the future. Top-line results of SURMOUNT-1 generated much excitement when Lilly reported them back in April, including a story in The New York Times.
Semaglutide, a Novo Nordisk drug, is approved in the United States for type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic at doses of either 1 mg or 2 mg per week) and also for weight loss, as Wegovy, at the higher dose of 2.4 mg per week. When Wegovy was given the green light by the Food and Drug Administration a year ago, it too was hailed as a “game changer” for obesity.
The weight-loss results seen in SURMOUNT-1 “put tirzepatide squarely in the range of weight loss achieved with bariatric surgery,” concluded Louis J. Aronne, MD, a coinvestigator on the trial, professor at Weill-Cornell Medicine in New York, and director of the Center for Weight Management and Metabolic Clinical Research of Weill-Cornell.
The results are “amazing,” and propel the weight-loss field into “a new era of obesity treatment,” commented Lee M. Kaplan, MD, who was not involved in the study and served as designated discussant for the trial.
Despite the lack of direct comparison, the findings indicate that “tirzepatide causes more weight loss than semaglutide,” and it provides “an opportunity to meet or exceed” the weight-loss effects of bariatric surgery, added Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Simultaneously with Dr. Jastreboff’s report at the meeting, the results were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
An accompanying editorial agrees with Dr. Kaplan: “It is remarkable that the magnitude of weight loss with tirzepatide was similar to that with gastric bypass, which raises the potential for alternative medical approaches to the treatment of obesity.”
“The tides are shifting, and there are now more options for people with obesity to lose weight,” write Clifford J. Rosen, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, and Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dual incretin agonism ‘enhances activity,’ says expert
Tirzepatide is the first agent on the U.S. market from a novel class of dual-incretin agonists, with a molecular structure engineered to activate both the glucagonlike protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), the two predominant incretins in the human gut. This combined activity has led to the twincretin nickname for tirzepatide.
Semaglutide is a single-incretin agonist, with its activity focused exclusively on the GLP-1 receptor.
Dr. Aronne tied the apparently superior efficacy of tirzepatide relative to semaglutide directly to the added incretin activity of tirzepatide. “The dual approach enhances efficacy,” he proposed during his presentation at the meeting.
The impressive efficacy and reassuring safety profile reported from SURMOUNT-1 opens the door to a new approach to treating obesity, which in the past has often taken a back seat to treatments for dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Now that we can treat obesity safely and effectively, it makes sense to treat obesity first,” Dr. Aronne recommended.
Dr. Jastreboff agreed: “Perhaps we can prevent diabetes by treating obesity head-on,” she remarked.
Weight-loss agents gain U.S. traction
There have been concerns about patient access to these newer weight-loss drugs in the United States, given that the retail cost of semaglutide for obesity exceeds $1,000/month, but Dr. Aronne reported data that painted a more optimistic picture.
His numbers showed that during the first months that semaglutide was on the U.S. market as a weight-loss agent, the number of U.S. prescriptions written for branded antiobesity medications roughly doubled, a spike that seemed mostly driven by the introduction and growing use of semaglutide.
With tirzepatide, every prespecified cardiometabolic parameter assessed in the trial showed clinically meaningful improvements, reported Dr. Jastreboff, including an average 17% reduction in waist circumference in patients on either of the highest two dosages, a 34% average drop in total fat mass, an average 0.5–percentage point cut in baseline hemoglobin A1c at the highest two dosages, substantial cuts in fasting plasma glucose and fasting insulin levels, an average 28% drop in triglyceride levels, and an average systolic blood pressure reduction of about 8 mm Hg that occurred within 24 weeks on treatment.
“I think that insurers will sign up” for tirzepatide coverage based on benefits like this, Dr. Aronne predicted.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 patients with obesity or with overweight plus at least one weight-related complication at any of 119 sites in nine countries. They had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or more, or 27 kg/m2 or more and at least one weight-related complication, excluding diabetes. They were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive once-weekly, subcutaneous tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or placebo for 72 weeks, including a 20-week dose-escalation period.
The study’s two primary endpoints were the average percentage change in body weight from entry to 72 weeks, and the percentage of participants reaching at least a 5% reduction in their baseline body weight by 72 weeks.
The most common adverse events with tirzepatide were gastrointestinal, and most were mild to moderate in severity, occurring primarily during dose escalation. Adverse events caused treatment discontinuation in 4.3%, 7.1%, 6.2%, and 2.6% of participants receiving 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg tirzepatide doses and placebo, respectively
The trial ran from December 2019 to April 2022, so during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, which Dr. Jastreboff described as an “amazing feat.”
Jamy Ard, MD, who chaired the SURMOUNT-1 session quipped, after hearing the results, “Wow; that’s exciting. If you’re not excited by the results, you’d better check your pulse.”
Dr. Ard is a professor at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., and codirector of the Wake Forest Baptist Health Weight Management Center in Winston-Salem.
SURMOUNT-1 was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an advisor or consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Scholar Rock, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Aronne has been a consultant or advisor to, speaker on behalf of, or received research funding from Eli Lilly as well as from Altimmune, Amgen, Allurion, Intellihealth, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and United Health group; he has an ownership interest in ERX, Gelesis, and Intellihealth; and he serves on the board of ERX, Jamieson Wellness, and Intellihealth. Dr. Kaplan has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Optum Health, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, the Obesity and Nutrition Institute, and Xeno Biosciences. Dr. Ard has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Nestle Health Sciences and Novo Nordisk, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Epitomee, Medical, and United Health Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – Treatment of people with obesity but no diabetes with the dual–incretin agonist tirzepatide safely produced “unprecedented” levels of weight loss in the vast majority of patients in SURMOUNT-1, a placebo-controlled trial with more than 2,500 people with obesity or overweight plus at least one weight-related complication.
Although the pivotal trial did not directly compare weekly subcutaneous injection with the twincretin tirzepatide (at 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) with either bariatric surgery or what has been the reigning champ of weight-loss agents, a 2.4-mg/week injection of semaglutide (Wegovy), the new findings are impressive because they eclipsed semaglutide’s past performance in at least three important ways, said Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, SURMOUNT-1’s lead investigator, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
First, the highest-tested dosage of tirzepatide, 15 mg/week, for 72 weeks, produced a 5% or greater loss in baseline weight in 91%-96% of patients, an effect “not previously seen” in any prior phase 3 trial of a weight-loss agent, noted Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and director of Weight Management & Obesity Prevention at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Second, the average level of weight loss among the 630 people who received 15 mg/week was 22.5% in the on-treatment analysis, and 20.9% in the intention-to-treat analysis, again a magnitude of effect never before seen with any other medical intervention.
And in an exploratory analysis, 40% of people who received the highest-tested tirzepatide dose of 15 mg/week had at least a 25% loss in baseline weight in the on-treatment analysis, another example of unprecedented weight-loss achievement, said Dr. Jastreboff.
Looking at the data another way, the average baseline weight of those in the trial was 104 kg (230 lb) at the start, and the average weight loss was between 35 and 52 lbs by 72 weeks on treatment, Dr. Jastreboff said in a press conference.
She noted, however, that not everyone will respond to tirzepatide, “but if you do respond to this medicine, you will feel full earlier, you won’t want to go back for seconds, and you may eat smaller amounts more often.”
Such weight-loss agents will need to be taken chronically, in the same way that medications are for hypertension or dyslipidemia, Dr. Jastreboff stressed. “If you stop the antiobesity medication then the body fat mass set point will go back up so this necessitates long-term treatment.”
A new era: Weight loss ‘in the range of bariatric surgery’
Tirzepatide, developed by Lilly, has recently been approved in the United States for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, under the brand name Mounjaro.
SURMOUNT-1 was designed to examine the effect of the agent in overweight/obesity, and the company will be filing for the additional indication of weight loss in the future. Top-line results of SURMOUNT-1 generated much excitement when Lilly reported them back in April, including a story in The New York Times.
Semaglutide, a Novo Nordisk drug, is approved in the United States for type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic at doses of either 1 mg or 2 mg per week) and also for weight loss, as Wegovy, at the higher dose of 2.4 mg per week. When Wegovy was given the green light by the Food and Drug Administration a year ago, it too was hailed as a “game changer” for obesity.
The weight-loss results seen in SURMOUNT-1 “put tirzepatide squarely in the range of weight loss achieved with bariatric surgery,” concluded Louis J. Aronne, MD, a coinvestigator on the trial, professor at Weill-Cornell Medicine in New York, and director of the Center for Weight Management and Metabolic Clinical Research of Weill-Cornell.
The results are “amazing,” and propel the weight-loss field into “a new era of obesity treatment,” commented Lee M. Kaplan, MD, who was not involved in the study and served as designated discussant for the trial.
Despite the lack of direct comparison, the findings indicate that “tirzepatide causes more weight loss than semaglutide,” and it provides “an opportunity to meet or exceed” the weight-loss effects of bariatric surgery, added Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Simultaneously with Dr. Jastreboff’s report at the meeting, the results were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
An accompanying editorial agrees with Dr. Kaplan: “It is remarkable that the magnitude of weight loss with tirzepatide was similar to that with gastric bypass, which raises the potential for alternative medical approaches to the treatment of obesity.”
“The tides are shifting, and there are now more options for people with obesity to lose weight,” write Clifford J. Rosen, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, and Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dual incretin agonism ‘enhances activity,’ says expert
Tirzepatide is the first agent on the U.S. market from a novel class of dual-incretin agonists, with a molecular structure engineered to activate both the glucagonlike protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), the two predominant incretins in the human gut. This combined activity has led to the twincretin nickname for tirzepatide.
Semaglutide is a single-incretin agonist, with its activity focused exclusively on the GLP-1 receptor.
Dr. Aronne tied the apparently superior efficacy of tirzepatide relative to semaglutide directly to the added incretin activity of tirzepatide. “The dual approach enhances efficacy,” he proposed during his presentation at the meeting.
The impressive efficacy and reassuring safety profile reported from SURMOUNT-1 opens the door to a new approach to treating obesity, which in the past has often taken a back seat to treatments for dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Now that we can treat obesity safely and effectively, it makes sense to treat obesity first,” Dr. Aronne recommended.
Dr. Jastreboff agreed: “Perhaps we can prevent diabetes by treating obesity head-on,” she remarked.
Weight-loss agents gain U.S. traction
There have been concerns about patient access to these newer weight-loss drugs in the United States, given that the retail cost of semaglutide for obesity exceeds $1,000/month, but Dr. Aronne reported data that painted a more optimistic picture.
His numbers showed that during the first months that semaglutide was on the U.S. market as a weight-loss agent, the number of U.S. prescriptions written for branded antiobesity medications roughly doubled, a spike that seemed mostly driven by the introduction and growing use of semaglutide.
With tirzepatide, every prespecified cardiometabolic parameter assessed in the trial showed clinically meaningful improvements, reported Dr. Jastreboff, including an average 17% reduction in waist circumference in patients on either of the highest two dosages, a 34% average drop in total fat mass, an average 0.5–percentage point cut in baseline hemoglobin A1c at the highest two dosages, substantial cuts in fasting plasma glucose and fasting insulin levels, an average 28% drop in triglyceride levels, and an average systolic blood pressure reduction of about 8 mm Hg that occurred within 24 weeks on treatment.
“I think that insurers will sign up” for tirzepatide coverage based on benefits like this, Dr. Aronne predicted.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 patients with obesity or with overweight plus at least one weight-related complication at any of 119 sites in nine countries. They had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or more, or 27 kg/m2 or more and at least one weight-related complication, excluding diabetes. They were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive once-weekly, subcutaneous tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or placebo for 72 weeks, including a 20-week dose-escalation period.
The study’s two primary endpoints were the average percentage change in body weight from entry to 72 weeks, and the percentage of participants reaching at least a 5% reduction in their baseline body weight by 72 weeks.
The most common adverse events with tirzepatide were gastrointestinal, and most were mild to moderate in severity, occurring primarily during dose escalation. Adverse events caused treatment discontinuation in 4.3%, 7.1%, 6.2%, and 2.6% of participants receiving 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg tirzepatide doses and placebo, respectively
The trial ran from December 2019 to April 2022, so during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, which Dr. Jastreboff described as an “amazing feat.”
Jamy Ard, MD, who chaired the SURMOUNT-1 session quipped, after hearing the results, “Wow; that’s exciting. If you’re not excited by the results, you’d better check your pulse.”
Dr. Ard is a professor at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., and codirector of the Wake Forest Baptist Health Weight Management Center in Winston-Salem.
SURMOUNT-1 was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an advisor or consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Scholar Rock, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Aronne has been a consultant or advisor to, speaker on behalf of, or received research funding from Eli Lilly as well as from Altimmune, Amgen, Allurion, Intellihealth, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and United Health group; he has an ownership interest in ERX, Gelesis, and Intellihealth; and he serves on the board of ERX, Jamieson Wellness, and Intellihealth. Dr. Kaplan has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Optum Health, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, the Obesity and Nutrition Institute, and Xeno Biosciences. Dr. Ard has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Nestle Health Sciences and Novo Nordisk, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Epitomee, Medical, and United Health Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – Treatment of people with obesity but no diabetes with the dual–incretin agonist tirzepatide safely produced “unprecedented” levels of weight loss in the vast majority of patients in SURMOUNT-1, a placebo-controlled trial with more than 2,500 people with obesity or overweight plus at least one weight-related complication.
Although the pivotal trial did not directly compare weekly subcutaneous injection with the twincretin tirzepatide (at 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) with either bariatric surgery or what has been the reigning champ of weight-loss agents, a 2.4-mg/week injection of semaglutide (Wegovy), the new findings are impressive because they eclipsed semaglutide’s past performance in at least three important ways, said Ania M. Jastreboff, MD, PhD, SURMOUNT-1’s lead investigator, at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
First, the highest-tested dosage of tirzepatide, 15 mg/week, for 72 weeks, produced a 5% or greater loss in baseline weight in 91%-96% of patients, an effect “not previously seen” in any prior phase 3 trial of a weight-loss agent, noted Dr. Jastreboff, an endocrinologist and director of Weight Management & Obesity Prevention at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
Second, the average level of weight loss among the 630 people who received 15 mg/week was 22.5% in the on-treatment analysis, and 20.9% in the intention-to-treat analysis, again a magnitude of effect never before seen with any other medical intervention.
And in an exploratory analysis, 40% of people who received the highest-tested tirzepatide dose of 15 mg/week had at least a 25% loss in baseline weight in the on-treatment analysis, another example of unprecedented weight-loss achievement, said Dr. Jastreboff.
Looking at the data another way, the average baseline weight of those in the trial was 104 kg (230 lb) at the start, and the average weight loss was between 35 and 52 lbs by 72 weeks on treatment, Dr. Jastreboff said in a press conference.
She noted, however, that not everyone will respond to tirzepatide, “but if you do respond to this medicine, you will feel full earlier, you won’t want to go back for seconds, and you may eat smaller amounts more often.”
Such weight-loss agents will need to be taken chronically, in the same way that medications are for hypertension or dyslipidemia, Dr. Jastreboff stressed. “If you stop the antiobesity medication then the body fat mass set point will go back up so this necessitates long-term treatment.”
A new era: Weight loss ‘in the range of bariatric surgery’
Tirzepatide, developed by Lilly, has recently been approved in the United States for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, under the brand name Mounjaro.
SURMOUNT-1 was designed to examine the effect of the agent in overweight/obesity, and the company will be filing for the additional indication of weight loss in the future. Top-line results of SURMOUNT-1 generated much excitement when Lilly reported them back in April, including a story in The New York Times.
Semaglutide, a Novo Nordisk drug, is approved in the United States for type 2 diabetes (as Ozempic at doses of either 1 mg or 2 mg per week) and also for weight loss, as Wegovy, at the higher dose of 2.4 mg per week. When Wegovy was given the green light by the Food and Drug Administration a year ago, it too was hailed as a “game changer” for obesity.
The weight-loss results seen in SURMOUNT-1 “put tirzepatide squarely in the range of weight loss achieved with bariatric surgery,” concluded Louis J. Aronne, MD, a coinvestigator on the trial, professor at Weill-Cornell Medicine in New York, and director of the Center for Weight Management and Metabolic Clinical Research of Weill-Cornell.
The results are “amazing,” and propel the weight-loss field into “a new era of obesity treatment,” commented Lee M. Kaplan, MD, who was not involved in the study and served as designated discussant for the trial.
Despite the lack of direct comparison, the findings indicate that “tirzepatide causes more weight loss than semaglutide,” and it provides “an opportunity to meet or exceed” the weight-loss effects of bariatric surgery, added Dr. Kaplan, director of the Obesity, Metabolism and Nutrition Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston.
Simultaneously with Dr. Jastreboff’s report at the meeting, the results were published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
An accompanying editorial agrees with Dr. Kaplan: “It is remarkable that the magnitude of weight loss with tirzepatide was similar to that with gastric bypass, which raises the potential for alternative medical approaches to the treatment of obesity.”
“The tides are shifting, and there are now more options for people with obesity to lose weight,” write Clifford J. Rosen, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, and Julie R. Ingelfinger, MD, of Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dual incretin agonism ‘enhances activity,’ says expert
Tirzepatide is the first agent on the U.S. market from a novel class of dual-incretin agonists, with a molecular structure engineered to activate both the glucagonlike protein-1 (GLP-1) receptor and the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), the two predominant incretins in the human gut. This combined activity has led to the twincretin nickname for tirzepatide.
Semaglutide is a single-incretin agonist, with its activity focused exclusively on the GLP-1 receptor.
Dr. Aronne tied the apparently superior efficacy of tirzepatide relative to semaglutide directly to the added incretin activity of tirzepatide. “The dual approach enhances efficacy,” he proposed during his presentation at the meeting.
The impressive efficacy and reassuring safety profile reported from SURMOUNT-1 opens the door to a new approach to treating obesity, which in the past has often taken a back seat to treatments for dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes.
“Now that we can treat obesity safely and effectively, it makes sense to treat obesity first,” Dr. Aronne recommended.
Dr. Jastreboff agreed: “Perhaps we can prevent diabetes by treating obesity head-on,” she remarked.
Weight-loss agents gain U.S. traction
There have been concerns about patient access to these newer weight-loss drugs in the United States, given that the retail cost of semaglutide for obesity exceeds $1,000/month, but Dr. Aronne reported data that painted a more optimistic picture.
His numbers showed that during the first months that semaglutide was on the U.S. market as a weight-loss agent, the number of U.S. prescriptions written for branded antiobesity medications roughly doubled, a spike that seemed mostly driven by the introduction and growing use of semaglutide.
With tirzepatide, every prespecified cardiometabolic parameter assessed in the trial showed clinically meaningful improvements, reported Dr. Jastreboff, including an average 17% reduction in waist circumference in patients on either of the highest two dosages, a 34% average drop in total fat mass, an average 0.5–percentage point cut in baseline hemoglobin A1c at the highest two dosages, substantial cuts in fasting plasma glucose and fasting insulin levels, an average 28% drop in triglyceride levels, and an average systolic blood pressure reduction of about 8 mm Hg that occurred within 24 weeks on treatment.
“I think that insurers will sign up” for tirzepatide coverage based on benefits like this, Dr. Aronne predicted.
SURMOUNT-1 randomized 2,539 patients with obesity or with overweight plus at least one weight-related complication at any of 119 sites in nine countries. They had a body mass index of 30 kg/m2 or more, or 27 kg/m2 or more and at least one weight-related complication, excluding diabetes. They were randomized in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive once-weekly, subcutaneous tirzepatide (5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg) or placebo for 72 weeks, including a 20-week dose-escalation period.
The study’s two primary endpoints were the average percentage change in body weight from entry to 72 weeks, and the percentage of participants reaching at least a 5% reduction in their baseline body weight by 72 weeks.
The most common adverse events with tirzepatide were gastrointestinal, and most were mild to moderate in severity, occurring primarily during dose escalation. Adverse events caused treatment discontinuation in 4.3%, 7.1%, 6.2%, and 2.6% of participants receiving 5-mg, 10-mg, and 15-mg tirzepatide doses and placebo, respectively
The trial ran from December 2019 to April 2022, so during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, which Dr. Jastreboff described as an “amazing feat.”
Jamy Ard, MD, who chaired the SURMOUNT-1 session quipped, after hearing the results, “Wow; that’s exciting. If you’re not excited by the results, you’d better check your pulse.”
Dr. Ard is a professor at Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C., and codirector of the Wake Forest Baptist Health Weight Management Center in Winston-Salem.
SURMOUNT-1 was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company that markets tirzepatide (Mounjaro). Dr. Jastreboff has been an advisor or consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, Scholar Rock, and Weight Watchers, and she has received research funding from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Aronne has been a consultant or advisor to, speaker on behalf of, or received research funding from Eli Lilly as well as from Altimmune, Amgen, Allurion, Intellihealth, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and United Health group; he has an ownership interest in ERX, Gelesis, and Intellihealth; and he serves on the board of ERX, Jamieson Wellness, and Intellihealth. Dr. Kaplan has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Optum Health, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, the Obesity and Nutrition Institute, and Xeno Biosciences. Dr. Ard has been a consultant to Eli Lilly, as well as to Nestle Health Sciences and Novo Nordisk, and he has received research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim, Epitomee, Medical, and United Health Group.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ADA 2022
Will tirzepatide slow kidney function decline in type 2 diabetes?
The “twincretin” tirzepatide might become part of the “arsenal” against diabetic kidney disease, new research suggests. Notably, the drug significantly reduced the likelihood of macroalbuminuria, in a prespecified subanalysis of the SURPASS-4 clinical trial.
“Once-per-week tirzepatide compared to [daily] insulin glargine treatment resulted in a meaningful improvement in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline and reduced urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and the risk of end stage kidney disease (ESKD) – with low risk of clinically relevant hypoglycemia in participants with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk and varying degrees of chronic kidney disease (CKD),” lead investigator Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, PhD, PharmD, summarized in an email to this news organization.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just approved tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Eli Lilly) – a novel, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combined with a glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist – to treat glycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, based on five pivotal SURPASS trials.
Dr. Heerspink presented the new findings about tirzepatide’s impact on kidney function in an oral session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
40% reduced risk of kidney function decline
The main results of SURPASS-4 were published in the Lancet in October 2021, and showed that tirzepatide appeared superior to insulin glargine in lowering hemoglobin A1c in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk who were inadequately controlled on oral diabetes treatments.
Now, Dr. Heerspink has shown that patients who received tirzepatide as opposed to insulin glargine were significantly less likely to have kidney function decline that included new-onset macroalbuminuria (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .05).
“These are very large benefits and clearly indicate the potential of tirzepatide to be a very strong kidney protective drug,” said Dr. Heerspink, from the department of clinical pharmacy and pharmacology, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands).
“Based on results from the SURPASS-4 trial, tirzepatide has significant kidney-protective effects in adults with type 2 diabetes with high cardiovascular risk and largely normal kidney function,” Christine Limonte, MD, chair of the session in which the analysis was presented, agreed, in an email to this news organization.
The approximate 40% reduced risk of kidney function decline in this population “is important because it suggests that this novel agent may contribute to the growing arsenal for preventing and treating diabetic kidney disease,” added Dr. Limonte, a clinical research fellow in the division of nephrology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“Over the last several years,” she noted, “sodium glucose cotransporter-2 [SGLT2] inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists have been identified as having significant kidney-protective effects in type 2 diabetes, and as such are becoming first-line agents in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease.”
Additional studies are needed, she added, to assess the impacts of tirzepatide compared to these agents (particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists, which overlap in their mechanism of action).
“With the growing number of therapeutic options for diabetic kidney disease, future research should also focus on identifying combinations of agents which benefit individuals in a ‘targeted’ manner,” according to Dr. Limonte.
“Ensuring accessibility to kidney-protective agents by promoting access to health care and reducing drug costs is essential to improving outcomes in diabetic kidney disease,” she added.
Strongest reduction seen in risk of new macroalbuminuria
One in three adults with diabetes has CKD, according to a press release issued by the ADA. Therefore, there is a need for therapies to reduce the development and progression of CKD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The prespecified analysis of SUPRESS-4 investigated potential renoprotective effects of tirzepatide.
The trial enrolled 1,995 patients with type 2 diabetes who were at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The patients had a mean age of 63.6 years and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.5%.
Most patients had normal kidney function. The mean eGFR based on the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation was 81.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Few patients (17%) had moderately or severely reduced kidney function (eGFR <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2). Around a quarter of the patients (28%) had microalbuminuria (UACR 30-300 mg/g) and 8% had macroalbuminuria (UACR >300 mg/g).
The patients were randomized to receive a weekly injection of 5, 10, or 15 mg tirzepatide or a daily individualized injection of insulin glargine starting at 10 IU/day at bedtime, titrated to a fasting blood glucose <100 mg/dL, in addition to existing oral glucose-lowering agents. The primary outcomes in the subanalysis were:
- Endpoint 1: a composite of ≥40% decline in eGFR from baseline, renal death, progression to ESKD, and new-onset macroalbuminuria.
- Endpoint 2: the same as endpoint 1 excluding new-onset macroalbuminuria.
During a median follow up of 85 weeks and up to 104 weeks, patients who received tirzepatide versus insulin glargine were significantly less likely to reach endpoint 1 but not endpoint 2.
In addition, tirzepatide “very strongly” reduced the risk of new-onset macroalbuminuria, compared to insulin glargine, by approximately 60% in the complete study cohort (hazard ratio, 0.41; P < .05), Dr. Limonte noted.
Tirzepatide also reduced the risk of a >40% decline in eGFR, but this effect was not statistically significant, possibly because this outcome was underpowered. There were also too few kidney deaths and progressions to ESKD to meaningfully assess the effects of tirzepatide on these outcomes.
Therefore, Dr. Limonte noted, “it is likely that tirzepatide’s significant benefit on composite endpoint 1 was largely driven by this agent’s impact on reducing macroalbuminuria onset [explaining why a significant benefit was not seen with composite endpoint 2, which excluded new-onset macroalbuminuria].”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Heerspink disclosed that he is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook Therapeutics, CSL Behring, Gilead Sciences, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen Research & Development, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mundipharma, and Traveere Pharmaceuticals, and has received research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novo Nordisk.
Dr. Limonte disclosed that she receives funds from the American Kidney Fund’s Clinical Scientist in Nephrology Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The “twincretin” tirzepatide might become part of the “arsenal” against diabetic kidney disease, new research suggests. Notably, the drug significantly reduced the likelihood of macroalbuminuria, in a prespecified subanalysis of the SURPASS-4 clinical trial.
“Once-per-week tirzepatide compared to [daily] insulin glargine treatment resulted in a meaningful improvement in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline and reduced urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and the risk of end stage kidney disease (ESKD) – with low risk of clinically relevant hypoglycemia in participants with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk and varying degrees of chronic kidney disease (CKD),” lead investigator Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, PhD, PharmD, summarized in an email to this news organization.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just approved tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Eli Lilly) – a novel, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combined with a glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist – to treat glycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, based on five pivotal SURPASS trials.
Dr. Heerspink presented the new findings about tirzepatide’s impact on kidney function in an oral session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
40% reduced risk of kidney function decline
The main results of SURPASS-4 were published in the Lancet in October 2021, and showed that tirzepatide appeared superior to insulin glargine in lowering hemoglobin A1c in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk who were inadequately controlled on oral diabetes treatments.
Now, Dr. Heerspink has shown that patients who received tirzepatide as opposed to insulin glargine were significantly less likely to have kidney function decline that included new-onset macroalbuminuria (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .05).
“These are very large benefits and clearly indicate the potential of tirzepatide to be a very strong kidney protective drug,” said Dr. Heerspink, from the department of clinical pharmacy and pharmacology, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands).
“Based on results from the SURPASS-4 trial, tirzepatide has significant kidney-protective effects in adults with type 2 diabetes with high cardiovascular risk and largely normal kidney function,” Christine Limonte, MD, chair of the session in which the analysis was presented, agreed, in an email to this news organization.
The approximate 40% reduced risk of kidney function decline in this population “is important because it suggests that this novel agent may contribute to the growing arsenal for preventing and treating diabetic kidney disease,” added Dr. Limonte, a clinical research fellow in the division of nephrology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“Over the last several years,” she noted, “sodium glucose cotransporter-2 [SGLT2] inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists have been identified as having significant kidney-protective effects in type 2 diabetes, and as such are becoming first-line agents in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease.”
Additional studies are needed, she added, to assess the impacts of tirzepatide compared to these agents (particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists, which overlap in their mechanism of action).
“With the growing number of therapeutic options for diabetic kidney disease, future research should also focus on identifying combinations of agents which benefit individuals in a ‘targeted’ manner,” according to Dr. Limonte.
“Ensuring accessibility to kidney-protective agents by promoting access to health care and reducing drug costs is essential to improving outcomes in diabetic kidney disease,” she added.
Strongest reduction seen in risk of new macroalbuminuria
One in three adults with diabetes has CKD, according to a press release issued by the ADA. Therefore, there is a need for therapies to reduce the development and progression of CKD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The prespecified analysis of SUPRESS-4 investigated potential renoprotective effects of tirzepatide.
The trial enrolled 1,995 patients with type 2 diabetes who were at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The patients had a mean age of 63.6 years and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.5%.
Most patients had normal kidney function. The mean eGFR based on the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation was 81.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Few patients (17%) had moderately or severely reduced kidney function (eGFR <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2). Around a quarter of the patients (28%) had microalbuminuria (UACR 30-300 mg/g) and 8% had macroalbuminuria (UACR >300 mg/g).
The patients were randomized to receive a weekly injection of 5, 10, or 15 mg tirzepatide or a daily individualized injection of insulin glargine starting at 10 IU/day at bedtime, titrated to a fasting blood glucose <100 mg/dL, in addition to existing oral glucose-lowering agents. The primary outcomes in the subanalysis were:
- Endpoint 1: a composite of ≥40% decline in eGFR from baseline, renal death, progression to ESKD, and new-onset macroalbuminuria.
- Endpoint 2: the same as endpoint 1 excluding new-onset macroalbuminuria.
During a median follow up of 85 weeks and up to 104 weeks, patients who received tirzepatide versus insulin glargine were significantly less likely to reach endpoint 1 but not endpoint 2.
In addition, tirzepatide “very strongly” reduced the risk of new-onset macroalbuminuria, compared to insulin glargine, by approximately 60% in the complete study cohort (hazard ratio, 0.41; P < .05), Dr. Limonte noted.
Tirzepatide also reduced the risk of a >40% decline in eGFR, but this effect was not statistically significant, possibly because this outcome was underpowered. There were also too few kidney deaths and progressions to ESKD to meaningfully assess the effects of tirzepatide on these outcomes.
Therefore, Dr. Limonte noted, “it is likely that tirzepatide’s significant benefit on composite endpoint 1 was largely driven by this agent’s impact on reducing macroalbuminuria onset [explaining why a significant benefit was not seen with composite endpoint 2, which excluded new-onset macroalbuminuria].”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Heerspink disclosed that he is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook Therapeutics, CSL Behring, Gilead Sciences, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen Research & Development, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mundipharma, and Traveere Pharmaceuticals, and has received research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novo Nordisk.
Dr. Limonte disclosed that she receives funds from the American Kidney Fund’s Clinical Scientist in Nephrology Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The “twincretin” tirzepatide might become part of the “arsenal” against diabetic kidney disease, new research suggests. Notably, the drug significantly reduced the likelihood of macroalbuminuria, in a prespecified subanalysis of the SURPASS-4 clinical trial.
“Once-per-week tirzepatide compared to [daily] insulin glargine treatment resulted in a meaningful improvement in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) decline and reduced urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and the risk of end stage kidney disease (ESKD) – with low risk of clinically relevant hypoglycemia in participants with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk and varying degrees of chronic kidney disease (CKD),” lead investigator Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, PhD, PharmD, summarized in an email to this news organization.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has just approved tirzepatide (Mounjaro, Eli Lilly) – a novel, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combined with a glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist – to treat glycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, based on five pivotal SURPASS trials.
Dr. Heerspink presented the new findings about tirzepatide’s impact on kidney function in an oral session at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association.
40% reduced risk of kidney function decline
The main results of SURPASS-4 were published in the Lancet in October 2021, and showed that tirzepatide appeared superior to insulin glargine in lowering hemoglobin A1c in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk who were inadequately controlled on oral diabetes treatments.
Now, Dr. Heerspink has shown that patients who received tirzepatide as opposed to insulin glargine were significantly less likely to have kidney function decline that included new-onset macroalbuminuria (hazard ratio, 0.59; P < .05).
“These are very large benefits and clearly indicate the potential of tirzepatide to be a very strong kidney protective drug,” said Dr. Heerspink, from the department of clinical pharmacy and pharmacology, University Medical Center Groningen (the Netherlands).
“Based on results from the SURPASS-4 trial, tirzepatide has significant kidney-protective effects in adults with type 2 diabetes with high cardiovascular risk and largely normal kidney function,” Christine Limonte, MD, chair of the session in which the analysis was presented, agreed, in an email to this news organization.
The approximate 40% reduced risk of kidney function decline in this population “is important because it suggests that this novel agent may contribute to the growing arsenal for preventing and treating diabetic kidney disease,” added Dr. Limonte, a clinical research fellow in the division of nephrology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“Over the last several years,” she noted, “sodium glucose cotransporter-2 [SGLT2] inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists have been identified as having significant kidney-protective effects in type 2 diabetes, and as such are becoming first-line agents in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease.”
Additional studies are needed, she added, to assess the impacts of tirzepatide compared to these agents (particularly GLP-1 receptor agonists, which overlap in their mechanism of action).
“With the growing number of therapeutic options for diabetic kidney disease, future research should also focus on identifying combinations of agents which benefit individuals in a ‘targeted’ manner,” according to Dr. Limonte.
“Ensuring accessibility to kidney-protective agents by promoting access to health care and reducing drug costs is essential to improving outcomes in diabetic kidney disease,” she added.
Strongest reduction seen in risk of new macroalbuminuria
One in three adults with diabetes has CKD, according to a press release issued by the ADA. Therefore, there is a need for therapies to reduce the development and progression of CKD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
The prespecified analysis of SUPRESS-4 investigated potential renoprotective effects of tirzepatide.
The trial enrolled 1,995 patients with type 2 diabetes who were at increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The patients had a mean age of 63.6 years and a mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.5%.
Most patients had normal kidney function. The mean eGFR based on the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation was 81.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Few patients (17%) had moderately or severely reduced kidney function (eGFR <60 mL/min per 1.73 m2). Around a quarter of the patients (28%) had microalbuminuria (UACR 30-300 mg/g) and 8% had macroalbuminuria (UACR >300 mg/g).
The patients were randomized to receive a weekly injection of 5, 10, or 15 mg tirzepatide or a daily individualized injection of insulin glargine starting at 10 IU/day at bedtime, titrated to a fasting blood glucose <100 mg/dL, in addition to existing oral glucose-lowering agents. The primary outcomes in the subanalysis were:
- Endpoint 1: a composite of ≥40% decline in eGFR from baseline, renal death, progression to ESKD, and new-onset macroalbuminuria.
- Endpoint 2: the same as endpoint 1 excluding new-onset macroalbuminuria.
During a median follow up of 85 weeks and up to 104 weeks, patients who received tirzepatide versus insulin glargine were significantly less likely to reach endpoint 1 but not endpoint 2.
In addition, tirzepatide “very strongly” reduced the risk of new-onset macroalbuminuria, compared to insulin glargine, by approximately 60% in the complete study cohort (hazard ratio, 0.41; P < .05), Dr. Limonte noted.
Tirzepatide also reduced the risk of a >40% decline in eGFR, but this effect was not statistically significant, possibly because this outcome was underpowered. There were also too few kidney deaths and progressions to ESKD to meaningfully assess the effects of tirzepatide on these outcomes.
Therefore, Dr. Limonte noted, “it is likely that tirzepatide’s significant benefit on composite endpoint 1 was largely driven by this agent’s impact on reducing macroalbuminuria onset [explaining why a significant benefit was not seen with composite endpoint 2, which excluded new-onset macroalbuminuria].”
The study was funded by Eli Lilly. Dr. Heerspink disclosed that he is a consultant for AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook Therapeutics, CSL Behring, Gilead Sciences, Goldfinch Bio, Janssen Research & Development, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Mundipharma, and Traveere Pharmaceuticals, and has received research support from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Novo Nordisk.
Dr. Limonte disclosed that she receives funds from the American Kidney Fund’s Clinical Scientist in Nephrology Award.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADA 2022

















