User login
Advanced Imaging Techniques Use in Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis: The Experience at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
Advanced Imaging Techniques Use in Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis: The Experience at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), the most commonly diagnosed systemic vasculitis, is a large- and medium-vessel vasculitis that can lead to significant morbidity due to aneurysm formation or vascular occlusion if not diagnosed in a timely manner.1,2 Diagnosis is typically based on clinical history and inflammatory markers. Laboratory inflammatory markers may be normal in the early stages of GCA but can be abnormal due to other unrelated reasons leading to a false positive diagnosis.3 Delayed treatment may lead to visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke.2 Initial treatment typically includes high-dose steroids that can lead to significant adverse reactions such as hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, premature atherosclerosis, and increased risk of infection.4-6
The 1990 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for GCA are widely recognized (Table 1).7 The criteria focuses on clinical manifestations, including new onset headache, temporal artery tenderness, age ≥ 50 years, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) ≥ 50 mm/hr, and temporal artery biopsy with positive anatomical findings.8 When 3 of the 5 1990 ACR criteria are present, the sensitivity and specificity is estimated to be > 90% for GCA vs alternative vasculitides.7

Although the 1990 ACR criteria do not include imaging, modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography angiography (CTA), 18F-FDG positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may be used in GCA diagnosis.8-10 These imaging modalities have been added to the proposed ACR classification criteria for GCA.11 For this updated point system standard, age ≥ 50 years is a requirement and includes a positive temporal artery biopsy or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound (+5 points), an ESR ≥ 50 mm/h or C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 10 mg/L (+3 points), or sudden visual loss (+3 points). Scalp tenderness, jaw or tongue claudication, new temporal headache, morning stiffness in shoulders or neck, temporal artery abnormality on vascular examination, bilateral axillary vessel involvement on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta are scored +2 points each. With these new criteria, a cumulative score ≥ 6 is classified as GCA. Diagnostic accuracy is further improved with imaging: ultrasonography (sensitivity 55% and specificity 95%) and 18F-FDG PET (sensitivity 69% and specificity 92%), CTA (sensitivity 71% and specificity 86%), and MRI/MRA (sensitivity 73% and specificity 88%).12-15
In recent years, clinicians have reported increased glucose uptake in arteries observed on PET imaging that suggests GCA.9,10,16-20 18F-FDG accumulates in cells with high metabolic activity rates, such as areas of inflammation. In assessing temporal arteries or other involved vasculature (eg, axillary or great vessels) for GCA, this modality indicates increased glucose uptake in the lining of vessel walls. The inflammation of vessel walls can then be visualized with PET. 18F-FDG PET presents a noninvasive imaging technique for evaluating GCA but its use has been limited in the United States due to its high cost.
Methods
Approval for a retrospective chart review of patients evaluated for suspected GCA was obtained from the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) Institutional Review Board. The review included patients who underwent diagnostic procedures such as ultrasound, MRI, CT angiogram, and PET studies from 2016 through 2022. International Classification of Diseases codes used for case identification included: M31.6, M31.5, I77.6, I77.8, I77.89, I67.7, and I68.2. The Current Procedural Terminology code used for temporal artery biopsy is 37609.
Results
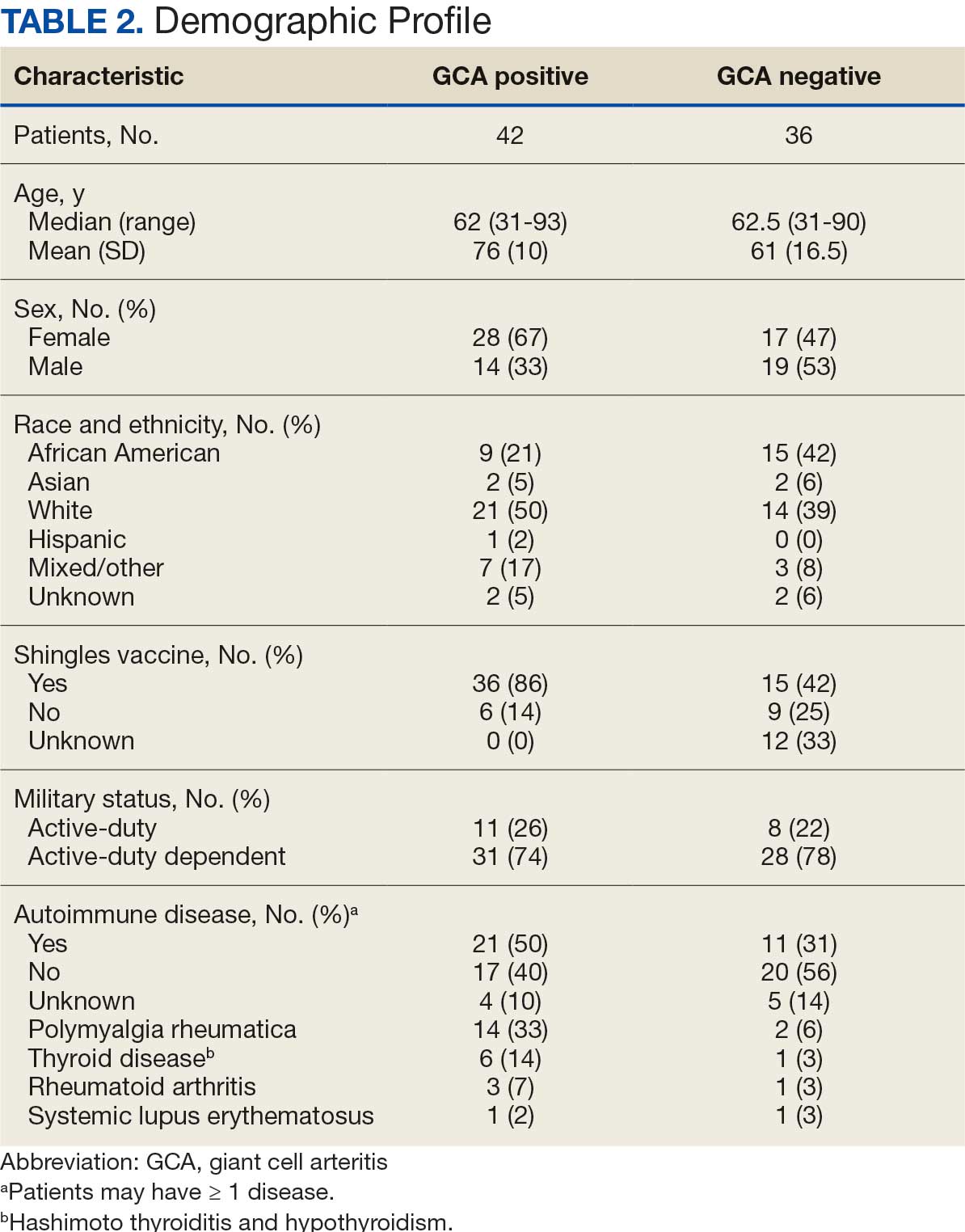
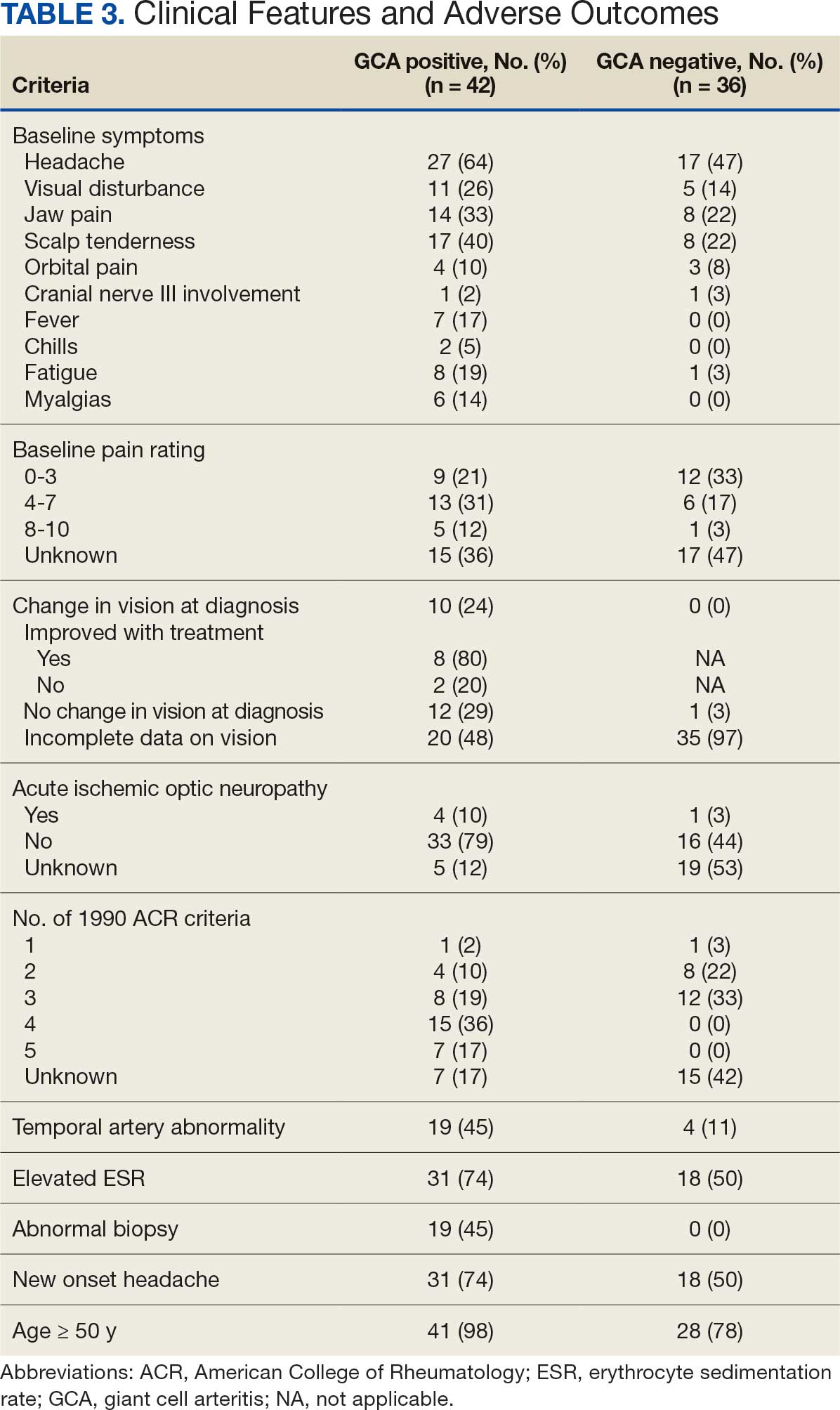
Seventy-eight charts were reviewed and 42 patients (54%) were diagnosed with GCA (Table 2). This study sample had a much higher proportion of African American subjects (31%) when compared with the civilian population, likely reflecting the higher representation of African Americans in the armed forces. Twenty-eight females (67%) were GCA positive. The most common presenting symptoms included 27 patients (64%) with headache, 17 (40%) with scalp tenderness, and 14 (33%) with jaw pain. The mean 1990 ACR score was 3.8 (range, 2-5). With respect to the score criteria: 41 patients (98%) were aged ≥ 50 years, 31 (74%) had new onset headache, and 31 (74%) had elevated ESR (Table 3). Acute ischemic optic neuropathy was documented in 4 patients (10%) with confirmed GCA. The mean ESR and CRP values at diagnosis were 66.2 mm/h (range, 7-122 mm/h) and 8.711 μg/mL (range, 0.054 – 92.690 μg/mL), respectively. Twenty-seven patients (64%) underwent biopsy: 24 (89%) were unilateral and 3 (11%) were bilateral (Table 4). Four patients with GCA (10%) were missing biopsy data. Nineteen patients with GCA (70%) had biopsies with pathologic findings consistent with GCA.
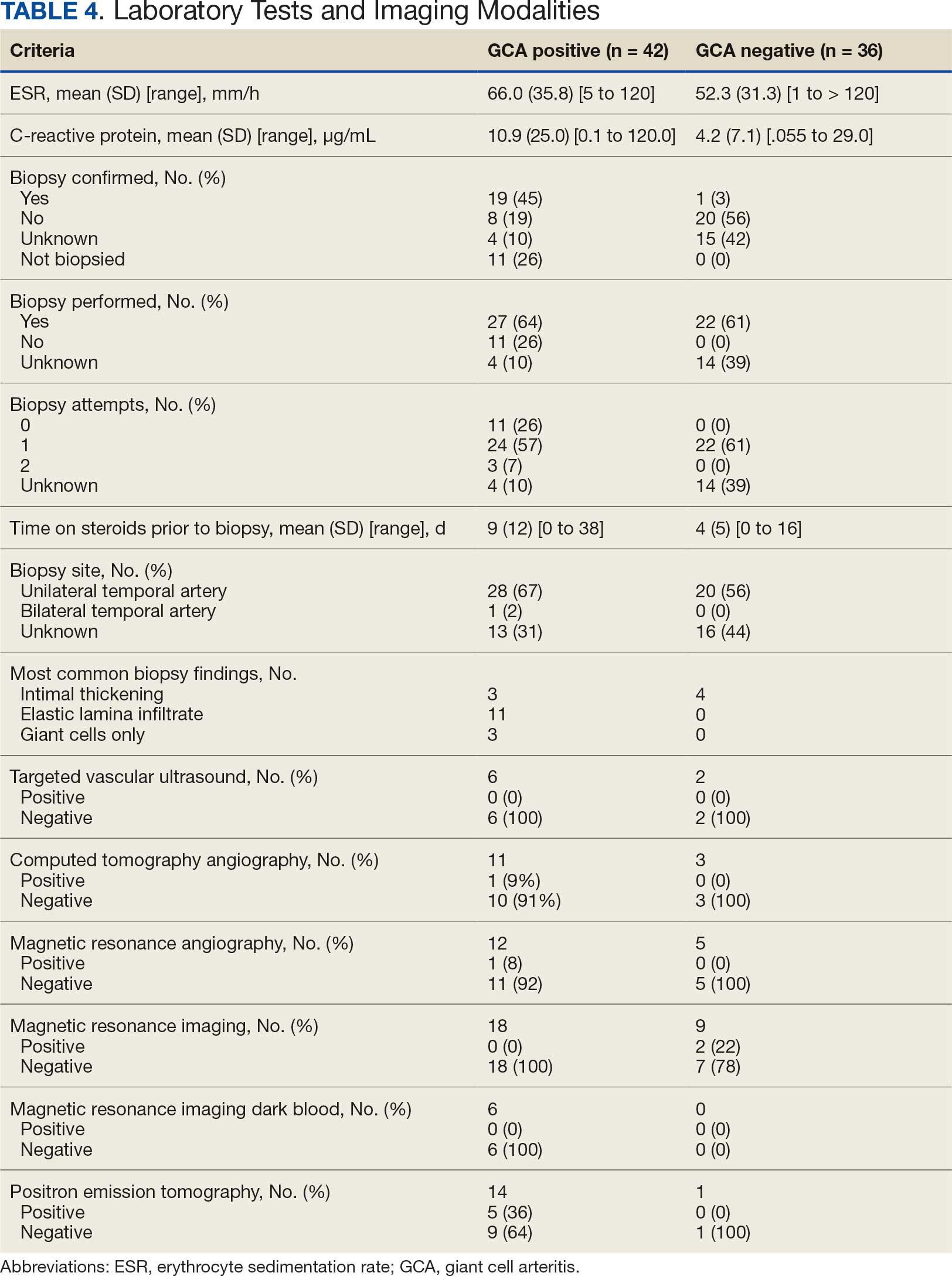
Twenty-five patients with GCA (60%) received ≥ 1 imaging modality. The most common imaging modality was MRI, which was used for 18 (43%) patients. Fourteen patients (33%) had 18F-FDG PET, 12 patients (29%) had MRA, and 11 patients (26%) had CTA. The small number of patients who underwent point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), brain MRI, or dark blood MRI were negative for disease. Five patients who underwent 18F-FDG PET had findings consistent with GCA. One patient with GCA had CTA of the head and neck with radiographic findings supportive of GCA.
Discussion
The available evidence supports the use of additional screening tests to increase the temporal artery biopsy yield for GCA. Inflammatory laboratory markers demonstrate some sensitivity but are nonspecific for GCA. In this study, only 60% of patients with GCA underwent diagnostic imaging as part of the workup. There are multiple factors that may contribute to the underutilization of advanced imaging in the diagnosis of GCA, including outdated standardized diagnostic criteria, limited resources (direct access to modalities), and lack of clinician awareness of diagnostic testing options. In this retrospective review, 30 patients (71%) were diagnosed with GCA with a 1990 ACR GCA score ≤ 3. Of these 30 patients, 19 underwent confirmatory biopsy followed by prolonged courses of steroid therapy. In addition, only 25 patients underwent advanced imaging to increase diagnostic accuracy of the suspected syndrome.
A large meta-analysis demonstrated a sensitivity of 77.3% (95% CI, 71.8-81.9%) for temporal artery biopsy.21 The overall yield was 40% in the meta-analysis. Advanced noninvasive imaging represents an appropriate method of evaluating GCA.8-20 In our study, 18F-FDG PET demonstrated the highest sensitivity (36%) for the diagnosis of GCA. Ultrasonography is recommended as an initial screening tool to identify the noncompressible halo sign (a hypoechoic circumferential wall thickening due to edema) as a cost-effective and widely available technology.22 Other research has corroborated the beneficial use of ultrasonography in improving diagnostic accuracy by detecting the noncompressible halo sign in temporal arteries.22,23 GCA diagnostic performance has been significantly improved with the use of B-mode probes ≥ 15 MHz as well as proposals to incorporate a compression sign or interrogating the axillary vessels, showing a sensitivity of 54% to 77%.23,24
POCUS may reduce the risk of a false-negative biopsy and improve yield with more frequent utilization. However, ultrasonography may be limited by operator skills and visualization of the great vessels. The accuracy of ultrasonography is dependent on the experience and adeptness of the operator. Additional studies are needed to establish a systematic standard for POCUS training to ensure accurate interpretation and uniform interrogation procedure.24 Artificial intelligence (AI) may aid in interpreting results of POCUS and bridging the operator skill gap among operators.25,26 AI and machine learning techniques can assist in detecting the noncompressible halo sign and compression sign in temporal arteries and other affected vessels.
In comparing the WRNMMC patient population with other US civilian GCA cohorts, there are some differences and similarities. There was a high representation of African American patients in the study, which may reflect a greater severity of autoimmune disease expression in this population.27 We also observed a higher number of females and an association with polymyalgia rheumatica in the data, consistent with previous reports.28,29 The females in this study were primarily civilians and therefore more similar to the general population of individuals with GCA. In contrast, male patients were more likely to be active-duty service members or have prior service experience with increased exposure to novel environmental factors linked to increased risk of autoimmune disease. This includes an increased risk of Guillain-Barré syndrome and Graves disease among Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange.30,31 Other studies have found that veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder are at increased risk for severe autoimmune diseases.32,33 As more women join the active-duty military, the impact of autoimmune disease in the military service population is expected to grow, requiring further research.
Conclusions
Early diagnosis and treatment of GCA are critical to preventing serious outcomes, such as visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke. The incidence of autoimmune disease is expected to rise in the armed forces and veteran populations due to exposure to novel environmental factors and the increasing representation of women in the military. The use of additional screening tools can aid in earlier diagnosis of GCA. The 2022 ACR classification criteria for GCA represent significant updates to the 1990 criteria, incorporating ancillary tests such as the temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound, bilateral axillary vessel screening on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta. The updated criteria require further validation and supports the adoption of a multidisciplinary approach that includes ultrasonography, vascular MRI/CT, and 18F-FDG PET. Furthermore, AI may play a future key role in ultrasound interpretation and study interrogation procedure. Ultimately, ultrasonography is a noninvasive and promising technique for the early diagnosis of GCA. A target goal is to increase the yield of positive temporal artery biopsies to ≥ 70%.
- Jennette JC. Overview of the 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013;17:603-606. doi:10.1007/s10157-013-0869-6
- Kale N, Eggenberger E. Diagnosis and management of giant cell arteritis: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010;21:417-422. doi:10.1097/ICU.0b013e32833eae8b
- Smetana GW, Shmerling RH. Does this patient have temporal arteritis? JAMA. 2002;287:92-101.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:23-43. doi:10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00297-8
- Curtis JR, Patkar N, Xie A, et al. Risk of serious bacterial infections among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1125-1133. doi:10.1002/art.22504
- Hoes JN, van der Goes MC, van Raalte DH, et al. Glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and ß-cell function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with or without low-to-medium dose glucocorticoids. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1887-1894. doi:10.1136/ard.2011.151464
- Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1122-1128. doi:10.1002/art.1780330810
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56:506-515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Slart RHJ, Nienhuis PH, Glaudemans AWJM, et al. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis and polymyalgia rheumatica. J Nucl Med. 2023;64:515-521. doi:10.2967/jnumed.122.265016
- Shimol JB, Amital H, Lidar M, Domachevsky L, Shoenfeld Y, Davidson T. The utility of PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17709. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73818-2
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR Classification Criteria for Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74:1881-1889. doi:10.1002/art.42325
- He J, Williamson L, Ng B, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of temporal artery ultrasound and temporal artery biopsy in giant cell arteritis: a single center Australian experience over 10 years. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022;25:447-453. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14288
- Stellingwerff MD, Brouwer E, Lensen KDF, et al. Different scoring methods of FDG PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: need for standardization. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1542. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001542
- Conway R, Smyth AE, Kavanagh RG, et al. Diagnostic utility of computed tomographic angiography in giant-cell arteritis. Stroke. 2018;49:2233-2236. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021995
- Duftner C, Dejaco C, Sepriano A, et al. Imaging in diagnosis, outcome prediction and monitoring of large vessel vasculitis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing the EULAR recommendations. RMD Open. 2018;4:e000612. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000612
- Rehak Z, Vasina J, Ptacek J, et al. PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: high 18F-FDG uptake in the temporal, occipital and vertebral arteries. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2016;35:398-401. doi:10.1016/j.remn.2016.03.007
- Salvarani C, Soriano A, Muratore F, et al. Is PET/CT essential in the diagnosis and follow-up of temporal arteritis? Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:1125-1130. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.007
- Brodmann M, Lipp RW, Passath A, et al. The role of 2-18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis of the temporal arteries. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:241-242. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh025
- Flaus A, Granjon D, Habouzit V, Gaultier JB, Prevot-Bitot N. Unusual and diffuse hypermetabolism in routine 18F-FDG PET/CT of the supra-aortic vessels in biopsy-positive giant cell arteritis. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43:e336-e337. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000002198
- Berger CT, Sommer G, Aschwanden M, et al. The clinical benefit of imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2018;148:w14661. doi:10.4414/smw.2018.14661
- Rubenstein E, Maldini C, Gonzalez-Chiappe S, et al. Sensitivity of temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:1011-1020. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez385
- Tsivgoulis G, Heliopoulos I, Vadikolias K, et al. Teaching neuroimages: ultrasound findings in giant-cell arteritis. Neurology. 2010;75:e67-e68. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f881e9
- Nakajima E, Moon FH, Canvas Jr N, et al. Accuracy of Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Rheumatol. 2023;63:5. doi:10.1186/s42358-023-00286-3
- Naumegni SR, Hoffmann C, Cornec D, et al. Temporal artery ultrasound to diagnose giant cell arteritis: a practical guide. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021;47:201-213. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.10.004
- Kim YH. Artificial intelligence in medical ultrasonography: driving on an unpaved road. Ultrasonography. 2021;40:313-317. doi:10.14366/usg.21031
- Sultan LR, Mohamed MH, Andronikou S. ChatGPT-4: a breakthrough in ultrasound image analysis. Radiol Adv. 2024;1:umae006. doi:10.1093/radadv/umae006
- Cipriani VP, Klein S. Clinical characteristics of multiple sclerosis in African-Americans. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19:87. doi:10.1007/s11910-019-1000-5
- Sturm A, Dechant C, Proft F, et al. Gender differences in giant cell arteritis: a case-control study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:S70-72.
- Li KJ, Semenov D, Turk M, et al. A meta-analysis of the epidemiology of giant cell arteritis across time and space. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:82. doi:10.1186/s13075-021-02450-w
- Nelson L, Gormley R, Riddle MS, Tribble DR, Porter CK. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in U.S. military personnel: a case-control study. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:171. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-171
- Spaulding SW. The possible roles of environmental factors and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the prevalence of thyroid diseases in Vietnam era veterans. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011;18:315-320.
- O’Donovan A, Cohen BE, Seal KH, et al. Elevated risk for autoimmune disorders in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:365-374. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.06.015
- Bookwalter DB, Roenfeldt KA, LeardMann CA, Kong SY, Riddle MS, Rull RP. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of selected autoimmune diseases among US military personnel. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:23. doi:10.1186/s12888-020-2432-9
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), the most commonly diagnosed systemic vasculitis, is a large- and medium-vessel vasculitis that can lead to significant morbidity due to aneurysm formation or vascular occlusion if not diagnosed in a timely manner.1,2 Diagnosis is typically based on clinical history and inflammatory markers. Laboratory inflammatory markers may be normal in the early stages of GCA but can be abnormal due to other unrelated reasons leading to a false positive diagnosis.3 Delayed treatment may lead to visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke.2 Initial treatment typically includes high-dose steroids that can lead to significant adverse reactions such as hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, premature atherosclerosis, and increased risk of infection.4-6
The 1990 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for GCA are widely recognized (Table 1).7 The criteria focuses on clinical manifestations, including new onset headache, temporal artery tenderness, age ≥ 50 years, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) ≥ 50 mm/hr, and temporal artery biopsy with positive anatomical findings.8 When 3 of the 5 1990 ACR criteria are present, the sensitivity and specificity is estimated to be > 90% for GCA vs alternative vasculitides.7

Although the 1990 ACR criteria do not include imaging, modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography angiography (CTA), 18F-FDG positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may be used in GCA diagnosis.8-10 These imaging modalities have been added to the proposed ACR classification criteria for GCA.11 For this updated point system standard, age ≥ 50 years is a requirement and includes a positive temporal artery biopsy or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound (+5 points), an ESR ≥ 50 mm/h or C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 10 mg/L (+3 points), or sudden visual loss (+3 points). Scalp tenderness, jaw or tongue claudication, new temporal headache, morning stiffness in shoulders or neck, temporal artery abnormality on vascular examination, bilateral axillary vessel involvement on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta are scored +2 points each. With these new criteria, a cumulative score ≥ 6 is classified as GCA. Diagnostic accuracy is further improved with imaging: ultrasonography (sensitivity 55% and specificity 95%) and 18F-FDG PET (sensitivity 69% and specificity 92%), CTA (sensitivity 71% and specificity 86%), and MRI/MRA (sensitivity 73% and specificity 88%).12-15
In recent years, clinicians have reported increased glucose uptake in arteries observed on PET imaging that suggests GCA.9,10,16-20 18F-FDG accumulates in cells with high metabolic activity rates, such as areas of inflammation. In assessing temporal arteries or other involved vasculature (eg, axillary or great vessels) for GCA, this modality indicates increased glucose uptake in the lining of vessel walls. The inflammation of vessel walls can then be visualized with PET. 18F-FDG PET presents a noninvasive imaging technique for evaluating GCA but its use has been limited in the United States due to its high cost.
Methods
Approval for a retrospective chart review of patients evaluated for suspected GCA was obtained from the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) Institutional Review Board. The review included patients who underwent diagnostic procedures such as ultrasound, MRI, CT angiogram, and PET studies from 2016 through 2022. International Classification of Diseases codes used for case identification included: M31.6, M31.5, I77.6, I77.8, I77.89, I67.7, and I68.2. The Current Procedural Terminology code used for temporal artery biopsy is 37609.
Results
Seventy-eight charts were reviewed and 42 patients (54%) were diagnosed with GCA (Table 2). This study sample had a much higher proportion of African American subjects (31%) when compared with the civilian population, likely reflecting the higher representation of African Americans in the armed forces. Twenty-eight females (67%) were GCA positive. The most common presenting symptoms included 27 patients (64%) with headache, 17 (40%) with scalp tenderness, and 14 (33%) with jaw pain. The mean 1990 ACR score was 3.8 (range, 2-5). With respect to the score criteria: 41 patients (98%) were aged ≥ 50 years, 31 (74%) had new onset headache, and 31 (74%) had elevated ESR (Table 3). Acute ischemic optic neuropathy was documented in 4 patients (10%) with confirmed GCA. The mean ESR and CRP values at diagnosis were 66.2 mm/h (range, 7-122 mm/h) and 8.711 μg/mL (range, 0.054 – 92.690 μg/mL), respectively. Twenty-seven patients (64%) underwent biopsy: 24 (89%) were unilateral and 3 (11%) were bilateral (Table 4). Four patients with GCA (10%) were missing biopsy data. Nineteen patients with GCA (70%) had biopsies with pathologic findings consistent with GCA.



Twenty-five patients with GCA (60%) received ≥ 1 imaging modality. The most common imaging modality was MRI, which was used for 18 (43%) patients. Fourteen patients (33%) had 18F-FDG PET, 12 patients (29%) had MRA, and 11 patients (26%) had CTA. The small number of patients who underwent point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), brain MRI, or dark blood MRI were negative for disease. Five patients who underwent 18F-FDG PET had findings consistent with GCA. One patient with GCA had CTA of the head and neck with radiographic findings supportive of GCA.
Discussion
The available evidence supports the use of additional screening tests to increase the temporal artery biopsy yield for GCA. Inflammatory laboratory markers demonstrate some sensitivity but are nonspecific for GCA. In this study, only 60% of patients with GCA underwent diagnostic imaging as part of the workup. There are multiple factors that may contribute to the underutilization of advanced imaging in the diagnosis of GCA, including outdated standardized diagnostic criteria, limited resources (direct access to modalities), and lack of clinician awareness of diagnostic testing options. In this retrospective review, 30 patients (71%) were diagnosed with GCA with a 1990 ACR GCA score ≤ 3. Of these 30 patients, 19 underwent confirmatory biopsy followed by prolonged courses of steroid therapy. In addition, only 25 patients underwent advanced imaging to increase diagnostic accuracy of the suspected syndrome.
A large meta-analysis demonstrated a sensitivity of 77.3% (95% CI, 71.8-81.9%) for temporal artery biopsy.21 The overall yield was 40% in the meta-analysis. Advanced noninvasive imaging represents an appropriate method of evaluating GCA.8-20 In our study, 18F-FDG PET demonstrated the highest sensitivity (36%) for the diagnosis of GCA. Ultrasonography is recommended as an initial screening tool to identify the noncompressible halo sign (a hypoechoic circumferential wall thickening due to edema) as a cost-effective and widely available technology.22 Other research has corroborated the beneficial use of ultrasonography in improving diagnostic accuracy by detecting the noncompressible halo sign in temporal arteries.22,23 GCA diagnostic performance has been significantly improved with the use of B-mode probes ≥ 15 MHz as well as proposals to incorporate a compression sign or interrogating the axillary vessels, showing a sensitivity of 54% to 77%.23,24
POCUS may reduce the risk of a false-negative biopsy and improve yield with more frequent utilization. However, ultrasonography may be limited by operator skills and visualization of the great vessels. The accuracy of ultrasonography is dependent on the experience and adeptness of the operator. Additional studies are needed to establish a systematic standard for POCUS training to ensure accurate interpretation and uniform interrogation procedure.24 Artificial intelligence (AI) may aid in interpreting results of POCUS and bridging the operator skill gap among operators.25,26 AI and machine learning techniques can assist in detecting the noncompressible halo sign and compression sign in temporal arteries and other affected vessels.
In comparing the WRNMMC patient population with other US civilian GCA cohorts, there are some differences and similarities. There was a high representation of African American patients in the study, which may reflect a greater severity of autoimmune disease expression in this population.27 We also observed a higher number of females and an association with polymyalgia rheumatica in the data, consistent with previous reports.28,29 The females in this study were primarily civilians and therefore more similar to the general population of individuals with GCA. In contrast, male patients were more likely to be active-duty service members or have prior service experience with increased exposure to novel environmental factors linked to increased risk of autoimmune disease. This includes an increased risk of Guillain-Barré syndrome and Graves disease among Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange.30,31 Other studies have found that veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder are at increased risk for severe autoimmune diseases.32,33 As more women join the active-duty military, the impact of autoimmune disease in the military service population is expected to grow, requiring further research.
Conclusions
Early diagnosis and treatment of GCA are critical to preventing serious outcomes, such as visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke. The incidence of autoimmune disease is expected to rise in the armed forces and veteran populations due to exposure to novel environmental factors and the increasing representation of women in the military. The use of additional screening tools can aid in earlier diagnosis of GCA. The 2022 ACR classification criteria for GCA represent significant updates to the 1990 criteria, incorporating ancillary tests such as the temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound, bilateral axillary vessel screening on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta. The updated criteria require further validation and supports the adoption of a multidisciplinary approach that includes ultrasonography, vascular MRI/CT, and 18F-FDG PET. Furthermore, AI may play a future key role in ultrasound interpretation and study interrogation procedure. Ultimately, ultrasonography is a noninvasive and promising technique for the early diagnosis of GCA. A target goal is to increase the yield of positive temporal artery biopsies to ≥ 70%.
Giant cell arteritis (GCA), the most commonly diagnosed systemic vasculitis, is a large- and medium-vessel vasculitis that can lead to significant morbidity due to aneurysm formation or vascular occlusion if not diagnosed in a timely manner.1,2 Diagnosis is typically based on clinical history and inflammatory markers. Laboratory inflammatory markers may be normal in the early stages of GCA but can be abnormal due to other unrelated reasons leading to a false positive diagnosis.3 Delayed treatment may lead to visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke.2 Initial treatment typically includes high-dose steroids that can lead to significant adverse reactions such as hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction, metabolic syndrome, premature atherosclerosis, and increased risk of infection.4-6
The 1990 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria for GCA are widely recognized (Table 1).7 The criteria focuses on clinical manifestations, including new onset headache, temporal artery tenderness, age ≥ 50 years, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) ≥ 50 mm/hr, and temporal artery biopsy with positive anatomical findings.8 When 3 of the 5 1990 ACR criteria are present, the sensitivity and specificity is estimated to be > 90% for GCA vs alternative vasculitides.7

Although the 1990 ACR criteria do not include imaging, modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography angiography (CTA), 18F-FDG positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)/magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may be used in GCA diagnosis.8-10 These imaging modalities have been added to the proposed ACR classification criteria for GCA.11 For this updated point system standard, age ≥ 50 years is a requirement and includes a positive temporal artery biopsy or temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound (+5 points), an ESR ≥ 50 mm/h or C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 10 mg/L (+3 points), or sudden visual loss (+3 points). Scalp tenderness, jaw or tongue claudication, new temporal headache, morning stiffness in shoulders or neck, temporal artery abnormality on vascular examination, bilateral axillary vessel involvement on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta are scored +2 points each. With these new criteria, a cumulative score ≥ 6 is classified as GCA. Diagnostic accuracy is further improved with imaging: ultrasonography (sensitivity 55% and specificity 95%) and 18F-FDG PET (sensitivity 69% and specificity 92%), CTA (sensitivity 71% and specificity 86%), and MRI/MRA (sensitivity 73% and specificity 88%).12-15
In recent years, clinicians have reported increased glucose uptake in arteries observed on PET imaging that suggests GCA.9,10,16-20 18F-FDG accumulates in cells with high metabolic activity rates, such as areas of inflammation. In assessing temporal arteries or other involved vasculature (eg, axillary or great vessels) for GCA, this modality indicates increased glucose uptake in the lining of vessel walls. The inflammation of vessel walls can then be visualized with PET. 18F-FDG PET presents a noninvasive imaging technique for evaluating GCA but its use has been limited in the United States due to its high cost.
Methods
Approval for a retrospective chart review of patients evaluated for suspected GCA was obtained from the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC) Institutional Review Board. The review included patients who underwent diagnostic procedures such as ultrasound, MRI, CT angiogram, and PET studies from 2016 through 2022. International Classification of Diseases codes used for case identification included: M31.6, M31.5, I77.6, I77.8, I77.89, I67.7, and I68.2. The Current Procedural Terminology code used for temporal artery biopsy is 37609.
Results
Seventy-eight charts were reviewed and 42 patients (54%) were diagnosed with GCA (Table 2). This study sample had a much higher proportion of African American subjects (31%) when compared with the civilian population, likely reflecting the higher representation of African Americans in the armed forces. Twenty-eight females (67%) were GCA positive. The most common presenting symptoms included 27 patients (64%) with headache, 17 (40%) with scalp tenderness, and 14 (33%) with jaw pain. The mean 1990 ACR score was 3.8 (range, 2-5). With respect to the score criteria: 41 patients (98%) were aged ≥ 50 years, 31 (74%) had new onset headache, and 31 (74%) had elevated ESR (Table 3). Acute ischemic optic neuropathy was documented in 4 patients (10%) with confirmed GCA. The mean ESR and CRP values at diagnosis were 66.2 mm/h (range, 7-122 mm/h) and 8.711 μg/mL (range, 0.054 – 92.690 μg/mL), respectively. Twenty-seven patients (64%) underwent biopsy: 24 (89%) were unilateral and 3 (11%) were bilateral (Table 4). Four patients with GCA (10%) were missing biopsy data. Nineteen patients with GCA (70%) had biopsies with pathologic findings consistent with GCA.



Twenty-five patients with GCA (60%) received ≥ 1 imaging modality. The most common imaging modality was MRI, which was used for 18 (43%) patients. Fourteen patients (33%) had 18F-FDG PET, 12 patients (29%) had MRA, and 11 patients (26%) had CTA. The small number of patients who underwent point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS), brain MRI, or dark blood MRI were negative for disease. Five patients who underwent 18F-FDG PET had findings consistent with GCA. One patient with GCA had CTA of the head and neck with radiographic findings supportive of GCA.
Discussion
The available evidence supports the use of additional screening tests to increase the temporal artery biopsy yield for GCA. Inflammatory laboratory markers demonstrate some sensitivity but are nonspecific for GCA. In this study, only 60% of patients with GCA underwent diagnostic imaging as part of the workup. There are multiple factors that may contribute to the underutilization of advanced imaging in the diagnosis of GCA, including outdated standardized diagnostic criteria, limited resources (direct access to modalities), and lack of clinician awareness of diagnostic testing options. In this retrospective review, 30 patients (71%) were diagnosed with GCA with a 1990 ACR GCA score ≤ 3. Of these 30 patients, 19 underwent confirmatory biopsy followed by prolonged courses of steroid therapy. In addition, only 25 patients underwent advanced imaging to increase diagnostic accuracy of the suspected syndrome.
A large meta-analysis demonstrated a sensitivity of 77.3% (95% CI, 71.8-81.9%) for temporal artery biopsy.21 The overall yield was 40% in the meta-analysis. Advanced noninvasive imaging represents an appropriate method of evaluating GCA.8-20 In our study, 18F-FDG PET demonstrated the highest sensitivity (36%) for the diagnosis of GCA. Ultrasonography is recommended as an initial screening tool to identify the noncompressible halo sign (a hypoechoic circumferential wall thickening due to edema) as a cost-effective and widely available technology.22 Other research has corroborated the beneficial use of ultrasonography in improving diagnostic accuracy by detecting the noncompressible halo sign in temporal arteries.22,23 GCA diagnostic performance has been significantly improved with the use of B-mode probes ≥ 15 MHz as well as proposals to incorporate a compression sign or interrogating the axillary vessels, showing a sensitivity of 54% to 77%.23,24
POCUS may reduce the risk of a false-negative biopsy and improve yield with more frequent utilization. However, ultrasonography may be limited by operator skills and visualization of the great vessels. The accuracy of ultrasonography is dependent on the experience and adeptness of the operator. Additional studies are needed to establish a systematic standard for POCUS training to ensure accurate interpretation and uniform interrogation procedure.24 Artificial intelligence (AI) may aid in interpreting results of POCUS and bridging the operator skill gap among operators.25,26 AI and machine learning techniques can assist in detecting the noncompressible halo sign and compression sign in temporal arteries and other affected vessels.
In comparing the WRNMMC patient population with other US civilian GCA cohorts, there are some differences and similarities. There was a high representation of African American patients in the study, which may reflect a greater severity of autoimmune disease expression in this population.27 We also observed a higher number of females and an association with polymyalgia rheumatica in the data, consistent with previous reports.28,29 The females in this study were primarily civilians and therefore more similar to the general population of individuals with GCA. In contrast, male patients were more likely to be active-duty service members or have prior service experience with increased exposure to novel environmental factors linked to increased risk of autoimmune disease. This includes an increased risk of Guillain-Barré syndrome and Graves disease among Vietnam veterans exposed to Agent Orange.30,31 Other studies have found that veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder are at increased risk for severe autoimmune diseases.32,33 As more women join the active-duty military, the impact of autoimmune disease in the military service population is expected to grow, requiring further research.
Conclusions
Early diagnosis and treatment of GCA are critical to preventing serious outcomes, such as visual loss, jaw or limb claudication, or ischemic stroke. The incidence of autoimmune disease is expected to rise in the armed forces and veteran populations due to exposure to novel environmental factors and the increasing representation of women in the military. The use of additional screening tools can aid in earlier diagnosis of GCA. The 2022 ACR classification criteria for GCA represent significant updates to the 1990 criteria, incorporating ancillary tests such as the temporal artery halo sign on ultrasound, bilateral axillary vessel screening on imaging, and 18F-FDG PET activity throughout the aorta. The updated criteria require further validation and supports the adoption of a multidisciplinary approach that includes ultrasonography, vascular MRI/CT, and 18F-FDG PET. Furthermore, AI may play a future key role in ultrasound interpretation and study interrogation procedure. Ultimately, ultrasonography is a noninvasive and promising technique for the early diagnosis of GCA. A target goal is to increase the yield of positive temporal artery biopsies to ≥ 70%.
- Jennette JC. Overview of the 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013;17:603-606. doi:10.1007/s10157-013-0869-6
- Kale N, Eggenberger E. Diagnosis and management of giant cell arteritis: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010;21:417-422. doi:10.1097/ICU.0b013e32833eae8b
- Smetana GW, Shmerling RH. Does this patient have temporal arteritis? JAMA. 2002;287:92-101.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:23-43. doi:10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00297-8
- Curtis JR, Patkar N, Xie A, et al. Risk of serious bacterial infections among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1125-1133. doi:10.1002/art.22504
- Hoes JN, van der Goes MC, van Raalte DH, et al. Glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and ß-cell function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with or without low-to-medium dose glucocorticoids. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1887-1894. doi:10.1136/ard.2011.151464
- Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1122-1128. doi:10.1002/art.1780330810
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56:506-515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Slart RHJ, Nienhuis PH, Glaudemans AWJM, et al. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis and polymyalgia rheumatica. J Nucl Med. 2023;64:515-521. doi:10.2967/jnumed.122.265016
- Shimol JB, Amital H, Lidar M, Domachevsky L, Shoenfeld Y, Davidson T. The utility of PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17709. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73818-2
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR Classification Criteria for Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74:1881-1889. doi:10.1002/art.42325
- He J, Williamson L, Ng B, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of temporal artery ultrasound and temporal artery biopsy in giant cell arteritis: a single center Australian experience over 10 years. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022;25:447-453. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14288
- Stellingwerff MD, Brouwer E, Lensen KDF, et al. Different scoring methods of FDG PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: need for standardization. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1542. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001542
- Conway R, Smyth AE, Kavanagh RG, et al. Diagnostic utility of computed tomographic angiography in giant-cell arteritis. Stroke. 2018;49:2233-2236. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021995
- Duftner C, Dejaco C, Sepriano A, et al. Imaging in diagnosis, outcome prediction and monitoring of large vessel vasculitis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing the EULAR recommendations. RMD Open. 2018;4:e000612. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000612
- Rehak Z, Vasina J, Ptacek J, et al. PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: high 18F-FDG uptake in the temporal, occipital and vertebral arteries. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2016;35:398-401. doi:10.1016/j.remn.2016.03.007
- Salvarani C, Soriano A, Muratore F, et al. Is PET/CT essential in the diagnosis and follow-up of temporal arteritis? Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:1125-1130. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.007
- Brodmann M, Lipp RW, Passath A, et al. The role of 2-18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis of the temporal arteries. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:241-242. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh025
- Flaus A, Granjon D, Habouzit V, Gaultier JB, Prevot-Bitot N. Unusual and diffuse hypermetabolism in routine 18F-FDG PET/CT of the supra-aortic vessels in biopsy-positive giant cell arteritis. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43:e336-e337. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000002198
- Berger CT, Sommer G, Aschwanden M, et al. The clinical benefit of imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2018;148:w14661. doi:10.4414/smw.2018.14661
- Rubenstein E, Maldini C, Gonzalez-Chiappe S, et al. Sensitivity of temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:1011-1020. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez385
- Tsivgoulis G, Heliopoulos I, Vadikolias K, et al. Teaching neuroimages: ultrasound findings in giant-cell arteritis. Neurology. 2010;75:e67-e68. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f881e9
- Nakajima E, Moon FH, Canvas Jr N, et al. Accuracy of Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Rheumatol. 2023;63:5. doi:10.1186/s42358-023-00286-3
- Naumegni SR, Hoffmann C, Cornec D, et al. Temporal artery ultrasound to diagnose giant cell arteritis: a practical guide. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021;47:201-213. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.10.004
- Kim YH. Artificial intelligence in medical ultrasonography: driving on an unpaved road. Ultrasonography. 2021;40:313-317. doi:10.14366/usg.21031
- Sultan LR, Mohamed MH, Andronikou S. ChatGPT-4: a breakthrough in ultrasound image analysis. Radiol Adv. 2024;1:umae006. doi:10.1093/radadv/umae006
- Cipriani VP, Klein S. Clinical characteristics of multiple sclerosis in African-Americans. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19:87. doi:10.1007/s11910-019-1000-5
- Sturm A, Dechant C, Proft F, et al. Gender differences in giant cell arteritis: a case-control study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:S70-72.
- Li KJ, Semenov D, Turk M, et al. A meta-analysis of the epidemiology of giant cell arteritis across time and space. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:82. doi:10.1186/s13075-021-02450-w
- Nelson L, Gormley R, Riddle MS, Tribble DR, Porter CK. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in U.S. military personnel: a case-control study. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:171. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-171
- Spaulding SW. The possible roles of environmental factors and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the prevalence of thyroid diseases in Vietnam era veterans. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011;18:315-320.
- O’Donovan A, Cohen BE, Seal KH, et al. Elevated risk for autoimmune disorders in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:365-374. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.06.015
- Bookwalter DB, Roenfeldt KA, LeardMann CA, Kong SY, Riddle MS, Rull RP. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of selected autoimmune diseases among US military personnel. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:23. doi:10.1186/s12888-020-2432-9
- Jennette JC. Overview of the 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2013;17:603-606. doi:10.1007/s10157-013-0869-6
- Kale N, Eggenberger E. Diagnosis and management of giant cell arteritis: a review. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2010;21:417-422. doi:10.1097/ICU.0b013e32833eae8b
- Smetana GW, Shmerling RH. Does this patient have temporal arteritis? JAMA. 2002;287:92-101.
- Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:23-43. doi:10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00297-8
- Curtis JR, Patkar N, Xie A, et al. Risk of serious bacterial infections among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1125-1133. doi:10.1002/art.22504
- Hoes JN, van der Goes MC, van Raalte DH, et al. Glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and ß-cell function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with or without low-to-medium dose glucocorticoids. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:1887-1894. doi:10.1136/ard.2011.151464
- Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1122-1128. doi:10.1002/art.1780330810
- Dejaco C, Duftner C, Buttgereit F, Matteson EL, Dasgupta B. The spectrum of giant cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica: revisiting the concept of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56:506-515. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kew273
- Slart RHJ, Nienhuis PH, Glaudemans AWJM, et al. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis and polymyalgia rheumatica. J Nucl Med. 2023;64:515-521. doi:10.2967/jnumed.122.265016
- Shimol JB, Amital H, Lidar M, Domachevsky L, Shoenfeld Y, Davidson T. The utility of PET/CT in large vessel vasculitis. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17709. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73818-2
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR Classification Criteria for Giant Cell Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74:1881-1889. doi:10.1002/art.42325
- He J, Williamson L, Ng B, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of temporal artery ultrasound and temporal artery biopsy in giant cell arteritis: a single center Australian experience over 10 years. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022;25:447-453. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.14288
- Stellingwerff MD, Brouwer E, Lensen KDF, et al. Different scoring methods of FDG PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: need for standardization. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94:e1542. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001542
- Conway R, Smyth AE, Kavanagh RG, et al. Diagnostic utility of computed tomographic angiography in giant-cell arteritis. Stroke. 2018;49:2233-2236. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021995
- Duftner C, Dejaco C, Sepriano A, et al. Imaging in diagnosis, outcome prediction and monitoring of large vessel vasculitis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing the EULAR recommendations. RMD Open. 2018;4:e000612. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2017-000612
- Rehak Z, Vasina J, Ptacek J, et al. PET/CT in giant cell arteritis: high 18F-FDG uptake in the temporal, occipital and vertebral arteries. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2016;35:398-401. doi:10.1016/j.remn.2016.03.007
- Salvarani C, Soriano A, Muratore F, et al. Is PET/CT essential in the diagnosis and follow-up of temporal arteritis? Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:1125-1130. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.007
- Brodmann M, Lipp RW, Passath A, et al. The role of 2-18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis of the temporal arteries. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004;43:241-242. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh025
- Flaus A, Granjon D, Habouzit V, Gaultier JB, Prevot-Bitot N. Unusual and diffuse hypermetabolism in routine 18F-FDG PET/CT of the supra-aortic vessels in biopsy-positive giant cell arteritis. Clin Nucl Med. 2018;43:e336-e337. doi:10.1097/RLU.0000000000002198
- Berger CT, Sommer G, Aschwanden M, et al. The clinical benefit of imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2018;148:w14661. doi:10.4414/smw.2018.14661
- Rubenstein E, Maldini C, Gonzalez-Chiappe S, et al. Sensitivity of temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59:1011-1020. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kez385
- Tsivgoulis G, Heliopoulos I, Vadikolias K, et al. Teaching neuroimages: ultrasound findings in giant-cell arteritis. Neurology. 2010;75:e67-e68. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f881e9
- Nakajima E, Moon FH, Canvas Jr N, et al. Accuracy of Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Rheumatol. 2023;63:5. doi:10.1186/s42358-023-00286-3
- Naumegni SR, Hoffmann C, Cornec D, et al. Temporal artery ultrasound to diagnose giant cell arteritis: a practical guide. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2021;47:201-213. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.10.004
- Kim YH. Artificial intelligence in medical ultrasonography: driving on an unpaved road. Ultrasonography. 2021;40:313-317. doi:10.14366/usg.21031
- Sultan LR, Mohamed MH, Andronikou S. ChatGPT-4: a breakthrough in ultrasound image analysis. Radiol Adv. 2024;1:umae006. doi:10.1093/radadv/umae006
- Cipriani VP, Klein S. Clinical characteristics of multiple sclerosis in African-Americans. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19:87. doi:10.1007/s11910-019-1000-5
- Sturm A, Dechant C, Proft F, et al. Gender differences in giant cell arteritis: a case-control study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34:S70-72.
- Li KJ, Semenov D, Turk M, et al. A meta-analysis of the epidemiology of giant cell arteritis across time and space. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23:82. doi:10.1186/s13075-021-02450-w
- Nelson L, Gormley R, Riddle MS, Tribble DR, Porter CK. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barré syndrome in U.S. military personnel: a case-control study. BMC Res Notes. 2009;2:171. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-2-171
- Spaulding SW. The possible roles of environmental factors and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the prevalence of thyroid diseases in Vietnam era veterans. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011;18:315-320.
- O’Donovan A, Cohen BE, Seal KH, et al. Elevated risk for autoimmune disorders in Iraq and Afghanistan veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:365-374. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.06.015
- Bookwalter DB, Roenfeldt KA, LeardMann CA, Kong SY, Riddle MS, Rull RP. Posttraumatic stress disorder and risk of selected autoimmune diseases among US military personnel. BMC Psychiatry. 2020;20:23. doi:10.1186/s12888-020-2432-9
Advanced Imaging Techniques Use in Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis: The Experience at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
Advanced Imaging Techniques Use in Giant Cell Arteritis Diagnosis: The Experience at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
Vasculitis Patients Need Multiple COVID Vaccine Boosters
People with vasculitis may need at least three or four vaccinations for COVID-19 before they start to show an immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection, new research has suggested.
In a longitudinal retrospective study, serum antibody neutralization against the Omicron variant of the virus and its descendants was found to be “largely absent” after the first two doses of COVID-19 vaccine had been given to patients. But increasing neutralizing antibody titers were seen after both the third and fourth vaccine boosters had been administered.
Results also showed that the more recently people had been treated with the B cell–depleting therapy rituximab, the lower the levels of immunogenicity that were achieved, and thus protection against SARS-CoV-2.
“Our results have significant implications for individuals treated with rituximab in the post-Omicron era, highlighting the value of additive boosters in affirming increasing protection in clinically vulnerable populations,” the team behind the work at the University of Cambridge in England, has reported in Science Advances.
Moreover, because the use of rituximab reduced the neutralization of not just wild-type (WT) Omicron but also the Omicron-descendant variants BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB, this highlights “the urgent need for additional adjunctive strategies to enhance vaccine-induced immunity as well as preferential access for such patients to updated vaccines using spike from now circulating Omicron lineages,” the team added.
Studying Humoral Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Corresponding author Ravindra K. Gupta, BMBCh, MA, MPH, PhD, told this news organization that studying humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in immunocompromised individuals such as those with vasculitis was important for two main reasons.
“It is really important at individual level for their own health, of course, but also because we know that variants of concern have often evolved and developed within patients and can then spread in wider populations,” he said.
Gupta, who is professor of clinical microbiology at the Cambridge Institute for Therapeutic Immunology & Infectious Disease added: “We believe that the variants of concern that we’re having to deal with right now, including Omicron, have come from such [immunocompromised] individuals.”
Omicron “was a big shift,” Gupta noted. “It had a lot of new mutations on it, so it was almost like a new strain of the virus.” Few studies have looked at the longitudinal immunogenicity proffered by COVID vaccines in the post-Omicron era, particularly in those with vasculitis who are often treated with immunosuppressive drugs, including rituximab.
Two-Pronged Study Approach
For the study, a population of immunocompromised individuals diagnosed with vasculitis who had been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years was identified. Just over half (58%) had received adenovirus-based AZD1222/ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca-Oxford; AZN) and 37% BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech; mRNA) as their primary vaccines. Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis comprised the majority of those who received rituximab (83%), compared with less than half of those who did not take rituximab (48%).
A two-pronged approach was taken with the researchers first measuring neutralizing antibody titers before and 30 days after four successive COVID vaccinations in a group of 32 individuals with available samples. They then performed a cross-sectional, case-control study in 95 individuals to look at neutralizing antibody titers and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in individuals who had (n = 64) and had not (n = 31) been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years and had samples available after their third and fourth COVID vaccinations.
The first analysis was done to see how people were responding to vaccination over time. “That told us that there was a problem with the first two doses and that we got some response after doses three and four, but the response was uniformly quite poor against the new variants of concern,” Gupta said.
A human embryonic kidney cell model had been used to determine individuals’ neutralizing antibody titers in response to WT, BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB pseudotyped viruses. After the first and second COVID vaccinations, the geometric mean titer (GMT) against each variant barely increased from a baseline of 40.0. The greatest increases in GMT was seen with the WT virus, at 43.7, 90.7, 256.3, and 394.2, after the first, second, third and fourth doses, respectively. The lowest increases in GMT were seen with the XBB variant, with respective values of 40.0, 40.8, 45.7, and 53.9.
Incremental Benefit Offers Some ‘Reassurance’
Vasculitis specialist Rona Smith, MA, MB BChir, MD, who was one of the authors of the paper, told this news organization separately that the results showed there was “an incremental benefit of having COVID vaccinations,” which “offers a little bit of reassurance” that there can be an immune response in people with vasculitis.
Although results of the cross-sectional study showed that there was a significant dampening effect of rituximab treatment on the immune response, “I don’t think it’s an isolated effect in our [vasculitis] patients,” Smith suggested, adding the results were “probably still relevant to patients who receive routine dosing of rituximab for other conditions.”
Neutralizing antibody titers were consistently lower among individuals who had been treated with rituximab vs those who had not, with treatment in the past 18 months found to significantly impair immunogenicity.
The ADCC response was better preserved than the neutralizing antibody response, Gupta said, although it was still significantly lower in the rituximab-treated than in the non–rituximab-treated patients.
When to Vaccinate in Vasculitis?
Regarding when to give vaccines to people with vasculitis, Smith said: “Current recommendations are that patients should receive any vaccines that they’re offered routinely, whether that be COVID vaccines, flu vaccines, pneumococcal vaccines.”
As for the timing of those vaccinations, she observed that the current thinking was that vaccinations should “ideally be at least 1 month before a rituximab treatment, and ideally 3-4 [months] after their last dose. However, as many patients are on a 6-month dosing cycle, it can be difficult for some of them to find a suitable time window to have the COVID vaccine when it is offered.”
Additional precautions, such as wearing masks in crowded places and avoiding visits to acutely unwell friends or relatives, may still be prudent, Smith acknowledged, but he was clear that people should not be locking themselves away as they did during the COVID-19 pandemic.
When advising patients, “our general recommendation is that it is better to have a vaccine than not, but we can’t guarantee how well you will respond to it, but some response is better than none,” Smith said.
The study was independently supported. Gupta had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Smith was a coauthor of the paper and has received research grant funding from Union Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline/Vir Biotechnology, Addenbrooke’s Charitable Trust, and Vasculitis UK. Another coauthor reported receiving research grants from CSL Vifor, Roche, and GlaxoSmithKline and advisory board, consultancy, and lecture fees from Roche and CSL Vifor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with vasculitis may need at least three or four vaccinations for COVID-19 before they start to show an immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection, new research has suggested.
In a longitudinal retrospective study, serum antibody neutralization against the Omicron variant of the virus and its descendants was found to be “largely absent” after the first two doses of COVID-19 vaccine had been given to patients. But increasing neutralizing antibody titers were seen after both the third and fourth vaccine boosters had been administered.
Results also showed that the more recently people had been treated with the B cell–depleting therapy rituximab, the lower the levels of immunogenicity that were achieved, and thus protection against SARS-CoV-2.
“Our results have significant implications for individuals treated with rituximab in the post-Omicron era, highlighting the value of additive boosters in affirming increasing protection in clinically vulnerable populations,” the team behind the work at the University of Cambridge in England, has reported in Science Advances.
Moreover, because the use of rituximab reduced the neutralization of not just wild-type (WT) Omicron but also the Omicron-descendant variants BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB, this highlights “the urgent need for additional adjunctive strategies to enhance vaccine-induced immunity as well as preferential access for such patients to updated vaccines using spike from now circulating Omicron lineages,” the team added.
Studying Humoral Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Corresponding author Ravindra K. Gupta, BMBCh, MA, MPH, PhD, told this news organization that studying humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in immunocompromised individuals such as those with vasculitis was important for two main reasons.
“It is really important at individual level for their own health, of course, but also because we know that variants of concern have often evolved and developed within patients and can then spread in wider populations,” he said.
Gupta, who is professor of clinical microbiology at the Cambridge Institute for Therapeutic Immunology & Infectious Disease added: “We believe that the variants of concern that we’re having to deal with right now, including Omicron, have come from such [immunocompromised] individuals.”
Omicron “was a big shift,” Gupta noted. “It had a lot of new mutations on it, so it was almost like a new strain of the virus.” Few studies have looked at the longitudinal immunogenicity proffered by COVID vaccines in the post-Omicron era, particularly in those with vasculitis who are often treated with immunosuppressive drugs, including rituximab.
Two-Pronged Study Approach
For the study, a population of immunocompromised individuals diagnosed with vasculitis who had been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years was identified. Just over half (58%) had received adenovirus-based AZD1222/ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca-Oxford; AZN) and 37% BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech; mRNA) as their primary vaccines. Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis comprised the majority of those who received rituximab (83%), compared with less than half of those who did not take rituximab (48%).
A two-pronged approach was taken with the researchers first measuring neutralizing antibody titers before and 30 days after four successive COVID vaccinations in a group of 32 individuals with available samples. They then performed a cross-sectional, case-control study in 95 individuals to look at neutralizing antibody titers and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in individuals who had (n = 64) and had not (n = 31) been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years and had samples available after their third and fourth COVID vaccinations.
The first analysis was done to see how people were responding to vaccination over time. “That told us that there was a problem with the first two doses and that we got some response after doses three and four, but the response was uniformly quite poor against the new variants of concern,” Gupta said.
A human embryonic kidney cell model had been used to determine individuals’ neutralizing antibody titers in response to WT, BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB pseudotyped viruses. After the first and second COVID vaccinations, the geometric mean titer (GMT) against each variant barely increased from a baseline of 40.0. The greatest increases in GMT was seen with the WT virus, at 43.7, 90.7, 256.3, and 394.2, after the first, second, third and fourth doses, respectively. The lowest increases in GMT were seen with the XBB variant, with respective values of 40.0, 40.8, 45.7, and 53.9.
Incremental Benefit Offers Some ‘Reassurance’
Vasculitis specialist Rona Smith, MA, MB BChir, MD, who was one of the authors of the paper, told this news organization separately that the results showed there was “an incremental benefit of having COVID vaccinations,” which “offers a little bit of reassurance” that there can be an immune response in people with vasculitis.
Although results of the cross-sectional study showed that there was a significant dampening effect of rituximab treatment on the immune response, “I don’t think it’s an isolated effect in our [vasculitis] patients,” Smith suggested, adding the results were “probably still relevant to patients who receive routine dosing of rituximab for other conditions.”
Neutralizing antibody titers were consistently lower among individuals who had been treated with rituximab vs those who had not, with treatment in the past 18 months found to significantly impair immunogenicity.
The ADCC response was better preserved than the neutralizing antibody response, Gupta said, although it was still significantly lower in the rituximab-treated than in the non–rituximab-treated patients.
When to Vaccinate in Vasculitis?
Regarding when to give vaccines to people with vasculitis, Smith said: “Current recommendations are that patients should receive any vaccines that they’re offered routinely, whether that be COVID vaccines, flu vaccines, pneumococcal vaccines.”
As for the timing of those vaccinations, she observed that the current thinking was that vaccinations should “ideally be at least 1 month before a rituximab treatment, and ideally 3-4 [months] after their last dose. However, as many patients are on a 6-month dosing cycle, it can be difficult for some of them to find a suitable time window to have the COVID vaccine when it is offered.”
Additional precautions, such as wearing masks in crowded places and avoiding visits to acutely unwell friends or relatives, may still be prudent, Smith acknowledged, but he was clear that people should not be locking themselves away as they did during the COVID-19 pandemic.
When advising patients, “our general recommendation is that it is better to have a vaccine than not, but we can’t guarantee how well you will respond to it, but some response is better than none,” Smith said.
The study was independently supported. Gupta had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Smith was a coauthor of the paper and has received research grant funding from Union Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline/Vir Biotechnology, Addenbrooke’s Charitable Trust, and Vasculitis UK. Another coauthor reported receiving research grants from CSL Vifor, Roche, and GlaxoSmithKline and advisory board, consultancy, and lecture fees from Roche and CSL Vifor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with vasculitis may need at least three or four vaccinations for COVID-19 before they start to show an immune response against SARS-CoV-2 infection, new research has suggested.
In a longitudinal retrospective study, serum antibody neutralization against the Omicron variant of the virus and its descendants was found to be “largely absent” after the first two doses of COVID-19 vaccine had been given to patients. But increasing neutralizing antibody titers were seen after both the third and fourth vaccine boosters had been administered.
Results also showed that the more recently people had been treated with the B cell–depleting therapy rituximab, the lower the levels of immunogenicity that were achieved, and thus protection against SARS-CoV-2.
“Our results have significant implications for individuals treated with rituximab in the post-Omicron era, highlighting the value of additive boosters in affirming increasing protection in clinically vulnerable populations,” the team behind the work at the University of Cambridge in England, has reported in Science Advances.
Moreover, because the use of rituximab reduced the neutralization of not just wild-type (WT) Omicron but also the Omicron-descendant variants BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB, this highlights “the urgent need for additional adjunctive strategies to enhance vaccine-induced immunity as well as preferential access for such patients to updated vaccines using spike from now circulating Omicron lineages,” the team added.
Studying Humoral Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines
Corresponding author Ravindra K. Gupta, BMBCh, MA, MPH, PhD, told this news organization that studying humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in immunocompromised individuals such as those with vasculitis was important for two main reasons.
“It is really important at individual level for their own health, of course, but also because we know that variants of concern have often evolved and developed within patients and can then spread in wider populations,” he said.
Gupta, who is professor of clinical microbiology at the Cambridge Institute for Therapeutic Immunology & Infectious Disease added: “We believe that the variants of concern that we’re having to deal with right now, including Omicron, have come from such [immunocompromised] individuals.”
Omicron “was a big shift,” Gupta noted. “It had a lot of new mutations on it, so it was almost like a new strain of the virus.” Few studies have looked at the longitudinal immunogenicity proffered by COVID vaccines in the post-Omicron era, particularly in those with vasculitis who are often treated with immunosuppressive drugs, including rituximab.
Two-Pronged Study Approach
For the study, a population of immunocompromised individuals diagnosed with vasculitis who had been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years was identified. Just over half (58%) had received adenovirus-based AZD1222/ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca-Oxford; AZN) and 37% BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech; mRNA) as their primary vaccines. Patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis comprised the majority of those who received rituximab (83%), compared with less than half of those who did not take rituximab (48%).
A two-pronged approach was taken with the researchers first measuring neutralizing antibody titers before and 30 days after four successive COVID vaccinations in a group of 32 individuals with available samples. They then performed a cross-sectional, case-control study in 95 individuals to look at neutralizing antibody titers and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in individuals who had (n = 64) and had not (n = 31) been treated with rituximab in the past 5 years and had samples available after their third and fourth COVID vaccinations.
The first analysis was done to see how people were responding to vaccination over time. “That told us that there was a problem with the first two doses and that we got some response after doses three and four, but the response was uniformly quite poor against the new variants of concern,” Gupta said.
A human embryonic kidney cell model had been used to determine individuals’ neutralizing antibody titers in response to WT, BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and XBB pseudotyped viruses. After the first and second COVID vaccinations, the geometric mean titer (GMT) against each variant barely increased from a baseline of 40.0. The greatest increases in GMT was seen with the WT virus, at 43.7, 90.7, 256.3, and 394.2, after the first, second, third and fourth doses, respectively. The lowest increases in GMT were seen with the XBB variant, with respective values of 40.0, 40.8, 45.7, and 53.9.
Incremental Benefit Offers Some ‘Reassurance’
Vasculitis specialist Rona Smith, MA, MB BChir, MD, who was one of the authors of the paper, told this news organization separately that the results showed there was “an incremental benefit of having COVID vaccinations,” which “offers a little bit of reassurance” that there can be an immune response in people with vasculitis.
Although results of the cross-sectional study showed that there was a significant dampening effect of rituximab treatment on the immune response, “I don’t think it’s an isolated effect in our [vasculitis] patients,” Smith suggested, adding the results were “probably still relevant to patients who receive routine dosing of rituximab for other conditions.”
Neutralizing antibody titers were consistently lower among individuals who had been treated with rituximab vs those who had not, with treatment in the past 18 months found to significantly impair immunogenicity.
The ADCC response was better preserved than the neutralizing antibody response, Gupta said, although it was still significantly lower in the rituximab-treated than in the non–rituximab-treated patients.
When to Vaccinate in Vasculitis?
Regarding when to give vaccines to people with vasculitis, Smith said: “Current recommendations are that patients should receive any vaccines that they’re offered routinely, whether that be COVID vaccines, flu vaccines, pneumococcal vaccines.”
As for the timing of those vaccinations, she observed that the current thinking was that vaccinations should “ideally be at least 1 month before a rituximab treatment, and ideally 3-4 [months] after their last dose. However, as many patients are on a 6-month dosing cycle, it can be difficult for some of them to find a suitable time window to have the COVID vaccine when it is offered.”
Additional precautions, such as wearing masks in crowded places and avoiding visits to acutely unwell friends or relatives, may still be prudent, Smith acknowledged, but he was clear that people should not be locking themselves away as they did during the COVID-19 pandemic.
When advising patients, “our general recommendation is that it is better to have a vaccine than not, but we can’t guarantee how well you will respond to it, but some response is better than none,” Smith said.
The study was independently supported. Gupta had no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Smith was a coauthor of the paper and has received research grant funding from Union Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline/Vir Biotechnology, Addenbrooke’s Charitable Trust, and Vasculitis UK. Another coauthor reported receiving research grants from CSL Vifor, Roche, and GlaxoSmithKline and advisory board, consultancy, and lecture fees from Roche and CSL Vifor.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SCIENCE ADVANCES
Real-World Data Question Low-Dose Steroid Use in ANCA Vasculitis
TOPLINE:
Compared with a standard dosing regimen, a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen is associated with an increased risk for disease progression, relapse, death, or kidney failure in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, particularly affecting patients receiving rituximab or those with elevated creatinine levels.
METHODOLOGY:
- The PEXIVAS trial demonstrated that a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen was noninferior to standard dosing in terms of death or end-stage kidney disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, the trial did not include disease progression or relapse as a primary endpoint, and cyclophosphamide was the primary induction therapy.
- Researchers conducted this retrospective study across 19 hospitals (18 in France and one in Luxembourg) between January 2018 and November 2022 to compare the effectiveness of a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen, as used in the PEXIVAS trial, with a standard-dose regimen in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis in the real-world setting.
- They included 234 patients aged > 15 years (51% men) with severe granulomatosis with polyangiitis (n = 141) or microscopic polyangiitis (n = 93) who received induction therapy with rituximab or cyclophosphamide; 126 and 108 patients received reduced-dose and standard-dose glucocorticoid regimens, respectively.
- Most patients (70%) had severe renal involvement.
- The primary composite outcome encompassed minor relapse, major relapse, disease progression before remission, end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis for > 12 weeks or transplantation, and death within 12 months post-induction.
TAKEAWAY:
- The primary composite outcome occurred in a higher proportion of patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoid therapy than in those receiving standard-dose therapy (33.3% vs 18.5%; hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.23-3.94).
- However, no significant association was found between reduced-dose glucocorticoids and the risk for death or end-stage kidney disease or the occurrence of serious infections.
- Among patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoids, serum creatinine levels > 300 μmol/L were associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 3.02; 95% CI, 1.28-7.11).
- In the rituximab induction subgroup, reduced-dose glucocorticoid was associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.18-4.71), compared with standard-dose glucocorticoids.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data suggest increased vigilance when using the [reduced-dose glucocorticoid] regimen, especially in the two subgroups of patients at higher risk of failure, that is, those receiving [rituximab] as induction therapy and those with a baseline serum creatinine greater than 300 μmol/L,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sophie Nagle, MD, National Referral Centre for Rare Autoimmune and Systemic Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Hôpital Cochin, Paris, France. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of this study may have introduced inherent limitations and potential selection bias. The study lacked data on patient comorbidities, which could have influenced treatment choice and outcomes. Additionally, about a quarter of patients did not receive methylprednisolone pulses prior to oral glucocorticoids, unlike the PEXIVAS trial protocol. The group receiving standard-dose glucocorticoids showed heterogeneity in glucocorticoid regimens, and the minimum follow-up was only 6 months.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any source of funding. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with a standard dosing regimen, a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen is associated with an increased risk for disease progression, relapse, death, or kidney failure in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, particularly affecting patients receiving rituximab or those with elevated creatinine levels.
METHODOLOGY:
- The PEXIVAS trial demonstrated that a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen was noninferior to standard dosing in terms of death or end-stage kidney disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, the trial did not include disease progression or relapse as a primary endpoint, and cyclophosphamide was the primary induction therapy.
- Researchers conducted this retrospective study across 19 hospitals (18 in France and one in Luxembourg) between January 2018 and November 2022 to compare the effectiveness of a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen, as used in the PEXIVAS trial, with a standard-dose regimen in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis in the real-world setting.
- They included 234 patients aged > 15 years (51% men) with severe granulomatosis with polyangiitis (n = 141) or microscopic polyangiitis (n = 93) who received induction therapy with rituximab or cyclophosphamide; 126 and 108 patients received reduced-dose and standard-dose glucocorticoid regimens, respectively.
- Most patients (70%) had severe renal involvement.
- The primary composite outcome encompassed minor relapse, major relapse, disease progression before remission, end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis for > 12 weeks or transplantation, and death within 12 months post-induction.
TAKEAWAY:
- The primary composite outcome occurred in a higher proportion of patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoid therapy than in those receiving standard-dose therapy (33.3% vs 18.5%; hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.23-3.94).
- However, no significant association was found between reduced-dose glucocorticoids and the risk for death or end-stage kidney disease or the occurrence of serious infections.
- Among patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoids, serum creatinine levels > 300 μmol/L were associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 3.02; 95% CI, 1.28-7.11).
- In the rituximab induction subgroup, reduced-dose glucocorticoid was associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.18-4.71), compared with standard-dose glucocorticoids.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data suggest increased vigilance when using the [reduced-dose glucocorticoid] regimen, especially in the two subgroups of patients at higher risk of failure, that is, those receiving [rituximab] as induction therapy and those with a baseline serum creatinine greater than 300 μmol/L,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sophie Nagle, MD, National Referral Centre for Rare Autoimmune and Systemic Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Hôpital Cochin, Paris, France. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of this study may have introduced inherent limitations and potential selection bias. The study lacked data on patient comorbidities, which could have influenced treatment choice and outcomes. Additionally, about a quarter of patients did not receive methylprednisolone pulses prior to oral glucocorticoids, unlike the PEXIVAS trial protocol. The group receiving standard-dose glucocorticoids showed heterogeneity in glucocorticoid regimens, and the minimum follow-up was only 6 months.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any source of funding. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Compared with a standard dosing regimen, a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen is associated with an increased risk for disease progression, relapse, death, or kidney failure in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, particularly affecting patients receiving rituximab or those with elevated creatinine levels.
METHODOLOGY:
- The PEXIVAS trial demonstrated that a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen was noninferior to standard dosing in terms of death or end-stage kidney disease in ANCA-associated vasculitis. However, the trial did not include disease progression or relapse as a primary endpoint, and cyclophosphamide was the primary induction therapy.
- Researchers conducted this retrospective study across 19 hospitals (18 in France and one in Luxembourg) between January 2018 and November 2022 to compare the effectiveness of a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen, as used in the PEXIVAS trial, with a standard-dose regimen in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis in the real-world setting.
- They included 234 patients aged > 15 years (51% men) with severe granulomatosis with polyangiitis (n = 141) or microscopic polyangiitis (n = 93) who received induction therapy with rituximab or cyclophosphamide; 126 and 108 patients received reduced-dose and standard-dose glucocorticoid regimens, respectively.
- Most patients (70%) had severe renal involvement.
- The primary composite outcome encompassed minor relapse, major relapse, disease progression before remission, end-stage kidney disease requiring dialysis for > 12 weeks or transplantation, and death within 12 months post-induction.
TAKEAWAY:
- The primary composite outcome occurred in a higher proportion of patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoid therapy than in those receiving standard-dose therapy (33.3% vs 18.5%; hazard ratio [HR], 2.20; 95% CI, 1.23-3.94).
- However, no significant association was found between reduced-dose glucocorticoids and the risk for death or end-stage kidney disease or the occurrence of serious infections.
- Among patients receiving reduced-dose glucocorticoids, serum creatinine levels > 300 μmol/L were associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 3.02; 95% CI, 1.28-7.11).
- In the rituximab induction subgroup, reduced-dose glucocorticoid was associated with an increased risk for the primary composite outcome (adjusted HR, 2.36; 95% CI, 1.18-4.71), compared with standard-dose glucocorticoids.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our data suggest increased vigilance when using the [reduced-dose glucocorticoid] regimen, especially in the two subgroups of patients at higher risk of failure, that is, those receiving [rituximab] as induction therapy and those with a baseline serum creatinine greater than 300 μmol/L,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sophie Nagle, MD, National Referral Centre for Rare Autoimmune and Systemic Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Hôpital Cochin, Paris, France. It was published online on November 20, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of this study may have introduced inherent limitations and potential selection bias. The study lacked data on patient comorbidities, which could have influenced treatment choice and outcomes. Additionally, about a quarter of patients did not receive methylprednisolone pulses prior to oral glucocorticoids, unlike the PEXIVAS trial protocol. The group receiving standard-dose glucocorticoids showed heterogeneity in glucocorticoid regimens, and the minimum follow-up was only 6 months.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not report any source of funding. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Need for Low-Dose Steroids to Prevent Relapse in GPA Vasculitis Depends on Treatment Regimen
WASHINGTON — Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) completely tapered off prednisone have a more than fourfold risk of relapse by 6 months, compared with those tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone; however, this benefit was only seen in patients not on rituximab, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
“For patients treated with rituximab, fully tapering off glucocorticoids is reasonable to consider as the first approach,” said Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, during his presentation of the findings.
Although a low dose of glucocorticoids can prevent some minor relapses in patients on other treatment regimens such as methotrexate or azathioprine, “fully tapering off prednisone presents relatively little risk of major relapse, and that major relapse can be treated rather quickly,” Merkel added.
The Assessment of Prednisone in Remission (TAPIR) trial enrolled 143 patients with GPA who were in remission (defined as a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score for Wegener’s Granulomatosis [BVAS/WG] of 0) within 1 year of treatment to induce remission for active disease and who were taking 5-10 mg of prednisone per day. After all patients tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone, 71 patients completely tapered off prednisone over 4 weeks and remained off glucocorticoids until month 6. The remaining patients maintained a 5-mg/day dose over the study period. Placement in either treatment group was randomized, and patients continued other immunosuppressive therapy during the study.
Researchers evaluated the rate of relapse by 6 months, defined as a physician’s decision to increase the dose of glucocorticoids to treat GPA, in both groups.
Across all participants, the median age was 58 years, and 52% of patients were male. Most patients were White, and 47% of all patients were prescribed rituximab.
At 6 months, 15.5% of participants who completely tapered off prednisone experienced a relapse of GPA, compared with 4.2% of those taking low-dose prednisone. Time to relapse was also shorter in the 0-mg prednisone group (P = .026), and relapses occurred continually over 6 months, Merkel said.
When stratified by rituximab use, relapse rates at 6 months between the 5-mg and 0-mg prednisone groups in patients taking rituximab showed no difference. Among patients not taking rituximab, those who completely stopped prednisone were nine and a half times as likely to experience relapse as those in the low-dose group.
Despite these differences in relapse rates, “surprisingly, there were no differences in patient-reported outcomes [such as pain interference, physical function, and fatigue],” Merkel said.
Across all patients, all but one relapse was characterized as minor. There were five serious adverse events and 10 infections in the 0-mg group versus one adverse event and 4 infections in the 5-mg group, but these differences were not statistically significant.
In patients who relapsed, musculoskeletal and ear, nose, and throat manifestations of GPA were most common, and these are “the kind of stuff we see that is helped by low-dose glucocorticoids,” Merkel said.
It’s a good sign that for patients who were completely weaned off glucocorticoids, nearly all relapses were minor, Galina Marder, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said in an interview. She was not involved with the research.
The study “can reinforce the message [of] trying to get them off steroids completely [when possible],” she said.
The findings also provide insight for future clinical trials, Merkel noted. For patients taking non–rituximab-based regimens, completely tapering off glucocorticoids or maintaining a low dose can affect study outcomes.
“[These data are] even more important for clinical trials because they are [reinforcing] the fact that you can have a diminishing signal if you allow some patients to stay on 5 mg prednisone” when GPA flares are the primary outcome, Marder added.
The Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium received funding for this research through grants from the National Institutes of Health. Merkel has disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, argenx, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cabaletta, ChemoCentryx, CSL Behring, Dynacure, Eicos, Electra, EMD Serono, Forbius, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, GSK, HI-Bio, Inmagene, InflaRx, Janssen, Kiniksa, Kyverna, Magenta, MiroBio, Neutrolis, Novartis, NS Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sparrow, Takeda, Talaris, UpToDate, and Visterra. Marder consults for Amgen and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) completely tapered off prednisone have a more than fourfold risk of relapse by 6 months, compared with those tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone; however, this benefit was only seen in patients not on rituximab, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
“For patients treated with rituximab, fully tapering off glucocorticoids is reasonable to consider as the first approach,” said Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, during his presentation of the findings.
Although a low dose of glucocorticoids can prevent some minor relapses in patients on other treatment regimens such as methotrexate or azathioprine, “fully tapering off prednisone presents relatively little risk of major relapse, and that major relapse can be treated rather quickly,” Merkel added.
The Assessment of Prednisone in Remission (TAPIR) trial enrolled 143 patients with GPA who were in remission (defined as a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score for Wegener’s Granulomatosis [BVAS/WG] of 0) within 1 year of treatment to induce remission for active disease and who were taking 5-10 mg of prednisone per day. After all patients tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone, 71 patients completely tapered off prednisone over 4 weeks and remained off glucocorticoids until month 6. The remaining patients maintained a 5-mg/day dose over the study period. Placement in either treatment group was randomized, and patients continued other immunosuppressive therapy during the study.
Researchers evaluated the rate of relapse by 6 months, defined as a physician’s decision to increase the dose of glucocorticoids to treat GPA, in both groups.
Across all participants, the median age was 58 years, and 52% of patients were male. Most patients were White, and 47% of all patients were prescribed rituximab.
At 6 months, 15.5% of participants who completely tapered off prednisone experienced a relapse of GPA, compared with 4.2% of those taking low-dose prednisone. Time to relapse was also shorter in the 0-mg prednisone group (P = .026), and relapses occurred continually over 6 months, Merkel said.
When stratified by rituximab use, relapse rates at 6 months between the 5-mg and 0-mg prednisone groups in patients taking rituximab showed no difference. Among patients not taking rituximab, those who completely stopped prednisone were nine and a half times as likely to experience relapse as those in the low-dose group.
Despite these differences in relapse rates, “surprisingly, there were no differences in patient-reported outcomes [such as pain interference, physical function, and fatigue],” Merkel said.
Across all patients, all but one relapse was characterized as minor. There were five serious adverse events and 10 infections in the 0-mg group versus one adverse event and 4 infections in the 5-mg group, but these differences were not statistically significant.
In patients who relapsed, musculoskeletal and ear, nose, and throat manifestations of GPA were most common, and these are “the kind of stuff we see that is helped by low-dose glucocorticoids,” Merkel said.
It’s a good sign that for patients who were completely weaned off glucocorticoids, nearly all relapses were minor, Galina Marder, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said in an interview. She was not involved with the research.
The study “can reinforce the message [of] trying to get them off steroids completely [when possible],” she said.
The findings also provide insight for future clinical trials, Merkel noted. For patients taking non–rituximab-based regimens, completely tapering off glucocorticoids or maintaining a low dose can affect study outcomes.
“[These data are] even more important for clinical trials because they are [reinforcing] the fact that you can have a diminishing signal if you allow some patients to stay on 5 mg prednisone” when GPA flares are the primary outcome, Marder added.
The Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium received funding for this research through grants from the National Institutes of Health. Merkel has disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, argenx, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cabaletta, ChemoCentryx, CSL Behring, Dynacure, Eicos, Electra, EMD Serono, Forbius, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, GSK, HI-Bio, Inmagene, InflaRx, Janssen, Kiniksa, Kyverna, Magenta, MiroBio, Neutrolis, Novartis, NS Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sparrow, Takeda, Talaris, UpToDate, and Visterra. Marder consults for Amgen and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) completely tapered off prednisone have a more than fourfold risk of relapse by 6 months, compared with those tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone; however, this benefit was only seen in patients not on rituximab, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR).
“For patients treated with rituximab, fully tapering off glucocorticoids is reasonable to consider as the first approach,” said Peter Merkel, MD, MPH, chief of the division of rheumatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, during his presentation of the findings.
Although a low dose of glucocorticoids can prevent some minor relapses in patients on other treatment regimens such as methotrexate or azathioprine, “fully tapering off prednisone presents relatively little risk of major relapse, and that major relapse can be treated rather quickly,” Merkel added.
The Assessment of Prednisone in Remission (TAPIR) trial enrolled 143 patients with GPA who were in remission (defined as a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score for Wegener’s Granulomatosis [BVAS/WG] of 0) within 1 year of treatment to induce remission for active disease and who were taking 5-10 mg of prednisone per day. After all patients tapered to 5 mg/day of prednisone, 71 patients completely tapered off prednisone over 4 weeks and remained off glucocorticoids until month 6. The remaining patients maintained a 5-mg/day dose over the study period. Placement in either treatment group was randomized, and patients continued other immunosuppressive therapy during the study.
Researchers evaluated the rate of relapse by 6 months, defined as a physician’s decision to increase the dose of glucocorticoids to treat GPA, in both groups.
Across all participants, the median age was 58 years, and 52% of patients were male. Most patients were White, and 47% of all patients were prescribed rituximab.
At 6 months, 15.5% of participants who completely tapered off prednisone experienced a relapse of GPA, compared with 4.2% of those taking low-dose prednisone. Time to relapse was also shorter in the 0-mg prednisone group (P = .026), and relapses occurred continually over 6 months, Merkel said.
When stratified by rituximab use, relapse rates at 6 months between the 5-mg and 0-mg prednisone groups in patients taking rituximab showed no difference. Among patients not taking rituximab, those who completely stopped prednisone were nine and a half times as likely to experience relapse as those in the low-dose group.
Despite these differences in relapse rates, “surprisingly, there were no differences in patient-reported outcomes [such as pain interference, physical function, and fatigue],” Merkel said.
Across all patients, all but one relapse was characterized as minor. There were five serious adverse events and 10 infections in the 0-mg group versus one adverse event and 4 infections in the 5-mg group, but these differences were not statistically significant.
In patients who relapsed, musculoskeletal and ear, nose, and throat manifestations of GPA were most common, and these are “the kind of stuff we see that is helped by low-dose glucocorticoids,” Merkel said.
It’s a good sign that for patients who were completely weaned off glucocorticoids, nearly all relapses were minor, Galina Marder, MD, a rheumatologist and associate professor of medicine at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said in an interview. She was not involved with the research.
The study “can reinforce the message [of] trying to get them off steroids completely [when possible],” she said.
The findings also provide insight for future clinical trials, Merkel noted. For patients taking non–rituximab-based regimens, completely tapering off glucocorticoids or maintaining a low dose can affect study outcomes.
“[These data are] even more important for clinical trials because they are [reinforcing] the fact that you can have a diminishing signal if you allow some patients to stay on 5 mg prednisone” when GPA flares are the primary outcome, Marder added.
The Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium received funding for this research through grants from the National Institutes of Health. Merkel has disclosed financial relationships with AbbVie/Abbott, Amgen, argenx, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cabaletta, ChemoCentryx, CSL Behring, Dynacure, Eicos, Electra, EMD Serono, Forbius, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, GSK, HI-Bio, Inmagene, InflaRx, Janssen, Kiniksa, Kyverna, Magenta, MiroBio, Neutrolis, Novartis, NS Pharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Sparrow, Takeda, Talaris, UpToDate, and Visterra. Marder consults for Amgen and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Rituximab Not Inferior to Cyclophosphamide in Pediatric Vasculitis
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infliximab vs Adalimumab: Which Is Best for Behçet Syndrome?
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No Benefit to High-Dose IV Vs Oral Steroids in Giant Cell Arteritis
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA), intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids alone does not improve visual acuity and increases the risk for diabetes within the first year. Survival rates do not differ with these two treatments.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a population-based retrospective study at three centers in Sweden to assess the clinical characteristics, treatment-related toxicity, and mortality in patients with GCA who were receiving high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone.
- A total of 419 patients with biopsy-confirmed GCA (mean age at diagnosis, 75 years; 69% women) diagnosed from 2004 to 2019 were included.
- Patients were treated with either intravenous methylprednisolone (n = 111) at a dose of 500-1000 mg per day for 3 consecutive days or oral glucocorticoids alone (n = 308).
- Ischemic visual complications considered to indicate visual involvement were confirmed by an ophthalmologist, and data on visual acuity were collected from ophthalmologic clinic records at initial consultations and follow-up at 3-18 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Despite a tendency toward improvement, no significant difference in visual acuity was observed with intravenous methylprednisolone compared with oral glucocorticoids.
- Patients treated with intravenous methylprednisolone had a higher risk for newly diagnosed diabetes within a year of GCA diagnosis (odds ratio [OR], 2.59; P = .01).
- The risk for diabetes remained elevated even after adjustment for the cumulative oral glucocorticoid dose at 3 months (adjusted OR, 3.30; P = .01).
- Survival rates did not significantly differ between the treatment groups over a mean follow-up of 6.6 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this study on the use of intravenous methylprednisolone treatment in GCA, we found no evidence of a beneficial effect in improving visual acuity or enabling more rapid tapering of the oral glucocorticoid dose,” the authors wrote. “The use of IVMP [intravenous methylprednisolone] was associated with an increased risk of diabetes during the first year compared with oral GC [glucocorticoid], raising questions about the value of IVMP in GCA treatment.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Hampus Henningson, Department of Clinical Sciences, Rheumatology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, was published online in Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The retrospective nature of the study may have resulted in missing data and difficulty in accurately quantifying the cumulative glucocorticoid doses. The study did not validate the diagnoses of comorbidities but relied solely on diagnostic codes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Swedish Research Council, Swedish Rheumatism Association, Swedish Medical Society, Alfred Österlund’s Foundation, and King Gustaf V’s 80-year foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Frailty, Not Just Advanced Age, Affects ANCA Vasculitis Outcomes
TOPLINE:
Older adults with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis face a higher risk for end-stage renal disease or mortality and severe infections. However, frailty, more than age, predicts severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham ANCA-associated vasculitis cohort in the United States.
- They included 234 individuals (median age, 75 years) with incident ANCA-associated vasculitis who were treated from January 2002 to December 2019.
- Baseline frailty was measured using a claims-based frailty index, with data collected in the year before treatment initiation; individuals were categorized as those who were nonfrail, prefrail, mildly frail, and moderately to severely frail.
- Frailty, either mild or moderate to severe, was noted in 44 of 118 individuals aged ≥ 75 years and in 25 of 116 individuals aged 65-74 years.
- The outcomes of interest were the incidences of end-stage renal disease or death and severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis. The association of age and frailty with clinical outcomes was assessed in those aged 65-74 years and ≥ 75 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Frailty was a significant predictor of severe infections within 2 years of ANCA-associated vasculitis diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 8.46; 95% CI, 3.95-18.14), showing a stronger association than seen for chronological age ≥ 75 years (aHR, 2.52; 95% CI, 1.26-5.04).
- The incidence of severe infections was higher in those with vs without frailty in the age groups 65-74 years (38.9 vs 0.8 cases per 100 person-years) and ≥ 75 years (61.9 vs 12.3 cases per 100 person-years).
- Older age (≥ 75 years) was associated with an increased risk for end-stage renal disease or death (aHR, 4.50; 95% CI, 1.83-11.09); however, frailty was not.
- The effect of frailty on end-stage renal disease or death varied by age, with a larger difference observed in individuals aged 65-74 years (frail vs nonfrail, 7.5 vs 2.0 cases per 100 person-years) than in those aged ≥ 75 years (13.5 vs 16.0 cases per 100 person-years).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results highlight the fact that assessment of frailty in the care of older adults with ANCA-associated vasculitis can distinguish a group of patients at increased risk of severe infections who might benefit from interventions to minimize infection risk and optimize outcomes,” the authors wrote.
“Incorporating frailty screening into the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis provides an opportunity to offer personalized, evidence-based care to frail older adults,” Alexandra Legge, MD, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, wrote in an associated comment published online in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. It was published online on September 18, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design and single-center setting limited the generalizability of the findings. Residual confounding may have been possible despite adjustments for relevant baseline factors. The requirement of at least one healthcare encounter before baseline may have underrepresented individuals without frailty. Differences in treatment patterns after the baseline period were not controlled for.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some authors reported receiving grants, research support, consulting fees, honoraria, or royalties or serving on advisory boards of pharmaceutical companies and other sources outside of the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Older adults with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis face a higher risk for end-stage renal disease or mortality and severe infections. However, frailty, more than age, predicts severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham ANCA-associated vasculitis cohort in the United States.
- They included 234 individuals (median age, 75 years) with incident ANCA-associated vasculitis who were treated from January 2002 to December 2019.
- Baseline frailty was measured using a claims-based frailty index, with data collected in the year before treatment initiation; individuals were categorized as those who were nonfrail, prefrail, mildly frail, and moderately to severely frail.
- Frailty, either mild or moderate to severe, was noted in 44 of 118 individuals aged ≥ 75 years and in 25 of 116 individuals aged 65-74 years.
- The outcomes of interest were the incidences of end-stage renal disease or death and severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis. The association of age and frailty with clinical outcomes was assessed in those aged 65-74 years and ≥ 75 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Frailty was a significant predictor of severe infections within 2 years of ANCA-associated vasculitis diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 8.46; 95% CI, 3.95-18.14), showing a stronger association than seen for chronological age ≥ 75 years (aHR, 2.52; 95% CI, 1.26-5.04).
- The incidence of severe infections was higher in those with vs without frailty in the age groups 65-74 years (38.9 vs 0.8 cases per 100 person-years) and ≥ 75 years (61.9 vs 12.3 cases per 100 person-years).
- Older age (≥ 75 years) was associated with an increased risk for end-stage renal disease or death (aHR, 4.50; 95% CI, 1.83-11.09); however, frailty was not.
- The effect of frailty on end-stage renal disease or death varied by age, with a larger difference observed in individuals aged 65-74 years (frail vs nonfrail, 7.5 vs 2.0 cases per 100 person-years) than in those aged ≥ 75 years (13.5 vs 16.0 cases per 100 person-years).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results highlight the fact that assessment of frailty in the care of older adults with ANCA-associated vasculitis can distinguish a group of patients at increased risk of severe infections who might benefit from interventions to minimize infection risk and optimize outcomes,” the authors wrote.
“Incorporating frailty screening into the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis provides an opportunity to offer personalized, evidence-based care to frail older adults,” Alexandra Legge, MD, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, wrote in an associated comment published online in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. It was published online on September 18, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design and single-center setting limited the generalizability of the findings. Residual confounding may have been possible despite adjustments for relevant baseline factors. The requirement of at least one healthcare encounter before baseline may have underrepresented individuals without frailty. Differences in treatment patterns after the baseline period were not controlled for.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some authors reported receiving grants, research support, consulting fees, honoraria, or royalties or serving on advisory boards of pharmaceutical companies and other sources outside of the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Older adults with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis face a higher risk for end-stage renal disease or mortality and severe infections. However, frailty, more than age, predicts severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham ANCA-associated vasculitis cohort in the United States.
- They included 234 individuals (median age, 75 years) with incident ANCA-associated vasculitis who were treated from January 2002 to December 2019.
- Baseline frailty was measured using a claims-based frailty index, with data collected in the year before treatment initiation; individuals were categorized as those who were nonfrail, prefrail, mildly frail, and moderately to severely frail.
- Frailty, either mild or moderate to severe, was noted in 44 of 118 individuals aged ≥ 75 years and in 25 of 116 individuals aged 65-74 years.
- The outcomes of interest were the incidences of end-stage renal disease or death and severe infections within 2 years of diagnosis. The association of age and frailty with clinical outcomes was assessed in those aged 65-74 years and ≥ 75 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Frailty was a significant predictor of severe infections within 2 years of ANCA-associated vasculitis diagnosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 8.46; 95% CI, 3.95-18.14), showing a stronger association than seen for chronological age ≥ 75 years (aHR, 2.52; 95% CI, 1.26-5.04).
- The incidence of severe infections was higher in those with vs without frailty in the age groups 65-74 years (38.9 vs 0.8 cases per 100 person-years) and ≥ 75 years (61.9 vs 12.3 cases per 100 person-years).
- Older age (≥ 75 years) was associated with an increased risk for end-stage renal disease or death (aHR, 4.50; 95% CI, 1.83-11.09); however, frailty was not.
- The effect of frailty on end-stage renal disease or death varied by age, with a larger difference observed in individuals aged 65-74 years (frail vs nonfrail, 7.5 vs 2.0 cases per 100 person-years) than in those aged ≥ 75 years (13.5 vs 16.0 cases per 100 person-years).
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results highlight the fact that assessment of frailty in the care of older adults with ANCA-associated vasculitis can distinguish a group of patients at increased risk of severe infections who might benefit from interventions to minimize infection risk and optimize outcomes,” the authors wrote.
“Incorporating frailty screening into the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis provides an opportunity to offer personalized, evidence-based care to frail older adults,” Alexandra Legge, MD, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, wrote in an associated comment published online in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Sebastian E. Sattui, MD, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. It was published online on September 18, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s observational design and single-center setting limited the generalizability of the findings. Residual confounding may have been possible despite adjustments for relevant baseline factors. The requirement of at least one healthcare encounter before baseline may have underrepresented individuals without frailty. Differences in treatment patterns after the baseline period were not controlled for.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Some authors reported receiving grants, research support, consulting fees, honoraria, or royalties or serving on advisory boards of pharmaceutical companies and other sources outside of the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Benralizumab Now FDA Approved to Treat EGPA Vasculitis
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved benralizumab (Fasenra) for the treatment of adults with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome.
The drug is the second approved biologic for the treatment of EGPA. The first, mepolizumab (Nucala), was approved in 2017.
“This disease has a devastating impact on patients and the quality of their life, and they need more treatment options. The approval of another treatment in EGPA is welcome news to the approximately 15,000 patients living in the US with this difficult-to-treat rare disease,” said Joyce Kullman, executive director of the Vasculitis Foundation, in a press release on September 18.
Benralizumab, developed by AstraZeneca, is a monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-5 alpha receptor expressed on eosinophils. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an add-on treatment for patients 12 years and older with severe eosinophilic asthma, and is now approved for use in children aged 6 years and older.
The new indication was based on positive results from a noninferiority trial comparing benralizumab and mepolizumab. For the trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier in 2024, 140 adults with relapsing or refractory EGPA were randomized to a 30-mg subcutaneous injection of benralizumab or three separate 100-mg mepolizumab injections every 4 weeks for 1 year. At weeks 36 and 48, 59% of patients in the benralizumab group and 56% of patients in the mepolizumab group achieved remission (95% CI, –13 to 18; P = .73 for superiority). From week 42 to 52, 41% of patients who received benralizumab completely stopped taking oral glucocorticoids, compared with 26% of those who received mepolizumab.
“Patients often rely on long-term oral corticosteroids, which can cause serious and lasting side effects. Benralizumab is a much-needed treatment option, with data showing that not only is remission an achievable goal for EGPA patients, but benralizumab can also help patients taper off steroid therapy,” Michael Wechsler, MD, director of The Asthma Institute at National Jewish Health in Denver, Colorado, and the international coordinating investigator for the clinical trial, said in the press release.
Benralizumab is administered via subcutaneous injection. In adults with EGPA, the recommended dosage is 30 mg every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then once every 8 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions include headache and pharyngitis, according to the prescribing information.
Benralizumab is also in development for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and hypereosinophilic syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved benralizumab (Fasenra) for the treatment of adults with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome.
The drug is the second approved biologic for the treatment of EGPA. The first, mepolizumab (Nucala), was approved in 2017.
“This disease has a devastating impact on patients and the quality of their life, and they need more treatment options. The approval of another treatment in EGPA is welcome news to the approximately 15,000 patients living in the US with this difficult-to-treat rare disease,” said Joyce Kullman, executive director of the Vasculitis Foundation, in a press release on September 18.
Benralizumab, developed by AstraZeneca, is a monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-5 alpha receptor expressed on eosinophils. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an add-on treatment for patients 12 years and older with severe eosinophilic asthma, and is now approved for use in children aged 6 years and older.
The new indication was based on positive results from a noninferiority trial comparing benralizumab and mepolizumab. For the trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier in 2024, 140 adults with relapsing or refractory EGPA were randomized to a 30-mg subcutaneous injection of benralizumab or three separate 100-mg mepolizumab injections every 4 weeks for 1 year. At weeks 36 and 48, 59% of patients in the benralizumab group and 56% of patients in the mepolizumab group achieved remission (95% CI, –13 to 18; P = .73 for superiority). From week 42 to 52, 41% of patients who received benralizumab completely stopped taking oral glucocorticoids, compared with 26% of those who received mepolizumab.
“Patients often rely on long-term oral corticosteroids, which can cause serious and lasting side effects. Benralizumab is a much-needed treatment option, with data showing that not only is remission an achievable goal for EGPA patients, but benralizumab can also help patients taper off steroid therapy,” Michael Wechsler, MD, director of The Asthma Institute at National Jewish Health in Denver, Colorado, and the international coordinating investigator for the clinical trial, said in the press release.
Benralizumab is administered via subcutaneous injection. In adults with EGPA, the recommended dosage is 30 mg every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then once every 8 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions include headache and pharyngitis, according to the prescribing information.
Benralizumab is also in development for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and hypereosinophilic syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved benralizumab (Fasenra) for the treatment of adults with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), formerly known as Churg-Strauss syndrome.
The drug is the second approved biologic for the treatment of EGPA. The first, mepolizumab (Nucala), was approved in 2017.
“This disease has a devastating impact on patients and the quality of their life, and they need more treatment options. The approval of another treatment in EGPA is welcome news to the approximately 15,000 patients living in the US with this difficult-to-treat rare disease,” said Joyce Kullman, executive director of the Vasculitis Foundation, in a press release on September 18.
Benralizumab, developed by AstraZeneca, is a monoclonal antibody against the interleukin-5 alpha receptor expressed on eosinophils. The drug was first approved in 2017 as an add-on treatment for patients 12 years and older with severe eosinophilic asthma, and is now approved for use in children aged 6 years and older.
The new indication was based on positive results from a noninferiority trial comparing benralizumab and mepolizumab. For the trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier in 2024, 140 adults with relapsing or refractory EGPA were randomized to a 30-mg subcutaneous injection of benralizumab or three separate 100-mg mepolizumab injections every 4 weeks for 1 year. At weeks 36 and 48, 59% of patients in the benralizumab group and 56% of patients in the mepolizumab group achieved remission (95% CI, –13 to 18; P = .73 for superiority). From week 42 to 52, 41% of patients who received benralizumab completely stopped taking oral glucocorticoids, compared with 26% of those who received mepolizumab.
“Patients often rely on long-term oral corticosteroids, which can cause serious and lasting side effects. Benralizumab is a much-needed treatment option, with data showing that not only is remission an achievable goal for EGPA patients, but benralizumab can also help patients taper off steroid therapy,” Michael Wechsler, MD, director of The Asthma Institute at National Jewish Health in Denver, Colorado, and the international coordinating investigator for the clinical trial, said in the press release.
Benralizumab is administered via subcutaneous injection. In adults with EGPA, the recommended dosage is 30 mg every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then once every 8 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions include headache and pharyngitis, according to the prescribing information.
Benralizumab is also in development for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps, and hypereosinophilic syndrome.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Has Five Unique Patient Clusters
TOPLINE:
A data-driven subclassification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis has identified five distinct clusters with varying degrees of kidney involvement and systemic inflammation, offering insights into improved patient stratification and treatment approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- ANCA-associated vasculitis is a rare and complex autoimmune disease that is traditionally classified into granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
- Researchers employed advanced artificial intelligence and big data techniques to identify phenotypically distinct subgroups of ANCA-associated vasculitis and developed a classification system using real-world patient data from the Federated Vasculitis Registry consortium.
- They included 3868 patients diagnosed with ANCA-associated vasculitis between November 1, 1966, and March 1, 2023 (mean age at diagnosis, 57.2 years; 51.9% men), across six European vasculitis registries; while a majority of patients (62.9%) were diagnosed with GPA, the remaining 37.1% were diagnosed with MPA.
- Overall, 17 clinical and demographic variables such as the age at diagnosis, gender, serum creatinine and C-reactive protein levels, the type of ANCA, and the involvement of various organ systems were used to create a model for categorizing patients into different clusters.
- The median follow-up duration was 4.2 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Five distinct clusters were identified in ANCA-associated vasculitis; three had significant kidney involvement (the severe kidney cluster, myeloperoxidase-ANCA-positive kidney cluster, and proteinase 3-ANCA-positive kidney cluster) and two had minimal kidney involvement (young respiratory cluster and inflammatory multisystem cluster).
- The clusters with significant kidney involvement were associated with poorer outcomes, including a higher risk for kidney failure and death. The severe kidney cluster had the poorest prognosis, with mortality and the rate of end-stage kidney failure being 30.5% and 41.6%, respectively.
- The young respiratory cluster, characterized by predominant ear-nose-throat involvement and low systemic inflammation, showed the best prognostic outcomes.
- This cluster membership model showed a greater predictive accuracy for patient and kidney survival than traditional methods based on clinical diagnosis or ANCA specificity.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the necessity of recognizing severe kidney disease at the time of diagnosis as an indicator of poor outcome, thereby necessitating intensified treatment approaches,” experts from the Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension), Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, wrote in an accompanying editorial published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Karl Gisslander, Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, and was published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on estimated glomerular filtration rate recovery in clusters with kidney disease were lacking. Populations from East Asia, where myeloperoxidase-ANCA positivity is more prevalent, were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the European Joint Programme on Rare Diseases. Some authors declared serving on advisory boards or receiving grants, contracts, travel support, consulting fees, payments, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A data-driven subclassification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis has identified five distinct clusters with varying degrees of kidney involvement and systemic inflammation, offering insights into improved patient stratification and treatment approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- ANCA-associated vasculitis is a rare and complex autoimmune disease that is traditionally classified into granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
- Researchers employed advanced artificial intelligence and big data techniques to identify phenotypically distinct subgroups of ANCA-associated vasculitis and developed a classification system using real-world patient data from the Federated Vasculitis Registry consortium.
- They included 3868 patients diagnosed with ANCA-associated vasculitis between November 1, 1966, and March 1, 2023 (mean age at diagnosis, 57.2 years; 51.9% men), across six European vasculitis registries; while a majority of patients (62.9%) were diagnosed with GPA, the remaining 37.1% were diagnosed with MPA.
- Overall, 17 clinical and demographic variables such as the age at diagnosis, gender, serum creatinine and C-reactive protein levels, the type of ANCA, and the involvement of various organ systems were used to create a model for categorizing patients into different clusters.
- The median follow-up duration was 4.2 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Five distinct clusters were identified in ANCA-associated vasculitis; three had significant kidney involvement (the severe kidney cluster, myeloperoxidase-ANCA-positive kidney cluster, and proteinase 3-ANCA-positive kidney cluster) and two had minimal kidney involvement (young respiratory cluster and inflammatory multisystem cluster).
- The clusters with significant kidney involvement were associated with poorer outcomes, including a higher risk for kidney failure and death. The severe kidney cluster had the poorest prognosis, with mortality and the rate of end-stage kidney failure being 30.5% and 41.6%, respectively.
- The young respiratory cluster, characterized by predominant ear-nose-throat involvement and low systemic inflammation, showed the best prognostic outcomes.
- This cluster membership model showed a greater predictive accuracy for patient and kidney survival than traditional methods based on clinical diagnosis or ANCA specificity.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the necessity of recognizing severe kidney disease at the time of diagnosis as an indicator of poor outcome, thereby necessitating intensified treatment approaches,” experts from the Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension), Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, wrote in an accompanying editorial published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Karl Gisslander, Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, and was published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on estimated glomerular filtration rate recovery in clusters with kidney disease were lacking. Populations from East Asia, where myeloperoxidase-ANCA positivity is more prevalent, were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the European Joint Programme on Rare Diseases. Some authors declared serving on advisory boards or receiving grants, contracts, travel support, consulting fees, payments, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A data-driven subclassification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis has identified five distinct clusters with varying degrees of kidney involvement and systemic inflammation, offering insights into improved patient stratification and treatment approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- ANCA-associated vasculitis is a rare and complex autoimmune disease that is traditionally classified into granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA).
- Researchers employed advanced artificial intelligence and big data techniques to identify phenotypically distinct subgroups of ANCA-associated vasculitis and developed a classification system using real-world patient data from the Federated Vasculitis Registry consortium.
- They included 3868 patients diagnosed with ANCA-associated vasculitis between November 1, 1966, and March 1, 2023 (mean age at diagnosis, 57.2 years; 51.9% men), across six European vasculitis registries; while a majority of patients (62.9%) were diagnosed with GPA, the remaining 37.1% were diagnosed with MPA.
- Overall, 17 clinical and demographic variables such as the age at diagnosis, gender, serum creatinine and C-reactive protein levels, the type of ANCA, and the involvement of various organ systems were used to create a model for categorizing patients into different clusters.
- The median follow-up duration was 4.2 years.
TAKEAWAY:
- Five distinct clusters were identified in ANCA-associated vasculitis; three had significant kidney involvement (the severe kidney cluster, myeloperoxidase-ANCA-positive kidney cluster, and proteinase 3-ANCA-positive kidney cluster) and two had minimal kidney involvement (young respiratory cluster and inflammatory multisystem cluster).
- The clusters with significant kidney involvement were associated with poorer outcomes, including a higher risk for kidney failure and death. The severe kidney cluster had the poorest prognosis, with mortality and the rate of end-stage kidney failure being 30.5% and 41.6%, respectively.
- The young respiratory cluster, characterized by predominant ear-nose-throat involvement and low systemic inflammation, showed the best prognostic outcomes.
- This cluster membership model showed a greater predictive accuracy for patient and kidney survival than traditional methods based on clinical diagnosis or ANCA specificity.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings highlight the necessity of recognizing severe kidney disease at the time of diagnosis as an indicator of poor outcome, thereby necessitating intensified treatment approaches,” experts from the Department of Internal Medicine IV (Nephrology and Hypertension), Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, wrote in an accompanying editorial published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Karl Gisslander, Department of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, and was published online on August 22, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Data on estimated glomerular filtration rate recovery in clusters with kidney disease were lacking. Populations from East Asia, where myeloperoxidase-ANCA positivity is more prevalent, were not included.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the European Joint Programme on Rare Diseases. Some authors declared serving on advisory boards or receiving grants, contracts, travel support, consulting fees, payments, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies and other institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.