User login
Moms’ cooing swapped with morphine for newborns in withdrawal
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Four years ago, Atrium Health, in Charlotte, N.C., embarked on a dramatic change in how it cares for newborns exposed to opioids in the womb.
Until then, most of the 700 or so babies who underwent opioid withdrawal each year in the hospital system spent their first weeks in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), isolated from their parents and treated with regular doses of morphine to ease their symptoms.
Now, most babies stay in the hospital for just a few days under a new approach called Eat, Sleep, Console. These young patients stay in private rooms where they can bond with their parents and volunteer caregivers. The usual course of treatment is no longer extended therapy with opioid replacements. Instead, mothers are encouraged to stay overnight and are taught how to sooth their babies with swaddling, rocking, and cooing.
As a result, the average length of stay for newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) has dropped from 12 days to 6. Use of morphine has fallen by 79%, from 2.25 to 0.45 mg/kg per stay, according to results of a quality improvement pilot project at one of Atrium’s community hospitals.
Similar outcomes from other hospitals around the country have led to widespread uptake of Eat, Sleep, Console since its advent in 2017. That year, according to federal data, seven newborns were diagnosed with NAS for every 1,000 births.
Advocates say the family-centric model helps parents feel less stigmatized and more confident in their ability to care for their babies, who can have symptoms such as irritability and difficulty feeding for months.
The approach “really empowers families to do what they do best, which is take care of each other,” Douglas Dodds, MD, a pediatrician who led the effort at Atrium, told this news organization.
Questioning the old protocols
Numerous state perinatal collaboratives, hospital associations, and health systems say the program is the new standard of care for infants with NAS and neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome (NOWS).
Twenty-six hospitals have adopted Eat, Sleep, Console as part of a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health and a program called Advancing Clinical Trials in Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome (ACT NOW). Researchers are comparing the approach to previous care protocols in regard to 12 outcomes, including time to medical readiness for discharge, frequency of opioid replacement therapy, and safety problems, such as seizures during treatment.
The transition has been swift. Less than a decade ago, most hospitals used the Finnegan Neonatal Abstinence Scoring System, which was developed in the 1970s to assess babies whose mothers had used heroin during pregnancy.
The Finnegan score entails monitoring babies every 3 hours for 21 symptoms, including high-pitched crying, sneezing, gastrointestinal problems, and yawning. If a baby scores an 8 or more three times in a row, most protocols using the traditional Finnegan approach recommend that providers move infants to an NICU, where they receive morphine or methadone. Once opioid replacement therapy is started, the protocols require a gradual weaning that lasts 3-4 weeks.
As the opioid epidemic grew and NICUs around the country began to fill with babies experiencing NAS or NOW, some clinicians began to question the Finnegan-driven approach.
“You have these miserable babies who are going through this really tough experience, and our first move is to separate them from their moms,” said Matthew Grossman, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Yale New Haven Children’s Hospital, New Haven, Conn., who created Eat, Sleep, Console.
Dr. Grossman, associate professor and vice chair for quality in the department of pediatrics at Yale University, said he noticed that when mothers stayed overnight with their babies, the infants tended to have fewer withdrawal symptoms. Indeed, previous studies had demonstrated the benefits of breastfeeding and allowing mothers and babies to share a room.
“If you think of mom as a medicine, then you can’t put the baby in a unit where the mom can’t be there,” Dr. Grossman told this news organization. “It would be like taking a kid with pneumonia and putting him in a unit that doesn’t have antibiotics.”
Despite its prominence, the Finnegan score has never been validated for guiding the treatment of NAS. In addition, Finnegan scores can be inconsistent, and the assessment requires disturbing an infant to check signs such as its startle reflex, which, as Dr. Grossman and his fellow researchers pointed out, flies in the face of American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations to prioritize swaddling and minimize stimulation for infants with NAS.
By contrast, Eat, Sleep, Console offers a simplified assessment. Interventions are called for if a baby eats less than an ounce of food at a time/does not breastfeed, sleeps less than an hour at a stretch, or takes more than 10 minutes to be consoled. After nonpharmacologic interventions have been tried, doses of medication are used as needed. Babies who are doing well can be discharged in as few as 4 days.
Quashing bias against parents with substance abuse disorder
Even with the promise of shorter stays and better care, switching to nonpharmacologic care presents hurdles for hospitals. Among these is a lack of physical space for mothers to room with their babies in a quiet environment.
“In many community hospitals, the only place for infants to go is a neonatal intensive care unit, outside of the newborn nursery,” said Stephen Patrick, MD, MPH, associate professor and director of the Center for Child Health Policy at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., who researches stigma associated with opioid use during pregnancy.
Administrators at SSM St. Mary’s Hospital in St. Louis initially balked at providing private rooms for mothers and their babies with NAS and NOWS, according to Kimberly Spence, MD, a neonatologist at SSM Health. She said the initial plan was to put the babies in a busy, brightly lit nursery.
But resistance waned as the hospital convinced health plans to pay for private rooms for the 5-7 days it typically takes a baby to go through withdrawal, said Dr. Spence, associate professor of pediatrics at Saint Louis University.
“We were able to provide enough data that this is evidence-based medicine and babies do better with their moms, and that ethically, this is the right thing to do, to reduce transfers to an NICU,” she said.
In addition, news stories about the family-centric approach and shorter stays for infants, along with SSM’s launch of an outpatient clinic to treat pregnant women with opioid use disorder, helped the system to attract more patients and increase its market share, said Dr. Spence.
Another challenge was getting physicians and nurses to set aside any judgments of parents with substance abuse disorder, according to Dr. Grossman and others.
“A lot of faculty and staff on the medical team didn’t feel like we should trust moms with their babies’ medical care” at SSM, Dr. Spence said.
Some hospitals conduct anti-bias training to teach providers that substance abuse is a disease that deserves proper medical treatment and not the moral failing of a patient. Such education may involve explaining that babies’ outcomes are improved when women undergo treatment with methadone or buprenorphine during pregnancy, even though use of those medications does pose a risk of NAS.
Creating a system that supports parents with substance abuse disorders may help to change perceptions. At Atrium Health, some staff members now enjoy working with these families because they can make a profound impact, Dr. Dodds said. He said they’ve learned that families suffering from substance abuse disorder “are not that different than any other family.”
Dr. Dodds, Dr. Patrick, Dr. Spence, and Dr. Grossman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart health poor for many U.S. children
U.S. children appear to be failing an important test – of their hearts, not minds.
New research from the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago shows that heart health is a concern for many long before adulthood because fewer than one-third of children aged 2-19 years scored highly on the American Heart Association’s checklist for ideal cardiovascular fitness.
“This study gives us a new baseline for children’s heart health in the United States,” said Amanda Perak, MD, pediatric cardiologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a coauthor of the study.
Dr. Perak and colleagues published their findings in the journal Circulation.
The researchers identified 9888 children who completed the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2013 and 2018. They analyzed the available data using the AHA’s Life’s Essential 8 – a 100-point assessment of eight predictors for measuring heart health, including sleep, nicotine exposure, and blood glucose.
Data for only three metrics were available for all children in the study: diet, physical activity, and body mass index. As children aged, more metrics were averaged to obtain the overall cardiovascular health score. For instance, cholesterol/lipid levels become available at age 6 years, and blood pressure can be measured starting at age 8 years.
Only 2.2% of children in the study had optimal heart health, according to the Life’s Essential 8 scoring system, which spans poor (0-49), moderate (50-79), and high (80-100). Fewer than one in three (29.1%) overall had high scores, and scores worsened with age.
In the 2- to 5-year age group, over half (56.5%) of the children had good heart health. However, only one-third (33.5%) of 6- to 11-year-olds scored highly. Meanwhile, only 14% of adolescents had good heart scores, Dr. Perak’s group found.
Heart health scores based on diet were lowest for every age group. In the youngest age group, the average cardiovascular health (CVH) score was about 61. In the 12- to 19-year age group, however, the average CVH score decreased to 28.5, the lowest measured score for any group in the study.
With such worrisome diet scores for the 12- to 19-year-old group, public health policies need to focus on changes, like removing sugar-sweetened beverage options from schools, according to Joseph Mahgerefteh, MD, director of preventive cardiology at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center, New York. He added that parents and their children also have a role to play.
“Some of our teenagers forget they can drink water when they are thirsty, and it is not necessary to drink sugar-sweetened beverages for thirst,” Dr. Mahgerefteh, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “Fresh vegetable intake is so low to a degree that some of our patients refuse to have any type of vegetable in their diet.”
“As a physician community caring for these patients, we need to be much more aggressive with our counseling and referral of these patients,” added Barry Love, MD, director of the congenital cardiac catheterization program at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center. “These youngsters will inevitably encounter the effect of these conditions – coronary artery disease and stroke – at a much earlier adult age.”
Dr. Perak, Dr. Mahgerefteh, and Dr. Love reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. children appear to be failing an important test – of their hearts, not minds.
New research from the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago shows that heart health is a concern for many long before adulthood because fewer than one-third of children aged 2-19 years scored highly on the American Heart Association’s checklist for ideal cardiovascular fitness.
“This study gives us a new baseline for children’s heart health in the United States,” said Amanda Perak, MD, pediatric cardiologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a coauthor of the study.
Dr. Perak and colleagues published their findings in the journal Circulation.
The researchers identified 9888 children who completed the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2013 and 2018. They analyzed the available data using the AHA’s Life’s Essential 8 – a 100-point assessment of eight predictors for measuring heart health, including sleep, nicotine exposure, and blood glucose.
Data for only three metrics were available for all children in the study: diet, physical activity, and body mass index. As children aged, more metrics were averaged to obtain the overall cardiovascular health score. For instance, cholesterol/lipid levels become available at age 6 years, and blood pressure can be measured starting at age 8 years.
Only 2.2% of children in the study had optimal heart health, according to the Life’s Essential 8 scoring system, which spans poor (0-49), moderate (50-79), and high (80-100). Fewer than one in three (29.1%) overall had high scores, and scores worsened with age.
In the 2- to 5-year age group, over half (56.5%) of the children had good heart health. However, only one-third (33.5%) of 6- to 11-year-olds scored highly. Meanwhile, only 14% of adolescents had good heart scores, Dr. Perak’s group found.
Heart health scores based on diet were lowest for every age group. In the youngest age group, the average cardiovascular health (CVH) score was about 61. In the 12- to 19-year age group, however, the average CVH score decreased to 28.5, the lowest measured score for any group in the study.
With such worrisome diet scores for the 12- to 19-year-old group, public health policies need to focus on changes, like removing sugar-sweetened beverage options from schools, according to Joseph Mahgerefteh, MD, director of preventive cardiology at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center, New York. He added that parents and their children also have a role to play.
“Some of our teenagers forget they can drink water when they are thirsty, and it is not necessary to drink sugar-sweetened beverages for thirst,” Dr. Mahgerefteh, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “Fresh vegetable intake is so low to a degree that some of our patients refuse to have any type of vegetable in their diet.”
“As a physician community caring for these patients, we need to be much more aggressive with our counseling and referral of these patients,” added Barry Love, MD, director of the congenital cardiac catheterization program at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center. “These youngsters will inevitably encounter the effect of these conditions – coronary artery disease and stroke – at a much earlier adult age.”
Dr. Perak, Dr. Mahgerefteh, and Dr. Love reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
U.S. children appear to be failing an important test – of their hearts, not minds.
New research from the Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago shows that heart health is a concern for many long before adulthood because fewer than one-third of children aged 2-19 years scored highly on the American Heart Association’s checklist for ideal cardiovascular fitness.
“This study gives us a new baseline for children’s heart health in the United States,” said Amanda Perak, MD, pediatric cardiologist at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and a coauthor of the study.
Dr. Perak and colleagues published their findings in the journal Circulation.
The researchers identified 9888 children who completed the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2013 and 2018. They analyzed the available data using the AHA’s Life’s Essential 8 – a 100-point assessment of eight predictors for measuring heart health, including sleep, nicotine exposure, and blood glucose.
Data for only three metrics were available for all children in the study: diet, physical activity, and body mass index. As children aged, more metrics were averaged to obtain the overall cardiovascular health score. For instance, cholesterol/lipid levels become available at age 6 years, and blood pressure can be measured starting at age 8 years.
Only 2.2% of children in the study had optimal heart health, according to the Life’s Essential 8 scoring system, which spans poor (0-49), moderate (50-79), and high (80-100). Fewer than one in three (29.1%) overall had high scores, and scores worsened with age.
In the 2- to 5-year age group, over half (56.5%) of the children had good heart health. However, only one-third (33.5%) of 6- to 11-year-olds scored highly. Meanwhile, only 14% of adolescents had good heart scores, Dr. Perak’s group found.
Heart health scores based on diet were lowest for every age group. In the youngest age group, the average cardiovascular health (CVH) score was about 61. In the 12- to 19-year age group, however, the average CVH score decreased to 28.5, the lowest measured score for any group in the study.
With such worrisome diet scores for the 12- to 19-year-old group, public health policies need to focus on changes, like removing sugar-sweetened beverage options from schools, according to Joseph Mahgerefteh, MD, director of preventive cardiology at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center, New York. He added that parents and their children also have a role to play.
“Some of our teenagers forget they can drink water when they are thirsty, and it is not necessary to drink sugar-sweetened beverages for thirst,” Dr. Mahgerefteh, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. “Fresh vegetable intake is so low to a degree that some of our patients refuse to have any type of vegetable in their diet.”
“As a physician community caring for these patients, we need to be much more aggressive with our counseling and referral of these patients,” added Barry Love, MD, director of the congenital cardiac catheterization program at the Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Heart Center. “These youngsters will inevitably encounter the effect of these conditions – coronary artery disease and stroke – at a much earlier adult age.”
Dr. Perak, Dr. Mahgerefteh, and Dr. Love reported no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Clinical characteristics of recurrent RIME elucidated in chart review
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
INDIANAPOLIS – , in a single-center retrospective study. In addition, 71% of patients with recurrent disease experienced 1-2 recurrences – episodes that were generally milder and occurred at variable intervals.
Those are among key findings from the study of 50 patients with RIME, presented by Catherina X. Pan at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Reactive infectious mucocutaneous eruption (RIME) is a novel term encompassing an array of rare, parainfectious mucositis diseases, noted Ms. Pan, a fourth-year medical student at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Previously known as Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced rash and mucositis (MIRM), common clinical characteristics of RIME include less than 10% body surface area involvement of polymorphic skin lesions (vesiculobullous or targetoid macules/papules); erosive oral, genital, and/or ocular mucositis involving more than two sites, and evidence of prior infection including but not limited to upper respiratory infection, fever, and cough.
In addition to M. pneumoniae, other pathogens have been implicated, she said. “While the underlying etiology of the disease is not entirely clear, it’s become increasingly known that RIME tends to recur in a subset of patients.”
A cohort study of 13 patients with RIME found that Black race, male sex, and older age were predominant among the five patients who developed recurrent disease.
The estimated recurrence rate is between 8% and 38%, but the clinical characteristics of patients who develop recurrent RIME tend to be poorly understood, Ms. Pan said.
Along with her mentor, Sadaf Hussain, MD, of the department of dermatology at Boston Children’s Hospital, Ms. Pan conducted a retrospective chart review to characterize the clinical history and course of disease in patients diagnosed with recurrent RIME. They extracted data between January of 2000 and March of 2022 using ICD-10 codes used by board-certified dermatologists at Boston Children’s Hospital, as well as a text search for RIME or MIRM in the dermatology notes. Patients were included if they had a RIME/MIRM diagnosis by a board-certified dermatologist and/or infection on PCR/serology and mucositis involvement with limited skin involvement.
The study population included 50 patients: 24 with recurrent RIME and 26 with isolated RIME. The majority (66%) were male, and the mean age of RIME onset was between 11 and 12 years old, which is up to two years younger than previously reported in the case series of 13 patients. Most of the study participants (79%) were White, but there were no significant differences in patients who had recurrent RIME and those who had isolated RIME in terms of age, sex, or race.
Isolated vs. recurrent RIME
However, compared with patients who had isolated RIME, a greater proportion of those with recurrent RIME had a history of atopic disease (46% vs. 23%, respectively; P = .136), as well as a history of tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy (25% vs. 4%; P = .045). “This has not been previously observed, but it may generate a hypothesis that patients with a history of frequent infection as well as amplified immune responses may be associated with disease recurrence,” Ms. Pan said.
The average number of episodes among patients with recurrent RIME was 3.5 and the interval between episodes was variable, at a mean of 10.2 months. Ms. Pan reported that 71% of recurrent RIME patients experienced 1-2 episodes, although one patient experienced 9 episodes.
Clinically, episodes among all patients with RIME were characterized by infectious prodromal symptoms (69%), oral lesions (95%), ocular lesions (60%), genital lesions (41%) and cutaneous lesions (40%). However, RIME recurrences were less severe and more atypical, with 49% involving only one mucosal surface and 29% involving two mucosal surfaces. Also, except for oral lesions, rates of infectious prodromal symptoms and other lesions significantly decreased among recurrences compared with initial RIME.
“Notably, we found that M. pneumoniae was the most common known cause of RIME, particularly among the initial episodes,” Ms. Pan said. “However, 61% of recurrent RIME episodes did not have a known cause in terms of infectious etiology. And, concordant with prior studies, we also found decreased severity [of RIME recurrences] as indicated by decreased rates of emergency department presentation, hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization.”
In other findings, psychiatric complications such as anxiety and depression followed the onset of RIME in 33% of those with recurrent disease and 22% of those with isolated disease. In addition, the three most common treatments among all 50 patients were systemic steroids, topical steroids, and M. pneumoniae-specific antibiotics.
“While RIME is considered as typically milder than Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis with low mortality rates, it can lead to severe complications including conjunctival shrinkage, corneal ulceration and scarring, blindness, and oral, ocular, urogenital synechiae,” Ms. Pan noted. “Increased use of corticosteroids and steroid-sparing agents such as IVIG have also been observed. Multidisciplinary care with ophthalmology, urology, and mental health services is critical.”
She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its retrospective, single-center design, and the possibility that milder cases may have been excluded due to a lack of accurate diagnosis or referral.
Carrie C. Coughlin, MD, who was asked to comment on the study results, pointed out that nearly half (24) of patients in the cohort experienced recurrent RIME. “This is a high proportion, suggesting counseling about the possibility of recurrence is more important than previously thought,” said Dr. Coughlin, director of the section of pediatric dermatology Washington University/St. Louis Children’s Hospital.
“Fortunately, recurrent cases tended to be less severe. However, many patients had more than one recurrence, making this challenging for affected patients.”
The researchers reported having no financial disclosures. Dr. Coughlin is on the board of the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) and the International Immunosuppression and Transplant Skin Cancer Collaborative.
AT SPD 2022
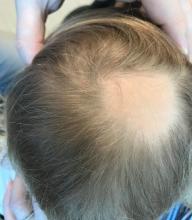
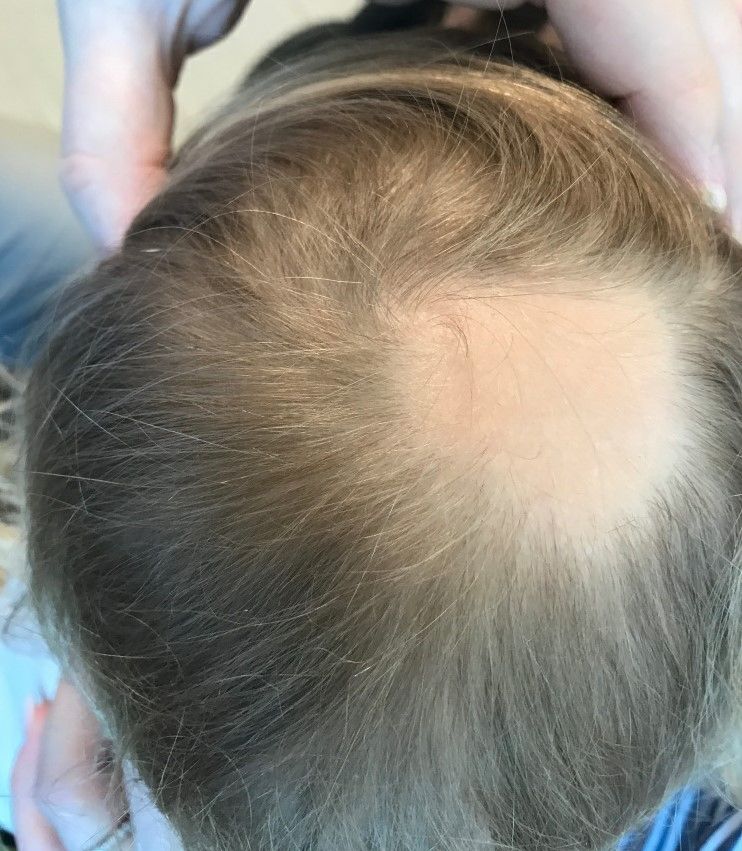
A toddler presents with patchy hair loss
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Given the history of sudden hair loss, with the exam revealing a well-circumscribed patch of focal alopecia without cutaneous inflammation, hairs with a narrow base and broad distal shaft, the diagnosis is alopecia areata (AA).
Alopecia areata (AA) is a nonscarring alopecia, within a set of diseases characterized by the preservation of hair follicles and therefore the potential for future hair regrowth.1 AA is believed to be caused by a breakdown of the immune-privileged nature of hair follicles, resulting in T-lymphocytes targeting the hair follicle directly, shifting follicles to early catagen or telogen phase, but sparing follicular stem cells, thereby allowing the follicle to regenerate in the future.1-3 Risk factors include family history of AA, thyroid disorders, as well as iron and vitamin D deficiency.4,5 It characteristically presents with focal, well-demarcated patches of hair loss in the scalp, typically with background skin normal to slightly pink.3,6 Exam can show “exclamation point” hairs consisting of hairs that are narrow at their base and wide at the distal end.3,7 Patients may also exhibit eyebrow and eyelash loss as well as nail changes including nail pitting and splitting.8 Diagnosis is typically made clinically but is supported by a positive hair pull test, where hairs are pulled from the periphery of an alopecic lesion; the presence of greater than 10% of hairs plucked from the scalp indicates a positive result.9,10
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of AA includes other nonscarring alopecias such as trichotillomania and telogen effluvium. Other possible diagnoses include lichen planopilaris and tinea capitis.
Trichotillomania results in irregularly bordered hair loss and broken hairs of different lengths because of an internal urge to remove one’s hair, resulting in nonscarring alopecia. It can be associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder, anxiety, or other body-altering behaviors like skin picking and nail biting (characterized as body-focused repetitive behavior disorders). Treatments include reassurance and education, behavior modification, or systemic therapy including tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs. Toddlers can engage in hair pulling behavior and trichotillomania can be difficult to differentiate from AA. However, the absence of broken hairs of varying lengths makes trichotillomania less likely in this patient.
Telogen effluvium is another form of nonscarring alopecia that presents as diffuse hair thinning across the entire scalp in response to acute psychological or physiological stress, hormonal changes, certain medications, systemic illness, or nutritional deficiency. The timing between the triggering event and hair loss can vary from weeks to months. Diagnosis requires detailed history-taking and may include evaluation for endocrinologic hair thinning (e.g. thyroid function tests) to identify reversible causes. Treatment involves directing therapy to the underlying etiology and most cases of telogen effluvium are self-limited. The presence of a well-circumscribed patch of hair loss in this patient makes AA more likely.
Lichen planopilaris (LPP) is a scarring, irreversible alopecia caused by T-lymphocytes attacking follicular hair stem cells. It is characterized by hair loss, pruritus, burning pain, scalp scaling, and multifocal scarring. Exam shows patches of alopecia with loss of follicular ostia centrally and perifollicular scale and erythema at the borders. Diagnosis is aided by biopsy of the affected scalp. Treatment of LPP requires the use of potent and superpotent topical corticosteroids and intralesional corticosteroids to decrease scalp inflammation and prevent further progression. The presence of follicular ostia and absence of perifollicular scale in this patient makes LPP highly unlikely.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp caused by dermatophytes including Trychophyton tonsurans and Microsporum canis. It presents with patches of alopecia with overlying scale and broken hairs and can have associated cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis can involve skin scraping and KOH prep to visualize branching hyphae as well as fungal culture to identify the causative organism. Because dermatophytes in tinea capitis invade hair follicles, topical antifungals are ineffective because of their lack of penetration. Therefore, systemic antifungals including oral terbinafine and griseofulvin are considered first-line agents for treatment.
What’s the management plan?
The diagnosis of AA is usually a clinical one, though assessment of alternative diagnoses is appropriate dependent on signs and symptoms. Workup of AA can include thyroid studies because of the association with autoimmune thyroid disease, though studies suggest limited screening benefits in children.11 Given its variable and unpredictable course, management can include “watchful waiting” because of its potential for spontaneous remission.6 For limited patchy loss, active treatment with mid to superpotent topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in older children and adolescents is reasonable.12 Other treatment options include topical or low-dose oral minoxidil and immunotherapy with diphenylcyclopropenone or squaric acid (inducing an allergic contact dermatitis).12 Management of therapies for more extensive AA is evolving, with ongoing studies of oral JAK-inhibitors and biologic agents.12,13
Our patient was started on topical fluocinonide 0.05% solution and achieved good disease control and hair regrowth over the course of 3 months.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Haft is an inflammatory skin disease fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at the university and Rady Children’s Hospital. They had no disclosures.
References
1. Bernardez C et al. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2015;106(3):158-67.
2. Rajabi F et al. Br J Dermatol. 2018;179(5):1033-48.
3. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):1-12.
4. Lee S et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019;80(2):466-77 e16.
5. MacLean KJ and Tidman MJ. Practitioner. 2013;257(1764):29-32, 3.
6. Pratt CH et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17011.
7. Gilhar A et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(16):1515-25.
8. Wyrwich KW et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(5):725-32.
9. Spano F and Donovan JC. Can Fam Physician. 2015;61(9):751-5.
10. Mounsey AL and Reed SW. Am Fam Physician. 2009;80(4):356-62.
11. Hordinsky MK. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2015;17(2):44-6.
12. Strazzulla LC et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(1):15-24.
13. Zhou C et al. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2021;61(3):403-23.
Examination findings of the scalp demonstrate a well-circumscribed alopecic patch on the vertex scalp without erythema or scale. Closer inspection of the patch with magnification or 'dermoscopy' reveals hair follicle ostia and hairs that are broader distally and narrower at their base. Nails and rest of the skin exam are unremarkable.
COVID-19 infection late in pregnancy linked to sevenfold risk of preterm birth
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Pregnant women who get infected with SARS-CoV-2 in their third trimester are almost three times as likely to have a preterm birth, while infection after 34 weeks’ gestation raises this risk sevenfold, based on the largest matched population-based cohort study published to date.
These findings support previous studies, underscoring the need for pregnant women and their families to take preventive measures against infection, lead author Noga Fallach, MA, of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, Tel Aviv, and colleagues reported.
Past research has suggested that COVID-19 may cause low birth weights and preterm birth in pregnant women, but those studies didn’t report outcomes for each trimester, the investigators wrote in PLoS ONE, noting that “timing of viral infection during fetal development may affect birth and other health outcomes.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators looked back at data from 2,703 pregnant women in Israel who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 from Feb. 21, 2020, to July 2, 2021. Pregnancy outcomes in these women were compared with outcomes in an equal number of uninfected pregnant women. Vaccination status was not reported.
Comparing the two groups showed that catching COVID-19 in the third trimester was linked with nearly triple the risk of preterm birth (odds ratio, 2.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.63-4.67), and more than quadruple the risk if COVID-19 symptoms were present (OR, 4.28; 95% CI, 1.94-9.41). Women who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 after 34 weeks’ gestation were seven times more likely than uninfected women to deliver early (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 2.44-20.61).
Pregnant women who caught COVID-19 in the first two trimesters were not significantly more likely to have a preterm birth. Infection was not associated with abnormally low birth rates, or pregnancy loss, in any trimester.
Tal Patalon, MD, coauthor and head of the Kahn-Sagol-Maccabi Research and Innovation Center, focused on these more optimistic findings in an interview.
“The results are encouraging, and reassuring that COVID-19 infection during pregnancy is not associated with any type of pregnancy loss,” Dr. Patalon said.
She also pointed out that the women in the study were infected with SARS-CoV-2 variants that are no longer common.
“It should be remembered that the research group tested the COVID-19 pre-Delta variants, and does not refer to the dominant variant today, which is Omicron,” Dr. Patalon said.
Still, the investigators concluded that the “results underline the importance of preventive measures taken against SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women and their families.”
Sonja A. Rasmussen, MD, of the University of Florida, Gainesville, said that the issue with out-of-date variants in published research has been one of the “real challenges” in studying the ever-evolving COVID-19 pandemic; however, it’s not a good enough reason to dismiss this study.
“I think at this point, we need to assume that it applies to Omicron too,” Dr. Rasmussen said, noting that other respiratory viruses, like influenza, have also been shown to increase the risk of preterm birth when contracted in late pregnancy.
While the present findings highlight the risk of infection in the third trimester, Dr. Rasmussen advised women in all stages of pregnancy to protect themselves against COVID-19, based on the knowledge that illness in a mother can affect normal growth and development in a fetus, even if it doesn’t lead to preterm birth.
“A mom getting sick during pregnancy is not good for the baby,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “The baby’s really dependent on the mom. So you want that baby to have good nutrition throughout the pregnancy. It’s just as important earlier on as later. And you want that baby to get good oxygenation no matter what time [in the pregnancy]. I know that people want a little bit of a break [from preventive measures]. But I would emphasize that if you’re pregnant, we do all sorts of things during pregnancy to make sure that our babies are safe and healthy, and I would continue that for the whole pregnancy.”
Specifically, Dr. Rasmussen advised social distancing, use of an N95 mask, and vaccination. Getting vaccinated during pregnancy helps newborns fight off infection until 6 months of age, she added, when they become eligible for vaccination themselves. This added benefit was recently reported in a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine , for which Dr. Rasmussen cowrote an editorial .
“Vaccines have been approved for 6 months and older,” Dr. Rasmussen said. “But what do you do in those first 6 months of life? That’s a high-risk time for kids.”
Despite these risks, convincing pregnant women to get vaccinated remains a key challenge for health care providers, according to Dr. Rasmussen, even with an abundance of safety data. “Early on [in the pandemic], we said we didn’t know a lot about risks. We knew that other vaccines were safe during pregnancy, but we didn’t have a lot of information about a COVID-19 vaccine. But now we have a lot of data on safety during pregnancy, and these vaccines appear to be completely safe, based on the information we have. There have been many, many pregnant women vaccinated in the United States and in other countries.”
For reluctant expecting mothers, Dr. Rasmussen offered some words of advice: “I know that you worry about anything you do when you’re pregnant. But this is something that you can do to help your baby – now, to make a preterm birth less likely, and later, after the baby is born.
“The most important thing is for the pregnant person to hear this [vaccine recommendation] from their doctor,” she added. “If they’re going to listen to anybody, they’re going to listen to their physician. That’s what the data have shown for a long time.”
The investigators and Dr. Rasmussen disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM PLOS ONE
Pediatric obesity treatment options: Beyond lifestyle modification
Pediatric obesity is a serious problem, not only in the United States but worldwide. Unfortunately, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the epidemic of childhood obesity. Solutions for treating the millions of children and adolescents with obesity are desperately needed because prevention efforts over the past several decades have not been sufficient in slowing the steady rise in obesity prevalence.
Lifestyle modification, including dietary changes, increases in activity, and behavioral modification, are the cornerstone of any obesity treatment, but they alone are not powerful enough to treat obesity by itself in the vast majority of children and adolescents. This is because obesity is not a lifestyle choice; rather, it is a disease, and a disease that has a tremendous amount of biology driving individuals toward weight gain and the propensity toward weight regain if weight is lost.
Fortunately, the tools to treat the underlying biology driving obesity are becoming safer, more effective, and more widely used every year. The two most effective biology-based treatments for pediatric obesity are antiobesity medications and bariatric surgery. These two treatments, when accompanied by lifestyle modification, have the potential to reduce not only body weight but also treat many other risk factors, such as prediabetes, diabetes, high blood pressure, poor cholesterol, liver disease, and sleep apnea, as well as others.
Rise in antiobesity medications
Antiobesity medications are developing at a rapid pace. Seven medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for adults, and three medications (phentermine, orlistat, and liraglutide) are now approved for children and adolescents.
The number of antiobesity medications for use in children and adolescents is expected to expand to five, with semaglutide and phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) both completing trials in adolescents in 2022. Each of these medications works by treating the biology that drives weight gain, whether it is decreasing impulsivity, reducing hunger and appetite hormone pathways, or improving energy regulation pathways. Weight loss at 1 year for currently FDA-approved medications in adolescents ranges from 3% to 6% on average, depending on the medications. The newer medications already FDA approved in adults that will soon, hopefully, be available in pediatrics result in 10%-16% weight loss on average.
A common parent and patient question regarding antiobesity medications is: “If I start an antiobesity medication, how long will I need to be on it?” The simple answer is: “Probably for the rest of your life.”
This can be a shock to hear, but obesity treatment is very similar to that of hypertension or diabetes. Using high blood pressure as an example: If a patient has high blood pressure (for example, 160/90 mm Hg), they will be prescribed a medication to treat it. Once blood pressure comes down to near-normal levels (for example, 120/80 mm Hg), a dose will be maintained, not removed, because that is the biological mediator keeping the blood pressure low. Removal of the medication would result in blood pressure going back to homeostasis (160/90 mm Hg in our example) in a short period of time).
The same can be said for obesity. For example, if a 16-year-old girl is prescribed liraglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, and loses 10% of her body weight at 1 year, that is great success. Why would we remove the medication that is treating the underlying biology causing successful weight loss?
In short, we would not want to do that. Even if our example patient only maintained that 10% initial weight loss, that would be very successful, just like someone maintaining their low blood pressure. As medications begin to develop at a rapid pace and become more available to pediatric patients, the messaging and conversation around anti-obesity medications must continue to focus on obesity being a biological disease and not a behavior for treatment to be effective and not stigmatized.
Bariatric surgery most effective treatment for pediatric obesity
Currently, the most effective treatment for pediatric obesity is bariatric surgery. The two most commonly used surgical procedures today are the sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Sleeve gastrectomy works by removing 75%-85% of the stomach and creating a new stomach, called a “sleeve.” Gastric bypass works by separating the stomach into two parts and connecting one part of the new stomach into the intestine.
Both surgeries are very effective at treating obesity in adolescents, with an average weight loss of 30%-35%. Surgery is not just a restrictive means of controlling body weight; it also changes key hormones for appetite and satiety that signal the brain. In fact, many of the same biological signals that are changed by surgery are the same signals being targeted by antiobesity medications. Long-term outcome of bariatric surgery in adolescents, provided by Teen-LABS, show it to be safe and maybe even more effective than in adults for treating diabetes and hypertension, with similar weight loss.
Does treatment outweigh the potential risks?
Although obesity surgery and antiobesity medications are more successful at treating obesity in children and adolescents than lifestyle medications, they do have some risks. Surgery, depending on the type of surgery, can cause nutritional deficiencies, reduce body mineral density, and is a life-changing medical procedure. Antiobesity medications, depending on the type, can cause nausea and vomiting and increase heart rate – and because they are relatively new, we do not fully understand the long-term impact of continued use past 1 year.
However, an important question to ask is: “Do the risks of obesity surgery and antiobesity medications outweigh the risk of having lifelong obesity?” The answer to me and many of my colleagues is: “Yes!” Although there are risks associated with the two best treatments for pediatric obesity, those risks under proper supervision of a medical professional far outweigh the risks of not properly treating obesity and allowing it to persist and get worse over many years to come. Obesity is a disease deeply rooted in biology, and we must use biology-based treatments to tackle this problem in children and adolescents, who deserve the best care and treatments possible.
Dr. Ryder is assistant professor of pediatrics and associate director of research, Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She reported receiving donations for clinical trials from Boehringer Ingelheim. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric obesity is a serious problem, not only in the United States but worldwide. Unfortunately, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the epidemic of childhood obesity. Solutions for treating the millions of children and adolescents with obesity are desperately needed because prevention efforts over the past several decades have not been sufficient in slowing the steady rise in obesity prevalence.
Lifestyle modification, including dietary changes, increases in activity, and behavioral modification, are the cornerstone of any obesity treatment, but they alone are not powerful enough to treat obesity by itself in the vast majority of children and adolescents. This is because obesity is not a lifestyle choice; rather, it is a disease, and a disease that has a tremendous amount of biology driving individuals toward weight gain and the propensity toward weight regain if weight is lost.
Fortunately, the tools to treat the underlying biology driving obesity are becoming safer, more effective, and more widely used every year. The two most effective biology-based treatments for pediatric obesity are antiobesity medications and bariatric surgery. These two treatments, when accompanied by lifestyle modification, have the potential to reduce not only body weight but also treat many other risk factors, such as prediabetes, diabetes, high blood pressure, poor cholesterol, liver disease, and sleep apnea, as well as others.
Rise in antiobesity medications
Antiobesity medications are developing at a rapid pace. Seven medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for adults, and three medications (phentermine, orlistat, and liraglutide) are now approved for children and adolescents.
The number of antiobesity medications for use in children and adolescents is expected to expand to five, with semaglutide and phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) both completing trials in adolescents in 2022. Each of these medications works by treating the biology that drives weight gain, whether it is decreasing impulsivity, reducing hunger and appetite hormone pathways, or improving energy regulation pathways. Weight loss at 1 year for currently FDA-approved medications in adolescents ranges from 3% to 6% on average, depending on the medications. The newer medications already FDA approved in adults that will soon, hopefully, be available in pediatrics result in 10%-16% weight loss on average.
A common parent and patient question regarding antiobesity medications is: “If I start an antiobesity medication, how long will I need to be on it?” The simple answer is: “Probably for the rest of your life.”
This can be a shock to hear, but obesity treatment is very similar to that of hypertension or diabetes. Using high blood pressure as an example: If a patient has high blood pressure (for example, 160/90 mm Hg), they will be prescribed a medication to treat it. Once blood pressure comes down to near-normal levels (for example, 120/80 mm Hg), a dose will be maintained, not removed, because that is the biological mediator keeping the blood pressure low. Removal of the medication would result in blood pressure going back to homeostasis (160/90 mm Hg in our example) in a short period of time).
The same can be said for obesity. For example, if a 16-year-old girl is prescribed liraglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, and loses 10% of her body weight at 1 year, that is great success. Why would we remove the medication that is treating the underlying biology causing successful weight loss?
In short, we would not want to do that. Even if our example patient only maintained that 10% initial weight loss, that would be very successful, just like someone maintaining their low blood pressure. As medications begin to develop at a rapid pace and become more available to pediatric patients, the messaging and conversation around anti-obesity medications must continue to focus on obesity being a biological disease and not a behavior for treatment to be effective and not stigmatized.
Bariatric surgery most effective treatment for pediatric obesity
Currently, the most effective treatment for pediatric obesity is bariatric surgery. The two most commonly used surgical procedures today are the sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Sleeve gastrectomy works by removing 75%-85% of the stomach and creating a new stomach, called a “sleeve.” Gastric bypass works by separating the stomach into two parts and connecting one part of the new stomach into the intestine.
Both surgeries are very effective at treating obesity in adolescents, with an average weight loss of 30%-35%. Surgery is not just a restrictive means of controlling body weight; it also changes key hormones for appetite and satiety that signal the brain. In fact, many of the same biological signals that are changed by surgery are the same signals being targeted by antiobesity medications. Long-term outcome of bariatric surgery in adolescents, provided by Teen-LABS, show it to be safe and maybe even more effective than in adults for treating diabetes and hypertension, with similar weight loss.
Does treatment outweigh the potential risks?
Although obesity surgery and antiobesity medications are more successful at treating obesity in children and adolescents than lifestyle medications, they do have some risks. Surgery, depending on the type of surgery, can cause nutritional deficiencies, reduce body mineral density, and is a life-changing medical procedure. Antiobesity medications, depending on the type, can cause nausea and vomiting and increase heart rate – and because they are relatively new, we do not fully understand the long-term impact of continued use past 1 year.
However, an important question to ask is: “Do the risks of obesity surgery and antiobesity medications outweigh the risk of having lifelong obesity?” The answer to me and many of my colleagues is: “Yes!” Although there are risks associated with the two best treatments for pediatric obesity, those risks under proper supervision of a medical professional far outweigh the risks of not properly treating obesity and allowing it to persist and get worse over many years to come. Obesity is a disease deeply rooted in biology, and we must use biology-based treatments to tackle this problem in children and adolescents, who deserve the best care and treatments possible.
Dr. Ryder is assistant professor of pediatrics and associate director of research, Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She reported receiving donations for clinical trials from Boehringer Ingelheim. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pediatric obesity is a serious problem, not only in the United States but worldwide. Unfortunately, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has worsened the epidemic of childhood obesity. Solutions for treating the millions of children and adolescents with obesity are desperately needed because prevention efforts over the past several decades have not been sufficient in slowing the steady rise in obesity prevalence.
Lifestyle modification, including dietary changes, increases in activity, and behavioral modification, are the cornerstone of any obesity treatment, but they alone are not powerful enough to treat obesity by itself in the vast majority of children and adolescents. This is because obesity is not a lifestyle choice; rather, it is a disease, and a disease that has a tremendous amount of biology driving individuals toward weight gain and the propensity toward weight regain if weight is lost.
Fortunately, the tools to treat the underlying biology driving obesity are becoming safer, more effective, and more widely used every year. The two most effective biology-based treatments for pediatric obesity are antiobesity medications and bariatric surgery. These two treatments, when accompanied by lifestyle modification, have the potential to reduce not only body weight but also treat many other risk factors, such as prediabetes, diabetes, high blood pressure, poor cholesterol, liver disease, and sleep apnea, as well as others.
Rise in antiobesity medications
Antiobesity medications are developing at a rapid pace. Seven medications have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for adults, and three medications (phentermine, orlistat, and liraglutide) are now approved for children and adolescents.
The number of antiobesity medications for use in children and adolescents is expected to expand to five, with semaglutide and phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia) both completing trials in adolescents in 2022. Each of these medications works by treating the biology that drives weight gain, whether it is decreasing impulsivity, reducing hunger and appetite hormone pathways, or improving energy regulation pathways. Weight loss at 1 year for currently FDA-approved medications in adolescents ranges from 3% to 6% on average, depending on the medications. The newer medications already FDA approved in adults that will soon, hopefully, be available in pediatrics result in 10%-16% weight loss on average.
A common parent and patient question regarding antiobesity medications is: “If I start an antiobesity medication, how long will I need to be on it?” The simple answer is: “Probably for the rest of your life.”
This can be a shock to hear, but obesity treatment is very similar to that of hypertension or diabetes. Using high blood pressure as an example: If a patient has high blood pressure (for example, 160/90 mm Hg), they will be prescribed a medication to treat it. Once blood pressure comes down to near-normal levels (for example, 120/80 mm Hg), a dose will be maintained, not removed, because that is the biological mediator keeping the blood pressure low. Removal of the medication would result in blood pressure going back to homeostasis (160/90 mm Hg in our example) in a short period of time).
The same can be said for obesity. For example, if a 16-year-old girl is prescribed liraglutide, a glucagonlike peptide–1 receptor agonist, and loses 10% of her body weight at 1 year, that is great success. Why would we remove the medication that is treating the underlying biology causing successful weight loss?
In short, we would not want to do that. Even if our example patient only maintained that 10% initial weight loss, that would be very successful, just like someone maintaining their low blood pressure. As medications begin to develop at a rapid pace and become more available to pediatric patients, the messaging and conversation around anti-obesity medications must continue to focus on obesity being a biological disease and not a behavior for treatment to be effective and not stigmatized.
Bariatric surgery most effective treatment for pediatric obesity
Currently, the most effective treatment for pediatric obesity is bariatric surgery. The two most commonly used surgical procedures today are the sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass. Sleeve gastrectomy works by removing 75%-85% of the stomach and creating a new stomach, called a “sleeve.” Gastric bypass works by separating the stomach into two parts and connecting one part of the new stomach into the intestine.
Both surgeries are very effective at treating obesity in adolescents, with an average weight loss of 30%-35%. Surgery is not just a restrictive means of controlling body weight; it also changes key hormones for appetite and satiety that signal the brain. In fact, many of the same biological signals that are changed by surgery are the same signals being targeted by antiobesity medications. Long-term outcome of bariatric surgery in adolescents, provided by Teen-LABS, show it to be safe and maybe even more effective than in adults for treating diabetes and hypertension, with similar weight loss.
Does treatment outweigh the potential risks?
Although obesity surgery and antiobesity medications are more successful at treating obesity in children and adolescents than lifestyle medications, they do have some risks. Surgery, depending on the type of surgery, can cause nutritional deficiencies, reduce body mineral density, and is a life-changing medical procedure. Antiobesity medications, depending on the type, can cause nausea and vomiting and increase heart rate – and because they are relatively new, we do not fully understand the long-term impact of continued use past 1 year.
However, an important question to ask is: “Do the risks of obesity surgery and antiobesity medications outweigh the risk of having lifelong obesity?” The answer to me and many of my colleagues is: “Yes!” Although there are risks associated with the two best treatments for pediatric obesity, those risks under proper supervision of a medical professional far outweigh the risks of not properly treating obesity and allowing it to persist and get worse over many years to come. Obesity is a disease deeply rooted in biology, and we must use biology-based treatments to tackle this problem in children and adolescents, who deserve the best care and treatments possible.
Dr. Ryder is assistant professor of pediatrics and associate director of research, Center for Pediatric Obesity Medicine, at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She reported receiving donations for clinical trials from Boehringer Ingelheim. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCOS in mothers tied to health problems in children
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HUMAN REPRODUCTION
Children and COVID: Does latest rise in new cases point toward stabilization?
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.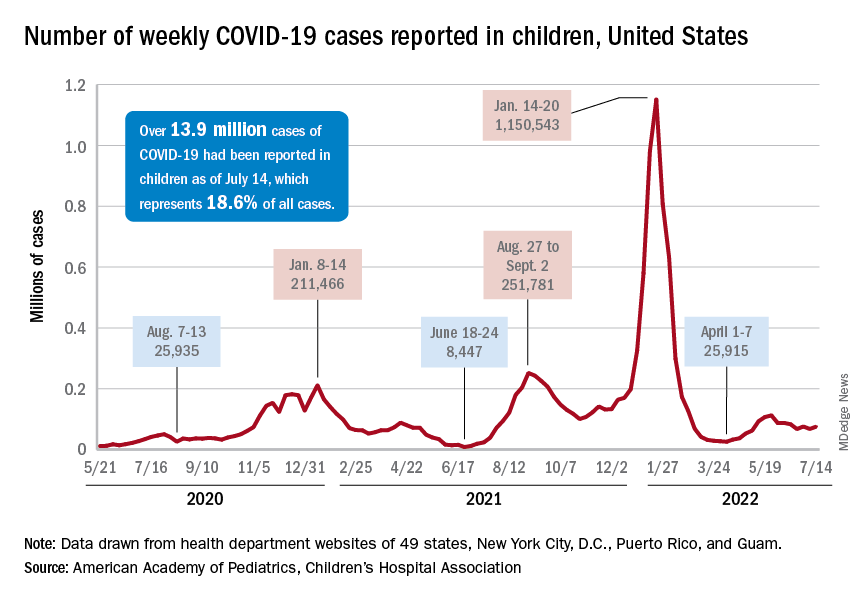
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
New COVID-19 cases rose for the second time in 3 weeks, as the effort to vaccinate the youngest children continued to slow after just 3 full weeks.
Nationally, over 75,000 children under age 5 years received their first dose of COVID-19 vaccine during the week of July 7-13. That number is down from the previous week – 118,000 from June 30 to July 6 – which, in turn, was lower than the 206,000 doses administered through the first 10 days after approval, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. That all adds up to just under 400,000 vaccinated children, or 2% of the eligible population under age 5, as of July 13.
State-level data, meanwhile, show considerable variation, the American Academy of Pediatrics noted in its weekly analysis of the CDC vaccine data. Vermont has already vaccinated 10.0% of children under age 5 years, and Massachusetts is at 9.5%, while Mississippi (0.3%), Alabama (0.5%), and Louisiana (0.8%) are still below 1%, the AAP said.
New cases show signs of steadying
The national count was up by 11.1% for the week of July 8-14, rising to 75,000 new cases, compared with 68,000 the previous week, but the recent trend seems to be leaning toward steadiness. The overall number has been between 67,000 and 76,000 over the past 4 weeks, alternating between rising and falling in that time span, according to data gathered by the AAP and the Children’s Hospital Association from state and territorial health departments.
the two groups said, also noting that several states have stopped updating their online dashboards over the past year, making the current total artificially low in comparison.
Taken with that grain of salt, the cumulative number of child cases since the start of the pandemic is just over 13.9 million, which represents 18.6% of all cases in the United States. That proportion has been declining in recent weeks and was as high as 19.0% as late as mid-May. “While COVID-19 cases are likely increasingly underreported for all age groups, this decline indicates that children are disproportionately undercounted in reported COVID-19 cases,” the AAP and CHA said.
Anxiety spreads from mother to daughter, father to son
The new findings suggest that children learn anxious behavior from their parents, study investigator Barbara Pavlova, PhD, clinical psychologist with Nova Scotia Health Authority, told this news organization.
“This means that transmission of anxiety from parents to children may be preventable,” said Dr. Pavlova, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada.
“Treating parents’ anxiety is not just important for their own health but also for the health of their children. This may be especially true if the child and the parent are the same sex,” Dr. Pavlova added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Parental anxiety a disruptor
Anxiety disorders run in families. Both genes and environment are thought to be at play, but there are few data on sex-specific transmission from parent to child.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 203 girls and 195 boys and their parents. The average age of the children was 11 years, and they had a familial risk for mood disorders.
Anxiety disorder in a same-sex parent was significantly associated with anxiety disorder in offspring (odds ratio, 2.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-5.34; P = .001) but not in an opposite-sex parent (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 0.81-2.81; P = .20).
Living with a same-sex parent without anxiety was associated with lower rates of offspring anxiety (OR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.22-0.67; P = .001).
Among all 398 children, 108 (27%) had been diagnosed with one or more anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (7.8%), social anxiety disorder (6.3%), separation anxiety disorder (8.6%), specific phobia (8%), and anxiety disorder not otherwise specified (5%).
Rates of anxiety disorders in children increased with age, from 14% in those younger than 9 years to 52% in those older than 15 years. Anxiety disorders were similarly common among boys (24%) and girls (30%).
Rates of anxiety disorders were lowest (24%) in children of two parents without anxiety disorders and highest (41%) in cases in which both parents had anxiety disorders.
The findings point to the possible role of environmental factors, “such as modeling and vicarious learning,” in the transmission of anxiety from parents to their children, the researchers note.
“A child receives [a] similar amount of genetic information from each biological parent. A strong same-sex parent effect suggests children learn resilience by modeling the behavior of their same-sex parent. A parent’s anxiety disorder may disrupt this protective learning,” said Dr. Pavlova.
Early diagnosis, treatment essential
Reached for comment, Jill Emanuele, PhD, vice president of clinical training for the Child MIND Institute, New York, said that when it comes to anxiety, it’s important to assess and treat both the parent and the child.
“We know that both environment and genetics play a role in anxiety disorders. From a clinical perspective, if we see a parent with an anxiety disorder, we know that there is a chance that that is also going to affect the child – whether or not the child has an anxiety disorder,” Dr. Emanuele said in an interview.
“Anxiety disorders are the most common psychiatric disorders diagnosed. We also know that anxiety disorders emerge earlier than mood disorders and certainly can emerge in childhood. It’s important to address anxiety early because those same problems can continue into adulthood if left untreated,” Dr. Emanuele added.
The study was supported by the Canada Research Chairs Program, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation, the Nova Scotia Health Research Foundation, and the Dalhousie Medical Research Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emanuele is a board member with the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new findings suggest that children learn anxious behavior from their parents, study investigator Barbara Pavlova, PhD, clinical psychologist with Nova Scotia Health Authority, told this news organization.
“This means that transmission of anxiety from parents to children may be preventable,” said Dr. Pavlova, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada.
“Treating parents’ anxiety is not just important for their own health but also for the health of their children. This may be especially true if the child and the parent are the same sex,” Dr. Pavlova added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Parental anxiety a disruptor
Anxiety disorders run in families. Both genes and environment are thought to be at play, but there are few data on sex-specific transmission from parent to child.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 203 girls and 195 boys and their parents. The average age of the children was 11 years, and they had a familial risk for mood disorders.
Anxiety disorder in a same-sex parent was significantly associated with anxiety disorder in offspring (odds ratio, 2.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-5.34; P = .001) but not in an opposite-sex parent (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 0.81-2.81; P = .20).
Living with a same-sex parent without anxiety was associated with lower rates of offspring anxiety (OR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.22-0.67; P = .001).
Among all 398 children, 108 (27%) had been diagnosed with one or more anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (7.8%), social anxiety disorder (6.3%), separation anxiety disorder (8.6%), specific phobia (8%), and anxiety disorder not otherwise specified (5%).
Rates of anxiety disorders in children increased with age, from 14% in those younger than 9 years to 52% in those older than 15 years. Anxiety disorders were similarly common among boys (24%) and girls (30%).
Rates of anxiety disorders were lowest (24%) in children of two parents without anxiety disorders and highest (41%) in cases in which both parents had anxiety disorders.
The findings point to the possible role of environmental factors, “such as modeling and vicarious learning,” in the transmission of anxiety from parents to their children, the researchers note.
“A child receives [a] similar amount of genetic information from each biological parent. A strong same-sex parent effect suggests children learn resilience by modeling the behavior of their same-sex parent. A parent’s anxiety disorder may disrupt this protective learning,” said Dr. Pavlova.
Early diagnosis, treatment essential
Reached for comment, Jill Emanuele, PhD, vice president of clinical training for the Child MIND Institute, New York, said that when it comes to anxiety, it’s important to assess and treat both the parent and the child.
“We know that both environment and genetics play a role in anxiety disorders. From a clinical perspective, if we see a parent with an anxiety disorder, we know that there is a chance that that is also going to affect the child – whether or not the child has an anxiety disorder,” Dr. Emanuele said in an interview.
“Anxiety disorders are the most common psychiatric disorders diagnosed. We also know that anxiety disorders emerge earlier than mood disorders and certainly can emerge in childhood. It’s important to address anxiety early because those same problems can continue into adulthood if left untreated,” Dr. Emanuele added.
The study was supported by the Canada Research Chairs Program, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation, the Nova Scotia Health Research Foundation, and the Dalhousie Medical Research Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emanuele is a board member with the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new findings suggest that children learn anxious behavior from their parents, study investigator Barbara Pavlova, PhD, clinical psychologist with Nova Scotia Health Authority, told this news organization.
“This means that transmission of anxiety from parents to children may be preventable,” said Dr. Pavlova, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada.
“Treating parents’ anxiety is not just important for their own health but also for the health of their children. This may be especially true if the child and the parent are the same sex,” Dr. Pavlova added.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Parental anxiety a disruptor
Anxiety disorders run in families. Both genes and environment are thought to be at play, but there are few data on sex-specific transmission from parent to child.
To investigate, the researchers conducted a cross-sectional study of 203 girls and 195 boys and their parents. The average age of the children was 11 years, and they had a familial risk for mood disorders.
Anxiety disorder in a same-sex parent was significantly associated with anxiety disorder in offspring (odds ratio, 2.85; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-5.34; P = .001) but not in an opposite-sex parent (OR, 1.51; 95% CI, 0.81-2.81; P = .20).
Living with a same-sex parent without anxiety was associated with lower rates of offspring anxiety (OR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.22-0.67; P = .001).
Among all 398 children, 108 (27%) had been diagnosed with one or more anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (7.8%), social anxiety disorder (6.3%), separation anxiety disorder (8.6%), specific phobia (8%), and anxiety disorder not otherwise specified (5%).
Rates of anxiety disorders in children increased with age, from 14% in those younger than 9 years to 52% in those older than 15 years. Anxiety disorders were similarly common among boys (24%) and girls (30%).
Rates of anxiety disorders were lowest (24%) in children of two parents without anxiety disorders and highest (41%) in cases in which both parents had anxiety disorders.
The findings point to the possible role of environmental factors, “such as modeling and vicarious learning,” in the transmission of anxiety from parents to their children, the researchers note.
“A child receives [a] similar amount of genetic information from each biological parent. A strong same-sex parent effect suggests children learn resilience by modeling the behavior of their same-sex parent. A parent’s anxiety disorder may disrupt this protective learning,” said Dr. Pavlova.
Early diagnosis, treatment essential
Reached for comment, Jill Emanuele, PhD, vice president of clinical training for the Child MIND Institute, New York, said that when it comes to anxiety, it’s important to assess and treat both the parent and the child.
“We know that both environment and genetics play a role in anxiety disorders. From a clinical perspective, if we see a parent with an anxiety disorder, we know that there is a chance that that is also going to affect the child – whether or not the child has an anxiety disorder,” Dr. Emanuele said in an interview.
“Anxiety disorders are the most common psychiatric disorders diagnosed. We also know that anxiety disorders emerge earlier than mood disorders and certainly can emerge in childhood. It’s important to address anxiety early because those same problems can continue into adulthood if left untreated,” Dr. Emanuele added.
The study was supported by the Canada Research Chairs Program, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation, the Nova Scotia Health Research Foundation, and the Dalhousie Medical Research Foundation. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Emanuele is a board member with the Anxiety and Depression Association of America.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC warns about potentially deadly virus in infants
The potentially fatal parechovirus is now circulating in multiple states, causing fevers, seizures, and sepsis-like symptoms, including confusion and extreme pain, according to the CDC.
Human parechoviruses are common in children and most have been infected before they start kindergarten, the CDC said. Between 6 months and 5 years of age, symptoms include an upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and rash.
But infants younger than 3 months may have more serious, and possibly fatal, infections. They may get “sepsis-like illness, seizures, and meningitis or meningoencephalitis, particularly in infants younger than 1 month,” the CDC said. At least one newborn has reportedly died from the infection.
Parechovirus can spread like other common germs, from feces that are later ingested – likely due to poor handwashing – and through droplets sent airborne by coughing or sneezing. It can be transmitted by people both with and without symptoms of the infection.
The microbe can reproduce for 1-3 weeks in the upper respiratory tract and up to 6 months in the gastrointestinal tract, the CDC said.
Kristina Angel Bryant, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Louisville Hospital, says parechoviruses often cause rashes on the hands and feet, which some experts refer to as “mittens and booties.”
The CDC is urging doctors to test for parechovirus if they recognize these symptoms in infants if there is no other explanation for what might be distressing them.
There is no specific treatment for parechovirus. And with no standard testing system in place, experts are unsure if the number of parechovirus cases is higher in 2022 than in previous years.
The message for parents, Dr. Bryant says, is: Don’t panic. “This is not a new virus.”
“One of the most common symptoms is fever, and in some kids, that is the only symptom,” she says. “Older infants and toddlers may have only cold symptoms, and some kids have no symptoms at all.”
Parents can take the usual steps to protect their child from the viral illness, including diligent handwashing and having less contact with people who are sick, Dr. Bryant says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The potentially fatal parechovirus is now circulating in multiple states, causing fevers, seizures, and sepsis-like symptoms, including confusion and extreme pain, according to the CDC.
Human parechoviruses are common in children and most have been infected before they start kindergarten, the CDC said. Between 6 months and 5 years of age, symptoms include an upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and rash.
But infants younger than 3 months may have more serious, and possibly fatal, infections. They may get “sepsis-like illness, seizures, and meningitis or meningoencephalitis, particularly in infants younger than 1 month,” the CDC said. At least one newborn has reportedly died from the infection.
Parechovirus can spread like other common germs, from feces that are later ingested – likely due to poor handwashing – and through droplets sent airborne by coughing or sneezing. It can be transmitted by people both with and without symptoms of the infection.
The microbe can reproduce for 1-3 weeks in the upper respiratory tract and up to 6 months in the gastrointestinal tract, the CDC said.
Kristina Angel Bryant, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Louisville Hospital, says parechoviruses often cause rashes on the hands and feet, which some experts refer to as “mittens and booties.”
The CDC is urging doctors to test for parechovirus if they recognize these symptoms in infants if there is no other explanation for what might be distressing them.
There is no specific treatment for parechovirus. And with no standard testing system in place, experts are unsure if the number of parechovirus cases is higher in 2022 than in previous years.
The message for parents, Dr. Bryant says, is: Don’t panic. “This is not a new virus.”
“One of the most common symptoms is fever, and in some kids, that is the only symptom,” she says. “Older infants and toddlers may have only cold symptoms, and some kids have no symptoms at all.”
Parents can take the usual steps to protect their child from the viral illness, including diligent handwashing and having less contact with people who are sick, Dr. Bryant says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The potentially fatal parechovirus is now circulating in multiple states, causing fevers, seizures, and sepsis-like symptoms, including confusion and extreme pain, according to the CDC.
Human parechoviruses are common in children and most have been infected before they start kindergarten, the CDC said. Between 6 months and 5 years of age, symptoms include an upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and rash.
But infants younger than 3 months may have more serious, and possibly fatal, infections. They may get “sepsis-like illness, seizures, and meningitis or meningoencephalitis, particularly in infants younger than 1 month,” the CDC said. At least one newborn has reportedly died from the infection.
Parechovirus can spread like other common germs, from feces that are later ingested – likely due to poor handwashing – and through droplets sent airborne by coughing or sneezing. It can be transmitted by people both with and without symptoms of the infection.
The microbe can reproduce for 1-3 weeks in the upper respiratory tract and up to 6 months in the gastrointestinal tract, the CDC said.
Kristina Angel Bryant, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Louisville Hospital, says parechoviruses often cause rashes on the hands and feet, which some experts refer to as “mittens and booties.”
The CDC is urging doctors to test for parechovirus if they recognize these symptoms in infants if there is no other explanation for what might be distressing them.
There is no specific treatment for parechovirus. And with no standard testing system in place, experts are unsure if the number of parechovirus cases is higher in 2022 than in previous years.
The message for parents, Dr. Bryant says, is: Don’t panic. “This is not a new virus.”
“One of the most common symptoms is fever, and in some kids, that is the only symptom,” she says. “Older infants and toddlers may have only cold symptoms, and some kids have no symptoms at all.”
Parents can take the usual steps to protect their child from the viral illness, including diligent handwashing and having less contact with people who are sick, Dr. Bryant says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.