User login
Cutis is a peer-reviewed clinical journal for the dermatologist, allergist, and general practitioner published monthly since 1965. Concise clinical articles present the practical side of dermatology, helping physicians to improve patient care. Cutis is referenced in Index Medicus/MEDLINE and is written and edited by industry leaders.
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')
A peer-reviewed, indexed journal for dermatologists with original research, image quizzes, cases and reviews, and columns.
Community Outreach Benefits Dermatology Residents and Their Patients
The sun often is rising in the rearview mirror as I travel with the University of New Mexico dermatology team from Albuquerque to our satellite clinic in Gallup, New Mexico. This twice-monthly trip—with a group usually comprising an attending physician, residents, and medical students—provides an invaluable opportunity for me to take part in delivering care to a majority Native American population and connects our institution and its trainees to the state’s rural and indigenous cultures and communities.
Community outreach is an important initiative for many dermatology residency training programs. Engaging with the community outside the clinic setting allows residents to hone their clinical skills, interact with and meet new people, and help to improve access to health care, especially for members of underserved populations.
Limited access to health care remains a pressing issue in the United States, especially for underserved and rural communities. There currently is no standardized way to measure access to care, but multiple contributing factors have been identified, including but not limited to patient wait times and throughput, provider turnover, ratio of dermatologists to patient population, insurance type, and patient outcomes.1 Fortunately, there are many ways for dermatology residents to get involved and improve access to dermatologic services in their communities, including skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology.
Skin Cancer Screenings
More than 40% of community outreach initiatives offered by dermatology residency programs are related to skin cancer screening and prevention.2 The American Academy of Dermatology’s free skin cancer check program (https://www.aad.org/member/career/volunteer/spot) offers a way to participate in or even host a skin cancer screening in your community. Since 1985, this program has identified nearly 300,000 suspicious lesions and more than 30,000 suspected melanomas. Resources for setting up a skin cancer screening in your community are available on the program’s website. Residents may take this opportunity to teach medical students how to perform full-body skin examinations and/or practice making independent decisions as the supervisor for medical trainees. Skin cancer screening events not only expand access to care in underserved communities but also help residents feel more connected to the local community, especially if they have moved to a new location for their residency training.
Free Clinics
Engaging in educational opportunities offered through residency programs is another way to participate in community outreach. In particular, many programs are affiliated with a School of Medicine within their institution that allows residents to spearhead volunteer opportunities such as working at a free clinic. In fact, more than 30% of initiatives offered at dermatology residency programs are free general dermatology clinics.2 Residents are in the unique position of being both learners themselves as well as educators to trainees.3 As part of our role, we can provide crucial specialty care to the community by working in concert with medical students and while also familiarizing ourselves with treating populations that we may not reach in our daily clinical work. For example, by participating in free clinics, we can provide care to vulnerable populations who typically may have financial or time barriers that prevent them from seeking care at the institution-associated clinic, including individuals experiencing homelessness, patients who are uninsured, and individuals who cannot take time off work to pursue medical care. Our presence in the community helps to reduce barriers to specialty care, particularly in the field of dermatology where the access shortage in the context of rising skin cancer rates prompts public health concerns.4
Teledermatology
Teledermatology became a way to extend our reach in the community more than ever before during the COVID-19 pandemic. Advances in audio, visual, and data telecommunication have been particularly helpful in dermatology, a specialty that relies heavily on visual cues for diagnosis. Synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid teledermatology services implemented during the pandemic have gained favor among patients and dermatologists and are still applied in current practice.5,6
For example, in the state of New Mexico (where there is a severe shortage of board-certified dermatologists to care for the state’s population), teledermatology has allowed rural providers of all specialties to consult University of New Mexico dermatologists by sending clinical photographs along with patient information and history via secure messaging. Instead of having the patient travel hundreds of miles to see the nearest dermatologist for their skin condition or endure long wait times to get in to see a specialist, primary providers now can initiate treatment or work-up for their patient’s skin issue in a timely manner with the use of teledermatology to consult specialists.
Teledermatology has demonstrated cost-effectiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in conveniently expanding access to care. It offers patients and dermatologists flexibility in receiving and delivering health care, respectively.7 As residents, learning how to navigate this technologic frontier in health care delivery is imperative, as it will remain a prevalent tool in the future care of our communities, particularly in underserved areas.
Final Thoughts
Through community outreach initiatives, dermatology residents have an opportunity not only to enrich our education but also to connect with and become closer to our patients. Skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology have provided ways to reach more communities and remain important aspects of dermatology residency.
- Patel B, Blalock TW. Defining “access to care” for dermatology at academic medical institutions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:627-628. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.03.014
- Fritsche M, Maglakelidze N, Zaenglein A, et al. Community outreach initiatives in dermatology: cross-sectional study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2693-2695. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02629-y
- Chiu LW. Teaching tips for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;113:E17-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.1046
- Duniphin DD. Limited access to dermatology specialty care: barriers and teledermatology. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023;13:E2023031. doi:10.5826/dpc.1301a31
- Ibrahim AE, Magdy M, Khalaf EM, et al. Teledermatology in the time of COVID-19. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75:e15000. doi:10.1111/ijcp.15000
- Farr MA, Duvic M, Joshi TP. Teledermatology during COVID-19: an updated review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:467-475. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00601-y
- Lipner SR. Optimizing patient care with teledermatology: improving access, efficiency, and satisfaction. Cutis. 2024;114:63-64. doi:10.12788/cutis.1073
The sun often is rising in the rearview mirror as I travel with the University of New Mexico dermatology team from Albuquerque to our satellite clinic in Gallup, New Mexico. This twice-monthly trip—with a group usually comprising an attending physician, residents, and medical students—provides an invaluable opportunity for me to take part in delivering care to a majority Native American population and connects our institution and its trainees to the state’s rural and indigenous cultures and communities.
Community outreach is an important initiative for many dermatology residency training programs. Engaging with the community outside the clinic setting allows residents to hone their clinical skills, interact with and meet new people, and help to improve access to health care, especially for members of underserved populations.
Limited access to health care remains a pressing issue in the United States, especially for underserved and rural communities. There currently is no standardized way to measure access to care, but multiple contributing factors have been identified, including but not limited to patient wait times and throughput, provider turnover, ratio of dermatologists to patient population, insurance type, and patient outcomes.1 Fortunately, there are many ways for dermatology residents to get involved and improve access to dermatologic services in their communities, including skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology.
Skin Cancer Screenings
More than 40% of community outreach initiatives offered by dermatology residency programs are related to skin cancer screening and prevention.2 The American Academy of Dermatology’s free skin cancer check program (https://www.aad.org/member/career/volunteer/spot) offers a way to participate in or even host a skin cancer screening in your community. Since 1985, this program has identified nearly 300,000 suspicious lesions and more than 30,000 suspected melanomas. Resources for setting up a skin cancer screening in your community are available on the program’s website. Residents may take this opportunity to teach medical students how to perform full-body skin examinations and/or practice making independent decisions as the supervisor for medical trainees. Skin cancer screening events not only expand access to care in underserved communities but also help residents feel more connected to the local community, especially if they have moved to a new location for their residency training.
Free Clinics
Engaging in educational opportunities offered through residency programs is another way to participate in community outreach. In particular, many programs are affiliated with a School of Medicine within their institution that allows residents to spearhead volunteer opportunities such as working at a free clinic. In fact, more than 30% of initiatives offered at dermatology residency programs are free general dermatology clinics.2 Residents are in the unique position of being both learners themselves as well as educators to trainees.3 As part of our role, we can provide crucial specialty care to the community by working in concert with medical students and while also familiarizing ourselves with treating populations that we may not reach in our daily clinical work. For example, by participating in free clinics, we can provide care to vulnerable populations who typically may have financial or time barriers that prevent them from seeking care at the institution-associated clinic, including individuals experiencing homelessness, patients who are uninsured, and individuals who cannot take time off work to pursue medical care. Our presence in the community helps to reduce barriers to specialty care, particularly in the field of dermatology where the access shortage in the context of rising skin cancer rates prompts public health concerns.4
Teledermatology
Teledermatology became a way to extend our reach in the community more than ever before during the COVID-19 pandemic. Advances in audio, visual, and data telecommunication have been particularly helpful in dermatology, a specialty that relies heavily on visual cues for diagnosis. Synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid teledermatology services implemented during the pandemic have gained favor among patients and dermatologists and are still applied in current practice.5,6
For example, in the state of New Mexico (where there is a severe shortage of board-certified dermatologists to care for the state’s population), teledermatology has allowed rural providers of all specialties to consult University of New Mexico dermatologists by sending clinical photographs along with patient information and history via secure messaging. Instead of having the patient travel hundreds of miles to see the nearest dermatologist for their skin condition or endure long wait times to get in to see a specialist, primary providers now can initiate treatment or work-up for their patient’s skin issue in a timely manner with the use of teledermatology to consult specialists.
Teledermatology has demonstrated cost-effectiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in conveniently expanding access to care. It offers patients and dermatologists flexibility in receiving and delivering health care, respectively.7 As residents, learning how to navigate this technologic frontier in health care delivery is imperative, as it will remain a prevalent tool in the future care of our communities, particularly in underserved areas.
Final Thoughts
Through community outreach initiatives, dermatology residents have an opportunity not only to enrich our education but also to connect with and become closer to our patients. Skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology have provided ways to reach more communities and remain important aspects of dermatology residency.
The sun often is rising in the rearview mirror as I travel with the University of New Mexico dermatology team from Albuquerque to our satellite clinic in Gallup, New Mexico. This twice-monthly trip—with a group usually comprising an attending physician, residents, and medical students—provides an invaluable opportunity for me to take part in delivering care to a majority Native American population and connects our institution and its trainees to the state’s rural and indigenous cultures and communities.
Community outreach is an important initiative for many dermatology residency training programs. Engaging with the community outside the clinic setting allows residents to hone their clinical skills, interact with and meet new people, and help to improve access to health care, especially for members of underserved populations.
Limited access to health care remains a pressing issue in the United States, especially for underserved and rural communities. There currently is no standardized way to measure access to care, but multiple contributing factors have been identified, including but not limited to patient wait times and throughput, provider turnover, ratio of dermatologists to patient population, insurance type, and patient outcomes.1 Fortunately, there are many ways for dermatology residents to get involved and improve access to dermatologic services in their communities, including skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology.
Skin Cancer Screenings
More than 40% of community outreach initiatives offered by dermatology residency programs are related to skin cancer screening and prevention.2 The American Academy of Dermatology’s free skin cancer check program (https://www.aad.org/member/career/volunteer/spot) offers a way to participate in or even host a skin cancer screening in your community. Since 1985, this program has identified nearly 300,000 suspicious lesions and more than 30,000 suspected melanomas. Resources for setting up a skin cancer screening in your community are available on the program’s website. Residents may take this opportunity to teach medical students how to perform full-body skin examinations and/or practice making independent decisions as the supervisor for medical trainees. Skin cancer screening events not only expand access to care in underserved communities but also help residents feel more connected to the local community, especially if they have moved to a new location for their residency training.
Free Clinics
Engaging in educational opportunities offered through residency programs is another way to participate in community outreach. In particular, many programs are affiliated with a School of Medicine within their institution that allows residents to spearhead volunteer opportunities such as working at a free clinic. In fact, more than 30% of initiatives offered at dermatology residency programs are free general dermatology clinics.2 Residents are in the unique position of being both learners themselves as well as educators to trainees.3 As part of our role, we can provide crucial specialty care to the community by working in concert with medical students and while also familiarizing ourselves with treating populations that we may not reach in our daily clinical work. For example, by participating in free clinics, we can provide care to vulnerable populations who typically may have financial or time barriers that prevent them from seeking care at the institution-associated clinic, including individuals experiencing homelessness, patients who are uninsured, and individuals who cannot take time off work to pursue medical care. Our presence in the community helps to reduce barriers to specialty care, particularly in the field of dermatology where the access shortage in the context of rising skin cancer rates prompts public health concerns.4
Teledermatology
Teledermatology became a way to extend our reach in the community more than ever before during the COVID-19 pandemic. Advances in audio, visual, and data telecommunication have been particularly helpful in dermatology, a specialty that relies heavily on visual cues for diagnosis. Synchronous, asynchronous, and hybrid teledermatology services implemented during the pandemic have gained favor among patients and dermatologists and are still applied in current practice.5,6
For example, in the state of New Mexico (where there is a severe shortage of board-certified dermatologists to care for the state’s population), teledermatology has allowed rural providers of all specialties to consult University of New Mexico dermatologists by sending clinical photographs along with patient information and history via secure messaging. Instead of having the patient travel hundreds of miles to see the nearest dermatologist for their skin condition or endure long wait times to get in to see a specialist, primary providers now can initiate treatment or work-up for their patient’s skin issue in a timely manner with the use of teledermatology to consult specialists.
Teledermatology has demonstrated cost-effectiveness, accuracy, and efficiency in conveniently expanding access to care. It offers patients and dermatologists flexibility in receiving and delivering health care, respectively.7 As residents, learning how to navigate this technologic frontier in health care delivery is imperative, as it will remain a prevalent tool in the future care of our communities, particularly in underserved areas.
Final Thoughts
Through community outreach initiatives, dermatology residents have an opportunity not only to enrich our education but also to connect with and become closer to our patients. Skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology have provided ways to reach more communities and remain important aspects of dermatology residency.
- Patel B, Blalock TW. Defining “access to care” for dermatology at academic medical institutions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:627-628. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.03.014
- Fritsche M, Maglakelidze N, Zaenglein A, et al. Community outreach initiatives in dermatology: cross-sectional study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2693-2695. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02629-y
- Chiu LW. Teaching tips for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;113:E17-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.1046
- Duniphin DD. Limited access to dermatology specialty care: barriers and teledermatology. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023;13:E2023031. doi:10.5826/dpc.1301a31
- Ibrahim AE, Magdy M, Khalaf EM, et al. Teledermatology in the time of COVID-19. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75:e15000. doi:10.1111/ijcp.15000
- Farr MA, Duvic M, Joshi TP. Teledermatology during COVID-19: an updated review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:467-475. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00601-y
- Lipner SR. Optimizing patient care with teledermatology: improving access, efficiency, and satisfaction. Cutis. 2024;114:63-64. doi:10.12788/cutis.1073
- Patel B, Blalock TW. Defining “access to care” for dermatology at academic medical institutions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;89:627-628. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.03.014
- Fritsche M, Maglakelidze N, Zaenglein A, et al. Community outreach initiatives in dermatology: cross-sectional study. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:2693-2695. doi:10.1007/s00403-023-02629-y
- Chiu LW. Teaching tips for dermatology residents. Cutis. 2024;113:E17-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.1046
- Duniphin DD. Limited access to dermatology specialty care: barriers and teledermatology. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023;13:E2023031. doi:10.5826/dpc.1301a31
- Ibrahim AE, Magdy M, Khalaf EM, et al. Teledermatology in the time of COVID-19. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75:e15000. doi:10.1111/ijcp.15000
- Farr MA, Duvic M, Joshi TP. Teledermatology during COVID-19: an updated review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22:467-475. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00601-y
- Lipner SR. Optimizing patient care with teledermatology: improving access, efficiency, and satisfaction. Cutis. 2024;114:63-64. doi:10.12788/cutis.1073
Resident Pearls
- Outreach initiatives can help residents feel more connected to their community and expand access to care.
- Skin cancer screenings, free clinics, and teledermatology are a few ways residents may get involved in their local communities.
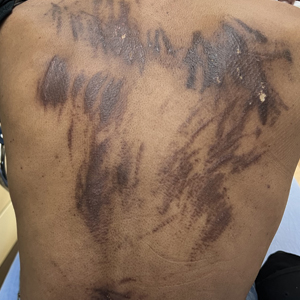
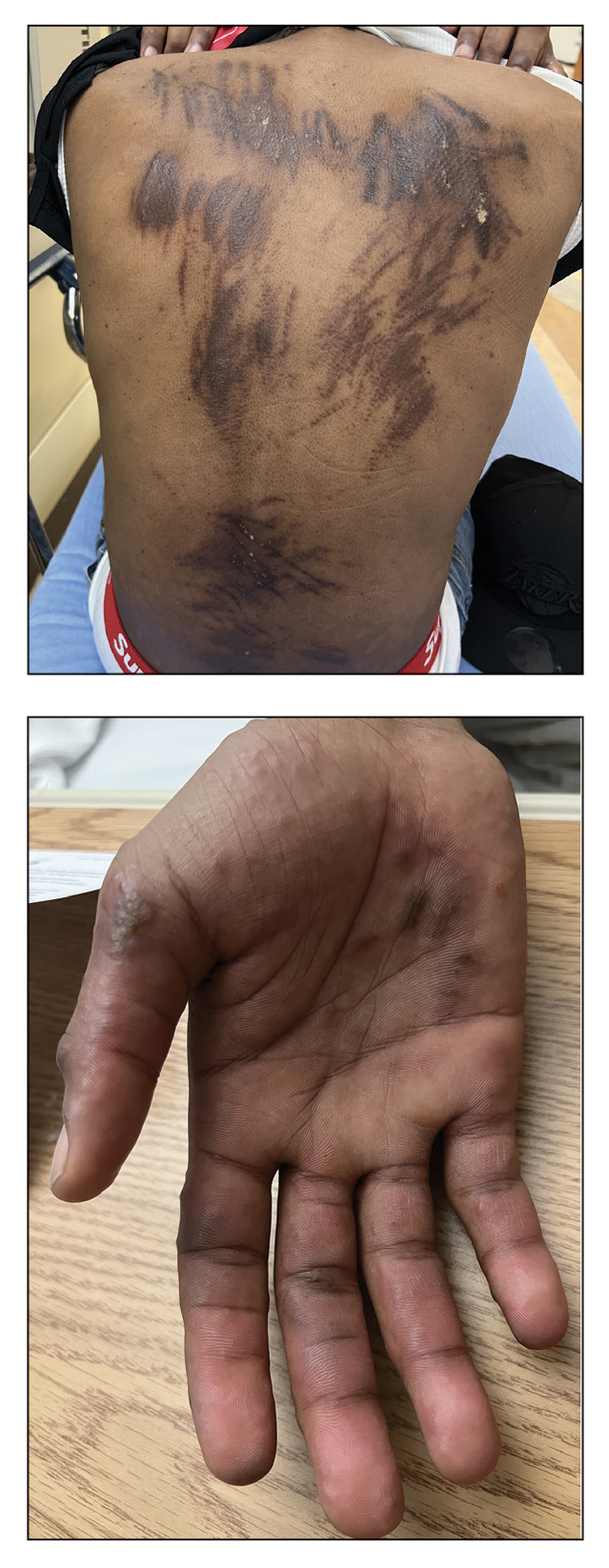
Eruption of Multiple Linear Hyperpigmented Plaques
THE DIAGNOSIS: Chemotherapy-Induced Flagellate Dermatitis
Based on the clinical presentation and temporal relation with chemotherapy, a diagnosis of bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis (FD) was made, as bleomycin is the only chemotherapeutic agent from this regimen that has been linked with FD.1,2 Laboratory findings revealed eosinophilia, further supporting a druginduced dermatitis. The patient was treated with oral steroids and diphenhydramine to alleviate itching and discomfort. The chemotherapy was temporarily discontinued until symptomatic improvement was observed within 2 to 3 days.
Flagellate dermatitis is characterized by unique erythematous, linear, intermingled streaks of adjoining firm papules—often preceded by a prodrome of global pruritus—that eventually become hyperpigmented as the erythema subsides. The clinical manifestation of FD can be idiopathic; true/mechanical (dermatitis artefacta, abuse, sadomasochism); chemotherapy induced (peplomycin, trastuzumab, cisplatin, docetaxel, bendamustine); toxin induced (shiitake mushroom, cnidarian stings, Paederus insects); related to rheumatologic diseases (dermatomyositis, adult-onset Still disease), dermatographism, phytophotodermatitis, or poison ivy dermatitis; or induced by chikungunya fever.1
The term flagellate originates from the Latin word flagellum, which pertains to the distinctive whiplike pattern. It was first described by Moulin et al3 in 1970 in reference to bleomycin-induced linear hyperpigmentation. Bleomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces verticillus, is used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and germ cell tumors. The worldwide incidence of bleomycin-induced FD is 8% to 22% and commonly is associated with a cumulative dose greater than 100 U.2 Clinical presentation is variable in terms of onset, distribution, and morphology of the eruption and could be independent of dose, route of administration, or type of malignancy being treated. The flagellate rash commonly involves the trunk, arms, and legs; can develop within hours to 6 months of starting bleomycin therapy; often is preceded by generalized itching; and eventually heals with hyperpigmentation.
Possible mechanisms of bleomycin-induced FD include localized melanogenesis, inflammatory pigmentary incontinence, alterations to normal pigmentation patterns, cytotoxic effects of the drug itself, minor trauma/ scratching leading to increased blood flow and causing local accumulation of bleomycin, heat recall, and reduced epidermal turnover leading to extended interaction between keratinocytes and melanocytes.2 Heat exposure can act as a trigger for bleomycin-induced skin rash recall even months after the treatment is stopped.
Apart from discontinuing the drug, there is no specific treatment available for bleomycin-induced FD. The primary objective of treatment is to alleviate pruritus, which often involves the use of topical or systemic corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s clinical response. Once treatment is discontinued, FD typically resolves within 6 to 8 months. However, there can be a permanent postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected area.4 Although there is a concern for increased mortality after postponement of chemotherapy,5 the decision to proceed with or discontinue the chemotherapy regimen necessitates a comprehensive interdisciplinary discussion and a meticulous assessment of the risks and benefits that is customized to each individual patient. Flagellate dermatitis can reoccur with bleomycin re-exposure; a combined approach of proactive topical and systemic steroid treatment seems to diminish the likelihood of FD recurrence.5
Our case underscores the importance of recognizing, detecting, and managing FD promptly in individuals undergoing bleomycin-based chemotherapy. Medical professionals should familiarize themselves with this distinct adverse effect linked to bleomycin, enabling prompt discontinuation if necessary, and educate patients about the condition’s typically temporary nature, thereby alleviating their concerns.
- Bhushan P, Manjul P, Baliyan V. Flagellate dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:149-152.
- Ziemer M, Goetze S, Juhasz K, et al. Flagellate dermatitis as a bleomycinspecific adverse effect of cytostatic therapy: a clinical-histopathologic correlation. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:68-76. doi:10.2165/11537080-000000000-00000
- Moulin G, Fière B, Beyvin A. Cutaneous pigmentation caused by bleomycin. Article in French. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:293-296.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.119358
- Hanna TP, King WD, Thibodeau S, et al. Mortality due to cancer treatment delay: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;371:m4087. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4087
THE DIAGNOSIS: Chemotherapy-Induced Flagellate Dermatitis
Based on the clinical presentation and temporal relation with chemotherapy, a diagnosis of bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis (FD) was made, as bleomycin is the only chemotherapeutic agent from this regimen that has been linked with FD.1,2 Laboratory findings revealed eosinophilia, further supporting a druginduced dermatitis. The patient was treated with oral steroids and diphenhydramine to alleviate itching and discomfort. The chemotherapy was temporarily discontinued until symptomatic improvement was observed within 2 to 3 days.
Flagellate dermatitis is characterized by unique erythematous, linear, intermingled streaks of adjoining firm papules—often preceded by a prodrome of global pruritus—that eventually become hyperpigmented as the erythema subsides. The clinical manifestation of FD can be idiopathic; true/mechanical (dermatitis artefacta, abuse, sadomasochism); chemotherapy induced (peplomycin, trastuzumab, cisplatin, docetaxel, bendamustine); toxin induced (shiitake mushroom, cnidarian stings, Paederus insects); related to rheumatologic diseases (dermatomyositis, adult-onset Still disease), dermatographism, phytophotodermatitis, or poison ivy dermatitis; or induced by chikungunya fever.1
The term flagellate originates from the Latin word flagellum, which pertains to the distinctive whiplike pattern. It was first described by Moulin et al3 in 1970 in reference to bleomycin-induced linear hyperpigmentation. Bleomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces verticillus, is used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and germ cell tumors. The worldwide incidence of bleomycin-induced FD is 8% to 22% and commonly is associated with a cumulative dose greater than 100 U.2 Clinical presentation is variable in terms of onset, distribution, and morphology of the eruption and could be independent of dose, route of administration, or type of malignancy being treated. The flagellate rash commonly involves the trunk, arms, and legs; can develop within hours to 6 months of starting bleomycin therapy; often is preceded by generalized itching; and eventually heals with hyperpigmentation.
Possible mechanisms of bleomycin-induced FD include localized melanogenesis, inflammatory pigmentary incontinence, alterations to normal pigmentation patterns, cytotoxic effects of the drug itself, minor trauma/ scratching leading to increased blood flow and causing local accumulation of bleomycin, heat recall, and reduced epidermal turnover leading to extended interaction between keratinocytes and melanocytes.2 Heat exposure can act as a trigger for bleomycin-induced skin rash recall even months after the treatment is stopped.
Apart from discontinuing the drug, there is no specific treatment available for bleomycin-induced FD. The primary objective of treatment is to alleviate pruritus, which often involves the use of topical or systemic corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s clinical response. Once treatment is discontinued, FD typically resolves within 6 to 8 months. However, there can be a permanent postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected area.4 Although there is a concern for increased mortality after postponement of chemotherapy,5 the decision to proceed with or discontinue the chemotherapy regimen necessitates a comprehensive interdisciplinary discussion and a meticulous assessment of the risks and benefits that is customized to each individual patient. Flagellate dermatitis can reoccur with bleomycin re-exposure; a combined approach of proactive topical and systemic steroid treatment seems to diminish the likelihood of FD recurrence.5
Our case underscores the importance of recognizing, detecting, and managing FD promptly in individuals undergoing bleomycin-based chemotherapy. Medical professionals should familiarize themselves with this distinct adverse effect linked to bleomycin, enabling prompt discontinuation if necessary, and educate patients about the condition’s typically temporary nature, thereby alleviating their concerns.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Chemotherapy-Induced Flagellate Dermatitis
Based on the clinical presentation and temporal relation with chemotherapy, a diagnosis of bleomycininduced flagellate dermatitis (FD) was made, as bleomycin is the only chemotherapeutic agent from this regimen that has been linked with FD.1,2 Laboratory findings revealed eosinophilia, further supporting a druginduced dermatitis. The patient was treated with oral steroids and diphenhydramine to alleviate itching and discomfort. The chemotherapy was temporarily discontinued until symptomatic improvement was observed within 2 to 3 days.
Flagellate dermatitis is characterized by unique erythematous, linear, intermingled streaks of adjoining firm papules—often preceded by a prodrome of global pruritus—that eventually become hyperpigmented as the erythema subsides. The clinical manifestation of FD can be idiopathic; true/mechanical (dermatitis artefacta, abuse, sadomasochism); chemotherapy induced (peplomycin, trastuzumab, cisplatin, docetaxel, bendamustine); toxin induced (shiitake mushroom, cnidarian stings, Paederus insects); related to rheumatologic diseases (dermatomyositis, adult-onset Still disease), dermatographism, phytophotodermatitis, or poison ivy dermatitis; or induced by chikungunya fever.1
The term flagellate originates from the Latin word flagellum, which pertains to the distinctive whiplike pattern. It was first described by Moulin et al3 in 1970 in reference to bleomycin-induced linear hyperpigmentation. Bleomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces verticillus, is used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and germ cell tumors. The worldwide incidence of bleomycin-induced FD is 8% to 22% and commonly is associated with a cumulative dose greater than 100 U.2 Clinical presentation is variable in terms of onset, distribution, and morphology of the eruption and could be independent of dose, route of administration, or type of malignancy being treated. The flagellate rash commonly involves the trunk, arms, and legs; can develop within hours to 6 months of starting bleomycin therapy; often is preceded by generalized itching; and eventually heals with hyperpigmentation.
Possible mechanisms of bleomycin-induced FD include localized melanogenesis, inflammatory pigmentary incontinence, alterations to normal pigmentation patterns, cytotoxic effects of the drug itself, minor trauma/ scratching leading to increased blood flow and causing local accumulation of bleomycin, heat recall, and reduced epidermal turnover leading to extended interaction between keratinocytes and melanocytes.2 Heat exposure can act as a trigger for bleomycin-induced skin rash recall even months after the treatment is stopped.
Apart from discontinuing the drug, there is no specific treatment available for bleomycin-induced FD. The primary objective of treatment is to alleviate pruritus, which often involves the use of topical or systemic corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s clinical response. Once treatment is discontinued, FD typically resolves within 6 to 8 months. However, there can be a permanent postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in the affected area.4 Although there is a concern for increased mortality after postponement of chemotherapy,5 the decision to proceed with or discontinue the chemotherapy regimen necessitates a comprehensive interdisciplinary discussion and a meticulous assessment of the risks and benefits that is customized to each individual patient. Flagellate dermatitis can reoccur with bleomycin re-exposure; a combined approach of proactive topical and systemic steroid treatment seems to diminish the likelihood of FD recurrence.5
Our case underscores the importance of recognizing, detecting, and managing FD promptly in individuals undergoing bleomycin-based chemotherapy. Medical professionals should familiarize themselves with this distinct adverse effect linked to bleomycin, enabling prompt discontinuation if necessary, and educate patients about the condition’s typically temporary nature, thereby alleviating their concerns.
- Bhushan P, Manjul P, Baliyan V. Flagellate dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:149-152.
- Ziemer M, Goetze S, Juhasz K, et al. Flagellate dermatitis as a bleomycinspecific adverse effect of cytostatic therapy: a clinical-histopathologic correlation. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:68-76. doi:10.2165/11537080-000000000-00000
- Moulin G, Fière B, Beyvin A. Cutaneous pigmentation caused by bleomycin. Article in French. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:293-296.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.119358
- Hanna TP, King WD, Thibodeau S, et al. Mortality due to cancer treatment delay: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;371:m4087. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4087
- Bhushan P, Manjul P, Baliyan V. Flagellate dermatoses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:149-152.
- Ziemer M, Goetze S, Juhasz K, et al. Flagellate dermatitis as a bleomycinspecific adverse effect of cytostatic therapy: a clinical-histopathologic correlation. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011;12:68-76. doi:10.2165/11537080-000000000-00000
- Moulin G, Fière B, Beyvin A. Cutaneous pigmentation caused by bleomycin. Article in French. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1970;77:293-296.
- Biswas A, Chaudhari PB, Sharma P, et al. Bleomycin induced flagellate erythema: revisiting a unique complication. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9:500-503. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.119358
- Hanna TP, King WD, Thibodeau S, et al. Mortality due to cancer treatment delay: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2020;371:m4087. doi:10.1136/bmj.m4087
A 28-year-old man presented for evaluation of an intensely itchy rash of 5 days’ duration involving the face, trunk, arms, and legs. The patient recently had been diagnosed with classical Hodgkin lymphoma and was started on a biweekly chemotherapy regimen of adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine 3 weeks prior. He reported that a red, itchy, papular rash had developed on the hands 1 week after starting chemotherapy and improved with antihistamines. Symptoms of the current rash included night sweats, occasional fever, substantial unintentional weight loss, and fatigue. He had no history of urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis, or nail changes.
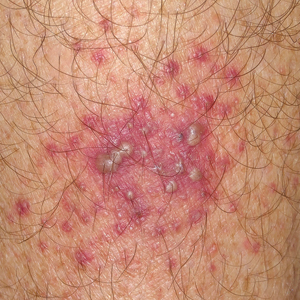
Physical examination revealed widespread, itchy, linear and curvilinear hyperpigmented plaques on the upper arms, shoulders, back (top), face, and thighs, as well as erythematous grouped papules on the bilateral palms (bottom). There was no mucosal or systemic involvement.
Asteraceae Dermatitis: Everyday Plants With Allergenic Potential
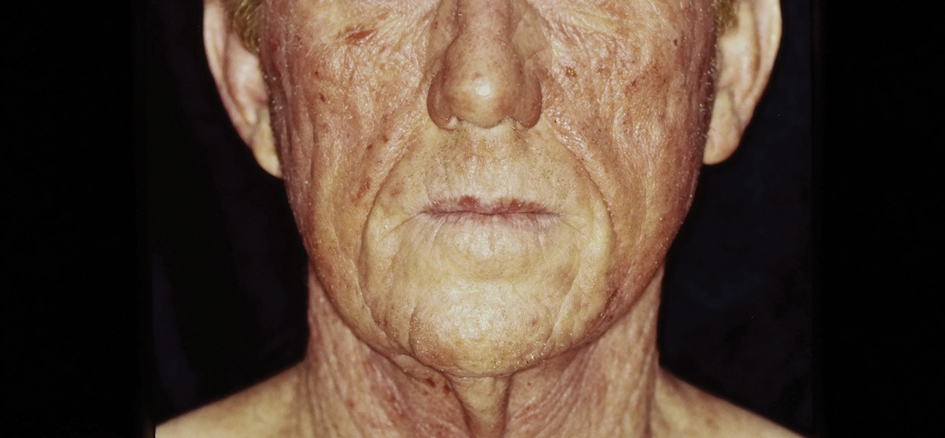
The Asteraceae (formerly Compositae) family of plants is derived from the ancient Greek word aster, meaning “star,” referring to the starlike arrangement of flower petals around a central disc known as a capitulum. What initially appears as a single flower is actually a composite of several smaller flowers, hence the former name Compositae.1 Well-known members of the Asteraceae family include ornamental annuals (eg, sunflowers, marigolds, cosmos), herbaceous perennials (eg, chrysanthemums, dandelions), vegetables (eg, lettuce, chicory, artichokes), herbs (eg, chamomile, tarragon), and weeds (eg, ragweed, horseweed, capeweed)(Figure 1).2
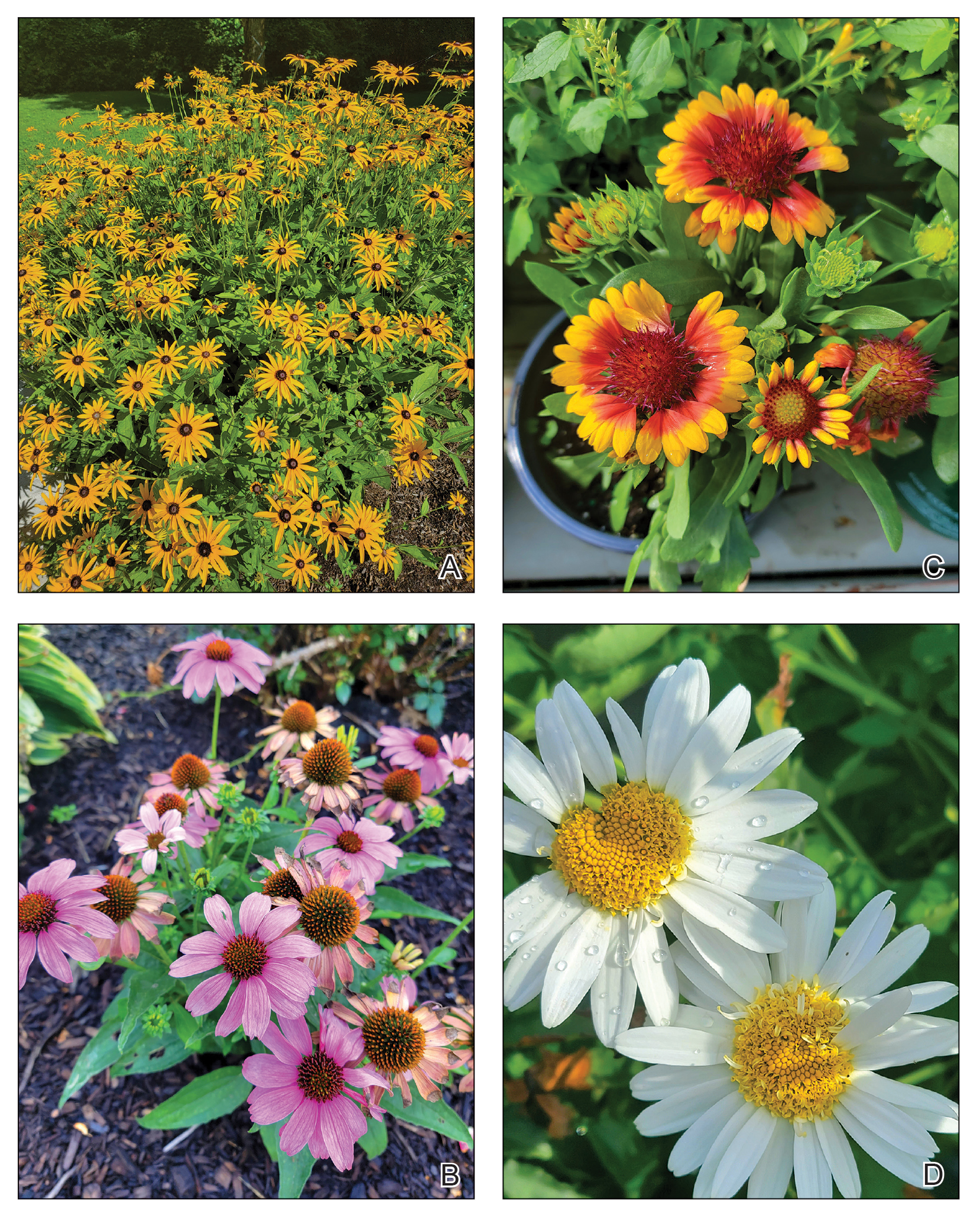

There are more than 25,000 species of Asteraceae plants that thrive in a wide range of climates worldwide. Cases of Asteraceae-induced skin reactions have been reported in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.3 Members of the Asteraceae family are ubiquitous in gardens, along roadsides, and in the wilderness. Occupational exposure commonly affects gardeners, florists, farmers, and forestry workers through either direct contact with plants or via airborne pollen. Furthermore, plants of the Asteraceae family are used in various products, including pediculicides (eg, insect repellents), cosmetics (eg, eye creams, body washes), and food products (eg, cooking oils, sweetening agents, coffee substitutes, herbal teas).4-6 These plants have substantial allergic potential, resulting in numerous cutaneous reactions.
Allergic Potential
Asteraceae plants can elicit both immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs); for instance, exposure to ragweed pollen may cause an IgE-mediated type 1 HSR manifesting as allergic rhinitis or a type IV HSR manifesting as airborne allergic contact dermatitis.7,8 The main contact allergens present in Asteraceae plants are sesquiterpene lactones, which are found in the leaves, stems, flowers, and pollen.9-11 Sesquiterpene lactones consist of an α-methyl group attached to a lactone ring combined with a sesquiterpene.12 Patch testing can be used to diagnose Asteraceae allergy; however, the results are not consistently reliable because there is no perfect screening allergen. Patch test preparations commonly used to detect Asteraceae allergy include Compositae mix (consisting of Anthemis nobilis extract, Chamomilla recutita extract, Achillea millefolium extract, Tanacetum vulgare extract, Arnica montana extract, and parthenolide) and sesquiterpene lactone mix (consisting of alantolactone, dehydrocostus lactone, and costunolide). In North America, the prevalence of positive patch tests to Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix is approximately 2% and 0.5%, respectively.13 When patch testing is performed, both Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix should be utilized to minimize the risk of missing Asteraceae allergy, as sesquiterpene lactone mix alone does not detect all Compositae-sensitized patients. Additionally, it may be necessary to test supplemental Asteraceae allergens, including preparations from specific plants to which the patient has been exposed. Exposure to Asteraceae-containing cosmetic products may lead to dermatitis, though this is highly dependent on the particular plant species involved. For instance, the prevalence of sensitization is high in arnica (tincture) and elecampane but low with more commonly used species such as German chamomile.14
Cutaneous Manifestations
Asteraceae dermatitis, which also is known as Australian bush dermatitis, weed dermatitis, and chrysanthemum dermatitis,2 can manifest on any area of the body that directly contacts the plant or is exposed to the pollen. Asteraceae dermatitis historically was reported in older adults with a recent history of plant exposure.6,15 However, recent data have shown a female preponderance and a younger mean age of onset (46–49 years).16
There are multiple distinct clinical manifestations of Asteraceae dermatitis. The most common cutaneous finding is localized vesicular or eczematous patches on the hands or wrists. Other variations include eczematous rashes on the exposed skin of the hands, arms, face, and neck; generalized eczema; and isolated facial eczema.16,17 These variations can be attributed to contact dermatitis caused by airborne pollen, which may mimic photodermatitis. However, airborne Asteraceae dermatitis can be distinguished clinically from photodermatitis by the involvement of sun-protected areas such as the skinfolds of the eyelids, retroauricular sulci, and nasolabial folds (Figure 2).2,9 In rare cases, systemic allergic contact dermatitis can occur if the Asteraceae allergen is ingested.2,18
Other diagnostic clues include dermatitis that flares during the summer, at the peak of the growing season, with remission in the cooler months. Potential risk factors include a childhood history of atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis.16 With prolonged exposure, patients may develop chronic actinic dermatitis, an immunologically mediated photodermatosis characterized by lichenified and pruritic eczematous plaques located predominantly on sun-exposed areas with notable sparing of the skin folds.19 The association between Asteraceae dermatitis and chronic actinic dermatitis is highly variable, with some studies reporting a 25% correlation and others finding a stronger association of up to 80%.2,15,20 Asteraceae allergy appears to be a relatively uncommon cause of photoallergy in North America. In one recent study, 16% (3/19) of patients with chronic actinic dermatitis had positive patch or photopatch tests to sesquiterpene lactone mix, but in another large study of photopatch testing it was reported to be a rare photoallergen.21,22
Parthenium dermatitis is an allergic contact dermatitis caused by exposure to Parthenium hysterophorus, a weed of the Asteraceae family that is responsible for 30% of cases of contact dermatitis in India.23,24 Unlike the more classic manifestation of Asteraceae dermatitis, which primarily affects the upper extremities in cases from North America and Europe, Parthenium dermatitis typically occurs in an airborne pattern distribution.24
Management
While complete avoidance of Asteraceae plants is ideal, it often is unrealistic due to their abundance in nature. Therefore, minimizing exposure to the causative plants is recommended. Primary preventive measures such as wearing protective gloves and clothing and applying bentonite clay prior to exposure should be taken when working outdoors. Promptly showering after contact with plants also can reduce the risk for Asteraceae dermatitis.
Symptomatic treatment is appropriate for mild cases and includes topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. For severe cases, systemic corticosteroids may be needed for acute flares, with azathioprine, mycophenolate, cyclosporine, or methotrexate available for recalcitrant disease. Verma et al25 found that treatment with azathioprine for 6 months resulted in greater than 60% clearance in all 12 patients, with a majority achieving 80% to 100% clearance. Methotrexate has been used at doses of 15 mg once weekly.26 Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have been effective in extensive cases; however, care should be exercised in patients with photosensitive dermatitis, who instead should practice strict photoprotection.27-29 Lakshmi et al30 reported the use of cyclosporine during the acute phase of Asteraceae dermatitis at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg daily for 4 to 8 weeks. There have been several case reports of dupilumab treating allergic contact dermatitis; however, there have been 3 cases of patients with atopic dermatitis developing Asteraceae dermatitis while taking dupilumab.31,32 Recently, oral Janus kinase inhibitors have shown success in treating refractory cases of airborne Asteraceae dermatitis.33,34 Further research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of dupilumab and Janus kinase inhibitors for treatment of Asteraceae dermatitis.
Final Thoughts
The Asteraceae plant family is vast and diverse, with more than 200 species reported to cause allergic contact dermatitis.12 Common modes of contact include gardening, occupational exposure, airborne pollen, and use of pediculicides and cosmetics that contain components of Asteraceae plants. Educating patients on how to minimize contact with Asteraceae plants is the most effective management strategy; topical agents and oral immunosuppressives can be used for symptomatic treatment.
- Morhardt S, Morhardt E. California Desert Flowers: An Introduction to Families, Genera, and Species. University of California Press; 2004.
- Gordon LA. Compositae dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 1999;40:123-130. doi:10.1046/j.1440-0960.1999.00341.x
- Denisow-Pietrzyk M, Pietrzyk Ł, Denisow B. Asteraceae species as potential environmental factors of allergy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26:6290-6300. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-04146-w
- Paulsen E, Chistensen LP, Andersen KE. Cosmetics and herbal remedies with Compositae plant extracts—are they tolerated by Compositae-allergic patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:15-23. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01250.x
- Burry JN, Reid JG, Kirk J. Australian bush dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1975;1:263-264. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1975.tb05422.x
- Punchihewa N, Palmer A, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: an Australian case series. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:356-362. doi:10.1111/cod.14162
- Chen KW, Marusciac L, Tamas PT, et al. Ragweed pollen allergy: burden, characteristics, and management of an imported allergen source in Europe. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176:163-180. doi:10.1159/000487997
- Schloemer JA, Zirwas MJ, Burkhart CG. Airborne contact dermatitis: common causes in the USA. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:271-274. doi:10.1111/ijd.12692
- Arlette J, Mitchell JC. Compositae dermatitis. current aspects. Contact Dermatitis. 1981;7:129-136. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1981.tb04584.x
- Mitchell JC, Dupuis G. Allergic contact dermatitis from sesquiterpenoids of the Compositae family of plants. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:139-150. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb06857.x
- Salapovic H, Geier J, Reznicek G. Quantification of Sesquiterpene lactones in Asteraceae plant extracts: evaluation of their allergenic potential. Sci Pharm. 2013;81:807-818. doi:10.3797/scipharm.1306-17
- Paulsen E. Compositae dermatitis: a survey. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;26:76-86. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb00888.x. Published correction appears in Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:208.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Paulsen E. Contact sensitization from Compositae-containing herbal remedies and cosmetics. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:189-198. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470401.x
- Frain-Bell W, Johnson BE. Contact allergic sensitivity to plants and the photosensitivity dermatitis and actinic reticuloid syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1979;101:503-512.
- Paulsen E, Andersen KE. Clinical patterns of Compositae dermatitis in Danish monosensitized patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:185-193. doi:10.1111/cod.12916
- Jovanovic´ M, Poljacki M. Compositae dermatitis. Med Pregl. 2003;56:43-49. doi:10.2298/mpns0302043j
- Krook G. Occupational dermatitis from Lactuca sativa (lettuce) and Cichorium (endive). simultaneous occurrence of immediate and delayed allergy as a cause of contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1977;3:27-36. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1977.tb03583.x
- Paek SY, Lim HW. Chronic actinic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:355-361, viii-ix. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.007
- du P Menagé H, Hawk JL, White IR. Sesquiterpene lactone mix contact sensitivity and its relationship to chronic actinic dermatitis: a follow-up study. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:119-122. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05859.x
- Wang CX, Belsito DV. Chronic actinic dermatitis revisited. Dermatitis. 2020;31:68-74. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000531
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291. doi:10.1111/phpp.12742
- McGovern TW, LaWarre S. Botanical briefs: the scourge of India—Parthenium hysterophorus L. Cutis. 2001;67:27-34. Published correction appears in Cutis. 2001;67:154.
- Sharma VK, Verma P, Maharaja K. Parthenium dermatitis. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2013;12:85-94. doi:10.1039/c2pp25186h
- Verma KK, Bansal A, Sethuraman G. Parthenium dermatitis treated with azathioprine weekly pulse doses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:24-27. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.19713
- Sharma VK, Bhat R, Sethuraman G, et al. Treatment of Parthenium dermatitis with methotrexate. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;57:118-119. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00950.x
- Burke DA, Corey G, Storrs FJ. Psoralen plus UVA protocol for Compositae photosensitivity. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:171-176.
- Lovell CR. Allergic contact dermatitis due to plants. In: Plants and the Skin. Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1993:96-254.
- Dogra S, Parsad D, Handa S. Narrowband ultraviolet B in airborne contact dermatitis: a ray of hope! Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:373-374. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05724.x
- Lakshmi C, Srinivas CR, Jayaraman A. Ciclosporin in Parthenium dermatitis—a report of 2 cases. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;59:245-248. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01208.x
- Hendricks AJ, Yosipovitch G, Shi VY. Dupilumab use in dermatologic conditions beyond atopic dermatitis—a systematic review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:19-28. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1689227
- Napolitano M, Fabbrocini G, Patruno C. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: a possible cause of dupilumab-associated facial and neck dermatitis in atopic dermatitis patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:473-474. doi:10.1111/cod.13898
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;88:150-152. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544. doi:10.1111/cod.14204
The Asteraceae (formerly Compositae) family of plants is derived from the ancient Greek word aster, meaning “star,” referring to the starlike arrangement of flower petals around a central disc known as a capitulum. What initially appears as a single flower is actually a composite of several smaller flowers, hence the former name Compositae.1 Well-known members of the Asteraceae family include ornamental annuals (eg, sunflowers, marigolds, cosmos), herbaceous perennials (eg, chrysanthemums, dandelions), vegetables (eg, lettuce, chicory, artichokes), herbs (eg, chamomile, tarragon), and weeds (eg, ragweed, horseweed, capeweed)(Figure 1).2

There are more than 25,000 species of Asteraceae plants that thrive in a wide range of climates worldwide. Cases of Asteraceae-induced skin reactions have been reported in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.3 Members of the Asteraceae family are ubiquitous in gardens, along roadsides, and in the wilderness. Occupational exposure commonly affects gardeners, florists, farmers, and forestry workers through either direct contact with plants or via airborne pollen. Furthermore, plants of the Asteraceae family are used in various products, including pediculicides (eg, insect repellents), cosmetics (eg, eye creams, body washes), and food products (eg, cooking oils, sweetening agents, coffee substitutes, herbal teas).4-6 These plants have substantial allergic potential, resulting in numerous cutaneous reactions.
Allergic Potential
Asteraceae plants can elicit both immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs); for instance, exposure to ragweed pollen may cause an IgE-mediated type 1 HSR manifesting as allergic rhinitis or a type IV HSR manifesting as airborne allergic contact dermatitis.7,8 The main contact allergens present in Asteraceae plants are sesquiterpene lactones, which are found in the leaves, stems, flowers, and pollen.9-11 Sesquiterpene lactones consist of an α-methyl group attached to a lactone ring combined with a sesquiterpene.12 Patch testing can be used to diagnose Asteraceae allergy; however, the results are not consistently reliable because there is no perfect screening allergen. Patch test preparations commonly used to detect Asteraceae allergy include Compositae mix (consisting of Anthemis nobilis extract, Chamomilla recutita extract, Achillea millefolium extract, Tanacetum vulgare extract, Arnica montana extract, and parthenolide) and sesquiterpene lactone mix (consisting of alantolactone, dehydrocostus lactone, and costunolide). In North America, the prevalence of positive patch tests to Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix is approximately 2% and 0.5%, respectively.13 When patch testing is performed, both Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix should be utilized to minimize the risk of missing Asteraceae allergy, as sesquiterpene lactone mix alone does not detect all Compositae-sensitized patients. Additionally, it may be necessary to test supplemental Asteraceae allergens, including preparations from specific plants to which the patient has been exposed. Exposure to Asteraceae-containing cosmetic products may lead to dermatitis, though this is highly dependent on the particular plant species involved. For instance, the prevalence of sensitization is high in arnica (tincture) and elecampane but low with more commonly used species such as German chamomile.14
Cutaneous Manifestations
Asteraceae dermatitis, which also is known as Australian bush dermatitis, weed dermatitis, and chrysanthemum dermatitis,2 can manifest on any area of the body that directly contacts the plant or is exposed to the pollen. Asteraceae dermatitis historically was reported in older adults with a recent history of plant exposure.6,15 However, recent data have shown a female preponderance and a younger mean age of onset (46–49 years).16
There are multiple distinct clinical manifestations of Asteraceae dermatitis. The most common cutaneous finding is localized vesicular or eczematous patches on the hands or wrists. Other variations include eczematous rashes on the exposed skin of the hands, arms, face, and neck; generalized eczema; and isolated facial eczema.16,17 These variations can be attributed to contact dermatitis caused by airborne pollen, which may mimic photodermatitis. However, airborne Asteraceae dermatitis can be distinguished clinically from photodermatitis by the involvement of sun-protected areas such as the skinfolds of the eyelids, retroauricular sulci, and nasolabial folds (Figure 2).2,9 In rare cases, systemic allergic contact dermatitis can occur if the Asteraceae allergen is ingested.2,18

Other diagnostic clues include dermatitis that flares during the summer, at the peak of the growing season, with remission in the cooler months. Potential risk factors include a childhood history of atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis.16 With prolonged exposure, patients may develop chronic actinic dermatitis, an immunologically mediated photodermatosis characterized by lichenified and pruritic eczematous plaques located predominantly on sun-exposed areas with notable sparing of the skin folds.19 The association between Asteraceae dermatitis and chronic actinic dermatitis is highly variable, with some studies reporting a 25% correlation and others finding a stronger association of up to 80%.2,15,20 Asteraceae allergy appears to be a relatively uncommon cause of photoallergy in North America. In one recent study, 16% (3/19) of patients with chronic actinic dermatitis had positive patch or photopatch tests to sesquiterpene lactone mix, but in another large study of photopatch testing it was reported to be a rare photoallergen.21,22
Parthenium dermatitis is an allergic contact dermatitis caused by exposure to Parthenium hysterophorus, a weed of the Asteraceae family that is responsible for 30% of cases of contact dermatitis in India.23,24 Unlike the more classic manifestation of Asteraceae dermatitis, which primarily affects the upper extremities in cases from North America and Europe, Parthenium dermatitis typically occurs in an airborne pattern distribution.24
Management
While complete avoidance of Asteraceae plants is ideal, it often is unrealistic due to their abundance in nature. Therefore, minimizing exposure to the causative plants is recommended. Primary preventive measures such as wearing protective gloves and clothing and applying bentonite clay prior to exposure should be taken when working outdoors. Promptly showering after contact with plants also can reduce the risk for Asteraceae dermatitis.
Symptomatic treatment is appropriate for mild cases and includes topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. For severe cases, systemic corticosteroids may be needed for acute flares, with azathioprine, mycophenolate, cyclosporine, or methotrexate available for recalcitrant disease. Verma et al25 found that treatment with azathioprine for 6 months resulted in greater than 60% clearance in all 12 patients, with a majority achieving 80% to 100% clearance. Methotrexate has been used at doses of 15 mg once weekly.26 Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have been effective in extensive cases; however, care should be exercised in patients with photosensitive dermatitis, who instead should practice strict photoprotection.27-29 Lakshmi et al30 reported the use of cyclosporine during the acute phase of Asteraceae dermatitis at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg daily for 4 to 8 weeks. There have been several case reports of dupilumab treating allergic contact dermatitis; however, there have been 3 cases of patients with atopic dermatitis developing Asteraceae dermatitis while taking dupilumab.31,32 Recently, oral Janus kinase inhibitors have shown success in treating refractory cases of airborne Asteraceae dermatitis.33,34 Further research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of dupilumab and Janus kinase inhibitors for treatment of Asteraceae dermatitis.
Final Thoughts
The Asteraceae plant family is vast and diverse, with more than 200 species reported to cause allergic contact dermatitis.12 Common modes of contact include gardening, occupational exposure, airborne pollen, and use of pediculicides and cosmetics that contain components of Asteraceae plants. Educating patients on how to minimize contact with Asteraceae plants is the most effective management strategy; topical agents and oral immunosuppressives can be used for symptomatic treatment.
The Asteraceae (formerly Compositae) family of plants is derived from the ancient Greek word aster, meaning “star,” referring to the starlike arrangement of flower petals around a central disc known as a capitulum. What initially appears as a single flower is actually a composite of several smaller flowers, hence the former name Compositae.1 Well-known members of the Asteraceae family include ornamental annuals (eg, sunflowers, marigolds, cosmos), herbaceous perennials (eg, chrysanthemums, dandelions), vegetables (eg, lettuce, chicory, artichokes), herbs (eg, chamomile, tarragon), and weeds (eg, ragweed, horseweed, capeweed)(Figure 1).2

There are more than 25,000 species of Asteraceae plants that thrive in a wide range of climates worldwide. Cases of Asteraceae-induced skin reactions have been reported in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.3 Members of the Asteraceae family are ubiquitous in gardens, along roadsides, and in the wilderness. Occupational exposure commonly affects gardeners, florists, farmers, and forestry workers through either direct contact with plants or via airborne pollen. Furthermore, plants of the Asteraceae family are used in various products, including pediculicides (eg, insect repellents), cosmetics (eg, eye creams, body washes), and food products (eg, cooking oils, sweetening agents, coffee substitutes, herbal teas).4-6 These plants have substantial allergic potential, resulting in numerous cutaneous reactions.
Allergic Potential
Asteraceae plants can elicit both immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs); for instance, exposure to ragweed pollen may cause an IgE-mediated type 1 HSR manifesting as allergic rhinitis or a type IV HSR manifesting as airborne allergic contact dermatitis.7,8 The main contact allergens present in Asteraceae plants are sesquiterpene lactones, which are found in the leaves, stems, flowers, and pollen.9-11 Sesquiterpene lactones consist of an α-methyl group attached to a lactone ring combined with a sesquiterpene.12 Patch testing can be used to diagnose Asteraceae allergy; however, the results are not consistently reliable because there is no perfect screening allergen. Patch test preparations commonly used to detect Asteraceae allergy include Compositae mix (consisting of Anthemis nobilis extract, Chamomilla recutita extract, Achillea millefolium extract, Tanacetum vulgare extract, Arnica montana extract, and parthenolide) and sesquiterpene lactone mix (consisting of alantolactone, dehydrocostus lactone, and costunolide). In North America, the prevalence of positive patch tests to Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix is approximately 2% and 0.5%, respectively.13 When patch testing is performed, both Compositae mix and sesquiterpene lactone mix should be utilized to minimize the risk of missing Asteraceae allergy, as sesquiterpene lactone mix alone does not detect all Compositae-sensitized patients. Additionally, it may be necessary to test supplemental Asteraceae allergens, including preparations from specific plants to which the patient has been exposed. Exposure to Asteraceae-containing cosmetic products may lead to dermatitis, though this is highly dependent on the particular plant species involved. For instance, the prevalence of sensitization is high in arnica (tincture) and elecampane but low with more commonly used species such as German chamomile.14
Cutaneous Manifestations
Asteraceae dermatitis, which also is known as Australian bush dermatitis, weed dermatitis, and chrysanthemum dermatitis,2 can manifest on any area of the body that directly contacts the plant or is exposed to the pollen. Asteraceae dermatitis historically was reported in older adults with a recent history of plant exposure.6,15 However, recent data have shown a female preponderance and a younger mean age of onset (46–49 years).16
There are multiple distinct clinical manifestations of Asteraceae dermatitis. The most common cutaneous finding is localized vesicular or eczematous patches on the hands or wrists. Other variations include eczematous rashes on the exposed skin of the hands, arms, face, and neck; generalized eczema; and isolated facial eczema.16,17 These variations can be attributed to contact dermatitis caused by airborne pollen, which may mimic photodermatitis. However, airborne Asteraceae dermatitis can be distinguished clinically from photodermatitis by the involvement of sun-protected areas such as the skinfolds of the eyelids, retroauricular sulci, and nasolabial folds (Figure 2).2,9 In rare cases, systemic allergic contact dermatitis can occur if the Asteraceae allergen is ingested.2,18

Other diagnostic clues include dermatitis that flares during the summer, at the peak of the growing season, with remission in the cooler months. Potential risk factors include a childhood history of atopic dermatitis and allergic rhinitis.16 With prolonged exposure, patients may develop chronic actinic dermatitis, an immunologically mediated photodermatosis characterized by lichenified and pruritic eczematous plaques located predominantly on sun-exposed areas with notable sparing of the skin folds.19 The association between Asteraceae dermatitis and chronic actinic dermatitis is highly variable, with some studies reporting a 25% correlation and others finding a stronger association of up to 80%.2,15,20 Asteraceae allergy appears to be a relatively uncommon cause of photoallergy in North America. In one recent study, 16% (3/19) of patients with chronic actinic dermatitis had positive patch or photopatch tests to sesquiterpene lactone mix, but in another large study of photopatch testing it was reported to be a rare photoallergen.21,22
Parthenium dermatitis is an allergic contact dermatitis caused by exposure to Parthenium hysterophorus, a weed of the Asteraceae family that is responsible for 30% of cases of contact dermatitis in India.23,24 Unlike the more classic manifestation of Asteraceae dermatitis, which primarily affects the upper extremities in cases from North America and Europe, Parthenium dermatitis typically occurs in an airborne pattern distribution.24
Management
While complete avoidance of Asteraceae plants is ideal, it often is unrealistic due to their abundance in nature. Therefore, minimizing exposure to the causative plants is recommended. Primary preventive measures such as wearing protective gloves and clothing and applying bentonite clay prior to exposure should be taken when working outdoors. Promptly showering after contact with plants also can reduce the risk for Asteraceae dermatitis.
Symptomatic treatment is appropriate for mild cases and includes topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors. For severe cases, systemic corticosteroids may be needed for acute flares, with azathioprine, mycophenolate, cyclosporine, or methotrexate available for recalcitrant disease. Verma et al25 found that treatment with azathioprine for 6 months resulted in greater than 60% clearance in all 12 patients, with a majority achieving 80% to 100% clearance. Methotrexate has been used at doses of 15 mg once weekly.26 Narrowband UVB and psoralen plus UVA have been effective in extensive cases; however, care should be exercised in patients with photosensitive dermatitis, who instead should practice strict photoprotection.27-29 Lakshmi et al30 reported the use of cyclosporine during the acute phase of Asteraceae dermatitis at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg daily for 4 to 8 weeks. There have been several case reports of dupilumab treating allergic contact dermatitis; however, there have been 3 cases of patients with atopic dermatitis developing Asteraceae dermatitis while taking dupilumab.31,32 Recently, oral Janus kinase inhibitors have shown success in treating refractory cases of airborne Asteraceae dermatitis.33,34 Further research is needed to determine the safety and efficacy of dupilumab and Janus kinase inhibitors for treatment of Asteraceae dermatitis.
Final Thoughts
The Asteraceae plant family is vast and diverse, with more than 200 species reported to cause allergic contact dermatitis.12 Common modes of contact include gardening, occupational exposure, airborne pollen, and use of pediculicides and cosmetics that contain components of Asteraceae plants. Educating patients on how to minimize contact with Asteraceae plants is the most effective management strategy; topical agents and oral immunosuppressives can be used for symptomatic treatment.
- Morhardt S, Morhardt E. California Desert Flowers: An Introduction to Families, Genera, and Species. University of California Press; 2004.
- Gordon LA. Compositae dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 1999;40:123-130. doi:10.1046/j.1440-0960.1999.00341.x
- Denisow-Pietrzyk M, Pietrzyk Ł, Denisow B. Asteraceae species as potential environmental factors of allergy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26:6290-6300. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-04146-w
- Paulsen E, Chistensen LP, Andersen KE. Cosmetics and herbal remedies with Compositae plant extracts—are they tolerated by Compositae-allergic patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:15-23. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01250.x
- Burry JN, Reid JG, Kirk J. Australian bush dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1975;1:263-264. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1975.tb05422.x
- Punchihewa N, Palmer A, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: an Australian case series. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:356-362. doi:10.1111/cod.14162
- Chen KW, Marusciac L, Tamas PT, et al. Ragweed pollen allergy: burden, characteristics, and management of an imported allergen source in Europe. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176:163-180. doi:10.1159/000487997
- Schloemer JA, Zirwas MJ, Burkhart CG. Airborne contact dermatitis: common causes in the USA. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:271-274. doi:10.1111/ijd.12692
- Arlette J, Mitchell JC. Compositae dermatitis. current aspects. Contact Dermatitis. 1981;7:129-136. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1981.tb04584.x
- Mitchell JC, Dupuis G. Allergic contact dermatitis from sesquiterpenoids of the Compositae family of plants. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:139-150. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb06857.x
- Salapovic H, Geier J, Reznicek G. Quantification of Sesquiterpene lactones in Asteraceae plant extracts: evaluation of their allergenic potential. Sci Pharm. 2013;81:807-818. doi:10.3797/scipharm.1306-17
- Paulsen E. Compositae dermatitis: a survey. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;26:76-86. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb00888.x. Published correction appears in Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:208.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Paulsen E. Contact sensitization from Compositae-containing herbal remedies and cosmetics. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:189-198. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470401.x
- Frain-Bell W, Johnson BE. Contact allergic sensitivity to plants and the photosensitivity dermatitis and actinic reticuloid syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1979;101:503-512.
- Paulsen E, Andersen KE. Clinical patterns of Compositae dermatitis in Danish monosensitized patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:185-193. doi:10.1111/cod.12916
- Jovanovic´ M, Poljacki M. Compositae dermatitis. Med Pregl. 2003;56:43-49. doi:10.2298/mpns0302043j
- Krook G. Occupational dermatitis from Lactuca sativa (lettuce) and Cichorium (endive). simultaneous occurrence of immediate and delayed allergy as a cause of contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1977;3:27-36. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1977.tb03583.x
- Paek SY, Lim HW. Chronic actinic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:355-361, viii-ix. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.007
- du P Menagé H, Hawk JL, White IR. Sesquiterpene lactone mix contact sensitivity and its relationship to chronic actinic dermatitis: a follow-up study. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:119-122. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05859.x
- Wang CX, Belsito DV. Chronic actinic dermatitis revisited. Dermatitis. 2020;31:68-74. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000531
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291. doi:10.1111/phpp.12742
- McGovern TW, LaWarre S. Botanical briefs: the scourge of India—Parthenium hysterophorus L. Cutis. 2001;67:27-34. Published correction appears in Cutis. 2001;67:154.
- Sharma VK, Verma P, Maharaja K. Parthenium dermatitis. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2013;12:85-94. doi:10.1039/c2pp25186h
- Verma KK, Bansal A, Sethuraman G. Parthenium dermatitis treated with azathioprine weekly pulse doses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:24-27. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.19713
- Sharma VK, Bhat R, Sethuraman G, et al. Treatment of Parthenium dermatitis with methotrexate. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;57:118-119. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00950.x
- Burke DA, Corey G, Storrs FJ. Psoralen plus UVA protocol for Compositae photosensitivity. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:171-176.
- Lovell CR. Allergic contact dermatitis due to plants. In: Plants and the Skin. Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1993:96-254.
- Dogra S, Parsad D, Handa S. Narrowband ultraviolet B in airborne contact dermatitis: a ray of hope! Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:373-374. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05724.x
- Lakshmi C, Srinivas CR, Jayaraman A. Ciclosporin in Parthenium dermatitis—a report of 2 cases. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;59:245-248. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01208.x
- Hendricks AJ, Yosipovitch G, Shi VY. Dupilumab use in dermatologic conditions beyond atopic dermatitis—a systematic review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:19-28. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1689227
- Napolitano M, Fabbrocini G, Patruno C. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: a possible cause of dupilumab-associated facial and neck dermatitis in atopic dermatitis patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:473-474. doi:10.1111/cod.13898
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;88:150-152. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544. doi:10.1111/cod.14204
- Morhardt S, Morhardt E. California Desert Flowers: An Introduction to Families, Genera, and Species. University of California Press; 2004.
- Gordon LA. Compositae dermatitis. Australas J Dermatol. 1999;40:123-130. doi:10.1046/j.1440-0960.1999.00341.x
- Denisow-Pietrzyk M, Pietrzyk Ł, Denisow B. Asteraceae species as potential environmental factors of allergy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26:6290-6300. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-04146-w
- Paulsen E, Chistensen LP, Andersen KE. Cosmetics and herbal remedies with Compositae plant extracts—are they tolerated by Compositae-allergic patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2008;58:15-23. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01250.x
- Burry JN, Reid JG, Kirk J. Australian bush dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1975;1:263-264. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1975.tb05422.x
- Punchihewa N, Palmer A, Nixon R. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: an Australian case series. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:356-362. doi:10.1111/cod.14162
- Chen KW, Marusciac L, Tamas PT, et al. Ragweed pollen allergy: burden, characteristics, and management of an imported allergen source in Europe. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176:163-180. doi:10.1159/000487997
- Schloemer JA, Zirwas MJ, Burkhart CG. Airborne contact dermatitis: common causes in the USA. Int J Dermatol. 2015;54:271-274. doi:10.1111/ijd.12692
- Arlette J, Mitchell JC. Compositae dermatitis. current aspects. Contact Dermatitis. 1981;7:129-136. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1981.tb04584.x
- Mitchell JC, Dupuis G. Allergic contact dermatitis from sesquiterpenoids of the Compositae family of plants. Br J Dermatol. 1971;84:139-150. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb06857.x
- Salapovic H, Geier J, Reznicek G. Quantification of Sesquiterpene lactones in Asteraceae plant extracts: evaluation of their allergenic potential. Sci Pharm. 2013;81:807-818. doi:10.3797/scipharm.1306-17
- Paulsen E. Compositae dermatitis: a survey. Contact Dermatitis. 1992;26:76-86. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1992.tb00888.x. Published correction appears in Contact Dermatitis. 1992;27:208.
- DeKoven JG, Silverberg JI, Warshaw EM, et al. North American Contact Dermatitis Group patch test results: 2017-2018. Dermatitis. 2021;32:111-123. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000729
- Paulsen E. Contact sensitization from Compositae-containing herbal remedies and cosmetics. Contact Dermatitis. 2002;47:189-198. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0536.2002.470401.x
- Frain-Bell W, Johnson BE. Contact allergic sensitivity to plants and the photosensitivity dermatitis and actinic reticuloid syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 1979;101:503-512.
- Paulsen E, Andersen KE. Clinical patterns of Compositae dermatitis in Danish monosensitized patients. Contact Dermatitis. 2018;78:185-193. doi:10.1111/cod.12916
- Jovanovic´ M, Poljacki M. Compositae dermatitis. Med Pregl. 2003;56:43-49. doi:10.2298/mpns0302043j
- Krook G. Occupational dermatitis from Lactuca sativa (lettuce) and Cichorium (endive). simultaneous occurrence of immediate and delayed allergy as a cause of contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 1977;3:27-36. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1977.tb03583.x
- Paek SY, Lim HW. Chronic actinic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin. 2014;32:355-361, viii-ix. doi:10.1016/j.det.2014.03.007
- du P Menagé H, Hawk JL, White IR. Sesquiterpene lactone mix contact sensitivity and its relationship to chronic actinic dermatitis: a follow-up study. Contact Dermatitis. 1998;39:119-122. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1998.tb05859.x
- Wang CX, Belsito DV. Chronic actinic dermatitis revisited. Dermatitis. 2020;31:68-74. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000531
- DeLeo VA, Adler BL, Warshaw EM, et al. Photopatch test results of the North American contact dermatitis group, 1999-2009. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2022;38:288-291. doi:10.1111/phpp.12742
- McGovern TW, LaWarre S. Botanical briefs: the scourge of India—Parthenium hysterophorus L. Cutis. 2001;67:27-34. Published correction appears in Cutis. 2001;67:154.
- Sharma VK, Verma P, Maharaja K. Parthenium dermatitis. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2013;12:85-94. doi:10.1039/c2pp25186h
- Verma KK, Bansal A, Sethuraman G. Parthenium dermatitis treated with azathioprine weekly pulse doses. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:24-27. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.19713
- Sharma VK, Bhat R, Sethuraman G, et al. Treatment of Parthenium dermatitis with methotrexate. Contact Dermatitis. 2007;57:118-119. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2006.00950.x
- Burke DA, Corey G, Storrs FJ. Psoralen plus UVA protocol for Compositae photosensitivity. Am J Contact Dermat. 1996;7:171-176.
- Lovell CR. Allergic contact dermatitis due to plants. In: Plants and the Skin. Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1993:96-254.
- Dogra S, Parsad D, Handa S. Narrowband ultraviolet B in airborne contact dermatitis: a ray of hope! Br J Dermatol. 2004;150:373-374. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05724.x
- Lakshmi C, Srinivas CR, Jayaraman A. Ciclosporin in Parthenium dermatitis—a report of 2 cases. Contact Dermatitis. 2008;59:245-248. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01208.x
- Hendricks AJ, Yosipovitch G, Shi VY. Dupilumab use in dermatologic conditions beyond atopic dermatitis—a systematic review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021;32:19-28. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1689227
- Napolitano M, Fabbrocini G, Patruno C. Allergic contact dermatitis to Compositae: a possible cause of dupilumab-associated facial and neck dermatitis in atopic dermatitis patients? Contact Dermatitis. 2021;85:473-474. doi:10.1111/cod.13898
- Muddebihal A, Sardana K, Sinha S, et al. Tofacitinib in refractory Parthenium-induced airborne allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis. 2023;88:150-152. doi:10.1111/cod.14234
- Baltazar D, Shinamoto SR, Hamann CP, et al. Occupational airborne allergic contact dermatitis to invasive Compositae species treated with abrocitinib: a case report. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;87:542-544. doi:10.1111/cod.14204
Practice Points
- Asteraceae dermatitis can occur from direct contact with plants of the Asteraceae family; through airborne pollen; or from exposure to topical medications, cooking products, and cosmetics.
- Patient education on primary prevention, especially protective clothing, is crucial, as these plants are ubiquitous outdoors and have diverse phenotypes.
- Management of mild Asteraceae dermatitis consists primarily of topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors, while systemic corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive agents are utilized for severe or recalcitrant cases.
Beware the Manchineel: A Case of Irritant Contact Dermatitis
What is the world’s most dangerous tree? According to Guinness World Records1 (and one unlucky contestant on the wilderness survival reality show Naked and Afraid,2 who got its sap in his eyes and needed to be evacuated for treatment), the manchineel tree (Hippomane mancinella) has earned this designation.1-3 Manchineel trees are part of the strand vegetation of islands in the West Indies and along the Caribbean coasts of South and Central America, where their copious root systems help reduce coastal erosion. In the United States, this poisonous tree grows along the southern edge of Florida’s Everglades National Park; the Florida Keys; and the US Virgin Islands, especially Virgin Islands National Park. Although the manchineel tree appears on several endangered species lists,4-6 there are places within its distribution where it is locally abundant and thus poses a risk to residents and visitors.
The first European description of manchineel toxicity was by Peter Martyr d’Anghiera, a court historian and geographer of Christopher Columbus’s patroness, Isabella I, Queen of Castile and Léon. In the early 1500s, Peter Martyr wrote that on Columbus’s second New World voyage in 1493, the crew encountered a mysterious tree that burned the skin and eyes of anyone who had contact with it.7 Columbus called the tree’s fruit manzanilla de la muerte (“little apple of death”) after several sailors became severely ill from eating the fruit.8,9 Manchineel lore is rife with tales of agonizing death after eating the applelike fruit, and several contemporaneous accounts describe indigenous Caribbean islanders using manchineel’s toxic sap as an arrow poison.10
Eating manchineel fruit is known to cause abdominal pain, burning sensations in the oropharynx, and esophageal spasms.11 Several case reports mention that consuming the fruit can create an exaggerated
Case Report
A 64-year-old physician (S.A.N.) came across a stand of manchineel trees while camping in the Virgin Islands National Park on St. John in the US Virgin Islands (Figure 1). The patient—who was knowledgeable about tropical ecology and was familiar with the tree—was curious about its purported cutaneous toxicity and applied the viscous white sap of a broken branchlet (Figure 2) to a patch of skin measuring 4 cm in diameter on the medial left calf. He took serial photographs of the site on days 2, 4 (Figure 3), 6, and 10 (Figure 4), showing the onset of erythema and the subsequent development of follicular pustules. On day 6, a 4-mm punch biopsy specimen was taken of the most prominent pustule. Histopathology showed a subcorneal acantholytic blister and epidermal spongiosis overlying a mixed perivascular infiltrate and follicular necrosis, which was consistent with irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 5). On day 8, the region became indurated and tender to pressure; however, there was no warmth, edema, purulent drainage, lymphangitic streaks, or other signs of infection. The region was never itchy; it was uncomfortable only with firm direct pressure. The patient applied hot compresses to the site for 10 minutes 1 to 2 times daily for roughly 2 weeks, and the affected area healed fully (without any additional intervention) in approximately 6 weeks.


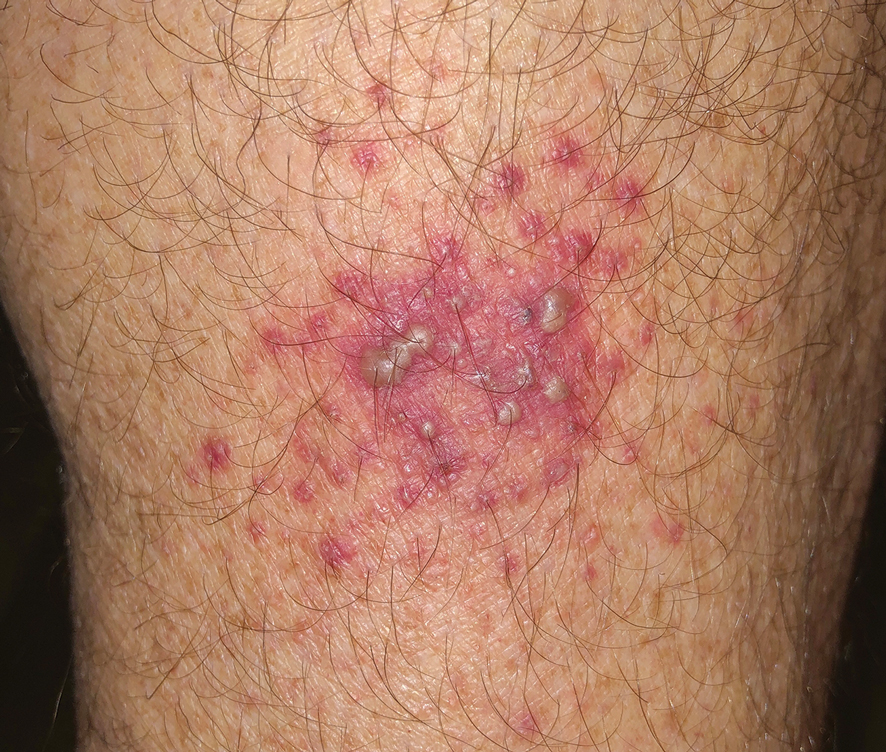
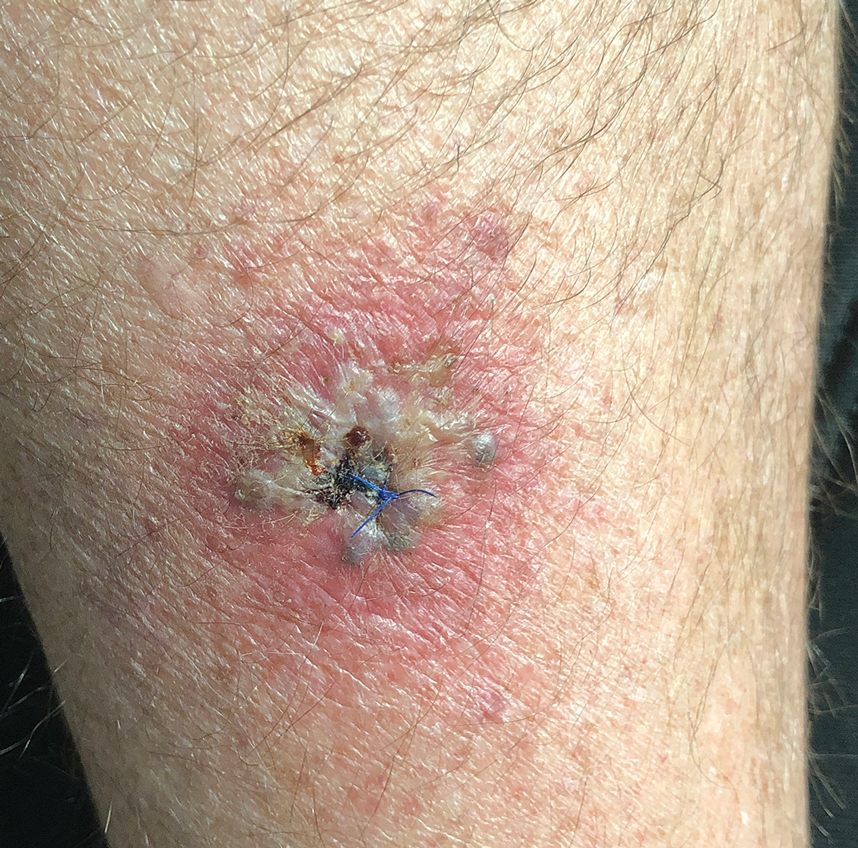
Comment
Manchineel is a member of the Euphorbiaceae (also known as the euphorb or spurge) family, a mainly tropical or subtropical plant family that includes many useful as well as many toxic species. Examples of useful plants include cassava (Manihot esculenta) and the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Many euphorbs have well-described toxicities, and many (eg, castor bean, Ricinus communis) are useful in some circumstances and toxic in others.6,12-14 Many euphorbs are known to cause skin reactions, usually due to toxins in the milky sap that directly irritate the skin or to latex compounds that can induce IgE-mediated contact dermatitis.9,14
Manchineel contains a complex mix of toxins, though no specific one has been identified as the main cause of the associated irritant contact dermatitis. Manchineel sap (and sap of many other euphorbs) contains phorbol esters that may cause direct pH-induced cytotoxicity leading to keratinocyte necrosis. Diterpenes may augment this cytotoxic effect via induction of proinflammatory cytokines.12 Pitts et al5 pointed to a mixture of oxygenated diterpene esters as the primary cause of toxicity and suggested that their water solubility explained occurrences of keratoconjunctivitis after contact with rainwater or dew from the manchineel tree.
All parts of the manchineel tree—fruit, leaves, wood, and sap—are poisonous. In a retrospective series of 97 cases of manchineel fruit ingestion, the most common symptoms were oropharyngeal pain (68% [66/97]), abdominal pain (42% [41/97]), and diarrhea (37% [36/97]). The same series identified 1 (1%) case of bradycardia and hypotension.3 Contact with the wood, exposure to sawdust, and inhalation of smoke from burning the wood can irritate the skin, conjunctivae, or nasopharynx. Rainwater or dew dripping from the leaves onto the skin can cause dermatitis and ophthalmitis, even without direct contact with the tree.4,5
Management—There is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis. Because it is an irritant reaction and not a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, topical corticosteroids have minimal benefit. A regimen consisting of a thorough cleansing, wet compresses, and observation, as most symptoms resolve spontaneously within a few days, has been recommended.4 Our patient used hot compresses, which he believes helped heal the site, although his symptoms lasted for several weeks.
Given that there is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis, the wisest approach is strict avoidance. On many Caribbean islands, visitors are warned about the manchineel tree, advised to avoid direct contact, and reminded to avoid standing beneath it during a rainstorm (Figure 6).

Conclusion
This article begins with a question: “What is the world’s most dangerous tree?” Many sources from the indexed medical literature as well as the popular press and social media state that it is the manchineel. Although all parts of the manchineel tree are highly toxic, human exposures are uncommon, and deaths are more apocryphal than actual.
- Most dangerous tree. Guinness World Records. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/most-dangerous-tree
- Naked and Afraid: Garden of Evil (S4E9). Discovery Channel. June 21, 2015. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://go.discovery.com/video/naked-and-afraid-discovery/garden-of-evil
- Boucaud-Maitre D, Cachet X, Bouzidi C, et al. Severity of manchineel fruit (Hippomane mancinella) poisoning: a retrospective case series of 97 patients from French Poison Control Centers. Toxicon. 2019;161:28-32. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.02.014
- Blue LM, Sailing C, Denapoles C, et al. Manchineel dermatitis in North American students in the Caribbean. J Travel Medicine. 2011;18:422-424. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2011.00568.x
- Pitts JF, Barker NH, Gibbons DC, et al. Manchineel keratoconjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1993;77:284-288. doi:10.1136/bjo.77.5.284
- Lauter WM, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella, L. I. historical review. J Pharm Sci. 1952;41:199-201. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.3030410412
- Martyr P. De Orbe Novo: the Eight Decades of Peter Martyr d’Anghera. Vol 1. FA MacNutt (translator). GP Putnam’s Sons; 1912. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://gutenberg.org/cache/epub/12425/pg12425.txt
- Fernandez de Ybarra AM. A forgotten medical worthy, Dr. Diego Alvarex Chanca, of Seville, Spain, and his letter describing the second voyage of Christopher Columbus to America. Med Library Hist J. 1906;4:246-263.
- Muscat MK. Manchineel apple of death. EJIFCC. 2019;30:346-348.
- Handler JS. Aspects of Amerindian ethnography in 17th century Barbados. Caribbean Studies. 1970;9:50-72.
- Howard RA. Three experiences with the manchineel (Hippomane spp., Euphorbiaceae). Biotropica. 1981;13:224-227. https://doi.org/10.2307/2388129
- Rao KV. Toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella. Planta Med. 1974;25:166-171. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1097927
- Lauter WM, Foote PA. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. II. Preliminary isolation of a toxic principle of the fruit. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1955;44:361-363. doi:10.1002/jps.3030440616
- Carroll MN Jr, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. III. Toxic actions of extracts of Hippomane mancinella L. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1957;46:93-97. doi:10.1002/jps.3030460206
What is the world’s most dangerous tree? According to Guinness World Records1 (and one unlucky contestant on the wilderness survival reality show Naked and Afraid,2 who got its sap in his eyes and needed to be evacuated for treatment), the manchineel tree (Hippomane mancinella) has earned this designation.1-3 Manchineel trees are part of the strand vegetation of islands in the West Indies and along the Caribbean coasts of South and Central America, where their copious root systems help reduce coastal erosion. In the United States, this poisonous tree grows along the southern edge of Florida’s Everglades National Park; the Florida Keys; and the US Virgin Islands, especially Virgin Islands National Park. Although the manchineel tree appears on several endangered species lists,4-6 there are places within its distribution where it is locally abundant and thus poses a risk to residents and visitors.
The first European description of manchineel toxicity was by Peter Martyr d’Anghiera, a court historian and geographer of Christopher Columbus’s patroness, Isabella I, Queen of Castile and Léon. In the early 1500s, Peter Martyr wrote that on Columbus’s second New World voyage in 1493, the crew encountered a mysterious tree that burned the skin and eyes of anyone who had contact with it.7 Columbus called the tree’s fruit manzanilla de la muerte (“little apple of death”) after several sailors became severely ill from eating the fruit.8,9 Manchineel lore is rife with tales of agonizing death after eating the applelike fruit, and several contemporaneous accounts describe indigenous Caribbean islanders using manchineel’s toxic sap as an arrow poison.10
Eating manchineel fruit is known to cause abdominal pain, burning sensations in the oropharynx, and esophageal spasms.11 Several case reports mention that consuming the fruit can create an exaggerated
Case Report
A 64-year-old physician (S.A.N.) came across a stand of manchineel trees while camping in the Virgin Islands National Park on St. John in the US Virgin Islands (Figure 1). The patient—who was knowledgeable about tropical ecology and was familiar with the tree—was curious about its purported cutaneous toxicity and applied the viscous white sap of a broken branchlet (Figure 2) to a patch of skin measuring 4 cm in diameter on the medial left calf. He took serial photographs of the site on days 2, 4 (Figure 3), 6, and 10 (Figure 4), showing the onset of erythema and the subsequent development of follicular pustules. On day 6, a 4-mm punch biopsy specimen was taken of the most prominent pustule. Histopathology showed a subcorneal acantholytic blister and epidermal spongiosis overlying a mixed perivascular infiltrate and follicular necrosis, which was consistent with irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 5). On day 8, the region became indurated and tender to pressure; however, there was no warmth, edema, purulent drainage, lymphangitic streaks, or other signs of infection. The region was never itchy; it was uncomfortable only with firm direct pressure. The patient applied hot compresses to the site for 10 minutes 1 to 2 times daily for roughly 2 weeks, and the affected area healed fully (without any additional intervention) in approximately 6 weeks.





Comment
Manchineel is a member of the Euphorbiaceae (also known as the euphorb or spurge) family, a mainly tropical or subtropical plant family that includes many useful as well as many toxic species. Examples of useful plants include cassava (Manihot esculenta) and the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Many euphorbs have well-described toxicities, and many (eg, castor bean, Ricinus communis) are useful in some circumstances and toxic in others.6,12-14 Many euphorbs are known to cause skin reactions, usually due to toxins in the milky sap that directly irritate the skin or to latex compounds that can induce IgE-mediated contact dermatitis.9,14
Manchineel contains a complex mix of toxins, though no specific one has been identified as the main cause of the associated irritant contact dermatitis. Manchineel sap (and sap of many other euphorbs) contains phorbol esters that may cause direct pH-induced cytotoxicity leading to keratinocyte necrosis. Diterpenes may augment this cytotoxic effect via induction of proinflammatory cytokines.12 Pitts et al5 pointed to a mixture of oxygenated diterpene esters as the primary cause of toxicity and suggested that their water solubility explained occurrences of keratoconjunctivitis after contact with rainwater or dew from the manchineel tree.
All parts of the manchineel tree—fruit, leaves, wood, and sap—are poisonous. In a retrospective series of 97 cases of manchineel fruit ingestion, the most common symptoms were oropharyngeal pain (68% [66/97]), abdominal pain (42% [41/97]), and diarrhea (37% [36/97]). The same series identified 1 (1%) case of bradycardia and hypotension.3 Contact with the wood, exposure to sawdust, and inhalation of smoke from burning the wood can irritate the skin, conjunctivae, or nasopharynx. Rainwater or dew dripping from the leaves onto the skin can cause dermatitis and ophthalmitis, even without direct contact with the tree.4,5
Management—There is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis. Because it is an irritant reaction and not a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, topical corticosteroids have minimal benefit. A regimen consisting of a thorough cleansing, wet compresses, and observation, as most symptoms resolve spontaneously within a few days, has been recommended.4 Our patient used hot compresses, which he believes helped heal the site, although his symptoms lasted for several weeks.
Given that there is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis, the wisest approach is strict avoidance. On many Caribbean islands, visitors are warned about the manchineel tree, advised to avoid direct contact, and reminded to avoid standing beneath it during a rainstorm (Figure 6).

Conclusion
This article begins with a question: “What is the world’s most dangerous tree?” Many sources from the indexed medical literature as well as the popular press and social media state that it is the manchineel. Although all parts of the manchineel tree are highly toxic, human exposures are uncommon, and deaths are more apocryphal than actual.
What is the world’s most dangerous tree? According to Guinness World Records1 (and one unlucky contestant on the wilderness survival reality show Naked and Afraid,2 who got its sap in his eyes and needed to be evacuated for treatment), the manchineel tree (Hippomane mancinella) has earned this designation.1-3 Manchineel trees are part of the strand vegetation of islands in the West Indies and along the Caribbean coasts of South and Central America, where their copious root systems help reduce coastal erosion. In the United States, this poisonous tree grows along the southern edge of Florida’s Everglades National Park; the Florida Keys; and the US Virgin Islands, especially Virgin Islands National Park. Although the manchineel tree appears on several endangered species lists,4-6 there are places within its distribution where it is locally abundant and thus poses a risk to residents and visitors.
The first European description of manchineel toxicity was by Peter Martyr d’Anghiera, a court historian and geographer of Christopher Columbus’s patroness, Isabella I, Queen of Castile and Léon. In the early 1500s, Peter Martyr wrote that on Columbus’s second New World voyage in 1493, the crew encountered a mysterious tree that burned the skin and eyes of anyone who had contact with it.7 Columbus called the tree’s fruit manzanilla de la muerte (“little apple of death”) after several sailors became severely ill from eating the fruit.8,9 Manchineel lore is rife with tales of agonizing death after eating the applelike fruit, and several contemporaneous accounts describe indigenous Caribbean islanders using manchineel’s toxic sap as an arrow poison.10
Eating manchineel fruit is known to cause abdominal pain, burning sensations in the oropharynx, and esophageal spasms.11 Several case reports mention that consuming the fruit can create an exaggerated
Case Report
A 64-year-old physician (S.A.N.) came across a stand of manchineel trees while camping in the Virgin Islands National Park on St. John in the US Virgin Islands (Figure 1). The patient—who was knowledgeable about tropical ecology and was familiar with the tree—was curious about its purported cutaneous toxicity and applied the viscous white sap of a broken branchlet (Figure 2) to a patch of skin measuring 4 cm in diameter on the medial left calf. He took serial photographs of the site on days 2, 4 (Figure 3), 6, and 10 (Figure 4), showing the onset of erythema and the subsequent development of follicular pustules. On day 6, a 4-mm punch biopsy specimen was taken of the most prominent pustule. Histopathology showed a subcorneal acantholytic blister and epidermal spongiosis overlying a mixed perivascular infiltrate and follicular necrosis, which was consistent with irritant contact dermatitis (Figure 5). On day 8, the region became indurated and tender to pressure; however, there was no warmth, edema, purulent drainage, lymphangitic streaks, or other signs of infection. The region was never itchy; it was uncomfortable only with firm direct pressure. The patient applied hot compresses to the site for 10 minutes 1 to 2 times daily for roughly 2 weeks, and the affected area healed fully (without any additional intervention) in approximately 6 weeks.





Comment
Manchineel is a member of the Euphorbiaceae (also known as the euphorb or spurge) family, a mainly tropical or subtropical plant family that includes many useful as well as many toxic species. Examples of useful plants include cassava (Manihot esculenta) and the rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). Many euphorbs have well-described toxicities, and many (eg, castor bean, Ricinus communis) are useful in some circumstances and toxic in others.6,12-14 Many euphorbs are known to cause skin reactions, usually due to toxins in the milky sap that directly irritate the skin or to latex compounds that can induce IgE-mediated contact dermatitis.9,14
Manchineel contains a complex mix of toxins, though no specific one has been identified as the main cause of the associated irritant contact dermatitis. Manchineel sap (and sap of many other euphorbs) contains phorbol esters that may cause direct pH-induced cytotoxicity leading to keratinocyte necrosis. Diterpenes may augment this cytotoxic effect via induction of proinflammatory cytokines.12 Pitts et al5 pointed to a mixture of oxygenated diterpene esters as the primary cause of toxicity and suggested that their water solubility explained occurrences of keratoconjunctivitis after contact with rainwater or dew from the manchineel tree.
All parts of the manchineel tree—fruit, leaves, wood, and sap—are poisonous. In a retrospective series of 97 cases of manchineel fruit ingestion, the most common symptoms were oropharyngeal pain (68% [66/97]), abdominal pain (42% [41/97]), and diarrhea (37% [36/97]). The same series identified 1 (1%) case of bradycardia and hypotension.3 Contact with the wood, exposure to sawdust, and inhalation of smoke from burning the wood can irritate the skin, conjunctivae, or nasopharynx. Rainwater or dew dripping from the leaves onto the skin can cause dermatitis and ophthalmitis, even without direct contact with the tree.4,5
Management—There is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis. Because it is an irritant reaction and not a type IV hypersensitivity reaction, topical corticosteroids have minimal benefit. A regimen consisting of a thorough cleansing, wet compresses, and observation, as most symptoms resolve spontaneously within a few days, has been recommended.4 Our patient used hot compresses, which he believes helped heal the site, although his symptoms lasted for several weeks.
Given that there is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis, the wisest approach is strict avoidance. On many Caribbean islands, visitors are warned about the manchineel tree, advised to avoid direct contact, and reminded to avoid standing beneath it during a rainstorm (Figure 6).

Conclusion
This article begins with a question: “What is the world’s most dangerous tree?” Many sources from the indexed medical literature as well as the popular press and social media state that it is the manchineel. Although all parts of the manchineel tree are highly toxic, human exposures are uncommon, and deaths are more apocryphal than actual.
- Most dangerous tree. Guinness World Records. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/most-dangerous-tree
- Naked and Afraid: Garden of Evil (S4E9). Discovery Channel. June 21, 2015. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://go.discovery.com/video/naked-and-afraid-discovery/garden-of-evil
- Boucaud-Maitre D, Cachet X, Bouzidi C, et al. Severity of manchineel fruit (Hippomane mancinella) poisoning: a retrospective case series of 97 patients from French Poison Control Centers. Toxicon. 2019;161:28-32. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.02.014
- Blue LM, Sailing C, Denapoles C, et al. Manchineel dermatitis in North American students in the Caribbean. J Travel Medicine. 2011;18:422-424. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2011.00568.x
- Pitts JF, Barker NH, Gibbons DC, et al. Manchineel keratoconjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1993;77:284-288. doi:10.1136/bjo.77.5.284
- Lauter WM, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella, L. I. historical review. J Pharm Sci. 1952;41:199-201. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.3030410412
- Martyr P. De Orbe Novo: the Eight Decades of Peter Martyr d’Anghera. Vol 1. FA MacNutt (translator). GP Putnam’s Sons; 1912. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://gutenberg.org/cache/epub/12425/pg12425.txt
- Fernandez de Ybarra AM. A forgotten medical worthy, Dr. Diego Alvarex Chanca, of Seville, Spain, and his letter describing the second voyage of Christopher Columbus to America. Med Library Hist J. 1906;4:246-263.
- Muscat MK. Manchineel apple of death. EJIFCC. 2019;30:346-348.
- Handler JS. Aspects of Amerindian ethnography in 17th century Barbados. Caribbean Studies. 1970;9:50-72.
- Howard RA. Three experiences with the manchineel (Hippomane spp., Euphorbiaceae). Biotropica. 1981;13:224-227. https://doi.org/10.2307/2388129
- Rao KV. Toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella. Planta Med. 1974;25:166-171. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1097927
- Lauter WM, Foote PA. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. II. Preliminary isolation of a toxic principle of the fruit. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1955;44:361-363. doi:10.1002/jps.3030440616
- Carroll MN Jr, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. III. Toxic actions of extracts of Hippomane mancinella L. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1957;46:93-97. doi:10.1002/jps.3030460206
- Most dangerous tree. Guinness World Records. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/most-dangerous-tree
- Naked and Afraid: Garden of Evil (S4E9). Discovery Channel. June 21, 2015. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://go.discovery.com/video/naked-and-afraid-discovery/garden-of-evil
- Boucaud-Maitre D, Cachet X, Bouzidi C, et al. Severity of manchineel fruit (Hippomane mancinella) poisoning: a retrospective case series of 97 patients from French Poison Control Centers. Toxicon. 2019;161:28-32. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.02.014
- Blue LM, Sailing C, Denapoles C, et al. Manchineel dermatitis in North American students in the Caribbean. J Travel Medicine. 2011;18:422-424. doi:10.1111/j.1708-8305.2011.00568.x
- Pitts JF, Barker NH, Gibbons DC, et al. Manchineel keratoconjunctivitis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1993;77:284-288. doi:10.1136/bjo.77.5.284
- Lauter WM, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella, L. I. historical review. J Pharm Sci. 1952;41:199-201. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.3030410412
- Martyr P. De Orbe Novo: the Eight Decades of Peter Martyr d’Anghera. Vol 1. FA MacNutt (translator). GP Putnam’s Sons; 1912. Accessed October 14, 2024. https://gutenberg.org/cache/epub/12425/pg12425.txt
- Fernandez de Ybarra AM. A forgotten medical worthy, Dr. Diego Alvarex Chanca, of Seville, Spain, and his letter describing the second voyage of Christopher Columbus to America. Med Library Hist J. 1906;4:246-263.
- Muscat MK. Manchineel apple of death. EJIFCC. 2019;30:346-348.
- Handler JS. Aspects of Amerindian ethnography in 17th century Barbados. Caribbean Studies. 1970;9:50-72.
- Howard RA. Three experiences with the manchineel (Hippomane spp., Euphorbiaceae). Biotropica. 1981;13:224-227. https://doi.org/10.2307/2388129
- Rao KV. Toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella. Planta Med. 1974;25:166-171. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1097927
- Lauter WM, Foote PA. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. II. Preliminary isolation of a toxic principle of the fruit. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1955;44:361-363. doi:10.1002/jps.3030440616
- Carroll MN Jr, Fox LE, Ariail WT. Investigation of the toxic principles of Hippomane mancinella L. III. Toxic actions of extracts of Hippomane mancinella L. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1957;46:93-97. doi:10.1002/jps.3030460206
PRACTICE POINTS
- Sap from the manchineel tree—found on the coasts of Caribbean islands, the Atlantic coastline of Central and northern South America, and parts of southernmost Florida—can cause severe dermatologic and ophthalmologic injuries. Eating its fruit can lead to oropharyngeal pain and diarrhea.
- Histopathology of manchineel dermatitis reveals a subcorneal acantholytic blister and epidermal spongiosis overlying a mixed perivascular infiltrate and follicular necrosis, which is consistent with irritant contact dermatitis.
- There is no specific treatment for manchineel dermatitis. Case reports advocate a thorough cleansing, application of wet compresses, and observation.
Projected 2023 Cost Reduction From Tumor Necrosis Factor α Inhibitor Biosimilars in Dermatology: A National Medicare Analysis
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).

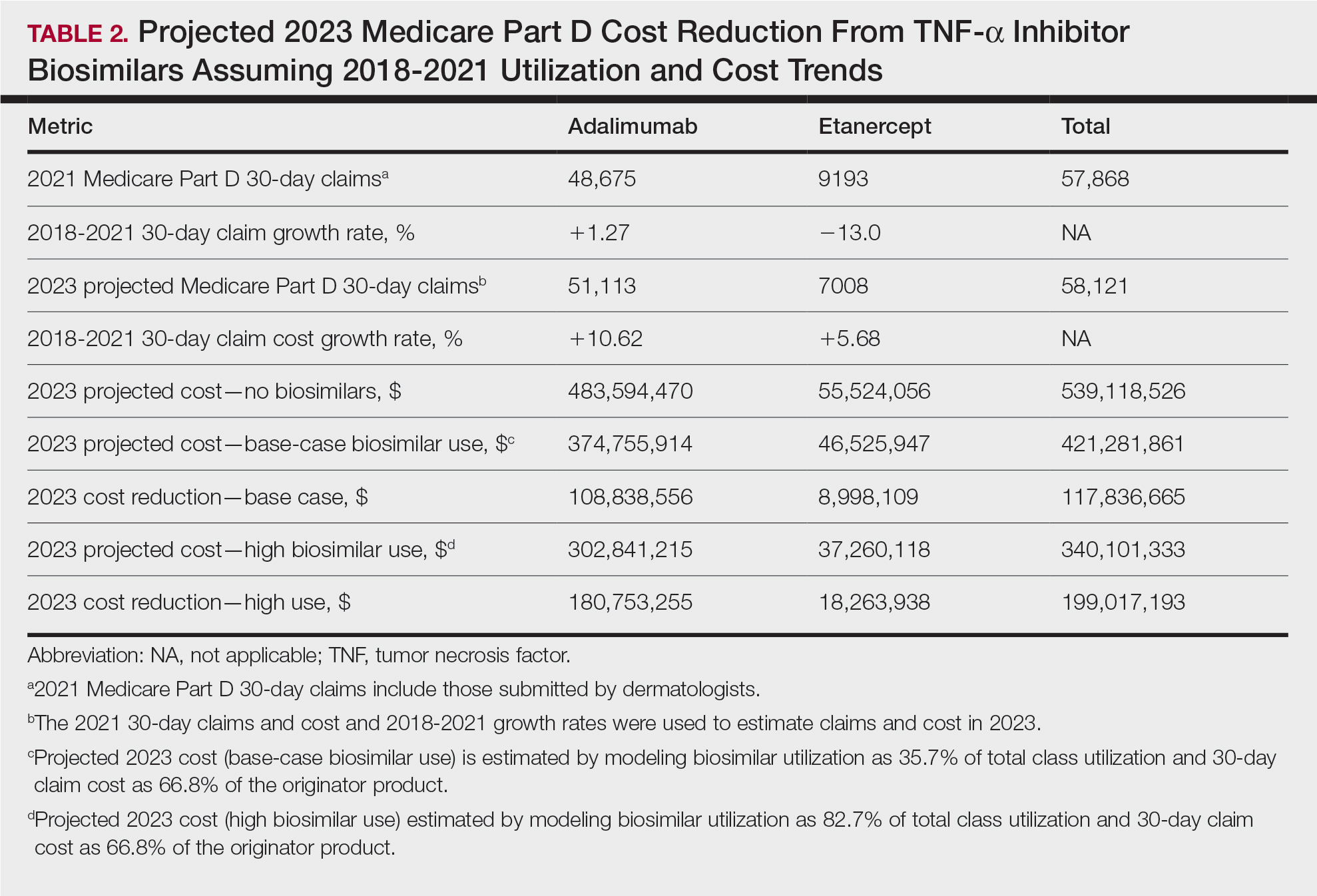
Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).


Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
To the Editor:
Although biologics provide major therapeutic benefits for dermatologic conditions, they also come with a substantial cost, making them among the most expensive medications available. Medicare and Medicaid spending on biologics for dermatologic conditions increased by 320% from 2012 to 2018, reaching a staggering $10.6 billion in 2018 alone.1 Biosimilars show promise in reducing health care spending for dermatologic conditions; however, their utilization has been limited due to multiple factors, including delayed market entry from patent thickets, exclusionary formulary contracts, and prescriber skepticism regarding their safety and efficacy.2 For instance, a national survey of 1201 US physicians in specialties that are high prescribers of biologics reported that 55% doubted the safety and appropriateness of biosimilars.3
US Food and Drug Administration approval of biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept offers the potential to reduce health care spending for dermatologic conditions. However, this cost reduction is dependent on utilization rates among dermatologists. In this national cross-sectional review of Medicare data, we predicted the impact of these biosimilars on dermatologic Medicare costs and demonstrated how differing utilization rates among dermatologists can influence potential savings.
To model 2023 utilization and cost reduction from biosimilars, we analyzed Medicare Part D data from 2020 on existing biosimilars, including granulocyte colony–stimulating factors, erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, and tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors.4 Methods in line with a 2021 report from the US Department of Health and Human Services5 as well as those of Yazdany et al6 were used. For each class, we calculated the 2020 distribution of biosimilar and originator drug claims as well as biosimilar cost reduction per 30-day claim. We utilized 2018-2021 annual growth rates for branded adalimumab and etanercept to estimate 30-day claims for 2023 and the cost of these branded agents in the absence of biosimilars. The hypothetical 2023 cost reduction from adalimumab and etanercept biosimilars was estimated by assuming 2020 biosimilar utilization rates and mean cost reduction per claim. This study utilized publicly available or aggregate summary data (not attributable to specific patients) and did not qualify as human subject research; therefore, institutional review board approval was not required.
In 2020, biosimilar utilization proportions ranged from 6.4% (tumor necrosis factor α inhibitors) to 82.7% (granulocyte colony–stimulating factors), with a mean across all classes of 35.7%. On average, the cost per 30-day claim of biosimilars was 66.8% of originator agents (Table 1). In 2021, we identified 57,868 30-day claims for branded adalimumab and etanercept submitted by dermatologists. From 2018 to 2021, 30-day branded adalimumab claims increased by 1.27% annually (cost + 10.62% annually), while claims for branded etanercept decreased by 13.0% annually (cost + 5.68% annually). Assuming these trends, the cost of branded adalimumab and etanercept was estimated to be $539 million in 2023. Applying the aforementioned 35.7% utilization, the introduction of biosimilars in dermatology would yield a cost reduction of approximately $118 million (21.9%). A high utilization rate (82.7%) of biosimilars among dermatologists would increase cost savings to $199 million (36.9%)(Table 2).


Our study demonstrates that the introduction of 2 biosimilars into dermatology may result in a notable reduction in Medicare expenditures. The savings observed are likely to translate to substantial cost savings for patients. A cross-sectional analysis of 2020 Medicare data indicated that coverage for psoriasis medications was 10.0% to 99.8% across different products and Medicare Part D plans. Consequently, patients faced considerable out-of-pocket expenses, amounting to $5653 and $5714 per year for adalimumab and etanercept, respectively.7
We found that the extent of savings from biosimilars was dependent on the utilization rates among dermatologists, with the highest utilization rate almost doubling the total savings of average utilization rates. Given the impact of high utilization and the wide variation observed, understanding the factors that have influenced uptake of biosimilars is important to increasing utilization as these medications become integrated into dermatology. For instance, limited uptake of infliximab initially may have been influenced by concerns about efficacy and increased adverse events.8,9 In contrast, the high utilization of filgrastim biosimilars (82.7%) may be attributed to its longevity in the market and familiarity to prescribers, as filgrastim was the first biosimilar to be approved in the United States.10
Promoting reasonable utilization of biosimilars may require prescriber education on their safety and approval processes, which could foster increased utilization and reduce skepticism.4 Under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act, the US Food and Drug Administration approves biosimilars only when they exhibit “high similarity” and show no “clinically meaningful differences” compared to the reference biologic, with no added safety risks or reduced efficacy.11 Moreover, a 2023 systematic review of 17 studies found no major difference in efficacy and safety between biosimilars and originators of etanercept, infliximab, and other biologics.12 Understanding these findings may reassure dermatologists and patients about the reliability and safety of biosimilars.
A limitation of our study is that it solely assesses Medicare data and estimates derived from existing (separate) biologic classes. It also does not account for potential expenditure shifts to newer biologic agents (eg, IL-12/17/23 inhibitors) or changes in manufacturer behavior or promotions. Nevertheless, it indicates notable financial savings from new biosimilar agents in dermatology; along with their compelling efficacy and safety profiles, this could represent a substantial benefit to patients and the health care system.
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
- Price KN, Atluri S, Hsiao JL, et al. Medicare and medicaid spending trends for immunomodulators prescribed for dermatologic conditions. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;33:575-579.
- Zhai MZ, Sarpatwari A, Kesselheim AS. Why are biosimilars not living up to their promise in the US? AMA J Ethics. 2019;21:E668-E678. doi:10.1001/amajethics.2019.668
- Cohen H, Beydoun D, Chien D, et al. Awareness, knowledge, and perceptions of biosimilars among specialty physicians. Adv Ther. 2017;33:2160-2172.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Part D prescribers— by provider and drug. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://data.cms.gov/provider-summary-by-type-of-service/medicare-part-d-prescribers/medicare-part-d-prescribers-by-provider-and-drug/data
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General. Medicare Part D and beneficiaries could realize significant spending reductions with increased biosimilar use. Accessed September 11, 2024. https://oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/OEI-05-20-00480.pdf
- Yazdany J, Dudley RA, Lin GA, et al. Out-of-pocket costs for infliximab and its biosimilar for rheumatoid arthritis under Medicare Part D. JAMA. 2018;320:931-933. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.7316
- Pourali SP, Nshuti L, Dusetzina SB. Out-of-pocket costs of specialty medications for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treatment in the medicare population. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1239-1241. doi:10.1001/ jamadermatol.2021.3616
- Lebwohl M. Biosimilars in dermatology. JAMA Dermatol. 2021; 157:641-642. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0219
- Westerkam LL, Tackett KJ, Sayed CJ. Comparing the effectiveness and safety associated with infliximab vs infliximab-abda therapy for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:708-711. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0220
- Awad M, Singh P, Hilas O. Zarxio (Filgrastim-sndz): the first biosimilar approved by the FDA. P T. 2017;42:19-23.
- Development of therapeutic protein biosimilars: comparative analytical assessment and other quality-related considerations guidance for industry. US Department of Health and Human Services website. Updated June 15, 2022. Accessed October 21, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/development-therapeutic-protein-biosimilars-comparative-analyticalassessment-and-other-quality
- Phan DB, Elyoussfi S, Stevenson M, et al. Biosimilars for the treatment of psoriasis: a systematic review of clinical trials and observational studies. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159:763-771. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.1338
Practice Points
- Biosimilars for adalimumab and etanercept are safe and effective alternatives with the potential to reduce health care costs in dermatology by approximately $118 million.
- A high utilization rate of biosimilars by dermatologists would increase cost savings even further.
Phenytoin-Induced DRESS Syndrome: Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.
Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.
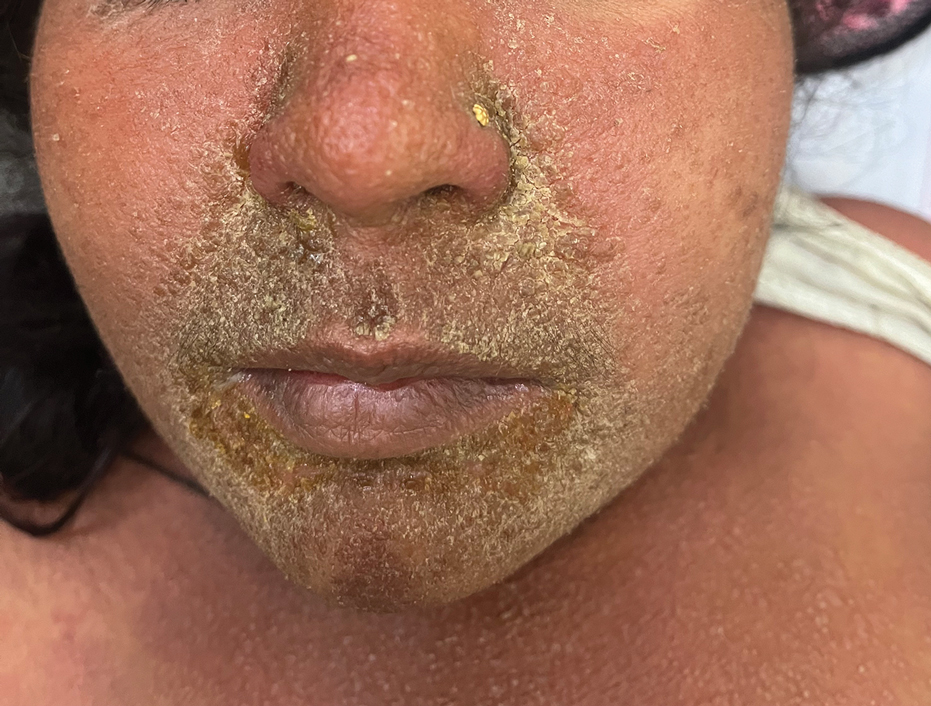
Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.

Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.

Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
To the Editor:
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome—a severe cutaneous adverse drug reaction—is characterized by a cutaneous rash and systemic upset in the form of various internal organ and hematologic disturbances. This delayed and idiosyncratic syndrome went by several names, including anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome, before Bocquet et al1 proposed the term DRESS syndrome.
Phenytoin, a hydantoin derivative used in neurology, was implicated in 41% of cases of DRESS syndrome in a study of 100 patients conducted in southern India.2,3 While DRESS syndrome is a newer name, the clinical picture of DRESS secondary to phenytoin use remains similar in that it manifests with a morbilliform rash and systemic upset. We sought to describe the clinical and laboratory characteristics of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome in this case series.
The analysis included 23 patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use who presented to a tertiary care institution in North India between July 2021 and December 2022, satisfied the European Registry of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reaction (RegiSCAR) criteria,4 and achieved a DRESS diagnostic score of more than 1. The mean age of the patients was 44 years (range, 14–74 years). There was a slight female predominance with a male to female ratio of 0.9:1. More than half of the patients (52.2% [12/23]) presented directly to the dermatology outpatient department; the remaining patients were referred from other departments (47.8% [11/23]). Patients primarily were receiving phenytoin for neurologic indications. Specific reasons included antiseizure prophylaxis following a traffic accident (34.8% [8/23]); epilepsy (26.1% [6/23]); and neoplastic (17.4% [4/23]), vascular (17.4% [4/23]), and infectious (4.3% [1/23]) causes. The mean latency period from drug intake to symptom onset was 29 days (range, 6–62 days), and the mean illness duration was 9 days (range, 1–45 days).
The majority of patients experienced pruritus (91.3% [21/23]) and fever (74.0% [17/23]), and all initially had a rash. Maculopapular morphology was seen in all patients. Erythema multiforme–like (17.4% [4/23]), erythrodermic (17.4% [4/23]), and vesicular (13.0% [3/23]) rashes also were documented (Figure 1). The trunk (100% [23/23]) and extremities (95.7% [22/23]) were involved most often, followed by the palms and soles (56.5% [13/23]). The mean total body surface area affected was 73.65%. Only 7 patients (30.4%) had mucosal involvement; nonhemorrhagic cheilitis was the most common manifestation.

Facial edema, a hallmark feature of DRESS syndrome, was noted in 69.6% (16/23) of patients (Figure 2). Lymphadenopathy was present in 43.5% (10/23) of patients; of those cases, the inguinal (40.0%; n=4) and cervical (30%; n=3) nodes most commonly were involved. Although DRESS syndrome can affect internal organs, this was an issue for only 2 (8.7%) patients who experienced mild hepatomegaly.

Laboratory investigations revealed a mean differential eosinophil percentage of 10.3% (reference range, 1%–4%), while the mean absolute eosinophil count was 1.0634×109/L (reference range, 0.02–0.5×109/L). Other hematologic findings included the mean percentages of neutrophils (60%; reference range, 50%–60%), lymphocytes (19.95%; reference range, 20%–50%), and monocytes (8.70%; reference range, 2%–8%).
Liver function tests revealed transaminitis5 as the most common finding, with mean aspartate aminotransferase levels of 109 U/L (reference range, 8–33 U/L), mean alanine aminotransferase of 97.9 U/L (reference range, 7–56 U/L), and mean alkaline phosphatase levels of 211.35 U/L (reference range, 44–147 U/L). Half of the patients had notable (>2 times the upper limit of normal) transaminitis.
Renal blood workup revealed slightly elevated blood urea nitrogen levels with a mean value of 28.4 mg/dL (reference range, 6–24 mg/dL), and mean serum creatinine was 0.78 mg/dL (reference range for men, 0.7–1.3 mg/dL; for women, 0.6–1.1 mg/dL).
All patients were treated with oral steroids (prednisolone 1 mg/kg/d) before tapering slowly over the following 6 to 8 weeks. The culprit drug (phenytoin) was stopped on the day of presentation. Resolution of rash and itching was seen in all patients by 3 weeks after presentation without any relapse by follow-up at 6 weeks from presentation to the hospital.
Our case series seeks to discuss the clinical and laboratory features of phenytoin-induced DRESS syndrome. Our patients had more erythrodermic and erythema multiforme–like morphologies, less mucosal involvement, more hepatic involvement, and earlier resolution.
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
- Bocquet H, Bagot M, Roujeau JC. Drug-induced pseudolymphoma and drug hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms: DRESS). Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1996;15:250-257. doi:10.1016/s1085-5629(96)80038-1
- Patocka J, Wu Q, Nepovimova E, et al. Phenytoin—an anti-seizure drug: overview of its chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;142:111393. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111393
- Sasidharanpillai S, Chathoth AT, Khader A, et al. Predictors of disease severity in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2019;85:266-275. doi:10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_482_17
- Kardaun SH, Sekula P, Valeyrie-Allanore L, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS): an original multisystem adverse drug reaction. Results from the prospective RegiSCAR study. Brit J Dermatol. 2013;169:1071-1080.
- Morán-Mariños C, Alva-Diaz C, De la Cruz Ramirez W, et al. Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) induced by phenytoin re-exposure: case report and systematic review. Acta Clin Belg. 2022;77:177-185. doi:10.1080/17843286.2020.1767459
Practice Points
- Phenytoin has been implicated in drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and common symptoms include rash, pruritus, and fever.
- Transaminitis may occur in patients with DRESS syndrome secondary to phenytoin use.
Spontaneously Draining Axillary Tumors in a Young Woman
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
A 19-year-old G1P1A0 woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of bilateral axillary swelling, pain, and spontaneous drainage of approximately 2 weeks’ duration. The patient, who was 2 weeks postpartum, reported that the symptoms were associated with lactation when breastfeeding. She denied any personal or family history of hidradenitis suppurativa or other formally diagnosed dermatologic condition. Physical examination revealed a soft, mildly tender, well-circumscribed, nonfluctuant mobile mass in each axilla. Both lesions had a single central sinus tract with thin lactescent discharge that spontaneously drained and was expressible. A single thin hyperpigmented papule was noted on the anterior aspect of each mass.

Utilization, Cost, and Prescription Trends of Antipsychotics Prescribed by Dermatologists for Medicare Patients
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).
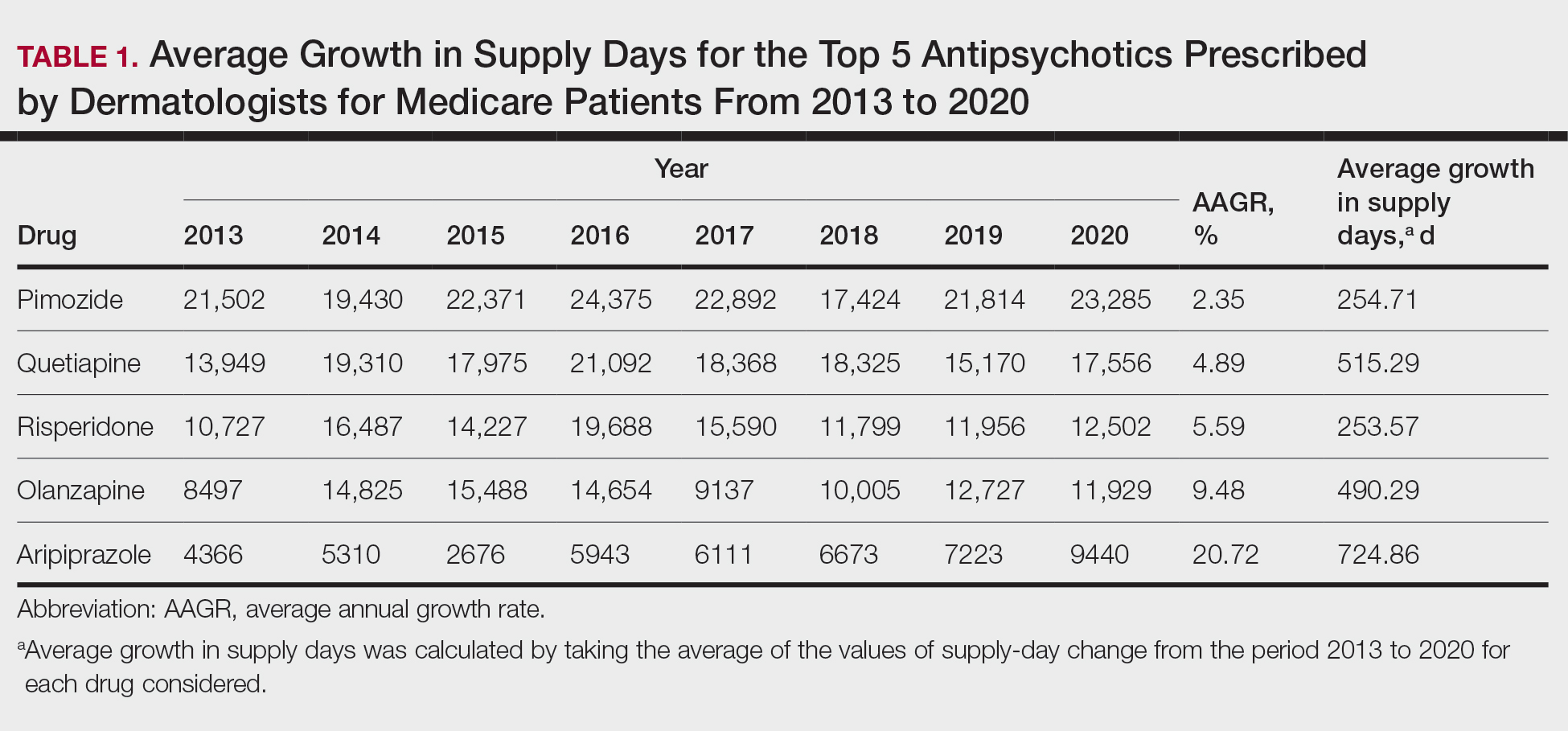
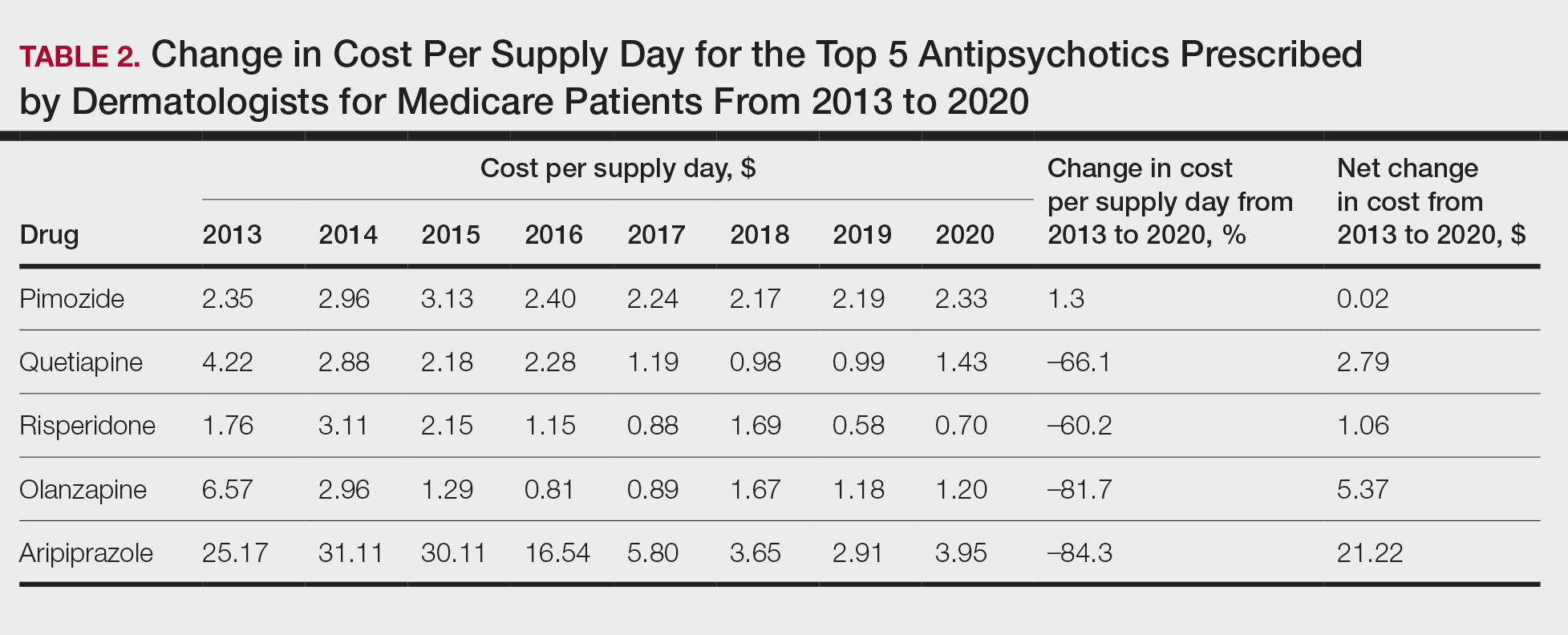
There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).


There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).


There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
Practice Points
- Dermatologists are frontline medical providers who can be useful in screening for primary psychiatric disorders in patients with dermatologic manifestations.
- Second-generation antipsychotics are effective for treating many psychiatric disorders.
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection of Pharyngeal Origin: Test All Anatomic Sites
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.
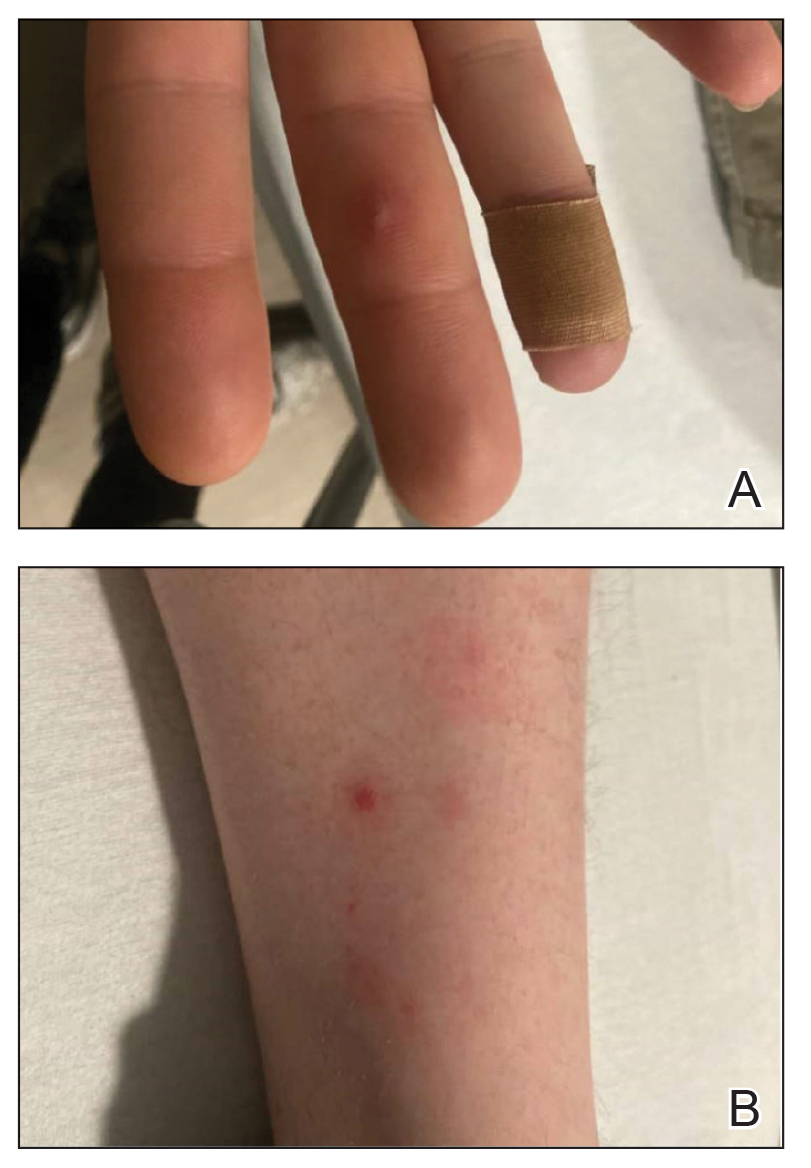
A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.
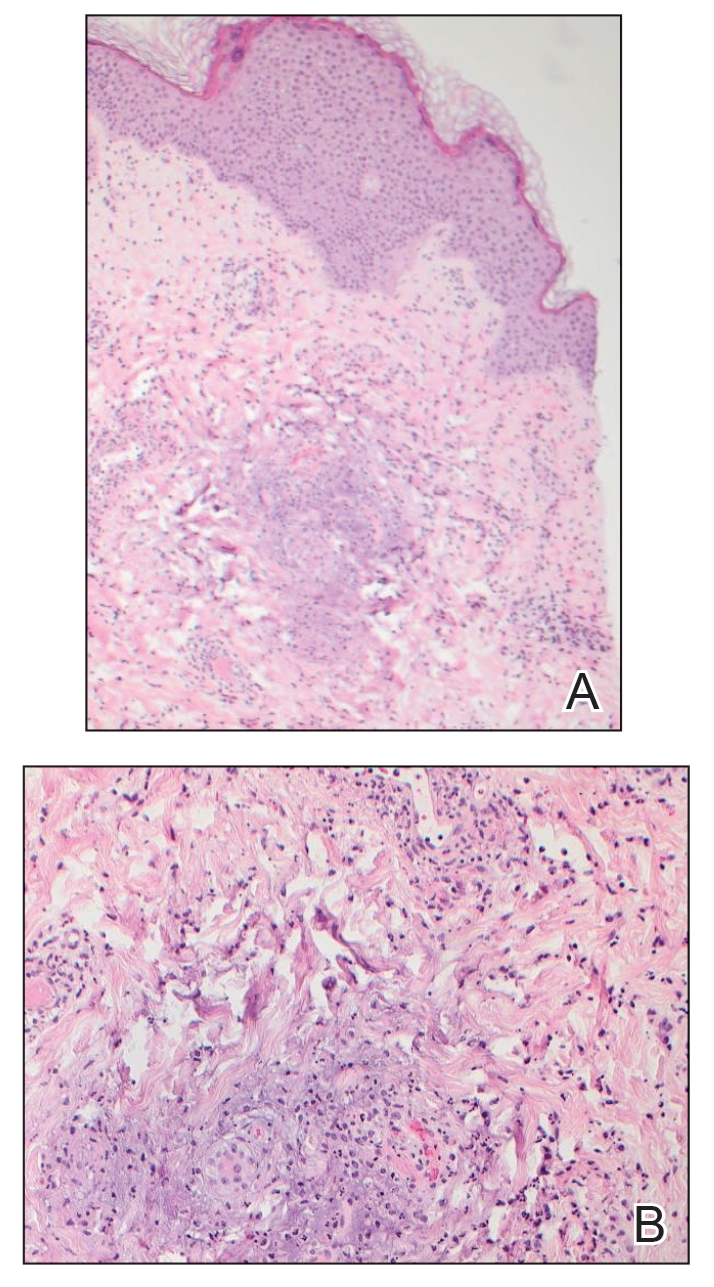
Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
Practice Points
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections of the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx can disseminate and cause fever, joint pain, and hemorrhagic papulovesicles that can mimic other serious conditions and require dermatologic expertise to confirm.
- Patients with suspected disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) as well as patients who are asymptomatic and at increased risk should have all possible anatomic sites of infection—the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx—tested with the appropriate molecular assays and culture when appropriate.
- Appropriate recognition and treatment of DGI is vital, as undertreatment can result in serious complications and contribute to the increasing global public health threat of antimicrobial-resistant gonococcal infections.
Considerations for the Use of Biologics in Pregnancy
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
Biologics have revolutionized dermatologic treatment, offering substantial relief from chronic and debilitating skin conditions such as psoriasis,
Biologics for Cutaneous Conditions
Biologics—tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α inhibitors; IL-17, IL-23, IL-12, and IL-36 inhibitors; and agents such as omalizumab and dupilumab—have shown remarkable efficacy in controlling severe or recalcitrant dermatologic conditions and typically are more effective than traditional systemic therapies.1 For instance, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-world data have shown that patients with psoriasis can achieve considerable skin clearance with biologics, greatly enhancing QOL.2 Adalimumab and secukinumab, which have been approved for use in moderate to severe cases of hidradenitis suppurativa, reduce the frequency of painful nodules and abscesses, thereby decreasing pain and improving QOL. Dupilumab, an IL-4/13 receptor antagonist, has revolutionized the treatment of AD by drastically reducing itch and skin lesions and improving QOL.3 For chronic urticaria, the anti-IgE antibody omalizumab has effectively reduced the incidence of hives and itching, providing pronounced symptom relief when traditional antihistamines fail.4 Use of rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, has led to remission in severe cases of pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid.5
Impact of Untreated Cutaneous Conditions in Pregnancy
When treating patients who are pregnant, dermatologists must consider the health of both the expectant mother and the developing fetus. This dual focus complicates decision-making, particularly with the use of biologics. Untreated cutaneous conditions can profoundly impact a pregnant patient’s health and QOL as well as lead to pregnancy complications affecting the fetus, such as preterm birth or low birth weight. In some studies, moderate to severe psoriasis has been associated with increased risk for complications during pregnancy, including preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction.6 Although specific data on hidradenitis suppurativa are lacking, the highly inflammatory nature of the condition suggests similar adverse effects on pregnancy.7 Atopic dermatitis can be exacerbated during pregnancy due to a shift in the immune system to become more allergic dominant.8 Generalized pustular psoriasis manifests with widespread pustules, fever, and systemic inflammation, posing serious risks to both the mother and the fetus if left untreated9; in such a life-threatening scenario, the use of potent treatments such as spesolimab, an IL-36 receptor antagonist, may be warranted. Therefore, managing these conditions effectively is crucial not only for the mother’s health but also for fetal well-being.
Which Biologics Can Dermatologists Safely Prescribe?
Despite the benefits, many dermatologists are hesitant to prescribe biologics to pregnant patients due to the lack of understanding and definitive safety data.10,11 Although there are no RCTs that involve pregnant patients, current evidence suggests that several biologics are not teratogenic and do not cause fetal malformations. Extensive postexposure data support the safety of TNF-α inhibitors during pregnancy.12 Research has shown that children exposed to these agents in utero have normal development, infection rates, and vaccination outcomes comparable to nonexposed children. For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis found no significant increase in the risk for major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions, or preterm births among patients exposed to anti–TNF-α agents during pregnancy.2 The Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project has provided valuable real-world data indicating that the use of TNF-α inhibitors in pregnancy, particularly during the first trimester, does not substantially elevate the risk for adverse outcomes.13 These findings have been corroborated by several other registry studies and RCTs, providing a robust safety profile for these agents during pregnancy.14
Similarly, postexposure data on IL-17 and IL-12/23 inhibitors indicate a favorable safety profile, though the sample sizes are smaller than those for anti–TNF-α agents.12,14 Studies of drugs such as secukinumab (IL-17 inhibitor), guselkumab (IL-23 inhibitor), or ustekinumab (IL-12/23 inhibitor) have shown no association with teratogenic effects or increased risk for miscarriage.14 However, agents such as spesolimab (IL-36 inhibitor) are relatively new, and ongoing studies are expected to provide more comprehensive safety data.15 Similarly, omalizumab and dupilumab have not been associated with increased risk for fetal malformations or adverse pregnancy outcomes. Omalizumab, indicated for chronic urticaria, has a good safety profile in pregnancy, with no significant increase in adverse outcomes reported in studies and registries.16 Dupilumab, used for AD, has demonstrated safety in pregnancy, with ongoing studies continuing to monitor outcomes.17
Conversely, rituximab (an anti-CD20 antibody for autoimmune bullous diseases) has shown evidence of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including fetal harm.18 Its use generally is discouraged unless deemed absolutely necessary, and no safer alternatives are available. Rituximab can cross the placenta, especially in the second and third trimesters, and has been associated with B-cell depletion in the fetus, leading to potential immunosuppression and increased risk for infections.5
Although the data on the safety of biologics in pregnancy are largely reassuring, it is essential to recognize that potential risks have not been ruled out entirely. There are extensive safety data for anti–TNF-α inhibitors, which provides a level of confidence; although newer agents such as IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors have shown promising early results, further research is required to solidify their safety profiles during pregnancy.
Dermatologists must balance the risks and benefits of using biologics in pregnant patients. This decision-making process involves careful consideration of the severity of the mother’s condition, the potential risks to the fetus, and the availability of alternative treatments. For many severe dermatologic conditions, the benefits of biologics in controlling disease activity and improving QOL may outweigh the potential risks, especially when other treatments have failed or are not suitable.
Final Thoughts
The increasing use of biologics in dermatology has undoubtedly improved the management of severe skin conditions, substantially enhancing patients’ QOL. As more data become available and clinical guidelines evolve, health care providers will be better equipped to make informed decisions about the use of biologics, particularly in pregnant patients. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists, obstetricians, and researchers will help refine treatment guidelines and ensure that pregnant patients with severe dermatologic conditions receive the best possible care.
For now, although the current evidence supports the safety of many biologics during pregnancy,10,11 individualized care and informed decision-making remain paramount. Careful management and adherence to current guidelines make it possible to navigate the complexities of treating severe dermatologic conditions in pregnant patients, ensuring the best outcomes for both mother and child.
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444
- Sehgal VN, Pandhi D, Khurana A. Biologics in dermatology: an integrated review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59:425-441. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.139859
- Mahadevan U, Wolf DC, Dubinsky M, et al. Placental transfer of anti-tumor necrosis factor agents in pregnant patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:286-292. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.11.011
- Simpson EL, Bieber T, Guttman-Yassky E, et al. Two phase 3 trials of dupilumab versus placebo in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2335-2348.
- Saini SS, Bindslev-Jensen C, Maurer M, et al. Efficacy and safety of omalizumab in patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria who remain symptomatic on H1 antihistamines: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135:67-75. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.306
- Mariette X, Forger F, Abraham B, et al. Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:228-233. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
- Yang Y-W, Chen C-S, Chen Y-H, et al. Psoriasis and pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;64:71-77.
- Zouboulis CC, Del Marmol V, Mrowietz U, et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa: criteria for diagnosis, severity assessment, classification and disease evaluation. Dermatology. 2015;231:184-190.
- Balakirski G, Novak N. Atopic dermatitis and pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:1185-1194. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.01.010
- Bachelez H, Choon S-E, Marrakchi S, et al. Inhibition of the interleukin-36 pathway for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:981-983.
- McMullan P, Yaghi M, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part I: pregnancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.072
- Yaghi M, McMullan P, Truong TM, et al. Safety of dermatologic medications in pregnancy and lactation: an update—part II: lactation. J Am Acad Dermatol. Published online January 25, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2023.10.071
- Owczarek W, Walecka I, Lesiak A, et al. The use of biological drugs in psoriasis patients prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy and lactation: a review of current clinical guidelines. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2020;37:821-830. doi:10.5114/ada.2020.102089
- Organization of Teratology Information Services (OTIS) Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00116272. Updated October 6, 2023. Accessed August 29, 2024. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00116272
- Sanchez-Garcia V, Hernandez-Quiles R, de-Miguel-Balsa E, et al. Exposure to biologic therapy before and during pregnancy in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1971-1990. doi:10.1111/jdv.19238
- Silverberg JI, Boguniewicz M, Hanifin J, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis is efficacious regardless of age of disease onset: a post hoc analysis of two phase 3 clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12:2731-2746. doi:10.1007/s13555-022-00822-x
- Levi-Schaffer F, Mankuta D. Omalizumab safety in pregnancy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;145:481-483. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.018
- Thaci D, Simpson EL, Beck LA, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis inadequately controlled by topical treatments: a randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging phase 2b trial. Lancet. 2016;387:40-52.
- Chakravarty EF, Murray ER, Kelman A, et al. Pregnancy outcomes after maternal exposure to rituximab. Blood. 2011;117:1499-1506. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-07-295444