User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Multiple Fungating Plaques on the Face, Arms, and Legs
Multiple Fungating Plaques on the Face, Arms, and Legs
THE DIAGNOSIS: Mpox
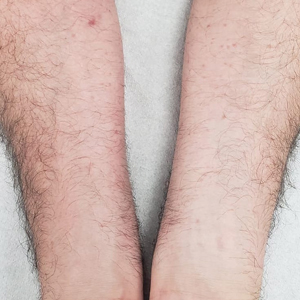
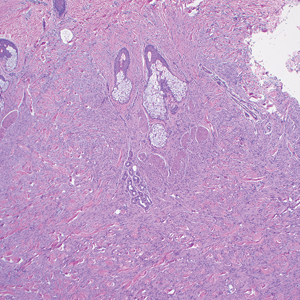
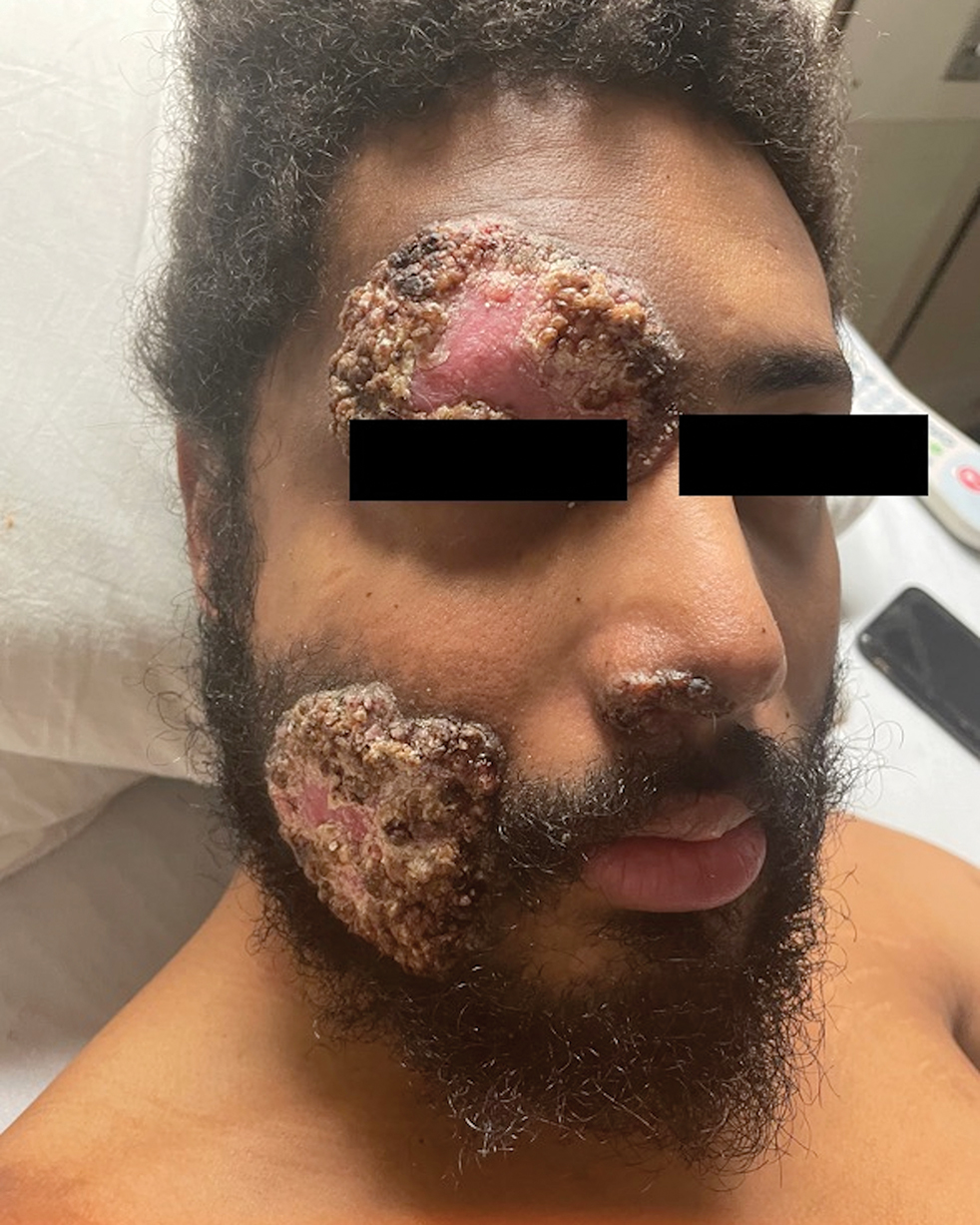
Histologic examination demonstrated dense aggregates of necrotic cellular debris composed of karyorrhectic nuclear fragments intermixed with neutrophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes. Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions also were observed (Figure 1). The bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial histologic special stains and cultures were negative. Three weeks after the initial visit with dermatology, the patient was admitted to the hospital for worsening symptoms of fever, chills, and painful erythema surrounding the skin lesions. Serology and viral workup revealed a positive mpox polymerase chain reaction test, suggesting a diagnosis of mpox. Following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention protocol, the patient was started on oral tecovirimat 200 mg twice daily for 3 weeks and intravenous infusions of cidofovir 345 mg once weekly for 2 weeks. After treatment was initiated, the skin lesions showed rapid improvement (Figure 2), and he was discharged from the hospital after finishing the second dose of cidofovir. Four months after the initial dermatology consultation, the lesions had resolved completely with residual scarring. At that time, the patient had full movement of the right eye.
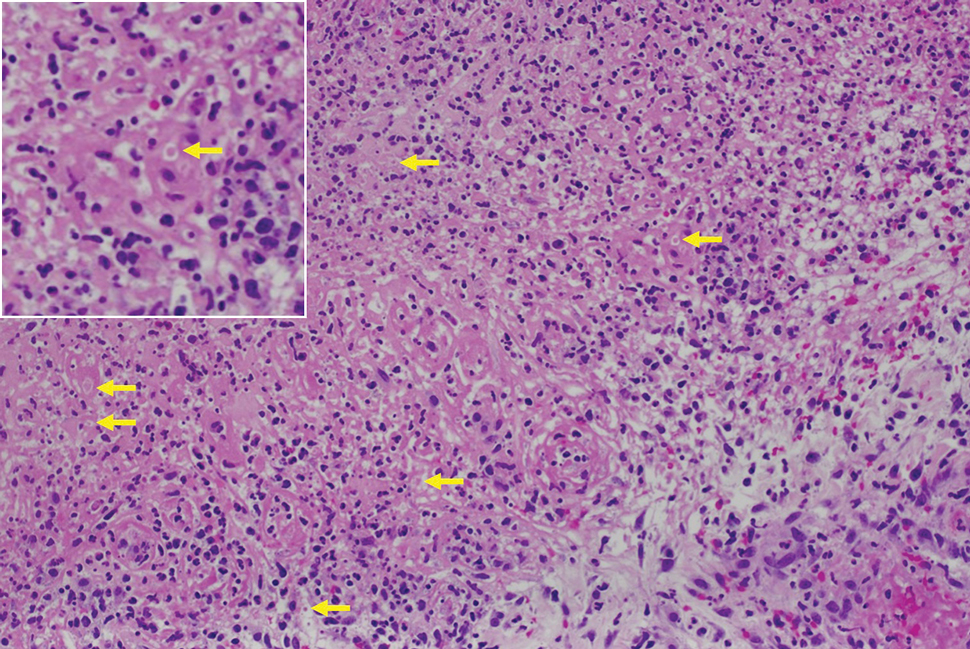
shows higher digital magnification of eosinophilic inclusions observed throughout the biopsy specimen (original magnification ×400).
Mpox virus is a member of the Poxviridae family of zoonotic viruses, which are transmitted from animals to humans. The mpox virus is brick-shaped (rectangular) and has a genome of linear double-stranded DNA encoding 180 proteins.1 Primates and rodents are the typical host reservoirs for viral circulation of mpox.2 Animal-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with mucous membranes, bodily fluids, or tissues of an infected animal. Human-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with infected mucous membranes, bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, and contaminated fomites.2
Symptoms typically occur within 1 week of exposure to the mpox virus. Prodromal symptoms of fever, sore throat, body aches, and headaches last for 3 days.1 Many patients experience a facial rash that spreads to the arms and legs over a period of 2 to 4 weeks. The rash initially manifests as small papules that progress to painful pustules and vesicles measuring 0.5 to 1.0 cm in diameter.3 The mpox virus is transmitted through these skin lesions until they crust over and re-epithelialize.1 The case fatality rate for mpox infection remains low (0.18%).4
Mpox outbreaks mainly were limited to central and western Africa prior to 2022. From May 17, 2022, through October 6, 2022, 26,384 cases of mpox were reported in the United States.5 During this outbreak, immunocompromised patients diagnosed with HIV and men who have sex with men were disproportionately affected.5
Due to the similarities between the smallpox virus and other orthopoxviruses, certain smallpox vaccines have been indicated for pre-exposure prophylaxis.6 The efficacy of prophylactic vaccination is believed to stem from the production of neutralizing antibodies that are cross-protective against other orthopoxviruses, including mpox.7 The 2 vaccines approved in the United States for mpox prophylaxis are JYNNEOS and ACAM2000, which are both live attenuated vaccines. Pre-exposure prophylaxis is indicated for patients at risk for severe disease, including men who have sex with men, individuals diagnosed with HIV or other immunosuppressive disorders, and individuals with recent diagnoses of one or more sexually transmitted diseases.8
Most mpox cases resolve within 2 to 4 weeks and only require supportive care (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, topical steroids, topical anesthetics) to treat pain.8 For patients at risk for severe disease, antiviral medications are warranted. Tecovirimat, brincidofovir, and cidofovir are antiviral medications used to treat smallpox that are thought to be effective against mpox.8,9 Tecovirimat and cidofovir have been shown to be effective against mpox in animal trials, but randomized or nonrandomized trials have not been performed in humans.9-11 Tecovirimat currently is available for the treatment of severe mpox in patients who meet the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Investigational New Drug protocol; for these patients, a 200-mg course is administered orally or intravenously every 12 hours for 2 weeks.8
- Lu J, Xing H, Wang C, et al. Mpox (formerly monkeypox): pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:458. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01675-
- Lim CK, Roberts J, Moso M, et al. Mpox diagnostics: review of current and emerging technologies. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28429. doi:10.1002/jmv.28429
- Brown K, Leggat PA. Human monkeypox: current state of knowledge and implications for the future. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2016;1:8. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed1010008
- World Health Organization. Mpox (monkeypox) World Health Organization. Published April 18, 2023. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/monkeypox
- Kava CM, Rohraff DM, Wallace B, et al. Epidemiologic features of the monkeypox outbreak and the public health response—United States, May 17–October 6, 2022. 2022:1449-1456. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7145a4.htm?s_cid=mm7145a4_w
- Rizk JG, Lippi G, Henry BM, et al. Prevention and treatment of monkeypox. Drugs. 2022;82:957-963. doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01742-y
- Edghill-Smith Y, Golding H, Manischewitz J, et al. Smallpox vaccine-induced antibodies are necessary and sufficient for protection against monkeypox virus. Nat Med. 2005;11:740-747. doi:10.1038 /nm1261
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox treatment information for healthcare professionals. Updated June 18, 2024. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/mpox/hcp/clinical-care/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/clinicians/treatment.html
- Mitja O, Ogoina D, Titanji BK, et al. Monkeypox. Lancet. 2023;401:60-74. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02075-X
- Huggins J, Goff A, Hensley L, et al. Nonhuman primates are protected from smallpox virus or monkeypox virus challenges by the antiviral drug ST-246. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2620-2625. doi:10.1128/aac.00021-09
- Grosenbach DW, Honeychurch K, Rose EA, et al. Oral tecovirimat for the treatment of smallpox. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:44-53. doi:10.1056 /nejmoa1705688
THE DIAGNOSIS: Mpox
Histologic examination demonstrated dense aggregates of necrotic cellular debris composed of karyorrhectic nuclear fragments intermixed with neutrophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes. Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions also were observed (Figure 1). The bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial histologic special stains and cultures were negative. Three weeks after the initial visit with dermatology, the patient was admitted to the hospital for worsening symptoms of fever, chills, and painful erythema surrounding the skin lesions. Serology and viral workup revealed a positive mpox polymerase chain reaction test, suggesting a diagnosis of mpox. Following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention protocol, the patient was started on oral tecovirimat 200 mg twice daily for 3 weeks and intravenous infusions of cidofovir 345 mg once weekly for 2 weeks. After treatment was initiated, the skin lesions showed rapid improvement (Figure 2), and he was discharged from the hospital after finishing the second dose of cidofovir. Four months after the initial dermatology consultation, the lesions had resolved completely with residual scarring. At that time, the patient had full movement of the right eye.

shows higher digital magnification of eosinophilic inclusions observed throughout the biopsy specimen (original magnification ×400).

Mpox virus is a member of the Poxviridae family of zoonotic viruses, which are transmitted from animals to humans. The mpox virus is brick-shaped (rectangular) and has a genome of linear double-stranded DNA encoding 180 proteins.1 Primates and rodents are the typical host reservoirs for viral circulation of mpox.2 Animal-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with mucous membranes, bodily fluids, or tissues of an infected animal. Human-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with infected mucous membranes, bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, and contaminated fomites.2
Symptoms typically occur within 1 week of exposure to the mpox virus. Prodromal symptoms of fever, sore throat, body aches, and headaches last for 3 days.1 Many patients experience a facial rash that spreads to the arms and legs over a period of 2 to 4 weeks. The rash initially manifests as small papules that progress to painful pustules and vesicles measuring 0.5 to 1.0 cm in diameter.3 The mpox virus is transmitted through these skin lesions until they crust over and re-epithelialize.1 The case fatality rate for mpox infection remains low (0.18%).4
Mpox outbreaks mainly were limited to central and western Africa prior to 2022. From May 17, 2022, through October 6, 2022, 26,384 cases of mpox were reported in the United States.5 During this outbreak, immunocompromised patients diagnosed with HIV and men who have sex with men were disproportionately affected.5
Due to the similarities between the smallpox virus and other orthopoxviruses, certain smallpox vaccines have been indicated for pre-exposure prophylaxis.6 The efficacy of prophylactic vaccination is believed to stem from the production of neutralizing antibodies that are cross-protective against other orthopoxviruses, including mpox.7 The 2 vaccines approved in the United States for mpox prophylaxis are JYNNEOS and ACAM2000, which are both live attenuated vaccines. Pre-exposure prophylaxis is indicated for patients at risk for severe disease, including men who have sex with men, individuals diagnosed with HIV or other immunosuppressive disorders, and individuals with recent diagnoses of one or more sexually transmitted diseases.8
Most mpox cases resolve within 2 to 4 weeks and only require supportive care (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, topical steroids, topical anesthetics) to treat pain.8 For patients at risk for severe disease, antiviral medications are warranted. Tecovirimat, brincidofovir, and cidofovir are antiviral medications used to treat smallpox that are thought to be effective against mpox.8,9 Tecovirimat and cidofovir have been shown to be effective against mpox in animal trials, but randomized or nonrandomized trials have not been performed in humans.9-11 Tecovirimat currently is available for the treatment of severe mpox in patients who meet the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Investigational New Drug protocol; for these patients, a 200-mg course is administered orally or intravenously every 12 hours for 2 weeks.8
THE DIAGNOSIS: Mpox
Histologic examination demonstrated dense aggregates of necrotic cellular debris composed of karyorrhectic nuclear fragments intermixed with neutrophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes. Eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions also were observed (Figure 1). The bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial histologic special stains and cultures were negative. Three weeks after the initial visit with dermatology, the patient was admitted to the hospital for worsening symptoms of fever, chills, and painful erythema surrounding the skin lesions. Serology and viral workup revealed a positive mpox polymerase chain reaction test, suggesting a diagnosis of mpox. Following the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention protocol, the patient was started on oral tecovirimat 200 mg twice daily for 3 weeks and intravenous infusions of cidofovir 345 mg once weekly for 2 weeks. After treatment was initiated, the skin lesions showed rapid improvement (Figure 2), and he was discharged from the hospital after finishing the second dose of cidofovir. Four months after the initial dermatology consultation, the lesions had resolved completely with residual scarring. At that time, the patient had full movement of the right eye.

shows higher digital magnification of eosinophilic inclusions observed throughout the biopsy specimen (original magnification ×400).

Mpox virus is a member of the Poxviridae family of zoonotic viruses, which are transmitted from animals to humans. The mpox virus is brick-shaped (rectangular) and has a genome of linear double-stranded DNA encoding 180 proteins.1 Primates and rodents are the typical host reservoirs for viral circulation of mpox.2 Animal-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with mucous membranes, bodily fluids, or tissues of an infected animal. Human-to-human transmission occurs through direct contact with infected mucous membranes, bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, and contaminated fomites.2
Symptoms typically occur within 1 week of exposure to the mpox virus. Prodromal symptoms of fever, sore throat, body aches, and headaches last for 3 days.1 Many patients experience a facial rash that spreads to the arms and legs over a period of 2 to 4 weeks. The rash initially manifests as small papules that progress to painful pustules and vesicles measuring 0.5 to 1.0 cm in diameter.3 The mpox virus is transmitted through these skin lesions until they crust over and re-epithelialize.1 The case fatality rate for mpox infection remains low (0.18%).4
Mpox outbreaks mainly were limited to central and western Africa prior to 2022. From May 17, 2022, through October 6, 2022, 26,384 cases of mpox were reported in the United States.5 During this outbreak, immunocompromised patients diagnosed with HIV and men who have sex with men were disproportionately affected.5
Due to the similarities between the smallpox virus and other orthopoxviruses, certain smallpox vaccines have been indicated for pre-exposure prophylaxis.6 The efficacy of prophylactic vaccination is believed to stem from the production of neutralizing antibodies that are cross-protective against other orthopoxviruses, including mpox.7 The 2 vaccines approved in the United States for mpox prophylaxis are JYNNEOS and ACAM2000, which are both live attenuated vaccines. Pre-exposure prophylaxis is indicated for patients at risk for severe disease, including men who have sex with men, individuals diagnosed with HIV or other immunosuppressive disorders, and individuals with recent diagnoses of one or more sexually transmitted diseases.8
Most mpox cases resolve within 2 to 4 weeks and only require supportive care (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, topical steroids, topical anesthetics) to treat pain.8 For patients at risk for severe disease, antiviral medications are warranted. Tecovirimat, brincidofovir, and cidofovir are antiviral medications used to treat smallpox that are thought to be effective against mpox.8,9 Tecovirimat and cidofovir have been shown to be effective against mpox in animal trials, but randomized or nonrandomized trials have not been performed in humans.9-11 Tecovirimat currently is available for the treatment of severe mpox in patients who meet the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Investigational New Drug protocol; for these patients, a 200-mg course is administered orally or intravenously every 12 hours for 2 weeks.8
- Lu J, Xing H, Wang C, et al. Mpox (formerly monkeypox): pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:458. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01675-
- Lim CK, Roberts J, Moso M, et al. Mpox diagnostics: review of current and emerging technologies. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28429. doi:10.1002/jmv.28429
- Brown K, Leggat PA. Human monkeypox: current state of knowledge and implications for the future. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2016;1:8. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed1010008
- World Health Organization. Mpox (monkeypox) World Health Organization. Published April 18, 2023. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/monkeypox
- Kava CM, Rohraff DM, Wallace B, et al. Epidemiologic features of the monkeypox outbreak and the public health response—United States, May 17–October 6, 2022. 2022:1449-1456. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7145a4.htm?s_cid=mm7145a4_w
- Rizk JG, Lippi G, Henry BM, et al. Prevention and treatment of monkeypox. Drugs. 2022;82:957-963. doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01742-y
- Edghill-Smith Y, Golding H, Manischewitz J, et al. Smallpox vaccine-induced antibodies are necessary and sufficient for protection against monkeypox virus. Nat Med. 2005;11:740-747. doi:10.1038 /nm1261
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox treatment information for healthcare professionals. Updated June 18, 2024. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/mpox/hcp/clinical-care/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/clinicians/treatment.html
- Mitja O, Ogoina D, Titanji BK, et al. Monkeypox. Lancet. 2023;401:60-74. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02075-X
- Huggins J, Goff A, Hensley L, et al. Nonhuman primates are protected from smallpox virus or monkeypox virus challenges by the antiviral drug ST-246. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2620-2625. doi:10.1128/aac.00021-09
- Grosenbach DW, Honeychurch K, Rose EA, et al. Oral tecovirimat for the treatment of smallpox. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:44-53. doi:10.1056 /nejmoa1705688
- Lu J, Xing H, Wang C, et al. Mpox (formerly monkeypox): pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:458. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01675-
- Lim CK, Roberts J, Moso M, et al. Mpox diagnostics: review of current and emerging technologies. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e28429. doi:10.1002/jmv.28429
- Brown K, Leggat PA. Human monkeypox: current state of knowledge and implications for the future. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2016;1:8. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed1010008
- World Health Organization. Mpox (monkeypox) World Health Organization. Published April 18, 2023. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/monkeypox
- Kava CM, Rohraff DM, Wallace B, et al. Epidemiologic features of the monkeypox outbreak and the public health response—United States, May 17–October 6, 2022. 2022:1449-1456. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/71/wr/mm7145a4.htm?s_cid=mm7145a4_w
- Rizk JG, Lippi G, Henry BM, et al. Prevention and treatment of monkeypox. Drugs. 2022;82:957-963. doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01742-y
- Edghill-Smith Y, Golding H, Manischewitz J, et al. Smallpox vaccine-induced antibodies are necessary and sufficient for protection against monkeypox virus. Nat Med. 2005;11:740-747. doi:10.1038 /nm1261
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Mpox treatment information for healthcare professionals. Updated June 18, 2024. Accessed May 28, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/mpox/hcp/clinical-care/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/clinicians/treatment.html
- Mitja O, Ogoina D, Titanji BK, et al. Monkeypox. Lancet. 2023;401:60-74. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02075-X
- Huggins J, Goff A, Hensley L, et al. Nonhuman primates are protected from smallpox virus or monkeypox virus challenges by the antiviral drug ST-246. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:2620-2625. doi:10.1128/aac.00021-09
- Grosenbach DW, Honeychurch K, Rose EA, et al. Oral tecovirimat for the treatment of smallpox. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:44-53. doi:10.1056 /nejmoa1705688
Multiple Fungating Plaques on the Face, Arms, and Legs
Multiple Fungating Plaques on the Face, Arms, and Legs
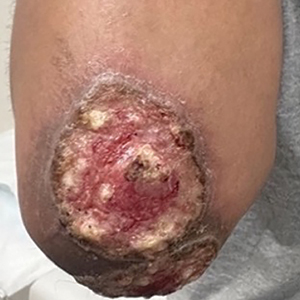
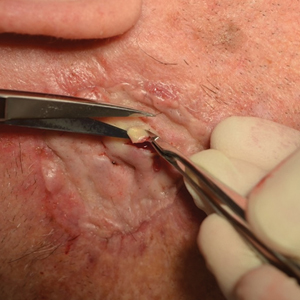
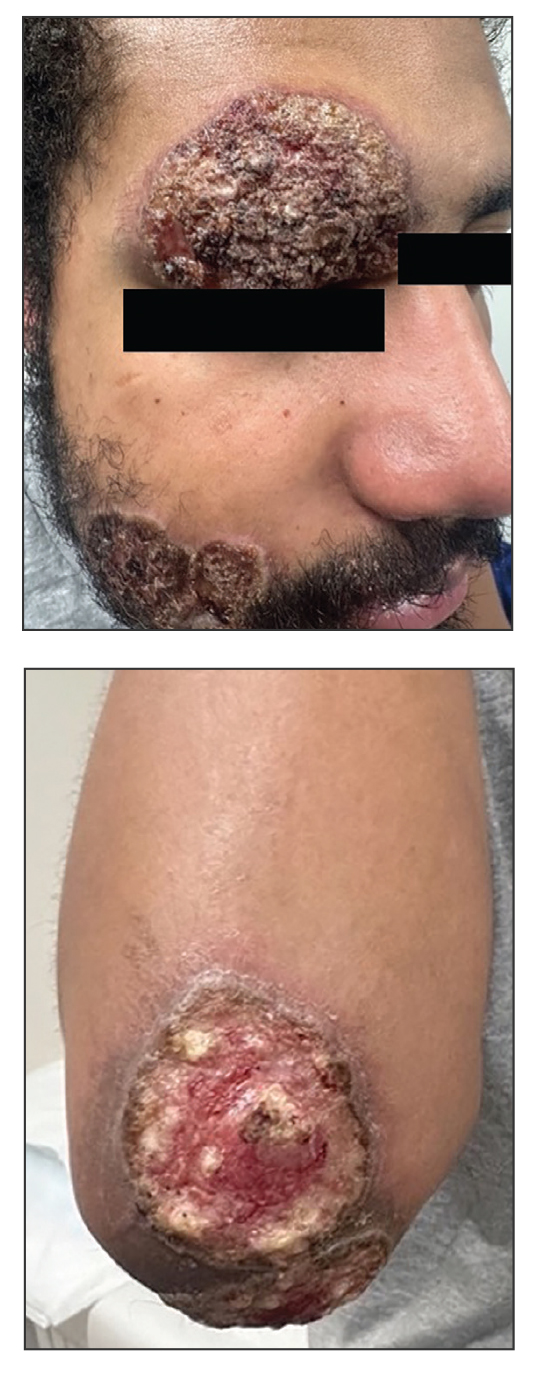
A 27-year-old man presented to his primary care physician after he was struck in the head by a tree branch while working outside. The next day, ulcerating lesions emerged on the right supraorbital ridge, along with subjective fevers, chills, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The patient reported a history of unprotected sexual intercourse with a male partner who was HIV positive. His medical history included syphilis status posttreatment with a course of 5 penicillin injections, hepatitis C, and HIV diagnosed one month prior to presentation (CD4 count, 169 cells/mm3 [reference range, 500-1500 cells/mm3]). A punch biopsy performed by the primary care physician revealed suppurative granulomatous inflammation, and the patient was prescribed antibiotics with mild improvement. He then was referred to dermatology for further evaluation of the ulcerating lesions.
Three months after the initial trauma, the patient presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of multiple large fungating plaques affecting multiple sites on the face (top), arms (bottom), and legs. Physical examination revealed large circinate verrucous plaques involving the right supraorbital ridge and eyelid. The patient was unable to fully open the right eye. Similar plaques also were observed on the right malar cheek, arms, and feet. Four 5-mm punch biopsies from lesions on the right elbow and left ankle were obtained with fungal and bacterial cultures.
Recommendations for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Recommendations for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic scarring inflammatory skin condition of the follicular epithelium that impacts 1% to 4% of the general population (eFigure).1-3 This statistic likely is an underrepresentation of the affected population due to missed and delayed diagnoses.1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been identified as having one of the strongest negative impacts on patients’ lives based on studied skin diseases.4 Its recurrent nature can negatively impact both the patient’s physical and mental state.3 Due to the debilitating effects of HS, we aimed to create updated recommendations for empiric antibotics based on affected anatomic locations in an effort to improve patient quality of life.
Methods
An institutional review board–approved retrospective medical chart review of 485 patients diagnosed with HS and evaluated at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston from January 2006 to December 2021 was conducted. Males and females of all ages (including pregnant and pediatric patients) were included. Only patients for whom anatomic locations of HS lesions or culture sites were not documented were excluded from the analysis. Locations of cultures were categorized into 5 groups: axilla; groin; buttocks; inframammary; and multiple sites of involvement, which included any combination of 2 or more sites. Types of bacteria collected from cultures and recorded included Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS), and other Gram-negative species. Sensitivity profiles also were analyzed for the most commonly cultured bacteria to create recommendations on antibiotic use based on the anatomic location of the lesions. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive statistics and bivariate analysis.
Results
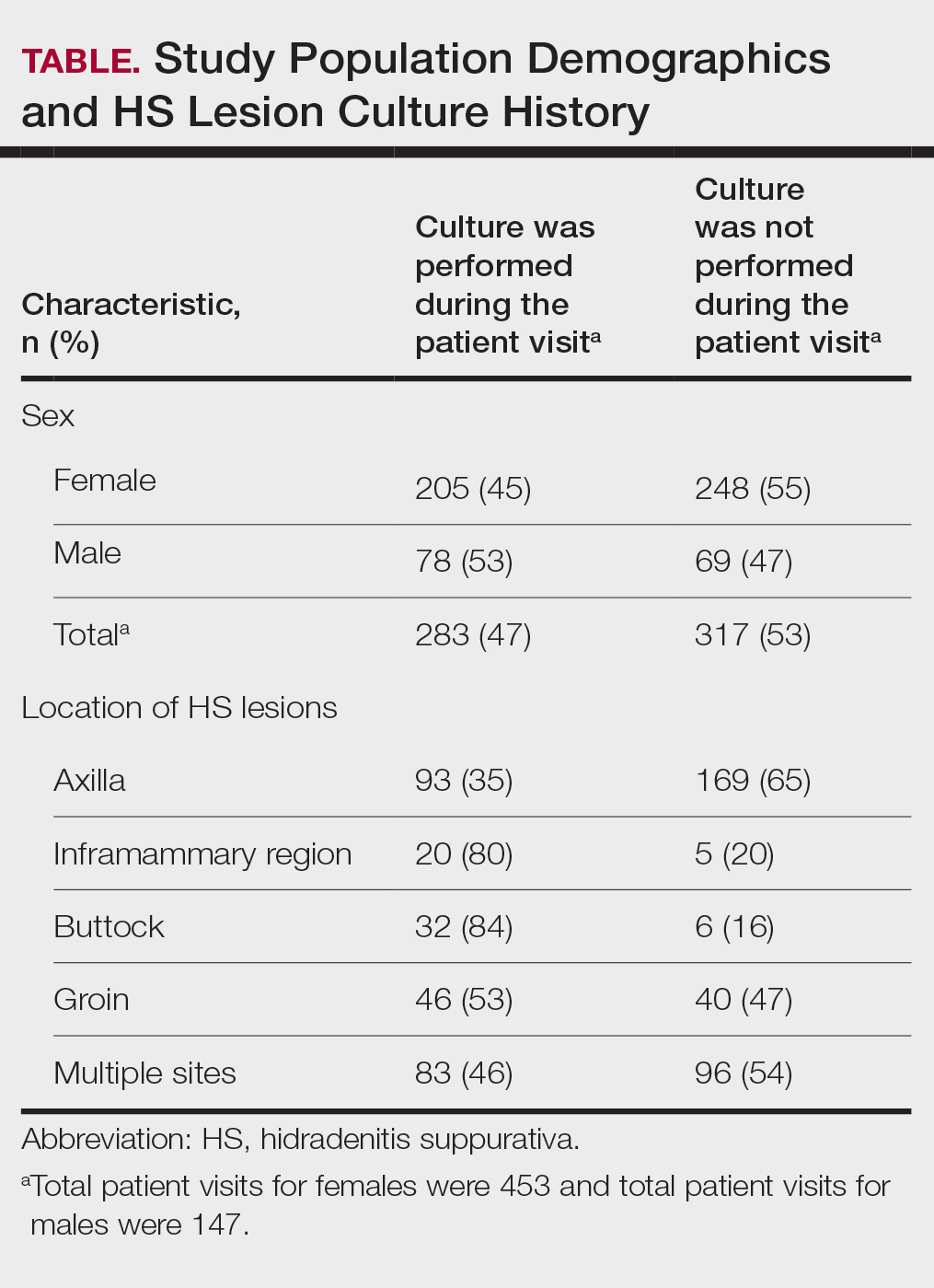
The analysis included 485 patients comprising 600 visits. Seventy-five percent (363/485) of the study population was female. The axilla was the most common anatomic location for HS lesions followed by multiple sites of involvement. In total, 283 cultures were performed; males were 1.1 times more likely than females to be cultured. While cultures were most frequently obtained in patients with axillary lesions only (93/262 [35%]) or from multiple sites of involvement (83/179 [46%]) as this was the most common presentation of HS in our patient population, cultures were more likely to be obtained when patients presented with only buttock (32/38 [84%]) and inframammary (20/25 [80%]) lesions (Table).
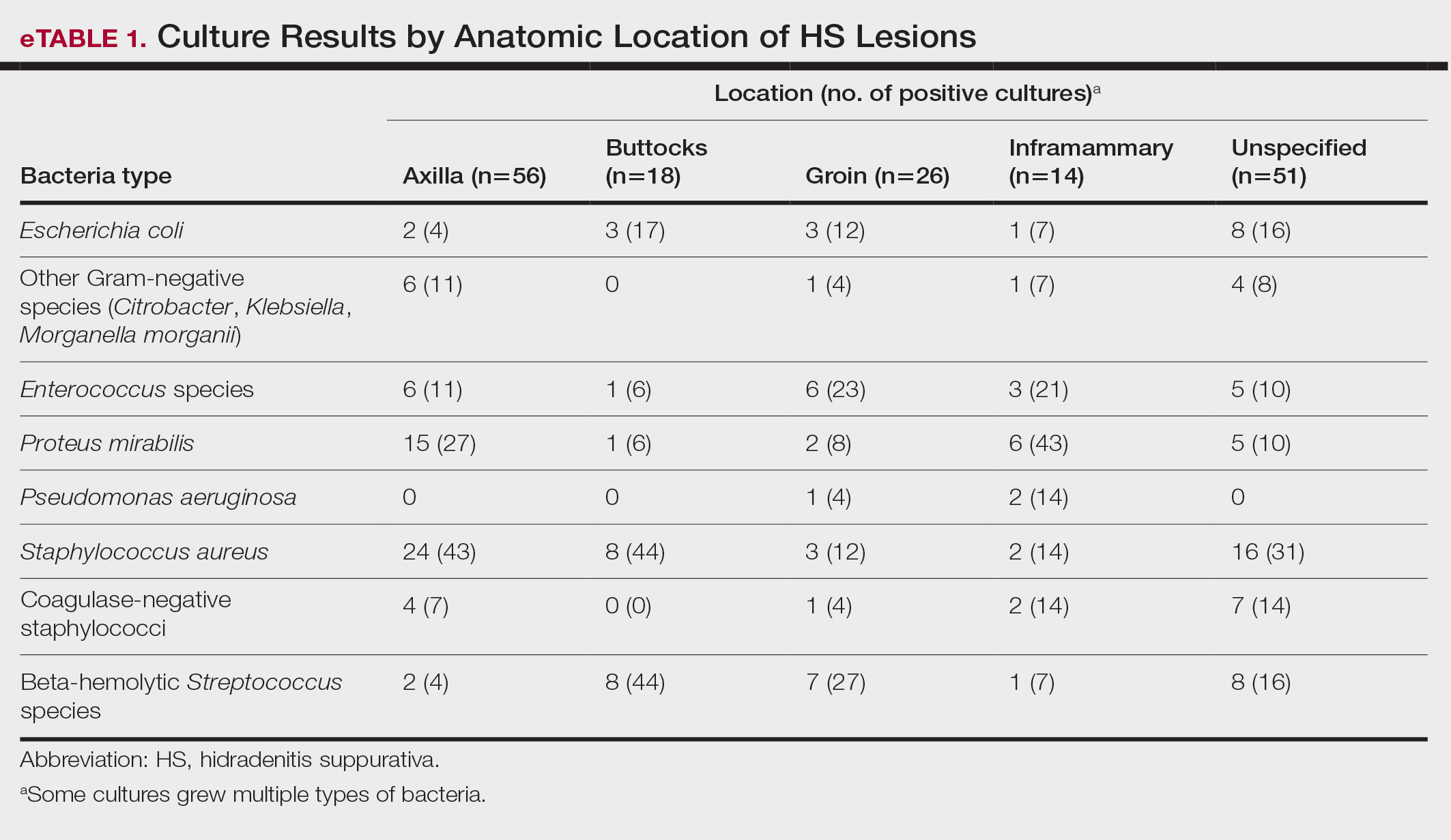
Staphylococcus aureus was the most commonly cultured bacteria in general (53/283 [19%]) as well as for HS located the axilla (24/56 [43%]) and in multiple sites (16/51 [31%]). Proteus mirabilis (29/283 [10%]) was the second most commonly cultured bacteria overall and was cultured most often in the axilla (15/56 [27%]) and inframammary region (6/14 [43%]). These were followed by beta-hemolytic Streptococcus species (26/283 [9%]) and Enterococcus species (21/283 [7%]), which was second to P mirabilis as the most commonly cultured bacteria in the inframammary region (6/14 [43%])(eTable 1).
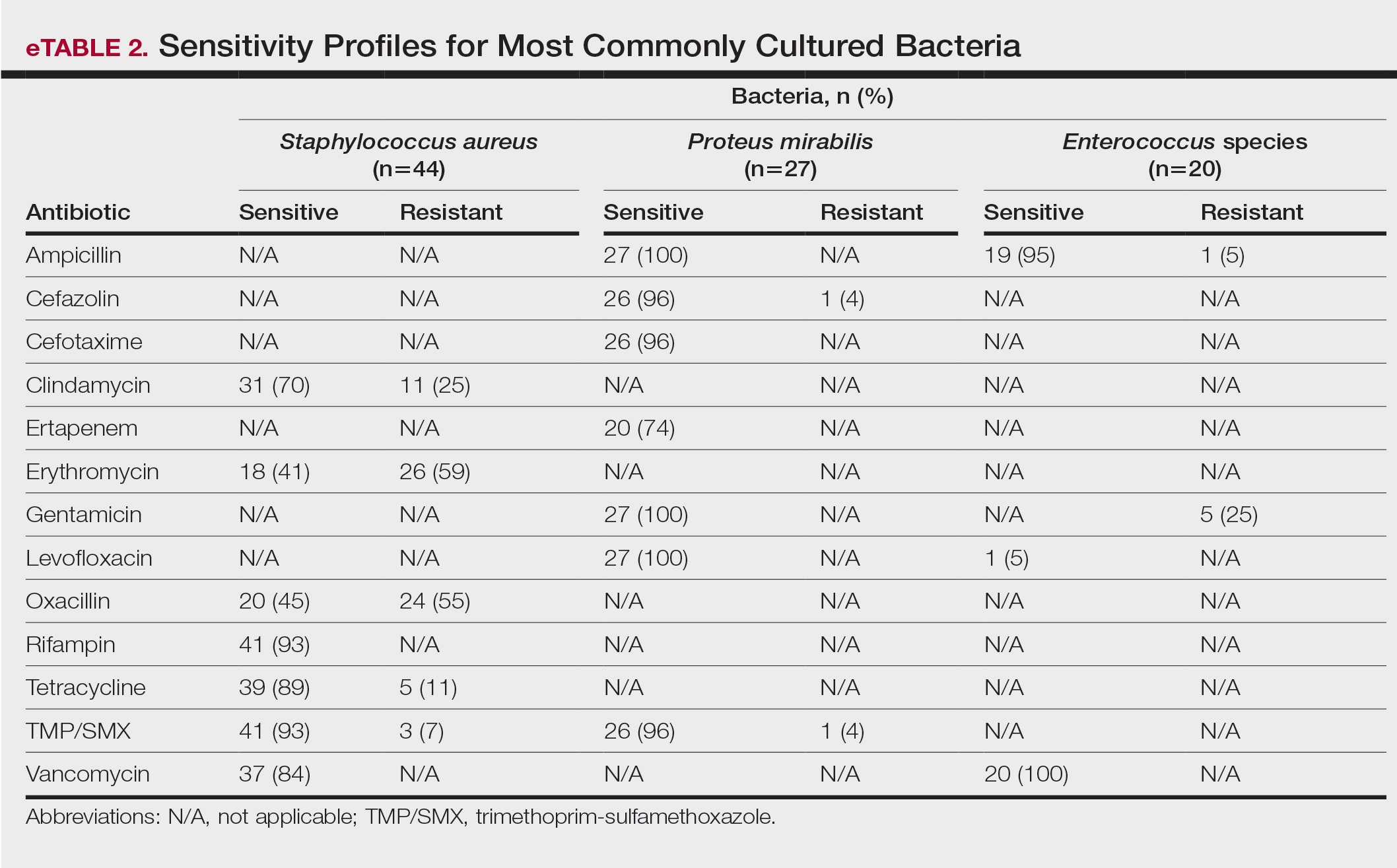
eTable 2 shows the sensitivity profiles for the most commonly cultured bacteria: S aureus, P mirabilis, and Enterococcus species. Staphylococcus aureus located in the axilla, buttocks, and groin was most sensitive to rifampin (41/44 [93%]), TMP/SMX (41/44 [93%]), and tetracycline (39/44 [89%]) and most resistant to erythromycin (26/44 [59%]) and oxacillin (24/44 [55%]). Proteus mirabilis in the inframammary region was most sensitive to ampicillin (27/27 [100%]), gentamicin (27/27 [100%]), levofloxacin (27/27 [100%]), and TMP/SMX (26/27 [96%]). Enterococcus species were most sensitive to vancomycin (20/20 [100%]) and ampicillin (19/20 [95%]) and most resistant to gentamicin (5/20 [25%]).
Comment
To treat HS, it is important to understand the cause of the condition. Although the pathogenesis of HS has many unknowns, bacterial colonization and biofilms are thought to play a role. Lipopolysaccharides found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria are pathogen-associated molecular patterns that present to the toll-like receptors of the human immune system. Once the toll-like receptors recognize the pathogen-associated molecular patterns, macrophages and keratinocytes are activated and release proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Persistent presentation of bacteria to the immune system increases immune-cell recruitment and worsens chronic inflammation in patients with HS. Evidence has revealed that bacteria initiate and sustain the inflammation seen in patients with HS; therefore, reducing the amount of bacteria could alleviate some of the symptoms of HS.5 It is important to continue learning about the pathophysiology of this disease as well as formulating tailored treatments to minimize patient discomfort and improve quality of life.
Based on the findings of the current study and the safety profile of the medication, tetracyclines may be considered for first-line empiric therapy in patients with HS involving the axilla only, buttocks only, or multiple sites. For additional coverage of P mirabilis in the axilla or inframammary region, TMP/SMX monotherapy or tetracycline plus ampicillin may be considered. For inframammary lesions only, empiric treatment with ampicillin or TMP/ SMX is recommended. For HS lesions in the groin area, coverage of Enterococcus species with ampicillin should be considered. Patients with multiple sites of involvement that include the inframammary or groin regions similarly should receive empiric antibiotics that cover both S aureus and Gram-negative bacteria, such as TMP/SMX or tetracycline and ampicillin, respectively; if the multiple sites do not include the inframammary or groin regions, Gram-negative coverage may not be indicated. Based on our findings, standardization of treatment for patients with HS can allow for earlier and potentially more effective treatment.
In a similar study conducted in 2016, bacteria species were isolated from the axilla, groin, and gluteus/perineum in patients with HS.5 In that study, the most prominent bacteria in the axilla was CoNS; in the groin, P mirabilis and E coli; and in the gluteus/perineum, E coli and CoNS. These results differed from ours, which found S aureus as the abundant bacteria in these areas. In the 2016 study, the highest rates of resistance were found for penicillin G, erythromycin, clindamycin, and ampicillin.5 In contrast, the current study found high sensitivities for clindamycin and ampicillin, but our results support the finding of high resistance for erythromycin. These differences could be accounted for by the lower sample size of patients in the 2016 study: 68 patients were analyzed for sensitivity results, and 171 patients were analyzed for frequency of bacterial species in patients with HS.5
Our study is limited by its relatively small sample size. Additionally, all patients were seen at 1 of 2 clinic sites, located in League City and Galveston, Texas, and the data from this geographic area may not be applicable to patients seen in different climates.
Conclusion
Outcomes for patients with HS improve with early intervention; however, HS treatment may be delayed by selection of ineffective antibiotic therapy. Our study provides clinicians with recommendations for empiric antibiotic treatment based on anatomic location of HS lesions and culture sensitivity profiles. Utilizing tailored antibiotic therapy on initial clinical evaluation may increase early disease control and improve morbidity and disease outcomes, thereby increasing patient quality of life.
- Vinkel C, Thomsen SF. Hidradenitis suppurativa: causes, features, and current treatments. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:17-23.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-563.
- Yazdanyar S, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of cause and treatment. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:118-123.
- Hessam S, Sand M, Georgas D, et al. Microbial profile and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria found in inflammatory hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2016; 29:161-167.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic scarring inflammatory skin condition of the follicular epithelium that impacts 1% to 4% of the general population (eFigure).1-3 This statistic likely is an underrepresentation of the affected population due to missed and delayed diagnoses.1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been identified as having one of the strongest negative impacts on patients’ lives based on studied skin diseases.4 Its recurrent nature can negatively impact both the patient’s physical and mental state.3 Due to the debilitating effects of HS, we aimed to create updated recommendations for empiric antibotics based on affected anatomic locations in an effort to improve patient quality of life.

Methods
An institutional review board–approved retrospective medical chart review of 485 patients diagnosed with HS and evaluated at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston from January 2006 to December 2021 was conducted. Males and females of all ages (including pregnant and pediatric patients) were included. Only patients for whom anatomic locations of HS lesions or culture sites were not documented were excluded from the analysis. Locations of cultures were categorized into 5 groups: axilla; groin; buttocks; inframammary; and multiple sites of involvement, which included any combination of 2 or more sites. Types of bacteria collected from cultures and recorded included Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS), and other Gram-negative species. Sensitivity profiles also were analyzed for the most commonly cultured bacteria to create recommendations on antibiotic use based on the anatomic location of the lesions. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive statistics and bivariate analysis.
Results
The analysis included 485 patients comprising 600 visits. Seventy-five percent (363/485) of the study population was female. The axilla was the most common anatomic location for HS lesions followed by multiple sites of involvement. In total, 283 cultures were performed; males were 1.1 times more likely than females to be cultured. While cultures were most frequently obtained in patients with axillary lesions only (93/262 [35%]) or from multiple sites of involvement (83/179 [46%]) as this was the most common presentation of HS in our patient population, cultures were more likely to be obtained when patients presented with only buttock (32/38 [84%]) and inframammary (20/25 [80%]) lesions (Table).

Staphylococcus aureus was the most commonly cultured bacteria in general (53/283 [19%]) as well as for HS located the axilla (24/56 [43%]) and in multiple sites (16/51 [31%]). Proteus mirabilis (29/283 [10%]) was the second most commonly cultured bacteria overall and was cultured most often in the axilla (15/56 [27%]) and inframammary region (6/14 [43%]). These were followed by beta-hemolytic Streptococcus species (26/283 [9%]) and Enterococcus species (21/283 [7%]), which was second to P mirabilis as the most commonly cultured bacteria in the inframammary region (6/14 [43%])(eTable 1).

eTable 2 shows the sensitivity profiles for the most commonly cultured bacteria: S aureus, P mirabilis, and Enterococcus species. Staphylococcus aureus located in the axilla, buttocks, and groin was most sensitive to rifampin (41/44 [93%]), TMP/SMX (41/44 [93%]), and tetracycline (39/44 [89%]) and most resistant to erythromycin (26/44 [59%]) and oxacillin (24/44 [55%]). Proteus mirabilis in the inframammary region was most sensitive to ampicillin (27/27 [100%]), gentamicin (27/27 [100%]), levofloxacin (27/27 [100%]), and TMP/SMX (26/27 [96%]). Enterococcus species were most sensitive to vancomycin (20/20 [100%]) and ampicillin (19/20 [95%]) and most resistant to gentamicin (5/20 [25%]).

Comment
To treat HS, it is important to understand the cause of the condition. Although the pathogenesis of HS has many unknowns, bacterial colonization and biofilms are thought to play a role. Lipopolysaccharides found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria are pathogen-associated molecular patterns that present to the toll-like receptors of the human immune system. Once the toll-like receptors recognize the pathogen-associated molecular patterns, macrophages and keratinocytes are activated and release proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Persistent presentation of bacteria to the immune system increases immune-cell recruitment and worsens chronic inflammation in patients with HS. Evidence has revealed that bacteria initiate and sustain the inflammation seen in patients with HS; therefore, reducing the amount of bacteria could alleviate some of the symptoms of HS.5 It is important to continue learning about the pathophysiology of this disease as well as formulating tailored treatments to minimize patient discomfort and improve quality of life.
Based on the findings of the current study and the safety profile of the medication, tetracyclines may be considered for first-line empiric therapy in patients with HS involving the axilla only, buttocks only, or multiple sites. For additional coverage of P mirabilis in the axilla or inframammary region, TMP/SMX monotherapy or tetracycline plus ampicillin may be considered. For inframammary lesions only, empiric treatment with ampicillin or TMP/ SMX is recommended. For HS lesions in the groin area, coverage of Enterococcus species with ampicillin should be considered. Patients with multiple sites of involvement that include the inframammary or groin regions similarly should receive empiric antibiotics that cover both S aureus and Gram-negative bacteria, such as TMP/SMX or tetracycline and ampicillin, respectively; if the multiple sites do not include the inframammary or groin regions, Gram-negative coverage may not be indicated. Based on our findings, standardization of treatment for patients with HS can allow for earlier and potentially more effective treatment.
In a similar study conducted in 2016, bacteria species were isolated from the axilla, groin, and gluteus/perineum in patients with HS.5 In that study, the most prominent bacteria in the axilla was CoNS; in the groin, P mirabilis and E coli; and in the gluteus/perineum, E coli and CoNS. These results differed from ours, which found S aureus as the abundant bacteria in these areas. In the 2016 study, the highest rates of resistance were found for penicillin G, erythromycin, clindamycin, and ampicillin.5 In contrast, the current study found high sensitivities for clindamycin and ampicillin, but our results support the finding of high resistance for erythromycin. These differences could be accounted for by the lower sample size of patients in the 2016 study: 68 patients were analyzed for sensitivity results, and 171 patients were analyzed for frequency of bacterial species in patients with HS.5
Our study is limited by its relatively small sample size. Additionally, all patients were seen at 1 of 2 clinic sites, located in League City and Galveston, Texas, and the data from this geographic area may not be applicable to patients seen in different climates.
Conclusion
Outcomes for patients with HS improve with early intervention; however, HS treatment may be delayed by selection of ineffective antibiotic therapy. Our study provides clinicians with recommendations for empiric antibiotic treatment based on anatomic location of HS lesions and culture sensitivity profiles. Utilizing tailored antibiotic therapy on initial clinical evaluation may increase early disease control and improve morbidity and disease outcomes, thereby increasing patient quality of life.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic scarring inflammatory skin condition of the follicular epithelium that impacts 1% to 4% of the general population (eFigure).1-3 This statistic likely is an underrepresentation of the affected population due to missed and delayed diagnoses.1 Hidradenitis suppurativa has been identified as having one of the strongest negative impacts on patients’ lives based on studied skin diseases.4 Its recurrent nature can negatively impact both the patient’s physical and mental state.3 Due to the debilitating effects of HS, we aimed to create updated recommendations for empiric antibotics based on affected anatomic locations in an effort to improve patient quality of life.

Methods
An institutional review board–approved retrospective medical chart review of 485 patients diagnosed with HS and evaluated at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston from January 2006 to December 2021 was conducted. Males and females of all ages (including pregnant and pediatric patients) were included. Only patients for whom anatomic locations of HS lesions or culture sites were not documented were excluded from the analysis. Locations of cultures were categorized into 5 groups: axilla; groin; buttocks; inframammary; and multiple sites of involvement, which included any combination of 2 or more sites. Types of bacteria collected from cultures and recorded included Escherichia coli, Enterococcus species, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS), and other Gram-negative species. Sensitivity profiles also were analyzed for the most commonly cultured bacteria to create recommendations on antibiotic use based on the anatomic location of the lesions. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive statistics and bivariate analysis.
Results
The analysis included 485 patients comprising 600 visits. Seventy-five percent (363/485) of the study population was female. The axilla was the most common anatomic location for HS lesions followed by multiple sites of involvement. In total, 283 cultures were performed; males were 1.1 times more likely than females to be cultured. While cultures were most frequently obtained in patients with axillary lesions only (93/262 [35%]) or from multiple sites of involvement (83/179 [46%]) as this was the most common presentation of HS in our patient population, cultures were more likely to be obtained when patients presented with only buttock (32/38 [84%]) and inframammary (20/25 [80%]) lesions (Table).

Staphylococcus aureus was the most commonly cultured bacteria in general (53/283 [19%]) as well as for HS located the axilla (24/56 [43%]) and in multiple sites (16/51 [31%]). Proteus mirabilis (29/283 [10%]) was the second most commonly cultured bacteria overall and was cultured most often in the axilla (15/56 [27%]) and inframammary region (6/14 [43%]). These were followed by beta-hemolytic Streptococcus species (26/283 [9%]) and Enterococcus species (21/283 [7%]), which was second to P mirabilis as the most commonly cultured bacteria in the inframammary region (6/14 [43%])(eTable 1).

eTable 2 shows the sensitivity profiles for the most commonly cultured bacteria: S aureus, P mirabilis, and Enterococcus species. Staphylococcus aureus located in the axilla, buttocks, and groin was most sensitive to rifampin (41/44 [93%]), TMP/SMX (41/44 [93%]), and tetracycline (39/44 [89%]) and most resistant to erythromycin (26/44 [59%]) and oxacillin (24/44 [55%]). Proteus mirabilis in the inframammary region was most sensitive to ampicillin (27/27 [100%]), gentamicin (27/27 [100%]), levofloxacin (27/27 [100%]), and TMP/SMX (26/27 [96%]). Enterococcus species were most sensitive to vancomycin (20/20 [100%]) and ampicillin (19/20 [95%]) and most resistant to gentamicin (5/20 [25%]).

Comment
To treat HS, it is important to understand the cause of the condition. Although the pathogenesis of HS has many unknowns, bacterial colonization and biofilms are thought to play a role. Lipopolysaccharides found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria are pathogen-associated molecular patterns that present to the toll-like receptors of the human immune system. Once the toll-like receptors recognize the pathogen-associated molecular patterns, macrophages and keratinocytes are activated and release proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Persistent presentation of bacteria to the immune system increases immune-cell recruitment and worsens chronic inflammation in patients with HS. Evidence has revealed that bacteria initiate and sustain the inflammation seen in patients with HS; therefore, reducing the amount of bacteria could alleviate some of the symptoms of HS.5 It is important to continue learning about the pathophysiology of this disease as well as formulating tailored treatments to minimize patient discomfort and improve quality of life.
Based on the findings of the current study and the safety profile of the medication, tetracyclines may be considered for first-line empiric therapy in patients with HS involving the axilla only, buttocks only, or multiple sites. For additional coverage of P mirabilis in the axilla or inframammary region, TMP/SMX monotherapy or tetracycline plus ampicillin may be considered. For inframammary lesions only, empiric treatment with ampicillin or TMP/ SMX is recommended. For HS lesions in the groin area, coverage of Enterococcus species with ampicillin should be considered. Patients with multiple sites of involvement that include the inframammary or groin regions similarly should receive empiric antibiotics that cover both S aureus and Gram-negative bacteria, such as TMP/SMX or tetracycline and ampicillin, respectively; if the multiple sites do not include the inframammary or groin regions, Gram-negative coverage may not be indicated. Based on our findings, standardization of treatment for patients with HS can allow for earlier and potentially more effective treatment.
In a similar study conducted in 2016, bacteria species were isolated from the axilla, groin, and gluteus/perineum in patients with HS.5 In that study, the most prominent bacteria in the axilla was CoNS; in the groin, P mirabilis and E coli; and in the gluteus/perineum, E coli and CoNS. These results differed from ours, which found S aureus as the abundant bacteria in these areas. In the 2016 study, the highest rates of resistance were found for penicillin G, erythromycin, clindamycin, and ampicillin.5 In contrast, the current study found high sensitivities for clindamycin and ampicillin, but our results support the finding of high resistance for erythromycin. These differences could be accounted for by the lower sample size of patients in the 2016 study: 68 patients were analyzed for sensitivity results, and 171 patients were analyzed for frequency of bacterial species in patients with HS.5
Our study is limited by its relatively small sample size. Additionally, all patients were seen at 1 of 2 clinic sites, located in League City and Galveston, Texas, and the data from this geographic area may not be applicable to patients seen in different climates.
Conclusion
Outcomes for patients with HS improve with early intervention; however, HS treatment may be delayed by selection of ineffective antibiotic therapy. Our study provides clinicians with recommendations for empiric antibiotic treatment based on anatomic location of HS lesions and culture sensitivity profiles. Utilizing tailored antibiotic therapy on initial clinical evaluation may increase early disease control and improve morbidity and disease outcomes, thereby increasing patient quality of life.
- Vinkel C, Thomsen SF. Hidradenitis suppurativa: causes, features, and current treatments. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:17-23.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-563.
- Yazdanyar S, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of cause and treatment. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:118-123.
- Hessam S, Sand M, Georgas D, et al. Microbial profile and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria found in inflammatory hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2016; 29:161-167.
- Vinkel C, Thomsen SF. Hidradenitis suppurativa: causes, features, and current treatments. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2018;11:17-23.
- Lee EY, Alhusayen R, Lansang P, et al. What is hidradenitis suppurativa? Can Fam Physician. 2017;63:114-120.
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:539-561; quiz 562-563.
- Yazdanyar S, Jemec GBE. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a review of cause and treatment. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2011;24:118-123.
- Hessam S, Sand M, Georgas D, et al. Microbial profile and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria found in inflammatory hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2016; 29:161-167.
Recommendations for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Recommendations for Empiric Antibiotic Therapy in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
PRACTICE POINTS
- The inflammation seen in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is initiated and sustained by bacteria; therefore, reducing the number of bacteria may alleviate some of the symptoms of HS.
- For HS involving the axillae or buttocks, tetracyclines should be recommended as first-line empiric therapy.
- Patients with HS with multiple sites affected that include the inframammary or groin regions should receive empiric antibiotics that cover both Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative bacteria, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or tetracycline plus ampicillin.
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
PRACTICE POINTS
- Addressing a lack of exposure to pediatric dermatology in medical school and increasing support for students who are interested in the field can help alleviate the shortage of physicians at the earliest point in training.
- Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources, such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities, could further broaden the medical student knowledge base.
- There is an opportunity to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants who are medical students interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology.
Eruptive Erythematous Papules on the Forearms
Eruptive Erythematous Papules on the Forearms
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Eruptive Syringoma
Syringomas are small, benign, often asymptomatic eccrine tumors that originate in the intraepidermal portion of eccrine sweat ducts.1 Clinically, they present as multiple symmetric white-to-yellow or discrete flesh-colored papules measuring 1 to 3 mm in diameter, often located on the face (most commonly on the eyelids), with a greater prevalence in middle-aged women. Occasionally, they manifest in other locations such as the cheeks, chest, axillae, abdomen, and groin.2
In 1987, Friedman and Butler3 developed a classification system categorizing syringomas into 4 clinical subtypes: familial syringoma, localized syringoma, Down syndrome–related syringoma, and generalized syringoma. The fourth subtype includes the variant of eruptive syringoma,3 a rare clinical manifestation that often develops before or during puberty with several flesh-colored or lightly pigmented papules on the neck, anterior chest, upper abdomen, axillae, periumbilical region, and/or genital region.1,4,5 The etiology of eruptive syringomas is unclear, although it has been linked to abnormal proliferation of sweat glands due to an underlying local inflammatory process.6
Acral distribution of syringomas is a rare variant that can manifest as part of generalized eruptive syringoma with consequent involvement of the arms and other areas.5,7 There are limited case reports on eruptive syringomas with predominant acral distribution.8 Compared to classic syringomas, the acral variant is associated with an older age of onset as well as a similar prevalence between men and women.9 Acral eruptive syringoma (AES) usually is isolated to the distal arms and legs. The most commonly affected region is the anterior surface of the forearms, although involvement of the dorsal hands, wrists, and feet also has been reported.10-16
The first known case of AES, which was reported in 1977, described eruptive syringomas on the dorsal hands of a healthy 31-year-old man.17 Several cases have been reported since then, mostly in patients aged 30 to 60 years, with predominant involvement of the dorsal hands and forearms.18-24 A review of Embase as well as PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms syringoma OR eccrine ductal tumor and eruptive OR acral OR arms OR forearms OR extremities identified 19 reported cases of AES between 1977 and 2023. For the reported AES cases, the mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 45.1 years (15.96 years), with patient ages ranging from 19 to 76 years. Notably, most cases occurred in individuals aged between 30 and 60 years, which deviates from the typical age of onset of localized syringomas, commonly seen during puberty or early adulthood.
Currently, AES is categorized within the clinical presentation of eruptive syringoma. Nevertheless, some authors have proposed classifying it as a distinct fifth clinical group due to specific features that distinguish it from generalized eruptive syringoma.9 This reclassification has considerable implications for the differential diagnosis, particularly because exclusive acral involvement poses a substantial diagnostic challenge and often requires histologic confirmation.
As shown in the Figure, histopathologic examination revealed tubular structures in the upper dermis with characteristic comma-shaped extensions. Some of these structures were lined with cuboidal cells and contained eosinophilic material within the lumen. There was no involvement of the epidermis or deeper dermis. The histologic features were consistent with syringoma, which is distinguished by its predominant involvement of the upper dermis and the presence of enlarged, dilated eccrine ducts, as observed in our case.
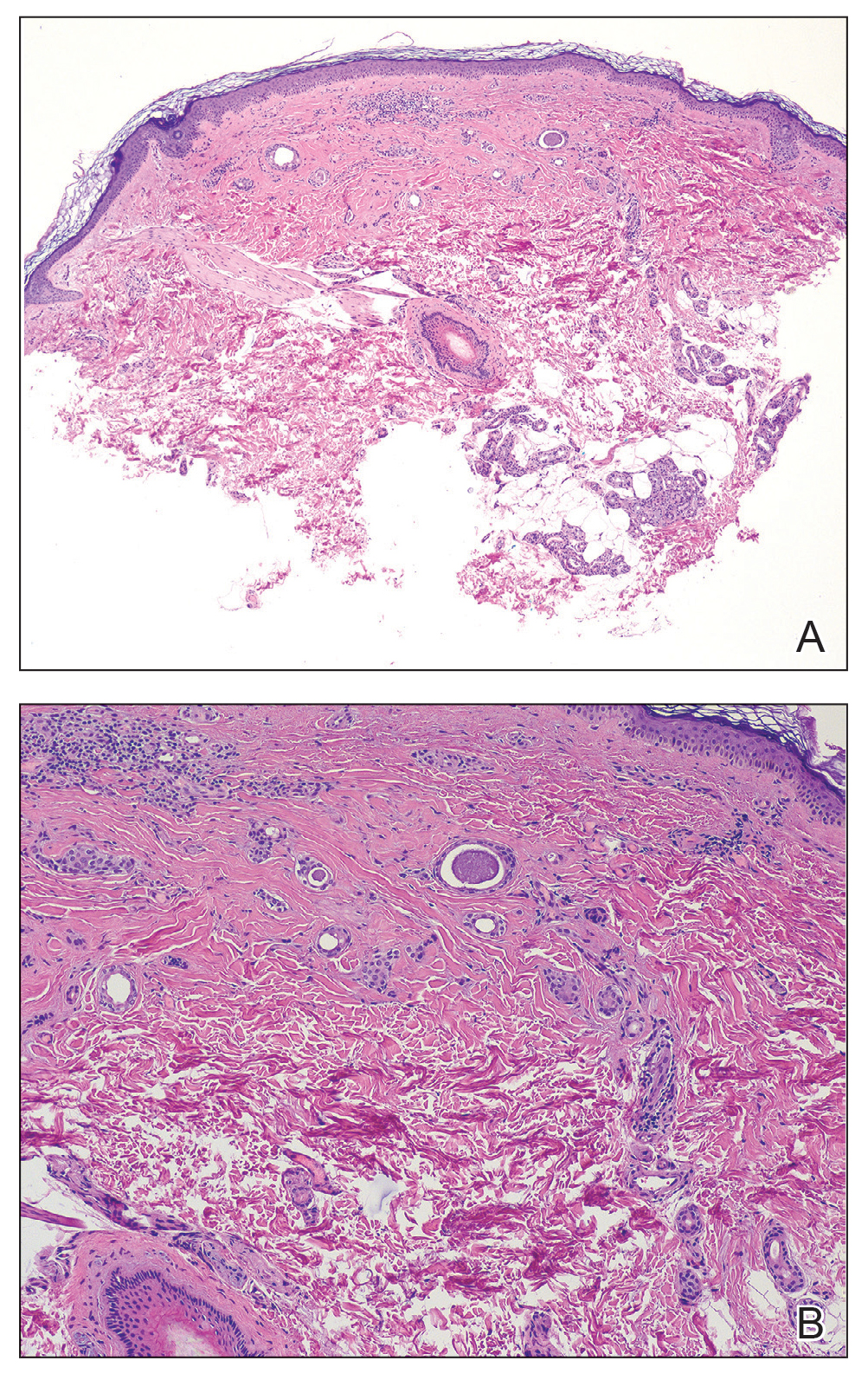
Treatment of syringomas often is challenging due to the high rate of recurrence and the risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Since the condition is benign, treatment typically is pursued for aesthetic reasons. Various therapeutic approaches have been reported, each with diverse response rates. The most common method involves surgical intervention, either with electrodesiccation or CO2 laser—both of which have shown satisfactory resolution of lesions without recurrence at 1-year follow-up, with no major scarring reported.25,26 Alternatively, topical management with retinoids daily over a 4-month period leads to flattening of the tumors with no further appearance of new lesions.27 Despite the availability of numerous management options, establishing a first-line treatment remains controversial due to the high risk for recurrence and the variability in the number and location of lesions among individual patients. In our case, given the benign nature of syringomas, the asymptomatic nature of the lesions, the involvement of noncritical aesthetic areas, and the limited response to noninvasive therapeutic options, the patient was informed of the diagnosis, and no further pharmacologic or surgical intervention was pursued.
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.E9. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Resende C, Araújo C, Santos R, et al. Late-onset of eruptive syringomas: a diagnostic challenge. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 suppl 1):239-241. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153899
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani HR. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.152586
- Ning WV, Bashey S, Cole C, et al. Multiple eruptive syringomas on the penis. Cutis. 2019;103:E15-E16.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Jamalipour M, Heidarpour M, Rajabi P. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:65-67. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.48992
- Mohaghegh F, Amiri A, Fatemi Naeini F, et al. Acral eruptive syringoma: an unusual presentation with misdiagnosis. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2020;2020:5416285. doi:10.1155/2020/5416285
- Valdivielso-Ramos M, de la Cueva P, Gimeno M, et al. Acral syringomas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:458-460.
- Patel K, Lundgren AD, Ahmed AM, et al. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities in a young woman. Cureus. 2018;10:E3619. doi:10.7759/cureus.3619
- Balci DD, Atik E, Altintas S. Coexistence of acral syringomas and multiple trichoepitheliomas on the face. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:169-171. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.08011
- Martín-García RF, Muñoz CM. Acral syringomas presenting as a photosensitive papular eruption. Cutis. 2006;77:33-36.
- Varas-Meis E, Prada-García C, Samaniego-González E, et al. Acral syringomas associated with hematological neoplasm. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:136. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.192961
- Berbis P, Fabre JF, Jancovici E, et al. Late-onset syringomas of the upper extremities associated with a carcinoid tumor. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:848-849.
- Metze D, Jurecka W, Gebhart W. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities. case history and immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Dermatologica. 1990;180:228-235. doi:10.1159/000248036
- Gómez-de Castro C, Vivanco Allende B, García-García B. Multiple acral syringomas. siringomas acrales múltiples. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:834-836. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2017.10.014
- Hughes PS, Apisarnthanarax P. Acral syringoma. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:1435-1436.
- Asai Y, Ishii M, Hamada T. Acral syringoma: electron microscopic studies on its origin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1982;62:64-68.
- van den Broek H, Lundquist CD. Syringomas of the upper extremities with onset in the sixth decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982,6:534-536. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(82)80368-X
- Garcia C, Krunic AL, Grichnik J, et al. Multiple acral syringomata with uniform involvement of the hands and feet. Cutis. 1997;59:213-214, 216.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Iglesias Sancho M, Serra Llobet J, Salleras Redonnet M, et al. Siringomas disem- inados de inicio acral, aparecidos en la octava década. Actas Dermosifiliofr. 1999;90:253-257.
- Muniesa C, Fortuño Y, Moreno A, et al. Papules on the dorsum of the fingers. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2008;99:812-813. doi:10.1016 /S1578-2190(08)70371-8
- Koh MJ. Multiple acral syringomas involving the hands. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03462.x
- Karam P, Benedetto AV. Syringomas: new approach to an old technique. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:219-220. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362 .1996.tb01647.x
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08111.x
- Gómez MI, Pérez B, Azaña JM, et al. Eruptive syringoma: treatment with topical tretinoin. Dermatology. 2009;189:105-106. doi:10.1159/000246803
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Eruptive Syringoma
Syringomas are small, benign, often asymptomatic eccrine tumors that originate in the intraepidermal portion of eccrine sweat ducts.1 Clinically, they present as multiple symmetric white-to-yellow or discrete flesh-colored papules measuring 1 to 3 mm in diameter, often located on the face (most commonly on the eyelids), with a greater prevalence in middle-aged women. Occasionally, they manifest in other locations such as the cheeks, chest, axillae, abdomen, and groin.2
In 1987, Friedman and Butler3 developed a classification system categorizing syringomas into 4 clinical subtypes: familial syringoma, localized syringoma, Down syndrome–related syringoma, and generalized syringoma. The fourth subtype includes the variant of eruptive syringoma,3 a rare clinical manifestation that often develops before or during puberty with several flesh-colored or lightly pigmented papules on the neck, anterior chest, upper abdomen, axillae, periumbilical region, and/or genital region.1,4,5 The etiology of eruptive syringomas is unclear, although it has been linked to abnormal proliferation of sweat glands due to an underlying local inflammatory process.6
Acral distribution of syringomas is a rare variant that can manifest as part of generalized eruptive syringoma with consequent involvement of the arms and other areas.5,7 There are limited case reports on eruptive syringomas with predominant acral distribution.8 Compared to classic syringomas, the acral variant is associated with an older age of onset as well as a similar prevalence between men and women.9 Acral eruptive syringoma (AES) usually is isolated to the distal arms and legs. The most commonly affected region is the anterior surface of the forearms, although involvement of the dorsal hands, wrists, and feet also has been reported.10-16
The first known case of AES, which was reported in 1977, described eruptive syringomas on the dorsal hands of a healthy 31-year-old man.17 Several cases have been reported since then, mostly in patients aged 30 to 60 years, with predominant involvement of the dorsal hands and forearms.18-24 A review of Embase as well as PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms syringoma OR eccrine ductal tumor and eruptive OR acral OR arms OR forearms OR extremities identified 19 reported cases of AES between 1977 and 2023. For the reported AES cases, the mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 45.1 years (15.96 years), with patient ages ranging from 19 to 76 years. Notably, most cases occurred in individuals aged between 30 and 60 years, which deviates from the typical age of onset of localized syringomas, commonly seen during puberty or early adulthood.
Currently, AES is categorized within the clinical presentation of eruptive syringoma. Nevertheless, some authors have proposed classifying it as a distinct fifth clinical group due to specific features that distinguish it from generalized eruptive syringoma.9 This reclassification has considerable implications for the differential diagnosis, particularly because exclusive acral involvement poses a substantial diagnostic challenge and often requires histologic confirmation.
As shown in the Figure, histopathologic examination revealed tubular structures in the upper dermis with characteristic comma-shaped extensions. Some of these structures were lined with cuboidal cells and contained eosinophilic material within the lumen. There was no involvement of the epidermis or deeper dermis. The histologic features were consistent with syringoma, which is distinguished by its predominant involvement of the upper dermis and the presence of enlarged, dilated eccrine ducts, as observed in our case.

Treatment of syringomas often is challenging due to the high rate of recurrence and the risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Since the condition is benign, treatment typically is pursued for aesthetic reasons. Various therapeutic approaches have been reported, each with diverse response rates. The most common method involves surgical intervention, either with electrodesiccation or CO2 laser—both of which have shown satisfactory resolution of lesions without recurrence at 1-year follow-up, with no major scarring reported.25,26 Alternatively, topical management with retinoids daily over a 4-month period leads to flattening of the tumors with no further appearance of new lesions.27 Despite the availability of numerous management options, establishing a first-line treatment remains controversial due to the high risk for recurrence and the variability in the number and location of lesions among individual patients. In our case, given the benign nature of syringomas, the asymptomatic nature of the lesions, the involvement of noncritical aesthetic areas, and the limited response to noninvasive therapeutic options, the patient was informed of the diagnosis, and no further pharmacologic or surgical intervention was pursued.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Eruptive Syringoma
Syringomas are small, benign, often asymptomatic eccrine tumors that originate in the intraepidermal portion of eccrine sweat ducts.1 Clinically, they present as multiple symmetric white-to-yellow or discrete flesh-colored papules measuring 1 to 3 mm in diameter, often located on the face (most commonly on the eyelids), with a greater prevalence in middle-aged women. Occasionally, they manifest in other locations such as the cheeks, chest, axillae, abdomen, and groin.2
In 1987, Friedman and Butler3 developed a classification system categorizing syringomas into 4 clinical subtypes: familial syringoma, localized syringoma, Down syndrome–related syringoma, and generalized syringoma. The fourth subtype includes the variant of eruptive syringoma,3 a rare clinical manifestation that often develops before or during puberty with several flesh-colored or lightly pigmented papules on the neck, anterior chest, upper abdomen, axillae, periumbilical region, and/or genital region.1,4,5 The etiology of eruptive syringomas is unclear, although it has been linked to abnormal proliferation of sweat glands due to an underlying local inflammatory process.6
Acral distribution of syringomas is a rare variant that can manifest as part of generalized eruptive syringoma with consequent involvement of the arms and other areas.5,7 There are limited case reports on eruptive syringomas with predominant acral distribution.8 Compared to classic syringomas, the acral variant is associated with an older age of onset as well as a similar prevalence between men and women.9 Acral eruptive syringoma (AES) usually is isolated to the distal arms and legs. The most commonly affected region is the anterior surface of the forearms, although involvement of the dorsal hands, wrists, and feet also has been reported.10-16
The first known case of AES, which was reported in 1977, described eruptive syringomas on the dorsal hands of a healthy 31-year-old man.17 Several cases have been reported since then, mostly in patients aged 30 to 60 years, with predominant involvement of the dorsal hands and forearms.18-24 A review of Embase as well as PubMed articles indexed for MEDLINE using the search terms syringoma OR eccrine ductal tumor and eruptive OR acral OR arms OR forearms OR extremities identified 19 reported cases of AES between 1977 and 2023. For the reported AES cases, the mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 45.1 years (15.96 years), with patient ages ranging from 19 to 76 years. Notably, most cases occurred in individuals aged between 30 and 60 years, which deviates from the typical age of onset of localized syringomas, commonly seen during puberty or early adulthood.
Currently, AES is categorized within the clinical presentation of eruptive syringoma. Nevertheless, some authors have proposed classifying it as a distinct fifth clinical group due to specific features that distinguish it from generalized eruptive syringoma.9 This reclassification has considerable implications for the differential diagnosis, particularly because exclusive acral involvement poses a substantial diagnostic challenge and often requires histologic confirmation.
As shown in the Figure, histopathologic examination revealed tubular structures in the upper dermis with characteristic comma-shaped extensions. Some of these structures were lined with cuboidal cells and contained eosinophilic material within the lumen. There was no involvement of the epidermis or deeper dermis. The histologic features were consistent with syringoma, which is distinguished by its predominant involvement of the upper dermis and the presence of enlarged, dilated eccrine ducts, as observed in our case.

Treatment of syringomas often is challenging due to the high rate of recurrence and the risk for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. Since the condition is benign, treatment typically is pursued for aesthetic reasons. Various therapeutic approaches have been reported, each with diverse response rates. The most common method involves surgical intervention, either with electrodesiccation or CO2 laser—both of which have shown satisfactory resolution of lesions without recurrence at 1-year follow-up, with no major scarring reported.25,26 Alternatively, topical management with retinoids daily over a 4-month period leads to flattening of the tumors with no further appearance of new lesions.27 Despite the availability of numerous management options, establishing a first-line treatment remains controversial due to the high risk for recurrence and the variability in the number and location of lesions among individual patients. In our case, given the benign nature of syringomas, the asymptomatic nature of the lesions, the involvement of noncritical aesthetic areas, and the limited response to noninvasive therapeutic options, the patient was informed of the diagnosis, and no further pharmacologic or surgical intervention was pursued.
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.E9. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Resende C, Araújo C, Santos R, et al. Late-onset of eruptive syringomas: a diagnostic challenge. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 suppl 1):239-241. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153899
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani HR. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.152586
- Ning WV, Bashey S, Cole C, et al. Multiple eruptive syringomas on the penis. Cutis. 2019;103:E15-E16.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Jamalipour M, Heidarpour M, Rajabi P. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:65-67. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.48992
- Mohaghegh F, Amiri A, Fatemi Naeini F, et al. Acral eruptive syringoma: an unusual presentation with misdiagnosis. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2020;2020:5416285. doi:10.1155/2020/5416285
- Valdivielso-Ramos M, de la Cueva P, Gimeno M, et al. Acral syringomas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:458-460.
- Patel K, Lundgren AD, Ahmed AM, et al. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities in a young woman. Cureus. 2018;10:E3619. doi:10.7759/cureus.3619
- Balci DD, Atik E, Altintas S. Coexistence of acral syringomas and multiple trichoepitheliomas on the face. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:169-171. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.08011
- Martín-García RF, Muñoz CM. Acral syringomas presenting as a photosensitive papular eruption. Cutis. 2006;77:33-36.
- Varas-Meis E, Prada-García C, Samaniego-González E, et al. Acral syringomas associated with hematological neoplasm. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:136. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.192961
- Berbis P, Fabre JF, Jancovici E, et al. Late-onset syringomas of the upper extremities associated with a carcinoid tumor. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:848-849.
- Metze D, Jurecka W, Gebhart W. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities. case history and immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Dermatologica. 1990;180:228-235. doi:10.1159/000248036
- Gómez-de Castro C, Vivanco Allende B, García-García B. Multiple acral syringomas. siringomas acrales múltiples. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:834-836. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2017.10.014
- Hughes PS, Apisarnthanarax P. Acral syringoma. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:1435-1436.
- Asai Y, Ishii M, Hamada T. Acral syringoma: electron microscopic studies on its origin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1982;62:64-68.
- van den Broek H, Lundquist CD. Syringomas of the upper extremities with onset in the sixth decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982,6:534-536. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(82)80368-X
- Garcia C, Krunic AL, Grichnik J, et al. Multiple acral syringomata with uniform involvement of the hands and feet. Cutis. 1997;59:213-214, 216.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Iglesias Sancho M, Serra Llobet J, Salleras Redonnet M, et al. Siringomas disem- inados de inicio acral, aparecidos en la octava década. Actas Dermosifiliofr. 1999;90:253-257.
- Muniesa C, Fortuño Y, Moreno A, et al. Papules on the dorsum of the fingers. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2008;99:812-813. doi:10.1016 /S1578-2190(08)70371-8
- Koh MJ. Multiple acral syringomas involving the hands. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03462.x
- Karam P, Benedetto AV. Syringomas: new approach to an old technique. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:219-220. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362 .1996.tb01647.x
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08111.x
- Gómez MI, Pérez B, Azaña JM, et al. Eruptive syringoma: treatment with topical tretinoin. Dermatology. 2009;189:105-106. doi:10.1159/000246803
- Williams K, Shinkai K. Evaluation and management of the patient with multiple syringomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1234-1240.E9. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2015.12.006
- Resende C, Araújo C, Santos R, et al. Late-onset of eruptive syringomas: a diagnostic challenge. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90(3 suppl 1):239-241. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20153899
- Friedman SJ, Butler DF. Syringoma presenting as milia. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987;16:310-314.
- Avhad G, Ghuge P, Jerajani HR. Generalized eruptive syringoma. Indian J Dermatol. 2015;60:214. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.152586
- Ning WV, Bashey S, Cole C, et al. Multiple eruptive syringomas on the penis. Cutis. 2019;103:E15-E16.
- Cohen PR, Tschen JA, Rapini RP. Penile syringoma: reports and review of patients with syringoma located on the penis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013;6:38-42.
- Jamalipour M, Heidarpour M, Rajabi P. Generalized eruptive syringomas. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:65-67. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.48992
- Mohaghegh F, Amiri A, Fatemi Naeini F, et al. Acral eruptive syringoma: an unusual presentation with misdiagnosis. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2020;2020:5416285. doi:10.1155/2020/5416285
- Valdivielso-Ramos M, de la Cueva P, Gimeno M, et al. Acral syringomas. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2010;101:458-460.
- Patel K, Lundgren AD, Ahmed AM, et al. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities in a young woman. Cureus. 2018;10:E3619. doi:10.7759/cureus.3619
- Balci DD, Atik E, Altintas S. Coexistence of acral syringomas and multiple trichoepitheliomas on the face. J Cutan Med Surg. 2009;13:169-171. doi:10.2310/7750.2008.08011
- Martín-García RF, Muñoz CM. Acral syringomas presenting as a photosensitive papular eruption. Cutis. 2006;77:33-36.
- Varas-Meis E, Prada-García C, Samaniego-González E, et al. Acral syringomas associated with hematological neoplasm. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2017;83:136. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.192961
- Berbis P, Fabre JF, Jancovici E, et al. Late-onset syringomas of the upper extremities associated with a carcinoid tumor. Arch Dermatol. 1989;125:848-849.
- Metze D, Jurecka W, Gebhart W. Disseminated syringomas of the upper extremities. case history and immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Dermatologica. 1990;180:228-235. doi:10.1159/000248036
- Gómez-de Castro C, Vivanco Allende B, García-García B. Multiple acral syringomas. siringomas acrales múltiples. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2018;109:834-836. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2017.10.014
- Hughes PS, Apisarnthanarax P. Acral syringoma. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:1435-1436.
- Asai Y, Ishii M, Hamada T. Acral syringoma: electron microscopic studies on its origin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1982;62:64-68.
- van den Broek H, Lundquist CD. Syringomas of the upper extremities with onset in the sixth decade. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982,6:534-536. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(82)80368-X
- Garcia C, Krunic AL, Grichnik J, et al. Multiple acral syringomata with uniform involvement of the hands and feet. Cutis. 1997;59:213-214, 216.
- Patrizi A, Neri I, Marzaduri S, et al. Syringoma: a review of twenty-nine cases. Acta Derm Venereol. 1998;78:460-462.
- Iglesias Sancho M, Serra Llobet J, Salleras Redonnet M, et al. Siringomas disem- inados de inicio acral, aparecidos en la octava década. Actas Dermosifiliofr. 1999;90:253-257.
- Muniesa C, Fortuño Y, Moreno A, et al. Papules on the dorsum of the fingers. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2008;99:812-813. doi:10.1016 /S1578-2190(08)70371-8
- Koh MJ. Multiple acral syringomas involving the hands. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:E438. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2009.03462.x
- Karam P, Benedetto AV. Syringomas: new approach to an old technique. Int J Dermatol. 1996;35:219-220. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4362 .1996.tb01647.x
- Wang JI, Roenigk HH. Treatment of multiple facial syringomas with the carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:136-139. doi:10.1046/j.1524-4725.1999.08111.x
- Gómez MI, Pérez B, Azaña JM, et al. Eruptive syringoma: treatment with topical tretinoin. Dermatology. 2009;189:105-106. doi:10.1159/000246803
Eruptive Erythematous Papules on the Forearms
Eruptive Erythematous Papules on the Forearms
A 44-year-old man presented to the dermatology department with multiple eruptive, nonconfluent, erythematous papules on the anterior forearms of 2 years’ duration. The patient’s medical history was notable for right-sided testicular cancer diagnosed in childhood and 3 excised basal cell carcinomas, the most recent of which was concurrent with the present case. The patient denied any recent pruritus, exposure to irritants, or use of over-the-counter medications. Physical examination was remarkable for numerous monomorphic, symmetric, nonconfluent, flesh-colored to slightly pigmented papules on the dorsal aspect of the forearms. No involvement of the fingers or lower extremities was observed. Two punch biopsies of representative lesions on the right and left forearms were taken. Histopathologic examination revealed eccrine ductal proliferations lined by cuboidal cells embedded within bundles of sclerotic collagen.
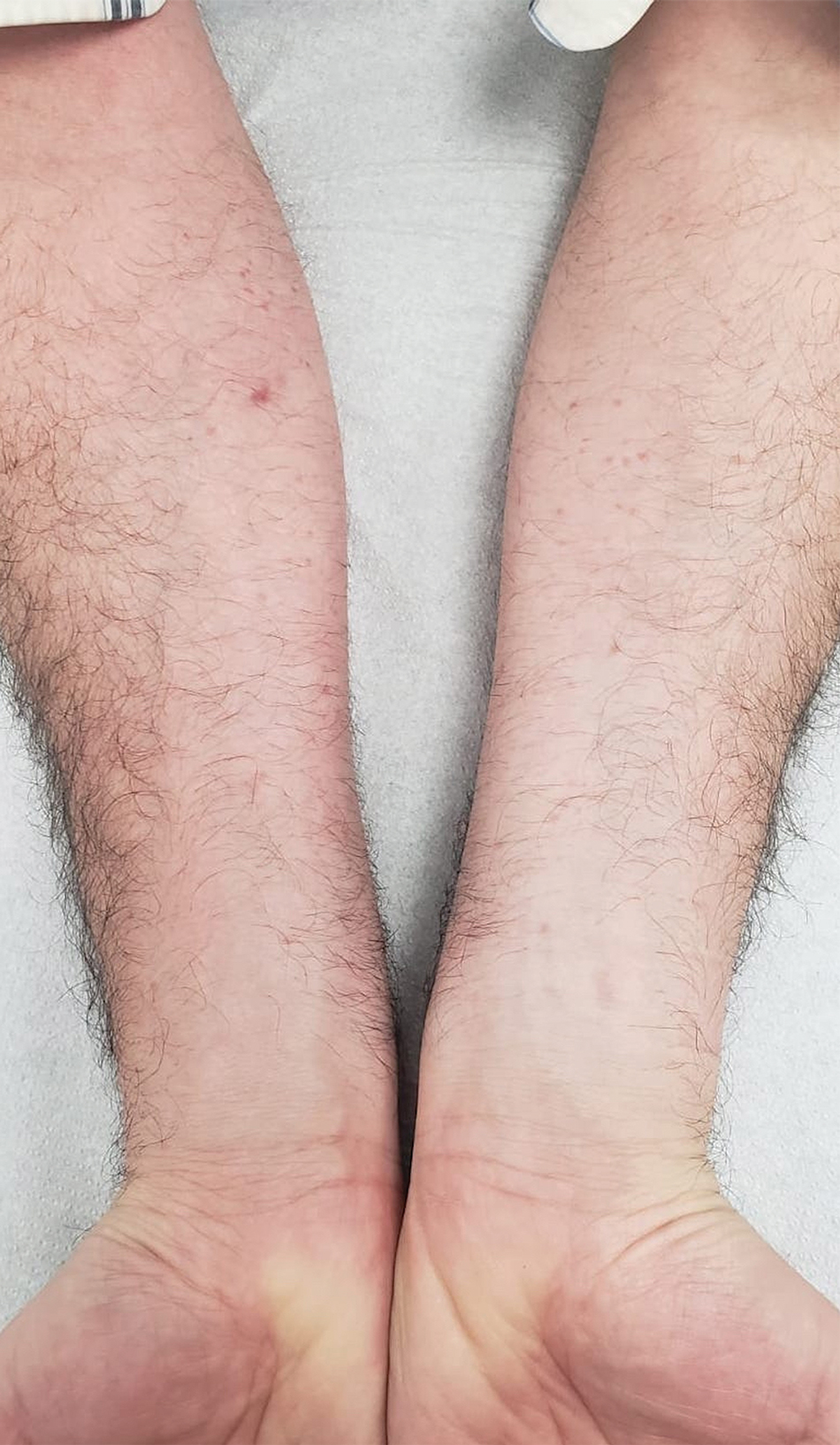
Actinic Keratosis Treatment With Diclofenac Gel 1%
Actinic Keratosis Treatment With Diclofenac Gel 1%
To the Editor:
Actinic keratoses (AKs) are keratinocyte neoplasms that manifest as rough, scaly, erythematous papules with ill-defined borders (commonly known as precancers) and develop due to long-term UV light exposure.1 They must be treated promptly due to the risk for progression to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). One US Department of Veterans Affairs study reported that 0.6% of AKs progress to SCC in 1 year and 2.6% progressed to SCC in 4 years.2 In 10% of AKs that will progress to SCC, one study reported progression in approximately 2 years.3
The risk for progression also increases in patients with multiple AKs; the risk is 4-fold higher in patients with 6 to 20 AKs and 11-fold higher in patients with more than 20 AKs.4 Common treatment options include lesion-directed therapies such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, surgery, and curettage, as well as field-directed therapies such as topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), diclofenac gel 3%, chemical peeling, topical imiquimod, and photodynamic therapy (PDT).4 When diclofenac gel is chosen as a treatment modality, it is commonly prescribed in the 3% formulation. Diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in the treatment of AKs,5,6 but diclofenac gel 1% has not been well described in the literature. We report the case of a patient with AKs on the lower legs who was treated with diclofenac gel after other therapies failed.
A 55-year-old woman presented for a routine skin check due to a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Her medical history also included palmar hyperhidrosis, disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis, and extensive actinic damage, as well as numerous biopsy-proven AKs. She had been evaluated every 3 months up to presentation due to the frequency of AK development over the past 5 years. The lesions were mainly localized to both lower legs, where the patient had acquired considerable lifetime sun exposure from tanning beds and sunbathing while boating. She also noted exposure to well water as a child, but none of her family members had a similar issue with AKs.
Prior to this visit, the patient had undergone 5 years of therapy for AKs. She initially was treated with multiple courses of topical 5-FU, but she consequently developed severe allergic contact dermatitis. Subsequent treatments included cryotherapy as well as application of tretinoin cream nightly for 2 weeks followed by PDT. She was unable to tolerate the tretinoin, which she reported led to dryness and irritation. She reported mild improvement after her first session of PDT but only minimal improvement after the next session. Ingenol mebutate was then prescribed for topical use on the legs for 2 days, which did not result in improvement. The patient continued to follow up for unresolved AKs on the legs and was prescribed acitretin to help reduce the risk for progression to SCC. At follow-up 3 months later, she reported decreased soreness from AKs after starting the acitretin and, aside from mild dryness, she tolerated the medication well; however, with continued use of acitretin, she began to experience adverse effects 6 months later, including thyroid suppression and hair loss, leading to discontinuation. Instead, 3 months later, she was recommended to start nicotinamide supplementation for prevention of SCC.
Due to continued AK development (Figure, A), we eventually prescribed diclofenac gel 3% twice daily for both legs 9 months after prescribing nicotinamide. This regimen was cost prohibitive, as the medication was not covered by her insurance and the cost was $300 for one tube. We recommended the patient instead apply the 3% gel to the right leg only due to greater severity of AKs on this leg and over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1% twice daily to the left leg. Approximately 5 months later, she reported a reduction in the discomfort from AKs as well as a reduction in the total number of AKs. She applied the 2 different products as instructed for the first month but did not notice a difference between them. She then continued to apply only the 1% gel on both legs for a total of 8 months with excellent response (Figure, B). At subsequent follow-up visits over a 2-year period, she has only required cryotherapy as spot treatment for AKs.
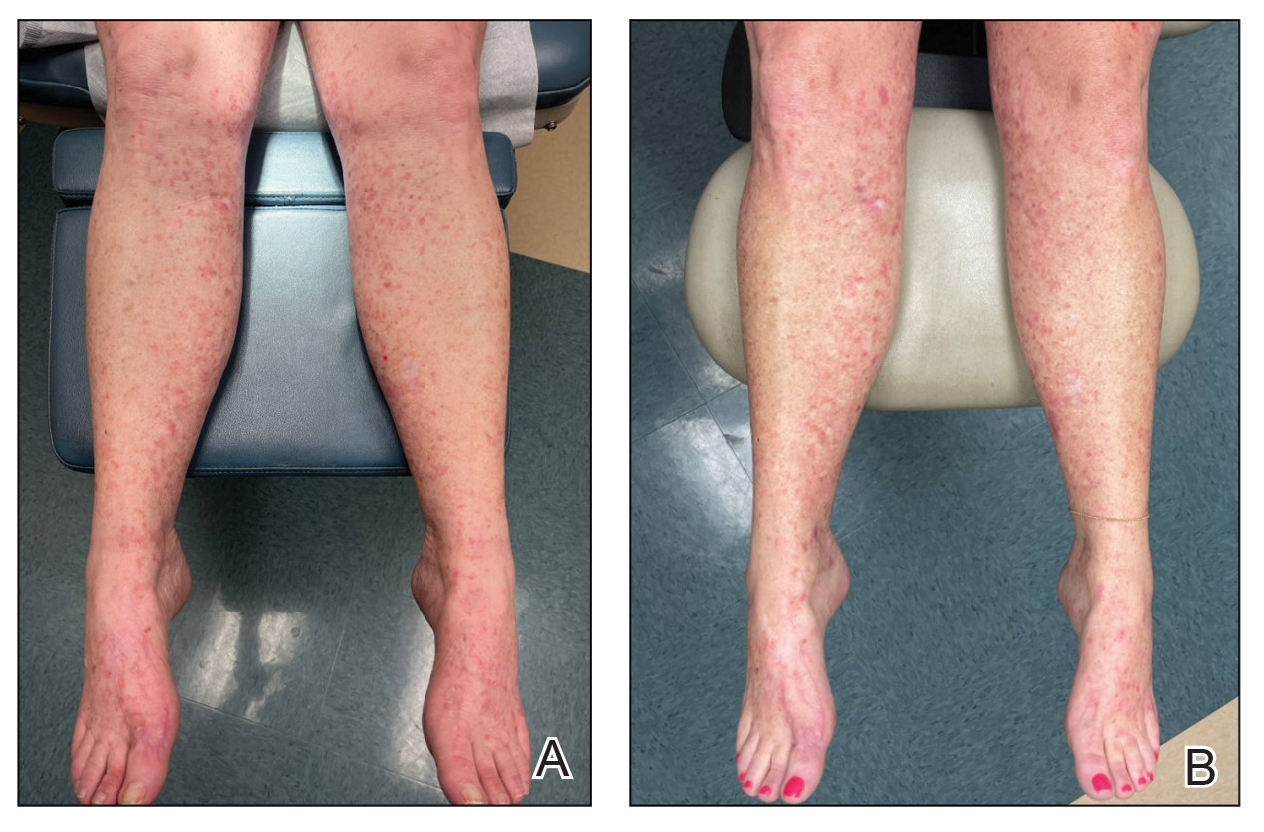
For 1 to a few discrete AKs, liquid nitrogen cryotherapy is considered first-line therapy.7 However, if multiple AKs are present, surrounding photodamaged skin also should be treated with field-directed therapy due to surrounding keratinocytes bearing a high mutational burden and risk of cancerization.8 Common field-directed therapies include topical 5-FU, topical imiquimod, topical tirbanibulin, PDT, retinoids, and topical diclofenac 3%.
One challenge in field-directed treatment of AKs is the side-effect profile seen in some patients, causing them to prematurely discontinue treatment. In our patient, 5-FU cream, tretinoin cream, and oral acitretin were not well tolerated. Topical diclofenac generally is well tolerated, with mostly mild local skin reactions and low risk for systemic adverse events. Adverse effects mainly consist of mild local skin reactions including pruritus (reported in 31%-52% of patients who used topical diclofenac), dryness (25%-27%), and irritation (less than 1%).9,10 Although diclofenac carries a black-box warning for serious cardiovascular thrombotic events and serious gastrointestinal tract bleeding, systemic absorption of topical diclofenac has been proven to be substantially lower (5- to 17-fold) compared to the oral formulation, and resulting serious adverse effects have been found to be largely reduced compared to the oral formulation.11,12 If allergic contact dermatitis develops, diclofenac should be discontinued.9,13
Diclofenac’s antineoplastic mechanism of action of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition involves induction of apoptosis as well as reduction in tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis.14,15 Topical diclofenac may result in decreased levels of lactate and amino acid in AK lesions, particularly in lesions responding to treatment.16 Topical diclofenac may alter immune infiltration by inducing infiltration of dermal CD8+ T cells along with high IFN-γ messenger RNA expression, suggesting improvement of T-cell function after topical diclofenac treatment.16
Although diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in treatment of AKs,5,6 diclofenac gel 1% has not yet been well studied. Use of the 1% gel is indicated for osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal pain by the US Food and Drug Administration.10,17 Efficacy of the 1% gel has been documented for these and other conditions including seborrheic keratoses.18-20
Because the 1% diclofenac formulation is available over-the-counter, it is more accessible to patients compared to the 3% formulation and often substantially decreases the cost of the medication for the patient. The cost of diclofenac gel 1% in the United States ranges from $0.04 to $0.31 per gram compared to $1.07 to $11.79 per gram for the 3% gel prescription formulation.17 Efficacy of the 1% formulation compared to the 3% formulation could represent an avenue to increase accessibility to field-directed therapy in the population for the treatment of AKs with a potentially well-tolerated, effective, and low-cost medication formulation.
This case represents the effectiveness of diclofenac gel 1% in treating AKs. Several treatment modalities failed in our case, but she experienced improvement with use of over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1%. She also noted no difference in response between the prescription 3% diclofenac formulation and the over-the-counter 1% formulation. Diclofenac gel 1% may represent an excellent therapeutic option in treatment-refractory cases of AKs. Larger randomized trials should be considered to assess safety and efficacy.
- FEisen DB, Asgari MM, Bennett DD, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:e209-e233.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Fuchs A, Marmur E. The kinetics of skin cancer: progression of actinic keratosis to squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33: 1099-1101.
- Dianzani C, Conforti C, Giuffrida R, et al. Current therapies for actinic keratosis. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:677-684.
- Javor S, Cozzani E, Parodi A. Topical treatment of actinic keratosis with 3.0% diclofenac in 2.5% hyaluronan gel: review of the literature about the cumulative evidence of its efficacy and safety. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:275-280.
- Martin GM, Stockfleth E. Diclofenac sodium 3% gel for the management of actinic keratosis: 10+ years of cumulative evidence of efficacy and safety. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:600-608.
- Arisi M, Guasco Pisani E, et al. Cryotherapy for actinic keratosis: basic principles and literature review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:357-365.
- Calzavara-Pinton P, Calzavara-Pinton I, Rovati C, et al. Topical pharmacotherapy for actinic keratoses in older adults. Drugs Aging. 2022;39:143-152.
- Beutner C, Forkel S, Kreipe K, et al. Contact allergy to topical diclofenac with systemic tolerance. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:41-43.
- Voltaren gel (diclofenac sodium topical gel). Prescribing information. Novartis Consumer Health, Inc; 2009. Accessed May 21, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/022122s006lbl.pdf
- Moreira SA, Liu DJ. Diclofenac systemic bioavailability of a topical 1% diclofenac + 3% menthol combination gel vs. an oral diclofenac tablet in healthy volunteers: a randomized, open-label, crossover study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;55:368-372.
- Kienzler JL, Gold M, Nollevaux F. Systemic bioavailability of topical diclofenac sodium gel 1% versus oral diclofenac sodium in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50:50-61.
- Gulin SJ, Chiriac A. Diclofenac-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a series of four patients. Drug Saf Case Rep. 2016;3:15.
- Fecker LF, Stockfleth E, Nindl I, et al. The role of apoptosis in therapy and prophylaxis of epithelial tumours by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Br J Dermatol. 2007;156(Suppl 3):25-33.
- Thomas GJ, Herranz P, Cruz SB, et al. Treatment of actinic keratosis through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: potential mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium 3% in hyaluronic acid 2.5. Dermatol Ther. 2019;32:e12800.
- Singer K, Dettmer K, Unger P, et al. Topical diclofenac reprograms metabolism and immune cell infiltration in actinic keratosis. Front Oncol. 2019;9:605.
- Diclofenac (topical). Drug information. UpToDate. https://www-uptodate-com.libraryaccess.elpaso.ttuhsc.edu/contents/diclofenac-topical-drug-information?source=auto_suggest&selectedTitle=1~3---3~4---diclofenac&search=diclofenac%20topical#F8017265
- Afify AA, Hana MR. Comparative evaluation of topical diclofenac sodium versus topical ibuprofen in the treatment of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14370.
- Yin F, Ma J, Xiao H, et al. Randomized, double-blind, noninferiority study of diclofenac diethylamine 2.32% gel applied twice daily versus diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% gel applied four times daily in patients with acute ankle sprain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23:1125.
- van Herwaarden N, van den Elsen GAH, de Jong ICA, et al. Topical NSAIDs: ineffective or undervalued? [in Dutch]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2021;165:D5317.
To the Editor:
Actinic keratoses (AKs) are keratinocyte neoplasms that manifest as rough, scaly, erythematous papules with ill-defined borders (commonly known as precancers) and develop due to long-term UV light exposure.1 They must be treated promptly due to the risk for progression to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). One US Department of Veterans Affairs study reported that 0.6% of AKs progress to SCC in 1 year and 2.6% progressed to SCC in 4 years.2 In 10% of AKs that will progress to SCC, one study reported progression in approximately 2 years.3
The risk for progression also increases in patients with multiple AKs; the risk is 4-fold higher in patients with 6 to 20 AKs and 11-fold higher in patients with more than 20 AKs.4 Common treatment options include lesion-directed therapies such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, surgery, and curettage, as well as field-directed therapies such as topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), diclofenac gel 3%, chemical peeling, topical imiquimod, and photodynamic therapy (PDT).4 When diclofenac gel is chosen as a treatment modality, it is commonly prescribed in the 3% formulation. Diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in the treatment of AKs,5,6 but diclofenac gel 1% has not been well described in the literature. We report the case of a patient with AKs on the lower legs who was treated with diclofenac gel after other therapies failed.
A 55-year-old woman presented for a routine skin check due to a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Her medical history also included palmar hyperhidrosis, disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis, and extensive actinic damage, as well as numerous biopsy-proven AKs. She had been evaluated every 3 months up to presentation due to the frequency of AK development over the past 5 years. The lesions were mainly localized to both lower legs, where the patient had acquired considerable lifetime sun exposure from tanning beds and sunbathing while boating. She also noted exposure to well water as a child, but none of her family members had a similar issue with AKs.
Prior to this visit, the patient had undergone 5 years of therapy for AKs. She initially was treated with multiple courses of topical 5-FU, but she consequently developed severe allergic contact dermatitis. Subsequent treatments included cryotherapy as well as application of tretinoin cream nightly for 2 weeks followed by PDT. She was unable to tolerate the tretinoin, which she reported led to dryness and irritation. She reported mild improvement after her first session of PDT but only minimal improvement after the next session. Ingenol mebutate was then prescribed for topical use on the legs for 2 days, which did not result in improvement. The patient continued to follow up for unresolved AKs on the legs and was prescribed acitretin to help reduce the risk for progression to SCC. At follow-up 3 months later, she reported decreased soreness from AKs after starting the acitretin and, aside from mild dryness, she tolerated the medication well; however, with continued use of acitretin, she began to experience adverse effects 6 months later, including thyroid suppression and hair loss, leading to discontinuation. Instead, 3 months later, she was recommended to start nicotinamide supplementation for prevention of SCC.
Due to continued AK development (Figure, A), we eventually prescribed diclofenac gel 3% twice daily for both legs 9 months after prescribing nicotinamide. This regimen was cost prohibitive, as the medication was not covered by her insurance and the cost was $300 for one tube. We recommended the patient instead apply the 3% gel to the right leg only due to greater severity of AKs on this leg and over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1% twice daily to the left leg. Approximately 5 months later, she reported a reduction in the discomfort from AKs as well as a reduction in the total number of AKs. She applied the 2 different products as instructed for the first month but did not notice a difference between them. She then continued to apply only the 1% gel on both legs for a total of 8 months with excellent response (Figure, B). At subsequent follow-up visits over a 2-year period, she has only required cryotherapy as spot treatment for AKs.

For 1 to a few discrete AKs, liquid nitrogen cryotherapy is considered first-line therapy.7 However, if multiple AKs are present, surrounding photodamaged skin also should be treated with field-directed therapy due to surrounding keratinocytes bearing a high mutational burden and risk of cancerization.8 Common field-directed therapies include topical 5-FU, topical imiquimod, topical tirbanibulin, PDT, retinoids, and topical diclofenac 3%.
One challenge in field-directed treatment of AKs is the side-effect profile seen in some patients, causing them to prematurely discontinue treatment. In our patient, 5-FU cream, tretinoin cream, and oral acitretin were not well tolerated. Topical diclofenac generally is well tolerated, with mostly mild local skin reactions and low risk for systemic adverse events. Adverse effects mainly consist of mild local skin reactions including pruritus (reported in 31%-52% of patients who used topical diclofenac), dryness (25%-27%), and irritation (less than 1%).9,10 Although diclofenac carries a black-box warning for serious cardiovascular thrombotic events and serious gastrointestinal tract bleeding, systemic absorption of topical diclofenac has been proven to be substantially lower (5- to 17-fold) compared to the oral formulation, and resulting serious adverse effects have been found to be largely reduced compared to the oral formulation.11,12 If allergic contact dermatitis develops, diclofenac should be discontinued.9,13
Diclofenac’s antineoplastic mechanism of action of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition involves induction of apoptosis as well as reduction in tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis.14,15 Topical diclofenac may result in decreased levels of lactate and amino acid in AK lesions, particularly in lesions responding to treatment.16 Topical diclofenac may alter immune infiltration by inducing infiltration of dermal CD8+ T cells along with high IFN-γ messenger RNA expression, suggesting improvement of T-cell function after topical diclofenac treatment.16
Although diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in treatment of AKs,5,6 diclofenac gel 1% has not yet been well studied. Use of the 1% gel is indicated for osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal pain by the US Food and Drug Administration.10,17 Efficacy of the 1% gel has been documented for these and other conditions including seborrheic keratoses.18-20
Because the 1% diclofenac formulation is available over-the-counter, it is more accessible to patients compared to the 3% formulation and often substantially decreases the cost of the medication for the patient. The cost of diclofenac gel 1% in the United States ranges from $0.04 to $0.31 per gram compared to $1.07 to $11.79 per gram for the 3% gel prescription formulation.17 Efficacy of the 1% formulation compared to the 3% formulation could represent an avenue to increase accessibility to field-directed therapy in the population for the treatment of AKs with a potentially well-tolerated, effective, and low-cost medication formulation.
This case represents the effectiveness of diclofenac gel 1% in treating AKs. Several treatment modalities failed in our case, but she experienced improvement with use of over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1%. She also noted no difference in response between the prescription 3% diclofenac formulation and the over-the-counter 1% formulation. Diclofenac gel 1% may represent an excellent therapeutic option in treatment-refractory cases of AKs. Larger randomized trials should be considered to assess safety and efficacy.
To the Editor:
Actinic keratoses (AKs) are keratinocyte neoplasms that manifest as rough, scaly, erythematous papules with ill-defined borders (commonly known as precancers) and develop due to long-term UV light exposure.1 They must be treated promptly due to the risk for progression to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). One US Department of Veterans Affairs study reported that 0.6% of AKs progress to SCC in 1 year and 2.6% progressed to SCC in 4 years.2 In 10% of AKs that will progress to SCC, one study reported progression in approximately 2 years.3
The risk for progression also increases in patients with multiple AKs; the risk is 4-fold higher in patients with 6 to 20 AKs and 11-fold higher in patients with more than 20 AKs.4 Common treatment options include lesion-directed therapies such as cryotherapy, laser therapy, surgery, and curettage, as well as field-directed therapies such as topical 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), diclofenac gel 3%, chemical peeling, topical imiquimod, and photodynamic therapy (PDT).4 When diclofenac gel is chosen as a treatment modality, it is commonly prescribed in the 3% formulation. Diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in the treatment of AKs,5,6 but diclofenac gel 1% has not been well described in the literature. We report the case of a patient with AKs on the lower legs who was treated with diclofenac gel after other therapies failed.
A 55-year-old woman presented for a routine skin check due to a history of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Her medical history also included palmar hyperhidrosis, disseminated superficial actinic porokeratosis, and extensive actinic damage, as well as numerous biopsy-proven AKs. She had been evaluated every 3 months up to presentation due to the frequency of AK development over the past 5 years. The lesions were mainly localized to both lower legs, where the patient had acquired considerable lifetime sun exposure from tanning beds and sunbathing while boating. She also noted exposure to well water as a child, but none of her family members had a similar issue with AKs.
Prior to this visit, the patient had undergone 5 years of therapy for AKs. She initially was treated with multiple courses of topical 5-FU, but she consequently developed severe allergic contact dermatitis. Subsequent treatments included cryotherapy as well as application of tretinoin cream nightly for 2 weeks followed by PDT. She was unable to tolerate the tretinoin, which she reported led to dryness and irritation. She reported mild improvement after her first session of PDT but only minimal improvement after the next session. Ingenol mebutate was then prescribed for topical use on the legs for 2 days, which did not result in improvement. The patient continued to follow up for unresolved AKs on the legs and was prescribed acitretin to help reduce the risk for progression to SCC. At follow-up 3 months later, she reported decreased soreness from AKs after starting the acitretin and, aside from mild dryness, she tolerated the medication well; however, with continued use of acitretin, she began to experience adverse effects 6 months later, including thyroid suppression and hair loss, leading to discontinuation. Instead, 3 months later, she was recommended to start nicotinamide supplementation for prevention of SCC.
Due to continued AK development (Figure, A), we eventually prescribed diclofenac gel 3% twice daily for both legs 9 months after prescribing nicotinamide. This regimen was cost prohibitive, as the medication was not covered by her insurance and the cost was $300 for one tube. We recommended the patient instead apply the 3% gel to the right leg only due to greater severity of AKs on this leg and over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1% twice daily to the left leg. Approximately 5 months later, she reported a reduction in the discomfort from AKs as well as a reduction in the total number of AKs. She applied the 2 different products as instructed for the first month but did not notice a difference between them. She then continued to apply only the 1% gel on both legs for a total of 8 months with excellent response (Figure, B). At subsequent follow-up visits over a 2-year period, she has only required cryotherapy as spot treatment for AKs.

For 1 to a few discrete AKs, liquid nitrogen cryotherapy is considered first-line therapy.7 However, if multiple AKs are present, surrounding photodamaged skin also should be treated with field-directed therapy due to surrounding keratinocytes bearing a high mutational burden and risk of cancerization.8 Common field-directed therapies include topical 5-FU, topical imiquimod, topical tirbanibulin, PDT, retinoids, and topical diclofenac 3%.
One challenge in field-directed treatment of AKs is the side-effect profile seen in some patients, causing them to prematurely discontinue treatment. In our patient, 5-FU cream, tretinoin cream, and oral acitretin were not well tolerated. Topical diclofenac generally is well tolerated, with mostly mild local skin reactions and low risk for systemic adverse events. Adverse effects mainly consist of mild local skin reactions including pruritus (reported in 31%-52% of patients who used topical diclofenac), dryness (25%-27%), and irritation (less than 1%).9,10 Although diclofenac carries a black-box warning for serious cardiovascular thrombotic events and serious gastrointestinal tract bleeding, systemic absorption of topical diclofenac has been proven to be substantially lower (5- to 17-fold) compared to the oral formulation, and resulting serious adverse effects have been found to be largely reduced compared to the oral formulation.11,12 If allergic contact dermatitis develops, diclofenac should be discontinued.9,13
Diclofenac’s antineoplastic mechanism of action of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition involves induction of apoptosis as well as reduction in tumor cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis.14,15 Topical diclofenac may result in decreased levels of lactate and amino acid in AK lesions, particularly in lesions responding to treatment.16 Topical diclofenac may alter immune infiltration by inducing infiltration of dermal CD8+ T cells along with high IFN-γ messenger RNA expression, suggesting improvement of T-cell function after topical diclofenac treatment.16
Although diclofenac gel 3% has been shown to be effective in treatment of AKs,5,6 diclofenac gel 1% has not yet been well studied. Use of the 1% gel is indicated for osteoarthritis and musculoskeletal pain by the US Food and Drug Administration.10,17 Efficacy of the 1% gel has been documented for these and other conditions including seborrheic keratoses.18-20
Because the 1% diclofenac formulation is available over-the-counter, it is more accessible to patients compared to the 3% formulation and often substantially decreases the cost of the medication for the patient. The cost of diclofenac gel 1% in the United States ranges from $0.04 to $0.31 per gram compared to $1.07 to $11.79 per gram for the 3% gel prescription formulation.17 Efficacy of the 1% formulation compared to the 3% formulation could represent an avenue to increase accessibility to field-directed therapy in the population for the treatment of AKs with a potentially well-tolerated, effective, and low-cost medication formulation.
This case represents the effectiveness of diclofenac gel 1% in treating AKs. Several treatment modalities failed in our case, but she experienced improvement with use of over-the-counter diclofenac gel 1%. She also noted no difference in response between the prescription 3% diclofenac formulation and the over-the-counter 1% formulation. Diclofenac gel 1% may represent an excellent therapeutic option in treatment-refractory cases of AKs. Larger randomized trials should be considered to assess safety and efficacy.
- FEisen DB, Asgari MM, Bennett DD, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:e209-e233.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Fuchs A, Marmur E. The kinetics of skin cancer: progression of actinic keratosis to squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33: 1099-1101.
- Dianzani C, Conforti C, Giuffrida R, et al. Current therapies for actinic keratosis. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:677-684.
- Javor S, Cozzani E, Parodi A. Topical treatment of actinic keratosis with 3.0% diclofenac in 2.5% hyaluronan gel: review of the literature about the cumulative evidence of its efficacy and safety. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:275-280.
- Martin GM, Stockfleth E. Diclofenac sodium 3% gel for the management of actinic keratosis: 10+ years of cumulative evidence of efficacy and safety. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:600-608.
- Arisi M, Guasco Pisani E, et al. Cryotherapy for actinic keratosis: basic principles and literature review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:357-365.
- Calzavara-Pinton P, Calzavara-Pinton I, Rovati C, et al. Topical pharmacotherapy for actinic keratoses in older adults. Drugs Aging. 2022;39:143-152.
- Beutner C, Forkel S, Kreipe K, et al. Contact allergy to topical diclofenac with systemic tolerance. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:41-43.
- Voltaren gel (diclofenac sodium topical gel). Prescribing information. Novartis Consumer Health, Inc; 2009. Accessed May 21, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/022122s006lbl.pdf
- Moreira SA, Liu DJ. Diclofenac systemic bioavailability of a topical 1% diclofenac + 3% menthol combination gel vs. an oral diclofenac tablet in healthy volunteers: a randomized, open-label, crossover study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;55:368-372.
- Kienzler JL, Gold M, Nollevaux F. Systemic bioavailability of topical diclofenac sodium gel 1% versus oral diclofenac sodium in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50:50-61.
- Gulin SJ, Chiriac A. Diclofenac-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a series of four patients. Drug Saf Case Rep. 2016;3:15.
- Fecker LF, Stockfleth E, Nindl I, et al. The role of apoptosis in therapy and prophylaxis of epithelial tumours by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Br J Dermatol. 2007;156(Suppl 3):25-33.
- Thomas GJ, Herranz P, Cruz SB, et al. Treatment of actinic keratosis through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: potential mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium 3% in hyaluronic acid 2.5. Dermatol Ther. 2019;32:e12800.
- Singer K, Dettmer K, Unger P, et al. Topical diclofenac reprograms metabolism and immune cell infiltration in actinic keratosis. Front Oncol. 2019;9:605.
- Diclofenac (topical). Drug information. UpToDate. https://www-uptodate-com.libraryaccess.elpaso.ttuhsc.edu/contents/diclofenac-topical-drug-information?source=auto_suggest&selectedTitle=1~3---3~4---diclofenac&search=diclofenac%20topical#F8017265
- Afify AA, Hana MR. Comparative evaluation of topical diclofenac sodium versus topical ibuprofen in the treatment of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14370.
- Yin F, Ma J, Xiao H, et al. Randomized, double-blind, noninferiority study of diclofenac diethylamine 2.32% gel applied twice daily versus diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% gel applied four times daily in patients with acute ankle sprain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23:1125.
- van Herwaarden N, van den Elsen GAH, de Jong ICA, et al. Topical NSAIDs: ineffective or undervalued? [in Dutch]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2021;165:D5317.
- FEisen DB, Asgari MM, Bennett DD, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of actinic keratosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;85:e209-e233.
- Criscione VD, Weinstock MA, Naylor MF, et al. Actinic keratoses: natural history and risk of malignant transformation in the Veterans Affairs Topical Tretinoin Chemoprevention Trial. Cancer. 2009;115:2523-2530.
- Fuchs A, Marmur E. The kinetics of skin cancer: progression of actinic keratosis to squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33: 1099-1101.
- Dianzani C, Conforti C, Giuffrida R, et al. Current therapies for actinic keratosis. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59:677-684.
- Javor S, Cozzani E, Parodi A. Topical treatment of actinic keratosis with 3.0% diclofenac in 2.5% hyaluronan gel: review of the literature about the cumulative evidence of its efficacy and safety. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2016;151:275-280.
- Martin GM, Stockfleth E. Diclofenac sodium 3% gel for the management of actinic keratosis: 10+ years of cumulative evidence of efficacy and safety. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11:600-608.
- Arisi M, Guasco Pisani E, et al. Cryotherapy for actinic keratosis: basic principles and literature review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022;15:357-365.
- Calzavara-Pinton P, Calzavara-Pinton I, Rovati C, et al. Topical pharmacotherapy for actinic keratoses in older adults. Drugs Aging. 2022;39:143-152.
- Beutner C, Forkel S, Kreipe K, et al. Contact allergy to topical diclofenac with systemic tolerance. Contact Dermatitis. 2022;86:41-43.
- Voltaren gel (diclofenac sodium topical gel). Prescribing information. Novartis Consumer Health, Inc; 2009. Accessed May 21, 2025. https:// www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/022122s006lbl.pdf
- Moreira SA, Liu DJ. Diclofenac systemic bioavailability of a topical 1% diclofenac + 3% menthol combination gel vs. an oral diclofenac tablet in healthy volunteers: a randomized, open-label, crossover study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;55:368-372.
- Kienzler JL, Gold M, Nollevaux F. Systemic bioavailability of topical diclofenac sodium gel 1% versus oral diclofenac sodium in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50:50-61.
- Gulin SJ, Chiriac A. Diclofenac-induced allergic contact dermatitis: a series of four patients. Drug Saf Case Rep. 2016;3:15.
- Fecker LF, Stockfleth E, Nindl I, et al. The role of apoptosis in therapy and prophylaxis of epithelial tumours by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Br J Dermatol. 2007;156(Suppl 3):25-33.
- Thomas GJ, Herranz P, Cruz SB, et al. Treatment of actinic keratosis through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2: potential mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium 3% in hyaluronic acid 2.5. Dermatol Ther. 2019;32:e12800.
- Singer K, Dettmer K, Unger P, et al. Topical diclofenac reprograms metabolism and immune cell infiltration in actinic keratosis. Front Oncol. 2019;9:605.
- Diclofenac (topical). Drug information. UpToDate. https://www-uptodate-com.libraryaccess.elpaso.ttuhsc.edu/contents/diclofenac-topical-drug-information?source=auto_suggest&selectedTitle=1~3---3~4---diclofenac&search=diclofenac%20topical#F8017265
- Afify AA, Hana MR. Comparative evaluation of topical diclofenac sodium versus topical ibuprofen in the treatment of seborrheic keratosis. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:e14370.
- Yin F, Ma J, Xiao H, et al. Randomized, double-blind, noninferiority study of diclofenac diethylamine 2.32% gel applied twice daily versus diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% gel applied four times daily in patients with acute ankle sprain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23:1125.
- van Herwaarden N, van den Elsen GAH, de Jong ICA, et al. Topical NSAIDs: ineffective or undervalued? [in Dutch]. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2021;165:D5317.
Actinic Keratosis Treatment With Diclofenac Gel 1%
Actinic Keratosis Treatment With Diclofenac Gel 1%
PRACTICE POINTS
- There are numerous field-directed therapies for actinic keratoses (AKs); however, efficacy and tolerability vary among the available treatments.
- Diclofenac gel 1% is an affordable option that could potentially increase accessibility and decrease cost of field therapy for the treatment of AKs, while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Painful Flesh-Colored Nodule on the Shoulder
Painful Flesh-Colored Nodule on the Shoulder
THE DIAGNOSIS: Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
The histologic findings showed fascicular proliferation of relatively monomorphic spindle cells with extensive entrapment of collagen and adipocytes. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the lesional cells were diffusely positive for CD34 and negative for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa. The decision was made to perform cytogenetic testing with fluorescence in situ hybridization to evaluate for the presence of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFB) polypeptide rearrangement, a key biomarker known to be positive in most patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).1 This rearrangement results in overproduction of PDGFB, continuous activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta, cellular proliferation, and tumor formation.2 In our patient, results were positive for the PDGFB polypeptide rearrangement, which confirmed suspected diagnosis of DFSP with fibrous histiocytoma like morphology. The patient was referred for Mohs micrographic surgery for proper management.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue tumor that involves the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and sometimes muscle and fascia.2 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans primarily affects young to middle-aged adults, with a slight predilection for individuals in the third to fifth decades of life.3 Lesions preferentially involve the trunk, particularly the shoulder and chest regions, and manifest as poorly circumscribed, locally aggressive mesenchymal neoplasms with a high local recurrence rate but low metastatic potential.4,5 Clinically, the lesions appear as flesh-colored, rubbery plaques or nodules. A diagnosis of DFSP requires a high index of clinical suspicion, and histologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular testing usually are required for confirmation.
On histopathologic examination, DFSP classically demonstrates uniform, spindle-shaped cells that traditionally are arranged in an intersecting pattern and primarily are based in the dermis (Figure 1).5 Infiltration into the underlying tissue is a common feature, with neoplastic extensions causing a classic honeycomb pattern6 that also can be seen in diffuse neurofibroma and may cause diagnostic challenges; however, the immunohistology staining of neurofibroma differs from DFSP in that it stains positive for CD34, SOX-100, and S100, while DFSP has strong and diffuse CD34 immunoreactivity with negative immunostaining for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa.2,6
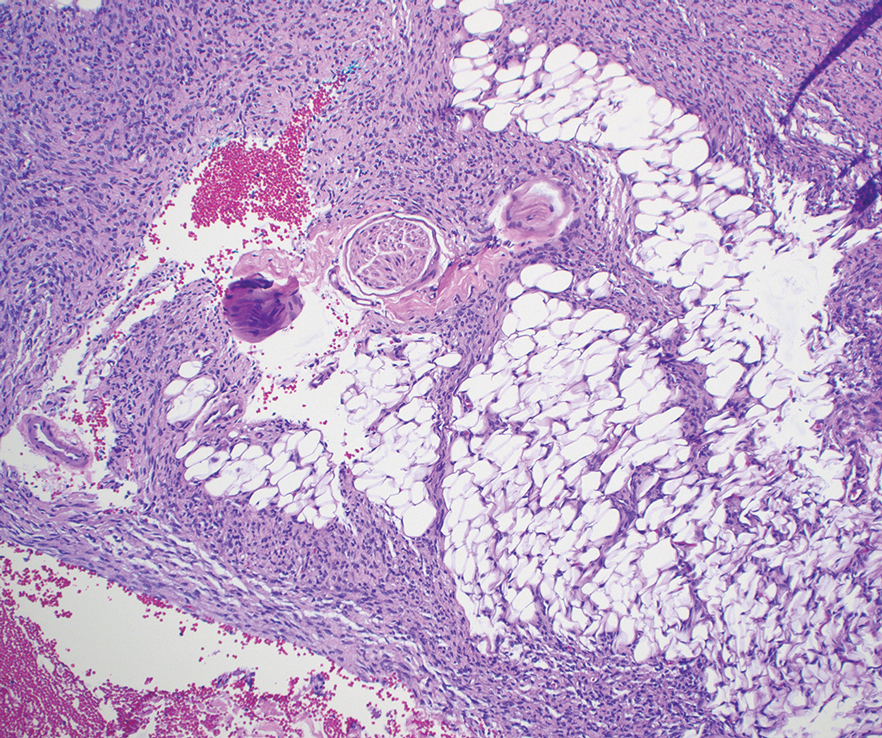
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can cause considerable fat infiltration compared to other soft-tissue neoplasms, making this finding suspicious for—if not characteristic of—DFSP. Collagen trapping also can be observed; however, this is more pathognomonic in cellular fibrous histiocytoma, which is a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas. Due to its similarity to other lesions, histopathologic examination along with immunostaining can assist in differentiating and accurately diagnosing DFSP.6
Cellular fibrous histiocytoma (CFH), a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas, is a benign tumor of mesenchymal origin that occurs more commonly on the trunk, arms, and legs. On histologic examination, CFH is composed of spindle-shaped cells with variable amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm and small, oval-shaped eosinophilic nuclei and collagen trapping (Figure 2).7,8 Most CFHs occupy the superficial dermis but can extend into the deep reticular dermis, thus mimicking the honeycomb pattern seen in DFSP. This neoplasm can show a similar architecture to DFSP, which is why further investigation including cytogenetics and immunohistochemical staining can help differentiate the two conditions. Cellular fibrous histiocytoma typically stains negative for CD34 and positive for factor XIIIa.9 However, CD34 can be positive in a subset of CFHs, with a considerable subset showing peripheral CD34 positivity and a smaller subset showing central CD34 the positivity.10 This suggests that CD34 cannot be the only factor differentiating these 2 lesions in making a proper dermatopathologic diagnosis.
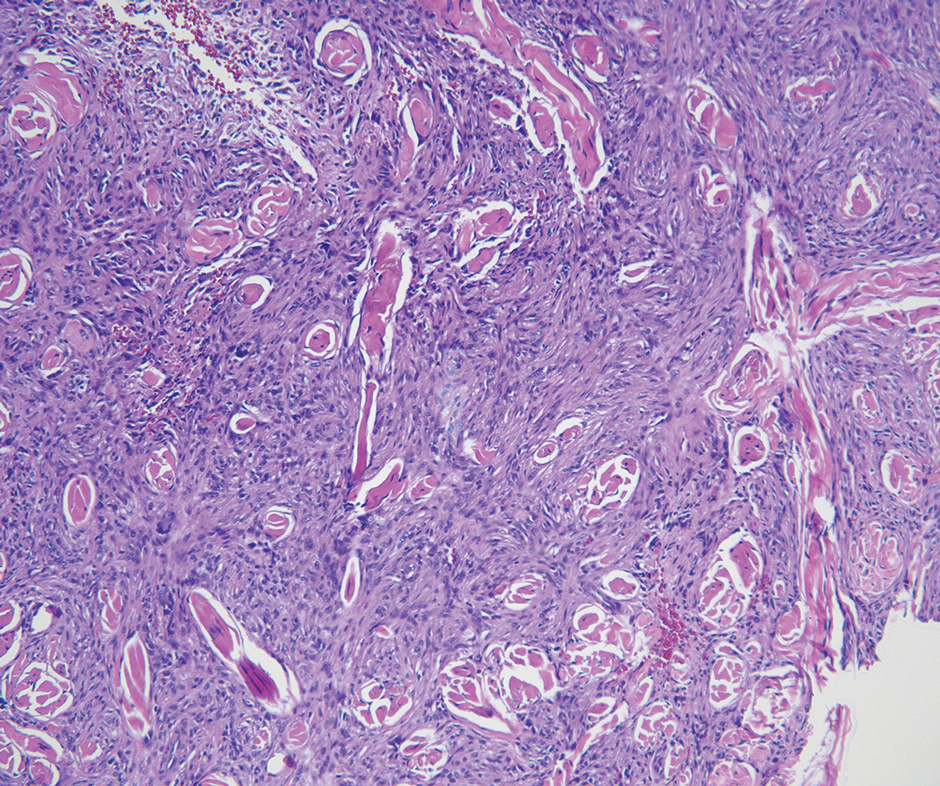
Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can occur anywhere on the body and typically manifests as a deep, painless, enlarging mass in adults aged 50 to 60 years.11 On histologic examination, SFT consists of randomly arranged cells with a spindle or ovoid shape within a collagenous stroma intermixed with blood vessels with a characteristic staghorn shape (Figure 3).11 Low-grade SFT shows a patternless arrangement with spindle cells, a low number of mitotic figures, and vessels with a staghorn appearance compared to high-grade SFT, which shows hypercellularity with nuclear pleomorphism and a high number of mitotic figures.11 Solitary fibrous tumors are positive for CD34 and STAT-6 and negative for CD31 and typically demonstrate NGFI-A binding protein 2 (NAB2)—signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT 6) gene fusion.11
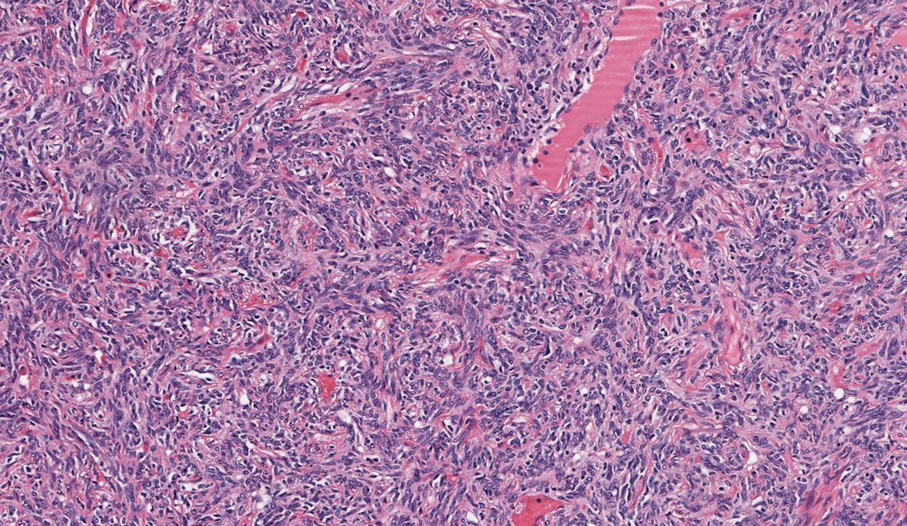
Spindle-cell lipomas are rare, benign, slow-growing, lipomatous tumors that typically manifest in men aged 40 to 70 years.12 These lesions originate most frequently in the subcutaneous tissue of the upper back, posterior neck, and shoulders. The histologic growth pattern of spindle-cell lipomas can mimic other spindle-cell and myxoid tumors, which is why cytogenetic analysis is crucial for differentiating these lesions. On histologic examination, spindle-cell lipomas exhibit a mixture of mature adipocytes, uniform spindle cells, and collagen bundles (eFigure). Spindle-cell lipoma stains positive for CD34 but negative for S100.13 In addition, spindle-cell lipomas tend to show structural rearrangements (mainly deletions) of the long arm of chromosome 13 or even losses of whole chromosome 13, which contains the retinoblastoma (RB1) gene.13
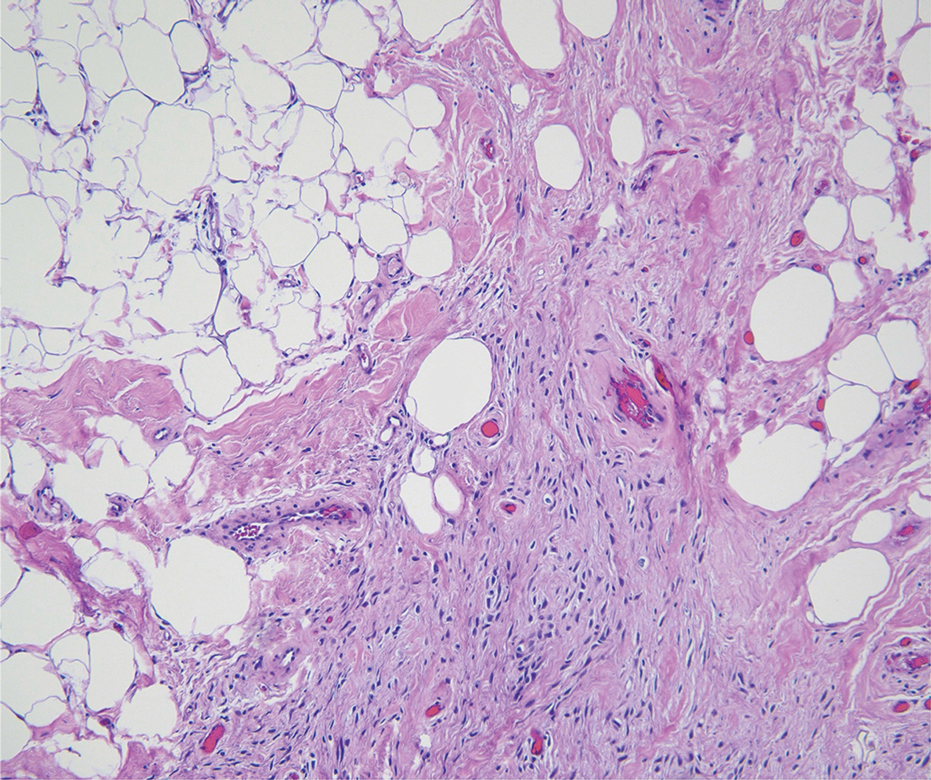
Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can appear clinically and histologically similar to atypical fibroxanthoma.14 This lesion often manifests in elderly patients and is strongly associated with chronic sun exposure.15 Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a locally aggressive tumor with metastatic potential to the skin or lymph nodes. On histologic examination, these tumors exhibit pleomorphic atypical epithelioid or spindle cells as well as multinucleated tumor giant cells with possible tumor necrosis, lymphovascular invasion, or perineural infiltration (Figure 4). Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma, typically a diagnosis of exclusion, requires immunohistochemistry to aid in proper identification.16 These lesions stain positive for CD10 and negative for cytokeratins, desmin, HMB45, CD34, p63, p40, SOX10, and S100.15,16
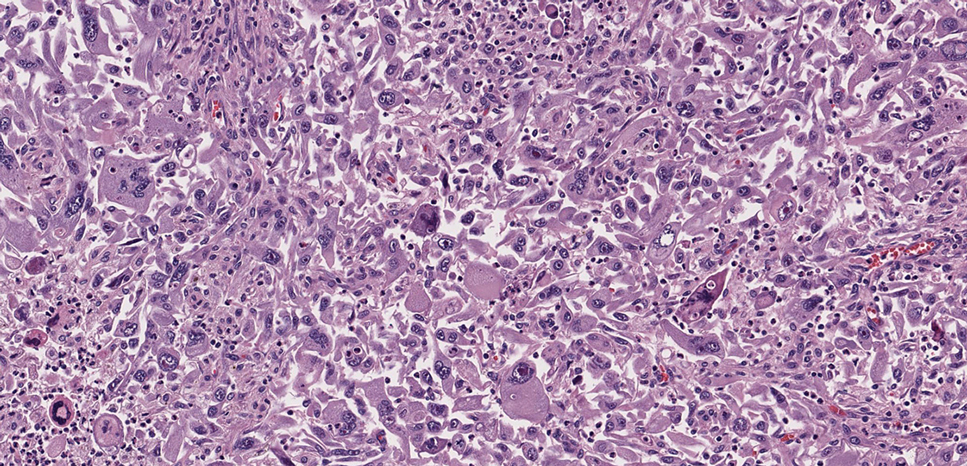
- Ugurel S, Kortmann R, Mohr P, et al. S1 guidelines for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)—update 2018. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2019;17:663-668. doi:10.1111/ddg.13849
- Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated April 18, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025.
- Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a clinicopathologic analysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer. 2000;88:2711-2720.
- Lim SX, Ramaiya A, Levell NJ, et al. Review of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;48:297-302. doi:10.1093/ced/llac111
- Trinidad CM, Wangsiricharoen S, Prieto VG, et al. Rare variants of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: clinical, histologic, and molecular features and diagnostic pitfalls. Dermatopathology. 2023;10:54-62. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology10010008
- Hao X, Billings SD, Wu F, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: update on the diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1752. doi:10.3390/jcm9061752
- Tsunoda K, Oikawa H, Maeda F, et al. A case of cellular fibrous histiocytoma on the right elbow with repeated relapse within a short period. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371790
- Calonje E, Mentzel T, Fletcher CD. Cellular benign fibrous histiocytoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 74 cases of a distinctive variant of cutaneous fibrous histiocytoma with frequent recurrence. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:668-676.
- Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ. CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathology. 1997;19:147-153. doi:10.1097/00000372-199704000-00008
- Volpicelli ER, Fletcher CD. Desmin and CD34 positivity in cellular fibrous histiocytoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 100 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:747-752. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01944.x
- Martin-Broto J, Mondaza-Hernandez JL, Moura DS, et al. A comprehensive review on solitary fibrous tumor: new insights for new horizons. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:2913. doi:10.3390/cancers13122913
- Machol JA, Cusic JG, O’Connor EA, et al. Spindle cell lipoma of the neck: review of the literature and case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E550. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000405
- Domanski HA, Carlén B, Jonsson K, et al. Distinct cytologic features of spindle cell lipoma. a cytologic-histologic study with clinical, radiologic, electron microscopic, and cytogenetic correlations. Cancer. 2001;93:381-389. doi:10.1002/cncr.10142
- Devine RL, Cameron A, Holden AM, et al. The pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: its management, follow-up and the need for more guidance. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;2:100046. doi:10.1016 /j.adoms.2021.100046
- Seretis K, Klaroudas A, Galani V, et al. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: it might be rare but it exists [published online August 4, 2023]. J Surg Case Rep. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjad374
- Miller K, Goodlad JR, Brenn T. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:1317-1326. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31825359e1
THE DIAGNOSIS: Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
The histologic findings showed fascicular proliferation of relatively monomorphic spindle cells with extensive entrapment of collagen and adipocytes. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the lesional cells were diffusely positive for CD34 and negative for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa. The decision was made to perform cytogenetic testing with fluorescence in situ hybridization to evaluate for the presence of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFB) polypeptide rearrangement, a key biomarker known to be positive in most patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).1 This rearrangement results in overproduction of PDGFB, continuous activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta, cellular proliferation, and tumor formation.2 In our patient, results were positive for the PDGFB polypeptide rearrangement, which confirmed suspected diagnosis of DFSP with fibrous histiocytoma like morphology. The patient was referred for Mohs micrographic surgery for proper management.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue tumor that involves the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and sometimes muscle and fascia.2 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans primarily affects young to middle-aged adults, with a slight predilection for individuals in the third to fifth decades of life.3 Lesions preferentially involve the trunk, particularly the shoulder and chest regions, and manifest as poorly circumscribed, locally aggressive mesenchymal neoplasms with a high local recurrence rate but low metastatic potential.4,5 Clinically, the lesions appear as flesh-colored, rubbery plaques or nodules. A diagnosis of DFSP requires a high index of clinical suspicion, and histologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular testing usually are required for confirmation.
On histopathologic examination, DFSP classically demonstrates uniform, spindle-shaped cells that traditionally are arranged in an intersecting pattern and primarily are based in the dermis (Figure 1).5 Infiltration into the underlying tissue is a common feature, with neoplastic extensions causing a classic honeycomb pattern6 that also can be seen in diffuse neurofibroma and may cause diagnostic challenges; however, the immunohistology staining of neurofibroma differs from DFSP in that it stains positive for CD34, SOX-100, and S100, while DFSP has strong and diffuse CD34 immunoreactivity with negative immunostaining for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa.2,6

Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can cause considerable fat infiltration compared to other soft-tissue neoplasms, making this finding suspicious for—if not characteristic of—DFSP. Collagen trapping also can be observed; however, this is more pathognomonic in cellular fibrous histiocytoma, which is a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas. Due to its similarity to other lesions, histopathologic examination along with immunostaining can assist in differentiating and accurately diagnosing DFSP.6
Cellular fibrous histiocytoma (CFH), a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas, is a benign tumor of mesenchymal origin that occurs more commonly on the trunk, arms, and legs. On histologic examination, CFH is composed of spindle-shaped cells with variable amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm and small, oval-shaped eosinophilic nuclei and collagen trapping (Figure 2).7,8 Most CFHs occupy the superficial dermis but can extend into the deep reticular dermis, thus mimicking the honeycomb pattern seen in DFSP. This neoplasm can show a similar architecture to DFSP, which is why further investigation including cytogenetics and immunohistochemical staining can help differentiate the two conditions. Cellular fibrous histiocytoma typically stains negative for CD34 and positive for factor XIIIa.9 However, CD34 can be positive in a subset of CFHs, with a considerable subset showing peripheral CD34 positivity and a smaller subset showing central CD34 the positivity.10 This suggests that CD34 cannot be the only factor differentiating these 2 lesions in making a proper dermatopathologic diagnosis.

Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can occur anywhere on the body and typically manifests as a deep, painless, enlarging mass in adults aged 50 to 60 years.11 On histologic examination, SFT consists of randomly arranged cells with a spindle or ovoid shape within a collagenous stroma intermixed with blood vessels with a characteristic staghorn shape (Figure 3).11 Low-grade SFT shows a patternless arrangement with spindle cells, a low number of mitotic figures, and vessels with a staghorn appearance compared to high-grade SFT, which shows hypercellularity with nuclear pleomorphism and a high number of mitotic figures.11 Solitary fibrous tumors are positive for CD34 and STAT-6 and negative for CD31 and typically demonstrate NGFI-A binding protein 2 (NAB2)—signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT 6) gene fusion.11

Spindle-cell lipomas are rare, benign, slow-growing, lipomatous tumors that typically manifest in men aged 40 to 70 years.12 These lesions originate most frequently in the subcutaneous tissue of the upper back, posterior neck, and shoulders. The histologic growth pattern of spindle-cell lipomas can mimic other spindle-cell and myxoid tumors, which is why cytogenetic analysis is crucial for differentiating these lesions. On histologic examination, spindle-cell lipomas exhibit a mixture of mature adipocytes, uniform spindle cells, and collagen bundles (eFigure). Spindle-cell lipoma stains positive for CD34 but negative for S100.13 In addition, spindle-cell lipomas tend to show structural rearrangements (mainly deletions) of the long arm of chromosome 13 or even losses of whole chromosome 13, which contains the retinoblastoma (RB1) gene.13

Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can appear clinically and histologically similar to atypical fibroxanthoma.14 This lesion often manifests in elderly patients and is strongly associated with chronic sun exposure.15 Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a locally aggressive tumor with metastatic potential to the skin or lymph nodes. On histologic examination, these tumors exhibit pleomorphic atypical epithelioid or spindle cells as well as multinucleated tumor giant cells with possible tumor necrosis, lymphovascular invasion, or perineural infiltration (Figure 4). Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma, typically a diagnosis of exclusion, requires immunohistochemistry to aid in proper identification.16 These lesions stain positive for CD10 and negative for cytokeratins, desmin, HMB45, CD34, p63, p40, SOX10, and S100.15,16

THE DIAGNOSIS: Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
The histologic findings showed fascicular proliferation of relatively monomorphic spindle cells with extensive entrapment of collagen and adipocytes. Immunohistochemical staining showed that the lesional cells were diffusely positive for CD34 and negative for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa. The decision was made to perform cytogenetic testing with fluorescence in situ hybridization to evaluate for the presence of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFB) polypeptide rearrangement, a key biomarker known to be positive in most patients with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP).1 This rearrangement results in overproduction of PDGFB, continuous activation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta, cellular proliferation, and tumor formation.2 In our patient, results were positive for the PDGFB polypeptide rearrangement, which confirmed suspected diagnosis of DFSP with fibrous histiocytoma like morphology. The patient was referred for Mohs micrographic surgery for proper management.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue tumor that involves the dermis, subcutaneous fat, and sometimes muscle and fascia.2 Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans primarily affects young to middle-aged adults, with a slight predilection for individuals in the third to fifth decades of life.3 Lesions preferentially involve the trunk, particularly the shoulder and chest regions, and manifest as poorly circumscribed, locally aggressive mesenchymal neoplasms with a high local recurrence rate but low metastatic potential.4,5 Clinically, the lesions appear as flesh-colored, rubbery plaques or nodules. A diagnosis of DFSP requires a high index of clinical suspicion, and histologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular testing usually are required for confirmation.
On histopathologic examination, DFSP classically demonstrates uniform, spindle-shaped cells that traditionally are arranged in an intersecting pattern and primarily are based in the dermis (Figure 1).5 Infiltration into the underlying tissue is a common feature, with neoplastic extensions causing a classic honeycomb pattern6 that also can be seen in diffuse neurofibroma and may cause diagnostic challenges; however, the immunohistology staining of neurofibroma differs from DFSP in that it stains positive for CD34, SOX-100, and S100, while DFSP has strong and diffuse CD34 immunoreactivity with negative immunostaining for SOX10, S100, desmin, and factor XIIIa.2,6

Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans can cause considerable fat infiltration compared to other soft-tissue neoplasms, making this finding suspicious for—if not characteristic of—DFSP. Collagen trapping also can be observed; however, this is more pathognomonic in cellular fibrous histiocytoma, which is a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas. Due to its similarity to other lesions, histopathologic examination along with immunostaining can assist in differentiating and accurately diagnosing DFSP.6
Cellular fibrous histiocytoma (CFH), a distinct clinical variant of dermatofibromas, is a benign tumor of mesenchymal origin that occurs more commonly on the trunk, arms, and legs. On histologic examination, CFH is composed of spindle-shaped cells with variable amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm and small, oval-shaped eosinophilic nuclei and collagen trapping (Figure 2).7,8 Most CFHs occupy the superficial dermis but can extend into the deep reticular dermis, thus mimicking the honeycomb pattern seen in DFSP. This neoplasm can show a similar architecture to DFSP, which is why further investigation including cytogenetics and immunohistochemical staining can help differentiate the two conditions. Cellular fibrous histiocytoma typically stains negative for CD34 and positive for factor XIIIa.9 However, CD34 can be positive in a subset of CFHs, with a considerable subset showing peripheral CD34 positivity and a smaller subset showing central CD34 the positivity.10 This suggests that CD34 cannot be the only factor differentiating these 2 lesions in making a proper dermatopathologic diagnosis.

Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can occur anywhere on the body and typically manifests as a deep, painless, enlarging mass in adults aged 50 to 60 years.11 On histologic examination, SFT consists of randomly arranged cells with a spindle or ovoid shape within a collagenous stroma intermixed with blood vessels with a characteristic staghorn shape (Figure 3).11 Low-grade SFT shows a patternless arrangement with spindle cells, a low number of mitotic figures, and vessels with a staghorn appearance compared to high-grade SFT, which shows hypercellularity with nuclear pleomorphism and a high number of mitotic figures.11 Solitary fibrous tumors are positive for CD34 and STAT-6 and negative for CD31 and typically demonstrate NGFI-A binding protein 2 (NAB2)—signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT 6) gene fusion.11

Spindle-cell lipomas are rare, benign, slow-growing, lipomatous tumors that typically manifest in men aged 40 to 70 years.12 These lesions originate most frequently in the subcutaneous tissue of the upper back, posterior neck, and shoulders. The histologic growth pattern of spindle-cell lipomas can mimic other spindle-cell and myxoid tumors, which is why cytogenetic analysis is crucial for differentiating these lesions. On histologic examination, spindle-cell lipomas exhibit a mixture of mature adipocytes, uniform spindle cells, and collagen bundles (eFigure). Spindle-cell lipoma stains positive for CD34 but negative for S100.13 In addition, spindle-cell lipomas tend to show structural rearrangements (mainly deletions) of the long arm of chromosome 13 or even losses of whole chromosome 13, which contains the retinoblastoma (RB1) gene.13

Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a rare mesenchymal tumor that can appear clinically and histologically similar to atypical fibroxanthoma.14 This lesion often manifests in elderly patients and is strongly associated with chronic sun exposure.15 Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma is a locally aggressive tumor with metastatic potential to the skin or lymph nodes. On histologic examination, these tumors exhibit pleomorphic atypical epithelioid or spindle cells as well as multinucleated tumor giant cells with possible tumor necrosis, lymphovascular invasion, or perineural infiltration (Figure 4). Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma, typically a diagnosis of exclusion, requires immunohistochemistry to aid in proper identification.16 These lesions stain positive for CD10 and negative for cytokeratins, desmin, HMB45, CD34, p63, p40, SOX10, and S100.15,16

- Ugurel S, Kortmann R, Mohr P, et al. S1 guidelines for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)—update 2018. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2019;17:663-668. doi:10.1111/ddg.13849
- Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated April 18, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025.
- Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a clinicopathologic analysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer. 2000;88:2711-2720.
- Lim SX, Ramaiya A, Levell NJ, et al. Review of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;48:297-302. doi:10.1093/ced/llac111
- Trinidad CM, Wangsiricharoen S, Prieto VG, et al. Rare variants of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: clinical, histologic, and molecular features and diagnostic pitfalls. Dermatopathology. 2023;10:54-62. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology10010008
- Hao X, Billings SD, Wu F, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: update on the diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1752. doi:10.3390/jcm9061752
- Tsunoda K, Oikawa H, Maeda F, et al. A case of cellular fibrous histiocytoma on the right elbow with repeated relapse within a short period. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371790
- Calonje E, Mentzel T, Fletcher CD. Cellular benign fibrous histiocytoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 74 cases of a distinctive variant of cutaneous fibrous histiocytoma with frequent recurrence. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:668-676.
- Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ. CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathology. 1997;19:147-153. doi:10.1097/00000372-199704000-00008
- Volpicelli ER, Fletcher CD. Desmin and CD34 positivity in cellular fibrous histiocytoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 100 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:747-752. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01944.x
- Martin-Broto J, Mondaza-Hernandez JL, Moura DS, et al. A comprehensive review on solitary fibrous tumor: new insights for new horizons. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:2913. doi:10.3390/cancers13122913
- Machol JA, Cusic JG, O’Connor EA, et al. Spindle cell lipoma of the neck: review of the literature and case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E550. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000405
- Domanski HA, Carlén B, Jonsson K, et al. Distinct cytologic features of spindle cell lipoma. a cytologic-histologic study with clinical, radiologic, electron microscopic, and cytogenetic correlations. Cancer. 2001;93:381-389. doi:10.1002/cncr.10142
- Devine RL, Cameron A, Holden AM, et al. The pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: its management, follow-up and the need for more guidance. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;2:100046. doi:10.1016 /j.adoms.2021.100046
- Seretis K, Klaroudas A, Galani V, et al. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: it might be rare but it exists [published online August 4, 2023]. J Surg Case Rep. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjad374
- Miller K, Goodlad JR, Brenn T. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:1317-1326. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31825359e1
- Ugurel S, Kortmann R, Mohr P, et al. S1 guidelines for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP)—update 2018. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2019;17:663-668. doi:10.1111/ddg.13849
- Brooks J, Ramsey ML. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Updated April 18, 2024. Accessed April 30, 2025.
- Bowne WB, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a clinicopathologic analysis of patients treated and followed at a single institution. Cancer. 2000;88:2711-2720.
- Lim SX, Ramaiya A, Levell NJ, et al. Review of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2022;48:297-302. doi:10.1093/ced/llac111
- Trinidad CM, Wangsiricharoen S, Prieto VG, et al. Rare variants of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: clinical, histologic, and molecular features and diagnostic pitfalls. Dermatopathology. 2023;10:54-62. doi:10.3390/dermatopathology10010008
- Hao X, Billings SD, Wu F, et al. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: update on the diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1752. doi:10.3390/jcm9061752
- Tsunoda K, Oikawa H, Maeda F, et al. A case of cellular fibrous histiocytoma on the right elbow with repeated relapse within a short period. Case Rep Dermatol. 2015;7:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371790
- Calonje E, Mentzel T, Fletcher CD. Cellular benign fibrous histiocytoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 74 cases of a distinctive variant of cutaneous fibrous histiocytoma with frequent recurrence. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994;18:668-676.
- Goldblum JR, Tuthill RJ. CD34 and factor-XIIIa immunoreactivity in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans and dermatofibroma. Am J Dermatopathology. 1997;19:147-153. doi:10.1097/00000372-199704000-00008
- Volpicelli ER, Fletcher CD. Desmin and CD34 positivity in cellular fibrous histiocytoma: an immunohistochemical analysis of 100 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2012;39:747-752. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01944.x
- Martin-Broto J, Mondaza-Hernandez JL, Moura DS, et al. A comprehensive review on solitary fibrous tumor: new insights for new horizons. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:2913. doi:10.3390/cancers13122913
- Machol JA, Cusic JG, O’Connor EA, et al. Spindle cell lipoma of the neck: review of the literature and case report. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2015;3:E550. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000405
- Domanski HA, Carlén B, Jonsson K, et al. Distinct cytologic features of spindle cell lipoma. a cytologic-histologic study with clinical, radiologic, electron microscopic, and cytogenetic correlations. Cancer. 2001;93:381-389. doi:10.1002/cncr.10142
- Devine RL, Cameron A, Holden AM, et al. The pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: its management, follow-up and the need for more guidance. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;2:100046. doi:10.1016 /j.adoms.2021.100046
- Seretis K, Klaroudas A, Galani V, et al. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: it might be rare but it exists [published online August 4, 2023]. J Surg Case Rep. doi:10.1093/jscr/rjad374
- Miller K, Goodlad JR, Brenn T. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:1317-1326. doi:10.1097/pas.0b013e31825359e1
Painful Flesh-Colored Nodule on the Shoulder
Painful Flesh-Colored Nodule on the Shoulder
A 26-year-old man with no notable medical history presented to the dermatology clinic with an inconspicuous, painful, raised lesion on the right posterior shoulder of 6 months’ duration. The patient reported that the lesion was tender to light palpation and bothersome in his daily activities. Physical examination revealed a firm, flesh-colored, 1.8-cm nodule with no erythema or pigmentation on the right shoulder. An elliptical excisional biopsy was performed and submitted for histologic evaluation.
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14
Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14

Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.

Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a highly contagious paramyxovirus that has neared elimination in the United States since 2000 due to widespread adoption of the measles vaccine; however, measles recently has made a comeback, with outbreaks reported in more than 60 countries. In the United States, vaccine hesitancy coupled with decreasing vaccination rates, international travel to endemic areas, and decreased funding and resources for monitoring and immunization programs likely led to a re-emergence of measles cases.1,2 The resurgence of measles is troubling given its infectiousness and potential severity in at-risk populations. Since measles has a basic reproduction number of 12 to 18 (ie, 1 infected individual will on average infect 12 to 18 others3), it has the capacity to spread quickly. This is why, prior to the development of the measles vaccine in the 1960s, it was responsible for millions of deaths across the globe.
Prior to the introduction of the measles vaccine, both physicians and the public generally were aware of the signs and symptoms of measles due to its prevalence; however, since there have been so few cases in recent decades, images and descriptions of patients presenting with measles can be found only in textbooks, and many physicians are ill-prepared to diagnose the disease.4 In response to the recent surge in measles cases, dermatologists—who often are among the first medical professionals to encounter febrile patients with rashes—must be prepared to bridge this divide. Herein, we review the clinical signs, diagnostic approach, operational precautions, and public health responsibilities that dermatologists must relearn amid the current measles outbreak.
Background
Measles is primarily transmitted via respiratory droplets and may remain airborne for up to 2 hours.5 It also can be transmitted through direct contact with secretions such as mucus. Indirect transmission via fomites, while certainly plausible, is thought to be the least effective mechanism of transmission.6 Following exposure, the incubation period ranges from 7 to 21 days, during which the virus replicates asymptomatically before causing clinical disease.7 Herd immunity for measles requires 93% immunity in the population; public health agencies typically target greater than 95% immunity.8 Humans are the only reservoir for the measles virus, making eradication possible.
The road to eradication began with the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963 and subsequent development of the combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine in 1971. As MMR is a live vaccine, 2 doses confer approximately 97% protection.9 The first dose is given at 12 to 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 to 6 years of age. Immunity is considered lifelong, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization do not recommend routine measles boosters for individuals who have completed the primary 2-dose series.10,11
Widespread vaccination led to a dramatic reduction in incidence, with many countries eliminating measles infections.7 The United States declared measles eliminated in 2000, with confirmed cases between 2000 and 2020 ranging from 37 to 1282.12 Vaccination progress stalled in the late 1990s due to vaccine hesitancy resulting from (subsequently debunked) reports of an association between the MMR vaccine and autism.13 Despite efforts to correct this misinformation, many patients continue to espouse these concerns.
Recognizing Measles: Clinical Presentation
Measles, which most often manifests in childhood but also can occur in adults, follows a distinctive clinical course. The prodromal phase is characterized by high fever, cough, coryza (nasal congestion), and conjunctivitis— conjunctivitis—the 3 “Cs” that serve as early warning signs of the disease. Patients may develop small white macules on the buccal mucosa known as Koplik spots (phonetically the fourth “C”), which appear just before the rash. Three to 5 days after the onset of systemic symptoms, patients will develop a classic morbilliform exanthem. In some cases, the exanthem manifests on the head and neck (Figure 1)—first behind the ears and along the hairline, then spreading caudally to the trunk and extremities. The lesions may become confluent, with patients presenting with diffuse erythema. The exanthem fades over several days to weeks, often accompanied by superficial desquamation.14

Given the nonspecificity of the early symptoms of measles, a high index of suspicion is needed for patients presenting with a febrile illness and a morbilliform eruption (Figure 2). Consideration of MMR vaccination status, exposure history, and local outbreak patterns can help guide risk stratification and the need for testing. Immunocompromised individuals, including those receiving immunosuppressive therapies for dermatologic conditions, may present atypically, lacking the prototypical exanthem or displaying milder signs and further complicating the diagnosis.15 The differential diagnosis for measles includes a drug reaction or other viral exanthem, and a detailed history may help elucidate the culprit.

Evaluation and Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of measles relies on both molecular and serologic testing. Nasopharyngeal swabs for measles polymerase chain reaction testing are obtained using synthetic (noncotton) swabs placed in a viral transport medium. Serum samples also should be collected for measles IgM and IgG antibody testing. Importantly, measles is a reportable illness, and testing may be coordinated with local departments of health.
Determining a patient’s immune status may be important for certain populations. Patients with documented 2-dose MMR vaccination, positive measles IgG serology, or a prior confirmed measles infection are considered immune. While a positive measles IgG indicates immunity, a negative result in an exposed patient should prompt consideration of postexposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin.
Many patients, specifically those presenting to dermatology, are taking immunomodulatory or immunosuppressive medications—a contraindication for vaccination with the live MMR vaccine. At the time of publication, there was a single reported case of a patient taking a tumor necrosis factor α inhibitor for rheumatoid arthritis who had acquired measles.16 While the benefits of titer assessment in patients who are starting or continuing immunomodulatory therapy are not known and currently it is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, dermatologists might consider checking MMR titers and vaccinating (or referring for vaccination) nonimmune patients.17
Infection Control
Early identification of a suspected measles case is paramount. Patients in whom measles is a possibility should be isolated as quickly as possible, and the patient and accompanying caregivers should be masked. Clinical staff should don appropriate personal protective equipment, including an N95 mask. Coordination with the local department of health must occur as soon as measles is suspected.
If testing is an option in the outpatient setting, a nasopharyngeal viral swab and serologic titers can be obtained. If testing is not available on site, patients should be sent to appropriate care facilities; prenotification is critical to prevent nosocomial outbreaks. Patients should be encouraged to isolate and avoid public spaces and/or public transport for 4 days following development of an exanthem.18 Offices should develop clinical protocols for suspected measles cases with training for clinical and office staff.
Final Thoughts
As measles outbreaks become more prevalent, it is incumbent upon physicians to remind ourselves of the signs and symptoms of this largely eliminated disease so that we may pursue early detection and intervention strategies. The primary cutaneous manifestations of measles make dermatologists critical to early recognition and containment efforts. Dermatologists should prepare for the arrival of patients with measles by maintaining vigilance for the classic signs of the disease, implementing stringent isolation protocols, verifying patient immunity when appropriate, and partnering closely with public health authorities.
More broadly, efforts to contain and re-establish a paradigm for eliminating measles outbreaks must be pursued. Encouraging vaccination and developing programs to help combat misinformation surrounding vaccines are critical to this effort. In an era of vaccine hesitancy, measles is a multidisciplinary public health emergency. Dermatologists must remain ready.
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
- Bedford H, Elliman D. Measles rates are rising again. BMJ. 2024;384.
- Harris E. Measles outbreaks grow amid declining vaccination rates. JAMA. 2023;330:2242.
- Guerra FM, Bolotin S, Lim G, et al. The basic reproduction number (R0) of measles: a systematic review. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:E420-E428.
- Swartz MK. Measles: public and professional education. J Pediatr Health Care. 2019;33:367-368.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim infection prevention and control recommendations for measles in healthcare settings. Accessed April 27, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/infection-control/hcp/measles/
- Moss WJ, Griffin DE, Feinstone WH. Measles. In: Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases. Elsevier; 2009: 551-565.
- Moss WJ. Measles. Lancet. 2017;390:2490-2502.
- Maintain the vaccination coverage level of 2 doses of the MMR vaccine for children in kindergarten— IID04. Healthy People 2030 website. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/vaccination/maintain-vaccination-coverage-level-2-doses-mmr-vaccine-children-kindergarten-iid-04
- Franconeri L, Antona D, Cauchemez S, et al. Two-dose measles vaccine effectiveness remains high over time: a French observational study, 2017–2019. Vaccine. 2023;41:5797-5804.
- World Health Organization. Measles. Accessed May 8, 2025. https:// www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles vaccine recommendations. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/vaccine-considerations/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Measles cases and outbreaks. Accessed May 6, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/cases-outbreaks.html
- Dyer C. Lancet retracts Wakefield’s MMR paper. BMJ. 2010;340.
- Alves Graber EM, Andrade FJ, Bost W, et al. An update and review of measles for emergency physicians. J Emerg Med. 2020;58:610-615.
- Kaplan LJ, Daum RS, Smaron M, et al. Severe measles in immunocompromised patients. JAMA. 1992;267:1237-1241.
- Takahashi E, Kurosaka D, Yoshida K, et al. Onset of modified measles after etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Japanese J Clin Immunol. 2010;33:37-41.
- Worth A, Waldman RA, Dieckhaus K, et al. Art of prevention: our approach to the measles-mumps-rubella vaccine in adult patients vaccinated against measles before 1968 on biologic therapy for the treatment of psoriasis. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019;6:94.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical overview of measles (rubeola). Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/measles/hcp/clinical-overview/index.html
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Measles Resurgence: A Dermatologist’s Guide
Immune Responses and Health Disparities Warrant Scabies Vaccine Development
Immune Responses and Health Disparities Warrant Scabies Vaccine Development
The scabies mite, originally known as Acarus scabiei,1 now is considered an arthropod of the class Arachnida, order Astigmata, and family Sarcoptidae.2 Scabies mites are able to adhere to the surface of human skin.3 The mites burrow and lay eggs in the top layer of the epidermis; most patients have 10 to 15 mites.3 The patient’s immune system incites an allergic reaction to the mite protein and feces in the skin, causing itching and rash.4
Scabies is common in indigenous populations and in low-income areas of developing countries.5 It is most prevalent in Africa, South America, Australia, and Southeast Asia, in part due to poverty, poor nutritional status, homelessness, and inadequate hygiene.2 In 2009, the World Health Organization declared scabies a neglected skin disease2; however, in 2010, 1.5 million disability adjusted life-years were attributed to scabies,6 and it is estimated that 200 million people worldwide have scabies at any given time. Children and elderly individuals in resource-poor communities are the most at risk. In fact, 5% to 50% of children in low-income areas have scabies.4
The purpose of this article is to provide background on scabies and its effect on the human immune system. We also discuss manipulation of the immune response for the purposes of creating a potential scabies vaccine.
Life Cycle and Transmission
The life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei consists of 4 stages. The first is the egg. As female scabies mites burrow under the skin, they lay 2 to 3 ovular eggs per day.3 The second stage is the larva. When the egg hatches, the larva has 3 pairs of legs and travels to the surface of the skin where it burrows into the stratum corneum, creating short, nearly invisible burrows called molting pouches. After 3 to 4 days, the larva molts into a nymph, which is the third stage. The nymph has 4 pairs of legs and will continue to grow before molting into an adult, which is the fourth stage. Both the larva and nymph may be found in hair follicles or molting pouches. The fourth stage is the adult, which is round and saclike and does not have eyes. Adult females are 0.30 mm to 0.45 mm long and 0.25 mm to 0.35 mm wide, which is half the size of adult males.3 On warm skin, the female mite can crawl at a rate of 2.5 cm per minute.7
Scabies mites mate via an active male penetrating the molting pouch of a female. This only occurs once but leaves the female fertile for the rest of her life. Once a female is pregnant, she leaves her molting pouch and travels along the surface of the skin looking for a place to make her permanent burrow.3 The most common sites for scabies burrows are the axillae, umbilicus, interdigital spaces, beltline, buttocks, flexor surfaces of the wrists, female nipples, and male penile shaft.5 Once she finds an acceptable location, the female scabies mite will create a serpentine burrow and lay her eggs. Once she burrows, she will stay there and continue to lay eggs for the rest of her life, lengthening the burrow as needed.3 Female mites lay their eggs in the superficial epidermis, and the eggs take approximately 2 to 3 weeks to hatch. Female mites die 30 to 60 days later.2
Scabies infestations typically spread via the transfer of pregnant adult females during skin-to-skin contact, but they also can spread via fomites.3 During all stages of their life cycle, scabies mites can secrete enzymes that allow them to penetrate the intact epidermis in less than 30 minutes; in fact, an otherwise healthy patient with scabies must have 15 to 20 minutes of close skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual for the disease to be transmitted.7 Because scabies mites can survive for more than 3 days outside the human body, it is thought that fomites also may be involved in transmission. Scabies mites also have been collected from clothing, bedding, and furniture, which further supports the idea that fomites are involved in disease transmission.7
Clinical Manifestation of Scabies
Scabies symptoms include severe pruritus as well as linear burrows and vesicles in the interdigital spaces on the hands, wrists, arms and legs, and lower abdomen. Infants and young children also can develop a rash on the palms, soles, ankles, and scalp. Men can develop inflammatory scabies nodules on the penis and scrotum, while women can develop these nodules on the nipple.4 Type I and type IV hypersensitivity reactions contribute to the rash and itching associated with scabies infestation via host allergic and inflammatory reactions to the mites and their byproducts. Patients with scabies typically are infested with fewer than 15 mites,6 but just a few can cause substantial pruritus and scratching, leading to hyperkeratosis.8
Additionally, when patients with scabies scratch the skin, they become vulnerable to bacterial infections.4 Scabies lesions can be coinfected with group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus,8 potentially leading to abscesses and septicemia. These secondary infections also can cause renal and cardiac complications; in fact, in tropical areas, scabies infections are considered a risk factor for kidney disease and rheumatic heart disease.4
The 2 main forms of scabies infestations are ordinary and crusted. The most common form is ordinary scabies, which typically manifests with fewer than 15 mites per patient; crusted scabies (CS) is the more rare and extreme form.6 Cases of CS present with thousands to millions of mites per patient, leading to more widespread and severe symptoms.4 Because of the large increase in the number of mites, CS is more contagious than ordinary scabies.6
Patients with CS typically present with hyperkeratotic skin disease, as evidenced by thick scaly crusts with large numbers of mites, which can lead to permanent skin disfiguration. Patients with CS also can develop deep fissuring of the crusts, within which other microbes can gain entry to the body and lead to secondary infection and possibly sepsis and death. Also, because of the increased number of mites as well as the crusted skin, patients with CS are contagious for longer. As it is more difficult to eradicate, reinfestation is common with CS.6
Patients with compromised immune systems are predisposed to CS. Specifically, patients with HIV or human T-lymphotropic virus 1 or those undergoing organ transplantation are thought to be the most at risk for CS.6 Crusted scabies also has been identified in large numbers in patients with Down syndrome and in Aboriginal Australians; however, the reasoning for this is poorly understood.6
Immune Response
The inflammatory reaction associated with scabies infestations occurs 4 to 6 weeks after initial exposure. It is hypothesized that scabies can alter parts of the host immune system, which contributes to the delayed onset of symptoms. Scabies mites also produce inactivated protease paralogues and serpins, which help to protect the mites from the host immune system by inhibiting the complement system.6
The complement system is part of the innate immune response and is the first line of defense against pathogens. Specifically with scabies infestations, C3 and C4 complement components have been found in skin lesions.6 C3a and C4a fragments cause local inflammation, while C3a and C5a activate mast cells to release histamine and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, further amplifying the inflammatory response; however, CS lesions show low C3 and C4, which can indicate immunodeficiency in patients with CS. It also can be due to the sheer number of mites in a CS infection causing the host immune system to be overloaded.6
Innate effector immune cells also are an important part of the innate immune response to scabies; for example, eosinophilia is seen in scabies infections. Specifically, in CS, eosinophils help modulate and sustain the T-helper (Th) 2 inflammatory response. One cytokine secreted by Th2 cells is IL-5, which is closely associated with the attraction, maturation, and survival of eosinophils.6 Eosinophils also can influence the Th1 inflammatory response in that they produce IL-12, interferon (IFN) γ, and several Toll-like receptors. Furthermore, eosinophilic expression of IL-2 can lead to expansion of regulatory T cells, while eosinophilic expression of IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF) Β also can suppress local inflammation by influencing regulatory T cells.6
Additionally, mast cells and basophils are important in the IgE-mediated allergic reaction as well as the host immune response to parasites. When activated, basophils and mast cells produce TNF-α, IL-6, Il-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which contribute to the Th2 inflammatory response; however, the role of mast cells and basophils in scabies infections still is poorly understood.6
Macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs) contribute to phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and differentiation of T cells, which also contribute to the inflammatory and allergic reactions associated with parasitic infections.6 Macrophages have been found in low numbers in scabies infestation, possibly due to immune-modulating molecules secreted by scabies mites. Early in an infestation, the mites secrete immune-modulating molecules, which inhibit macrophage migration to the site of inflammation, allowing the mites to grow.6 Neutrophils and DCs also are involved in the host immune response to scabies. Neutrophils are the predominant inflammatory cell infiltrate in scabies lesions. The scabies protein SMSB4 inhibits neutrophil opsonization and phagocytosis, thus suppressing bacterial killing.6 Some of the first antigen-presenting cells encountered by the antigen are DCs. They are involved in preparing the antigens for presentation to effector T cells, which leads to T-cell differentiation and activation.6
Cytokines are another important factor in the innate immune response. The host immune response to ordinary scabies is Th1-cell mediated, during which CD4+ and CD8+ T cells secrete IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2.6 Therefore, IFN- γ and TNF-α are elevated in the serum of patients with ordinary scabies. Conversely, the host immune response to CS is Th2-cell mediated. T-helper 2 cells are needed in IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, and they secrete IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. In the serum of patients with CS, IL-l4, IL-5, and IL-13 are elevated while IFN-γ is decreased.6 Additionally, IL-6, TGF-Β, IL-23, IL-1Β, or IL-18 can induce Th17 cells to generate and secrete IL-17, which enhances the inflammatory response by inducing further expression of TNF-α, IL-1Β, IL-6, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts. T-helper 17 and IL-17 also are involved in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, as well as Leishmania major and Schistosoma japonicum.6
Regulatory T cells Tregs secrete TGF-Β and IL-10, which suppress pathologic inflammation, and IL-10 is substantially reduced in patients with CS compared to those with ordinary scabies and uninfected control patients. Additionally, IL-10 can inhibit the synthesis of TNF-γ and IFN-α. Reduced IL-10 expression can lead to proliferation of IL-17 secretion, resulting in a regulatory T cell/Th17 dysfunctional immune response.6
Immunoglobulins are antibodies that are involved in the host’s adaptive immune response. The first antibody to appear in response to an antigen is IgM, and IgM bound to scabies antigens is present in 74%6 of patients with ordinary scabies. Because IgM is the first antibody to appear in response to a scabies infection, detection of serum IgM may allow for earlier detection of scabies; however, IgM has a high cross-reactivity between scabies mites and dust mites, which can hinder scabies diagnosis via IgM detection.6
Both patients with ordinary scabies and CS also show an increased circulatory IgG concentration compared to control groups; patients with CS have higher concentrations. Increased IgG also can be in part due to concurrent bacterial infections.6 When IgG or IgM antibodies bind to a pathogen, they activate the complement cascade, which further enhances the activity of these antibodies.9
Additionally, IgA is important in mucosal immune function. In both patients with ordinary scabies and CS, there is increased IgA binding to recombinant scabies mite antigens.6Sarcoptes scabiei proteases that are localized in the mite’s gut and scybala suggest their involvement in mite digestion and burrowing. The increased secretion of these proteases into the host skin may contribute to the increased IgA,9 and these increased IgA levels have been shown to be positively correlated with severity of scabies infection.6
Also essential in allergic and parasitic inflammation, IgE is observed at higher levels in secondary infections of scabies compared to primary infections.6 Additionally, T-cell infiltrates are implicated in adaptive immune response to scabies. CD4+ T cells are the most prevalent T cells in ordinary scabies skin lesions; however, CD4+ T cells are minimal and CD8+ T cells are elevated in CS skin lesions. The increased CD8+ T cells may cause apoptosis of keratinocytes, leading to epidermal hyperproliferation. The apoptotic keratinocytes can secrete cytokines, which can lead to tissue damage.6 These T cells also may be involved in the failure of the skin’s immune system to mount an effective response to the parasite infestation, leading to uncontrolled parasitic growth. Because patients with AIDS who are infected with scabies mites often develop CS, it is also thought that CD4+ T cells are essential in the immune response to scabies.6
Diagnosis and Current Treatment Options
Current diagnosis of scabies is based on mites, eggs, and fecal matter from the host’s skin. Dermoscopy and fluorescent dermoscopy can be helpful in identifying the mites, eggs, and feces on the patient’s skin. Scabies treatment sometimes may be based solely on symptoms without any positive tests.8
Acaricides are the current method of treatment for scabies infestations.5 Acaricides can be expensive and toxic to the environment and food sources,10 and some agents have been associated with neurotoxicity5 in children or the development of certain cancers.11 Although topical acaricides are the standard form of treatment, oral ivermectin also can be used. Ivermectin is not associated with selective fetal toxicity, but there are limited safety data in pregnant women and in children weighing less than 15 kg (33 lb). Additionally, because symptoms typically are not present during an early infection, treating everyone in the household and those who had close contact with the patient can help prevent reinfection.4
Although these drugs have been shown to be effective at treating scabies, scabies mites are becoming increasingly resistant to acaricides.5 There are 4 main proposed mechanisms for why this occurs.12 The first is through voltage-gated sodium channels, which are involved in the normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Permethrin, a type of acaricide, binds to voltage-gated sodium channels when it is in an open or active state and prevents it from closing. This creates repetitive neuron firing and hyperactivity, which ultimately kills the scabies mite. Some mites have mutated to close this channel, which reduces the binding potential of permethrin. Glutathione S-transferase is another mechanism of resistance. It catalyzes a bond that tags drugs for elimination. Increased activity or expressivity of glutathione S-transferase by scabies mites can lead to drug resistance.12 Adenosine triphosphate– binding cassette (ABC) transporters also may contribute to this resistance. The ABC transporters use adenosine triphosphate to facilitate the import or export of molecules. Scabies mites express a protein called the multidrug-resistant protein, which is an ABC transporter that is associated with drug resistance and is present in scabies mites.12 Lastly, ligand-gated chloride channels have been implicated in scabies resistance to acaricides. Ligand-gated chloride channels also are important in normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Some antiparasitic drugs act on these channels, leading to a continuous influx of chloride, but some scabies mites have mutated this pathway.12
Pesticides and the Risk for Cancer
Pesticides commonly are used to treat scabies; however, a link between pesticide exposure and leukemia and lymphoma has been seen through epidemiologic studies, and there also is increasing biological evidence to suggest this.11 For example, the pesticide permethrin, which works by paralyzing the nervous system of insects,13 has been associated with an increased risk for leukemia and lymphoma in humans. Permethrin is a pyrethroid and, compared to control patients, children with leukemia had higher levels of pyrethroid metabolites in their blood.14 Numerical and structural chromosomal aberrations that give rise to gene fusions are the most common abnormalities seen in leukemia, and permethrin has been shown to induce DNA breaks, chromosome aberrations, and sister chromatid exchanges.14 Permethrin also has been associated with an increased risk for multiple myeloma.13
Furthermore, in utero exposure to pesticides has been associated with an increased risk for childhood leukemia.15 Pesticide exposure shortly before conception, during pregnancy, and after birth is associated with an increased risk for acute lymphocytic leukemia.16 In fact, the children of mothers who were exposed to pesticides 3 months before conception have been found to be at least twice as likely to be diagnosed with acute lymphocytic leukemia within the first year of life compared with children whose mothers were not exposed to pesticides.17 It is hypothesized that permethrin can cross the placenta and alter the hematopoietic precursor cells in the fetus, resulting in leukemogenesis.18 Pyrethroid metabolites also have been detected in umbilical cord blood samples and breast milk.15
In contrast to the research demonstrating a link between permethrin and cancer, other studies have found no association between permethrin19 and leukemia20; non-Hodgkin lymphoma19; or cancers of the colon, rectum, pancreas, lungs, skin, female breast, prostate, and urinary bladder.20 Because of conflicting research on the link between permethrin and cancer, more research is needed.,20
Importance of a Scabies Vaccine
Because scabies mites are developing increasing treatment resistance, more radical approaches such as vaccines are becoming important. While a scabies vaccine is still aspirational, animals that have been infected for a second time with scabies demonstrate a milder response to the second infection compared to the first infection, which could mean there is a potential for disease prevention through a vaccine.21 While educating patients and physicians, reporting cases of infection, and improving drug supply and access can help decrease scabies infestations, these are costly and difficult to implement. Scabies already is most prevalent in low-income areas, so costly interventions are even less feasible. An effective, one-dose vaccine would cost less than these efforts and therefore could be implemented more easily.9
In older adults, scabies more often manifests atypically and is more likely to progress to CS. Aged care centers are prone to institutional outbreaks, even in developed countries, so a vaccine also would greatly help this population. Additionally, the number of children attending day care centers, which also are prone to scabies outbreaks, is increasing. When a child contracts scabies, all close contacts need to be treated, so a preventive vaccine can be useful.9
One potential candidate for a scabies vaccine is total mite extract. Studies show that rabbits immunized with a total mite extract induce antibodies to more antigens than rabbits naturally infested with scabies mites; however, the mites cannot be cultured in vitro, which makes obtaining a large amount of their total extract difficult. Therefore, recombinant vaccines also have been proposed, as they are more easily available.22 One recombinant vaccine candidate is recombinant S scabiei serpin (rSs-serpin). Immunization with rSs-serpin has strong immunogenicity and produced immune protection in rabbits.22
Two other recombinant vaccine candidates are the rSs chitinaselike protein (CLP) 12 and the rSsCLP5. Chitinaselike proteins are very similar to chitinases; however, they are unable to degrade chitin. They are involved in immune reactions to infections, and CLPs from scabies mites have been shown to induce the host immune response.22 For example, in a particular rabbit study, rSsCLP5 demonstrated high immunoreactivity and immunogenicity. In fact, after exposure to S scabiei, 74.3% of rabbits who were vaccinated with rSsCLP5 had no detectable lesions.5 Also, after immunization with rSsCLP5 and rSsCLP12, there were increased levels of specific IgG and IgE antibodies produced and decreased numbers of infesting mites.22 Weight loss also is associated with severe scabies infection. Rabbits vaccinated with rSsCLP5 and exposed to the parasite gained weight, indicating protection via rSsCLP5. Even rabbits who did develop symptoms of scabies after immunization with rSsCLP5 and exposure to S scabiei showed less serious manifestations.5
A combination vaccine cocktail of rSs-serpin, rSsCLP12, and rSsCLP5 also has been proposed by Shen et al.22 Four test groups and a control group (n=12 per group) were included in a vaccine trial. Between 83.33% and 91.67% of rabbits vaccinated with this mixed recombinant cocktail vaccine had no detectable skin lesions from scabies. After immunization with the cocktail vaccine, the specific serum IgG and IgE antibodies also increased. For both IgG and IgE, increased levels were first detected at 1 week postimmunization and peaked at 2 weeks postimmunization.22 A multiepitope vaccine derived from these 3 recombinant proteins also was explored by Shen et al22; fewer rabbits vaccinated with it had no detectable scabies skin lesions compared to those treated with the vaccine cocktail. Although the multiepitope vaccine yielded less immume protection, it was associated with a slower disease course and milder symptoms compared with no vaccination.22
Two more proposed scabies recombinant vaccine candidates are derived from the antigens Ssag1 and Ssag2; however, rabbits vaccinated with Ssag1 or Ssag2 showed no immune protection or mite burden reduction.22 The lack of protection could be due to denaturation or degradation of the protective antigens. It also can be due to the low abundance of these antigens, meaning they may not be vital for the mite’s survival—survival—a potential avenue for future research. The antigens also could have lost their native structure and immunogenic properties during the purification and production process. Therefore, more research is needed to investigate how to purify these vaccines to keep the peptides more structurally similar to their native makeups.10 More research also is needed to better understand the antigen or antigens and their mechanisms that elicit a protective immune response.9
Final Thoughts
Scabies causes severe pruritus in mild cases but also can lead to severe disfigurement, sepsis, and even death. Scabies infestations are seen disproportionately more often in low-income and resource-poor communities, and the current treatment options are less accessible to these populations. Scabies infestations induce a complex immune response that involves multiple aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune systems and can be targeted to create a scabies vaccine. Development of a scabies vaccine is crucial considering the growing resistance to current standard treatments. Acaricides potentially are associated with an increased risk for malignancy, which further amplifies the need for a scabies vaccine. There currently are multiple promising scabies vaccine candidates; however, more research is needed to better understand the host’s immune response to scabies as well as how to more accurately and efficiently produce the vaccine. The development of a safe, effective, economical vaccine that can be mass distributed would be beneficial in the treatment of scabies, especially in resource-poor communities.
- Arlian LG, Morgan MS. A review of Sarcoptes scabiei: past, present and future. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:297. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2234-1
- Murray RL, Crane JS. Scabies. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 31, 2023.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC—scabies—biology. November 2, 2010. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/scabies/index.html
- World Health Organization. Scabies. May 31, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/scabies
- Shen N, Zhang H, Ren Y, et al. A chitinase-like protein from Sarcoptes scabiei as a candidate anti-mite vaccine that contributes to immune protection in rabbits. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:599. doi:10.1186/s13071- 018-3184-y
- Bhat SA, Mounsey KE, Liu X, et al. Host immune responses to the itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei, in humans. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:385. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2320-4
- Hicks MI, Elston DM. Scabies. Dermatolog Ther. 2009;22:279-292. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01243.x
- Morgan MS, Arlian LG, Rider SD, et al. A proteomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei (acari: Sarcoptidae). J Med Entomol. 2016;53:553-561. doi:10.1093/jme/tjv247
- Liu X, Walton S, Mounsey K. Vaccine against scabies: necessity and possibility. Parasitology. 2014;141:725-732. doi:10.1017 /s0031182013002047
- Casais R, Granda V, Balseiro A, et al. Vaccination of rabbits with immunodominant antigens from Sarcoptes scabiei induced high levels of humoral responses and pro-inflammatory cytokines but confers limited protection. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:435. doi:10.1186 /s13071-016-1717-9?
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Pedraza-Meléndez AI, Salas-Labadía C, et al. Low concentrations of permethrin and malathion induce numerical and structural abnormalities in KMT2A and IGH genes in vitro. J Appl Toxicol. 2018;38:1262-1270. doi:10.1002/jat.3638
- Khalil S, Abbas O, Kibbi AG, et al. Scabies in the age of increasing drug resistance. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:E0005920. doi:10.1371 /journal.pntd.0005920
- Rusiecki JA, Patel R, Koutros S, et al. Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to permethrin in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:581-586. doi:10.1289 /ehp.11318
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Salas-Labadía C, Sanabrais-Jiménez M, et al. Exposure to the insecticides permethrin and malathion induces leukemia and lymphoma-associated gene aberrations in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;44:17-26. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2017.06.013
- Navarrete-Meneses MDP, Pérez-Vera P. Pyrethroid pesticide exposure and hematological cancer: epidemiological, biological and molecular evidence. Rev Environ Health. 2019;34:197-210. doi:10.1515 /reveh-2018-0070
- Madrigal JM, Jones RR, Gunier RB, et al. Residential exposure to carbamate, organophosphate, and pyrethroid insecticides in house dust and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Environ Res. 2021;201:111501. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111501
- Ferreira JD, Couto AC, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, et al. In utero pesticide exposure and leukemia in Brazilian children <2 years of age. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121:269-275. doi:10.1289/ehp.1103942
- Borkhardt A, Wilda M, Fuchs U, et al. Congenital leukaemia after heavy abuse of permethrin during pregnancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003;88:F436-F437. doi:10.1136/fn.88.5.f436
- De Roos AJ, Schinasi LH, Miligi L, et al. Occupational insecticide exposure and risk of non]Hodgkin lymphoma: a pooled case]control study from the InterLymph consortium. Int J Cancer. 2021;149:1768-1786. doi:10.1002/ijc.33740
- Boffett, P, Desai V. Exposure to permethrin and cancer risk: a systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018;48:433-442. doi:10.1080/1040 8444.2018.1439449
- Adji A, Rumokoy LJM, Salaki CL. Scabies vaccine as a new breakthrough for the challenge of acaricides resistance. Adv Biolog Sci Res. 2020;8:208-213. doi:10.2991/absr.k.200513.036
- Shen N, Wei W, Chen Y, et al. Vaccination with a cocktail vaccine elicits significant protection against Sarcoptes scabiei in rabbits, whereas the multi-epitope vaccine offers limited protection. Exp Parasitol. 2023;245:108442. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2022.108442
The scabies mite, originally known as Acarus scabiei,1 now is considered an arthropod of the class Arachnida, order Astigmata, and family Sarcoptidae.2 Scabies mites are able to adhere to the surface of human skin.3 The mites burrow and lay eggs in the top layer of the epidermis; most patients have 10 to 15 mites.3 The patient’s immune system incites an allergic reaction to the mite protein and feces in the skin, causing itching and rash.4
Scabies is common in indigenous populations and in low-income areas of developing countries.5 It is most prevalent in Africa, South America, Australia, and Southeast Asia, in part due to poverty, poor nutritional status, homelessness, and inadequate hygiene.2 In 2009, the World Health Organization declared scabies a neglected skin disease2; however, in 2010, 1.5 million disability adjusted life-years were attributed to scabies,6 and it is estimated that 200 million people worldwide have scabies at any given time. Children and elderly individuals in resource-poor communities are the most at risk. In fact, 5% to 50% of children in low-income areas have scabies.4
The purpose of this article is to provide background on scabies and its effect on the human immune system. We also discuss manipulation of the immune response for the purposes of creating a potential scabies vaccine.
Life Cycle and Transmission
The life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei consists of 4 stages. The first is the egg. As female scabies mites burrow under the skin, they lay 2 to 3 ovular eggs per day.3 The second stage is the larva. When the egg hatches, the larva has 3 pairs of legs and travels to the surface of the skin where it burrows into the stratum corneum, creating short, nearly invisible burrows called molting pouches. After 3 to 4 days, the larva molts into a nymph, which is the third stage. The nymph has 4 pairs of legs and will continue to grow before molting into an adult, which is the fourth stage. Both the larva and nymph may be found in hair follicles or molting pouches. The fourth stage is the adult, which is round and saclike and does not have eyes. Adult females are 0.30 mm to 0.45 mm long and 0.25 mm to 0.35 mm wide, which is half the size of adult males.3 On warm skin, the female mite can crawl at a rate of 2.5 cm per minute.7
Scabies mites mate via an active male penetrating the molting pouch of a female. This only occurs once but leaves the female fertile for the rest of her life. Once a female is pregnant, she leaves her molting pouch and travels along the surface of the skin looking for a place to make her permanent burrow.3 The most common sites for scabies burrows are the axillae, umbilicus, interdigital spaces, beltline, buttocks, flexor surfaces of the wrists, female nipples, and male penile shaft.5 Once she finds an acceptable location, the female scabies mite will create a serpentine burrow and lay her eggs. Once she burrows, she will stay there and continue to lay eggs for the rest of her life, lengthening the burrow as needed.3 Female mites lay their eggs in the superficial epidermis, and the eggs take approximately 2 to 3 weeks to hatch. Female mites die 30 to 60 days later.2
Scabies infestations typically spread via the transfer of pregnant adult females during skin-to-skin contact, but they also can spread via fomites.3 During all stages of their life cycle, scabies mites can secrete enzymes that allow them to penetrate the intact epidermis in less than 30 minutes; in fact, an otherwise healthy patient with scabies must have 15 to 20 minutes of close skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual for the disease to be transmitted.7 Because scabies mites can survive for more than 3 days outside the human body, it is thought that fomites also may be involved in transmission. Scabies mites also have been collected from clothing, bedding, and furniture, which further supports the idea that fomites are involved in disease transmission.7
Clinical Manifestation of Scabies
Scabies symptoms include severe pruritus as well as linear burrows and vesicles in the interdigital spaces on the hands, wrists, arms and legs, and lower abdomen. Infants and young children also can develop a rash on the palms, soles, ankles, and scalp. Men can develop inflammatory scabies nodules on the penis and scrotum, while women can develop these nodules on the nipple.4 Type I and type IV hypersensitivity reactions contribute to the rash and itching associated with scabies infestation via host allergic and inflammatory reactions to the mites and their byproducts. Patients with scabies typically are infested with fewer than 15 mites,6 but just a few can cause substantial pruritus and scratching, leading to hyperkeratosis.8
Additionally, when patients with scabies scratch the skin, they become vulnerable to bacterial infections.4 Scabies lesions can be coinfected with group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus,8 potentially leading to abscesses and septicemia. These secondary infections also can cause renal and cardiac complications; in fact, in tropical areas, scabies infections are considered a risk factor for kidney disease and rheumatic heart disease.4
The 2 main forms of scabies infestations are ordinary and crusted. The most common form is ordinary scabies, which typically manifests with fewer than 15 mites per patient; crusted scabies (CS) is the more rare and extreme form.6 Cases of CS present with thousands to millions of mites per patient, leading to more widespread and severe symptoms.4 Because of the large increase in the number of mites, CS is more contagious than ordinary scabies.6
Patients with CS typically present with hyperkeratotic skin disease, as evidenced by thick scaly crusts with large numbers of mites, which can lead to permanent skin disfiguration. Patients with CS also can develop deep fissuring of the crusts, within which other microbes can gain entry to the body and lead to secondary infection and possibly sepsis and death. Also, because of the increased number of mites as well as the crusted skin, patients with CS are contagious for longer. As it is more difficult to eradicate, reinfestation is common with CS.6
Patients with compromised immune systems are predisposed to CS. Specifically, patients with HIV or human T-lymphotropic virus 1 or those undergoing organ transplantation are thought to be the most at risk for CS.6 Crusted scabies also has been identified in large numbers in patients with Down syndrome and in Aboriginal Australians; however, the reasoning for this is poorly understood.6
Immune Response
The inflammatory reaction associated with scabies infestations occurs 4 to 6 weeks after initial exposure. It is hypothesized that scabies can alter parts of the host immune system, which contributes to the delayed onset of symptoms. Scabies mites also produce inactivated protease paralogues and serpins, which help to protect the mites from the host immune system by inhibiting the complement system.6
The complement system is part of the innate immune response and is the first line of defense against pathogens. Specifically with scabies infestations, C3 and C4 complement components have been found in skin lesions.6 C3a and C4a fragments cause local inflammation, while C3a and C5a activate mast cells to release histamine and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, further amplifying the inflammatory response; however, CS lesions show low C3 and C4, which can indicate immunodeficiency in patients with CS. It also can be due to the sheer number of mites in a CS infection causing the host immune system to be overloaded.6
Innate effector immune cells also are an important part of the innate immune response to scabies; for example, eosinophilia is seen in scabies infections. Specifically, in CS, eosinophils help modulate and sustain the T-helper (Th) 2 inflammatory response. One cytokine secreted by Th2 cells is IL-5, which is closely associated with the attraction, maturation, and survival of eosinophils.6 Eosinophils also can influence the Th1 inflammatory response in that they produce IL-12, interferon (IFN) γ, and several Toll-like receptors. Furthermore, eosinophilic expression of IL-2 can lead to expansion of regulatory T cells, while eosinophilic expression of IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF) Β also can suppress local inflammation by influencing regulatory T cells.6
Additionally, mast cells and basophils are important in the IgE-mediated allergic reaction as well as the host immune response to parasites. When activated, basophils and mast cells produce TNF-α, IL-6, Il-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which contribute to the Th2 inflammatory response; however, the role of mast cells and basophils in scabies infections still is poorly understood.6
Macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs) contribute to phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and differentiation of T cells, which also contribute to the inflammatory and allergic reactions associated with parasitic infections.6 Macrophages have been found in low numbers in scabies infestation, possibly due to immune-modulating molecules secreted by scabies mites. Early in an infestation, the mites secrete immune-modulating molecules, which inhibit macrophage migration to the site of inflammation, allowing the mites to grow.6 Neutrophils and DCs also are involved in the host immune response to scabies. Neutrophils are the predominant inflammatory cell infiltrate in scabies lesions. The scabies protein SMSB4 inhibits neutrophil opsonization and phagocytosis, thus suppressing bacterial killing.6 Some of the first antigen-presenting cells encountered by the antigen are DCs. They are involved in preparing the antigens for presentation to effector T cells, which leads to T-cell differentiation and activation.6
Cytokines are another important factor in the innate immune response. The host immune response to ordinary scabies is Th1-cell mediated, during which CD4+ and CD8+ T cells secrete IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2.6 Therefore, IFN- γ and TNF-α are elevated in the serum of patients with ordinary scabies. Conversely, the host immune response to CS is Th2-cell mediated. T-helper 2 cells are needed in IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, and they secrete IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. In the serum of patients with CS, IL-l4, IL-5, and IL-13 are elevated while IFN-γ is decreased.6 Additionally, IL-6, TGF-Β, IL-23, IL-1Β, or IL-18 can induce Th17 cells to generate and secrete IL-17, which enhances the inflammatory response by inducing further expression of TNF-α, IL-1Β, IL-6, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts. T-helper 17 and IL-17 also are involved in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, as well as Leishmania major and Schistosoma japonicum.6
Regulatory T cells Tregs secrete TGF-Β and IL-10, which suppress pathologic inflammation, and IL-10 is substantially reduced in patients with CS compared to those with ordinary scabies and uninfected control patients. Additionally, IL-10 can inhibit the synthesis of TNF-γ and IFN-α. Reduced IL-10 expression can lead to proliferation of IL-17 secretion, resulting in a regulatory T cell/Th17 dysfunctional immune response.6
Immunoglobulins are antibodies that are involved in the host’s adaptive immune response. The first antibody to appear in response to an antigen is IgM, and IgM bound to scabies antigens is present in 74%6 of patients with ordinary scabies. Because IgM is the first antibody to appear in response to a scabies infection, detection of serum IgM may allow for earlier detection of scabies; however, IgM has a high cross-reactivity between scabies mites and dust mites, which can hinder scabies diagnosis via IgM detection.6
Both patients with ordinary scabies and CS also show an increased circulatory IgG concentration compared to control groups; patients with CS have higher concentrations. Increased IgG also can be in part due to concurrent bacterial infections.6 When IgG or IgM antibodies bind to a pathogen, they activate the complement cascade, which further enhances the activity of these antibodies.9
Additionally, IgA is important in mucosal immune function. In both patients with ordinary scabies and CS, there is increased IgA binding to recombinant scabies mite antigens.6Sarcoptes scabiei proteases that are localized in the mite’s gut and scybala suggest their involvement in mite digestion and burrowing. The increased secretion of these proteases into the host skin may contribute to the increased IgA,9 and these increased IgA levels have been shown to be positively correlated with severity of scabies infection.6
Also essential in allergic and parasitic inflammation, IgE is observed at higher levels in secondary infections of scabies compared to primary infections.6 Additionally, T-cell infiltrates are implicated in adaptive immune response to scabies. CD4+ T cells are the most prevalent T cells in ordinary scabies skin lesions; however, CD4+ T cells are minimal and CD8+ T cells are elevated in CS skin lesions. The increased CD8+ T cells may cause apoptosis of keratinocytes, leading to epidermal hyperproliferation. The apoptotic keratinocytes can secrete cytokines, which can lead to tissue damage.6 These T cells also may be involved in the failure of the skin’s immune system to mount an effective response to the parasite infestation, leading to uncontrolled parasitic growth. Because patients with AIDS who are infected with scabies mites often develop CS, it is also thought that CD4+ T cells are essential in the immune response to scabies.6
Diagnosis and Current Treatment Options
Current diagnosis of scabies is based on mites, eggs, and fecal matter from the host’s skin. Dermoscopy and fluorescent dermoscopy can be helpful in identifying the mites, eggs, and feces on the patient’s skin. Scabies treatment sometimes may be based solely on symptoms without any positive tests.8
Acaricides are the current method of treatment for scabies infestations.5 Acaricides can be expensive and toxic to the environment and food sources,10 and some agents have been associated with neurotoxicity5 in children or the development of certain cancers.11 Although topical acaricides are the standard form of treatment, oral ivermectin also can be used. Ivermectin is not associated with selective fetal toxicity, but there are limited safety data in pregnant women and in children weighing less than 15 kg (33 lb). Additionally, because symptoms typically are not present during an early infection, treating everyone in the household and those who had close contact with the patient can help prevent reinfection.4
Although these drugs have been shown to be effective at treating scabies, scabies mites are becoming increasingly resistant to acaricides.5 There are 4 main proposed mechanisms for why this occurs.12 The first is through voltage-gated sodium channels, which are involved in the normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Permethrin, a type of acaricide, binds to voltage-gated sodium channels when it is in an open or active state and prevents it from closing. This creates repetitive neuron firing and hyperactivity, which ultimately kills the scabies mite. Some mites have mutated to close this channel, which reduces the binding potential of permethrin. Glutathione S-transferase is another mechanism of resistance. It catalyzes a bond that tags drugs for elimination. Increased activity or expressivity of glutathione S-transferase by scabies mites can lead to drug resistance.12 Adenosine triphosphate– binding cassette (ABC) transporters also may contribute to this resistance. The ABC transporters use adenosine triphosphate to facilitate the import or export of molecules. Scabies mites express a protein called the multidrug-resistant protein, which is an ABC transporter that is associated with drug resistance and is present in scabies mites.12 Lastly, ligand-gated chloride channels have been implicated in scabies resistance to acaricides. Ligand-gated chloride channels also are important in normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Some antiparasitic drugs act on these channels, leading to a continuous influx of chloride, but some scabies mites have mutated this pathway.12
Pesticides and the Risk for Cancer
Pesticides commonly are used to treat scabies; however, a link between pesticide exposure and leukemia and lymphoma has been seen through epidemiologic studies, and there also is increasing biological evidence to suggest this.11 For example, the pesticide permethrin, which works by paralyzing the nervous system of insects,13 has been associated with an increased risk for leukemia and lymphoma in humans. Permethrin is a pyrethroid and, compared to control patients, children with leukemia had higher levels of pyrethroid metabolites in their blood.14 Numerical and structural chromosomal aberrations that give rise to gene fusions are the most common abnormalities seen in leukemia, and permethrin has been shown to induce DNA breaks, chromosome aberrations, and sister chromatid exchanges.14 Permethrin also has been associated with an increased risk for multiple myeloma.13
Furthermore, in utero exposure to pesticides has been associated with an increased risk for childhood leukemia.15 Pesticide exposure shortly before conception, during pregnancy, and after birth is associated with an increased risk for acute lymphocytic leukemia.16 In fact, the children of mothers who were exposed to pesticides 3 months before conception have been found to be at least twice as likely to be diagnosed with acute lymphocytic leukemia within the first year of life compared with children whose mothers were not exposed to pesticides.17 It is hypothesized that permethrin can cross the placenta and alter the hematopoietic precursor cells in the fetus, resulting in leukemogenesis.18 Pyrethroid metabolites also have been detected in umbilical cord blood samples and breast milk.15
In contrast to the research demonstrating a link between permethrin and cancer, other studies have found no association between permethrin19 and leukemia20; non-Hodgkin lymphoma19; or cancers of the colon, rectum, pancreas, lungs, skin, female breast, prostate, and urinary bladder.20 Because of conflicting research on the link between permethrin and cancer, more research is needed.,20
Importance of a Scabies Vaccine
Because scabies mites are developing increasing treatment resistance, more radical approaches such as vaccines are becoming important. While a scabies vaccine is still aspirational, animals that have been infected for a second time with scabies demonstrate a milder response to the second infection compared to the first infection, which could mean there is a potential for disease prevention through a vaccine.21 While educating patients and physicians, reporting cases of infection, and improving drug supply and access can help decrease scabies infestations, these are costly and difficult to implement. Scabies already is most prevalent in low-income areas, so costly interventions are even less feasible. An effective, one-dose vaccine would cost less than these efforts and therefore could be implemented more easily.9
In older adults, scabies more often manifests atypically and is more likely to progress to CS. Aged care centers are prone to institutional outbreaks, even in developed countries, so a vaccine also would greatly help this population. Additionally, the number of children attending day care centers, which also are prone to scabies outbreaks, is increasing. When a child contracts scabies, all close contacts need to be treated, so a preventive vaccine can be useful.9
One potential candidate for a scabies vaccine is total mite extract. Studies show that rabbits immunized with a total mite extract induce antibodies to more antigens than rabbits naturally infested with scabies mites; however, the mites cannot be cultured in vitro, which makes obtaining a large amount of their total extract difficult. Therefore, recombinant vaccines also have been proposed, as they are more easily available.22 One recombinant vaccine candidate is recombinant S scabiei serpin (rSs-serpin). Immunization with rSs-serpin has strong immunogenicity and produced immune protection in rabbits.22
Two other recombinant vaccine candidates are the rSs chitinaselike protein (CLP) 12 and the rSsCLP5. Chitinaselike proteins are very similar to chitinases; however, they are unable to degrade chitin. They are involved in immune reactions to infections, and CLPs from scabies mites have been shown to induce the host immune response.22 For example, in a particular rabbit study, rSsCLP5 demonstrated high immunoreactivity and immunogenicity. In fact, after exposure to S scabiei, 74.3% of rabbits who were vaccinated with rSsCLP5 had no detectable lesions.5 Also, after immunization with rSsCLP5 and rSsCLP12, there were increased levels of specific IgG and IgE antibodies produced and decreased numbers of infesting mites.22 Weight loss also is associated with severe scabies infection. Rabbits vaccinated with rSsCLP5 and exposed to the parasite gained weight, indicating protection via rSsCLP5. Even rabbits who did develop symptoms of scabies after immunization with rSsCLP5 and exposure to S scabiei showed less serious manifestations.5
A combination vaccine cocktail of rSs-serpin, rSsCLP12, and rSsCLP5 also has been proposed by Shen et al.22 Four test groups and a control group (n=12 per group) were included in a vaccine trial. Between 83.33% and 91.67% of rabbits vaccinated with this mixed recombinant cocktail vaccine had no detectable skin lesions from scabies. After immunization with the cocktail vaccine, the specific serum IgG and IgE antibodies also increased. For both IgG and IgE, increased levels were first detected at 1 week postimmunization and peaked at 2 weeks postimmunization.22 A multiepitope vaccine derived from these 3 recombinant proteins also was explored by Shen et al22; fewer rabbits vaccinated with it had no detectable scabies skin lesions compared to those treated with the vaccine cocktail. Although the multiepitope vaccine yielded less immume protection, it was associated with a slower disease course and milder symptoms compared with no vaccination.22
Two more proposed scabies recombinant vaccine candidates are derived from the antigens Ssag1 and Ssag2; however, rabbits vaccinated with Ssag1 or Ssag2 showed no immune protection or mite burden reduction.22 The lack of protection could be due to denaturation or degradation of the protective antigens. It also can be due to the low abundance of these antigens, meaning they may not be vital for the mite’s survival—survival—a potential avenue for future research. The antigens also could have lost their native structure and immunogenic properties during the purification and production process. Therefore, more research is needed to investigate how to purify these vaccines to keep the peptides more structurally similar to their native makeups.10 More research also is needed to better understand the antigen or antigens and their mechanisms that elicit a protective immune response.9
Final Thoughts
Scabies causes severe pruritus in mild cases but also can lead to severe disfigurement, sepsis, and even death. Scabies infestations are seen disproportionately more often in low-income and resource-poor communities, and the current treatment options are less accessible to these populations. Scabies infestations induce a complex immune response that involves multiple aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune systems and can be targeted to create a scabies vaccine. Development of a scabies vaccine is crucial considering the growing resistance to current standard treatments. Acaricides potentially are associated with an increased risk for malignancy, which further amplifies the need for a scabies vaccine. There currently are multiple promising scabies vaccine candidates; however, more research is needed to better understand the host’s immune response to scabies as well as how to more accurately and efficiently produce the vaccine. The development of a safe, effective, economical vaccine that can be mass distributed would be beneficial in the treatment of scabies, especially in resource-poor communities.
The scabies mite, originally known as Acarus scabiei,1 now is considered an arthropod of the class Arachnida, order Astigmata, and family Sarcoptidae.2 Scabies mites are able to adhere to the surface of human skin.3 The mites burrow and lay eggs in the top layer of the epidermis; most patients have 10 to 15 mites.3 The patient’s immune system incites an allergic reaction to the mite protein and feces in the skin, causing itching and rash.4
Scabies is common in indigenous populations and in low-income areas of developing countries.5 It is most prevalent in Africa, South America, Australia, and Southeast Asia, in part due to poverty, poor nutritional status, homelessness, and inadequate hygiene.2 In 2009, the World Health Organization declared scabies a neglected skin disease2; however, in 2010, 1.5 million disability adjusted life-years were attributed to scabies,6 and it is estimated that 200 million people worldwide have scabies at any given time. Children and elderly individuals in resource-poor communities are the most at risk. In fact, 5% to 50% of children in low-income areas have scabies.4
The purpose of this article is to provide background on scabies and its effect on the human immune system. We also discuss manipulation of the immune response for the purposes of creating a potential scabies vaccine.
Life Cycle and Transmission
The life cycle of Sarcoptes scabiei consists of 4 stages. The first is the egg. As female scabies mites burrow under the skin, they lay 2 to 3 ovular eggs per day.3 The second stage is the larva. When the egg hatches, the larva has 3 pairs of legs and travels to the surface of the skin where it burrows into the stratum corneum, creating short, nearly invisible burrows called molting pouches. After 3 to 4 days, the larva molts into a nymph, which is the third stage. The nymph has 4 pairs of legs and will continue to grow before molting into an adult, which is the fourth stage. Both the larva and nymph may be found in hair follicles or molting pouches. The fourth stage is the adult, which is round and saclike and does not have eyes. Adult females are 0.30 mm to 0.45 mm long and 0.25 mm to 0.35 mm wide, which is half the size of adult males.3 On warm skin, the female mite can crawl at a rate of 2.5 cm per minute.7
Scabies mites mate via an active male penetrating the molting pouch of a female. This only occurs once but leaves the female fertile for the rest of her life. Once a female is pregnant, she leaves her molting pouch and travels along the surface of the skin looking for a place to make her permanent burrow.3 The most common sites for scabies burrows are the axillae, umbilicus, interdigital spaces, beltline, buttocks, flexor surfaces of the wrists, female nipples, and male penile shaft.5 Once she finds an acceptable location, the female scabies mite will create a serpentine burrow and lay her eggs. Once she burrows, she will stay there and continue to lay eggs for the rest of her life, lengthening the burrow as needed.3 Female mites lay their eggs in the superficial epidermis, and the eggs take approximately 2 to 3 weeks to hatch. Female mites die 30 to 60 days later.2
Scabies infestations typically spread via the transfer of pregnant adult females during skin-to-skin contact, but they also can spread via fomites.3 During all stages of their life cycle, scabies mites can secrete enzymes that allow them to penetrate the intact epidermis in less than 30 minutes; in fact, an otherwise healthy patient with scabies must have 15 to 20 minutes of close skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual for the disease to be transmitted.7 Because scabies mites can survive for more than 3 days outside the human body, it is thought that fomites also may be involved in transmission. Scabies mites also have been collected from clothing, bedding, and furniture, which further supports the idea that fomites are involved in disease transmission.7
Clinical Manifestation of Scabies
Scabies symptoms include severe pruritus as well as linear burrows and vesicles in the interdigital spaces on the hands, wrists, arms and legs, and lower abdomen. Infants and young children also can develop a rash on the palms, soles, ankles, and scalp. Men can develop inflammatory scabies nodules on the penis and scrotum, while women can develop these nodules on the nipple.4 Type I and type IV hypersensitivity reactions contribute to the rash and itching associated with scabies infestation via host allergic and inflammatory reactions to the mites and their byproducts. Patients with scabies typically are infested with fewer than 15 mites,6 but just a few can cause substantial pruritus and scratching, leading to hyperkeratosis.8
Additionally, when patients with scabies scratch the skin, they become vulnerable to bacterial infections.4 Scabies lesions can be coinfected with group A streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus,8 potentially leading to abscesses and septicemia. These secondary infections also can cause renal and cardiac complications; in fact, in tropical areas, scabies infections are considered a risk factor for kidney disease and rheumatic heart disease.4
The 2 main forms of scabies infestations are ordinary and crusted. The most common form is ordinary scabies, which typically manifests with fewer than 15 mites per patient; crusted scabies (CS) is the more rare and extreme form.6 Cases of CS present with thousands to millions of mites per patient, leading to more widespread and severe symptoms.4 Because of the large increase in the number of mites, CS is more contagious than ordinary scabies.6
Patients with CS typically present with hyperkeratotic skin disease, as evidenced by thick scaly crusts with large numbers of mites, which can lead to permanent skin disfiguration. Patients with CS also can develop deep fissuring of the crusts, within which other microbes can gain entry to the body and lead to secondary infection and possibly sepsis and death. Also, because of the increased number of mites as well as the crusted skin, patients with CS are contagious for longer. As it is more difficult to eradicate, reinfestation is common with CS.6
Patients with compromised immune systems are predisposed to CS. Specifically, patients with HIV or human T-lymphotropic virus 1 or those undergoing organ transplantation are thought to be the most at risk for CS.6 Crusted scabies also has been identified in large numbers in patients with Down syndrome and in Aboriginal Australians; however, the reasoning for this is poorly understood.6
Immune Response
The inflammatory reaction associated with scabies infestations occurs 4 to 6 weeks after initial exposure. It is hypothesized that scabies can alter parts of the host immune system, which contributes to the delayed onset of symptoms. Scabies mites also produce inactivated protease paralogues and serpins, which help to protect the mites from the host immune system by inhibiting the complement system.6
The complement system is part of the innate immune response and is the first line of defense against pathogens. Specifically with scabies infestations, C3 and C4 complement components have been found in skin lesions.6 C3a and C4a fragments cause local inflammation, while C3a and C5a activate mast cells to release histamine and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, further amplifying the inflammatory response; however, CS lesions show low C3 and C4, which can indicate immunodeficiency in patients with CS. It also can be due to the sheer number of mites in a CS infection causing the host immune system to be overloaded.6
Innate effector immune cells also are an important part of the innate immune response to scabies; for example, eosinophilia is seen in scabies infections. Specifically, in CS, eosinophils help modulate and sustain the T-helper (Th) 2 inflammatory response. One cytokine secreted by Th2 cells is IL-5, which is closely associated with the attraction, maturation, and survival of eosinophils.6 Eosinophils also can influence the Th1 inflammatory response in that they produce IL-12, interferon (IFN) γ, and several Toll-like receptors. Furthermore, eosinophilic expression of IL-2 can lead to expansion of regulatory T cells, while eosinophilic expression of IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF) Β also can suppress local inflammation by influencing regulatory T cells.6
Additionally, mast cells and basophils are important in the IgE-mediated allergic reaction as well as the host immune response to parasites. When activated, basophils and mast cells produce TNF-α, IL-6, Il-4, IL-5, and IL-13, which contribute to the Th2 inflammatory response; however, the role of mast cells and basophils in scabies infections still is poorly understood.6
Macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs) contribute to phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and differentiation of T cells, which also contribute to the inflammatory and allergic reactions associated with parasitic infections.6 Macrophages have been found in low numbers in scabies infestation, possibly due to immune-modulating molecules secreted by scabies mites. Early in an infestation, the mites secrete immune-modulating molecules, which inhibit macrophage migration to the site of inflammation, allowing the mites to grow.6 Neutrophils and DCs also are involved in the host immune response to scabies. Neutrophils are the predominant inflammatory cell infiltrate in scabies lesions. The scabies protein SMSB4 inhibits neutrophil opsonization and phagocytosis, thus suppressing bacterial killing.6 Some of the first antigen-presenting cells encountered by the antigen are DCs. They are involved in preparing the antigens for presentation to effector T cells, which leads to T-cell differentiation and activation.6
Cytokines are another important factor in the innate immune response. The host immune response to ordinary scabies is Th1-cell mediated, during which CD4+ and CD8+ T cells secrete IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2.6 Therefore, IFN- γ and TNF-α are elevated in the serum of patients with ordinary scabies. Conversely, the host immune response to CS is Th2-cell mediated. T-helper 2 cells are needed in IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, and they secrete IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13. In the serum of patients with CS, IL-l4, IL-5, and IL-13 are elevated while IFN-γ is decreased.6 Additionally, IL-6, TGF-Β, IL-23, IL-1Β, or IL-18 can induce Th17 cells to generate and secrete IL-17, which enhances the inflammatory response by inducing further expression of TNF-α, IL-1Β, IL-6, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts. T-helper 17 and IL-17 also are involved in psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, as well as Leishmania major and Schistosoma japonicum.6
Regulatory T cells Tregs secrete TGF-Β and IL-10, which suppress pathologic inflammation, and IL-10 is substantially reduced in patients with CS compared to those with ordinary scabies and uninfected control patients. Additionally, IL-10 can inhibit the synthesis of TNF-γ and IFN-α. Reduced IL-10 expression can lead to proliferation of IL-17 secretion, resulting in a regulatory T cell/Th17 dysfunctional immune response.6
Immunoglobulins are antibodies that are involved in the host’s adaptive immune response. The first antibody to appear in response to an antigen is IgM, and IgM bound to scabies antigens is present in 74%6 of patients with ordinary scabies. Because IgM is the first antibody to appear in response to a scabies infection, detection of serum IgM may allow for earlier detection of scabies; however, IgM has a high cross-reactivity between scabies mites and dust mites, which can hinder scabies diagnosis via IgM detection.6
Both patients with ordinary scabies and CS also show an increased circulatory IgG concentration compared to control groups; patients with CS have higher concentrations. Increased IgG also can be in part due to concurrent bacterial infections.6 When IgG or IgM antibodies bind to a pathogen, they activate the complement cascade, which further enhances the activity of these antibodies.9
Additionally, IgA is important in mucosal immune function. In both patients with ordinary scabies and CS, there is increased IgA binding to recombinant scabies mite antigens.6Sarcoptes scabiei proteases that are localized in the mite’s gut and scybala suggest their involvement in mite digestion and burrowing. The increased secretion of these proteases into the host skin may contribute to the increased IgA,9 and these increased IgA levels have been shown to be positively correlated with severity of scabies infection.6
Also essential in allergic and parasitic inflammation, IgE is observed at higher levels in secondary infections of scabies compared to primary infections.6 Additionally, T-cell infiltrates are implicated in adaptive immune response to scabies. CD4+ T cells are the most prevalent T cells in ordinary scabies skin lesions; however, CD4+ T cells are minimal and CD8+ T cells are elevated in CS skin lesions. The increased CD8+ T cells may cause apoptosis of keratinocytes, leading to epidermal hyperproliferation. The apoptotic keratinocytes can secrete cytokines, which can lead to tissue damage.6 These T cells also may be involved in the failure of the skin’s immune system to mount an effective response to the parasite infestation, leading to uncontrolled parasitic growth. Because patients with AIDS who are infected with scabies mites often develop CS, it is also thought that CD4+ T cells are essential in the immune response to scabies.6
Diagnosis and Current Treatment Options
Current diagnosis of scabies is based on mites, eggs, and fecal matter from the host’s skin. Dermoscopy and fluorescent dermoscopy can be helpful in identifying the mites, eggs, and feces on the patient’s skin. Scabies treatment sometimes may be based solely on symptoms without any positive tests.8
Acaricides are the current method of treatment for scabies infestations.5 Acaricides can be expensive and toxic to the environment and food sources,10 and some agents have been associated with neurotoxicity5 in children or the development of certain cancers.11 Although topical acaricides are the standard form of treatment, oral ivermectin also can be used. Ivermectin is not associated with selective fetal toxicity, but there are limited safety data in pregnant women and in children weighing less than 15 kg (33 lb). Additionally, because symptoms typically are not present during an early infection, treating everyone in the household and those who had close contact with the patient can help prevent reinfection.4
Although these drugs have been shown to be effective at treating scabies, scabies mites are becoming increasingly resistant to acaricides.5 There are 4 main proposed mechanisms for why this occurs.12 The first is through voltage-gated sodium channels, which are involved in the normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Permethrin, a type of acaricide, binds to voltage-gated sodium channels when it is in an open or active state and prevents it from closing. This creates repetitive neuron firing and hyperactivity, which ultimately kills the scabies mite. Some mites have mutated to close this channel, which reduces the binding potential of permethrin. Glutathione S-transferase is another mechanism of resistance. It catalyzes a bond that tags drugs for elimination. Increased activity or expressivity of glutathione S-transferase by scabies mites can lead to drug resistance.12 Adenosine triphosphate– binding cassette (ABC) transporters also may contribute to this resistance. The ABC transporters use adenosine triphosphate to facilitate the import or export of molecules. Scabies mites express a protein called the multidrug-resistant protein, which is an ABC transporter that is associated with drug resistance and is present in scabies mites.12 Lastly, ligand-gated chloride channels have been implicated in scabies resistance to acaricides. Ligand-gated chloride channels also are important in normal functioning of neurons and myocytes. Some antiparasitic drugs act on these channels, leading to a continuous influx of chloride, but some scabies mites have mutated this pathway.12
Pesticides and the Risk for Cancer
Pesticides commonly are used to treat scabies; however, a link between pesticide exposure and leukemia and lymphoma has been seen through epidemiologic studies, and there also is increasing biological evidence to suggest this.11 For example, the pesticide permethrin, which works by paralyzing the nervous system of insects,13 has been associated with an increased risk for leukemia and lymphoma in humans. Permethrin is a pyrethroid and, compared to control patients, children with leukemia had higher levels of pyrethroid metabolites in their blood.14 Numerical and structural chromosomal aberrations that give rise to gene fusions are the most common abnormalities seen in leukemia, and permethrin has been shown to induce DNA breaks, chromosome aberrations, and sister chromatid exchanges.14 Permethrin also has been associated with an increased risk for multiple myeloma.13
Furthermore, in utero exposure to pesticides has been associated with an increased risk for childhood leukemia.15 Pesticide exposure shortly before conception, during pregnancy, and after birth is associated with an increased risk for acute lymphocytic leukemia.16 In fact, the children of mothers who were exposed to pesticides 3 months before conception have been found to be at least twice as likely to be diagnosed with acute lymphocytic leukemia within the first year of life compared with children whose mothers were not exposed to pesticides.17 It is hypothesized that permethrin can cross the placenta and alter the hematopoietic precursor cells in the fetus, resulting in leukemogenesis.18 Pyrethroid metabolites also have been detected in umbilical cord blood samples and breast milk.15
In contrast to the research demonstrating a link between permethrin and cancer, other studies have found no association between permethrin19 and leukemia20; non-Hodgkin lymphoma19; or cancers of the colon, rectum, pancreas, lungs, skin, female breast, prostate, and urinary bladder.20 Because of conflicting research on the link between permethrin and cancer, more research is needed.,20
Importance of a Scabies Vaccine
Because scabies mites are developing increasing treatment resistance, more radical approaches such as vaccines are becoming important. While a scabies vaccine is still aspirational, animals that have been infected for a second time with scabies demonstrate a milder response to the second infection compared to the first infection, which could mean there is a potential for disease prevention through a vaccine.21 While educating patients and physicians, reporting cases of infection, and improving drug supply and access can help decrease scabies infestations, these are costly and difficult to implement. Scabies already is most prevalent in low-income areas, so costly interventions are even less feasible. An effective, one-dose vaccine would cost less than these efforts and therefore could be implemented more easily.9
In older adults, scabies more often manifests atypically and is more likely to progress to CS. Aged care centers are prone to institutional outbreaks, even in developed countries, so a vaccine also would greatly help this population. Additionally, the number of children attending day care centers, which also are prone to scabies outbreaks, is increasing. When a child contracts scabies, all close contacts need to be treated, so a preventive vaccine can be useful.9
One potential candidate for a scabies vaccine is total mite extract. Studies show that rabbits immunized with a total mite extract induce antibodies to more antigens than rabbits naturally infested with scabies mites; however, the mites cannot be cultured in vitro, which makes obtaining a large amount of their total extract difficult. Therefore, recombinant vaccines also have been proposed, as they are more easily available.22 One recombinant vaccine candidate is recombinant S scabiei serpin (rSs-serpin). Immunization with rSs-serpin has strong immunogenicity and produced immune protection in rabbits.22
Two other recombinant vaccine candidates are the rSs chitinaselike protein (CLP) 12 and the rSsCLP5. Chitinaselike proteins are very similar to chitinases; however, they are unable to degrade chitin. They are involved in immune reactions to infections, and CLPs from scabies mites have been shown to induce the host immune response.22 For example, in a particular rabbit study, rSsCLP5 demonstrated high immunoreactivity and immunogenicity. In fact, after exposure to S scabiei, 74.3% of rabbits who were vaccinated with rSsCLP5 had no detectable lesions.5 Also, after immunization with rSsCLP5 and rSsCLP12, there were increased levels of specific IgG and IgE antibodies produced and decreased numbers of infesting mites.22 Weight loss also is associated with severe scabies infection. Rabbits vaccinated with rSsCLP5 and exposed to the parasite gained weight, indicating protection via rSsCLP5. Even rabbits who did develop symptoms of scabies after immunization with rSsCLP5 and exposure to S scabiei showed less serious manifestations.5
A combination vaccine cocktail of rSs-serpin, rSsCLP12, and rSsCLP5 also has been proposed by Shen et al.22 Four test groups and a control group (n=12 per group) were included in a vaccine trial. Between 83.33% and 91.67% of rabbits vaccinated with this mixed recombinant cocktail vaccine had no detectable skin lesions from scabies. After immunization with the cocktail vaccine, the specific serum IgG and IgE antibodies also increased. For both IgG and IgE, increased levels were first detected at 1 week postimmunization and peaked at 2 weeks postimmunization.22 A multiepitope vaccine derived from these 3 recombinant proteins also was explored by Shen et al22; fewer rabbits vaccinated with it had no detectable scabies skin lesions compared to those treated with the vaccine cocktail. Although the multiepitope vaccine yielded less immume protection, it was associated with a slower disease course and milder symptoms compared with no vaccination.22
Two more proposed scabies recombinant vaccine candidates are derived from the antigens Ssag1 and Ssag2; however, rabbits vaccinated with Ssag1 or Ssag2 showed no immune protection or mite burden reduction.22 The lack of protection could be due to denaturation or degradation of the protective antigens. It also can be due to the low abundance of these antigens, meaning they may not be vital for the mite’s survival—survival—a potential avenue for future research. The antigens also could have lost their native structure and immunogenic properties during the purification and production process. Therefore, more research is needed to investigate how to purify these vaccines to keep the peptides more structurally similar to their native makeups.10 More research also is needed to better understand the antigen or antigens and their mechanisms that elicit a protective immune response.9
Final Thoughts
Scabies causes severe pruritus in mild cases but also can lead to severe disfigurement, sepsis, and even death. Scabies infestations are seen disproportionately more often in low-income and resource-poor communities, and the current treatment options are less accessible to these populations. Scabies infestations induce a complex immune response that involves multiple aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune systems and can be targeted to create a scabies vaccine. Development of a scabies vaccine is crucial considering the growing resistance to current standard treatments. Acaricides potentially are associated with an increased risk for malignancy, which further amplifies the need for a scabies vaccine. There currently are multiple promising scabies vaccine candidates; however, more research is needed to better understand the host’s immune response to scabies as well as how to more accurately and efficiently produce the vaccine. The development of a safe, effective, economical vaccine that can be mass distributed would be beneficial in the treatment of scabies, especially in resource-poor communities.
- Arlian LG, Morgan MS. A review of Sarcoptes scabiei: past, present and future. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:297. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2234-1
- Murray RL, Crane JS. Scabies. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 31, 2023.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC—scabies—biology. November 2, 2010. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/scabies/index.html
- World Health Organization. Scabies. May 31, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/scabies
- Shen N, Zhang H, Ren Y, et al. A chitinase-like protein from Sarcoptes scabiei as a candidate anti-mite vaccine that contributes to immune protection in rabbits. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:599. doi:10.1186/s13071- 018-3184-y
- Bhat SA, Mounsey KE, Liu X, et al. Host immune responses to the itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei, in humans. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:385. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2320-4
- Hicks MI, Elston DM. Scabies. Dermatolog Ther. 2009;22:279-292. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01243.x
- Morgan MS, Arlian LG, Rider SD, et al. A proteomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei (acari: Sarcoptidae). J Med Entomol. 2016;53:553-561. doi:10.1093/jme/tjv247
- Liu X, Walton S, Mounsey K. Vaccine against scabies: necessity and possibility. Parasitology. 2014;141:725-732. doi:10.1017 /s0031182013002047
- Casais R, Granda V, Balseiro A, et al. Vaccination of rabbits with immunodominant antigens from Sarcoptes scabiei induced high levels of humoral responses and pro-inflammatory cytokines but confers limited protection. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:435. doi:10.1186 /s13071-016-1717-9?
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Pedraza-Meléndez AI, Salas-Labadía C, et al. Low concentrations of permethrin and malathion induce numerical and structural abnormalities in KMT2A and IGH genes in vitro. J Appl Toxicol. 2018;38:1262-1270. doi:10.1002/jat.3638
- Khalil S, Abbas O, Kibbi AG, et al. Scabies in the age of increasing drug resistance. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:E0005920. doi:10.1371 /journal.pntd.0005920
- Rusiecki JA, Patel R, Koutros S, et al. Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to permethrin in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:581-586. doi:10.1289 /ehp.11318
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Salas-Labadía C, Sanabrais-Jiménez M, et al. Exposure to the insecticides permethrin and malathion induces leukemia and lymphoma-associated gene aberrations in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;44:17-26. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2017.06.013
- Navarrete-Meneses MDP, Pérez-Vera P. Pyrethroid pesticide exposure and hematological cancer: epidemiological, biological and molecular evidence. Rev Environ Health. 2019;34:197-210. doi:10.1515 /reveh-2018-0070
- Madrigal JM, Jones RR, Gunier RB, et al. Residential exposure to carbamate, organophosphate, and pyrethroid insecticides in house dust and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Environ Res. 2021;201:111501. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111501
- Ferreira JD, Couto AC, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, et al. In utero pesticide exposure and leukemia in Brazilian children <2 years of age. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121:269-275. doi:10.1289/ehp.1103942
- Borkhardt A, Wilda M, Fuchs U, et al. Congenital leukaemia after heavy abuse of permethrin during pregnancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003;88:F436-F437. doi:10.1136/fn.88.5.f436
- De Roos AJ, Schinasi LH, Miligi L, et al. Occupational insecticide exposure and risk of non]Hodgkin lymphoma: a pooled case]control study from the InterLymph consortium. Int J Cancer. 2021;149:1768-1786. doi:10.1002/ijc.33740
- Boffett, P, Desai V. Exposure to permethrin and cancer risk: a systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018;48:433-442. doi:10.1080/1040 8444.2018.1439449
- Adji A, Rumokoy LJM, Salaki CL. Scabies vaccine as a new breakthrough for the challenge of acaricides resistance. Adv Biolog Sci Res. 2020;8:208-213. doi:10.2991/absr.k.200513.036
- Shen N, Wei W, Chen Y, et al. Vaccination with a cocktail vaccine elicits significant protection against Sarcoptes scabiei in rabbits, whereas the multi-epitope vaccine offers limited protection. Exp Parasitol. 2023;245:108442. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2022.108442
- Arlian LG, Morgan MS. A review of Sarcoptes scabiei: past, present and future. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:297. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2234-1
- Murray RL, Crane JS. Scabies. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Updated July 31, 2023.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC—scabies—biology. November 2, 2010. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/scabies/index.html
- World Health Organization. Scabies. May 31, 2023. Accessed May 8, 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/scabies
- Shen N, Zhang H, Ren Y, et al. A chitinase-like protein from Sarcoptes scabiei as a candidate anti-mite vaccine that contributes to immune protection in rabbits. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11:599. doi:10.1186/s13071- 018-3184-y
- Bhat SA, Mounsey KE, Liu X, et al. Host immune responses to the itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei, in humans. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:385. doi:10.1186/s13071-017-2320-4
- Hicks MI, Elston DM. Scabies. Dermatolog Ther. 2009;22:279-292. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2009.01243.x
- Morgan MS, Arlian LG, Rider SD, et al. A proteomic analysis of Sarcoptes scabiei (acari: Sarcoptidae). J Med Entomol. 2016;53:553-561. doi:10.1093/jme/tjv247
- Liu X, Walton S, Mounsey K. Vaccine against scabies: necessity and possibility. Parasitology. 2014;141:725-732. doi:10.1017 /s0031182013002047
- Casais R, Granda V, Balseiro A, et al. Vaccination of rabbits with immunodominant antigens from Sarcoptes scabiei induced high levels of humoral responses and pro-inflammatory cytokines but confers limited protection. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:435. doi:10.1186 /s13071-016-1717-9?
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Pedraza-Meléndez AI, Salas-Labadía C, et al. Low concentrations of permethrin and malathion induce numerical and structural abnormalities in KMT2A and IGH genes in vitro. J Appl Toxicol. 2018;38:1262-1270. doi:10.1002/jat.3638
- Khalil S, Abbas O, Kibbi AG, et al. Scabies in the age of increasing drug resistance. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:E0005920. doi:10.1371 /journal.pntd.0005920
- Rusiecki JA, Patel R, Koutros S, et al. Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to permethrin in the Agricultural Health Study. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:581-586. doi:10.1289 /ehp.11318
- Navarrete-Meneses MP, Salas-Labadía C, Sanabrais-Jiménez M, et al. Exposure to the insecticides permethrin and malathion induces leukemia and lymphoma-associated gene aberrations in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;44:17-26. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2017.06.013
- Navarrete-Meneses MDP, Pérez-Vera P. Pyrethroid pesticide exposure and hematological cancer: epidemiological, biological and molecular evidence. Rev Environ Health. 2019;34:197-210. doi:10.1515 /reveh-2018-0070
- Madrigal JM, Jones RR, Gunier RB, et al. Residential exposure to carbamate, organophosphate, and pyrethroid insecticides in house dust and risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Environ Res. 2021;201:111501. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111501
- Ferreira JD, Couto AC, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, et al. In utero pesticide exposure and leukemia in Brazilian children <2 years of age. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121:269-275. doi:10.1289/ehp.1103942
- Borkhardt A, Wilda M, Fuchs U, et al. Congenital leukaemia after heavy abuse of permethrin during pregnancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003;88:F436-F437. doi:10.1136/fn.88.5.f436
- De Roos AJ, Schinasi LH, Miligi L, et al. Occupational insecticide exposure and risk of non]Hodgkin lymphoma: a pooled case]control study from the InterLymph consortium. Int J Cancer. 2021;149:1768-1786. doi:10.1002/ijc.33740
- Boffett, P, Desai V. Exposure to permethrin and cancer risk: a systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018;48:433-442. doi:10.1080/1040 8444.2018.1439449
- Adji A, Rumokoy LJM, Salaki CL. Scabies vaccine as a new breakthrough for the challenge of acaricides resistance. Adv Biolog Sci Res. 2020;8:208-213. doi:10.2991/absr.k.200513.036
- Shen N, Wei W, Chen Y, et al. Vaccination with a cocktail vaccine elicits significant protection against Sarcoptes scabiei in rabbits, whereas the multi-epitope vaccine offers limited protection. Exp Parasitol. 2023;245:108442. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2022.108442
Immune Responses and Health Disparities Warrant Scabies Vaccine Development
Immune Responses and Health Disparities Warrant Scabies Vaccine Development
PRACTICE POINTS
- Dermatologists should be aware of the impact scabies has on patients, especially on those in lower socioeconomic groups.
- Physicians and patients should be educated on scabies prevention and treatment to help decrease the spread of scabies infections.
Managing Seromas Following Skin Graft Placement in Dermatologic Surgery
Managing Seromas Following Skin Graft Placement in Dermatologic Surgery
A seroma is a collection of serous lymphatic fluid that forms in an anatomic or surgically created dead space—a void left between tissue layers, such as between the skin and underlying tissue, where fluid can accumulate. Seromas represent possible postoperative complications in many types of procedures, including general, oncologic, reconstructive, and dermatologic surgeries.1-3 While seroma formation following dermatologic surgery generally is uncommon, associated procedures include placement of split- or full-thickness skin grafts or liposuction.4,5 Many seromas follow a self-limited course. In some cases, seromas may cause discomfort, recur, or possibly become infected. Surgical techniques for prevention of seroma formation have been described in the dermatologic literature, but discussion of seroma management, particularly in dermatology, is not well documented. In this article, we describe a management approach for primary, recurrent, or late-stage seromas following placement of split- and full-thickness skin grafts in dermatologic surgery.
Practice Gap
To minimize the risk for seroma formation, attention should be paid to reducing dead space during graft placement. Small slits may be created in the skin graft after placement if the graft is larger than 2 to 3 cm in diameter to facilitate fluid drainage.6 Additionally, a tie-over bolster dressing that provides sustained even pressure over the entire graft should be applied and left in place for 1 week.7 Adjunctive measures, such as the use of fibrin sealants or quilting sutures, may further reduce the likelihood of fluid accumulation.7,8 Factors such as obesity, smoking, limited mobility, and inadequate elevation of the extremities undergoing surgery also should be addressed preoperatively to optimize outcomes of skin grafts.
Although these preventive strategies can be used during skin graft placement, seromas still can occur. Seromas typically manifest during the postoperative period after the removal of the protective dressings, including the bolster. The characteristic finding is the formation of a fluid-filled bulla under the graft. The associated serous lymphatic collection usually is yellow-tinged but may appear violaceous if bleeding has occurred beneath the graft. If the patient presents within 24 to 48 hours of seroma formation, the bulla may be tense or slightly tense; however, if days to weeks have passed since the seroma formed, the lesion may undergo fibrosis with thickening of the overlying tissue. If untreated, fibrosis may progress for several weeks, eventually resulting in nodule formation. Chronic seromas with retained fluid will persist for months. Seromas are more likely to develop under larger skin grafts (typically those exceeding 5-10 cm in diameter) or grafts placed in dependent positions, such as areas below the level of the heart where fluid pooling is more likely, especially on the arms and legs with associated movement.
The Technique
Our approach to seroma management is based on the timeline at presentation and whether the seroma is primary or recurrent or demonstrates late fibrosis. Successful management of primary seromas is centered on prompt drainage. Complete drainage using a #11 surgical blade may be accomplished with a single puncture to create a 2- to 3-mm opening for smaller seromas. Larger or multiple seromas under larger skin grafts may require creating multiple small punctures or small slits (ie, 5-10 mm) to allow for adequate drainage and reduce the incidence of seroma reaccumulation. Once successful drainage has occurred, a pressure dressing consisting of a thin layer of petroleum based ointment, a nonadherent dressing, gauze, and secure tape can help reduce the risk for reaccumulation.
Infrequently, seromas will reaccumulate under a skin graft. If this occurs, the graft may appear fibrous with lumps and loculations of seroma fluid separated by intact graft tissue, resulting in a “bound down” appearance (eFigure 1). This may require creating adequate slits for drainage in the graft. Multiple slits should be created if the seroma is larger (typically more than 3-4 cm in diameter) or loculations are present. If the fluid continues to reaccumulate and the drainage slits reseal, the next step is to cut a small hole in the graft to allow for uninterrupted drainage (eFigure 2). Manual digital pressure with moist gauze can assist in decompressing the seroma and removing residual fluid and gelatinous contents, promoting continuous drainage and preventing further fluid buildup (eFigure 3). These openings heal by secondary intention (eFigure 4). Local care during this time also is achieved with a thin layer of ointment, a nonstick pad, gauze, and secure tape. Dressings should be changed every 1 to 2 days until healing is complete.
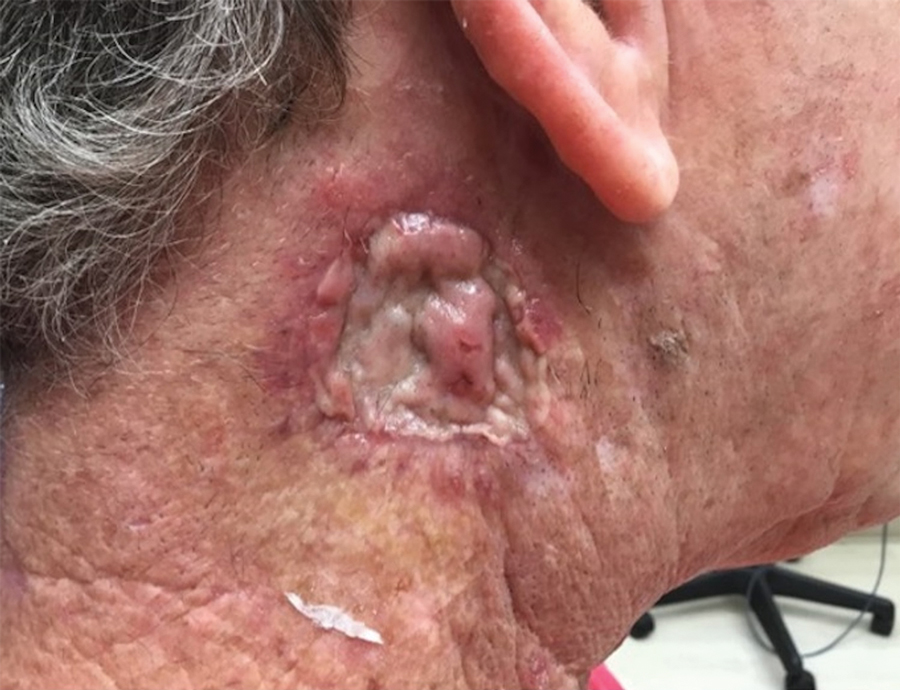
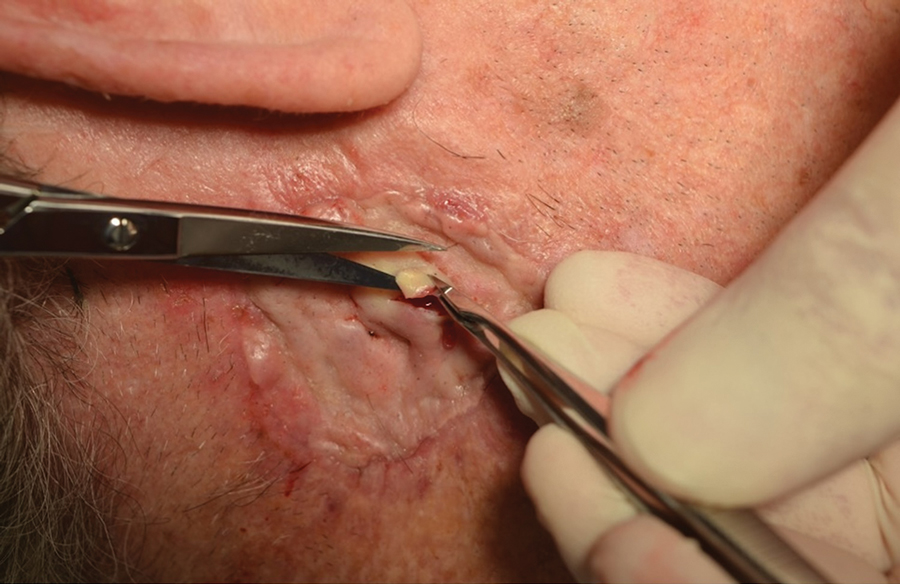
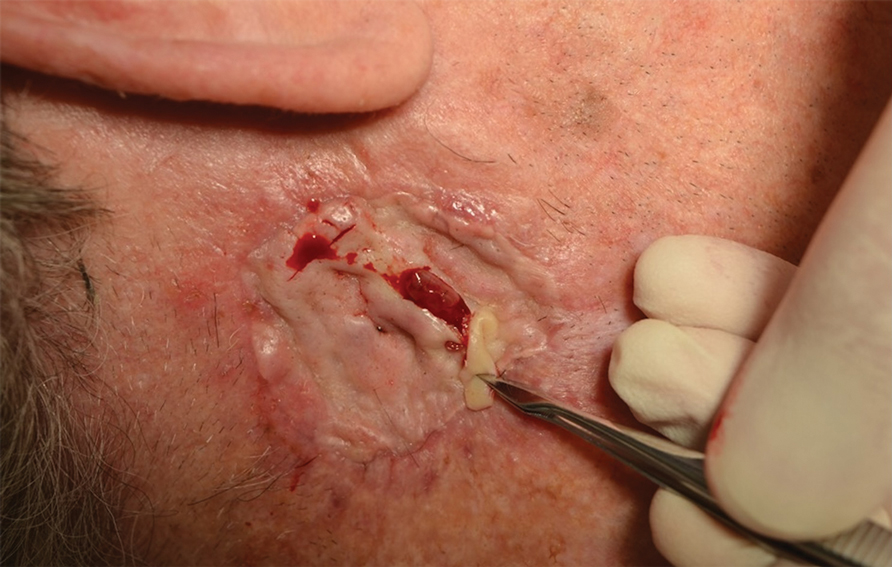
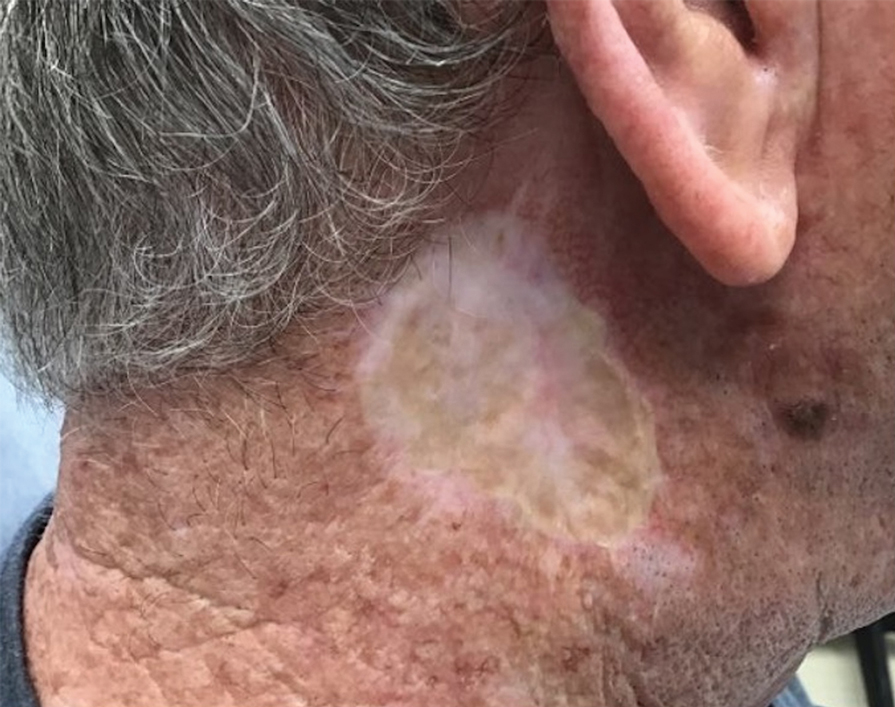
Seromas that lead to fibrotic nodule formation—typically occurring within several weeks to months if untreated—require additional steps for resolution. Once fibrosis occurs, these nodules can be managed by (1) placing adequate local anesthesia, (2) tangentially excising the nodules using either a skin biopsy blade or a #10 or #15 surgical blade, (3) using a handheld heat cautery or electrocautery device to achieve hemostasis, and (4) performing local care, as with any shave or tangential biopsy, until healing is complete. Typically, this requires a single treatment.
Practice Implications
While conservative management with continued compression dressings can be considered for postoperative seroma formation, interventional management sometimes is required. The size and duration of the seroma often guide management. For small seromas (typically less than 2-3 cm in diameter), a small slit incision with a #11 surgical blade may be performed at the dependent point of the seroma. Gentle pressure with a cotton-tipped applicator or moist gauze can be useful to express serous fluid; however, care should be taken not to disrupt adherence of the graft. Recurrent seromas or those with late fibrosis benefit from creation of a surgical window to allow uninterrupted drainage and removal of fibrous components, then can be left to heal by secondary intention with conservative local care.
- DeWitt C, Norris I, Fischer A, et al. A dermatologic approach to a recurrent auricular seroma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1033-1035. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001390
- Woodworth PA, McBoyle MF, Helmer SD, et al. Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery: incidence and predicting factors. Am Surg. 2000;66:444-451.
- Salari N, Fatahi B, Bartina Y, et al. The global prevalence of seroma after abdominoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45:2821-2836. doi:10.1007/s00266-021-02365-6
- Bolognia J, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018.
- Taha AA, Wahba MM, Tahseen H. Liposuction: drains, are they adequate? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020;8:E2677. doi:10.1097/ GOX.0000000000002677
- Ishii N, Sakai S, Kishi K. A simple and safe method to create a drainage hole for thick skin grafts. Eplasty. 2017;17:ic27.
- Davis M, Baird D, Hill D, et al. Management of full-thickness skin grafts. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021;34:683-686. doi:10.1080 /08998280.2021.1953867
- Mittermayr R, Wassermann E, Thurnher M, et al. Skin graft fixation by slow clotting fibrin sealant applied as a thin layer. Burns. 2006; 32:305-311. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2005.10.010
A seroma is a collection of serous lymphatic fluid that forms in an anatomic or surgically created dead space—a void left between tissue layers, such as between the skin and underlying tissue, where fluid can accumulate. Seromas represent possible postoperative complications in many types of procedures, including general, oncologic, reconstructive, and dermatologic surgeries.1-3 While seroma formation following dermatologic surgery generally is uncommon, associated procedures include placement of split- or full-thickness skin grafts or liposuction.4,5 Many seromas follow a self-limited course. In some cases, seromas may cause discomfort, recur, or possibly become infected. Surgical techniques for prevention of seroma formation have been described in the dermatologic literature, but discussion of seroma management, particularly in dermatology, is not well documented. In this article, we describe a management approach for primary, recurrent, or late-stage seromas following placement of split- and full-thickness skin grafts in dermatologic surgery.
Practice Gap
To minimize the risk for seroma formation, attention should be paid to reducing dead space during graft placement. Small slits may be created in the skin graft after placement if the graft is larger than 2 to 3 cm in diameter to facilitate fluid drainage.6 Additionally, a tie-over bolster dressing that provides sustained even pressure over the entire graft should be applied and left in place for 1 week.7 Adjunctive measures, such as the use of fibrin sealants or quilting sutures, may further reduce the likelihood of fluid accumulation.7,8 Factors such as obesity, smoking, limited mobility, and inadequate elevation of the extremities undergoing surgery also should be addressed preoperatively to optimize outcomes of skin grafts.
Although these preventive strategies can be used during skin graft placement, seromas still can occur. Seromas typically manifest during the postoperative period after the removal of the protective dressings, including the bolster. The characteristic finding is the formation of a fluid-filled bulla under the graft. The associated serous lymphatic collection usually is yellow-tinged but may appear violaceous if bleeding has occurred beneath the graft. If the patient presents within 24 to 48 hours of seroma formation, the bulla may be tense or slightly tense; however, if days to weeks have passed since the seroma formed, the lesion may undergo fibrosis with thickening of the overlying tissue. If untreated, fibrosis may progress for several weeks, eventually resulting in nodule formation. Chronic seromas with retained fluid will persist for months. Seromas are more likely to develop under larger skin grafts (typically those exceeding 5-10 cm in diameter) or grafts placed in dependent positions, such as areas below the level of the heart where fluid pooling is more likely, especially on the arms and legs with associated movement.
The Technique
Our approach to seroma management is based on the timeline at presentation and whether the seroma is primary or recurrent or demonstrates late fibrosis. Successful management of primary seromas is centered on prompt drainage. Complete drainage using a #11 surgical blade may be accomplished with a single puncture to create a 2- to 3-mm opening for smaller seromas. Larger or multiple seromas under larger skin grafts may require creating multiple small punctures or small slits (ie, 5-10 mm) to allow for adequate drainage and reduce the incidence of seroma reaccumulation. Once successful drainage has occurred, a pressure dressing consisting of a thin layer of petroleum based ointment, a nonadherent dressing, gauze, and secure tape can help reduce the risk for reaccumulation.
Infrequently, seromas will reaccumulate under a skin graft. If this occurs, the graft may appear fibrous with lumps and loculations of seroma fluid separated by intact graft tissue, resulting in a “bound down” appearance (eFigure 1). This may require creating adequate slits for drainage in the graft. Multiple slits should be created if the seroma is larger (typically more than 3-4 cm in diameter) or loculations are present. If the fluid continues to reaccumulate and the drainage slits reseal, the next step is to cut a small hole in the graft to allow for uninterrupted drainage (eFigure 2). Manual digital pressure with moist gauze can assist in decompressing the seroma and removing residual fluid and gelatinous contents, promoting continuous drainage and preventing further fluid buildup (eFigure 3). These openings heal by secondary intention (eFigure 4). Local care during this time also is achieved with a thin layer of ointment, a nonstick pad, gauze, and secure tape. Dressings should be changed every 1 to 2 days until healing is complete.




Seromas that lead to fibrotic nodule formation—typically occurring within several weeks to months if untreated—require additional steps for resolution. Once fibrosis occurs, these nodules can be managed by (1) placing adequate local anesthesia, (2) tangentially excising the nodules using either a skin biopsy blade or a #10 or #15 surgical blade, (3) using a handheld heat cautery or electrocautery device to achieve hemostasis, and (4) performing local care, as with any shave or tangential biopsy, until healing is complete. Typically, this requires a single treatment.
Practice Implications
While conservative management with continued compression dressings can be considered for postoperative seroma formation, interventional management sometimes is required. The size and duration of the seroma often guide management. For small seromas (typically less than 2-3 cm in diameter), a small slit incision with a #11 surgical blade may be performed at the dependent point of the seroma. Gentle pressure with a cotton-tipped applicator or moist gauze can be useful to express serous fluid; however, care should be taken not to disrupt adherence of the graft. Recurrent seromas or those with late fibrosis benefit from creation of a surgical window to allow uninterrupted drainage and removal of fibrous components, then can be left to heal by secondary intention with conservative local care.
A seroma is a collection of serous lymphatic fluid that forms in an anatomic or surgically created dead space—a void left between tissue layers, such as between the skin and underlying tissue, where fluid can accumulate. Seromas represent possible postoperative complications in many types of procedures, including general, oncologic, reconstructive, and dermatologic surgeries.1-3 While seroma formation following dermatologic surgery generally is uncommon, associated procedures include placement of split- or full-thickness skin grafts or liposuction.4,5 Many seromas follow a self-limited course. In some cases, seromas may cause discomfort, recur, or possibly become infected. Surgical techniques for prevention of seroma formation have been described in the dermatologic literature, but discussion of seroma management, particularly in dermatology, is not well documented. In this article, we describe a management approach for primary, recurrent, or late-stage seromas following placement of split- and full-thickness skin grafts in dermatologic surgery.
Practice Gap
To minimize the risk for seroma formation, attention should be paid to reducing dead space during graft placement. Small slits may be created in the skin graft after placement if the graft is larger than 2 to 3 cm in diameter to facilitate fluid drainage.6 Additionally, a tie-over bolster dressing that provides sustained even pressure over the entire graft should be applied and left in place for 1 week.7 Adjunctive measures, such as the use of fibrin sealants or quilting sutures, may further reduce the likelihood of fluid accumulation.7,8 Factors such as obesity, smoking, limited mobility, and inadequate elevation of the extremities undergoing surgery also should be addressed preoperatively to optimize outcomes of skin grafts.
Although these preventive strategies can be used during skin graft placement, seromas still can occur. Seromas typically manifest during the postoperative period after the removal of the protective dressings, including the bolster. The characteristic finding is the formation of a fluid-filled bulla under the graft. The associated serous lymphatic collection usually is yellow-tinged but may appear violaceous if bleeding has occurred beneath the graft. If the patient presents within 24 to 48 hours of seroma formation, the bulla may be tense or slightly tense; however, if days to weeks have passed since the seroma formed, the lesion may undergo fibrosis with thickening of the overlying tissue. If untreated, fibrosis may progress for several weeks, eventually resulting in nodule formation. Chronic seromas with retained fluid will persist for months. Seromas are more likely to develop under larger skin grafts (typically those exceeding 5-10 cm in diameter) or grafts placed in dependent positions, such as areas below the level of the heart where fluid pooling is more likely, especially on the arms and legs with associated movement.
The Technique
Our approach to seroma management is based on the timeline at presentation and whether the seroma is primary or recurrent or demonstrates late fibrosis. Successful management of primary seromas is centered on prompt drainage. Complete drainage using a #11 surgical blade may be accomplished with a single puncture to create a 2- to 3-mm opening for smaller seromas. Larger or multiple seromas under larger skin grafts may require creating multiple small punctures or small slits (ie, 5-10 mm) to allow for adequate drainage and reduce the incidence of seroma reaccumulation. Once successful drainage has occurred, a pressure dressing consisting of a thin layer of petroleum based ointment, a nonadherent dressing, gauze, and secure tape can help reduce the risk for reaccumulation.
Infrequently, seromas will reaccumulate under a skin graft. If this occurs, the graft may appear fibrous with lumps and loculations of seroma fluid separated by intact graft tissue, resulting in a “bound down” appearance (eFigure 1). This may require creating adequate slits for drainage in the graft. Multiple slits should be created if the seroma is larger (typically more than 3-4 cm in diameter) or loculations are present. If the fluid continues to reaccumulate and the drainage slits reseal, the next step is to cut a small hole in the graft to allow for uninterrupted drainage (eFigure 2). Manual digital pressure with moist gauze can assist in decompressing the seroma and removing residual fluid and gelatinous contents, promoting continuous drainage and preventing further fluid buildup (eFigure 3). These openings heal by secondary intention (eFigure 4). Local care during this time also is achieved with a thin layer of ointment, a nonstick pad, gauze, and secure tape. Dressings should be changed every 1 to 2 days until healing is complete.




Seromas that lead to fibrotic nodule formation—typically occurring within several weeks to months if untreated—require additional steps for resolution. Once fibrosis occurs, these nodules can be managed by (1) placing adequate local anesthesia, (2) tangentially excising the nodules using either a skin biopsy blade or a #10 or #15 surgical blade, (3) using a handheld heat cautery or electrocautery device to achieve hemostasis, and (4) performing local care, as with any shave or tangential biopsy, until healing is complete. Typically, this requires a single treatment.
Practice Implications
While conservative management with continued compression dressings can be considered for postoperative seroma formation, interventional management sometimes is required. The size and duration of the seroma often guide management. For small seromas (typically less than 2-3 cm in diameter), a small slit incision with a #11 surgical blade may be performed at the dependent point of the seroma. Gentle pressure with a cotton-tipped applicator or moist gauze can be useful to express serous fluid; however, care should be taken not to disrupt adherence of the graft. Recurrent seromas or those with late fibrosis benefit from creation of a surgical window to allow uninterrupted drainage and removal of fibrous components, then can be left to heal by secondary intention with conservative local care.
- DeWitt C, Norris I, Fischer A, et al. A dermatologic approach to a recurrent auricular seroma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1033-1035. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001390
- Woodworth PA, McBoyle MF, Helmer SD, et al. Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery: incidence and predicting factors. Am Surg. 2000;66:444-451.
- Salari N, Fatahi B, Bartina Y, et al. The global prevalence of seroma after abdominoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45:2821-2836. doi:10.1007/s00266-021-02365-6
- Bolognia J, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018.
- Taha AA, Wahba MM, Tahseen H. Liposuction: drains, are they adequate? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020;8:E2677. doi:10.1097/ GOX.0000000000002677
- Ishii N, Sakai S, Kishi K. A simple and safe method to create a drainage hole for thick skin grafts. Eplasty. 2017;17:ic27.
- Davis M, Baird D, Hill D, et al. Management of full-thickness skin grafts. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021;34:683-686. doi:10.1080 /08998280.2021.1953867
- Mittermayr R, Wassermann E, Thurnher M, et al. Skin graft fixation by slow clotting fibrin sealant applied as a thin layer. Burns. 2006; 32:305-311. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2005.10.010
- DeWitt C, Norris I, Fischer A, et al. A dermatologic approach to a recurrent auricular seroma. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:1033-1035. doi:10.1097/DSS.0000000000001390
- Woodworth PA, McBoyle MF, Helmer SD, et al. Seroma formation after breast cancer surgery: incidence and predicting factors. Am Surg. 2000;66:444-451.
- Salari N, Fatahi B, Bartina Y, et al. The global prevalence of seroma after abdominoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2021;45:2821-2836. doi:10.1007/s00266-021-02365-6
- Bolognia J, Cerroni L, Schaffer JV. Dermatology. Elsevier; 2018.
- Taha AA, Wahba MM, Tahseen H. Liposuction: drains, are they adequate? Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2020;8:E2677. doi:10.1097/ GOX.0000000000002677
- Ishii N, Sakai S, Kishi K. A simple and safe method to create a drainage hole for thick skin grafts. Eplasty. 2017;17:ic27.
- Davis M, Baird D, Hill D, et al. Management of full-thickness skin grafts. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2021;34:683-686. doi:10.1080 /08998280.2021.1953867
- Mittermayr R, Wassermann E, Thurnher M, et al. Skin graft fixation by slow clotting fibrin sealant applied as a thin layer. Burns. 2006; 32:305-311. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2005.10.010
Managing Seromas Following Skin Graft Placement in Dermatologic Surgery
Managing Seromas Following Skin Graft Placement in Dermatologic Surgery
PRACTICE POINTS
- If seromas are identified early (within 24 to 48 hours postoperatively), prompt drainage with a small incision can prevent complications, such as fibrosis or nodule formation, and improve patient comfort.
- For larger or recurrent seromas, multiple small slits or a surgical window should be created to ensure continuous drainage and prevent reaccumulation. Manual compression with moist gauze also can aid in fluid removal.
- If fibrosis develops and leads to nodule formation, early excision of the fibrotic tissue with local anesthesia is essential for resolution. This approach typically requires a single treatment, with secondary intention healing.
Advocacy and Compliance Issues Impacting Dermatology in 2025
Advocacy and Compliance Issues Impacting Dermatology in 2025
The US health care system presents major administrative burdens—particularly in coding, billing, and reimbursement—that impact clinical efficiency and patient access. Dermatologists have experienced disproportionate reimbursement declines. A longitudinal review of 20 dermatologic service codes found a 10% average decline in Medicare reimbursement between 2000 and 2020.1 A recent cross-sectional study showed a 4.7% average decline in reimbursement rates from 2007 to 2021 for commonly performed dermatologic procedures, with variation across procedure categories.2 These reductions threaten practice sustainability and highlight the urgent need for comprehensive, long-term payment reform to preserve access to high-quality dermatologic care.
In dermatopathology, policy changes to reimbursement and laboratory oversight directly impact practice operations. Specialty-specific advocacy remains vital in driving policy changes. In this article, we highlight a recent advocacy win—the reversal of immunohistochemistry (IHC) stain denials—and provide updates on a new position statement on IHC guidance. We also outline regulatory changes to the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988 and College of American Pathologists (CAP) laboratory director requirements and emphasize the importance of continued legislative advocacy.
Reversal of Reimbursement Denials for IHC Stains
EviCore, a medical benefits management company serving over one-third of insured individuals in the United States, is hired by an extensive network of insurance companies to develop clinical and laboratory guidelines and utilization and payment integrity programs.3 EviCore’s laboratory management guidelines for 2024 denied IHC stains (Current Procedural Terminology codes 88341 and 88342) as not medically necessary when associated with specific International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, skin lesion codes (eTable 1).3-5 These policies caused major disruption to dermatopathology services nationwide, impacting both academic and private laboratories (eTable 2).5 The implementation of such blanket denials interferes with clinical decision-making, compromising diagnostic quality by restricting medically necessary and essential laboratory and pathology services. The American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) and CAP leadership formally objected to the policy, citing how these reimbursement denials fail to account for the importance of clinical judgment and diagnostic nuance.6
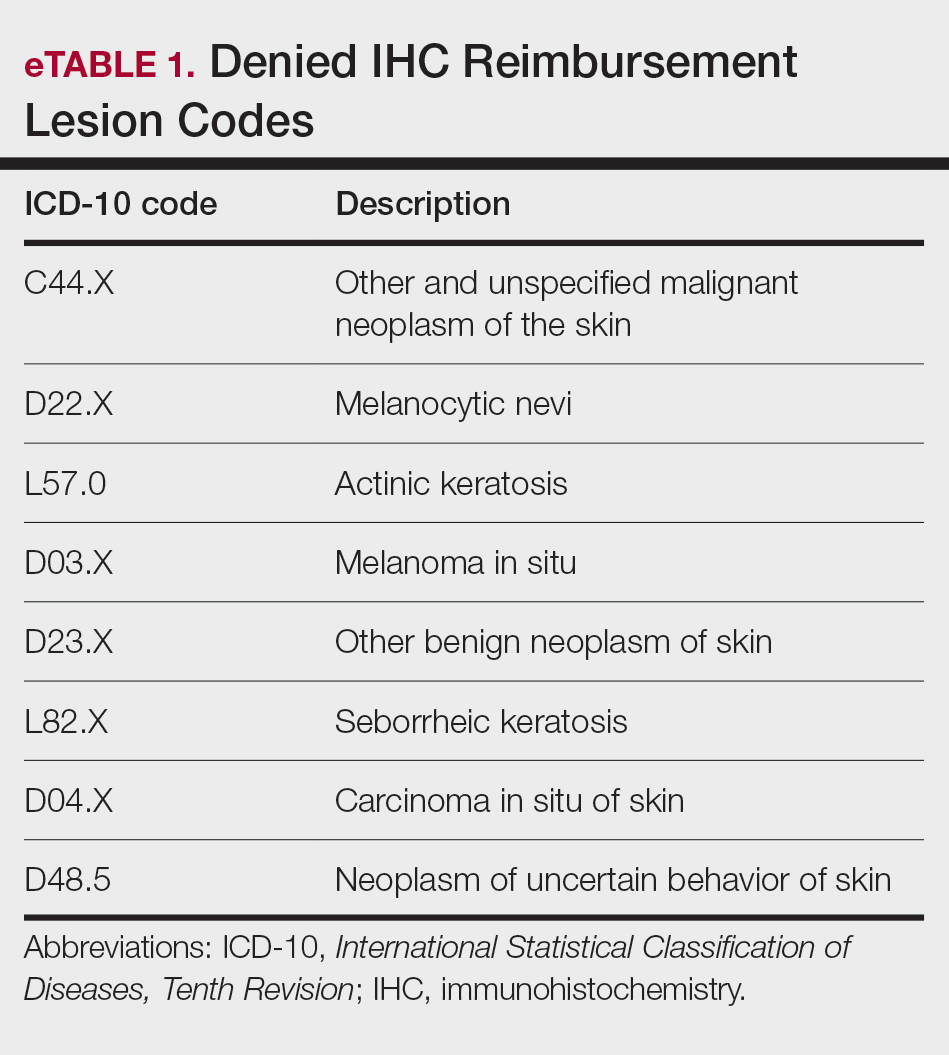

Thanks to broad advocacy efforts, EviCore updated its guidelines effective January 1, 2025. The skin-related International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were removed from IHC coverage restrictions, with automatic payment reinstated retroactive to March 15, 2024. EviCore also rescinded language denying reimbursement if a diagnosis could be made without the use of IHC stains.7 While this reversal is a notable achievement, ongoing monitoring of emerging trends in claim denials remains crucial. Continued advocacy, proper documentation, and adherence to American Society of Dermatopathology (ASDP) Appropriate Use Criteria is essential to protecting clinical autonomy.
The AADA’s Dermatopathology Committee developed a new position statement on IHC utilization supporting the advocacy efforts with payers, who recently have tried to implement restrictive limitations.8 Immunohistochemistry is considered a valuable tool for dermatopathology diagnosis, and its utility aids in the confirmation, exclusion, or change in diagnosis.9 By clearly outlining the clinical value of IHC in dermatopathology, this statement reinforces the need to advocate against restrictive payer policies to preserve physician autonomy and promote appropriate, evidence-based use of IHC stains.8
In addition, the ASDP Standards of Practice Committee is working with the Johns Hopkins–Global Appropriateness Measures data-powered analytics platform to develop physician-led IHC benchmarks. The ASDP Appropriate Use Criteria mobile application is a valuable clinical tool for dermatopathologists, general pathologists, dermatologists, and other providers, offering case-based recommendations for test utilization grounded in current evidence.9
Legislative Advocacy: Support for H.R. 879
Physician payment cuts have reached a critical tipping point. Since 2001, physicians have experienced a 33% average reduction in Medicare reimbursement, unadjusted for inflation or rising overhead.10 In January 2025, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) imposed a further 2.83% cut, despite projecting a 3.5% increase in the Medicare Economic Index.11,12 Dermatologists and other physician groups cannot continue to absorb these reductions, as they have several consequences, including the inability to maintain practices, forcing some physicians out of business, driving health care consolidation, and limiting patient access.
The Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act (H.R. 879)13 is bipartisan legislation that seeks to stop the 2.8% Medicare physician payment cut that went into effect in January 2025, provide physicians with an additional 2% inflation-adjusted payment increase for 2025, and help stabilize Medicare reimbursement rates.13,14 As the impact of continued cuts threatens both patient access and practice viability, member engagement is essential to advancing federal physician payment reform. To support sustainable payment reform and protect access to care, visit the AADA Advocacy Action Center online.14
2025 CLIA and CAP Laboratory Director Requirements: What’s Changing?
As of December 28, 2024, updated CLIA regulations took effect for all laboratories performing moderate- or high-complexity testing. These revisions aim to modernize outdated requirements and update regulations to incorporate technological advancements such as automation and artificial intelligence.15 New CLIA standards require laboratory directors with Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of Osteopathy degrees to be certified in anatomic and/or clinical pathology by the American Board of Pathology or the American Osteopathic Board of Pathology.15 For physicians who do not hold these board-certified qualifications, there are alternative pathways to becoming a laboratory director based on experience and education for physicians licensed to practice in the jurisdiction where the laboratory is located. For high-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 2 years of experience directing or supervising high-complexity testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities. For moderate-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 1 year of experience supervising nonwaived laboratory testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities.16
If the current laboratory director is not board certified in pathology, the new regulation will permit the grandfathering of current laboratory directors if existing laboratory directors have remained continuously employed in their current role since December 28, 2024.16 Therefore, individuals who were already employed in qualifying positions as of December 28, 2024, will be grandfathered in and will not need to meet the new educational requirements if they remain employed without interruption. All individuals qualifying after December 28, 2024, will be required to do so under the new provisions stated earlier.
The CMS updated laboratory personnel requirements, thereby impacting all CLIA-certified laboratories and those seeking CLIA certification. Likewise, laboratories seeking accreditation by the CAP must meet the new laboratory personnel requirements.17 In some cases, CAP requirements are more stringent than the CLIA regulations (CAP accreditation is more stringent in areas of quality control, personnel qualifications, proficiency testing, and in oversight of laboratory developed tests).15-17 If more stringent state or local regulations are in place for personnel qualifications, including requirements for state licensure, they must be followed.
The AADA formed an ad hoc workgroup to address the CLIA laboratory director requirements and is actively engaging CMS to amend these requirements immediately. Formal objections have been submitted, and direct dialogue with CMS leadership is under way in collaboration with the American Board of Dermatology and leading dermatology and pathology societies.
Final Thoughts
Advocacy remains essential to the future of dermatology. From payer policy reversals to laboratory compliance reforms and federal payment advocacy, physicians must remain engaged. Whether it is safeguarding diagnostic autonomy or securing financial sustainability, we must continue to put “skin in the game.”
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358.
- Miller TC, Rucker P, Armstrong D. “Not medically necessary”: inside the company helping America’s biggest health insurers deny coverage for care. ProPublica. October 23, 2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.propublica.org/article/evicore-health-insurance-denials-cigna-unitedhealthcare-aetna-prior-authorizations
- EviCore healthcare. Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Lab Management Guidelines v2.0.2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/MOL.CS_.104.A_Immunohistochemistry%20%28IHC%29_V2.0.2024_eff11.01.2024_pub12.31.2024.pdf
- EviCore. Laboratory management. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/provider/clinical-guidelines-details?solution=laboratory%20management
- Saad AJ. College of American Pathologists. December 12, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents /Wellmark-Letter- https://documents.cap.org/documents/wellmarkcap-letter2023.pdf
- EviCore healthcare. Clinical Guidelines: Lab Management Program. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/Cigna_LabMgmt_V1.0.2025_eff01.01.2025_pub08.22.2024_0.pdf
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Position statement on immunohistochemistry utilization. Accessed May 9, 2024. https://server.aad.org/forms/policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Immunohistochemistry%20Utilization.pdf
- Naert KA, Trotter MJ. Utilization and utility of immunohistochemistry in dermatopathology. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:74-77.
- American Medical Association. Medicare physician payment continues to fall further behind practice cost inflation. Accessed April 23, 2025. https:// www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2025-medicare-updates-inflation-chart.pdf
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2025-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-final-rule
- American Medical Association. The Medicare Economic Index. Accessed April 23 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/medicare-basics-medicare-economic-index.pdf
- Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act, HR 879, 119th Cong (2025). Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/house-bill/879
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AADA advocacy action center. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/take-action
- Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) fees; histocompatibility, personnel, and alternative sanctions for certificate of waiver laboratories. Fed Regist. 2023;88:89976-90044.
- College of American Pathologists. CAP accreditation checklists – 2024 edition. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2024-Checklist-Summary.pdf?_gl=1*1b4rei9*_ga*NDc0NjYwNjM5LjE3NDQ3NTI4NjA.*_ga_97ZFJSQQ0X*MTc0NDc2OTc3My40LjEuMTc0NDc2OTgyOC4wLjAuMA
- Bennett SA, Conn CM, Gill HE, et al. Regulatory requirements for laboratory developed tests in the United States. J Immunol Methods. 2025;537:113813.
The US health care system presents major administrative burdens—particularly in coding, billing, and reimbursement—that impact clinical efficiency and patient access. Dermatologists have experienced disproportionate reimbursement declines. A longitudinal review of 20 dermatologic service codes found a 10% average decline in Medicare reimbursement between 2000 and 2020.1 A recent cross-sectional study showed a 4.7% average decline in reimbursement rates from 2007 to 2021 for commonly performed dermatologic procedures, with variation across procedure categories.2 These reductions threaten practice sustainability and highlight the urgent need for comprehensive, long-term payment reform to preserve access to high-quality dermatologic care.
In dermatopathology, policy changes to reimbursement and laboratory oversight directly impact practice operations. Specialty-specific advocacy remains vital in driving policy changes. In this article, we highlight a recent advocacy win—the reversal of immunohistochemistry (IHC) stain denials—and provide updates on a new position statement on IHC guidance. We also outline regulatory changes to the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988 and College of American Pathologists (CAP) laboratory director requirements and emphasize the importance of continued legislative advocacy.
Reversal of Reimbursement Denials for IHC Stains
EviCore, a medical benefits management company serving over one-third of insured individuals in the United States, is hired by an extensive network of insurance companies to develop clinical and laboratory guidelines and utilization and payment integrity programs.3 EviCore’s laboratory management guidelines for 2024 denied IHC stains (Current Procedural Terminology codes 88341 and 88342) as not medically necessary when associated with specific International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, skin lesion codes (eTable 1).3-5 These policies caused major disruption to dermatopathology services nationwide, impacting both academic and private laboratories (eTable 2).5 The implementation of such blanket denials interferes with clinical decision-making, compromising diagnostic quality by restricting medically necessary and essential laboratory and pathology services. The American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) and CAP leadership formally objected to the policy, citing how these reimbursement denials fail to account for the importance of clinical judgment and diagnostic nuance.6


Thanks to broad advocacy efforts, EviCore updated its guidelines effective January 1, 2025. The skin-related International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were removed from IHC coverage restrictions, with automatic payment reinstated retroactive to March 15, 2024. EviCore also rescinded language denying reimbursement if a diagnosis could be made without the use of IHC stains.7 While this reversal is a notable achievement, ongoing monitoring of emerging trends in claim denials remains crucial. Continued advocacy, proper documentation, and adherence to American Society of Dermatopathology (ASDP) Appropriate Use Criteria is essential to protecting clinical autonomy.
The AADA’s Dermatopathology Committee developed a new position statement on IHC utilization supporting the advocacy efforts with payers, who recently have tried to implement restrictive limitations.8 Immunohistochemistry is considered a valuable tool for dermatopathology diagnosis, and its utility aids in the confirmation, exclusion, or change in diagnosis.9 By clearly outlining the clinical value of IHC in dermatopathology, this statement reinforces the need to advocate against restrictive payer policies to preserve physician autonomy and promote appropriate, evidence-based use of IHC stains.8
In addition, the ASDP Standards of Practice Committee is working with the Johns Hopkins–Global Appropriateness Measures data-powered analytics platform to develop physician-led IHC benchmarks. The ASDP Appropriate Use Criteria mobile application is a valuable clinical tool for dermatopathologists, general pathologists, dermatologists, and other providers, offering case-based recommendations for test utilization grounded in current evidence.9
Legislative Advocacy: Support for H.R. 879
Physician payment cuts have reached a critical tipping point. Since 2001, physicians have experienced a 33% average reduction in Medicare reimbursement, unadjusted for inflation or rising overhead.10 In January 2025, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) imposed a further 2.83% cut, despite projecting a 3.5% increase in the Medicare Economic Index.11,12 Dermatologists and other physician groups cannot continue to absorb these reductions, as they have several consequences, including the inability to maintain practices, forcing some physicians out of business, driving health care consolidation, and limiting patient access.
The Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act (H.R. 879)13 is bipartisan legislation that seeks to stop the 2.8% Medicare physician payment cut that went into effect in January 2025, provide physicians with an additional 2% inflation-adjusted payment increase for 2025, and help stabilize Medicare reimbursement rates.13,14 As the impact of continued cuts threatens both patient access and practice viability, member engagement is essential to advancing federal physician payment reform. To support sustainable payment reform and protect access to care, visit the AADA Advocacy Action Center online.14
2025 CLIA and CAP Laboratory Director Requirements: What’s Changing?
As of December 28, 2024, updated CLIA regulations took effect for all laboratories performing moderate- or high-complexity testing. These revisions aim to modernize outdated requirements and update regulations to incorporate technological advancements such as automation and artificial intelligence.15 New CLIA standards require laboratory directors with Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of Osteopathy degrees to be certified in anatomic and/or clinical pathology by the American Board of Pathology or the American Osteopathic Board of Pathology.15 For physicians who do not hold these board-certified qualifications, there are alternative pathways to becoming a laboratory director based on experience and education for physicians licensed to practice in the jurisdiction where the laboratory is located. For high-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 2 years of experience directing or supervising high-complexity testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities. For moderate-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 1 year of experience supervising nonwaived laboratory testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities.16
If the current laboratory director is not board certified in pathology, the new regulation will permit the grandfathering of current laboratory directors if existing laboratory directors have remained continuously employed in their current role since December 28, 2024.16 Therefore, individuals who were already employed in qualifying positions as of December 28, 2024, will be grandfathered in and will not need to meet the new educational requirements if they remain employed without interruption. All individuals qualifying after December 28, 2024, will be required to do so under the new provisions stated earlier.
The CMS updated laboratory personnel requirements, thereby impacting all CLIA-certified laboratories and those seeking CLIA certification. Likewise, laboratories seeking accreditation by the CAP must meet the new laboratory personnel requirements.17 In some cases, CAP requirements are more stringent than the CLIA regulations (CAP accreditation is more stringent in areas of quality control, personnel qualifications, proficiency testing, and in oversight of laboratory developed tests).15-17 If more stringent state or local regulations are in place for personnel qualifications, including requirements for state licensure, they must be followed.
The AADA formed an ad hoc workgroup to address the CLIA laboratory director requirements and is actively engaging CMS to amend these requirements immediately. Formal objections have been submitted, and direct dialogue with CMS leadership is under way in collaboration with the American Board of Dermatology and leading dermatology and pathology societies.
Final Thoughts
Advocacy remains essential to the future of dermatology. From payer policy reversals to laboratory compliance reforms and federal payment advocacy, physicians must remain engaged. Whether it is safeguarding diagnostic autonomy or securing financial sustainability, we must continue to put “skin in the game.”
The US health care system presents major administrative burdens—particularly in coding, billing, and reimbursement—that impact clinical efficiency and patient access. Dermatologists have experienced disproportionate reimbursement declines. A longitudinal review of 20 dermatologic service codes found a 10% average decline in Medicare reimbursement between 2000 and 2020.1 A recent cross-sectional study showed a 4.7% average decline in reimbursement rates from 2007 to 2021 for commonly performed dermatologic procedures, with variation across procedure categories.2 These reductions threaten practice sustainability and highlight the urgent need for comprehensive, long-term payment reform to preserve access to high-quality dermatologic care.
In dermatopathology, policy changes to reimbursement and laboratory oversight directly impact practice operations. Specialty-specific advocacy remains vital in driving policy changes. In this article, we highlight a recent advocacy win—the reversal of immunohistochemistry (IHC) stain denials—and provide updates on a new position statement on IHC guidance. We also outline regulatory changes to the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988 and College of American Pathologists (CAP) laboratory director requirements and emphasize the importance of continued legislative advocacy.
Reversal of Reimbursement Denials for IHC Stains
EviCore, a medical benefits management company serving over one-third of insured individuals in the United States, is hired by an extensive network of insurance companies to develop clinical and laboratory guidelines and utilization and payment integrity programs.3 EviCore’s laboratory management guidelines for 2024 denied IHC stains (Current Procedural Terminology codes 88341 and 88342) as not medically necessary when associated with specific International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, skin lesion codes (eTable 1).3-5 These policies caused major disruption to dermatopathology services nationwide, impacting both academic and private laboratories (eTable 2).5 The implementation of such blanket denials interferes with clinical decision-making, compromising diagnostic quality by restricting medically necessary and essential laboratory and pathology services. The American Academy of Dermatology Association (AADA) and CAP leadership formally objected to the policy, citing how these reimbursement denials fail to account for the importance of clinical judgment and diagnostic nuance.6


Thanks to broad advocacy efforts, EviCore updated its guidelines effective January 1, 2025. The skin-related International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, codes were removed from IHC coverage restrictions, with automatic payment reinstated retroactive to March 15, 2024. EviCore also rescinded language denying reimbursement if a diagnosis could be made without the use of IHC stains.7 While this reversal is a notable achievement, ongoing monitoring of emerging trends in claim denials remains crucial. Continued advocacy, proper documentation, and adherence to American Society of Dermatopathology (ASDP) Appropriate Use Criteria is essential to protecting clinical autonomy.
The AADA’s Dermatopathology Committee developed a new position statement on IHC utilization supporting the advocacy efforts with payers, who recently have tried to implement restrictive limitations.8 Immunohistochemistry is considered a valuable tool for dermatopathology diagnosis, and its utility aids in the confirmation, exclusion, or change in diagnosis.9 By clearly outlining the clinical value of IHC in dermatopathology, this statement reinforces the need to advocate against restrictive payer policies to preserve physician autonomy and promote appropriate, evidence-based use of IHC stains.8
In addition, the ASDP Standards of Practice Committee is working with the Johns Hopkins–Global Appropriateness Measures data-powered analytics platform to develop physician-led IHC benchmarks. The ASDP Appropriate Use Criteria mobile application is a valuable clinical tool for dermatopathologists, general pathologists, dermatologists, and other providers, offering case-based recommendations for test utilization grounded in current evidence.9
Legislative Advocacy: Support for H.R. 879
Physician payment cuts have reached a critical tipping point. Since 2001, physicians have experienced a 33% average reduction in Medicare reimbursement, unadjusted for inflation or rising overhead.10 In January 2025, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) imposed a further 2.83% cut, despite projecting a 3.5% increase in the Medicare Economic Index.11,12 Dermatologists and other physician groups cannot continue to absorb these reductions, as they have several consequences, including the inability to maintain practices, forcing some physicians out of business, driving health care consolidation, and limiting patient access.
The Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act (H.R. 879)13 is bipartisan legislation that seeks to stop the 2.8% Medicare physician payment cut that went into effect in January 2025, provide physicians with an additional 2% inflation-adjusted payment increase for 2025, and help stabilize Medicare reimbursement rates.13,14 As the impact of continued cuts threatens both patient access and practice viability, member engagement is essential to advancing federal physician payment reform. To support sustainable payment reform and protect access to care, visit the AADA Advocacy Action Center online.14
2025 CLIA and CAP Laboratory Director Requirements: What’s Changing?
As of December 28, 2024, updated CLIA regulations took effect for all laboratories performing moderate- or high-complexity testing. These revisions aim to modernize outdated requirements and update regulations to incorporate technological advancements such as automation and artificial intelligence.15 New CLIA standards require laboratory directors with Doctor of Medicine or Doctor of Osteopathy degrees to be certified in anatomic and/or clinical pathology by the American Board of Pathology or the American Osteopathic Board of Pathology.15 For physicians who do not hold these board-certified qualifications, there are alternative pathways to becoming a laboratory director based on experience and education for physicians licensed to practice in the jurisdiction where the laboratory is located. For high-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 2 years of experience directing or supervising high-complexity testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities. For moderate-complexity laboratories, individuals need at least 1 year of experience supervising nonwaived laboratory testing and at least 20 continuing education credit hours in laboratory practice that cover director responsibilities.16
If the current laboratory director is not board certified in pathology, the new regulation will permit the grandfathering of current laboratory directors if existing laboratory directors have remained continuously employed in their current role since December 28, 2024.16 Therefore, individuals who were already employed in qualifying positions as of December 28, 2024, will be grandfathered in and will not need to meet the new educational requirements if they remain employed without interruption. All individuals qualifying after December 28, 2024, will be required to do so under the new provisions stated earlier.
The CMS updated laboratory personnel requirements, thereby impacting all CLIA-certified laboratories and those seeking CLIA certification. Likewise, laboratories seeking accreditation by the CAP must meet the new laboratory personnel requirements.17 In some cases, CAP requirements are more stringent than the CLIA regulations (CAP accreditation is more stringent in areas of quality control, personnel qualifications, proficiency testing, and in oversight of laboratory developed tests).15-17 If more stringent state or local regulations are in place for personnel qualifications, including requirements for state licensure, they must be followed.
The AADA formed an ad hoc workgroup to address the CLIA laboratory director requirements and is actively engaging CMS to amend these requirements immediately. Formal objections have been submitted, and direct dialogue with CMS leadership is under way in collaboration with the American Board of Dermatology and leading dermatology and pathology societies.
Final Thoughts
Advocacy remains essential to the future of dermatology. From payer policy reversals to laboratory compliance reforms and federal payment advocacy, physicians must remain engaged. Whether it is safeguarding diagnostic autonomy or securing financial sustainability, we must continue to put “skin in the game.”
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358.
- Miller TC, Rucker P, Armstrong D. “Not medically necessary”: inside the company helping America’s biggest health insurers deny coverage for care. ProPublica. October 23, 2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.propublica.org/article/evicore-health-insurance-denials-cigna-unitedhealthcare-aetna-prior-authorizations
- EviCore healthcare. Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Lab Management Guidelines v2.0.2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/MOL.CS_.104.A_Immunohistochemistry%20%28IHC%29_V2.0.2024_eff11.01.2024_pub12.31.2024.pdf
- EviCore. Laboratory management. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/provider/clinical-guidelines-details?solution=laboratory%20management
- Saad AJ. College of American Pathologists. December 12, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents /Wellmark-Letter- https://documents.cap.org/documents/wellmarkcap-letter2023.pdf
- EviCore healthcare. Clinical Guidelines: Lab Management Program. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/Cigna_LabMgmt_V1.0.2025_eff01.01.2025_pub08.22.2024_0.pdf
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Position statement on immunohistochemistry utilization. Accessed May 9, 2024. https://server.aad.org/forms/policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Immunohistochemistry%20Utilization.pdf
- Naert KA, Trotter MJ. Utilization and utility of immunohistochemistry in dermatopathology. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:74-77.
- American Medical Association. Medicare physician payment continues to fall further behind practice cost inflation. Accessed April 23, 2025. https:// www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2025-medicare-updates-inflation-chart.pdf
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2025-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-final-rule
- American Medical Association. The Medicare Economic Index. Accessed April 23 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/medicare-basics-medicare-economic-index.pdf
- Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act, HR 879, 119th Cong (2025). Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/house-bill/879
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AADA advocacy action center. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/take-action
- Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) fees; histocompatibility, personnel, and alternative sanctions for certificate of waiver laboratories. Fed Regist. 2023;88:89976-90044.
- College of American Pathologists. CAP accreditation checklists – 2024 edition. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2024-Checklist-Summary.pdf?_gl=1*1b4rei9*_ga*NDc0NjYwNjM5LjE3NDQ3NTI4NjA.*_ga_97ZFJSQQ0X*MTc0NDc2OTc3My40LjEuMTc0NDc2OTgyOC4wLjAuMA
- Bennett SA, Conn CM, Gill HE, et al. Regulatory requirements for laboratory developed tests in the United States. J Immunol Methods. 2025;537:113813.
- Pollock JR, Chen JY, Dorius DA, et al. Decreasing physician Medicare reimbursement for dermatology services. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:1154-1156.
- Mazmudar RS, Sheth A, Tripathi R, et al. Inflation-adjusted trends in Medicare reimbursement for common dermatologic procedures, 2007-2021. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1355-1358.
- Miller TC, Rucker P, Armstrong D. “Not medically necessary”: inside the company helping America’s biggest health insurers deny coverage for care. ProPublica. October 23, 2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.propublica.org/article/evicore-health-insurance-denials-cigna-unitedhealthcare-aetna-prior-authorizations
- EviCore healthcare. Immunohistochemistry (IHC). Lab Management Guidelines v2.0.2024. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/MOL.CS_.104.A_Immunohistochemistry%20%28IHC%29_V2.0.2024_eff11.01.2024_pub12.31.2024.pdf
- EviCore. Laboratory management. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/provider/clinical-guidelines-details?solution=laboratory%20management
- Saad AJ. College of American Pathologists. December 12, 2023. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents /Wellmark-Letter- https://documents.cap.org/documents/wellmarkcap-letter2023.pdf
- EviCore healthcare. Clinical Guidelines: Lab Management Program. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.evicore.com/sites/default/files/clinical-guidelines/2024-08/Cigna_LabMgmt_V1.0.2025_eff01.01.2025_pub08.22.2024_0.pdf
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. Position statement on immunohistochemistry utilization. Accessed May 9, 2024. https://server.aad.org/forms/policies/Uploads/PS/PS-Immunohistochemistry%20Utilization.pdf
- Naert KA, Trotter MJ. Utilization and utility of immunohistochemistry in dermatopathology. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013;35:74-77.
- American Medical Association. Medicare physician payment continues to fall further behind practice cost inflation. Accessed April 23, 2025. https:// www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2025-medicare-updates-inflation-chart.pdf
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Calendar year (CY) 2025 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule final rule. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/calendar-year-cy-2025-medicare-physician-fee-schedule-final-rule
- American Medical Association. The Medicare Economic Index. Accessed April 23 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/medicare-basics-medicare-economic-index.pdf
- Medicare Patient Access and Practice Stabilization Act, HR 879, 119th Cong (2025). Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/house-bill/879
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AADA advocacy action center. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://www.aad.org/member/advocacy/take-action
- Department of Health and Human Services. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA) fees; histocompatibility, personnel, and alternative sanctions for certificate of waiver laboratories. Fed Regist. 2023;88:89976-90044.
- College of American Pathologists. CAP accreditation checklists – 2024 edition. Accessed April 23, 2025. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2024-Checklist-Summary.pdf?_gl=1*1b4rei9*_ga*NDc0NjYwNjM5LjE3NDQ3NTI4NjA.*_ga_97ZFJSQQ0X*MTc0NDc2OTc3My40LjEuMTc0NDc2OTgyOC4wLjAuMA
- Bennett SA, Conn CM, Gill HE, et al. Regulatory requirements for laboratory developed tests in the United States. J Immunol Methods. 2025;537:113813.
Advocacy and Compliance Issues Impacting Dermatology in 2025
Advocacy and Compliance Issues Impacting Dermatology in 2025
PRACTICE POINTS
- Recent advocacy efforts have led to the reversal of widespread insurer denials for immunohistochemistry stains; however, continued vigilance is necessary, as restrictive coverage policies may re-emerge.
- Laboratory directors must comply with updated Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 and College of American Pathologists personnel requirements effective December 28, 2024, including stricter board certification and 2 years of laboratory training or experience and 20 hours of continuing education requirements.
- The American Society of Dermatopathology Appropriate Use Criteria mobile application provides physicians with evidence-based guidance for test selection in dermatopathology.