User login
AVAHO
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]


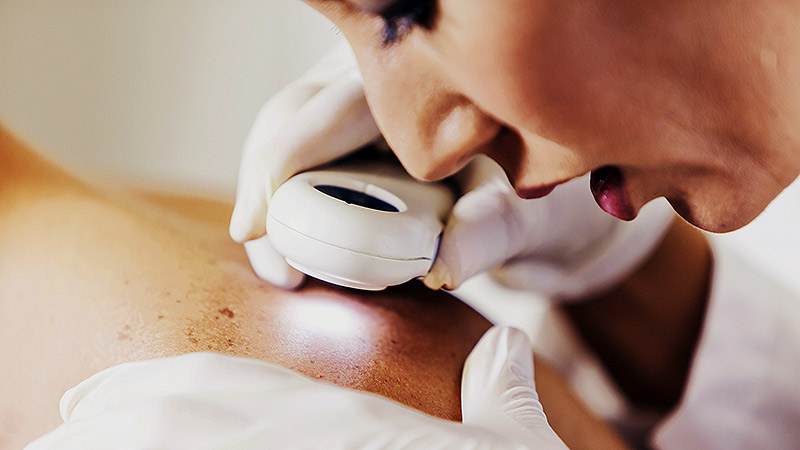
Population vs Tailored Skin Cancer Screening: Which Is Best?
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ATHENS, Greece — At the 11th World Congress of Melanoma and 21st EADO Congress 2025, experts presented divergent perspectives on the merits of population-wide skin cancer screening programs vs more targeted approaches. The debate highlighted concerns about healthcare resource allocation, overdiagnosis, and the true impact of mass skin cancer screening on mortality.
Arguing against widespread screening, particularly in low-to-medium incidence countries like Spain, was Susana Puig, MD, the head of Dermatology at Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, University of Barcelona, and a dermatologist at Barnaclínic+, Barcelona, Spain.
“It’s not efficient. We visit too many healthy individuals to detect melanoma,” she said. “We need to focus on treating patients, not checking healthy people without any risk.”
Championing for population-wide screening was Peter Mohr, MD, a dermatologist at the Clinic of Dermatology in Elbe Klinikum Buxtehude, Buxtehude, Germany, who noted a disproportionate focus on treatment rather than prevention. “The ultimate goal of screening,” he said, “is to prevent advanced disease and reduce melanoma-specific mortality.”
Avoid Population-Based Screening
Presenting data from Germany, Puig noted that population-based screening starting at any age requires examining more than 600 people and performing over 24 excisions to detect one melanoma. When setting screening to start at the age of 35 years, the number of people needed to screen to detect one melanoma decreased slightly to 559.
These findings highlight that population-based screening will include many people who don’t need it and can increase the potential for overdiagnosis, she argued.
Studies and guidelines from the United States align with Puig’s concern about broad-based screening likely leading to overdiagnosis. “The incidence of melanoma has risen sixfold in the past 40 years in the United States, while mortality has remained largely flat, an epidemiological signature consistent with overdiagnosis,” according to Adewole Adamson, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine, in the Division of Dermatology at Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, Texas, who published findings to this effect in 2022.
“We cannot saturate the system with healthy people,” Puig said. Instead, “we need to use strategies to identify high-risk patients.” She proposed being more selective about who to screen by identifying those at higher risk of developing melanoma.
Identifying risk factors, such as the presence of atypical nevi and a personal or family history of melanoma, can help hone who is screened, she explained. Patients with a personal history of melanoma, in particular, face a higher risk of developing subsequent melanomas. Data show that patients with two or more primary melanomas had almost three times the risk of developing a subsequent one than those with one prior melanoma — 25.7% vs 8.6%. Puig also pointed out the significant correlation between age and melanoma risk, with people over 70 years exhibiting a 93-fold higher probability of diagnosis than those younger than 30 years.
Citing the German data, she noted that screening people 20 years and older with one risk factor reduced the number needed to screen by more than threefold — from more than 600 to 178.
Puig suggested dedicated surveillance programs for high-risk individuals alongside opportunistic screening during routine medical encounters.
“This would lead to a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources and better outcomes for those most vulnerable to melanoma,” Puig concluded.
Perform Population-Based Screening
In contrast, Mohr presented a defense of population-based skin cancer screening. Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the United States and is prevalent worldwide, with more than 1.5 million new cases diagnosed globally in 2022.
Screening people and identifying the disease in its earliest stages is important, he said.
Mohr highlighted a recent study exploring biennial skin cancer screening in Germany and found that 4.2% of those screened had a skin cancer finding, but the number of interval melanomas was similar in both screened and unscreened populations.
However, a large retrospective cohort study from Germany involving about 1.4 million people showed a decrease in locoregional metastasis (from 13% to 4%), distant metastases (from 8% to 4%), and systemic treatments (from 21% to 11%) in screened vs unscreened people, as well as better overall survival rates in the screened population.
Mohr highlighted how Germany, in particular, is well-equipped for more broad-based, preventative screening.
Germany has had long-standing primary prevention programs, which have existed for about 24 years and involve extensive public awareness campaigns. Access to dermatologists is significantly better in Germany compared with the Netherlands, with an average waiting time for screening of around 6 weeks and only 1.2 weeks for suspicious lesions, compared with 14 weeks and 3.5 weeks, respectively, in the Netherlands. This access may make a broader screening strategy more feasible in a country like Germany.
However, Mohr did note that there are “no large, randomized trials to show us the value of skin cancer screening.”
A Role for Primary Care Physicians?
Although they disagreed about the utility of screening, both Puig and Mohr agreed on the important role primary care physicians play in improving early melanoma detection. “We cannot do it alone, and general practitioners are really fundamental,” Puig said.
Mohr said that continuous education for primary care physicians can dramatically improve their diagnostic skills. In Germany, an 8-hour training session significantly improved their ability to detect basal cell carcinoma and melanomas. However, he cautioned that this improved accuracy tended to wane within a year.
In Spain, Puig highlighted the successful implementation of teledermatology to support general practitioners. “We train them with dermoscopy, and we answer all teledermatology requests in 1 week, reducing in-person visits by 50%,” she explained. This approach allows general practitioners to assess potential skin cancer efficiently and streamline referrals.
Puig reported being on advisory boards for Almirall, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma. She conducts research and trials with AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, BMS, Biofrontera, Canfield, Cantabria, Fotofinder, GSK, ISDIN, La Roche-Posay, Leo Pharma, MSD, MEDA, Novartis, Pfizer, Polychem, Sanofi, Roche, and Regeneron. She is involved with Athena Technology Solutions and Dermavision Solutions. Mohr reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM WCM-EADO 2025
Million Veteran Program Drives Prostate Cancer Research
About 15,000 veterans are annually diagnosed with prostate cancer. Fortunately, those veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Million Veteran Program (MVP) provide researchers with a deep pool of genetic data that can help identify causes, aid diagnosis, and guide targeted treatments.
More than 1,000,000 veterans have enrolled in MVP and donated their anonymized DNA to foster research. It is also one of the most genetically diverse health-related databases: 20% of participants identify as Black, 8% as Hispanic, 2% as Asian American, and 1% as Native American.
Ethnically and racially diverse data are particularly important for advancing the treatment of underserved groups. In a 2020 review, researchers found a number of areas where Black veterans differed from White veterans, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, incidence (almost 60% higher), clinical course, and mortality rate (2 to 3 times greater). To facilitate research, the MVP developed the “DNA chip,” a custom-designed tool that tests for > 750,000 genetic variants, including > 300,000 that are more common in minority populations.
“The whole thing about understanding genetics and diversity is like a circular feedback loop,” Director of MVP Dr. Sumitra Muralidhar said in a VA news article. “The more people you have represented from different racial and ethnic backgrounds, the more we’ll be able to discover genetic variants that contribute to their health. The more we discover, the more we can help that group. It’s a complete circular feedback loop.”
In addition to veterans’ blood samples and 600,000-plus baseline surveys on lifestyle, military service, and health, the MVP has collected upwards of 825,000 germline DNA samples, which have helped inform research into prostate cancer, the most commonly diagnosed solid tumor among veterans. By mining these data, researchers have built more evidence of how genes add to risk and disease progression.
In one study preprint that has not been peer reviewed, VA researchers investigated the significance of high polygenic hazard scores. The scores are strongly associated with age at diagnosis of any prostate cancer, as well as lifetime risk of metastatic and fatal prostate cancer. However, because they’re associated with any prostate cancer, the researchers say, there is concern that screening men with high polygenic risk could increase overdiagnosis of indolent cancers.
The researchers analyzed genetic and phenotypic data from 69,901 men in the MVP who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer (6413 metastatic). They found their hypothesis to be correct: Among men eventually diagnosed with prostate cancer, those with higher polygenic risk were more likely to develop metastatic disease.
Genetic risk scores like PHS601, a 601-variant polygenic score, can be performed on a saliva sample at any time during a person’s life, the researchers note. Thus, the scores provide the earliest information about age-specific risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. These scores might be useful, they suggest, to support clinical decisions not only about whom to screen but also at what age.
Another study led by Stanford University researchers and published in Nature Genetics aimed to make screening more targeted, in this case prostate specific antigen screening. Estimates about PSA heritability vary from 40% to 45%, with genome-wide evaluations putting it at 25% to 30%, suggesting that incorporating genetic factors could improve screening.
This study involved 296,754 men (211,342 with European ancestry, 58,236 with African ancestry, 23,546 with Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 3630 with Asian ancestry; 96.5% of participants were from MVP)—a sample size more than triple that in previous work.
The researchers detected 448 genome-wide significant variants, including 295 that were novel (to the best of their knowledge). The variance explained by genome-wide polygenic risk scores ranged from 11.6% to 16.6% for European ancestry, 5.5% to 9.5% for African ancestry, 13.5% to 18.2% for Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 8.6% to 15.3% for Asian ancestry, and decreased with increasing age. Midlife genetically adjusted PSA levels were more strongly associated with overall and aggressive prostate cancer than unadjusted PSA levels.
The researchers say their study highlights how including higher proportions of participants from underrepresented populations can improve genetic prediction of PSA levels, offering the potential to personalize prostate cancer screening. Adjusting PSA for individuals’ predispositions in the absence of prostate cancer could improve the specificity (to reduce overdiagnosis) and sensitivity (to prevent more deaths) of screening.
Their findings, the researchers suggest, also explain additional variation in PSA, especially among men of African heritage, who experience the highest prostate cancer morbidity and mortality. They note that this work “moved us closer to leveraging genetic information to personalize PSA and substantially improved our understanding of PSA across diverse ancestries.”
A third study from a team at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System also investigated the risk of inheriting a predisposition to prostate cancer. These researchers explored pathogenic variants using both genome-wide single-allele and identity-by-descent analytic approaches. They then tested their candidate variants for replication across independent biobanks, including MVP.
The researchers discovered the gene WNT9B E152K more than doubled the risk of familial prostate cancer. Meta-analysis, collectively encompassing 500,000 patients, confirmed the genome-wide significance. The researchers say WNT9B shares an “unexpected commonality” with the previously established prostate cancer risk genes HOXB13 and HNF1B: Each are required for embryonic prostate development. Based on that finding, the researchers also evaluated 2 additional genes, KMT2D and DHCR7, which are known to cause Mendelian genitourinary developmental defects. They, too, were nominally associated with prostate cancer under meta-analyses.
Tens of thousands of participants in MVP have had prostate cancer. The genetic research they participate in advances detection, prediction, and treatment for themselves and others, and science in general. The research is not only about finding causes, but what to do if the cancer develops. An “acting on MVP prostate cancer findings” study at VA Puget Sound Health Care System is testing how communicating with veterans about MVP prostate cancer results will affect their care. Those with prostate cancer will be screened to determine genetic contributions to their cancers. Those found to have a gene-based cancer diagnosis will be offered genetic counseling. Their immediate family will also be offered screening to test for inherited prostate cancer risk.
In 2016, the VA partnered with the Prostate Cancer Foundation to establish the Precision Oncology Program for Cancer of the Prostate (POPCaP). In collaboration with MVP and the Genomic Medicine Service, the program uses genetic information to individualize treatments for veterans with advanced prostate cancer.
US Army Veteran James Perry is one of the beneficiaries of the program. First diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2001, he was initially treated with radiation therapy, but the cancer recurred and spread to his lung. The John J. Cochran Veterans Hospital in St. Louis sent a sample of Perry's lung tumor to the laboratory for genetic testing, where they discovered he had a BRCA1 gene mutation.
His oncologist, Dr. Martin Schoen, recommended Perry enroll in AMPLITUDE, a clinical trial testing the effectiveness of poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, a new class of drugs to treat hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. One year later, Perry’s lung tumor could barely be seen on computed tomography, and his PSA levels were undetectable.
"I would highly recommend enrolling in a trial," Perry told VA Research Currents. “If a veteran has that opportunity, I would encourage it—anything that is going to give you a few more days is worth it.” In the interview, Perry said he enjoyed being part of the trial because he knows he is getting the most advanced care possible and is proud to help others like himself.
"We are honored to support VA's work to improve the lives of veterans who are living with advanced prostate cancer," Vice President and National Director of the PCF Veterans Health Initiative Rebecca Levine said. "Clinical trials play a vital role in bringing new treatments to patients who need them most. Mr. Perry's experience illustrates VA's commitment to provide state-of-the-art cancer care to all veterans who need it."
About 15,000 veterans are annually diagnosed with prostate cancer. Fortunately, those veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Million Veteran Program (MVP) provide researchers with a deep pool of genetic data that can help identify causes, aid diagnosis, and guide targeted treatments.
More than 1,000,000 veterans have enrolled in MVP and donated their anonymized DNA to foster research. It is also one of the most genetically diverse health-related databases: 20% of participants identify as Black, 8% as Hispanic, 2% as Asian American, and 1% as Native American.
Ethnically and racially diverse data are particularly important for advancing the treatment of underserved groups. In a 2020 review, researchers found a number of areas where Black veterans differed from White veterans, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, incidence (almost 60% higher), clinical course, and mortality rate (2 to 3 times greater). To facilitate research, the MVP developed the “DNA chip,” a custom-designed tool that tests for > 750,000 genetic variants, including > 300,000 that are more common in minority populations.
“The whole thing about understanding genetics and diversity is like a circular feedback loop,” Director of MVP Dr. Sumitra Muralidhar said in a VA news article. “The more people you have represented from different racial and ethnic backgrounds, the more we’ll be able to discover genetic variants that contribute to their health. The more we discover, the more we can help that group. It’s a complete circular feedback loop.”
In addition to veterans’ blood samples and 600,000-plus baseline surveys on lifestyle, military service, and health, the MVP has collected upwards of 825,000 germline DNA samples, which have helped inform research into prostate cancer, the most commonly diagnosed solid tumor among veterans. By mining these data, researchers have built more evidence of how genes add to risk and disease progression.
In one study preprint that has not been peer reviewed, VA researchers investigated the significance of high polygenic hazard scores. The scores are strongly associated with age at diagnosis of any prostate cancer, as well as lifetime risk of metastatic and fatal prostate cancer. However, because they’re associated with any prostate cancer, the researchers say, there is concern that screening men with high polygenic risk could increase overdiagnosis of indolent cancers.
The researchers analyzed genetic and phenotypic data from 69,901 men in the MVP who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer (6413 metastatic). They found their hypothesis to be correct: Among men eventually diagnosed with prostate cancer, those with higher polygenic risk were more likely to develop metastatic disease.
Genetic risk scores like PHS601, a 601-variant polygenic score, can be performed on a saliva sample at any time during a person’s life, the researchers note. Thus, the scores provide the earliest information about age-specific risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. These scores might be useful, they suggest, to support clinical decisions not only about whom to screen but also at what age.
Another study led by Stanford University researchers and published in Nature Genetics aimed to make screening more targeted, in this case prostate specific antigen screening. Estimates about PSA heritability vary from 40% to 45%, with genome-wide evaluations putting it at 25% to 30%, suggesting that incorporating genetic factors could improve screening.
This study involved 296,754 men (211,342 with European ancestry, 58,236 with African ancestry, 23,546 with Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 3630 with Asian ancestry; 96.5% of participants were from MVP)—a sample size more than triple that in previous work.
The researchers detected 448 genome-wide significant variants, including 295 that were novel (to the best of their knowledge). The variance explained by genome-wide polygenic risk scores ranged from 11.6% to 16.6% for European ancestry, 5.5% to 9.5% for African ancestry, 13.5% to 18.2% for Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 8.6% to 15.3% for Asian ancestry, and decreased with increasing age. Midlife genetically adjusted PSA levels were more strongly associated with overall and aggressive prostate cancer than unadjusted PSA levels.
The researchers say their study highlights how including higher proportions of participants from underrepresented populations can improve genetic prediction of PSA levels, offering the potential to personalize prostate cancer screening. Adjusting PSA for individuals’ predispositions in the absence of prostate cancer could improve the specificity (to reduce overdiagnosis) and sensitivity (to prevent more deaths) of screening.
Their findings, the researchers suggest, also explain additional variation in PSA, especially among men of African heritage, who experience the highest prostate cancer morbidity and mortality. They note that this work “moved us closer to leveraging genetic information to personalize PSA and substantially improved our understanding of PSA across diverse ancestries.”
A third study from a team at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System also investigated the risk of inheriting a predisposition to prostate cancer. These researchers explored pathogenic variants using both genome-wide single-allele and identity-by-descent analytic approaches. They then tested their candidate variants for replication across independent biobanks, including MVP.
The researchers discovered the gene WNT9B E152K more than doubled the risk of familial prostate cancer. Meta-analysis, collectively encompassing 500,000 patients, confirmed the genome-wide significance. The researchers say WNT9B shares an “unexpected commonality” with the previously established prostate cancer risk genes HOXB13 and HNF1B: Each are required for embryonic prostate development. Based on that finding, the researchers also evaluated 2 additional genes, KMT2D and DHCR7, which are known to cause Mendelian genitourinary developmental defects. They, too, were nominally associated with prostate cancer under meta-analyses.
Tens of thousands of participants in MVP have had prostate cancer. The genetic research they participate in advances detection, prediction, and treatment for themselves and others, and science in general. The research is not only about finding causes, but what to do if the cancer develops. An “acting on MVP prostate cancer findings” study at VA Puget Sound Health Care System is testing how communicating with veterans about MVP prostate cancer results will affect their care. Those with prostate cancer will be screened to determine genetic contributions to their cancers. Those found to have a gene-based cancer diagnosis will be offered genetic counseling. Their immediate family will also be offered screening to test for inherited prostate cancer risk.
In 2016, the VA partnered with the Prostate Cancer Foundation to establish the Precision Oncology Program for Cancer of the Prostate (POPCaP). In collaboration with MVP and the Genomic Medicine Service, the program uses genetic information to individualize treatments for veterans with advanced prostate cancer.
US Army Veteran James Perry is one of the beneficiaries of the program. First diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2001, he was initially treated with radiation therapy, but the cancer recurred and spread to his lung. The John J. Cochran Veterans Hospital in St. Louis sent a sample of Perry's lung tumor to the laboratory for genetic testing, where they discovered he had a BRCA1 gene mutation.
His oncologist, Dr. Martin Schoen, recommended Perry enroll in AMPLITUDE, a clinical trial testing the effectiveness of poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, a new class of drugs to treat hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. One year later, Perry’s lung tumor could barely be seen on computed tomography, and his PSA levels were undetectable.
"I would highly recommend enrolling in a trial," Perry told VA Research Currents. “If a veteran has that opportunity, I would encourage it—anything that is going to give you a few more days is worth it.” In the interview, Perry said he enjoyed being part of the trial because he knows he is getting the most advanced care possible and is proud to help others like himself.
"We are honored to support VA's work to improve the lives of veterans who are living with advanced prostate cancer," Vice President and National Director of the PCF Veterans Health Initiative Rebecca Levine said. "Clinical trials play a vital role in bringing new treatments to patients who need them most. Mr. Perry's experience illustrates VA's commitment to provide state-of-the-art cancer care to all veterans who need it."
About 15,000 veterans are annually diagnosed with prostate cancer. Fortunately, those veterans enrolled in the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Million Veteran Program (MVP) provide researchers with a deep pool of genetic data that can help identify causes, aid diagnosis, and guide targeted treatments.
More than 1,000,000 veterans have enrolled in MVP and donated their anonymized DNA to foster research. It is also one of the most genetically diverse health-related databases: 20% of participants identify as Black, 8% as Hispanic, 2% as Asian American, and 1% as Native American.
Ethnically and racially diverse data are particularly important for advancing the treatment of underserved groups. In a 2020 review, researchers found a number of areas where Black veterans differed from White veterans, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, incidence (almost 60% higher), clinical course, and mortality rate (2 to 3 times greater). To facilitate research, the MVP developed the “DNA chip,” a custom-designed tool that tests for > 750,000 genetic variants, including > 300,000 that are more common in minority populations.
“The whole thing about understanding genetics and diversity is like a circular feedback loop,” Director of MVP Dr. Sumitra Muralidhar said in a VA news article. “The more people you have represented from different racial and ethnic backgrounds, the more we’ll be able to discover genetic variants that contribute to their health. The more we discover, the more we can help that group. It’s a complete circular feedback loop.”
In addition to veterans’ blood samples and 600,000-plus baseline surveys on lifestyle, military service, and health, the MVP has collected upwards of 825,000 germline DNA samples, which have helped inform research into prostate cancer, the most commonly diagnosed solid tumor among veterans. By mining these data, researchers have built more evidence of how genes add to risk and disease progression.
In one study preprint that has not been peer reviewed, VA researchers investigated the significance of high polygenic hazard scores. The scores are strongly associated with age at diagnosis of any prostate cancer, as well as lifetime risk of metastatic and fatal prostate cancer. However, because they’re associated with any prostate cancer, the researchers say, there is concern that screening men with high polygenic risk could increase overdiagnosis of indolent cancers.
The researchers analyzed genetic and phenotypic data from 69,901 men in the MVP who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer (6413 metastatic). They found their hypothesis to be correct: Among men eventually diagnosed with prostate cancer, those with higher polygenic risk were more likely to develop metastatic disease.
Genetic risk scores like PHS601, a 601-variant polygenic score, can be performed on a saliva sample at any time during a person’s life, the researchers note. Thus, the scores provide the earliest information about age-specific risk of developing aggressive prostate cancer. These scores might be useful, they suggest, to support clinical decisions not only about whom to screen but also at what age.
Another study led by Stanford University researchers and published in Nature Genetics aimed to make screening more targeted, in this case prostate specific antigen screening. Estimates about PSA heritability vary from 40% to 45%, with genome-wide evaluations putting it at 25% to 30%, suggesting that incorporating genetic factors could improve screening.
This study involved 296,754 men (211,342 with European ancestry, 58,236 with African ancestry, 23,546 with Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 3630 with Asian ancestry; 96.5% of participants were from MVP)—a sample size more than triple that in previous work.
The researchers detected 448 genome-wide significant variants, including 295 that were novel (to the best of their knowledge). The variance explained by genome-wide polygenic risk scores ranged from 11.6% to 16.6% for European ancestry, 5.5% to 9.5% for African ancestry, 13.5% to 18.2% for Hispanic/Latino ancestry, and 8.6% to 15.3% for Asian ancestry, and decreased with increasing age. Midlife genetically adjusted PSA levels were more strongly associated with overall and aggressive prostate cancer than unadjusted PSA levels.
The researchers say their study highlights how including higher proportions of participants from underrepresented populations can improve genetic prediction of PSA levels, offering the potential to personalize prostate cancer screening. Adjusting PSA for individuals’ predispositions in the absence of prostate cancer could improve the specificity (to reduce overdiagnosis) and sensitivity (to prevent more deaths) of screening.
Their findings, the researchers suggest, also explain additional variation in PSA, especially among men of African heritage, who experience the highest prostate cancer morbidity and mortality. They note that this work “moved us closer to leveraging genetic information to personalize PSA and substantially improved our understanding of PSA across diverse ancestries.”
A third study from a team at the VA Tennessee Valley Healthcare System also investigated the risk of inheriting a predisposition to prostate cancer. These researchers explored pathogenic variants using both genome-wide single-allele and identity-by-descent analytic approaches. They then tested their candidate variants for replication across independent biobanks, including MVP.
The researchers discovered the gene WNT9B E152K more than doubled the risk of familial prostate cancer. Meta-analysis, collectively encompassing 500,000 patients, confirmed the genome-wide significance. The researchers say WNT9B shares an “unexpected commonality” with the previously established prostate cancer risk genes HOXB13 and HNF1B: Each are required for embryonic prostate development. Based on that finding, the researchers also evaluated 2 additional genes, KMT2D and DHCR7, which are known to cause Mendelian genitourinary developmental defects. They, too, were nominally associated with prostate cancer under meta-analyses.
Tens of thousands of participants in MVP have had prostate cancer. The genetic research they participate in advances detection, prediction, and treatment for themselves and others, and science in general. The research is not only about finding causes, but what to do if the cancer develops. An “acting on MVP prostate cancer findings” study at VA Puget Sound Health Care System is testing how communicating with veterans about MVP prostate cancer results will affect their care. Those with prostate cancer will be screened to determine genetic contributions to their cancers. Those found to have a gene-based cancer diagnosis will be offered genetic counseling. Their immediate family will also be offered screening to test for inherited prostate cancer risk.
In 2016, the VA partnered with the Prostate Cancer Foundation to establish the Precision Oncology Program for Cancer of the Prostate (POPCaP). In collaboration with MVP and the Genomic Medicine Service, the program uses genetic information to individualize treatments for veterans with advanced prostate cancer.
US Army Veteran James Perry is one of the beneficiaries of the program. First diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2001, he was initially treated with radiation therapy, but the cancer recurred and spread to his lung. The John J. Cochran Veterans Hospital in St. Louis sent a sample of Perry's lung tumor to the laboratory for genetic testing, where they discovered he had a BRCA1 gene mutation.
His oncologist, Dr. Martin Schoen, recommended Perry enroll in AMPLITUDE, a clinical trial testing the effectiveness of poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, a new class of drugs to treat hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. One year later, Perry’s lung tumor could barely be seen on computed tomography, and his PSA levels were undetectable.
"I would highly recommend enrolling in a trial," Perry told VA Research Currents. “If a veteran has that opportunity, I would encourage it—anything that is going to give you a few more days is worth it.” In the interview, Perry said he enjoyed being part of the trial because he knows he is getting the most advanced care possible and is proud to help others like himself.
"We are honored to support VA's work to improve the lives of veterans who are living with advanced prostate cancer," Vice President and National Director of the PCF Veterans Health Initiative Rebecca Levine said. "Clinical trials play a vital role in bringing new treatments to patients who need them most. Mr. Perry's experience illustrates VA's commitment to provide state-of-the-art cancer care to all veterans who need it."
AVAHO Encourages Members to Make Voices Heard
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
Advocacy for veterans with cancer has always been a central part of the Association for VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO) mission, but that advocacy has now taken on a new focus: the fate of US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) employees. The advocacy portal provides templated letters, a search function to find local Senators and Members of Congress, a search function to find regional media outlets, updates on voting and elections, and information on key legislation relevant to VA health care.
To ensure its members’ concerns are heard, AVAHO is encouraging members, in their own time and as private citizens, to contact their local representatives to inform them about the real impact of recent policy changes on VA employees and the veterans they care for. Members can select any of 4 letters focused on reductions in force, cancellation of VA contracts, the return to office mandate, and the National Institutes of Health’s proposed cap on indirect cost for research grants: “AVAHO recognizes the power of the individual voice. Our members have an important role in shaping the health care services provided to veterans across our nation.”
"The contracts that have been canceled and continue to be canceled included critical services related to cancer care," AVAHO notes on its Advocacy page. "We know these impacted contracts have hindered the VA’s ability to implement research protocols, process and report pharmacogenomic results, manage Electronic Health Record Modernization workgroups responsible for safety improvements, and execute new oncology services through the Close to Me initiative, just to name a few."
Service Connection Expanded to Additional Cancers
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is "lowering the burden of proof" for thousands, making acute and chronic leukemias, multiple myelomas, myelodysplastic syndromes, myelofibrosis, urinary bladder, ureter, and related genitourinary cancers presumptive for service connection.
The Jan. 8 decision included Gulf War veterans, those who served in Somalia or the Southwest Asia theater of operations during the Persian Gulf War on or after Aug. 2, 1990; and post-9/11 veterans, those who served in Afghanistan, Iraq, Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, or Uzbekistan and the airspace above these locations during the Gulf War on or after Sept. 11, 2001. It also includes veterans who served at the Karshi-Khanabad (K2) base in Uzbekistan after Sept. 11, 2001.
Veterans no longer must prove their service caused their condition to receive benefits. This landmark decision allows them access to free health care for that condition.
According to the VA, these steps are also part of a comprehensive effort to ensure that K2 veterans—and their survivors—receive the care and benefits they deserve. K2 veterans have higher claim and approval rates than any other cohort of veterans: 13,002 are enrolled in VA health care, and the average K2 veteran is service connected for 14.6 conditions.
The 2022 PACT Act was the largest expansion of veteran benefits in generations. The VA then made millions of veterans eligible for health care and benefits years earlier than called for by the law. It also launched the largest outreach campaign in the history of the VA to encourage veterans to apply.
Nearly 890,000 veterans have signed up for VA health care since the bill was signed into law, a nearly 40% increase over the previous equivalent period, and veterans have submitted > 4.8 million applications for VA benefits (a 42% increase over the previous equivalent period and an all-time record). The VA has delivered > $600 billion in earned benefits directly to veterans, their families, and survivors during that time.
The VA encourages all eligible veterans—including those with previously denied claims—to apply for benefits. To apply for benefits, veterans and survivors may visit VA.gov or call 1-800-MYVA411.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is "lowering the burden of proof" for thousands, making acute and chronic leukemias, multiple myelomas, myelodysplastic syndromes, myelofibrosis, urinary bladder, ureter, and related genitourinary cancers presumptive for service connection.
The Jan. 8 decision included Gulf War veterans, those who served in Somalia or the Southwest Asia theater of operations during the Persian Gulf War on or after Aug. 2, 1990; and post-9/11 veterans, those who served in Afghanistan, Iraq, Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, or Uzbekistan and the airspace above these locations during the Gulf War on or after Sept. 11, 2001. It also includes veterans who served at the Karshi-Khanabad (K2) base in Uzbekistan after Sept. 11, 2001.
Veterans no longer must prove their service caused their condition to receive benefits. This landmark decision allows them access to free health care for that condition.
According to the VA, these steps are also part of a comprehensive effort to ensure that K2 veterans—and their survivors—receive the care and benefits they deserve. K2 veterans have higher claim and approval rates than any other cohort of veterans: 13,002 are enrolled in VA health care, and the average K2 veteran is service connected for 14.6 conditions.
The 2022 PACT Act was the largest expansion of veteran benefits in generations. The VA then made millions of veterans eligible for health care and benefits years earlier than called for by the law. It also launched the largest outreach campaign in the history of the VA to encourage veterans to apply.
Nearly 890,000 veterans have signed up for VA health care since the bill was signed into law, a nearly 40% increase over the previous equivalent period, and veterans have submitted > 4.8 million applications for VA benefits (a 42% increase over the previous equivalent period and an all-time record). The VA has delivered > $600 billion in earned benefits directly to veterans, their families, and survivors during that time.
The VA encourages all eligible veterans—including those with previously denied claims—to apply for benefits. To apply for benefits, veterans and survivors may visit VA.gov or call 1-800-MYVA411.
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) is "lowering the burden of proof" for thousands, making acute and chronic leukemias, multiple myelomas, myelodysplastic syndromes, myelofibrosis, urinary bladder, ureter, and related genitourinary cancers presumptive for service connection.
The Jan. 8 decision included Gulf War veterans, those who served in Somalia or the Southwest Asia theater of operations during the Persian Gulf War on or after Aug. 2, 1990; and post-9/11 veterans, those who served in Afghanistan, Iraq, Djibouti, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, or Uzbekistan and the airspace above these locations during the Gulf War on or after Sept. 11, 2001. It also includes veterans who served at the Karshi-Khanabad (K2) base in Uzbekistan after Sept. 11, 2001.
Veterans no longer must prove their service caused their condition to receive benefits. This landmark decision allows them access to free health care for that condition.
According to the VA, these steps are also part of a comprehensive effort to ensure that K2 veterans—and their survivors—receive the care and benefits they deserve. K2 veterans have higher claim and approval rates than any other cohort of veterans: 13,002 are enrolled in VA health care, and the average K2 veteran is service connected for 14.6 conditions.
The 2022 PACT Act was the largest expansion of veteran benefits in generations. The VA then made millions of veterans eligible for health care and benefits years earlier than called for by the law. It also launched the largest outreach campaign in the history of the VA to encourage veterans to apply.
Nearly 890,000 veterans have signed up for VA health care since the bill was signed into law, a nearly 40% increase over the previous equivalent period, and veterans have submitted > 4.8 million applications for VA benefits (a 42% increase over the previous equivalent period and an all-time record). The VA has delivered > $600 billion in earned benefits directly to veterans, their families, and survivors during that time.
The VA encourages all eligible veterans—including those with previously denied claims—to apply for benefits. To apply for benefits, veterans and survivors may visit VA.gov or call 1-800-MYVA411.
Highlights in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia From ASH 2024
Highlights in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia From ASH 2024

Studies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment in frontline and relapsed/refractory settings, presented at the American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2024 Annual Meeting and Exposition, are discussed by Dr Muhammad Jawad Javed of Albany Medical Center and Stratton VA.
Dr Javed begins with the AMPLIFY trial, the first phase 3 study to evaluate a fixed-duration regimen of venetoclax with a second-generation BTK inhibitor. AMPLIFY compares three frontline treatment arms: (1) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax (AV); (2) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax plus obinutuzumab (AVO); and (3) chemoimmunotherapy. Results showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the AV and AVO groups.
The next frontline treatment study he discusses examined use of minimal residual disease testing to guide treatment duration of a venetoclax/obinutuzumab regimen. The study found that shorter treatment duration led to PFS comparable to that achieved by longer duration.
Dr Javed next turns to a retrospective analysis of the impact of first-line treatment choice on the risk for other malignancies, using data from the Department of US Veteran Affairs Central Cancer Registry.
In relapsed/refractory disease, Dr Javed highlights the BRUIN CLL-321 study of the noncovalent reversible BTK inhibitor pirtobrutinib. Pirtobrutinib improved PFS compared with chemoimmunotherapy.
Last, he discusses epcoritamab, which yielded encouraging complete response data in heavily pretreated CLL patients.
--
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, Albany Medical Center/Stratton VA Albany, Department of Medicine; Resident Physician, Department of Internal Medicine, Albany Medical Center, Albany, New York
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships

Studies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment in frontline and relapsed/refractory settings, presented at the American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2024 Annual Meeting and Exposition, are discussed by Dr Muhammad Jawad Javed of Albany Medical Center and Stratton VA.
Dr Javed begins with the AMPLIFY trial, the first phase 3 study to evaluate a fixed-duration regimen of venetoclax with a second-generation BTK inhibitor. AMPLIFY compares three frontline treatment arms: (1) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax (AV); (2) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax plus obinutuzumab (AVO); and (3) chemoimmunotherapy. Results showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the AV and AVO groups.
The next frontline treatment study he discusses examined use of minimal residual disease testing to guide treatment duration of a venetoclax/obinutuzumab regimen. The study found that shorter treatment duration led to PFS comparable to that achieved by longer duration.
Dr Javed next turns to a retrospective analysis of the impact of first-line treatment choice on the risk for other malignancies, using data from the Department of US Veteran Affairs Central Cancer Registry.
In relapsed/refractory disease, Dr Javed highlights the BRUIN CLL-321 study of the noncovalent reversible BTK inhibitor pirtobrutinib. Pirtobrutinib improved PFS compared with chemoimmunotherapy.
Last, he discusses epcoritamab, which yielded encouraging complete response data in heavily pretreated CLL patients.
--
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, Albany Medical Center/Stratton VA Albany, Department of Medicine; Resident Physician, Department of Internal Medicine, Albany Medical Center, Albany, New York
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships

Studies in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment in frontline and relapsed/refractory settings, presented at the American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2024 Annual Meeting and Exposition, are discussed by Dr Muhammad Jawad Javed of Albany Medical Center and Stratton VA.
Dr Javed begins with the AMPLIFY trial, the first phase 3 study to evaluate a fixed-duration regimen of venetoclax with a second-generation BTK inhibitor. AMPLIFY compares three frontline treatment arms: (1) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax (AV); (2) acalabrutinib plus venetoclax plus obinutuzumab (AVO); and (3) chemoimmunotherapy. Results showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the AV and AVO groups.
The next frontline treatment study he discusses examined use of minimal residual disease testing to guide treatment duration of a venetoclax/obinutuzumab regimen. The study found that shorter treatment duration led to PFS comparable to that achieved by longer duration.
Dr Javed next turns to a retrospective analysis of the impact of first-line treatment choice on the risk for other malignancies, using data from the Department of US Veteran Affairs Central Cancer Registry.
In relapsed/refractory disease, Dr Javed highlights the BRUIN CLL-321 study of the noncovalent reversible BTK inhibitor pirtobrutinib. Pirtobrutinib improved PFS compared with chemoimmunotherapy.
Last, he discusses epcoritamab, which yielded encouraging complete response data in heavily pretreated CLL patients.
--
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, Albany Medical Center/Stratton VA Albany, Department of Medicine; Resident Physician, Department of Internal Medicine, Albany Medical Center, Albany, New York
Muhammad Jawad Javed, MBBS, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships
Highlights in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia From ASH 2024
Highlights in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia From ASH 2024

Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
VA Cancer Clinical Trials as a Strategy for Increasing Accrual of Racial and Ethnic Underrepresented Groups
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.

Patient Navigators for Serious Illnesses Can Now Bill Under New Medicare Codes
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a move that acknowledges the gauntlet the US health system poses for people facing serious and fatal illnesses, Medicare will pay for a new class of workers to help patients manage treatments for conditions like cancer and heart failure.
The 2024 Medicare physician fee schedule includes new billing codes, including G0023, to pay for 60 minutes a month of care coordination by certified or trained auxiliary personnel working under the direction of a clinician.
A diagnosis of cancer or another serious illness takes a toll beyond the physical effects of the disease. Patients often scramble to make adjustments in family and work schedules to manage treatment, said Samyukta Mullangi, MD, MBA, medical director of oncology at Thyme Care, a Nashville, Tennessee–based firm that provides navigation and coordination services to oncology practices and insurers.
“It just really does create a bit of a pressure cooker for patients,” Dr. Mullangi told this news organization.
Medicare has for many years paid for medical professionals to help patients cope with the complexities of disease, such as chronic care management (CCM) provided by physicians, nurses, and physician assistants.
The new principal illness navigation (PIN) payments are intended to pay for work that to date typically has been done by people without medical degrees, including those involved in peer support networks and community health programs. The US Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services(CMS) expects these navigators will undergo training and work under the supervision of clinicians.
The new navigators may coordinate care transitions between medical settings, follow up with patients after emergency department (ED) visits, or communicate with skilled nursing facilities regarding the psychosocial needs and functional deficits of a patient, among other functions.
CMS expects the new navigators may:
- Conduct assessments to understand a patient’s life story, strengths, needs, goals, preferences, and desired outcomes, including understanding cultural and linguistic factors.
- Provide support to accomplish the clinician’s treatment plan.
- Coordinate the receipt of needed services from healthcare facilities, home- and community-based service providers, and caregivers.
Peers as Navigators
The new navigators can be former patients who have undergone similar treatments for serious diseases, CMS said. This approach sets the new program apart from other care management services Medicare already covers, program officials wrote in the 2024 physician fee schedule.
“For some conditions, patients are best able to engage with the healthcare system and access care if they have assistance from a single, dedicated individual who has ‘lived experience,’ ” according to the rule.
The agency has taken a broad initial approach in defining what kinds of illnesses a patient may have to qualify for services. Patients must have a serious condition that is expected to last at least 3 months, such as cancer, heart failure, or substance use disorder.
But those without a definitive diagnosis may also qualify to receive navigator services.
In the rule, CMS cited a case in which a CT scan identified a suspicious mass in a patient’s colon. A clinician might decide this person would benefit from navigation services due to the potential risks for an undiagnosed illness.
“Regardless of the definitive diagnosis of the mass, presence of a colonic mass for that patient may be a serious high-risk condition that could, for example, cause obstruction and lead the patient to present to the emergency department, as well as be potentially indicative of an underlying life-threatening illness such as colon cancer,” CMS wrote in the rule.
Navigators often start their work when cancer patients are screened and guide them through initial diagnosis, potential surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, said Sharon Gentry, MSN, RN, a former nurse navigator who is now the editor in chief of the Journal of the Academy of Oncology Nurse & Patient Navigators.
The navigators are meant to be a trusted and continual presence for patients, who otherwise might be left to start anew in finding help at each phase of care.
The navigators “see the whole picture. They see the whole journey the patient takes, from pre-diagnosis all the way through diagnosis care out through survival,” Ms. Gentry said.
Gaining a special Medicare payment for these kinds of services will elevate this work, she said.
Many newer drugs can target specific mechanisms and proteins of cancer. Often, oncology treatment involves testing to find out if mutations are allowing the cancer cells to evade a patient’s immune system.
Checking these biomarkers takes time, however. Patients sometimes become frustrated because they are anxious to begin treatment. Patients may receive inaccurate information from friends or family who went through treatment previously. Navigators can provide knowledge on the current state of care for a patient’s disease, helping them better manage anxieties.
“You have to explain to them that things have changed since the guy you drink coffee with was diagnosed with cancer, and there may be a drug that could target that,” Ms. Gentry said.
Potential Challenges
Initial uptake of the new PIN codes may be slow going, however, as clinicians and health systems may already use well-established codes. These include CCM and principal care management services, which may pay higher rates, Mullangi said.
“There might be sensitivity around not wanting to cannibalize existing programs with a new program,” Dr. Mullangi said.
In addition, many patients will have a copay for the services of principal illness navigators, Dr. Mullangi said.
While many patients have additional insurance that would cover the service, not all do. People with traditional Medicare coverage can sometimes pay 20% of the cost of some medical services.
“I think that may give patients pause, particularly if they’re already feeling the financial burden of a cancer treatment journey,” Dr. Mullangi said.
Pay rates for PIN services involve calculations of regional price differences, which are posted publicly by CMS, and potential added fees for services provided by hospital-affiliated organizations.
Consider payments for code G0023, covering 60 minutes of principal navigation services provided in a single month.
A set reimbursement for patients cared for in independent medical practices exists, with variation for local costs. Medicare’s non-facility price for G0023 would be $102.41 in some parts of Silicon Valley in California, including San Jose. In Arkansas, where costs are lower, reimbursement would be $73.14 for this same service.
Patients who get services covered by code G0023 in independent medical practices would have monthly copays of about $15-$20, depending on where they live.
The tab for patients tends to be higher for these same services if delivered through a medical practice owned by a hospital, as this would trigger the addition of facility fees to the payments made to cover the services. Facility fees are difficult for the public to ascertain before getting a treatment or service.
Dr. Mullangi and Ms. Gentry reported no relevant financial disclosures outside of their employers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

Improving Colorectal Cancer Screening via Mailed Fecal Immunochemical Testing in a Veterans Affairs Health System
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is among the most common cancers and causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States.1 Reflective of a nationwide trend, CRC screening rates at the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System (VACHS) decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic.2-5 Contributing factors to this decrease included cancellations of elective colonoscopies during the initial phase of the pandemic and concurrent turnover of endoscopists. In 2021, the US Preventive Services Task Force lowered the recommended initial CRC screening age from 50 years to 45 years, further increasing the backlog of unscreened patients.6
Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) is a noninvasive screening method in which antibodies are used to detect hemoglobin in the stool. The sensitivity and specificity of 1-time FIT are 79% to 80% and 94%, respectively, for the detection of CRC, with sensitivity improving with successive testing.7,8 Annual FIT is recognized as a tier 1 preferred screening method by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer.7,9 Programs that mail FIT kits to eligible patients outside of physician visits have been successfully implemented in health care systems.10,11
The VACHS designed and implemented a mailed FIT program using existing infrastructure and staffing.
Program Description
A team of local stakeholders comprised of VACHS leadership, primary care, nursing, and gastroenterology staff, as well as representatives from laboratory, informatics, mail services, and group practice management, was established to execute the project. The team met monthly to plan the project.
The team developed a dataset consisting of patients aged 45 to 75 years who were at average risk for CRC and due for CRC screening. Patients were defined as due for CRC screening if they had not had a colonoscopy in the previous 9 years or a FIT or fecal occult blood test in the previous 11 months. Average risk for CRC was defined by excluding patients with associated diagnosis codes for CRC, colectomy, inflammatory bowel disease, and anemia. The program also excluded patients with diagnosis codes associated with dementia, deferring discussions about cancer screening to their primary care practitioners (PCPs). Patients with invalid mailing addresses were also excluded, as well as those whose PCPs had indicated in the electronic health record that the patient received CRC screening outside the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) system.
Letter Templates
Two patient letter electronic health record templates were developed. The first was a primer letter, which was mailed to patients 2 to 3 weeks before the mailed FIT kit as an introduction to the program.12 The purpose of the primer letter was to give advance notice to patients that they could expect a FIT kit to arrive in the mail. The goal was to prepare patients to complete FIT when the kit arrived and prompt them to call the VA to opt out of the mailed FIT program if they were up to date with CRC screening or if they had a condition which made them at high risk for CRC.
The second FIT letter arrived with the FIT kit, introduced FIT and described the importance of CRC screening. The letter detailed instructions for completing FIT and automatically created a FIT order. It also included a list of common conditions that may exclude patients, with a recommendation for patients to contact their medical team if they felt they were not candidates for FIT.
Staff Education
A previous VACHS pilot project demonstrated the success of a mailed FIT program to increase FIT use. Implemented as part of the pilot program, staff education consisted of a session for clinicians about the role of FIT in CRC screening and an all-staff education session. An additional education session about CRC and FIT for all staff was repeated with the program launch.
Program Launch
The mailed FIT program was introduced during a VACHS primary care all-staff meeting. After the meeting, each patient aligned care team (PACT) received an encrypted email that included a list of the patients on their team who were candidates for the program, a patient-facing FIT instruction sheet, detailed instructions on how to send the FIT primer letter, and a FIT package consisting of the labeled FIT kit, FIT letter, and patient instruction sheet. A reminder letter was sent to each patient 3 weeks after the FIT package was mailed. The patient lists were populated into a shared, encrypted Microsoft Teams folder that was edited in real time by PACT teams and viewed by VACHS leadership to track progress.
Program Metrics
At program launch, the VACHS had 4642 patients due for CRC screening who were eligible for the mailed FIT program. On March 7, 2023, the data consisting of FIT tests ordered between December 2022 and May 2023—3 months before and after the launch of the program—were reviewed and categorized. In the 3 months before program launch, 1528 FIT were ordered and 714 were returned (46.7%). In the 3 months after the launch of the program, 4383 FIT were ordered and 1712 were returned (39.1%) (Figure). Test orders increased 287% from the preintervention to the postintervention period. The mean (SD) number of monthly FIT tests prelaunch was 509 (32.7), which increased to 1461 (331.6) postlaunch.
At the VACHS, 61.4% of patients aged 45 to 75 years were up to date with CRC screening before the program launch. In the 3 months after program launch, the rate increased to 63.8% among patients aged 45 to 75 years, the highest rate in our Veterans Integrated Services Network and exceeding the VA national average CRC screening rate, according to unpublished VA Monthly Management Report data.
In the 3 months following the program launch, 139 FIT kits tested positive for potential CRC. Of these, 79 (56.8%) patients had completed a diagnostic colonoscopy. PACT PCPs and nurses received reports on patients with positive FIT tests and those with no colonoscopy scheduled or completed and were asked to follow up.
Discussion
Through a proactive, population-based CRC screening program centered on mailed FIT kits outside of the traditional patient visit, the VACHS increased the use of FIT and rates of CRC screening. The numbers of FIT kits ordered and completed substantially increased in the 3 months after program launch.
Compared to mailed FIT programs described in the literature that rely on centralized processes in that a separate team operates the mailed FIT program for the entire organization, this program used existing PACT infrastructure and staff.10,11 This strategy allowed VACHS to design and implement the program in several months. Not needing to hire new staff or create a central team for the sole purpose of implementing the program allowed us to save on any organizational funding and efforts that would have accompanied the additional staff. The program described in this article may be more attainable for primary care practices or smaller health systems that do not have the capacity for the creation of a centralized process.
Limitations
Although the total number of FIT completions substantially increased during the program, the rate of FIT completion during the mailed FIT program was lower than the rate of completion prior to program launch. This decreased rate of FIT kit completion may be related to separation from a patient visit and potential loss of real-time education with a clinician. The program’s decentralized design increased the existing workload for primary care staff, and as a result, consideration must be given to local staffing levels. Additionally, the report of eligible patients depended on diagnosis codes and may have captured patients with higher-than-average risk of CRC, such as patients with prior history of adenomatous polyps, family history of CRC, or other medical or genetic conditions. We attempted to mitigate this by including a list of conditions that would exclude patients from FIT eligibility in the FIT letter and giving them the option to opt out.
Conclusions
CRC screening rates improved following implementation of a primary care team-centered quality improvement process to proactively identify patients appropriate for FIT and mail them FIT kits. This project highlights that population-health interventions around CRC screening via use of FIT can be successful within a primary care patient-centered medical home model, considering the increases in both CRC screening rates and increase in FIT tests ordered.
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
1. American Cancer Society. Key statistics for colorectal cancer. Revised January 29, 2024. Accessed June 11, 2024. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/colon-rectal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
2. Chen RC, Haynes K, Du S, Barron J, Katz AJ. Association of cancer screening deficit in the United States with the COVID-19 pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(6):878-884. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.0884
3. Mazidimoradi A, Tiznobaik A, Salehiniya H. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: a systematic review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2022;53(3):730-744. doi:10.1007/s12029-021-00679-x
4. Adams MA, Kurlander JE, Gao Y, Yankey N, Saini SD. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on screening colonoscopy utilization in a large integrated health system. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(7):2098-2100.e2. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.02.034
5. Sundaram S, Olson S, Sharma P, Rajendra S. A review of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening: implications and solutions. Pathogens. 2021;10(11):558. doi:10.3390/pathogens10111508
6. US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
7. Robertson DJ, Lee JK, Boland CR, et al. Recommendations on fecal immunochemical testing to screen for colorectal neoplasia: a consensus statement by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(1):2-21.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.025
8. Lee JK, Liles EG, Bent S, Levin TR, Corley DA. Accuracy of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(3):171. doi:10.7326/M13-1484
9. Rex DK, Boland CR, Dominitz JA, et al. Colorectal cancer screening: recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(1):307-323. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.013
10. Deeds SA, Moore CB, Gunnink EJ, et al. Implementation of a mailed faecal immunochemical test programme for colorectal cancer screening among veterans. BMJ Open Qual. 2022;11(4):e001927. doi:10.1136/bmjoq-2022-001927
11. Selby K, Jensen CD, Levin TR, et al. Program components and results from an organized colorectal cancer screening program using annual fecal immunochemical testing. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(1):145-152. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.042
12. Deeds S, Liu T, Schuttner L, et al. A postcard primer prior to mailed fecal immunochemical test among veterans: a randomized controlled trial. J Gen Intern Med. 2023:38(14):3235-3241. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08248-7
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The War on Cancer, declared by President Richard Nixon some 50 years ago, has been canceled during the second Trump administration in 2025 — so saith The New York Times Sunday magazine cover story on September 14, 2025. This war seems now to be best described as "The War on Cancer Research."
To our horror and disbelief, we've witnessed the slow but persistent drift of much of the United States citizenry away from science and the sudden and severe movement of the US government to crush much medical research. But it is not as if we were not warned.
In August 2024, on these pages and without political bias, I urged Medscape readers to pay attention to Project 2025. A great deal of what we as a population are now experiencing was laid out as a carefully constructed plan.
What is surprising is the cruel ruthlessness of the "move fast and break things" approach, taken with little apparent concern about the resultant human tragedies (workforce and patients) and no clear care about the resulting fallout. As we've now learned, destroying something as grand as our cancer research enterprise can be accomplished very quickly. Rebuilding it is certain to be slow and difficult and perhaps can never be accomplished.
In this new anti-science, anti-research, and anti-researcher reality, what can we now do?
First and foremost, we must recognize that the war on cancer is not over. Cancer is not canceled, even if much of the US government's research effort/funding has been. Those of us in medicine and public health often speak in quantification of causes of death of our populations. As such, I'll remind Medscape readers that cancer afflicts some 20 million humans worldwide each year, killing nearly 10 million. Although two-thirds of Americans diagnosed with a potentially lethal malignancy are cured, cancer still kills roughly 600,000 Americans each year. Cancer has been the second most frequent cause of death of Americans for 75 years.
Being inevitable and immutable, death itself is not the enemy. We all die. Disease, disability, pain, and human suffering are the real enemies of us all. Cancer maims, pains, diabetes, and torments some 20 million humans worldwide each year. That is a huge humanitarian problem that should be recognized by individuals of all creeds and backgrounds.
With this depletion of our domestic government basic and applied cancer research program, what can we do?
- Think globally and look to the international scientific research enterprises — relying on them, much as they have relied on us.
- Defend the universal importance of reliable and available literature on medical science.
- Continue to translate and apply the vast amount of available published research in clinical practice and publish the results.
- Urge private industries to expand their research budgets into areas of study that may not produce quickly tangible positive bottom-line results.
- Remind the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services (for whom chronic diseases seem paramount) that cancer is the second leading American chronic disease by morbidity.
- Redouble efforts of cancer prevention, especially urging the FDA to ban combustible tobacco and strive more diligently to decrease obesity.
- Appeal to our vast philanthropic universe to increase its funding of nonprofit organizations active in the cancer investigation, diagnosis, and management space.
One such 501c3 organization is California-based Cancer Commons. (Disclosure: I named it in 2010 and serve as its editor in chief).
A commons is a space shared by a community to use for the common interest. As we originally envisioned it, a cancer commons is an open access internet location where individuals and organizations (eg, corporations, universities, government agencies, philanthropies) will voluntarily share their data to work together to defeat the common enemy of humans: cancer.
On September 8, 2025, Cancer Commons was the 15th annual Lundberg Institute Lecturer at the Commonwealth Club of California in San Francisco. At the lecture, Cancer Commons founder (and long-term survivor of metastatic malignant melanoma), Jay Martin "Martin" Tenenbaum, PhD, spoke of the need for a cancer commons and the founder's vision. Emma Shtivelman, PhD, the long-time compassionate chief scientist, described some of the thousands of patients with advanced cancer that she has helped — all free of charge. And newly named CEO Clifford Reid, MBA, PhD, used his entrepreneurial prowess to envision an ambitious future.
Cancer Commons has always focused on patients with cancer who are beyond standards of curative care. As Cancer Commons evolves, it anticipates focusing on patients with cancer who are beyond National Comprehensive Cancer Network Guidelines. The organization intends to greatly expand its 1000 patients per year with "high touch" engagement with PhD clinical scientists to many thousands by including artificial intelligence. It plans to extend its N-of-One approach to create new knowledge — especially regarding the hundreds of drugs that are FDA-approved for use in treating cancer but have not been further assessed for the utility in actually treating patients with cancer.
The war on cancer is not over. It remains a persistent foe that causes immense disability, pain, and human suffering. With government support depleted, the burden now shifts to the private sector and philanthropic organizations, such as Cancer Commons, to serve as the new vital infrastructure in the fight for a cure. Now, we must redouble our efforts to ensure that these research endeavors are supported if the US government will not do its part.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity
Turning the Cancer Research Problem Into an Opportunity