User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Seven ways doctors could get better payment from insurers
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say experts in physician-payer contracts.
Many doctors sign long-term agreements and then forget about them, says Marcia Brauchler, president and founder of Physicians’ Ally, Littleton, Colorado, a health care consulting company. “The average doctor is trying to run a practice on 2010 rates because they haven’t touched their insurance contracts for 10 years,” she says.
Payers also make a lot of money by adopting dozens of unilateral policy and procedure changes every year that they know physicians are too busy to read. They are counting on the fact that few doctors will understand what the policy changes are and that even fewer will contest them, says Greg Brodek, JD, chair of the health law practice group and head of the managed care litigation practice at Duane Morris, who represents doctors in disputes with payers.
These experts say doctors can push back on one-sided payer contracts and negotiate changes. Mr. Brodek says some practices have more leverage than others to influence payers – if they are larger, in a specialty that the payer needs in its network, or located in a remote area where the payer has limited options.
Here are seven key areas to pay attention to:
1. Long-term contracts. Most doctors sign multiyear “evergreen” contracts that renew automatically every year. This allows insurers to continue to pay doctors the same rate for years.
To avoid this, doctors should negotiate new rates when their agreements renew or, if they prefer, ask that a cost-of-living adjustment be included in the multiyear contract that applies to subsequent years, says Ms. Brauchler.
2. Fee schedules. Payers will “whitewash” what they’re paying you by saying it’s 100% of the payer fee schedule. When it comes to Medicare, they may be paying you a lot less, says Ms. Brauchler.
“My biggest takeaway is to compare the CPT codes of the payer’s fee schedule against what Medicare allows. For example, for CPT code 99213, a 15-minute established office visit, if Medicare pays you $100 and Aetna pays you $75.00, you’re getting 75% of Medicare,” says Ms. Brauchler. To avoid this, doctors should ask that the contract state that reimbursement be made according to Medicare’s medical policies rather than the payer’s.
3. Audits. Commercial payers will claim they have a contractual right to conduct pre- and post-payment audits of physicians’ claims that can result in reduced payments. The contract only states that if doctors correctly submit claims, they will get paid, not that they will have to go through extra steps, which is a breach of their agreement, says Mr. Brodek.
In his experience, 90% of payers back down when asked to provide the contractual basis to conduct these audits. “Or, they take the position that it’s not in the contract but that they have a policy.”
4. Contract amendments versus policies and procedures. This is a huge area that needs to be clarified in contracts and monitored by providers throughout their relationships with payers. Contracts have three elements: the parties, the services provided, and the payment. Changing any one of those terms requires an amendment and advance written notice that has to be delivered to the other party in a certain way, such as by overnight delivery, says Mr. Brodek.
In addition, both parties have to sign that they agree to an amendment. “But, that’s too cumbersome and complicated for payers who have decided to adopt policies instead. These are unilateral changes made with no advance notice given, since the payer typically posts the change on its website,” says Mr. Brodek.
5. Recoupment efforts. Payers will review claims after they’re paid and contact the doctor saying they found a mistake, such as inappropriate coding. They will claim that the doctor now owes them a large sum of money based on a percentage of claims reviewed. “They typically send the doctor a letter that ends with, ‘If you do not pay this amount within 30 days, we will offset the amount due against future payments that we would otherwise make to you,’” says Mr. Brodek.
He recommends that contracts include the doctors’ right to contest an audit so the “payer doesn’t have the unilateral right to disregard the initial coding that the doctor appropriately assigned to the claim and recoup the money anyway,” says Mr. Brodek.
6. Medical network rentals and products. Most contracts say that payers can rent out their medical networks to other health plans, such as HMOs, and that the clinicians agree to comply with all of their policies and procedures. The agreement may also cover the products of other plans.
“The problem is that physicians are not given information about the other plans, including their terms and conditions for getting paid,” says Mr. Brodek. If a problem with payment arises, they have no written agreement with that plan, which makes it harder to enforce.
“That’s why we recommend that doctors negotiate agreements that only cover the main payer. Most of the time, the payer is amenable to putting that language in the contract,” he says.
7. Payer products. In the past several years, a typical contract has included appendices that list the payer’s products, such as Medicare, workers compensation, auto insurance liability, or health care exchange products. Many clinicians don’t realize they can pick the plans they want to participate in by accepting or opting out, says Mr. Brodek.
“We advise clients to limit the contract to what you want covered and to make informed decisions, because some products have low fees set by the states, such as workers compensation and health care exchanges,” says Mr. Brodek.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gut bacteria linked with long COVID
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
While links have been found between the gut’s microbiome and COVID-19, as well as other diseases, this is the first published research to show a link specifically to COVID’s long-term effects, the investigators, based at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, wrote in Gut.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that altered gut microbiome composition is strongly associated with persistent symptoms in patients with COVID-19 up to 6 months after clearance of SARS-CoV-2 virus,” said Siew Ng, MBBS, PhD, associate director at the university’s Center for Gut Microbiota Research.
At three hospitals, the researchers enrolled 106 patients with COVID-19 from February to August 2020 with stool samples at admission and at 1 month and 6 months after discharge, and compared them with people who did not have COVID, recruited in 2019. The severity of COVID in the enrolled patients was mostly mild to moderate.
At 3 months, 86 of the patients with COVID had post–acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS) – defined as at least one persistent, otherwise unexplained symptom 4 weeks after clearance of the virus. And 81 patients had PACS at 6 months, most commonly fatigue, poor memory, hair loss, anxiety, and trouble sleeping.
Using stool samples for their analysis, the researchers found that, broadly, the diversity of the types of bacteria, and the abundance of these bacteria, were significantly lower at 6 months for those with PACS, compared with those without PACS and with controls (P < .05 and P < .0001, respectively). Among those with PACS, 28 bacteria species were diminished and 14 were enriched, both at baseline and follow-up. Those patients who had COVID but not PACS showed just 25 alterations of bacteria species at the time of hospital admission, and they all normalized by 6 months.
Having respiratory symptoms at 6 months was linked with higher levels of opportunistic pathogens such as Streptococcus anginosus and S. vestibularis. Neuropsychiatric symptoms and fatigue were associated with nosocomial pathogens that are linked to opportunistic infections, such as Clostridium innocuum and Actinomyces naeslundii (P < .05).
Bacteria known for producing butyrate, a beneficial fatty acid, were significantly depleted in those patients with hair loss. And certain of these bacteria, including Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, had the largest inverse correlations with PACS at 6 months (P < .05), the researchers found.
“Particular gut microbial profiles may indicate heightened susceptibility,” Dr. Ng said.
Although the findings were drawn from patients with earlier strains of the COVID-19 virus, the findings still apply to new variants, including Omicron, since these pose the same problem of persistent disruption of the immune system, Dr. Ng said.
Her group is conducting trials to look at how modulating the microbiome might prevent long COVID and boost antibodies after vaccination in high-risk people, she said.
“Gut microbiota influences the health of the host,” Dr. Ng said. “It provides crucial benefits in the form of immune system development, prevention of infections, nutrient acquisition, and brain and nervous system functionality. Considering the millions of people infected during the ongoing pandemic, our findings are a strong impetus for consideration of microbiota modulation to facilitate timely recovery and reduce the burden of post–acute COVID-19 syndrome.”
John Haran, MD, PhD, associate professor of microbiology and physiological systems and emergency medicine at the University of Massachusetts, Worcester, said the research adds to the evidence base on the gut microbiome’s links to COVID, but there was likely be no clinical impact yet. Still, he said the findings linking specific species to specific symptoms was particularly interesting.
“Very early on during hospitalization, [the researchers] saw these differences and correlated out with people who have longer symptoms, and especially different groups of people that have longer symptoms, too,” said Dr. Haran, who has done research on the topic. “It’s very different if you have different symptoms, for example, you keep coughing for months versus you have brain fog and fatigue, or other debilitating symptoms.”
Dr. Haran noted that the findings didn’t identify bacteria types especially linked to COVID, but rather species that have already been found to be associated with a “bad” microbiome. He also pointed out that the patients enrolled in the study were not vaccinated, because vaccines weren’t available at the time. Still, further study to see whether modulation of gut bacteria can be a therapy seems worthwhile.
“Microbiome modulation is pretty safe, and that’s really the next big step that needs to be taken in this,” he said.
For now, the findings don’t give the clinician much new ammunition for treatment.
“We’re not there yet,” he added. “It’s not as if clinicians are going to tell their COVID patients: ‘Go out and buy some kale.’ ”
Eugene Chang, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Chicago, who has studied the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal disease, said it’s “too preliminary” to say whether the findings could lead to a clinical impact. The measures used merely identify the microbes present, but not what they are doing.
“These measures are unlikely to perform well enough to be useful for risk assessment or predicting clinical outcomes,” he said. “That being said, advances in technology are being made where next generations of metrics could be developed and useful as stratifiers and predictors of risk.”
Seeing shifting patterns associated with certain symptoms, he said, is “notable because it suggests that the disturbances of the gut microbiota in PACS are significant.”
But he said it’s important to know whether these changes are a cause of PACS in some way or just an effect of it.
“If causative or contributory – this has to be proven – then ‘microbiota modulation’ would make sense and could be a priority for development,” he said. “If merely an effect, these metrics and better ones to come could be useful as predictors or measures of the patient’s general state of health.”
As seen in his group’s work and other work, he said, “the gut microbiota is highly sensitive to changes in their ecosystem, which is influenced by the health state of the patient.”
Dr. Ng, Dr. Haran, and Dr. Chang reported no relevant disclosures.
This article was updated Jan. 27, 2022.
FROM GUT
‘Post-truth era’ hurts COVID-19 response, trust in science
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Can you tell which of the following statements are true and which are false?
COVID-19 is not a threat to younger people, and only those who have other medical conditions are dying from it.
The mRNA vaccines developed to prevent the coronavirus alter your genes, can make your body “magnetic,” and are killing more people than the virus itself.
President Joe Biden’s climate change plan calls for a ban on meat consumption to cut greenhouse gas emissions.
The 2020 presidential election was rigged and stolen.
If you guessed that all of these claims are false, you’re right – take a bow. Not a single one of these statements has any factual support, according to scientific research, legal rulings, and legitimate government authorities.
And yet public opinion surveys show millions of Americans, and others around the world, believe some of these falsehoods are true and can’t be convinced otherwise.
Social media, politicians and partisan websites, TV programs, and commentators have widely circulated these and other unfounded claims so frequently that many people say they simply can’t tell what’s objectively true and not anymore.
So much so,
The new study – The Rise and Fall of Rationality in Language, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences – found that facts have become less important in public discourse.
As a result, unsupported beliefs have taken precedent over readily identifiable truths in discussions of health, science, and politics. The upshot: “Feelings trump facts” in social media, news reports, books, and other sources of information.
And here’s the kicker: The trend did not begin with the rise of former President Donald Trump, the COVID-19 pandemic, or the advent of social media; in fact, it has been growing for much longer than you might think.
“While the current ‘post-truth era’ has taken many by surprise, the study shows that over the past 40 years, public interest has undergone an accelerating shift from the collective to the individual, and from rationality towards emotion,” concluded the researchers from Indiana University and Wageningen University & Research in the Netherlands.
“Our work suggests that the societal balance between emotion and reason has shifted back to what it used to be around 150 years ago,” says lead researcher Marten Scheffer, PhD, a professor in the department of environmental sciences at WUR. “This implies that scientists, experts, and policymakers will have to think about the best way to respond to that social change.”
Researchers surprised by findings
The findings are based on a very detailed analysis of language from millions of books, newspaper articles, Google searches, TV reports, social media posts, and other sources dating back to 1850.
The researchers analyzed how often the 5,000 most used words appeared over the past 170 years and found that the use of those having to do with facts and reasoning, such as “determine” and “conclusion,” has fallen dramatically since 1980. Meanwhile, the use of words related to human emotion, such as “feel” and “believe,” have skyrocketed.
Dr. Scheffer notes rapid developments in science and technology from 1850 to 1980 had profound social and economic benefits that helped boost the status of the scientific approach. That shift in public attitudes had ripple effects on culture, society, education, politics, and religion – and “the role of spiritualism dwindled” in the modern world, he says.
But since 1980, that trend has seen a major reversal, with beliefs becoming more important than facts to many people, he says. At the same time, trust in science and scientists has fallen.
Dr. Scheffer says the researchers expected to find some evidence of a swing toward more belief-based sentiments during the Trump era but were surprised to discover how strong it is and that the trend has actually been a long time coming.
“The shift in interest from rational to intuitive/emotional is pretty obvious now in the post-truth political and social media discussion,” he says. “However, our work shows that it already started in the 1980s. For me personally, that went under the radar, except perhaps for the rise of alternative (to religion) forms of spirituality.
“We were especially struck by how strong the patterns are and how universal they appear across languages, nonfiction and fiction, and even in The New York Times.”
In the political world, the implications are significant enough – impacting policies and politicians on both sides of the aisle and across the globe. Just look at the deepening political divisions during the Trump presidency.
But for health and science, the spread of misinformation and falsehoods can be matters of life or death, as we have seen in the politically charged debates over how best to combat COVID-19 and global climate change.
“Our public debate seems increasingly driven by what people want to be true rather than what is actually true. As a scientist, that worries me,” says study co-author Johan Bollen, PhD, a professor of informatics at Indiana University.
“As a society, we are now faced with major collective problems that we need to approach from a pragmatic, rational, and objective perspective to be successful,” he says. “After all, global warming doesn’t care about whether you believe in it or not … but we will all suffer as a society if we fail to take adequate measures.”
For WUR co-researcher Ingrid van de Leemput, the trend isn’t merely academic; she’s seen it play out in her personal life.
“I do speak to people that, for instance, think the vaccines are poison,” she says. “I’m also on Twitter, and there, I’m every day surprised about how easily many people form their opinions, based on feelings, on what others say, or on some unfounded source.”
Public health experts say the embrace of personal beliefs over facts is one reason only 63% of Americans have been vaccinated against COVID-19. The result: millions of preventable infections among those who downplay the risks of the virus and reject the strong scientific evidence of vaccine safety and effectiveness.
“None of this really surprises me,” Johns Hopkins University social and behavioral scientist Rupali Limaye, PhD, says of the new study findings. Dr. Limaye coauthored a paper in 2016 in JAMA Pediatrics about how to talk to parents about vaccine hesitancy and the fact that we’re living in what they called “this post-truth era.”
Dr. Limaye says the trend has made it difficult for doctors, scientists, and health authorities to make fact-based arguments for COVID-19 vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and other measures to control the virus.
“It’s been really hard being a scientist to hear people say, ‘Well, that’s not true’ when we say something very basic that I think all of us can agree on – like the grass is green,” she says. “To be honest, I worry that a lot of scientists are going to quit being in science because they’re exhausted.”
What’s driving the trend?
So, what’s behind the embrace of “alternative facts,” as former White House counselor Kellyanne Conway put it so brazenly in 2017, in defending the White House’s false claims that Trump’s inauguration crowd was the largest ever?
Dr. Scheffer and colleagues identified a handful of things that have encouraged the embrace of falsehoods over facts in recent years.
- The Internet: Its rise in the late 1980s, and its growing role as a primary source of news and information, has allowed more belief-based misinformation to flourish and spread like wildfire.
- Social media: The new study found the use of sentiment- and intuition-related words accelerated around 2007, along with a global surge in social media that catapulted Facebook, Twitter, and others into the mainstream, replacing more traditional fact-based media (i.e., newspapers and magazines).
- The 2007 financial crisis: The downturn in the global economy meant more people were dealing with job stress, investment losses, and other problems that fed the interest in belief-based, anti-establishment social media posts.
- Conspiracy theories: Falsehoods involving hidden political agendas, shadow “elites,” and wealthy people with dark motives tend to thrive during times of crisis and societal anxiety. “Conspiracy theories originate particularly in times of uncertainty and crisis and generally depict established institutions as hiding the truth and sustaining an unfair situation,” the researchers noted. “As a result, they may find fertile grounds on social media platforms promulgating a sense of unfairness, subsequently feeding anti-system sentiments.”
Dr. Scheffer says that growing political divisions during the Trump era have widened the fact-vs.-fiction divide. The ex-president voiced many anti-science views on global climate change, for instance, and spread so many falsehoods about COVID-19 and the 2020 election that Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube suspended his accounts.
Yet Trump remains a popular figure among Republicans, with most saying in a December poll they believe his baseless claims that the 2020 election was “rigged” and “stolen,” despite all credible, easily accessible evidence that it was secure, according to a recent poll by the University of Massachusetts at Amherst.
More than 60 courts have rejected Trump’s lawsuits seeking to overturn the election results. All 50 states, the District of Columbia, and both branches of Congress have certified the election results, giving Biden the White House. Even Trump’s own Justice Department confirmed that the 2020 election was free and fair.
Nevertheless, the University of Massachusetts survey found that most Republicans believe one or more conspiracy theories floated by the former president and those pushing his “big lie” that Democrats rigged the election to elect Biden.
Ed Berliner, an Emmy Award-winning broadcast journalist and media consultant, suggests something else is driving the spread of misinformation: the pursuit of ratings by cable TV and media companies to boost ad and subscriber revenues.
As a former executive producer and syndicated cable TV show host, he says he has seen firsthand how facts are often lost in opinion-driven news programs, even on network programs claiming to offer “fair and balanced” journalism.
“Propaganda is the new currency in America, and those who do not fight back against it are doomed to be overrun by the misinformation,” says Mr. Berliner, host of The Man in the Arena and CEO of Entourage Media LLC.
“The broadcast news media has to stop this incessant ‘infotainment’ prattle, stop trying to nuzzle up to a soft side, and bear down on hard facts, exposing the lies and refusing to back down.”
Public health implications
Public health and media experts alike say the PNAS study findings are disheartening but underscore the need for doctors and scientists to do a better job of communicating about COVID-19 and other pressing issues.
Dr. Limaye, from Johns Hopkins, is particularly concerned about the rise in conspiracy theories that has led to COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy.
“When we speak to individuals about getting the COVID vaccine…the types of concerns that come up now are very different than they were 8 years ago,” she says. “The comments we used to hear were much more related to vaccine safety. [People] would say, ‘I’m worried about an ingredient in the vaccine’ or ‘I’m worried that my kiddo has to get three different shots within 6 months to have a series dose completed.’”
But now, a lot of comments they receive are about government and pharma conspiracies.
What that means is doctors and scientists must do more than simply say “here are the facts” and “trust me, I’m a doctor or a scientist,” she says. And these approaches don’t only apply to public health.
“It’s funny, because when we talk to climate change scientists, as vaccine [specialists], we’ll say we can’t believe that people think COVID is a hoax,” she says. “And they’re like, ‘Hold my beer, we’ve been dealing with this for 20 years. Hello, it’s just your guys’ turn to deal with this public denial of science.’”
Dr. Limaye is also concerned about the impacts on funding for scientific research.
“There’s always been a really strong bipartisan effort with regards to funding for science, when you look at Congress and when you look at appropriations,” she says. “But what ended up happening, especially with the Trump administration, was that there was a real shift in that. We’ve never really seen that before in past generations.”
So, what’s the big take-home message?
Dr. Limaye believes doctors and public health experts must show more empathy – and not be combative or arrogant – in communicating science in one-on-one conversations. This month, she’s launching a new course for parents, school administrators, and nurses on how to do precisely that.
“It’s really all about how to have hard conversations with people who might be anti-science,” she says. “It’s being empathetic and not being dismissive. But it’s hard work, and I think a lot of people are just not cut out for it and just don’t have the time for it…You can’t just say, ‘Well, this is science, and I’m a doctor’ – that doesn’t work anymore.”
Brendan Nyhan, PhD, a Dartmouth College political scientist, echoes those sentiments in a separate paper recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In fact, he suggests that providing accurate, fact-based information to counter false claims may actually backfire and reinforce some people’s unfounded beliefs.
“One response to the prevalence of mistaken beliefs is to try to set the record straight by providing accurate information – for instance, by providing evidence of the scientific consensus on climate change,” he writes. “The failures of this approach, which is sometimes referred to as the ‘deficit model’ in science communication, are well-known.”
Dr. Nyhan argues two things make some people more prone to believe falsehoods:
What scientists call “ingrouping,” a kind of tribal mentality that makes some people choose social identity or politics over truth-seeking and demonize others who don’t agree with their views
The rise of high-profile political figures, such as Trump, who encourage their followers to indulge in their desire for “identify-affirming misinformation”
Dr. Scheffer says the most important thing for doctors, health experts, and scientists to recognize is that it’s crucial to gain the trust of someone who may believe fictions over facts to make any persuasive argument on COVID-19 or any other issue.
He also has a standard response to those who present falsehoods to him as facts that he suggests anyone can use: “That is interesting. Would you mind helping me understand how you came to that opinion?”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Medtronic recalls HawkOne directional atherectomy system
Medtronic has recalled 95,110 HawkOne Directional Atherectomy Systems because of the risk of the guidewire within the catheter moving downward or prolapsing during use, which may damage the tip of the catheter.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a Class I recall, the most serious type, because of the potential for serious injury or death.
The HawkOne Directional Atherectomy system is used during procedures intended to remove blockage from peripheral arteries and improve blood flow.
If the guideline moves downward or prolapses during use, the “catheter tip may break off or separate, and this could lead to serious adverse events, including a tear along the inside wall of an artery (arterial dissection), a rupture or breakage of an artery (arterial rupture), decrease in blood flow to a part of the body because of a blocked artery (ischemia), and/or blood vessel complications that could require surgical repair and additional procedures to capture and remove the detached and/or migrated (embolized) tip,” the FDA says in a recall notice posted today on its website.
To date, there have been 55 injuries, no deaths, and 163 complaints reported for this device.
The recalled devices were distributed in the United States between Jan. 22, 2018 and Oct. 4, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers pertaining to the devices are listed on the FDA website.
Medtronic sent an urgent field safety notice to customers Dec. 6, 2021, requesting that they alert parties of the defect, review the instructions for use before using the device, and note the warnings and precautions listed in the letter.
Customers were also asked to complete the enclosed confirmation form and email to rs.cfqfca@medtronic.com.
Health care providers can report adverse reactions or quality problems they experience using these devices to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medtronic has recalled 95,110 HawkOne Directional Atherectomy Systems because of the risk of the guidewire within the catheter moving downward or prolapsing during use, which may damage the tip of the catheter.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a Class I recall, the most serious type, because of the potential for serious injury or death.
The HawkOne Directional Atherectomy system is used during procedures intended to remove blockage from peripheral arteries and improve blood flow.
If the guideline moves downward or prolapses during use, the “catheter tip may break off or separate, and this could lead to serious adverse events, including a tear along the inside wall of an artery (arterial dissection), a rupture or breakage of an artery (arterial rupture), decrease in blood flow to a part of the body because of a blocked artery (ischemia), and/or blood vessel complications that could require surgical repair and additional procedures to capture and remove the detached and/or migrated (embolized) tip,” the FDA says in a recall notice posted today on its website.
To date, there have been 55 injuries, no deaths, and 163 complaints reported for this device.
The recalled devices were distributed in the United States between Jan. 22, 2018 and Oct. 4, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers pertaining to the devices are listed on the FDA website.
Medtronic sent an urgent field safety notice to customers Dec. 6, 2021, requesting that they alert parties of the defect, review the instructions for use before using the device, and note the warnings and precautions listed in the letter.
Customers were also asked to complete the enclosed confirmation form and email to rs.cfqfca@medtronic.com.
Health care providers can report adverse reactions or quality problems they experience using these devices to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medtronic has recalled 95,110 HawkOne Directional Atherectomy Systems because of the risk of the guidewire within the catheter moving downward or prolapsing during use, which may damage the tip of the catheter.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has identified this as a Class I recall, the most serious type, because of the potential for serious injury or death.
The HawkOne Directional Atherectomy system is used during procedures intended to remove blockage from peripheral arteries and improve blood flow.
If the guideline moves downward or prolapses during use, the “catheter tip may break off or separate, and this could lead to serious adverse events, including a tear along the inside wall of an artery (arterial dissection), a rupture or breakage of an artery (arterial rupture), decrease in blood flow to a part of the body because of a blocked artery (ischemia), and/or blood vessel complications that could require surgical repair and additional procedures to capture and remove the detached and/or migrated (embolized) tip,” the FDA says in a recall notice posted today on its website.
To date, there have been 55 injuries, no deaths, and 163 complaints reported for this device.
The recalled devices were distributed in the United States between Jan. 22, 2018 and Oct. 4, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers pertaining to the devices are listed on the FDA website.
Medtronic sent an urgent field safety notice to customers Dec. 6, 2021, requesting that they alert parties of the defect, review the instructions for use before using the device, and note the warnings and precautions listed in the letter.
Customers were also asked to complete the enclosed confirmation form and email to rs.cfqfca@medtronic.com.
Health care providers can report adverse reactions or quality problems they experience using these devices to the FDA’s MedWatch program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician burnout, depression compounded by COVID: Survey
In 2020, it was hard to imagine that the situation could get worse for doctors.
But 2021 presented a new set of challenges. As quarantines lifted and physicians tried to get back to work, they were forced to deal with reduced staff, continuing COVID stress, and pandemic-related anxieties about family and loved ones.
Medscape’s National Burnout and Depression Report 2022 asked more than 13,000 physicians from 29 specialties to share details about their lives and struggles with burnout and depression in 2021. The results paint a picture of physicians trying to fulfill their mission to care for patients, but struggling to maintain their own well-being amid a global pandemic.
Burnout bump
In 2021’s report, 42% of physicians said they were burned out. In 2022, that number increased to 47%. Perhaps not surprisingly, burnout among emergency physicians took the biggest leap, increasing from 43% to 60%. Critical care (56%), ob.gyn. (53%), and infectious disease and family medicine (both at 51%) rounded out the top five specialties with doctors experiencing burnout in 2021.
Burnout has typically been a greater problem for women than men physicians, and the pandemic hasn’t changed that. “There’s no question that women have reported far more role strain during the pandemic than men,” says Carol A. Bernstein, MD, psychiatrist at Montefiore Health System and professor and vice chair for faculty development and well-being at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York. And indeed, 56% of women and 41% of men reported burnout in the 2022 survey.
The causes, however, weren’t especially pandemic related – or at least not directly. As in previous surveys, the major contributing factor to burnout was too much paperwork (60%), such as charting and other bureaucratic tasks. Treating COVID-19 patients was cited as the major source of stress by 10% of respondents. About 34% said too many hours at work was the biggest contributing factor to burnout.
The nature of the beast
What is burnout like for these doctors? One described the conditions that lead to burnout like this: “I barely spend enough time with most patients, just running from one to the next; and then after work, I spend hours documenting, charting, dealing with reports. I feel like an overpaid clerk.” Another said: “Where’s the relationships with patients that used to make this worthwhile?” Others fingered staffing shortages at work or an overwhelming home life: “Staff calls in sick; we’re all running around trying to find things and get things done. It never ends.”
Of those who do experience burnout, the problem reaches beyond the workplace, with 54% saying that their burnout has a strong/severe impact on life and 68% reporting that burnout affects their relationships. One respondent said: “I’m always tired; I have trouble concentrating, no time for the children, more arguments with my hubby.” Another put it this way: “Home is just as busy and chaotic as work. I can never relax.”
It doesn’t help matters that physicians are likely to think they’re the only professionals experiencing job burnout. For example, only 36% of respondents believe teachers experience comparable burnout, yet more than 41% of teachers leave the profession within 5 years of starting – often because of burnout.
When it comes to methods for coping with burnout, exercise is the clear favorite, with 63% of respondents saying exercise helps maintain their mental health. About 41% talk with family members or close friends. However, less healthy coping mechanisms were cited as well, such as isolating themselves from others (45%), sleeping (41%), and eating junk food (35%) or drinking alcohol (24%).
When it comes to trying to alleviate burnout, 29% have tried meditation or similar stress-reduction techniques, while others have reduced their work hours (29%) or changed their work settings (19%).
‘Now I feel like there’s no hope’
About a fifth of physicians (21%) said they suffered from clinical depression, and 64% reported feeling “blue, down, or sad.” One physician characterized their depression this way: “I used to think my life would be great. Now I feel like there’s no hope, this will never get better, I’ll never be happy.”
Of doctors reporting depression, 53% said their illness did not affect their interactions with patients, while 34% said depression caused them to be more easily exasperated by patients.
When asked about seeking help for depression, about half (49%) said they believed they could deal with emotional stress on their own. Unfortunately, fear of medical boards finding out keeps 43% of physicians from reaching out for help, according to the survey.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2020, it was hard to imagine that the situation could get worse for doctors.
But 2021 presented a new set of challenges. As quarantines lifted and physicians tried to get back to work, they were forced to deal with reduced staff, continuing COVID stress, and pandemic-related anxieties about family and loved ones.
Medscape’s National Burnout and Depression Report 2022 asked more than 13,000 physicians from 29 specialties to share details about their lives and struggles with burnout and depression in 2021. The results paint a picture of physicians trying to fulfill their mission to care for patients, but struggling to maintain their own well-being amid a global pandemic.
Burnout bump
In 2021’s report, 42% of physicians said they were burned out. In 2022, that number increased to 47%. Perhaps not surprisingly, burnout among emergency physicians took the biggest leap, increasing from 43% to 60%. Critical care (56%), ob.gyn. (53%), and infectious disease and family medicine (both at 51%) rounded out the top five specialties with doctors experiencing burnout in 2021.
Burnout has typically been a greater problem for women than men physicians, and the pandemic hasn’t changed that. “There’s no question that women have reported far more role strain during the pandemic than men,” says Carol A. Bernstein, MD, psychiatrist at Montefiore Health System and professor and vice chair for faculty development and well-being at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York. And indeed, 56% of women and 41% of men reported burnout in the 2022 survey.
The causes, however, weren’t especially pandemic related – or at least not directly. As in previous surveys, the major contributing factor to burnout was too much paperwork (60%), such as charting and other bureaucratic tasks. Treating COVID-19 patients was cited as the major source of stress by 10% of respondents. About 34% said too many hours at work was the biggest contributing factor to burnout.
The nature of the beast
What is burnout like for these doctors? One described the conditions that lead to burnout like this: “I barely spend enough time with most patients, just running from one to the next; and then after work, I spend hours documenting, charting, dealing with reports. I feel like an overpaid clerk.” Another said: “Where’s the relationships with patients that used to make this worthwhile?” Others fingered staffing shortages at work or an overwhelming home life: “Staff calls in sick; we’re all running around trying to find things and get things done. It never ends.”
Of those who do experience burnout, the problem reaches beyond the workplace, with 54% saying that their burnout has a strong/severe impact on life and 68% reporting that burnout affects their relationships. One respondent said: “I’m always tired; I have trouble concentrating, no time for the children, more arguments with my hubby.” Another put it this way: “Home is just as busy and chaotic as work. I can never relax.”
It doesn’t help matters that physicians are likely to think they’re the only professionals experiencing job burnout. For example, only 36% of respondents believe teachers experience comparable burnout, yet more than 41% of teachers leave the profession within 5 years of starting – often because of burnout.
When it comes to methods for coping with burnout, exercise is the clear favorite, with 63% of respondents saying exercise helps maintain their mental health. About 41% talk with family members or close friends. However, less healthy coping mechanisms were cited as well, such as isolating themselves from others (45%), sleeping (41%), and eating junk food (35%) or drinking alcohol (24%).
When it comes to trying to alleviate burnout, 29% have tried meditation or similar stress-reduction techniques, while others have reduced their work hours (29%) or changed their work settings (19%).
‘Now I feel like there’s no hope’
About a fifth of physicians (21%) said they suffered from clinical depression, and 64% reported feeling “blue, down, or sad.” One physician characterized their depression this way: “I used to think my life would be great. Now I feel like there’s no hope, this will never get better, I’ll never be happy.”
Of doctors reporting depression, 53% said their illness did not affect their interactions with patients, while 34% said depression caused them to be more easily exasperated by patients.
When asked about seeking help for depression, about half (49%) said they believed they could deal with emotional stress on their own. Unfortunately, fear of medical boards finding out keeps 43% of physicians from reaching out for help, according to the survey.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2020, it was hard to imagine that the situation could get worse for doctors.
But 2021 presented a new set of challenges. As quarantines lifted and physicians tried to get back to work, they were forced to deal with reduced staff, continuing COVID stress, and pandemic-related anxieties about family and loved ones.
Medscape’s National Burnout and Depression Report 2022 asked more than 13,000 physicians from 29 specialties to share details about their lives and struggles with burnout and depression in 2021. The results paint a picture of physicians trying to fulfill their mission to care for patients, but struggling to maintain their own well-being amid a global pandemic.
Burnout bump
In 2021’s report, 42% of physicians said they were burned out. In 2022, that number increased to 47%. Perhaps not surprisingly, burnout among emergency physicians took the biggest leap, increasing from 43% to 60%. Critical care (56%), ob.gyn. (53%), and infectious disease and family medicine (both at 51%) rounded out the top five specialties with doctors experiencing burnout in 2021.
Burnout has typically been a greater problem for women than men physicians, and the pandemic hasn’t changed that. “There’s no question that women have reported far more role strain during the pandemic than men,” says Carol A. Bernstein, MD, psychiatrist at Montefiore Health System and professor and vice chair for faculty development and well-being at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, both in New York. And indeed, 56% of women and 41% of men reported burnout in the 2022 survey.
The causes, however, weren’t especially pandemic related – or at least not directly. As in previous surveys, the major contributing factor to burnout was too much paperwork (60%), such as charting and other bureaucratic tasks. Treating COVID-19 patients was cited as the major source of stress by 10% of respondents. About 34% said too many hours at work was the biggest contributing factor to burnout.
The nature of the beast
What is burnout like for these doctors? One described the conditions that lead to burnout like this: “I barely spend enough time with most patients, just running from one to the next; and then after work, I spend hours documenting, charting, dealing with reports. I feel like an overpaid clerk.” Another said: “Where’s the relationships with patients that used to make this worthwhile?” Others fingered staffing shortages at work or an overwhelming home life: “Staff calls in sick; we’re all running around trying to find things and get things done. It never ends.”
Of those who do experience burnout, the problem reaches beyond the workplace, with 54% saying that their burnout has a strong/severe impact on life and 68% reporting that burnout affects their relationships. One respondent said: “I’m always tired; I have trouble concentrating, no time for the children, more arguments with my hubby.” Another put it this way: “Home is just as busy and chaotic as work. I can never relax.”
It doesn’t help matters that physicians are likely to think they’re the only professionals experiencing job burnout. For example, only 36% of respondents believe teachers experience comparable burnout, yet more than 41% of teachers leave the profession within 5 years of starting – often because of burnout.
When it comes to methods for coping with burnout, exercise is the clear favorite, with 63% of respondents saying exercise helps maintain their mental health. About 41% talk with family members or close friends. However, less healthy coping mechanisms were cited as well, such as isolating themselves from others (45%), sleeping (41%), and eating junk food (35%) or drinking alcohol (24%).
When it comes to trying to alleviate burnout, 29% have tried meditation or similar stress-reduction techniques, while others have reduced their work hours (29%) or changed their work settings (19%).
‘Now I feel like there’s no hope’
About a fifth of physicians (21%) said they suffered from clinical depression, and 64% reported feeling “blue, down, or sad.” One physician characterized their depression this way: “I used to think my life would be great. Now I feel like there’s no hope, this will never get better, I’ll never be happy.”
Of doctors reporting depression, 53% said their illness did not affect their interactions with patients, while 34% said depression caused them to be more easily exasperated by patients.
When asked about seeking help for depression, about half (49%) said they believed they could deal with emotional stress on their own. Unfortunately, fear of medical boards finding out keeps 43% of physicians from reaching out for help, according to the survey.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doc’s botched surgery leads to incontinence and $10 million judgment; more
Early in December 2021 a jury awarded a couple $10 million in a case involving a hysterectomy that went badly wrong, according to a story in the New York Post, among other news sites.
In October 2018, Michele Nugent, 41, of New York, underwent the procedure at Richmond University Medical Center. After giving birth to four children via cesarean delivery, she had developed scarring and was suffering from excessive and painful uterine bleeding.
A few days after her hysterectomy, however, Ms. Nugent experienced what she described as the worst pain of her life, along with nausea, vomiting, and urinary leakage. She was brought to the hospital emergency department, where she was reportedly told by staff there that her symptoms were normal complications of her surgery and that the treating gynecologist, Eli Serur, MD, would soon be in touch.
Despite these reassurances, Ms. Nugent’s postsurgical issues continued to worsen over the next 10 days. Among other things, she lost almost complete control of her bladder, which required her to wear adult diapers. Still, her doctor’s office told her to put off visiting until her next scheduled appointment.
At that meeting, which took place 13 days after Ms. Nugent’s surgery, Dr. Serur diagnosed a urinary tract infection and placed her on antibiotics. He also encouraged her to return to work the following week.
Ms. Nugent’s problems persisted, however. At an office meeting that included 20 men, she suddenly lost complete control of her bladder, despite going regularly to the bathroom and wearing adult diapers. “Out of nowhere,” she testified at trial, “I urinated all over myself and had to leave.” The experience left her humiliated and embarrassed.
Several weeks later, Ms. Nugent consulted with a urologist, who soon repaired the cause of her urinary problems – a fistula between her vagina and bladder.
Though successful, the procedure still left Ms. Nugent with, what are for now at least, intractable symptoms. At night, she’s forced to make multiple trips to the bathroom, and sex with her husband has become all but impossible because of the pain it elicits.
In reaching its verdict, the jury of four women and two men faulted Dr. Serur for not only performing a faulty surgery but for failing to identify and correct his mistake. In so doing, it concluded, he had departed “from good and accepted medical practice.”
Jurors divided the $10 million judgment against him into two parts: $6.5 million for Ms. Nugent’s past and future suffering, and $3.5 million to her husband for his past and future loss of consortium – that is, his loss of intimacy with his wife.
As for the medical center, the Nugents agreed to dismiss it from the case prior to trial.
Physician accused of gross negligence finally surrenders his license
A California doctor under investigation multiple times during the past 2 decades has surrendered his medical license, as a story reported by Valley Public Radio indicates.
Since 1999, the Medical Board of California has opened three investigations against Bakersfield ob.gyn. Arthur Park, MD, each involving accusations of gross negligence “following the deaths of mothers and/or their babies during childbirth.” In 2000, and again in 2020, the board voted that Dr. Park should lose his license but then suspended its decision, which enabled Dr. Park to continue practicing under probation and on condition that he complete remedial education.
Early in 2021, however, the board filed yet another accusation against him, this one involving the 2019 death of Demi Dominguez and her newborn baby. According to the accusation, Ms. Dominguez died of preeclampsia because Dr. Park and a colleague failed to treat her high blood pressure prior to delivery. While doctors attempted to resuscitate her, Ms. Dominguez’s son was delivered by emergency cesarean but died only a few hours later. The board said that Dr. Park was “grossly negligent in his care and treatment” and that his actions constituted “an extreme departure from the applicable standard of care.”
Early in December 2021, even before the board and attorney general’s office had completed their investigations, Dr. Park agreed to surrender his medical license.
Patient advocates were pleased by the doctor’s decision but also disappointed that he’d no longer be compelled to stand before a judge, as he had been scheduled to do in connection with the Dominguez case.
A review of public records by Valley Public Radio indicates that – between the various board accusations against him and an additional nine lawsuits alleging malpractice and other issues – at least two mothers and five children have died while under Dr. Park’s care. Others whose delivery he oversaw claim their children were permanently injured during childbirth.
Although Dr. Park will be eligible to reapply for his license after 2 years, a representative of his medical office said Dr. Park had decided to retire from practicing medicine.
Delayed cancer diagnosis prompts med-mal suit
An Illinois woman who claims her doctor and his staff failed to follow up on her abnormal Pap smear has filed a malpractice suit against them and their medical group, reports a story in the Madison-St. Clair Record.
In early 2019, Lisa Albright visited the medical group after she had experienced pain during intercourse. A family nurse practitioner at the practice performed a Pap smear, and Ms. Albright was instructed to wait a few days and check her patient portal for the results. In her suit, Ms. Albright claims those results were abnormal. Despite this, neither the nurse practitioner nor anyone else at the practice scheduled a follow-up test or other diagnostic assessment.
Approximately 5 months later, Ms. Albright consulted a new physician, whose follow-up testing indicated that Ms. Albright had a cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Ms. Albright’s suit alleges that the diagnostic delay has, among other things, caused her to undergo multiple surgical procedures and treatments, face a shorter life expectancy, and endure a loss in the quality of her life.
At press time, Ms. Albright and her legal representative have not yet determined the amount they will ask for – it will be set after the severity and permanency of Ms. Albright’s injuries have been more thoroughly investigated. But it’s expected that they will seek damages, along with all legal and court expenses.
The defendants haven’t responded to the plaintiff’s suit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early in December 2021 a jury awarded a couple $10 million in a case involving a hysterectomy that went badly wrong, according to a story in the New York Post, among other news sites.
In October 2018, Michele Nugent, 41, of New York, underwent the procedure at Richmond University Medical Center. After giving birth to four children via cesarean delivery, she had developed scarring and was suffering from excessive and painful uterine bleeding.
A few days after her hysterectomy, however, Ms. Nugent experienced what she described as the worst pain of her life, along with nausea, vomiting, and urinary leakage. She was brought to the hospital emergency department, where she was reportedly told by staff there that her symptoms were normal complications of her surgery and that the treating gynecologist, Eli Serur, MD, would soon be in touch.
Despite these reassurances, Ms. Nugent’s postsurgical issues continued to worsen over the next 10 days. Among other things, she lost almost complete control of her bladder, which required her to wear adult diapers. Still, her doctor’s office told her to put off visiting until her next scheduled appointment.
At that meeting, which took place 13 days after Ms. Nugent’s surgery, Dr. Serur diagnosed a urinary tract infection and placed her on antibiotics. He also encouraged her to return to work the following week.
Ms. Nugent’s problems persisted, however. At an office meeting that included 20 men, she suddenly lost complete control of her bladder, despite going regularly to the bathroom and wearing adult diapers. “Out of nowhere,” she testified at trial, “I urinated all over myself and had to leave.” The experience left her humiliated and embarrassed.
Several weeks later, Ms. Nugent consulted with a urologist, who soon repaired the cause of her urinary problems – a fistula between her vagina and bladder.
Though successful, the procedure still left Ms. Nugent with, what are for now at least, intractable symptoms. At night, she’s forced to make multiple trips to the bathroom, and sex with her husband has become all but impossible because of the pain it elicits.
In reaching its verdict, the jury of four women and two men faulted Dr. Serur for not only performing a faulty surgery but for failing to identify and correct his mistake. In so doing, it concluded, he had departed “from good and accepted medical practice.”
Jurors divided the $10 million judgment against him into two parts: $6.5 million for Ms. Nugent’s past and future suffering, and $3.5 million to her husband for his past and future loss of consortium – that is, his loss of intimacy with his wife.
As for the medical center, the Nugents agreed to dismiss it from the case prior to trial.
Physician accused of gross negligence finally surrenders his license
A California doctor under investigation multiple times during the past 2 decades has surrendered his medical license, as a story reported by Valley Public Radio indicates.
Since 1999, the Medical Board of California has opened three investigations against Bakersfield ob.gyn. Arthur Park, MD, each involving accusations of gross negligence “following the deaths of mothers and/or their babies during childbirth.” In 2000, and again in 2020, the board voted that Dr. Park should lose his license but then suspended its decision, which enabled Dr. Park to continue practicing under probation and on condition that he complete remedial education.
Early in 2021, however, the board filed yet another accusation against him, this one involving the 2019 death of Demi Dominguez and her newborn baby. According to the accusation, Ms. Dominguez died of preeclampsia because Dr. Park and a colleague failed to treat her high blood pressure prior to delivery. While doctors attempted to resuscitate her, Ms. Dominguez’s son was delivered by emergency cesarean but died only a few hours later. The board said that Dr. Park was “grossly negligent in his care and treatment” and that his actions constituted “an extreme departure from the applicable standard of care.”
Early in December 2021, even before the board and attorney general’s office had completed their investigations, Dr. Park agreed to surrender his medical license.
Patient advocates were pleased by the doctor’s decision but also disappointed that he’d no longer be compelled to stand before a judge, as he had been scheduled to do in connection with the Dominguez case.
A review of public records by Valley Public Radio indicates that – between the various board accusations against him and an additional nine lawsuits alleging malpractice and other issues – at least two mothers and five children have died while under Dr. Park’s care. Others whose delivery he oversaw claim their children were permanently injured during childbirth.
Although Dr. Park will be eligible to reapply for his license after 2 years, a representative of his medical office said Dr. Park had decided to retire from practicing medicine.
Delayed cancer diagnosis prompts med-mal suit
An Illinois woman who claims her doctor and his staff failed to follow up on her abnormal Pap smear has filed a malpractice suit against them and their medical group, reports a story in the Madison-St. Clair Record.
In early 2019, Lisa Albright visited the medical group after she had experienced pain during intercourse. A family nurse practitioner at the practice performed a Pap smear, and Ms. Albright was instructed to wait a few days and check her patient portal for the results. In her suit, Ms. Albright claims those results were abnormal. Despite this, neither the nurse practitioner nor anyone else at the practice scheduled a follow-up test or other diagnostic assessment.
Approximately 5 months later, Ms. Albright consulted a new physician, whose follow-up testing indicated that Ms. Albright had a cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Ms. Albright’s suit alleges that the diagnostic delay has, among other things, caused her to undergo multiple surgical procedures and treatments, face a shorter life expectancy, and endure a loss in the quality of her life.
At press time, Ms. Albright and her legal representative have not yet determined the amount they will ask for – it will be set after the severity and permanency of Ms. Albright’s injuries have been more thoroughly investigated. But it’s expected that they will seek damages, along with all legal and court expenses.
The defendants haven’t responded to the plaintiff’s suit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early in December 2021 a jury awarded a couple $10 million in a case involving a hysterectomy that went badly wrong, according to a story in the New York Post, among other news sites.
In October 2018, Michele Nugent, 41, of New York, underwent the procedure at Richmond University Medical Center. After giving birth to four children via cesarean delivery, she had developed scarring and was suffering from excessive and painful uterine bleeding.
A few days after her hysterectomy, however, Ms. Nugent experienced what she described as the worst pain of her life, along with nausea, vomiting, and urinary leakage. She was brought to the hospital emergency department, where she was reportedly told by staff there that her symptoms were normal complications of her surgery and that the treating gynecologist, Eli Serur, MD, would soon be in touch.
Despite these reassurances, Ms. Nugent’s postsurgical issues continued to worsen over the next 10 days. Among other things, she lost almost complete control of her bladder, which required her to wear adult diapers. Still, her doctor’s office told her to put off visiting until her next scheduled appointment.
At that meeting, which took place 13 days after Ms. Nugent’s surgery, Dr. Serur diagnosed a urinary tract infection and placed her on antibiotics. He also encouraged her to return to work the following week.
Ms. Nugent’s problems persisted, however. At an office meeting that included 20 men, she suddenly lost complete control of her bladder, despite going regularly to the bathroom and wearing adult diapers. “Out of nowhere,” she testified at trial, “I urinated all over myself and had to leave.” The experience left her humiliated and embarrassed.
Several weeks later, Ms. Nugent consulted with a urologist, who soon repaired the cause of her urinary problems – a fistula between her vagina and bladder.
Though successful, the procedure still left Ms. Nugent with, what are for now at least, intractable symptoms. At night, she’s forced to make multiple trips to the bathroom, and sex with her husband has become all but impossible because of the pain it elicits.
In reaching its verdict, the jury of four women and two men faulted Dr. Serur for not only performing a faulty surgery but for failing to identify and correct his mistake. In so doing, it concluded, he had departed “from good and accepted medical practice.”
Jurors divided the $10 million judgment against him into two parts: $6.5 million for Ms. Nugent’s past and future suffering, and $3.5 million to her husband for his past and future loss of consortium – that is, his loss of intimacy with his wife.
As for the medical center, the Nugents agreed to dismiss it from the case prior to trial.
Physician accused of gross negligence finally surrenders his license
A California doctor under investigation multiple times during the past 2 decades has surrendered his medical license, as a story reported by Valley Public Radio indicates.
Since 1999, the Medical Board of California has opened three investigations against Bakersfield ob.gyn. Arthur Park, MD, each involving accusations of gross negligence “following the deaths of mothers and/or their babies during childbirth.” In 2000, and again in 2020, the board voted that Dr. Park should lose his license but then suspended its decision, which enabled Dr. Park to continue practicing under probation and on condition that he complete remedial education.
Early in 2021, however, the board filed yet another accusation against him, this one involving the 2019 death of Demi Dominguez and her newborn baby. According to the accusation, Ms. Dominguez died of preeclampsia because Dr. Park and a colleague failed to treat her high blood pressure prior to delivery. While doctors attempted to resuscitate her, Ms. Dominguez’s son was delivered by emergency cesarean but died only a few hours later. The board said that Dr. Park was “grossly negligent in his care and treatment” and that his actions constituted “an extreme departure from the applicable standard of care.”
Early in December 2021, even before the board and attorney general’s office had completed their investigations, Dr. Park agreed to surrender his medical license.
Patient advocates were pleased by the doctor’s decision but also disappointed that he’d no longer be compelled to stand before a judge, as he had been scheduled to do in connection with the Dominguez case.
A review of public records by Valley Public Radio indicates that – between the various board accusations against him and an additional nine lawsuits alleging malpractice and other issues – at least two mothers and five children have died while under Dr. Park’s care. Others whose delivery he oversaw claim their children were permanently injured during childbirth.
Although Dr. Park will be eligible to reapply for his license after 2 years, a representative of his medical office said Dr. Park had decided to retire from practicing medicine.
Delayed cancer diagnosis prompts med-mal suit
An Illinois woman who claims her doctor and his staff failed to follow up on her abnormal Pap smear has filed a malpractice suit against them and their medical group, reports a story in the Madison-St. Clair Record.
In early 2019, Lisa Albright visited the medical group after she had experienced pain during intercourse. A family nurse practitioner at the practice performed a Pap smear, and Ms. Albright was instructed to wait a few days and check her patient portal for the results. In her suit, Ms. Albright claims those results were abnormal. Despite this, neither the nurse practitioner nor anyone else at the practice scheduled a follow-up test or other diagnostic assessment.
Approximately 5 months later, Ms. Albright consulted a new physician, whose follow-up testing indicated that Ms. Albright had a cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Ms. Albright’s suit alleges that the diagnostic delay has, among other things, caused her to undergo multiple surgical procedures and treatments, face a shorter life expectancy, and endure a loss in the quality of her life.
At press time, Ms. Albright and her legal representative have not yet determined the amount they will ask for – it will be set after the severity and permanency of Ms. Albright’s injuries have been more thoroughly investigated. But it’s expected that they will seek damages, along with all legal and court expenses.
The defendants haven’t responded to the plaintiff’s suit.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antimicrobial resistance linked to 1.2 million global deaths in 2019
More than HIV, more than malaria.
In terms of preventable deaths, 1.27 million people could have been saved if drug-resistant infections were replaced with infections susceptible to current antibiotics. Furthermore, 4.95 million fewer people would have died if drug-resistant infections were replaced by no infections, researchers estimated.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic took some focus off the AMR burden worldwide over the past 2 years, the urgency to address risk to public health did not ebb. In fact, based on the findings, the researchers noted that AMR is now a leading cause of death worldwide.
“If left unchecked, the spread of AMR could make many bacterial pathogens much more lethal in the future than they are today,” the researchers noted in the study, published online Jan. 20, 2022, in The Lancet.
“These findings are a warning signal that antibiotic resistance is placing pressure on health care systems and leading to significant health loss,” study author Kevin Ikuta, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“We need to continue to adhere to and support infection prevention and control programs, be thoughtful about our antibiotic use, and advocate for increased funding to vaccine discovery and the antibiotic development pipeline,” added Dr. Ikuta, health sciences assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Although many investigators have studied AMR, this study is the largest in scope, covering 204 countries and territories and incorporating data on a comprehensive range of pathogens and pathogen-drug combinations.
Dr. Ikuta, lead author Christopher J.L. Murray, DPhil, and colleagues estimated the global burden of AMR using the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019. They specifically looked at rates of death directly attributed to and separately those associated with resistance.
Regional differences
Broken down by 21 regions, Australasia had 6.5 deaths per 100,000 people attributable to AMR, the lowest rate reported. This region also had 28 deaths per 100,000 associated with AMR.
Researchers found the highest rates in western sub-Saharan Africa. Deaths attributable to AMR were 27.3 per 100,000 and associated death rate was 114.8 per 100,000.
Lower- and middle-income regions had the highest AMR death rates, although resistance remains a high-priority issue for high-income countries as well.
“It’s important to take a global perspective on resistant infections because we can learn about regions and countries that are experiencing the greatest burden, information that was previously unknown,” Dr. Ikuta said. “With these estimates policy makers can prioritize regions that are hotspots and would most benefit from additional interventions.”
Furthermore, the study emphasized the global nature of AMR. “We’ve seen over the last 2 years with COVID-19 that this sort of problem doesn’t respect country borders, and high rates of resistance in one location can spread across a region or spread globally pretty quickly,” Dr. Ikuta said.
Leading resistant infections
Lower respiratory and thorax infections, bloodstream infections, and intra-abdominal infections together accounted for almost 79% of such deaths linked to AMR.
The six leading pathogens are likely household names among infectious disease specialists. The researchers found Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, each responsible for more than 250,000 AMR-associated deaths.
The study also revealed that resistance to several first-line antibiotic agents often used empirically to treat infections accounted for more than 70% of the AMR-attributable deaths. These included fluoroquinolones and beta-lactam antibiotics such as carbapenems, cephalosporins, and penicillins.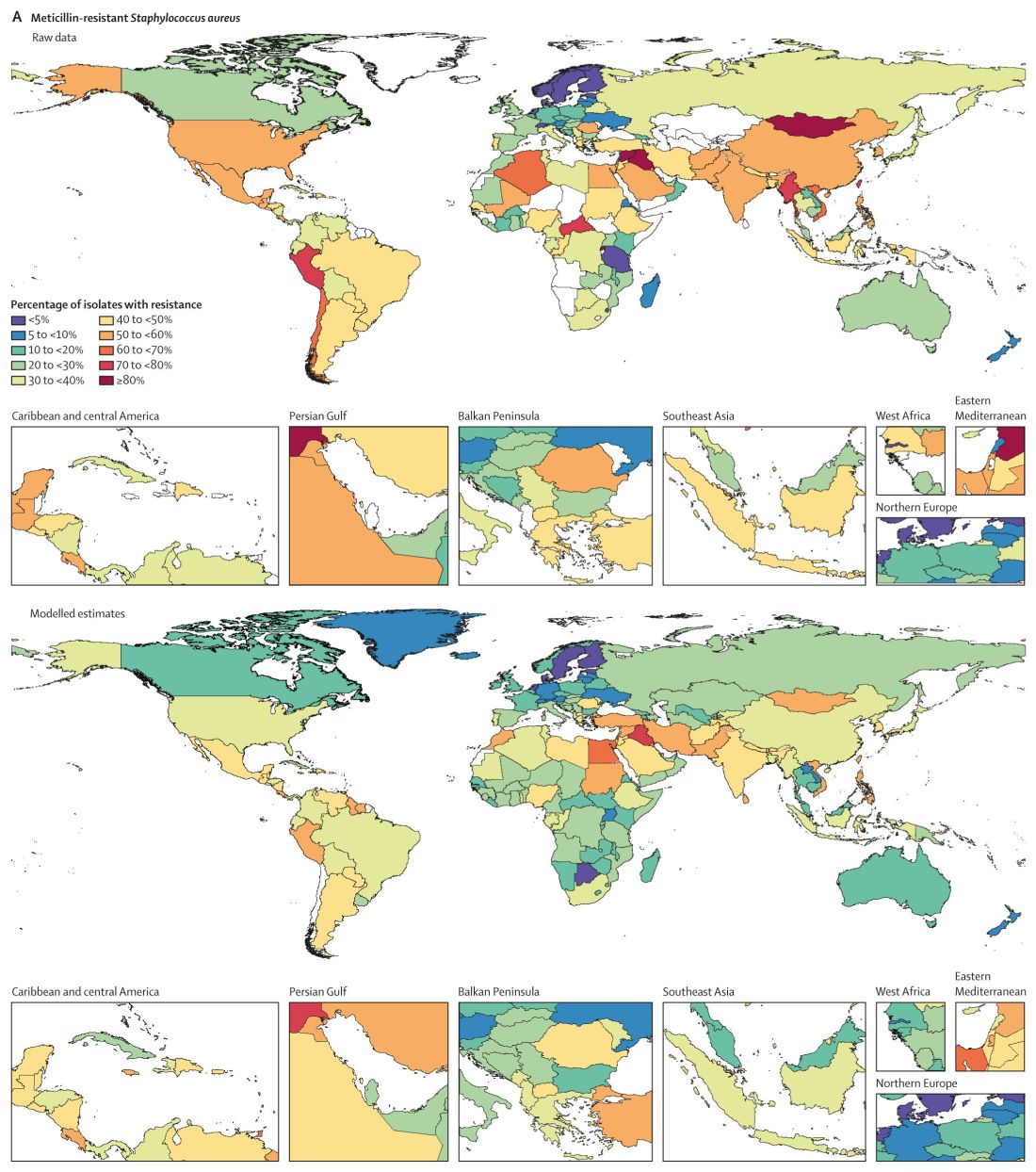
Consistent with previous studies, MRSA stood out as a major cause of mortality. Of 88 different pathogen-drug combinations evaluated, MRSA was responsible for the most mortality: more than 100,000 deaths and 3·5 million disability-adjusted life-years.
The current study findings on MRSA “being a particularly nasty culprit” in AMR infections validates previous work that reported similar results, Vance Fowler, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment on the research. “That is reassuring.”
Potential solutions offered
Dr. Murray and colleagues outlined five strategies to address the challenge of bacterial AMR:
- Infection prevention and control remain paramount in minimizing infections in general and AMR infections in particular.
- More vaccines are needed to reduce the need for antibiotics. “Vaccines are available for only one of the six leading pathogens (S. pneumoniae), although new vaccine programs are underway for S. aureus, E. coli, and others,” the researchers wrote.
- Reduce antibiotic use unrelated to treatment of human disease.
- Avoid using antibiotics for viral infections and other unnecessary indications.
- Invest in new antibiotic development and ensure access to second-line agents in areas without widespread access.
“Identifying strategies that can work to reduce the burden of bacterial AMR – either across a wide range of settings or those that are specifically tailored to the resources available and leading pathogen-drug combinations in a particular setting – is an urgent priority,” the researchers noted.
Admirable AMR research
The results of the study are “startling, but not surprising,” said Dr. Fowler, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
The authors did a “nice job” of addressing both deaths attributable and associated with AMR, Dr. Fowler added. “Those two categories unlock applications, not just in terms of how you interpret it but also what you do about it.”
The deaths attributable to AMR show that there is more work to be done regarding infection control and prevention, Dr. Fowler said, including in areas of the world like lower- and middle-income countries where infection resistance is most pronounced.
The deaths associated with AMR can be more challenging to calculate – people with infections can die for multiple reasons. However, Dr. Fowler applauded the researchers for doing “as good a job as you can” in estimating the extent of associated mortality.
‘The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance’
In an accompanying editorial in The Lancet, Ramanan Laxminarayan, PhD, MPH, wrote: “As COVID-19 rages on, the pandemic of antimicrobial resistance continues in the shadows. The toll taken by AMR on patients and their families is largely invisible but is reflected in prolonged bacterial infections that extend hospital stays and cause needless deaths.”
Dr. Laxminarayan pointed out an irony with AMR in different regions. Some of the AMR burden in sub-Saharan Africa is “probably due to inadequate access to antibiotics and high infection levels, albeit at low levels of resistance, whereas in south Asia and Latin America, it is because of high resistance even with good access to antibiotics.”
More funding to address AMR is needed, Dr. Laxminarayan noted. “Even the lower end of 911,000 deaths estimated by Murray and colleagues is higher than the number of deaths from HIV, which attracts close to U.S. $50 billion each year. However, global spending on addressing AMR is probably much lower than that.” Dr. Laxminarayan is an economist and epidemiologist affiliated with the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy in Washington, D.C., and the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership in Geneva.
An overlap with COVID-19
The Lancet report is likely “to bring more attention to AMR, especially since so many people have been distracted by COVID, and rightly so,” Dr. Fowler predicted. “The world has had its hands full with COVID.”
The two infections interact in direct ways, Dr. Fowler added. For example, some people hospitalized for COVID-19 for an extended time could develop progressively drug-resistant bacteria – leading to a superinfection.
The overlap could be illustrated by a Venn diagram, he said. A yellow circle could illustrate people with COVID-19 who are asymptomatic or who remain outpatients. Next to that would be a blue circle showing people who develop AMR infections. Where the two circles overlap would be green for those hospitalized who – because of receiving steroids, being on a ventilator, or getting a central line – develop a superinfection.
Official guidance continues
The study comes in the context of recent guidance and federal action on AMR. For example, the Infectious Diseases Society of America released new guidelines for AMR in November 2021 as part of ongoing advice on prevention and treatment of this “ongoing crisis.”
This most recent IDSA guidance addresses three pathogens in particular: AmpC beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
Also in November, the World Health Organization released an updated fact sheet on antimicrobial resistance. The WHO declared AMR one of the world’s top 10 global public health threats. The agency emphasized that misuse and overuse of antimicrobials are the main drivers in the development of drug-resistant pathogens. The WHO also pointed out that lack of clean water and sanitation in many areas of the world contribute to spread of microbes, including those resistant to current treatment options.
In September 2021, the Biden administration acknowledged the threat of AMR with allocation of more than $2 billion of the American Rescue Plan money for prevention and treatment of these infections.
Asked if there are any reasons for hope or optimism at this point, Dr. Ikuta said: “Definitely. We know what needs to be done to combat the spread of resistance. COVID-19 has demonstrated the importance of global commitment to infection control measures, such as hand washing and surveillance, and rapid investments in treatments, which can all be applied to antimicrobial resistance.”
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the U.K. Department of Health and Social Care using U.K. aid funding managed by the Fleming Fund and other organizations provided funding for the study. Dr. Ikuta and Dr. Laxminarayan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fowler reported receiving grants or honoraria, as well as serving as a consultant, for numerous sources. He also reported a patent pending in sepsis diagnostics and serving as chair of the V710 Scientific Advisory Committee (Merck).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than HIV, more than malaria.
In terms of preventable deaths, 1.27 million people could have been saved if drug-resistant infections were replaced with infections susceptible to current antibiotics. Furthermore, 4.95 million fewer people would have died if drug-resistant infections were replaced by no infections, researchers estimated.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic took some focus off the AMR burden worldwide over the past 2 years, the urgency to address risk to public health did not ebb. In fact, based on the findings, the researchers noted that AMR is now a leading cause of death worldwide.
“If left unchecked, the spread of AMR could make many bacterial pathogens much more lethal in the future than they are today,” the researchers noted in the study, published online Jan. 20, 2022, in The Lancet.
“These findings are a warning signal that antibiotic resistance is placing pressure on health care systems and leading to significant health loss,” study author Kevin Ikuta, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“We need to continue to adhere to and support infection prevention and control programs, be thoughtful about our antibiotic use, and advocate for increased funding to vaccine discovery and the antibiotic development pipeline,” added Dr. Ikuta, health sciences assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Although many investigators have studied AMR, this study is the largest in scope, covering 204 countries and territories and incorporating data on a comprehensive range of pathogens and pathogen-drug combinations.
Dr. Ikuta, lead author Christopher J.L. Murray, DPhil, and colleagues estimated the global burden of AMR using the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019. They specifically looked at rates of death directly attributed to and separately those associated with resistance.
Regional differences
Broken down by 21 regions, Australasia had 6.5 deaths per 100,000 people attributable to AMR, the lowest rate reported. This region also had 28 deaths per 100,000 associated with AMR.
Researchers found the highest rates in western sub-Saharan Africa. Deaths attributable to AMR were 27.3 per 100,000 and associated death rate was 114.8 per 100,000.
Lower- and middle-income regions had the highest AMR death rates, although resistance remains a high-priority issue for high-income countries as well.
“It’s important to take a global perspective on resistant infections because we can learn about regions and countries that are experiencing the greatest burden, information that was previously unknown,” Dr. Ikuta said. “With these estimates policy makers can prioritize regions that are hotspots and would most benefit from additional interventions.”
Furthermore, the study emphasized the global nature of AMR. “We’ve seen over the last 2 years with COVID-19 that this sort of problem doesn’t respect country borders, and high rates of resistance in one location can spread across a region or spread globally pretty quickly,” Dr. Ikuta said.
Leading resistant infections
Lower respiratory and thorax infections, bloodstream infections, and intra-abdominal infections together accounted for almost 79% of such deaths linked to AMR.
The six leading pathogens are likely household names among infectious disease specialists. The researchers found Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, each responsible for more than 250,000 AMR-associated deaths.
The study also revealed that resistance to several first-line antibiotic agents often used empirically to treat infections accounted for more than 70% of the AMR-attributable deaths. These included fluoroquinolones and beta-lactam antibiotics such as carbapenems, cephalosporins, and penicillins.
Consistent with previous studies, MRSA stood out as a major cause of mortality. Of 88 different pathogen-drug combinations evaluated, MRSA was responsible for the most mortality: more than 100,000 deaths and 3·5 million disability-adjusted life-years.
The current study findings on MRSA “being a particularly nasty culprit” in AMR infections validates previous work that reported similar results, Vance Fowler, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment on the research. “That is reassuring.”
Potential solutions offered
Dr. Murray and colleagues outlined five strategies to address the challenge of bacterial AMR:
- Infection prevention and control remain paramount in minimizing infections in general and AMR infections in particular.
- More vaccines are needed to reduce the need for antibiotics. “Vaccines are available for only one of the six leading pathogens (S. pneumoniae), although new vaccine programs are underway for S. aureus, E. coli, and others,” the researchers wrote.
- Reduce antibiotic use unrelated to treatment of human disease.
- Avoid using antibiotics for viral infections and other unnecessary indications.
- Invest in new antibiotic development and ensure access to second-line agents in areas without widespread access.
“Identifying strategies that can work to reduce the burden of bacterial AMR – either across a wide range of settings or those that are specifically tailored to the resources available and leading pathogen-drug combinations in a particular setting – is an urgent priority,” the researchers noted.
Admirable AMR research
The results of the study are “startling, but not surprising,” said Dr. Fowler, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
The authors did a “nice job” of addressing both deaths attributable and associated with AMR, Dr. Fowler added. “Those two categories unlock applications, not just in terms of how you interpret it but also what you do about it.”
The deaths attributable to AMR show that there is more work to be done regarding infection control and prevention, Dr. Fowler said, including in areas of the world like lower- and middle-income countries where infection resistance is most pronounced.
The deaths associated with AMR can be more challenging to calculate – people with infections can die for multiple reasons. However, Dr. Fowler applauded the researchers for doing “as good a job as you can” in estimating the extent of associated mortality.
‘The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance’
In an accompanying editorial in The Lancet, Ramanan Laxminarayan, PhD, MPH, wrote: “As COVID-19 rages on, the pandemic of antimicrobial resistance continues in the shadows. The toll taken by AMR on patients and their families is largely invisible but is reflected in prolonged bacterial infections that extend hospital stays and cause needless deaths.”
Dr. Laxminarayan pointed out an irony with AMR in different regions. Some of the AMR burden in sub-Saharan Africa is “probably due to inadequate access to antibiotics and high infection levels, albeit at low levels of resistance, whereas in south Asia and Latin America, it is because of high resistance even with good access to antibiotics.”
More funding to address AMR is needed, Dr. Laxminarayan noted. “Even the lower end of 911,000 deaths estimated by Murray and colleagues is higher than the number of deaths from HIV, which attracts close to U.S. $50 billion each year. However, global spending on addressing AMR is probably much lower than that.” Dr. Laxminarayan is an economist and epidemiologist affiliated with the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy in Washington, D.C., and the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership in Geneva.
An overlap with COVID-19
The Lancet report is likely “to bring more attention to AMR, especially since so many people have been distracted by COVID, and rightly so,” Dr. Fowler predicted. “The world has had its hands full with COVID.”
The two infections interact in direct ways, Dr. Fowler added. For example, some people hospitalized for COVID-19 for an extended time could develop progressively drug-resistant bacteria – leading to a superinfection.
The overlap could be illustrated by a Venn diagram, he said. A yellow circle could illustrate people with COVID-19 who are asymptomatic or who remain outpatients. Next to that would be a blue circle showing people who develop AMR infections. Where the two circles overlap would be green for those hospitalized who – because of receiving steroids, being on a ventilator, or getting a central line – develop a superinfection.
Official guidance continues
The study comes in the context of recent guidance and federal action on AMR. For example, the Infectious Diseases Society of America released new guidelines for AMR in November 2021 as part of ongoing advice on prevention and treatment of this “ongoing crisis.”
This most recent IDSA guidance addresses three pathogens in particular: AmpC beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
Also in November, the World Health Organization released an updated fact sheet on antimicrobial resistance. The WHO declared AMR one of the world’s top 10 global public health threats. The agency emphasized that misuse and overuse of antimicrobials are the main drivers in the development of drug-resistant pathogens. The WHO also pointed out that lack of clean water and sanitation in many areas of the world contribute to spread of microbes, including those resistant to current treatment options.
In September 2021, the Biden administration acknowledged the threat of AMR with allocation of more than $2 billion of the American Rescue Plan money for prevention and treatment of these infections.
Asked if there are any reasons for hope or optimism at this point, Dr. Ikuta said: “Definitely. We know what needs to be done to combat the spread of resistance. COVID-19 has demonstrated the importance of global commitment to infection control measures, such as hand washing and surveillance, and rapid investments in treatments, which can all be applied to antimicrobial resistance.”
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the U.K. Department of Health and Social Care using U.K. aid funding managed by the Fleming Fund and other organizations provided funding for the study. Dr. Ikuta and Dr. Laxminarayan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fowler reported receiving grants or honoraria, as well as serving as a consultant, for numerous sources. He also reported a patent pending in sepsis diagnostics and serving as chair of the V710 Scientific Advisory Committee (Merck).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More than HIV, more than malaria.
In terms of preventable deaths, 1.27 million people could have been saved if drug-resistant infections were replaced with infections susceptible to current antibiotics. Furthermore, 4.95 million fewer people would have died if drug-resistant infections were replaced by no infections, researchers estimated.
Although the COVID-19 pandemic took some focus off the AMR burden worldwide over the past 2 years, the urgency to address risk to public health did not ebb. In fact, based on the findings, the researchers noted that AMR is now a leading cause of death worldwide.
“If left unchecked, the spread of AMR could make many bacterial pathogens much more lethal in the future than they are today,” the researchers noted in the study, published online Jan. 20, 2022, in The Lancet.
“These findings are a warning signal that antibiotic resistance is placing pressure on health care systems and leading to significant health loss,” study author Kevin Ikuta, MD, MPH, told this news organization.
“We need to continue to adhere to and support infection prevention and control programs, be thoughtful about our antibiotic use, and advocate for increased funding to vaccine discovery and the antibiotic development pipeline,” added Dr. Ikuta, health sciences assistant clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Although many investigators have studied AMR, this study is the largest in scope, covering 204 countries and territories and incorporating data on a comprehensive range of pathogens and pathogen-drug combinations.
Dr. Ikuta, lead author Christopher J.L. Murray, DPhil, and colleagues estimated the global burden of AMR using the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2019. They specifically looked at rates of death directly attributed to and separately those associated with resistance.
Regional differences
Broken down by 21 regions, Australasia had 6.5 deaths per 100,000 people attributable to AMR, the lowest rate reported. This region also had 28 deaths per 100,000 associated with AMR.
Researchers found the highest rates in western sub-Saharan Africa. Deaths attributable to AMR were 27.3 per 100,000 and associated death rate was 114.8 per 100,000.
Lower- and middle-income regions had the highest AMR death rates, although resistance remains a high-priority issue for high-income countries as well.
“It’s important to take a global perspective on resistant infections because we can learn about regions and countries that are experiencing the greatest burden, information that was previously unknown,” Dr. Ikuta said. “With these estimates policy makers can prioritize regions that are hotspots and would most benefit from additional interventions.”
Furthermore, the study emphasized the global nature of AMR. “We’ve seen over the last 2 years with COVID-19 that this sort of problem doesn’t respect country borders, and high rates of resistance in one location can spread across a region or spread globally pretty quickly,” Dr. Ikuta said.
Leading resistant infections
Lower respiratory and thorax infections, bloodstream infections, and intra-abdominal infections together accounted for almost 79% of such deaths linked to AMR.
The six leading pathogens are likely household names among infectious disease specialists. The researchers found Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, each responsible for more than 250,000 AMR-associated deaths.
The study also revealed that resistance to several first-line antibiotic agents often used empirically to treat infections accounted for more than 70% of the AMR-attributable deaths. These included fluoroquinolones and beta-lactam antibiotics such as carbapenems, cephalosporins, and penicillins.
Consistent with previous studies, MRSA stood out as a major cause of mortality. Of 88 different pathogen-drug combinations evaluated, MRSA was responsible for the most mortality: more than 100,000 deaths and 3·5 million disability-adjusted life-years.
The current study findings on MRSA “being a particularly nasty culprit” in AMR infections validates previous work that reported similar results, Vance Fowler, MD, told this news organization when asked to comment on the research. “That is reassuring.”
Potential solutions offered
Dr. Murray and colleagues outlined five strategies to address the challenge of bacterial AMR:
- Infection prevention and control remain paramount in minimizing infections in general and AMR infections in particular.
- More vaccines are needed to reduce the need for antibiotics. “Vaccines are available for only one of the six leading pathogens (S. pneumoniae), although new vaccine programs are underway for S. aureus, E. coli, and others,” the researchers wrote.
- Reduce antibiotic use unrelated to treatment of human disease.
- Avoid using antibiotics for viral infections and other unnecessary indications.
- Invest in new antibiotic development and ensure access to second-line agents in areas without widespread access.
“Identifying strategies that can work to reduce the burden of bacterial AMR – either across a wide range of settings or those that are specifically tailored to the resources available and leading pathogen-drug combinations in a particular setting – is an urgent priority,” the researchers noted.
Admirable AMR research
The results of the study are “startling, but not surprising,” said Dr. Fowler, professor of medicine at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
The authors did a “nice job” of addressing both deaths attributable and associated with AMR, Dr. Fowler added. “Those two categories unlock applications, not just in terms of how you interpret it but also what you do about it.”
The deaths attributable to AMR show that there is more work to be done regarding infection control and prevention, Dr. Fowler said, including in areas of the world like lower- and middle-income countries where infection resistance is most pronounced.
The deaths associated with AMR can be more challenging to calculate – people with infections can die for multiple reasons. However, Dr. Fowler applauded the researchers for doing “as good a job as you can” in estimating the extent of associated mortality.
‘The overlooked pandemic of antimicrobial resistance’
In an accompanying editorial in The Lancet, Ramanan Laxminarayan, PhD, MPH, wrote: “As COVID-19 rages on, the pandemic of antimicrobial resistance continues in the shadows. The toll taken by AMR on patients and their families is largely invisible but is reflected in prolonged bacterial infections that extend hospital stays and cause needless deaths.”
Dr. Laxminarayan pointed out an irony with AMR in different regions. Some of the AMR burden in sub-Saharan Africa is “probably due to inadequate access to antibiotics and high infection levels, albeit at low levels of resistance, whereas in south Asia and Latin America, it is because of high resistance even with good access to antibiotics.”
More funding to address AMR is needed, Dr. Laxminarayan noted. “Even the lower end of 911,000 deaths estimated by Murray and colleagues is higher than the number of deaths from HIV, which attracts close to U.S. $50 billion each year. However, global spending on addressing AMR is probably much lower than that.” Dr. Laxminarayan is an economist and epidemiologist affiliated with the Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics & Policy in Washington, D.C., and the Global Antibiotic Research and Development Partnership in Geneva.
An overlap with COVID-19
The Lancet report is likely “to bring more attention to AMR, especially since so many people have been distracted by COVID, and rightly so,” Dr. Fowler predicted. “The world has had its hands full with COVID.”
The two infections interact in direct ways, Dr. Fowler added. For example, some people hospitalized for COVID-19 for an extended time could develop progressively drug-resistant bacteria – leading to a superinfection.
The overlap could be illustrated by a Venn diagram, he said. A yellow circle could illustrate people with COVID-19 who are asymptomatic or who remain outpatients. Next to that would be a blue circle showing people who develop AMR infections. Where the two circles overlap would be green for those hospitalized who – because of receiving steroids, being on a ventilator, or getting a central line – develop a superinfection.
Official guidance continues
The study comes in the context of recent guidance and federal action on AMR. For example, the Infectious Diseases Society of America released new guidelines for AMR in November 2021 as part of ongoing advice on prevention and treatment of this “ongoing crisis.”
This most recent IDSA guidance addresses three pathogens in particular: AmpC beta-lactamase–producing Enterobacterales, carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
Also in November, the World Health Organization released an updated fact sheet on antimicrobial resistance. The WHO declared AMR one of the world’s top 10 global public health threats. The agency emphasized that misuse and overuse of antimicrobials are the main drivers in the development of drug-resistant pathogens. The WHO also pointed out that lack of clean water and sanitation in many areas of the world contribute to spread of microbes, including those resistant to current treatment options.
In September 2021, the Biden administration acknowledged the threat of AMR with allocation of more than $2 billion of the American Rescue Plan money for prevention and treatment of these infections.
Asked if there are any reasons for hope or optimism at this point, Dr. Ikuta said: “Definitely. We know what needs to be done to combat the spread of resistance. COVID-19 has demonstrated the importance of global commitment to infection control measures, such as hand washing and surveillance, and rapid investments in treatments, which can all be applied to antimicrobial resistance.”
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the U.K. Department of Health and Social Care using U.K. aid funding managed by the Fleming Fund and other organizations provided funding for the study. Dr. Ikuta and Dr. Laxminarayan have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Fowler reported receiving grants or honoraria, as well as serving as a consultant, for numerous sources. He also reported a patent pending in sepsis diagnostics and serving as chair of the V710 Scientific Advisory Committee (Merck).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID at 2 years: Preparing for a different ‘normal’
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.
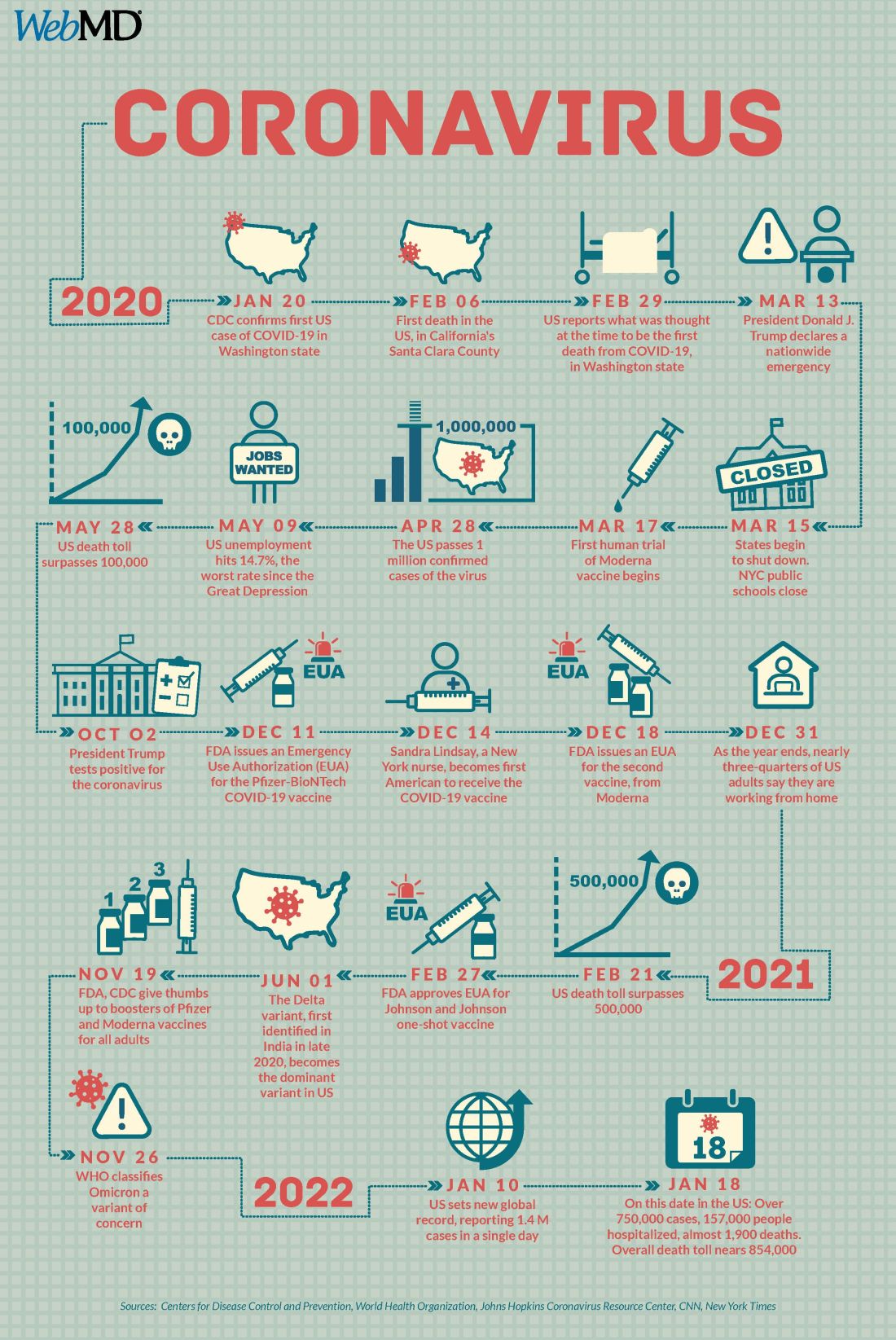
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Detransition, baby: Examining factors leading to ‘detransitioning’ and regret in the transgender community
Over the holiday season I had the pleasure of finally reading the national bestseller, Detransition, Baby. On the surface, the story depicts the complex relationships between Reese, a transgender woman who strongly desires a family, her ex-wife, Ames – a transgender woman who detransitioned to live as a cisgender man – and Ames’ cisgender female partner, who is unexpectedly pregnant with his child. The story delves much deeper than the relationships between these characters, as it exceptionally articulates many of the emotional intricacies of the transgender experience and addresses one of the most taboo topics in the transgender community – detransitioning and regret.
The terms “transition” and “detransition” have fallen out of favor in the vernacular of the transgender population as they incorrectly imply that gender identity is contingent upon gender-affirmation processes.1,2 More importantly, the terms “detransition” and regret are not synonymous. Conflating these terms has undermined the intrinsic nature of gender identity, which has resulted in political and legal consequences seeking to limit or outright ban care for transgender patients.
As a gender-affirming surgeon, one of the most common questions I get asked is the rate of regret patients have after their surgeries. While I have no issue answering the question when it is presented, I do not hesitate to point out some of the problematic subtext inherent in such inquiries. Within the line of questioning, many often comment, “It’s so permanent,” “I can’t believe people can do this to their bodies,” or “How sure are patients before undergoing these surgeries?” While these comments and queries can be downright offensive, they seem to stem from the difficulty people have comprehending gender dysphoria and the painstaking steps people take to affirm their identity. The implication of these comments also reveals a more deep-seated issue – general distrust of individual bodily autonomy, personal identity, and choice.
For the obstetrician-gynecologist, understanding the concept of autonomous, patient-centered decision-making should be second nature, as we face a similar line of interrogation when discussing abortion, contraception, and pregnancy. No other field faces this level of scrutiny when it comes to defending a patient’s bodily autonomy. For example, given the history of reproductive injustice with tubal ligation procedures, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has issued clear guidelines regarding counseling of women while acknowledging the tenuous history of these procedures with minority subgroups. According to their committee opinion, ethical counseling for such a permanent procedure involves understanding the content of information presented to the patient, how that information is conveyed, and self-reflection on the part of the provider.3 The approach to counseling and understanding gender-affirming care is no different.
I want to be clear that regret after gender-affirming surgery is rare, occurring in 0%-3.8% of patients.4-6 In a separate study, 91% of patients expressed significant improvement in quality of life after surgery.7 However, what is disheartening about patients who experience surgical regret is that it originates from continued difficulty from the transition process itself and ongoing discrimination – even though the patient’s physical characteristics match their gender identity.4-6 Similarly, in another survey which examined 17,151 participants who had pursued gender affirmation (broadly defined), approximately 2,242 (13.1%) reported a history of detransition.2 Among these adults, the vast majority (82.5%), cited external factors such as school harassment, sexual violence, family pressure, and social stigma as reasons for detransitioning.2 Other associated factors included male sex assigned at birth, nonbinary gender identity, bisexual orientation, and having an unsupportive family.2
When Ames is explaining his “detransition” to his cisfemale partner, he states: “I got sick of living as trans …[sic]… I am trans, but I don’t need to do trans.”8 While there is still more research needed to further understand detransitioning and surgical regret, these few studies demonstrate a heart-breaking reality – in many aspects of our society it is still extremely difficult to live as a transgender person.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. She did not report any disclosures.
References
1. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center, A program of the Fenway Institute: LGBTQIA+ glossary of terms for health care teams. 2020. Available at www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Glossary-2020.08.30.pdf. Accessed Dec. 30, 2021.
2. Turban JL et al. LGBT Health 2021;8(4):273-80.
3. Sterilization of women: Ethical issues and considerations. Committee Opinion No. 695. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2017;129:e109-16.
4. Ruppin U, Pfafflin F. Arch Sex Behav. 2015;44:1321-9.
5. Lawrence AA. Arch Sex Behav. 2003;32:299-315.
6. Landen M et al. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1998;97:284-9.
7. Papdopulos NA et al. J Sex Med. 2017;14(5):721-30.
8. Peters T. Detransition, Baby. New York: Penguin Random House, 2021.
Over the holiday season I had the pleasure of finally reading the national bestseller, Detransition, Baby. On the surface, the story depicts the complex relationships between Reese, a transgender woman who strongly desires a family, her ex-wife, Ames – a transgender woman who detransitioned to live as a cisgender man – and Ames’ cisgender female partner, who is unexpectedly pregnant with his child. The story delves much deeper than the relationships between these characters, as it exceptionally articulates many of the emotional intricacies of the transgender experience and addresses one of the most taboo topics in the transgender community – detransitioning and regret.
The terms “transition” and “detransition” have fallen out of favor in the vernacular of the transgender population as they incorrectly imply that gender identity is contingent upon gender-affirmation processes.1,2 More importantly, the terms “detransition” and regret are not synonymous. Conflating these terms has undermined the intrinsic nature of gender identity, which has resulted in political and legal consequences seeking to limit or outright ban care for transgender patients.
As a gender-affirming surgeon, one of the most common questions I get asked is the rate of regret patients have after their surgeries. While I have no issue answering the question when it is presented, I do not hesitate to point out some of the problematic subtext inherent in such inquiries. Within the line of questioning, many often comment, “It’s so permanent,” “I can’t believe people can do this to their bodies,” or “How sure are patients before undergoing these surgeries?” While these comments and queries can be downright offensive, they seem to stem from the difficulty people have comprehending gender dysphoria and the painstaking steps people take to affirm their identity. The implication of these comments also reveals a more deep-seated issue – general distrust of individual bodily autonomy, personal identity, and choice.
For the obstetrician-gynecologist, understanding the concept of autonomous, patient-centered decision-making should be second nature, as we face a similar line of interrogation when discussing abortion, contraception, and pregnancy. No other field faces this level of scrutiny when it comes to defending a patient’s bodily autonomy. For example, given the history of reproductive injustice with tubal ligation procedures, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has issued clear guidelines regarding counseling of women while acknowledging the tenuous history of these procedures with minority subgroups. According to their committee opinion, ethical counseling for such a permanent procedure involves understanding the content of information presented to the patient, how that information is conveyed, and self-reflection on the part of the provider.3 The approach to counseling and understanding gender-affirming care is no different.
I want to be clear that regret after gender-affirming surgery is rare, occurring in 0%-3.8% of patients.4-6 In a separate study, 91% of patients expressed significant improvement in quality of life after surgery.7 However, what is disheartening about patients who experience surgical regret is that it originates from continued difficulty from the transition process itself and ongoing discrimination – even though the patient’s physical characteristics match their gender identity.4-6 Similarly, in another survey which examined 17,151 participants who had pursued gender affirmation (broadly defined), approximately 2,242 (13.1%) reported a history of detransition.2 Among these adults, the vast majority (82.5%), cited external factors such as school harassment, sexual violence, family pressure, and social stigma as reasons for detransitioning.2 Other associated factors included male sex assigned at birth, nonbinary gender identity, bisexual orientation, and having an unsupportive family.2
When Ames is explaining his “detransition” to his cisfemale partner, he states: “I got sick of living as trans …[sic]… I am trans, but I don’t need to do trans.”8 While there is still more research needed to further understand detransitioning and surgical regret, these few studies demonstrate a heart-breaking reality – in many aspects of our society it is still extremely difficult to live as a transgender person.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. She did not report any disclosures.
References
1. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center, A program of the Fenway Institute: LGBTQIA+ glossary of terms for health care teams. 2020. Available at www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Glossary-2020.08.30.pdf. Accessed Dec. 30, 2021.
2. Turban JL et al. LGBT Health 2021;8(4):273-80.
3. Sterilization of women: Ethical issues and considerations. Committee Opinion No. 695. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2017;129:e109-16.
4. Ruppin U, Pfafflin F. Arch Sex Behav. 2015;44:1321-9.
5. Lawrence AA. Arch Sex Behav. 2003;32:299-315.
6. Landen M et al. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1998;97:284-9.
7. Papdopulos NA et al. J Sex Med. 2017;14(5):721-30.
8. Peters T. Detransition, Baby. New York: Penguin Random House, 2021.
Over the holiday season I had the pleasure of finally reading the national bestseller, Detransition, Baby. On the surface, the story depicts the complex relationships between Reese, a transgender woman who strongly desires a family, her ex-wife, Ames – a transgender woman who detransitioned to live as a cisgender man – and Ames’ cisgender female partner, who is unexpectedly pregnant with his child. The story delves much deeper than the relationships between these characters, as it exceptionally articulates many of the emotional intricacies of the transgender experience and addresses one of the most taboo topics in the transgender community – detransitioning and regret.
The terms “transition” and “detransition” have fallen out of favor in the vernacular of the transgender population as they incorrectly imply that gender identity is contingent upon gender-affirmation processes.1,2 More importantly, the terms “detransition” and regret are not synonymous. Conflating these terms has undermined the intrinsic nature of gender identity, which has resulted in political and legal consequences seeking to limit or outright ban care for transgender patients.
As a gender-affirming surgeon, one of the most common questions I get asked is the rate of regret patients have after their surgeries. While I have no issue answering the question when it is presented, I do not hesitate to point out some of the problematic subtext inherent in such inquiries. Within the line of questioning, many often comment, “It’s so permanent,” “I can’t believe people can do this to their bodies,” or “How sure are patients before undergoing these surgeries?” While these comments and queries can be downright offensive, they seem to stem from the difficulty people have comprehending gender dysphoria and the painstaking steps people take to affirm their identity. The implication of these comments also reveals a more deep-seated issue – general distrust of individual bodily autonomy, personal identity, and choice.
For the obstetrician-gynecologist, understanding the concept of autonomous, patient-centered decision-making should be second nature, as we face a similar line of interrogation when discussing abortion, contraception, and pregnancy. No other field faces this level of scrutiny when it comes to defending a patient’s bodily autonomy. For example, given the history of reproductive injustice with tubal ligation procedures, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has issued clear guidelines regarding counseling of women while acknowledging the tenuous history of these procedures with minority subgroups. According to their committee opinion, ethical counseling for such a permanent procedure involves understanding the content of information presented to the patient, how that information is conveyed, and self-reflection on the part of the provider.3 The approach to counseling and understanding gender-affirming care is no different.
I want to be clear that regret after gender-affirming surgery is rare, occurring in 0%-3.8% of patients.4-6 In a separate study, 91% of patients expressed significant improvement in quality of life after surgery.7 However, what is disheartening about patients who experience surgical regret is that it originates from continued difficulty from the transition process itself and ongoing discrimination – even though the patient’s physical characteristics match their gender identity.4-6 Similarly, in another survey which examined 17,151 participants who had pursued gender affirmation (broadly defined), approximately 2,242 (13.1%) reported a history of detransition.2 Among these adults, the vast majority (82.5%), cited external factors such as school harassment, sexual violence, family pressure, and social stigma as reasons for detransitioning.2 Other associated factors included male sex assigned at birth, nonbinary gender identity, bisexual orientation, and having an unsupportive family.2
When Ames is explaining his “detransition” to his cisfemale partner, he states: “I got sick of living as trans …[sic]… I am trans, but I don’t need to do trans.”8 While there is still more research needed to further understand detransitioning and surgical regret, these few studies demonstrate a heart-breaking reality – in many aspects of our society it is still extremely difficult to live as a transgender person.
Dr. Brandt is an ob.gyn. and fellowship-trained gender-affirming surgeon in West Reading, Pa. She did not report any disclosures.
References
1. National LGBTQIA+ Health Education Center, A program of the Fenway Institute: LGBTQIA+ glossary of terms for health care teams. 2020. Available at www.lgbtqiahealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Glossary-2020.08.30.pdf. Accessed Dec. 30, 2021.
2. Turban JL et al. LGBT Health 2021;8(4):273-80.
3. Sterilization of women: Ethical issues and considerations. Committee Opinion No. 695. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2017;129:e109-16.
4. Ruppin U, Pfafflin F. Arch Sex Behav. 2015;44:1321-9.
5. Lawrence AA. Arch Sex Behav. 2003;32:299-315.
6. Landen M et al. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1998;97:284-9.
7. Papdopulos NA et al. J Sex Med. 2017;14(5):721-30.
8. Peters T. Detransition, Baby. New York: Penguin Random House, 2021.
Make America beautiful: Support mask mandates
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.










