User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Why is a healthy diet so hard to maintain?
Does this surprise anyone?
Although first publicized in 1975, the diet really didn’t gain attention until the 1990s. But, since then, the evidence in its favor has steadily grown.
Granted, while it was codified into a diet then, the benefits of fruits and vegetables weren’t exactly a secret beforehand. I’m pretty sure all of us remember being told to eat our vegetables (often repeatedly) while growing up.
So it’s not like we, both medical and nonmedical people, should be surprised at the results.
Is it really going to change anyone’s dietary habits?
Of course it will! It’s the beginning of the new year, and this time people are actually going to stick with their resolutions! For the first time they understand that ... who am I kidding?
For some people (hopefully myself included) there will be success at eating better and taking care of themselves. For most it will be Groundhog Day, both literally and figuratively, when February comes around.
It makes me wonder why this is. We all know what’s good for us. The evidence to support the Mediterranean diet is solid. The foods on it are widely available, often at lower cost than the usual American protein-heavy and processed foods habits. They’re flexible, and, generally taste good.
Yet, for all the evidence behind it, most won’t stick with it. Too many years of habits. Too many stressful days at work that lower our willpower to stick with it. Too many convenient reasons to count.
The question really isn’t “what’s the best diet?” That’s been answered. Realistically I don’t see that changing anytime soon.
The real question is “how do I stick with it?”
And another 5, 10, or 20 years of annually trying to figure out what the best diet is won’t change that.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Does this surprise anyone?
Although first publicized in 1975, the diet really didn’t gain attention until the 1990s. But, since then, the evidence in its favor has steadily grown.
Granted, while it was codified into a diet then, the benefits of fruits and vegetables weren’t exactly a secret beforehand. I’m pretty sure all of us remember being told to eat our vegetables (often repeatedly) while growing up.
So it’s not like we, both medical and nonmedical people, should be surprised at the results.
Is it really going to change anyone’s dietary habits?
Of course it will! It’s the beginning of the new year, and this time people are actually going to stick with their resolutions! For the first time they understand that ... who am I kidding?
For some people (hopefully myself included) there will be success at eating better and taking care of themselves. For most it will be Groundhog Day, both literally and figuratively, when February comes around.
It makes me wonder why this is. We all know what’s good for us. The evidence to support the Mediterranean diet is solid. The foods on it are widely available, often at lower cost than the usual American protein-heavy and processed foods habits. They’re flexible, and, generally taste good.
Yet, for all the evidence behind it, most won’t stick with it. Too many years of habits. Too many stressful days at work that lower our willpower to stick with it. Too many convenient reasons to count.
The question really isn’t “what’s the best diet?” That’s been answered. Realistically I don’t see that changing anytime soon.
The real question is “how do I stick with it?”
And another 5, 10, or 20 years of annually trying to figure out what the best diet is won’t change that.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Does this surprise anyone?
Although first publicized in 1975, the diet really didn’t gain attention until the 1990s. But, since then, the evidence in its favor has steadily grown.
Granted, while it was codified into a diet then, the benefits of fruits and vegetables weren’t exactly a secret beforehand. I’m pretty sure all of us remember being told to eat our vegetables (often repeatedly) while growing up.
So it’s not like we, both medical and nonmedical people, should be surprised at the results.
Is it really going to change anyone’s dietary habits?
Of course it will! It’s the beginning of the new year, and this time people are actually going to stick with their resolutions! For the first time they understand that ... who am I kidding?
For some people (hopefully myself included) there will be success at eating better and taking care of themselves. For most it will be Groundhog Day, both literally and figuratively, when February comes around.
It makes me wonder why this is. We all know what’s good for us. The evidence to support the Mediterranean diet is solid. The foods on it are widely available, often at lower cost than the usual American protein-heavy and processed foods habits. They’re flexible, and, generally taste good.
Yet, for all the evidence behind it, most won’t stick with it. Too many years of habits. Too many stressful days at work that lower our willpower to stick with it. Too many convenient reasons to count.
The question really isn’t “what’s the best diet?” That’s been answered. Realistically I don’t see that changing anytime soon.
The real question is “how do I stick with it?”
And another 5, 10, or 20 years of annually trying to figure out what the best diet is won’t change that.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
FDA approves second antiamyloid for Alzheimer’s disease
Like its controversial cousin aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen/Eisai), lecanemab was approved under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway, which can be used to fast-track a drug that provides a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments for a serious or life-threatening illness.
Unlike aducanumab, however, there was no formal FDA advisory committee meeting on lecanemab prior to approval.
“Alzheimer’s disease immeasurably incapacitates the lives of those who suffer from it and has devastating effects on their loved ones,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
“This treatment option is the latest therapy to target and affect the underlying disease process of Alzheimer’s, instead of only treating the symptoms of the disease,” Dr. Dunn added.
Eisai has reported that lecanemab will cost $26,500 a year.
Modest benefit, adverse events
The FDA noted, “The labeling states that treatment with Leqembi should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was studied in clinical trials.”
The agency approved the treatment on the basis of findings from the CLARITY AD trial, which showed modest cognitive benefit for patients with early AD – but at a cost of increased risk for amyloid-related edema and effusions.
The trial enrolled 1,795 adults with mild cognitive impairment or early Alzheimer’s disease in whom amyloid pathology in the brain had been confirmed. Treatment consisted of lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly or matching placebo.
After 18 months of treatment, lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27%, compared with placebo, as measured by the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB). This was an absolute difference of 0.45 points (change from baseline, 1.21 for lecanemab vs. 1.66 with placebo; P < .001).
While the results are “welcome news,” a 0.45-point difference on the CDR-SB might not be clinically meaningful, authors of a recent editorial in The Lancet cautioned.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities that manifest as edema or microhemorrhages also occurred in one in five patients taking lecanemab.
In addition, a newly published case report in The New England Journal of Medicine describes a patient with Alzheimer’s disease who was taking lecanemab and who died after experiencing numerous intracerebral hemorrhages during treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) for acute ischemic stroke.
“The findings raise the possibility of cerebral hemorrhages and necrotizing vasculopathy associated with tPA infusion in a patient with cerebrovascular amyloid who had received lecanemab,” the authors wrote.
Alzheimer’s Association reaction
Still, in anticipation of accelerated approval of lecanemab and the antiamyloid drug donanemab (Eli Lilly), which the FDA has also fast-tracked, the Alzheimer’s Association filed a formal request last month with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services asking that it provide full and unrestricted coverage for FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments.
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, the association asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release at the time.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike added.
After news of today’s approval was released, Dr. Pike noted in a new release, “The Alzheimer’s Association welcomes and celebrates this action by the FDA. We now have a second approved treatment that changes the course of Alzheimer’s disease in a meaningful way for people in the early stages of the disease.”
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Association, called today’s approval “a milestone achievement.”
“The progress we’ve seen in not only this class of treatments but also in the diversification of treatment types and targets over the past few years is exciting and provides real hope to those impacted by this devastating disease,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Critical issues
Commenting on the approval, Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer at Linus Health, said FDA approval of lecanemab and its adoption in the clinic represent a “very exciting development and prospect; but arguably some critical issues need to be considered.”
He noted that the health care system “is not currently prepared to cope with the challenges and demands of lecanemab,” as well as future pharmacologic agents.
“First, we need better workflows to identify suitable patients who can most benefit from this treatment,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone. He added that beyond identification of cognitive difficulties, amyloid status will need to be determined.
“Presently, this requires expensive and invasive tests,” such as positron-emission tomography scans or lumbar punctures for cerebrospinal fluid analysis. However, these are not fully covered by insurance companies and would be challenging to fully scale, he noted.
“In addition to screening, health systems will need to resolve the logistics challenges around the administration of lecanemab with twice-monthly infusions and the need for careful longitudinal evaluations for potential side effects,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone.
“While lecanemab may represent the first disease-modifying therapy widely available for early Alzheimer’s disease, the likely more promising approach is the addition of other therapies to lecanemab as part of a multi-intervention strategy combining pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions,” he added.
Dr. Pascual-Leone has served as a paid member on scientific advisory boards for Neuroelectrics, Magstim, TetraNeuron, Skin2Neuron, MedRhythms, and Hearts Radiant and is a cofounder of TI Solutions and Linus Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 1/9/23.
Like its controversial cousin aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen/Eisai), lecanemab was approved under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway, which can be used to fast-track a drug that provides a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments for a serious or life-threatening illness.
Unlike aducanumab, however, there was no formal FDA advisory committee meeting on lecanemab prior to approval.
“Alzheimer’s disease immeasurably incapacitates the lives of those who suffer from it and has devastating effects on their loved ones,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
“This treatment option is the latest therapy to target and affect the underlying disease process of Alzheimer’s, instead of only treating the symptoms of the disease,” Dr. Dunn added.
Eisai has reported that lecanemab will cost $26,500 a year.
Modest benefit, adverse events
The FDA noted, “The labeling states that treatment with Leqembi should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was studied in clinical trials.”
The agency approved the treatment on the basis of findings from the CLARITY AD trial, which showed modest cognitive benefit for patients with early AD – but at a cost of increased risk for amyloid-related edema and effusions.
The trial enrolled 1,795 adults with mild cognitive impairment or early Alzheimer’s disease in whom amyloid pathology in the brain had been confirmed. Treatment consisted of lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly or matching placebo.
After 18 months of treatment, lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27%, compared with placebo, as measured by the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB). This was an absolute difference of 0.45 points (change from baseline, 1.21 for lecanemab vs. 1.66 with placebo; P < .001).
While the results are “welcome news,” a 0.45-point difference on the CDR-SB might not be clinically meaningful, authors of a recent editorial in The Lancet cautioned.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities that manifest as edema or microhemorrhages also occurred in one in five patients taking lecanemab.
In addition, a newly published case report in The New England Journal of Medicine describes a patient with Alzheimer’s disease who was taking lecanemab and who died after experiencing numerous intracerebral hemorrhages during treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) for acute ischemic stroke.
“The findings raise the possibility of cerebral hemorrhages and necrotizing vasculopathy associated with tPA infusion in a patient with cerebrovascular amyloid who had received lecanemab,” the authors wrote.
Alzheimer’s Association reaction
Still, in anticipation of accelerated approval of lecanemab and the antiamyloid drug donanemab (Eli Lilly), which the FDA has also fast-tracked, the Alzheimer’s Association filed a formal request last month with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services asking that it provide full and unrestricted coverage for FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments.
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, the association asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release at the time.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike added.
After news of today’s approval was released, Dr. Pike noted in a new release, “The Alzheimer’s Association welcomes and celebrates this action by the FDA. We now have a second approved treatment that changes the course of Alzheimer’s disease in a meaningful way for people in the early stages of the disease.”
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Association, called today’s approval “a milestone achievement.”
“The progress we’ve seen in not only this class of treatments but also in the diversification of treatment types and targets over the past few years is exciting and provides real hope to those impacted by this devastating disease,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Critical issues
Commenting on the approval, Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer at Linus Health, said FDA approval of lecanemab and its adoption in the clinic represent a “very exciting development and prospect; but arguably some critical issues need to be considered.”
He noted that the health care system “is not currently prepared to cope with the challenges and demands of lecanemab,” as well as future pharmacologic agents.
“First, we need better workflows to identify suitable patients who can most benefit from this treatment,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone. He added that beyond identification of cognitive difficulties, amyloid status will need to be determined.
“Presently, this requires expensive and invasive tests,” such as positron-emission tomography scans or lumbar punctures for cerebrospinal fluid analysis. However, these are not fully covered by insurance companies and would be challenging to fully scale, he noted.
“In addition to screening, health systems will need to resolve the logistics challenges around the administration of lecanemab with twice-monthly infusions and the need for careful longitudinal evaluations for potential side effects,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone.
“While lecanemab may represent the first disease-modifying therapy widely available for early Alzheimer’s disease, the likely more promising approach is the addition of other therapies to lecanemab as part of a multi-intervention strategy combining pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions,” he added.
Dr. Pascual-Leone has served as a paid member on scientific advisory boards for Neuroelectrics, Magstim, TetraNeuron, Skin2Neuron, MedRhythms, and Hearts Radiant and is a cofounder of TI Solutions and Linus Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 1/9/23.
Like its controversial cousin aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen/Eisai), lecanemab was approved under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway, which can be used to fast-track a drug that provides a meaningful therapeutic advantage over existing treatments for a serious or life-threatening illness.
Unlike aducanumab, however, there was no formal FDA advisory committee meeting on lecanemab prior to approval.
“Alzheimer’s disease immeasurably incapacitates the lives of those who suffer from it and has devastating effects on their loved ones,” Billy Dunn, MD, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a press release.
“This treatment option is the latest therapy to target and affect the underlying disease process of Alzheimer’s, instead of only treating the symptoms of the disease,” Dr. Dunn added.
Eisai has reported that lecanemab will cost $26,500 a year.
Modest benefit, adverse events
The FDA noted, “The labeling states that treatment with Leqembi should be initiated in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of disease, the population in which treatment was studied in clinical trials.”
The agency approved the treatment on the basis of findings from the CLARITY AD trial, which showed modest cognitive benefit for patients with early AD – but at a cost of increased risk for amyloid-related edema and effusions.
The trial enrolled 1,795 adults with mild cognitive impairment or early Alzheimer’s disease in whom amyloid pathology in the brain had been confirmed. Treatment consisted of lecanemab 10 mg/kg biweekly or matching placebo.
After 18 months of treatment, lecanemab slowed cognitive decline by 27%, compared with placebo, as measured by the Clinical Dementia Rating–Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB). This was an absolute difference of 0.45 points (change from baseline, 1.21 for lecanemab vs. 1.66 with placebo; P < .001).
While the results are “welcome news,” a 0.45-point difference on the CDR-SB might not be clinically meaningful, authors of a recent editorial in The Lancet cautioned.
Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities that manifest as edema or microhemorrhages also occurred in one in five patients taking lecanemab.
In addition, a newly published case report in The New England Journal of Medicine describes a patient with Alzheimer’s disease who was taking lecanemab and who died after experiencing numerous intracerebral hemorrhages during treatment with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) for acute ischemic stroke.
“The findings raise the possibility of cerebral hemorrhages and necrotizing vasculopathy associated with tPA infusion in a patient with cerebrovascular amyloid who had received lecanemab,” the authors wrote.
Alzheimer’s Association reaction
Still, in anticipation of accelerated approval of lecanemab and the antiamyloid drug donanemab (Eli Lilly), which the FDA has also fast-tracked, the Alzheimer’s Association filed a formal request last month with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services asking that it provide full and unrestricted coverage for FDA-approved Alzheimer’s disease treatments.
In a letter addressed to CMS administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure, the association asked the agency to remove the requirements for “coverage with evidence development” in its national coverage determination for FDA-approved antiamyloid monoclonal antibodies.
“Each day matters when it comes to slowing the progression of this disease,” Joanne Pike, DrPH, president and CEO for the Alzheimer’s Association, noted in a news release at the time.
“The current CMS policy to severely limit access to these treatments eliminates people’s options, is resulting in continued irreversible disease progression, and contributes to greater health inequities. That’s not acceptable,” Dr. Pike added.
After news of today’s approval was released, Dr. Pike noted in a new release, “The Alzheimer’s Association welcomes and celebrates this action by the FDA. We now have a second approved treatment that changes the course of Alzheimer’s disease in a meaningful way for people in the early stages of the disease.”
Maria C. Carrillo, PhD, chief science officer at the Alzheimer’s Association, called today’s approval “a milestone achievement.”
“The progress we’ve seen in not only this class of treatments but also in the diversification of treatment types and targets over the past few years is exciting and provides real hope to those impacted by this devastating disease,” Dr. Carrillo said.
Critical issues
Commenting on the approval, Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and chief medical officer at Linus Health, said FDA approval of lecanemab and its adoption in the clinic represent a “very exciting development and prospect; but arguably some critical issues need to be considered.”
He noted that the health care system “is not currently prepared to cope with the challenges and demands of lecanemab,” as well as future pharmacologic agents.
“First, we need better workflows to identify suitable patients who can most benefit from this treatment,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone. He added that beyond identification of cognitive difficulties, amyloid status will need to be determined.
“Presently, this requires expensive and invasive tests,” such as positron-emission tomography scans or lumbar punctures for cerebrospinal fluid analysis. However, these are not fully covered by insurance companies and would be challenging to fully scale, he noted.
“In addition to screening, health systems will need to resolve the logistics challenges around the administration of lecanemab with twice-monthly infusions and the need for careful longitudinal evaluations for potential side effects,” said Dr. Pascual-Leone.
“While lecanemab may represent the first disease-modifying therapy widely available for early Alzheimer’s disease, the likely more promising approach is the addition of other therapies to lecanemab as part of a multi-intervention strategy combining pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic interventions,” he added.
Dr. Pascual-Leone has served as a paid member on scientific advisory boards for Neuroelectrics, Magstim, TetraNeuron, Skin2Neuron, MedRhythms, and Hearts Radiant and is a cofounder of TI Solutions and Linus Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated 1/9/23.
Five thoughts on the Damar Hamlin collapse
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The obvious first statement is that it’s neither wise nor appropriate to speculate on the specifics of Damar Hamlin’s cardiac event during a football game on Jan. 2 (including the possibility of commotio cordis) or his ongoing care. The public nature of his collapse induces intense curiosity but people with illness deserve privacy. Privacy in health care is in short supply. I disagree strongly with those who say his doctors ought to be giving public updates. That’s up to the family.
But there are important general concepts to consider about this incident. These include ...
Cardiac arrest can happen to anyone
People with structural heart disease or other chronic illnesses have a higher risk of arrhythmia, but the notion that athletes are immune from cardiac arrest is wrong. This sentence almost seems too obvious to write, but to this day, I hear clinicians express surprise that an athletic person has heart disease.
Survival turns on rapid and effective intervention
In the old days of electrophysiology, we used to test implantable cardioverter-defibrillators during an implant procedure by inducing ventricular fibrillation (VF) and watching the device convert it. Thankfully, trials have shown that this is no longer necessary for most implants.
When you induce VF In the EP lab, you learn quickly that a) it causes loss of consciousness in a matter of seconds, b) rapid defibrillation restores consciousness, often without the patients knowing or remembering they passed out, and c) the failure of the shock to terminate VF results in deterioration in a matter of 1-2 minutes. Even 1 minute in VF feels so long.
Need is an appropriate word in VF treatment
Clinicians often use the verb need. As in, this patient needs this pill or this procedure. It’s rarely appropriate.
But in the case of treating VF, patients truly need rapid defibrillation. Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is low because there just aren’t enough automated external defibrillators (AEDs) or people trained to use them. A study of patients who had out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Denmark found that 30-day survival almost doubled (28.8% vs. 16.4%), when the nearest AED was accessible.
Bystanders must act
The public messages are simple: If a person loses consciousness in front of you, and is not breathing normally, assume it is a cardiac arrest, call 911 to get professional help, and start hands-only chest compressions. Don’t spend time checking for a pulse or trying to wake the person. If this is not a cardiac arrest, they will soon tell you to stop compressing their chest. Seconds matter.
Chest compressions are important but what is really needed is defibrillation. A crucial step in CPR is to send someone to get an AED and get the pads attached. If this is a shockable rhythm, deliver the shock. Hamlin’s collapse emphasizes the importance of the AED; without it, his survival to the hospital would have been unlikely.
Widespread preparticipation screening of young athletes remains a bad idea
Whenever cardiac arrest occurs in an athlete, in such a public way, people think about prevention. Surely it is better to prevent such an event than react to it, goes the thinking. The argument against this idea has four prongs:
The incidence of cardiac disease in a young athlete is extremely low, which sets up a situation where most “positive” tests are false positive. A false positive screening ECG or echocardiogram can create harm in multiple ways. One is the risk from downstream procedures, but worse is the inappropriate disqualification from sport. Healthwise, few harms could be greater than creating long-term fear of exercise in someone.
There is also the problem of false-negative screening tests. An ECG may be normal in the setting of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. And a normal echocardiogram does not exclude arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy or other genetic causes of cardiac arrest. In a 2018 study from a major sports cardiology center in London, 6 of the 8 sudden cardiac deaths in their series were in athletes who had no detectable abnormalities on screening.
Even when disease is found, it’s not clear that prohibiting participation in sports prevents sudden death. Many previous class III recommendations against participation in sport now carry class II – may be considered – designations.
Finally, screening for any disease loses value as treatments improve. Public education regarding rapid intervention with CPR and AED use is the best treatment option. A great example is the case of Christian Erikson, a Danish soccer player who suffered cardiac arrest during a match at the European Championships in 2021 and was rapidly defibrillated on the field. Therapy was so effective that he was conscious and able to wave to fans on his way out of the stadium. He has now returned to elite competition.
Proponents of screening might oppose my take by saying that National Football League players are intensely screened. But this is different from widespread screening of high school and college athletes. It might sound harsh to say, but professional teams have dualities of interests in the health of their athletes given the million-dollar contracts.
What’s more, professional teams can afford to hire expert cardiologists to perform the testing. This would likely reduce the rate of false-positive findings, compared with screening in the community setting. I often have young people referred to me because of asymptomatic bradycardia found during athletic screening – an obviously normal finding.
Conclusions
As long as there are sports, there will be athletes who suffer cardiac arrest.
We can both hope for Hamlin’s full recovery and learn lessons to help reduce the rate of death from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This mostly involves education on how to help fellow humans and a public health commitment to access to AEDs.
John Mandrola, MD, practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky. and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Compulsively checking social media linked with altered brain patterns in teens
Teens who compulsively checked social media networks showed different development patterns in parts of the brain that involve reward and punishment than did those who didn’t check their platforms as often, new research suggests.
Results were published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Researchers, led by Maria T. Maza, of the department of psychology and neuroscience at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, included 169 6th- and 7th-grade students recruited from three public middle schools in rural North Carolina in a 3-year longitudinal cohort.
Participants reported how frequently they checked Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat. Answers were grouped into eight score groups depending on their per-day check times: less than 1; 1; 2-3; 4-5; 6-10; 11-15; 16-20; or more than 20 times. Those groups were then broken into three categories: low (nonhabitual); moderate; and high (habitual).
Imaging shows reactions
Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to see how different areas of the brain react when participants looked at a series of indicators, such as happy and angry faces, which mimic social media rewards, punishments, or neutral feedback.
The research team focused on adolescents, for whom social media participation and neural sensitivity to social feedback from peers are high.
They found that participants who frequently checked social media showed distinct brain patterns when anticipating social feedback compared with those who had moderate or low use, “suggesting that habitual social media checking early in adolescence is associated with divergent brain development over time.”
The affected regions of the brain included the networks that respond to motivation and cognitive control.
However, the study was not able to determine whether the differences are a good or bad thing.
“While for some individuals with habitual checking behaviors, an initial hyposensitivity to potential social rewards and punishments followed by hypersensitivity may contribute to checking behaviors on social media becoming compulsive and problematic, for others, this change in sensitivity may reflect an adaptive behavior that allows them to better navigate their increasingly digital environment,” the authors wrote.
Chicken-and-egg questions
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at the Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, who was not part of this research, said in an interview that it’s not clear from this study which came first – different brain development in the teens prior to this study that caused compulsive checking, or checking behaviors that caused different brain development. The authors acknowledge this is a limitation of the study.
“Hopefully, someday researchers will look at some of these brain activation patterns before kids have been exposed to social media to help us sort some of these questions out,” Dr. Rettew said.
“It wasn’t as though the groups looked the same at baseline and then diverged as they used more and more social media,” Dr. Rettew said. “It looked like there were some baseline differences that could be traced back maybe years before the study even started.”
People hear “divergent brain development” associated with social media and naturally get alarmed, he acknowledged.
“I get that, but the study isn’t really equipped to tell us what should be happening in the brain and what changes may have implications for other parts of an adolescent’s life,” Dr. Rettew said, “In the end, what we have is an association between heavy social media use and certain brain activation patterns which is cool to see and measure.”
He agrees with the authors, however, that overuse of social media is concerning and studying its effects is important.
Seventy-eight percent of early adolescents check every hour
According to the paper, 78% of 13- to 17-year-olds report checking their devices at least every hour and 46% check “almost constantly.”
“Regardless of which brain regions light up when looking at various emoji responses to their Instagram post, I think it is valid already to have some concerns about youth who can’t stay off their phone for more than 10 minutes,” Dr. Rettew said. “Technology is here to stay, but how we can learn to use it rather than have it use us is probably the more pressing question at this point.”
One coauthor reports grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) during the conduct of the study and grants from NIDA and the National Science Foundation outside the submitted work; a coauthor reports grants from the Winston Family Foundation; and a coauthor reports a grant from NIDA and funds from the Winston Family Foundation – both during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
Teens who compulsively checked social media networks showed different development patterns in parts of the brain that involve reward and punishment than did those who didn’t check their platforms as often, new research suggests.
Results were published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Researchers, led by Maria T. Maza, of the department of psychology and neuroscience at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, included 169 6th- and 7th-grade students recruited from three public middle schools in rural North Carolina in a 3-year longitudinal cohort.
Participants reported how frequently they checked Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat. Answers were grouped into eight score groups depending on their per-day check times: less than 1; 1; 2-3; 4-5; 6-10; 11-15; 16-20; or more than 20 times. Those groups were then broken into three categories: low (nonhabitual); moderate; and high (habitual).
Imaging shows reactions
Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to see how different areas of the brain react when participants looked at a series of indicators, such as happy and angry faces, which mimic social media rewards, punishments, or neutral feedback.
The research team focused on adolescents, for whom social media participation and neural sensitivity to social feedback from peers are high.
They found that participants who frequently checked social media showed distinct brain patterns when anticipating social feedback compared with those who had moderate or low use, “suggesting that habitual social media checking early in adolescence is associated with divergent brain development over time.”
The affected regions of the brain included the networks that respond to motivation and cognitive control.
However, the study was not able to determine whether the differences are a good or bad thing.
“While for some individuals with habitual checking behaviors, an initial hyposensitivity to potential social rewards and punishments followed by hypersensitivity may contribute to checking behaviors on social media becoming compulsive and problematic, for others, this change in sensitivity may reflect an adaptive behavior that allows them to better navigate their increasingly digital environment,” the authors wrote.
Chicken-and-egg questions
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at the Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, who was not part of this research, said in an interview that it’s not clear from this study which came first – different brain development in the teens prior to this study that caused compulsive checking, or checking behaviors that caused different brain development. The authors acknowledge this is a limitation of the study.
“Hopefully, someday researchers will look at some of these brain activation patterns before kids have been exposed to social media to help us sort some of these questions out,” Dr. Rettew said.
“It wasn’t as though the groups looked the same at baseline and then diverged as they used more and more social media,” Dr. Rettew said. “It looked like there were some baseline differences that could be traced back maybe years before the study even started.”
People hear “divergent brain development” associated with social media and naturally get alarmed, he acknowledged.
“I get that, but the study isn’t really equipped to tell us what should be happening in the brain and what changes may have implications for other parts of an adolescent’s life,” Dr. Rettew said, “In the end, what we have is an association between heavy social media use and certain brain activation patterns which is cool to see and measure.”
He agrees with the authors, however, that overuse of social media is concerning and studying its effects is important.
Seventy-eight percent of early adolescents check every hour
According to the paper, 78% of 13- to 17-year-olds report checking their devices at least every hour and 46% check “almost constantly.”
“Regardless of which brain regions light up when looking at various emoji responses to their Instagram post, I think it is valid already to have some concerns about youth who can’t stay off their phone for more than 10 minutes,” Dr. Rettew said. “Technology is here to stay, but how we can learn to use it rather than have it use us is probably the more pressing question at this point.”
One coauthor reports grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) during the conduct of the study and grants from NIDA and the National Science Foundation outside the submitted work; a coauthor reports grants from the Winston Family Foundation; and a coauthor reports a grant from NIDA and funds from the Winston Family Foundation – both during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
Teens who compulsively checked social media networks showed different development patterns in parts of the brain that involve reward and punishment than did those who didn’t check their platforms as often, new research suggests.
Results were published online in JAMA Pediatrics.
Researchers, led by Maria T. Maza, of the department of psychology and neuroscience at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, included 169 6th- and 7th-grade students recruited from three public middle schools in rural North Carolina in a 3-year longitudinal cohort.
Participants reported how frequently they checked Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat. Answers were grouped into eight score groups depending on their per-day check times: less than 1; 1; 2-3; 4-5; 6-10; 11-15; 16-20; or more than 20 times. Those groups were then broken into three categories: low (nonhabitual); moderate; and high (habitual).
Imaging shows reactions
Researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to see how different areas of the brain react when participants looked at a series of indicators, such as happy and angry faces, which mimic social media rewards, punishments, or neutral feedback.
The research team focused on adolescents, for whom social media participation and neural sensitivity to social feedback from peers are high.
They found that participants who frequently checked social media showed distinct brain patterns when anticipating social feedback compared with those who had moderate or low use, “suggesting that habitual social media checking early in adolescence is associated with divergent brain development over time.”
The affected regions of the brain included the networks that respond to motivation and cognitive control.
However, the study was not able to determine whether the differences are a good or bad thing.
“While for some individuals with habitual checking behaviors, an initial hyposensitivity to potential social rewards and punishments followed by hypersensitivity may contribute to checking behaviors on social media becoming compulsive and problematic, for others, this change in sensitivity may reflect an adaptive behavior that allows them to better navigate their increasingly digital environment,” the authors wrote.
Chicken-and-egg questions
David Rettew, MD, a child and adolescent psychiatrist at the Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, who was not part of this research, said in an interview that it’s not clear from this study which came first – different brain development in the teens prior to this study that caused compulsive checking, or checking behaviors that caused different brain development. The authors acknowledge this is a limitation of the study.
“Hopefully, someday researchers will look at some of these brain activation patterns before kids have been exposed to social media to help us sort some of these questions out,” Dr. Rettew said.
“It wasn’t as though the groups looked the same at baseline and then diverged as they used more and more social media,” Dr. Rettew said. “It looked like there were some baseline differences that could be traced back maybe years before the study even started.”
People hear “divergent brain development” associated with social media and naturally get alarmed, he acknowledged.
“I get that, but the study isn’t really equipped to tell us what should be happening in the brain and what changes may have implications for other parts of an adolescent’s life,” Dr. Rettew said, “In the end, what we have is an association between heavy social media use and certain brain activation patterns which is cool to see and measure.”
He agrees with the authors, however, that overuse of social media is concerning and studying its effects is important.
Seventy-eight percent of early adolescents check every hour
According to the paper, 78% of 13- to 17-year-olds report checking their devices at least every hour and 46% check “almost constantly.”
“Regardless of which brain regions light up when looking at various emoji responses to their Instagram post, I think it is valid already to have some concerns about youth who can’t stay off their phone for more than 10 minutes,” Dr. Rettew said. “Technology is here to stay, but how we can learn to use it rather than have it use us is probably the more pressing question at this point.”
One coauthor reports grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) during the conduct of the study and grants from NIDA and the National Science Foundation outside the submitted work; a coauthor reports grants from the Winston Family Foundation; and a coauthor reports a grant from NIDA and funds from the Winston Family Foundation – both during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported. Dr. Rettew is author of the book, “Parenting Made Complicated: What Science Really Knows about the Greatest Debates of Early Childhood.”
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
ED doctors call private equity staffing practices illegal and seek to ban them
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Thirty-three states plus the District of Columbia have rules on their books against the so-called corporate practice of medicine. But over the years, critics say, companies have successfully sidestepped bans on owning medical practices by buying or establishing local staffing groups that are nominally owned by doctors and restricting the physicians’ authority so they have no direct control.
These laws and regulations, which started appearing nearly a century ago, were meant to fight the commercialization of medicine, maintain the independence and authority of physicians, and prioritize the doctor-patient relationship over the interests of investors and shareholders.
Those campaigning for stiffer enforcement of the laws say that physician-staffing firms owned by private equity investors are the most egregious offenders. Private equity-backed staffing companies manage a quarter of the nation’s emergency departments, according to a Raleigh, N.C.–based doctor who runs a job site for ED physicians. The two largest are Nashville, Tenn.–based Envision Healthcare, owned by investment giant KKR & Co., and Knoxville, Tenn.–based TeamHealth, owned by Blackstone.
Court filings in multiple states, including California, Missouri, Texas, and Tennessee, have called out Envision and TeamHealth for allegedly using doctor groups as straw men to sidestep corporate practice laws. But those filings have typically been in financial cases involving wrongful termination, breach of contract, and overbilling.
Now, physicians and consumer advocates around the country are anticipating a California lawsuit against Envision, scheduled to start in January 2024 in federal court. The plaintiff in the case, Milwaukee-based American Academy of Emergency Medicine Physician Group, alleges that Envision uses shell business structures to retain de facto ownership of ED staffing groups, and it is asking the court to declare them illegal.
“We’re not asking them to pay money, and we will not accept being paid to drop the case,” said David Millstein, lead attorney for the plaintiff. “We are simply asking the court to ban this practice model.”
‘Possibility to reverberate throughout the country’
The physician group believes a victory would lead to a prohibition of the practice across California – and not just in ERs, but for other staff provided by Envision and TeamHealth, including in anesthesiology and hospital medicine. The California Medical Association supports the lawsuit, saying it “will shape the boundaries of California’s prohibition on the corporate practice of medicine.”
The plaintiff – along with many doctors, nurses, and consumer advocates, as well as some lawmakers – hopes that success in the case will spur regulators and prosecutors in other states to take corporate medicine prohibitions more seriously. “Any decision anywhere in the country that says the corporate ownership of a medical practice is illegal has the possibility to reverberate throughout the country, absolutely – and I hope that it would,” said Julie Mayfield, a state senator in North Carolina.
But the push to reinvigorate laws restricting the corporate practice of medicine has plenty of skeptics, who view it as an effort to return to a golden era in medicine that is long gone or may never have existed to begin with. The genie is out of the bottle, they say, noting that the profit motive has penetrated every corner of health care and that nearly 70% of physicians in the United States are now employed by corporations and hospitals.
The corporate practice of medicine doctrine has “a very interesting and not a very flattering history,” said Barak Richman, a law professor at Duke University. “The medical profession was trying to assert its professional dominance that accrued a lot of benefits to itself in ways that were not terribly beneficial to patients or to the market.”
The California case involves Placentia-Linda Hospital in Orange County, where the plaintiff physician group lost its ED management contract to Envision. The complaint alleges that Envision uses the same business model at numerous hospitals around the state.
“Envision exercises profound and pervasive direct and indirect control and/or influence over the medical practice, making decisions which bear directly and indirectly on the practice of medicine, rendering physicians as mere employees, and diminishing physician independence and freedom from commercial interests,” according to the complaint.
Envision said the company is compliant with state laws and that its operating structure is common in the health care industry. “Legal challenges to that structure have proved meritless,” Envision wrote in an email. It added that “care decisions have and always will be between clinicians and patients.”
TeamHealth, an indirect target in the case, said its “world-class operating team” provides management services that “allow clinicians to focus on the practice of medicine and patient care through a structure commonly utilized by hospitals, health systems, and other providers across the country.”
State rules vary widely
State laws and regulations governing the corporate practice of medicine vary widely on multiple factors, including whether there are exceptions for nonprofit organizations, how much of doctors’ revenue outside management firms can keep, who can own the equipment, and how violations are punished. New York, Texas, and California are considered to have among the toughest restrictions, while Florida and 16 other states have none.
Kirk Ogrosky, a partner at the law firm Goodwin Procter, said this kind of management structure predates the arrival of private equity in the industry. “I would be surprised if a company that is interested in investing in this space screwed up the formation documents; it would shock me,” Mr. Ogrosky said.
Private equity–backed firms have been attracted to EDs in recent years because they are profitable and because they have been able to charge inflated amounts for out-of-network care – at least until a federal law cracked down on surprise billing. Envision and TeamHealth prioritize profits, critics say, by maximizing revenue, cutting costs, and consolidating smaller practices into ever-larger groups – to the point of regional dominance.
Envision and TeamHealth are privately owned, which makes it difficult to find reliable data on their finances and the extent of their market penetration.
Leon Adelman, MD, cofounder and CEO of Ivy Clinicians, a Raleigh, N.C.–based startup job site for emergency physicians, has spent 18 months piecing together data and found that private equity–backed staffing firms run 25% of the nation’s EDs. TeamHealth and Envision have the two largest shares, with 8.6% and 8.3%, respectively, Dr. Adelman said.
Other estimates put private equity’s penetration of ERs at closer to 40%.
Doctors push for investigations
So far, efforts by emergency physicians and others to challenge private equity staffing firms over their alleged violations have yielded frustrating results.
An advocacy group called Take Medicine Back, formed last year by a handful of ED physicians, sent a letter in July to North Carolina Attorney General Josh Stein, asking him to investigate violations of the ban on the corporate practice of medicine. And because Mr. Stein holds a senior position at the National Association of Attorneys General, the letter also asked him to take the lead in persuading his fellow AGs to “launch a multi-state investigation into the widespread lack of enforcement” of corporate practice of medicine laws.
The group’s leader, Mitchell Li, MD, said he was initially disappointed by the response he received from Mr. Stein’s office, which promised to review his request, saying it raised complex legal issues about the corporate practice of medicine in the state. But Dr. Li is now more hopeful, since he has secured a January appointment with officials in Mr. Stein’s office.
Robert McNamara, MD, a cofounder of Dr. Li’s group and chair of emergency medicine at Temple University’s Lewis Katz School of Medicine, drafted complaints to the Texas Medical Board, along with Houston physician David Hoyer, MD, asking the board to intervene against two doctors accused of fronting for professional entities controlled by Envision and TeamHealth. In both cases, the board declined to intervene.
Dr. McNamara, who serves as the chief medical officer of the physicians’ group in the California Envision case, also filed a complaint with Pennsylvania Attorney General Josh Shapiro, alleging that a group called Emergency Care Services of Pennsylvania PC, which was trying to contract with ED physicians of the Crozer Keystone Health System, was wholly owned by TeamHealth and serving as a shell to avoid scrutiny.
A senior official in Mr. Shapiro’s office responded, saying the complaint had been referred to two state agencies, but Dr. McNamara said he has heard nothing back in more than 3 years.
Differing views on private equity’s role
Proponents of private equity ownership say it has brought a lot of good to health care. Jamal Hagler, vice president of research at the American Investment Council, said private equity brings expertise to hospital systems, “whether it’s to hire new staff, grow and open up to new markets, integrate new technologies, or develop new technologies.”
But many physicians who have worked for private equity companies say their mission is not compatible with the best practice of medicine. They cite an emphasis on speed and high patient volume over safety; a preference for lesser-trained, cheaper medical providers; and treatment protocols unsuitable for certain patients.
Sean Jones, MD, an emergency physician in Asheville, N.C., said his first full-time job was at a Florida hospital, where EmCare, a subsidiary of Envision, ran the ED. Dr. Jones said EmCare, in collaboration with the hospital’s owner, pushed doctors to meet performance goals related to wait times and treatments, which were not always good for patients.
For example, if a patient came in with abnormally high heart and respiratory rates – signs of sepsis – doctors were expected to give them large amounts of fluids and antibiotics within an hour, Dr. Jones said. But those symptoms could also be caused by a panic attack or heart failure.
“You don’t want to give a patient with heart failure 2 or 3 liters of fluid, and I would get emails saying, ‘You didn’t do this,’ ” he said. “Well, no, I didn’t, because the reason they couldn’t breathe was they had too much fluid in their lungs.”
Envision said the company’s 25,000 clinicians, “like all clinicians, exercise their independent judgment to provide quality, compassionate, clinically appropriate care.”
Dr. Jones felt otherwise. “We don’t need some MBAs telling us what to do,” he said.
This story was produced by KHN, which publishes California Healthline, an editorially independent service of the California Health Care Foundation. Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit national health policy news service. It is an editorially independent program of the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
Medical practice gave 8,000 patients cancer for Christmas
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy heart failure
Does anyone really like it when places of business send out cards or messages for the holidays? A card from a truly small family business is one thing, but when you start getting emails from multibillion dollar corporations, it feels a bit dishonest. And that’s not even mentioning the potential blowback when things go wrong.
Now, you may wonder how a company could possibly mess up something so simple. “We wish you a merry Christmas and a happy New Year.” Not that difficult. Unless you’re Askern Medical Practice in Doncaster, England. Instead of expressing a simple expression of joy for the holiday season, Askern informed all 8,000 of its patients that they had aggressive lung cancer with metastases and they needed to fill out a DS1500 form, which entitles terminal patients to certain benefits.
It only took an hour for Askern to recognize its mistake and send a second text apologizing and adding in the appropriate season’s greetings, but obviously the damage was done. Presumably patients who were last at the doctor to have their cold treated were able to shrug off the text, or simply didn’t see it before the correction came through, but obviously many patients had concerns directly related to cancer and panicked. They called in but were by and large unable to reach anyone at the practice. Some patients close by even went to center itself to clear things up.
One patient, Mr. Carl Chegwin, raised an excellent point about the debacle: “What if that message was meant for someone, and then they are told it’s a Christmas message, then again told, ‘Oh no, that was actually meant for you?’ ” The old double backtrack into yes, you actually do have cancer has got to be a candidate for worst Christmas gift of all. Yes, even worse than socks.
Genes know it: You are when you eat
There’s been a lot of recent research on intermittent fasting and what it can and can’t do for one’s health. Much of it has focused on participants’ metabolic rates, but a study just published in Cell Metabolism shows how time-restricted feeding (TRF) has an impact on gene expression, the process through which genes are activated and respond to their environment by creating proteins.
The research conducted by Satchidananda Panda, PhD, of the Salk Institute and his team involved two groups of mice, one with free access to food and the other with a daily 9-hour feeding window. Analysis of tissue samples collected from 22 organ groups revealed that nearly 80% of mouse genes responded to TRF. Interestingly, 40% of the genes in the hypothalamus, adrenal gland, and pancreas, which handle hormone regulation, were affected, suggesting that TRF could potentially aid in diabetes and stress disorder management, the investigators said in a written statement.
The researchers also found that TRF aligned the circadian rhythms of multiple organs of the body, which brings sleep into the picture. “Time-restricted eating synchronized the circadian rhythms to have two major waves: one during fasting, and another just after eating. We suspect this allows the body to coordinate different processes,” said Dr. Panda, whose previous research looked at TRF in firefighters, who typically work on shift schedules.
Time-restricted eating, it appears, affects gene expression throughout the body and allows interconnected organ systems to work smoothly. It’s not just about eating. Go figure.
This group practice reduced stress for everyone
It’s been awhile since we checked in on the good folks at Maharishi International University in Fairfield, Iowa – fictional home of the Fighting Transcendentalists [MAHARISHI RULES!] – but we just have to mention their long-term effort to reduce the national stress.
Way back in the year 2000, a group from MIU began practicing transcendental meditation. The size of the group increased over the next few years and eventually reached 1,725 in 2006. That number is important because it represents the square root of 1% of the U.S. population. When that “transition threshold was achieved,” the university explained in a written statement, “all stress indicators immediately started decreasing.”
By stress indicators they mean the U.S. stress index, the mean of eight variables – murder, rape, assault, robbery, infant mortality, drug deaths, vehicle fatalities, and child deaths by injuries – that the study investigators used to track the effectiveness of the meditation program, they said in the World Journal of Social Science.
After 2011, “when the size of the group size began to decline the rate of decrease in stress slowed and then it reversed and began to increase,” MIU reported.
Coauthor Dr. Kenneth Cavanaugh of MIU explained the process: “This study used state-of-the-art methods of time series regression analysis for eliminating potential alternative explanations due to intrinsic preexisting trends and fluctuations in the data. We carefully studied potential alternative explanations in terms of changes in economic conditions, political leadership, population demographics, and policing strategies. None of these factors could account for the results.”
Since we here at LOTME are serious professional journalists, the use of quotes means we are not making this up. Here’s one more thing in quotes: “A grant for 75 million dollars from the Howard and Alice Settle Foundation provided stipends for participants to be in the group and provided funding to bring several hundred visiting [meditation] experts from India to further augment the MIU group.”
Who needs to make up stuff? Not us.
Best diets in 2023: Mediterranean diet wins again
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After all, weight loss usually lands one of the top spots on New Year’s resolution surveys.
And just in time, there’s guidance to pick the best plan, as U.S. News & World Report’s annual rankings of the best diet plans were released on Jan. 3.
Once again, the Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, olive oil, and fish, got the top spot, as best diet overall. It’s the sixth consecutive year for that win. But many other diets got top marks as well.
In 2023, U.S. News, with the help of more than 30 nutritionists, doctors, and epidemiologists, ranked 24 diets in several categories to help people find a plan that meets their goals, whether it’s finding the best weight loss diet, easiest one to follow, or plans for other goals, such as managing diabetes or heart disease. Two new categories were added: Best Diets for Bone & Joint Health and Best Family-Friendly Diets.
In previous years, the publication ranked 40 diets. Even if a diet is no longer ranked, its profile with detailed information remains on the site.
“Each year we ask ourselves what we can do better or differently next time,” said Gretel Schueller, managing editor of health for U.S. News. When the publication got feedback from their experts this year, they had requests to consider sustainability of diets and whether they meet a busy family’s needs, in addition to considering many other factors.
This year’s report ranks plans in 11 categories.
The winners and the categories:
Best diets overall
After the Mediterranean diet, two others tied for second place:
- DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which fights high blood pressure and emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
- Flexitarian diet, which focuses on fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods but also allows occasional meat.
Best weight-loss diets
WW, formerly known as Weight Watchers, got first place. The plan emphasizes not only weight loss but healthier eating and regular activity. The Points program, which assigns specific points to foods, with a daily Points budget, is more personalized than in the past.
- DASH got second place.
- Mayo Clinic Diet and TLC diet tied for third place. The Mayo Clinic Diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It helps people improve their eating habits. The TLC diet (Therapeutic Lifestyle Changes) focuses on vegetables, fruit, lean protein, and reducing cholesterol levels.
Best fast weight-loss diets
The keto diet got first place. It’s a high-fat, low-carb diet that aims to achieve weight loss through fat burning. Four others tied for second place:
- Atkins, a diet created by the cardiologist Robert Atkins, which begins with very few carbs and then recommends progressively eating more until the weight loss goal is achieved
- Nutrisystem, a commercial program that includes prepackaged meals and focuses on high-protein, lower-glycemic foods to stabilize blood sugar levels
- Optavia, a plan focused on low-carb, low-calorie foods and including fortified meal replacements
- SlimFast Diet, a plan of shakes, smoothies, and meal bars to replace two of three meals a day
Best diets for healthy eating
- Mediterranean
- DASH
- Flexitarian
Best heart-healthy diets
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian and Ornish tied for third. The Ornish Diet focuses on plant-based and whole foods and limiting animal products. It recommends daily exercise and stress reduction.
Best diets for diabetes
- DASH
- Mediterranean
- Flexitarian
Best diets for bone and joint health
DASH and Mediterranean are in a first-place tie, followed by the flexitarian diet.
Best family-friendly diets
This category has a three-way tie: the flexitarian, Mediterranean, and TLC diets.
Best plant-based diets
Mediterranean was first, then flexitarian and the MIND diet. The MIND diet combines the DASH and Mediterranean diets and focuses on “brain-healthy” foods.
Easiest diets to follow
Flexitarian and TLC tied for first, followed by a tie between DASH and Mediterranean.
Best diet programs (formerly called commercial plans)
- WW
- There was a tie for second place between Jenny Craig and Noom, the latter of which focuses on low-calorie foods, with personalized calorie ranges and coaching to help meet goals.
Methodology
A variety of factors were considered, such as whether a diet includes all food groups, how easy it is to follow, whether it can be customized to meet cultural and personal preferences, and if it has a realistic timeline for weight loss.
Response from diet plans
Representatives from two plans that received mixed reviews in the rankings responded.
Jenny Craig was ranked second for best diet program but much lower for family friendly, landing at 22nd place of 24.
“Our program is designed to address the needs of the individual through personalized experiences,” Jenny Craig CEO Mandy Dowson said. “We have many families that participate in our program together but are still evaluated separately to determine appropriate individual goals.”
Its high ranking for best diet program reflects feedback from satisfied members, she said. Among advances will be the new Jenny Fresh program, a line of entrées prepared fresh and delivered to customers’ doors.
Atkins got second place for best fast weight loss but ranked near the bottom for best overall, best weight loss, diabetes, healthy eating, and heart health. In response, Colette Heimowitz, vice president of nutrition and education for Simply Good Foods, which makes Atkins’s food products, said that low-carb eating approaches are a viable option for anyone today.
“There are more than 130 independent, peer-reviewed published studies that show the efficacy and safety of low-carb eating,” she said. “The studies have been conducted for several decades and counting.”
Expert perspective
Samantha Cassetty, a registered dietitian, nutritionist, and wellness expert in New York and author of Sugar Shock, reviewed the report for this news organization. She was not involved in the rankings.
“I think what this shows you is, the best diet overall is also the best for various conditions,” she said. For instance, the Mediterranean, the No. 1 overall, also got high ranking for diabetes, heart health, and bone and joint health.
For consumers trying to lose weight: “If you see fast weight loss, that should be a red flag. A healthy diet for weight loss is one you can sustain,” she said.
She’s not a fan of the programs with prepackaged foods. “It takes the guesswork out, but the portion sizes tend to be unsatisfying. They don’t teach you how to deal with some of the challenges [such as realizing an ‘ideal’ portion size].”
How to use the report
Ms. Schueller’s advice: “Recognize that no diet fits everyone.” When considering which plan to choose, she suggests thinking long-term.
“Whatever we choose has to work in the long run,” she said.
Consumers should consider expenses, meal prep time, and whether the diet fits their lifestyle.
Ideally, she said, the best diet “teaches you smart food preparation and how to make healthy choices, allows the flexibility to be social and eat with groups, whether family or friends.”
Before choosing a diet to follow, consult a medical professional for input on the decision, U.S. News cautioned.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA considers regulating CBD products
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The products can have drug-like effects on the body and contain CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). Both CBD and THC can be derived from hemp, which was legalized by Congress in 2018.
“Given what we know about the safety of CBD so far, it raises concerns for FDA about whether these existing regulatory pathways for food and dietary supplements are appropriate for this substance,” FDA Principal Deputy Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, told The Wall Street Journal.
A 2021 FDA report valued the CBD market at $4.6 billion and projected it to quadruple by 2026. The only FDA-approved CBD product is an oil called Epidiolex, which can be prescribed for the seizure-associated disease epilepsy. Research on CBD to treat other diseases is ongoing.
Food, beverage, and beauty products containing CBD are sold in stores and online in many forms, including oils, vaporized liquids, and oil-based capsules, but “research supporting the drug’s benefits is still limited,” the Mayo Clinic said.
Recently, investigations have found that many CBD products also contain THC, which can be derived from legal hemp in a form that is referred to as Delta 8 and produces a psychoactive high. The CDC warned in 2022 that people “mistook” THC products for CBD products, which are often sold at the same stores, and experienced “adverse events.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and FDA warn that much is unknown about CBD and delta-8 products. The CDC says known CBD risks include liver damage; interference with other drugs you are taking, which may lead to injury or serious side effects; drowsiness or sleepiness; diarrhea or changes in appetite; changes in mood, such as crankiness; potential negative effects on fetuses during pregnancy or on babies during breastfeeding; or unintentional poisoning of children when mistaking THC products for CBD products or due to containing other ingredients such as THC or pesticides.
“I don’t think that we can have the perfect be the enemy of the good when we’re looking at such a vast market that is so available and utilized,” Norman Birenbaum, a senior FDA adviser who is working on the regulatory issue, told the Journal. “You’ve got a widely unregulated market.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Antiepileptic drugs tied to increased Parkinson’s disease risk
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.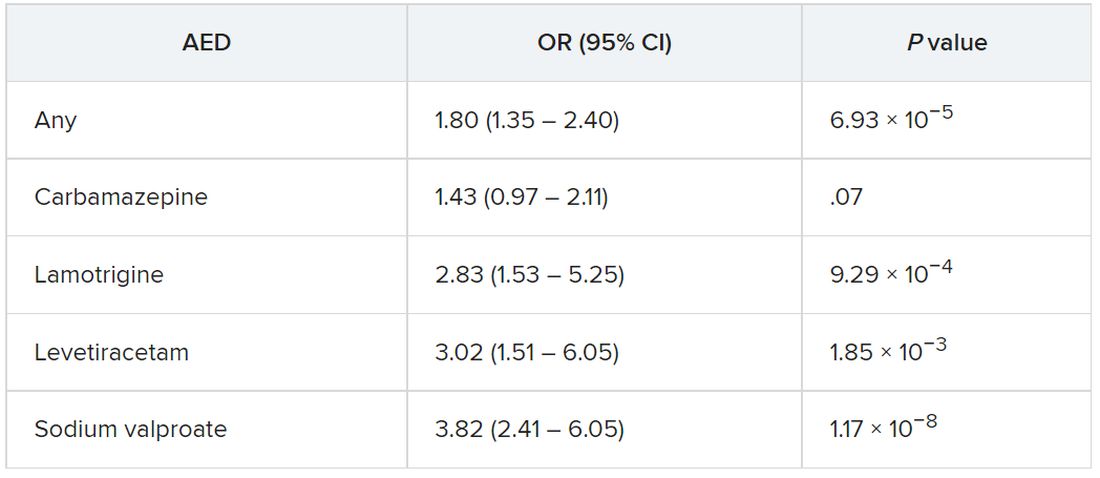
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests.
Drawing on data from the UK Biobank, investigators compared more than 1,400 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with matched control persons and found a considerably higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease among those who had taken AEDs in comparison with those who had not. There was a trend linking a greater number of AED prescriptions and multiple AEDs associated with a greater risk for Parkinson’s disease.
“We observed an association between the most commonly prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the U.K. and Parkinson’s disease using data from UK Biobank,” said senior author Alastair Noyce, PhD, professor of neurology and neuroepidemiology and honorary consultant neurologist, Queen Mary University of London.
“This is the first time that a comprehensive study of the link between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has been undertaken,” said Dr. Noyce.
He added that the findings have no immediate clinical implications, “but further research is definitely needed, [as] this is an interesting observation made in a research setting.”
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Plausible, but unclear link
Recent observational studies have found a “temporal association” between epilepsy and incident Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanism underlying this association is “unclear,” the authors wrote.
It is “plausible” that AEDs “may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease” and that movement disorders are potential side effects of AEDs, but the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease has “not been well studied,” so it remains “unclear” whether AEDs play a role in the association.
“We have previously reported an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease in several different datasets. Here, we wanted to see if it could be explained by an association with the drugs used to treat epilepsy rather than epilepsy per se,” Dr. Noyce explained.
Are AEDs the culprit?
The researchers used data from the UK Biobank, a longitudinal cohort study with more than 500,000 participants, as well as linked primary care medication data to conduct a nested case-control study to investigate this potential association. Participants ranged in age from 40 to 69 years and were recruited between 2006 and 2010.
The researchers compared 1,433 individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease with 8,598 control persons who were matched in a 6:1 ratio for age, sex, race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status (median [interquartile range] age, 71 [65-75] years; 60.9% men; 97.5% White).
Of those with Parkinson’s disease, 4.3% had been prescribed an AED prior to the date of their being diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease, compared with 2.5% in the control group; 4.4% had been diagnosed with epilepsy, compared with 1% of the control persons.
The strongest evidence was for the association between lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and sodium valproate and Parkinson’s disease. There was “weaker evidence” for carbamazepine, although all the AEDs were associated with a higher risk of Parkinson’s disease.
The odds of incident Parkinson’s disease were higher among those who were prescribed one or more AEDs and among individuals who were issued a higher number of prescriptions, the authors reported.
It is possible that it is the epilepsy itself that is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease, rather than the drugs, and that “likely explains part of the association we are seeing,” said Dr. Noyce.
“The bottom line is that more research into the links between epilepsy – and drugs used to treat epilepsy – and Parkinson’s disease is needed,” he said.
Moreover, “only with time will we work out whether the findings hold any real clinical relevance,” he added.
Alternative explanations
Commenting on the research, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association, said, “It has been established in prior research that there is an association between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.” The current study “shows that having had a prescription written for one of four antiepileptic medications was associated with subsequently receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.”
Although one possible conclusion is that the AEDs themselves increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease, “there seem to be other alternative explanations as to why a person who had been prescribed AEDs has an increased risk of receiving a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Gilbert, an associate professor of neurology at Bellevue Hospital Center, New York, who was not involved with the current study.
For example, pre-motor changes in the brain of persons with Parkinson’s disease “may increase the risk of requiring an AED by potentially increasing the risk of having a seizure,” and “changes in the brain caused by the seizures for which AEDs are prescribed may increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease.”
Moreover, psychiatric changes related to Parkinson’s disease may have led to the prescription for AEDs, because at least two of the AEDs are also prescribed for mood stabilization, Dr. Gilbert suggested.
“An unanswered question that the paper acknowledges is, what about people who receive AEDs for reasons other than seizures? Do they also have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease? This would be an interesting population to focus on because it would remove the link between AEDs and seizure and focus on the association between AEDs and Parkinson’s disease,” Dr. Gilbert said.
She emphasized that people who take AEDs for seizures “should not jump to the conclusion that they must come off these medications so as not to increase their risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.” She noted that having seizures “can be dangerous – injuries can occur during a seizure, and if a seizure can’t be stopped or a number occur in rapid succession, brain injury may result.”
For these reasons, people with “a tendency to have seizures need to protect themselves with AEDs” and “should certainly reach out to their neurologists with any questions,” Dr. Gilbert said.
The Preventive Neurology Unit is funded by Barts Charity. The Apocrita High Performance Cluster facility, supported by Queen Mary University London Research–IT Services, was used for this research. Dr. Noyce has received grants from Barts Charity, Parkinson’s UK, Cure Parkinson’s, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, Innovate UK, Solvemed, and Alchemab and personal fees from AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Zambon, BIAL, uMedeor, Alchemab, Britannia, and Charco Neurotech outside the submitted work. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original article. Dr. Gilbert reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Stem cell transplant superior to DMTs for secondary progressive MS
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Results from a retrospective study show that more than 60% of patients with SPMS who received AHSCT were free from disability progression at 5 years. Also for these patients, improvement was more likely to be maintained for years after treatment.
The investigators noted that patients with secondary progressive disease often show little benefit from other DMTs, so interest in other treatments is high. While AHSCT is known to offer good results for patients with relapsing remitting MS, studies of its efficacy for SPMS have yielded conflicting results.
The new findings suggest it may be time to take another look at this therapy for patients with active, more severe disease, the researchers wrote.
“AHSCT may become a treatment option in secondary progressive MS patients with inflammatory activity who have failed available treatments,” said coinvestigator Matilde Inglese, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Genoa (Italy).
“Patients selection is very important to ensure the best treatment response and minimize safety issues, including transplant-related mortality,” Dr. Inglese added.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Class III evidence
In the retrospective, propensity-matching study, researchers used two Italian registries to identify 79 patients who were treated off label with AHSCT and 1,975 patients who received another therapy.
Other DMTs included in the control-group analysis were beta-interferons, azathioprine, glatiramer acetate, mitoxantrone, fingolimod, natalizumab, methotrexate, teriflunomide, cyclophosphamide, dimethyl fumarate, or alemtuzumab.
Results showed that time to first disability progression was significantly longer for patients who had received transplants (hazard ratio, 0.5; P = .005); 61.7% of the AHSCT group were free of disability progression at 5 years versus 46.3% of the control group.
Among patients who received AHSCT, relapse rates were lower in comparison with those who received other DMTs (P < .001), and disability scores were lower over 10 years (P < .001).
The transplant group was also significantly more likely than the other-DMTs group to achieve sustained improvement in disability 3 years after treatment (34.7% vs. 4.6%; P < .001).
“This study provides Class III evidence that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplants prolonged the time to confirmed disability progression compared to other disease-modifying therapies,” the investigators wrote.
Extends the treatment population
Commenting on the study, Jeff Cohen, MD, director of experimental therapeutics at the Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said the research “extends the population for which hematopoietic stem cell transplant should be considered.”
Although previous studies did not show a benefit for patients with severe progressive MS, participants in the current study had secondary progressive MS and superimposed relapse activity, said Dr. Cohen, who was not involved with the research.
“We think that indicates a greater likelihood of benefit” from AHSCT, he noted. “The fact that someone has overt progression or somewhat more severe disability doesn’t preclude the use of stem cell transplant.”
Dr. Cohen pointed out, however, that the study is not without limitations. The exclusion of patients taking B-cell therapies from the SPMS control group raises the question of whether similar results would come from a comparison with AHSCT.
In addition, Dr. Cohen noted there are safety concerns about the therapy, which has yielded higher transplant-related mortality among patients with SPMS – although only one patient in the current study died following the transplant.
Still, the findings are promising, Dr. Cohen added.
“I think as more data accumulate that supports its benefit and reasonable safety in a variety of populations, we’ll see it used more,” he said.
The study was funded by the Italian Multiple Sclerosis Foundation. Dr. Inglese has received fees for consultation from Roche, Genzyme, Merck, Biogen, and Novartis. Dr. Cohen reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY







