User login
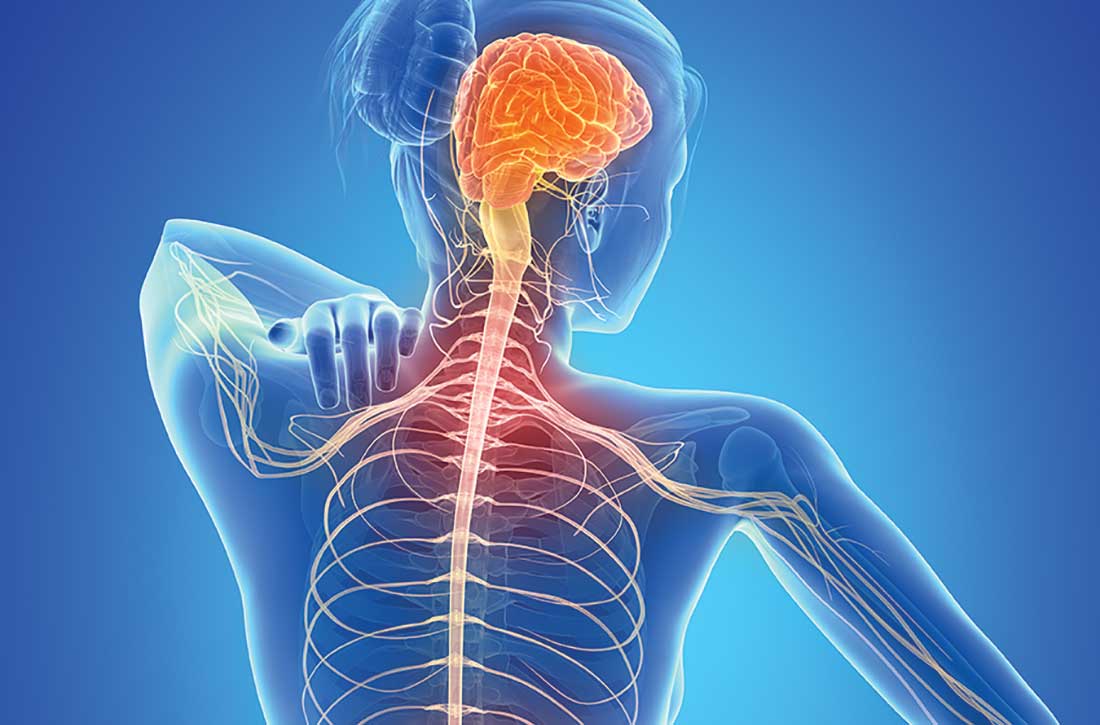
‘Smart inhalers’ may help diagnose and treat asthma – if used
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
After years going on and off medications for occasional asthma symptoms, things went downhill for Brian Blome in November 2020. The retired carpenter started feeling short of breath and wheezing during bike rides. At home, he struggled with chores.
“I was having a hard time climbing a flight of stairs, just doing laundry,” said Mr. Blome, who lives in the Chicago suburb of Palatine.
To get things under control, he saw an allergist and started regular medications – two tablets, two nasal sprays, and inhaled corticosteroids each day, plus an albuterol inhaler for flare-ups.
The inhalers have an extra feature: an electronic monitor that attaches to the device and automatically tracks where and when the medication is used. Bluetooth sends this information to an app on the patient’s mobile phone and to a dashboard where the medical team can see, at a glance, when symptoms are popping up and how regularly medications are taken – leading to the devices often being called “smart inhalers.”
At the 2022 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology conference in Phoenix, researchers explained how digital monitoring devices can help diagnose and treat hard-to-control asthma, potentially reducing the need for oral steroids or biologic therapies.
Even though electric monitors have been on the market for years, their use has been slow to catch on because of uncertainties around insurance coverage, liability, and how to manage and best use the data. One recent study said these devices cost $100-$500, but that price depends on many things, such as insurance.
About 17% of adult asthma patients have “difficult-to-control” asthma, meaning they limit their activity because of breathing symptoms and use reliever medications multiple times a week.
But research suggests that correcting inhaling technique and sticking to the use of the medications can cut that 17% down to just 3.7%, said Mr. Blome’s allergist, Giselle Mosnaim, MD, of NorthShore University HealthSystem in Glenview, Ill. Dr. Mosnaim spoke about digital monitoring at a conference session on digital technologies for asthma management.
A study of more than 5,000 asthma patients “showed that, if you have critical errors in inhaler technique, this leads to worse asthma outcomes and increased asthma exacerbations,” she said. It also shows that, despite new devices and new technologies, “we still have poor inhaler technique.”
Yet adherence is poorly gauged by doctors and patient self-reporting. “The ideal measure of adherence should be objective, accurate, and unobtrusive to minimize impact on patient behavior and allow reliable data collection in real-world settings,” Dr. Mosnaim said. “So electronic medication monitors are the gold standard.”
Improving use
Patients not following instructions or guidelines “is something we saw nonstop with kids,” said Caroline Moassessi, founder of the allergy and asthma blog Gratefulfoodie.com who formerly served on a regional board of the American Lung Association. She’s also the mother of two asthmatic children, now in college, who years ago used electronic medication monitors as part of a research trial.
They were “unimpressed – mostly since I think they thought their asthma was controlled,” she said. “When patients are not in crisis, they don’t manage their asthma well.”
Even in research studies such as the one Rachelle Ramsey, PhD, presented at the conference, it’s not only hard to determine if better adherence leads to improved health, but when.
“For example, does your adherence this week impact your asthma control this week, or does it impact your asthma control next week? Or is it even further out? Do you need to have some level of adherence over the course of a month in order to have better outcomes at the end of that month?” said Dr. Ramsey, a pediatric research psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. “I think it’s a little complicated.”
That said, results from several small studies do show a connection between remote monitoring and better clinical outcomes. One study enrolled asthma patients in the United Kingdom, and another was done by Dr. Mosnaim with Chicago-area patients.
In the U.K. quality improvement project, nurses asked patients with difficult-to-control asthma if they knew how to use their inhalers and were following treatment guidelines.
Those who said “yes” were invited to swap their steroid/inhalers for a controller fitted with a device that tracks use and measures acoustics to test inhaler technique. After 28 days of monitoring, many people in the study had better clinical outcomes.
And after 3 months of digital monitoring, patients didn’t use their rescue medication quite as often.
Mr. Blome has seen a marked improvement in his asthma since starting regular appointments and getting back on daily medications a year and a half ago. He says that now and then, he has wheezing and shortness of breath, usually while biking or exercising. But those symptoms aren’t as severe or frequent as before.
From a doctor’s perspective, “digital inhaler systems allow me to discern patterns in order to determine what triggers his asthma symptoms and to adjust medications at different times of the year,” Dr. Mosnaim said.
Electronic systems can monitor pollen counts and air quality as well as how often a patient uses a quick reliever medication. Thus, she said, tracking these measures year-round could raise attention to impending asthma attacks and suggest when to increase the dose of controller medications or add other treatments.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Adjunctive confocal microscopy found to reduce unnecessary skin excisions
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
results from a large randomized clinical trial showed.
“Skin cancer management exerts a sizable burden on health systems,” researchers led by Giovanni Pellacani, MD, wrote in an article published in JAMA Dermatology. “The systematic application of RCM in the triage of high-risk patients should improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce unnecessary excisions for histopathological diagnostic confirmation, thereby reducing costs, surgical waiting lists, and delayed diagnoses.”
However, they added, “the clinical application of RCM has mainly been limited to retrospective and prospective observational studies producing hypothetical estimates of clinical applicability without intention to affect clinical and therapeutic patient pathways.”
For the current study, Dr. Pellacani, who chairs the department of dermatology at Sapienza University, Rome, and colleagues hypothesized that RCM would reduce unnecessary excisions by more than 30% and would identify all melanoma lesions 0.5 mm or thinner at baseline. They enrolled 3,165 patients with suspect lesions from three dermatology referral centers between January 2017 and December 2019, with a mean follow-up of 9.6 months in the study. Participants were randomly assigned 1:1 to standard therapeutic care, which consisted of clinical and dermoscopy evaluation with or without adjunctive RCM, a novel noninvasive technology that provides in vivo imaging of the skin, with a high diagnostic accuracy.
Histopathologic examination of all excised lesions was performed at the pathology department of the referral center. Resulting information guided prospective clinical decision-making (excision or follow-up). The mean age of patients was 49 years, 49% were women, 21% had a personal history of melanoma, and 51% had Fitzpatrick phototype 2 skin.
When compared with standard therapeutic care only, adjunctive RCM was associated with a higher positive predictive value (18.9 vs. 33.3, respectively), lower benign to malignant ratio (3.7:1.0 vs. 1.8:1.0), and a reduction in the number needed to excise of 43.4% (5.3 vs. 3.0). In addition, all 15 lesions with delayed melanoma diagnoses were thinner than 0.5 mm. Of these, eight were diagnosed as melanoma in situ.
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., who was asked to comment on the study, said that a strength of the analysis was its follow-up and histopathologic evaluation, “which are both essentially forms of feedback. Good, relevant feedback is necessary for all of us to improve.”
She pointed out that, while RCM does appear to reduce the number of benign lesions unnecessarily removed and increase the number of skin cancers appropriately excised, the authors acknowledged that they had at least 4 years of experience with RCM. “The study also does not address the time factor (the procedure takes about 7 minutes per lesion) and the financial cost of reflectance confocal microscopy, as compared to the cost of standard follow-up alone with an increased number of excisions.”
She added that the findings “are not yet applicable to general dermatology across the world, as the authors comment, given that reflectance confocal microscopy is not yet widely available.”
The Italian Ministry of Health supported the study. Neither the researchers nor Dr. Ko reported having relevant financial conflicts.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Tin in permanent contraception implants causes toxicity
Essure implants arrived on the market in 2002 as permanent contraception for women older than age 45 years with children. They were recalled in 2017. Presented as an alternative to laparoscopic tubal ligation, this medical device resulted in rare side effects affecting thousands of women, most notably the nervous system, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, and musculoskeletal system.
Implant analysis protocol
“My research focuses on a variety of medical devices, mostly joint replacements, and more specifically, hip replacements. I look at how these materials behave in humans and how the wear debris affects the body,” explained Ana Maria Trunfio-Sfarghiu, bioengineering expert and research associate with the French National Center for Scientific Research at the Lyon National Institute of Applied Sciences’ Contact and Structure Mechanics Laboratory.
“The problems with Essure implants started with a woman who had been using one for about 10 years and was experiencing side effects such as trouble concentrating and focusing, significant vaginal bleeding, extreme tiredness, hair loss, etc. She had the implant removed, and we retrieved it from her gynecologist and analyzed it alongside other implants,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
“Together with the hospital, we set up an implant analysis protocol. We visited hospital teams to demonstrate how to prepare the biopsies, embedded in paraffin blocks, before sending them to us for analysis. We gave the same specimen preparation instructions for all subjects,” Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu explained.
After a year of clinical analysis, the Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology published an article about 18 cases.
Implant weld corrosion
The Essure implant measures a few centimeters long and resembles a small spring. Once it is released inside the fallopian tube, its goal is to create inflammation and block the tube. It triggers fibrosis, which prevents the sperm from reaching the egg. Premarketing tests had shown that the fibrosis surrounding the implant would keep it from moving. However, the pharmaceutical company hadn’t assessed the mechanical integrity of the spring weld, which was made of silver-tin.
During their analysis in collaboration with the Minapath laboratory, Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s team found that the weld had corroded and that tin particles had been released into the subjects’ bodies. “The study included about 40 women, and we found tin in all of them,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
This weld corrosion has several possible consequences. “When the implant degrades, it can travel anywhere in the pelvis, like a needle moving through the body with no apparent destination. The surgeons who operate to remove it describe similar surgeries in military medicine when the patient has been hit by a bullet!”
Organotin toxicity
Although tin is not especially toxic for the body when ingested, it can bind to organic compounds if it passes through to the blood. “When tin binds to a carbon atom, it becomes organotin, a neurotoxin,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
She said that this organotin can travel to the brain and trigger symptoms like those found in patients with Essure implants. “For the time being, there is insufficient data to assert that we found organotin in all subjects. Another more in-depth study would be needed to assess migration to the brain. For the past 2 years, we have tried to obtain academic funding to continue our research, so far without success. Academic and political authorities seem to be a bit scared of what we’ve found,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
For her, “it’s how the implant was marketed that is problematic. The implant was designed to create local inflammation, inflammation in itself being difficult to control. Some women need to have their entire uterus and ovaries removed to resolve problems caused by the implant.”
Harm in the United States
Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s research has helped American victims obtain acknowledgment of their suffering in the United States. “But the harm caused to women by defective implants has yet to be acknowledged in France,” she added.
She explained that Essure was recalled in 2017 because sales were poor, not because it was deemed dangerous. Her conclusion? “No implant that creates inflammation should be authorized, especially if there is a surgical alternative, which there is here: tubal ligation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape French edition.
Essure implants arrived on the market in 2002 as permanent contraception for women older than age 45 years with children. They were recalled in 2017. Presented as an alternative to laparoscopic tubal ligation, this medical device resulted in rare side effects affecting thousands of women, most notably the nervous system, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, and musculoskeletal system.
Implant analysis protocol
“My research focuses on a variety of medical devices, mostly joint replacements, and more specifically, hip replacements. I look at how these materials behave in humans and how the wear debris affects the body,” explained Ana Maria Trunfio-Sfarghiu, bioengineering expert and research associate with the French National Center for Scientific Research at the Lyon National Institute of Applied Sciences’ Contact and Structure Mechanics Laboratory.
“The problems with Essure implants started with a woman who had been using one for about 10 years and was experiencing side effects such as trouble concentrating and focusing, significant vaginal bleeding, extreme tiredness, hair loss, etc. She had the implant removed, and we retrieved it from her gynecologist and analyzed it alongside other implants,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
“Together with the hospital, we set up an implant analysis protocol. We visited hospital teams to demonstrate how to prepare the biopsies, embedded in paraffin blocks, before sending them to us for analysis. We gave the same specimen preparation instructions for all subjects,” Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu explained.
After a year of clinical analysis, the Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology published an article about 18 cases.
Implant weld corrosion
The Essure implant measures a few centimeters long and resembles a small spring. Once it is released inside the fallopian tube, its goal is to create inflammation and block the tube. It triggers fibrosis, which prevents the sperm from reaching the egg. Premarketing tests had shown that the fibrosis surrounding the implant would keep it from moving. However, the pharmaceutical company hadn’t assessed the mechanical integrity of the spring weld, which was made of silver-tin.
During their analysis in collaboration with the Minapath laboratory, Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s team found that the weld had corroded and that tin particles had been released into the subjects’ bodies. “The study included about 40 women, and we found tin in all of them,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
This weld corrosion has several possible consequences. “When the implant degrades, it can travel anywhere in the pelvis, like a needle moving through the body with no apparent destination. The surgeons who operate to remove it describe similar surgeries in military medicine when the patient has been hit by a bullet!”
Organotin toxicity
Although tin is not especially toxic for the body when ingested, it can bind to organic compounds if it passes through to the blood. “When tin binds to a carbon atom, it becomes organotin, a neurotoxin,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
She said that this organotin can travel to the brain and trigger symptoms like those found in patients with Essure implants. “For the time being, there is insufficient data to assert that we found organotin in all subjects. Another more in-depth study would be needed to assess migration to the brain. For the past 2 years, we have tried to obtain academic funding to continue our research, so far without success. Academic and political authorities seem to be a bit scared of what we’ve found,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
For her, “it’s how the implant was marketed that is problematic. The implant was designed to create local inflammation, inflammation in itself being difficult to control. Some women need to have their entire uterus and ovaries removed to resolve problems caused by the implant.”
Harm in the United States
Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s research has helped American victims obtain acknowledgment of their suffering in the United States. “But the harm caused to women by defective implants has yet to be acknowledged in France,” she added.
She explained that Essure was recalled in 2017 because sales were poor, not because it was deemed dangerous. Her conclusion? “No implant that creates inflammation should be authorized, especially if there is a surgical alternative, which there is here: tubal ligation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape French edition.
Essure implants arrived on the market in 2002 as permanent contraception for women older than age 45 years with children. They were recalled in 2017. Presented as an alternative to laparoscopic tubal ligation, this medical device resulted in rare side effects affecting thousands of women, most notably the nervous system, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, and musculoskeletal system.
Implant analysis protocol
“My research focuses on a variety of medical devices, mostly joint replacements, and more specifically, hip replacements. I look at how these materials behave in humans and how the wear debris affects the body,” explained Ana Maria Trunfio-Sfarghiu, bioengineering expert and research associate with the French National Center for Scientific Research at the Lyon National Institute of Applied Sciences’ Contact and Structure Mechanics Laboratory.
“The problems with Essure implants started with a woman who had been using one for about 10 years and was experiencing side effects such as trouble concentrating and focusing, significant vaginal bleeding, extreme tiredness, hair loss, etc. She had the implant removed, and we retrieved it from her gynecologist and analyzed it alongside other implants,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
“Together with the hospital, we set up an implant analysis protocol. We visited hospital teams to demonstrate how to prepare the biopsies, embedded in paraffin blocks, before sending them to us for analysis. We gave the same specimen preparation instructions for all subjects,” Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu explained.
After a year of clinical analysis, the Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology published an article about 18 cases.
Implant weld corrosion
The Essure implant measures a few centimeters long and resembles a small spring. Once it is released inside the fallopian tube, its goal is to create inflammation and block the tube. It triggers fibrosis, which prevents the sperm from reaching the egg. Premarketing tests had shown that the fibrosis surrounding the implant would keep it from moving. However, the pharmaceutical company hadn’t assessed the mechanical integrity of the spring weld, which was made of silver-tin.
During their analysis in collaboration with the Minapath laboratory, Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s team found that the weld had corroded and that tin particles had been released into the subjects’ bodies. “The study included about 40 women, and we found tin in all of them,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
This weld corrosion has several possible consequences. “When the implant degrades, it can travel anywhere in the pelvis, like a needle moving through the body with no apparent destination. The surgeons who operate to remove it describe similar surgeries in military medicine when the patient has been hit by a bullet!”
Organotin toxicity
Although tin is not especially toxic for the body when ingested, it can bind to organic compounds if it passes through to the blood. “When tin binds to a carbon atom, it becomes organotin, a neurotoxin,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
She said that this organotin can travel to the brain and trigger symptoms like those found in patients with Essure implants. “For the time being, there is insufficient data to assert that we found organotin in all subjects. Another more in-depth study would be needed to assess migration to the brain. For the past 2 years, we have tried to obtain academic funding to continue our research, so far without success. Academic and political authorities seem to be a bit scared of what we’ve found,” said Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu.
For her, “it’s how the implant was marketed that is problematic. The implant was designed to create local inflammation, inflammation in itself being difficult to control. Some women need to have their entire uterus and ovaries removed to resolve problems caused by the implant.”
Harm in the United States
Ms. Trunfio-Sfarghiu’s research has helped American victims obtain acknowledgment of their suffering in the United States. “But the harm caused to women by defective implants has yet to be acknowledged in France,” she added.
She explained that Essure was recalled in 2017 because sales were poor, not because it was deemed dangerous. Her conclusion? “No implant that creates inflammation should be authorized, especially if there is a surgical alternative, which there is here: tubal ligation.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com. This article was translated from the Medscape French edition.
Journalism or medicine: Why not both?
I had an early attraction to newspapers. As a child growing up in Jersey City, N.J., I delivered them door-to-door. I was editor-in-chief of my high school newspaper and worked as a copy boy and sports reporter on the daily Jersey Journal. At Princeton, I joined the University Press Club, working as a string reporter for the New York Herald Tribune, Philadelphia Inquirer, and Associated Press.
I thought I might become a journalist, but medicine was too strong a calling. During my GI elective as a senior medical resident at New York Hospital, I was able to work with some of the first commercial fiberoptic instruments, which presaged my academic career in endoscopic innovation. I was editor-in-chief of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy from 1988 to 1996, and have been the consulting editor for GI Endoscopy Clinics of North America since 1997.
As the first editor-in-chief of GI & Hepatology News, I had the opportunity to combine a background in peer review with my early newspaper experience. My vision for the new publication was to provide information curated and vetted by experts, in contrast to the torrent pouring down from the Internet that was (pertinent to our specialty) “indigestible.” I put in much effort selecting stories provided by Elsevier Global Medical News, especially in constructing the front page. AGA Institute provided strong support, allowing me to choose an editorial board covering all subspecialties. I wanted to highlight the excitement of researchers balanced by expert review and commentary. The digital version added search features, and I tried to promote the “browse factor” that would also encourage advertising, critical to the success of any newspaper. At the end of my term, I felt I had laid a strong foundation, and have been delighted to see the publication continue to thrive.
Charles Lightdale, MD, is professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest.
I had an early attraction to newspapers. As a child growing up in Jersey City, N.J., I delivered them door-to-door. I was editor-in-chief of my high school newspaper and worked as a copy boy and sports reporter on the daily Jersey Journal. At Princeton, I joined the University Press Club, working as a string reporter for the New York Herald Tribune, Philadelphia Inquirer, and Associated Press.
I thought I might become a journalist, but medicine was too strong a calling. During my GI elective as a senior medical resident at New York Hospital, I was able to work with some of the first commercial fiberoptic instruments, which presaged my academic career in endoscopic innovation. I was editor-in-chief of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy from 1988 to 1996, and have been the consulting editor for GI Endoscopy Clinics of North America since 1997.
As the first editor-in-chief of GI & Hepatology News, I had the opportunity to combine a background in peer review with my early newspaper experience. My vision for the new publication was to provide information curated and vetted by experts, in contrast to the torrent pouring down from the Internet that was (pertinent to our specialty) “indigestible.” I put in much effort selecting stories provided by Elsevier Global Medical News, especially in constructing the front page. AGA Institute provided strong support, allowing me to choose an editorial board covering all subspecialties. I wanted to highlight the excitement of researchers balanced by expert review and commentary. The digital version added search features, and I tried to promote the “browse factor” that would also encourage advertising, critical to the success of any newspaper. At the end of my term, I felt I had laid a strong foundation, and have been delighted to see the publication continue to thrive.
Charles Lightdale, MD, is professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest.
I had an early attraction to newspapers. As a child growing up in Jersey City, N.J., I delivered them door-to-door. I was editor-in-chief of my high school newspaper and worked as a copy boy and sports reporter on the daily Jersey Journal. At Princeton, I joined the University Press Club, working as a string reporter for the New York Herald Tribune, Philadelphia Inquirer, and Associated Press.
I thought I might become a journalist, but medicine was too strong a calling. During my GI elective as a senior medical resident at New York Hospital, I was able to work with some of the first commercial fiberoptic instruments, which presaged my academic career in endoscopic innovation. I was editor-in-chief of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy from 1988 to 1996, and have been the consulting editor for GI Endoscopy Clinics of North America since 1997.
As the first editor-in-chief of GI & Hepatology News, I had the opportunity to combine a background in peer review with my early newspaper experience. My vision for the new publication was to provide information curated and vetted by experts, in contrast to the torrent pouring down from the Internet that was (pertinent to our specialty) “indigestible.” I put in much effort selecting stories provided by Elsevier Global Medical News, especially in constructing the front page. AGA Institute provided strong support, allowing me to choose an editorial board covering all subspecialties. I wanted to highlight the excitement of researchers balanced by expert review and commentary. The digital version added search features, and I tried to promote the “browse factor” that would also encourage advertising, critical to the success of any newspaper. At the end of my term, I felt I had laid a strong foundation, and have been delighted to see the publication continue to thrive.
Charles Lightdale, MD, is professor of medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York. He disclosed having no conflicts of interest.
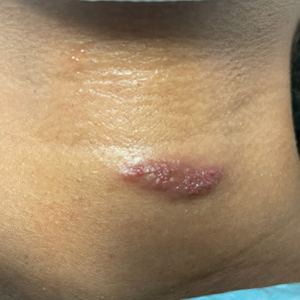
Vascular Plaque in a Pregnant Patient With a History of Breast Cancer
The Diagnosis: Tufted Angioma
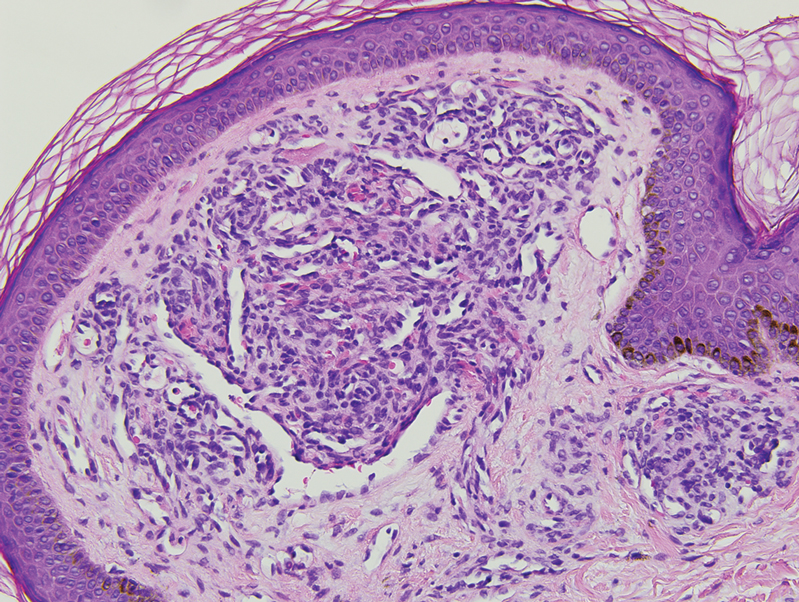
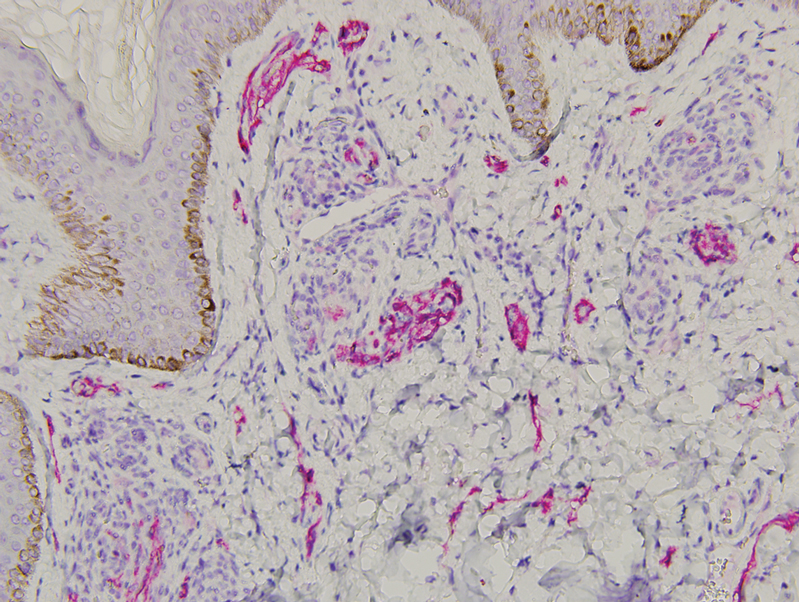
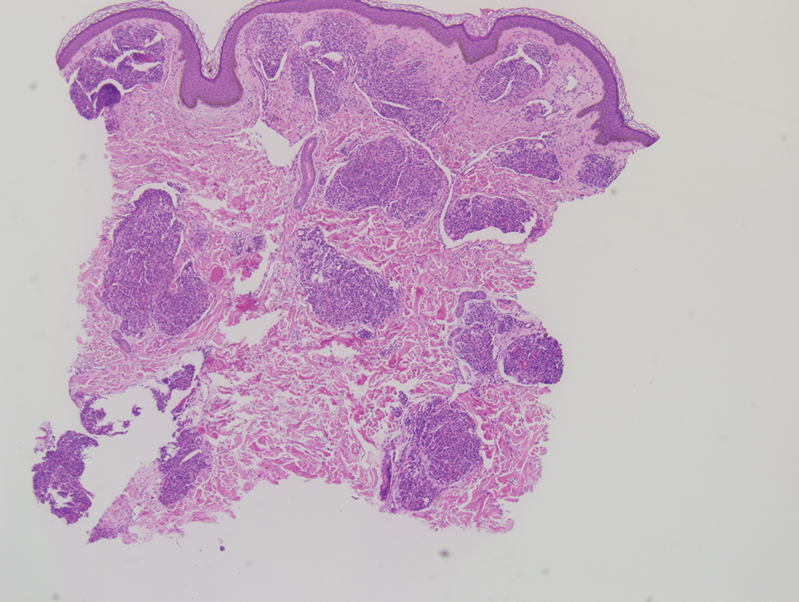
Histopathology revealed discrete lobules of closely packed capillaries with bland endothelial cells throughout the upper and lower dermis (Figure 1). The surrounding crescentlike vessels and lymphatics stained with D2-40 (Figure 2). These histologic findings were consistent with tufted angioma, and the patient elected for observation.
Tufted angiomas are benign vascular lesions named for the tufted appearance of capillaries on histology.1 They commonly present in children, with a lower incidence in adults and rare cases in pregnancy.2 Tufted angiomas typically present as solitary, slowly expanding, erythematous macules, plaques, or nodules on the neck or trunk ranging in size from less than 1 to 10 cm.2-4 They can be histologically distinguished from other vascular tumors, including aggressive malignant neoplasms.1
Tufted angiomas are identified by characteristic “cannon ball tufts” of capillaries in the dermis and subcutis at low power.3,5 Distinct cellular lobules may be found bulging into thin-walled vascular channels at the margins of the lobules in the dermis and subcutis (Figure 3).4 The lobules are formed by cells with spindle-shaped nuclei.6 Some mitotic figures may be present, but no cellular atypia is seen.2 The capillaries at the periphery appear as dilated semilunar vessels.4 Dilated lymphatics, which stain with D2-40, can be found at the periphery of the tufted capillaries and throughout the remaining dermis.3,4
Tufted angiomas may arise independently in adults but also have been associated with conditions such as pregnancy. Omori et al7 identified an acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy that was positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors. Reports of tufted angiomas in pregnancy vary; some are multiple lesions, some regress postpartum, and some undergo successful surgical treatment.3,5
Vascular lesions such as tufted angiomas specifically may appear in pregnancy due to a high-volume state with vasodilation and increased vascular proliferation. Although tumor angiogenesis has been linked to specific growth factors and cytokines, it has been hypothesized that the systemic hormones of pregnancy such as human chorionic gonadotropin, estradiol, and progesterone also shift the body to a more angiogenic state.8 In a study of cutaneous changes in pregnant women (N=905), 41% developed a vascular skin change, including spider veins, varicosities, hemangiomas, and granulomas.9 The most common vascular tumor in pregnancy is pyogenic granuloma. Pyogenic granulomas are small, solitary, friable papules that commonly are found on the hands, forearms, face, or in the mouth; histologically they demonstrate dilated capillaries in lobular structures accompanied by larger thick-walled vessels.3,10,11
Tufted angiomas may mimic a variety of other conditions. Epithelioid hemangioma, considered by some to be on the same morphologic spectrum as angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, classically occurs in young adults on the head and in the neck region. It histologically demonstrates a lobular appearance at low power; however, these lobules are made up of vessels with histiocytoid to epithelioid endothelial cells surrounded by a prominent inflammatory infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils.12
Kaposi sarcoma may appear on the neck but most often presents as macules and patches on the extremities that may form nodules with a rubbery consistency. In tufted angiomas, the cellular nodules with dilated channels at the margins bear a resemblance to Kaposi sarcoma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma; however, in tufted angiomas the lobules are composed of bland spindle cells and slitlike vessels at the periphery.3,13,14 Tufted angiomas are negative for human herpesvirus 8 and typically do not have an associated inflammatory infiltrate with plasma cells.11,15
Moreover, it is important to differentiate tufted angioma from a cutaneous manifestation of an underlying malignancy, which has been described previously in cases of breast cancer.16,17 Our case illustrates a rare vascular tumor arising in the novel context of a pregnant patient with breast cancer. Distinguishing tufted angioma from other benign or malignant vascular tumors is necessary to avoid inappropriate therapeutic interventions.
- Jones EW, Orkin M. Tufted angioma (angioblastoma). a benign progressive angioma, not to be confused with Kaposi’s sarcoma or low-grade angiosarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 pt 1):214-225.
- Lee B, Chiu M, Soriano T, et al. Adult-onset tufted angioma: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:341-345.
- Kim YK, Kim HJ, Lee KG. Acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:458-459.
- Feito-Rodriguez M, Sanchez-Orta A, De Lucas R, et al. Congenital tufted angioma: a multicenter retrospective study of 30 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:808-816.
- Pietroletti R, Leardi S, Simi M. Perianal acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy: case report. Tech Coloproctol. 2002;6:117-119.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Omori M, Bito T, Nishigori C. Acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy showing expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors. Eur J Dermatol. 2013;23:898-899.
- Boeldt DS, Bird IM. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J Endocrinol. 2017;232:R27-R44.
- Fernandes LB, Amaral W. Clinical study of skin changes in low and high risk pregnant women. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:822-826.
- Walker JL, Wang AR, Kroumpouzos G, et al. Cutaneous tumors in pregnancy. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:359-367.
- Sarwal P, Lapumnuaypol K. Pyogenic granuloma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Ortins-Pina A, Llamas-Velasco M, Turpin S, et al. FOSB immunoreactivity in endothelia of epithelioid hemangioma (angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia). J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:395-402.
- Arai E, Kuramochi A, Tsuchida T, et al. Usefulness of D2-40 immunohistochemistry for differentiation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:492-497.
- Grassi S, Carugno A, Vignini M, et al. Adult-onset tufted angiomas associated with an arteriovenous malformation in a renal transplant recipient: case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:162-165.
- Lyons LL, North PE, Mac-Moune Lai F, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: a study of 33 cases emphasizing its pathologic, immunophenotypic, and biologic uniqueness from juvenile hemangioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:559-568.
- Putra HP, Djawad K, Nurdin AR. Cutaneous lesions as the first manifestation of breast cancer: a rare case. Pan Afr Med J. 2020;37:383.
- Thiers BH, Sahn RE, Callen JP. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancy. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:73-98.
The Diagnosis: Tufted Angioma
Histopathology revealed discrete lobules of closely packed capillaries with bland endothelial cells throughout the upper and lower dermis (Figure 1). The surrounding crescentlike vessels and lymphatics stained with D2-40 (Figure 2). These histologic findings were consistent with tufted angioma, and the patient elected for observation.
Tufted angiomas are benign vascular lesions named for the tufted appearance of capillaries on histology.1 They commonly present in children, with a lower incidence in adults and rare cases in pregnancy.2 Tufted angiomas typically present as solitary, slowly expanding, erythematous macules, plaques, or nodules on the neck or trunk ranging in size from less than 1 to 10 cm.2-4 They can be histologically distinguished from other vascular tumors, including aggressive malignant neoplasms.1
Tufted angiomas are identified by characteristic “cannon ball tufts” of capillaries in the dermis and subcutis at low power.3,5 Distinct cellular lobules may be found bulging into thin-walled vascular channels at the margins of the lobules in the dermis and subcutis (Figure 3).4 The lobules are formed by cells with spindle-shaped nuclei.6 Some mitotic figures may be present, but no cellular atypia is seen.2 The capillaries at the periphery appear as dilated semilunar vessels.4 Dilated lymphatics, which stain with D2-40, can be found at the periphery of the tufted capillaries and throughout the remaining dermis.3,4
Tufted angiomas may arise independently in adults but also have been associated with conditions such as pregnancy. Omori et al7 identified an acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy that was positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors. Reports of tufted angiomas in pregnancy vary; some are multiple lesions, some regress postpartum, and some undergo successful surgical treatment.3,5
Vascular lesions such as tufted angiomas specifically may appear in pregnancy due to a high-volume state with vasodilation and increased vascular proliferation. Although tumor angiogenesis has been linked to specific growth factors and cytokines, it has been hypothesized that the systemic hormones of pregnancy such as human chorionic gonadotropin, estradiol, and progesterone also shift the body to a more angiogenic state.8 In a study of cutaneous changes in pregnant women (N=905), 41% developed a vascular skin change, including spider veins, varicosities, hemangiomas, and granulomas.9 The most common vascular tumor in pregnancy is pyogenic granuloma. Pyogenic granulomas are small, solitary, friable papules that commonly are found on the hands, forearms, face, or in the mouth; histologically they demonstrate dilated capillaries in lobular structures accompanied by larger thick-walled vessels.3,10,11
Tufted angiomas may mimic a variety of other conditions. Epithelioid hemangioma, considered by some to be on the same morphologic spectrum as angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, classically occurs in young adults on the head and in the neck region. It histologically demonstrates a lobular appearance at low power; however, these lobules are made up of vessels with histiocytoid to epithelioid endothelial cells surrounded by a prominent inflammatory infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils.12
Kaposi sarcoma may appear on the neck but most often presents as macules and patches on the extremities that may form nodules with a rubbery consistency. In tufted angiomas, the cellular nodules with dilated channels at the margins bear a resemblance to Kaposi sarcoma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma; however, in tufted angiomas the lobules are composed of bland spindle cells and slitlike vessels at the periphery.3,13,14 Tufted angiomas are negative for human herpesvirus 8 and typically do not have an associated inflammatory infiltrate with plasma cells.11,15
Moreover, it is important to differentiate tufted angioma from a cutaneous manifestation of an underlying malignancy, which has been described previously in cases of breast cancer.16,17 Our case illustrates a rare vascular tumor arising in the novel context of a pregnant patient with breast cancer. Distinguishing tufted angioma from other benign or malignant vascular tumors is necessary to avoid inappropriate therapeutic interventions.
The Diagnosis: Tufted Angioma
Histopathology revealed discrete lobules of closely packed capillaries with bland endothelial cells throughout the upper and lower dermis (Figure 1). The surrounding crescentlike vessels and lymphatics stained with D2-40 (Figure 2). These histologic findings were consistent with tufted angioma, and the patient elected for observation.
Tufted angiomas are benign vascular lesions named for the tufted appearance of capillaries on histology.1 They commonly present in children, with a lower incidence in adults and rare cases in pregnancy.2 Tufted angiomas typically present as solitary, slowly expanding, erythematous macules, plaques, or nodules on the neck or trunk ranging in size from less than 1 to 10 cm.2-4 They can be histologically distinguished from other vascular tumors, including aggressive malignant neoplasms.1
Tufted angiomas are identified by characteristic “cannon ball tufts” of capillaries in the dermis and subcutis at low power.3,5 Distinct cellular lobules may be found bulging into thin-walled vascular channels at the margins of the lobules in the dermis and subcutis (Figure 3).4 The lobules are formed by cells with spindle-shaped nuclei.6 Some mitotic figures may be present, but no cellular atypia is seen.2 The capillaries at the periphery appear as dilated semilunar vessels.4 Dilated lymphatics, which stain with D2-40, can be found at the periphery of the tufted capillaries and throughout the remaining dermis.3,4
Tufted angiomas may arise independently in adults but also have been associated with conditions such as pregnancy. Omori et al7 identified an acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy that was positive for estrogen and progesterone receptors. Reports of tufted angiomas in pregnancy vary; some are multiple lesions, some regress postpartum, and some undergo successful surgical treatment.3,5
Vascular lesions such as tufted angiomas specifically may appear in pregnancy due to a high-volume state with vasodilation and increased vascular proliferation. Although tumor angiogenesis has been linked to specific growth factors and cytokines, it has been hypothesized that the systemic hormones of pregnancy such as human chorionic gonadotropin, estradiol, and progesterone also shift the body to a more angiogenic state.8 In a study of cutaneous changes in pregnant women (N=905), 41% developed a vascular skin change, including spider veins, varicosities, hemangiomas, and granulomas.9 The most common vascular tumor in pregnancy is pyogenic granuloma. Pyogenic granulomas are small, solitary, friable papules that commonly are found on the hands, forearms, face, or in the mouth; histologically they demonstrate dilated capillaries in lobular structures accompanied by larger thick-walled vessels.3,10,11
Tufted angiomas may mimic a variety of other conditions. Epithelioid hemangioma, considered by some to be on the same morphologic spectrum as angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia, classically occurs in young adults on the head and in the neck region. It histologically demonstrates a lobular appearance at low power; however, these lobules are made up of vessels with histiocytoid to epithelioid endothelial cells surrounded by a prominent inflammatory infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes and eosinophils.12
Kaposi sarcoma may appear on the neck but most often presents as macules and patches on the extremities that may form nodules with a rubbery consistency. In tufted angiomas, the cellular nodules with dilated channels at the margins bear a resemblance to Kaposi sarcoma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma; however, in tufted angiomas the lobules are composed of bland spindle cells and slitlike vessels at the periphery.3,13,14 Tufted angiomas are negative for human herpesvirus 8 and typically do not have an associated inflammatory infiltrate with plasma cells.11,15
Moreover, it is important to differentiate tufted angioma from a cutaneous manifestation of an underlying malignancy, which has been described previously in cases of breast cancer.16,17 Our case illustrates a rare vascular tumor arising in the novel context of a pregnant patient with breast cancer. Distinguishing tufted angioma from other benign or malignant vascular tumors is necessary to avoid inappropriate therapeutic interventions.
- Jones EW, Orkin M. Tufted angioma (angioblastoma). a benign progressive angioma, not to be confused with Kaposi’s sarcoma or low-grade angiosarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 pt 1):214-225.
- Lee B, Chiu M, Soriano T, et al. Adult-onset tufted angioma: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:341-345.
- Kim YK, Kim HJ, Lee KG. Acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:458-459.
- Feito-Rodriguez M, Sanchez-Orta A, De Lucas R, et al. Congenital tufted angioma: a multicenter retrospective study of 30 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:808-816.
- Pietroletti R, Leardi S, Simi M. Perianal acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy: case report. Tech Coloproctol. 2002;6:117-119.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Omori M, Bito T, Nishigori C. Acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy showing expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors. Eur J Dermatol. 2013;23:898-899.
- Boeldt DS, Bird IM. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J Endocrinol. 2017;232:R27-R44.
- Fernandes LB, Amaral W. Clinical study of skin changes in low and high risk pregnant women. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:822-826.
- Walker JL, Wang AR, Kroumpouzos G, et al. Cutaneous tumors in pregnancy. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:359-367.
- Sarwal P, Lapumnuaypol K. Pyogenic granuloma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Ortins-Pina A, Llamas-Velasco M, Turpin S, et al. FOSB immunoreactivity in endothelia of epithelioid hemangioma (angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia). J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:395-402.
- Arai E, Kuramochi A, Tsuchida T, et al. Usefulness of D2-40 immunohistochemistry for differentiation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:492-497.
- Grassi S, Carugno A, Vignini M, et al. Adult-onset tufted angiomas associated with an arteriovenous malformation in a renal transplant recipient: case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:162-165.
- Lyons LL, North PE, Mac-Moune Lai F, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: a study of 33 cases emphasizing its pathologic, immunophenotypic, and biologic uniqueness from juvenile hemangioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:559-568.
- Putra HP, Djawad K, Nurdin AR. Cutaneous lesions as the first manifestation of breast cancer: a rare case. Pan Afr Med J. 2020;37:383.
- Thiers BH, Sahn RE, Callen JP. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancy. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:73-98.
- Jones EW, Orkin M. Tufted angioma (angioblastoma). a benign progressive angioma, not to be confused with Kaposi’s sarcoma or low-grade angiosarcoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20(2 pt 1):214-225.
- Lee B, Chiu M, Soriano T, et al. Adult-onset tufted angioma: a case report and review of the literature. Cutis. 2006;78:341-345.
- Kim YK, Kim HJ, Lee KG. Acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:458-459.
- Feito-Rodriguez M, Sanchez-Orta A, De Lucas R, et al. Congenital tufted angioma: a multicenter retrospective study of 30 cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018;35:808-816.
- Pietroletti R, Leardi S, Simi M. Perianal acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy: case report. Tech Coloproctol. 2002;6:117-119.
- Osio A, Fraitag S, Hadj-Rabia S, et al. Clinical spectrum of tufted angiomas in childhood: a report of 13 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 2010;146:758-763.
- Omori M, Bito T, Nishigori C. Acquired tufted angioma in pregnancy showing expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors. Eur J Dermatol. 2013;23:898-899.
- Boeldt DS, Bird IM. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J Endocrinol. 2017;232:R27-R44.
- Fernandes LB, Amaral W. Clinical study of skin changes in low and high risk pregnant women. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:822-826.
- Walker JL, Wang AR, Kroumpouzos G, et al. Cutaneous tumors in pregnancy. Clin Dermatol. 2016;34:359-367.
- Sarwal P, Lapumnuaypol K. Pyogenic granuloma. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Ortins-Pina A, Llamas-Velasco M, Turpin S, et al. FOSB immunoreactivity in endothelia of epithelioid hemangioma (angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia). J Cutan Pathol. 2018;45:395-402.
- Arai E, Kuramochi A, Tsuchida T, et al. Usefulness of D2-40 immunohistochemistry for differentiation between kaposiform hemangioendothelioma and tufted angioma. J Cutan Pathol. 2006;33:492-497.
- Grassi S, Carugno A, Vignini M, et al. Adult-onset tufted angiomas associated with an arteriovenous malformation in a renal transplant recipient: case report and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015;37:162-165.
- Lyons LL, North PE, Mac-Moune Lai F, et al. Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: a study of 33 cases emphasizing its pathologic, immunophenotypic, and biologic uniqueness from juvenile hemangioma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:559-568.
- Putra HP, Djawad K, Nurdin AR. Cutaneous lesions as the first manifestation of breast cancer: a rare case. Pan Afr Med J. 2020;37:383.
- Thiers BH, Sahn RE, Callen JP. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancy. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:73-98.
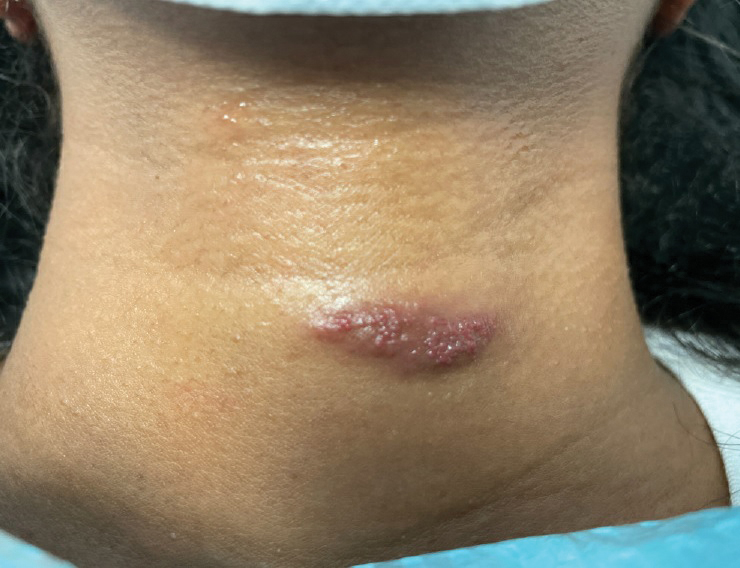
A 31-year-old woman at 34 weeks’ gestation presented with skin discoloration of the anterior neck of 7 months’ duration. Her pregnancy had been complicated by a diagnosis of invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast with unilateral complete mastectomy and negative sentinel lymph node biopsy in the first trimester. The lesion was tender, darkening, and rapidly enlarging. Physical examination demonstrated a linear, violaceous, vascular, and indurated plaque with microvesiculation that was 3.5 cm in width. She had no history of blistering sunburns, frequent UV exposure, or skin cancer.
Hand outcomes similar with distal or proximal radial cardiac cath
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
FROM SCAI 2022
FDA clears Abbott Freestyle Libre 3 glucose sensor
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has cleared Abbot’s Freestyle Libre 3 system for use by people aged 4 years and older with diabetes.
The new system was cleared for use for both iOS- and Android-compatible mobile apps, enabling real-time glucose readings in contrast to the “intermittently scanned” capability of prior Libre versions. The Libre 3 allows for optional alarms and notifications of urgent low or high glucose levels, as well as remote monitoring by health care professionals or the patient’s family members and/or friends.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 was granted a CE Mark in Europe in October 2020.
Smaller, thinner, and better integration
According to Abbott, the Libre 3 is the first continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to show a mean absolute relative difference (MARD) of less than 8% compared with a gold-standard glucose measure. The average Libre 3 MARD is 7.9%, compared with 9.3% for the Libre 2. The Libre 3 is also the “smallest and thinnest” CGM, roughly the size of two stacked U.S. pennies, worn on the upper arm.
And, the company said, the Libre 3 has a Bluetooth integration of up to 33 feet, a range 50% further than other CGMs.
This version follows the FreeStyle Libre 2, approved in June 2020, and its compatible iPhone app, approved in August 2021.
The Libre 3 will be priced the same as the Libre 2, at about one-third the cost of other CGM systems. However, it is not currently eligible for Medicare reimbursement. Medicaid eligibility may vary by state.
“I applaud Abbott for making their CGM system the most affordable and addressing disparities in care so patients living with diabetes can avoid complications and optimize their quality of life,” Eugene E. Wright Jr., MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said in an Abbott statement.
“I have seen real-world evidence that diabetes technologies like CGMs have helped my patients safely achieve improved glycemic control,” he said.
The FreeStyle Libre 3 sensor will be available at participating pharmacies later this year.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paraphilic disorders and sexual criminality
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5
Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.
A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).
Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5
Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.
A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).
Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
Mr. J, age 23, presents to an outpatient mental health clinic for treatment of anxiety. He has no psychiatric history, is dressed neatly, and recently finished graduate school with a degree in accounting. Mr. J is reserved during the initial psychiatric evaluation and provides only basic facts about his developmental history.
Mr. J comes from a middle-class household with no history of trauma or substance use. He does not report any symptoms consistent with anxiety, but discloses a history of sexual preoccupations. Mr. J says that during adolescence he developed a predilection for observing others engage in sexual activity. In his late teens, he began following couples to their homes in the hope of witnessing sexual intimacy. In the rare instance that his voyeuristic fantasy comes to fruition, he masturbates and achieves sexual gratification he is incapable of experiencing otherwise. Mr. J notes that he has not yet been caught, but he expresses concern and embarrassment related to his actions. He concludes by noting that he seeks help because the frequency of this behavior has steadily increased.
How would you treat Mr. J? Where does the line exist between a normophilic sexual interest, fantasy or urge, and a paraphilia? Does Mr. J qualify as a sexually violent predator?
From The Rocky Horror Picture Show to Fifty Shades of Grey, sensationalized portrayals of sexual deviancy have long been present in popular culture. The continued popularity of serial killers years after their crimes seems in part related to the extreme sexual torture their victims often endure. However, a sexual offense does not always qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1 In fact, many individuals with paraphilic disorders never engage in illegal activity. Additionally, experiencing sexually deviant thoughts alone does not qualify as a paraphilic disorder.1
A thorough psychiatric evaluation should include a discussion of the patient’s sexual history, including the potential of sexual dysfunction and abnormal desires or behaviors. Most individuals with sexual dysfunction do not have a paraphilic disorder.2 DSM-5 and ICD-11 classify sexual dysfunction and paraphilic disorders in different categories. However, previous editions grouped them together under sexual and gender identity disorders. Individuals with paraphilic disorders may not originally present to the outpatient setting for a paraphilic disorder, but instead may first seek treatment for a more common comorbid disorder, such as a mood disorder, personality disorder, or substance use disorder.3
Diagnostically speaking, if individuals do not experience distress or issues with functionality and lack legal charges (suggesting that they have not violated the rights of others), they are categorized as having an atypical sexual interest but do not necessarily meet the criteria for a disorder.4 This article provides an overview of paraphilic disorders as well as forensic considerations when examining individuals with sexually deviant behaviors.
Overview of paraphilic disorders
DSM-5 characterizes a paraphilic disorder as “recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors generally involving nonhuman objects or nonconsenting partners for at least 6 months. The individual must have acted on the thought and/or it caused clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.” DSM-5 outlines 9 categories of paraphilic disorders, which are described in Table 1.4,5
Continue to: Paraphilic disorders are more common...
Paraphilic disorders are more common in men than in women; the 2 most prevalent are voyeuristic disorder and frotteuristic disorder.6 The incidence of paraphilias in the general outpatient setting varies by disorder. Approximately 45% of individuals with pedophilic disorder seek treatment, whereas only 1% of individuals with zoophilia seek treatment.6 The incidence of paraphilic acts also varies drastically; individuals with exhibitionistic disorder engaged in an average of 50 acts vs only 3 for individuals with sexual sadism.6 Not all individuals with paraphilic disorders commit crimes. Approximately 58% of sexual offenders meet the criteria for a paraphilic disorder, but antisocial personality disorder is a far more common diagnosis.7
Sexual psychopath statutes: Phase 1
In 1937, Michigan became the first state to enact sexual psychopath statutes, allowing for indeterminate sentencing and the civil commitment/treatment of sex offenders with repeated convictions. By the 1970s, more than 30 states had enacted similar statutes. It was not until 1967, in Specht v Patterson,8 that the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled that the Fourteenth Amendment Due Process Clause was violated when Francis Eddie Specht faced life in prison following his conviction for indecent liberties under the Colorado Sex Offenders Act.
Specht was convicted in 1959 for indecent liberties after pleading guilty to enticing a child younger than age 16 into an office and engaging in sexual activities with them. At the time of Specht’s conviction, the crime of indecent liberties carried a punishment of 10 years. However, Specht was sentenced under the Sexual Offenders Act, which allowed for an indeterminate sentence of 1 day to life in prison. The Supreme Court noted that Specht was denied the right to be present with counsel, to confront the evidence against him, to cross-examine witnesses, and to offer his own evidence, which was a violation of his constitutionally guaranteed Fourteenth Amendment right to Procedural Due Process. The decision led most states to repeal early sexual psychopath statutes.8
Sexually violent predator laws: Phase 2
After early sexual psychopath statutes were repealed, many states pushed to update sex offender laws in response to the Earl Shriner case.9 In 1989, Shriner was released from prison after serving a 10-year sentence for sexually assaulting 2 teenage girls. At the time, he did not meet the criteria for civil commitment in the state of Washington. On the day he was released, Shriner cut off a young boy’s penis and left him to die. Washington subsequently became the first of many states to enact sexually violent predator (SVP) laws. Table 210 shows states and districts that have SVP civil commitment laws.
A series of United States Supreme Court cases solidified current sexual offender civil commitment laws (Table 38,11-15).
Continue to: Allen v Illinois
Allen v Illinois (1986).11 The Court ruled that forcing an individual to participate in a psychiatric evaluation prior to a sexually dangerous person’s commitment hearing did not violate the individual’s Fifth Amendment right against self-incrimination because the purpose of the evaluation was to provide treatment, not punishment.
Kansas v Hendricks (1997).12 The Court upheld that the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act was constitutional and noted that the use of the broad term “mental abnormality” (in lieu of the more specific term “mental illness”) does not violate an individual’s Fourteenth Amendment right to substantive due process. Additionally, the Court opined that the constitutional ban on double jeopardy and ex post facto lawmaking does not apply because the procedures are civil, not criminal.
Kansas v Crane (2002).13 The Court upheld the Kansas Sexually Violent Predator Act, stating that mental illness and dangerousness are essential elements to meet the criteria for civil commitment. The Court added that proof of partial (not total) “volitional impairment” is all that is required to meet the threshold of sexual dangerousness.
McKune v Lile (2002).14 The Court ruled that a policy requiring participation in polygraph testing, which would lead to the disclosure of sexual crimes (even those that have not been prosecuted), does not violate an individual’s Fifth Amendment rights because it serves a vital penological purpose.
Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 200616; United States v Comstock (2010).15 This act and subsequent case reinforced the federal government’s right to civilly commit sexually dangerous persons approaching the end of their prison sentences.
Continue to: What is requiried for civil commitment?
What is required for civil commitment?
SVP laws require 4 conditions to be met for the civil commitment of sexual offenders (Table 417). In criteria 1, “charges” is a key word, because this allows individuals found Not Guilty by Reason of Insanity or Incompetent to Stand Trial to be civilly committed. Criteria 2 defines “mental abnormality” as a “congenital or acquired condition affecting the emotional or volitional capacity which predisposes the person to commit criminal sexual acts in a degree constituting such person a menace to the health and safety of others.”18 This is a broad definition, and allows individuals with personality disorders to be civilly committed (although most sexual offenders are committed for having a paraphilic disorder). To determine risk, various actuarial instruments are used to assess for sexually violent recidivism, including (but not limited to) the Static-99R, Sexual Violence Risk-20, and the Sex Offender Risk Appraisal Guide.19
Although the percentages vary, sex offenders rarely are civilly committed following their criminal sentence. In California, approximately 1.5% of sex offenders are civilly committed.17 The standard of proof for civil commitment varies by state between “clear and convincing evidence” and “beyond a reasonable doubt.” As sex offenders approach the end of their sentence, sexually violent offenders are identified to the general population and referred for a psychiatric evaluation. If the individual meets the 4 criteria for commitment (Table 417), their case is sent to the prosecuting attorney’s office. If accepted, the court holds a probable cause hearing, followed by a full trial.
Pornography and sex offenders
Pornography has long been considered a risk factor for sexual offending, and the role of pornography in influencing sexual behavior has drawn recent interest in research towards predicting future offenses. However, a 2019 systematic review by Mellor et al20 on the relationship between pornography and sexual offending suggested that early exposure to pornography is not a risk factor for sexual offending, nor is the risk of offending increased shortly after pornography exposure. Additionally, pornography use did not predict recidivism in low-risk sexual offenders, but did in high-risk offenders.
The use of child pornography presents a set of new risk factors. Prohibited by federal and state law, child pornography is defined under Section 2256 of Title 18, United States Code, as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a minor (someone <age 18). Visual depictions include photographs, videos, digital or computer-generated images indistinguishable from an actual minor, and images created to depict a minor. The law does not require an image of a child engaging in sexual activity for the image to be characterized as child pornography. Offenders are also commonly charged with the distribution of child pornography. A conviction of child pornography possession carries a 15- to 30-year sentence, and distribution carries a 5- to 20-year sentence.21 The individual must also file for the sex offender registry, which may restrict their employment and place of residency.
It is unclear what percentage of individuals charged with child pornography have a history of prior sexual offenses. Numerous studies suggest there is a low risk of online offenders without prior offenses becoming contact offenders. Characteristics of online-only offenders include being White, a single male, age 20 to 30, well-educated, and employed, and having antisocial traits and a history of sexual deviancy.22 Contact offenders tend to be married with easy access to children, unemployed, uneducated, and to have a history of mental illness or criminal offenses.22
Continue to: Recidivism and treatment
Recidivism and treatment
The recidivism rate among sexual offenders averages 13.7% at 3- to 6-year follow-up,although rates vary by type of sexual offense.23 Individuals who committed rape have the highest rate of recidivism, while those who engaged in incest have the lowest. Three key points about sexual offender recidivism are:
- it declines over time and with increased age.
- sexual offenders are more like to commit a nonsexual offense than a sexual offense.
- sexual offenders who have undergone treatment are 26.3% less likely to reoffend.23
Although there is no standard of treatment, current interventions include external control, reduction of sexual drive, treatment of comorbid conditions, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and dynamic psychotherapy. External control relies on an outside entity that affects the individual’s behavior. For sexually deviant behaviors, simply making the act illegal or involving the law may inhibit many individuals from acting on a thought. Additional external control may include pharmacotherapy, which ranges from nonhormonal options such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) to hormonal options. Therapy tends to focus on social skills training, sex education, cognitive restructuring, and identifying triggers, as well as victim empathy. The best indicators for successful treatment include an absence of comorbidities, increased age, and adult interpersonal relationships.24
Treatment choice may be predicated on the severity of the paraphilia. Psychotherapy alone is recommended for individuals able to maintain functioning if it does not affect their conventional sexual activity. Common treatment for low-risk individuals is psychotherapy and an SSRI. As risk increases, so does treatment with pharmacologic agents. Beyond SSRIs, moderate offenders may be treated with an SSRI and a low-dose antiandrogen. This is escalated in high-risk violent offenders to long-acting gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs and synthetic steroidal analogs.25
An evolving class of disorders
With the evolution and accessibility of pornography, uncommon sexual practices have become more common, gaining notoriety and increased social acceptance. As a result, mental health professionals may be tasked with evaluating patients for possible paraphilic disorders. A common misconception is that individuals with sexually deviant thoughts, sexual offenders, and patients with paraphilic disorders are all the same. However, more commonly, sexual offenders do not have a paraphilic disorder. In the case of SVPs, outside of imprisonment, civil commitment remains a consideration for possible treatment. To meet the threshold of civil commitment, a sexual offender must have a “mental abnormality,” which is most commonly a paraphilic disorder. The treatment of paraphilic disorders remains a difficult task and includes a mixture of psychotherapy and medication options.
CASE CONTINUED
Mr. J begins weekly CBT to gain control of his voyeuristic fantasies without impacting his conventional sexual activity and desire. He responds well to treatment, and after 18 months, begins a typical sexual relationship with a woman. Although his voyeuristic thoughts remain, the urge to act on the thoughts decreases as Mr. J develops coping mechanisms. He does not require pharmacologic treatment.
Bottom Line
Individuals with paraphilic disorders are too often portrayed as sexual deviants or criminals. Psychiatrists must review each case with careful consideration of individual risk factors, such as the patient’s sexual history, to evaluate potential treatment options while determining if they pose a threat to the public.
Related Resources
- Sorrentino R, Abramowitz J. Minor-attracted persons: a neglected population. Current Psychiatry. 2021;20(7):21-27. doi:10.12788/cp.0149
- Berlin FS. Paraphilic disorders: a better understanding. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(4):22-26,28.
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
1. Federoff JP. The paraphilias. In: Gelder MG, Andreasen NC, López-Ibor JJ Jr, Geddes JR, eds. New Oxford Textbook of Psychiatry. 2nd ed. Oxford University Press; 2012:832-842.
2. Grubin D. Medical models and interventions in sexual deviance. In: Laws R, O’Donohue WT, eds. Sexual Deviance: Theory, Assessment and Treatment. 2nd ed. Guilford Press; 2008:594-610.
3. Guidry LL, Saleh FM. Clinical considerations of paraphilic sex offenders with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2004;11(1-2):21-34.
4. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
5. Balon R. Paraphilic disorders. In: Roberts LW, Hales RE, Yudofsky SC, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychiatry. 7th ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2019:749-770.
6. Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, Ruiz P. Paraphilic disorders. Kaplan and Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry. 11th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2015:593-599.
7. First MB, Halon RL. Use of DSM paraphilia diagnosis in sexually violent predator commitment cases. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2008;36(4):443-454.
8. Specht v Patterson, 386 US 605 (1967).
9. Ra EP. The civil confinement of sexual predators: a delicate balance. J Civ Rts Econ Dev. 2007;22(1):335-372.
10. Felthous AR, Ko J. Sexually violent predator law in the United States. East Asian Arch Psychiatry. 2018;28(4):159-173.
11. Allen v Illinois, 478 US 364 (1986).
12. Kansas v Hendricks, 521 US 346 (1997).
13. Kansas v Crane, 534 US 407 (2002).
14. McKune v Lile, 536 US 24 (2002).
15. United States v Comstock, 560 US 126 (2010).
16. Adam Walsh Child Protection and Safety Act of 2006, HR 4472, 109th Cong (2006). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/4472
17. Tucker DE, Brakel SJ. Sexually violent predator laws. In: Rosner R, Scott C, eds. Principles and Practice of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. CRC Press; 2017:823-831.
18. Wash. Rev. Code. Ann. §71.09.020(8)
19. Bradford J, de Amorim Levin GV, Booth BD, et al. Forensic assessment of sex offenders. In: Gold LH, Frierson RL, eds. The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Forensic Psychiatry. 3rd ed. American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2017:382-397.
20. Mellor E, Duff S. The use of pornography and the relationship between pornography exposure and sexual offending in males: a systematic review. Aggress Violent Beh. 2019;46:116-126.
21. Failure To Register, 18 USC § 2250 (2012). Accessed April 25, 2022. https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/USCODE-2011-title18/USCODE-2011-title18-partI-chap109B-sec2250
22. Hirschtritt ME, Tucker D, Binder RL. Risk assessment of online child sexual exploitation offenders. J Am Acad Psychiatry Law. 2019;47(2):155-164.
23. Blasko BL. Overview of sexual offender typologies, recidivism, and treatment. In: Jeglic EL, Calkins C, eds. Sexual Violence: Evidence Based Policy and Prevention. Springer; 2016:11-29.
24. Thibaut F, Cosyns P, Fedoroff JP, et al; WFSBP Task Force on Paraphilias. The World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) 2020 guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of paraphilic disorders. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2020;21(6):412-490.
25. Holoyda B. Paraphilias: from diagnosis to treatment. Psychiatric Times. 2019;36(12).
Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: A hypothesis (Part 2)
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (
Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16
Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (
Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16
Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
There is a need to connect mental and physical symptoms in the diagnosis and treatment of psychiatric disorders. Obviously, we are not yet equipped to clearly recognize which neurotransmitters cause which symptoms. The science of defining the underlying mechanisms is lagging behind the clinical needs. However, in this article, we present a few hypothetical clinical cases to emphasize a possible way of analyzing symptoms in order to identify underlying pathology and guide more effective treatment. Our descriptions do not reflect the entire set of symptoms caused by these neurotransmitters; we created them based on what is presently known (or suspected). Additional research is needed to confirm or disprove the hypotheses we present.
In Part 1 (
Endorphin excess (Table 11-16)
Ms. R is a frustrated chronic pain patient who bitterly complains that despite having seen more than 20 physicians, she does not have an answer to what causes her “all over” pain and headache.4,5,11 She does not believe that all her laboratory test are normal, and insists that “something is missing.” She aches all over but says she can actually tolerate more pain than others and experiences only a little discomfort during an electromyogram or dental interventions. Though Ms. R is not very susceptible to acute pain,4,5,9,16 pain all over without an identifiable cause is part of her life.4,5,11 She says that listening to music and social interactions help decrease her pain.4,5,10 Ms. R states that opioid medications do not help her pain, though she has a history of opioid overuse and opioid-induced hyperalgesia.6,11,16
Ms. R tends to overdo pleasureful activities to achieve satisfaction.2 She says exercise is particularly satisfying, to the point that she experiences euphoria and a loss of time.9 She is angry that her neurologist suggested she see a psychiatrist. Her depression bothers her more than her anxiety.2,5,7
Ms. R clearly has a self-image problem, alternating between high and low self-esteem. She has a low appetite1,12,14-16 and sleeps excessively.2,4,7,9,10 Her mother privately tells you that Ms. R has a history of childhood sexual abuse and lagged in life due to a lack of motivation. Ms. R used to self-mutilate “to feel normal.”12 Her primary care physician chronically addresses Ms. R’s poorly explained cholestasis and pruritus8 as well as dysregulation of blood pressure and heart rate, both of which tend to be low.12,13,16
Impression. Ms. R shows multiple symptoms associated with endorphin excess. A trial of an opioid antagonist may be reasonable. Dopamine blockade helps with endorphin suppression and also may be used for this patient. Using a low starting dose and a slow titration of such medications would be beneficial due to frequent intolerance issues, especially nausea. Gamma aminobutyric acid-ergic medications modulate the opioid system and may be considered. A serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) or mirtazapine may help patients such as Ms. R to control mood and pain through norepinephrine’s influence on endorphins.
Endorphin deficiency (Table 11,16-24)
Mr. J complains of low back pain, diffuse body pain, depression, and moodiness.19,20,24 He is sluggish and plagued by psychomotor retardation.24 All his life, a heightened perception of pain has caused him problems,19,20 but has not stopped him from engaging in self-mutilation
Continue to: Mr. J responds to treatment...
Mr. J responds to treatment with opioids16,20 but comments that his mood, and not necessarily his pain, improves when he takes these medications.20 He tends to overuse his pain medications, and had run into trouble with his previous pain management physician. Nitrous oxide is remarkably effective during dental procedures.19 Acupuncture helps to control his pain and mood.17 Exercise is also rewarding.18
Mr. J has difficulty achieving orgasm, a decreased sexual drive, and emotional sensitivity.24 He is impulsive.19,20,24 His baseline mood is low-grade; anxiety bothers him more than depression.23,24 Mr. J is thin, has a poor appetite,1,16 and sleeps poorly.24 His primary care physician struggles to help Mr. J to control dysregulation of his heart rate, blood pressure,21 and urinary retention,16,22 as well as episodes of hypoglycemia.1,16 He reluctantly admits to abusing alcohol, but explains that it helps with his mood and pain better than his prescribed medications.18,23
Impression. Mr. J exhibits multiple symptoms associated with endorphin deficiency. Short-term use of opioids is warranted, but he should avoid long-term opioid use, and he and his physician should work together to establish strict control of their intake. Buprenorphine would be the opioid of choice for such a patient. Psychiatric treatment, including for alcohol use disorder, should be a mandatory part of his treatment regimen. Behavioral therapy with a focus on finding healthy ways to achieve gratification would be effective. Alternative treatments such as acupuncture may be of value.
Norepinephrine excess (Table 216,25-30)
Mr. G comes to the office irritable and angry28,30 because no one can help him with his intractable headaches.
Comment. Norepinephrine and dopamine functions are connected through common neuronal and glial uptake mechanisms. This is a foundation of norepinephrine excess symptoms crossing over with symptoms of dopamine deficiency.
Continue to: Impression
Impression. Mr. G shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine excess. It is important to avoid caffeine intake in patients with clinical signs of excessive norepinephrine. Beta-blockers and alpha-2 agonists work well in patients such as Mr. G. Benzodiazepines indirectly decrease norepinephrine activity, but need to be used carefully due to the potential for misuse and addiction. In particular, short-acting benzodiazepines such as alprazolam and lorazepam must be avoided due to the induction of CNS instability with rapidly changing medication blood levels. Chlordiazepoxide may be a good choice for a patient such as Mr. G because it has the fewest adverse effects and the lowest abuse potential compared with other benzodiazepines. Avoid SNRIs in such a patient. Using mood-stabilizing antipsychotic medications may be especially warranted in treating Mr. G’s depression and pain.
Norepinephrine deficiency (Table 216,26,31-39)
Two years ago, Ms. A was diagnosed with chronic fatigue31 and fibromyalgia. She also had been diagnosed with depression and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). She presents with concerns of “brain fog,” no energy, low sex drive, and daytime sleepiness.33,35 Allodynia is widespread.16,36,37 Ms. A suffers from bulimia; she eats once a day but is still overweight.26 She has orthostatic hypotension in addition to baseline low blood pressure and bradycardia.16,38,39 Her pupils are almost pinpoint, even when she does not take opioid medications.
Comment. As mentioned earlier, because of the norepinephrine/dopamine relationship, symptoms of excess dopamine overlap with symptoms of norepinephrine deficiency.
Impression. Ms. A shows multiple symptoms associated with norepinephrine deficiency. The use of noradrenergic antidepressants (such as SNRIs and mirtazapine)26 and stimulants may be warranted. Physical exercise, participating in social activities, massage, acupuncture, and family support may help with Ms. A’s pain as well as her depression, as might vasopressors.
In Part 3, we will address gamma aminobutyric acid and glutamate.
Bottom Line
Both high and low levels of endorphins and norepinephrine may be associated with certain psychiatric and medical symptoms and disorders. An astute clinician may judge which neurotransmitter is dysfunctional based on the patient’s presentation, and tailor treatment accordingly.
Related Resources
- Arbuck DM, Salmerón JM, Mueller R. Neurotransmitter-based diagnosis and treatment: a hypothesis (Part 1). Current Psychiatry. 2022;21(5):30-36. doi:10.12788/cp.0242
Drug Brand Names
Alprazolam • Xanax
Chlordiazepoxide • Librium
Lorazepam • Ativan
Mirtazapine • Remeron
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
1. Applyard SM, Hayward M, Young JI, et al. A role for the endogenous opioid beta-endorphin in energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2003;144(5):1753-1760.
2. Craft LL, Perna FM. The benefits of exercise for the clinically depressed. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;6(3):104-111.
3. Dabo F, Nyberg F, Qin Zhou, et al. Plasma levels of beta-endorphin during pregnancy and use of labor analgesia. Reprod Sci. 2010;17(8):742-747.
4. Dunbar RI, Kaskatis K, MacDonald I, et al. Performance of music elevates pain threshold and positive affect: implications for the evolutionary function of music. Evol Psychol. 2012;10(4):688-702.
5. Dunbar RIM, Baron R, Frangou A, et al. Social laughter is correlated with an elevated pain threshold. Proc Biol Sci. 2012;279(1731):1161-1167.
6. Grisel JE, Bartels JL, Allen SA, et al. Influence of beta-Endorphin on anxious behavior in mice: interaction with EtOH. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008;200(1):105-115.
7. Zorrilla EP, DeRubeis RJ, Redei E. High self-esteem, hardiness, and affective stability are associated with higher basal pituitary-adrenal hormone levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1995;20(6):591-601.
8. Li X, Zhu J, Tao Y, et al. Elevated endogenous opioids in obstructive jaundice: the possible skin mechanisms. Med Hypotheses. 2018;116:119-121.
9. Hicks SD, Jacob P, Perez O, et al. The transcriptional signature of a runner’s high. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(5):970-978.
10. Dunbar RIM. The anatomy of friendship. Trends Cogn Sci. 2018;22(1):32-51.
11. Stephan BC, Parsa FD. Avoiding opioids and their harmful side effects in the postoperative patient: exogenous opioids, endogenous endorphins, wellness, mood, and their relation to postoperative pain. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2016;75(3):63-70.
12. Cuthbert BN, Holaday JW, Meyerhoff J, et al. Intravenous beta-endorphin: behavioral and physiological effects in conscious monkeys. Peptides. 1989;10(4):729-734.
13. Levin ER, Mills S, Weber MA. Endogenous opioids and opiate antagonists modulate the blood pressure of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Peptides. 1986;(6):977-981.
14. Davis JM, Lowy MT, Yim GK, et al. Relationship between plasma concentrations of immunoreactive beta-endorphin and food intake in rats. Peptides. 1983;4(1):79-83.
15. Leibowitz SF, Hor L. Endorphinergic and alpha-noradrenergic systems in the paraventricular nucleus: effects on eating behavior. Peptides. 1982;3(3): 421-428.
16. Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th ed. Spanish version. Elsevier; 2011:587-588.
17. Han JS. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci Lett. 2004;361(1-3):258-261.
18. Harte JL, Eifert GH, Smith R. The effects of running and meditation on beta-endorphin, corticotropin-releasing hormone and cortisol in plasma, and on mood. Biol Psychol. 1995;40(3):251-265.
19. Petrizzo R, Mohr J, Mantione K, et al. The role of endogenous morphine and nitric oxide in pain management. Pract Pain Manag. 2014;14(9).
20. Sprouse-Blum AS, Smith G, Sugai D, et al. Understanding endorphins and their importance in pain management. Hawaii Med J. 2010;69(3):70-100.
21. Dontsov AV. The influence of deficit of endogenous neuropeptides on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2017;95(2):127-131. In Russian.
22. Dray A, Metsch R, Davis TP. Endorphins and the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Peptides. 1984;5(3):645-647.
23. Zalewska-Kaszubska J, Czarnecka E. Deficit in beta-endorphin peptide and tendency to alcohol abuse. Peptides. 2005;26(4):701-705.
24. McLay RN, Pan W, Kastin AJ. Effects of peptides on animal and human behavior: a review of studies published in the first twenty years of the journal Peptides. Peptides. 2001;22(12):2181-2255.
25. Wong-Riley MT. Neuroscience Secrets. 1st ed. Spanish version. Hanley & Belfus; 1999:424-428.
26. Brewerton TD. Clinical Handbook of Eating Disorders: An Integrated Approach. CRC Press; 2004:257-281.
27. Winklewski PJ, Radkowski M, Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, et al. Stress response, brain noradrenergic system and cognition. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;980:67-74.
28. McCall JG, Al-Hasani R, Siuda ER, et al. Engagement of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system mediates stress-induced anxiety. Neuron. 2015;87(3):605-620.
29. Wszedybyl-Winklewska M, Wolf J, Szarmach A, et al. Central sympathetic nervous system reinforcement in obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;39:143-154.
30. Yamamoto K, Shinba T, Yoshii M. Psychiatric symptoms of noradrenergic dysfunction: a pathophysiological view. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2014;201(68):1-20.
31. Stone EA, Lin Y, Sarfraz Y, et al. The role of the central noradrenergic system in behavioral inhibition. Brain Res Rev. 2011;67(1-2):193-208.
32. Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C. Effect of the alpha-2 adrenoceptor antagonist mirtazapine on the 5-hydroxytryptamine system in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:861-871.
33. De Carvalho D, Patrone LG, Taxini CL, et al. Neurochemical and electrical modulation of the locus coeruleus: contribution to CO2 drive to breathe. Front Physiol. 2014;5(288):1-13.
34. Markianos M, Evangelopoulos ME, Koutsis G, et al. Evidence for involvement of central noradrenergic activity in crying proneness. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;23:403-408.
35. Cao S, Fisher DW, Yu T, et al. The link between chronic pain and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;(16):204-215.
36. Caraci F, Merlo S, Drago F, et al. Rescue of noradrenergic system as a novel pharmacological strategy in the treatment of chronic pain: focus on microglia activation. Front Pharmacol. 2019;(10):1024.
37. Hayashida KI, Obata H. Strategies to treat chronic pain and strengthen impaired descending noradrenergic inhibitory system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):822.
38. Kur’yanova EV, Tryasuchev AV, Stupin VO, et al. Effect of atropine on adrenergic responsiveness of erythrocyte and heart rhythm variability in outbred rats with stimulation of the central neurotransmitter systems. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;165(5):165(5):597-601.
39. Peterson AC, Li CR. Noradrenergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: an overview of imaging studies. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;(10):127.
A PSYCHIATRIC MANIFESTO: Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
Having witnessed the devastating impact of stigma on patients with mental illness throughout my psychiatric career, I am fed up and disgusted with this malevolent scourge.
I regard the stigma that engulfs neuropsychiatric disorders as a malignancy that mutilates patients’ souls and hastens their mortality.
Stigma is hate speech
How would you feel if you had a serious medical illness, a disabling brain disorder such as schizophrenia, depression, or anxiety, and people refer to you with pejorative and insulting terms such as crazy, deranged, lunatic, unhinged, nutty, insane, wacky, berserk, cuckoo, bonkers, flaky, screwball, or unglued? This is hate speech generated by stigma against people with mental illness. Individuals with heart disease, cancer, or diabetes never get called such disgraceful and stigmatizing terms that shame, stain, besmirch, and scar them, which happens daily to persons with psychiatric brain disorders.
The damage and harm of the discriminatory stigma on our patients is multifaceted. It is painful, detrimental, pernicious, and deleterious. It is corrosive to their spirits, crippling to their self-image, and subversive to their self-confidence. Hate speech is not simply words, but a menacing weapon that assaults the core humanity of medically ill psychiatric patients.
Although hate speech is punishable by law, there are rarely any legal actions against those who hurl hate speech at psychiatric patients every day. Society has institutionalized the stigma of mental illness and takes it in stride instead of recognizing it as an illegal, harmful act.
Long before the stresses of the COVID-19 pandemic, 43% of the population had been shown to experience a diagnosable psychiatric disorder over the course of their life.1 Thus, tens of millions of people are burdened by stigma and the hate speech associated with it. This is directly related to massive ignorance about mental illness being the result of a neurobiological condition due to either genetic or intrauterine adverse events that disrupt brain development. Delusions and hallucinations are symptoms of a malfunctioning brain, depression is not a sign of personal weakness, anxiety is the most prevalent mental disorder in the world, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is not odd behavior but the result of dysfunction of neural circuits. Correcting public misperceptions about psychiatric brain disorders can mitigate stigma, but it has yet to happen.
Stigma is a hate crime
Stigma can accelerate physical death and premature mortality. Many studies have confirmed that persons with schizophrenia do not receive basic primary care treatments for the life-shortening medical conditions that often afflict them, such as diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.2 Stigma is responsible for a significant disparity of medical3-5 and intensive care6 among individuals with mental illness compared to the general population. It’s no wonder most psychiatric disorders are associated with accelerated mortality.7 A recent study during the pandemic by Balasuriya et al8 reported that patients with depression had poor access to care. Stigma interferes with or delays necessary medical care, leading to clinical deterioration and unnecessary, preventable death. Stigma shortens life and is a hate crime.
Continue to: The extremely high suicide rates...
The extremely high suicide rates among individuals with serious mental illness, who live under the oppressiveness of stigma, is another example of how stigma is a hate crime that can cause patients with psychiatric disorders to give up and end their lives. Zaheer et al9 found that young patients with schizophrenia had an astronomical suicide rate compared to the general population (1 in 52 in individuals with schizophrenia, compared to 12 in 100,000 in the general population, roughly a 200-fold increase!). This is clearly a consequence of stigma and discrimination,10 which leads to demoralization, shame, loneliness, distress, and hopelessness. Stigma can be fatal, and that makes it a hate crime.
Stigma also limits vocational opportunities for individuals with mental illness. They are either not hired, or quickly fired. Even highly educated professionals such as physicians, nurses, lawyers, or teachers can lose their jobs if they divulge a history of a psychiatric disorder or alcohol or substance abuse, regardless of whether they are receiving treatment and are medically in remission. Even highly qualified politicians have been deemed “ineligible” for higher office if they disclose a history of psychiatric treatment. Stigma is loaded with outrageous discrimination that deprives our patients of “the pursuit of happiness,” a fundamental constitutional right.
Stigma surrounding the mental health professions
Stigma also engulfs mental health professionals, simply because they deal with psychiatric patients every day. In a classic article titled “The Enigma of Stigma,”11 Dr. Paul Fink, past president of the American Psychiatric Association (1988-1989), described how psychiatrists are perceived as “different” from other physicians by the public and by the media. He said psychiatrists are tarred by the same brush as their patients as “undesirables” in society. And movies such as Psycho and One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest reinforce the stigma against both psychiatric patients and the psychiatrists and nurses who treat them. The health care system that carves out “behavioral health” from the umbrella of “medical care” further accentuates the stigma by portraying the “separateness” of psychiatry, a genuine medical specialty, from its fellow medical disciplines. This becomes fodder for the antipsychiatry movement at every turn and can even lead to questioning the existence of mental illness, as Thomas Szasz12 did by declaring that mental illness is a myth and describing psychiatry as “the science of lies.” No other medical specialty endures abuse and insults like psychiatry, and that’s a direct result of stigma.
Extinguishing stigma is a societal imperative
So what can be done to squelch stigma and defeat it once and for all, so that psychiatric patients can be treated with dignity and compassion, like people with cancer, heart attacks, diabetes, or brain tumors? The pandemic, terrible as it has been for the entire world, did have the silver lining of raising awareness about the ubiquity of psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety and depression, across all ages, genders, educational and religious backgrounds, and socioeconomic classes. But there should also be a robust legal battle against the damaging effects of stigma. There are laws to sanction and penalize hate speech and hate crimes that must be implemented when stigma is documented. There are also parity laws, but they have no teeth and have not ameliorated the insurance discrepancies and economic burden of psychiatric disorders. A bold step would be to reclassify serious psychiatric brain disorders (schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, OCD, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, generalized anxiety disorder/panic attacks, and borderline personality disorder) as neurologic disorders, which would automatically give patients with these disorders broad access to medical care, which happened when autism was reclassified as a neurologic disorder. Finally, a much more intensive public education must be disseminated about the neurobiological etiologies, brain structure, and function in psychiatric disorders, and the psychiatric symptoms associated with all neurologic disorders. Regrettably, empathy can be difficult to teach.
Stigma is hate speech and a hate crime. It must be permanently eliminated by effective laws and by erasing the widespread ignorance about the medical and neurologic roots of mental disorders, and by emphasizing the fact that they are as treatable as other general medical conditions.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.
1. Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(6):593-602.
2. Nasrallah HA, Meyer JM, Goff DC, et al. Low rates of treatment for hypertension, dyslipidemia and diabetes in schizophrenia: data from the CATIE schizophrenia trial sample at baseline. Schizophr Res. 2006;86(1-3):15-22.
3. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Use of medical services by veterans with mental disorders. Psychosomatics. 1997;38(5):451-458.
4. Druss BG, Rosenheck RA. Mental disorders and access to medical care in the United States. Am J Psychiatry. 1998;155(12):1775-1777.
5. Druss BG, Bradford WD, Rosenheck RA, et al. Quality of medical care and excess mortality in older patients with mental disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2001;58(6):565-572.
6. Druss BG, Bradford DW, Rosenheck RA, et al. Mental disorders and use of cardiovascular procedures after myocardial infarction. JAMA. 2000;283(4):506-511.
7. Nasrallah HA. Transformative advances are unfolding in psychiatry. Current Psychiatry. 2019;18(9):10-12.
8. Balasuriya L, Quinton JK, Canavan ME, et al. The association between history of depression and access to care among Medicare beneficiaries during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(12):3778-3785.
9. Zaheer J, Olfson M, Mallia E, et al. Predictors of suicide at time of diagnosis in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a 20-year total population study in Ontario, Canada. Schizophr Res. 2020;222:382-388.
10. Brohan E, Thornicroft G, Rüsch N, et al. Measuring discrimination experienced by people with a mental illness: replication of the short-form DISCUS in six world regions. Psychol Med. 2022:1-11. doi:10.1017/S0033291722000630
11. Fink P. The enigma of stigma and its relation to psychiatric education. Psychiatric Annals. 1983;13(9):669-690.
12. Szasz T. The Myth of Mental Illness. Harper Collins; 1960.