User login
Intracranial atherosclerosis finding on MRA linked to stroke
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
An incidental diagnosis of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in stroke-free individuals should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, according to the authors of a study identifying risk factors and vascular event risk in asymptomatic ICAS.
That conclusion emerged from data collected on more than 1,000 stroke-free participants in NOMAS (Northern Manhattan Study), a trial that prospectively followed participants who underwent a brain magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) during 2003-2008.
In ICAS patients with stenosis of at least 70%, even with aggressive medical therapy, the annual stroke recurrence rate is 10%-20% in those with occlusions and at least three or more vascular risk factors. This high rate of recurrent vascular events in patients with stroke caused by ICAS warrants greater focus on primary prevention and targeted interventions for stroke-free individuals at highest risk for ICAS-related events, the investigators concluded.
Identify high-risk ICAS
Using NOMAS data, the investigators, led by Jose Gutierrez, MD, MPH, tested the hypothesis that stroke-free subjects at high risk of stroke and vascular events could be identified through the presence of asymptomatic ICAS. NOMAS is an ongoing, population-based epidemiologic study among randomly selected people with home telephones living in northern Manhattan.
During 2003-2008, investigators invited participants who were at least 50 years old, stroke free, and without contraindications to undergo brain MRA. The 1,211 study members were followed annually via telephone and in-person adjudication of events. A control group of 79 patients with no MRA was also identified with similar rates of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and current smoking.
Mean age was about 71 years (59% female, 65% Hispanic, 45% any stenosis). At the time of MRA, 78% had hypertension, 25% had diabetes, 81% had hypercholesterolemia, and 11% were current smokers.
Researchers rated stenoses in 11 brain arteries as 0, with no stenosis; 1, with less than 50% stenosis or luminal irregularities; 2, 50%-69% stenosis; and 3, at least 70% stenosis or flow gap. Outcomes included vascular death, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, cardioembolic stroke, intracranial artery disease stroke (which combined intracranial small and large artery disease strokes), and any vascular events (defined as a composite of vascular death, any stroke, or MI).
Greater stenosis denotes higher risk
Analysis found ICAS to be associated with older age (odds ratio, 1.02 per year; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-1.04), hypertension duration (OR, 1.01 per year; 95% CI, 1.00-1.02), higher number of glucose-lowering drugs (OR, 1.64 per each medication; 95% CI, 1.24-2.15), and HDL cholesterol(OR, 0.96 per mg/dL; 95% CI, 0.92-0.99). Event risk was greater among participants with ICAS of at least 70% (5.5% annual risk of vascular events; HR, 2.1; 95% CI, 1.4-3.2; compared with those with no ICAS), the investigators reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Furthermore, 80% of incident strokes initially classified as small artery disease occurred among individuals with evidence of any degree of ICAS at their baseline MRI, the investigators noted. They found also that individuals with ICAS who had a primary care physician at the time of their initial MRI had a lower risk of events. Frequent primary care visits, they observed, might imply greater control of risk factors and other unmeasured confounders, such as health literacy, health care trust, access, and availability.
Incidental ICAS should trigger vascular assessment
An incidental diagnosis of ICAS in stroke-free subjects should trigger a thorough assessment of vascular health, the investigators concluded. They commented also that prophylaxis of first-ever stroke at this asymptomatic stage “may magnify the societal benefits of vascular prevention and decrease stroke-related disability and vascular death in our communities.”
“The big gap in our knowledge,” Tanya N. Turan, MD, professor of neurology at Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, wrote in an accompanying editorial “is understanding the pathophysiological triggers for an asymptomatic stenosis to become a high-risk symptomatic stenosis. Until that question is answered, screening for asymptomatic ICAS is unlikely to change management among patients with known vascular risk factors.” In an interview, she observed further that “MRI plaque imaging could be a useful research tool to see if certain plaque features in an asymptomatic lesion are high risk for causing stroke. If that were proven, then it would make more sense to screen for ICAS and develop specific therapeutic strategies targeting high-risk asymptomatic plaque.”
Focus on recurrent stroke misplaced
Dr. Gutierrez said in an interview: “In the stroke world, most of what we do focuses on preventing recurrent stroke. Nonetheless, three-fourths of strokes in this country are new strokes, so to me it doesn’t make much sense to spend most of our efforts and attention to prevent the smallest fractions of strokes that occur in our society.”
He stressed that “the first immediate application of our results is that if people having a brain MRA for other reasons are found to have incidental, and therefore asymptomatic, ICAS, then they should be aggressively treated for vascular risk factors.” Secondly, “we hope to identify the patients at the highest risk of prevalent ICAS before they have a stroke. Among them, a brain MRI/MRA evaluating the phenotype would determine how aggressively to treat LDL.”
Dr. Gutierrez, professor of neurology at Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York, noted that educating patients of their underlying high risk of events may have the effect of engaging them more in their own care. “There is evidence that actually showing people scans increases compliance and health literacy. It’s not yet standard of care, but we hope our future projects will help advance the field in the primary prevention direction,” he said.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health. The authors reported that they had no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: AML August 2021
CPX-351 is a liposomal cytarabine and daunorubicin. It was FDA approved in 2017 for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed therapy-related AML (t-AML) or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The approval was based on the results from a randomized trial comparing CPX-351 vs standard 7 +3 chemotherapy in patients older that 65 with t-AML or AML-MRC. The 5-year results from that study were recently published by Lancet et al. At 5 years of follow-up, CPX-351 continued to show benefit in older patients with t-AML or AML-MRC vs standard chemotherapy with cytarabine for 7 days and daunorubicin for 3 days (7+3) . The median OS in favor of CPX-351 vs 7+3 group was maintained (hazard ratio, 0.70; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55-0.91). At 5 years, survival estimates were higher for CPX-351 vs 7+3 (18% [95% CI, 12%-25%] vs 8% [95% CI, 4%-13%]). Overall, 5% of deaths in both groups were considered related to the study treatment. Overall, more patients treated with CPX-351 were able to proceed to stem cell transplantation (SCT) compared to those treated with 7 + 3 (35% vs 25%).
The 3-year overall survival from SCT was 56% vs 23% for patients treated with CPX-351 vs 7 +3. Of the responding patients who did not proceed to SCT, only 3 patients were alive at 5 years. Although this data is encouraging, it demonstrates that we have a long way to go to improve the outcome of these patients. In addition, more patients who achieve remission should proceed to SCT in order to improve the survival of this patient population (Lancet JE et al). In terms of supportive care during induction chemotherapy, two published studies this month evaluated two approaches to aiming to decrease the morbidity from infections: prospective monitoring for fungal infections and the use of romyelocel with G-CSF. Prospectively monitoring for fungal infections was performed as an observation study imbedded within a phase 3 Children’s Oncology Group trial (ACCL0933). The study included 471 patients with AML (age, 3 months-30 years) receiving fluconazole (n=235) or caspofungin (n=236).
Twice-weekly surveillance with galactomannan enzyme immunoassay (GM-EIA) and b-D-glucan (BDG) assay were performed in all patients. The negative predictive value was greater than 99% for an individual or combination of GM-EIA and BDG assays. However, true positive results were not observed in any sample collected within 7 days of an invasive aspergillosis/candidiasis diagnosis, resulting in sensitivity and positive predictive value for each test of 0%. This approach was ineffective at detecting invasive fungal diseases (IFDs) in children, adolescents, and young adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) receiving antifungal prophylaxis (Fisher BT et al).
A different approach to reduce infection morbidity and mortality during induction chemotherapy is the administration of romyelocel. Myeloid progenitor cells are cells that can produce granulocytes but have no long-term reconstitution capability. Romyelocel is a cryopreserved product, of MPC manufactured by ex vivo expansion of CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. Romyelocel is capable of producing granulocytes, and thereby may reduce the severity or duration of neutropenic fevers. This phase 2 study included 163 patients with de novo AML receiving induction chemotherapy. Evaluable patients (n=120) were randomly assigned to receive either romyelocel-L plus G-CSF (n=59) or G-CSF monotherapy (n=61). From days 15 to 28, romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy significantly reduced the mean duration of febrile episodes (2.36 days vs 3.90 days; P = .02) and incidence of infections (6.8% vs 27.9%; P = .0013). Length of hospitalization was significantly shorter in the romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy group (25.5 days vs 28.7 days; P = .002). These results are encouraging, and a phase III trial is suggested by the authors. (Desai PM et al).
Finally, a study by MDACC reported disappointing results with the use of venetoclax in patients with tp53 mutation. Findings are from a retrospective analysis of 238 patients with newly diagnosed TP53-mutated AML treated with either VEN-based (n=58) or non-VEN-based (n=180) therapies. The addition of venetoclax to standard treatment regimens (VEN-based) did not improve clinical outcomes in patients with TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML), highlighting the need for novel therapies in this patient population. Overall, there was no significant differences in overall survival (median, 5.7 months vs 6.6 months; P = .4), relapse-free survival (median, 3.5 months vs 4.7 months; P = .43), 4-week mortality (7% vs 10%; P = .5), and 8-week mortality (22% vs 17%; P = .4) in patients receiving VEN-based vs non-VEN-based therapies (Venugopal S et al). Clearly, better therapies are needed for this patient population.
CPX-351 is a liposomal cytarabine and daunorubicin. It was FDA approved in 2017 for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed therapy-related AML (t-AML) or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The approval was based on the results from a randomized trial comparing CPX-351 vs standard 7 +3 chemotherapy in patients older that 65 with t-AML or AML-MRC. The 5-year results from that study were recently published by Lancet et al. At 5 years of follow-up, CPX-351 continued to show benefit in older patients with t-AML or AML-MRC vs standard chemotherapy with cytarabine for 7 days and daunorubicin for 3 days (7+3) . The median OS in favor of CPX-351 vs 7+3 group was maintained (hazard ratio, 0.70; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55-0.91). At 5 years, survival estimates were higher for CPX-351 vs 7+3 (18% [95% CI, 12%-25%] vs 8% [95% CI, 4%-13%]). Overall, 5% of deaths in both groups were considered related to the study treatment. Overall, more patients treated with CPX-351 were able to proceed to stem cell transplantation (SCT) compared to those treated with 7 + 3 (35% vs 25%).
The 3-year overall survival from SCT was 56% vs 23% for patients treated with CPX-351 vs 7 +3. Of the responding patients who did not proceed to SCT, only 3 patients were alive at 5 years. Although this data is encouraging, it demonstrates that we have a long way to go to improve the outcome of these patients. In addition, more patients who achieve remission should proceed to SCT in order to improve the survival of this patient population (Lancet JE et al). In terms of supportive care during induction chemotherapy, two published studies this month evaluated two approaches to aiming to decrease the morbidity from infections: prospective monitoring for fungal infections and the use of romyelocel with G-CSF. Prospectively monitoring for fungal infections was performed as an observation study imbedded within a phase 3 Children’s Oncology Group trial (ACCL0933). The study included 471 patients with AML (age, 3 months-30 years) receiving fluconazole (n=235) or caspofungin (n=236).
Twice-weekly surveillance with galactomannan enzyme immunoassay (GM-EIA) and b-D-glucan (BDG) assay were performed in all patients. The negative predictive value was greater than 99% for an individual or combination of GM-EIA and BDG assays. However, true positive results were not observed in any sample collected within 7 days of an invasive aspergillosis/candidiasis diagnosis, resulting in sensitivity and positive predictive value for each test of 0%. This approach was ineffective at detecting invasive fungal diseases (IFDs) in children, adolescents, and young adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) receiving antifungal prophylaxis (Fisher BT et al).
A different approach to reduce infection morbidity and mortality during induction chemotherapy is the administration of romyelocel. Myeloid progenitor cells are cells that can produce granulocytes but have no long-term reconstitution capability. Romyelocel is a cryopreserved product, of MPC manufactured by ex vivo expansion of CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. Romyelocel is capable of producing granulocytes, and thereby may reduce the severity or duration of neutropenic fevers. This phase 2 study included 163 patients with de novo AML receiving induction chemotherapy. Evaluable patients (n=120) were randomly assigned to receive either romyelocel-L plus G-CSF (n=59) or G-CSF monotherapy (n=61). From days 15 to 28, romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy significantly reduced the mean duration of febrile episodes (2.36 days vs 3.90 days; P = .02) and incidence of infections (6.8% vs 27.9%; P = .0013). Length of hospitalization was significantly shorter in the romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy group (25.5 days vs 28.7 days; P = .002). These results are encouraging, and a phase III trial is suggested by the authors. (Desai PM et al).
Finally, a study by MDACC reported disappointing results with the use of venetoclax in patients with tp53 mutation. Findings are from a retrospective analysis of 238 patients with newly diagnosed TP53-mutated AML treated with either VEN-based (n=58) or non-VEN-based (n=180) therapies. The addition of venetoclax to standard treatment regimens (VEN-based) did not improve clinical outcomes in patients with TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML), highlighting the need for novel therapies in this patient population. Overall, there was no significant differences in overall survival (median, 5.7 months vs 6.6 months; P = .4), relapse-free survival (median, 3.5 months vs 4.7 months; P = .43), 4-week mortality (7% vs 10%; P = .5), and 8-week mortality (22% vs 17%; P = .4) in patients receiving VEN-based vs non-VEN-based therapies (Venugopal S et al). Clearly, better therapies are needed for this patient population.
CPX-351 is a liposomal cytarabine and daunorubicin. It was FDA approved in 2017 for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed therapy-related AML (t-AML) or AML with myelodysplasia-related changes (AML-MRC). The approval was based on the results from a randomized trial comparing CPX-351 vs standard 7 +3 chemotherapy in patients older that 65 with t-AML or AML-MRC. The 5-year results from that study were recently published by Lancet et al. At 5 years of follow-up, CPX-351 continued to show benefit in older patients with t-AML or AML-MRC vs standard chemotherapy with cytarabine for 7 days and daunorubicin for 3 days (7+3) . The median OS in favor of CPX-351 vs 7+3 group was maintained (hazard ratio, 0.70; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55-0.91). At 5 years, survival estimates were higher for CPX-351 vs 7+3 (18% [95% CI, 12%-25%] vs 8% [95% CI, 4%-13%]). Overall, 5% of deaths in both groups were considered related to the study treatment. Overall, more patients treated with CPX-351 were able to proceed to stem cell transplantation (SCT) compared to those treated with 7 + 3 (35% vs 25%).
The 3-year overall survival from SCT was 56% vs 23% for patients treated with CPX-351 vs 7 +3. Of the responding patients who did not proceed to SCT, only 3 patients were alive at 5 years. Although this data is encouraging, it demonstrates that we have a long way to go to improve the outcome of these patients. In addition, more patients who achieve remission should proceed to SCT in order to improve the survival of this patient population (Lancet JE et al). In terms of supportive care during induction chemotherapy, two published studies this month evaluated two approaches to aiming to decrease the morbidity from infections: prospective monitoring for fungal infections and the use of romyelocel with G-CSF. Prospectively monitoring for fungal infections was performed as an observation study imbedded within a phase 3 Children’s Oncology Group trial (ACCL0933). The study included 471 patients with AML (age, 3 months-30 years) receiving fluconazole (n=235) or caspofungin (n=236).
Twice-weekly surveillance with galactomannan enzyme immunoassay (GM-EIA) and b-D-glucan (BDG) assay were performed in all patients. The negative predictive value was greater than 99% for an individual or combination of GM-EIA and BDG assays. However, true positive results were not observed in any sample collected within 7 days of an invasive aspergillosis/candidiasis diagnosis, resulting in sensitivity and positive predictive value for each test of 0%. This approach was ineffective at detecting invasive fungal diseases (IFDs) in children, adolescents, and young adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) receiving antifungal prophylaxis (Fisher BT et al).
A different approach to reduce infection morbidity and mortality during induction chemotherapy is the administration of romyelocel. Myeloid progenitor cells are cells that can produce granulocytes but have no long-term reconstitution capability. Romyelocel is a cryopreserved product, of MPC manufactured by ex vivo expansion of CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells. Romyelocel is capable of producing granulocytes, and thereby may reduce the severity or duration of neutropenic fevers. This phase 2 study included 163 patients with de novo AML receiving induction chemotherapy. Evaluable patients (n=120) were randomly assigned to receive either romyelocel-L plus G-CSF (n=59) or G-CSF monotherapy (n=61). From days 15 to 28, romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy significantly reduced the mean duration of febrile episodes (2.36 days vs 3.90 days; P = .02) and incidence of infections (6.8% vs 27.9%; P = .0013). Length of hospitalization was significantly shorter in the romyelocel-L plus G-CSF vs G-CSF monotherapy group (25.5 days vs 28.7 days; P = .002). These results are encouraging, and a phase III trial is suggested by the authors. (Desai PM et al).
Finally, a study by MDACC reported disappointing results with the use of venetoclax in patients with tp53 mutation. Findings are from a retrospective analysis of 238 patients with newly diagnosed TP53-mutated AML treated with either VEN-based (n=58) or non-VEN-based (n=180) therapies. The addition of venetoclax to standard treatment regimens (VEN-based) did not improve clinical outcomes in patients with TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML), highlighting the need for novel therapies in this patient population. Overall, there was no significant differences in overall survival (median, 5.7 months vs 6.6 months; P = .4), relapse-free survival (median, 3.5 months vs 4.7 months; P = .43), 4-week mortality (7% vs 10%; P = .5), and 8-week mortality (22% vs 17%; P = .4) in patients receiving VEN-based vs non-VEN-based therapies (Venugopal S et al). Clearly, better therapies are needed for this patient population.
Short sleep is linked to future dementia
, according to a new analysis of data from the Whitehall II cohort study.
Previous work had identified links between short sleep duration and dementia risk, but few studies examined sleep habits long before onset of dementia. Those that did produced inconsistent results, according to Séverine Sabia, PhD, who is a research associate at Inserm (France) and the University College London.
“One potential reason for these inconstancies is the large range of ages of the study populations, and the small number of participants within each sleep duration group. The novelty of our study is to examine this association among almost 8,000 participants with a follow-up of 30 years, using repeated measures of sleep duration starting in midlife to consider sleep duration at specific ages,” Dr. Sabia said in an interview. She presented the research at the 2021 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Those previous studies found a U-shaped association between sleep duration and dementia risk, with lowest risk associated with 7-8 hours of sleep, but greater risk for shorter and longer durations. However, because the studies had follow-up periods shorter than 10 years, they are at greater risk of reverse causation bias. Longer follow-up studies tended to have small sample sizes or to focus on older adults.
The longer follow-up in the current study makes for a more compelling case, said Claire Sexton, DPhil, director of Scientific Programs & Outreach for the Alzheimer’s Association. Observations of short or long sleep closer to the onset of symptoms could just be a warning sign of dementia. “But looking at age 50, age 60 ... if you’re seeing those relationships, then it’s less likely that it is just purely prodromal,” said Dr. Sexton. But it still doesn’t necessarily confirm causation. “It could also be a risk factor,” Dr. Sexton added.
Multifactorial risk
Dr. Sabia also noted that the magnitude of risk was similar to that seen with smoking or obesity, and many factors play a role in dementia risk. “Even if the risk of dementia was 30% higher in those with persistent short sleep duration, in absolute terms, the percentage of those with persistent short duration who developed dementia was 8%, and 6% in those with persistent sleep duration of 7 hours. Dementia is a multifactorial disease, which means that several factors are likely to influence its onset. Sleep duration is one of them, but if a person has poor sleep and does not manage to increase it, there are other important prevention measures. It is important to keep a healthy lifestyle and cardiometabolic measures in the normal range. All together it is likely to be beneficial for brain health in later life,” she said.
Dr. Sexton agreed. “With sleep we’re still trying to tease apart what aspect of sleep is important. Is it the sleep duration? Is it the quality of sleep? Is it certain sleep stages?” she said.
Regardless of sleep’s potential influence on dementia risk, both Dr. Sexton and Dr. Sabia noted the importance of sleep for general health. “These types of problems are very prevalent, so it’s good for people to be aware of them. And then if they notice any problems with their sleep, or any changes, to go and see their health care provider, and to be discussing them, and then to be investigating the cause, and to see whether changes in sleep hygiene and treatments for insomnia could address these sleep problems,” said Dr. Sexton.
Decades of data
During the Whitehall II study, researchers assessed average sleep duration (“How many hours of sleep do you have on an average weeknight?”) six times over 30 years of follow-up. Dr. Sabia’s group extracted self-reported sleep duration data at ages 50, 60, and 70. Short sleep duration was defined as fewer than 5 hours, or 6 hours. Normal sleep duration was defined as 7 hours. Long duration was defined as 8 hours or more.
A questioner during the Q&A period noted that this grouping is a little unusual. Many studies define 7-8 hours as normal. Dr. Sabia answered that they were unable to examine periods of 9 hours or more due to the nature of the data, and the lowest associated risk was found at 7 hours.
The researchers analyzed data from 7,959 participants (33.0% women). At age 50, compared with 7 hours of sleep, 6 or few hours of sleep was associated with a higher risk of dementia over the ensuing 25 years of follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.48). The same was true at age 60 (15 years of follow-up HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.10-1.72). There was a trend at age 70 (8 years follow-up; HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.98-1.57). For 8 or more hours of sleep, there were trends toward increased risk at age 50 (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.98-1.60). Long sleep at age 60 and 70 was associated with heightened risk, but the confidence intervals were well outside statistical significance.
Twenty percent of participants had persistent short sleep over the course of follow-up, 37% had persistent normal sleep, and 7% had persistent long sleep. Seven percent of participants experienced a change from normal sleep to short sleep, 16% had a change from short sleep to normal sleep, and 13% had a change from normal sleep to long sleep.
Persistent short sleep between age 50 and 70 was associated with a 30% increased risk of dementia (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.00-1.69). There were no statistically significant associations between dementia risk and any of the changing sleep pattern groups.
Dr. Sabia and Dr. Sexton have no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new analysis of data from the Whitehall II cohort study.
Previous work had identified links between short sleep duration and dementia risk, but few studies examined sleep habits long before onset of dementia. Those that did produced inconsistent results, according to Séverine Sabia, PhD, who is a research associate at Inserm (France) and the University College London.
“One potential reason for these inconstancies is the large range of ages of the study populations, and the small number of participants within each sleep duration group. The novelty of our study is to examine this association among almost 8,000 participants with a follow-up of 30 years, using repeated measures of sleep duration starting in midlife to consider sleep duration at specific ages,” Dr. Sabia said in an interview. She presented the research at the 2021 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Those previous studies found a U-shaped association between sleep duration and dementia risk, with lowest risk associated with 7-8 hours of sleep, but greater risk for shorter and longer durations. However, because the studies had follow-up periods shorter than 10 years, they are at greater risk of reverse causation bias. Longer follow-up studies tended to have small sample sizes or to focus on older adults.
The longer follow-up in the current study makes for a more compelling case, said Claire Sexton, DPhil, director of Scientific Programs & Outreach for the Alzheimer’s Association. Observations of short or long sleep closer to the onset of symptoms could just be a warning sign of dementia. “But looking at age 50, age 60 ... if you’re seeing those relationships, then it’s less likely that it is just purely prodromal,” said Dr. Sexton. But it still doesn’t necessarily confirm causation. “It could also be a risk factor,” Dr. Sexton added.
Multifactorial risk
Dr. Sabia also noted that the magnitude of risk was similar to that seen with smoking or obesity, and many factors play a role in dementia risk. “Even if the risk of dementia was 30% higher in those with persistent short sleep duration, in absolute terms, the percentage of those with persistent short duration who developed dementia was 8%, and 6% in those with persistent sleep duration of 7 hours. Dementia is a multifactorial disease, which means that several factors are likely to influence its onset. Sleep duration is one of them, but if a person has poor sleep and does not manage to increase it, there are other important prevention measures. It is important to keep a healthy lifestyle and cardiometabolic measures in the normal range. All together it is likely to be beneficial for brain health in later life,” she said.
Dr. Sexton agreed. “With sleep we’re still trying to tease apart what aspect of sleep is important. Is it the sleep duration? Is it the quality of sleep? Is it certain sleep stages?” she said.
Regardless of sleep’s potential influence on dementia risk, both Dr. Sexton and Dr. Sabia noted the importance of sleep for general health. “These types of problems are very prevalent, so it’s good for people to be aware of them. And then if they notice any problems with their sleep, or any changes, to go and see their health care provider, and to be discussing them, and then to be investigating the cause, and to see whether changes in sleep hygiene and treatments for insomnia could address these sleep problems,” said Dr. Sexton.
Decades of data
During the Whitehall II study, researchers assessed average sleep duration (“How many hours of sleep do you have on an average weeknight?”) six times over 30 years of follow-up. Dr. Sabia’s group extracted self-reported sleep duration data at ages 50, 60, and 70. Short sleep duration was defined as fewer than 5 hours, or 6 hours. Normal sleep duration was defined as 7 hours. Long duration was defined as 8 hours or more.
A questioner during the Q&A period noted that this grouping is a little unusual. Many studies define 7-8 hours as normal. Dr. Sabia answered that they were unable to examine periods of 9 hours or more due to the nature of the data, and the lowest associated risk was found at 7 hours.
The researchers analyzed data from 7,959 participants (33.0% women). At age 50, compared with 7 hours of sleep, 6 or few hours of sleep was associated with a higher risk of dementia over the ensuing 25 years of follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.48). The same was true at age 60 (15 years of follow-up HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.10-1.72). There was a trend at age 70 (8 years follow-up; HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.98-1.57). For 8 or more hours of sleep, there were trends toward increased risk at age 50 (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.98-1.60). Long sleep at age 60 and 70 was associated with heightened risk, but the confidence intervals were well outside statistical significance.
Twenty percent of participants had persistent short sleep over the course of follow-up, 37% had persistent normal sleep, and 7% had persistent long sleep. Seven percent of participants experienced a change from normal sleep to short sleep, 16% had a change from short sleep to normal sleep, and 13% had a change from normal sleep to long sleep.
Persistent short sleep between age 50 and 70 was associated with a 30% increased risk of dementia (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.00-1.69). There were no statistically significant associations between dementia risk and any of the changing sleep pattern groups.
Dr. Sabia and Dr. Sexton have no relevant financial disclosures.
, according to a new analysis of data from the Whitehall II cohort study.
Previous work had identified links between short sleep duration and dementia risk, but few studies examined sleep habits long before onset of dementia. Those that did produced inconsistent results, according to Séverine Sabia, PhD, who is a research associate at Inserm (France) and the University College London.
“One potential reason for these inconstancies is the large range of ages of the study populations, and the small number of participants within each sleep duration group. The novelty of our study is to examine this association among almost 8,000 participants with a follow-up of 30 years, using repeated measures of sleep duration starting in midlife to consider sleep duration at specific ages,” Dr. Sabia said in an interview. She presented the research at the 2021 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference.
Those previous studies found a U-shaped association between sleep duration and dementia risk, with lowest risk associated with 7-8 hours of sleep, but greater risk for shorter and longer durations. However, because the studies had follow-up periods shorter than 10 years, they are at greater risk of reverse causation bias. Longer follow-up studies tended to have small sample sizes or to focus on older adults.
The longer follow-up in the current study makes for a more compelling case, said Claire Sexton, DPhil, director of Scientific Programs & Outreach for the Alzheimer’s Association. Observations of short or long sleep closer to the onset of symptoms could just be a warning sign of dementia. “But looking at age 50, age 60 ... if you’re seeing those relationships, then it’s less likely that it is just purely prodromal,” said Dr. Sexton. But it still doesn’t necessarily confirm causation. “It could also be a risk factor,” Dr. Sexton added.
Multifactorial risk
Dr. Sabia also noted that the magnitude of risk was similar to that seen with smoking or obesity, and many factors play a role in dementia risk. “Even if the risk of dementia was 30% higher in those with persistent short sleep duration, in absolute terms, the percentage of those with persistent short duration who developed dementia was 8%, and 6% in those with persistent sleep duration of 7 hours. Dementia is a multifactorial disease, which means that several factors are likely to influence its onset. Sleep duration is one of them, but if a person has poor sleep and does not manage to increase it, there are other important prevention measures. It is important to keep a healthy lifestyle and cardiometabolic measures in the normal range. All together it is likely to be beneficial for brain health in later life,” she said.
Dr. Sexton agreed. “With sleep we’re still trying to tease apart what aspect of sleep is important. Is it the sleep duration? Is it the quality of sleep? Is it certain sleep stages?” she said.
Regardless of sleep’s potential influence on dementia risk, both Dr. Sexton and Dr. Sabia noted the importance of sleep for general health. “These types of problems are very prevalent, so it’s good for people to be aware of them. And then if they notice any problems with their sleep, or any changes, to go and see their health care provider, and to be discussing them, and then to be investigating the cause, and to see whether changes in sleep hygiene and treatments for insomnia could address these sleep problems,” said Dr. Sexton.
Decades of data
During the Whitehall II study, researchers assessed average sleep duration (“How many hours of sleep do you have on an average weeknight?”) six times over 30 years of follow-up. Dr. Sabia’s group extracted self-reported sleep duration data at ages 50, 60, and 70. Short sleep duration was defined as fewer than 5 hours, or 6 hours. Normal sleep duration was defined as 7 hours. Long duration was defined as 8 hours or more.
A questioner during the Q&A period noted that this grouping is a little unusual. Many studies define 7-8 hours as normal. Dr. Sabia answered that they were unable to examine periods of 9 hours or more due to the nature of the data, and the lowest associated risk was found at 7 hours.
The researchers analyzed data from 7,959 participants (33.0% women). At age 50, compared with 7 hours of sleep, 6 or few hours of sleep was associated with a higher risk of dementia over the ensuing 25 years of follow-up (hazard ratio [HR], 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01-1.48). The same was true at age 60 (15 years of follow-up HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.10-1.72). There was a trend at age 70 (8 years follow-up; HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.98-1.57). For 8 or more hours of sleep, there were trends toward increased risk at age 50 (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.98-1.60). Long sleep at age 60 and 70 was associated with heightened risk, but the confidence intervals were well outside statistical significance.
Twenty percent of participants had persistent short sleep over the course of follow-up, 37% had persistent normal sleep, and 7% had persistent long sleep. Seven percent of participants experienced a change from normal sleep to short sleep, 16% had a change from short sleep to normal sleep, and 13% had a change from normal sleep to long sleep.
Persistent short sleep between age 50 and 70 was associated with a 30% increased risk of dementia (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.00-1.69). There were no statistically significant associations between dementia risk and any of the changing sleep pattern groups.
Dr. Sabia and Dr. Sexton have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM AAIC 2021
DOACs best aspirin after ventricular ablation: STROKE-VT
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Catheter ablation has been around a lot longer for ventricular arrhythmia than for atrial fibrillation, but far less is settled about what antithrombotic therapy should follow ventricular ablations, as there have been no big, randomized trials for guidance.
But the evidence base grew stronger this week, and it favors postprocedure treatment with a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) over antiplatelet therapy with aspirin for patients undergoing radiofrequency (RF) ablation to treat left ventricular (LV) arrhythmias.
The 30-day risk for ischemic stroke or transient ischemia attack (TIA) was sharply higher for patients who took daily aspirin after RF ablation for ventricular tachycardia (VT) or premature ventricular contractions (PVC) in a multicenter randomized trial.
Those of its 246 patients who received aspirin were also far more likely to show asymptomatic lesions on cerebral MRI scans performed both 24 hours and 30 days after the procedure.
The findings show the importance of DOAC therapy after ventricular ablation procedures, a setting for which there are no evidence-based guidelines, “to mitigate the risk of systemic thromboembolic events,” said Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute, Overland Park. He spoke at a media presentation on the trial, called STROKE-VT, during the Heart Rhythm Society 2021 Scientific Sessions, held virtually and on-site in Boston.
The risk for stroke and TIA went up in association with several procedural issues, including some that operators might be able to change in order to reach for better outcomes, Dr. Lakkireddy observed.
“Prolonged radiofrequency ablation times, especially in those with low left ventricle ejection fractions, are definitely higher risk,” as are procedures that involved the retrograde transaortic approach for advancing the ablation catheter, rather than a trans-septal approach.
The retrograde transaortic approach should be avoided in such procedures, “whenever it can be avoided,” said Dr. Lakkireddy, who formally presented STROKE-VT at the HRS sessions and is lead author on its report published about the same time in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
The trial has limitations, but “it’s a very important study, and I think that this could become our standard of care for managing anticoagulation after VT and PVC left-sided ablations,” Mina K. Chung, MD, Cleveland Clinic, said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s presentation.
How patients are treated with antithrombotics after ventricular ablations can vary widely, sometimes based on the operator’s “subjective feeling of how extensive the ablation is,” Christine M. Albert, MD, MPH, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, not involved in the study, said during the STROKE-VT media briefing.
That’s consistent with the guidelines, which propose oral anticoagulation therapy after more extensive ventricular ablations and antiplatelets when the ablation is more limited – based more on consensus than firm evidence – as described by Jeffrey R. Winterfield, MD, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and Usha Tedrow, MD, MSc, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
“This is really the first randomized trial data, that I know of, that we have on this. So I do think it will be guideline-influencing,” Dr. Albert said.
“This should change practice,” agreed Jonathan P. Piccini, MD, MHS, Duke University, Durham, N.C., also not part of STROKE-VT. “A lot of evidence in the trial is consistent and provides a compelling story, not to mention that, in my opinion, the study probably underestimates the value of DOACs,” he told this news organization.
That’s because patients assigned to DOACs had far longer ablation times, “so their risk was even greater than in the aspirin arm,” Dr. Piccini said. Ablation times averaged 2,095 seconds in the DOAC group, compared with only 1,708 seconds in the aspirin group, probably because the preponderance of VT over PVC ablations for those getting a DOAC was even greater in the aspirin group.
Of the 246 patients assigned to either aspirin or a DOAC, usually a factor Xa inhibitor, 75% had undergone VT ablation and the remainder ablation for PVCs. Their mean age was 60 years and only 18% were women. None had experienced a cerebrovascular event in the previous 3 months.
The 30-day odds ratio for TIA or ischemic stroke in patients who received aspirin, compared with a DOAC, was 12.6 (95% confidence interval, 4.10-39.11; P < .001).
The corresponding OR for asymptomatic cerebral lesions by MRI at 24 hours was 2.15 (95% CI, 1.02-4.54; P = .04) and at 30 days was 3.48 (95% CI, 1.38-8.80; P = .008).
The rate of stroke or TIA was similar in patients who underwent ablation for VT and for PVCs (14% vs. 16%, respectively; P = .70). There were fewer asymptomatic cerebrovascular events by MRI at 24 hours for those undergoing VT ablations (14.7% and 25.8%, respectively; P = .046); but difference between rates attenuated by 30 days (11.4% and 14.5%, respectively; P = .52).
The OR for TIA or stroke associated with the retrograde transaortic approach, performed in about 40% of the patients, compared with the trans-septal approach in the remainder was 2.60 (95% CI, 1.06-6.37; P = .04).
“The study tells us it’s safe and indeed preferable to anticoagulate after an ablation procedure. But the more important finding, perhaps, wasn’t the one related to the core hypothesis. And that was the effect of retrograde access,” Paul A. Friedman, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said as an invited discussant after Dr. Lakkireddy’s formal presentation of the trial.
Whether a ventricular ablation is performed using the retrograde transaortic or trans-septal approach often depends on the location of the ablation targets in the left ventricle. But in some cases it’s a matter of operator preference, Dr. Piccini observed.
“There are some situations where, really, it is better to do retrograde aortic, and there are some cases that are better to do trans-septal. But now there’s going to be a higher burden of proof,” he said. Given the findings of STROKE-VT, operators may need to consider that a ventricular ablation procedure that can be done by the trans-septal route perhaps ought to be consistently done that way.
Dr. Lakkireddy discloses financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Biosense Webster, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and more. Dr. Chung had “nothing relevant to disclose.” Dr. Piccini discloses receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Sanofi, Abbott, ARCA Biopharma, Medtronic, Philips, Biotronik, Allergan, LivaNova, and Myokardia; and research in conjunction with Bayer Healthcare, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. Dr. Friedman discloses conducting research in conjunction with Medtronic and Abbott; holding intellectual property rights with AliveCor, Inference, Medicool, Eko, and Anumana; and receiving honoraria or speaking or consulting fees from Boston Scientific. Dr. Winterfield and Dr. Tedrow had no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bronchitis the leader at putting children in the hospital
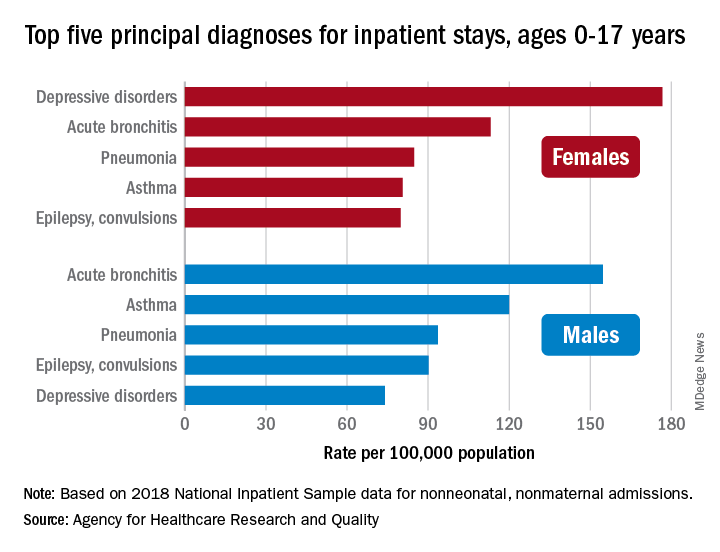
About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.

About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.

About 7% (99,000) of the 1.47 million nonmaternal, nonneonatal hospital stays in children aged 0-17 years involved a primary diagnosis of acute bronchitis in 2018, representing the leading cause of admissions in boys (154.7 stays per 100,000 population) and the second-leading diagnosis in girls (113.1 stays per 100,000), Kimberly W. McDermott, PhD, and Marc Roemer, MS, said in a statistical brief.
Depressive disorders were the most common primary diagnosis in girls, with a rate of 176.7 stays per 100,000, and the second-leading diagnosis overall, although the rate was less than half that (74.0 per 100,000) in boys. Two other respiratory conditions, asthma and pneumonia, were among the top five for both girls and boys, as was epilepsy, they reported.
The combined rate for all diagnoses was slightly higher for boys, 2,051 per 100,000, compared with 1,922 for girls, they said based on data from the National Inpatient Sample.
“Identifying the most frequent primary conditions for which patients are admitted to the hospital is important to the implementation and improvement of health care delivery, quality initiatives, and health policy,” said Dr. McDermott of IBM Watson Health and Mr. Roemer of the AHRQ.
Physicians wearing white coats rated more experienced
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
Physicians wearing white coats were rated as significantly more experienced and professional than peers wearing casual attire. Regardless of their attire, however, female physicians were more likely to be judged as appearing less professional and were more likely to be misidentified as medical technicians, physician assistants, or nurses, found research published in JAMA Network Open.
“A white coat with scrubs attire was most preferred for surgeons (mean preference index, 1.3), whereas a white coat with business attire was preferred for family physicians and dermatologists (mean preference indexes, 1.6 and 1.2, respectively; P < .001),” Helen Xun, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote. “A male model wearing business inner wear with a white coat, fleece jacket, or softshell jacket was perceived as significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire (mean professionalism score: male, 65.8; female, 56.2; mean difference in professionalism score: white coat, 12.06; fleece, 7.89; softshell, 8.82; P < .001). ... A male model wearing hospital scrubs or fashion scrubs alone was also perceived as more professional than a female model in the same attire.”
While casual attire, such as fleece or softshell jackets emblazoned with the names of the institution and wearer, has become more popular attire for physicians in recent years, the researchers noted theirs is the first published research to identify associations between gender, attire, and how people distinguish between various health care roles. The study authors launched their web-based survey from May to June 2020 and asked people aged 18 years and older to rate a series of photographs of deidentified models wearing health care attire. Inner wear choices were business attire versus scrubs with and without outer wear options of a long white coat, gray fleece jacket, or black softshell jackets. Survey respondents ranked the images on a 6-point Likert scale with 1 being the least experienced, professional, and friendly and 6 being the most experienced, professional, and friendly. Survey respondents also viewed individual images of male or female models and were asked to rate their professionalism on a scale of 0-100 – with 100 as the “most professional” as well as to identify their profession as either physician, surgeon, nurse, medical technician, or physician assistant.
The study team included 487 (93.3%) of 522 completed surveys in their analyses. Respondents’ mean age was 36.2 years; 260 (53.4%) were female; 372 (76.4%) were White; 33 (6.8%) were Black or African American. Younger respondents and those living in the Western United States who had more exposure to physician casual attire appeared more accepting of it, the authors wrote.
“I remember attending my white-coat ceremony as a medical student, and the symbolism of it all representing me entering the profession. It felt very emotional and heavy and I felt very proud to be there. I also remember taking a ‘selfie’ in my long white coat as a doctor for the first time before my first shift as a resident. But, I’ve also been wearing that same white coat, and a large badge with a ‘DOCTOR’ label on it, and been mistaken by a patient or parent for something other than the physician,” Alexandra M. Sims, a pediatrician and health equity researcher in Cincinnati, said in an interview. “So, I’d really hope that the take-home here is not simply that we must wear our white coats to be considered more professional. I think we have to unpack and dismantle how we’ve even built this notion of ‘professionalism’ in the first place. Women, people of color, and other marginalized groups were certainly not a part of the defining, but we must be a part of the reimagining of an equitable health care profession in this new era.”
As sartorial trends usher in more casual attire, clinicians should redouble efforts to build rapport and enhance communication with patients, such as clarifying team members’ roles when introducing themselves. Dr. Xun and coauthors noted that addressing gender bias is important for all clinicians – not just women – and point to the need for institutional and organizational support for disciplines where gender bias is “especially prevalent,” like surgery. “This responsibility should not be undertaken only by the individuals that experience the biases, which may result in additional cumulative career disadvantages. The promotion of equality and diversity begins with recognition, characterization, and evidence-supported interventions and is a community operation,” Dr. Xun and colleagues concluded.
“I do not equate attire to professionalism or experience, nor is it connected to my satisfaction with the physician. For myself and my daughter, it is the experience of care that ultimately influences our perceptions regarding the professionalism of the physician,” Hala H. Durrah, MTA, parent to a chronically ill child with special health care needs and a Patient and Family Engagement Consultant, said in an interview. “My respect for a physician will ultimately be determined by how my daughter and I were treated, not just from a clinical perspective, but how we felt during those interactions.”
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
How diet affects NASH-to-HCC progression
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
A new study sought to establish a new, clinically relevant mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that closely reflects human disease as well as the multitissue dynamics involved in the progression and regression of the condition, according to the researchers. This study focused on the association between progression of NASH and consumption of a Western diet, as well as the development of HCC.
The study used a model consisting of hyperphagic mice that lacked a functional ALMS1 gene (Foz/Foz), in addition to wild-type littermates. The model ultimately defined “the key signaling and cytokine pathways that are critical for disease development and resolution” associated with NASH, wrote Souradipta Ganguly, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. The report was published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
According to the researchers, this study is unique given “current rodent models of NASH do not reproduce the complete spectrum of metabolic and histologic” nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) phenotypes. Likewise, the lack of “systemic studies in a single rodent model of NASH that closely recapitulates the human pathology” reinforces the importance of the new model, the researchers added.
Over time, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies that fed wild-type mice a Western diet have largely failed to mimic the full pathology of NASH to fibrosis to HCC. In addition, the models in these studies fail to reflect the multitissue injuries frequently observed in NASH.
To circumvent these challenges, Dr. Ganguly and colleagues used ALMS1-mutated mice to develop a rodent model of metabolic syndrome that included NASH with fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. The ALMS1 mutation also resulted in the mice becoming hyperphagic, which increases hunger and leads to early-onset obesity, among other conditions characteristic of metabolic syndrome.
Researchers fed the hyperphagic Foz/Foz mice and wild-type littermates a Western diet or standard diet during a 12-week period for NASH/fibrosis and a 24-week period for HCC. After NASH was established, mice were switched back to normal chow to see if the condition regressed.
Macronutrient distribution of the study’s Western diet included 40% fat, 15% protein, and 44% carbohydrates, based on total caloric content. In contrast, the standard chow included 12% fat, 23% protein, and 65% carbohydrates from total calories.
Within 1-2 weeks, Foz mice fed the Western diet were considered steatotic. These mice subsequently developed NASH by 4 weeks of the study and grade 3 fibrosis by 12 weeks. The researchers concurrently observed the development of chronic kidney injury in the animals. Mice continuing to the 24 weeks ultimately progressed to cirrhosis and HCC; these mice demonstrated reduced survival due to cardiac dysfunction.
Mice that developed NASH were then switched to a diet consisting of normal chow. Following this switch, NASH began to regress, and survival improved. These mice did not appear to develop HCC, and total liver weight was significantly reduced compared with the mice that didn’t enter the regression phase of the study. The researchers wrote that the resolution of hepatic steatosis was also consistent with improved glucose tolerance.
In transcriptomic and histologic analyses, the researchers found strong concordance between Foz/Foz mice NASH liver and human NASH.
The study also found that early disruption of gut barrier, microbial dysbiosis, lipopolysaccharide leakage, and intestinal inflammation preceded NASH in the Foz/Foz mice fed the Western diet, resulting in acute-phase liver inflammation. The early inflammation was reflected by an increase in several chemokines and cytokines by 1-2 weeks. As NASH progressed, the liver cytokine/chemokine profile continued to evolve, leading to monocyte recruitment predominance. “Further studies will elaborate the roles of these NASH-specific microbiomial features in the development and progression of NASH fibrosis,” wrote the researchers.
The study received financial support Janssen, in addition to funding from an ALF Liver Scholar award, ACTRI/National Institutes of Health, the SDDRC, and the NIAAA/National Institutes of Health. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
FROM CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Treating the unvaccinated
The following is not anything I’m doing. It’s written solely as a thought exercise.
I don’t think it’s illegal, any more than if I refused to see smokers, or gum chewers. I mean, it’s my practice. I’m the only one here.
It’s certainly unethical, though. Part of being a doctor is caring for those who need our help. I’m vaccinated, so hopefully I’m at lower risk of getting sick if exposed. But that’s not a guarantee.
The vaccine is 95% effective. But that still means 1 in 20 vaccinated people can still contract the disease. Of course, people who aren’t vaccinated have no protection at all, aside from their immune system.
If the decision to not vaccinate, or not wear a mask, only affected themselves, I wouldn’t have as much of an issue with it. Like bungee jumping, the consequences of something going wrong affect only the person who made the choice (not including costs to the health care system or loved ones, now caretakers).
But with an easily spread infectious disease, a better analogy is probably that of drunk drivers. Their actions affect not only themselves, but everyone else on (or near) the road: other drivers, their passengers, pedestrians. ...
In a neurology practice not all of my patients have great immune systems. Sure, there are healthy migraine patients, but I also see patients with multiple sclerosis (on drugs like Ocrevus), patients with myasthenia gravis (on steroids or Imuran), and other folks whose survival depends on keeping their immune systems working at a suboptimal level. Not to mention those with malignancies, leukemias, and lymphomas.
These people have no real defense against the virus, and many of them can’t even get the vaccine. They depend on precautions, herd immunity, and luck. So, to protect them, maybe I should keep the unvaccinated out. Granted, this isn’t a guarantee, either, and doesn’t protect them during more mundane activities, such as grocery shopping or filling up their car.
Besides, the unvaccinated have their own, unrelated, neurological issues. Migraines, seizures, neuropathy, and so they need to see me. My job is to help anyone who needs me. Isn’t that what being a doctor is all about?
It’s an interesting question. Like most things in medicine, there is no black or white, just different shades of gray.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The following is not anything I’m doing. It’s written solely as a thought exercise.
I don’t think it’s illegal, any more than if I refused to see smokers, or gum chewers. I mean, it’s my practice. I’m the only one here.
It’s certainly unethical, though. Part of being a doctor is caring for those who need our help. I’m vaccinated, so hopefully I’m at lower risk of getting sick if exposed. But that’s not a guarantee.
The vaccine is 95% effective. But that still means 1 in 20 vaccinated people can still contract the disease. Of course, people who aren’t vaccinated have no protection at all, aside from their immune system.
If the decision to not vaccinate, or not wear a mask, only affected themselves, I wouldn’t have as much of an issue with it. Like bungee jumping, the consequences of something going wrong affect only the person who made the choice (not including costs to the health care system or loved ones, now caretakers).
But with an easily spread infectious disease, a better analogy is probably that of drunk drivers. Their actions affect not only themselves, but everyone else on (or near) the road: other drivers, their passengers, pedestrians. ...
In a neurology practice not all of my patients have great immune systems. Sure, there are healthy migraine patients, but I also see patients with multiple sclerosis (on drugs like Ocrevus), patients with myasthenia gravis (on steroids or Imuran), and other folks whose survival depends on keeping their immune systems working at a suboptimal level. Not to mention those with malignancies, leukemias, and lymphomas.
These people have no real defense against the virus, and many of them can’t even get the vaccine. They depend on precautions, herd immunity, and luck. So, to protect them, maybe I should keep the unvaccinated out. Granted, this isn’t a guarantee, either, and doesn’t protect them during more mundane activities, such as grocery shopping or filling up their car.
Besides, the unvaccinated have their own, unrelated, neurological issues. Migraines, seizures, neuropathy, and so they need to see me. My job is to help anyone who needs me. Isn’t that what being a doctor is all about?
It’s an interesting question. Like most things in medicine, there is no black or white, just different shades of gray.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
The following is not anything I’m doing. It’s written solely as a thought exercise.
I don’t think it’s illegal, any more than if I refused to see smokers, or gum chewers. I mean, it’s my practice. I’m the only one here.
It’s certainly unethical, though. Part of being a doctor is caring for those who need our help. I’m vaccinated, so hopefully I’m at lower risk of getting sick if exposed. But that’s not a guarantee.
The vaccine is 95% effective. But that still means 1 in 20 vaccinated people can still contract the disease. Of course, people who aren’t vaccinated have no protection at all, aside from their immune system.
If the decision to not vaccinate, or not wear a mask, only affected themselves, I wouldn’t have as much of an issue with it. Like bungee jumping, the consequences of something going wrong affect only the person who made the choice (not including costs to the health care system or loved ones, now caretakers).
But with an easily spread infectious disease, a better analogy is probably that of drunk drivers. Their actions affect not only themselves, but everyone else on (or near) the road: other drivers, their passengers, pedestrians. ...
In a neurology practice not all of my patients have great immune systems. Sure, there are healthy migraine patients, but I also see patients with multiple sclerosis (on drugs like Ocrevus), patients with myasthenia gravis (on steroids or Imuran), and other folks whose survival depends on keeping their immune systems working at a suboptimal level. Not to mention those with malignancies, leukemias, and lymphomas.
These people have no real defense against the virus, and many of them can’t even get the vaccine. They depend on precautions, herd immunity, and luck. So, to protect them, maybe I should keep the unvaccinated out. Granted, this isn’t a guarantee, either, and doesn’t protect them during more mundane activities, such as grocery shopping or filling up their car.
Besides, the unvaccinated have their own, unrelated, neurological issues. Migraines, seizures, neuropathy, and so they need to see me. My job is to help anyone who needs me. Isn’t that what being a doctor is all about?
It’s an interesting question. Like most things in medicine, there is no black or white, just different shades of gray.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
MR elastography could predict cirrhosis in NAFLD
Liver stiffness measurement with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) may prove predictive of future cirrhosis risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“These data expand the role of MRE from an accurate diagnostic method to a prognostic noninvasive imaging biomarker that can risk-stratify patients with NAFLD and guide the timing of surveillance and further refine their clinical management,” wrote Tolga Gidener, MD, and colleagues. The study authors added that the research further expands “the role of MRE beyond liver fibrosis estimation by adding a predictive feature to improve individualized disease monitoring and patient counseling.” Their study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Currently, there are no established noninvasive strategies that can effectively identify patients with NAFLD who are at high risk of progression to cirrhosis and liver-related complications. While fibrosis stage on histology may predict liver-associated outcomes in these patients, this approach is invasive, time consuming, and is generally not well tolerated by patients.
Although the technique has been noted for its high success rate and excellent levels of reliability and reproducibility, a possible limitation of MRE is its cost. That said, standalone MRE is reimbursed under Medicare Category I Current Procedural Terminology code 76391 with a cost of $240.02. However, there is also a lack of data on whether baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE can predict progression of NAFLD to cirrhosis.
To gauge the role of baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE, Dr. Gidener and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study that evaluated hard liver–related outcomes in 829 adult patients with NAFLD with or without cirrhosis (median age, 58 years; 54% female) who underwent MRE during 2007-2019.
Patients in the study were followed from the first MRE until death, last clinical encounter, or the end of the study. Clinical outcomes assessed in individual chart review included cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, and death.
At baseline, the median liver stiffness measurement was 2.8 kPa in 639 patients with NAFLD but without cirrhosis. Over a median 4-year follow-up period, a total of 20 patients developed cirrhosis, with an overall annual incidence rate of 1%.
Baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was significantly predictive of subsequent cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 2.93; 95% confidence interval, 1.86-4.62; P < .0001) per 1-kPa difference in liver stiffness measurement at baseline.
According to the researchers, the probability of future cirrhosis development can be ascertained using current liver stiffness measurement. As such, a greater than 1% probability threshold can be reached in 5 years in patients with a measurement of 2 kPa, 3 years in patients with a measurement of 3 kPA, and 1 year in patients with 4-5 kPa. “These time frames inform about estimated time to progression to hard outcomes and provide guidance for subsequent noninvasive monitoring for disease progression,” wrote the researchers.
The baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was also significantly predictive of future hepatic decompensation or death (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.13-1.56; P = .0007) per 1-kPa increment in the liver stiffness measurement. Likewise, the 1-year probability of subsequent hepatic decompensation or death in patients with cirrhosis and baseline liver stiffness measurement of 5 kPa versus 8 kPa was 9% versus 20%, respectively. In terms of covariates, age was the only factor that increased the risk of hepatic decompensation or death.
While the current study offers a glimpse into the potential clinical implications of liver stiffness measurement by MRE in NAFLD, the researchers suggest the applicability of the findings are limited by the study’s small sample size, relatively short follow-up duration, and the small number of cirrhosis events.
The researchers received study funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, National Institutes of Health, and the Department of Defense. The researchers disclosed no other relevant conflicts of interest.
Liver stiffness measurement with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) may prove predictive of future cirrhosis risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“These data expand the role of MRE from an accurate diagnostic method to a prognostic noninvasive imaging biomarker that can risk-stratify patients with NAFLD and guide the timing of surveillance and further refine their clinical management,” wrote Tolga Gidener, MD, and colleagues. The study authors added that the research further expands “the role of MRE beyond liver fibrosis estimation by adding a predictive feature to improve individualized disease monitoring and patient counseling.” Their study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Currently, there are no established noninvasive strategies that can effectively identify patients with NAFLD who are at high risk of progression to cirrhosis and liver-related complications. While fibrosis stage on histology may predict liver-associated outcomes in these patients, this approach is invasive, time consuming, and is generally not well tolerated by patients.
Although the technique has been noted for its high success rate and excellent levels of reliability and reproducibility, a possible limitation of MRE is its cost. That said, standalone MRE is reimbursed under Medicare Category I Current Procedural Terminology code 76391 with a cost of $240.02. However, there is also a lack of data on whether baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE can predict progression of NAFLD to cirrhosis.
To gauge the role of baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE, Dr. Gidener and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study that evaluated hard liver–related outcomes in 829 adult patients with NAFLD with or without cirrhosis (median age, 58 years; 54% female) who underwent MRE during 2007-2019.
Patients in the study were followed from the first MRE until death, last clinical encounter, or the end of the study. Clinical outcomes assessed in individual chart review included cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, and death.
At baseline, the median liver stiffness measurement was 2.8 kPa in 639 patients with NAFLD but without cirrhosis. Over a median 4-year follow-up period, a total of 20 patients developed cirrhosis, with an overall annual incidence rate of 1%.
Baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was significantly predictive of subsequent cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 2.93; 95% confidence interval, 1.86-4.62; P < .0001) per 1-kPa difference in liver stiffness measurement at baseline.
According to the researchers, the probability of future cirrhosis development can be ascertained using current liver stiffness measurement. As such, a greater than 1% probability threshold can be reached in 5 years in patients with a measurement of 2 kPa, 3 years in patients with a measurement of 3 kPA, and 1 year in patients with 4-5 kPa. “These time frames inform about estimated time to progression to hard outcomes and provide guidance for subsequent noninvasive monitoring for disease progression,” wrote the researchers.
The baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was also significantly predictive of future hepatic decompensation or death (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.13-1.56; P = .0007) per 1-kPa increment in the liver stiffness measurement. Likewise, the 1-year probability of subsequent hepatic decompensation or death in patients with cirrhosis and baseline liver stiffness measurement of 5 kPa versus 8 kPa was 9% versus 20%, respectively. In terms of covariates, age was the only factor that increased the risk of hepatic decompensation or death.
While the current study offers a glimpse into the potential clinical implications of liver stiffness measurement by MRE in NAFLD, the researchers suggest the applicability of the findings are limited by the study’s small sample size, relatively short follow-up duration, and the small number of cirrhosis events.
The researchers received study funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, National Institutes of Health, and the Department of Defense. The researchers disclosed no other relevant conflicts of interest.
Liver stiffness measurement with magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) may prove predictive of future cirrhosis risk in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), according to researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
“These data expand the role of MRE from an accurate diagnostic method to a prognostic noninvasive imaging biomarker that can risk-stratify patients with NAFLD and guide the timing of surveillance and further refine their clinical management,” wrote Tolga Gidener, MD, and colleagues. The study authors added that the research further expands “the role of MRE beyond liver fibrosis estimation by adding a predictive feature to improve individualized disease monitoring and patient counseling.” Their study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Currently, there are no established noninvasive strategies that can effectively identify patients with NAFLD who are at high risk of progression to cirrhosis and liver-related complications. While fibrosis stage on histology may predict liver-associated outcomes in these patients, this approach is invasive, time consuming, and is generally not well tolerated by patients.
Although the technique has been noted for its high success rate and excellent levels of reliability and reproducibility, a possible limitation of MRE is its cost. That said, standalone MRE is reimbursed under Medicare Category I Current Procedural Terminology code 76391 with a cost of $240.02. However, there is also a lack of data on whether baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE can predict progression of NAFLD to cirrhosis.
To gauge the role of baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE, Dr. Gidener and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study that evaluated hard liver–related outcomes in 829 adult patients with NAFLD with or without cirrhosis (median age, 58 years; 54% female) who underwent MRE during 2007-2019.
Patients in the study were followed from the first MRE until death, last clinical encounter, or the end of the study. Clinical outcomes assessed in individual chart review included cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation, and death.
At baseline, the median liver stiffness measurement was 2.8 kPa in 639 patients with NAFLD but without cirrhosis. Over a median 4-year follow-up period, a total of 20 patients developed cirrhosis, with an overall annual incidence rate of 1%.
Baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was significantly predictive of subsequent cirrhosis (hazard ratio, 2.93; 95% confidence interval, 1.86-4.62; P < .0001) per 1-kPa difference in liver stiffness measurement at baseline.
According to the researchers, the probability of future cirrhosis development can be ascertained using current liver stiffness measurement. As such, a greater than 1% probability threshold can be reached in 5 years in patients with a measurement of 2 kPa, 3 years in patients with a measurement of 3 kPA, and 1 year in patients with 4-5 kPa. “These time frames inform about estimated time to progression to hard outcomes and provide guidance for subsequent noninvasive monitoring for disease progression,” wrote the researchers.
The baseline liver stiffness measurement by MRE was also significantly predictive of future hepatic decompensation or death (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.13-1.56; P = .0007) per 1-kPa increment in the liver stiffness measurement. Likewise, the 1-year probability of subsequent hepatic decompensation or death in patients with cirrhosis and baseline liver stiffness measurement of 5 kPa versus 8 kPa was 9% versus 20%, respectively. In terms of covariates, age was the only factor that increased the risk of hepatic decompensation or death.
While the current study offers a glimpse into the potential clinical implications of liver stiffness measurement by MRE in NAFLD, the researchers suggest the applicability of the findings are limited by the study’s small sample size, relatively short follow-up duration, and the small number of cirrhosis events.
The researchers received study funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, National Institutes of Health, and the Department of Defense. The researchers disclosed no other relevant conflicts of interest.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Modest calorie reduction plus exercise linked with improved vascular health
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
Finding applies to seniors with obesity, who were part of a new study
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
The authors of the paper, published in Circulation, found a link between greater vascular benefits and exercise with modest – rather than intense – calorie restriction (CR) in elderly individuals with obesity.
“The finding that higher-intensity calorie restriction may not be necessary or advised has important implications for weight loss recommendations,” noted Tina E. Brinkley, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate professor of gerontology and geriatric medicine at the Sticht Center for Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Prevention at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, N.C.
It’s “not entirely clear” why greater calorie restriction did not translate to greater vascular benefit, but it “could be related in part to potentially adverse effects of severe CR on vascular function,” she noted. “These findings have important implications for reducing cardiovascular risk with nonpharmacological interventions in high-risk populations.”
Methods and findings
The study included 160 men and women aged 65-79 years, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 to 45 kg/m2. The subjects were randomized to one of three groups for 20 weeks of aerobic exercise only, aerobic exercise plus moderate CR, or aerobic exercise plus more intensive CR. Their exercise regimen involved 30 minutes of supervised treadmill walking for 4 days per week at 65%-70% of heart rate reserve.
Subjects in the moderate CR group decreased caloric intake by 250 kcals a day, while the intense calorie reduction group cut 600 kcals per day. Their meals contained less than 30% of calories from fat and at least 0.8 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight. They were also provided with supplemental calcium (1,200 mg/day) and vitamin D (800 IU/day).
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging was used to assess various aspects of aortic structure and function, including aortic arch pulse wave velocity, aortic distensibility and dimensions, and periaortic fat.
Weight loss was greater among subjects with CR plus exercise, compared with that of patients in the exercise-only group. The degree of weight loss was not significantly different between those with moderate versus intense CR ( 8.02 kg vs. 8.98 kg).
Among the exercise-only group, researchers observed no changes in aortic stiffness. However, adding moderate CR significantly improved this measure, while intense CR did not.
Specifically, subjects in the moderate-CR group had a “robust” 21% increase in distensibility in the descending aorta (DA), and an 8% decrease in aortic arch pulse wave velocity, whereas there were no significant vascular changes in the intense-CR group.
Bests results seen in exercise plus modest CR group
“Collectively, these data suggest that combining exercise with modest CR (as opposed to more intensive CR or no CR) provides the greatest benefit for proximal aortic stiffness, while also optimizing weight loss and improvements in body composition and body fat distribution,” noted the authors in their paper.
“Our data support the growing number of studies indicating that intentional weight loss can be safe for older adults with obesity and extend our previous findings, suggesting that obesity may blunt the beneficial effects of exercise for not only cardiorespiratory fitness, but likely vascular health as well.”
William E. Kraus, MD, professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology at Duke University Medical Center, in Durham, NC, described the study as important and interesting for several reasons.
“First, it demonstrates one can change aortic vascular function with a combined diet and exercise program, even in older, obese Americans. This implies it is never too late to make meaningful lifestyle changes that will benefit cardiovascular health,” he said. “Second, it is among an increasing number of studies demonstrating that more is not always better than less in exercise and diet lifestyle changes - and in fact the converse is true.”
“This gives hope that more people can benefit from modest lifestyle changes - in this case following guidelines for physical activity and only a modest reduction of 250 kilocalories per day resulted in benefit,” Dr. Kraus added.
The authors of the paper and Dr. Kraus disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM CIRCULATION