User login
To meme or not to meme: The likability and ‘virability’ of memes
As the famous saying goes, “laughter is the best medicine.”
So it’s no surprise that humor is a great way to connect with different people and across various groups.
Memes are usually conveyed as images and texts that communicate ideas or thoughts. A meme, or “imitated thing” (translation from the Greek mimeme), was reappropriated from Richard Dawkins in his book The Selfish Gene;
I am a big fan of memes. In fact, I can confidently say that one-third of my camera roll is dedicated to saved memes from Facebook, Instagram, and friends. Shameless to say, I’m also part of a few online groups dedicated to memes. They are relatable, as well as quick and fun ways to make light of an otherwise dull or upsetting situation.
Memes are contagious. From the moment they are created, they can be shared from one person to another, be edited or changed to adapt to the current situation, and become viral. They can be used to augment a conversation or replace the need for text communication entirely – in a sense, they are an entire language in and of themselves. They are constantly undergoing selection, repacking, and filtration. As a result, the most popular, successful, and, usually, relatable meme comes out on top, whereas the others fall behind and become “extinct.”
Memes generally adopt a form of word- or image-play that resonates well with people. The type of content varies from general lighthearted harmless animal humor to wry political and/or social commentary. They can be nearly universal or target specific groups (for example, students).
The popularity of memes depends on two factors: likability and “viralability.” Likability refers to how stimulating or engaging the content is, whereas “viralability” refers to the ability of the content to create a similar effect of user engagement across multiple people. Both factors are dynamic and can be quantified on the basis of the number of likes, shares, and/or comments.
In a content analysis of 1,000 memes on Facebook, researchers found that affiliative and aggressive humor styles were the most prevalent. Affiliative humor refers to a style of banter or joke that portrays others in a positive light, whereas aggressive humor achieves the opposite (that is, portrays others in a negative light). Interestingly, the type of humor that achieved the average most likes and shares was self-defeating humor (that is, disparaging one’s own situation in a negative perspective).
Self-defeating memes are suggested to have higher meme fitness. Meme fitness refers to the replicability of a meme. In this context, self-defeating memes have a unique ability to resonate with peoples’ thoughts and feelings in a sarcastic way and create laughter in contexts of general hardships (for example, failed relationships, academic hardships, or general life weaknesses). In a way, I’ve found that self-defeating memes offer a branch of support; to know that I am not going through certain problems alone, and that others can understand these difficulties, is comforting.
Memes can target emotional pain, neutralize the threat, and turn discomfort into a discourse of playfulness and warmth. Especially during times of great uncertainty, a bit of banter and wry humor may be just what we need to make light of difficult situations.
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc student.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the famous saying goes, “laughter is the best medicine.”
So it’s no surprise that humor is a great way to connect with different people and across various groups.
Memes are usually conveyed as images and texts that communicate ideas or thoughts. A meme, or “imitated thing” (translation from the Greek mimeme), was reappropriated from Richard Dawkins in his book The Selfish Gene;
I am a big fan of memes. In fact, I can confidently say that one-third of my camera roll is dedicated to saved memes from Facebook, Instagram, and friends. Shameless to say, I’m also part of a few online groups dedicated to memes. They are relatable, as well as quick and fun ways to make light of an otherwise dull or upsetting situation.
Memes are contagious. From the moment they are created, they can be shared from one person to another, be edited or changed to adapt to the current situation, and become viral. They can be used to augment a conversation or replace the need for text communication entirely – in a sense, they are an entire language in and of themselves. They are constantly undergoing selection, repacking, and filtration. As a result, the most popular, successful, and, usually, relatable meme comes out on top, whereas the others fall behind and become “extinct.”
Memes generally adopt a form of word- or image-play that resonates well with people. The type of content varies from general lighthearted harmless animal humor to wry political and/or social commentary. They can be nearly universal or target specific groups (for example, students).
The popularity of memes depends on two factors: likability and “viralability.” Likability refers to how stimulating or engaging the content is, whereas “viralability” refers to the ability of the content to create a similar effect of user engagement across multiple people. Both factors are dynamic and can be quantified on the basis of the number of likes, shares, and/or comments.
In a content analysis of 1,000 memes on Facebook, researchers found that affiliative and aggressive humor styles were the most prevalent. Affiliative humor refers to a style of banter or joke that portrays others in a positive light, whereas aggressive humor achieves the opposite (that is, portrays others in a negative light). Interestingly, the type of humor that achieved the average most likes and shares was self-defeating humor (that is, disparaging one’s own situation in a negative perspective).
Self-defeating memes are suggested to have higher meme fitness. Meme fitness refers to the replicability of a meme. In this context, self-defeating memes have a unique ability to resonate with peoples’ thoughts and feelings in a sarcastic way and create laughter in contexts of general hardships (for example, failed relationships, academic hardships, or general life weaknesses). In a way, I’ve found that self-defeating memes offer a branch of support; to know that I am not going through certain problems alone, and that others can understand these difficulties, is comforting.
Memes can target emotional pain, neutralize the threat, and turn discomfort into a discourse of playfulness and warmth. Especially during times of great uncertainty, a bit of banter and wry humor may be just what we need to make light of difficult situations.
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc student.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As the famous saying goes, “laughter is the best medicine.”
So it’s no surprise that humor is a great way to connect with different people and across various groups.
Memes are usually conveyed as images and texts that communicate ideas or thoughts. A meme, or “imitated thing” (translation from the Greek mimeme), was reappropriated from Richard Dawkins in his book The Selfish Gene;
I am a big fan of memes. In fact, I can confidently say that one-third of my camera roll is dedicated to saved memes from Facebook, Instagram, and friends. Shameless to say, I’m also part of a few online groups dedicated to memes. They are relatable, as well as quick and fun ways to make light of an otherwise dull or upsetting situation.
Memes are contagious. From the moment they are created, they can be shared from one person to another, be edited or changed to adapt to the current situation, and become viral. They can be used to augment a conversation or replace the need for text communication entirely – in a sense, they are an entire language in and of themselves. They are constantly undergoing selection, repacking, and filtration. As a result, the most popular, successful, and, usually, relatable meme comes out on top, whereas the others fall behind and become “extinct.”
Memes generally adopt a form of word- or image-play that resonates well with people. The type of content varies from general lighthearted harmless animal humor to wry political and/or social commentary. They can be nearly universal or target specific groups (for example, students).
The popularity of memes depends on two factors: likability and “viralability.” Likability refers to how stimulating or engaging the content is, whereas “viralability” refers to the ability of the content to create a similar effect of user engagement across multiple people. Both factors are dynamic and can be quantified on the basis of the number of likes, shares, and/or comments.
In a content analysis of 1,000 memes on Facebook, researchers found that affiliative and aggressive humor styles were the most prevalent. Affiliative humor refers to a style of banter or joke that portrays others in a positive light, whereas aggressive humor achieves the opposite (that is, portrays others in a negative light). Interestingly, the type of humor that achieved the average most likes and shares was self-defeating humor (that is, disparaging one’s own situation in a negative perspective).
Self-defeating memes are suggested to have higher meme fitness. Meme fitness refers to the replicability of a meme. In this context, self-defeating memes have a unique ability to resonate with peoples’ thoughts and feelings in a sarcastic way and create laughter in contexts of general hardships (for example, failed relationships, academic hardships, or general life weaknesses). In a way, I’ve found that self-defeating memes offer a branch of support; to know that I am not going through certain problems alone, and that others can understand these difficulties, is comforting.
Memes can target emotional pain, neutralize the threat, and turn discomfort into a discourse of playfulness and warmth. Especially during times of great uncertainty, a bit of banter and wry humor may be just what we need to make light of difficult situations.
Leanna M.W. Lui, HBSc, completed an HBSc global health specialist degree at the University of Toronto, where she is now an MSc student.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Guidelines for dementia and age-related cognitive changes
It is estimated that by the year 2060, 13.9 million Americans over the age of 65 will be diagnosed with dementia. Few good treatments are currently available.
Earlier this year, the American Psychological Association (APA) Task Force issued clinical guidelines “for the Evaluation of Dementia and Age-Related Cognitive Change.” While these 16 guidelines are aimed at psychologists, primary care doctors are often the first ones to evaluate a patient who may have dementia. As a family physician, I find having these guidelines especially helpful.
Neuropsychiatric testing and defining severity and type
This new guidance places emphasis on neuropsychiatric testing and defining the severity and type of dementia present.
Over the past 2 decades, diagnoses of mild neurocognitive disorders have increased, and this, in part, is due to diagnosing these problems earlier and with greater precision. It is also important to know that biomarkers are being increasingly researched, and it is imperative that we stay current with this research.
Cognitive decline may also occur with the coexistence of other mental health disorders, such as depression, so it is important that we screen for these as well. This is often difficult given the behavioral changes that can arise in dementia, but, as primary care doctors, we must differentiate these to treat our patients appropriately.
Informed consent
Informed consent can become an issue with patients with dementia. It must be assessed whether the patient has the capacity to make an informed decision and can competently communicate that decision.
The diagnosis of dementia alone does not preclude a patient from giving informed consent. A patient’s mental capacity must be determined, and if they are not capable of making an informed decision, the person legally responsible for giving informed consent on behalf of the patient must be identified.
Patients with dementia often have other medical comorbidities and take several medications. It is imperative to keep accurate medical records and medication lists. Sometimes, patients with dementia cannot provide this information. If that is the case, every attempt should be made to obtain records from every possible source.
Cultural competence
The guidelines also stress that there may be cultural differences when applying neuropsychiatric tests. It is our duty to maintain cultural competence and understand these differences. We all need to work to ensure we control our biases, and it is suggested that we review relevant evidence-based literature.
While ageism is common in our society, it shouldn’t be in our practices. For these reasons, outreach in at-risk populations is very important.
Pertinent data
The guidelines also suggest obtaining all possible information in our evaluation, especially when the patient is unable to give it to us.
Often, as primary care physicians, we refer these patients to other providers, and we should be providing all pertinent data to those we are referring these patients to. If all information is not available at the time of evaluation, follow-up visits should be scheduled.
If possible, family members should be present at the time of visit. They often provide valuable information regarding the extent and progression of the decline. Also, they know how the patient is functioning in the home setting and how much assistance they need with activities of daily living.
Caretaker support
Another important factor to consider is caretaker burnout. Caretakers are often under a lot of stress and have high rates of depression. It is important to provide them with education and support, as well as resources that may be available to them. For some, accepting the diagnosis that their loved one has dementia may be a struggle.
As doctors treating dementia patients, we need to know the resources that are available to assist dementia patients and their families. There are many local organizations that can help.
Also, research into dementia is ongoing and we need to stay current. The diagnosis of dementia should be made as early as possible using appropriate screening tools. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the quicker interventions can be started and the family members, as well as the patient, can come to accept the diagnosis.
As the population ages, we can expect the demands of dementia to rise as well. Primary care doctors are in a unique position to diagnose dementia once it starts to appear.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
It is estimated that by the year 2060, 13.9 million Americans over the age of 65 will be diagnosed with dementia. Few good treatments are currently available.
Earlier this year, the American Psychological Association (APA) Task Force issued clinical guidelines “for the Evaluation of Dementia and Age-Related Cognitive Change.” While these 16 guidelines are aimed at psychologists, primary care doctors are often the first ones to evaluate a patient who may have dementia. As a family physician, I find having these guidelines especially helpful.
Neuropsychiatric testing and defining severity and type
This new guidance places emphasis on neuropsychiatric testing and defining the severity and type of dementia present.
Over the past 2 decades, diagnoses of mild neurocognitive disorders have increased, and this, in part, is due to diagnosing these problems earlier and with greater precision. It is also important to know that biomarkers are being increasingly researched, and it is imperative that we stay current with this research.
Cognitive decline may also occur with the coexistence of other mental health disorders, such as depression, so it is important that we screen for these as well. This is often difficult given the behavioral changes that can arise in dementia, but, as primary care doctors, we must differentiate these to treat our patients appropriately.
Informed consent
Informed consent can become an issue with patients with dementia. It must be assessed whether the patient has the capacity to make an informed decision and can competently communicate that decision.
The diagnosis of dementia alone does not preclude a patient from giving informed consent. A patient’s mental capacity must be determined, and if they are not capable of making an informed decision, the person legally responsible for giving informed consent on behalf of the patient must be identified.
Patients with dementia often have other medical comorbidities and take several medications. It is imperative to keep accurate medical records and medication lists. Sometimes, patients with dementia cannot provide this information. If that is the case, every attempt should be made to obtain records from every possible source.
Cultural competence
The guidelines also stress that there may be cultural differences when applying neuropsychiatric tests. It is our duty to maintain cultural competence and understand these differences. We all need to work to ensure we control our biases, and it is suggested that we review relevant evidence-based literature.
While ageism is common in our society, it shouldn’t be in our practices. For these reasons, outreach in at-risk populations is very important.
Pertinent data
The guidelines also suggest obtaining all possible information in our evaluation, especially when the patient is unable to give it to us.
Often, as primary care physicians, we refer these patients to other providers, and we should be providing all pertinent data to those we are referring these patients to. If all information is not available at the time of evaluation, follow-up visits should be scheduled.
If possible, family members should be present at the time of visit. They often provide valuable information regarding the extent and progression of the decline. Also, they know how the patient is functioning in the home setting and how much assistance they need with activities of daily living.
Caretaker support
Another important factor to consider is caretaker burnout. Caretakers are often under a lot of stress and have high rates of depression. It is important to provide them with education and support, as well as resources that may be available to them. For some, accepting the diagnosis that their loved one has dementia may be a struggle.
As doctors treating dementia patients, we need to know the resources that are available to assist dementia patients and their families. There are many local organizations that can help.
Also, research into dementia is ongoing and we need to stay current. The diagnosis of dementia should be made as early as possible using appropriate screening tools. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the quicker interventions can be started and the family members, as well as the patient, can come to accept the diagnosis.
As the population ages, we can expect the demands of dementia to rise as well. Primary care doctors are in a unique position to diagnose dementia once it starts to appear.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
It is estimated that by the year 2060, 13.9 million Americans over the age of 65 will be diagnosed with dementia. Few good treatments are currently available.
Earlier this year, the American Psychological Association (APA) Task Force issued clinical guidelines “for the Evaluation of Dementia and Age-Related Cognitive Change.” While these 16 guidelines are aimed at psychologists, primary care doctors are often the first ones to evaluate a patient who may have dementia. As a family physician, I find having these guidelines especially helpful.
Neuropsychiatric testing and defining severity and type
This new guidance places emphasis on neuropsychiatric testing and defining the severity and type of dementia present.
Over the past 2 decades, diagnoses of mild neurocognitive disorders have increased, and this, in part, is due to diagnosing these problems earlier and with greater precision. It is also important to know that biomarkers are being increasingly researched, and it is imperative that we stay current with this research.
Cognitive decline may also occur with the coexistence of other mental health disorders, such as depression, so it is important that we screen for these as well. This is often difficult given the behavioral changes that can arise in dementia, but, as primary care doctors, we must differentiate these to treat our patients appropriately.
Informed consent
Informed consent can become an issue with patients with dementia. It must be assessed whether the patient has the capacity to make an informed decision and can competently communicate that decision.
The diagnosis of dementia alone does not preclude a patient from giving informed consent. A patient’s mental capacity must be determined, and if they are not capable of making an informed decision, the person legally responsible for giving informed consent on behalf of the patient must be identified.
Patients with dementia often have other medical comorbidities and take several medications. It is imperative to keep accurate medical records and medication lists. Sometimes, patients with dementia cannot provide this information. If that is the case, every attempt should be made to obtain records from every possible source.
Cultural competence
The guidelines also stress that there may be cultural differences when applying neuropsychiatric tests. It is our duty to maintain cultural competence and understand these differences. We all need to work to ensure we control our biases, and it is suggested that we review relevant evidence-based literature.
While ageism is common in our society, it shouldn’t be in our practices. For these reasons, outreach in at-risk populations is very important.
Pertinent data
The guidelines also suggest obtaining all possible information in our evaluation, especially when the patient is unable to give it to us.
Often, as primary care physicians, we refer these patients to other providers, and we should be providing all pertinent data to those we are referring these patients to. If all information is not available at the time of evaluation, follow-up visits should be scheduled.
If possible, family members should be present at the time of visit. They often provide valuable information regarding the extent and progression of the decline. Also, they know how the patient is functioning in the home setting and how much assistance they need with activities of daily living.
Caretaker support
Another important factor to consider is caretaker burnout. Caretakers are often under a lot of stress and have high rates of depression. It is important to provide them with education and support, as well as resources that may be available to them. For some, accepting the diagnosis that their loved one has dementia may be a struggle.
As doctors treating dementia patients, we need to know the resources that are available to assist dementia patients and their families. There are many local organizations that can help.
Also, research into dementia is ongoing and we need to stay current. The diagnosis of dementia should be made as early as possible using appropriate screening tools. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the quicker interventions can be started and the family members, as well as the patient, can come to accept the diagnosis.
As the population ages, we can expect the demands of dementia to rise as well. Primary care doctors are in a unique position to diagnose dementia once it starts to appear.
Dr. Girgis practices family medicine in South River, N.J., and is a clinical assistant professor of family medicine at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J. You can contact her at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Let’s talk about healthy aging (but where to begin?)
This month’s cover story, “A 4-pronged approach to foster healthy aging in older adults,” by Wilson and colleagues (page 376) provides a wealth of information about aspects of healthy aging that we should consider when we see our older patients. After reading this manuscript, I was a bit overwhelmed by the amount of information presented and, more so, by the thought of attempting to incorporate into my practice all of the possible screenings and interventions available to help older adults improve and maintain their health.
There is no debate about the importance of issues such as diet, exercise and mobility, mental health and cognition, vision and hearing, and strong social connections for maintaining health as we age. The difficulty comes in deciding how to spend our limited time with older patients during office encounters. Most older adults have several chronic diseases that need our attention, and they often have various medications that need to be monitored for effectiveness and safety, which can be time consuming. And, of course, we need to take time to screen for cardiovascular risk and cancer, too. Where to start?
Dr. Wilson’s solution makes sense to me: Take advantage of the annual wellness visit to discuss diet, exercise, mental health, vision and hearing, and social relationships. I am not so sure, however, if using formal screening instruments is the best way to do this, especially since there is no strong research that demonstrates improved patient-relevant outcomes using screening instruments, except, perhaps, for periodically screening for anxiety and depression.
It may be as effective to use what I will call the “chat technique.” Start with open-ended questions and statements, such as: “How are things going for you?” “Tell me about your family.” “What do you do for physical activity?” and “How has your mood been lately?”
An excellent complement to the chat technique is the goal-setting approach championed by geriatrician and family physician Jim Mold.1 His premise is that health itself is not the most important goal for most people, but rather a means to an end. That end is very specific to every person. An elderly, frail woman’s main life goal, for example, might be to remain in her own home for as long as possible or to live long enough to attend her great-grandson’s wedding.
Goal setting provides an excellent context for true shared decision-making. I agree with Dr. Wilson’s closing statement:
“As family physicians, it is important to capitalize on longitudinal relationships with patients and begin educating younger patients using this multidimensional framework to promote living ‘a productive and meaningful life’at any age.”
1. Mold, JW. Goal-Oriented Medical Care: Helping Patients Achieve Their Personal Health Goals. Full Court Press; 2017.
This month’s cover story, “A 4-pronged approach to foster healthy aging in older adults,” by Wilson and colleagues (page 376) provides a wealth of information about aspects of healthy aging that we should consider when we see our older patients. After reading this manuscript, I was a bit overwhelmed by the amount of information presented and, more so, by the thought of attempting to incorporate into my practice all of the possible screenings and interventions available to help older adults improve and maintain their health.
There is no debate about the importance of issues such as diet, exercise and mobility, mental health and cognition, vision and hearing, and strong social connections for maintaining health as we age. The difficulty comes in deciding how to spend our limited time with older patients during office encounters. Most older adults have several chronic diseases that need our attention, and they often have various medications that need to be monitored for effectiveness and safety, which can be time consuming. And, of course, we need to take time to screen for cardiovascular risk and cancer, too. Where to start?
Dr. Wilson’s solution makes sense to me: Take advantage of the annual wellness visit to discuss diet, exercise, mental health, vision and hearing, and social relationships. I am not so sure, however, if using formal screening instruments is the best way to do this, especially since there is no strong research that demonstrates improved patient-relevant outcomes using screening instruments, except, perhaps, for periodically screening for anxiety and depression.
It may be as effective to use what I will call the “chat technique.” Start with open-ended questions and statements, such as: “How are things going for you?” “Tell me about your family.” “What do you do for physical activity?” and “How has your mood been lately?”
An excellent complement to the chat technique is the goal-setting approach championed by geriatrician and family physician Jim Mold.1 His premise is that health itself is not the most important goal for most people, but rather a means to an end. That end is very specific to every person. An elderly, frail woman’s main life goal, for example, might be to remain in her own home for as long as possible or to live long enough to attend her great-grandson’s wedding.
Goal setting provides an excellent context for true shared decision-making. I agree with Dr. Wilson’s closing statement:
“As family physicians, it is important to capitalize on longitudinal relationships with patients and begin educating younger patients using this multidimensional framework to promote living ‘a productive and meaningful life’at any age.”
This month’s cover story, “A 4-pronged approach to foster healthy aging in older adults,” by Wilson and colleagues (page 376) provides a wealth of information about aspects of healthy aging that we should consider when we see our older patients. After reading this manuscript, I was a bit overwhelmed by the amount of information presented and, more so, by the thought of attempting to incorporate into my practice all of the possible screenings and interventions available to help older adults improve and maintain their health.
There is no debate about the importance of issues such as diet, exercise and mobility, mental health and cognition, vision and hearing, and strong social connections for maintaining health as we age. The difficulty comes in deciding how to spend our limited time with older patients during office encounters. Most older adults have several chronic diseases that need our attention, and they often have various medications that need to be monitored for effectiveness and safety, which can be time consuming. And, of course, we need to take time to screen for cardiovascular risk and cancer, too. Where to start?
Dr. Wilson’s solution makes sense to me: Take advantage of the annual wellness visit to discuss diet, exercise, mental health, vision and hearing, and social relationships. I am not so sure, however, if using formal screening instruments is the best way to do this, especially since there is no strong research that demonstrates improved patient-relevant outcomes using screening instruments, except, perhaps, for periodically screening for anxiety and depression.
It may be as effective to use what I will call the “chat technique.” Start with open-ended questions and statements, such as: “How are things going for you?” “Tell me about your family.” “What do you do for physical activity?” and “How has your mood been lately?”
An excellent complement to the chat technique is the goal-setting approach championed by geriatrician and family physician Jim Mold.1 His premise is that health itself is not the most important goal for most people, but rather a means to an end. That end is very specific to every person. An elderly, frail woman’s main life goal, for example, might be to remain in her own home for as long as possible or to live long enough to attend her great-grandson’s wedding.
Goal setting provides an excellent context for true shared decision-making. I agree with Dr. Wilson’s closing statement:
“As family physicians, it is important to capitalize on longitudinal relationships with patients and begin educating younger patients using this multidimensional framework to promote living ‘a productive and meaningful life’at any age.”
1. Mold, JW. Goal-Oriented Medical Care: Helping Patients Achieve Their Personal Health Goals. Full Court Press; 2017.
1. Mold, JW. Goal-Oriented Medical Care: Helping Patients Achieve Their Personal Health Goals. Full Court Press; 2017.
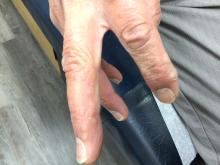
A 70-year-old man presents with firm papules on his hand and fingers
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
, although women are more often affected than men. GA most commonly appears in the first 3 decades of life. Although the etiology is not known, GA may represent a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. A link between GA and diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, dyslipidemia, and rarely, malignancy may exist.
GA is most commonly localized, presenting as an asymptomatic, erythematous, annular plaque with a firm border and central clearing localized to the wrists, ankles, and dorsal hands or feet. This form is the type most often seen in children. Generalized GA is far less common and presents later in life as multiple asymptomatic or pruritic papules and plaques on the trunk and extremities. Less common variants include subcutaneous GA, patch GA, atypical GA, and perforating GA. Perforating GA occurs on the dorsal hands and presents as (umbilicated) papules, and seems consistent with this patient’s clinical presentation. Histologically, transepidermal elimination of collagen is typically seen in perforating GA.1
Histology in this patient’s biopsy revealed a granulomatous dermatitis consistent with granuloma annulare. A palisaded arrangement of histiocytic cells surrounding altered collagen with increased dermal mucin was seen. There was associated perivascular mononuclear inflammatory infiltrates. The overlying epidermis was unremarkable.
Granuloma annulare often spontaneously resolves without sequelae. In some cases, atrophy may result. Lesions may also recur. Localized GA is often treated with high-potency topical corticosteroids or intralesional corticosteroids. For generalized GA, topical or intralesional corticosteroids may be used for select lesions. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, light therapy, cryotherapy, imiquimod, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin, and dapsone have also been reported in the literature as possible treatments.
This case and photo were provided by Dr. Berke, of Three Rivers Dermatology, Pittsburgh, and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1 Alves J, Barreiros H, Bartolo E. Healthcare (Basel). 2014 Sep 4;2(3):338-45.
2. Bolognia J et al. Dermatology (St. Louis: Mosby/Elsevier, 2008).
3. “Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin,” 13th ed. James W et al. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier, 2006.
Teen boy’s knee lesion has changed
A biopsy of the lesion was performed which showed an increased number of eccrine glands and blood vessels within the dermis. Some areas showed an increase in adipocytes and smooth muscle bundles. The changes were consistent with eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH).
The boy was referred to vascular laser therapy for treatment of the lesion.
EAH is a rare benign vascular growth characterized by an increased number of mature eccrine glands and blood vessels in the dermis and subcutis. The lesions are mostly present on the extremities, but cases of diffuse congenital lesions and lesions on the face and trunk have also been described. The lesions can be seen at birth or during the first years of life in about half of the cases, and the others tend to occur later in puberty and rarely in adulthood.1
Clinically, EAH lesions present as red, yellow to brown papules and plaques. Different dermoscopic patterns have been described which include the popcorn pattern that presents as yellow, confluent nodules with popcornlike shapes over a background of erythema, and linear arborizing vessels. The spitzoid pattern are brown globules on a background of erythema and pseudoreticular pigmentation around the globules. The verrucous hemangiomalike pattern has a bluish-white hue, reddish-blue or bluish lacunae, as seen in our patient.2-4
Most of the lesions are asymptomatic, but in some patients, they can be associated with pain, hyperhidrosis, and sometimes bleeding. Hyperhidrosis has been reported early in the presentation or during puberty or pregnancy. Our patient had started on amphetamines when hyperhidrosis occurred. Hyperhidrosis is a knowns side effect of this type of medication and may have had a role in the increased sweating noted on the hamartoma.
EAH can clinically look like verrucous hemangiomas, angiokeratomas, and vascular malformations, and histopathology may be needed to differentiate between them. Eccrine nevi and EAH can be similar. Hyperhidrosis is an early and predominant component of eccrine nevi, compared with one-third of EAH.
The exact etiology of this lesion is not known. It is thought to be caused by an abnormal differentiation of the epithelium, adnexal structure, and the mesenchyme during organogenesis.3 No other associated conditions have been described with EAH.
EAH are benign lesions that rarely require treatment. If the lesions are symptomatic or because of cosmetic reasons, they can be removed surgically. There are some reports of successful treatment with pulse dual-wavelength sequential 595- and 1064-nm lasers.5 Botulinum toxin has also been used in cases of symptomatic hyperhidrosis.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no conflicts. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Smith SD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Nov;36(6):909-12.
2. Patterson AT et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:413-7.
3. Garcıa-Garcıa SC et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(2):165-7.
4. Awatef Kelati et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(8)835-6.
5. Felgueiras J et al. Dermatol Surg. 2015 Mar;41(3):428-30.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed which showed an increased number of eccrine glands and blood vessels within the dermis. Some areas showed an increase in adipocytes and smooth muscle bundles. The changes were consistent with eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH).
The boy was referred to vascular laser therapy for treatment of the lesion.
EAH is a rare benign vascular growth characterized by an increased number of mature eccrine glands and blood vessels in the dermis and subcutis. The lesions are mostly present on the extremities, but cases of diffuse congenital lesions and lesions on the face and trunk have also been described. The lesions can be seen at birth or during the first years of life in about half of the cases, and the others tend to occur later in puberty and rarely in adulthood.1
Clinically, EAH lesions present as red, yellow to brown papules and plaques. Different dermoscopic patterns have been described which include the popcorn pattern that presents as yellow, confluent nodules with popcornlike shapes over a background of erythema, and linear arborizing vessels. The spitzoid pattern are brown globules on a background of erythema and pseudoreticular pigmentation around the globules. The verrucous hemangiomalike pattern has a bluish-white hue, reddish-blue or bluish lacunae, as seen in our patient.2-4
Most of the lesions are asymptomatic, but in some patients, they can be associated with pain, hyperhidrosis, and sometimes bleeding. Hyperhidrosis has been reported early in the presentation or during puberty or pregnancy. Our patient had started on amphetamines when hyperhidrosis occurred. Hyperhidrosis is a knowns side effect of this type of medication and may have had a role in the increased sweating noted on the hamartoma.
EAH can clinically look like verrucous hemangiomas, angiokeratomas, and vascular malformations, and histopathology may be needed to differentiate between them. Eccrine nevi and EAH can be similar. Hyperhidrosis is an early and predominant component of eccrine nevi, compared with one-third of EAH.
The exact etiology of this lesion is not known. It is thought to be caused by an abnormal differentiation of the epithelium, adnexal structure, and the mesenchyme during organogenesis.3 No other associated conditions have been described with EAH.
EAH are benign lesions that rarely require treatment. If the lesions are symptomatic or because of cosmetic reasons, they can be removed surgically. There are some reports of successful treatment with pulse dual-wavelength sequential 595- and 1064-nm lasers.5 Botulinum toxin has also been used in cases of symptomatic hyperhidrosis.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no conflicts. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Smith SD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Nov;36(6):909-12.
2. Patterson AT et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:413-7.
3. Garcıa-Garcıa SC et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(2):165-7.
4. Awatef Kelati et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(8)835-6.
5. Felgueiras J et al. Dermatol Surg. 2015 Mar;41(3):428-30.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed which showed an increased number of eccrine glands and blood vessels within the dermis. Some areas showed an increase in adipocytes and smooth muscle bundles. The changes were consistent with eccrine angiomatous hamartoma (EAH).
The boy was referred to vascular laser therapy for treatment of the lesion.
EAH is a rare benign vascular growth characterized by an increased number of mature eccrine glands and blood vessels in the dermis and subcutis. The lesions are mostly present on the extremities, but cases of diffuse congenital lesions and lesions on the face and trunk have also been described. The lesions can be seen at birth or during the first years of life in about half of the cases, and the others tend to occur later in puberty and rarely in adulthood.1
Clinically, EAH lesions present as red, yellow to brown papules and plaques. Different dermoscopic patterns have been described which include the popcorn pattern that presents as yellow, confluent nodules with popcornlike shapes over a background of erythema, and linear arborizing vessels. The spitzoid pattern are brown globules on a background of erythema and pseudoreticular pigmentation around the globules. The verrucous hemangiomalike pattern has a bluish-white hue, reddish-blue or bluish lacunae, as seen in our patient.2-4
Most of the lesions are asymptomatic, but in some patients, they can be associated with pain, hyperhidrosis, and sometimes bleeding. Hyperhidrosis has been reported early in the presentation or during puberty or pregnancy. Our patient had started on amphetamines when hyperhidrosis occurred. Hyperhidrosis is a knowns side effect of this type of medication and may have had a role in the increased sweating noted on the hamartoma.
EAH can clinically look like verrucous hemangiomas, angiokeratomas, and vascular malformations, and histopathology may be needed to differentiate between them. Eccrine nevi and EAH can be similar. Hyperhidrosis is an early and predominant component of eccrine nevi, compared with one-third of EAH.
The exact etiology of this lesion is not known. It is thought to be caused by an abnormal differentiation of the epithelium, adnexal structure, and the mesenchyme during organogenesis.3 No other associated conditions have been described with EAH.
EAH are benign lesions that rarely require treatment. If the lesions are symptomatic or because of cosmetic reasons, they can be removed surgically. There are some reports of successful treatment with pulse dual-wavelength sequential 595- and 1064-nm lasers.5 Botulinum toxin has also been used in cases of symptomatic hyperhidrosis.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. She has no conflicts. Email her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Smith SD et al. Pediatr Dermatol. 2019 Nov;36(6):909-12.
2. Patterson AT et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2016;38:413-7.
3. Garcıa-Garcıa SC et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(2):165-7.
4. Awatef Kelati et al. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4(8)835-6.
5. Felgueiras J et al. Dermatol Surg. 2015 Mar;41(3):428-30.
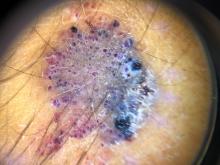
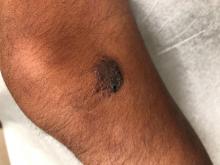
A 14-year-old male was referred to our pediatric dermatology clinic for evaluation of a lesion on the left knee that appeared at 1 year of age. The lesion has been growing with him and was not symptomatic until 6 months prior to the consultation, when it started bleeding and feeling wet.
He has a history of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder managed with dextroamphetamine-amphetamine. The changes noted on the knee lesion seem to occur at the same time that his ADHD medication was started.
On physical exam he had a violaceous circular plaque on the left knee.
On dermoscopy the lesion showed multiple dilated red and violaceous lacunae and whitish blue hue.
Sleep apnea has many faces
Fortunately her problem stemmed from sleep apnea, and resolved with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy.
Wallace and Bucks performed a meta analysis of 42 studies of memory in patients with sleep apnea and found sleep apnea patients were impaired when compared to healthy controls on verbal episodic memory (immediate recall, delayed recall, learning, and recognition) and visuospatial episodic memory (immediate and delayed recall).1 A meta-analysis by Olaithe and associates found an improvement in executive function in patients with sleep apnea who were treated with CPAP.2 I think this is worth considering especially in your patients who have subjective memory disturbances and do not appear to have a mild cognitive impairment or dementia.
About 15 years ago I saw a 74-year-old man for nocturia. He had seen two urologists and had a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) without any real change in his nocturia. I trialed him on all sorts of medications, and he seemed to improve temporarily a little on trazodone (went from seven episodes a night to four).
Eventually, after several years, I sent him for a sleep study. He had severe sleep apnea (Apnea Hypopnea Index, 65; O2 saturations as low as 60%). With treatment, his nocturia resolved. He went from seven episodes to two each night.
Zhou and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 13 studies looking at the association of sleep apnea with nocturia.3 They found that men with sleep apnea have a high incidence of nocturia.
Miyazato and colleagues looked at the effect of CPAP treatment on nighttime urine production in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.4 In this small study of 40 patients, mean nighttime voiding episodes decreased from 2.1 to 1.2 (P < .01).
I have seen several patients with night sweats who ended up having sleep apnea. These patients have had a resolution of their night sweats with sleep apnea treatment.
Arnardottir and colleagues found that obstructive sleep apnea was associated with frequent nocturnal sweating.5 They found that 31% of men and 33% of women with OSA had nocturnal sweating, compared with about 10% of the general population.
When the OSA patients were treated with positive airway pressure, the prevalence of nocturnal sweating decreased to 11.5%, which is similar to general population numbers. Given how common both sleep apnea and night sweats are, this is an important consideration as you evaluate night sweats.
I have seen many patients who have had atrial fibrillation and sleep apnea. Shapira-Daniels and colleagues did a prospective study of 188 patients with atrial fibrillation without a history of sleep apnea who were referred for ablation.6 All patients had home sleep studies, and testing was consistent with sleep apnea in 82% of patients.
Kanagala and associates found that patients with untreated sleep apnea had a greater chance of recurrent atrial fibrillation after cardioversion.7 Recurrence of atrial fibrillation at 12 months was 82% in untreated OSA patients, higher than the 42% recurrence in the treated OSA group (P = .013) and the 53% recurrence in control patients.
I think sleep apnea evaluation should be strongly considered in patients with atrial fibrillation and should be done before referral for ablations.
Pearl: Consider sleep apnea as a possible cause of or contributing factor to the common primary care problems of cognitive concerns, nocturia, night sweats, and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as 3rd-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at imnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Wallace A and Bucks RS. Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(2):203. Epub 2013 Feb 1.
2. Olaithe M and Bucks RS. Executive dysfunction in OSA before and after treatment: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(9):1297. Epub 2013 Sep 1.
3. Zhou J et al. Association between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and nocturia: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2020 Dec;24(4):1293-8.
4. Miyauchi Y et al. Effect of the continuous positive airway pressure on the nocturnal urine volume or night-time frequency in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Urology 2015;85:333.
5. Arnardottir ES et al. Nocturnal sweating–a common symptom of obstructive sleep apnoea: the Icelandic sleep apnoea cohort. BMJ Open. 2013 May 14;3(5):e002795. BMJ Open 2013;3:e002795
6. Shapira-Daniels A et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed sleep apnea in patients with atrial fibrillation and its impact on therapy. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(12):1499. Epub 2020 Aug 12.
7. Kanagala R et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and the recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;107(20):2589. Epub 2003 May 12.
Fortunately her problem stemmed from sleep apnea, and resolved with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy.
Wallace and Bucks performed a meta analysis of 42 studies of memory in patients with sleep apnea and found sleep apnea patients were impaired when compared to healthy controls on verbal episodic memory (immediate recall, delayed recall, learning, and recognition) and visuospatial episodic memory (immediate and delayed recall).1 A meta-analysis by Olaithe and associates found an improvement in executive function in patients with sleep apnea who were treated with CPAP.2 I think this is worth considering especially in your patients who have subjective memory disturbances and do not appear to have a mild cognitive impairment or dementia.
About 15 years ago I saw a 74-year-old man for nocturia. He had seen two urologists and had a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) without any real change in his nocturia. I trialed him on all sorts of medications, and he seemed to improve temporarily a little on trazodone (went from seven episodes a night to four).
Eventually, after several years, I sent him for a sleep study. He had severe sleep apnea (Apnea Hypopnea Index, 65; O2 saturations as low as 60%). With treatment, his nocturia resolved. He went from seven episodes to two each night.
Zhou and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 13 studies looking at the association of sleep apnea with nocturia.3 They found that men with sleep apnea have a high incidence of nocturia.
Miyazato and colleagues looked at the effect of CPAP treatment on nighttime urine production in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.4 In this small study of 40 patients, mean nighttime voiding episodes decreased from 2.1 to 1.2 (P < .01).
I have seen several patients with night sweats who ended up having sleep apnea. These patients have had a resolution of their night sweats with sleep apnea treatment.
Arnardottir and colleagues found that obstructive sleep apnea was associated with frequent nocturnal sweating.5 They found that 31% of men and 33% of women with OSA had nocturnal sweating, compared with about 10% of the general population.
When the OSA patients were treated with positive airway pressure, the prevalence of nocturnal sweating decreased to 11.5%, which is similar to general population numbers. Given how common both sleep apnea and night sweats are, this is an important consideration as you evaluate night sweats.
I have seen many patients who have had atrial fibrillation and sleep apnea. Shapira-Daniels and colleagues did a prospective study of 188 patients with atrial fibrillation without a history of sleep apnea who were referred for ablation.6 All patients had home sleep studies, and testing was consistent with sleep apnea in 82% of patients.
Kanagala and associates found that patients with untreated sleep apnea had a greater chance of recurrent atrial fibrillation after cardioversion.7 Recurrence of atrial fibrillation at 12 months was 82% in untreated OSA patients, higher than the 42% recurrence in the treated OSA group (P = .013) and the 53% recurrence in control patients.
I think sleep apnea evaluation should be strongly considered in patients with atrial fibrillation and should be done before referral for ablations.
Pearl: Consider sleep apnea as a possible cause of or contributing factor to the common primary care problems of cognitive concerns, nocturia, night sweats, and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as 3rd-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at imnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Wallace A and Bucks RS. Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(2):203. Epub 2013 Feb 1.
2. Olaithe M and Bucks RS. Executive dysfunction in OSA before and after treatment: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(9):1297. Epub 2013 Sep 1.
3. Zhou J et al. Association between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and nocturia: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2020 Dec;24(4):1293-8.
4. Miyauchi Y et al. Effect of the continuous positive airway pressure on the nocturnal urine volume or night-time frequency in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Urology 2015;85:333.
5. Arnardottir ES et al. Nocturnal sweating–a common symptom of obstructive sleep apnoea: the Icelandic sleep apnoea cohort. BMJ Open. 2013 May 14;3(5):e002795. BMJ Open 2013;3:e002795
6. Shapira-Daniels A et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed sleep apnea in patients with atrial fibrillation and its impact on therapy. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(12):1499. Epub 2020 Aug 12.
7. Kanagala R et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and the recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;107(20):2589. Epub 2003 May 12.
Fortunately her problem stemmed from sleep apnea, and resolved with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy.
Wallace and Bucks performed a meta analysis of 42 studies of memory in patients with sleep apnea and found sleep apnea patients were impaired when compared to healthy controls on verbal episodic memory (immediate recall, delayed recall, learning, and recognition) and visuospatial episodic memory (immediate and delayed recall).1 A meta-analysis by Olaithe and associates found an improvement in executive function in patients with sleep apnea who were treated with CPAP.2 I think this is worth considering especially in your patients who have subjective memory disturbances and do not appear to have a mild cognitive impairment or dementia.
About 15 years ago I saw a 74-year-old man for nocturia. He had seen two urologists and had a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) without any real change in his nocturia. I trialed him on all sorts of medications, and he seemed to improve temporarily a little on trazodone (went from seven episodes a night to four).
Eventually, after several years, I sent him for a sleep study. He had severe sleep apnea (Apnea Hypopnea Index, 65; O2 saturations as low as 60%). With treatment, his nocturia resolved. He went from seven episodes to two each night.
Zhou and colleagues performed a meta-analysis of 13 studies looking at the association of sleep apnea with nocturia.3 They found that men with sleep apnea have a high incidence of nocturia.
Miyazato and colleagues looked at the effect of CPAP treatment on nighttime urine production in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.4 In this small study of 40 patients, mean nighttime voiding episodes decreased from 2.1 to 1.2 (P < .01).
I have seen several patients with night sweats who ended up having sleep apnea. These patients have had a resolution of their night sweats with sleep apnea treatment.
Arnardottir and colleagues found that obstructive sleep apnea was associated with frequent nocturnal sweating.5 They found that 31% of men and 33% of women with OSA had nocturnal sweating, compared with about 10% of the general population.
When the OSA patients were treated with positive airway pressure, the prevalence of nocturnal sweating decreased to 11.5%, which is similar to general population numbers. Given how common both sleep apnea and night sweats are, this is an important consideration as you evaluate night sweats.
I have seen many patients who have had atrial fibrillation and sleep apnea. Shapira-Daniels and colleagues did a prospective study of 188 patients with atrial fibrillation without a history of sleep apnea who were referred for ablation.6 All patients had home sleep studies, and testing was consistent with sleep apnea in 82% of patients.
Kanagala and associates found that patients with untreated sleep apnea had a greater chance of recurrent atrial fibrillation after cardioversion.7 Recurrence of atrial fibrillation at 12 months was 82% in untreated OSA patients, higher than the 42% recurrence in the treated OSA group (P = .013) and the 53% recurrence in control patients.
I think sleep apnea evaluation should be strongly considered in patients with atrial fibrillation and should be done before referral for ablations.
Pearl: Consider sleep apnea as a possible cause of or contributing factor to the common primary care problems of cognitive concerns, nocturia, night sweats, and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and serves as 3rd-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at imnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Wallace A and Bucks RS. Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(2):203. Epub 2013 Feb 1.
2. Olaithe M and Bucks RS. Executive dysfunction in OSA before and after treatment: a meta-analysis. Sleep. 2013;36(9):1297. Epub 2013 Sep 1.
3. Zhou J et al. Association between obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and nocturia: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2020 Dec;24(4):1293-8.
4. Miyauchi Y et al. Effect of the continuous positive airway pressure on the nocturnal urine volume or night-time frequency in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Urology 2015;85:333.
5. Arnardottir ES et al. Nocturnal sweating–a common symptom of obstructive sleep apnoea: the Icelandic sleep apnoea cohort. BMJ Open. 2013 May 14;3(5):e002795. BMJ Open 2013;3:e002795
6. Shapira-Daniels A et al. Prevalence of undiagnosed sleep apnea in patients with atrial fibrillation and its impact on therapy. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(12):1499. Epub 2020 Aug 12.
7. Kanagala R et al. Obstructive sleep apnea and the recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003;107(20):2589. Epub 2003 May 12.
An integrated response to Surfside: Lessons learned
The catastrophic collapse of the Surfside, Fla., Champlain Towers South left ambiguous loss, trauma, grief, and other psychiatric and psychological sequelae in its wake.
Now that a few months have passed since the tragedy, which took the lives of 98 residents, it is helpful to examine the psychiatric and psychological support efforts that emerged.
We can think of those support efforts as operating on two tracks: one was pursued by mental health professionals representing numerous organizations; the other was pursued by local, regional, and international first responders – specifically, by Israeli Defense Force (IDF) members who came to our community at the request of Surfside families.
Those efforts were guided by existing frameworks for crisis response designed to provide containment amid the naturally disorganizing effects of the trauma and ambiguous loss. In retrospect, it was clear that the mechanisms by which those frameworks coalesced and functioned were more implicit and organically synchronous than explicitly coordinated and agreed upon. key themes emerged and revealed intrinsic links between the first-responder/search and rescue and psychological strategies.
In this article, we discuss relevant themes and parallels between the psychological intervention/strategies and the first-responder disaster response and the practical utility of implementing an integrated strategy. Our hope is that a better understanding of these strategies will help future therapists and responders who respond to crises.
Setting the frame
The importance of setting a psychotherapeutic frame is indisputable regardless of theoretical orientation or therapeutic modality. Predictable, consistent conditions under which therapy takes place support a patient’s capacity to tolerate the ambiguous and unpredictable aspects of the process. Those “rules of engagement” provide a structure where subjective experiences can be formulated, organized, understood, and integrated. Twice-daily briefs held in a centralized location (dubbed the Surfside “family center”) paralleled this frame and served that same containing function by offering structure, order, and predictability amid the palpable chaos of ambiguous loss and traumatic grief. Those briefs provided key information on the status of the operation and described the rescue strategy. These were led by the Miami-Dade assistant fire chief and IDF colonel (E.E.), who presented a unified front and consistent presence.
It is essential that briefings such as these be coordinated (and unified) with clear expectations about ground rules, much like what is involved in therapeutic informed consent. In this context, rules included permissions related to documentation of meetings, information sharing, and rules of communication with the media in an effort to protect the vulnerable.
The centralized meeting location served as an important center of gravity and unified place of waiting and information receipt. It provided a dedicated space to meet with humanitarian aid organizations and government officials, and symbolized continuity, consistency, ease of information transmission, and a place where practical needs could be addressed. Meals, toiletries, and other supplies were provided to simplify and maintain daily routines. Those are otherwise unremarkable practices that seemed impossible to manage amid a crisis, yet can be inherently grounding and emotionally organizing when facing deep psychological fragmentation.
Meeting in person allowed the IDF to offer operational visuals to allow those affected to feel less helpless and cultivate a sense of purpose by being part of the strategy/mission. Their strategy included “population intelligence,” which was aimed at both information gathering to practically facilitate the rescue/recovery process (for example, locating victims, property, and recreating a visual of how the building fell), and inspiring people to participate. This engagement helped many transition from a place of denial/repression to acknowledging loss/grief, and from a passive to active part of the effort, in a way that was safe and realistic – as opposed to going to the site and aiding themselves, as some had requested.
Naturally, a central location made it possible to offer immediate psychological assistance and support. Clinicians responding to crisis should be carefully selected in light of the immense suffering, emotional vulnerability, and heightened reactivity of those affected. People were overwhelmed by deep sorrow, fear, anger, and uncertainty, vacillating between hope and despair, and mobilized by a desire to help. Those providing support need to be interpersonally skilled and able to regulate their own emotions. They must be able to formulate – in real time – an understanding of what is needed, and implement a strategic plan. Like first responders, it is also key for providers to be easily accessible and identifiable in uniform so that people in the grip of a survival response can easily identify and elicit support.
The power of strategy
The Israeli delegation and mental health approaches were aligned with respect to cultivating a team identity and keeping the team spirit elevated. The delegation’s approach was to deemphasize rank during the mission in that everyone was responsible for anything that was needed and no task was below anyone’s rank. The same was true for the mental health support response: Early interventions were focused on addressing practical needs – providing blankets, water, chargers, food, and a calming presence to counter the initial chaos. No task was too small, regardless of title or role. As more structure and order ensued, it was possible to offer more traditional crisis-related interventions aimed at grounding those affected.
Both teams worked to ensure 24-hour coverage, which was crucial given the need for consistency and continuity. Our commitment was to support the victims’ families and survivors by fully embracing the chaos and the situational demands, offering attunement and support, and satisfying both basic and higher-level needs. We divided and conquered work, observed signals of need, offered immediate support where necessary, and coordinated longer-term care plans when possible. The importance of ongoing self-care, consultation, and debriefing while doing this work cannot be overstated. Time to address basic needs and the impact of vicarious trauma as a team must be built in.
Importance of flexibility
This tragedy came with unique complexities and sensitivities that needed to be identified expediently and addressed with a concrete, comprehensive plan. This was true for both the rescue and psychological support efforts, and flexibility was key. There was nothing traditional about our work from a therapeutic perspective – we found quiet corners and empty offices, went for walks, met in lobbies, and checked in by phone. The interventions were brief.
Roles shifted often between aiding in addressing practical needs, advocating for victims and connecting them to appropriate resources, supporting the police in making death notifications, providing support and space for processing during and after briefings, and more.
Similarly, the rescue team constantly reevaluated their strategy because of what they discovered as they dismantled the collapsed building, in addition to managing external impacting factors (heat, rain, lightning, and the threat of the remaining structure falling).
Language matters
The iteration of commitment to the families/victims/mission and to work speedily and efficiently was important for both rescuers and therapists. It was key during the briefings for the chief and colonel (E.E.) to share information in a manner that was professional, discreet, honest and explicit. Their willingness and ability to be vulnerable and to share their personal feelings as active rescuers humanized them. Their approach was matter of fact, yet warm, loving, and containing, all of which conveyed dignity and respect.
Word choice mattered, and the IDF’s intentional choice to refer to recovered victims as “souls,” rather than “bodies,” conveyed their sensitivity to the intensity of anguish, depth of loss, and gravity of the situation. From a psychological perspective, the transition between “rescue” efforts signifying the potential saving of lives to “recovery” of bodies or remains was significant and demarcated a dramatic shift. The weeks-long efforts, once painfully slow, then felt too abrupt to process.
One extraordinary moment was the chief’s response to the families’ discomfort at the news of the switch from rescue to recovery. The families were anxious about losing the structure that the briefings provided and were apprehensive about the handoff from fire to the police department. With great compassion and attunement, he assured them that he would stay with them, and they together, as a family, would decide when to conclude the in-person briefings. The colonel (E.E.), too, provided assurance that neither procedure nor the urgency of the recovery would change. It was both heart-warming and containing that information related to the operation was shared in a clear manner, and that the thought process and rationale behind major decisions (e.g., demolishing the remaining building, decision to pause operations, switch from rescue to recovery) was shared. It was useful for the clinicians to be aware of this rationale in helping individuals metabolize the information and process the associated trauma and grief.
Unification is key
Surfside has left an indelible impact on us. We saw and experienced unity in many respects – clinicians from various backgrounds collaborating, families bonding and caring for one another, community support and solidarity, and the cooperation and coordination of the search and rescue teams. The diverse groups providing support came to feel like a family, and the importance of inter- and intrateam integration cannot be overstated. We were transformed both by our professional collaborations and authentic connections with those affected, and will forever cherish the experience, one another, the families, and the souls lost.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures. Col. Edri is the Israeli Defense Forces District Commander of the Home Front Command Haifa District. He served as the deputy commander for the Israeli Defense Forces Search and Rescue Delegation, which was brought in to provide international aid to the local and domestic forces responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. Col. Edri has no disclosures. Dr. Davidtz is a licensed psychologist and associate professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she is director of internship training for the Psychology Services Center and director of psychological services for the emotionally distressed, a specialty clinic that serves people with serious mental illness and personality disorders. She also maintains a part-time private practice specializing in the treatment of complex posttraumatic conditions and personality disorders. Dr. Davidtz has no disclosures.
The catastrophic collapse of the Surfside, Fla., Champlain Towers South left ambiguous loss, trauma, grief, and other psychiatric and psychological sequelae in its wake.
Now that a few months have passed since the tragedy, which took the lives of 98 residents, it is helpful to examine the psychiatric and psychological support efforts that emerged.
We can think of those support efforts as operating on two tracks: one was pursued by mental health professionals representing numerous organizations; the other was pursued by local, regional, and international first responders – specifically, by Israeli Defense Force (IDF) members who came to our community at the request of Surfside families.
Those efforts were guided by existing frameworks for crisis response designed to provide containment amid the naturally disorganizing effects of the trauma and ambiguous loss. In retrospect, it was clear that the mechanisms by which those frameworks coalesced and functioned were more implicit and organically synchronous than explicitly coordinated and agreed upon. key themes emerged and revealed intrinsic links between the first-responder/search and rescue and psychological strategies.
In this article, we discuss relevant themes and parallels between the psychological intervention/strategies and the first-responder disaster response and the practical utility of implementing an integrated strategy. Our hope is that a better understanding of these strategies will help future therapists and responders who respond to crises.
Setting the frame
The importance of setting a psychotherapeutic frame is indisputable regardless of theoretical orientation or therapeutic modality. Predictable, consistent conditions under which therapy takes place support a patient’s capacity to tolerate the ambiguous and unpredictable aspects of the process. Those “rules of engagement” provide a structure where subjective experiences can be formulated, organized, understood, and integrated. Twice-daily briefs held in a centralized location (dubbed the Surfside “family center”) paralleled this frame and served that same containing function by offering structure, order, and predictability amid the palpable chaos of ambiguous loss and traumatic grief. Those briefs provided key information on the status of the operation and described the rescue strategy. These were led by the Miami-Dade assistant fire chief and IDF colonel (E.E.), who presented a unified front and consistent presence.
It is essential that briefings such as these be coordinated (and unified) with clear expectations about ground rules, much like what is involved in therapeutic informed consent. In this context, rules included permissions related to documentation of meetings, information sharing, and rules of communication with the media in an effort to protect the vulnerable.
The centralized meeting location served as an important center of gravity and unified place of waiting and information receipt. It provided a dedicated space to meet with humanitarian aid organizations and government officials, and symbolized continuity, consistency, ease of information transmission, and a place where practical needs could be addressed. Meals, toiletries, and other supplies were provided to simplify and maintain daily routines. Those are otherwise unremarkable practices that seemed impossible to manage amid a crisis, yet can be inherently grounding and emotionally organizing when facing deep psychological fragmentation.
Meeting in person allowed the IDF to offer operational visuals to allow those affected to feel less helpless and cultivate a sense of purpose by being part of the strategy/mission. Their strategy included “population intelligence,” which was aimed at both information gathering to practically facilitate the rescue/recovery process (for example, locating victims, property, and recreating a visual of how the building fell), and inspiring people to participate. This engagement helped many transition from a place of denial/repression to acknowledging loss/grief, and from a passive to active part of the effort, in a way that was safe and realistic – as opposed to going to the site and aiding themselves, as some had requested.
Naturally, a central location made it possible to offer immediate psychological assistance and support. Clinicians responding to crisis should be carefully selected in light of the immense suffering, emotional vulnerability, and heightened reactivity of those affected. People were overwhelmed by deep sorrow, fear, anger, and uncertainty, vacillating between hope and despair, and mobilized by a desire to help. Those providing support need to be interpersonally skilled and able to regulate their own emotions. They must be able to formulate – in real time – an understanding of what is needed, and implement a strategic plan. Like first responders, it is also key for providers to be easily accessible and identifiable in uniform so that people in the grip of a survival response can easily identify and elicit support.
The power of strategy
The Israeli delegation and mental health approaches were aligned with respect to cultivating a team identity and keeping the team spirit elevated. The delegation’s approach was to deemphasize rank during the mission in that everyone was responsible for anything that was needed and no task was below anyone’s rank. The same was true for the mental health support response: Early interventions were focused on addressing practical needs – providing blankets, water, chargers, food, and a calming presence to counter the initial chaos. No task was too small, regardless of title or role. As more structure and order ensued, it was possible to offer more traditional crisis-related interventions aimed at grounding those affected.
Both teams worked to ensure 24-hour coverage, which was crucial given the need for consistency and continuity. Our commitment was to support the victims’ families and survivors by fully embracing the chaos and the situational demands, offering attunement and support, and satisfying both basic and higher-level needs. We divided and conquered work, observed signals of need, offered immediate support where necessary, and coordinated longer-term care plans when possible. The importance of ongoing self-care, consultation, and debriefing while doing this work cannot be overstated. Time to address basic needs and the impact of vicarious trauma as a team must be built in.
Importance of flexibility
This tragedy came with unique complexities and sensitivities that needed to be identified expediently and addressed with a concrete, comprehensive plan. This was true for both the rescue and psychological support efforts, and flexibility was key. There was nothing traditional about our work from a therapeutic perspective – we found quiet corners and empty offices, went for walks, met in lobbies, and checked in by phone. The interventions were brief.
Roles shifted often between aiding in addressing practical needs, advocating for victims and connecting them to appropriate resources, supporting the police in making death notifications, providing support and space for processing during and after briefings, and more.
Similarly, the rescue team constantly reevaluated their strategy because of what they discovered as they dismantled the collapsed building, in addition to managing external impacting factors (heat, rain, lightning, and the threat of the remaining structure falling).
Language matters
The iteration of commitment to the families/victims/mission and to work speedily and efficiently was important for both rescuers and therapists. It was key during the briefings for the chief and colonel (E.E.) to share information in a manner that was professional, discreet, honest and explicit. Their willingness and ability to be vulnerable and to share their personal feelings as active rescuers humanized them. Their approach was matter of fact, yet warm, loving, and containing, all of which conveyed dignity and respect.
Word choice mattered, and the IDF’s intentional choice to refer to recovered victims as “souls,” rather than “bodies,” conveyed their sensitivity to the intensity of anguish, depth of loss, and gravity of the situation. From a psychological perspective, the transition between “rescue” efforts signifying the potential saving of lives to “recovery” of bodies or remains was significant and demarcated a dramatic shift. The weeks-long efforts, once painfully slow, then felt too abrupt to process.
One extraordinary moment was the chief’s response to the families’ discomfort at the news of the switch from rescue to recovery. The families were anxious about losing the structure that the briefings provided and were apprehensive about the handoff from fire to the police department. With great compassion and attunement, he assured them that he would stay with them, and they together, as a family, would decide when to conclude the in-person briefings. The colonel (E.E.), too, provided assurance that neither procedure nor the urgency of the recovery would change. It was both heart-warming and containing that information related to the operation was shared in a clear manner, and that the thought process and rationale behind major decisions (e.g., demolishing the remaining building, decision to pause operations, switch from rescue to recovery) was shared. It was useful for the clinicians to be aware of this rationale in helping individuals metabolize the information and process the associated trauma and grief.
Unification is key
Surfside has left an indelible impact on us. We saw and experienced unity in many respects – clinicians from various backgrounds collaborating, families bonding and caring for one another, community support and solidarity, and the cooperation and coordination of the search and rescue teams. The diverse groups providing support came to feel like a family, and the importance of inter- and intrateam integration cannot be overstated. We were transformed both by our professional collaborations and authentic connections with those affected, and will forever cherish the experience, one another, the families, and the souls lost.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures. Col. Edri is the Israeli Defense Forces District Commander of the Home Front Command Haifa District. He served as the deputy commander for the Israeli Defense Forces Search and Rescue Delegation, which was brought in to provide international aid to the local and domestic forces responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. Col. Edri has no disclosures. Dr. Davidtz is a licensed psychologist and associate professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she is director of internship training for the Psychology Services Center and director of psychological services for the emotionally distressed, a specialty clinic that serves people with serious mental illness and personality disorders. She also maintains a part-time private practice specializing in the treatment of complex posttraumatic conditions and personality disorders. Dr. Davidtz has no disclosures.
The catastrophic collapse of the Surfside, Fla., Champlain Towers South left ambiguous loss, trauma, grief, and other psychiatric and psychological sequelae in its wake.
Now that a few months have passed since the tragedy, which took the lives of 98 residents, it is helpful to examine the psychiatric and psychological support efforts that emerged.
We can think of those support efforts as operating on two tracks: one was pursued by mental health professionals representing numerous organizations; the other was pursued by local, regional, and international first responders – specifically, by Israeli Defense Force (IDF) members who came to our community at the request of Surfside families.
Those efforts were guided by existing frameworks for crisis response designed to provide containment amid the naturally disorganizing effects of the trauma and ambiguous loss. In retrospect, it was clear that the mechanisms by which those frameworks coalesced and functioned were more implicit and organically synchronous than explicitly coordinated and agreed upon. key themes emerged and revealed intrinsic links between the first-responder/search and rescue and psychological strategies.
In this article, we discuss relevant themes and parallels between the psychological intervention/strategies and the first-responder disaster response and the practical utility of implementing an integrated strategy. Our hope is that a better understanding of these strategies will help future therapists and responders who respond to crises.
Setting the frame
The importance of setting a psychotherapeutic frame is indisputable regardless of theoretical orientation or therapeutic modality. Predictable, consistent conditions under which therapy takes place support a patient’s capacity to tolerate the ambiguous and unpredictable aspects of the process. Those “rules of engagement” provide a structure where subjective experiences can be formulated, organized, understood, and integrated. Twice-daily briefs held in a centralized location (dubbed the Surfside “family center”) paralleled this frame and served that same containing function by offering structure, order, and predictability amid the palpable chaos of ambiguous loss and traumatic grief. Those briefs provided key information on the status of the operation and described the rescue strategy. These were led by the Miami-Dade assistant fire chief and IDF colonel (E.E.), who presented a unified front and consistent presence.
It is essential that briefings such as these be coordinated (and unified) with clear expectations about ground rules, much like what is involved in therapeutic informed consent. In this context, rules included permissions related to documentation of meetings, information sharing, and rules of communication with the media in an effort to protect the vulnerable.
The centralized meeting location served as an important center of gravity and unified place of waiting and information receipt. It provided a dedicated space to meet with humanitarian aid organizations and government officials, and symbolized continuity, consistency, ease of information transmission, and a place where practical needs could be addressed. Meals, toiletries, and other supplies were provided to simplify and maintain daily routines. Those are otherwise unremarkable practices that seemed impossible to manage amid a crisis, yet can be inherently grounding and emotionally organizing when facing deep psychological fragmentation.
Meeting in person allowed the IDF to offer operational visuals to allow those affected to feel less helpless and cultivate a sense of purpose by being part of the strategy/mission. Their strategy included “population intelligence,” which was aimed at both information gathering to practically facilitate the rescue/recovery process (for example, locating victims, property, and recreating a visual of how the building fell), and inspiring people to participate. This engagement helped many transition from a place of denial/repression to acknowledging loss/grief, and from a passive to active part of the effort, in a way that was safe and realistic – as opposed to going to the site and aiding themselves, as some had requested.
Naturally, a central location made it possible to offer immediate psychological assistance and support. Clinicians responding to crisis should be carefully selected in light of the immense suffering, emotional vulnerability, and heightened reactivity of those affected. People were overwhelmed by deep sorrow, fear, anger, and uncertainty, vacillating between hope and despair, and mobilized by a desire to help. Those providing support need to be interpersonally skilled and able to regulate their own emotions. They must be able to formulate – in real time – an understanding of what is needed, and implement a strategic plan. Like first responders, it is also key for providers to be easily accessible and identifiable in uniform so that people in the grip of a survival response can easily identify and elicit support.
The power of strategy
The Israeli delegation and mental health approaches were aligned with respect to cultivating a team identity and keeping the team spirit elevated. The delegation’s approach was to deemphasize rank during the mission in that everyone was responsible for anything that was needed and no task was below anyone’s rank. The same was true for the mental health support response: Early interventions were focused on addressing practical needs – providing blankets, water, chargers, food, and a calming presence to counter the initial chaos. No task was too small, regardless of title or role. As more structure and order ensued, it was possible to offer more traditional crisis-related interventions aimed at grounding those affected.
Both teams worked to ensure 24-hour coverage, which was crucial given the need for consistency and continuity. Our commitment was to support the victims’ families and survivors by fully embracing the chaos and the situational demands, offering attunement and support, and satisfying both basic and higher-level needs. We divided and conquered work, observed signals of need, offered immediate support where necessary, and coordinated longer-term care plans when possible. The importance of ongoing self-care, consultation, and debriefing while doing this work cannot be overstated. Time to address basic needs and the impact of vicarious trauma as a team must be built in.
Importance of flexibility
This tragedy came with unique complexities and sensitivities that needed to be identified expediently and addressed with a concrete, comprehensive plan. This was true for both the rescue and psychological support efforts, and flexibility was key. There was nothing traditional about our work from a therapeutic perspective – we found quiet corners and empty offices, went for walks, met in lobbies, and checked in by phone. The interventions were brief.
Roles shifted often between aiding in addressing practical needs, advocating for victims and connecting them to appropriate resources, supporting the police in making death notifications, providing support and space for processing during and after briefings, and more.
Similarly, the rescue team constantly reevaluated their strategy because of what they discovered as they dismantled the collapsed building, in addition to managing external impacting factors (heat, rain, lightning, and the threat of the remaining structure falling).
Language matters
The iteration of commitment to the families/victims/mission and to work speedily and efficiently was important for both rescuers and therapists. It was key during the briefings for the chief and colonel (E.E.) to share information in a manner that was professional, discreet, honest and explicit. Their willingness and ability to be vulnerable and to share their personal feelings as active rescuers humanized them. Their approach was matter of fact, yet warm, loving, and containing, all of which conveyed dignity and respect.
Word choice mattered, and the IDF’s intentional choice to refer to recovered victims as “souls,” rather than “bodies,” conveyed their sensitivity to the intensity of anguish, depth of loss, and gravity of the situation. From a psychological perspective, the transition between “rescue” efforts signifying the potential saving of lives to “recovery” of bodies or remains was significant and demarcated a dramatic shift. The weeks-long efforts, once painfully slow, then felt too abrupt to process.
One extraordinary moment was the chief’s response to the families’ discomfort at the news of the switch from rescue to recovery. The families were anxious about losing the structure that the briefings provided and were apprehensive about the handoff from fire to the police department. With great compassion and attunement, he assured them that he would stay with them, and they together, as a family, would decide when to conclude the in-person briefings. The colonel (E.E.), too, provided assurance that neither procedure nor the urgency of the recovery would change. It was both heart-warming and containing that information related to the operation was shared in a clear manner, and that the thought process and rationale behind major decisions (e.g., demolishing the remaining building, decision to pause operations, switch from rescue to recovery) was shared. It was useful for the clinicians to be aware of this rationale in helping individuals metabolize the information and process the associated trauma and grief.
Unification is key
Surfside has left an indelible impact on us. We saw and experienced unity in many respects – clinicians from various backgrounds collaborating, families bonding and caring for one another, community support and solidarity, and the cooperation and coordination of the search and rescue teams. The diverse groups providing support came to feel like a family, and the importance of inter- and intrateam integration cannot be overstated. We were transformed both by our professional collaborations and authentic connections with those affected, and will forever cherish the experience, one another, the families, and the souls lost.
Dr. Feldman is a licensed clinical psychologist in private practice in Miami. She is an adjunct professor in the college of psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she teaches clinical psychology doctoral students. She also serves on the board of directors of The Southeast Florida Association for Psychoanalytic Psychology. Dr. Feldman has no disclosures. Col. Edri is the Israeli Defense Forces District Commander of the Home Front Command Haifa District. He served as the deputy commander for the Israeli Defense Forces Search and Rescue Delegation, which was brought in to provide international aid to the local and domestic forces responding to the Surfside, Fla., building collapse. Col. Edri has no disclosures. Dr. Davidtz is a licensed psychologist and associate professor in the College of Psychology at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., where she is director of internship training for the Psychology Services Center and director of psychological services for the emotionally distressed, a specialty clinic that serves people with serious mental illness and personality disorders. She also maintains a part-time private practice specializing in the treatment of complex posttraumatic conditions and personality disorders. Dr. Davidtz has no disclosures.
Timeless stories
Let me tell you a story. In 5 billion years the sun will run out of hydrogen, the fuel it is currently burning to power my solar panels amongst other things. At that time, the sun will no longer be able to keep its core contracted and will expand into a fiery, red giant, engulfing earth and obliterating any sign that we ever existed. No buildings. No blog posts. No mausoleums. No stories. Nothing of us will remain.
Well, here for a moment anyway, I’ve gotten you to think about something other than COVID. You’re welcome.
Fascinatingly, the image in your mind’s eye right now of a barren scorched landscape was put there by me. Simply by placing a few words together I have caused new thoughts in your head. You might even share this story with someone else – I would have actually changed your behavior through the power of language. This miraculous phenomenon seems to be unique to us humans; we are the only ones who can create whole worlds in another individual’s head just by making a few sounds. We in medicine have the privilege of experiencing this miracle every day.
Last week, a 97-year-old pale, frail, white man saw me for a basal cell carcinoma on his cheek. While performing a simple electrodesiccation and curettage, I asked if he remembers getting a lot of sunburns when he was young. He certainly remembered one. On a blustery sunny day, he fell asleep for hours on the deck of the USS West Virginia while in the Philippines. As a radio man, he was exhausted from days of conflict and he recalled how warm breezes lulled him asleep. He was so sunburned that for days he forgot how afraid he was of the Japanese.
After listening to his story, I had an image in my mind of palm trees swaying in the tropical winds while hundreds of hulking gray castles sat hidden in the vast surrounding oceans awaiting one of the greatest naval conflicts in history. I got to hear it from surely one of the last remaining people in existence to be able to tell that story. Listening to a patient’s tales is one of the benefits of being a physician. Not only do they help bond us with our patients, but also help lessen our burden of having to make diagnosis after diagnosis and write note after note for hours on end. Somehow performing yet another biopsy that day is made just a bit easier if I’m also learning about what it was like at the Battle of Leyte Gulf.
Encouraging patients to talk more can be risky. No physician, not even allergists, can afford to be waylaid by a retiree with nothing else to do today. But meaningful encounters can not only be a vaccine against burnout, they also lead to better patient adherence and satisfaction. Sometimes, there is simply not time. But often there is a little window during a procedure or when you’re reasonably caught up and don’t expect delays ahead. And like every story, they literally transform us, the listener. In a true physical sense, their stories live on in me, and now that I’ve shared this one in writing, also with you for perpetuity. That is at least for the next 5 billion years when it, too, will be swallowed by the sun, leaving only a crispy, smoking rock where we once existed.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Let me tell you a story. In 5 billion years the sun will run out of hydrogen, the fuel it is currently burning to power my solar panels amongst other things. At that time, the sun will no longer be able to keep its core contracted and will expand into a fiery, red giant, engulfing earth and obliterating any sign that we ever existed. No buildings. No blog posts. No mausoleums. No stories. Nothing of us will remain.
Well, here for a moment anyway, I’ve gotten you to think about something other than COVID. You’re welcome.
Fascinatingly, the image in your mind’s eye right now of a barren scorched landscape was put there by me. Simply by placing a few words together I have caused new thoughts in your head. You might even share this story with someone else – I would have actually changed your behavior through the power of language. This miraculous phenomenon seems to be unique to us humans; we are the only ones who can create whole worlds in another individual’s head just by making a few sounds. We in medicine have the privilege of experiencing this miracle every day.
Last week, a 97-year-old pale, frail, white man saw me for a basal cell carcinoma on his cheek. While performing a simple electrodesiccation and curettage, I asked if he remembers getting a lot of sunburns when he was young. He certainly remembered one. On a blustery sunny day, he fell asleep for hours on the deck of the USS West Virginia while in the Philippines. As a radio man, he was exhausted from days of conflict and he recalled how warm breezes lulled him asleep. He was so sunburned that for days he forgot how afraid he was of the Japanese.
After listening to his story, I had an image in my mind of palm trees swaying in the tropical winds while hundreds of hulking gray castles sat hidden in the vast surrounding oceans awaiting one of the greatest naval conflicts in history. I got to hear it from surely one of the last remaining people in existence to be able to tell that story. Listening to a patient’s tales is one of the benefits of being a physician. Not only do they help bond us with our patients, but also help lessen our burden of having to make diagnosis after diagnosis and write note after note for hours on end. Somehow performing yet another biopsy that day is made just a bit easier if I’m also learning about what it was like at the Battle of Leyte Gulf.
Encouraging patients to talk more can be risky. No physician, not even allergists, can afford to be waylaid by a retiree with nothing else to do today. But meaningful encounters can not only be a vaccine against burnout, they also lead to better patient adherence and satisfaction. Sometimes, there is simply not time. But often there is a little window during a procedure or when you’re reasonably caught up and don’t expect delays ahead. And like every story, they literally transform us, the listener. In a true physical sense, their stories live on in me, and now that I’ve shared this one in writing, also with you for perpetuity. That is at least for the next 5 billion years when it, too, will be swallowed by the sun, leaving only a crispy, smoking rock where we once existed.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Let me tell you a story. In 5 billion years the sun will run out of hydrogen, the fuel it is currently burning to power my solar panels amongst other things. At that time, the sun will no longer be able to keep its core contracted and will expand into a fiery, red giant, engulfing earth and obliterating any sign that we ever existed. No buildings. No blog posts. No mausoleums. No stories. Nothing of us will remain.
Well, here for a moment anyway, I’ve gotten you to think about something other than COVID. You’re welcome.
Fascinatingly, the image in your mind’s eye right now of a barren scorched landscape was put there by me. Simply by placing a few words together I have caused new thoughts in your head. You might even share this story with someone else – I would have actually changed your behavior through the power of language. This miraculous phenomenon seems to be unique to us humans; we are the only ones who can create whole worlds in another individual’s head just by making a few sounds. We in medicine have the privilege of experiencing this miracle every day.
Last week, a 97-year-old pale, frail, white man saw me for a basal cell carcinoma on his cheek. While performing a simple electrodesiccation and curettage, I asked if he remembers getting a lot of sunburns when he was young. He certainly remembered one. On a blustery sunny day, he fell asleep for hours on the deck of the USS West Virginia while in the Philippines. As a radio man, he was exhausted from days of conflict and he recalled how warm breezes lulled him asleep. He was so sunburned that for days he forgot how afraid he was of the Japanese.
After listening to his story, I had an image in my mind of palm trees swaying in the tropical winds while hundreds of hulking gray castles sat hidden in the vast surrounding oceans awaiting one of the greatest naval conflicts in history. I got to hear it from surely one of the last remaining people in existence to be able to tell that story. Listening to a patient’s tales is one of the benefits of being a physician. Not only do they help bond us with our patients, but also help lessen our burden of having to make diagnosis after diagnosis and write note after note for hours on end. Somehow performing yet another biopsy that day is made just a bit easier if I’m also learning about what it was like at the Battle of Leyte Gulf.
Encouraging patients to talk more can be risky. No physician, not even allergists, can afford to be waylaid by a retiree with nothing else to do today. But meaningful encounters can not only be a vaccine against burnout, they also lead to better patient adherence and satisfaction. Sometimes, there is simply not time. But often there is a little window during a procedure or when you’re reasonably caught up and don’t expect delays ahead. And like every story, they literally transform us, the listener. In a true physical sense, their stories live on in me, and now that I’ve shared this one in writing, also with you for perpetuity. That is at least for the next 5 billion years when it, too, will be swallowed by the sun, leaving only a crispy, smoking rock where we once existed.
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Substance use or substance use disorder: A question of judgment
Substance use disorders can be a thorny topic in residency because of our role as gatekeepers of mental hospitals during our training. Intoxicated patients often get dismissed as a burden and distraction, malingering their way into a comfortable place to regain sobriety. This is extremely prevalent, often constituting the majority of patients seen during an emergency department call.
A typical interview may elicit any or all symptoms in the DSM yet be best explained by substance use intoxication or withdrawal. Alcohol and other CNS depressants commonly cause feelings of sadness and/or suicidality. Methamphetamine and other CNS stimulants commonly cause symptoms of psychosis or mania, followed by feelings of sadness and/or suicidality.
Different EDs have different degrees of patience for individuals in the process of becoming sober. Some departments will pressure clinicians into quickly discarding those patients and often frown upon any attempt at providing solace by raising the concern of reinforcing maladaptive behavior. A mystery-meat sandwich of admirable blandness may be the extent of help offered. Some more fortunate patients also receive a juice box or even a taxi voucher in an especially generous ED. This is always against our better judgment, of course, as we are told those gestures encourage abuse.
Other EDs will permit patients to remain until sober, allowing for another evaluation without the influence of controlled substances. We are reminded of many conversations with patients with substance use disorders, where topics discussed included: 1. Recommendation to seek substance use services, which are often nonexistent or with wait lists spanning months; 2. Education on the role of mental health hospitals and how patients’ despair in the context of intoxication does not meet some scriptural criteria; 3. Pep talks aided by such previously described sandwiches and juice boxes to encourage a sobering patient to leave the facility of their own will.
Methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol are rarely one-and-done endeavors. We sparingly see our patients for their very first ED visit while intoxicated or crashing. They know how the system runs and which ED will more readily allow them an overnight stay. The number of times they have been recommended for substance use treatment is beyond counting – they may have been on a wait list a handful of times. They are aware of our reluctance to provide inpatient psychiatric treatment for substance use, but it is worth a shot trying, anyway – sometimes they get lucky. Usually it is the pep talk, relief from hunger pangs, and daylight that get them out the doors – until next time.
It is under this context that many trainees become psychiatrists, a process that solidifies the separation between drug use and mental illness. Many graduate from residency practically equating substance use disorder with malingering or futility. This can take on a surreal quality as many localities have recently adopted particular forms or requirements like the dispensation of naloxone syringes to all patients with substance use disorders. While the desire and effort are noble, it may suggest to a patient presenting for help that society’s main interest is to avoid seeing them die rather than help with available resources for maintaining sobriety.
Therein lies the conundrum, a conundrum that spans psychiatry to society. The conundrum is our ambivalence between punishing the choice of drug use or healing the substance use disorder. Should we discharge the intoxicated patient as soon as they are safe to walk out, or should we make every effort possible to find long-term solutions?
The calculation becomes more complex
A defining moment appears to have been society’s reconsideration of its stance on substance use disorders when affluent White teenagers started dying in the suburbs from pain pills overdoses. Suddenly, those children needed and deserved treatment, not punishment. We find ourselves far away from a time when the loudest societal commentary on substance use entailed mothers advocating for harsher sentences against drunk drivers.
More recently, as psychiatry and large contingents of society have decided to take up the mantle of equity and social justice, we have begun to make progress in decriminalizing substance use in an effort to reverse systemic discrimination toward minority groups. This has taken many shapes, including drug legalization, criminal justice reform, and even the provision of clean substance use paraphernalia for safer use of IV drugs. Police reform has led to reluctance to arrest or press charges for nonviolent crimes and reduced police presence in minority neighborhoods. The “rich White teenager” approach is now recommended in all neighborhoods.
Society’s attempt at decriminalizing drug use has run parallel with psychiatry’s recent attempts at reduced pathologizing of behaviors more prevalent in underprivileged groups and cultures. This runs the gamut, from avoiding the use of the term “agitated” because of its racial connotations, to advocating for reduced rates of schizophrenia diagnoses in Black males.1 A diagnosis of substance use disorder carries with it similar troublesome societal implications. Decriminalization, legalization, provision of substances to the population, normalization, and other societal reforms will likely have an impact on the prevalence of substance use disorder diagnoses, which involve many criteria dependent on societal context.
It would be expected that criteria such as hazardous use, social problems, and attempts to quit will decrease as social acceptance increases. How might this affect access to substance use treatment, an already extremely limited resource?
Now, as forensic psychiatrists, we find ourselves adjudicating on the role of drugs at a time when society is wrestling with its attitude on the breadth of responsibility possessed by people who use drugs. In California, as in many other states, insanity laws exclude those who were insane as a result of drug use, as a testament to or possibly a remnant of how society feels about the role of choice and responsibility in the use of drugs. Yet another defendant who admits to drug use may on the contrary receive a much more lenient plea deal if willing to commit to sobriety. But in a never-ending maze of differing judgments and opinions, a less understanding district attorney may argue that the additional risk posed by the use of drugs and resulting impulsivity may actually warrant a heavier sentence.
In a recent attempt at atonement for our past punitive stance on drug users, we have found a desire to protect those who use drugs by punishing those who sell, at times forgetting that these populations are deeply intertwined. A recent law permits the federal charge of distribution of fentanyl resulting in death, which carries the mandatory minimum of 20 years in prison. Yet, if the user whom we are trying to protect by this law is also the one selling, what are we left with?
Fentanyl has been a particularly tragic development in the history of mankind and drug use. Substance use has rarely been so easily linked to accidental death. While many physicians can easily explain the safety of fentanyl when used as prescribed and in controlled settings, this is certainly not the case in the community. Measuring micrograms of fentanyl is outside the knowledge and capabilities of most drug dealers, who are not equipped with pharmacy-grade scales. Yet, as a result, they sell and customers buy quantities of fentanyl that range from homeopathically low to lethally high because of a mixture of negligence and deliberate indifference.
Another effort at atonement has been attempts at decriminalizing drug use and releasing many nonviolent offenders. This can, however, encourage bystanders to report more acts as crime rather than public intoxication, to ensure a police response when confronted by intoxicated people. Whereas previously an inebriated person who is homeless may have been called for and asked to seek shelter, they now get called on, and subsequently charged for, allegedly mumbling a threat by a frustrated bystander.
The release of offenders has its limits. Many placements on probation require sobriety and result in longer sentences for the use of substances that are otherwise decriminalized. The decriminalization and reexamination of substance use by society should widen the scope from simply considering crime to examining the use of drugs throughout the legal system and even beyond.
The DSM and psychiatry are not intended or equipped to adjudicate disputes on where the lines should be drawn between determinism and free will. We are knowledgeable of patients with substance use disorders, the effect of intoxicating substances, and the capacity of patients with substance use disorders to act in law-abiding ways. Our field can inform without simply advocating whether our patients should be punished. While society is currently struggling with how to apportion blame, psychiatry should resist the urge to impose medical solutions to social problems. Our solutions would almost certainly be grossly limited as we are still struggling to repent for lobotomizing “uppity” young women2 and using electroshock therapy to disrupt perverse impulses in homosexual males.3 Social norms and political zeitgeists change over time while the psychological and physiological principles underlying our understanding of mental illness should, in theory, stay relatively constant. Psychiatry’s answers for societal ills do not usually improve with time but rather have a tendency to be humbling.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1.Medlock MM et al., eds. “Racism and Psychiatry: Contemporary Issues and Interventions” (New York: Springer, 2018).
2. Tone A and Koziol M. CMAJ. 2018:190(20):e624-5.
3. McGuire RJ and Vallance M. BMJ. 1964;1(5376):151-3.
Substance use disorders can be a thorny topic in residency because of our role as gatekeepers of mental hospitals during our training. Intoxicated patients often get dismissed as a burden and distraction, malingering their way into a comfortable place to regain sobriety. This is extremely prevalent, often constituting the majority of patients seen during an emergency department call.
A typical interview may elicit any or all symptoms in the DSM yet be best explained by substance use intoxication or withdrawal. Alcohol and other CNS depressants commonly cause feelings of sadness and/or suicidality. Methamphetamine and other CNS stimulants commonly cause symptoms of psychosis or mania, followed by feelings of sadness and/or suicidality.
Different EDs have different degrees of patience for individuals in the process of becoming sober. Some departments will pressure clinicians into quickly discarding those patients and often frown upon any attempt at providing solace by raising the concern of reinforcing maladaptive behavior. A mystery-meat sandwich of admirable blandness may be the extent of help offered. Some more fortunate patients also receive a juice box or even a taxi voucher in an especially generous ED. This is always against our better judgment, of course, as we are told those gestures encourage abuse.
Other EDs will permit patients to remain until sober, allowing for another evaluation without the influence of controlled substances. We are reminded of many conversations with patients with substance use disorders, where topics discussed included: 1. Recommendation to seek substance use services, which are often nonexistent or with wait lists spanning months; 2. Education on the role of mental health hospitals and how patients’ despair in the context of intoxication does not meet some scriptural criteria; 3. Pep talks aided by such previously described sandwiches and juice boxes to encourage a sobering patient to leave the facility of their own will.
Methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol are rarely one-and-done endeavors. We sparingly see our patients for their very first ED visit while intoxicated or crashing. They know how the system runs and which ED will more readily allow them an overnight stay. The number of times they have been recommended for substance use treatment is beyond counting – they may have been on a wait list a handful of times. They are aware of our reluctance to provide inpatient psychiatric treatment for substance use, but it is worth a shot trying, anyway – sometimes they get lucky. Usually it is the pep talk, relief from hunger pangs, and daylight that get them out the doors – until next time.
It is under this context that many trainees become psychiatrists, a process that solidifies the separation between drug use and mental illness. Many graduate from residency practically equating substance use disorder with malingering or futility. This can take on a surreal quality as many localities have recently adopted particular forms or requirements like the dispensation of naloxone syringes to all patients with substance use disorders. While the desire and effort are noble, it may suggest to a patient presenting for help that society’s main interest is to avoid seeing them die rather than help with available resources for maintaining sobriety.
Therein lies the conundrum, a conundrum that spans psychiatry to society. The conundrum is our ambivalence between punishing the choice of drug use or healing the substance use disorder. Should we discharge the intoxicated patient as soon as they are safe to walk out, or should we make every effort possible to find long-term solutions?
The calculation becomes more complex
A defining moment appears to have been society’s reconsideration of its stance on substance use disorders when affluent White teenagers started dying in the suburbs from pain pills overdoses. Suddenly, those children needed and deserved treatment, not punishment. We find ourselves far away from a time when the loudest societal commentary on substance use entailed mothers advocating for harsher sentences against drunk drivers.
More recently, as psychiatry and large contingents of society have decided to take up the mantle of equity and social justice, we have begun to make progress in decriminalizing substance use in an effort to reverse systemic discrimination toward minority groups. This has taken many shapes, including drug legalization, criminal justice reform, and even the provision of clean substance use paraphernalia for safer use of IV drugs. Police reform has led to reluctance to arrest or press charges for nonviolent crimes and reduced police presence in minority neighborhoods. The “rich White teenager” approach is now recommended in all neighborhoods.
Society’s attempt at decriminalizing drug use has run parallel with psychiatry’s recent attempts at reduced pathologizing of behaviors more prevalent in underprivileged groups and cultures. This runs the gamut, from avoiding the use of the term “agitated” because of its racial connotations, to advocating for reduced rates of schizophrenia diagnoses in Black males.1 A diagnosis of substance use disorder carries with it similar troublesome societal implications. Decriminalization, legalization, provision of substances to the population, normalization, and other societal reforms will likely have an impact on the prevalence of substance use disorder diagnoses, which involve many criteria dependent on societal context.
It would be expected that criteria such as hazardous use, social problems, and attempts to quit will decrease as social acceptance increases. How might this affect access to substance use treatment, an already extremely limited resource?
Now, as forensic psychiatrists, we find ourselves adjudicating on the role of drugs at a time when society is wrestling with its attitude on the breadth of responsibility possessed by people who use drugs. In California, as in many other states, insanity laws exclude those who were insane as a result of drug use, as a testament to or possibly a remnant of how society feels about the role of choice and responsibility in the use of drugs. Yet another defendant who admits to drug use may on the contrary receive a much more lenient plea deal if willing to commit to sobriety. But in a never-ending maze of differing judgments and opinions, a less understanding district attorney may argue that the additional risk posed by the use of drugs and resulting impulsivity may actually warrant a heavier sentence.
In a recent attempt at atonement for our past punitive stance on drug users, we have found a desire to protect those who use drugs by punishing those who sell, at times forgetting that these populations are deeply intertwined. A recent law permits the federal charge of distribution of fentanyl resulting in death, which carries the mandatory minimum of 20 years in prison. Yet, if the user whom we are trying to protect by this law is also the one selling, what are we left with?
Fentanyl has been a particularly tragic development in the history of mankind and drug use. Substance use has rarely been so easily linked to accidental death. While many physicians can easily explain the safety of fentanyl when used as prescribed and in controlled settings, this is certainly not the case in the community. Measuring micrograms of fentanyl is outside the knowledge and capabilities of most drug dealers, who are not equipped with pharmacy-grade scales. Yet, as a result, they sell and customers buy quantities of fentanyl that range from homeopathically low to lethally high because of a mixture of negligence and deliberate indifference.
Another effort at atonement has been attempts at decriminalizing drug use and releasing many nonviolent offenders. This can, however, encourage bystanders to report more acts as crime rather than public intoxication, to ensure a police response when confronted by intoxicated people. Whereas previously an inebriated person who is homeless may have been called for and asked to seek shelter, they now get called on, and subsequently charged for, allegedly mumbling a threat by a frustrated bystander.
The release of offenders has its limits. Many placements on probation require sobriety and result in longer sentences for the use of substances that are otherwise decriminalized. The decriminalization and reexamination of substance use by society should widen the scope from simply considering crime to examining the use of drugs throughout the legal system and even beyond.
The DSM and psychiatry are not intended or equipped to adjudicate disputes on where the lines should be drawn between determinism and free will. We are knowledgeable of patients with substance use disorders, the effect of intoxicating substances, and the capacity of patients with substance use disorders to act in law-abiding ways. Our field can inform without simply advocating whether our patients should be punished. While society is currently struggling with how to apportion blame, psychiatry should resist the urge to impose medical solutions to social problems. Our solutions would almost certainly be grossly limited as we are still struggling to repent for lobotomizing “uppity” young women2 and using electroshock therapy to disrupt perverse impulses in homosexual males.3 Social norms and political zeitgeists change over time while the psychological and physiological principles underlying our understanding of mental illness should, in theory, stay relatively constant. Psychiatry’s answers for societal ills do not usually improve with time but rather have a tendency to be humbling.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1.Medlock MM et al., eds. “Racism and Psychiatry: Contemporary Issues and Interventions” (New York: Springer, 2018).
2. Tone A and Koziol M. CMAJ. 2018:190(20):e624-5.
3. McGuire RJ and Vallance M. BMJ. 1964;1(5376):151-3.
Substance use disorders can be a thorny topic in residency because of our role as gatekeepers of mental hospitals during our training. Intoxicated patients often get dismissed as a burden and distraction, malingering their way into a comfortable place to regain sobriety. This is extremely prevalent, often constituting the majority of patients seen during an emergency department call.
A typical interview may elicit any or all symptoms in the DSM yet be best explained by substance use intoxication or withdrawal. Alcohol and other CNS depressants commonly cause feelings of sadness and/or suicidality. Methamphetamine and other CNS stimulants commonly cause symptoms of psychosis or mania, followed by feelings of sadness and/or suicidality.
Different EDs have different degrees of patience for individuals in the process of becoming sober. Some departments will pressure clinicians into quickly discarding those patients and often frown upon any attempt at providing solace by raising the concern of reinforcing maladaptive behavior. A mystery-meat sandwich of admirable blandness may be the extent of help offered. Some more fortunate patients also receive a juice box or even a taxi voucher in an especially generous ED. This is always against our better judgment, of course, as we are told those gestures encourage abuse.
Other EDs will permit patients to remain until sober, allowing for another evaluation without the influence of controlled substances. We are reminded of many conversations with patients with substance use disorders, where topics discussed included: 1. Recommendation to seek substance use services, which are often nonexistent or with wait lists spanning months; 2. Education on the role of mental health hospitals and how patients’ despair in the context of intoxication does not meet some scriptural criteria; 3. Pep talks aided by such previously described sandwiches and juice boxes to encourage a sobering patient to leave the facility of their own will.
Methamphetamine, heroin, and alcohol are rarely one-and-done endeavors. We sparingly see our patients for their very first ED visit while intoxicated or crashing. They know how the system runs and which ED will more readily allow them an overnight stay. The number of times they have been recommended for substance use treatment is beyond counting – they may have been on a wait list a handful of times. They are aware of our reluctance to provide inpatient psychiatric treatment for substance use, but it is worth a shot trying, anyway – sometimes they get lucky. Usually it is the pep talk, relief from hunger pangs, and daylight that get them out the doors – until next time.
It is under this context that many trainees become psychiatrists, a process that solidifies the separation between drug use and mental illness. Many graduate from residency practically equating substance use disorder with malingering or futility. This can take on a surreal quality as many localities have recently adopted particular forms or requirements like the dispensation of naloxone syringes to all patients with substance use disorders. While the desire and effort are noble, it may suggest to a patient presenting for help that society’s main interest is to avoid seeing them die rather than help with available resources for maintaining sobriety.
Therein lies the conundrum, a conundrum that spans psychiatry to society. The conundrum is our ambivalence between punishing the choice of drug use or healing the substance use disorder. Should we discharge the intoxicated patient as soon as they are safe to walk out, or should we make every effort possible to find long-term solutions?
The calculation becomes more complex
A defining moment appears to have been society’s reconsideration of its stance on substance use disorders when affluent White teenagers started dying in the suburbs from pain pills overdoses. Suddenly, those children needed and deserved treatment, not punishment. We find ourselves far away from a time when the loudest societal commentary on substance use entailed mothers advocating for harsher sentences against drunk drivers.
More recently, as psychiatry and large contingents of society have decided to take up the mantle of equity and social justice, we have begun to make progress in decriminalizing substance use in an effort to reverse systemic discrimination toward minority groups. This has taken many shapes, including drug legalization, criminal justice reform, and even the provision of clean substance use paraphernalia for safer use of IV drugs. Police reform has led to reluctance to arrest or press charges for nonviolent crimes and reduced police presence in minority neighborhoods. The “rich White teenager” approach is now recommended in all neighborhoods.
Society’s attempt at decriminalizing drug use has run parallel with psychiatry’s recent attempts at reduced pathologizing of behaviors more prevalent in underprivileged groups and cultures. This runs the gamut, from avoiding the use of the term “agitated” because of its racial connotations, to advocating for reduced rates of schizophrenia diagnoses in Black males.1 A diagnosis of substance use disorder carries with it similar troublesome societal implications. Decriminalization, legalization, provision of substances to the population, normalization, and other societal reforms will likely have an impact on the prevalence of substance use disorder diagnoses, which involve many criteria dependent on societal context.
It would be expected that criteria such as hazardous use, social problems, and attempts to quit will decrease as social acceptance increases. How might this affect access to substance use treatment, an already extremely limited resource?
Now, as forensic psychiatrists, we find ourselves adjudicating on the role of drugs at a time when society is wrestling with its attitude on the breadth of responsibility possessed by people who use drugs. In California, as in many other states, insanity laws exclude those who were insane as a result of drug use, as a testament to or possibly a remnant of how society feels about the role of choice and responsibility in the use of drugs. Yet another defendant who admits to drug use may on the contrary receive a much more lenient plea deal if willing to commit to sobriety. But in a never-ending maze of differing judgments and opinions, a less understanding district attorney may argue that the additional risk posed by the use of drugs and resulting impulsivity may actually warrant a heavier sentence.
In a recent attempt at atonement for our past punitive stance on drug users, we have found a desire to protect those who use drugs by punishing those who sell, at times forgetting that these populations are deeply intertwined. A recent law permits the federal charge of distribution of fentanyl resulting in death, which carries the mandatory minimum of 20 years in prison. Yet, if the user whom we are trying to protect by this law is also the one selling, what are we left with?
Fentanyl has been a particularly tragic development in the history of mankind and drug use. Substance use has rarely been so easily linked to accidental death. While many physicians can easily explain the safety of fentanyl when used as prescribed and in controlled settings, this is certainly not the case in the community. Measuring micrograms of fentanyl is outside the knowledge and capabilities of most drug dealers, who are not equipped with pharmacy-grade scales. Yet, as a result, they sell and customers buy quantities of fentanyl that range from homeopathically low to lethally high because of a mixture of negligence and deliberate indifference.
Another effort at atonement has been attempts at decriminalizing drug use and releasing many nonviolent offenders. This can, however, encourage bystanders to report more acts as crime rather than public intoxication, to ensure a police response when confronted by intoxicated people. Whereas previously an inebriated person who is homeless may have been called for and asked to seek shelter, they now get called on, and subsequently charged for, allegedly mumbling a threat by a frustrated bystander.
The release of offenders has its limits. Many placements on probation require sobriety and result in longer sentences for the use of substances that are otherwise decriminalized. The decriminalization and reexamination of substance use by society should widen the scope from simply considering crime to examining the use of drugs throughout the legal system and even beyond.
The DSM and psychiatry are not intended or equipped to adjudicate disputes on where the lines should be drawn between determinism and free will. We are knowledgeable of patients with substance use disorders, the effect of intoxicating substances, and the capacity of patients with substance use disorders to act in law-abiding ways. Our field can inform without simply advocating whether our patients should be punished. While society is currently struggling with how to apportion blame, psychiatry should resist the urge to impose medical solutions to social problems. Our solutions would almost certainly be grossly limited as we are still struggling to repent for lobotomizing “uppity” young women2 and using electroshock therapy to disrupt perverse impulses in homosexual males.3 Social norms and political zeitgeists change over time while the psychological and physiological principles underlying our understanding of mental illness should, in theory, stay relatively constant. Psychiatry’s answers for societal ills do not usually improve with time but rather have a tendency to be humbling.
Dr. Badre is a clinical and forensic psychiatrist in San Diego. He holds teaching positions at the University of California, San Diego, and the University of San Diego. He teaches medical education, psychopharmacology, ethics in psychiatry, and correctional care. Dr. Badre can be reached at his website, BadreMD.com.
Dr. Compton is a psychiatry resident at University of California, San Diego. His background includes medical education, mental health advocacy, work with underserved populations, and brain cancer research.
References
1.Medlock MM et al., eds. “Racism and Psychiatry: Contemporary Issues and Interventions” (New York: Springer, 2018).
2. Tone A and Koziol M. CMAJ. 2018:190(20):e624-5.
3. McGuire RJ and Vallance M. BMJ. 1964;1(5376):151-3.