User login
Acne treatment may vary based on race, gender, insurance
based on findings from a retrospective, cohort study of 29,928 individuals with acne.
“Our findings suggest the presence of racial/ethnic, sex, and insurance-based disparities in health care use and treatment for acne and raise particular concern for undertreatment among racial/ethnic minority and female patients,” John S. Barbieri, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Data from previous studies have suggested racial disparities in the management of several dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but associations between social demographics and prescribing patterns have not been well studied for acne treatment, the authors noted.
For the current study, the researchers used deidentified data from the Optum electronic health record from Jan. 1, 2007 to June 30, 2017. In all, 29,928 patients aged 15-35 years and who were being treated for acne were included in the study. Of that total, 64% were women, 8% were non-Hispanic black and 68% were white, with the remaining patients grouped as non-Hispanic Asian, Hispanic, or other.
Non-Hispanic black patients were significantly more likely to be seen by a dermatologist, compared with non-Hispanic white patients, who were designated as the reference (odds ratio, 1.20). However, the black patients were less likely to receive prescriptions for any acne medication (incidence rate ratio, 0.89).
Non-Hispanic black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic white patients to be prescribed topical retinoids or topical antibiotics (OR, 1.25 and 1.35, respectively). They were also were less likely than their white counterparts to be prescribed oral antibiotics, spironolactone, and isotretinoin (OR, 0.80, 0.68, and 0.39, respectively).
Overall, men were more than twice as likely as women to receive prescriptions for isotretinoin (OR, 2.44). They were also more likely to receive prescriptions for the other treatments, but the differences were not as high as those for isotretinoin.
In addition, patients with Medicaid insurance were significantly less likely than those with commercial insurance (the reference) to see a dermatologist (OR, 0.46). Medicaid patients also were less likely to be prescribed topical retinoids, oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin (OR, 0.82, 0.87, 0.50, and 0.43, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors, among them, the use of automated pharmacy data without confirmation that patients had picked up the medications they had been prescribed, the researchers said. The study also lacked data on acne severity, clinical outcomes, and the use of over-the-counter acne treatments.
“Further study is needed to confirm our findings, provide understanding of the reasons for these potential disparities, and develop strategies to ensure equitable care for patients with acne,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, and by a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Barbieri had no financial conflicts to disclose. One of the study coauthors disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Barbieri JS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 5. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818.
based on findings from a retrospective, cohort study of 29,928 individuals with acne.
“Our findings suggest the presence of racial/ethnic, sex, and insurance-based disparities in health care use and treatment for acne and raise particular concern for undertreatment among racial/ethnic minority and female patients,” John S. Barbieri, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Data from previous studies have suggested racial disparities in the management of several dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but associations between social demographics and prescribing patterns have not been well studied for acne treatment, the authors noted.
For the current study, the researchers used deidentified data from the Optum electronic health record from Jan. 1, 2007 to June 30, 2017. In all, 29,928 patients aged 15-35 years and who were being treated for acne were included in the study. Of that total, 64% were women, 8% were non-Hispanic black and 68% were white, with the remaining patients grouped as non-Hispanic Asian, Hispanic, or other.
Non-Hispanic black patients were significantly more likely to be seen by a dermatologist, compared with non-Hispanic white patients, who were designated as the reference (odds ratio, 1.20). However, the black patients were less likely to receive prescriptions for any acne medication (incidence rate ratio, 0.89).
Non-Hispanic black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic white patients to be prescribed topical retinoids or topical antibiotics (OR, 1.25 and 1.35, respectively). They were also were less likely than their white counterparts to be prescribed oral antibiotics, spironolactone, and isotretinoin (OR, 0.80, 0.68, and 0.39, respectively).
Overall, men were more than twice as likely as women to receive prescriptions for isotretinoin (OR, 2.44). They were also more likely to receive prescriptions for the other treatments, but the differences were not as high as those for isotretinoin.
In addition, patients with Medicaid insurance were significantly less likely than those with commercial insurance (the reference) to see a dermatologist (OR, 0.46). Medicaid patients also were less likely to be prescribed topical retinoids, oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin (OR, 0.82, 0.87, 0.50, and 0.43, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors, among them, the use of automated pharmacy data without confirmation that patients had picked up the medications they had been prescribed, the researchers said. The study also lacked data on acne severity, clinical outcomes, and the use of over-the-counter acne treatments.
“Further study is needed to confirm our findings, provide understanding of the reasons for these potential disparities, and develop strategies to ensure equitable care for patients with acne,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, and by a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Barbieri had no financial conflicts to disclose. One of the study coauthors disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Barbieri JS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 5. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818.
based on findings from a retrospective, cohort study of 29,928 individuals with acne.
“Our findings suggest the presence of racial/ethnic, sex, and insurance-based disparities in health care use and treatment for acne and raise particular concern for undertreatment among racial/ethnic minority and female patients,” John S. Barbieri, MD, a dermatology research fellow at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues wrote in a study published in JAMA Dermatology.
Data from previous studies have suggested racial disparities in the management of several dermatologic conditions, including atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but associations between social demographics and prescribing patterns have not been well studied for acne treatment, the authors noted.
For the current study, the researchers used deidentified data from the Optum electronic health record from Jan. 1, 2007 to June 30, 2017. In all, 29,928 patients aged 15-35 years and who were being treated for acne were included in the study. Of that total, 64% were women, 8% were non-Hispanic black and 68% were white, with the remaining patients grouped as non-Hispanic Asian, Hispanic, or other.
Non-Hispanic black patients were significantly more likely to be seen by a dermatologist, compared with non-Hispanic white patients, who were designated as the reference (odds ratio, 1.20). However, the black patients were less likely to receive prescriptions for any acne medication (incidence rate ratio, 0.89).
Non-Hispanic black patients were more likely than non-Hispanic white patients to be prescribed topical retinoids or topical antibiotics (OR, 1.25 and 1.35, respectively). They were also were less likely than their white counterparts to be prescribed oral antibiotics, spironolactone, and isotretinoin (OR, 0.80, 0.68, and 0.39, respectively).
Overall, men were more than twice as likely as women to receive prescriptions for isotretinoin (OR, 2.44). They were also more likely to receive prescriptions for the other treatments, but the differences were not as high as those for isotretinoin.
In addition, patients with Medicaid insurance were significantly less likely than those with commercial insurance (the reference) to see a dermatologist (OR, 0.46). Medicaid patients also were less likely to be prescribed topical retinoids, oral antibiotics, spironolactone, or isotretinoin (OR, 0.82, 0.87, 0.50, and 0.43, respectively).
The study findings were limited by several factors, among them, the use of automated pharmacy data without confirmation that patients had picked up the medications they had been prescribed, the researchers said. The study also lacked data on acne severity, clinical outcomes, and the use of over-the-counter acne treatments.
“Further study is needed to confirm our findings, provide understanding of the reasons for these potential disparities, and develop strategies to ensure equitable care for patients with acne,” the researchers concluded.
The study was supported in part by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, and by a Pfizer Fellowship in Dermatology Patient Oriented Research grant to the Trustees of the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Barbieri had no financial conflicts to disclose. One of the study coauthors disclosed relationships with Pfizer, Eli Lilly, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Barbieri JS et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Feb 5. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4818.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Baby’s Got Back Rash
ANSWER
The correct answer is psoriasis vulgaris (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
At least 30% of patients with psoriasis have a family history of the disease—a meaningful clue in developing a differential. Besides asking about the history, always look for corroborating signs in areas where the disease is commonly seen (eg, the fingernails). In this case, further corroboration was provided by the history of illness at the time of the rash’s onset; what was initially strep-driven guttate psoriasis morphed into full-blown psoriasis vulgaris.
The heavy scales, with their salmon-pink base, tipped the scales in favor of psoriasis as the diagnosis. The pinpoint bleeding (known as the Auspitz sign), although not pathognomic for psoriasis, is certainly suggestive of it.
In adults, these findings would probably have been sufficient to settle on psoriasis. But before labeling a young child with a serious, lifelong diagnosis, it was necessary to be sure. For one thing, advanced psoriasis is very unusual in children as young as this patient, and for another, treatment would likely be problematic. Fortunately for clarity’s sake, the biopsy was consistent with psoriasis and inconsistent with the other items in the differential.
TREATMENT
The patient was prescribed a topical steroid cream to apply every other day, alternating with vitamin D–derived ointment. In addition, he was advised to increase his exposure to natural sunlight. Phototherapy with narrow-band ultraviolet light B would be a superior option, but his family lives too far from the clinic to make 3 roundtrips per week for such treatment.
If these measures fail, a biologic agent may be appropriate. Unfortunately, the patient’s insurance carrier requires the failure of several other modalities before it will approve use of such therapy.
ANSWER
The correct answer is psoriasis vulgaris (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
At least 30% of patients with psoriasis have a family history of the disease—a meaningful clue in developing a differential. Besides asking about the history, always look for corroborating signs in areas where the disease is commonly seen (eg, the fingernails). In this case, further corroboration was provided by the history of illness at the time of the rash’s onset; what was initially strep-driven guttate psoriasis morphed into full-blown psoriasis vulgaris.
The heavy scales, with their salmon-pink base, tipped the scales in favor of psoriasis as the diagnosis. The pinpoint bleeding (known as the Auspitz sign), although not pathognomic for psoriasis, is certainly suggestive of it.
In adults, these findings would probably have been sufficient to settle on psoriasis. But before labeling a young child with a serious, lifelong diagnosis, it was necessary to be sure. For one thing, advanced psoriasis is very unusual in children as young as this patient, and for another, treatment would likely be problematic. Fortunately for clarity’s sake, the biopsy was consistent with psoriasis and inconsistent with the other items in the differential.
TREATMENT
The patient was prescribed a topical steroid cream to apply every other day, alternating with vitamin D–derived ointment. In addition, he was advised to increase his exposure to natural sunlight. Phototherapy with narrow-band ultraviolet light B would be a superior option, but his family lives too far from the clinic to make 3 roundtrips per week for such treatment.
If these measures fail, a biologic agent may be appropriate. Unfortunately, the patient’s insurance carrier requires the failure of several other modalities before it will approve use of such therapy.
ANSWER
The correct answer is psoriasis vulgaris (choice “a”).
DISCUSSION
At least 30% of patients with psoriasis have a family history of the disease—a meaningful clue in developing a differential. Besides asking about the history, always look for corroborating signs in areas where the disease is commonly seen (eg, the fingernails). In this case, further corroboration was provided by the history of illness at the time of the rash’s onset; what was initially strep-driven guttate psoriasis morphed into full-blown psoriasis vulgaris.
The heavy scales, with their salmon-pink base, tipped the scales in favor of psoriasis as the diagnosis. The pinpoint bleeding (known as the Auspitz sign), although not pathognomic for psoriasis, is certainly suggestive of it.
In adults, these findings would probably have been sufficient to settle on psoriasis. But before labeling a young child with a serious, lifelong diagnosis, it was necessary to be sure. For one thing, advanced psoriasis is very unusual in children as young as this patient, and for another, treatment would likely be problematic. Fortunately for clarity’s sake, the biopsy was consistent with psoriasis and inconsistent with the other items in the differential.
TREATMENT
The patient was prescribed a topical steroid cream to apply every other day, alternating with vitamin D–derived ointment. In addition, he was advised to increase his exposure to natural sunlight. Phototherapy with narrow-band ultraviolet light B would be a superior option, but his family lives too far from the clinic to make 3 roundtrips per week for such treatment.
If these measures fail, a biologic agent may be appropriate. Unfortunately, the patient’s insurance carrier requires the failure of several other modalities before it will approve use of such therapy.
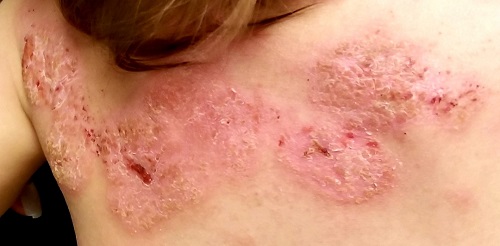
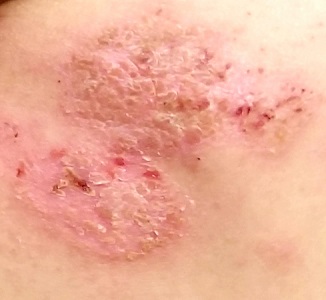
Several months ago, a rash of numerous small, red, scaly papules and patches manifested on this 3-year-old boy’s back and shoulders. At the time, he had been ill for about a week, and his primary care provider diagnosed chickenpox—even though the child had been immunized.
Although the patient’s health soon improved, the appearance of the rash worsened. Treatment with various products—including calamine lotion, OTC tolnaftate and miconazole, and a 2-week course of oral antibiotics—was of no help. Finally, the patient was referred to dermatology.
Family history is positive for psoriasis. However, the parents are quick to note that the boy’s rash appears far different from that of affected family members, and previous providers have dismissed this diagnosis from the differential. There is no family or personal history of atopy.
Examination reveals a dense papulosquamous rash mainly confined to the child’s back and posterior shoulders (the area over the scapula). No other areas are similarly affected, but 1 fingernail is mildly pitted.
A #10 blade lifts the edge of one of the scales gently (and painlessly) until there is pinpoint bleeding from 2 tiny foci. A 5-mm full-thickness punch biopsy with primary closure shows marked parakeratosis, collections of neutrophils on the crests of dermal papillae, and fusing of rete ridges, which effectively obscure the normal wave-like pattern of the dermoepidermal junction.
Psoriasis ointment helped with itch, healing in phase 2 EB study
LONDON – , in a small, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study.
More importantly, use of the ointment promoted wound healing in those with the severe skin-blistering condition. Indeed, compared with placebo, a greater reduction in wound size was observed after 2 weeks when the ointment was applied (a mean reduction of 65.5% vs. 88.4%; P less than .006). However, at 1 month, no significant differences were seen in the size of the wounds between the two treatment arms.
“Calcipotriol is a vitamin D analog and it is well known that vitamin D is a very critical factor for skin homeostasis and proper wound healing,” Christina Guttmann-Gruber, PhD, said at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, a group lead researcher for EB House Austria, which is based at the Salzburg (Austria) University Clinic for Dermatology, noted that vitamin D also helps with tissue repair and immune modulation, and enhances local antimicrobial activity.
During an oral poster presentation at the meeting, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber explained that in previous in vitro studies, it was found that low concentrations (100 nmol) of calcipotriol inhibited proliferation of RDEB tumor cells (Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 7;8:13430). Calcipotriol (also known as calcipotriene) also was found to improve the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promote wound closure. “Therefore, we thought that applying calcipotriol at the site of injury, on chronic wounds prone to superinfection where it is needed, might be beneficial for our patients.”
She and her associates designed a two-arm, randomized, double-blind crossover study to assess the effects of an existing calcipotriol-containing ointment on wound healing in patients with RDEB. The ointment used in the study is approved for treating psoriasis but was adapted by the in-house pharmacy team to reduce the concentration of calcipotriol to about 0.05 mcg/g, or around 121 nmol. The reason for the reduction was that, at higher doses, keratinocyte proliferation was reduced, which would be detrimental in RDEB patients.
Nine patients were included in the study and were randomized to either apply 1 g of the active or placebo ointment to each of two designated wounds, of at least 6 cm2 in size, every day for 4 weeks. A 2-month washout period then followed before the groups switched to use the other ointment for 1 month. Six out of the nine patients completed both treatment phases. The reasons for the patients not completing both intervention phases were not related to the drug.
Calcipotriol treatment resulted in a significant and steady reduction in itch over the entire course of treatment, which was not seen among those on placebo, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber observed. The reduction in itch was “striking,” but only while the treatment was being used, she said. Results for pain were less clear, with a significant reduction in pain after 2 weeks seen only in the placebo group, while both treatments reduced pain to the same degree by 1 month.
No serious adverse events were observed at any time point and topical use of the low-dose calcipotriol did not significantly change serum levels of calcium or vitamin D in the two patients in which this was studied, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said.
“This is an approved drug; it’s used in psoriasis, but at a very high concentration. We were able to use it off label and make a diluted version,” she observed. “Any pharmacy can do it.” Although it was applied topically, it could be done by applying it to the dressing rather directly onto the wounded skin, she said.
Data on the skin microbiome response to treatment were also collected but were not available to analyze in time for presentation, but it appeared that there was improvement with the low-dose calcipotriol treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said. “When the wounds are healing, the microbial flora is improving.”
The next step will probably be to plan a multicenter trial of this treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said in an interview. The questions is whether such a trial would get the financial backing it needed, but if an orphan drug designation could be obtained for calcipotriol for EB, then it would be possible to conduct such a trial.
The study was funded by DEBRA Austria. The presenting author, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Guttmann-Gruber C et al. EB World Congress 2020. Poster 34.
LONDON – , in a small, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study.
More importantly, use of the ointment promoted wound healing in those with the severe skin-blistering condition. Indeed, compared with placebo, a greater reduction in wound size was observed after 2 weeks when the ointment was applied (a mean reduction of 65.5% vs. 88.4%; P less than .006). However, at 1 month, no significant differences were seen in the size of the wounds between the two treatment arms.
“Calcipotriol is a vitamin D analog and it is well known that vitamin D is a very critical factor for skin homeostasis and proper wound healing,” Christina Guttmann-Gruber, PhD, said at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, a group lead researcher for EB House Austria, which is based at the Salzburg (Austria) University Clinic for Dermatology, noted that vitamin D also helps with tissue repair and immune modulation, and enhances local antimicrobial activity.
During an oral poster presentation at the meeting, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber explained that in previous in vitro studies, it was found that low concentrations (100 nmol) of calcipotriol inhibited proliferation of RDEB tumor cells (Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 7;8:13430). Calcipotriol (also known as calcipotriene) also was found to improve the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promote wound closure. “Therefore, we thought that applying calcipotriol at the site of injury, on chronic wounds prone to superinfection where it is needed, might be beneficial for our patients.”
She and her associates designed a two-arm, randomized, double-blind crossover study to assess the effects of an existing calcipotriol-containing ointment on wound healing in patients with RDEB. The ointment used in the study is approved for treating psoriasis but was adapted by the in-house pharmacy team to reduce the concentration of calcipotriol to about 0.05 mcg/g, or around 121 nmol. The reason for the reduction was that, at higher doses, keratinocyte proliferation was reduced, which would be detrimental in RDEB patients.
Nine patients were included in the study and were randomized to either apply 1 g of the active or placebo ointment to each of two designated wounds, of at least 6 cm2 in size, every day for 4 weeks. A 2-month washout period then followed before the groups switched to use the other ointment for 1 month. Six out of the nine patients completed both treatment phases. The reasons for the patients not completing both intervention phases were not related to the drug.
Calcipotriol treatment resulted in a significant and steady reduction in itch over the entire course of treatment, which was not seen among those on placebo, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber observed. The reduction in itch was “striking,” but only while the treatment was being used, she said. Results for pain were less clear, with a significant reduction in pain after 2 weeks seen only in the placebo group, while both treatments reduced pain to the same degree by 1 month.
No serious adverse events were observed at any time point and topical use of the low-dose calcipotriol did not significantly change serum levels of calcium or vitamin D in the two patients in which this was studied, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said.
“This is an approved drug; it’s used in psoriasis, but at a very high concentration. We were able to use it off label and make a diluted version,” she observed. “Any pharmacy can do it.” Although it was applied topically, it could be done by applying it to the dressing rather directly onto the wounded skin, she said.
Data on the skin microbiome response to treatment were also collected but were not available to analyze in time for presentation, but it appeared that there was improvement with the low-dose calcipotriol treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said. “When the wounds are healing, the microbial flora is improving.”
The next step will probably be to plan a multicenter trial of this treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said in an interview. The questions is whether such a trial would get the financial backing it needed, but if an orphan drug designation could be obtained for calcipotriol for EB, then it would be possible to conduct such a trial.
The study was funded by DEBRA Austria. The presenting author, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Guttmann-Gruber C et al. EB World Congress 2020. Poster 34.
LONDON – , in a small, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study.
More importantly, use of the ointment promoted wound healing in those with the severe skin-blistering condition. Indeed, compared with placebo, a greater reduction in wound size was observed after 2 weeks when the ointment was applied (a mean reduction of 65.5% vs. 88.4%; P less than .006). However, at 1 month, no significant differences were seen in the size of the wounds between the two treatment arms.
“Calcipotriol is a vitamin D analog and it is well known that vitamin D is a very critical factor for skin homeostasis and proper wound healing,” Christina Guttmann-Gruber, PhD, said at the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA). Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, a group lead researcher for EB House Austria, which is based at the Salzburg (Austria) University Clinic for Dermatology, noted that vitamin D also helps with tissue repair and immune modulation, and enhances local antimicrobial activity.
During an oral poster presentation at the meeting, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber explained that in previous in vitro studies, it was found that low concentrations (100 nmol) of calcipotriol inhibited proliferation of RDEB tumor cells (Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 7;8:13430). Calcipotriol (also known as calcipotriene) also was found to improve the expression of antimicrobial peptides and promote wound closure. “Therefore, we thought that applying calcipotriol at the site of injury, on chronic wounds prone to superinfection where it is needed, might be beneficial for our patients.”
She and her associates designed a two-arm, randomized, double-blind crossover study to assess the effects of an existing calcipotriol-containing ointment on wound healing in patients with RDEB. The ointment used in the study is approved for treating psoriasis but was adapted by the in-house pharmacy team to reduce the concentration of calcipotriol to about 0.05 mcg/g, or around 121 nmol. The reason for the reduction was that, at higher doses, keratinocyte proliferation was reduced, which would be detrimental in RDEB patients.
Nine patients were included in the study and were randomized to either apply 1 g of the active or placebo ointment to each of two designated wounds, of at least 6 cm2 in size, every day for 4 weeks. A 2-month washout period then followed before the groups switched to use the other ointment for 1 month. Six out of the nine patients completed both treatment phases. The reasons for the patients not completing both intervention phases were not related to the drug.
Calcipotriol treatment resulted in a significant and steady reduction in itch over the entire course of treatment, which was not seen among those on placebo, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber observed. The reduction in itch was “striking,” but only while the treatment was being used, she said. Results for pain were less clear, with a significant reduction in pain after 2 weeks seen only in the placebo group, while both treatments reduced pain to the same degree by 1 month.
No serious adverse events were observed at any time point and topical use of the low-dose calcipotriol did not significantly change serum levels of calcium or vitamin D in the two patients in which this was studied, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said.
“This is an approved drug; it’s used in psoriasis, but at a very high concentration. We were able to use it off label and make a diluted version,” she observed. “Any pharmacy can do it.” Although it was applied topically, it could be done by applying it to the dressing rather directly onto the wounded skin, she said.
Data on the skin microbiome response to treatment were also collected but were not available to analyze in time for presentation, but it appeared that there was improvement with the low-dose calcipotriol treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said. “When the wounds are healing, the microbial flora is improving.”
The next step will probably be to plan a multicenter trial of this treatment, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber said in an interview. The questions is whether such a trial would get the financial backing it needed, but if an orphan drug designation could be obtained for calcipotriol for EB, then it would be possible to conduct such a trial.
The study was funded by DEBRA Austria. The presenting author, Dr. Guttmann-Gruber, had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Guttmann-Gruber C et al. EB World Congress 2020. Poster 34.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
Nonspecific musculoskeletal symptoms might indicate early PsA
People with psoriatic arthritis can be symptomatic for years before the condition is diagnosed, according to two recent reports.
There are no reliable diagnostic biomarkers, and sometimes patients have vague symptoms with only minimal physical findings, which makes it hard for physicians to recognize the problem and refer to rheumatology.
In the meantime, the longer it takes to diagnose psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and treat it properly, the worse off patients are when it’s finally caught. They “present with a greater rate of clinical progression and worse physical function, compared with patients with an undelayed diagnosis,” and more radiographic joint damage, according to investigators led by rheumatologist Alexis Ogdie, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Ogdie’s study in BMC Rheumatology, and a second one from Arthritis Care & Research, both described the early phase of psoriatic arthritis, before formal diagnosis, to help with early recognition.
Delay associated with misdiagnosis
Dr. Ogdie’s team surveyed 203 adults with PsA – average age of 52 years, mostly white, and over 80% women – about their diagnosis history. The time between seeking medical attention for PsA-related symptoms and receiving a diagnosis was less than 6 months for 69 participants, 6 months to 4 years for 68, and 5 years or more for 66.
Typical symptoms, like joint pain, swollen joints, reduced range of motion, and dactylitis, were associated with quicker diagnosis. Turning early to dermatologists and rheumatologists – instead of general practitioners, orthopedics, chiropractors, and others – sped diagnosis, as well. People diagnosed within 6 months also tended to be slightly older, were less likely to be disabled or unemployed, have more education, and were more likely to make $100,000 per year or more.
Vaguer symptoms, such as stiffness, fatigue, and enthesitis-associated foot pain, delayed diagnosis. The longer PsA went unrecognized, the more likely people were to be misdiagnosed with osteoarthritis, psychosomatic disorders, and other problems.
“Increased recognition of heterogeneous symptoms associated with PsA, as well as understanding existing diagnostic barriers, may lead to prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate treatment that may improve outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
A prodromal phase
In the Arthritis Care & Research study, investigators led by Lihi Eder, MD, PhD, codirector of the cardio-rheumatology program at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, used health records and databases to compare primary care histories of 462 Canadian PsA patients in the 5 years before they were diagnosed with 2,310 age- and sex-matched controls without PsA and treated by the same family physicians. The mean age in the study was 54 years, and just over half the subjects were women. Socioeconomic status and rurality were similar between the two groups.
The mean time from the initial primary care visit for a musculoskeletal complaint to rheumatology referral was 513 days among PsA patients, “which was substantially longer than for other inflammatory arthritic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Eder and associates noted.
PsA patients were more than twice as likely to visit primary care for nonspecific musculoskeletal issues in the year before their diagnosis, and more likely in the 5 years prior. The odds of visits to musculoskeletal specialists, joint injections, joint imaging, and ED visits, was also higher as early as 5 years before PsA recognition, and hinted at the impending diagnosis.
“Our study characterized a prediagnosis period in PsA and supports the notion that a prodromal PsA phase occurs in a significant proportion of patients. ... This pattern reveals some of the underlying causes of diagnosis delays of PsA and highlights the need for diagnostic strategies and novel reliable biomarkers to aid in early diagnosis of PsA,” the investigators concluded.
Dr. Ogdie and colleagues suggested that community case searches, public awareness programs, patient education, and referral guidelines for primary care providers might help. They also suggested greater use of validated screening tools, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool, in primary care.
Dr. Eder had no disclosures, and her study was funded by the Canadian Rheumatology Association. Dr. Ogdie’s study was funded by Novartis, maker of secukinumab (Cosentyx), which is indicated for PsA. She is a consultant for Novartis and has received grant support from the company. One author is an employee.
SOURCES: Ogdie A et al. BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1186/s41927-019-0102-7; Eder L et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1002/acr.24146.
People with psoriatic arthritis can be symptomatic for years before the condition is diagnosed, according to two recent reports.
There are no reliable diagnostic biomarkers, and sometimes patients have vague symptoms with only minimal physical findings, which makes it hard for physicians to recognize the problem and refer to rheumatology.
In the meantime, the longer it takes to diagnose psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and treat it properly, the worse off patients are when it’s finally caught. They “present with a greater rate of clinical progression and worse physical function, compared with patients with an undelayed diagnosis,” and more radiographic joint damage, according to investigators led by rheumatologist Alexis Ogdie, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Ogdie’s study in BMC Rheumatology, and a second one from Arthritis Care & Research, both described the early phase of psoriatic arthritis, before formal diagnosis, to help with early recognition.
Delay associated with misdiagnosis
Dr. Ogdie’s team surveyed 203 adults with PsA – average age of 52 years, mostly white, and over 80% women – about their diagnosis history. The time between seeking medical attention for PsA-related symptoms and receiving a diagnosis was less than 6 months for 69 participants, 6 months to 4 years for 68, and 5 years or more for 66.
Typical symptoms, like joint pain, swollen joints, reduced range of motion, and dactylitis, were associated with quicker diagnosis. Turning early to dermatologists and rheumatologists – instead of general practitioners, orthopedics, chiropractors, and others – sped diagnosis, as well. People diagnosed within 6 months also tended to be slightly older, were less likely to be disabled or unemployed, have more education, and were more likely to make $100,000 per year or more.
Vaguer symptoms, such as stiffness, fatigue, and enthesitis-associated foot pain, delayed diagnosis. The longer PsA went unrecognized, the more likely people were to be misdiagnosed with osteoarthritis, psychosomatic disorders, and other problems.
“Increased recognition of heterogeneous symptoms associated with PsA, as well as understanding existing diagnostic barriers, may lead to prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate treatment that may improve outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
A prodromal phase
In the Arthritis Care & Research study, investigators led by Lihi Eder, MD, PhD, codirector of the cardio-rheumatology program at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, used health records and databases to compare primary care histories of 462 Canadian PsA patients in the 5 years before they were diagnosed with 2,310 age- and sex-matched controls without PsA and treated by the same family physicians. The mean age in the study was 54 years, and just over half the subjects were women. Socioeconomic status and rurality were similar between the two groups.
The mean time from the initial primary care visit for a musculoskeletal complaint to rheumatology referral was 513 days among PsA patients, “which was substantially longer than for other inflammatory arthritic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Eder and associates noted.
PsA patients were more than twice as likely to visit primary care for nonspecific musculoskeletal issues in the year before their diagnosis, and more likely in the 5 years prior. The odds of visits to musculoskeletal specialists, joint injections, joint imaging, and ED visits, was also higher as early as 5 years before PsA recognition, and hinted at the impending diagnosis.
“Our study characterized a prediagnosis period in PsA and supports the notion that a prodromal PsA phase occurs in a significant proportion of patients. ... This pattern reveals some of the underlying causes of diagnosis delays of PsA and highlights the need for diagnostic strategies and novel reliable biomarkers to aid in early diagnosis of PsA,” the investigators concluded.
Dr. Ogdie and colleagues suggested that community case searches, public awareness programs, patient education, and referral guidelines for primary care providers might help. They also suggested greater use of validated screening tools, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool, in primary care.
Dr. Eder had no disclosures, and her study was funded by the Canadian Rheumatology Association. Dr. Ogdie’s study was funded by Novartis, maker of secukinumab (Cosentyx), which is indicated for PsA. She is a consultant for Novartis and has received grant support from the company. One author is an employee.
SOURCES: Ogdie A et al. BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1186/s41927-019-0102-7; Eder L et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1002/acr.24146.
People with psoriatic arthritis can be symptomatic for years before the condition is diagnosed, according to two recent reports.
There are no reliable diagnostic biomarkers, and sometimes patients have vague symptoms with only minimal physical findings, which makes it hard for physicians to recognize the problem and refer to rheumatology.
In the meantime, the longer it takes to diagnose psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and treat it properly, the worse off patients are when it’s finally caught. They “present with a greater rate of clinical progression and worse physical function, compared with patients with an undelayed diagnosis,” and more radiographic joint damage, according to investigators led by rheumatologist Alexis Ogdie, MD, an associate professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Dr. Ogdie’s study in BMC Rheumatology, and a second one from Arthritis Care & Research, both described the early phase of psoriatic arthritis, before formal diagnosis, to help with early recognition.
Delay associated with misdiagnosis
Dr. Ogdie’s team surveyed 203 adults with PsA – average age of 52 years, mostly white, and over 80% women – about their diagnosis history. The time between seeking medical attention for PsA-related symptoms and receiving a diagnosis was less than 6 months for 69 participants, 6 months to 4 years for 68, and 5 years or more for 66.
Typical symptoms, like joint pain, swollen joints, reduced range of motion, and dactylitis, were associated with quicker diagnosis. Turning early to dermatologists and rheumatologists – instead of general practitioners, orthopedics, chiropractors, and others – sped diagnosis, as well. People diagnosed within 6 months also tended to be slightly older, were less likely to be disabled or unemployed, have more education, and were more likely to make $100,000 per year or more.
Vaguer symptoms, such as stiffness, fatigue, and enthesitis-associated foot pain, delayed diagnosis. The longer PsA went unrecognized, the more likely people were to be misdiagnosed with osteoarthritis, psychosomatic disorders, and other problems.
“Increased recognition of heterogeneous symptoms associated with PsA, as well as understanding existing diagnostic barriers, may lead to prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate treatment that may improve outcomes,” the investigators concluded.
A prodromal phase
In the Arthritis Care & Research study, investigators led by Lihi Eder, MD, PhD, codirector of the cardio-rheumatology program at Women’s College Hospital, Toronto, used health records and databases to compare primary care histories of 462 Canadian PsA patients in the 5 years before they were diagnosed with 2,310 age- and sex-matched controls without PsA and treated by the same family physicians. The mean age in the study was 54 years, and just over half the subjects were women. Socioeconomic status and rurality were similar between the two groups.
The mean time from the initial primary care visit for a musculoskeletal complaint to rheumatology referral was 513 days among PsA patients, “which was substantially longer than for other inflammatory arthritic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Eder and associates noted.
PsA patients were more than twice as likely to visit primary care for nonspecific musculoskeletal issues in the year before their diagnosis, and more likely in the 5 years prior. The odds of visits to musculoskeletal specialists, joint injections, joint imaging, and ED visits, was also higher as early as 5 years before PsA recognition, and hinted at the impending diagnosis.
“Our study characterized a prediagnosis period in PsA and supports the notion that a prodromal PsA phase occurs in a significant proportion of patients. ... This pattern reveals some of the underlying causes of diagnosis delays of PsA and highlights the need for diagnostic strategies and novel reliable biomarkers to aid in early diagnosis of PsA,” the investigators concluded.
Dr. Ogdie and colleagues suggested that community case searches, public awareness programs, patient education, and referral guidelines for primary care providers might help. They also suggested greater use of validated screening tools, such as the Psoriasis Epidemiology Screening Tool, in primary care.
Dr. Eder had no disclosures, and her study was funded by the Canadian Rheumatology Association. Dr. Ogdie’s study was funded by Novartis, maker of secukinumab (Cosentyx), which is indicated for PsA. She is a consultant for Novartis and has received grant support from the company. One author is an employee.
SOURCES: Ogdie A et al. BMC Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 10. doi: 10.1186/s41927-019-0102-7; Eder L et al. Arthritis Care Res. 2020 Jan 21. doi: 10.1002/acr.24146.
FROM BMC RHEUMATOLOGY AND ARTHRITIS CARE & RESEARCH
Tildrakizumab signals safe for pregnant psoriasis patients
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
A post hoc analysis of .
“Although contraception in female patients of childbearing age was mandatory before initiation of and during tildrakizumab therapy, some pregnancies occurred during the tildrakizumab clinical development program as protocol violations,” wrote Kathleen Haycraft, MD, of Riverside Dermatology & Spa, Hannibal, Mo., and colleagues.
Tildrakizumab (Ilumya), an interleukin-23 antagonist, was approved in 2018 by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. Effects on birth outcomes or on neonates exposed during pregnancy have not been studied, the researchers said.
“Tildrakizumab plasma half-life after subcutaneous administration is approximately 25 days; therefore, tildrakizumab administered even in the first trimester may cross the placental barrier,” they noted.
In a research letter published in the British Journal of Dermatology, the investigators reviewed data from nine phase 1, 2, and 3 clinical trials and identified 528 women of childbearing age who received tildrakizumab. Fourteen pregnancies were reported among these women: six from a contraceptive failure, and eight for lack of contraception use. (One of the phase 1 trials was in patients with Crohn’s disease, which included one of the pregnancies; the rest were in patients with psoriasis.)
The 14 pregnancy outcomes included 2 spontaneous abortions (14.3%), 4 elective abortions (28.6%), and 8 live births (57.1%), which included 1 premature birth, with “no identifiable congenital anomalies,” the authors wrote. The longest duration of exposure to tildrakizumab in a pregnant woman was 1,196 days; this pregnancy resulted in a premature live birth at 36 weeks with no anomalies. The spontaneous abortion rate was similar to the rate in the general population, which is 12%-15%, the authors noted.
While the study “adds to the existing evidence on the outcomes of biologic treatment of psoriasis,” the findings were limited by several factors including the small number of pregnancies, short duration of exposure to tildrakizumab, variations in dosing, and lack of controls, the researchers noted. “Additional data from a larger population following tildrakizumab exposure are required to fully evaluate the safety and tolerability of tildrakizumab treatment during pregnancy,” they said. In the meantime, they advised women of childbearing age with psoriasis to continue to avoid pregnancy and follow practice guidelines for contraceptive use while taking the biologic therapy.
The studies were supported by Merck Sharp & Dohme, a Merck & Co. subsidiary; analyses were supported by Sun Pharmaceutical Industries. Lead author Dr. Haycraft disclosed relationships with companies including Sun, Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Ortho-Derm, and Pfizer. Other authors disclosed relationships with Novartis, Celgene, Ortho Dermatologics, Janssen, and Merck; two authors are Sun employees.
dermnews@mdedge.com
SOURCE: Haycraft K et al. Br J Dermatol. 2020 Jan 29. doi: 10.1111/bjd.18897.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGY
Consider allergic contact dermatitis in children with AD with disease flares, new rash
ORLANDO – Do you have ? Consider patch testing to assess whether they have allergic contact dermatitis.
“Of the patients who are sent to me by local pediatric dermatologists, 50% of them are positive” for allergens, said Jonathan H. Zippin, MD, PhD, director of the contact, occupational, and photodermatitis service at Cornell University, New York.
Speaking at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, and Surgical Conference, Dr. Zippin noted the prevalence of allergen sensitization is between 13% and 25% among children who are asymptomatic, while the prevalence of sensitization to at least one allergen among children with suspected allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is between 25% and 96%. In 2014, a study from the National American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) showed that of 883 children who were patch tested, 56.7% had at least one relevant positive patch test (RPPT) result.
“The take-home message here is that pediatric contact dermatitis is common, much more common than a lot of people realize,” Dr. Zippin said.
He described three common scenarios to keep in mind: a worsening rash, a new rash, and failure of a rash to improve after the patient avoids all of his or her positive allergens.
When a rash worsens, patch testing is likely to offer answers. In an analysis of 1,142 patients with suspected ACD aged 18 years or younger (mean age, 10.5 years; 64% female) in the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry study database, 65% had at least one positive patch test, and 48% had at least 1 RPPT (Dermatitis 2016; 27[5] 293-302).
But not all patch testing is the same: The study also found that 24% of the RPPT cases would have been missed if assessed with the T.R.U.E. TEST compared with extended patch testing. If a T.R.U.E. TEST fails to explain generalized atopic dermatitis, the patient should be sent for more comprehensive testing where available, Dr. Zippin advised.
Pediatric patients also have unique allergens clinicians should consider. In the same study, children had a number of allergens similar to those of adults as reported in previous studies, such as nickel, cobalt, and neomycin. However, propylene glycol and cocamidopropyl betaine were allergens identified as unique to the pediatric population.
Another study looking at the same group of patients found that compared with children who did not have AD, children with AD had 7.4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to cocamidopropyl betaine, 7.6 times higher odds of having an RPPT to parthenolide, 5.3 times higher odds of having an RPPT to tixocortol pivalate, 4.2 times higher odds of having an RPPT to wool alcohols, and 4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to lanolin (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[8]:765-70).
All of these are components of topical medicaments used to treat AD, “either components of emollients that we recommend, or components of steroids that we recommend,” Dr. Zippin pointed out.
One of these allergens could be the culprit when a child develops a new rash but there are no new apparent changes in products, exposures, and activities. Lanolin, also called wool grease, is used in many skin care products, for example. Dr. Zippin described the case of a 6-year-old girl with a history of AD, who presented with a new rash on her scalp and behind her ears, not explained by any obvious changes to products, exposures, or activities. Subsequent patch testing determined that the rash was caused by baby shampoo, which contained cocamidopropyl betaine, which is used in hypoallergenic products. The rash resolved after a different shampoo was used.
“Sometimes, we really have to be thinking when the rash is getting worse, is there something they’re being exposed to that might be an allergen?” Dr. Zippin said.
In patients who have avoided all their positive allergens but a rash has not improved, clinicians should consider systemic contact dermatitis (SCD). Patients can develop SCD through different types of exposures, including transepidermal, transmucosal, oral, intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, inhalation, and implantation routes.
SCD also has a variety of presentations, including pompholyx/dyshidrosis/vesicular dermatitis, maculopapular eruption, chronic pruritus, exfoliative erythroderma/toxiderma, chronic urticaria, erythema multiforme and vasculitis, hyperkeratotic papules of the elbows, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and pruritus ani, according to Dr. Zippin.
SCD should be considered when a patient has a positive patch test to an allergen that is known to cause SCD, and does not clear after avoiding cutaneous exposure to the allergen, Dr. Zippin advised.
Patients will most often develop SCD from plants and herbs, Dr. Zippin noted. Chrysanthemums and chamomile tea are common culprits for compositae allergy and can trigger SCD; other causes are Anacardiaceae, Balsam of Peru, and propolis. Metals (nickel, cobalt, gold, and chromium), medications (aminoglycosides, corticosteroids, and ethylenediamine), and other sources (formaldehyde, propylene glycol in frozen foods, gallates, and methylisothiazolinone) can cause SCD as well.
Methylisothiazolinone in particular is a very common sensitizer, Dr. Zippin said. “If you have a patient who is positive to this, it’s almost always the cause of their problem.”
Balsam of Peru is in a number of different foods, and patients who need to follow a diet free of Balsam of Peru should avoid a long list of foods including citrus; bakery goods; Danish pastry; candy; gum; spices such as cinnamon, cloves, vanilla, curry, allspice, anise, and ginger; spicy condiments such as ketchup, chili sauce, barbecue sauce; chili, pizza, and foods with red sauces; tomatoes; pickles; alcohol (wine, beer, gin, vermouth); tea (perfumed or flavored); tobacco; chocolate and ice cream; and soft drinks (cola or spiced soft drinks).
Patients starting a nickel-free diet should avoid soy, peanuts and other nuts, legumes, chocolate, cocoa, oats, fish, and whole wheat flours. Any elimination diet should last for 3 months but should at least be tried for 3-4 weeks, with gradual reintroduction of foods suspected as triggers once per week. Any type I allergies that are discovered or suspected can be referred to an allergist for allergen challenge and desensitization therapy.
For more information, Dr. Zippin recommended the American Contact Dermatitis Society website for more information.
Dr. Zippin reported that he is the founder and holds stock options at CEP Biotech; is on the medical advisory board and receives stock options from YouV Labs., is a paid consultant and performs industry-sponsored research for Pfizer, receives stock options from Regeneron, and is on the medical advisory board for Hoth Therapeutics Inc. He is on the board of directors for the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
ORLANDO – Do you have ? Consider patch testing to assess whether they have allergic contact dermatitis.
“Of the patients who are sent to me by local pediatric dermatologists, 50% of them are positive” for allergens, said Jonathan H. Zippin, MD, PhD, director of the contact, occupational, and photodermatitis service at Cornell University, New York.
Speaking at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, and Surgical Conference, Dr. Zippin noted the prevalence of allergen sensitization is between 13% and 25% among children who are asymptomatic, while the prevalence of sensitization to at least one allergen among children with suspected allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is between 25% and 96%. In 2014, a study from the National American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) showed that of 883 children who were patch tested, 56.7% had at least one relevant positive patch test (RPPT) result.
“The take-home message here is that pediatric contact dermatitis is common, much more common than a lot of people realize,” Dr. Zippin said.
He described three common scenarios to keep in mind: a worsening rash, a new rash, and failure of a rash to improve after the patient avoids all of his or her positive allergens.
When a rash worsens, patch testing is likely to offer answers. In an analysis of 1,142 patients with suspected ACD aged 18 years or younger (mean age, 10.5 years; 64% female) in the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry study database, 65% had at least one positive patch test, and 48% had at least 1 RPPT (Dermatitis 2016; 27[5] 293-302).
But not all patch testing is the same: The study also found that 24% of the RPPT cases would have been missed if assessed with the T.R.U.E. TEST compared with extended patch testing. If a T.R.U.E. TEST fails to explain generalized atopic dermatitis, the patient should be sent for more comprehensive testing where available, Dr. Zippin advised.
Pediatric patients also have unique allergens clinicians should consider. In the same study, children had a number of allergens similar to those of adults as reported in previous studies, such as nickel, cobalt, and neomycin. However, propylene glycol and cocamidopropyl betaine were allergens identified as unique to the pediatric population.
Another study looking at the same group of patients found that compared with children who did not have AD, children with AD had 7.4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to cocamidopropyl betaine, 7.6 times higher odds of having an RPPT to parthenolide, 5.3 times higher odds of having an RPPT to tixocortol pivalate, 4.2 times higher odds of having an RPPT to wool alcohols, and 4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to lanolin (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[8]:765-70).
All of these are components of topical medicaments used to treat AD, “either components of emollients that we recommend, or components of steroids that we recommend,” Dr. Zippin pointed out.
One of these allergens could be the culprit when a child develops a new rash but there are no new apparent changes in products, exposures, and activities. Lanolin, also called wool grease, is used in many skin care products, for example. Dr. Zippin described the case of a 6-year-old girl with a history of AD, who presented with a new rash on her scalp and behind her ears, not explained by any obvious changes to products, exposures, or activities. Subsequent patch testing determined that the rash was caused by baby shampoo, which contained cocamidopropyl betaine, which is used in hypoallergenic products. The rash resolved after a different shampoo was used.
“Sometimes, we really have to be thinking when the rash is getting worse, is there something they’re being exposed to that might be an allergen?” Dr. Zippin said.
In patients who have avoided all their positive allergens but a rash has not improved, clinicians should consider systemic contact dermatitis (SCD). Patients can develop SCD through different types of exposures, including transepidermal, transmucosal, oral, intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, inhalation, and implantation routes.
SCD also has a variety of presentations, including pompholyx/dyshidrosis/vesicular dermatitis, maculopapular eruption, chronic pruritus, exfoliative erythroderma/toxiderma, chronic urticaria, erythema multiforme and vasculitis, hyperkeratotic papules of the elbows, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and pruritus ani, according to Dr. Zippin.
SCD should be considered when a patient has a positive patch test to an allergen that is known to cause SCD, and does not clear after avoiding cutaneous exposure to the allergen, Dr. Zippin advised.
Patients will most often develop SCD from plants and herbs, Dr. Zippin noted. Chrysanthemums and chamomile tea are common culprits for compositae allergy and can trigger SCD; other causes are Anacardiaceae, Balsam of Peru, and propolis. Metals (nickel, cobalt, gold, and chromium), medications (aminoglycosides, corticosteroids, and ethylenediamine), and other sources (formaldehyde, propylene glycol in frozen foods, gallates, and methylisothiazolinone) can cause SCD as well.
Methylisothiazolinone in particular is a very common sensitizer, Dr. Zippin said. “If you have a patient who is positive to this, it’s almost always the cause of their problem.”
Balsam of Peru is in a number of different foods, and patients who need to follow a diet free of Balsam of Peru should avoid a long list of foods including citrus; bakery goods; Danish pastry; candy; gum; spices such as cinnamon, cloves, vanilla, curry, allspice, anise, and ginger; spicy condiments such as ketchup, chili sauce, barbecue sauce; chili, pizza, and foods with red sauces; tomatoes; pickles; alcohol (wine, beer, gin, vermouth); tea (perfumed or flavored); tobacco; chocolate and ice cream; and soft drinks (cola or spiced soft drinks).
Patients starting a nickel-free diet should avoid soy, peanuts and other nuts, legumes, chocolate, cocoa, oats, fish, and whole wheat flours. Any elimination diet should last for 3 months but should at least be tried for 3-4 weeks, with gradual reintroduction of foods suspected as triggers once per week. Any type I allergies that are discovered or suspected can be referred to an allergist for allergen challenge and desensitization therapy.
For more information, Dr. Zippin recommended the American Contact Dermatitis Society website for more information.
Dr. Zippin reported that he is the founder and holds stock options at CEP Biotech; is on the medical advisory board and receives stock options from YouV Labs., is a paid consultant and performs industry-sponsored research for Pfizer, receives stock options from Regeneron, and is on the medical advisory board for Hoth Therapeutics Inc. He is on the board of directors for the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
ORLANDO – Do you have ? Consider patch testing to assess whether they have allergic contact dermatitis.
“Of the patients who are sent to me by local pediatric dermatologists, 50% of them are positive” for allergens, said Jonathan H. Zippin, MD, PhD, director of the contact, occupational, and photodermatitis service at Cornell University, New York.
Speaking at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, and Surgical Conference, Dr. Zippin noted the prevalence of allergen sensitization is between 13% and 25% among children who are asymptomatic, while the prevalence of sensitization to at least one allergen among children with suspected allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is between 25% and 96%. In 2014, a study from the National American Contact Dermatitis Group (NACDG) showed that of 883 children who were patch tested, 56.7% had at least one relevant positive patch test (RPPT) result.
“The take-home message here is that pediatric contact dermatitis is common, much more common than a lot of people realize,” Dr. Zippin said.
He described three common scenarios to keep in mind: a worsening rash, a new rash, and failure of a rash to improve after the patient avoids all of his or her positive allergens.
When a rash worsens, patch testing is likely to offer answers. In an analysis of 1,142 patients with suspected ACD aged 18 years or younger (mean age, 10.5 years; 64% female) in the Pediatric Contact Dermatitis Registry study database, 65% had at least one positive patch test, and 48% had at least 1 RPPT (Dermatitis 2016; 27[5] 293-302).
But not all patch testing is the same: The study also found that 24% of the RPPT cases would have been missed if assessed with the T.R.U.E. TEST compared with extended patch testing. If a T.R.U.E. TEST fails to explain generalized atopic dermatitis, the patient should be sent for more comprehensive testing where available, Dr. Zippin advised.
Pediatric patients also have unique allergens clinicians should consider. In the same study, children had a number of allergens similar to those of adults as reported in previous studies, such as nickel, cobalt, and neomycin. However, propylene glycol and cocamidopropyl betaine were allergens identified as unique to the pediatric population.
Another study looking at the same group of patients found that compared with children who did not have AD, children with AD had 7.4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to cocamidopropyl betaine, 7.6 times higher odds of having an RPPT to parthenolide, 5.3 times higher odds of having an RPPT to tixocortol pivalate, 4.2 times higher odds of having an RPPT to wool alcohols, and 4 times higher odds of having an RPPT to lanolin (JAMA Dermatology 2017;153[8]:765-70).
All of these are components of topical medicaments used to treat AD, “either components of emollients that we recommend, or components of steroids that we recommend,” Dr. Zippin pointed out.
One of these allergens could be the culprit when a child develops a new rash but there are no new apparent changes in products, exposures, and activities. Lanolin, also called wool grease, is used in many skin care products, for example. Dr. Zippin described the case of a 6-year-old girl with a history of AD, who presented with a new rash on her scalp and behind her ears, not explained by any obvious changes to products, exposures, or activities. Subsequent patch testing determined that the rash was caused by baby shampoo, which contained cocamidopropyl betaine, which is used in hypoallergenic products. The rash resolved after a different shampoo was used.
“Sometimes, we really have to be thinking when the rash is getting worse, is there something they’re being exposed to that might be an allergen?” Dr. Zippin said.
In patients who have avoided all their positive allergens but a rash has not improved, clinicians should consider systemic contact dermatitis (SCD). Patients can develop SCD through different types of exposures, including transepidermal, transmucosal, oral, intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, inhalation, and implantation routes.
SCD also has a variety of presentations, including pompholyx/dyshidrosis/vesicular dermatitis, maculopapular eruption, chronic pruritus, exfoliative erythroderma/toxiderma, chronic urticaria, erythema multiforme and vasculitis, hyperkeratotic papules of the elbows, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and pruritus ani, according to Dr. Zippin.
SCD should be considered when a patient has a positive patch test to an allergen that is known to cause SCD, and does not clear after avoiding cutaneous exposure to the allergen, Dr. Zippin advised.
Patients will most often develop SCD from plants and herbs, Dr. Zippin noted. Chrysanthemums and chamomile tea are common culprits for compositae allergy and can trigger SCD; other causes are Anacardiaceae, Balsam of Peru, and propolis. Metals (nickel, cobalt, gold, and chromium), medications (aminoglycosides, corticosteroids, and ethylenediamine), and other sources (formaldehyde, propylene glycol in frozen foods, gallates, and methylisothiazolinone) can cause SCD as well.
Methylisothiazolinone in particular is a very common sensitizer, Dr. Zippin said. “If you have a patient who is positive to this, it’s almost always the cause of their problem.”
Balsam of Peru is in a number of different foods, and patients who need to follow a diet free of Balsam of Peru should avoid a long list of foods including citrus; bakery goods; Danish pastry; candy; gum; spices such as cinnamon, cloves, vanilla, curry, allspice, anise, and ginger; spicy condiments such as ketchup, chili sauce, barbecue sauce; chili, pizza, and foods with red sauces; tomatoes; pickles; alcohol (wine, beer, gin, vermouth); tea (perfumed or flavored); tobacco; chocolate and ice cream; and soft drinks (cola or spiced soft drinks).
Patients starting a nickel-free diet should avoid soy, peanuts and other nuts, legumes, chocolate, cocoa, oats, fish, and whole wheat flours. Any elimination diet should last for 3 months but should at least be tried for 3-4 weeks, with gradual reintroduction of foods suspected as triggers once per week. Any type I allergies that are discovered or suspected can be referred to an allergist for allergen challenge and desensitization therapy.
For more information, Dr. Zippin recommended the American Contact Dermatitis Society website for more information.
Dr. Zippin reported that he is the founder and holds stock options at CEP Biotech; is on the medical advisory board and receives stock options from YouV Labs., is a paid consultant and performs industry-sponsored research for Pfizer, receives stock options from Regeneron, and is on the medical advisory board for Hoth Therapeutics Inc. He is on the board of directors for the American Contact Dermatitis Society.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ODAC 2020
Abdominal rash
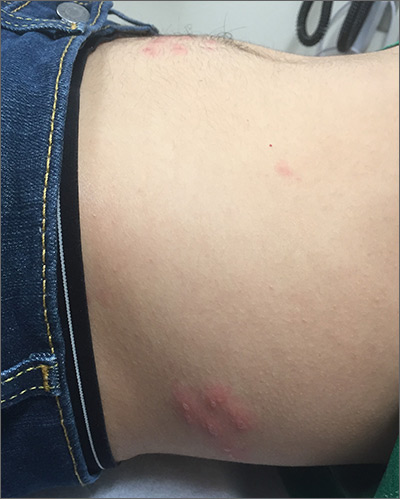
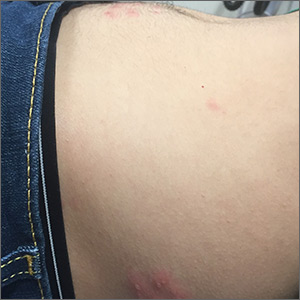
The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.

The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.

The pruritic prodrome, which evolved into painful vesicles, on an erythematous base in a dermatomal distribution was a classic presentation of herpes zoster.
Although herpes zoster is usually thought of as a disease that strikes older individuals, a study by Kawai et al found that of 8000 patients experiencing an outbreak, 43% were < 50 years of age. Additionally, this study found that the rate of herpes zoster infection had increased 4-fold in the past 60 years, and the rise had not been affected by the introduction of varicella vaccination. In Kawai’s series, 6.6% of the cases were in immunocompromised individuals.
In this case, the patient began antiviral therapy (Valacyclovir 1g tid for 7 days) to treat the active lesions. In further discussion with the patient, he indicated that he was concerned he might have an underlying undiagnosed autoimmune condition or human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. His provider completed routine health care maintenance recommendations including an HIV screen, which was negative. Since he was otherwise asymptomatic, with no history of recurrent infections, no additional testing was warranted. However, since the patient worked with immunocompromised patients at a local hospital, he was placed on medical leave (per the facility’s protocol) until the lesions had crusted over. By Day 10, his lesions had crusted over and he returned to work.
Text courtesy of Brent Gillespie, PAC, University of New Mexico. Photo and editing courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.
Kawai K, Yawn BP, Wollan P, et al. Increasing incidence of herpes zoster over a 60-year period from a population-based study. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:221-226.
Measles, scarlet fever among infectious diseases to watch for in 2020
ORLANDO – – leading into 2020, Justin Finch, MD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, & Surgical Conference.
While group A streptococcus has declined over the past century, there has been “an unprecedented” resurgence in severe, invasive group A streptococcal infections and severe epidemics of scarlet fever worldwide, including in industrialized regions like the United Kingdom. Shedding some light on why this may be occurring, Dr. Finch referred to a recently published population-based molecular epidemiologic study identified a new dominant emm1UK lineage of Streptococcus pyogenes associated with such cases in England (Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;19(11):1209-18). This new lineage of S. pyogenes was genotypically distinct from other emm1 isolates and had greatly increased expression of the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A, one of the exotoxins responsible for the clinical features of scarlet fever.
“We have not, to my knowledge, seen the strain yet in the United States,” said Dr. Finch, of Central Connecticut Dermatology in Cromwell. “Have it on your radar. With all of the worldwide travel patterns, I expect that you will see this in the United States at some point in the not-too-distant future.”
Also in 2019, promising data on the safety and effectiveness of the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine in immunocompromised patients became available for the first time. A randomized clinical trial published in JAMA of 1,846 patients who were immunosuppressed after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and received two doses of a recombinant zoster vaccine found that the patients had a reduced incidence of herpes zoster after a median follow-up of 21 months (JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322[2]:123-33). The study found that the recombinant vaccine was both safe and effective in these immunocompromised patients, “so we can easily generalize this to our dermatology population as well,” Dr. Finch said. In comparing the live attenuated and recombinant vaccines, he noted the recombinant vaccine requires two doses but appears to be slightly more effective. “The number needed to treat to prevent [one case] of zoster is about half as high as that for the live vaccine, and most importantly for us is, it’s safe in immunocompromised patients.”
2019 also saw a record high in the number of measles cases in the United States, the highest since 1993, Dr. Finch pointed out. Most cases were seen in the area in and around New York City, but the percentage of people across the United States who are vaccinated against measles is below the threshold for herd immunity to protect immunocompromised patients. Measles requires a population vaccination rate of 94%, and less than half of U.S. counties in 2014 and 2015 reached that vaccination rate.
“Furthermore, if we look at that over the last 20 years, comparing the domestic measles cases to imported measles cases, we are increasingly breeding these measles epidemics right here at home, whereas they used to be imported from throughout the world,” said Dr. Finch. Patients with measles can be treated with vitamin A, he added, referring to a Cochrane review showing that 200,000 units of vitamin A given daily for 2 days decreased the mortality rate of measles by about 80%. Measles is on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s list of reportable diseases, so should be reported to local health authorities, and will be followed up with confirmatory testing.
In 2019, a study examining herd protection of oral human papillomavirus infection in men and women compared the prevalence of oral HPV infection based on the 4 HPV types present in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine with 33 nonvaccine types from 2009 to 2016. There was no change in the prevalence of nonvaccine type oral HPV infections among men who were unvaccinated, but the prevalence of oral HPV infections because of the four strains in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine declined from 2.7% in 2009-2010 to 1.6% in 2015-2016 (JAMA. 2019 Sep 10;322[10]:977-9). Among unvaccinated women, the prevalence of nonvaccine- and vaccine-type oral HPV infections did not change between the two time periods.
“Notably, this only occurred in men,” Dr. Finch said. Herd immunity is being achieved in men “because we’re vaccinating all women, [but] we’re not seeing that herd immunity in women. Which begs the question: Why are we still vaccinating only half of our population?”
One study published in 2019 (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov;181[5]:1093-5) described a patient with CARD9 mutations, which predispose individuals to deep invasive infections – a disseminated Microsporum infection in this case, Dr. Finch said. “You shouldn’t see that,” he added, noting that these mutations are known to predispose individuals to severe Trichophyton infections and familial candidiasis.
“What I think is interesting about this is that, as we look forward to 2020, we’re going to increasingly see studies like this that are identifying specific mutations in our community that underlie a lot of these weird infections,” he added. “I wouldn’t be surprised if within the span of our careers, we find that a lot of those severe treatment-refractory reports that so commonly plague your everyday clinic have some underlying, specific immunity.”
Dr. Finch reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – – leading into 2020, Justin Finch, MD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, & Surgical Conference.
While group A streptococcus has declined over the past century, there has been “an unprecedented” resurgence in severe, invasive group A streptococcal infections and severe epidemics of scarlet fever worldwide, including in industrialized regions like the United Kingdom. Shedding some light on why this may be occurring, Dr. Finch referred to a recently published population-based molecular epidemiologic study identified a new dominant emm1UK lineage of Streptococcus pyogenes associated with such cases in England (Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;19(11):1209-18). This new lineage of S. pyogenes was genotypically distinct from other emm1 isolates and had greatly increased expression of the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A, one of the exotoxins responsible for the clinical features of scarlet fever.
“We have not, to my knowledge, seen the strain yet in the United States,” said Dr. Finch, of Central Connecticut Dermatology in Cromwell. “Have it on your radar. With all of the worldwide travel patterns, I expect that you will see this in the United States at some point in the not-too-distant future.”
Also in 2019, promising data on the safety and effectiveness of the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine in immunocompromised patients became available for the first time. A randomized clinical trial published in JAMA of 1,846 patients who were immunosuppressed after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and received two doses of a recombinant zoster vaccine found that the patients had a reduced incidence of herpes zoster after a median follow-up of 21 months (JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322[2]:123-33). The study found that the recombinant vaccine was both safe and effective in these immunocompromised patients, “so we can easily generalize this to our dermatology population as well,” Dr. Finch said. In comparing the live attenuated and recombinant vaccines, he noted the recombinant vaccine requires two doses but appears to be slightly more effective. “The number needed to treat to prevent [one case] of zoster is about half as high as that for the live vaccine, and most importantly for us is, it’s safe in immunocompromised patients.”
2019 also saw a record high in the number of measles cases in the United States, the highest since 1993, Dr. Finch pointed out. Most cases were seen in the area in and around New York City, but the percentage of people across the United States who are vaccinated against measles is below the threshold for herd immunity to protect immunocompromised patients. Measles requires a population vaccination rate of 94%, and less than half of U.S. counties in 2014 and 2015 reached that vaccination rate.
“Furthermore, if we look at that over the last 20 years, comparing the domestic measles cases to imported measles cases, we are increasingly breeding these measles epidemics right here at home, whereas they used to be imported from throughout the world,” said Dr. Finch. Patients with measles can be treated with vitamin A, he added, referring to a Cochrane review showing that 200,000 units of vitamin A given daily for 2 days decreased the mortality rate of measles by about 80%. Measles is on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s list of reportable diseases, so should be reported to local health authorities, and will be followed up with confirmatory testing.
In 2019, a study examining herd protection of oral human papillomavirus infection in men and women compared the prevalence of oral HPV infection based on the 4 HPV types present in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine with 33 nonvaccine types from 2009 to 2016. There was no change in the prevalence of nonvaccine type oral HPV infections among men who were unvaccinated, but the prevalence of oral HPV infections because of the four strains in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine declined from 2.7% in 2009-2010 to 1.6% in 2015-2016 (JAMA. 2019 Sep 10;322[10]:977-9). Among unvaccinated women, the prevalence of nonvaccine- and vaccine-type oral HPV infections did not change between the two time periods.
“Notably, this only occurred in men,” Dr. Finch said. Herd immunity is being achieved in men “because we’re vaccinating all women, [but] we’re not seeing that herd immunity in women. Which begs the question: Why are we still vaccinating only half of our population?”
One study published in 2019 (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov;181[5]:1093-5) described a patient with CARD9 mutations, which predispose individuals to deep invasive infections – a disseminated Microsporum infection in this case, Dr. Finch said. “You shouldn’t see that,” he added, noting that these mutations are known to predispose individuals to severe Trichophyton infections and familial candidiasis.
“What I think is interesting about this is that, as we look forward to 2020, we’re going to increasingly see studies like this that are identifying specific mutations in our community that underlie a lot of these weird infections,” he added. “I wouldn’t be surprised if within the span of our careers, we find that a lot of those severe treatment-refractory reports that so commonly plague your everyday clinic have some underlying, specific immunity.”
Dr. Finch reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – – leading into 2020, Justin Finch, MD, said at the ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, & Surgical Conference.
While group A streptococcus has declined over the past century, there has been “an unprecedented” resurgence in severe, invasive group A streptococcal infections and severe epidemics of scarlet fever worldwide, including in industrialized regions like the United Kingdom. Shedding some light on why this may be occurring, Dr. Finch referred to a recently published population-based molecular epidemiologic study identified a new dominant emm1UK lineage of Streptococcus pyogenes associated with such cases in England (Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Nov;19(11):1209-18). This new lineage of S. pyogenes was genotypically distinct from other emm1 isolates and had greatly increased expression of the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A, one of the exotoxins responsible for the clinical features of scarlet fever.
“We have not, to my knowledge, seen the strain yet in the United States,” said Dr. Finch, of Central Connecticut Dermatology in Cromwell. “Have it on your radar. With all of the worldwide travel patterns, I expect that you will see this in the United States at some point in the not-too-distant future.”
Also in 2019, promising data on the safety and effectiveness of the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine in immunocompromised patients became available for the first time. A randomized clinical trial published in JAMA of 1,846 patients who were immunosuppressed after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and received two doses of a recombinant zoster vaccine found that the patients had a reduced incidence of herpes zoster after a median follow-up of 21 months (JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322[2]:123-33). The study found that the recombinant vaccine was both safe and effective in these immunocompromised patients, “so we can easily generalize this to our dermatology population as well,” Dr. Finch said. In comparing the live attenuated and recombinant vaccines, he noted the recombinant vaccine requires two doses but appears to be slightly more effective. “The number needed to treat to prevent [one case] of zoster is about half as high as that for the live vaccine, and most importantly for us is, it’s safe in immunocompromised patients.”
2019 also saw a record high in the number of measles cases in the United States, the highest since 1993, Dr. Finch pointed out. Most cases were seen in the area in and around New York City, but the percentage of people across the United States who are vaccinated against measles is below the threshold for herd immunity to protect immunocompromised patients. Measles requires a population vaccination rate of 94%, and less than half of U.S. counties in 2014 and 2015 reached that vaccination rate.
“Furthermore, if we look at that over the last 20 years, comparing the domestic measles cases to imported measles cases, we are increasingly breeding these measles epidemics right here at home, whereas they used to be imported from throughout the world,” said Dr. Finch. Patients with measles can be treated with vitamin A, he added, referring to a Cochrane review showing that 200,000 units of vitamin A given daily for 2 days decreased the mortality rate of measles by about 80%. Measles is on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s list of reportable diseases, so should be reported to local health authorities, and will be followed up with confirmatory testing.
In 2019, a study examining herd protection of oral human papillomavirus infection in men and women compared the prevalence of oral HPV infection based on the 4 HPV types present in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine with 33 nonvaccine types from 2009 to 2016. There was no change in the prevalence of nonvaccine type oral HPV infections among men who were unvaccinated, but the prevalence of oral HPV infections because of the four strains in the quadrivalent HPV vaccine declined from 2.7% in 2009-2010 to 1.6% in 2015-2016 (JAMA. 2019 Sep 10;322[10]:977-9). Among unvaccinated women, the prevalence of nonvaccine- and vaccine-type oral HPV infections did not change between the two time periods.
“Notably, this only occurred in men,” Dr. Finch said. Herd immunity is being achieved in men “because we’re vaccinating all women, [but] we’re not seeing that herd immunity in women. Which begs the question: Why are we still vaccinating only half of our population?”
One study published in 2019 (Br J Dermatol. 2019 Nov;181[5]:1093-5) described a patient with CARD9 mutations, which predispose individuals to deep invasive infections – a disseminated Microsporum infection in this case, Dr. Finch said. “You shouldn’t see that,” he added, noting that these mutations are known to predispose individuals to severe Trichophyton infections and familial candidiasis.
“What I think is interesting about this is that, as we look forward to 2020, we’re going to increasingly see studies like this that are identifying specific mutations in our community that underlie a lot of these weird infections,” he added. “I wouldn’t be surprised if within the span of our careers, we find that a lot of those severe treatment-refractory reports that so commonly plague your everyday clinic have some underlying, specific immunity.”
Dr. Finch reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM ODAC 2020
Losartan showing promise in pediatric epidermolysis bullosa trial
LONDON – Treatment with the in an early clinical study.
In the ongoing phase 1/2 REFLECT (Recessive dystrophic EB: Mechanisms of fibrosis and its prevention with Losartan in vivo) trial, involving 29 children, no severe complications have been noted so far, according to one of the study investigators, Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, of the University of Freiburg, Germany. At the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), she presented interim data on 18 patients in the trial, emphasizing that the primary aim of the trial was to evaluate the safety of this treatment approach.
Over the 2 years the trial has been underway, 65 adverse events have been reported, of which 4 have been severe. Two of these were bacterial infections that required hospital treatment and the other two were a reduction in the general health condition of the child.
Losartan is an angiotensin-II receptor blocker (ARB) that has been in clinical use for more than 25 years in adults and 15 years in children over the age of 6 years.
The drug may be used for treating recessive dystrophic EB (RDEB) in the future, Dr. Kiritsi said, because it attenuates tumor necrosis factor–beta (TGF-beta) signaling, which is thought to be involved in the fibrotic process. So while it may not target the genetic defect, it could help ameliorate the effects of the disease.
The precursor to REFLECT was a study performed in a mouse disease model of EB (EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:1211-28) where a reduction in fibrotic scarring was seen with losartan with “remarkable effects” on “mitten” deformity, Dr. Kiritsi said. The results of that study suggested that the earlier treatment with losartan was started in the course of the disease, the better the effect, she added. (Mitten deformity is the result of fused skin between the fingers or toes, and the subsequent buildup of fibrotic tissue causes the hand or foot to contract.)
REFLECT is an investigator-initiated trial that started in 2017 and is being funded by DEBRA International. It is a dual-center, nonrandomized, single-arm study in which children aged 3-16 years with RDEB are treated with losartan for 10 months, with follow-up at 3 months.
Various secondary endpoints were included to look for the first signs of any efficacy: the Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA), the Birmingham Epidermolysis Bullosa Severity Score (BEBS), the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI), the Itch Assessment Scale for the Pediatric Burn Patients, and two quality of life indices: the Quality of Life in EB (QOLEB) questionnaire and the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI).
Dr. Kiritsi highlighted a few of the secondary endpoint findings, saying that reduced BEBS scores showed there was “amelioration of the patients’ phenotype” and that EBDASI scores also decreased, with “nearly 60% of the patients having significant improvement of their skin disease.” Importantly, itch improved in most of the patients, she said. Reductions in CDLQI were observed, “meaning that quality of life was significantly better at the end of the trial.” There were also decreases in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and TNF-alpha.
Although there is no validated tool available to assess hand function, Dr. Kiritsi and her team used their own morphometric scoring instrument to measure how far the hand could stretch; their evaluations suggested that this measure improved – or at least did not worsen – with losartan treatment, she noted.
A larger, randomized trial is needed to confirm if there is any benefit of losartan, but first, a new, easy-to-swallow losartan formulation needs to be developed specifically for EB in the pediatric population, Dr. Kiritsi said. Although a pediatric suspension of losartan was previously available, it is no longer on the market, so the next step is to develop a formulation that could be used in a pivotal clinical trial, she noted.
“Losartan faces fewer technical hurdles compared to other novel treatments as it is an established medicine,” Dr. Kiritsi and associates observed in a poster presentation. There are still economic hurdles, however, since “with losartan patents expired, companies cannot expect to recoup an investment into clinical studies” and alternative funding sources are needed.
In 2019, losartan was granted an orphan drug designation for the treatment of EB from both the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, but its use remains off label in children. “We decided to treat children,” Dr. Kiritsi said, “because we wanted to start as early as possible. If you already have mitten deformities, these cannot be reversed.”
DEBRA International funded the study. Dr. Kiritsi received research support from Rheacell GmbH and honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt Pharma and Rheacell GmbH. She has received other support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz Thyssen Stiftung, German Research Foundation (funding of research projects), and 3R Pharma Consulting and Midas Pharma GmbH (consultation for losartan new drug formulation).
SOURCE: Kiritsi D et al. EB 2020. Poster 47.
LONDON – Treatment with the in an early clinical study.
In the ongoing phase 1/2 REFLECT (Recessive dystrophic EB: Mechanisms of fibrosis and its prevention with Losartan in vivo) trial, involving 29 children, no severe complications have been noted so far, according to one of the study investigators, Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, of the University of Freiburg, Germany. At the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), she presented interim data on 18 patients in the trial, emphasizing that the primary aim of the trial was to evaluate the safety of this treatment approach.
Over the 2 years the trial has been underway, 65 adverse events have been reported, of which 4 have been severe. Two of these were bacterial infections that required hospital treatment and the other two were a reduction in the general health condition of the child.
Losartan is an angiotensin-II receptor blocker (ARB) that has been in clinical use for more than 25 years in adults and 15 years in children over the age of 6 years.
The drug may be used for treating recessive dystrophic EB (RDEB) in the future, Dr. Kiritsi said, because it attenuates tumor necrosis factor–beta (TGF-beta) signaling, which is thought to be involved in the fibrotic process. So while it may not target the genetic defect, it could help ameliorate the effects of the disease.
The precursor to REFLECT was a study performed in a mouse disease model of EB (EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:1211-28) where a reduction in fibrotic scarring was seen with losartan with “remarkable effects” on “mitten” deformity, Dr. Kiritsi said. The results of that study suggested that the earlier treatment with losartan was started in the course of the disease, the better the effect, she added. (Mitten deformity is the result of fused skin between the fingers or toes, and the subsequent buildup of fibrotic tissue causes the hand or foot to contract.)
REFLECT is an investigator-initiated trial that started in 2017 and is being funded by DEBRA International. It is a dual-center, nonrandomized, single-arm study in which children aged 3-16 years with RDEB are treated with losartan for 10 months, with follow-up at 3 months.
Various secondary endpoints were included to look for the first signs of any efficacy: the Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA), the Birmingham Epidermolysis Bullosa Severity Score (BEBS), the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI), the Itch Assessment Scale for the Pediatric Burn Patients, and two quality of life indices: the Quality of Life in EB (QOLEB) questionnaire and the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI).
Dr. Kiritsi highlighted a few of the secondary endpoint findings, saying that reduced BEBS scores showed there was “amelioration of the patients’ phenotype” and that EBDASI scores also decreased, with “nearly 60% of the patients having significant improvement of their skin disease.” Importantly, itch improved in most of the patients, she said. Reductions in CDLQI were observed, “meaning that quality of life was significantly better at the end of the trial.” There were also decreases in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and TNF-alpha.
Although there is no validated tool available to assess hand function, Dr. Kiritsi and her team used their own morphometric scoring instrument to measure how far the hand could stretch; their evaluations suggested that this measure improved – or at least did not worsen – with losartan treatment, she noted.
A larger, randomized trial is needed to confirm if there is any benefit of losartan, but first, a new, easy-to-swallow losartan formulation needs to be developed specifically for EB in the pediatric population, Dr. Kiritsi said. Although a pediatric suspension of losartan was previously available, it is no longer on the market, so the next step is to develop a formulation that could be used in a pivotal clinical trial, she noted.
“Losartan faces fewer technical hurdles compared to other novel treatments as it is an established medicine,” Dr. Kiritsi and associates observed in a poster presentation. There are still economic hurdles, however, since “with losartan patents expired, companies cannot expect to recoup an investment into clinical studies” and alternative funding sources are needed.
In 2019, losartan was granted an orphan drug designation for the treatment of EB from both the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, but its use remains off label in children. “We decided to treat children,” Dr. Kiritsi said, “because we wanted to start as early as possible. If you already have mitten deformities, these cannot be reversed.”
DEBRA International funded the study. Dr. Kiritsi received research support from Rheacell GmbH and honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt Pharma and Rheacell GmbH. She has received other support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz Thyssen Stiftung, German Research Foundation (funding of research projects), and 3R Pharma Consulting and Midas Pharma GmbH (consultation for losartan new drug formulation).
SOURCE: Kiritsi D et al. EB 2020. Poster 47.
LONDON – Treatment with the in an early clinical study.
In the ongoing phase 1/2 REFLECT (Recessive dystrophic EB: Mechanisms of fibrosis and its prevention with Losartan in vivo) trial, involving 29 children, no severe complications have been noted so far, according to one of the study investigators, Dimitra Kiritsi, MD, of the University of Freiburg, Germany. At the EB World Congress, organized by the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Association (DEBRA), she presented interim data on 18 patients in the trial, emphasizing that the primary aim of the trial was to evaluate the safety of this treatment approach.
Over the 2 years the trial has been underway, 65 adverse events have been reported, of which 4 have been severe. Two of these were bacterial infections that required hospital treatment and the other two were a reduction in the general health condition of the child.
Losartan is an angiotensin-II receptor blocker (ARB) that has been in clinical use for more than 25 years in adults and 15 years in children over the age of 6 years.
The drug may be used for treating recessive dystrophic EB (RDEB) in the future, Dr. Kiritsi said, because it attenuates tumor necrosis factor–beta (TGF-beta) signaling, which is thought to be involved in the fibrotic process. So while it may not target the genetic defect, it could help ameliorate the effects of the disease.
The precursor to REFLECT was a study performed in a mouse disease model of EB (EMBO Mol Med. 2015;7:1211-28) where a reduction in fibrotic scarring was seen with losartan with “remarkable effects” on “mitten” deformity, Dr. Kiritsi said. The results of that study suggested that the earlier treatment with losartan was started in the course of the disease, the better the effect, she added. (Mitten deformity is the result of fused skin between the fingers or toes, and the subsequent buildup of fibrotic tissue causes the hand or foot to contract.)
REFLECT is an investigator-initiated trial that started in 2017 and is being funded by DEBRA International. It is a dual-center, nonrandomized, single-arm study in which children aged 3-16 years with RDEB are treated with losartan for 10 months, with follow-up at 3 months.
Various secondary endpoints were included to look for the first signs of any efficacy: the Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA), the Birmingham Epidermolysis Bullosa Severity Score (BEBS), the Epidermolysis Bullosa Disease Activity and Scarring Index (EBDASI), the Itch Assessment Scale for the Pediatric Burn Patients, and two quality of life indices: the Quality of Life in EB (QOLEB) questionnaire and the Children’s Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI).
Dr. Kiritsi highlighted a few of the secondary endpoint findings, saying that reduced BEBS scores showed there was “amelioration of the patients’ phenotype” and that EBDASI scores also decreased, with “nearly 60% of the patients having significant improvement of their skin disease.” Importantly, itch improved in most of the patients, she said. Reductions in CDLQI were observed, “meaning that quality of life was significantly better at the end of the trial.” There were also decreases in inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and TNF-alpha.
Although there is no validated tool available to assess hand function, Dr. Kiritsi and her team used their own morphometric scoring instrument to measure how far the hand could stretch; their evaluations suggested that this measure improved – or at least did not worsen – with losartan treatment, she noted.
A larger, randomized trial is needed to confirm if there is any benefit of losartan, but first, a new, easy-to-swallow losartan formulation needs to be developed specifically for EB in the pediatric population, Dr. Kiritsi said. Although a pediatric suspension of losartan was previously available, it is no longer on the market, so the next step is to develop a formulation that could be used in a pivotal clinical trial, she noted.
“Losartan faces fewer technical hurdles compared to other novel treatments as it is an established medicine,” Dr. Kiritsi and associates observed in a poster presentation. There are still economic hurdles, however, since “with losartan patents expired, companies cannot expect to recoup an investment into clinical studies” and alternative funding sources are needed.
In 2019, losartan was granted an orphan drug designation for the treatment of EB from both the Food and Drug Administration and the European Medicines Agency, but its use remains off label in children. “We decided to treat children,” Dr. Kiritsi said, “because we wanted to start as early as possible. If you already have mitten deformities, these cannot be reversed.”
DEBRA International funded the study. Dr. Kiritsi received research support from Rheacell GmbH and honoraria or consultation fees from Amryt Pharma and Rheacell GmbH. She has received other support from DEBRA International, EB Research Partnership, Fritz Thyssen Stiftung, German Research Foundation (funding of research projects), and 3R Pharma Consulting and Midas Pharma GmbH (consultation for losartan new drug formulation).
SOURCE: Kiritsi D et al. EB 2020. Poster 47.
REPORTING FROM EB 2020
New Barbie lineup includes a doll with vitiligo
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.
A new line of Barbie dolls unveiled by Mattel earlier this month includes one with vitiligo, much to the delight of clinicians who treat children and adolescents with the condition.
“When I see young children and adolescents with vitiligo, it is very common for me to feel their emotional suffering from their skin condition,” Seemal R. Desai, MD, a dermatologist at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas said in an interview. “Kids can be cruel. Name calling, social ostracizing, [and] effects on self-esteem are all things I have seen amongst my patients and their families in their own struggles with vitiligo.”
According to a brand communications representative from toymaker Mattel, which began manufacturing Barbie dolls in 1959, the company worked with a board-certified dermatologist to include a doll with vitiligo in its 2020 “Fashionistas” line. “As we continue to redefine what it means to be a ‘Barbie’ or look like Barbie, offering a doll with vitiligo in our main doll line allows kids to play out even more stories they see in the world around them,” the representative wrote in an email message. Other dolls debuting as part of the lineup include one with no hair, one with a darker skin tone that uses a gold prosthetic limb, and a Ken doll with long rooted hair (think Jeff Spicoli in “Fast Times at Ridgemont High,” but about six inches longer).
Such efforts to celebrate diversity and inclusiveness go far in helping children and young adults to embrace their skin and their own identities, said Dr. Desai, the immediate past president of the Skin of Color Society and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology board of directors. “One nuance, perhaps even more important, is that the Barbie can help to break down barriers, create awareness, and potentially even reduce bullying, stigma, and lack of knowledge about vitiligo amongst the general public who don’t understand vitiligo,” he said. “I hope the public and social media will embrace this new Barbie. Who knows? Pretty soon, vitiligo may no longer be a ‘thing’ that causes ‘stares’ and ‘glares.’ ”
Referring to the Barbie with no hair in the new line of dolls, the Mattel statement said, “ if a girl is experiencing hair loss for any reason, she can see herself reflected in the line.”
In 2019, Mattel introduced a lineup of Barbie dolls reflecting permanent disabilities, including one with a prosthetic limb. For that effort, the company collaborated with then-12-year-old Jordan Reeves, the “Born Just Right” coauthor “who is on a mission to build creative solutions that help kids with disabilities, to create a play experience that is as representative as possible,” the Mattel representative wrote.