User login
More evidence shows COVID-19’s link to risk for autoimmune disease
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Research from South Korea provides additional evidence for the connection between COVID-19 and an increased risk for autoimmune conditions post infection.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this retrospective study, researchers identified 354,527 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 via polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing from Oct. 8, 2020, to Dec. 31, 2021.
- Researchers compared the COVID-19 group with 6,134,940 healthy individuals who had no evidence of COVID-19 to quantify the risk for autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders.
- Patients were followed until diagnosis, death, or end of study period (Dec. 31, 2021).
TAKEAWAY:
- Risks for alopecia areata, alopecia totalis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis, Crohn’s disease, and sarcoidosis were higher in the COVID-19 group.
- Patients with more severe COVID-19 (admitted to the ICU) were at greater risk for many autoimmune conditions, including alopecia totalis, psoriasis, vitiligo, and vasculitis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results emphasize the need to focus on managing not only the acute stages of COVID-19 itself but also autoimmune diseases as complications of COVID-19,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
Sung Ha Lim, MD, of Yonsei University, Wonju, South Korea, was the first author of the study, published in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and was composed almost exclusively of individuals from a single ethnicity. The study could have included individuals with COVID-19 in the control group who did not undergo PCR testing. The analysis did not include detailed information on each patient, including genetic information, that could have contributed to autoimmune disease risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by a fund from the research program of the Korea Medical Institute and by grants from the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, the Korean Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation of Korea. The authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Respiratory infections, asthma rise before type 2 diabetes
HAMBURG, GERMANY – , shows a longitudinal study looking at comorbidities both 25 years before and 25 years after a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
About 40% of people had respiratory tract infections at the time of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes, compared with 4% who were not diagnosed. Likewise, ear, nose, and throat infections were present in 20% of people at type 2 diabetes diagnosis, compared with around 2% who were not diagnosed. A similar pattern was seen with asthma.
Taken together, the data suggest that subacute inflammation manifesting in asthma as well as the onset of asthma or an acute infection may be a precursor to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
“We have also found that in the years prior to diagnosis, there are associations with infections and inflammatory disorders to a much greater degree than in those people who do not get a diabetes diagnosis but who have very similar demographics,” Adrian Heald, MD, study lead and diabetes consultant from Salford (England) Royal Hospital, said in an interview.
Five years prior to diagnosis, respiratory tract infections were documented in around 23% of patients who were later diagnosed with type 2 diabetes versus 2.5% in those not diagnosed, and a similar pattern was seen for ear, nose, and throat infections and asthma. The findings suggest that patients reporting infections, in addition to other known risk factors for type 2 diabetes, might benefit from diabetes tests and early interventions, if needed.
“These novel insights offer a fascinating and fresh perspective on the onset and natural progression to type 2 diabetes and beyond, suggesting an early phase of inflammation-related disease activity long before any clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made.”
Dr. Heald points out that clinicians may intervene to stave off progression to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis in at risk patients. “At this point, an intervention could relate to lifestyle changes and involve highlighting to the patient that the morbidity they have already accumulated is suggestive of diabetes risk,” he said, adding that, “they may have dyslipidemia, hypertension, and most often excess weight so annual checks of their HbA1c, weight management, and blood pressure would need checking,” he explained.
Moderator Coen Stehouwer, MD, professor of internal medicine at Maastricht University, the Netherlands, commented, “Before clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes there is often a lengthy period of undiagnosed disease and before that, prediabetes, because glucose can be abnormal up to 10 years prior to clinical diagnosis.”
But he added that, “It’s not entirely clear whether the rise seen before clinical diagnosis in this study correlates with undiagnosed diabetes or prediabetes or even if it precedes type 2 diabetes – it might be because inflammation is a common origin for type 2 diabetes and various comorbidities. This might explain how they go together.”
Longitudinal study 25 years before and 25 years after type 2 diagnosis
Dr. Heald presented the findings at a session on inflammation in diabetes at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. The work was also published in Diabetes Therapy.
The researchers wanted to investigate the pattern of comorbidities in the years and decades prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes as well as after: “With the database we used, called DARE [Diabetes Alliance for Research in England], we are able to explore phenomena longitudinally going right back to the beginning of their digital health records, looking at phenotypes over time.”
By mapping significant health issues in people who went on to develop type 2 diabetes alongside those that did not, Dr. Heald managed to develop a continuum spanning 25 years prior and 25 years after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. The researchers also examined relationships between sociodemographic factors and longitudinal health outcomes of relevance to cardiac conditions and lower respiratory tract infections. His talk in Hamburg primarily addressed clinical phenotypes before the point of diagnosis.
Data were drawn from 1,932 people with (1,196) and without (736) type 2 diabetes. Participants in both groups were aged 66-67 years, 43%-46% were women, age at diagnosis was 50-52 years, and participants lived in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom.
In the years leading up to type 2 diagnosis, individuals consistently exhibited a considerable increase in several clinical phenotypes, reported Dr. Heald. Of note, he added, “immediately prior to type 2 diagnosis, there was a significantly greater proportion of hypertension at 35%, respiratory tract infection at 34%, heart disease at 17%, ear, nose, and throat infection at 19%, and asthma at 12%. And by comparison, the corresponding disease trajectory in matched controls was much less dramatic.”
“There is a huge difference in people who went on to receive a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and those who did not, and not just what we’d expect – so hypertension for example or manifestations of renal disease, but importantly inflammatory disorders are more common,” he emphasized.
In addition, a larger signal for ischemic heart disease was seen just before type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
These data suggest that longitudinal clinical histories prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes might offer new information, both genetic and nongenetic, about development of type 2 diabetes in relation to comorbidities.
After type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the proportion of people exhibiting coronary artery disease, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, and infections climbed rapidly before plateauing, reported Dr. Heald. “We also know that individuals with coronary artery disease are more highly represented in socially disadvantaged groups, and this is borne out in the data at 25 years prior and after type 2 diagnosis.”
Dr. Heald has received speaker fees or contributed to advisory boards from Lilly, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Besins, Bayer, Sanofi, and Recordati. Research grants from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Besins. Professor Stehouwer has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, GERMANY – , shows a longitudinal study looking at comorbidities both 25 years before and 25 years after a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
About 40% of people had respiratory tract infections at the time of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes, compared with 4% who were not diagnosed. Likewise, ear, nose, and throat infections were present in 20% of people at type 2 diabetes diagnosis, compared with around 2% who were not diagnosed. A similar pattern was seen with asthma.
Taken together, the data suggest that subacute inflammation manifesting in asthma as well as the onset of asthma or an acute infection may be a precursor to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
“We have also found that in the years prior to diagnosis, there are associations with infections and inflammatory disorders to a much greater degree than in those people who do not get a diabetes diagnosis but who have very similar demographics,” Adrian Heald, MD, study lead and diabetes consultant from Salford (England) Royal Hospital, said in an interview.
Five years prior to diagnosis, respiratory tract infections were documented in around 23% of patients who were later diagnosed with type 2 diabetes versus 2.5% in those not diagnosed, and a similar pattern was seen for ear, nose, and throat infections and asthma. The findings suggest that patients reporting infections, in addition to other known risk factors for type 2 diabetes, might benefit from diabetes tests and early interventions, if needed.
“These novel insights offer a fascinating and fresh perspective on the onset and natural progression to type 2 diabetes and beyond, suggesting an early phase of inflammation-related disease activity long before any clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made.”
Dr. Heald points out that clinicians may intervene to stave off progression to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis in at risk patients. “At this point, an intervention could relate to lifestyle changes and involve highlighting to the patient that the morbidity they have already accumulated is suggestive of diabetes risk,” he said, adding that, “they may have dyslipidemia, hypertension, and most often excess weight so annual checks of their HbA1c, weight management, and blood pressure would need checking,” he explained.
Moderator Coen Stehouwer, MD, professor of internal medicine at Maastricht University, the Netherlands, commented, “Before clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes there is often a lengthy period of undiagnosed disease and before that, prediabetes, because glucose can be abnormal up to 10 years prior to clinical diagnosis.”
But he added that, “It’s not entirely clear whether the rise seen before clinical diagnosis in this study correlates with undiagnosed diabetes or prediabetes or even if it precedes type 2 diabetes – it might be because inflammation is a common origin for type 2 diabetes and various comorbidities. This might explain how they go together.”
Longitudinal study 25 years before and 25 years after type 2 diagnosis
Dr. Heald presented the findings at a session on inflammation in diabetes at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. The work was also published in Diabetes Therapy.
The researchers wanted to investigate the pattern of comorbidities in the years and decades prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes as well as after: “With the database we used, called DARE [Diabetes Alliance for Research in England], we are able to explore phenomena longitudinally going right back to the beginning of their digital health records, looking at phenotypes over time.”
By mapping significant health issues in people who went on to develop type 2 diabetes alongside those that did not, Dr. Heald managed to develop a continuum spanning 25 years prior and 25 years after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. The researchers also examined relationships between sociodemographic factors and longitudinal health outcomes of relevance to cardiac conditions and lower respiratory tract infections. His talk in Hamburg primarily addressed clinical phenotypes before the point of diagnosis.
Data were drawn from 1,932 people with (1,196) and without (736) type 2 diabetes. Participants in both groups were aged 66-67 years, 43%-46% were women, age at diagnosis was 50-52 years, and participants lived in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom.
In the years leading up to type 2 diagnosis, individuals consistently exhibited a considerable increase in several clinical phenotypes, reported Dr. Heald. Of note, he added, “immediately prior to type 2 diagnosis, there was a significantly greater proportion of hypertension at 35%, respiratory tract infection at 34%, heart disease at 17%, ear, nose, and throat infection at 19%, and asthma at 12%. And by comparison, the corresponding disease trajectory in matched controls was much less dramatic.”
“There is a huge difference in people who went on to receive a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and those who did not, and not just what we’d expect – so hypertension for example or manifestations of renal disease, but importantly inflammatory disorders are more common,” he emphasized.
In addition, a larger signal for ischemic heart disease was seen just before type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
These data suggest that longitudinal clinical histories prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes might offer new information, both genetic and nongenetic, about development of type 2 diabetes in relation to comorbidities.
After type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the proportion of people exhibiting coronary artery disease, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, and infections climbed rapidly before plateauing, reported Dr. Heald. “We also know that individuals with coronary artery disease are more highly represented in socially disadvantaged groups, and this is borne out in the data at 25 years prior and after type 2 diagnosis.”
Dr. Heald has received speaker fees or contributed to advisory boards from Lilly, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Besins, Bayer, Sanofi, and Recordati. Research grants from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Besins. Professor Stehouwer has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HAMBURG, GERMANY – , shows a longitudinal study looking at comorbidities both 25 years before and 25 years after a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
About 40% of people had respiratory tract infections at the time of diagnosis with type 2 diabetes, compared with 4% who were not diagnosed. Likewise, ear, nose, and throat infections were present in 20% of people at type 2 diabetes diagnosis, compared with around 2% who were not diagnosed. A similar pattern was seen with asthma.
Taken together, the data suggest that subacute inflammation manifesting in asthma as well as the onset of asthma or an acute infection may be a precursor to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
“We have also found that in the years prior to diagnosis, there are associations with infections and inflammatory disorders to a much greater degree than in those people who do not get a diabetes diagnosis but who have very similar demographics,” Adrian Heald, MD, study lead and diabetes consultant from Salford (England) Royal Hospital, said in an interview.
Five years prior to diagnosis, respiratory tract infections were documented in around 23% of patients who were later diagnosed with type 2 diabetes versus 2.5% in those not diagnosed, and a similar pattern was seen for ear, nose, and throat infections and asthma. The findings suggest that patients reporting infections, in addition to other known risk factors for type 2 diabetes, might benefit from diabetes tests and early interventions, if needed.
“These novel insights offer a fascinating and fresh perspective on the onset and natural progression to type 2 diabetes and beyond, suggesting an early phase of inflammation-related disease activity long before any clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is made.”
Dr. Heald points out that clinicians may intervene to stave off progression to a type 2 diabetes diagnosis in at risk patients. “At this point, an intervention could relate to lifestyle changes and involve highlighting to the patient that the morbidity they have already accumulated is suggestive of diabetes risk,” he said, adding that, “they may have dyslipidemia, hypertension, and most often excess weight so annual checks of their HbA1c, weight management, and blood pressure would need checking,” he explained.
Moderator Coen Stehouwer, MD, professor of internal medicine at Maastricht University, the Netherlands, commented, “Before clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes there is often a lengthy period of undiagnosed disease and before that, prediabetes, because glucose can be abnormal up to 10 years prior to clinical diagnosis.”
But he added that, “It’s not entirely clear whether the rise seen before clinical diagnosis in this study correlates with undiagnosed diabetes or prediabetes or even if it precedes type 2 diabetes – it might be because inflammation is a common origin for type 2 diabetes and various comorbidities. This might explain how they go together.”
Longitudinal study 25 years before and 25 years after type 2 diagnosis
Dr. Heald presented the findings at a session on inflammation in diabetes at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. The work was also published in Diabetes Therapy.
The researchers wanted to investigate the pattern of comorbidities in the years and decades prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes as well as after: “With the database we used, called DARE [Diabetes Alliance for Research in England], we are able to explore phenomena longitudinally going right back to the beginning of their digital health records, looking at phenotypes over time.”
By mapping significant health issues in people who went on to develop type 2 diabetes alongside those that did not, Dr. Heald managed to develop a continuum spanning 25 years prior and 25 years after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. The researchers also examined relationships between sociodemographic factors and longitudinal health outcomes of relevance to cardiac conditions and lower respiratory tract infections. His talk in Hamburg primarily addressed clinical phenotypes before the point of diagnosis.
Data were drawn from 1,932 people with (1,196) and without (736) type 2 diabetes. Participants in both groups were aged 66-67 years, 43%-46% were women, age at diagnosis was 50-52 years, and participants lived in Greater Manchester, United Kingdom.
In the years leading up to type 2 diagnosis, individuals consistently exhibited a considerable increase in several clinical phenotypes, reported Dr. Heald. Of note, he added, “immediately prior to type 2 diagnosis, there was a significantly greater proportion of hypertension at 35%, respiratory tract infection at 34%, heart disease at 17%, ear, nose, and throat infection at 19%, and asthma at 12%. And by comparison, the corresponding disease trajectory in matched controls was much less dramatic.”
“There is a huge difference in people who went on to receive a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and those who did not, and not just what we’d expect – so hypertension for example or manifestations of renal disease, but importantly inflammatory disorders are more common,” he emphasized.
In addition, a larger signal for ischemic heart disease was seen just before type 2 diabetes diagnosis.
These data suggest that longitudinal clinical histories prior to a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes might offer new information, both genetic and nongenetic, about development of type 2 diabetes in relation to comorbidities.
After type 2 diabetes diagnosis, the proportion of people exhibiting coronary artery disease, hypertension, chronic kidney disease, retinopathy, and infections climbed rapidly before plateauing, reported Dr. Heald. “We also know that individuals with coronary artery disease are more highly represented in socially disadvantaged groups, and this is borne out in the data at 25 years prior and after type 2 diagnosis.”
Dr. Heald has received speaker fees or contributed to advisory boards from Lilly, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Besins, Bayer, Sanofi, and Recordati. Research grants from Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and Besins. Professor Stehouwer has declared no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2023
Updated guidance from USPSTF on PrEP for HIV prevention
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recently released their final recommendation update on the use of antiretroviral therapy to prevent HIV infection in adolescents and adults who are at increased risk.1 The Task Force last addressed this topic in 2019; since then, 2 additional antiretroviral regimens have been approved for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The update also includes revised wording on who should consider receiving PrEP.
HIV remains a significant public health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV, and approximately 30,000 new infections occur each year.2 Men who have sex with men account for 68% of new infections, and there are marked racial disparities in both incidence and prevalence of infection, with Black/African Americans accounting for 42% of new infections.2
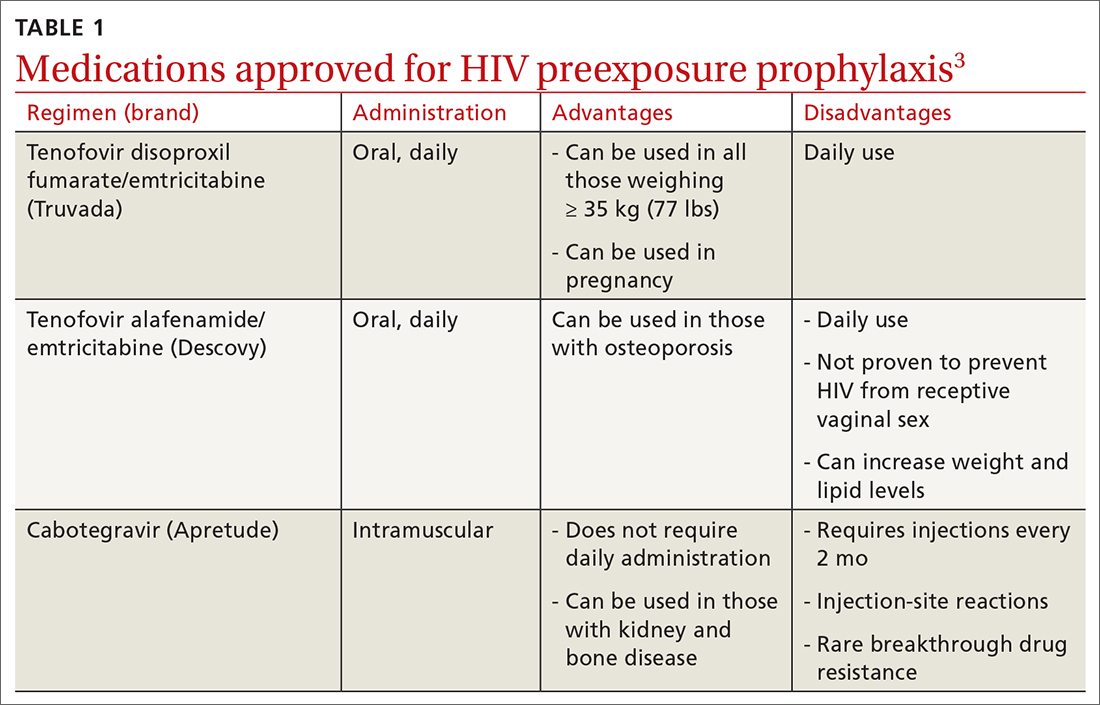
PrEP decreases the risk for HIV by about 50% overall, with higher rates of protection correlated to higher adherence (close to 100% protection with daily adherence to oral regimens).3 The 3 approved regimens for PrEP are outlined in TABLE 13.
Who’s at increased risk? The USPSTF did not find any risk assessment tools with proven accuracy in identifying those at increased risk for HIV infection but did document risk factors and behaviors that can be used to predict risk. They encourage discussion about HIV prevention with all adults and adolescents who are sexually active or who inject drugs.
Those people for whom the Task Force recommends considering PrEP are listed in TABLE 21. However, the USPSTF recommends providing PrEP to anyone who requests it, as they may not want to disclose their risk factors.

What to keep in mind. Family physicians are encouraged to read the full USPSTF report and refer to CDC guidelines on prescribing PrEP, which provide details on each regimen and the routine laboratory testing that should be performed.4 The most important clinical considerations described in the USPSTF report are:
- Before starting PrEP, document a negative HIV antigen/antibody test result and continue to test for HIV every 3 months. PrEP regimens should not be used to treat HIV.
- Document a negative HIV RNA assay if the patient has taken oral PrEP in the past 3 months or injectable PrEP in the past 12 months.
- At PrEP initiation, consider ordering other recommended tests, such as those for kidney function, chronic hepatitis B infection (if using tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine), lipid levels (if using tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine), and other sexually transmitted infection (STIs).
- Encourage the use of condoms, as PrEP does not protect from other STIs.
- Follow up regularly, and at each patient visit stress the need for medication adherence to achieve maximum protection.
1. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final recommendation statement. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
2. CDC. HIV surveillance report: diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2020. Published May 2022. Accessed September 29, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance-report-2020-updated-vol-33.pdf
3. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final evidence review. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
4. CDC. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update: a clinical practice guideline. Accessed September 28, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recently released their final recommendation update on the use of antiretroviral therapy to prevent HIV infection in adolescents and adults who are at increased risk.1 The Task Force last addressed this topic in 2019; since then, 2 additional antiretroviral regimens have been approved for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The update also includes revised wording on who should consider receiving PrEP.
HIV remains a significant public health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV, and approximately 30,000 new infections occur each year.2 Men who have sex with men account for 68% of new infections, and there are marked racial disparities in both incidence and prevalence of infection, with Black/African Americans accounting for 42% of new infections.2
PrEP decreases the risk for HIV by about 50% overall, with higher rates of protection correlated to higher adherence (close to 100% protection with daily adherence to oral regimens).3 The 3 approved regimens for PrEP are outlined in TABLE 13.

Who’s at increased risk? The USPSTF did not find any risk assessment tools with proven accuracy in identifying those at increased risk for HIV infection but did document risk factors and behaviors that can be used to predict risk. They encourage discussion about HIV prevention with all adults and adolescents who are sexually active or who inject drugs.
Those people for whom the Task Force recommends considering PrEP are listed in TABLE 21. However, the USPSTF recommends providing PrEP to anyone who requests it, as they may not want to disclose their risk factors.

What to keep in mind. Family physicians are encouraged to read the full USPSTF report and refer to CDC guidelines on prescribing PrEP, which provide details on each regimen and the routine laboratory testing that should be performed.4 The most important clinical considerations described in the USPSTF report are:
- Before starting PrEP, document a negative HIV antigen/antibody test result and continue to test for HIV every 3 months. PrEP regimens should not be used to treat HIV.
- Document a negative HIV RNA assay if the patient has taken oral PrEP in the past 3 months or injectable PrEP in the past 12 months.
- At PrEP initiation, consider ordering other recommended tests, such as those for kidney function, chronic hepatitis B infection (if using tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine), lipid levels (if using tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine), and other sexually transmitted infection (STIs).
- Encourage the use of condoms, as PrEP does not protect from other STIs.
- Follow up regularly, and at each patient visit stress the need for medication adherence to achieve maximum protection.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recently released their final recommendation update on the use of antiretroviral therapy to prevent HIV infection in adolescents and adults who are at increased risk.1 The Task Force last addressed this topic in 2019; since then, 2 additional antiretroviral regimens have been approved for preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The update also includes revised wording on who should consider receiving PrEP.
HIV remains a significant public health problem in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV, and approximately 30,000 new infections occur each year.2 Men who have sex with men account for 68% of new infections, and there are marked racial disparities in both incidence and prevalence of infection, with Black/African Americans accounting for 42% of new infections.2
PrEP decreases the risk for HIV by about 50% overall, with higher rates of protection correlated to higher adherence (close to 100% protection with daily adherence to oral regimens).3 The 3 approved regimens for PrEP are outlined in TABLE 13.

Who’s at increased risk? The USPSTF did not find any risk assessment tools with proven accuracy in identifying those at increased risk for HIV infection but did document risk factors and behaviors that can be used to predict risk. They encourage discussion about HIV prevention with all adults and adolescents who are sexually active or who inject drugs.
Those people for whom the Task Force recommends considering PrEP are listed in TABLE 21. However, the USPSTF recommends providing PrEP to anyone who requests it, as they may not want to disclose their risk factors.

What to keep in mind. Family physicians are encouraged to read the full USPSTF report and refer to CDC guidelines on prescribing PrEP, which provide details on each regimen and the routine laboratory testing that should be performed.4 The most important clinical considerations described in the USPSTF report are:
- Before starting PrEP, document a negative HIV antigen/antibody test result and continue to test for HIV every 3 months. PrEP regimens should not be used to treat HIV.
- Document a negative HIV RNA assay if the patient has taken oral PrEP in the past 3 months or injectable PrEP in the past 12 months.
- At PrEP initiation, consider ordering other recommended tests, such as those for kidney function, chronic hepatitis B infection (if using tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine), lipid levels (if using tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine), and other sexually transmitted infection (STIs).
- Encourage the use of condoms, as PrEP does not protect from other STIs.
- Follow up regularly, and at each patient visit stress the need for medication adherence to achieve maximum protection.
1. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final recommendation statement. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
2. CDC. HIV surveillance report: diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2020. Published May 2022. Accessed September 29, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance-report-2020-updated-vol-33.pdf
3. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final evidence review. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
4. CDC. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update: a clinical practice guideline. Accessed September 28, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
1. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final recommendation statement. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
2. CDC. HIV surveillance report: diagnoses of HIV infection in the United States and dependent areas, 2020. Published May 2022. Accessed September 29, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/library/reports/surveillance/cdc-hiv-surveillance-report-2020-updated-vol-33.pdf
3. USPSTF. Prevention of acquisition of HIV: preexposure prophylaxis. Final evidence review. Published August 22, 2023. Accessed September 28, 2023. https://uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/document/final-evidence-review/prevention-of-human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-pre-exposure-prophylaxis
4. CDC. Preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2021 update: a clinical practice guideline. Accessed September 28, 2023. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/risk/prep/cdc-hiv-prep-guidelines-2021.pdf
Severity score predicts mortality in pulmonary tuberculosis
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
, based on data from approximately 400 individuals.
Although a mortality risk-prediction score could improve treatment for pulmonary tuberculosis patients, such a score has not been previously reported, wrote Takeshi Osawa, MD, of Fukujuji Hospital, Tokyo, and colleagues.
In a study published in the journal CHEST, the researchers used 252 patients from a previous perspective study of newly diagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis as the development cohort, and recruited 165 additional patients between March 2021 and September 2022.
The primary endpoint was all-cause in-hospital mortality. Based on data from the development group, the researchers found that age 65 years and older and age 80 years and older, hypoxemia, activities of daily living, bilateral pulmonary lesions, lymphocyte count of less than 720 microliters, serum albumin less than 2.86 mg/dL, C-reactive protein (CRP) 3.97 mg/dL or higher, and procalcitonin (PCT) 0.130 ng/mL or higher were predictors of all-cause in hospital mortality.
The researchers used this information to create the disease severity score, known as the AHL score. The AHL included three clinical parameters: activity in daily living (semi-dependent, 1 point; totally dependent, 2 points); hypoxemia (1 point) and lymphocytes (< 720 /mcL, 1 point).
The scoring systems for the three parameters were, respectively, 1 point for semi-dependent and 2 points totally dependent (for activity in daily living), 1 point for presence of hypoxemia, and 1 point for lymphocytes less than 720 per microliter. The researchers stratified the scores into levels of low, intermediate, and high risk, with scores of 0, 1-2, and 3-4, respectively.
All-cause in hospital mortality occurred in 39 (15.5%) and 17 (10.3%) of patients in the developmental and validation cohorts, respectively.
The AHL score effectively predicted mortality, dividing patients into three groups of 1.3% low-risk, 8.9% intermediate risk, and 39.3% high-risk in the validation cohort, with a Harrell’s c-statistic of 0.842.
The corresponding numbers for the development cohort were 0, 13.5%, and 55.8%, with a c-statistic of 0.902.
The findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of data from “smear-negative” patients who were treated as outpatients, and more research is needed to determine the applicability of the AHL score in an outpatient population, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on long-term mortality in surviving patients who were discharged, and the reliance on assessments that can be performed only in clinical settings in developed countries, they said.
However, the results support the feasibility of the AHL score in clinical settings to accurately predict mortality in patients with pulmonary TB, and may help optimize treatments for this population, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. All authors disclosed nonfinancial support in the form of measuring reagents from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation during the study but had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST
Pulmonary aspergillosis predicts poor outcomes in critically ill flu patients
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Critically ill influenza patients with associated pulmonary aspergillosis were more than twice as likely to die in intensive care than those without the added infection, based on data from a meta-analysis of more than 1,700 individuals.
Reports of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (IAPA) are rising in critically ill patients, but data on risk factors, clinical features, and outcomes are limited, Lawrence Y. Lu, MD, of The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane, Australia, and colleagues wrote. In addition, diagnosis of IAPA can be challenging, and many clinicians report low awareness of the condition.
In a study published in the journal Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 10 observational studies including 1,720 critically ill influenza patients aged 16 years and older; of these, 331 had IAPA, for a prevalence of 19.2%. The primary outcomes were all-cause mortality in the hospital and in the ICU. Secondary outcomes included ICU length of stay, hospital length of stay, and the need for supportive care (invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, pressor support, and extracorporeal membranous oxygenation).
Overall, mortality among flu patients in the ICU was significantly higher for those with IAPA than those without IAPA (45.0% vs. 23.8%, respectively), as was all-cause mortality (46.4% vs. 26.2%, respectively; odds ratio, 2.6 and P < .001 for both ICU and all-cause mortality).
Factors significantly associated with an increased risk for IAPA included organ transplant (OR, 4.8), hematogenous malignancy (OR, 2.5), being immunocompromised in some way (OR, 2.2), and prolonged corticosteroid use prior to hospital admission (OR, 2.4).
IAPA also was associated with more severe disease, a higher rate of complications, longer ICU stays, and a greater need for organ supports, the researchers noted. Clinical features not significantly more common in patients with IAPA included fever, hemoptysis, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
The findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design of the included studies and inability to control for all potential confounders, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the variations in study design, variability of practice patterns across locations, and inclusion of data mainly from countries of high socioeconomic status.
“Given the apparent waning of the COVID-19 pandemic and re-emergence of influenza, our analysis also revealed other gaps in the current literature, including the need to validate newer diagnostic methods and to develop a system to measure severity of IAPA,” the researchers added.
However, the current study results reflect IAPA prevalence from previous studies, and support the need to have a lower threshold for IAPA testing and initiation of antifungal treatment, even with limited data for clinical guidance, they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL CHEST
Preparing for the viral trifecta: RSV, influenza, and COVID-19
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
New armamentaria available to fight an old disease.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
In July 2023, nirsevimab (Beyfortus), a monoclonal antibody, was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the prevention of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease in infants and children younger than 2 years of age. On Aug. 3, 2023, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended routine use of it for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during or entering their first RSV season. Its use is also recommended for certain children 8-19 months of age who are at increased risk for severe RSV disease at the start of their second RSV season. Hearing the approval, I immediately had a flashback to residency, recalling the multiple infants admitted each fall and winter exhibiting classic symptoms including cough, rhinorrhea, nasal flaring, retractions, and wheezing with many having oxygen requirements and others needing intubation. Only supportive care was available.
RSV is the leading cause of infant hospitalizations. Annually, the CDC estimates there are 50,000-80,000 RSV hospitalizations and 100-300 RSV-related deaths in the United States in persons younger than 5 years of age. While premature infants have the highest rates of hospitalization (three times a term infant) about 79% of hospitalized children younger than 2 years have no underlying medical risks.1 The majority of children will experience RSV as an upper respiratory infection within the first 2 years of life. However, severe disease requiring hospitalization is more likely to occur in premature infants and children younger than 6 months; children younger than 2 with congenital heart disease and/or chronic lung disease; children with severe cystic fibrosis; as well as the immunocompromised child and individuals with neuromuscular disorders that preclude clearing mucous secretions or have difficulty swallowing.
Palivizumab (Synagis), the first monoclonal antibody to prevent RSV in infants was licensed in 1998. Its use was limited to infants meeting specific criteria developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Only 5% of infants had access to it. It was a short-acting agent requiring monthly injections, which were very costly ($1,661-$2,584 per dose). Eligible infants could receive up to five injections per season. Several studies proved its use was not cost beneficial.
What are the advantages of nirsevimab? It’s a long-acting monoclonal antibody. Only one dose is required per season. Costs will significantly diminish. It is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months of age born during RSV season. Those children 8-19 months at risk for severe RSV disease can receive it prior to the start of their second RSV season. During RSV season (October 1 to March 31), the initial dose should be administered to newborns just prior to hospital discharge. Older infants and newborns who did not receive it prior to hospital discharge can receive it at their medical home. Newborns should receive it within the first week of life. It is covered by the Vaccine for Children Program. Simultaneous administration with routine childhood immunizations is recommended. Finally, RSV season may vary in tropical areas (Southern Florida, Puerto Rico. etc.) and Alaska. The timing of nirsevimab administration should be based on local RSV activity provided by state and local authorities.
In addition, the FDA approved an RSV vaccine (Abrysvo) for use in adults at least 60 years of age and in pregnant women at 32-36 weeks’ gestation. The latter is administered to prevent lower respiratory tract infection in infants from birth to 6 months. Recommendations have been published for administration in nonpregnant adults. Specific information is forthcoming in terms timing of administration of nirsevimab in infants whose mothers receive Abrysvo.
RSV season is quickly approaching. Detailed recommendations for administration and FAQ questions related to nirsevimab and palivizumab can be found at https://www.aap.org or https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
Influenza
So, what about influenza? Vaccine composition has been tweaked to match the circulating viruses but the recommended age for annual routine administration remains unchanged. All persons at least 6 months of age should be vaccinated. Children between 6 months and 8 years need two doses at least 4 weeks apart when receiving vaccine for the first time. Immunizing everyone in the household is encouraged especially if there are household contacts at risk for developing severe disease, including infants too young to be vaccinated. Keep in mind children may be coinfected with multiple viruses. Adams and colleagues reviewed the prevalence of coinfection of influenza and Sars-CoV-2 in persons younger than 18 years reported to three CDC surveillance platforms during the 2021-2022 season.2 Thirty-two of 575 hospitalized (6%) coinfections were analyzed and 7 of 44 (16%) deaths. Compared with patients without coinfections, the coinfected patients were more likely to require mechanical ventilation (13% vs. 4%) or CPAP (16% vs. 6%). Only 4 of 23 who were influenza vaccine eligible were vaccinated. Of seven coinfected children who died, none had received influenza vaccine and only one received an antiviral. Only 5 of 31 (16%) infected only with influenza were vaccinated.3
Influenza activity was lower than usual during the 2021-2022 season. However, this report revealed underuse of both influenza vaccine and antiviral therapy, both of which are routinely recommended.
COVID-19
What’s new with COVID-19? On Sept. 12, 2023, ACIP recommended that everyone at least 6 months of age receive the 2023-2024 (monovalent, XBB containing) COVID-19 vaccines. Children at least 5 years of age need one dose and those younger need one or two doses depending on the number of doses previously received. Why the change? Circulating variants continue to change. There is a current uptick in cases including hospitalizations (7.7%) and deaths (4.5%) and it’s just the beginning of the season.4 Symptoms, risk groups and complications have not changed. The primary goal is to prevent infection, hospitalization, long term complications, and death.
We are now armed with the most up-to-date interventions to help prevent the acquisition of these three viruses. Our next step is recommending and delivering them to our patients.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She reported no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1.Suh M et al. J Infect Dis. 2022;226(Suppl 2):S154-36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiac120.
2. Adams K et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:1589-96. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7150a4.
3. Pingali C et al. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Aug 25;72:912-9. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7234a3.
4. CDC Covid Data Tracker.
No need to restrict hep C DAA therapy based on alcohol use
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Alcohol use at any level, including alcohol use disorder (AUD), is not associated with decreased odds of a sustained virologic response (SVR) to direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Therefore, DAA therapy should not be withheld from patients who consume alcohol.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers examined electronic health records for 69,229 patients (mean age, 63 years; 97% men; 50% non-Hispanic White) who started DAA therapy through the Department of Veterans Affairs between 2014 and 2018.
- Alcohol use categories were abstinent without history of AUD, abstinent with history of AUD, lower-risk consumption, moderate-risk consumption, and high-risk consumption or AUD.
- The primary outcome was SVR, which was defined as undetectable HCV RNA for 12 weeks to 6 months after completion of DAA treatment.
TAKEAWAY:
- Close to half (46.6%) of patients were abstinent without AUD, 13.3% were abstinent with AUD, 19.4% had lower-risk consumption, 4.5% had moderate-risk consumption, and 16.2% had high-risk consumption or AUD.
- Overall, 94.4% of those who started on DAA treatment achieved SVR.
- After adjustment, there was no evidence that any alcohol category was significantly associated with decreased odds of achieving SVR. The odds ratios were 1.09 for abstinent without AUD history, 0.92 for abstinent with AUD history, 0.96 for moderate-risk consumption, and 0.95 for high-risk consumption or AUD.
- SVR did not differ by baseline stage of hepatic fibrosis, as measured by Fibrosis-4 score of 3.25 or less versus greater than 3.25.
IN PRACTICE:
“Achieving SVR has been shown to be associated with reduced risk of post-SVR outcomes, including hepatocellular carcinoma, liver-related mortality, and all-cause mortality. Our findings suggest that DAA therapy should be provided and reimbursed despite alcohol consumption or history of AUD. Restricting access to DAA therapy according to alcohol consumption or AUD creates an unnecessary barrier to patients accessing DAA therapy and challenges HCV elimination goals,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
Emily J. Cartwright, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, led the study, which was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was observational and subject to potential residual confounding. To define SVR, HCV RNA was measured 6 months after DAA treatment ended, which may have resulted in a misclassification of patients who experienced viral relapse. Most participants were men born between 1945 and 1965, and the results may not be generalizable to women and/or older and younger patients.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Dr. Cartwright reported no disclosures. Two coauthors disclosed fees from pharmaceutical companies outside the submitted work.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
As U.S. syphilis cases rise, those at the epicenter scramble
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It was just a routine checkup – or so she thought. But this time, Marnina Miller’s love interest came along. The pair headed to an STD clinic in Houston, where Ms. Miller worked, to get tested for syphilis and HIV. With an already compromised immune system because of an HIV diagnosis 9 years ago, it is critical for Ms. Miller to ensure she is clear of any other diseases. She tested negative for syphilis. Her partner, on the other hand, tested positive for latent (or stage 3) syphilis.
Syphilis has been on the rise in the United States for more than 2 decades. From 2017 to 2021, the number of cases shot up 75% (to 176,713), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. particularly among women and people of color, according to the Houston Health Department. This summer, drugmaker Pfizer reported a widespread shortage of the antibiotic penicillin, which is used to cure early-stage syphilis and treat latent syphilis.
“I was immediately scared,” Ms. Miller said. “I was nervous about what that meant for me because we did kiss before. And, although I am openly living with HIV, there is little education around syphilis and how it is contracted.”
The Houston Health Department has been warning Houstonites to take this public health crisis seriously by practicing safe sex and getting tested if they’re sexually active. There has also been a ninefold increase in congenital syphilis in Houston and Harris County, Tex. To help curb the spread, residents can now get free testing for sexually transmitted diseases at Houston health clinics.
“It is crucial for pregnant women to seek prenatal care and syphilis testing to protect themselves from an infection that could result in the deaths of their babies,” said Marlene McNeese Ward, deputy assistant director of the Houston Health Department’s Bureau of HIV/STI and Viral Hepatitis Prevention. She said a pregnant woman needs to get tested for syphilis three times during her pregnancy.
There are four stages of syphilis: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Oral, anal, and vaginal sex are some of the ways the disease can spread. Some people who contract syphilis never have symptoms and could have the disease for years without knowing.
Penicillin can cure both syphilis and congenital syphilis. The antibiotic cannot reverse damage done to organs via infection, especially if the disease has greatly progressed before treatment.
Sergino Nicolas, MD, creates TikTok videos and Instagram reels to raise awareness about the outbreak. The Pittsburgh-based emergency medical doctor said there is often a “nonchalant” attitude toward STDs among some people in their 20s and 30s. Being unaware of the consequences of syphilis could drive that attitude. “With thoughts like ‘I can just get treated,’ I think there is danger in that, because when you have these infections, [irreversible] complications can occur,” he said.
Preconceived notions among this age group that oral sex is a safer alternative to vaginal or anal sex is also common, Dr. Nicolas said. “Any time you might have infected secretions or be exposed to mucosa, including the vaginal mucosa, that can result in spreading the infection.”
Women of color have been particularly impacted by the outbreak. Syphilis has a wide range of signs and symptoms, and that could play a major role, Dr. Nicolas said. Lack of education on the dangers of unprotected sex, particularly with multiple sexual partners, could be another reason, as this increases rates of yeast infections and STDs, he said.
Another potential factor: Sexually explicit music and entertainment can also cloud judgment on whether to engage in sexual activity, Dr. Nicolas said. Younger generations can especially fall prey to this. “There have been new artists over the past few months that have really been pushing for ‘female empowerment’ in a sense,” he said. “At the same time, they can also push a narrative more so pertaining to promiscuity, which could result in certain psychological effects” that could lead to unsafe sex practices.
Public health activists in Houston are spreading the word on the importance of getting tested for STDs. Kevin Anderson is the founder of the T.R.U.T.H. Project, a Houston-based nonprofit that educates and mobilizes LGBTQ communities of color through social arts that promote sexual, mental, and physical health.
While celebrating its 10th anniversary, T.R.U.T.H. Project is creatively promoting syphilis education and awareness. The organization’s recent events have included an open-mic night called “Heart and Soul,” with free STD testing on site for attendees. It also hosted a sex-positive night aiming to educate attendees about STDs and safe sex practices. Self-love, self-care, and self-awareness of one’s body is one of the group’s most prominent messages. “If something feels or looks different, love yourself enough to be proactive in following up to find out what’s going on – because avoidance leads to outbreaks,” Mr. Anderson said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Three antibiotic regimens show similar effectiveness for CAP
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adults with nonsevere community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) responded nearly equally to three first-line and alternative antibiotic regimens, based on data from more than 23,000 individuals.
Current recommendations for the treatment of CAP vary across guidelines, wrote Anthony D. Bai, MD, of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ont., and colleagues. However, most guidelines were based on studies that were not powered to examine the effect of treatments on mortality, they said.
“Large observational studies could fill this gap by comparing multiple treatment arms, including patients not well represented in trials, and having a large sample size powered to detect a difference in mortality,” they noted.
In a study published in Chest, the researchers reviewed data from 23,512 consecutive patients admitted to 19 hospitals in Canada for CAP between 2015 and 2021. Patients were treated with one of four initial antibiotic regimens: beta-lactam plus macrolide (BL+M), beta-lactam alone (BL), respiratory fluoroquinolone (FQ), or beta-lactam plus doxycycline (BL+D). Of these, BL+M is generally considered the first-line regimen, the researchers noted.
Patients were divided into four groups according to their initial antibiotic treatment within 48 hours of admission; 9,340 patients received BL+M, 9,146 received BL, 4,510 received FQ, and 516 received BL+D. The duration of any antibiotic that was active against CAP was at least 4 days, or until hospital discharge or death.
The primary outcome was all-cause in-hospital mortality, which was 7.5%, 9.7%, 6.7%, and 6.0% for patients in each of the four treatment groups, respectively. Relative to the first-line therapy of BL+M, the adjusted risk differences for BL, FQ, and BL+D were 1.5%, –0.9%, and –1.9%, respectively.
The adjusted in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between BL+M and either FQ or BL+D, but the difference of 1.5% seen with BL alone suggested a “small but clinically important difference,” the researchers noted.
Key secondary outcomes were the length of hospital stay and being discharged alive. The median length of stay was 4.6 days for BL+M, 5.2 days for BL, 4.6 days for FQ, and 6.0 days for BL+D. Patients treated with BL also had a longer time to hospital discharge, which suggests that BL may not be as effective as the other regimens, the researchers said. In addition, patients in the BL group had a subdistribution hazard ratio of 0.90 for being discharged alive, compared with the BL+M group after adjustment with propensity scores and overlap weighting.
Overall, the results support dropping BL as a first-line regimen in the current ATS/IDSA guidelines, and support the recommendation of BL+M, FQ, and BL+D as similarly effective options as listed in other guidelines, applied according to other patient characteristics. For example, “Doxycycline may be preferred over a macrolide in many cases such as macrolide allergy, prolonged QT, or high [Clostridioides] difficile risk,” the researchers said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the lack of follow-up data after hospital discharge.
However, the results were strengthened by the large sample size and use of a comprehensive database that allowed adjustment for many variables, as well as the availability of complete follow-up data for the time spent in the hospital. Based on this study, clinicians may choose a respiratory fluoroquinolone, a beta-lactam plus macrolide, or a beta-lactam plus doxycycline for equally effective antibiotic treatment of CAP, based on the best fit for each individual patient, the researchers concluded.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM CHEST
Creatine may improve key long COVID symptoms: Small study
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
Taking creatine as a supplement for 6 months appears to significantly improve clinical features of post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome (PVFS or long COVID), a small randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded study suggests.
Researchers, led by Jelena Slankamenac, with Applied Bioenergetics Lab, Faculty of Sport and PE, University of Novi Sad, Serbia, published their findings in Food, Science & Nutrition .
“This is the first human study known to the authors that evaluated the efficacy and safety of supplemental creatine for fatigue, tissue bioenergetics, and patient-reported outcomes in patients with post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
They say the findings may be attributed to creatine’s “energy-replenishing and neuroprotective activity.”
Significant reductions in symptoms
Researchers randomized the 12 participants into two groups of 6 each. The creatine group received 4 g creatine monohydrate per day, while the placebo group received the same amount of inulin.
At 3 months, dietary creatine supplements produced a significant reduction in fatigue, compared with baseline values ( P = .04) and significantly improved scores for several long COVID–related symptoms, including loss of taste, breathing difficulties, body aches, headache, and difficulties concentrating) ( P < .05), the researchers report.
Intervention effect sizes were assessed by Cohen statistics, with a d of at least 0.8 indicating a large effect.
Among highlights of the results were that patients reported a significant 77.8% drop in scores for concentration difficulties at the 3-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 1.19) and no concentration difficulties at the 6-month follow-up (Cohen’s effect, d = 2.46).
Total creatine levels increased in several locations across the brain (as much as 33% for right parietal white matter). No changes in tissue creatine levels were found in the placebo group during the trial.
“Since PVFS is characterized by impaired tissue bioenergetics ..., supplemental creatine might be an effective dietary intervention to uphold brain creatine in post–COVID-19 fatigue syndrome,” the authors write.
The authors add that creatine supplements for long COVID patients could benefit organs beyond the brain as participants saw “a significant drop in lung and body pain after the intervention.”
Unanswered questions
Some experts said the results should be interpreted with caution.
“This research paper is very interesting,” says Nisha Viswanathan, MD, director of the long COVID program at University of California, Los Angeles, “but the limited number of patients makes the results difficult to generalize.”
Dr. Viswanathan, who was not part of the study, pointed out that the patients included in this study had a recent COVID infection (under 3 months).
“Acute COVID infection can take up to 3 months to resolve,” she says. “We define patients with long COVID as those with symptoms lasting greater than 3 months. Therefore, these patients could have had improvements in their fatigue due to the natural course of the illness rather than creatine supplementation.”
Alba Azola, MD, assistant professor in the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said she also was troubled by the window of 3 months for recent COVID infection.
She said she would like to see results for patients who have ongoing symptoms for at least 6 months after infection, especially given creatine supplements’ history in research.
Creatine supplements for other conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome, have been tested for nearly 2 decades, she pointed out, with conflicting findings, something the authors acknowledge in the paper.
“I think it’s premature to say (creatine) is the key,” she says. She added that the small sample size is important to consider given the heterogeneity of patients with long COVID.
That said, Dr. Azola says, she applauds all efforts to find treatments for long COVID, especially randomized, controlled studies like this one.
No major side effects
No major side effects were reported for either intervention, except for transient mild nausea reported by one patient after taking creatine.
Compliance with the intervention was 90.6% ± 3.5% in the creatine group and 95.3% ± 5.0% in the control group (P = .04).
Participants were eligible for inclusion if they were 18-65 years old, had a positive COVID test within the last 3 months (documented by a valid polymerase chain reaction [PCR] or antigen test performed in a COVID-19–certified lab); had moderate to severe fatigue; and at least one additional COVID-related symptom, including loss of taste or smell, breathing trouble, lung pain, body aches, headaches, or difficulties concentrating.
The authors acknowledge that they selected a sample of young to middle-aged adults experiencing moderate long COVID symptoms, and it’s unknown whether creatine is equally effective in other PVFS populations, such as elderly people, children, or patients with less or more severe disease.
Senior author Dr. Sergei Ostojic serves as a member of the Scientific Advisory Board on creatine in health and medicine (AlzChem LLC). He co-owns a patent for “Supplements Based on Liquid Creatine” at the European Patent Office. He has received research support related to creatine during the past 36 months from the Serbian Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development; Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Scientific Research; Alzchem GmbH; ThermoLife International; and Hueston Hennigan LLP. He does not own stocks and shares in any organization. Other authors declare no known relevant financial interests. Dr. Viswanathan and Dr. Azola report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM FOOD, SCIENCE & NUTRITION


