User login
For MD-IQ use only
Cannabis in Cancer: What Oncologists and Patients Should Know
first, and oncologists may be hesitant to broach the topic with their patients.
Updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) on the use of cannabis and cannabinoids in adults with cancer stress that it’s an important conversation to have.
According to the ASCO expert panel, access to and use of cannabis alongside cancer care have outpaced the science on evidence-based indications, and overall high-quality data on the effects of cannabis during cancer care are lacking. While several observational studies support cannabis use to help ease chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, the literature remains more divided on other potential benefits, such as alleviating cancer pain and sleep problems, and some evidence points to potential downsides of cannabis use.
Oncologists should “absolutely talk to patients” about cannabis, Brooke Worster, MD, medical director for the Master of Science in Medical Cannabis Science & Business program at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, told Medscape Medical News.
“Patients are interested, and they are going to find access to information. As a medical professional, it’s our job to help guide them through these spaces in a safe, nonjudgmental way.”
But, Worster noted, oncologists don’t have to be experts on cannabis to begin the conversation with patients.
So, “let yourself off the hook,” Worster urged.
Plus, avoiding the conversation won’t stop patients from using cannabis. In a recent study, Worster and her colleagues found that nearly one third of patients at 12 National Cancer Institute-designated cancer centers had used cannabis since their diagnosis — most often for sleep disturbance, pain, stress, and anxiety. Most (60%) felt somewhat or extremely comfortable talking to their healthcare provider about it, but only 21.5% said they had done so. Even fewer — about 10% — had talked to their treating oncologist.
Because patients may not discuss cannabis use, it’s especially important for oncologists to open up a line of communication, said Worster, also the enterprise director of supportive oncology at the Thomas Jefferson University.
Evidence on Cannabis During Cancer Care
A substantial proportion of people with cancer believe cannabis can help manage cancer-related symptoms.
In Worster’s recent survey study, regardless of whether patients had used cannabis, almost 90% of those surveyed reported a perceived benefit. Although 65% also reported perceived risks for cannabis use, including difficulty concentrating, lung damage, and impaired memory, the perceived benefits outweighed the risks.
Despite generally positive perceptions, the overall literature on the benefits of cannabis in patients with cancer paints a less clear picture.
The ASCO guidelines, which were based on 13 systematic reviews and five additional primary studies, reported that cannabis can improve refractory, chemotherapy-induced nausea or vomiting when added to guideline-concordant antiemetic regimens, but that there is no clear evidence of benefit or harm for other supportive care outcomes.
The “certainty of evidence for most outcomes was low or very low,” the ASCO authors wrote.
The ASCO experts explained that, outside the context of a clinical trial, the evidence is not sufficient to recommend cannabis or cannabinoids for managing cancer pain, sleep issues, appetite loss, or anxiety and depression. For these outcomes, some studies indicate a benefit, while others don’t.
Real-world data from a large registry study, for instance, have indicated that medical cannabis is “a safe and effective complementary treatment for pain relief in patients with cancer.” However, a 2020 meta-analysis found that, in studies with a low risk for bias, adding cannabinoids to opioids did not reduce cancer pain in adults with advanced cancer.
There can be downsides to cannabis use, too. In one recent study, some patients reported feeling worse physically and psychologically compared with those who didn’t use cannabis. Another study found that oral cannabis was associated with “bothersome” side effects, including sedation, dizziness, and transient anxiety.
The ASCO guidelines also made it clear that cannabis or cannabinoids should not be used as cancer-directed treatment, outside of a clinical trial.
Talking to Patients About Cannabis
Given the level of evidence and patient interest in cannabis, it is important for oncologists to raise the topic of cannabis use with their patients.
To help inform decision-making and approaches to care, the ASCO guidelines suggest that oncologists can guide care themselves or direct patients to appropriate “unbiased, evidence-based” resources. For those who use cannabis or cannabinoids outside of evidence-based indications or clinician recommendations, it’s important to explore patients’ goals, educate them, and try to minimize harm.
One strategy for broaching the topic, Worster suggested, is to simply ask patients if they have tried or considered trying cannabis to control symptoms like nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, or cancer pain.
The conversation with patients should then include an overview of the potential benefits and potential risks for cannabis use as well as risk reduction strategies, Worster noted.
But “approach it in an open and nonjudgmental frame of mind,” she said. “Just have a conversation.”
Discussing the formulation and concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) in products matters as well.
Will the product be inhaled, ingested, or topical? Inhaled cannabis is not ideal but is sometimes what patients have access to, Worster explained. Inhaled formulations tend to have faster onset, which might be preferable for treating chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, whereas edible formulations may take a while to start working.
It’s also important to warn patients about taking too much, she said, explaining that inhaling THC at higher doses can increase the risk for cardiovascular effects, anxiety, paranoia, panic, and psychosis.
CBD, on the other hand, is anti-inflammatory, but early data suggest it may blunt immune responses in high doses and should be used cautiously by patients receiving immunotherapy.
Worster noted that as laws change and the science advances, new cannabis products and formulations will emerge, as will artificial intelligence tools for helping to guide patients and clinicians in optimal use of cannabis for cancer care. State websites are a particularly helpful tool for providing state-specific medical education related to cannabis laws and use, as well, she said.
The bottom line, she said, is that talking to patients about the ins and outs of cannabis use “really matters.”
Worster disclosed that she is a medical consultant for EO Care.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
first, and oncologists may be hesitant to broach the topic with their patients.
Updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) on the use of cannabis and cannabinoids in adults with cancer stress that it’s an important conversation to have.
According to the ASCO expert panel, access to and use of cannabis alongside cancer care have outpaced the science on evidence-based indications, and overall high-quality data on the effects of cannabis during cancer care are lacking. While several observational studies support cannabis use to help ease chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, the literature remains more divided on other potential benefits, such as alleviating cancer pain and sleep problems, and some evidence points to potential downsides of cannabis use.
Oncologists should “absolutely talk to patients” about cannabis, Brooke Worster, MD, medical director for the Master of Science in Medical Cannabis Science & Business program at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, told Medscape Medical News.
“Patients are interested, and they are going to find access to information. As a medical professional, it’s our job to help guide them through these spaces in a safe, nonjudgmental way.”
But, Worster noted, oncologists don’t have to be experts on cannabis to begin the conversation with patients.
So, “let yourself off the hook,” Worster urged.
Plus, avoiding the conversation won’t stop patients from using cannabis. In a recent study, Worster and her colleagues found that nearly one third of patients at 12 National Cancer Institute-designated cancer centers had used cannabis since their diagnosis — most often for sleep disturbance, pain, stress, and anxiety. Most (60%) felt somewhat or extremely comfortable talking to their healthcare provider about it, but only 21.5% said they had done so. Even fewer — about 10% — had talked to their treating oncologist.
Because patients may not discuss cannabis use, it’s especially important for oncologists to open up a line of communication, said Worster, also the enterprise director of supportive oncology at the Thomas Jefferson University.
Evidence on Cannabis During Cancer Care
A substantial proportion of people with cancer believe cannabis can help manage cancer-related symptoms.
In Worster’s recent survey study, regardless of whether patients had used cannabis, almost 90% of those surveyed reported a perceived benefit. Although 65% also reported perceived risks for cannabis use, including difficulty concentrating, lung damage, and impaired memory, the perceived benefits outweighed the risks.
Despite generally positive perceptions, the overall literature on the benefits of cannabis in patients with cancer paints a less clear picture.
The ASCO guidelines, which were based on 13 systematic reviews and five additional primary studies, reported that cannabis can improve refractory, chemotherapy-induced nausea or vomiting when added to guideline-concordant antiemetic regimens, but that there is no clear evidence of benefit or harm for other supportive care outcomes.
The “certainty of evidence for most outcomes was low or very low,” the ASCO authors wrote.
The ASCO experts explained that, outside the context of a clinical trial, the evidence is not sufficient to recommend cannabis or cannabinoids for managing cancer pain, sleep issues, appetite loss, or anxiety and depression. For these outcomes, some studies indicate a benefit, while others don’t.
Real-world data from a large registry study, for instance, have indicated that medical cannabis is “a safe and effective complementary treatment for pain relief in patients with cancer.” However, a 2020 meta-analysis found that, in studies with a low risk for bias, adding cannabinoids to opioids did not reduce cancer pain in adults with advanced cancer.
There can be downsides to cannabis use, too. In one recent study, some patients reported feeling worse physically and psychologically compared with those who didn’t use cannabis. Another study found that oral cannabis was associated with “bothersome” side effects, including sedation, dizziness, and transient anxiety.
The ASCO guidelines also made it clear that cannabis or cannabinoids should not be used as cancer-directed treatment, outside of a clinical trial.
Talking to Patients About Cannabis
Given the level of evidence and patient interest in cannabis, it is important for oncologists to raise the topic of cannabis use with their patients.
To help inform decision-making and approaches to care, the ASCO guidelines suggest that oncologists can guide care themselves or direct patients to appropriate “unbiased, evidence-based” resources. For those who use cannabis or cannabinoids outside of evidence-based indications or clinician recommendations, it’s important to explore patients’ goals, educate them, and try to minimize harm.
One strategy for broaching the topic, Worster suggested, is to simply ask patients if they have tried or considered trying cannabis to control symptoms like nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, or cancer pain.
The conversation with patients should then include an overview of the potential benefits and potential risks for cannabis use as well as risk reduction strategies, Worster noted.
But “approach it in an open and nonjudgmental frame of mind,” she said. “Just have a conversation.”
Discussing the formulation and concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) in products matters as well.
Will the product be inhaled, ingested, or topical? Inhaled cannabis is not ideal but is sometimes what patients have access to, Worster explained. Inhaled formulations tend to have faster onset, which might be preferable for treating chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, whereas edible formulations may take a while to start working.
It’s also important to warn patients about taking too much, she said, explaining that inhaling THC at higher doses can increase the risk for cardiovascular effects, anxiety, paranoia, panic, and psychosis.
CBD, on the other hand, is anti-inflammatory, but early data suggest it may blunt immune responses in high doses and should be used cautiously by patients receiving immunotherapy.
Worster noted that as laws change and the science advances, new cannabis products and formulations will emerge, as will artificial intelligence tools for helping to guide patients and clinicians in optimal use of cannabis for cancer care. State websites are a particularly helpful tool for providing state-specific medical education related to cannabis laws and use, as well, she said.
The bottom line, she said, is that talking to patients about the ins and outs of cannabis use “really matters.”
Worster disclosed that she is a medical consultant for EO Care.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
first, and oncologists may be hesitant to broach the topic with their patients.
Updated guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) on the use of cannabis and cannabinoids in adults with cancer stress that it’s an important conversation to have.
According to the ASCO expert panel, access to and use of cannabis alongside cancer care have outpaced the science on evidence-based indications, and overall high-quality data on the effects of cannabis during cancer care are lacking. While several observational studies support cannabis use to help ease chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, the literature remains more divided on other potential benefits, such as alleviating cancer pain and sleep problems, and some evidence points to potential downsides of cannabis use.
Oncologists should “absolutely talk to patients” about cannabis, Brooke Worster, MD, medical director for the Master of Science in Medical Cannabis Science & Business program at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, told Medscape Medical News.
“Patients are interested, and they are going to find access to information. As a medical professional, it’s our job to help guide them through these spaces in a safe, nonjudgmental way.”
But, Worster noted, oncologists don’t have to be experts on cannabis to begin the conversation with patients.
So, “let yourself off the hook,” Worster urged.
Plus, avoiding the conversation won’t stop patients from using cannabis. In a recent study, Worster and her colleagues found that nearly one third of patients at 12 National Cancer Institute-designated cancer centers had used cannabis since their diagnosis — most often for sleep disturbance, pain, stress, and anxiety. Most (60%) felt somewhat or extremely comfortable talking to their healthcare provider about it, but only 21.5% said they had done so. Even fewer — about 10% — had talked to their treating oncologist.
Because patients may not discuss cannabis use, it’s especially important for oncologists to open up a line of communication, said Worster, also the enterprise director of supportive oncology at the Thomas Jefferson University.
Evidence on Cannabis During Cancer Care
A substantial proportion of people with cancer believe cannabis can help manage cancer-related symptoms.
In Worster’s recent survey study, regardless of whether patients had used cannabis, almost 90% of those surveyed reported a perceived benefit. Although 65% also reported perceived risks for cannabis use, including difficulty concentrating, lung damage, and impaired memory, the perceived benefits outweighed the risks.
Despite generally positive perceptions, the overall literature on the benefits of cannabis in patients with cancer paints a less clear picture.
The ASCO guidelines, which were based on 13 systematic reviews and five additional primary studies, reported that cannabis can improve refractory, chemotherapy-induced nausea or vomiting when added to guideline-concordant antiemetic regimens, but that there is no clear evidence of benefit or harm for other supportive care outcomes.
The “certainty of evidence for most outcomes was low or very low,” the ASCO authors wrote.
The ASCO experts explained that, outside the context of a clinical trial, the evidence is not sufficient to recommend cannabis or cannabinoids for managing cancer pain, sleep issues, appetite loss, or anxiety and depression. For these outcomes, some studies indicate a benefit, while others don’t.
Real-world data from a large registry study, for instance, have indicated that medical cannabis is “a safe and effective complementary treatment for pain relief in patients with cancer.” However, a 2020 meta-analysis found that, in studies with a low risk for bias, adding cannabinoids to opioids did not reduce cancer pain in adults with advanced cancer.
There can be downsides to cannabis use, too. In one recent study, some patients reported feeling worse physically and psychologically compared with those who didn’t use cannabis. Another study found that oral cannabis was associated with “bothersome” side effects, including sedation, dizziness, and transient anxiety.
The ASCO guidelines also made it clear that cannabis or cannabinoids should not be used as cancer-directed treatment, outside of a clinical trial.
Talking to Patients About Cannabis
Given the level of evidence and patient interest in cannabis, it is important for oncologists to raise the topic of cannabis use with their patients.
To help inform decision-making and approaches to care, the ASCO guidelines suggest that oncologists can guide care themselves or direct patients to appropriate “unbiased, evidence-based” resources. For those who use cannabis or cannabinoids outside of evidence-based indications or clinician recommendations, it’s important to explore patients’ goals, educate them, and try to minimize harm.
One strategy for broaching the topic, Worster suggested, is to simply ask patients if they have tried or considered trying cannabis to control symptoms like nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, or cancer pain.
The conversation with patients should then include an overview of the potential benefits and potential risks for cannabis use as well as risk reduction strategies, Worster noted.
But “approach it in an open and nonjudgmental frame of mind,” she said. “Just have a conversation.”
Discussing the formulation and concentration of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) in products matters as well.
Will the product be inhaled, ingested, or topical? Inhaled cannabis is not ideal but is sometimes what patients have access to, Worster explained. Inhaled formulations tend to have faster onset, which might be preferable for treating chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting, whereas edible formulations may take a while to start working.
It’s also important to warn patients about taking too much, she said, explaining that inhaling THC at higher doses can increase the risk for cardiovascular effects, anxiety, paranoia, panic, and psychosis.
CBD, on the other hand, is anti-inflammatory, but early data suggest it may blunt immune responses in high doses and should be used cautiously by patients receiving immunotherapy.
Worster noted that as laws change and the science advances, new cannabis products and formulations will emerge, as will artificial intelligence tools for helping to guide patients and clinicians in optimal use of cannabis for cancer care. State websites are a particularly helpful tool for providing state-specific medical education related to cannabis laws and use, as well, she said.
The bottom line, she said, is that talking to patients about the ins and outs of cannabis use “really matters.”
Worster disclosed that she is a medical consultant for EO Care.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
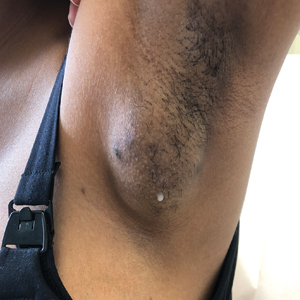
Spontaneously Draining Axillary Tumors in a Young Woman
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Ectopic (Accessory) Breast Tissue
Ectopic (accessory) breast tissue (EBT) is a phenomenon caused by failed regression of one or more components of the embryonic mammary ridges— paired ectodermal thickenings that eventually develop into definitive breast tissue including the nipples, areolae, and parenchyma. Ectopic breast tissue is more common in women than men and is believed to be sporadic, although an autosomal-dominant inheritance mechanism with incomplete penetrance has been proposed for some cases.1 The reported incidence of EBT varies greatly among racial and ethnic groups but is most common in individuals of Asian descent. The incidence across all types of EBT is estimated at 0.25% to 6% in the general population.2
Observed clinical variations of EBT range from simple polythelia (additional nipple[s] without associated parenchyma) to complete polymastia (organized and differentiated accessory breasts). Some types of EBT are rarer than others: One report of gynecologic cancer screenings in 1660 patients found polymastia and polythelia incidences of 0.12% and 5.48%, respectively.3 Of the symptomatic variations, isolated parenchymal EBT without a nipple or areolar complex is the most common and may manifest clinically as unilateral or bilateral tender, mildly erythematous nodules or masses often located in the axillae. Ectopic breast tissue generally is observed along the milk line, a developmental regional designation corresponding to the embryologic mammary ridge and extending linearly from the anterior axilla to the inguinal fold on both sides of the body; however, there have been rare reports of EBT manifesting in areas outside the milk line, such as the face, neck, back, vulva, and extremities.2,3
Given that the underlying elements of EBT usually are hormone responsive (as with normal breast tissue), the initial symptom onset and subsequent manifestation frequently coincide with pubertal milestones, pregnancy, or lactation. Furthermore, some patients with EBT may experience symptom fluctuations in concordance with monthly menstrual phases. Many cases of EBT are selflimited and resolve within weeks to months after the end of a pregnancy or lactation, but some cases may persist. Continued observation and follow-up are advisable in all patients, as EBT symptoms often recur and the tissue is susceptible to the same disease processes that affect normal breasts, the most concerning of which is malignancy.4 Although the true incidence is limited by available data, primary ectopic breast malignancy has been estimated to account for 0.3% to 3.8% of diagnosed breast malignancies.2 Cases of malignancy arising from EBT often are of higher grade and poorer prognosis, a finding that may be attributable to diagnostic delays caused by oversight or misdiagnosis of EBT rather than inherent differences in the biologic profile of the tumors.2,4 Patients with a documented history of EBT may benefit from having their routine breast cancer screenings expanded to include areas with EBT foci.
Potential misdiagnoses for EBT include subcutaneous lipoma, axillary lymphadenopathy, abscess, hidradenitis suppurativa, or malignancy. Features that are suggestive of EBT include symptom association with hormone fluctuations (eg, menstrual phases), absence of fever, and lactescent rather than purulent drainage. Among reported EBT cases, spontaneous lactation rarely is described and, if present, often is associated with a history of prior trauma (eg, core needle biopsy or local abscess formation).5 This trauma creates an aberrant connection known as a milk fistula between the underlying parenchyma and the skin surface. Interestingly, our patient denied any history of axillary trauma, but she was noted to be lactating from an apparent milk fistula rather than an organized secretory duct system.
Though a patient history and clinical examination may be sufficient to diagnose EBT cases that are more physically apparent and well correlated with hormone fluctuations, many cases require additional diagnostic studies for confirmation. Of the tools available, ultrasonography generally is considered first-line due to its noninvasive nature, low cost, minimal risk, and high diagnostic value.2 Ultrasonography quickly differentiates between abscesses and cystlike processes, which may appear as discrete areas of decreased echogenicity, and breast tissue, which manifests with fibroglandular tissue and lobules of fat.2,6 Additionally, ultrasonography may demonstrate the secretion of milk through ducts or fistulae, if present. Should examination with ultrasonography prove inconclusive, follow-up studies using conventional radiographic mammography or magnetic resonance imaging may be warranted. Biopsy of EBT foci generally is not indicated unless first-line noninvasive studies fail to yield a conclusive diagnosis; however, biopsy also may be warranted if initial imaging is suggestive of malignancy arising from EBT.2
Management of EBT generally is conservative, and symptoms often resolve without intervention.4 Symptomatic relief may be achieved through techniques such as application of warm/cold compresses, avoidance of mechanical stimulation, and use of over-the-counter pain medicine. In cases that are persistent, frequently recurrent, or associated with severe symptoms or that cause considerable cosmetic impact, management with surgical excision and/or liposuction may be warranted.7 In our patient, the symptoms were not bothersome enough to warrant surgical intervention, so she was managed conservatively and did not return for follow-up.
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
- Leung AK. Familial supernumerary nipples. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:631-635. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320310318
- Visconti G, Eltahir Y, Van Ginkel RJ, et al. Approach and management of primary ectopic breast carcinoma in the axilla: where are we? a comprehensive historical literature review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64:E1-E11. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2010.08.015
- Göttlicher S. Incidence and location of polythelias, polymastias and mammae aberratae. a prospective one year study of 1,660 patients of a gynecologic practice. Article in German. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1986;46:697-699. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1035944
- Ghosn SH, Khatri KA, Bhawan J. Bilateral aberrant axillary breast tissue mimicking lipomas: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(suppl 1):9-13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2006.00713.x
- Firat D, Idiz O, Isik A, et al. Spontaneous milk fistula from an accessory breast: an extremely rare case. Breast J. 2015;21:554-555. doi:10.1111/tbj.12452
- Lim HS, Kim SJ, Baek JM, et al. Sonographic findings of accessory breast tissue in axilla and related diseases. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36:1469-1478. doi:10.7863/ultra.16.06056
- Gentile P, Izzo V, Cervelli V. Fibroadenoma in the bilateral accessory axillary breast. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010;34:657-659. doi:10.1007/ s00266-010-9505-y
A 19-year-old G1P1A0 woman presented to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of bilateral axillary swelling, pain, and spontaneous drainage of approximately 2 weeks’ duration. The patient, who was 2 weeks postpartum, reported that the symptoms were associated with lactation when breastfeeding. She denied any personal or family history of hidradenitis suppurativa or other formally diagnosed dermatologic condition. Physical examination revealed a soft, mildly tender, well-circumscribed, nonfluctuant mobile mass in each axilla. Both lesions had a single central sinus tract with thin lactescent discharge that spontaneously drained and was expressible. A single thin hyperpigmented papule was noted on the anterior aspect of each mass.

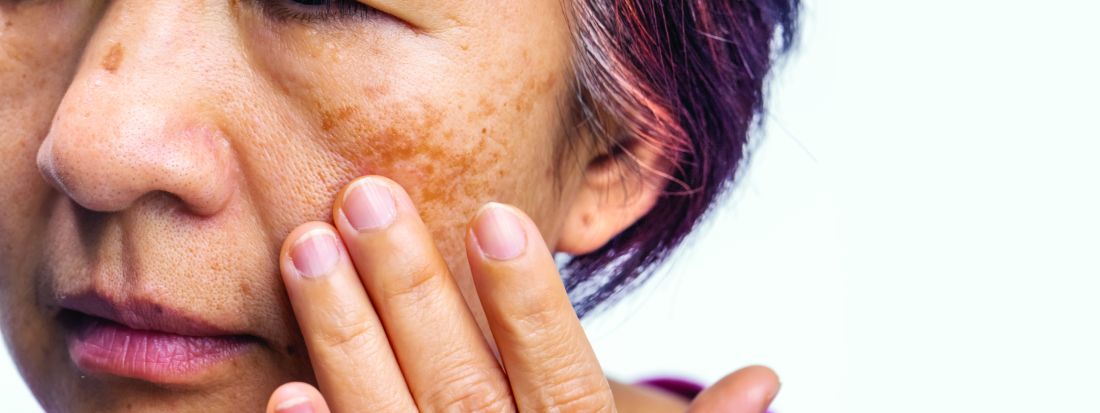
New Cosmeceutical as Effective as Cysteamine for Facial Melasma
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) 2024 Congress.
“Melasyl is a new potent melanogenesis inhibitor that exhibits a unique mode of action while preserving melanocyte integrity,” Mukta Sachdev, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology at Manipal Hospital in Bangalore, India, said at a late-breaking news session.
Both the serum and the cysteamine cream lightened participants’ skin to a similar extent, according to the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), with respective reductions of 4.19 and 3.81 points over a period of 4 months from baseline values of 11.15 and 10.93.
The mMASI score ranges from 0 to 24, with the lowest score representing the least and the highest score the most severe hyperpigmentation of the skin.
But the serum performed better than the cream by another measure. Judged by investigators blinded to which preparation study participants had been using, there was a significantly higher reduction in the Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score from baseline among those treated with the serum than among those treated with the cream (−51.85% vs −39.06%; P = .0163).
Moreover, after 4 months of treatment, there were significantly more participants with clear or almost clear skin with the serum than with the cream (17.46% vs 7.81%; P = .0163), Sachdev reported.
Other skin parameters relative to melasma, such as the brightness of skin tone and evenness of the improvement, improved more in the participants using the serum vs cream, she said.
With “no side effects, no local skin reactions,” Sachdev said, “quality of life improved significantly and similarly, and almost all subjects in both groups were very satisfied with their treatment options.”
Active Ingredients
Margarida Gonçalo, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Coimbra, in Portugal, who co-chaired the late-breaking news session, commented: “It’s really nice to have new products to treat such a devastating disease.”
Session co-chair, Lidia Rudnicka, MD, head of the Department of Dermatology, Medical University of Warsaw, in Poland, and president of the Polish Dermatological Society, wanted to know more about the active ingredients of the serum and the study’s design.
Sachdev replied that the serum also contains other ingredients that provide “antioxidant protection” and moisturization. These include retinyl palmitate, which works on the dermal-epidermal junction, and hyaluronic acid, as well as “soothing agents,” such as the medicinal herb Centella asiatica, she said.
Study Design
Conducted at a single center in India, the study involved 127 adults aged 20-50 years with melasma. For inclusion, the participants had to have facial epidermal or mixed melasma (phototypes III-V) for more than 1 year; those with dermal melasma were excluded.
Participants were randomly allocated to receive either the serum, which was applied topically to the areas of interest twice a day in the morning and then at bedtime (n = 63), or cysteamine cream (n = 64), which was applied once a day in addition to a neutral moisturizer. Treatment was for 4 months, with an on-site visit every month.
All participants were supplied with the same sunscreen/ultraviolet protector applied twice a day (once in the morning and again at midday) and a neutral hydrating cleanser that was used in the morning and evening.
Practical Implications
Over 4 months, both products showed significant improvement in melasma without reaching a plateau, Sachdev reported, with the serum demonstrating superior efficacy and tolerability, as judged by the investigators.
The study suggests that the serum is a promising non-hydroquinone treatment for melasma, she said. Hydroquinone-containing topical preparations are used to depigment the skin, but their long-term use can be limited for safety reasons.
“When products like this demonstrate improvement, it is something for the dermatologist to think about because we now have newer ingredients, which are safer and well tolerated,” she continued, noting that there appeared to be no risk for exogenous ochronosis, which can occur with long-term application of hydroquinone.
“So, I think the armamentarium of non-hydroquinone products for the treatment of melasma is rapidly expanding, and there are studies now with clinically proven efficacy,” Sachdev concluded.
The study was supported by L’Oréal France La Roche-Posay, which launched Melasyl in March 2024. Sachdev reported receipt of research support and honoraria from the company. Gonçalo and Rudnicka were not involved in the study and had no relevant conflicts of interest to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Risk Assessment Tool Can Help Predict Fractures in Cancer
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer-specific guidelines recommend using FRAX to assess fracture risk, but its applicability in patients with cancer remains unclear.
- This retrospective cohort study included 9877 patients with cancer (mean age, 67.1 years) and 45,875 matched control individuals without cancer (mean age, 66.2 years). All participants had dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans.
- Researchers collected data on bone mineral density and fractures. The 10-year probabilities of major osteoporotic fractures and hip fractures were calculated using FRAX, and the observed 10-year probabilities of these fractures were compared with FRAX-derived probabilities.
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a shorter mean follow-up duration (8.5 vs 7.6 years), a slightly higher mean body mass index, and a higher percentage of parental hip fractures (7.0% vs 8.2%); additionally, patients with cancer were more likely to have secondary causes of osteoporosis (10% vs 38.4%) and less likely to receive osteoporosis medication (9.9% vs 4.2%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a significantly higher incidence rate of major fractures (12.9 vs 14.5 per 1000 person-years) and hip fractures (3.5 vs 4.2 per 1000 person-years).
- FRAX with bone mineral density exhibited excellent calibration for predicting major osteoporotic fractures (slope, 1.03) and hip fractures (0.97) in patients with cancer, regardless of the site of cancer diagnosis. FRAX without bone mineral density, however, underestimated the risk for both major (0.87) and hip fractures (0.72).
- In patients with cancer, FRAX with bone mineral density findings were associated with incident major osteoporotic fractures (hazard ratio [HR] per SD, 1.84) and hip fractures (HR per SD, 3.61).
- When models were adjusted for FRAX with bone mineral density, patients with cancer had an increased risk for both major osteoporotic fractures (HR, 1.17) and hip fractures (HR, 1.30). No difference was found in the risk for fracture between patients with and individuals without cancer when the models were adjusted for FRAX without bone mineral density, even when considering osteoporosis medication use.
IN PRACTICE:
“This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that individuals with cancer are at higher risk of fracture than individuals without cancer and that FRAX, particularly with BMD [bone mineral density], may accurately predict fracture risk in this population. These results, along with the known mortality risk of osteoporotic fractures among cancer survivors, further emphasize the clinical importance of closing the current osteoporosis care gap among cancer survivors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Carrie Ye, MD, MPH, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study cohort included a selected group of cancer survivors who were referred for DXA scans and may not represent the general cancer population. The cohort consisted predominantly of women, limiting the generalizability to men with cancer. Given the heterogeneity of the population, the findings may not be applicable to all cancer subgroups. Information on cancer stage or the presence of bone metastases at the time of fracture risk assessment was lacking, which could have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. Three authors reported having ties with various sources, including two who received grants from various organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer-specific guidelines recommend using FRAX to assess fracture risk, but its applicability in patients with cancer remains unclear.
- This retrospective cohort study included 9877 patients with cancer (mean age, 67.1 years) and 45,875 matched control individuals without cancer (mean age, 66.2 years). All participants had dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans.
- Researchers collected data on bone mineral density and fractures. The 10-year probabilities of major osteoporotic fractures and hip fractures were calculated using FRAX, and the observed 10-year probabilities of these fractures were compared with FRAX-derived probabilities.
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a shorter mean follow-up duration (8.5 vs 7.6 years), a slightly higher mean body mass index, and a higher percentage of parental hip fractures (7.0% vs 8.2%); additionally, patients with cancer were more likely to have secondary causes of osteoporosis (10% vs 38.4%) and less likely to receive osteoporosis medication (9.9% vs 4.2%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a significantly higher incidence rate of major fractures (12.9 vs 14.5 per 1000 person-years) and hip fractures (3.5 vs 4.2 per 1000 person-years).
- FRAX with bone mineral density exhibited excellent calibration for predicting major osteoporotic fractures (slope, 1.03) and hip fractures (0.97) in patients with cancer, regardless of the site of cancer diagnosis. FRAX without bone mineral density, however, underestimated the risk for both major (0.87) and hip fractures (0.72).
- In patients with cancer, FRAX with bone mineral density findings were associated with incident major osteoporotic fractures (hazard ratio [HR] per SD, 1.84) and hip fractures (HR per SD, 3.61).
- When models were adjusted for FRAX with bone mineral density, patients with cancer had an increased risk for both major osteoporotic fractures (HR, 1.17) and hip fractures (HR, 1.30). No difference was found in the risk for fracture between patients with and individuals without cancer when the models were adjusted for FRAX without bone mineral density, even when considering osteoporosis medication use.
IN PRACTICE:
“This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that individuals with cancer are at higher risk of fracture than individuals without cancer and that FRAX, particularly with BMD [bone mineral density], may accurately predict fracture risk in this population. These results, along with the known mortality risk of osteoporotic fractures among cancer survivors, further emphasize the clinical importance of closing the current osteoporosis care gap among cancer survivors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Carrie Ye, MD, MPH, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study cohort included a selected group of cancer survivors who were referred for DXA scans and may not represent the general cancer population. The cohort consisted predominantly of women, limiting the generalizability to men with cancer. Given the heterogeneity of the population, the findings may not be applicable to all cancer subgroups. Information on cancer stage or the presence of bone metastases at the time of fracture risk assessment was lacking, which could have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. Three authors reported having ties with various sources, including two who received grants from various organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer-specific guidelines recommend using FRAX to assess fracture risk, but its applicability in patients with cancer remains unclear.
- This retrospective cohort study included 9877 patients with cancer (mean age, 67.1 years) and 45,875 matched control individuals without cancer (mean age, 66.2 years). All participants had dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans.
- Researchers collected data on bone mineral density and fractures. The 10-year probabilities of major osteoporotic fractures and hip fractures were calculated using FRAX, and the observed 10-year probabilities of these fractures were compared with FRAX-derived probabilities.
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a shorter mean follow-up duration (8.5 vs 7.6 years), a slightly higher mean body mass index, and a higher percentage of parental hip fractures (7.0% vs 8.2%); additionally, patients with cancer were more likely to have secondary causes of osteoporosis (10% vs 38.4%) and less likely to receive osteoporosis medication (9.9% vs 4.2%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with individuals without cancer, patients with cancer had a significantly higher incidence rate of major fractures (12.9 vs 14.5 per 1000 person-years) and hip fractures (3.5 vs 4.2 per 1000 person-years).
- FRAX with bone mineral density exhibited excellent calibration for predicting major osteoporotic fractures (slope, 1.03) and hip fractures (0.97) in patients with cancer, regardless of the site of cancer diagnosis. FRAX without bone mineral density, however, underestimated the risk for both major (0.87) and hip fractures (0.72).
- In patients with cancer, FRAX with bone mineral density findings were associated with incident major osteoporotic fractures (hazard ratio [HR] per SD, 1.84) and hip fractures (HR per SD, 3.61).
- When models were adjusted for FRAX with bone mineral density, patients with cancer had an increased risk for both major osteoporotic fractures (HR, 1.17) and hip fractures (HR, 1.30). No difference was found in the risk for fracture between patients with and individuals without cancer when the models were adjusted for FRAX without bone mineral density, even when considering osteoporosis medication use.
IN PRACTICE:
“This retrospective cohort study demonstrates that individuals with cancer are at higher risk of fracture than individuals without cancer and that FRAX, particularly with BMD [bone mineral density], may accurately predict fracture risk in this population. These results, along with the known mortality risk of osteoporotic fractures among cancer survivors, further emphasize the clinical importance of closing the current osteoporosis care gap among cancer survivors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study, led by Carrie Ye, MD, MPH, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada, was published online in JAMA Oncology.
LIMITATIONS:
This study cohort included a selected group of cancer survivors who were referred for DXA scans and may not represent the general cancer population. The cohort consisted predominantly of women, limiting the generalizability to men with cancer. Given the heterogeneity of the population, the findings may not be applicable to all cancer subgroups. Information on cancer stage or the presence of bone metastases at the time of fracture risk assessment was lacking, which could have affected the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. Three authors reported having ties with various sources, including two who received grants from various organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Topical JAK Inhibitor Shows Benefits in Small Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Study
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM —
“This is an exciting avenue for FFA if the data are recapitulated in a larger population. It could be an important new treatment option,” said Maryanne Senna, MD, director at Lahey Hospital & Medical Center’s Hair Loss Center of Excellence, Burlington, Massachusetts, and assistant dermatology professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts.
In a design characterized as “exploratory,” the trial had two parts: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled intervention for 12 weeks, followed by an open-label extension of topical delgocitinib for all participants for another 12 weeks.
The primary efficacy endpoint was change in the molecular signature of FFA inflammation at 12 weeks. Clinical improvement was monitored with both trichoscopic images capturing the numbers of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks and clinical severity scores through week 24. In a topical cream formulation, the Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) delgocitinib was associated with favorable activity for both.
Some Hair Regrowth for All
“At 24 weeks, all patients achieved some degree of hair regrowth and a stabilization of disease based on hairline measurements,” Senna reported in a late-breaking news session at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) Congress.
On the clinical endpoints, Senna noted an upward trajectory in clinical improvement at the completion of the study.
The 30 participants were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive delgocitinib cream in a concentration of 20 mg/g or vehicle cream applied twice daily for 12 weeks. At the end of this double-blind period, patients on vehicle were crossed over to the active therapy, and all patients were monitored for another 12 weeks in an open-label extension.
The change from baseline in FFA biomarkers was selected as the primary endpoint based on previous work showing up-regulation in the expression of the Th1 biomarkers CXCL9, CXCL10, and interferon gamma in lesional vs nonlesional scalp in patients with FFA.
When biopsies at the end of 12 weeks in the double-blind phase of the study were compared with the baseline biopsies, researchers found a decrease in expression of the three local inflammation markers in all patients receiving the JAKi, but not in those receiving the vehicle cream. In this small patient sample, only the reduction in expression of CXCL9, a cytokine known for differentiation and promotion of leukocytes, reached statistical significance (P < .05).
But in an analysis involving the expression of multiple genes, “lesions treated with delgocitinib had a 4% improvement in normalization toward a nonlesional transcriptomic profile, while patients treated with vehicle had a 33% worsening,” Senna reported. The difference was highly significant (P < .001).
Furthermore, the decrease in total Lichen Planopilaris Activity Index and FFA severity scores were numerically and statistically greater (P = .023) in the active-treatment arm than in the vehicle arm by the end of the double-blind part of the trial, she said.
On trichoscopy, there was an increased number of hairs and follicular units at 12 weeks relative to baseline among those treated with topical delgocitinib but a reduction in those treated with vehicle.
JAKi Patients Gained Hair, Vehicle Patients Lost Hair
On the basis of hair count per square centimeter from baseline, delgocitinib-treated patients gained on average of seven hairs whereas vehicle recipients lost an average of 11 hairs at 24 weeks, Senna reported.
Patients originally treated with vehicle did improve in most outcome measures in the open-label extension of the experimental treatment after crossover, but they did not catch up to those initially randomized to delgocitinib because of further accrual of favorable changes in the active-treatment group over time.
“There were no adverse events associated with active therapy or vehicle, including application-site reactions,” Senna said. The one between-group difference was a higher rate of COVID-19, but this was greater in the control arm.
All 30 of the participants in this study were women, and all had moderate to severe disease at enrollment. The median age was 64 years. Because of the predominant population at the hair loss center, all but one of the participants were White, and one participant was Asian.
Characterizing FFA as “devastating and disfiguring,” Senna, who specializes in the care of alopecia, noted that this a difficult disease to control with the off-label strategies that are now used. The slow progress to identify treatments for FFA is illustrated by the fact that only one other double-blind and randomized trial has ever been conducted in FFA, she said.
Exploratory Study Supports Anecdotal Experience
On the basis of prior anecdotal experience with JAKi treatment for FFA, Senna said, “I do think that it is possible to get largely clear skin with this therapy.” However, she is now hoping for definitive trials to better characterize the efficacy and safety of oral and topical therapies, perhaps used sequentially to maintain clinical improvement.
In light of the limited current options, Menno de Rie, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands, called these data “very inspiring and hopeful.” He suggested the promise of this therapy was reinforced by the upward trajectory of the biomarkers and clinical improvement over the study period.
“Any improvement in treatment options would be welcome, because we do not [have] any reliable therapies for this condition,” de Rie, who was not an investigator, said in an interview after the presentation.
Ultimately, Senna said, once effective therapy is established, the goal will be to start as early as possible in the disease process. She noted that there is evidence that prompt therapy can reverse the disorder, not just prevent progression.
“If you can get to the hair follicles before the point of no return, there is [a] chance [of] follicular rescue,” she said.
Delgocitinib cream (Anzupgo) was approved in Europe for treating chronic hand eczema in late September and is under review for the same indication in the United States.
Senna has financial relationships with Arena, Concert, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, and Leo Pharma, which provided funding for this study. de Rie reported no potential conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Nodules Respond to As Needed Topical JAK Inhibitor
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AMSTERDAM — Following the report of results from a randomized trial in which a topically applied Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor was highly active in
“Ruxolitinib cream may be a novel approach to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of milder HS for which there are no currently approved treatments,” reported Martina L. Porter, MD, assistant professor of dermatology, Harvard Medical School, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston, Massachusetts.
In the earlier 16-week, double-blind, randomized period of this phase 2b study, 69 adults with mild to moderate HS were randomized to 1.5% ruxolitinib cream or vehicle, applied twice daily for 16 weeks. The new results are from the open-label extension period, where those on the vehicle were crossed over to topical ruxolitinib and treatment was continued for another 16 weeks.
Over 80% Meet Primary Endpoint at 32 Weeks
Entry criteria for the study included Hurley stage I or II HS with no draining tunnels. Hurley stage III patients were not eligible. Patients had to have an abscess or inflammatory nodule (AN) count of 3 lesions concentrated in a single anatomic area or up to 10 lesions if disseminated. The median AN count of those enrolled was 5.4.
In the randomized portion of the study and in the open-label extension, the recommendation for application was to apply the medication to nodules and a 1-cm area of surrounding skin. As-needed treatment was only recommended in the extension portion of the study and rescue medication was not allowed.
The goal of the open-label extension was to evaluate how long the improvements were sustained, according to Dr. Porter, who presented the results at the 2024 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) meeting.
The primary endpoints of AN50, signaling at least a 50% reduction in AN count from baseline, among those initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream climbed slightly from 79.2% at the end of 16 weeks to 81.0% at the end of 32 weeks.
This shows that the benefits recorded in the randomized phase of the trial were sustained during the open-label extension, Dr. Porter said.
For those randomized to vehicle, there was a substantial response of 56.3% for AN50 during the randomized portion of the study, but catchup in the vehicle group to those on active therapy occurred rapidly over the open-label extension. By the end of 32 weeks, the score among the crossover patients slightly exceeded that of those on continuous therapy (88.5% vs 81.0%).
AN75 responses at week 32 were 66.7% and 61.5% in the continuous arm and crossover arm, respectively. The proportion of patients reaching an AN90 or AN100 response, meaning clear or almost clear, were 19% and 38.5%, in continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
One of the secondary endpoints was the HS Clinical Response 50, indicating at least a 50% reduction in the AN count with no increase in abscesses or draining fistulae. At 32 weeks, the proportions of patients who met this endpoint were 81.0% and 88.5% in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
The mean reduction in International HS Severity Scoring System scores from baseline were 4.1 and 4.5 in the continuous treatment and crossover arms, respectively.
Patients in the Study Mostly Women, 42% Black Individuals
Most (94%) of the participants were women; about 45% and 42% were White and Black individuals, respectively. Most of the remaining patients were Asian individuals. The median age at entry was 29 years, and the mean body mass index was approximately 34 kg/m2. A substantial proportion of patients had systemic comorbidities, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that about 25% had anxiety, depression, or both.
“This phenotype — a high proportion of women with nodules but no draining tunnels and a substantial number of comorbidities — is one we often see in patients with mild HS,” Dr. Porter said.
The safety and tolerability profile of ruxolitinib cream was quite good, according to Dr. Porter, who noted that there were fewer treatment-related adverse events in the open-label extension. Overall, the number of treatment-related adverse events (3.6%), including application site reactions leading to discontinuation (1.8%) was low.
Although there is a growing list of therapies now approved for HS, Dr. Porter emphasized that all have been developed for moderate to severe disease. She suggested that there is a sizable group of patients with mild disease for whom such therapies as biologics might not be warranted even if symptom relief is needed.
Given this unmet need, she said phase 3 trials are warranted to confirm the benefits and the safety of a topical therapy that can be used as needed to control intermittent HS flares.
Asked to comment, the lead author of a recently published review article on the “evolving treatment landscape” of HS, James G. Krueger, MD, professor in clinical investigation at Rockefeller University, New York City, agreed that there is an unmet need for effective and safe therapies in milder HS.
“I agree with the premise,” said Dr. Krueger, indicating that phase 3 data will be essential to confirm the promise of this approach. Dr. Krueger, who did not hear the results presented at the EADV meeting, listed several JAK inhibitors in his review that have shown promising efficacy as oral agents and support JAK signaling as a target of HS treatment.
Topical ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is currently approved in the United States for treating nonsegmental vitiligo in patients aged ≥ 12 years and for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in patients aged ≥ 12 years. In Europe, it is approved for treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo with facial involvement in patients aged ≥ 12 years.
Dr. Porter reported no potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Krueger reported financial relationships with more than 25 pharmaceutical companies not including Incyte, which is developing ruxolitinib cream.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EADV 2024
Is BMI Underestimating Breast Cancer Risk in Postmenopausal Women?
TOPLINE:
Accurate body fat measures are crucial for effective cancer prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study including 1033 breast cancer cases and 1143 postmenopausal population controls from the MCC-Spain study.
- Participants were aged 20-85 years. BMI was calculated as the ratio of weight to height squared and categorized using World Health Organization standards: < 25, 25-29.9, 30-34.9, and ≥ 35.
- CUN-BAE was calculated using a specific equation and categorized according to the estimated percentage of body fat: < 35%, 35%-39.9%, 40%-44.9%, and ≥ 45%.
- Odds ratios (ORs) were estimated with 95% CIs for both measures (BMI and CUN-BAE) for breast cancer cases using unconditional logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Excess body weight attributable to the risk for breast cancer was 23% when assessed using a BMI value > 30 and 38% when assessed using a CUN-BAE value > 40% body fat.
- Hormone receptor stratification showed that these differences in population-attributable fractions were only observed in hormone receptor–positive cases, with an estimated burden of 19.9% for BMI and 41.9% for CUN-BAE.
- The highest categories of CUN-BAE showed an increase in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer (OR, 2.13 for body fat ≥ 45% compared with the reference category < 35%).
- No similar trend was observed for BMI, as the gradient declined after a BMI ≥ 35.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of our study indicate that excess body fat is a significant risk factor for hormone receptor–positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Our findings suggest that the population impact could be underestimated when using traditional BMI estimates, and that more accurate measures of body fat, such as CUN-BAE, should be considered,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Verónica Dávila-Batista, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain. It was published online in Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design of the study may have limited the ability to establish causal relationships. BMI was self-reported at the time of the interview for controls and 1 year before diagnosis for cancer cases, which may have introduced recall bias. The formula for CUN-BAE was calculated from a sedentary convenience sample, which may not have been representative of the general population. The small sample size of cases that did not express hormone receptors was another limitation. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to non-White populations as non-White participants were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
Dávila-Batista disclosed receiving grants from the Carlos III Health Institute. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Accurate body fat measures are crucial for effective cancer prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study including 1033 breast cancer cases and 1143 postmenopausal population controls from the MCC-Spain study.
- Participants were aged 20-85 years. BMI was calculated as the ratio of weight to height squared and categorized using World Health Organization standards: < 25, 25-29.9, 30-34.9, and ≥ 35.
- CUN-BAE was calculated using a specific equation and categorized according to the estimated percentage of body fat: < 35%, 35%-39.9%, 40%-44.9%, and ≥ 45%.
- Odds ratios (ORs) were estimated with 95% CIs for both measures (BMI and CUN-BAE) for breast cancer cases using unconditional logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Excess body weight attributable to the risk for breast cancer was 23% when assessed using a BMI value > 30 and 38% when assessed using a CUN-BAE value > 40% body fat.
- Hormone receptor stratification showed that these differences in population-attributable fractions were only observed in hormone receptor–positive cases, with an estimated burden of 19.9% for BMI and 41.9% for CUN-BAE.
- The highest categories of CUN-BAE showed an increase in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer (OR, 2.13 for body fat ≥ 45% compared with the reference category < 35%).
- No similar trend was observed for BMI, as the gradient declined after a BMI ≥ 35.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of our study indicate that excess body fat is a significant risk factor for hormone receptor–positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Our findings suggest that the population impact could be underestimated when using traditional BMI estimates, and that more accurate measures of body fat, such as CUN-BAE, should be considered,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Verónica Dávila-Batista, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain. It was published online in Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design of the study may have limited the ability to establish causal relationships. BMI was self-reported at the time of the interview for controls and 1 year before diagnosis for cancer cases, which may have introduced recall bias. The formula for CUN-BAE was calculated from a sedentary convenience sample, which may not have been representative of the general population. The small sample size of cases that did not express hormone receptors was another limitation. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to non-White populations as non-White participants were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
Dávila-Batista disclosed receiving grants from the Carlos III Health Institute. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Accurate body fat measures are crucial for effective cancer prevention.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study including 1033 breast cancer cases and 1143 postmenopausal population controls from the MCC-Spain study.
- Participants were aged 20-85 years. BMI was calculated as the ratio of weight to height squared and categorized using World Health Organization standards: < 25, 25-29.9, 30-34.9, and ≥ 35.
- CUN-BAE was calculated using a specific equation and categorized according to the estimated percentage of body fat: < 35%, 35%-39.9%, 40%-44.9%, and ≥ 45%.
- Odds ratios (ORs) were estimated with 95% CIs for both measures (BMI and CUN-BAE) for breast cancer cases using unconditional logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Excess body weight attributable to the risk for breast cancer was 23% when assessed using a BMI value > 30 and 38% when assessed using a CUN-BAE value > 40% body fat.
- Hormone receptor stratification showed that these differences in population-attributable fractions were only observed in hormone receptor–positive cases, with an estimated burden of 19.9% for BMI and 41.9% for CUN-BAE.
- The highest categories of CUN-BAE showed an increase in the risk for postmenopausal breast cancer (OR, 2.13 for body fat ≥ 45% compared with the reference category < 35%).
- No similar trend was observed for BMI, as the gradient declined after a BMI ≥ 35.
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of our study indicate that excess body fat is a significant risk factor for hormone receptor–positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Our findings suggest that the population impact could be underestimated when using traditional BMI estimates, and that more accurate measures of body fat, such as CUN-BAE, should be considered,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Verónica Dávila-Batista, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain. It was published online in Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
LIMITATIONS:
The case-control design of the study may have limited the ability to establish causal relationships. BMI was self-reported at the time of the interview for controls and 1 year before diagnosis for cancer cases, which may have introduced recall bias. The formula for CUN-BAE was calculated from a sedentary convenience sample, which may not have been representative of the general population. The small sample size of cases that did not express hormone receptors was another limitation. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to non-White populations as non-White participants were excluded.
DISCLOSURES:
Dávila-Batista disclosed receiving grants from the Carlos III Health Institute. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The New Cancer Stats Might Look Like a Death Sentence. They Aren’t.
Cancer is becoming more common in younger generations. Data show that people under 50 are experiencing higher rates of cancer than any generation before them. As a genetic counselor, I hoped these upward trends in early-onset malignancies would slow with a better understanding of risk factors and prevention strategies. Unfortunately, the opposite is happening. Recent findings from the American Cancer Society reveal that the incidence of at least 17 of 34 cancer types is rising among GenX and Millennials.
These statistics are alarming. I appreciate how easy it is for patients to get lost in the headlines about cancer, which may shape how they approach their healthcare. Each year, millions of Americans miss critical cancer screenings, with many citing fear of a positive test result as a leading reason. Others believe, despite the statistics, that cancer is not something they need to worry about until they are older. And then, of course, getting screened is not as easy as it should be.
In my work, I meet with people from both younger and older generations who have either faced cancer themselves or witnessed a loved one experience the disease. One of the most common sentiments I hear from these patients is the desire to catch cancer earlier. My answer is always this: The first and most important step everyone can take is understanding their risk.
For some, knowing they are at increased risk for cancer means starting screenings earlier — sometimes as early as age 25 — or getting screened with a more sensitive test.
This proactive approach is the right one. It also significantly reduces the burden of total and cancer-specific healthcare costs. While screening may carry some potential risks, clinicians can minimize these risks by adhering to evidence-based guidelines, such as those from the American Cancer Society, and ensuring there is appropriate discussion of treatment options when a diagnosis is made.
Normalizing Cancer Risk Assessment and Screening
A detailed cancer risk assessment and education about signs and symptoms should be part of every preventive care visit, regardless of someone’s age. Further, that cancer risk assessment should lead to clear recommendations and support for taking the next steps.
This is where care advocacy and patient navigation come in. Care advocacy can improve outcomes at every stage of the cancer journey, from increasing screening rates to improving quality of life for survivors. I’ve seen first-hand how care advocates help patients overcome hurdles like long wait times for appointments they need, making both screening and diagnostic care easier to access.
Now, with the finalization of a new rule from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, providers can bill for oncology navigation services that occur under their supervision. This formal recognition of care navigation affirms the value of these services not just clinically but financially as well. It will be through methods like care navigation, targeted outreach, and engaging educational resources — built into and covered by health plans — that patients will feel more in control over their health and have tools to help minimize the effects of cancer on the rest of their lives.
These services benefit healthcare providers as well. Care navigation supports clinical care teams, from primary care providers to oncologists, by ensuring patients are seen before their cancer progresses to a more advanced stage. And even if patients follow screening recommendations for the rest of their lives and never get a positive result, they’ve still gained something invaluable: peace of mind, knowing they’ve taken an active role in their health.
Fighting Fear With Routine
Treating cancer as a normal part of young people’s healthcare means helping them envision the disease as a condition that can be treated, much like a diagnosis of diabetes or high cholesterol. This mindset shift means quickly following up on a concerning symptom or screening result and reducing the time to start treatment if needed. And with treatment options and success rates for some cancers being better than ever, survivorship support must be built into every treatment plan from the start. Before treatment begins, healthcare providers should make time to talk about sometimes-overlooked key topics, such as reproductive options for people whose fertility may be affected by their cancer treatment, about plans for returning to work during or after treatment, and finding the right mental health support.
Where we can’t prevent cancer, both primary care providers and oncologists can work together to help patients receive the right diagnosis and treatment as quickly as possible. Knowing insurance coverage has a direct effect on how early cancer is caught, for example, younger people need support in understanding and accessing benefits and resources that may be available through their existing healthcare channels, like some employer-sponsored health plans. Even if getting treated for cancer is inevitable for some, taking immediate action to get screened when it’s appropriate is the best thing we can do to lessen the impact of these rising cancer incidences across the country. At the end of the day, being afraid of cancer doesn’t decrease the chances of getting sick or dying from it. Proactive screening and early detection do.
Brockman, Genetic Counselor, Color Health, Buffalo, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer is becoming more common in younger generations. Data show that people under 50 are experiencing higher rates of cancer than any generation before them. As a genetic counselor, I hoped these upward trends in early-onset malignancies would slow with a better understanding of risk factors and prevention strategies. Unfortunately, the opposite is happening. Recent findings from the American Cancer Society reveal that the incidence of at least 17 of 34 cancer types is rising among GenX and Millennials.
These statistics are alarming. I appreciate how easy it is for patients to get lost in the headlines about cancer, which may shape how they approach their healthcare. Each year, millions of Americans miss critical cancer screenings, with many citing fear of a positive test result as a leading reason. Others believe, despite the statistics, that cancer is not something they need to worry about until they are older. And then, of course, getting screened is not as easy as it should be.
In my work, I meet with people from both younger and older generations who have either faced cancer themselves or witnessed a loved one experience the disease. One of the most common sentiments I hear from these patients is the desire to catch cancer earlier. My answer is always this: The first and most important step everyone can take is understanding their risk.
For some, knowing they are at increased risk for cancer means starting screenings earlier — sometimes as early as age 25 — or getting screened with a more sensitive test.
This proactive approach is the right one. It also significantly reduces the burden of total and cancer-specific healthcare costs. While screening may carry some potential risks, clinicians can minimize these risks by adhering to evidence-based guidelines, such as those from the American Cancer Society, and ensuring there is appropriate discussion of treatment options when a diagnosis is made.
Normalizing Cancer Risk Assessment and Screening
A detailed cancer risk assessment and education about signs and symptoms should be part of every preventive care visit, regardless of someone’s age. Further, that cancer risk assessment should lead to clear recommendations and support for taking the next steps.
This is where care advocacy and patient navigation come in. Care advocacy can improve outcomes at every stage of the cancer journey, from increasing screening rates to improving quality of life for survivors. I’ve seen first-hand how care advocates help patients overcome hurdles like long wait times for appointments they need, making both screening and diagnostic care easier to access.
Now, with the finalization of a new rule from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, providers can bill for oncology navigation services that occur under their supervision. This formal recognition of care navigation affirms the value of these services not just clinically but financially as well. It will be through methods like care navigation, targeted outreach, and engaging educational resources — built into and covered by health plans — that patients will feel more in control over their health and have tools to help minimize the effects of cancer on the rest of their lives.
These services benefit healthcare providers as well. Care navigation supports clinical care teams, from primary care providers to oncologists, by ensuring patients are seen before their cancer progresses to a more advanced stage. And even if patients follow screening recommendations for the rest of their lives and never get a positive result, they’ve still gained something invaluable: peace of mind, knowing they’ve taken an active role in their health.
Fighting Fear With Routine
Treating cancer as a normal part of young people’s healthcare means helping them envision the disease as a condition that can be treated, much like a diagnosis of diabetes or high cholesterol. This mindset shift means quickly following up on a concerning symptom or screening result and reducing the time to start treatment if needed. And with treatment options and success rates for some cancers being better than ever, survivorship support must be built into every treatment plan from the start. Before treatment begins, healthcare providers should make time to talk about sometimes-overlooked key topics, such as reproductive options for people whose fertility may be affected by their cancer treatment, about plans for returning to work during or after treatment, and finding the right mental health support.
Where we can’t prevent cancer, both primary care providers and oncologists can work together to help patients receive the right diagnosis and treatment as quickly as possible. Knowing insurance coverage has a direct effect on how early cancer is caught, for example, younger people need support in understanding and accessing benefits and resources that may be available through their existing healthcare channels, like some employer-sponsored health plans. Even if getting treated for cancer is inevitable for some, taking immediate action to get screened when it’s appropriate is the best thing we can do to lessen the impact of these rising cancer incidences across the country. At the end of the day, being afraid of cancer doesn’t decrease the chances of getting sick or dying from it. Proactive screening and early detection do.
Brockman, Genetic Counselor, Color Health, Buffalo, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer is becoming more common in younger generations. Data show that people under 50 are experiencing higher rates of cancer than any generation before them. As a genetic counselor, I hoped these upward trends in early-onset malignancies would slow with a better understanding of risk factors and prevention strategies. Unfortunately, the opposite is happening. Recent findings from the American Cancer Society reveal that the incidence of at least 17 of 34 cancer types is rising among GenX and Millennials.
These statistics are alarming. I appreciate how easy it is for patients to get lost in the headlines about cancer, which may shape how they approach their healthcare. Each year, millions of Americans miss critical cancer screenings, with many citing fear of a positive test result as a leading reason. Others believe, despite the statistics, that cancer is not something they need to worry about until they are older. And then, of course, getting screened is not as easy as it should be.
In my work, I meet with people from both younger and older generations who have either faced cancer themselves or witnessed a loved one experience the disease. One of the most common sentiments I hear from these patients is the desire to catch cancer earlier. My answer is always this: The first and most important step everyone can take is understanding their risk.
For some, knowing they are at increased risk for cancer means starting screenings earlier — sometimes as early as age 25 — or getting screened with a more sensitive test.
This proactive approach is the right one. It also significantly reduces the burden of total and cancer-specific healthcare costs. While screening may carry some potential risks, clinicians can minimize these risks by adhering to evidence-based guidelines, such as those from the American Cancer Society, and ensuring there is appropriate discussion of treatment options when a diagnosis is made.
Normalizing Cancer Risk Assessment and Screening
A detailed cancer risk assessment and education about signs and symptoms should be part of every preventive care visit, regardless of someone’s age. Further, that cancer risk assessment should lead to clear recommendations and support for taking the next steps.
This is where care advocacy and patient navigation come in. Care advocacy can improve outcomes at every stage of the cancer journey, from increasing screening rates to improving quality of life for survivors. I’ve seen first-hand how care advocates help patients overcome hurdles like long wait times for appointments they need, making both screening and diagnostic care easier to access.
Now, with the finalization of a new rule from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, providers can bill for oncology navigation services that occur under their supervision. This formal recognition of care navigation affirms the value of these services not just clinically but financially as well. It will be through methods like care navigation, targeted outreach, and engaging educational resources — built into and covered by health plans — that patients will feel more in control over their health and have tools to help minimize the effects of cancer on the rest of their lives.
These services benefit healthcare providers as well. Care navigation supports clinical care teams, from primary care providers to oncologists, by ensuring patients are seen before their cancer progresses to a more advanced stage. And even if patients follow screening recommendations for the rest of their lives and never get a positive result, they’ve still gained something invaluable: peace of mind, knowing they’ve taken an active role in their health.
Fighting Fear With Routine
Treating cancer as a normal part of young people’s healthcare means helping them envision the disease as a condition that can be treated, much like a diagnosis of diabetes or high cholesterol. This mindset shift means quickly following up on a concerning symptom or screening result and reducing the time to start treatment if needed. And with treatment options and success rates for some cancers being better than ever, survivorship support must be built into every treatment plan from the start. Before treatment begins, healthcare providers should make time to talk about sometimes-overlooked key topics, such as reproductive options for people whose fertility may be affected by their cancer treatment, about plans for returning to work during or after treatment, and finding the right mental health support.
Where we can’t prevent cancer, both primary care providers and oncologists can work together to help patients receive the right diagnosis and treatment as quickly as possible. Knowing insurance coverage has a direct effect on how early cancer is caught, for example, younger people need support in understanding and accessing benefits and resources that may be available through their existing healthcare channels, like some employer-sponsored health plans. Even if getting treated for cancer is inevitable for some, taking immediate action to get screened when it’s appropriate is the best thing we can do to lessen the impact of these rising cancer incidences across the country. At the end of the day, being afraid of cancer doesn’t decrease the chances of getting sick or dying from it. Proactive screening and early detection do.
Brockman, Genetic Counselor, Color Health, Buffalo, New York, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Utilization, Cost, and Prescription Trends of Antipsychotics Prescribed by Dermatologists for Medicare Patients
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).
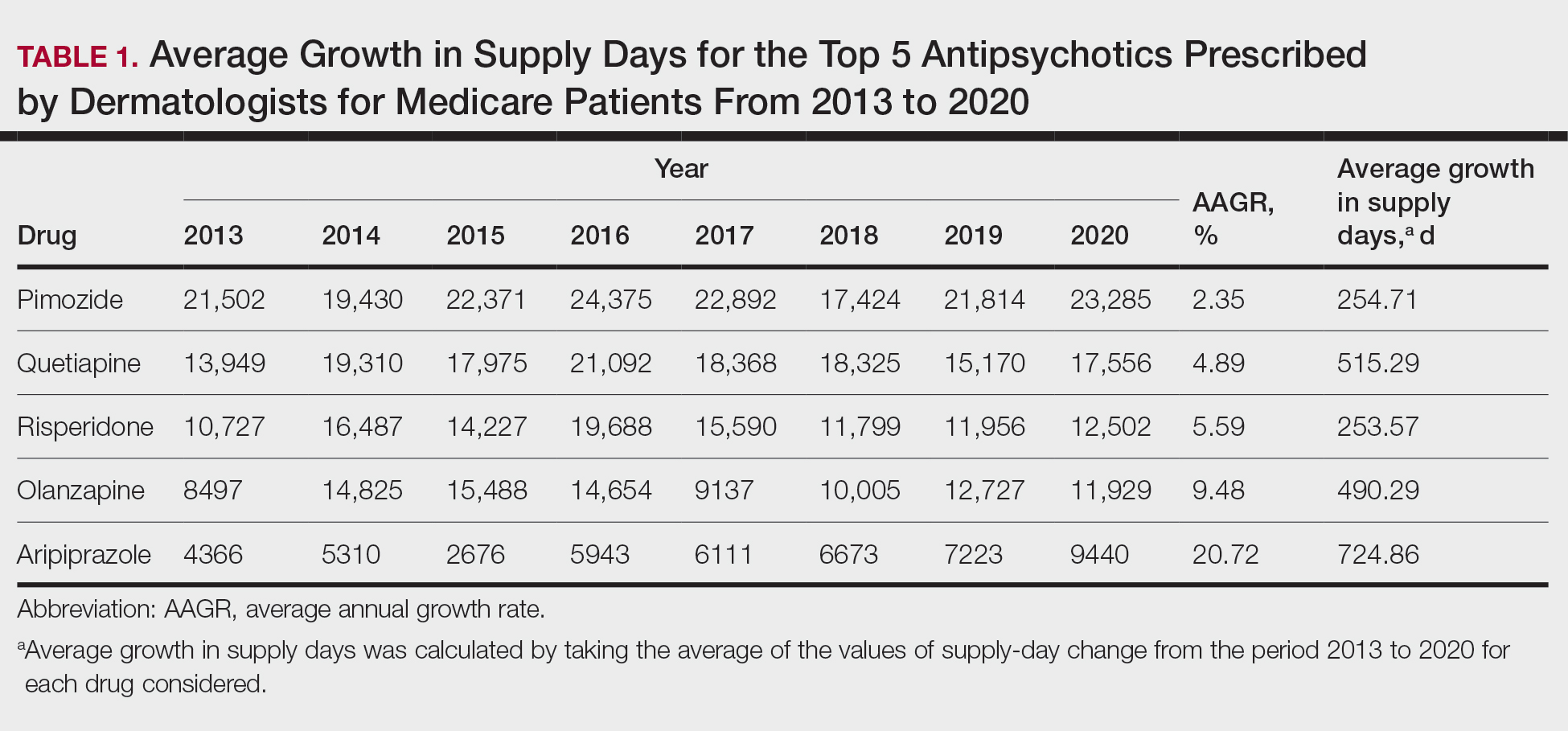
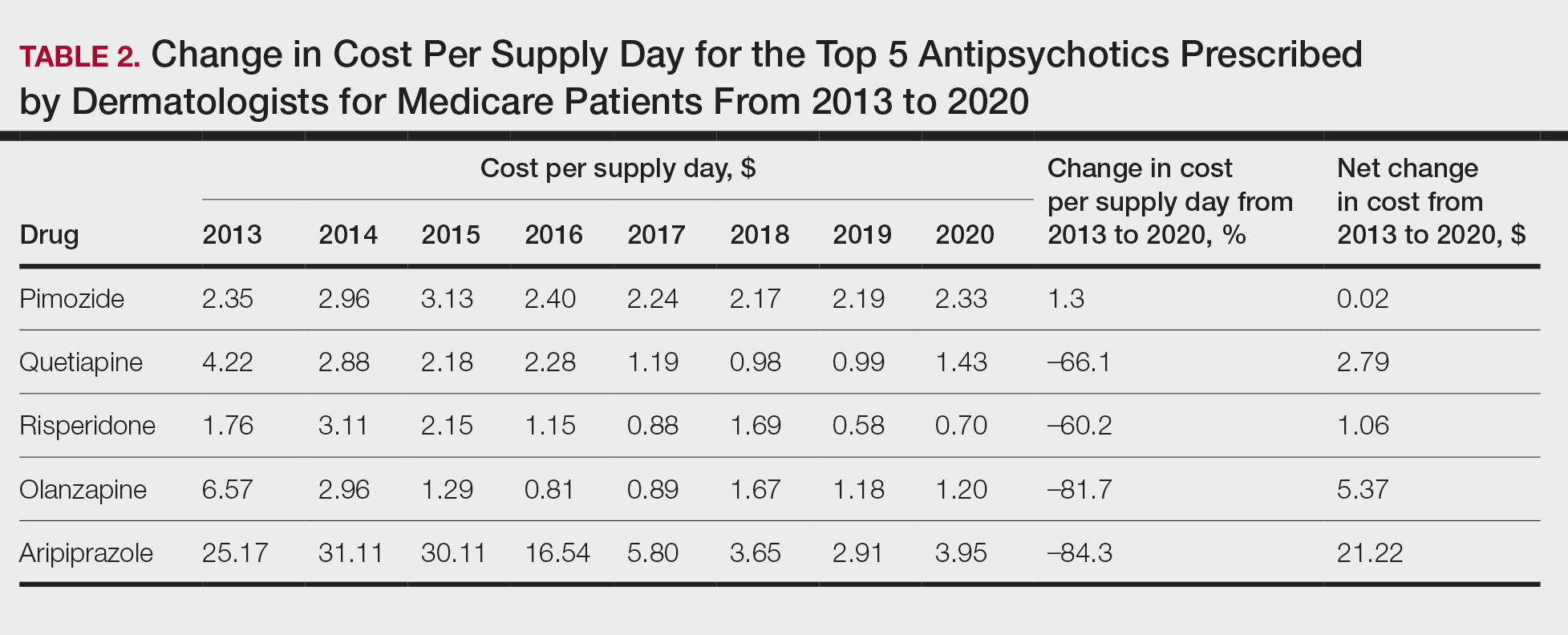
There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).


There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
To the Editor:
Patients with primary psychiatric disorders with dermatologic manifestations often seek treatment from dermatologists instead of psychiatrists.1 For example, patients with delusions of parasitosis may lack insight into the underlying etiology of their disease and instead fixate on establishing an organic cause for their symptoms. As a result, it is an increasingly common practice for dermatologists to diagnose and treat psychiatric conditions.1 The goal of this study was to evaluate trends for the top 5 antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists in the Medicare Part D database.
In this retrospective analysis, we consulted the Medicare Provider Utilization and Payment Data for January 2013 through December 2020, which is provided to the public by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.2 Only prescribing data from dermatologists were included in this study by using the built-in filter on the website to select “dermatology” as the prescriber type. All other provider types were excluded. We chose the top 5 most prescribed antipsychotics based on the number of supply days reported. Supply days—defined by Medicare as the number of days’ worth of medication that is prescribed—were used as a metric for utilization; therefore, each drug’s total supply days prescribed by dermatologists were calculated using this combined filter of drug name and total supply days using the database.
To analyze utilization over time, the annual average growth rate (AAGR) was calculated by determining the growth rate in total supply days annually from 2013 to 2020 and then averaging those rates to determine the overall AAGR. For greater clinical relevance, we calculated the average growth in supply days for the entire study period by determining the difference in the number of supply days for each year and then averaging these values. This was done to consider overall trends across dermatology rather than individual dermatologist prescribing patterns.
Based on our analysis, the antipsychotics most frequently prescribed by dermatologists for Medicare patients from January 2013 to December 2020 were pimozide, quetiapine, risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. The AAGR for each drug was 2.35%, 4.89%, 5.59%, 9.48%, and 20.72%, respectively, which is consistent with increased utilization over the study period for all 5 drugs (Table 1). The change in cost per supply day for the same period was 1.3%, –66.1%, –60.2%, –81.7%, and –84.3%, respectively. The net difference in cost per supply day over this entire period was $0.02, –$2.79, –$1.06, –$5.37, and –$21.22, respectively (Table 2).


There were several limitations to our study. Our analysis was limited to the Medicare population. Uninsured patients and those with Medicare Advantage or private health insurance plans were not included. In the Medicare database, only prescribers who prescribed a medication 10 times or more were recorded; therefore, some prescribers were not captured.
Although there was an increase in the dermatologic use of all 5 drugs in this study, perhaps the most marked growth was exhibited by aripiprazole, which had an AAGR of 20.72% (Table 1). Affordability may have been a factor, as the most marked reduction in price per supply day was noted for aripiprazole during the study period. Pimozide, which traditionally has been the first-line therapy for delusions of parasitosis, is the only first-generation antipsychotic drug among the 5 most frequently prescribed antipsychotics.3 Interestingly, pimozide had the lowest AAGR compared with the 4 second-generation antipsychotics. This finding also is corroborated by the average growth in supply days. While pimozide is a first-generation antipsychotic and had the lowest AAGR, pimozide still was the most prescribed antipsychotic in this study. Considering the average growth in Medicare beneficiaries during the study period was 2.70% per year,2 the AAGR of the 4 other drugs excluding pimozide shows that this growth was larger than what can be attributed to an increase in population size.
The most common conditions for which dermatologists prescribe antipsychotics are primary delusional infestation disorders as well as a range of self-inflicted dermatologic manifestations of dermatitis artefacta.4 Particularly, dermatologist-prescribed antipsychotics are first-line for these conditions in which perception of a persistent disease state is present.4 Importantly, dermatologists must differentiate between other dermatology-related psychiatric conditions such as trichotillomania and body dysmorphic disorder, which tend to respond better to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.4 Our data suggest that dermatologists are increasing their utilization of second-generation antipsychotics at a higher rate than first-generation antipsychotics, likely due to the lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. Patients are more willing to initiate a trial of psychiatric medication when it is prescribed by a dermatologist vs a psychiatrist due to lack of perceived stigma, which can lead to greater treatment compliance rates.5 As mentioned previously, as part of the differential, dermatologists also can effectively prescribe medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for symptoms including anxiety, trichotillomania, body dysmorphic disorder, or secondary psychiatric disorders as a result of the burden of skin disease.5
In many cases, a dermatologist may be the first and only specialist to evaluate patients with conditions that overlap within the jurisdiction of dermatology and psychiatry. It is imperative that dermatologists feel comfortable treating this vulnerable patient population. As demonstrated by Medicare prescription data, the increasing utilization of antipsychotics in our specialty demands that dermatologists possess an adequate working knowledge of psychopharmacology, which may be accomplished during residency training through several directives, including focused didactic sessions, elective rotations in psychiatry, increased exposure to psychocutaneous lectures at national conferences, and finally through the establishment of joint dermatology-psychiatry clinics with interdepartmental collaboration.
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
- Weber MB, Recuero JK, Almeida CS. Use of psychiatric drugs in dermatology. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95:133-143. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.12.002
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare provider utilization and payment data: part D prescriber. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed October 7, 2024. https://www.cms.gov/data -research/statistics-trends-and-reports/medicare-provider-utilization-payment-data/part-d-prescriber
- Bolognia J, Schaffe JV, Lorenzo C. Dermatology. In: Duncan KO, Koo JYM, eds. Psychocutaneous Diseases. Elsevier; 2017:128-136.
- Gupta MA, Vujcic B, Pur DR, et al. Use of antipsychotic drugs in dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:765-773. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.08.006
- Jafferany M, Stamu-O’Brien C, Mkhoyan R, et al. Psychotropic drugs in dermatology: a dermatologist’s approach and choice of medications. Dermatol Ther. 2020;33:E13385. doi:10.1111/dth.13385
Practice Points
- Dermatologists are frontline medical providers who can be useful in screening for primary psychiatric disorders in patients with dermatologic manifestations.
- Second-generation antipsychotics are effective for treating many psychiatric disorders.
How to Treat Cancer While Preserving Fertility
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.