User login
A 16-Year-Old Hispanic Male with a History of Hyperlipidemia Reports a Pruritic Rash on His Neck and Chest
Discussion
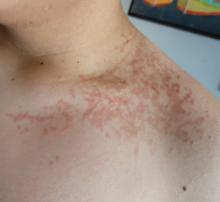
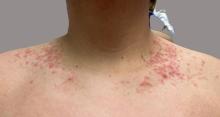
Given the patient’s recent dietary changes, particularly his switch to a ketogenic diet, he was diagnosed with prurigo pigmentosa and treated with doxycycline, which cleared the rash. Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare inflammatory dermatosis characterized by net-like or reticulated pink, and later hyperpigmented, papules and plaques. Although the condition predominantly affects young women of East Asian descent, cases have been reported worldwide, highlighting the importance of considering this diagnosis in diverse populations, including children. Here, we describe a case of prurigo pigmentosa in a young male who had recently adopted a ketogenic diet for weight loss.
The association between prurigo pigmentosa and dietary changes, particularly ketosis, is becoming increasingly recognized. This condition is strongly linked to ketosis, a metabolic state marked by the production of ketone bodies (e.g., beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate) during carbohydrate restriction, fasting, or ketogenic diets, as seen in our patient. These ketone bodies may act as irritants or trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory cascades in the skin.
Ketoacidosis, particularly in prolonged or intense ketosis, is thought to alter the local skin microenvironment, promoting activation of inflammatory cytokines and immune cells. The ketogenic state is believed to generate oxidative stress through increased free fatty acid oxidation, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can induce apoptosis of keratinocytes and inflammation in the epidermis, which is predominantly mediated by neutrophilic infiltration, as seen in histopathological findings. Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), have been implicated in neutrophil recruitment and activation. IL-8 is particularly important for guiding neutrophils to areas of injury.
Secondary hyperpigmentation, a hallmark of this condition, is thought to result from melanin-laden macrophages and persistent melanocyte activation in response to inflammation at the dermo-epidermal junction.
The condition progresses in three stages. In the early stage, lesions appear as pruritic, urticarial plaques. These evolve into crusted erythematous papules and papulovesicles in the middle stage, as observed in our patient. Finally, in the late stage, the lesions mature into smooth, hyperpigmented plaques. Each stage of prurigo pigmentosa has distinct histopathological features.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for prurigo pigmentosa includes several conditions that may present similarly. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can initially mimic the erythematous papules of prurigo pigmentosa, but the absence of a clear allergen exposure and failure to improve with avoidance measures makes ACD less likely. Psoriasis is another possibility, as its erythematous plaques may overlap with prurigo pigmentosa. However, the lack of silvery scales and chronicity makes psoriasis less likely in this case. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, typically presents with pruritic, ill-defined plaques, often in flexural areas, which were not observed in this patient. Flagellate dermatitis, often caused by exposure to bleomycin or consumption of shiitake mushrooms, can present with linear erythematous lesions resembling prurigo pigmentosa. However, the absence of relevant exposures and a flagellate pattern in this patient rules out this diagnosis.
This case highlights the growing recognition of prurigo pigmentosa in the context of dietary trends, especially ketogenic diets, which have become popular for weight loss and other health benefits. Pediatric populations, in particular, may adopt such diets for various reasons and require careful monitoring, as their physiological responses may differ from those in adults. Prurigo pigmentosa has also been reported in a teenager girl with a history of anorexia nervosa, who was in a ketotic state.
Treatment options for prurigo pigmentosa include antibiotics such as minocycline or doxycycline, or macrolides for 4–10 weeks. Other treatment modalities include dapsone, Q-switch Nd:YAG laser, narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) phototherapy, and topical treatments like crisaborole and tacrolimus.
Early recognition of this condition is crucial to avoid unnecessary interventions and to allow for resolution through dietary modification. Dermatologists and pediatricians should maintain a high index of suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa in patients presenting with characteristic eruptions and a history of dietary ketosis.
Catalina Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
1. Mufti A et al. Clinical Manifestations and Treatment Outcomes in Prurigo Pigmentosa (Nagashima Disease): A Systematic Review of the Literature. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10:3:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003.
2. Yang J et al. Use of Minocycline for the Treatment of Prurigo Pigmentosa with Intraepidermal Vesiculation: A Case Report. J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211015593. doi: 10.1177/03000605211015593.
3. Capucilli P et al. Prurigo Pigmentosa: An Itchy, Urticarial Eruption Confused for Food Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018 Jul-Aug;6(4):1381-1382. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2018.02.033.
Discussion
Given the patient’s recent dietary changes, particularly his switch to a ketogenic diet, he was diagnosed with prurigo pigmentosa and treated with doxycycline, which cleared the rash. Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare inflammatory dermatosis characterized by net-like or reticulated pink, and later hyperpigmented, papules and plaques. Although the condition predominantly affects young women of East Asian descent, cases have been reported worldwide, highlighting the importance of considering this diagnosis in diverse populations, including children. Here, we describe a case of prurigo pigmentosa in a young male who had recently adopted a ketogenic diet for weight loss.
The association between prurigo pigmentosa and dietary changes, particularly ketosis, is becoming increasingly recognized. This condition is strongly linked to ketosis, a metabolic state marked by the production of ketone bodies (e.g., beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate) during carbohydrate restriction, fasting, or ketogenic diets, as seen in our patient. These ketone bodies may act as irritants or trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory cascades in the skin.
Ketoacidosis, particularly in prolonged or intense ketosis, is thought to alter the local skin microenvironment, promoting activation of inflammatory cytokines and immune cells. The ketogenic state is believed to generate oxidative stress through increased free fatty acid oxidation, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can induce apoptosis of keratinocytes and inflammation in the epidermis, which is predominantly mediated by neutrophilic infiltration, as seen in histopathological findings. Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), have been implicated in neutrophil recruitment and activation. IL-8 is particularly important for guiding neutrophils to areas of injury.
Secondary hyperpigmentation, a hallmark of this condition, is thought to result from melanin-laden macrophages and persistent melanocyte activation in response to inflammation at the dermo-epidermal junction.
The condition progresses in three stages. In the early stage, lesions appear as pruritic, urticarial plaques. These evolve into crusted erythematous papules and papulovesicles in the middle stage, as observed in our patient. Finally, in the late stage, the lesions mature into smooth, hyperpigmented plaques. Each stage of prurigo pigmentosa has distinct histopathological features.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for prurigo pigmentosa includes several conditions that may present similarly. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can initially mimic the erythematous papules of prurigo pigmentosa, but the absence of a clear allergen exposure and failure to improve with avoidance measures makes ACD less likely. Psoriasis is another possibility, as its erythematous plaques may overlap with prurigo pigmentosa. However, the lack of silvery scales and chronicity makes psoriasis less likely in this case. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, typically presents with pruritic, ill-defined plaques, often in flexural areas, which were not observed in this patient. Flagellate dermatitis, often caused by exposure to bleomycin or consumption of shiitake mushrooms, can present with linear erythematous lesions resembling prurigo pigmentosa. However, the absence of relevant exposures and a flagellate pattern in this patient rules out this diagnosis.
This case highlights the growing recognition of prurigo pigmentosa in the context of dietary trends, especially ketogenic diets, which have become popular for weight loss and other health benefits. Pediatric populations, in particular, may adopt such diets for various reasons and require careful monitoring, as their physiological responses may differ from those in adults. Prurigo pigmentosa has also been reported in a teenager girl with a history of anorexia nervosa, who was in a ketotic state.
Treatment options for prurigo pigmentosa include antibiotics such as minocycline or doxycycline, or macrolides for 4–10 weeks. Other treatment modalities include dapsone, Q-switch Nd:YAG laser, narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) phototherapy, and topical treatments like crisaborole and tacrolimus.
Early recognition of this condition is crucial to avoid unnecessary interventions and to allow for resolution through dietary modification. Dermatologists and pediatricians should maintain a high index of suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa in patients presenting with characteristic eruptions and a history of dietary ketosis.
Catalina Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
1. Mufti A et al. Clinical Manifestations and Treatment Outcomes in Prurigo Pigmentosa (Nagashima Disease): A Systematic Review of the Literature. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10:3:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003.
2. Yang J et al. Use of Minocycline for the Treatment of Prurigo Pigmentosa with Intraepidermal Vesiculation: A Case Report. J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211015593. doi: 10.1177/03000605211015593.
3. Capucilli P et al. Prurigo Pigmentosa: An Itchy, Urticarial Eruption Confused for Food Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018 Jul-Aug;6(4):1381-1382. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2018.02.033.
Discussion
Given the patient’s recent dietary changes, particularly his switch to a ketogenic diet, he was diagnosed with prurigo pigmentosa and treated with doxycycline, which cleared the rash. Prurigo pigmentosa is a rare inflammatory dermatosis characterized by net-like or reticulated pink, and later hyperpigmented, papules and plaques. Although the condition predominantly affects young women of East Asian descent, cases have been reported worldwide, highlighting the importance of considering this diagnosis in diverse populations, including children. Here, we describe a case of prurigo pigmentosa in a young male who had recently adopted a ketogenic diet for weight loss.
The association between prurigo pigmentosa and dietary changes, particularly ketosis, is becoming increasingly recognized. This condition is strongly linked to ketosis, a metabolic state marked by the production of ketone bodies (e.g., beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate) during carbohydrate restriction, fasting, or ketogenic diets, as seen in our patient. These ketone bodies may act as irritants or trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory cascades in the skin.
Ketoacidosis, particularly in prolonged or intense ketosis, is thought to alter the local skin microenvironment, promoting activation of inflammatory cytokines and immune cells. The ketogenic state is believed to generate oxidative stress through increased free fatty acid oxidation, leading to the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS can induce apoptosis of keratinocytes and inflammation in the epidermis, which is predominantly mediated by neutrophilic infiltration, as seen in histopathological findings. Elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), have been implicated in neutrophil recruitment and activation. IL-8 is particularly important for guiding neutrophils to areas of injury.
Secondary hyperpigmentation, a hallmark of this condition, is thought to result from melanin-laden macrophages and persistent melanocyte activation in response to inflammation at the dermo-epidermal junction.
The condition progresses in three stages. In the early stage, lesions appear as pruritic, urticarial plaques. These evolve into crusted erythematous papules and papulovesicles in the middle stage, as observed in our patient. Finally, in the late stage, the lesions mature into smooth, hyperpigmented plaques. Each stage of prurigo pigmentosa has distinct histopathological features.
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for prurigo pigmentosa includes several conditions that may present similarly. Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) can initially mimic the erythematous papules of prurigo pigmentosa, but the absence of a clear allergen exposure and failure to improve with avoidance measures makes ACD less likely. Psoriasis is another possibility, as its erythematous plaques may overlap with prurigo pigmentosa. However, the lack of silvery scales and chronicity makes psoriasis less likely in this case. Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, typically presents with pruritic, ill-defined plaques, often in flexural areas, which were not observed in this patient. Flagellate dermatitis, often caused by exposure to bleomycin or consumption of shiitake mushrooms, can present with linear erythematous lesions resembling prurigo pigmentosa. However, the absence of relevant exposures and a flagellate pattern in this patient rules out this diagnosis.
This case highlights the growing recognition of prurigo pigmentosa in the context of dietary trends, especially ketogenic diets, which have become popular for weight loss and other health benefits. Pediatric populations, in particular, may adopt such diets for various reasons and require careful monitoring, as their physiological responses may differ from those in adults. Prurigo pigmentosa has also been reported in a teenager girl with a history of anorexia nervosa, who was in a ketotic state.
Treatment options for prurigo pigmentosa include antibiotics such as minocycline or doxycycline, or macrolides for 4–10 weeks. Other treatment modalities include dapsone, Q-switch Nd:YAG laser, narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB) phototherapy, and topical treatments like crisaborole and tacrolimus.
Early recognition of this condition is crucial to avoid unnecessary interventions and to allow for resolution through dietary modification. Dermatologists and pediatricians should maintain a high index of suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa in patients presenting with characteristic eruptions and a history of dietary ketosis.
Catalina Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
Suggested Reading
1. Mufti A et al. Clinical Manifestations and Treatment Outcomes in Prurigo Pigmentosa (Nagashima Disease): A Systematic Review of the Literature. JAAD Int. 2021 Apr 10:3:79-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003.
2. Yang J et al. Use of Minocycline for the Treatment of Prurigo Pigmentosa with Intraepidermal Vesiculation: A Case Report. J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211015593. doi: 10.1177/03000605211015593.
3. Capucilli P et al. Prurigo Pigmentosa: An Itchy, Urticarial Eruption Confused for Food Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018 Jul-Aug;6(4):1381-1382. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2018.02.033.
Case Report
A 16-year-old Hispanic male with a history of hyperlipidemia presents to his pediatrician's office for a routine well-child check-up. He reports a pruritic rash on his neck and chest that has been present for the past 1.5 weeks. The rash is itchy, and although a cream from Mexico initially helped, it has not been effective recently. The patient mentions that he has increased his gym workouts and has been training for basketball. He has a history of obesity but has lost almost 100 pounds in the last 6 months. Most recently, he has stopped consuming carbohydrates and has been fasting in the mornings.
There is no history of eczema or psoriasis, either in the patient or his family.
Physical Examination
The patient weighs 147 pounds, a significant decrease from his previous weight of 270 pounds 6 months ago. Other vital signs are within normal limits.
On physical examination, the patient presents with net-like, pink, scaly plaques on his neck, with no other rashes on the body (see Pictures 1 and 2).
Survey Highlights Trends in Pediatric Cosmetic Dermatology Procedures
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- An anonymous online survey conducted with SurveyMonkey targeted healthcare providers who routinely used lasers to treat cutaneous conditions in pediatric patients.
- The survey included members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and Surgery, as well as fellowship directors and current fellows of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery.
- A total of 85 practitioners responded to the survey, with 86% answering all questions; respondents primarily included pediatric dermatologists (77.65%), general dermatologists (18.82%), cosmetic dermatologists (8.24%), and dermatologic/Mohs surgeons (1.18%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Hypertrophic or traumatic scars ranked as the most frequently treated pediatric cosmetic condition (95.29%), followed by acne (89.41%), axillary and facial hyperhidrosis (77.65%), hypertrichosis/hirsutism (67.06%), and pigmented lesion removal (64.71%).
- The most common procedures performed were vascular lasers (77.65%), laser hair removal (50.59%), lasers for pigmentation (28.24%), neuromodulators (25.88%), and laser skin resurfacing (22.35%).
- Additional treatments respondents performed included chemical peels (20.00%), radiofrequency microneedling (16.47%), soft tissue fillers (4.71%), and cryolipolysis/body contouring (4.17%).
- About 50% of respondents said they would start cosmetic treatment of acne, and about 66% said they would start laser hair removal treatment between the ages of 12 and 15 years.
IN PRACTICE:
Noting that the survey results provided insight into the types of cosmetic procedures being performed for pediatric patients, the authors wrote, “These interventions can play a significant role in addressing the emotional and social challenges faced by pediatric patients with cosmetic concerns, allowing them to navigate social interactions more confidently and positively.” Before any procedure, they added, “It is important that any comorbid conditions be addressed,” they added, and “ethical considerations regarding informed consent, patient autonomy, and long-term consequences should be carefully weighed, given the vulnerable nature of pediatric patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lauren Hoffman, MD, who practices dermatology in Great Neck, New York. It was published online in December 2024 in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was subjective in nature and had a small sample size, and the exact number of survey recipients was unclear, hindering an accurate calculation of the response rate. The absolute number of responses accounted for a small portion of the total memberships of the participating societies. Also, the data collection periods varied among the three academic societies, and dermatologists’ practice types may have influenced the range and nature of treated conditions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose funding information. They declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- An anonymous online survey conducted with SurveyMonkey targeted healthcare providers who routinely used lasers to treat cutaneous conditions in pediatric patients.
- The survey included members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and Surgery, as well as fellowship directors and current fellows of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery.
- A total of 85 practitioners responded to the survey, with 86% answering all questions; respondents primarily included pediatric dermatologists (77.65%), general dermatologists (18.82%), cosmetic dermatologists (8.24%), and dermatologic/Mohs surgeons (1.18%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Hypertrophic or traumatic scars ranked as the most frequently treated pediatric cosmetic condition (95.29%), followed by acne (89.41%), axillary and facial hyperhidrosis (77.65%), hypertrichosis/hirsutism (67.06%), and pigmented lesion removal (64.71%).
- The most common procedures performed were vascular lasers (77.65%), laser hair removal (50.59%), lasers for pigmentation (28.24%), neuromodulators (25.88%), and laser skin resurfacing (22.35%).
- Additional treatments respondents performed included chemical peels (20.00%), radiofrequency microneedling (16.47%), soft tissue fillers (4.71%), and cryolipolysis/body contouring (4.17%).
- About 50% of respondents said they would start cosmetic treatment of acne, and about 66% said they would start laser hair removal treatment between the ages of 12 and 15 years.
IN PRACTICE:
Noting that the survey results provided insight into the types of cosmetic procedures being performed for pediatric patients, the authors wrote, “These interventions can play a significant role in addressing the emotional and social challenges faced by pediatric patients with cosmetic concerns, allowing them to navigate social interactions more confidently and positively.” Before any procedure, they added, “It is important that any comorbid conditions be addressed,” they added, and “ethical considerations regarding informed consent, patient autonomy, and long-term consequences should be carefully weighed, given the vulnerable nature of pediatric patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lauren Hoffman, MD, who practices dermatology in Great Neck, New York. It was published online in December 2024 in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was subjective in nature and had a small sample size, and the exact number of survey recipients was unclear, hindering an accurate calculation of the response rate. The absolute number of responses accounted for a small portion of the total memberships of the participating societies. Also, the data collection periods varied among the three academic societies, and dermatologists’ practice types may have influenced the range and nature of treated conditions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose funding information. They declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- An anonymous online survey conducted with SurveyMonkey targeted healthcare providers who routinely used lasers to treat cutaneous conditions in pediatric patients.
- The survey included members of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery and Surgery, as well as fellowship directors and current fellows of the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery.
- A total of 85 practitioners responded to the survey, with 86% answering all questions; respondents primarily included pediatric dermatologists (77.65%), general dermatologists (18.82%), cosmetic dermatologists (8.24%), and dermatologic/Mohs surgeons (1.18%).
TAKEAWAY:
- Hypertrophic or traumatic scars ranked as the most frequently treated pediatric cosmetic condition (95.29%), followed by acne (89.41%), axillary and facial hyperhidrosis (77.65%), hypertrichosis/hirsutism (67.06%), and pigmented lesion removal (64.71%).
- The most common procedures performed were vascular lasers (77.65%), laser hair removal (50.59%), lasers for pigmentation (28.24%), neuromodulators (25.88%), and laser skin resurfacing (22.35%).
- Additional treatments respondents performed included chemical peels (20.00%), radiofrequency microneedling (16.47%), soft tissue fillers (4.71%), and cryolipolysis/body contouring (4.17%).
- About 50% of respondents said they would start cosmetic treatment of acne, and about 66% said they would start laser hair removal treatment between the ages of 12 and 15 years.
IN PRACTICE:
Noting that the survey results provided insight into the types of cosmetic procedures being performed for pediatric patients, the authors wrote, “These interventions can play a significant role in addressing the emotional and social challenges faced by pediatric patients with cosmetic concerns, allowing them to navigate social interactions more confidently and positively.” Before any procedure, they added, “It is important that any comorbid conditions be addressed,” they added, and “ethical considerations regarding informed consent, patient autonomy, and long-term consequences should be carefully weighed, given the vulnerable nature of pediatric patients.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lauren Hoffman, MD, who practices dermatology in Great Neck, New York. It was published online in December 2024 in Dermatologic Surgery.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was subjective in nature and had a small sample size, and the exact number of survey recipients was unclear, hindering an accurate calculation of the response rate. The absolute number of responses accounted for a small portion of the total memberships of the participating societies. Also, the data collection periods varied among the three academic societies, and dermatologists’ practice types may have influenced the range and nature of treated conditions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not disclose funding information. They declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Approves IL-31 Inhibitor for Atopic Dermatitis
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a press release from the manufacturer, Galderma.
Nemolizumab (Nemluvio), a monoclonal antibody administered subcutaneously, targets the interleukin (IL)–31 receptor. IL-31 is known to promote itching and inflammation in atopic dermatitis, according to the company.
Approval was based on data from the phase 3 ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2 clinical trials, recently published in The Lancet, which included 1728 patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis and pruritus who had an inadequate response to topical steroids.
At week 16, significantly more patients randomized to nemolizumab every 4 weeks met the co-primary endpoints, compared with those taking placebo. The co-primary endpoints were an Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score of 0 (clear skin) or 1 (almost clear skin), with an improvement of at least 2 points from baseline to 16 weeks, and an improvement of at least 75% on the Eczema Area and Severity Index score from baseline to 16 weeks (EASI-75 response). All patients in both trials also received background treatment with topical corticosteroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors.
At 16 weeks, 36% and 38% of patients taking nemolizumab met the IGA criteria in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, compared with 25% and 26% of those taking placebo. Similarly, 44% and 42% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, achieved EASI-75, compared with 29% and 30% of those taking placebo. Differences between treatment and placebo groups were significant in both studies.
In addition, patients reported significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints, including itch, as early as week 1, and improvement in sleep by week 16, according to the study findings.
Safety profiles were similar between the treatment and placebo groups in both studies; the most common adverse reactions (reported by at least 1% of patients in each group) were headache (5% vs 4%), followed by arthralgia, urticaria, and myalgia (2% or less). In ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, 50% and 41% of patients taking nemolizumab reported at least one treatment-emergent adverse event, similar to the placebo groups (45% and 44%, respectively).
Serious treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 1% and 3% of those taking nemolizumab in ARCADIA 1 and ARCADIA 2, respectively, and 1% in the placebo groups in both studies. Ten serious treatment-emergent adverse events potentially related to nemolizumab were reported in five patients in ARCADIA 2. No deaths were reported in either study.
According to the prescribing information, safety profiles were similar between treatment and placebo groups in the subset of adolescents aged 12-17 years.
In August 2024, the FDA approved nemolizumab for the treatment of prurigo nodularis in adults. Authorization applications for nemolizumab for atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are under review by regulatory authorities in Australia, Singapore, Switzerland, Canada, Brazil, and South Korea, according to Galderma.
ARCADIA is funded by Galderma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Communicating with Angry Parents
There has been a lot of talk about polarization in America in the past year and how hard it can be to talk with someone with a different world view. It also seems that the COVID pandemic and a move to non–face-to-face communication has eroded social skills, increased disinformation, and made people irritable. As pediatric providers dealing with all kinds of people we have to increasingly deal with difficult communications.
We pediatric providers tend to be a friendly bunch with a mission of helping the health and well-being of children whose problems are no fault of their own. What’s not to like about us? Hence, one of the most difficult situations is a parent approaching us in anger. [All that follows also applies generally to adults, teens, and children but I here focus on parents.]
Health problems are often very frustrating. Parents mainly want their child’s problem fixed, yet that is not easy. Frustration with the health condition is compounded by having to wait, costs for care, life interruption, and confusing information. Anger and aggression are natural results of frustration (remember the Frustration-Aggression paradigm in animals?). Frustration is cumulative — a health problem may be the last straw, especially when social stressors or past trauma, also out of their control, were already present. Individuals with mental disorders or substance use are especially vulnerable to anger reactions.
Allaying Anger
As providers, we don’t know how anger may have been reinforced in the individual’s past. Anger may have scared others into giving in to them and thus became a familiar weapon. Sometimes angry outbursts get people to the front of the line. Expressing anger is also a kind of relief valve for emotions. Acknowledging that their situation is “very upsetting” and “frustrating” and that you will try to get a solution is the first step in effective communication.
Anger also comes from anxiety or fear. Anxiety is often a missed cause of childhood aggressive behavior. Parents are scared about poor short-and long-term outcomes of health problems in their child. Asking “What worries you the most about this illness?” or “What have you heard about this illness?” can elicit reports of fears you may be able to debunk or put in perspective.
Keeping their child healthy and safe are parents’ top priorities, so feeling helpless and out of control when an illness or injury occurs is very disturbing. Being a good parent is partly driven by guilt, which may be unrealistic, or from omission (eg, did not bring the child in sooner), or commission (eg, shouldn’t have taken her to that birthday party where she caught it). This is where you may normalize their actions such as saying “a child really can’t grow up in a bubble” or “symptoms can mean many things. I usually tell parents they don’t need to call unless the temperature is over 101,” for example. If appropriate, you might clarify what actions they should take in the future and provide a handout or instructions for sources of reliable information (and perhaps what is unreliable, such as TikTok!) to give them more power.
Feeling helpless may also evoke memories from the past when, as a child themselves, they were not able to help a loved one suffering from an accident or a health or mental health issue. They may have been helpless in the face of bullying, domestic violence, or racism. Even a hint of helplessness now can tap into the previous emotions, accelerating their reactivity. Promising to “work on this together” lends them your agency.
Of course, the main thing angry parents need is to have their child’s issue resolved. But this may not be a quick fix, especially if they are too incensed to cooperate. But what we can always do is address their need to be heard — both in content and emotion — and to help them regain a sense of control.
Pacing Can Help
One strategy that may seem counterintuitive is called “pacing.” Instead of begging the parent to calm down, which denigrates their strong feelings, we can echo their concerns while mirroring their emotions (within limits) to demonstrate that we understand them. Mirroring emotions may include your physical posture, volume and speed of speech, as well as use of similar sensory modalities. As for the modality component, you may notice that people tend to use visual, auditory or kinesthetic (feeling or action) words. So, for example, for an angry parent “screaming that no one has looked at the lab results yet” we might posture as they do, increase our volume, and use visual words such as saying “You are upset because you don’t see anyone looking over the labs in all this time.” As you hear more, you can continue to paraphrase and summarize what they are saying including their examples or wording. You can then change your own tone and posture progressively downshifting, bringing them along, and establishing rapport as they can tell that you are understanding them. Validating their emotions does not mean you have to agree with what they are saying; it demonstrates that you hear them.
Other strategies to demonstrate listening that can be helpful include sitting down side by side, and taking notes they can see, asking if you are getting the details correct. Using open-ended questions to elicit answers other than yes/no conveys openness to hear their story and may also reveal some of the causes for the upset. Sitting side by side conveys collaboration, whereas face to face implies more confrontation. Keep your arms down and arms and legs uncrossed and your head nodding and tilted somewhat down. These positions and verbal techniques demonstrate that you are listening to both their content and feelings.
Next Steps
The other main component to communication with an angry parent is providing action on the issue, especially involving them in a way that gives them some sense of control. Once they can tell that you understand them, it is then key to stay focused on solutions, bringing the discussion back if it veers off. There may be things they can do or you can do together such as log in to their portal, get on the phone with a relevant staff person such as a referral coordinator, or set a time for a follow-up appointment or call. Any action step they can do, even asking that they record a temperature every 6 hours, reduces helplessness.
It is crucial to elicit the parents’ criteria for satisfaction of their complaint. You may try asking: “What would tell you that your child’s problem is being adequately addressed?” Write down these criteria as part of the overall plan, making sure they are detailed, measurable, feasible, time related, and relevant. Include actions for the parent to take, if possible. By setting criteria and times for follow-up you establish accountability that also gives them a sense of control.
There are certain communications that can make things worse with an angry parent, some of which you may not even know occurred. Their anger may well have sparked a reaction in our staff, who are getting it full force before we even start our visit. Not only you but also your staff need to avoid making excuses for what happened (or didn’t happen) to the patient, blame the family for the child’s issue, imply that the parent’s feelings are invalid, or react as though their anger was a personal affront.
Setting Boundaries
There are certainly times when a parent’s behavior is unacceptable or even dangerous. It is important to have policies about what action to take so that we can verbally refer to these, if needed. We should all avoid threatening expulsion from the practice or calling security. Instead, assertively state the boundaries and rules and tell them what will happen if the behavior continues or exceeds a limit, such as frightening other patients or damaging equipment. It is essential to use respectful language and address them by name and certainly not make comments about them personally or criticize them, as these raise defensiveness. Suggesting they or you “take a break,” give them “some space” for a few minutes in a safe private room, or leave and come back in 15 minutes allows the upset parent to save face and gather themselves. All these things also work with children and teens.
Health care is stressful, especially with short staffing, and is often intensely personal and emotional. The human struggles we deal with may also be present in our own and our staff’s experiences.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
There has been a lot of talk about polarization in America in the past year and how hard it can be to talk with someone with a different world view. It also seems that the COVID pandemic and a move to non–face-to-face communication has eroded social skills, increased disinformation, and made people irritable. As pediatric providers dealing with all kinds of people we have to increasingly deal with difficult communications.
We pediatric providers tend to be a friendly bunch with a mission of helping the health and well-being of children whose problems are no fault of their own. What’s not to like about us? Hence, one of the most difficult situations is a parent approaching us in anger. [All that follows also applies generally to adults, teens, and children but I here focus on parents.]
Health problems are often very frustrating. Parents mainly want their child’s problem fixed, yet that is not easy. Frustration with the health condition is compounded by having to wait, costs for care, life interruption, and confusing information. Anger and aggression are natural results of frustration (remember the Frustration-Aggression paradigm in animals?). Frustration is cumulative — a health problem may be the last straw, especially when social stressors or past trauma, also out of their control, were already present. Individuals with mental disorders or substance use are especially vulnerable to anger reactions.
Allaying Anger
As providers, we don’t know how anger may have been reinforced in the individual’s past. Anger may have scared others into giving in to them and thus became a familiar weapon. Sometimes angry outbursts get people to the front of the line. Expressing anger is also a kind of relief valve for emotions. Acknowledging that their situation is “very upsetting” and “frustrating” and that you will try to get a solution is the first step in effective communication.
Anger also comes from anxiety or fear. Anxiety is often a missed cause of childhood aggressive behavior. Parents are scared about poor short-and long-term outcomes of health problems in their child. Asking “What worries you the most about this illness?” or “What have you heard about this illness?” can elicit reports of fears you may be able to debunk or put in perspective.
Keeping their child healthy and safe are parents’ top priorities, so feeling helpless and out of control when an illness or injury occurs is very disturbing. Being a good parent is partly driven by guilt, which may be unrealistic, or from omission (eg, did not bring the child in sooner), or commission (eg, shouldn’t have taken her to that birthday party where she caught it). This is where you may normalize their actions such as saying “a child really can’t grow up in a bubble” or “symptoms can mean many things. I usually tell parents they don’t need to call unless the temperature is over 101,” for example. If appropriate, you might clarify what actions they should take in the future and provide a handout or instructions for sources of reliable information (and perhaps what is unreliable, such as TikTok!) to give them more power.
Feeling helpless may also evoke memories from the past when, as a child themselves, they were not able to help a loved one suffering from an accident or a health or mental health issue. They may have been helpless in the face of bullying, domestic violence, or racism. Even a hint of helplessness now can tap into the previous emotions, accelerating their reactivity. Promising to “work on this together” lends them your agency.
Of course, the main thing angry parents need is to have their child’s issue resolved. But this may not be a quick fix, especially if they are too incensed to cooperate. But what we can always do is address their need to be heard — both in content and emotion — and to help them regain a sense of control.
Pacing Can Help
One strategy that may seem counterintuitive is called “pacing.” Instead of begging the parent to calm down, which denigrates their strong feelings, we can echo their concerns while mirroring their emotions (within limits) to demonstrate that we understand them. Mirroring emotions may include your physical posture, volume and speed of speech, as well as use of similar sensory modalities. As for the modality component, you may notice that people tend to use visual, auditory or kinesthetic (feeling or action) words. So, for example, for an angry parent “screaming that no one has looked at the lab results yet” we might posture as they do, increase our volume, and use visual words such as saying “You are upset because you don’t see anyone looking over the labs in all this time.” As you hear more, you can continue to paraphrase and summarize what they are saying including their examples or wording. You can then change your own tone and posture progressively downshifting, bringing them along, and establishing rapport as they can tell that you are understanding them. Validating their emotions does not mean you have to agree with what they are saying; it demonstrates that you hear them.
Other strategies to demonstrate listening that can be helpful include sitting down side by side, and taking notes they can see, asking if you are getting the details correct. Using open-ended questions to elicit answers other than yes/no conveys openness to hear their story and may also reveal some of the causes for the upset. Sitting side by side conveys collaboration, whereas face to face implies more confrontation. Keep your arms down and arms and legs uncrossed and your head nodding and tilted somewhat down. These positions and verbal techniques demonstrate that you are listening to both their content and feelings.
Next Steps
The other main component to communication with an angry parent is providing action on the issue, especially involving them in a way that gives them some sense of control. Once they can tell that you understand them, it is then key to stay focused on solutions, bringing the discussion back if it veers off. There may be things they can do or you can do together such as log in to their portal, get on the phone with a relevant staff person such as a referral coordinator, or set a time for a follow-up appointment or call. Any action step they can do, even asking that they record a temperature every 6 hours, reduces helplessness.
It is crucial to elicit the parents’ criteria for satisfaction of their complaint. You may try asking: “What would tell you that your child’s problem is being adequately addressed?” Write down these criteria as part of the overall plan, making sure they are detailed, measurable, feasible, time related, and relevant. Include actions for the parent to take, if possible. By setting criteria and times for follow-up you establish accountability that also gives them a sense of control.
There are certain communications that can make things worse with an angry parent, some of which you may not even know occurred. Their anger may well have sparked a reaction in our staff, who are getting it full force before we even start our visit. Not only you but also your staff need to avoid making excuses for what happened (or didn’t happen) to the patient, blame the family for the child’s issue, imply that the parent’s feelings are invalid, or react as though their anger was a personal affront.
Setting Boundaries
There are certainly times when a parent’s behavior is unacceptable or even dangerous. It is important to have policies about what action to take so that we can verbally refer to these, if needed. We should all avoid threatening expulsion from the practice or calling security. Instead, assertively state the boundaries and rules and tell them what will happen if the behavior continues or exceeds a limit, such as frightening other patients or damaging equipment. It is essential to use respectful language and address them by name and certainly not make comments about them personally or criticize them, as these raise defensiveness. Suggesting they or you “take a break,” give them “some space” for a few minutes in a safe private room, or leave and come back in 15 minutes allows the upset parent to save face and gather themselves. All these things also work with children and teens.
Health care is stressful, especially with short staffing, and is often intensely personal and emotional. The human struggles we deal with may also be present in our own and our staff’s experiences.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
There has been a lot of talk about polarization in America in the past year and how hard it can be to talk with someone with a different world view. It also seems that the COVID pandemic and a move to non–face-to-face communication has eroded social skills, increased disinformation, and made people irritable. As pediatric providers dealing with all kinds of people we have to increasingly deal with difficult communications.
We pediatric providers tend to be a friendly bunch with a mission of helping the health and well-being of children whose problems are no fault of their own. What’s not to like about us? Hence, one of the most difficult situations is a parent approaching us in anger. [All that follows also applies generally to adults, teens, and children but I here focus on parents.]
Health problems are often very frustrating. Parents mainly want their child’s problem fixed, yet that is not easy. Frustration with the health condition is compounded by having to wait, costs for care, life interruption, and confusing information. Anger and aggression are natural results of frustration (remember the Frustration-Aggression paradigm in animals?). Frustration is cumulative — a health problem may be the last straw, especially when social stressors or past trauma, also out of their control, were already present. Individuals with mental disorders or substance use are especially vulnerable to anger reactions.
Allaying Anger
As providers, we don’t know how anger may have been reinforced in the individual’s past. Anger may have scared others into giving in to them and thus became a familiar weapon. Sometimes angry outbursts get people to the front of the line. Expressing anger is also a kind of relief valve for emotions. Acknowledging that their situation is “very upsetting” and “frustrating” and that you will try to get a solution is the first step in effective communication.
Anger also comes from anxiety or fear. Anxiety is often a missed cause of childhood aggressive behavior. Parents are scared about poor short-and long-term outcomes of health problems in their child. Asking “What worries you the most about this illness?” or “What have you heard about this illness?” can elicit reports of fears you may be able to debunk or put in perspective.
Keeping their child healthy and safe are parents’ top priorities, so feeling helpless and out of control when an illness or injury occurs is very disturbing. Being a good parent is partly driven by guilt, which may be unrealistic, or from omission (eg, did not bring the child in sooner), or commission (eg, shouldn’t have taken her to that birthday party where she caught it). This is where you may normalize their actions such as saying “a child really can’t grow up in a bubble” or “symptoms can mean many things. I usually tell parents they don’t need to call unless the temperature is over 101,” for example. If appropriate, you might clarify what actions they should take in the future and provide a handout or instructions for sources of reliable information (and perhaps what is unreliable, such as TikTok!) to give them more power.
Feeling helpless may also evoke memories from the past when, as a child themselves, they were not able to help a loved one suffering from an accident or a health or mental health issue. They may have been helpless in the face of bullying, domestic violence, or racism. Even a hint of helplessness now can tap into the previous emotions, accelerating their reactivity. Promising to “work on this together” lends them your agency.
Of course, the main thing angry parents need is to have their child’s issue resolved. But this may not be a quick fix, especially if they are too incensed to cooperate. But what we can always do is address their need to be heard — both in content and emotion — and to help them regain a sense of control.
Pacing Can Help
One strategy that may seem counterintuitive is called “pacing.” Instead of begging the parent to calm down, which denigrates their strong feelings, we can echo their concerns while mirroring their emotions (within limits) to demonstrate that we understand them. Mirroring emotions may include your physical posture, volume and speed of speech, as well as use of similar sensory modalities. As for the modality component, you may notice that people tend to use visual, auditory or kinesthetic (feeling or action) words. So, for example, for an angry parent “screaming that no one has looked at the lab results yet” we might posture as they do, increase our volume, and use visual words such as saying “You are upset because you don’t see anyone looking over the labs in all this time.” As you hear more, you can continue to paraphrase and summarize what they are saying including their examples or wording. You can then change your own tone and posture progressively downshifting, bringing them along, and establishing rapport as they can tell that you are understanding them. Validating their emotions does not mean you have to agree with what they are saying; it demonstrates that you hear them.
Other strategies to demonstrate listening that can be helpful include sitting down side by side, and taking notes they can see, asking if you are getting the details correct. Using open-ended questions to elicit answers other than yes/no conveys openness to hear their story and may also reveal some of the causes for the upset. Sitting side by side conveys collaboration, whereas face to face implies more confrontation. Keep your arms down and arms and legs uncrossed and your head nodding and tilted somewhat down. These positions and verbal techniques demonstrate that you are listening to both their content and feelings.
Next Steps
The other main component to communication with an angry parent is providing action on the issue, especially involving them in a way that gives them some sense of control. Once they can tell that you understand them, it is then key to stay focused on solutions, bringing the discussion back if it veers off. There may be things they can do or you can do together such as log in to their portal, get on the phone with a relevant staff person such as a referral coordinator, or set a time for a follow-up appointment or call. Any action step they can do, even asking that they record a temperature every 6 hours, reduces helplessness.
It is crucial to elicit the parents’ criteria for satisfaction of their complaint. You may try asking: “What would tell you that your child’s problem is being adequately addressed?” Write down these criteria as part of the overall plan, making sure they are detailed, measurable, feasible, time related, and relevant. Include actions for the parent to take, if possible. By setting criteria and times for follow-up you establish accountability that also gives them a sense of control.
There are certain communications that can make things worse with an angry parent, some of which you may not even know occurred. Their anger may well have sparked a reaction in our staff, who are getting it full force before we even start our visit. Not only you but also your staff need to avoid making excuses for what happened (or didn’t happen) to the patient, blame the family for the child’s issue, imply that the parent’s feelings are invalid, or react as though their anger was a personal affront.
Setting Boundaries
There are certainly times when a parent’s behavior is unacceptable or even dangerous. It is important to have policies about what action to take so that we can verbally refer to these, if needed. We should all avoid threatening expulsion from the practice or calling security. Instead, assertively state the boundaries and rules and tell them what will happen if the behavior continues or exceeds a limit, such as frightening other patients or damaging equipment. It is essential to use respectful language and address them by name and certainly not make comments about them personally or criticize them, as these raise defensiveness. Suggesting they or you “take a break,” give them “some space” for a few minutes in a safe private room, or leave and come back in 15 minutes allows the upset parent to save face and gather themselves. All these things also work with children and teens.
Health care is stressful, especially with short staffing, and is often intensely personal and emotional. The human struggles we deal with may also be present in our own and our staff’s experiences.
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Special Considerations Needed in Applying Lupus Nephritis Guideline to Children
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON — When the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) released its updated guideline for management of lupus nephritis (LN) at its 2024 Annual Meeting, they included recommendations for managing pediatric LN for the first time.
The pediatric recommendations use the same classification criteria, outcome measures, and treatments as in adults — including the first-line triple therapy recommendation — but there remain important differences between pediatric and adult LN, Mary Beth Son, MD, clinical chief of immunology and section chief of rheumatology at Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts, and an associate professor of pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston, told attendees.
“In general, kids and adolescents with lupus are sicker,” Son said. They are more likely to have renal manifestations and neuropsychiatric lupus at diagnosis, compared with adults. Further, “although the disease is the same, it’s happening to kids and adolescents who are undergoing critical periods of growth and development.”
Medication risk profiles also shift for younger patients, Son noted.
“Importantly, they’re at risk for higher cumulative dosing of both glucocorticoids and cyclophosphamide,” Son said. “When we give an adolescent a course of cyclophosphamide, we have to be aware that this might be the first of a few courses over the course of the lifetime disease, and with increasing numbers of cyclophosphamide courses, you have increased risk for infertility and malignancy.”
Son also acknowledged challenges of pediatric literature, including differences in definitions of pediatric lupus, very few randomized controlled trials, and fewer pediatric studies in general, with fewer participants. Given these research gaps, the guideline panels included pediatric rheumatologists and nephrologists, and the patient panel included several patients with childhood-onset disease.
Son also addressed differences in pediatric drug development. Dosing studies also do not always directly translate from adults to children because children have larger drug volume distribution and differences in drug clearance, and they may need different formulations, she said. Children tend to tolerate medications better than adults because they usually have fewer comorbidities, but the assessment of a drug’s safety must take its impact on growth and development into consideration.
During a press conference after the session where the guideline was presented, Linda Hiraki, MD, ScD, a clinician-scientist in rheumatology at the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, said the panel took into consideration that pediatric patients receive their diagnosis during a critical time of development, so considerations of medication risks include the fact that children “have much more life to live.”
Triple Therapy Recommended
As with adults, the pediatric LN guideline recommends a triple therapy approach: glucocorticoids plus mycophenolate mofetil and belimumab, in addition to the usual renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and hydroxychloroquine. But Son acknowledged limitations of applying the new guideline to children. For one, voclosporin has not been studied in or approved for pediatric patients, although there exists modest evidence for other calcineurin inhibitors, mainly tacrolimus, in children.
“The other important consideration is that the lower dose of prednisone that’s being offered by the guidelines of 40 mg per day as a starting dose has not been studied in pediatric lupus nephritis patients,” Son said. “However, I would offer that, given that we know that kids get higher doses and longer courses, it’s even more important to consider a lower dose to begin with in the setting of other immunosuppressants.”
Good Practice Statements for Pediatric LN
Son also reviewed three good practice statements for pediatric LN. First, “glucocorticoid regimens should use pediatric-appropriate doses for children, as reduction of human glucocorticoid dosing is critically important given the early age of pediatric lupus onset and attendant comorbidities,” she said.
That statement is based on both common sense and some literature, including awareness that children are more likely to receive higher doses of steroids and that children’s higher damage scores are driven in part by steroid-related toxicity, such as avascular necrosis and cataracts. In addition, glucocorticoids can have profound effects on body mass index, mood, and height attainment.
“This is during a period of emerging self-identity and struggles with appearance; steroids exacerbate that” as well as mood issues already associated with puberty, Son said.
The second good practice statement recommends that clinicians monitor patients “for delayed pubertal onset and decreased growth velocity that can result from disease activity and glucocorticoid treatment and consider referral to pediatric endocrinology if indicated.” The third states that “a structured, intentional transition from pediatric to adult rheumatology care is indicated to avoid poor outcomes during this vulnerable period.”
During the press conference, Hiraki said that pediatric rheumatologists already recognize the need for discussions about transfer to adult care to begin very early, even years before patients are ready to transfer.
“The transition from being a pediatric patient to being an adult patient is very challenging for a number of reasons,” starting with loss of insurance coverage, added Bonnie Bermas, MD, a professor of internal medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas. When adult rheumatologists take on these patients, they may not have had care for 2 or 3 years, she said.
Rebecca Sadun, MD, PhD, an associate professor of pediatrics in rheumatology at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina, and vice-chair of the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Committee for the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance, was not involved in the guideline development process but reviewed the new guideline.
“We appreciate that the ACR took care to involve pediatric rheumatologists, pediatric nephrologists, and patients with childhood-onset lupus in the development of the newest lupus nephritis treatment guidelines,” she said in an interview. She also noted, however, that “the dearth of pediatric-specific clinical trial data means that we continue to wonder when it is appropriate to extrapolate from adult data regarding the efficacy, safety, and dosing of certain medications, including steroids and voclosporin.” She also noted that voclosporin use can increase pill burden and therefore be difficult to use in pediatrics.
“Children, adolescents, and young adults are a unique population with unique challenges, including significant struggles with adherence to complex medication regimens,” she said. Sadun drew attention to two themes from the guideline that she found particularly applicable to management of pediatric LN.
“First, we must remain wary of the serious consequences of long-term, high-dose glucocorticoids, and we should continue to look towards steroid-sparing strategies that will reduce reliance on glucocorticoids,” Sadun said. “Second, we are likely to see better outcomes, including better renal response, when we take advantage of combination immunosuppression earlier in the disease course.”
Son, Bermas, and Sadun had no disclosures. Hiraki has consulted for Janssen. The guideline development did not involve outside funding.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACR 2024
Smart Mattress to Reduce SUDEP?
LOS ANGELES — says one of the experts involved in its development.
When used along with a seizure detection device, Jong Woo Lee, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, estimates the smart mattress could cut SUDEP by more than 50%.
In addition, early results from an observational study are backing this up, he said.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
Most SUDEP Cases Found Face Down
SUDEP is the leading cause of death in children with epilepsy and in otherwise healthy adult patients with epilepsy. When his fifth patient died of SUDEP, Lee decided it was time to try to tackle the high mortality rate associated with these unexpected deaths. “I desperately wanted to help, ” he said.
About 70% of SUDEP occurs during sleep, and victims are found face down, or in the prone position, 90% of the time, said Lee.
“Of course, the best way to prevent SUDEP is not to have a seizure, but once you have a seizure and once you’re face down, your risk for death goes up by somewhere between 30 and 100 times,” he explained.
Lee was convinced SUDEP could be prevented by simple interventions that stimulate the patient and turn them over. He noted the incidence of sudden infant death syndrome, “which has similar characteristics” to SUDEP, has been reduced by up to 75% through campaigns that simply advise placing babies on their backs.
“Most of SUDEP happens because your arousal system is knocked out and you just don’t take the breath that you’re supposed to. Just the act of turning people over and vibrating the bed will stimulate them,” he said.
However, it’s crucial that this be done quickly, said Lee. “When you look at patients who died on video and see the EEGs, everybody took their last breath within 3 minutes.”
Because the window of opportunity is so short, “we think that seizure detection devices alone are not going to really be effective because you just can’t get there or react within those 3 minutes.”
There are currently no products that detect the prone position or have the ability to reposition a patient quickly into the recovery sideways position.
Lee and his colleagues developed a smart system that can be embedded in a mattress that detects when someone is having a seizure, determines if that person is face down, and if so, safely stimulates and repositions them.
The mattress is made up of a series of programmable inflatable blocks or “cells” that have pressure, vibration, temperature, and humidity sensors embedded within. “Based on the pressure readings, we can figure out whether the patient is right side up, on their right side, on their left side, or face down,” said Lee.
If the person is face down, he or she can be repositioned within a matter of seconds. “Each of the cells can lift 1000 pounds,” he said. The mattress is “very comfortable,” said Lee, who has tried it out himself.
Eighteen normative control participants have been enrolled for development and training purposes. To date, 10 of these individuals, aged 18-53 years, weighing 100-182 lb, and with a height of 5 ft 2 in to 6 ft 1 in, underwent extensive formal testing on the prototype bed.
Researchers found the mattress responded quickly to different body positions and weights. “We were able to reposition everybody in around 20 seconds,” said Lee.
The overall accuracy of detecting the prone position was 96.8%. There were no cases of a supine or prone position being mistaken for each other.
Researchers are refining the algorithm to improve the accuracy for detecting the prone position and expect to have a completely functional prototype within a few years.
Big Step Forward
Commenting on the research, Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor, Division of Epilepsy, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the study “is a big step forward in the race to provide an actionable tool to prevent SUDEP.”
The technology “appears to mostly be doing what it’s intended to do, with relatively minor technical errors being made,” he said.
However, it is not clear if this technology can truly save lives, said Goldenholz. “The data we have suggests that lying face down in bed after a seizure is correlated with SUDEP, but that does not mean that if we can simply flip people over, they for sure won’t die.”
Even if the new technology “works perfectly,” it’s still an open question, said Goldenholz. If it does save lives, “this will be a major breakthrough, and one that has been needed for a long time.”
However, even if it does not, he congratulates the team for trying to determine if reducing the prone position can help prevent SUDEP. He would like to see more “high-risk, high-reward” studies in the epilepsy field. “We are in so much need of new innovations.”
He said he was “personally very inspired” by this work. “People are dying from this terrible disease, and this team is building what they hope might save lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The mattress is being developed by Soterya. Lee reported no equity in Soterya. Goldenholz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — says one of the experts involved in its development.
When used along with a seizure detection device, Jong Woo Lee, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, estimates the smart mattress could cut SUDEP by more than 50%.
In addition, early results from an observational study are backing this up, he said.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
Most SUDEP Cases Found Face Down
SUDEP is the leading cause of death in children with epilepsy and in otherwise healthy adult patients with epilepsy. When his fifth patient died of SUDEP, Lee decided it was time to try to tackle the high mortality rate associated with these unexpected deaths. “I desperately wanted to help, ” he said.
About 70% of SUDEP occurs during sleep, and victims are found face down, or in the prone position, 90% of the time, said Lee.
“Of course, the best way to prevent SUDEP is not to have a seizure, but once you have a seizure and once you’re face down, your risk for death goes up by somewhere between 30 and 100 times,” he explained.
Lee was convinced SUDEP could be prevented by simple interventions that stimulate the patient and turn them over. He noted the incidence of sudden infant death syndrome, “which has similar characteristics” to SUDEP, has been reduced by up to 75% through campaigns that simply advise placing babies on their backs.
“Most of SUDEP happens because your arousal system is knocked out and you just don’t take the breath that you’re supposed to. Just the act of turning people over and vibrating the bed will stimulate them,” he said.
However, it’s crucial that this be done quickly, said Lee. “When you look at patients who died on video and see the EEGs, everybody took their last breath within 3 minutes.”
Because the window of opportunity is so short, “we think that seizure detection devices alone are not going to really be effective because you just can’t get there or react within those 3 minutes.”
There are currently no products that detect the prone position or have the ability to reposition a patient quickly into the recovery sideways position.
Lee and his colleagues developed a smart system that can be embedded in a mattress that detects when someone is having a seizure, determines if that person is face down, and if so, safely stimulates and repositions them.
The mattress is made up of a series of programmable inflatable blocks or “cells” that have pressure, vibration, temperature, and humidity sensors embedded within. “Based on the pressure readings, we can figure out whether the patient is right side up, on their right side, on their left side, or face down,” said Lee.
If the person is face down, he or she can be repositioned within a matter of seconds. “Each of the cells can lift 1000 pounds,” he said. The mattress is “very comfortable,” said Lee, who has tried it out himself.
Eighteen normative control participants have been enrolled for development and training purposes. To date, 10 of these individuals, aged 18-53 years, weighing 100-182 lb, and with a height of 5 ft 2 in to 6 ft 1 in, underwent extensive formal testing on the prototype bed.
Researchers found the mattress responded quickly to different body positions and weights. “We were able to reposition everybody in around 20 seconds,” said Lee.
The overall accuracy of detecting the prone position was 96.8%. There were no cases of a supine or prone position being mistaken for each other.
Researchers are refining the algorithm to improve the accuracy for detecting the prone position and expect to have a completely functional prototype within a few years.
Big Step Forward
Commenting on the research, Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor, Division of Epilepsy, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the study “is a big step forward in the race to provide an actionable tool to prevent SUDEP.”
The technology “appears to mostly be doing what it’s intended to do, with relatively minor technical errors being made,” he said.
However, it is not clear if this technology can truly save lives, said Goldenholz. “The data we have suggests that lying face down in bed after a seizure is correlated with SUDEP, but that does not mean that if we can simply flip people over, they for sure won’t die.”
Even if the new technology “works perfectly,” it’s still an open question, said Goldenholz. If it does save lives, “this will be a major breakthrough, and one that has been needed for a long time.”
However, even if it does not, he congratulates the team for trying to determine if reducing the prone position can help prevent SUDEP. He would like to see more “high-risk, high-reward” studies in the epilepsy field. “We are in so much need of new innovations.”
He said he was “personally very inspired” by this work. “People are dying from this terrible disease, and this team is building what they hope might save lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The mattress is being developed by Soterya. Lee reported no equity in Soterya. Goldenholz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — says one of the experts involved in its development.
When used along with a seizure detection device, Jong Woo Lee, MD, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, Massachusetts, estimates the smart mattress could cut SUDEP by more than 50%.
In addition, early results from an observational study are backing this up, he said.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
Most SUDEP Cases Found Face Down
SUDEP is the leading cause of death in children with epilepsy and in otherwise healthy adult patients with epilepsy. When his fifth patient died of SUDEP, Lee decided it was time to try to tackle the high mortality rate associated with these unexpected deaths. “I desperately wanted to help, ” he said.
About 70% of SUDEP occurs during sleep, and victims are found face down, or in the prone position, 90% of the time, said Lee.
“Of course, the best way to prevent SUDEP is not to have a seizure, but once you have a seizure and once you’re face down, your risk for death goes up by somewhere between 30 and 100 times,” he explained.
Lee was convinced SUDEP could be prevented by simple interventions that stimulate the patient and turn them over. He noted the incidence of sudden infant death syndrome, “which has similar characteristics” to SUDEP, has been reduced by up to 75% through campaigns that simply advise placing babies on their backs.
“Most of SUDEP happens because your arousal system is knocked out and you just don’t take the breath that you’re supposed to. Just the act of turning people over and vibrating the bed will stimulate them,” he said.
However, it’s crucial that this be done quickly, said Lee. “When you look at patients who died on video and see the EEGs, everybody took their last breath within 3 minutes.”
Because the window of opportunity is so short, “we think that seizure detection devices alone are not going to really be effective because you just can’t get there or react within those 3 minutes.”
There are currently no products that detect the prone position or have the ability to reposition a patient quickly into the recovery sideways position.
Lee and his colleagues developed a smart system that can be embedded in a mattress that detects when someone is having a seizure, determines if that person is face down, and if so, safely stimulates and repositions them.
The mattress is made up of a series of programmable inflatable blocks or “cells” that have pressure, vibration, temperature, and humidity sensors embedded within. “Based on the pressure readings, we can figure out whether the patient is right side up, on their right side, on their left side, or face down,” said Lee.
If the person is face down, he or she can be repositioned within a matter of seconds. “Each of the cells can lift 1000 pounds,” he said. The mattress is “very comfortable,” said Lee, who has tried it out himself.
Eighteen normative control participants have been enrolled for development and training purposes. To date, 10 of these individuals, aged 18-53 years, weighing 100-182 lb, and with a height of 5 ft 2 in to 6 ft 1 in, underwent extensive formal testing on the prototype bed.
Researchers found the mattress responded quickly to different body positions and weights. “We were able to reposition everybody in around 20 seconds,” said Lee.
The overall accuracy of detecting the prone position was 96.8%. There were no cases of a supine or prone position being mistaken for each other.
Researchers are refining the algorithm to improve the accuracy for detecting the prone position and expect to have a completely functional prototype within a few years.
Big Step Forward
Commenting on the research, Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor, Division of Epilepsy, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the study “is a big step forward in the race to provide an actionable tool to prevent SUDEP.”
The technology “appears to mostly be doing what it’s intended to do, with relatively minor technical errors being made,” he said.
However, it is not clear if this technology can truly save lives, said Goldenholz. “The data we have suggests that lying face down in bed after a seizure is correlated with SUDEP, but that does not mean that if we can simply flip people over, they for sure won’t die.”
Even if the new technology “works perfectly,” it’s still an open question, said Goldenholz. If it does save lives, “this will be a major breakthrough, and one that has been needed for a long time.”
However, even if it does not, he congratulates the team for trying to determine if reducing the prone position can help prevent SUDEP. He would like to see more “high-risk, high-reward” studies in the epilepsy field. “We are in so much need of new innovations.”
He said he was “personally very inspired” by this work. “People are dying from this terrible disease, and this team is building what they hope might save lives.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. The mattress is being developed by Soterya. Lee reported no equity in Soterya. Goldenholz reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AES 2024
Sleep Apnea Linked to Heightened Mortality in Epilepsy
LOS ANGELES — according to a new analysis of over 2 million patient-years drawn from the Komodo Health Claims Database.
“A 10-year-old with uncontrolled epilepsy and central sleep apnea is about 200 times more likely to die than a general population 10-year-old. That’s comparable to a 10-year-old with {epilepsy and} congestive heart failure. Noncentral sleep apnea is comparable to being paralyzed. It’s a huge risk factor,” said poster presenter Dan Lloyd, advanced analytics lead at UCB, which sponsored the research.
The ordering of sleep apnea tests for patients with epilepsy is widely variable, according to Stefanie Dedeurwaerdere, PhD, who is the innovation and value creation lead at UCB. “Some doctors do that as a general practice, and some don’t. There’s no coherency in the way these studies are requested for epilepsy patients. We want to create some awareness around this topic,” she said, and added that treatment of sleep apnea may improve epileptic seizures.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
The study included mortality rates between January 2018 and December 2022, with a total of 2,355,410 patient-years and 968,993 patients, with an age distribution of 19.1% age 1 to less than 18 years, 23.7% age 18-35 years, and 57.2% age 36 years or older. Sleep apnea prevalences were 0.7% for central sleep apnea (CSA), 14.0% for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and 85.3% with no sleep apnea.
Among those aged 1-18 years, the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) for those with uncontrolled epilepsy was 27.7. For those with comorbid OSA, the SMR was 74.2, and for comorbid CSA, the SMR was 135.9. The association was less pronounced in older groups, dipping to 7.0, 11.3, and 19.5 in those aged 18-35 years, and 3.3, 3.1, and 2.8 among those aged 36 years or older.
Among the 1-18 age group, SMRs for other comorbidities included 132.3 for heart failure, 74.9 for hemiplegia/paraplegia, 55.3 for cerebrovascular disease, and 44.6 for chronic pulmonary disease.
Asked for comment, Gordon Buchanan, MD, PhD, welcomed the new work. “The results did not surprise me. I study sleep, epilepsy, and [sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP)] in particular ... and every time I speak on these topics, someone asks me about risk of SUDEP in patients with sleep apnea. It’s great to finally have some data,” said Buchanan, a professor of neurology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The authors found that patients undergoing continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)/bi-level positive airway pressure therapy had a higher mortality risk than those not undergoing CPAP therapy but cautioned that uncontrolled confounders may be contributing to the effect.
Buchanan wondered if treatment with CPAP would be associated with a decreased mortality risk. “I think that would be interesting, but I know that, especially in children, it can be difficult to get them to remain compliant with CPAP. I think that would be interesting to know, if pushing harder to get the kids to comply with CPAP would reduce mortality,” he said.
The specific finding of heightened mortality associated with CSA is interesting, according to Buchanan. “We think of seizures propagating through the brain, maybe through direct synaptic connections or through spreading depolarization. So I think it would make sense that it would hit central regions that would then lead to sleep apnea.”
The relationship between OSA and epilepsy is likely complex. Epilepsy medications and special diets may influence body composition, which could in turn affect the risk for OSA, as could medications associated with psychiatric comorbidities, according to Buchanan.
The study is retrospective and based on claims data. It does not prove causation, and claims data do not fully capture mortality, which may lead to conservative SMR estimates. The researchers did not control for socioeconomic status, treatment status, and other comorbidities or conditions.
Lloyd and Dedeurwaerdere are employees of UCB, which sponsored the study. Buchanan had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — according to a new analysis of over 2 million patient-years drawn from the Komodo Health Claims Database.
“A 10-year-old with uncontrolled epilepsy and central sleep apnea is about 200 times more likely to die than a general population 10-year-old. That’s comparable to a 10-year-old with {epilepsy and} congestive heart failure. Noncentral sleep apnea is comparable to being paralyzed. It’s a huge risk factor,” said poster presenter Dan Lloyd, advanced analytics lead at UCB, which sponsored the research.
The ordering of sleep apnea tests for patients with epilepsy is widely variable, according to Stefanie Dedeurwaerdere, PhD, who is the innovation and value creation lead at UCB. “Some doctors do that as a general practice, and some don’t. There’s no coherency in the way these studies are requested for epilepsy patients. We want to create some awareness around this topic,” she said, and added that treatment of sleep apnea may improve epileptic seizures.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
The study included mortality rates between January 2018 and December 2022, with a total of 2,355,410 patient-years and 968,993 patients, with an age distribution of 19.1% age 1 to less than 18 years, 23.7% age 18-35 years, and 57.2% age 36 years or older. Sleep apnea prevalences were 0.7% for central sleep apnea (CSA), 14.0% for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and 85.3% with no sleep apnea.
Among those aged 1-18 years, the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) for those with uncontrolled epilepsy was 27.7. For those with comorbid OSA, the SMR was 74.2, and for comorbid CSA, the SMR was 135.9. The association was less pronounced in older groups, dipping to 7.0, 11.3, and 19.5 in those aged 18-35 years, and 3.3, 3.1, and 2.8 among those aged 36 years or older.
Among the 1-18 age group, SMRs for other comorbidities included 132.3 for heart failure, 74.9 for hemiplegia/paraplegia, 55.3 for cerebrovascular disease, and 44.6 for chronic pulmonary disease.
Asked for comment, Gordon Buchanan, MD, PhD, welcomed the new work. “The results did not surprise me. I study sleep, epilepsy, and [sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP)] in particular ... and every time I speak on these topics, someone asks me about risk of SUDEP in patients with sleep apnea. It’s great to finally have some data,” said Buchanan, a professor of neurology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The authors found that patients undergoing continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)/bi-level positive airway pressure therapy had a higher mortality risk than those not undergoing CPAP therapy but cautioned that uncontrolled confounders may be contributing to the effect.
Buchanan wondered if treatment with CPAP would be associated with a decreased mortality risk. “I think that would be interesting, but I know that, especially in children, it can be difficult to get them to remain compliant with CPAP. I think that would be interesting to know, if pushing harder to get the kids to comply with CPAP would reduce mortality,” he said.
The specific finding of heightened mortality associated with CSA is interesting, according to Buchanan. “We think of seizures propagating through the brain, maybe through direct synaptic connections or through spreading depolarization. So I think it would make sense that it would hit central regions that would then lead to sleep apnea.”
The relationship between OSA and epilepsy is likely complex. Epilepsy medications and special diets may influence body composition, which could in turn affect the risk for OSA, as could medications associated with psychiatric comorbidities, according to Buchanan.
The study is retrospective and based on claims data. It does not prove causation, and claims data do not fully capture mortality, which may lead to conservative SMR estimates. The researchers did not control for socioeconomic status, treatment status, and other comorbidities or conditions.
Lloyd and Dedeurwaerdere are employees of UCB, which sponsored the study. Buchanan had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — according to a new analysis of over 2 million patient-years drawn from the Komodo Health Claims Database.
“A 10-year-old with uncontrolled epilepsy and central sleep apnea is about 200 times more likely to die than a general population 10-year-old. That’s comparable to a 10-year-old with {epilepsy and} congestive heart failure. Noncentral sleep apnea is comparable to being paralyzed. It’s a huge risk factor,” said poster presenter Dan Lloyd, advanced analytics lead at UCB, which sponsored the research.
The ordering of sleep apnea tests for patients with epilepsy is widely variable, according to Stefanie Dedeurwaerdere, PhD, who is the innovation and value creation lead at UCB. “Some doctors do that as a general practice, and some don’t. There’s no coherency in the way these studies are requested for epilepsy patients. We want to create some awareness around this topic,” she said, and added that treatment of sleep apnea may improve epileptic seizures.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
The study included mortality rates between January 2018 and December 2022, with a total of 2,355,410 patient-years and 968,993 patients, with an age distribution of 19.1% age 1 to less than 18 years, 23.7% age 18-35 years, and 57.2% age 36 years or older. Sleep apnea prevalences were 0.7% for central sleep apnea (CSA), 14.0% for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and 85.3% with no sleep apnea.
Among those aged 1-18 years, the standardized mortality ratio (SMR) for those with uncontrolled epilepsy was 27.7. For those with comorbid OSA, the SMR was 74.2, and for comorbid CSA, the SMR was 135.9. The association was less pronounced in older groups, dipping to 7.0, 11.3, and 19.5 in those aged 18-35 years, and 3.3, 3.1, and 2.8 among those aged 36 years or older.
Among the 1-18 age group, SMRs for other comorbidities included 132.3 for heart failure, 74.9 for hemiplegia/paraplegia, 55.3 for cerebrovascular disease, and 44.6 for chronic pulmonary disease.
Asked for comment, Gordon Buchanan, MD, PhD, welcomed the new work. “The results did not surprise me. I study sleep, epilepsy, and [sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP)] in particular ... and every time I speak on these topics, someone asks me about risk of SUDEP in patients with sleep apnea. It’s great to finally have some data,” said Buchanan, a professor of neurology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City.
The authors found that patients undergoing continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)/bi-level positive airway pressure therapy had a higher mortality risk than those not undergoing CPAP therapy but cautioned that uncontrolled confounders may be contributing to the effect.
Buchanan wondered if treatment with CPAP would be associated with a decreased mortality risk. “I think that would be interesting, but I know that, especially in children, it can be difficult to get them to remain compliant with CPAP. I think that would be interesting to know, if pushing harder to get the kids to comply with CPAP would reduce mortality,” he said.
The specific finding of heightened mortality associated with CSA is interesting, according to Buchanan. “We think of seizures propagating through the brain, maybe through direct synaptic connections or through spreading depolarization. So I think it would make sense that it would hit central regions that would then lead to sleep apnea.”
The relationship between OSA and epilepsy is likely complex. Epilepsy medications and special diets may influence body composition, which could in turn affect the risk for OSA, as could medications associated with psychiatric comorbidities, according to Buchanan.
The study is retrospective and based on claims data. It does not prove causation, and claims data do not fully capture mortality, which may lead to conservative SMR estimates. The researchers did not control for socioeconomic status, treatment status, and other comorbidities or conditions.
Lloyd and Dedeurwaerdere are employees of UCB, which sponsored the study. Buchanan had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AES 2024
Noise and Artificial Light
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
If you’ve ever taken a red-eye flight you have probably received a little packet of items the airline hopes will make your night flight more comfortable. If you had shelled out for “extra leg room” or “more comfort” seating, your little kit may have included some one-size-never-fits-all socks, a toothbrush large enough to brush one tooth at a time, and a miniature tube of toothpaste the GEICO gecko would laugh at. I have no personal knowledge what the folks in first class are getting, but I suspect it comes in a calf skin Gucci pouch. But, regardless of where you are sitting, at a minimum your night comfort kit will come with an eye mask and ear plugs. Unfortunately, these freebies are wasted on me because I already use a sleep mask every night and simply turn off my hearing aids to mute the noise. But I appreciate their effort.
Light and sound are well-known sleep disruptors. Temperature gets less attention, but is nonetheless a potent contributor to a poor night’s sleep in my experience. Just by chance while I was recovering from my most recent jet lag, I encountered two papers from investigators who were curious about the association between healthy sleep and ambient light and noise.
The first paper looked at the relationship between artificial light at night (ALAN) and the incidence of insomnia. Looking at more than 300 Chinese cities, the investigators measured ALAN using satellite images and correlated the data with insomnia-related posts on social media. The researchers found when ALAN increased insomnia, related posts also increased. Not surprisingly, this relationship was greater in less populated cities during extreme temperatures and when air quality was poor.
The second paper came from University of Texas at Houston. Using Fitbit data from more than 3000 adolescents, the researchers looked for correlations between blood pressure, sleep health, and “median nighttime anthropogenic noise levels by ZIP code.” Turns out the Federal Highway Administration has a readily available map of these noise levels.
What the investigators found was that adequate sleep significantly reduces the risk of hypertension in adolescents. Not an unexpected finding to an ex-pediatrician like myself who is obsessed with the importance of sleep deprivation. However, the investigators and I were surprised that they had found no association between neighborhood noise alone or in combination with sleep health. I still suspect there is an association lurking there in the weeds of their data, but obviously it is not robust enough to float to the surface. It may be that in an acute situation noise can contribute to hypertension, but over time individuals adjust to the new sound level and their blood pressure settles down. Sleep is such a critical factor that it is not something our cardiovascular system can adapt to so easily. For various reasons most of us may already be functioning at the margins of sleep deprivation.
How then do we respond to observations by these two research teams? Do we take an approach similar to that the airlines have taken and prescribe, hand out, or sell ear plugs and sleep masks to every patient, or at least those with hypertension? This is what we could call the put-the-onus-on-the-patient approach, which seems to be the default when we lack the political will to take a bolder step.
The other path we could call the socio-environmental approach. The airlines have made a passing attempt at this by turning the cabin lights down on red-eye flights. I recently wrote about the “exposome,” which some investigators define as the total non-genetic exposures an individual endures during a lifetime and which in many situations has a negative effect on the individual’s health. These two papers clearly demonstrate that noise and nighttime artificial light are potent features of an uncountable number of individuals’ exposomes.
Unfortunately, it is going to require something far beyond these two relatively obscure studies to move the needle in the direction of a healthier population. It’s is not a stretch to put obesity and the attention deficit phenomenon under this same umbrella where our society needs to look at itself for the answers.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Childhood Atopic Dermatitis Doesn’t Delay Puberty
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a nationwide cohort study among 15,534 children in Denmark whose pubertal development was assessed every 6 months with a web-based questionnaire starting at the age of 11 years.
- The children were classified into three groups: No atopic dermatitis; self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (maternal report of a doctor diagnosis at 6 months, 18 months, and/or 7 years of age); hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (registry data showing it as the primary reason for hospital contact up to the age of 8 years), representing mainly severe cases.
- The main outcome was the age difference averaged across a range of pubertal milestones (attainment of Tanner stages; development of axillary hair, acne, and voice break; and occurrence of first ejaculation and menarche).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 21.5% of the children had self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis and 0.7% had hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis.
- Relative to girls without atopic dermatitis, girls with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones at the same age, with a mean difference of 0.0 months, and girls with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- Relative to boys without atopic dermatitis, boys with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones a mean of 0.1 month later and boys with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- A more stringent definition of atopic dermatitis — persistent or recurrent atopic dermatitis at 7 years of age (assumed more likely to affect sleep and disrupt the skin barrier near the start of puberty) — was also not associated with delayed pubertal development.
IN PRACTICE:
“Previous studies on atopic dermatitis and puberty are limited, some suggest a link between atopic dermatitis and delayed puberty, akin to other chronic inflammatory diseases in childhood,” the authors wrote. “The results of the present study are reassuring for young patients with atopic dermatitis approaching puberty and reproductive health in adult life,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Camilla Lomholt Kjersgaard, MD, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a lack of information on treatment, the use of analyses that did not address missing data, and a possible misclassification of self-reported pubertal development.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research; Aarhus University; and Fonden af Fam. Kjærsgaard, Sunds; and was cofunded by the European Union. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a nationwide cohort study among 15,534 children in Denmark whose pubertal development was assessed every 6 months with a web-based questionnaire starting at the age of 11 years.
- The children were classified into three groups: No atopic dermatitis; self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (maternal report of a doctor diagnosis at 6 months, 18 months, and/or 7 years of age); hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (registry data showing it as the primary reason for hospital contact up to the age of 8 years), representing mainly severe cases.
- The main outcome was the age difference averaged across a range of pubertal milestones (attainment of Tanner stages; development of axillary hair, acne, and voice break; and occurrence of first ejaculation and menarche).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 21.5% of the children had self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis and 0.7% had hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis.
- Relative to girls without atopic dermatitis, girls with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones at the same age, with a mean difference of 0.0 months, and girls with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- Relative to boys without atopic dermatitis, boys with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones a mean of 0.1 month later and boys with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- A more stringent definition of atopic dermatitis — persistent or recurrent atopic dermatitis at 7 years of age (assumed more likely to affect sleep and disrupt the skin barrier near the start of puberty) — was also not associated with delayed pubertal development.
IN PRACTICE:
“Previous studies on atopic dermatitis and puberty are limited, some suggest a link between atopic dermatitis and delayed puberty, akin to other chronic inflammatory diseases in childhood,” the authors wrote. “The results of the present study are reassuring for young patients with atopic dermatitis approaching puberty and reproductive health in adult life,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Camilla Lomholt Kjersgaard, MD, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a lack of information on treatment, the use of analyses that did not address missing data, and a possible misclassification of self-reported pubertal development.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research; Aarhus University; and Fonden af Fam. Kjærsgaard, Sunds; and was cofunded by the European Union. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a nationwide cohort study among 15,534 children in Denmark whose pubertal development was assessed every 6 months with a web-based questionnaire starting at the age of 11 years.
- The children were classified into three groups: No atopic dermatitis; self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (maternal report of a doctor diagnosis at 6 months, 18 months, and/or 7 years of age); hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis (registry data showing it as the primary reason for hospital contact up to the age of 8 years), representing mainly severe cases.
- The main outcome was the age difference averaged across a range of pubertal milestones (attainment of Tanner stages; development of axillary hair, acne, and voice break; and occurrence of first ejaculation and menarche).
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, 21.5% of the children had self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis and 0.7% had hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis.
- Relative to girls without atopic dermatitis, girls with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones at the same age, with a mean difference of 0.0 months, and girls with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- Relative to boys without atopic dermatitis, boys with self-reported doctor-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached the milestones a mean of 0.1 month later and boys with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis reached them a mean of 0.3 months earlier.
- A more stringent definition of atopic dermatitis — persistent or recurrent atopic dermatitis at 7 years of age (assumed more likely to affect sleep and disrupt the skin barrier near the start of puberty) — was also not associated with delayed pubertal development.
IN PRACTICE:
“Previous studies on atopic dermatitis and puberty are limited, some suggest a link between atopic dermatitis and delayed puberty, akin to other chronic inflammatory diseases in childhood,” the authors wrote. “The results of the present study are reassuring for young patients with atopic dermatitis approaching puberty and reproductive health in adult life,” they concluded.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Camilla Lomholt Kjersgaard, MD, Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark, and was published online in JAAD International.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included a lack of information on treatment, the use of analyses that did not address missing data, and a possible misclassification of self-reported pubertal development.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research; Aarhus University; and Fonden af Fam. Kjærsgaard, Sunds; and was cofunded by the European Union. The authors reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Measurement-Based Treatment to Target Approaches
Clinical Scenario
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school. Over the course of a month after a romantic and then a friend-group breakup, her parents have been concerned about her increasing tearfulness every day and retreat from activities to avoid social interactions with others that she once enjoyed so much. She has been missing more and more school, saying that she can’t bear to go, and staying in bed during the days, even on weekends. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment in 2 weeks with you and then again in another 2 weeks. Her parents and she tell you, “I thought she would be better by now.” You feel stuck with how to proceed in the visit. You have correctly identified the problem as depression, started the recommended evidence-based treatments, but the parents and Lilly are looking to you for something more or different. There are not many or other local resources. When and how do you all determine what “better” looks and feels like? Where do you go from here?
Metrics Can Guide Next Steps
This clinical scenario is not uncommon. As a psychiatrist consultant in primary care, I often encounter the following comment and question: “Someone isn’t feeling better. I have them taking an SSRI and doing psychotherapy. What is the next thing to do?” In discussions with supervisees and in training residents, I often say that you will know that your consultations have made a real impact on providers’ practices when these questions shift from “what’s the next medication or treatment” to a more robust baseline and follow-up inventory of symptoms via common and available metrics (PHQ9A, PSC-17 or 30, SCARED) shared with you at the start, the middle, and at other times of treatment. Such metrics can more meaningfully guide your collaborative clinical discussions and decisions.
Tracking baseline metrics and follow-up with treatment interventions is a transformative approach to clinical care. But, in primary care, it’s common that the question around mental health care may not receive the same robust screening and tracking of symptoms which have the power to more thoughtfully guide decision-making, even though this is common in other forms of patient care which have more routine use of more objective data.
Measurement-based treatment to target approaches are well-studied, but not often or always implemented. They involve providing a baseline metric (PHQ9A, Pediatric Symptom Checklist 17 or 30, GAD7, or SCARED), and tracking that metric for response over time using specific scores for decision points.
An Alternative Clinical Scenario
Consider the following alternative scenario for the above patient using a measurement-based treatment to target approach:
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school with symptoms concerning for depression. A PHQ9A is administered in your appointment, and she scores 20 out of 30, exceeding the threshold score for 11 for depression. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment with you in 2 weeks and then again in another 2 weeks. You obtain a PHQ9A at each appointment, and track the change with her and her parents over time.
You share with her and the family that it is common that there will be fluctuations in measurements, and you know that a score change on the PHQ9A greater than 7 is considered a clinically significant, reliable change. So, a PHQ9 score reduction from 20 to 13 would be meaningful progress. While seeking a score within the normal and non-clinical range, the progress can be tracked in a way that allows a more robust monitoring of treatment response. If the scores do not improve, you can see that and act accordingly. This way of using metrics shifts the conversation from “how are you feeling now and today” to tracking symptoms more broadly and tracking those individual symptoms over time, some of which may improve and some which may be trickier to target.
Such a way of tracking common mental health symptoms with a focus on having data at baseline and throughout treatment allows a provider to change or adapt interventions, and to not chase something that can feel ephemeral, such as “feeling happy or looking better.”
For additional information on the measurement-based treatment to target approach, there are resources that share in more depth the research informing this approach, and other and broader real ways to integrate these practices into your own visits:
- Is Treatment Working? Detecting Real Change in the Treatment of Child and Adolescent Depression
- AACAP Clinical Update: Collaborative Mental Health Care for Children and Adolescents in Primary Care
Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine.
Clinical Scenario
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school. Over the course of a month after a romantic and then a friend-group breakup, her parents have been concerned about her increasing tearfulness every day and retreat from activities to avoid social interactions with others that she once enjoyed so much. She has been missing more and more school, saying that she can’t bear to go, and staying in bed during the days, even on weekends. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment in 2 weeks with you and then again in another 2 weeks. Her parents and she tell you, “I thought she would be better by now.” You feel stuck with how to proceed in the visit. You have correctly identified the problem as depression, started the recommended evidence-based treatments, but the parents and Lilly are looking to you for something more or different. There are not many or other local resources. When and how do you all determine what “better” looks and feels like? Where do you go from here?
Metrics Can Guide Next Steps
This clinical scenario is not uncommon. As a psychiatrist consultant in primary care, I often encounter the following comment and question: “Someone isn’t feeling better. I have them taking an SSRI and doing psychotherapy. What is the next thing to do?” In discussions with supervisees and in training residents, I often say that you will know that your consultations have made a real impact on providers’ practices when these questions shift from “what’s the next medication or treatment” to a more robust baseline and follow-up inventory of symptoms via common and available metrics (PHQ9A, PSC-17 or 30, SCARED) shared with you at the start, the middle, and at other times of treatment. Such metrics can more meaningfully guide your collaborative clinical discussions and decisions.
Tracking baseline metrics and follow-up with treatment interventions is a transformative approach to clinical care. But, in primary care, it’s common that the question around mental health care may not receive the same robust screening and tracking of symptoms which have the power to more thoughtfully guide decision-making, even though this is common in other forms of patient care which have more routine use of more objective data.
Measurement-based treatment to target approaches are well-studied, but not often or always implemented. They involve providing a baseline metric (PHQ9A, Pediatric Symptom Checklist 17 or 30, GAD7, or SCARED), and tracking that metric for response over time using specific scores for decision points.
An Alternative Clinical Scenario
Consider the following alternative scenario for the above patient using a measurement-based treatment to target approach:
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school with symptoms concerning for depression. A PHQ9A is administered in your appointment, and she scores 20 out of 30, exceeding the threshold score for 11 for depression. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment with you in 2 weeks and then again in another 2 weeks. You obtain a PHQ9A at each appointment, and track the change with her and her parents over time.
You share with her and the family that it is common that there will be fluctuations in measurements, and you know that a score change on the PHQ9A greater than 7 is considered a clinically significant, reliable change. So, a PHQ9 score reduction from 20 to 13 would be meaningful progress. While seeking a score within the normal and non-clinical range, the progress can be tracked in a way that allows a more robust monitoring of treatment response. If the scores do not improve, you can see that and act accordingly. This way of using metrics shifts the conversation from “how are you feeling now and today” to tracking symptoms more broadly and tracking those individual symptoms over time, some of which may improve and some which may be trickier to target.
Such a way of tracking common mental health symptoms with a focus on having data at baseline and throughout treatment allows a provider to change or adapt interventions, and to not chase something that can feel ephemeral, such as “feeling happy or looking better.”
For additional information on the measurement-based treatment to target approach, there are resources that share in more depth the research informing this approach, and other and broader real ways to integrate these practices into your own visits:
- Is Treatment Working? Detecting Real Change in the Treatment of Child and Adolescent Depression
- AACAP Clinical Update: Collaborative Mental Health Care for Children and Adolescents in Primary Care
Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine.
Clinical Scenario
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school. Over the course of a month after a romantic and then a friend-group breakup, her parents have been concerned about her increasing tearfulness every day and retreat from activities to avoid social interactions with others that she once enjoyed so much. She has been missing more and more school, saying that she can’t bear to go, and staying in bed during the days, even on weekends. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment in 2 weeks with you and then again in another 2 weeks. Her parents and she tell you, “I thought she would be better by now.” You feel stuck with how to proceed in the visit. You have correctly identified the problem as depression, started the recommended evidence-based treatments, but the parents and Lilly are looking to you for something more or different. There are not many or other local resources. When and how do you all determine what “better” looks and feels like? Where do you go from here?
Metrics Can Guide Next Steps
This clinical scenario is not uncommon. As a psychiatrist consultant in primary care, I often encounter the following comment and question: “Someone isn’t feeling better. I have them taking an SSRI and doing psychotherapy. What is the next thing to do?” In discussions with supervisees and in training residents, I often say that you will know that your consultations have made a real impact on providers’ practices when these questions shift from “what’s the next medication or treatment” to a more robust baseline and follow-up inventory of symptoms via common and available metrics (PHQ9A, PSC-17 or 30, SCARED) shared with you at the start, the middle, and at other times of treatment. Such metrics can more meaningfully guide your collaborative clinical discussions and decisions.
Tracking baseline metrics and follow-up with treatment interventions is a transformative approach to clinical care. But, in primary care, it’s common that the question around mental health care may not receive the same robust screening and tracking of symptoms which have the power to more thoughtfully guide decision-making, even though this is common in other forms of patient care which have more routine use of more objective data.
Measurement-based treatment to target approaches are well-studied, but not often or always implemented. They involve providing a baseline metric (PHQ9A, Pediatric Symptom Checklist 17 or 30, GAD7, or SCARED), and tracking that metric for response over time using specific scores for decision points.
An Alternative Clinical Scenario
Consider the following alternative scenario for the above patient using a measurement-based treatment to target approach:
Lilly is a 15-year-old girl in her sophomore year of high school with symptoms concerning for depression. A PHQ9A is administered in your appointment, and she scores 20 out of 30, exceeding the threshold score for 11 for depression. You start her on an SSRI and recommend psychotherapy in the form of CBT offered through your office. She returns to the appointment with you in 2 weeks and then again in another 2 weeks. You obtain a PHQ9A at each appointment, and track the change with her and her parents over time.
You share with her and the family that it is common that there will be fluctuations in measurements, and you know that a score change on the PHQ9A greater than 7 is considered a clinically significant, reliable change. So, a PHQ9 score reduction from 20 to 13 would be meaningful progress. While seeking a score within the normal and non-clinical range, the progress can be tracked in a way that allows a more robust monitoring of treatment response. If the scores do not improve, you can see that and act accordingly. This way of using metrics shifts the conversation from “how are you feeling now and today” to tracking symptoms more broadly and tracking those individual symptoms over time, some of which may improve and some which may be trickier to target.
Such a way of tracking common mental health symptoms with a focus on having data at baseline and throughout treatment allows a provider to change or adapt interventions, and to not chase something that can feel ephemeral, such as “feeling happy or looking better.”
For additional information on the measurement-based treatment to target approach, there are resources that share in more depth the research informing this approach, and other and broader real ways to integrate these practices into your own visits:
- Is Treatment Working? Detecting Real Change in the Treatment of Child and Adolescent Depression
- AACAP Clinical Update: Collaborative Mental Health Care for Children and Adolescents in Primary Care
Pawlowski is a child and adolescent consulting psychiatrist. She is a division chief at the University of Vermont Medical Center where she focuses on primary care mental health integration within primary care pediatrics, internal medicine, and family medicine.