User login
When Your First Job Isn’t Forever: Lessons from My Journey and What Early-Career GIs Need to Know
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Introduction
For many of us in gastroenterology, landing that first attending job feels like the ultimate victory lap — the reward for all those years of training. We sign the contract, relocate, and imagine this will be our “forever job.” Reality often plays out differently.
In fact, 43% of physicians change jobs within five years, while 83% changed employers at least once in their careers.1 Even within our field — which is always in demand — turnover is high; 1 in 3 gastroenterologists are planning to leave their current role within two years.2 Why does this happen? More importantly, how do we navigate this transition with clarity and confidence as an early-career GI?
My Story: When I Dared to Change My “Forever Job”
When I signed my first attending contract, I didn’t negotiate a single thing. My priorities were simple: family in Toronto and visa requirements. After a decade of medical school, residency, and fellowship, everything else felt secondary. I was happy to be back home.
The job itself was good — reasonable hours, flexible colleagues, and ample opportunity to enhance my procedural skills. As I started carving out my niche in endobariatrics, the support I needed to grow further was not there. I kept telling myself that this job fulfilled my values and I needed to be patient: “this is my forever job. I am close to my family and that’s what matters.”
Then, during a suturing course at the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, I had a casual chat with the course director (now my boss). It took me by surprise, but as the conversation continued, he offered me a job. It was tempting: the chance to build my own endobariatrics program with real institutional backing. The catch? It was in a city I had never been to, with no family or friends around. I politely said “no, thank you, I can’t.” He smiled, gave me his number, and said, “think about it.”
For the first time, I allowed myself to ask, “could I really leave my forever job?”
The Power of a Circle and a Spreadsheet
I leaned on my circle — a close group of fellowship friends who each took a turn being someone’s lifeline. We have monthly Zoom calls to talk about jobs, family, and career aspirations. When I shared my dilemma, I realized I wasn’t alone; one friend was also unhappy with her first job. Suddenly, we were asking one another, “can we really leave?”
I hired a career consultant familiar with physician visa issues — hands down, the best money I ever invested. The job search felt like dating: each interview was a first date; some needed a second or third date before I knew if it could be a match.
After every interview, I’d jump on Zoom with my circle. We’d screen-share my giant Excel spreadsheet — our decision matrix — with columns for everything I cared about:
- Institute
- Administrative Time
- Endobariatric support
- Director Title
- Salary
- On-call
- Vacation
- Proximity to airport
- Cost of living
- RVU percentage
- Endoscopy center buy-in
- Contract duration
- Support staff
- CME
We scored each job, line by line, and not a single job checked all the boxes. As I sat there in a state of decision paralysis, it became clear that this was not a simple decision.
The GI Community: A Small, Supportive World
The GI community is incredibly close-knit and kind-hearted. At every conference, I made a point to chat with as many colleagues as I could, to hear their perspectives on jobs and how they made tough career moves. Those conversations were real — no Google search or Excel sheet could offer the perspective and insight I gained by simply asking and leaning on the GI community.
Meanwhile, the person who had first offered me that job kept checking in, catching up at conferences, and bonding over our love for food and baking. With him, I never felt like I was being ‘interviewed’ — I felt valued. It did not feel like he was trying to fill a position with just anyone to improve the call pool. He genuinely wanted to understand what my goals were and how I envisioned my future. Through those conversations, he reminded me of my original passions, which were sidelined when so immersed in the daily routine.
I’ve learned that feeling valued doesn’t come from grand gestures in recruitment. It’s in the quiet signs of respect, trust, and being seen. He wasn’t looking for just anyone; he was looking for someone whose goals aligned with his group’s and someone in whom he wanted to invest. While others might chase the highest salary, the most flexible schedule, or the strongest ancillary support, I realized I valued something I did not realize that I was lacking until then: mentorship.
What I Learned: There is No Such Thing As “The Perfect Job”
After a full year of spreadsheets, Zoom calls, conference chats, and overthinking, I came to a big realization: there’s no perfect job — there’s no such thing as an ideal “forever job.” The only constant for humans is change. Our circumstances change, our priorities shift, our interests shuffle, and our finances evolve. The best job is simply the one that fits the stage of life you’re in at that given moment. For me, mentorship and growth became my top priorities, even if it meant moving away from family.
What Physicians Value Most in a Second Job
After their first job, early-career gastroenterologists often reevaluate what really matters. Recent surveys highlight four key priorities:
- Work-life balance:
In a 2022 CompHealth Group healthcare survey, 85% of physicians ranked work-life balance as their top job priority.3
- Mentorship and growth:
Nearly 1 in 3 physicians cited lack of mentorship or career advancement as their reason for leaving a first job, per the 2023 MGMA/Jackson Physician Search report.4
- Compensation:
While not always the main reason for leaving, 77% of physicians now list compensation as a top priority — a big jump from prior years.3
- Practice support:
Poor infrastructure, administrative overload, or understaffed teams are common dealbreakers. In the second job, physicians look for well-run practices with solid support staff and reduced burnout risk.5
Conclusion
Welcome the uncertainty, talk to your circle, lean on your community, and use a spreadsheet if you need to — but don’t forget to trust your gut. There’s no forever job or the perfect path, only the next move that feels most true to who you are in that moment.
Dr. Ismail (@mayyismail) is Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine (Gastroenterology) at Temple University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She declares no conflicts of interest.
References
1. CHG Healthcare. Survey: 62% of physicians made a career change in the last two years. CHG Healthcare blog. June 10, 2024. Accessed August 5, 2025.
2. Berg S. Physicians in these 10 specialties are less likely to quit. AMA News. Published June 24, 2025. Accessed July 2025.
3. Saley C. Survey: Work/life balance is #1 priority in physicians’ job search. CHG Healthcare Insights. March 10, 2022. Accessed August 2025.
4. Medical Group Management Association; Jackson Physician Search. Early‑Career Physician Recruiting & Retention Playbook. October 23, 2023. Accessed August 2025.
5. Von Rosenvinge EC, et al. A crisis in scope: Recruitment and retention challenges reported by VA gastroenterology section chiefs. Fed Pract. 2024 Aug. doi:10.12788/fp.0504.
Developing the Next Generation of GI Leaders

In this episode of Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. Naresh Gunaratnam, current president and board chair of Digestive Health Physician Association, speaks with Dr. Larry Kim, current president of AGA, about .

In this episode of Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. Naresh Gunaratnam, current president and board chair of Digestive Health Physician Association, speaks with Dr. Larry Kim, current president of AGA, about .

In this episode of Private Practice Perspectives, Dr. Naresh Gunaratnam, current president and board chair of Digestive Health Physician Association, speaks with Dr. Larry Kim, current president of AGA, about .
Physician Compensation: Gains Small, Gaps Large
Few would deny that physicians today face many challenges: a growing and aging patient population, personnel shortages, mounting paperwork, regulatory and reimbursement pressures, and personal burnout. Collectively these could work to worsen patient access to care. Yet despite these headwinds, Doximity’s survey-based Physician Compensation Report 2025 found that more than three-quarters of physicians polled would still choose to enter their profession.
“Physician burnout isn’t new. It’s been a persistent problem over the past decade,” said Amit Phull, MD, chief clinical experience officer at Doximity. “In a Doximity poll of nearly 2,000 physicians conducted in May 2025, 85% reported they feel overworked, up from 73% just four years ago. As a result, about 68% of physicians said they are looking for an employment change or considering early retirement.”
Greater awareness of contemporary trends may help physicians make more-informed career decisions and more effectively advocate for both themselves and the patients who need them, the report’s authors stated.
Compensation Lag May Impact Care
A small overall average compensation increase of 3.7% from 2023 to 2024 – a slightly lower increase than the 5.9% in the prior year – has done little to close existing pay gaps across the profession.
In 2024, average compensation for men rose 5.7% over 2023, compared with just 1.7% for women – widening the gender pay gap to 26% vs 23% in 2023 and matching the gender gap seen in 2022. And significant disparities persist between physicians caring for adults vs children. In some specialties, the pay gap between pediatric and adult specialists exceeded 80% despite practitioners’ similar levels of training and clinical complexity.
Nearly 60% of respondents said reimbursement pressures could affect their ability to serve Medicare or Medicaid patients in the next year. Additionally, 81% reported that reimbursement policies have significantly contributed to the decline of private practices, and more than a third said they could stifle practice growth with compensation concerns forcing them to delay or cancel hiring or expansion plans. Almost 90% reported an adverse impact from physician shortages, with more citing an inability or limited ability to accept new patients.
Narrowing the Gap for Primary Care?
Over the past three years, the percent pay gap between primary care and specialist medicine declined modestly, the report noted. In 2024, surgical specialists earned 87% more than primary care physicians, down from 100% in 2022. Non-surgical specialists, emergency medicine physicians, and Ob/Gyns also continued to earn significantly more than primary care physicians, though the gaps have narrowed slightly.
“These trends come at a time when primary care remains critical to meeting high patient demand, especially amid ongoing physician shortages,” the report stated. “Primary care physicians continue to earn considerably less than many of their medical colleagues despite their essential role in the healthcare system.”
Significantly, many physicians believe that current reimbursement policies have contributed to the steady decline of independent practices in their fields. According to the American Medical Association, the share of physicians working in private practices dropped by 18 percentage points from 60.1% to 42.2% from 2012 to 2024.
The Specialties
This year’s review found that among 20 specialties, the highest average compensation occurred in surgical and procedural specialties, while the lowest paid were, as mentioned, pediatric medicine and primary care. Pediatric nephrology saw the largest average compensation growth in 2024 at 15.6%, yet compensation still lagged behind adult nephrology with a 40% pay gap.
By medical discipline, gastroenterologists ranked 13th overall in average annual compensation. Gastroenterology remained in the top 20 compensated specialties, with average annual compensation of $537,870 – an increase from $514,208 in 2024, representing a 4.5% growth rate over 2023. Neurosurgeons topped the list at $749,140, followed by thoracic surgeons at $689,969 and orthopedic surgeons at $679,517.
The three lowest-paid branches were all pediatric: endocrinology at $230,426, rheumatology at $231,574, and infectious diseases at $248,322. Pediatric gastroenterology paid somewhat higher at $298,457.
The largest disparities were seen in hematology and oncology, where adult specialists earned 93% more than their pediatric peers. Pediatric gastroenterology showed an 80% pay gap. There were also substantial pay differences across cardiology, pulmonology, and rheumatology. “These gaps appear to reflect a systemic lag in pay for pediatric specialty care, even as demand for pediatric subspecialists continues to rise,” the report stated.
Practice Setting and Location
Where a doctor practices impacts the bottom line, too: in 2024 the highest compensation reported for a metro area was in Rochester, Minnesota (the Mayo Clinic effect?), at $495,532, while the lowest reported was in Durham-Chapel Hill, North Carolina, at $368,782. St. Louis, Missouri ($484,883) and Los Angeles, California ($470,198) were 2nd and 3rd at the top of the list. Rochester, Minnesota, also emerged as best for annual compensation after cost-of-living adjustment, while Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the bottom rung.
The Gender Effect
With a women’s pay increase in 2024 of just 1.7%, the gender gap returned to its 2022-level disparity of 26%, with women physicians earning an average of $120,917 less than men after adjusting for specialty, location, and years of experience.
Doximity’s analysis of data from 2014 to 2019 estimated that on average men make at least $2 million more than women over the course of a 40-year career. This gap is often attributed to the fewer hours worked by female physician with their generally heavier familial responsibilities, “but Doximity’s gender wage gap analysis controls for the number of hours worked and career stage, along with specialty, work type, employment status, region, and credentials,” Phull said.
Women physicians had lower average earnings than men physicians across all specialties, a trend consistent with prior years. As a percentage of pay, the largest gender disparity was seen in pediatric nephrology (16.5%), a specialty that in fact saw the largest annual growth in physician pay. Neurosurgery had the smallest gender gap at 11.3%, while infectious diseases came in at 11.5% and oncology at 12%.
According to Maria T. Abreu, MD, AGAF, executive director of the F. Widjaja Inflammatory Bowel Disease Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and past president of AGA, the remuneration gender gap in gastroenterology is being taken seriously by AGA and several other GI societies. “The discrepancies in pay start from the beginning and therefore are magnified over time. We are helping to empower women to negotiate better as well as to gather data on the roots of inequity, she told GI & Hepatology News.
The AGA Women’s Committee has developed a project to support the advancement of women in gastroenterology, Abreu said. The initiative, which includes the AGA Gender Equity Framework and Gender Equity Road Map. focuses attention on disparities in the workplace and promotes opportunities for women’s leadership, career advancement, mentorship and physician health and wellness, she added.
Are these disparities due mainly to the “motherhood penalty,” with career interruption and time lost to maternity leave and fewer hours worked owing to the greater parenting burden of physician mothers? Or are they due to the systemic effects of gender expectations around compensation?
Hours worked appear to be a factor. A 2017 study of dual physician couples found that among childless respondents men worked an average of 57 hours and women 52 hours weekly. Compared with childless men, men with children worked similar numbers of hours weekly. However, compared with childless physicians, mothers worked significantly fewer hours – roughly 40 to 43 hours weekly – depending on the age of their youngest child.
Abreu pushed back on this stereotype. “Most women physicians, including gastroenterologists, do not take the maternity leave they are allowed because they are concerned about burdening their colleagues,” she said. “Thus, it is unlikely to explain the disparities. Many systemic issues remain challenging, but we want women to be empowered to advocate for themselves at the time of hiring and along the arc of their career paths.”
In Abreu’s view, having women assume more leadership roles in the field of gastroenterology provides an opportunity to focus on reducing the disparities in compensation.
Regardless of gender, among all physicians surveyed, autonomy and work-life balance appeared to be a high priority: 77% of doctors said they would be willing to accept or have already accepted lower pay for more autonomy or work-life balance. “Overwork appears to be especially prevalent among women physicians,” said Phull, noting that 91% of women respondents reported being overworked compared with 80% of men. “This overwork has compelled 74% of women to consider making a career change, compared with 62% of men.” Differences emerged among specialties as well: 90% of primary care physicians said they are overworked compared with 84% of surgeons and 83% of non-surgical specialists.
Looking ahead, the report raised an important question. Are we relying too heavily on physicians rather than addressing the underlying need for policies that support a healthier, more sustainable future for all? “Building that future will take more than physician dedication alone,” Phull said. “It will require meaningful collaboration across the entire health care ecosystem – including health systems, hospitals, payors, and policymakers. And physicians must not only have a voice in shaping the path forward; they must have a seat at the table.”
Abreu reported no conflicts of interest in regard to her comments.
Few would deny that physicians today face many challenges: a growing and aging patient population, personnel shortages, mounting paperwork, regulatory and reimbursement pressures, and personal burnout. Collectively these could work to worsen patient access to care. Yet despite these headwinds, Doximity’s survey-based Physician Compensation Report 2025 found that more than three-quarters of physicians polled would still choose to enter their profession.
“Physician burnout isn’t new. It’s been a persistent problem over the past decade,” said Amit Phull, MD, chief clinical experience officer at Doximity. “In a Doximity poll of nearly 2,000 physicians conducted in May 2025, 85% reported they feel overworked, up from 73% just four years ago. As a result, about 68% of physicians said they are looking for an employment change or considering early retirement.”
Greater awareness of contemporary trends may help physicians make more-informed career decisions and more effectively advocate for both themselves and the patients who need them, the report’s authors stated.
Compensation Lag May Impact Care
A small overall average compensation increase of 3.7% from 2023 to 2024 – a slightly lower increase than the 5.9% in the prior year – has done little to close existing pay gaps across the profession.
In 2024, average compensation for men rose 5.7% over 2023, compared with just 1.7% for women – widening the gender pay gap to 26% vs 23% in 2023 and matching the gender gap seen in 2022. And significant disparities persist between physicians caring for adults vs children. In some specialties, the pay gap between pediatric and adult specialists exceeded 80% despite practitioners’ similar levels of training and clinical complexity.
Nearly 60% of respondents said reimbursement pressures could affect their ability to serve Medicare or Medicaid patients in the next year. Additionally, 81% reported that reimbursement policies have significantly contributed to the decline of private practices, and more than a third said they could stifle practice growth with compensation concerns forcing them to delay or cancel hiring or expansion plans. Almost 90% reported an adverse impact from physician shortages, with more citing an inability or limited ability to accept new patients.
Narrowing the Gap for Primary Care?
Over the past three years, the percent pay gap between primary care and specialist medicine declined modestly, the report noted. In 2024, surgical specialists earned 87% more than primary care physicians, down from 100% in 2022. Non-surgical specialists, emergency medicine physicians, and Ob/Gyns also continued to earn significantly more than primary care physicians, though the gaps have narrowed slightly.
“These trends come at a time when primary care remains critical to meeting high patient demand, especially amid ongoing physician shortages,” the report stated. “Primary care physicians continue to earn considerably less than many of their medical colleagues despite their essential role in the healthcare system.”
Significantly, many physicians believe that current reimbursement policies have contributed to the steady decline of independent practices in their fields. According to the American Medical Association, the share of physicians working in private practices dropped by 18 percentage points from 60.1% to 42.2% from 2012 to 2024.
The Specialties
This year’s review found that among 20 specialties, the highest average compensation occurred in surgical and procedural specialties, while the lowest paid were, as mentioned, pediatric medicine and primary care. Pediatric nephrology saw the largest average compensation growth in 2024 at 15.6%, yet compensation still lagged behind adult nephrology with a 40% pay gap.
By medical discipline, gastroenterologists ranked 13th overall in average annual compensation. Gastroenterology remained in the top 20 compensated specialties, with average annual compensation of $537,870 – an increase from $514,208 in 2024, representing a 4.5% growth rate over 2023. Neurosurgeons topped the list at $749,140, followed by thoracic surgeons at $689,969 and orthopedic surgeons at $679,517.
The three lowest-paid branches were all pediatric: endocrinology at $230,426, rheumatology at $231,574, and infectious diseases at $248,322. Pediatric gastroenterology paid somewhat higher at $298,457.
The largest disparities were seen in hematology and oncology, where adult specialists earned 93% more than their pediatric peers. Pediatric gastroenterology showed an 80% pay gap. There were also substantial pay differences across cardiology, pulmonology, and rheumatology. “These gaps appear to reflect a systemic lag in pay for pediatric specialty care, even as demand for pediatric subspecialists continues to rise,” the report stated.
Practice Setting and Location
Where a doctor practices impacts the bottom line, too: in 2024 the highest compensation reported for a metro area was in Rochester, Minnesota (the Mayo Clinic effect?), at $495,532, while the lowest reported was in Durham-Chapel Hill, North Carolina, at $368,782. St. Louis, Missouri ($484,883) and Los Angeles, California ($470,198) were 2nd and 3rd at the top of the list. Rochester, Minnesota, also emerged as best for annual compensation after cost-of-living adjustment, while Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the bottom rung.
The Gender Effect
With a women’s pay increase in 2024 of just 1.7%, the gender gap returned to its 2022-level disparity of 26%, with women physicians earning an average of $120,917 less than men after adjusting for specialty, location, and years of experience.
Doximity’s analysis of data from 2014 to 2019 estimated that on average men make at least $2 million more than women over the course of a 40-year career. This gap is often attributed to the fewer hours worked by female physician with their generally heavier familial responsibilities, “but Doximity’s gender wage gap analysis controls for the number of hours worked and career stage, along with specialty, work type, employment status, region, and credentials,” Phull said.
Women physicians had lower average earnings than men physicians across all specialties, a trend consistent with prior years. As a percentage of pay, the largest gender disparity was seen in pediatric nephrology (16.5%), a specialty that in fact saw the largest annual growth in physician pay. Neurosurgery had the smallest gender gap at 11.3%, while infectious diseases came in at 11.5% and oncology at 12%.
According to Maria T. Abreu, MD, AGAF, executive director of the F. Widjaja Inflammatory Bowel Disease Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and past president of AGA, the remuneration gender gap in gastroenterology is being taken seriously by AGA and several other GI societies. “The discrepancies in pay start from the beginning and therefore are magnified over time. We are helping to empower women to negotiate better as well as to gather data on the roots of inequity, she told GI & Hepatology News.
The AGA Women’s Committee has developed a project to support the advancement of women in gastroenterology, Abreu said. The initiative, which includes the AGA Gender Equity Framework and Gender Equity Road Map. focuses attention on disparities in the workplace and promotes opportunities for women’s leadership, career advancement, mentorship and physician health and wellness, she added.
Are these disparities due mainly to the “motherhood penalty,” with career interruption and time lost to maternity leave and fewer hours worked owing to the greater parenting burden of physician mothers? Or are they due to the systemic effects of gender expectations around compensation?
Hours worked appear to be a factor. A 2017 study of dual physician couples found that among childless respondents men worked an average of 57 hours and women 52 hours weekly. Compared with childless men, men with children worked similar numbers of hours weekly. However, compared with childless physicians, mothers worked significantly fewer hours – roughly 40 to 43 hours weekly – depending on the age of their youngest child.
Abreu pushed back on this stereotype. “Most women physicians, including gastroenterologists, do not take the maternity leave they are allowed because they are concerned about burdening their colleagues,” she said. “Thus, it is unlikely to explain the disparities. Many systemic issues remain challenging, but we want women to be empowered to advocate for themselves at the time of hiring and along the arc of their career paths.”
In Abreu’s view, having women assume more leadership roles in the field of gastroenterology provides an opportunity to focus on reducing the disparities in compensation.
Regardless of gender, among all physicians surveyed, autonomy and work-life balance appeared to be a high priority: 77% of doctors said they would be willing to accept or have already accepted lower pay for more autonomy or work-life balance. “Overwork appears to be especially prevalent among women physicians,” said Phull, noting that 91% of women respondents reported being overworked compared with 80% of men. “This overwork has compelled 74% of women to consider making a career change, compared with 62% of men.” Differences emerged among specialties as well: 90% of primary care physicians said they are overworked compared with 84% of surgeons and 83% of non-surgical specialists.
Looking ahead, the report raised an important question. Are we relying too heavily on physicians rather than addressing the underlying need for policies that support a healthier, more sustainable future for all? “Building that future will take more than physician dedication alone,” Phull said. “It will require meaningful collaboration across the entire health care ecosystem – including health systems, hospitals, payors, and policymakers. And physicians must not only have a voice in shaping the path forward; they must have a seat at the table.”
Abreu reported no conflicts of interest in regard to her comments.
Few would deny that physicians today face many challenges: a growing and aging patient population, personnel shortages, mounting paperwork, regulatory and reimbursement pressures, and personal burnout. Collectively these could work to worsen patient access to care. Yet despite these headwinds, Doximity’s survey-based Physician Compensation Report 2025 found that more than three-quarters of physicians polled would still choose to enter their profession.
“Physician burnout isn’t new. It’s been a persistent problem over the past decade,” said Amit Phull, MD, chief clinical experience officer at Doximity. “In a Doximity poll of nearly 2,000 physicians conducted in May 2025, 85% reported they feel overworked, up from 73% just four years ago. As a result, about 68% of physicians said they are looking for an employment change or considering early retirement.”
Greater awareness of contemporary trends may help physicians make more-informed career decisions and more effectively advocate for both themselves and the patients who need them, the report’s authors stated.
Compensation Lag May Impact Care
A small overall average compensation increase of 3.7% from 2023 to 2024 – a slightly lower increase than the 5.9% in the prior year – has done little to close existing pay gaps across the profession.
In 2024, average compensation for men rose 5.7% over 2023, compared with just 1.7% for women – widening the gender pay gap to 26% vs 23% in 2023 and matching the gender gap seen in 2022. And significant disparities persist between physicians caring for adults vs children. In some specialties, the pay gap between pediatric and adult specialists exceeded 80% despite practitioners’ similar levels of training and clinical complexity.
Nearly 60% of respondents said reimbursement pressures could affect their ability to serve Medicare or Medicaid patients in the next year. Additionally, 81% reported that reimbursement policies have significantly contributed to the decline of private practices, and more than a third said they could stifle practice growth with compensation concerns forcing them to delay or cancel hiring or expansion plans. Almost 90% reported an adverse impact from physician shortages, with more citing an inability or limited ability to accept new patients.
Narrowing the Gap for Primary Care?
Over the past three years, the percent pay gap between primary care and specialist medicine declined modestly, the report noted. In 2024, surgical specialists earned 87% more than primary care physicians, down from 100% in 2022. Non-surgical specialists, emergency medicine physicians, and Ob/Gyns also continued to earn significantly more than primary care physicians, though the gaps have narrowed slightly.
“These trends come at a time when primary care remains critical to meeting high patient demand, especially amid ongoing physician shortages,” the report stated. “Primary care physicians continue to earn considerably less than many of their medical colleagues despite their essential role in the healthcare system.”
Significantly, many physicians believe that current reimbursement policies have contributed to the steady decline of independent practices in their fields. According to the American Medical Association, the share of physicians working in private practices dropped by 18 percentage points from 60.1% to 42.2% from 2012 to 2024.
The Specialties
This year’s review found that among 20 specialties, the highest average compensation occurred in surgical and procedural specialties, while the lowest paid were, as mentioned, pediatric medicine and primary care. Pediatric nephrology saw the largest average compensation growth in 2024 at 15.6%, yet compensation still lagged behind adult nephrology with a 40% pay gap.
By medical discipline, gastroenterologists ranked 13th overall in average annual compensation. Gastroenterology remained in the top 20 compensated specialties, with average annual compensation of $537,870 – an increase from $514,208 in 2024, representing a 4.5% growth rate over 2023. Neurosurgeons topped the list at $749,140, followed by thoracic surgeons at $689,969 and orthopedic surgeons at $679,517.
The three lowest-paid branches were all pediatric: endocrinology at $230,426, rheumatology at $231,574, and infectious diseases at $248,322. Pediatric gastroenterology paid somewhat higher at $298,457.
The largest disparities were seen in hematology and oncology, where adult specialists earned 93% more than their pediatric peers. Pediatric gastroenterology showed an 80% pay gap. There were also substantial pay differences across cardiology, pulmonology, and rheumatology. “These gaps appear to reflect a systemic lag in pay for pediatric specialty care, even as demand for pediatric subspecialists continues to rise,” the report stated.
Practice Setting and Location
Where a doctor practices impacts the bottom line, too: in 2024 the highest compensation reported for a metro area was in Rochester, Minnesota (the Mayo Clinic effect?), at $495,532, while the lowest reported was in Durham-Chapel Hill, North Carolina, at $368,782. St. Louis, Missouri ($484,883) and Los Angeles, California ($470,198) were 2nd and 3rd at the top of the list. Rochester, Minnesota, also emerged as best for annual compensation after cost-of-living adjustment, while Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the bottom rung.
The Gender Effect
With a women’s pay increase in 2024 of just 1.7%, the gender gap returned to its 2022-level disparity of 26%, with women physicians earning an average of $120,917 less than men after adjusting for specialty, location, and years of experience.
Doximity’s analysis of data from 2014 to 2019 estimated that on average men make at least $2 million more than women over the course of a 40-year career. This gap is often attributed to the fewer hours worked by female physician with their generally heavier familial responsibilities, “but Doximity’s gender wage gap analysis controls for the number of hours worked and career stage, along with specialty, work type, employment status, region, and credentials,” Phull said.
Women physicians had lower average earnings than men physicians across all specialties, a trend consistent with prior years. As a percentage of pay, the largest gender disparity was seen in pediatric nephrology (16.5%), a specialty that in fact saw the largest annual growth in physician pay. Neurosurgery had the smallest gender gap at 11.3%, while infectious diseases came in at 11.5% and oncology at 12%.
According to Maria T. Abreu, MD, AGAF, executive director of the F. Widjaja Inflammatory Bowel Disease Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles and past president of AGA, the remuneration gender gap in gastroenterology is being taken seriously by AGA and several other GI societies. “The discrepancies in pay start from the beginning and therefore are magnified over time. We are helping to empower women to negotiate better as well as to gather data on the roots of inequity, she told GI & Hepatology News.
The AGA Women’s Committee has developed a project to support the advancement of women in gastroenterology, Abreu said. The initiative, which includes the AGA Gender Equity Framework and Gender Equity Road Map. focuses attention on disparities in the workplace and promotes opportunities for women’s leadership, career advancement, mentorship and physician health and wellness, she added.
Are these disparities due mainly to the “motherhood penalty,” with career interruption and time lost to maternity leave and fewer hours worked owing to the greater parenting burden of physician mothers? Or are they due to the systemic effects of gender expectations around compensation?
Hours worked appear to be a factor. A 2017 study of dual physician couples found that among childless respondents men worked an average of 57 hours and women 52 hours weekly. Compared with childless men, men with children worked similar numbers of hours weekly. However, compared with childless physicians, mothers worked significantly fewer hours – roughly 40 to 43 hours weekly – depending on the age of their youngest child.
Abreu pushed back on this stereotype. “Most women physicians, including gastroenterologists, do not take the maternity leave they are allowed because they are concerned about burdening their colleagues,” she said. “Thus, it is unlikely to explain the disparities. Many systemic issues remain challenging, but we want women to be empowered to advocate for themselves at the time of hiring and along the arc of their career paths.”
In Abreu’s view, having women assume more leadership roles in the field of gastroenterology provides an opportunity to focus on reducing the disparities in compensation.
Regardless of gender, among all physicians surveyed, autonomy and work-life balance appeared to be a high priority: 77% of doctors said they would be willing to accept or have already accepted lower pay for more autonomy or work-life balance. “Overwork appears to be especially prevalent among women physicians,” said Phull, noting that 91% of women respondents reported being overworked compared with 80% of men. “This overwork has compelled 74% of women to consider making a career change, compared with 62% of men.” Differences emerged among specialties as well: 90% of primary care physicians said they are overworked compared with 84% of surgeons and 83% of non-surgical specialists.
Looking ahead, the report raised an important question. Are we relying too heavily on physicians rather than addressing the underlying need for policies that support a healthier, more sustainable future for all? “Building that future will take more than physician dedication alone,” Phull said. “It will require meaningful collaboration across the entire health care ecosystem – including health systems, hospitals, payors, and policymakers. And physicians must not only have a voice in shaping the path forward; they must have a seat at the table.”
Abreu reported no conflicts of interest in regard to her comments.
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
As the health care landscape continues to shift, direct care (also known as direct pay) models have emerged as attractive alternatives to traditional insurance-based practice. For dermatology residents poised to enter the workforce, the direct care model offers potential advantages in autonomy, patient relationships, and work-life balance, but not without considerable risks and operational challenges. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
The transition from dermatology residency to clinical practice allows for a variety of paths, from large academic institutions to private practice to corporate entities (private equity–owned groups). In recent years, the direct care model has gained traction, particularly among physicians seeking greater autonomy and a more sustainable pace of practice.
Direct care dermatology practices operate outside the constraints of third-party payers, offering patients transparent pricing and direct access to care in exchange for fees paid out of pocket. By eliminating insurance companies as the middleman, it allows for less overhead, longer visits with patients, and increased access to care; however, though this model may seem appealing, direct care practices are not without their own set of challenges, especially amid rising concerns over physician burnout and administrative burden.
This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of starting a direct care dermatology practice, providing a framework to help early-career dermatologists determine whether this path aligns with their personal and professional goals.
Despite its appeal, starting a direct care practice is not without substantial risks and hurdles—particularly for residents just out of training. These challenges include financial risks and startup costs, market uncertainty, lack of mentorship or support, and limitations in treating complex dermatologic conditions.
Before committing to practicing via a direct care model, dermatology residents should reflect on the following:
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable navigating the business and financial risk?
- Location: Does your target community have patients willing and able to pay out of pocket?
- Scope of interest: Will a direct care practice align with your clinical passions?
- Support systems: Do you have access to mentors, legal and financial advisors, and operational support?
- Long-term goals: Are you building a lifestyle practice, a scalable business, or a stepping stone to a future opportunity?
Ultimately, the decision to pursue a direct care model requires careful reflection on personal values, financial preparedness, and the unique needs of the community one intends to serve.
The direct care dermatology model offers an appealing alternative to traditional practice, especially for those prioritizing autonomy, patient connection, and work-life balance; however, it demands an entrepreneurial spirit as well as careful planning and an acceptance of financial uncertainty—factors that may pose challenges for new graduates. For dermatology residents, the decision to pursue direct care should be grounded in personal values, practical considerations, and a clear understanding of both the opportunities and limitations of this evolving practice model.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
- Sinsky CA, Colligan L, Li L, et al. Allocation of physician time in ambulatory practice: a time and motion study in 4 specialties. Ann Intern Med.
- Dorrell DN, Feldman S, Wei-ting Huang W. The most common causes of burnout among US academic dermatologists based on a survey study. J Am Acad of Dermatol. 2019;81:269-270.
- Carlasare LE. Defining the place of direct primary care in a value-based care system. WMJ. 2018;117:106-110.
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
Direct Care Dermatology: Weighing the Pros and Cons for the Early-Career Physician
PRACTICE POINTS
- Direct care practices may be the new horizon of health care.
- Starting a direct care practice offers autonomy but demands entrepreneurial readiness.
- New dermatologists can enjoy control over scheduling, pricing, and patient care, but success requires business acumen, financial planning, and comfort with risk.
Letter: Another View on Private Equity in GI
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
An October 1 article in GI & Hepatology News cautioned physicians against partnering with private equity firms, warning that they target “quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care.”
But several recent studies – and my own experience – show that .
A 2024 study conducted by Avalere Health found that per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated practice model to a PE-affiliated model declined by $963 in the 12 months following the transition. By contrast, per-beneficiary Medicare expenditures for physicians who shifted from an unaffiliated model to a hospital-affiliated one increased more than $1,300.
A 2025 peer-reviewed study published in Journal of Market Access & Health Policy found that physicians affiliated with private equity were far more likely to perform common high-volume procedures in the lowest-cost site of care – an ambulatory surgery center or medical office – than in higher-cost hospital outpatient departments. Physicians affiliated with hospitals were far more likely to perform procedures in HOPDs.
Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization has enabled my practice to afford advanced technologies we never could have deployed on our own. Those technologies have helped improve our polyp detection rates, reduce the incidence of colon cancer, and more efficiently care for patients with ulcerative colitis. We also now provide patients seamless access to digital platforms that help them better manage chronic conditions.
Independent medical practice is under duress. Partnering with a private equity-backed management services organization is one of the most effective ways for a physician practice to retain its independence – and continue offering patients affordable, high-quality care.
George Dickstein, MD, AGAF, is senior vice president of clinical affairs, Massachusetts, for Gastro Health, and chairperson of Gastro Health’s Physician Leadership Council. He is based in Framingham, Mass. GI & Hepatology News encourages readers to submit letters to the editor to debate topics raised in the newspaper.
Shaping the Future of Dermatology Practice: Leadership Insight From Susan C. Taylor, MD
Shaping the Future of Dermatology Practice: Leadership Insight From Susan C. Taylor, MD
What are the American Academy of Dermatology’s (AAD’s) top advocacy priorities related to Medicare physician reimbursement?
Dr. Taylor: Medicare physician payment has failed to keep up with inflation, threatening the viability of medical practices. The AAD urges Congress to stabilize the Medicare payment system to ensure continued patient access to essential health care by
What is the AAD’s stance on transitioning from traditional fee-for-service to value-based care models in dermatology under Medicare?
Dr. Taylor: Current value-based programs are extremely burdensome, have not demonstrated improved patient care, and are not clinically relevant to physicians or patients. The AAD has serious concerns about the viability and effectiveness of the Quality Payment Program (QPP), especially the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS). Numerous studies have highlighted persistent challenges associated with MIPS, including practices serving high-risk patients and those that are small or in rural areas. For instance, researchers examined whether MIPS disproportionately penalized surgeons who care for these patients and found a connection between caring for these patients, lower MIPS scores, and a higher likelihood of facing negative payment adjustments.
Additionally, the US Government Accountability Office was tasked with reviewing several aspects concerning small and rural practices in relation to Medicare payment incentive programs, including MIPS. Findings indicated that physician practices with 15 or fewer providers, whether located in rural or nonrural areas, had a higher likelihood of receiving negative payment adjustments in Medicare incentive programs compared to larger practices. To maximize participation and facilitate the best possible outcomes for dermatologists within the MIPS program, the AAD maintains that we must continue to develop and advocate that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approve dermatology-specific measures for MIPS reporting.
Does the AAD have plans to develop or expand dermatology-specific quality measures that are more clinically relevant and less administratively taxing?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is committed to ensuring that dermatologists can be successful in the QPP and its MIPS Value Pathways and Advanced Alternative Payment Model programs. These payment pathways for QPP-eligible participants allow physicians to increase their future Medicare reimbursements but also penalize those who do not meet performance objectives. The AAD is constantly reviewing and proposing new dermatology-specific quality measures to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services based on member feedback to reduce administrative burdens of MIPS reporting. All of our quality measures are developed by dermatologists for dermatologists.
How is the AAD supporting practices dealing with insurer-mandated switch policies that disrupt continuity of care and increase documentation burden?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD works with private payers to alleviate administrative burdens for dermatologists, maintain appropriate reimbursement for services provided, and ensure patients can access covered quality care by building and maintaining relationships with public and private payers. This critical collaboration addresses immediate needs affecting our members’ ability to deliver care, such as when policy changes affect claims and formulary coverage or payment. Our coordinated strategy ensures payer policies align with everyday practice for dermatologists so they can focus on treating patients. The AAD has resources and tools to guide dermatology practices in appropriate documentation and coding.
What initiatives is the AAD pursuing to specifically support independent or small dermatology practices in coping with administrative overload?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is continuously advocating for our small and independent dermatology practices. In every comment letter we submit on proposed medical practice reporting regulation, we demand small practice exemptions. Moreover, the AAD has resources and practical tools for all types of practices to cope with administrative burdens, including MIPS reporting requirements. These resources and tools were created by dermatologists for dermatologists to take the guesswork out of administrative compliance. DataDerm is the AAD’s clinical data registry used for MIPS reporting. Since its launch in 2016, DataDerm has become dermatology’s largest clinical data registry, capturing information on more than 16 million unique patients and 69 million encounters. It supports the advancement of skin disease diagnosis and treatment, informs clinical practice, streamlines MIPS reporting, and drives clinically relevant research using real-world data.
What are the biggest contributors to physician burnout right now? What resources does AAD offer to support dermatologists in managing burnout?
Dr. Taylor: The biggest contributors to burnout that dermatologists are facing are demanding workloads, administrative burdens, and loss of autonomy. Dermatologists welcome medical challenges, but they face growing administrative and regulatory burdens that take time away from patient care and contribute to burnout. Taking a wellness-centered approach can help, which is why the AAD includes both practical tools to reduce burdens and strategies to sustain your practice in its online resources. The burnout and wellness section of the AAD website can help with administrative burdens, building a supportive work culture, recognizing drivers of burnout, reconnecting with your purpose, and more.
How is the AAD working to ensure that the expanding scope of practice does not compromise patient safety, particularly when it comes to diagnosis and treatment of complex skin cancers or prescribing systemic medications?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD advocates to ensure that each member of the care team is practicing at a level consistent with their training and education and opposes scope-of-practice expansions for physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other nonphysician clinicians that threaten patient safety by allowing them to practice independently and advertise as skin experts. Each state has its own scope-of-practice laws governing what nonphysicians can do, whether supervision is required, and how they can represent their training, both in advertising and in a medical practice. The AAD supports appropriate safeguards to ensure patient safety and a focus on the highest-quality appropriate care as the nonphysician workforce expands. The AAD encourages patients to report adverse outcomes to the appropriate state licensing boards.
Is the AAD developing or recommending best practices for dermatologists who supervise NPs or PAs, especially in large practices or retail clinics where oversight can be inconsistent?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD firmly believes that the optimal quality of medical care is delivered when a qualified and licensed physician provides direct on-site supervision to all qualified nonphysician personnel. A medical director of a medical spa facility should be a physician licensed in the state where the facility is located and also should be clearly identified by state licensure and any state-recognized board certification as well as by medical specialty, training, and education. The individual also should be identified as the medical director in all marketing materials and on websites and social media accounts related to the medical spa facility. The AAD would like to see policies that would provide increased transparency in state licensure and specialty board certification including requiring disclosure that a physician is certified or eligible for certification by a private or public board, parent association, or multidisciplinary board or association; requiring disclosure of the certifying board or association with one’s field of study or specialty; requiring display of visible identification—including one’s state licensure, professional degree, field of study, and the use of clarifying titles—in facilities, in marketing materials, and on websites and social media; and requiring all personnel in private medical practices, hospitals, clinics, or other settings employing physicians and/or other personnel that offer medical, surgical, or aesthetic procedures to wear a photo identification name tag during all patient encounters.
What are the American Academy of Dermatology’s (AAD’s) top advocacy priorities related to Medicare physician reimbursement?
Dr. Taylor: Medicare physician payment has failed to keep up with inflation, threatening the viability of medical practices. The AAD urges Congress to stabilize the Medicare payment system to ensure continued patient access to essential health care by
What is the AAD’s stance on transitioning from traditional fee-for-service to value-based care models in dermatology under Medicare?
Dr. Taylor: Current value-based programs are extremely burdensome, have not demonstrated improved patient care, and are not clinically relevant to physicians or patients. The AAD has serious concerns about the viability and effectiveness of the Quality Payment Program (QPP), especially the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS). Numerous studies have highlighted persistent challenges associated with MIPS, including practices serving high-risk patients and those that are small or in rural areas. For instance, researchers examined whether MIPS disproportionately penalized surgeons who care for these patients and found a connection between caring for these patients, lower MIPS scores, and a higher likelihood of facing negative payment adjustments.
Additionally, the US Government Accountability Office was tasked with reviewing several aspects concerning small and rural practices in relation to Medicare payment incentive programs, including MIPS. Findings indicated that physician practices with 15 or fewer providers, whether located in rural or nonrural areas, had a higher likelihood of receiving negative payment adjustments in Medicare incentive programs compared to larger practices. To maximize participation and facilitate the best possible outcomes for dermatologists within the MIPS program, the AAD maintains that we must continue to develop and advocate that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approve dermatology-specific measures for MIPS reporting.
Does the AAD have plans to develop or expand dermatology-specific quality measures that are more clinically relevant and less administratively taxing?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is committed to ensuring that dermatologists can be successful in the QPP and its MIPS Value Pathways and Advanced Alternative Payment Model programs. These payment pathways for QPP-eligible participants allow physicians to increase their future Medicare reimbursements but also penalize those who do not meet performance objectives. The AAD is constantly reviewing and proposing new dermatology-specific quality measures to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services based on member feedback to reduce administrative burdens of MIPS reporting. All of our quality measures are developed by dermatologists for dermatologists.
How is the AAD supporting practices dealing with insurer-mandated switch policies that disrupt continuity of care and increase documentation burden?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD works with private payers to alleviate administrative burdens for dermatologists, maintain appropriate reimbursement for services provided, and ensure patients can access covered quality care by building and maintaining relationships with public and private payers. This critical collaboration addresses immediate needs affecting our members’ ability to deliver care, such as when policy changes affect claims and formulary coverage or payment. Our coordinated strategy ensures payer policies align with everyday practice for dermatologists so they can focus on treating patients. The AAD has resources and tools to guide dermatology practices in appropriate documentation and coding.
What initiatives is the AAD pursuing to specifically support independent or small dermatology practices in coping with administrative overload?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is continuously advocating for our small and independent dermatology practices. In every comment letter we submit on proposed medical practice reporting regulation, we demand small practice exemptions. Moreover, the AAD has resources and practical tools for all types of practices to cope with administrative burdens, including MIPS reporting requirements. These resources and tools were created by dermatologists for dermatologists to take the guesswork out of administrative compliance. DataDerm is the AAD’s clinical data registry used for MIPS reporting. Since its launch in 2016, DataDerm has become dermatology’s largest clinical data registry, capturing information on more than 16 million unique patients and 69 million encounters. It supports the advancement of skin disease diagnosis and treatment, informs clinical practice, streamlines MIPS reporting, and drives clinically relevant research using real-world data.
What are the biggest contributors to physician burnout right now? What resources does AAD offer to support dermatologists in managing burnout?
Dr. Taylor: The biggest contributors to burnout that dermatologists are facing are demanding workloads, administrative burdens, and loss of autonomy. Dermatologists welcome medical challenges, but they face growing administrative and regulatory burdens that take time away from patient care and contribute to burnout. Taking a wellness-centered approach can help, which is why the AAD includes both practical tools to reduce burdens and strategies to sustain your practice in its online resources. The burnout and wellness section of the AAD website can help with administrative burdens, building a supportive work culture, recognizing drivers of burnout, reconnecting with your purpose, and more.
How is the AAD working to ensure that the expanding scope of practice does not compromise patient safety, particularly when it comes to diagnosis and treatment of complex skin cancers or prescribing systemic medications?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD advocates to ensure that each member of the care team is practicing at a level consistent with their training and education and opposes scope-of-practice expansions for physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other nonphysician clinicians that threaten patient safety by allowing them to practice independently and advertise as skin experts. Each state has its own scope-of-practice laws governing what nonphysicians can do, whether supervision is required, and how they can represent their training, both in advertising and in a medical practice. The AAD supports appropriate safeguards to ensure patient safety and a focus on the highest-quality appropriate care as the nonphysician workforce expands. The AAD encourages patients to report adverse outcomes to the appropriate state licensing boards.
Is the AAD developing or recommending best practices for dermatologists who supervise NPs or PAs, especially in large practices or retail clinics where oversight can be inconsistent?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD firmly believes that the optimal quality of medical care is delivered when a qualified and licensed physician provides direct on-site supervision to all qualified nonphysician personnel. A medical director of a medical spa facility should be a physician licensed in the state where the facility is located and also should be clearly identified by state licensure and any state-recognized board certification as well as by medical specialty, training, and education. The individual also should be identified as the medical director in all marketing materials and on websites and social media accounts related to the medical spa facility. The AAD would like to see policies that would provide increased transparency in state licensure and specialty board certification including requiring disclosure that a physician is certified or eligible for certification by a private or public board, parent association, or multidisciplinary board or association; requiring disclosure of the certifying board or association with one’s field of study or specialty; requiring display of visible identification—including one’s state licensure, professional degree, field of study, and the use of clarifying titles—in facilities, in marketing materials, and on websites and social media; and requiring all personnel in private medical practices, hospitals, clinics, or other settings employing physicians and/or other personnel that offer medical, surgical, or aesthetic procedures to wear a photo identification name tag during all patient encounters.
What are the American Academy of Dermatology’s (AAD’s) top advocacy priorities related to Medicare physician reimbursement?
Dr. Taylor: Medicare physician payment has failed to keep up with inflation, threatening the viability of medical practices. The AAD urges Congress to stabilize the Medicare payment system to ensure continued patient access to essential health care by
What is the AAD’s stance on transitioning from traditional fee-for-service to value-based care models in dermatology under Medicare?
Dr. Taylor: Current value-based programs are extremely burdensome, have not demonstrated improved patient care, and are not clinically relevant to physicians or patients. The AAD has serious concerns about the viability and effectiveness of the Quality Payment Program (QPP), especially the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System (MIPS). Numerous studies have highlighted persistent challenges associated with MIPS, including practices serving high-risk patients and those that are small or in rural areas. For instance, researchers examined whether MIPS disproportionately penalized surgeons who care for these patients and found a connection between caring for these patients, lower MIPS scores, and a higher likelihood of facing negative payment adjustments.
Additionally, the US Government Accountability Office was tasked with reviewing several aspects concerning small and rural practices in relation to Medicare payment incentive programs, including MIPS. Findings indicated that physician practices with 15 or fewer providers, whether located in rural or nonrural areas, had a higher likelihood of receiving negative payment adjustments in Medicare incentive programs compared to larger practices. To maximize participation and facilitate the best possible outcomes for dermatologists within the MIPS program, the AAD maintains that we must continue to develop and advocate that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services approve dermatology-specific measures for MIPS reporting.
Does the AAD have plans to develop or expand dermatology-specific quality measures that are more clinically relevant and less administratively taxing?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is committed to ensuring that dermatologists can be successful in the QPP and its MIPS Value Pathways and Advanced Alternative Payment Model programs. These payment pathways for QPP-eligible participants allow physicians to increase their future Medicare reimbursements but also penalize those who do not meet performance objectives. The AAD is constantly reviewing and proposing new dermatology-specific quality measures to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services based on member feedback to reduce administrative burdens of MIPS reporting. All of our quality measures are developed by dermatologists for dermatologists.
How is the AAD supporting practices dealing with insurer-mandated switch policies that disrupt continuity of care and increase documentation burden?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD works with private payers to alleviate administrative burdens for dermatologists, maintain appropriate reimbursement for services provided, and ensure patients can access covered quality care by building and maintaining relationships with public and private payers. This critical collaboration addresses immediate needs affecting our members’ ability to deliver care, such as when policy changes affect claims and formulary coverage or payment. Our coordinated strategy ensures payer policies align with everyday practice for dermatologists so they can focus on treating patients. The AAD has resources and tools to guide dermatology practices in appropriate documentation and coding.
What initiatives is the AAD pursuing to specifically support independent or small dermatology practices in coping with administrative overload?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD is continuously advocating for our small and independent dermatology practices. In every comment letter we submit on proposed medical practice reporting regulation, we demand small practice exemptions. Moreover, the AAD has resources and practical tools for all types of practices to cope with administrative burdens, including MIPS reporting requirements. These resources and tools were created by dermatologists for dermatologists to take the guesswork out of administrative compliance. DataDerm is the AAD’s clinical data registry used for MIPS reporting. Since its launch in 2016, DataDerm has become dermatology’s largest clinical data registry, capturing information on more than 16 million unique patients and 69 million encounters. It supports the advancement of skin disease diagnosis and treatment, informs clinical practice, streamlines MIPS reporting, and drives clinically relevant research using real-world data.
What are the biggest contributors to physician burnout right now? What resources does AAD offer to support dermatologists in managing burnout?
Dr. Taylor: The biggest contributors to burnout that dermatologists are facing are demanding workloads, administrative burdens, and loss of autonomy. Dermatologists welcome medical challenges, but they face growing administrative and regulatory burdens that take time away from patient care and contribute to burnout. Taking a wellness-centered approach can help, which is why the AAD includes both practical tools to reduce burdens and strategies to sustain your practice in its online resources. The burnout and wellness section of the AAD website can help with administrative burdens, building a supportive work culture, recognizing drivers of burnout, reconnecting with your purpose, and more.
How is the AAD working to ensure that the expanding scope of practice does not compromise patient safety, particularly when it comes to diagnosis and treatment of complex skin cancers or prescribing systemic medications?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD advocates to ensure that each member of the care team is practicing at a level consistent with their training and education and opposes scope-of-practice expansions for physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and other nonphysician clinicians that threaten patient safety by allowing them to practice independently and advertise as skin experts. Each state has its own scope-of-practice laws governing what nonphysicians can do, whether supervision is required, and how they can represent their training, both in advertising and in a medical practice. The AAD supports appropriate safeguards to ensure patient safety and a focus on the highest-quality appropriate care as the nonphysician workforce expands. The AAD encourages patients to report adverse outcomes to the appropriate state licensing boards.
Is the AAD developing or recommending best practices for dermatologists who supervise NPs or PAs, especially in large practices or retail clinics where oversight can be inconsistent?
Dr. Taylor: The AAD firmly believes that the optimal quality of medical care is delivered when a qualified and licensed physician provides direct on-site supervision to all qualified nonphysician personnel. A medical director of a medical spa facility should be a physician licensed in the state where the facility is located and also should be clearly identified by state licensure and any state-recognized board certification as well as by medical specialty, training, and education. The individual also should be identified as the medical director in all marketing materials and on websites and social media accounts related to the medical spa facility. The AAD would like to see policies that would provide increased transparency in state licensure and specialty board certification including requiring disclosure that a physician is certified or eligible for certification by a private or public board, parent association, or multidisciplinary board or association; requiring disclosure of the certifying board or association with one’s field of study or specialty; requiring display of visible identification—including one’s state licensure, professional degree, field of study, and the use of clarifying titles—in facilities, in marketing materials, and on websites and social media; and requiring all personnel in private medical practices, hospitals, clinics, or other settings employing physicians and/or other personnel that offer medical, surgical, or aesthetic procedures to wear a photo identification name tag during all patient encounters.
Shaping the Future of Dermatology Practice: Leadership Insight From Susan C. Taylor, MD
Shaping the Future of Dermatology Practice: Leadership Insight From Susan C. Taylor, MD
Medicolegal Concerns in Contemporary Private GI Practice
The need for gastroenterology (GI) services is on the rise in the US, with growing rates of colonoscopy, earlier-onset colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. This increase is taking place in the context of a changing regulatory landscape.
, and to that end, a recent educational practice management update was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology by Erin Smith Aebel, JD, a health law specialist with Trenam Law in Tampa, Florida. Aebel has been a speaker at several national GI conferences and has addressed GI trainees on these issues in medical schools.
“Healthcare regulation continues to evolve and it’s a complicated area,” Aebel told GI & Hepatology News. “Some physician investors in healthcare ventures see the potential profits but are not fully aware of how a physician’s license and livelihood could be affected by noncompliance.”
Aebel has seen some medical business owners and institutions pushing physicians to their limits in order to maximize profits. “They’re failing to allow them the meaningful things that allow for a long-term productive and successful practice that provides great patient care,” she said. “A current issue I’m dealing with is employers’ taking away physicians’ administrative time and not respecting the work that is necessary for the physician to be efficient and provide great care,” she said. “If too many physicians get squeezed in this manner, they will eventually walk away from big employers to something they can better control.”
Aebel noted that private-equity acquisitions of medical practices — a fast-growing US trend — are often targeted at quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care. “A question to be asked by physicians and patients is who is benefiting from this transaction?” she said. “Sometimes retired physicians can see a great benefit in private equity, but newer physicians can get tied up with a strong noncompete agreement. The best deals are ones that try to find wins for all involved, including patients.”
Many independent gastroenterologists focusing on the demands of daily practice are less aware than they should be of the legal and business administration sides. “I often get clients who come to me complaining about their contracts after they’ve signed them. I don’t have leverage to do as much for them,” she admitted.
From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control. These could relate to compensation and bonuses, as well as opportunities to invest in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs).
Aebel’s overarching messages to gastroenterologists are as follows: “Be aware. Learn basic health law. Read your contracts before you sign them. And invest in good counsel before you sign agreements,” she said. “In addition, GI practitioners need to have a working knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the federal Stark Law and how they could be commonly applied in their practices.”
These are designed to protect government-funded patient care from monetary influence. The False Claims Act is another federal buttress against fraud and abuse, she said.
Update Details
Though not intended to be legal advice, Aebel’s update touches on several important medicolegal areas.
Stark Law on Self-Referrals
Gastroenterologists should be familiar with this federal law, a self-referral civil penalty statute regulating how physicians can pay themselves in practices that provide designated health services covered by federal healthcare programs such as Medicare or Medicaid.
For a Stark penalty to apply, there must be a physician referral to an entity (eg, lab, hospital, nutrition service, physiotherapy or radiotherapy center) in which the physician or a close family member has a financial interest.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Another common area vulnerable to federal fraud and abuse regulation is investment in ASCs. “Generally speaking, it is a felony to pay or be paid anything of value for Medicare or Medicaid business referrals,” Aebel wrote. This provision relates to the general restriction of the federal AKB statute.
A gastroenterologist referring Medicare patients to a center where that physician has an investment could technically violate this law because the physician will receive profit distributions from the referral. In addition to constituting a felony with potential jail time, violation of this statute is grounds for substantial civil monetary penalties and/or exclusion from the government coverage program.
Fortunately, Aebel noted, legal safe harbors cover many financial relationships, including investment in an ASC. The financial arrangement is protected from prosecution if it meets five safe harbor requirements, including nondiscriminatory treatment of government-insured patients and physician investment unrelated to a center’s volume or the value of referrals. If even one aspect is not met, that will automatically constitute a crime.
“However, the government will look at facts and circumstances to determine whether there was an intent to pay for a referral,” Aebel wrote.
The safe harbor designates requirements for four types of ASCs: surgeon-owned, single-specialty, multispecialty, and hospital/physician ASCs.
Private-Equity Investment
With mergers and acquisitions of US medical practices and networks by private-equity firms becoming more common, gastroenterologists need to be aware of the legal issues involved in such investment.
Most states abide by corporate practice of medicine doctrines, which prohibit unlicensed people from direct ownership in a medical practice. These doctrines vary by state, but their primary goal is to ensure that medical decisions are made solely based on patient care and not influenced by corporate interests. The aim is to shield the physician-patient relationship from commercial influence.
“Accordingly, this creates additional complicated structures necessary for private-equity investment in gastroenterology practices,” Aebel wrote. Usually, such investors will invest in a management services organization (MSO), which takes much of the practice’s value via management fees. Gastroenterologists may or may not have an opportunity to invest in the practice and the MSO in this scenario.
Under corporate practice of medicine doctrine, physicians must control the clinical aspects of patient care. Therefore, some states may have restrictions on private-equity companies’ control of the use of medical devices, pricing, medical protocols, or other issues of patient care.
“This needs to be considered when reviewing the investment documents and structural documents proposed by private equity companies,” the advisory stated. From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control over their clinical practice. “This could relate to their compensation, bonuses, and investment opportunities in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ASCs.”
Offering a gastroenterologist’s perspective on the paper, Camille Thélin, MD, MSc, an associate professor in the Division of Digestive Diseases and Health at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, who also practices privately, said, that “what Erin Aebel reminds us is that the business side of GI can be just as tricky as the clinical side. Ancillary services like capsule studies or office labs fall under strict Stark rules, ASC ownership has Anti-Kickback Law restrictions, and private-equity deals may affect both your paycheck and your autonomy.”
Thélin’s main takeaway advice is that business opportunities can be valuable but carry real legal risks if not structured correctly. “This isn’t just abstract compliance law — it’s about protecting one’s ability to practice medicine, earn fairly, and avoid devastating penalties,” she told GI & Hepatology News. “This article reinforces the need for proactive legal review and careful structuring of business arrangements so physicians can focus on patient care without stumbling into avoidable legal pitfalls. With the right legal structure, ancillaries, ASCs, and private equity can strengthen your GI practice without risking compliance.”
The bottom line, said Aebel, is that gastroenterologists already in private practice or considering entering one must navigate a complex landscape of compliance and regulatory requirements — particularly when providing ancillary services, investing in ASCs, or engaging with private equity.
Understanding the Stark law, the AKB statute, and the intricacies of private-equity investment is essential to mitigate risks and avoid severe penalties, the advisory stressed. By proactively seeking expert legal and business guidance, gastroenterologists can structure their financial and ownership arrangements in a compliant manner, safeguarding their practices while capitalizing on growth opportunities.
This paper listed no external funding. Neither Aebel nor Thélin had any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The need for gastroenterology (GI) services is on the rise in the US, with growing rates of colonoscopy, earlier-onset colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. This increase is taking place in the context of a changing regulatory landscape.
, and to that end, a recent educational practice management update was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology by Erin Smith Aebel, JD, a health law specialist with Trenam Law in Tampa, Florida. Aebel has been a speaker at several national GI conferences and has addressed GI trainees on these issues in medical schools.
“Healthcare regulation continues to evolve and it’s a complicated area,” Aebel told GI & Hepatology News. “Some physician investors in healthcare ventures see the potential profits but are not fully aware of how a physician’s license and livelihood could be affected by noncompliance.”
Aebel has seen some medical business owners and institutions pushing physicians to their limits in order to maximize profits. “They’re failing to allow them the meaningful things that allow for a long-term productive and successful practice that provides great patient care,” she said. “A current issue I’m dealing with is employers’ taking away physicians’ administrative time and not respecting the work that is necessary for the physician to be efficient and provide great care,” she said. “If too many physicians get squeezed in this manner, they will eventually walk away from big employers to something they can better control.”
Aebel noted that private-equity acquisitions of medical practices — a fast-growing US trend — are often targeted at quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care. “A question to be asked by physicians and patients is who is benefiting from this transaction?” she said. “Sometimes retired physicians can see a great benefit in private equity, but newer physicians can get tied up with a strong noncompete agreement. The best deals are ones that try to find wins for all involved, including patients.”
Many independent gastroenterologists focusing on the demands of daily practice are less aware than they should be of the legal and business administration sides. “I often get clients who come to me complaining about their contracts after they’ve signed them. I don’t have leverage to do as much for them,” she admitted.
From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control. These could relate to compensation and bonuses, as well as opportunities to invest in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs).
Aebel’s overarching messages to gastroenterologists are as follows: “Be aware. Learn basic health law. Read your contracts before you sign them. And invest in good counsel before you sign agreements,” she said. “In addition, GI practitioners need to have a working knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the federal Stark Law and how they could be commonly applied in their practices.”
These are designed to protect government-funded patient care from monetary influence. The False Claims Act is another federal buttress against fraud and abuse, she said.
Update Details
Though not intended to be legal advice, Aebel’s update touches on several important medicolegal areas.
Stark Law on Self-Referrals
Gastroenterologists should be familiar with this federal law, a self-referral civil penalty statute regulating how physicians can pay themselves in practices that provide designated health services covered by federal healthcare programs such as Medicare or Medicaid.
For a Stark penalty to apply, there must be a physician referral to an entity (eg, lab, hospital, nutrition service, physiotherapy or radiotherapy center) in which the physician or a close family member has a financial interest.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Another common area vulnerable to federal fraud and abuse regulation is investment in ASCs. “Generally speaking, it is a felony to pay or be paid anything of value for Medicare or Medicaid business referrals,” Aebel wrote. This provision relates to the general restriction of the federal AKB statute.
A gastroenterologist referring Medicare patients to a center where that physician has an investment could technically violate this law because the physician will receive profit distributions from the referral. In addition to constituting a felony with potential jail time, violation of this statute is grounds for substantial civil monetary penalties and/or exclusion from the government coverage program.
Fortunately, Aebel noted, legal safe harbors cover many financial relationships, including investment in an ASC. The financial arrangement is protected from prosecution if it meets five safe harbor requirements, including nondiscriminatory treatment of government-insured patients and physician investment unrelated to a center’s volume or the value of referrals. If even one aspect is not met, that will automatically constitute a crime.
“However, the government will look at facts and circumstances to determine whether there was an intent to pay for a referral,” Aebel wrote.
The safe harbor designates requirements for four types of ASCs: surgeon-owned, single-specialty, multispecialty, and hospital/physician ASCs.
Private-Equity Investment
With mergers and acquisitions of US medical practices and networks by private-equity firms becoming more common, gastroenterologists need to be aware of the legal issues involved in such investment.
Most states abide by corporate practice of medicine doctrines, which prohibit unlicensed people from direct ownership in a medical practice. These doctrines vary by state, but their primary goal is to ensure that medical decisions are made solely based on patient care and not influenced by corporate interests. The aim is to shield the physician-patient relationship from commercial influence.
“Accordingly, this creates additional complicated structures necessary for private-equity investment in gastroenterology practices,” Aebel wrote. Usually, such investors will invest in a management services organization (MSO), which takes much of the practice’s value via management fees. Gastroenterologists may or may not have an opportunity to invest in the practice and the MSO in this scenario.
Under corporate practice of medicine doctrine, physicians must control the clinical aspects of patient care. Therefore, some states may have restrictions on private-equity companies’ control of the use of medical devices, pricing, medical protocols, or other issues of patient care.
“This needs to be considered when reviewing the investment documents and structural documents proposed by private equity companies,” the advisory stated. From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control over their clinical practice. “This could relate to their compensation, bonuses, and investment opportunities in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ASCs.”
Offering a gastroenterologist’s perspective on the paper, Camille Thélin, MD, MSc, an associate professor in the Division of Digestive Diseases and Health at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, who also practices privately, said, that “what Erin Aebel reminds us is that the business side of GI can be just as tricky as the clinical side. Ancillary services like capsule studies or office labs fall under strict Stark rules, ASC ownership has Anti-Kickback Law restrictions, and private-equity deals may affect both your paycheck and your autonomy.”
Thélin’s main takeaway advice is that business opportunities can be valuable but carry real legal risks if not structured correctly. “This isn’t just abstract compliance law — it’s about protecting one’s ability to practice medicine, earn fairly, and avoid devastating penalties,” she told GI & Hepatology News. “This article reinforces the need for proactive legal review and careful structuring of business arrangements so physicians can focus on patient care without stumbling into avoidable legal pitfalls. With the right legal structure, ancillaries, ASCs, and private equity can strengthen your GI practice without risking compliance.”
The bottom line, said Aebel, is that gastroenterologists already in private practice or considering entering one must navigate a complex landscape of compliance and regulatory requirements — particularly when providing ancillary services, investing in ASCs, or engaging with private equity.
Understanding the Stark law, the AKB statute, and the intricacies of private-equity investment is essential to mitigate risks and avoid severe penalties, the advisory stressed. By proactively seeking expert legal and business guidance, gastroenterologists can structure their financial and ownership arrangements in a compliant manner, safeguarding their practices while capitalizing on growth opportunities.
This paper listed no external funding. Neither Aebel nor Thélin had any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The need for gastroenterology (GI) services is on the rise in the US, with growing rates of colonoscopy, earlier-onset colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. This increase is taking place in the context of a changing regulatory landscape.
, and to that end, a recent educational practice management update was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology by Erin Smith Aebel, JD, a health law specialist with Trenam Law in Tampa, Florida. Aebel has been a speaker at several national GI conferences and has addressed GI trainees on these issues in medical schools.
“Healthcare regulation continues to evolve and it’s a complicated area,” Aebel told GI & Hepatology News. “Some physician investors in healthcare ventures see the potential profits but are not fully aware of how a physician’s license and livelihood could be affected by noncompliance.”
Aebel has seen some medical business owners and institutions pushing physicians to their limits in order to maximize profits. “They’re failing to allow them the meaningful things that allow for a long-term productive and successful practice that provides great patient care,” she said. “A current issue I’m dealing with is employers’ taking away physicians’ administrative time and not respecting the work that is necessary for the physician to be efficient and provide great care,” she said. “If too many physicians get squeezed in this manner, they will eventually walk away from big employers to something they can better control.”
Aebel noted that private-equity acquisitions of medical practices — a fast-growing US trend — are often targeted at quick profits and quick exits, which can be inconsistent with quality long-term patient care. “A question to be asked by physicians and patients is who is benefiting from this transaction?” she said. “Sometimes retired physicians can see a great benefit in private equity, but newer physicians can get tied up with a strong noncompete agreement. The best deals are ones that try to find wins for all involved, including patients.”
Many independent gastroenterologists focusing on the demands of daily practice are less aware than they should be of the legal and business administration sides. “I often get clients who come to me complaining about their contracts after they’ve signed them. I don’t have leverage to do as much for them,” she admitted.
From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control. These could relate to compensation and bonuses, as well as opportunities to invest in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs).
Aebel’s overarching messages to gastroenterologists are as follows: “Be aware. Learn basic health law. Read your contracts before you sign them. And invest in good counsel before you sign agreements,” she said. “In addition, GI practitioners need to have a working knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the federal Stark Law and how they could be commonly applied in their practices.”
These are designed to protect government-funded patient care from monetary influence. The False Claims Act is another federal buttress against fraud and abuse, she said.
Update Details
Though not intended to be legal advice, Aebel’s update touches on several important medicolegal areas.
Stark Law on Self-Referrals
Gastroenterologists should be familiar with this federal law, a self-referral civil penalty statute regulating how physicians can pay themselves in practices that provide designated health services covered by federal healthcare programs such as Medicare or Medicaid.
For a Stark penalty to apply, there must be a physician referral to an entity (eg, lab, hospital, nutrition service, physiotherapy or radiotherapy center) in which the physician or a close family member has a financial interest.
Ambulatory Surgery Centers
Another common area vulnerable to federal fraud and abuse regulation is investment in ASCs. “Generally speaking, it is a felony to pay or be paid anything of value for Medicare or Medicaid business referrals,” Aebel wrote. This provision relates to the general restriction of the federal AKB statute.
A gastroenterologist referring Medicare patients to a center where that physician has an investment could technically violate this law because the physician will receive profit distributions from the referral. In addition to constituting a felony with potential jail time, violation of this statute is grounds for substantial civil monetary penalties and/or exclusion from the government coverage program.
Fortunately, Aebel noted, legal safe harbors cover many financial relationships, including investment in an ASC. The financial arrangement is protected from prosecution if it meets five safe harbor requirements, including nondiscriminatory treatment of government-insured patients and physician investment unrelated to a center’s volume or the value of referrals. If even one aspect is not met, that will automatically constitute a crime.
“However, the government will look at facts and circumstances to determine whether there was an intent to pay for a referral,” Aebel wrote.
The safe harbor designates requirements for four types of ASCs: surgeon-owned, single-specialty, multispecialty, and hospital/physician ASCs.
Private-Equity Investment
With mergers and acquisitions of US medical practices and networks by private-equity firms becoming more common, gastroenterologists need to be aware of the legal issues involved in such investment.
Most states abide by corporate practice of medicine doctrines, which prohibit unlicensed people from direct ownership in a medical practice. These doctrines vary by state, but their primary goal is to ensure that medical decisions are made solely based on patient care and not influenced by corporate interests. The aim is to shield the physician-patient relationship from commercial influence.
“Accordingly, this creates additional complicated structures necessary for private-equity investment in gastroenterology practices,” Aebel wrote. Usually, such investors will invest in a management services organization (MSO), which takes much of the practice’s value via management fees. Gastroenterologists may or may not have an opportunity to invest in the practice and the MSO in this scenario.
Under corporate practice of medicine doctrine, physicians must control the clinical aspects of patient care. Therefore, some states may have restrictions on private-equity companies’ control of the use of medical devices, pricing, medical protocols, or other issues of patient care.
“This needs to be considered when reviewing the investment documents and structural documents proposed by private equity companies,” the advisory stated. From a business standpoint, gastroenterologists need to understand where they can negotiate for financial gain and control over their clinical practice. “This could relate to their compensation, bonuses, and investment opportunities in the practice, the practice management company, and possibly real estate or ASCs.”
Offering a gastroenterologist’s perspective on the paper, Camille Thélin, MD, MSc, an associate professor in the Division of Digestive Diseases and Health at the University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, who also practices privately, said, that “what Erin Aebel reminds us is that the business side of GI can be just as tricky as the clinical side. Ancillary services like capsule studies or office labs fall under strict Stark rules, ASC ownership has Anti-Kickback Law restrictions, and private-equity deals may affect both your paycheck and your autonomy.”
Thélin’s main takeaway advice is that business opportunities can be valuable but carry real legal risks if not structured correctly. “This isn’t just abstract compliance law — it’s about protecting one’s ability to practice medicine, earn fairly, and avoid devastating penalties,” she told GI & Hepatology News. “This article reinforces the need for proactive legal review and careful structuring of business arrangements so physicians can focus on patient care without stumbling into avoidable legal pitfalls. With the right legal structure, ancillaries, ASCs, and private equity can strengthen your GI practice without risking compliance.”
The bottom line, said Aebel, is that gastroenterologists already in private practice or considering entering one must navigate a complex landscape of compliance and regulatory requirements — particularly when providing ancillary services, investing in ASCs, or engaging with private equity.
Understanding the Stark law, the AKB statute, and the intricacies of private-equity investment is essential to mitigate risks and avoid severe penalties, the advisory stressed. By proactively seeking expert legal and business guidance, gastroenterologists can structure their financial and ownership arrangements in a compliant manner, safeguarding their practices while capitalizing on growth opportunities.
This paper listed no external funding. Neither Aebel nor Thélin had any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.
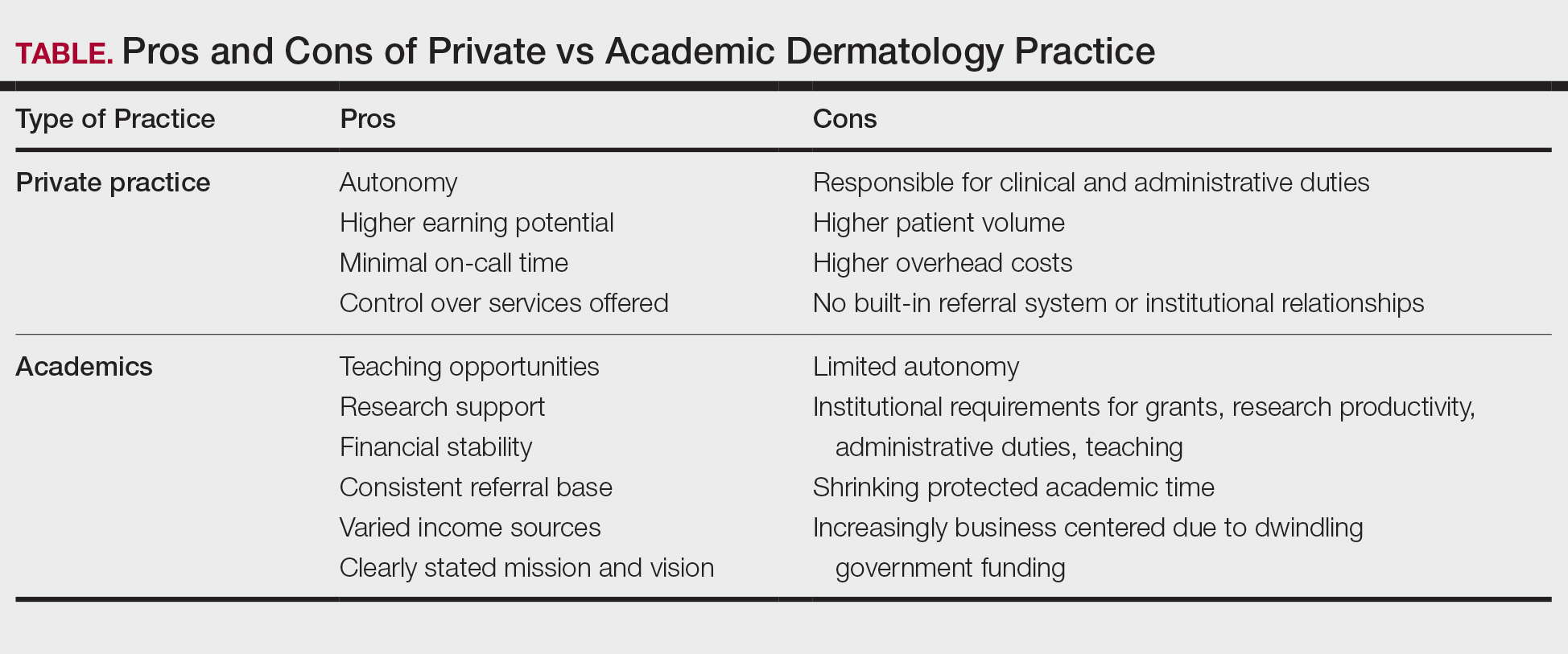
Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.

Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
Dermatology is a rapidly growing, highly competitive specialty with patients that can be served via private practice, academic medicine, hybrid settings, and rural health clinics. Medical residents’ choice of a career path has been rapidly evolving alongside shifts in health care policy, increasing demand for dermatologic services, stagnant fees falling behind inflation for more than a decade, and payment methods that no longer reflect the traditional fee-for-service model. This places a lot of pressure on young dermatologists to evaluate which practice structure best fits their career goals. A nuanced understanding of the strengths and limitations of each practice model is essential for dermatologists to make informed career decisions that are aligned with their values.
While there are many health care practice models, the first decision dermatology residents must make is whether they would prefer working in the private sector or an academic practice. Of course, it is not uncommon for academic dermatologists to embark on a midcareer segue into private practice and, less commonly, for private dermatologists to culminate their careers with a move to academics. The private sector includes private practice, private equity (PE)–owned group practices that often are single-specialty focused, and hospital-owned group practices that usually are multispecialty. Traditionally, private practices are health care businesses owned by one physician (solo practice) or a group of physicians (group practice) operated independently from hospitals, health systems, or private investors. Financially, these practices rely heavily on volume-based services, especially clinic visits and cosmetic procedures, which provide higher reimbursement rates and usually cash payments at the time of service.1 Roughly 35% of dermatologists in the United States work in private practice, and a dwindling 15% work in solo practice.2,3
Medical practices that are not self-owned by physicians vary widely, and they include hospital- or medical center–owned, private equity, and university-based academic practices. Private equity practices typically are characterized as profit driven. Hospital-owned practices shoulder business decisions and administrative duties for the physician at the cost of provider autonomy. Academic medicine is the most different from the other practice types. In contrast to private practice dermatologists, university-based dermatologists practice at academic medical centers (AMCs) with the core goals of patient care, education, and research. Compensation generally is based on the relative value unit (RVU), which is supplemented by government support and research grants.
As evidenced in this brief discussion, health care practice models are complex, and choosing the right model to align with professional goals can pose a major challenge for many physicians. The advantages and disadvantages of various practice models will be reviewed, highlighting trends and emerging models.
Solo or Small-Group Single-Specialty Private Practice
Private practice offers dermatologists the advantage of higher income potential but with greater economic risk; it often requires physicians to be more involved in the business aspects of dermatologic practice. In the early 1990s, a survey of private practice dermatologists revealed that income was the first or second most important factor that contributed to their career choice of private vs academic practice.4 Earning potential in private practice largely is driven by the autonomy afforded in this setting. Physicians have the liberty of choosing their practice location, structure, schedule, and staff in addition to tailoring services toward profitability; this typically leads to a higher volume of cosmetic and procedural visits, which may be attractive to providers wishing to focus on aesthetics. Private practice dermatologists also are not subject to institutional requirements that may include the preparation of grant submissions, research productivity targets, and devotion of time to teaching. Many private dermatologists find satisfaction in tailoring their work environments to align with personal values and goals and in cultivating long-term relationships with patients in a more personal and less bureaucratic context.
There also are drawbacks to private practice. The profitability often can be attributed to the higher patient load and more hours devoted to practice.5 A 2006 study found that academics saw 32% to 41% fewer patients per week than private practice dermatologists.6 Along with the opportunity for financial gain is the risk of financial ruin. Cost is the largest hurdle for establishing a practice, and most practices do not turn a profit for the first few years.1,5 The financial burden of running a practice includes pressure from the federal government to adopt expensive electronic health record systems to achieve maximum Medicare payment through the Merit-Based Incentive Payment System, liability insurance, health insurance, and staff salaries.7 These challenges require strong business acumen, including managing overhead costs, navigating insurance negotiations, marketing a practice, and maintaining compliance with evolving health care regulations. The purchase of a $100,000 laser could be a boon or bust, requiring the development of a business plan that ensures a positive return on investment. Additionally, private practice profitability has the potential to dwindle as governmental reimbursements fail to match inflation rates. Securing business advisors or even obtaining a Master of Business Administration degree can be helpful.
Insurance and government agencies also are infringing upon some of the autonomy of private practice dermatologists, as evidenced by a 2017 survey of dermatologists that found that more than half of respondents altered treatment plans based on insurance coverage more than 20% of the time.2 Private equity firms also could infringe on private practice autonomy, as providers are beholden to the firm’s restrictions—from which company’s product will be stocked to which partner will be on call. Lastly, private practice is less conducive to consistent referral patterns and strong relationships with specialists when compared to academic practice. Additionally, reliance on high patient throughput or cosmetic services for financial sustainability can shift focus away from complex medical dermatology, which often is referred to AMCs.
Academic Medicine
Academic dermatology offers a stimulating and collaborative environment with opportunities to advance the field through research and education. Often, the opportunity to teach medical students, residents, and peers is the deciding factor for academic dermatologists, as supported by a 2016 survey that found teaching opportunities are a major influence on career decision.8 The mixture of patient care, education, and research roles can be satisfying when compared to the grind of seeing large numbers of patients every day. Because they typically are salaried with an RVU-based income, academic dermatologists often are less concerned with the costs associated with medical treatment, and they typically treat more medically complex patients and underserved populations.9 The salary structure of academic roles also provides the benefit of a stable and predictable income. Physicians in this setting often are considered experts in their field, positioning them to have a strong built-in referral system along with frequent participation in multidisciplinary care alongside colleagues in rheumatology, oncology, and infectious diseases. The benefits of downstream income from dermatopathology, Mohs surgery, and other ancillary testing can provide great financial advantages for an academic or large group practice.10 Academic medical centers also afford the benefit of resources, such as research offices, clinical trial units, and institutional support for scholarly publication.
Despite its benefits, academic dermatology is not without unique demands. The resources afforded by research work come with grant application deadlines and the pressure to maintain research productivity as measured by grant dollars. Academic providers also must navigate institutional political dynamics and deal with limits on autonomy. Additionally, the administrative burden associated with committee work, mentorship obligations, and publishing requirements further limit clinical time and contribute to burnout. According to Loo et al,5 92% of 89 dermatology department chairmen responding to a poll believed that the lower compensation was the primary factor preventing more residents from pursuing academia.
The adoption of RVU-based and incentive compensation models at many AMCs, along with dwindling government funds available for research, also have created pressure to increase patient volume, sometimes at the expense of teaching and research. Of those academic dermatologists spending more than half their time seeing patients, a majority reported that they lack the time to also conduct research, teach, and mentor students and resident physicians.6 A survey of academic dermatologists suggested that, for those already serving in academic positions, salary was less of a concern than the lack of protected academic time.4 While competing demands can erode the appeal of academic dermatology, academia continues to offer a meaningful and fulfilling career path for those motivated by scholarship, mentorship, teaching opportunities, and systemic impact.
Hybrid and Emerging Models
To reconcile the trade-offs inherent in private and academic models, hybrid roles are becoming increasingly common. In these arrangements, dermatologists split their time between private practice and academic appointments settings, allowing for participation in resident education and research while also benefiting from the operational and financial structure of a private office. In some cases, private groups formally affiliate with academic institutions, creating academic-private practices that host trainees and produce scholarly work while operating financially outside of traditional hospital systems. Individual dermatologists also may choose to accept part-time academic roles that allow residents and medical students to rotate in their offices. Hybrid roles may be of most interest to individuals who feel that they are missing out on the mentorship and teaching opportunities afforded at AMCs.
Government-funded systems such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals offer another alternative. Dermatologists at VA hospitals often hold faculty appointments, treat a wide range of conditions in a population with great need, and engage in teaching without the intensity of productivity requirements seen at AMCs. These roles can be attractive to physicians who value public service, work-life balance, and minimal malpractice risk, as well as dermatologists who wish to introduce variety in their practice through an additional clinical setting. Notably, these roles are limited, as roughly 80% of VA hospitals employ part-time dermatologists and 72% reported being understaffed.11 Despite the challenges of limited resources and increased bureaucracy, the VA is the largest health care delivery system in the United States, offering the benefits of protection from most malpractice risk and participation in medical education at 80% of VA hospitals.12 A VA-based practice may be most attractive to physicians with prior military service or those looking for a stable practice that serves the underserved and the mission of medical education.
Similarly, rural health clinics are private practices with special subsidies from the federal government that bring Medicaid payments up to the level of Medicare.13 Rural dermatology also mirrors that of a VA-based practice by offering the opportunity to treat an array of conditions in a population of great need, as rural patients often are in care deserts and would otherwise need to travel for miles to receive dermatologic care. There is a shortage of dermatologists working in rural areas, and rural dermatologists are more likely than those in suburban or urban areas to practice alone.2 Although potentially more physically isolating, rural dermatology offers providers the opportunity to establish a lucrative practice with minimal competition and development of meaningful patient relationships.
The most rapidly increasing practice model emerging in dermatology over the past decade is the private equity (PE) group. Rajabi-Estarabadi et al14 estimated that at least 184 dermatology practices have been acquired by PE groups between 2010 and 2019. An estimated 15% of all PE acquisitions in health care have been within the field of dermatology.9 Private equity firms typically acquire 1 or more practices, then consolidate the operations with the short-term goals of reducing costs and maximizing profits and longer-term goals of selling the practice for further profit in 3 to 7 years.9 They often rely heavily on a dermatologist supervising a number of nurse practitioners.15 While PE acquisition may provide additional financial stability and income, providers have less autonomy and potentially risk a shift in their focus from patient care to profit.
The blurred lines between practice settings reflect a broader shift in the profession. Dermatologists have increasingly crafted flexible, individualized careers that align with their goals and values while drawing from both academic and private models. Hybrid roles may prove critical in preserving the educational and research missions of dermatology while adapting to economic and institutional realities.
Gender Trends, Career Satisfaction, and Other Factors Influencing Career Choice
The gender demographics of dermatology have changed greatly in recent decades. In the years 2010 to 2021, the percentage of women in the field rose from 41% to 52.2%, mirroring the rise in female medical students.16 Despite this, gender disparities persist through differences in pay, promotion rates, leadership opportunities, and research productivity.17 Women who are academic dermatologists are less likely to have protected research time and often shoulder a disproportionate share of mentorship and administrative responsibilities, which frequently are undervalued in promotion and compensation structures. Similarly, women physicians are less likely to own their own private practice.18 Notably, women physicians work part-time more often than their male counterparts, which likely impacts their income.19 Interestingly, no differences were noted in job satisfaction between men and women in academic or private practice settings, suggesting that dermatology is a fulfilling field for female physicians.16 Similar data were observed in the field of dermatopathology; in fact, there is no difference in job satisfaction when comparing providers in academics vs private practice.20
Geographic factors also influence career decisions. Some dermatologists may choose private practice to remain close to family or serve a rural area, while some choose academic centers typically located in major metropolitan areas. Others are drawn to AMCs due to their reputation, resources, or opportunities for specialization. The number of practicing dermatologists in an area also may be considered, as areas with fewer providers likely have more individuals seeking a provider and thus more earning potential.
In summary, career satisfaction is influenced by many factors, including practice setting, colleagues, institutional leadership, work environment, and professional goals. For individuals who are seeking intellectual stimulation and teaching opportunities, academic dermatology may be a great career option. Academic or large group practices may come with a large group of clinical dermatologists to provide a steady stream of specimens. Private practice appeals to those seeking autonomy, reduced bureaucracy, and higher earning potential. Tierney et al21 found that the greatest predictor of a future career in academics among Mohs surgeons was the number of publications a fellow had before and during fellowship training. These data suggest that personal interests greatly influence career decisions.
The Role of Mentorship in Career Decision-Making
Just as personal preferences guide career decisions, so too do interpersonal interactions. Mentorship plays a large role in career success, and the involvement of faculty mentors in society meetings and editorial boards has been shown to positively correlate with the number of residents pursuing academia.14 Similarly, negative interactions have strong impacts, as the top cited reason for Mohs surgeons leaving academia was lack of support from their academic chair.21 While many academic dermatologists report fulfillment from the collegial environment, retention remains an issue. Tierney et al21 found that, among 455 academic Mohs surgeons, only 28% of those who began in academia remained in those roles over the long term, and this trend of low retention holds true across the field of academic dermatology. Lack of autonomy, insufficient institutional support, and more lucrative private practice opportunities were all cited as reasons for leaving. For dermatologists seeking separation from academics but continued research opportunities, data suggest that private practice allows for continued research and publications, indicating that scholarly engagement is not exclusive to academic settings. These trends point to the increasing viability of hybrid or academic-private models that combine academic productivity with greater flexibility and financial stability.
Final Thoughts
Academic and private practice dermatology each offer compelling advantages and distinct challenges (Table). The growing popularity of hybrid models reflects a desire among dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment associated with academic medicine with professional sustainability and autonomy of private practice. Whether through part-time academic appointments, rural health clinics, VA employment, or affiliations between private groups and academic institutions, these emerging roles offer a flexible and adaptive approach to career development.

Ultimately, the ideal practice model is one that aligns with a physician’s personal values, long-term goals, and lifestyle preferences. No single path fits all, but thoughtful career planning supported by mentorship and institutional transparency can help dermatologists thrive in a rapidly evolving health care landscape.
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
- Kaplan J. Part I: private practice versus academic medicine. BoardVitals Blog. June 5, 2018. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.boardvitals.com/blog/private-practice-academic-medicine/
- Ehrlich A, Kostecki J, Olkaba H. Trends in dermatology practices and the implications for the workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77:746-752. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.06.030
- Parthasarathy V, Pollock JR, McNeely GL, et al. A cross-sectional analysis of trends in dermatology practice size in the United States from 2012 to 2020. Arch Dermatol Res. 2022;315:223-229. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02344-0
- Bergstresser PR. Perceptions of the academic environment: a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991;25:1092-1096. doi:10.1016/0190-9622(91)70311-o
- Loo DS, Liu CL, Geller AC, et al. Academic dermatology manpower: issues of recruitment and retention. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:341-347. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.3.341
- Resneck JS, Tierney EP, Kimball AB. Challenges facing academic dermatology: survey data on the faculty workforce. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:211-216. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2005.10.013
- Salmen N, Brodell R, Brodell Dolohanty L. The electronic health record: should small practices adopt this technology? J of Skin. 2024;8:1269-1273. doi:10.25251/skin.8.1.8
- Morales-Pico BM, Cotton CC, Morrell DS. Factors correlated with residents’ decisions to enter academic dermatology. Dermatol Online J. 2016;22:13030/qt7295783b.
- DeWane ME, Mostow E, Grant-Kels JM. The corporatization of care in academic dermatology. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:289-295. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.02.003
- Pearlman RL, Nahar VK, Sisson WT, et al. Understanding downstream service profitability generated by dermatology faculty in an academic medical center: a key driver to promotion of access-to-care. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315:1425-1427. doi:10.1007/s00403-022-02406-3
- Huang WW, Tsoukas MM, Bhutani T, et al. Benchmarking U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs dermatologic services: a nationwide survey of VA dermatologists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:50-54. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.035
- 20 reasons doctors like working for the Veterans Health Administration. US Department of Veterans Affairs. August 2016. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/docs/20ReasonsVHA_508_IB10935.pdf
- Rural health clinics (RHCs). Rural Health Information Hub. Updated April 7, 2025. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www .ruralhealthinfo.org/topics/rural-health-clinics
- Rajabi-Estarabadi A, Jones VA, Zheng C, et al. Dermatologist transitions: academics into private practices and vice versa. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:541-546. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.05.012
- Bruch JD, Foot C, Singh Y, et al. Workforce composition in private equity–acquired versus non–private equity–acquired physician practices. Health Affairs. 2023;42:121-129. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2022.00308
- Zlakishvili B, Horev A. Gender disparities in high-quality dermatology research over the past 15 years. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2024;10:e160. doi:10.1097/JW9.0000000000000160
- Jambusaria-Pahlajani A, Crow LD, Levender MM, et al. Practice patterns and job satisfaction of Mohs surgeons: a gender-based survey. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16:1103-1108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29140863/
- Kane CK. Policy Research Perspectives. Recent changes in physician practice arrangements: shifts away from private practice and towards larger practice size continue through 2022. American Medical Association website. 2023. Accessed August 5, 2025. https://www.ama-assn.org/system/files/2022-prp-practice-arrangement.pdf
- Frank E, Zhao Z, Sen S, et al. Gender disparities in work and parental status among early career physicians. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e198340. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8340
- Boyd AS, Fang F. A survey-based evaluation of dermatopathology in the United States. Am J Dermatopathol. 2011;33:173-176. doi:10.1097/dad.0b013e3181f0ed84
- Tierney EP, Hanke CW, Kimball AB. Career trajectory and job satisfaction trends in Mohs micrographic surgeons. Dermatol Surg. 2011;37:1229-1238. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02076.x
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
Advantages and Disadvantages of Private vs Academic Dermatology Practices
PRACTICE POINTS
- In the field of dermatology, solo and small-group single-specialty private practices are shrinking while academic medicine is growing.
- Hybrid models reflect a desire among some dermatologists to balance the intellectual fulfillment and sustainability associated with academic medicine and the professional autonomy of private practice.
Medical Liability for the Gastroenterologist
While nearly 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties and 99% of physicians in high-risk specialties may face a malpractice claim in their careers,1 malpractice is rarely discussed openly in medical school, residency, fellowship, or even amongst colleagues. Indeed, one study suggested that more than 10% of practicing gastroenterologists may face a malpractice claim,2 with gastroenterologists expected to spend 10-15% of their careers with an outstanding malpractice claim3 as cases may take 27-29 months to resolve on average.4
Believing that if a physician is sued, one must have done something “wrong” or that speaking about one’s experience may implicate a colleague, creates an intense stigma and isolation that only serves to aggravate the “second victim syndrome” (SVS) that is well documented in the surgical literature.2 Herein,
What is Malpractice? Why Do Physicians Get Sued?
Malpractice is defined as negligence on the part of a physician which causes physical or emotional damage to the patient. This requires a variety of legal issues to be evaluated (e.g. breach of duty between the physicians and patient, breach of standard of care), that often center around the question: would a “reasonable, careful, and prudent” doctor behave in the same manner in the same circumstance?
While some fields of medicine lend themselves better to algorithmic applications of highly evidence-based guidelines, many aspects of GI care and endoscopic practice are highly physician/patient-specific, dependent on local expertise, and based on low-quality evidence. As a result, an assessment of negligence may be quite subjective, depending on the expert retained by a plaintiff. Conflicting expert testimony on what professional custom is and whether practice deviates may hinge on technical details that may or may not be appreciated by a lay jury.
Plaintiffs must prove both that they have sustained an injury and that the injury (emotional or physical) was due to the physician’s negligence. While this may be straightforward in a “slip-and-fall” tort claim, medical malpractice claims usually involve sick patients with multiple comorbidities, where assigning causality to a single intervention/misinterpretation/missed opportunity is difficult to weigh against competing causes of adverse outcomes. Assessing a specific liability requires that the plaintiff prove this to a “more likely than not” standard which may be part of the reason why only 30% of cases are closed with indemnity payments, a figure that has not changed significantly in the past decade.4
While the perception amongst physicians is that tort legislation is ever increasing, data from the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) demonstrates that the number of paid claims against physicians has decreased by 75% in the last 20 years.5 This may reflect a progressive improvement in the quality of care delivered or success of “tort reform” on the state level to limit damages and “nuisance” lawsuits. However, another more problematic possibility is that with the corporatization of medicine, an untold number of physicians may be removed from litigation as a named party, with their institution shielding them from reporting. While the number of cases may or may not be declining, the average indemnity payment appears to be rising to $330,000 on average,4 with one study suggesting a significant growth in paid claims in gastroenterology.6
Historically, studies of closed malpractice claims have demonstrated that 59% involved diagnostic errors involving a cancer diagnosis,7 though why this actually happens may be for a wide variety of reasons including errors in the development of a differential diagnosis, ordering of an appropriate diagnostic test, interpretation of the diagnostic test, or follow-up of an abnormality identified.
What are the Intended/Unintended Consequences of Litigation?
The objective of our tort system is to compensate patients for economic damages (medical costs and lost wages) and non-economic damages (pain and suffering), and to ideally deter negligent behavior of providers. Interestingly, data from the NPDB have suggested that approximately 1% of all physicians account for 32% of all paid claims, with the same study showing that among physicians with paid claims, 4% had at least 3.8
While certain fields are obviously more prone to litigation, the risk of additional claims on a physician with 3 prior claims was more than 3 times that of physicians with 1 lifetime claim. One would assume that the system was built to drive out a small proportion of “bad actors.” Indeed, similar data from the NPDB has demonstrated that the number of claims against physicians was associated both with their leaving the practice of medicine and relocating to smaller practice settings.9
Another frequent question is whether the threat of litigation drives “defensive medicine” (i.e. medical care that is not beneficial) or avoidance medicine (i.e. excluding high risk patients and procedures from ones’ practice). These behaviors have been well documented in physicians around the world,10 as well as several surveys of gastroenterologists specifically suggesting regular ordering of unnecessary imaging/endoscopy and referrals of patients to specialists that may not be necessary.11,12
However, does defensive medicine work: does spending more prevent you from being the target of a lawsuit? In an observational study in Florida from 2000-2009, researchers demonstrated that across specialties, greater average spending by physicians was associated with a reduced risk of incurring a malpractice claim. Indeed, the likelihood of a top quintile spending internist having a malpractice incident vs a bottom quintile spending internist was 0.3% vs 1.5%.13
Approximately 10.4-43.3% of physicians may experience SVS, experiencing trauma after an adverse patient event/medical error, manifesting with psychological trauma (shame, guilt, anxiety) and cognitive limitations (burnout, stress).2 Significant emotional consequences are common on the part of the physician and have well-documented stages to recovery,14 which if ignored may lead to long-term detrimental mental/emotional health of the physician and their future patients.
Specifically, in one study, 80.8% of physicians who had a closed malpractice claim reported significant emotional distress (regardless of the legal outcome), with frequent reports of mood symptoms that affected professional conduct.15 Recognizing these effects and implementing peer counseling and institutional support may help to expedite recovery and mitigate future adverse career outcomes.14
Anatomy/Timeline of a Liability Lawsuit
Medical malpractice cases are heard in state courts, in the jurisdictions where the care was provided. From the time an event occurs to when a jury verdict may be rendered may take 4-5 years or more depending on the local statute of limitations, discovery process, backlog of the local case docket, and specific circumstances of the case. The length of time is important to consider given the likelihood that a physician may advance in training or move practice locations during the course of litigation. Several common myths surrounding this process are summarized in the accompanying box, titled “Myths Surrounding Medical Liability Litigation.”
The plaintiff faces a statute of limitations to file a lawsuit that may range from 1-6 years depending on the state. The first indication that legal action may be pending will generally be a plaintiff’s formal request for medical records. After these records are reviewed, the plaintiff’s attorney will consult one or more experts (often credentialed in the same specialty) to assess if the case is viable and to ultimately form the basis of an affidavit of merit from a plaintiff expert.
Once the lawsuit is filed, the physician(s) named will be assigned an attorney by their employer/insurance company. A state medical board malpractice questionnaire will generally follow that will seek to independently evaluate the alleged malpractice with interrogatives to determine if censure is warranted. There is a formal response to the plaintiff’s petition by the defense and then the discovery phase begins where both sides depose the defendants/plaintiffs and retain medical experts that are favorable to their arguments.
In choosing potential “experts,” physicians must ensure that they are willing/able to be present for a potential trial, do not have any personal/professional/academic conflicts with the defendants, and are willing to provide compelling testimony to a jury. A pre-trial conference and trial date is set which may be >12 months away depending on the local docket. While the amount of time a trial may take is variable, it may be up to 5-7 days that the defendants are expected to be in court in addition to days where depositions are being taken.
During the discovery process, dismissal of the physician from the lawsuit is pursued. In addition, settlement negotiations generally proceed in parallel with discovery process and may result in a pre-trial/pre-verdict settlement. Once a verdict is reached, whether for the plaintiff or the defendant, the case may be appealed, and the trial preparation process may be repeated.
Conclusions
Awareness of the medical liability process is critical for trainees and attendings alike, given the high likelihood of litigation in a gastroenterologist’s career. Specific considerations like local tort law and malpractice coverage are important to be familiar. Ongoing health services research help to shape our understanding on the intended and unintended consequences of litigation on medicine, though detailed data on outcomes/settlements are limited by confidentiality agreements, which may hamper efforts to improve patient safety.
Dr. Das is associate professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. He has served as a consultant for Olympus, but has no other relevant conflicts.
References
1. Jena AB, et al. Malpractice Risk According to Physician Specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1012370.
2. Chong RIH, et al. Scoping review of the second victim syndrome among surgeons: Understanding the impact, responses, and support systems. Am J Surg 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.09.045.
3. Seabury S, et al. On Average, Physicians Spend Nearly 11 Percent Of Their 40-Year Careers With An Open, Unresolved Malpractice Claim. Health Aff Proj Hope. 2013 Jan. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2012.0967.
4. CRICO Strategies. Medical Malpractice in America: A 10-Year Asessment with Insights. 2018. Accessed Apr 28, 2025.
5. Studdert DM, Hall MA. Medical Malpractice Law — Doctrine and Dynamics. N Engl J Med 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2201675.
6. Schaffer AC, et al. Rates and Characteristics of Paid Malpractice Claims Among US Physicians by Specialty, 1992-2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 May. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311.
7. Gandhi TK, et al. Missed and Delayed Diagnoses in the Ambulatory Setting: A Study of Closed Malpractice Claims. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-7-200610030-00006.
8. Studdert DM, et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Physicians Prone to Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1506137.
9. Studdert DM, et al. Changes in Practice among Physicians with Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1809981.
10. Ries NM, Jansen J. Physicians’ views and experiences of defensive medicine: An international review of empirical research. Health Policy. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2021.02.005.
11. Hiyama T, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7671.
12. Elli L, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Lombardy: Between lawsuits and the economic crisis. Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.004.
13. Jena AB, et al. Physician spending and subsequent risk of malpractice claims: observational study. BMJ. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h5516.
14. Scott SD, et al. The natural history of recovery for the healthcare provider “second victim” after adverse patient events. BMJ Qual Saf. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2009.032870.
15. Gómez-Durán EL, et al. Physicians as second victims after a malpractice claim: An important issue in need of attention. J Healthc Qual Res. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jhqr.2018.06.002.
While nearly 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties and 99% of physicians in high-risk specialties may face a malpractice claim in their careers,1 malpractice is rarely discussed openly in medical school, residency, fellowship, or even amongst colleagues. Indeed, one study suggested that more than 10% of practicing gastroenterologists may face a malpractice claim,2 with gastroenterologists expected to spend 10-15% of their careers with an outstanding malpractice claim3 as cases may take 27-29 months to resolve on average.4
Believing that if a physician is sued, one must have done something “wrong” or that speaking about one’s experience may implicate a colleague, creates an intense stigma and isolation that only serves to aggravate the “second victim syndrome” (SVS) that is well documented in the surgical literature.2 Herein,
What is Malpractice? Why Do Physicians Get Sued?
Malpractice is defined as negligence on the part of a physician which causes physical or emotional damage to the patient. This requires a variety of legal issues to be evaluated (e.g. breach of duty between the physicians and patient, breach of standard of care), that often center around the question: would a “reasonable, careful, and prudent” doctor behave in the same manner in the same circumstance?
While some fields of medicine lend themselves better to algorithmic applications of highly evidence-based guidelines, many aspects of GI care and endoscopic practice are highly physician/patient-specific, dependent on local expertise, and based on low-quality evidence. As a result, an assessment of negligence may be quite subjective, depending on the expert retained by a plaintiff. Conflicting expert testimony on what professional custom is and whether practice deviates may hinge on technical details that may or may not be appreciated by a lay jury.
Plaintiffs must prove both that they have sustained an injury and that the injury (emotional or physical) was due to the physician’s negligence. While this may be straightforward in a “slip-and-fall” tort claim, medical malpractice claims usually involve sick patients with multiple comorbidities, where assigning causality to a single intervention/misinterpretation/missed opportunity is difficult to weigh against competing causes of adverse outcomes. Assessing a specific liability requires that the plaintiff prove this to a “more likely than not” standard which may be part of the reason why only 30% of cases are closed with indemnity payments, a figure that has not changed significantly in the past decade.4
While the perception amongst physicians is that tort legislation is ever increasing, data from the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) demonstrates that the number of paid claims against physicians has decreased by 75% in the last 20 years.5 This may reflect a progressive improvement in the quality of care delivered or success of “tort reform” on the state level to limit damages and “nuisance” lawsuits. However, another more problematic possibility is that with the corporatization of medicine, an untold number of physicians may be removed from litigation as a named party, with their institution shielding them from reporting. While the number of cases may or may not be declining, the average indemnity payment appears to be rising to $330,000 on average,4 with one study suggesting a significant growth in paid claims in gastroenterology.6
Historically, studies of closed malpractice claims have demonstrated that 59% involved diagnostic errors involving a cancer diagnosis,7 though why this actually happens may be for a wide variety of reasons including errors in the development of a differential diagnosis, ordering of an appropriate diagnostic test, interpretation of the diagnostic test, or follow-up of an abnormality identified.
What are the Intended/Unintended Consequences of Litigation?
The objective of our tort system is to compensate patients for economic damages (medical costs and lost wages) and non-economic damages (pain and suffering), and to ideally deter negligent behavior of providers. Interestingly, data from the NPDB have suggested that approximately 1% of all physicians account for 32% of all paid claims, with the same study showing that among physicians with paid claims, 4% had at least 3.8
While certain fields are obviously more prone to litigation, the risk of additional claims on a physician with 3 prior claims was more than 3 times that of physicians with 1 lifetime claim. One would assume that the system was built to drive out a small proportion of “bad actors.” Indeed, similar data from the NPDB has demonstrated that the number of claims against physicians was associated both with their leaving the practice of medicine and relocating to smaller practice settings.9
Another frequent question is whether the threat of litigation drives “defensive medicine” (i.e. medical care that is not beneficial) or avoidance medicine (i.e. excluding high risk patients and procedures from ones’ practice). These behaviors have been well documented in physicians around the world,10 as well as several surveys of gastroenterologists specifically suggesting regular ordering of unnecessary imaging/endoscopy and referrals of patients to specialists that may not be necessary.11,12
However, does defensive medicine work: does spending more prevent you from being the target of a lawsuit? In an observational study in Florida from 2000-2009, researchers demonstrated that across specialties, greater average spending by physicians was associated with a reduced risk of incurring a malpractice claim. Indeed, the likelihood of a top quintile spending internist having a malpractice incident vs a bottom quintile spending internist was 0.3% vs 1.5%.13
Approximately 10.4-43.3% of physicians may experience SVS, experiencing trauma after an adverse patient event/medical error, manifesting with psychological trauma (shame, guilt, anxiety) and cognitive limitations (burnout, stress).2 Significant emotional consequences are common on the part of the physician and have well-documented stages to recovery,14 which if ignored may lead to long-term detrimental mental/emotional health of the physician and their future patients.
Specifically, in one study, 80.8% of physicians who had a closed malpractice claim reported significant emotional distress (regardless of the legal outcome), with frequent reports of mood symptoms that affected professional conduct.15 Recognizing these effects and implementing peer counseling and institutional support may help to expedite recovery and mitigate future adverse career outcomes.14
Anatomy/Timeline of a Liability Lawsuit
Medical malpractice cases are heard in state courts, in the jurisdictions where the care was provided. From the time an event occurs to when a jury verdict may be rendered may take 4-5 years or more depending on the local statute of limitations, discovery process, backlog of the local case docket, and specific circumstances of the case. The length of time is important to consider given the likelihood that a physician may advance in training or move practice locations during the course of litigation. Several common myths surrounding this process are summarized in the accompanying box, titled “Myths Surrounding Medical Liability Litigation.”
The plaintiff faces a statute of limitations to file a lawsuit that may range from 1-6 years depending on the state. The first indication that legal action may be pending will generally be a plaintiff’s formal request for medical records. After these records are reviewed, the plaintiff’s attorney will consult one or more experts (often credentialed in the same specialty) to assess if the case is viable and to ultimately form the basis of an affidavit of merit from a plaintiff expert.
Once the lawsuit is filed, the physician(s) named will be assigned an attorney by their employer/insurance company. A state medical board malpractice questionnaire will generally follow that will seek to independently evaluate the alleged malpractice with interrogatives to determine if censure is warranted. There is a formal response to the plaintiff’s petition by the defense and then the discovery phase begins where both sides depose the defendants/plaintiffs and retain medical experts that are favorable to their arguments.
In choosing potential “experts,” physicians must ensure that they are willing/able to be present for a potential trial, do not have any personal/professional/academic conflicts with the defendants, and are willing to provide compelling testimony to a jury. A pre-trial conference and trial date is set which may be >12 months away depending on the local docket. While the amount of time a trial may take is variable, it may be up to 5-7 days that the defendants are expected to be in court in addition to days where depositions are being taken.
During the discovery process, dismissal of the physician from the lawsuit is pursued. In addition, settlement negotiations generally proceed in parallel with discovery process and may result in a pre-trial/pre-verdict settlement. Once a verdict is reached, whether for the plaintiff or the defendant, the case may be appealed, and the trial preparation process may be repeated.
Conclusions
Awareness of the medical liability process is critical for trainees and attendings alike, given the high likelihood of litigation in a gastroenterologist’s career. Specific considerations like local tort law and malpractice coverage are important to be familiar. Ongoing health services research help to shape our understanding on the intended and unintended consequences of litigation on medicine, though detailed data on outcomes/settlements are limited by confidentiality agreements, which may hamper efforts to improve patient safety.
Dr. Das is associate professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. He has served as a consultant for Olympus, but has no other relevant conflicts.
References
1. Jena AB, et al. Malpractice Risk According to Physician Specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1012370.
2. Chong RIH, et al. Scoping review of the second victim syndrome among surgeons: Understanding the impact, responses, and support systems. Am J Surg 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.09.045.
3. Seabury S, et al. On Average, Physicians Spend Nearly 11 Percent Of Their 40-Year Careers With An Open, Unresolved Malpractice Claim. Health Aff Proj Hope. 2013 Jan. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2012.0967.
4. CRICO Strategies. Medical Malpractice in America: A 10-Year Asessment with Insights. 2018. Accessed Apr 28, 2025.
5. Studdert DM, Hall MA. Medical Malpractice Law — Doctrine and Dynamics. N Engl J Med 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2201675.
6. Schaffer AC, et al. Rates and Characteristics of Paid Malpractice Claims Among US Physicians by Specialty, 1992-2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 May. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311.
7. Gandhi TK, et al. Missed and Delayed Diagnoses in the Ambulatory Setting: A Study of Closed Malpractice Claims. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-7-200610030-00006.
8. Studdert DM, et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Physicians Prone to Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1506137.
9. Studdert DM, et al. Changes in Practice among Physicians with Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1809981.
10. Ries NM, Jansen J. Physicians’ views and experiences of defensive medicine: An international review of empirical research. Health Policy. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2021.02.005.
11. Hiyama T, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7671.
12. Elli L, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Lombardy: Between lawsuits and the economic crisis. Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.004.
13. Jena AB, et al. Physician spending and subsequent risk of malpractice claims: observational study. BMJ. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h5516.
14. Scott SD, et al. The natural history of recovery for the healthcare provider “second victim” after adverse patient events. BMJ Qual Saf. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2009.032870.
15. Gómez-Durán EL, et al. Physicians as second victims after a malpractice claim: An important issue in need of attention. J Healthc Qual Res. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jhqr.2018.06.002.
While nearly 75% of physicians in low-risk specialties and 99% of physicians in high-risk specialties may face a malpractice claim in their careers,1 malpractice is rarely discussed openly in medical school, residency, fellowship, or even amongst colleagues. Indeed, one study suggested that more than 10% of practicing gastroenterologists may face a malpractice claim,2 with gastroenterologists expected to spend 10-15% of their careers with an outstanding malpractice claim3 as cases may take 27-29 months to resolve on average.4
Believing that if a physician is sued, one must have done something “wrong” or that speaking about one’s experience may implicate a colleague, creates an intense stigma and isolation that only serves to aggravate the “second victim syndrome” (SVS) that is well documented in the surgical literature.2 Herein,
What is Malpractice? Why Do Physicians Get Sued?
Malpractice is defined as negligence on the part of a physician which causes physical or emotional damage to the patient. This requires a variety of legal issues to be evaluated (e.g. breach of duty between the physicians and patient, breach of standard of care), that often center around the question: would a “reasonable, careful, and prudent” doctor behave in the same manner in the same circumstance?
While some fields of medicine lend themselves better to algorithmic applications of highly evidence-based guidelines, many aspects of GI care and endoscopic practice are highly physician/patient-specific, dependent on local expertise, and based on low-quality evidence. As a result, an assessment of negligence may be quite subjective, depending on the expert retained by a plaintiff. Conflicting expert testimony on what professional custom is and whether practice deviates may hinge on technical details that may or may not be appreciated by a lay jury.
Plaintiffs must prove both that they have sustained an injury and that the injury (emotional or physical) was due to the physician’s negligence. While this may be straightforward in a “slip-and-fall” tort claim, medical malpractice claims usually involve sick patients with multiple comorbidities, where assigning causality to a single intervention/misinterpretation/missed opportunity is difficult to weigh against competing causes of adverse outcomes. Assessing a specific liability requires that the plaintiff prove this to a “more likely than not” standard which may be part of the reason why only 30% of cases are closed with indemnity payments, a figure that has not changed significantly in the past decade.4
While the perception amongst physicians is that tort legislation is ever increasing, data from the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) demonstrates that the number of paid claims against physicians has decreased by 75% in the last 20 years.5 This may reflect a progressive improvement in the quality of care delivered or success of “tort reform” on the state level to limit damages and “nuisance” lawsuits. However, another more problematic possibility is that with the corporatization of medicine, an untold number of physicians may be removed from litigation as a named party, with their institution shielding them from reporting. While the number of cases may or may not be declining, the average indemnity payment appears to be rising to $330,000 on average,4 with one study suggesting a significant growth in paid claims in gastroenterology.6
Historically, studies of closed malpractice claims have demonstrated that 59% involved diagnostic errors involving a cancer diagnosis,7 though why this actually happens may be for a wide variety of reasons including errors in the development of a differential diagnosis, ordering of an appropriate diagnostic test, interpretation of the diagnostic test, or follow-up of an abnormality identified.
What are the Intended/Unintended Consequences of Litigation?
The objective of our tort system is to compensate patients for economic damages (medical costs and lost wages) and non-economic damages (pain and suffering), and to ideally deter negligent behavior of providers. Interestingly, data from the NPDB have suggested that approximately 1% of all physicians account for 32% of all paid claims, with the same study showing that among physicians with paid claims, 4% had at least 3.8
While certain fields are obviously more prone to litigation, the risk of additional claims on a physician with 3 prior claims was more than 3 times that of physicians with 1 lifetime claim. One would assume that the system was built to drive out a small proportion of “bad actors.” Indeed, similar data from the NPDB has demonstrated that the number of claims against physicians was associated both with their leaving the practice of medicine and relocating to smaller practice settings.9
Another frequent question is whether the threat of litigation drives “defensive medicine” (i.e. medical care that is not beneficial) or avoidance medicine (i.e. excluding high risk patients and procedures from ones’ practice). These behaviors have been well documented in physicians around the world,10 as well as several surveys of gastroenterologists specifically suggesting regular ordering of unnecessary imaging/endoscopy and referrals of patients to specialists that may not be necessary.11,12
However, does defensive medicine work: does spending more prevent you from being the target of a lawsuit? In an observational study in Florida from 2000-2009, researchers demonstrated that across specialties, greater average spending by physicians was associated with a reduced risk of incurring a malpractice claim. Indeed, the likelihood of a top quintile spending internist having a malpractice incident vs a bottom quintile spending internist was 0.3% vs 1.5%.13
Approximately 10.4-43.3% of physicians may experience SVS, experiencing trauma after an adverse patient event/medical error, manifesting with psychological trauma (shame, guilt, anxiety) and cognitive limitations (burnout, stress).2 Significant emotional consequences are common on the part of the physician and have well-documented stages to recovery,14 which if ignored may lead to long-term detrimental mental/emotional health of the physician and their future patients.
Specifically, in one study, 80.8% of physicians who had a closed malpractice claim reported significant emotional distress (regardless of the legal outcome), with frequent reports of mood symptoms that affected professional conduct.15 Recognizing these effects and implementing peer counseling and institutional support may help to expedite recovery and mitigate future adverse career outcomes.14
Anatomy/Timeline of a Liability Lawsuit
Medical malpractice cases are heard in state courts, in the jurisdictions where the care was provided. From the time an event occurs to when a jury verdict may be rendered may take 4-5 years or more depending on the local statute of limitations, discovery process, backlog of the local case docket, and specific circumstances of the case. The length of time is important to consider given the likelihood that a physician may advance in training or move practice locations during the course of litigation. Several common myths surrounding this process are summarized in the accompanying box, titled “Myths Surrounding Medical Liability Litigation.”
The plaintiff faces a statute of limitations to file a lawsuit that may range from 1-6 years depending on the state. The first indication that legal action may be pending will generally be a plaintiff’s formal request for medical records. After these records are reviewed, the plaintiff’s attorney will consult one or more experts (often credentialed in the same specialty) to assess if the case is viable and to ultimately form the basis of an affidavit of merit from a plaintiff expert.
Once the lawsuit is filed, the physician(s) named will be assigned an attorney by their employer/insurance company. A state medical board malpractice questionnaire will generally follow that will seek to independently evaluate the alleged malpractice with interrogatives to determine if censure is warranted. There is a formal response to the plaintiff’s petition by the defense and then the discovery phase begins where both sides depose the defendants/plaintiffs and retain medical experts that are favorable to their arguments.
In choosing potential “experts,” physicians must ensure that they are willing/able to be present for a potential trial, do not have any personal/professional/academic conflicts with the defendants, and are willing to provide compelling testimony to a jury. A pre-trial conference and trial date is set which may be >12 months away depending on the local docket. While the amount of time a trial may take is variable, it may be up to 5-7 days that the defendants are expected to be in court in addition to days where depositions are being taken.
During the discovery process, dismissal of the physician from the lawsuit is pursued. In addition, settlement negotiations generally proceed in parallel with discovery process and may result in a pre-trial/pre-verdict settlement. Once a verdict is reached, whether for the plaintiff or the defendant, the case may be appealed, and the trial preparation process may be repeated.
Conclusions
Awareness of the medical liability process is critical for trainees and attendings alike, given the high likelihood of litigation in a gastroenterologist’s career. Specific considerations like local tort law and malpractice coverage are important to be familiar. Ongoing health services research help to shape our understanding on the intended and unintended consequences of litigation on medicine, though detailed data on outcomes/settlements are limited by confidentiality agreements, which may hamper efforts to improve patient safety.
Dr. Das is associate professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. He has served as a consultant for Olympus, but has no other relevant conflicts.
References
1. Jena AB, et al. Malpractice Risk According to Physician Specialty. N Engl J Med. 2011 Aug. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1012370.
2. Chong RIH, et al. Scoping review of the second victim syndrome among surgeons: Understanding the impact, responses, and support systems. Am J Surg 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.09.045.
3. Seabury S, et al. On Average, Physicians Spend Nearly 11 Percent Of Their 40-Year Careers With An Open, Unresolved Malpractice Claim. Health Aff Proj Hope. 2013 Jan. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2012.0967.
4. CRICO Strategies. Medical Malpractice in America: A 10-Year Asessment with Insights. 2018. Accessed Apr 28, 2025.
5. Studdert DM, Hall MA. Medical Malpractice Law — Doctrine and Dynamics. N Engl J Med 2022 Oct. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2201675.
6. Schaffer AC, et al. Rates and Characteristics of Paid Malpractice Claims Among US Physicians by Specialty, 1992-2014. JAMA Intern Med. 2017 May. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311.
7. Gandhi TK, et al. Missed and Delayed Diagnoses in the Ambulatory Setting: A Study of Closed Malpractice Claims. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-7-200610030-00006.
8. Studdert DM, et al. Prevalence and Characteristics of Physicians Prone to Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1506137.
9. Studdert DM, et al. Changes in Practice among Physicians with Malpractice Claims. N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1809981.
10. Ries NM, Jansen J. Physicians’ views and experiences of defensive medicine: An international review of empirical research. Health Policy. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2021.02.005.
11. Hiyama T, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Japan. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i47.7671.
12. Elli L, et al. Defensive medicine practices among gastroenterologists in Lombardy: Between lawsuits and the economic crisis. Dig Liver Dis. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.004.
13. Jena AB, et al. Physician spending and subsequent risk of malpractice claims: observational study. BMJ. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h5516.
14. Scott SD, et al. The natural history of recovery for the healthcare provider “second victim” after adverse patient events. BMJ Qual Saf. 2009 Oct. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2009.032870.
15. Gómez-Durán EL, et al. Physicians as second victims after a malpractice claim: An important issue in need of attention. J Healthc Qual Res. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.jhqr.2018.06.002.
Positioning Yourself For Success in Private Practice

In this video, Peter Naas, MD, of Gastroenterology Associates in Greenville, South Carolina, shares insights on how young physicians can best position themselves for a successful career in private practice gastroenterology.

In this video, Peter Naas, MD, of Gastroenterology Associates in Greenville, South Carolina, shares insights on how young physicians can best position themselves for a successful career in private practice gastroenterology.

In this video, Peter Naas, MD, of Gastroenterology Associates in Greenville, South Carolina, shares insights on how young physicians can best position themselves for a successful career in private practice gastroenterology.








