User login
Counseling on cannabis use in pregnancy
A flurry of research papers published this year has simultaneously documented a rise in the use of cannabis during pregnancy and offered more data about its potential harms. This confluence of findings is concerning and highlights the importance of screening our patients for cannabis use and engaging with them in a way in which we can maintain their trust and their commitment to prenatal care.
A retrospective cohort study involving 661,617 women in Ontario found a significant association between self-reported cannabis use in pregnancy and an increased risk of preterm birth (relative risk, 1.41), as well as a greater likelihood of small-for-gestational-age babies (RR, 1.53), placental abruption (RR, 1.72), and transfer to neonatal intensive care (RR, 1.40).1 The study, reported in JAMA in July 2019, carefully matched users with nonusers who had the same characteristics – for example, tobacco use or not.
This new information builds upon other meta-analyses that have demonstrated a decrease in birth weight and greater admittance to the neonatal ICU associated with cannabis use in pregnancy – and it supplements what some research suggests about long-term neurologic development and a potentially increased risk of attention and behavioral problems. Other outcomes that have been noted in long-term neurologic studies of children who were exposed to cannabis in utero include impaired visual acuity, verbal reasoning and comprehension, and short-term memory.2
Increases in use were recently documented in two studies. One, an analysis of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) published in JAMA in June 2019, showed that, between 2002-2003 and 2016-2017, the use of cannabis “in the past month” increased from 3.4% to 7.0% among pregnant women overall, and from 6% to 12% during the first trimester.3
The use of cannabis on a daily or near-daily basis, moreover, increased from 0.9% to 3% among pregnant women overall and from 2% to 5% during the first trimester. The data were collected during face-to-face interviews and were adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, and family income.
In the second study – a cross-sectional study of 367,403 pregnancies among women who filled out a questionnaire on cannabis use during standard prenatal care at Kaiser Permanente Northern California – the adjusted prevalence of use in the year before pregnancy increased from 7% in 2009 to 13% in 2017, and the adjusted prevalence during pregnancy increased from 2% to 3%.4
As in the NSDUH analysis, daily use increased most rapidly (compared with weekly or monthly) such that, by 2017, 25% of those who reported using cannabis in the year before pregnancy – and 21% of those who used cannabis during pregnancy – were daily users. It is notable that Kaiser’s population is diverse in all respects, and that the annual relative rates of increase in cannabis use before and during pregnancy (at each level of frequency) were consistent across racial/ethnic and household income groups.
It’s also worth noting that, in earlier research covering a similar time period (2009-2016), the investigators found significant increases in use via urine toxicology testing that occurs at the first prenatal visit at Kaiser. The increase found through questionnaires, therefore, reflects more than a greater willingness to self-report.
Choosing a screening tool
Universal prenatal substance use screening is recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but we don’t have any specific recommendations on what this means. Who should be screening, and what should that screening look like? Should we use a biologic screen, a standardized screening tool, or simply ask patients whether they use illicit substances?
Screening tools seem advantageous in that they are low cost, noninvasive, potentially comprehensive, and not subject to false-positive results as biologic screens can be – but which tool or tools are best? There are several validated screening tools that can be used outside of pregnancy to determine an individual’s use of illicit substances and whether or not that use is problematic, but previous studies have not used biologic markers to validate substance use screeners in pregnancy. Nor have studies compared screeners in pregnancy.
In our prenatal population in Baltimore, we have not been getting the answers we want using various nonvalidated screening tools. Approximately 30% of patients are positive for cannabis by urine screen, but only half tell us about their use.
Through research in our two prenatal care practices (one serving mostly privately insured and the other serving primarily Medicaid-eligible patients), we assessed both the accuracy and the acceptability of three substance use screening tools that are brief and that have been validated (for the general population) by the World Health Organization for screening of multiple substances: the 4P’s Plus (Parents, Partner, Past, and Pregnancy), the National Institute on Drug Abuse Quick Screen–ASSIST (Modified Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test), and the SURP-P (Substance Use Risk Profile–Pregnancy) scale.
In one study, published in May 2019 in Obstetrics & Gynecology, we recruited 500 pregnant women and administered these three tests to each of them.5 We then compared results with those of urine and hair drug testing, and checked the test-retest reliability of each test by readministering them (albeit by telephone) a week later. Although hair testing is not an indicator of current substance use, we used it to validate the screening tools on less-recent use.
The tests with the highest sensitivity and negative predictive values – the qualities we most want for screening – were the SURP-P and the 4P’s Plus (sensitivity of 92.4% and 90.2%, respectively). Overall they were highly sensitive screening tools across all trimesters, races, and age groups, making them more ideal screening tests than the NIDA Quick Screen–ASSIST.
Of the two tests, the 4P’s Plus screening tool was the one preferred by staff from both practices. In a companion qualitative study, we conducted focus-group discussions with 40 practice staff who were responsible for administering or overseeing patient screening.6 The staff, who were unaware of the sensitivity findings, were asked what they thought about the acceptability to patients of each of the three tools and their usability in practice.
Most of the participating staff preferred the 4P’s Plus screening tool for several reasons: It is easy to understand, is brief and to the point, and it has nonjudgmental language and tone. The screener first asks the patient about her parents’ and her partner’s use of alcohol and drugs, and then asks the patient about her own use of alcohol and tobacco. Affirmative responses to these questions lead to additional questions.
The premise is that one’s genetics, history, and current exposures – as well as one’s own use of tobacco and alcohol – are significantly associated with the use of illicit substances. If the patient reports no parental history or partner usage, and has never drank or smoked before, it’s extremely unlikely that she is using other drugs. The progression of questions does indeed seem less judgmental than immediately asking: “Do you use drugs?”
For us, the insight from this staff perception study combined with the findings on accuracy mean that the 4P’s Plus may be the most useful and acceptable screening tool for routine use in prenatal care.
Talking with our patients
The increase in the use of cannabis before and after pregnancy parallels the movement toward state legalization and decriminalization. Historically, clinicians often have relied on illegality as their main focus of counseling when giving recommendations for cessation and abstinence in pregnancy.2 This approach not only leads to punitive counseling, which can fracture the doctor-patient relationship, but increasingly it is no longer valid. In our changing legal climate, we need to provide medically based counseling and be very clear with our patients that legalization does not equate to safety.
It is important that we neither minimize nor overstate the risks. The evidence base for adverse birth outcomes of cannabis use in pregnancy is quite robust, but the associations can be subtle and are moderated by other behaviors and environmental factors that continue to challenge researchers.
As with alcohol, there likely are dose-or trimester-dependent differences in perinatal outcomes, and it’s quite possible that different cannabis products and routes of consumption have different effects. At this point, however, we don’t know the full story, nor do we know the extent to which the literature is biased toward positive correlations – the reporting of adverse effects – compared with negative findings. It is our job as medical care providers to be comfortable in that gray area and to still counsel patients on what we do know, providing the best-possible medical advice based on the information available to us.
In talking with patients, I explain that cannabis may cause a spectrum of problems and that there certainly are risks. I also tell them that we’re uncertain about the conditions and magnitude of that risk and that some babies who are exposed to cannabis in utero may have no perceivable consequences. Such honesty is important for maintaining trust, especially as some patients may see friends and relatives who also are cannabis users have normal pregnancy outcomes.
Much of my concern about cannabis in pregnancy centers on its effect on the developing brain and on long-term neurologic development. I share this with patients – I tell them that cannabis crosses the placenta and may well affect their baby’s brain as it is developing. I explain that I do not know whether this effect would be big or small, but that it’s not a chance I’m willing to take for their baby.
It is also important to educate patients that cannabis products are untested and unregulated and that they may be contaminated with heavy metals, pesticides, and other toxins that may be harmful to themselves and their babies. Patients also should know that the potency of cannabis has been dramatically increasing; research shows that the tetrahydrocannabinol – the psychoactive component – concentration has tripled over the past 2 decades.7
Research tells us that women who use illicit drugs and alcohol categorically engage in some form of harm reduction once they learn they are pregnant, and the same is true for cannabis. This is seen in dramatically different rates of first- and third-trimester use in the new analysis of NSDUH data; third-trimester use is approximately halved.
Some women will not be able to discontinue use, however, or they may try to quit and fail in their attempts. As we should with substance use more broadly, we must meet patients where they are, view cannabis use as a chronic medical problem, offer our assistance in helping them reduce harms of their use, and understand that quitting is a process.
Screening for mental health disorders and trauma is, of course, especially important in patients who use cannabis and other substances recreationally. In cases of medical marijuana usage, I recommend, as ACOG and other have done, that we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing cannabis versus shifting to alternative medications if options exist.
All patients should be welcomed, congratulated on their pregnancy and on coming for prenatal care, and engaged in the overall process of optimizing their health and the health of their baby. Like any other health issue during pregnancy, cannabis use needs to be screened for and treated in an evidence-based manner, but it does not define the trajectory or success of a woman’s pregnancy or her ability to be a successful parent.
Dr. Mark is associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):145-52.
2. Preventive Medicine 2017 May 18;104:46-9.
3. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):167-9.
4. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e196471.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):952-61.
6. J. Addict Med. 2019 May 10. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000543.
7. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
A flurry of research papers published this year has simultaneously documented a rise in the use of cannabis during pregnancy and offered more data about its potential harms. This confluence of findings is concerning and highlights the importance of screening our patients for cannabis use and engaging with them in a way in which we can maintain their trust and their commitment to prenatal care.
A retrospective cohort study involving 661,617 women in Ontario found a significant association between self-reported cannabis use in pregnancy and an increased risk of preterm birth (relative risk, 1.41), as well as a greater likelihood of small-for-gestational-age babies (RR, 1.53), placental abruption (RR, 1.72), and transfer to neonatal intensive care (RR, 1.40).1 The study, reported in JAMA in July 2019, carefully matched users with nonusers who had the same characteristics – for example, tobacco use or not.
This new information builds upon other meta-analyses that have demonstrated a decrease in birth weight and greater admittance to the neonatal ICU associated with cannabis use in pregnancy – and it supplements what some research suggests about long-term neurologic development and a potentially increased risk of attention and behavioral problems. Other outcomes that have been noted in long-term neurologic studies of children who were exposed to cannabis in utero include impaired visual acuity, verbal reasoning and comprehension, and short-term memory.2
Increases in use were recently documented in two studies. One, an analysis of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) published in JAMA in June 2019, showed that, between 2002-2003 and 2016-2017, the use of cannabis “in the past month” increased from 3.4% to 7.0% among pregnant women overall, and from 6% to 12% during the first trimester.3
The use of cannabis on a daily or near-daily basis, moreover, increased from 0.9% to 3% among pregnant women overall and from 2% to 5% during the first trimester. The data were collected during face-to-face interviews and were adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, and family income.
In the second study – a cross-sectional study of 367,403 pregnancies among women who filled out a questionnaire on cannabis use during standard prenatal care at Kaiser Permanente Northern California – the adjusted prevalence of use in the year before pregnancy increased from 7% in 2009 to 13% in 2017, and the adjusted prevalence during pregnancy increased from 2% to 3%.4
As in the NSDUH analysis, daily use increased most rapidly (compared with weekly or monthly) such that, by 2017, 25% of those who reported using cannabis in the year before pregnancy – and 21% of those who used cannabis during pregnancy – were daily users. It is notable that Kaiser’s population is diverse in all respects, and that the annual relative rates of increase in cannabis use before and during pregnancy (at each level of frequency) were consistent across racial/ethnic and household income groups.
It’s also worth noting that, in earlier research covering a similar time period (2009-2016), the investigators found significant increases in use via urine toxicology testing that occurs at the first prenatal visit at Kaiser. The increase found through questionnaires, therefore, reflects more than a greater willingness to self-report.
Choosing a screening tool
Universal prenatal substance use screening is recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but we don’t have any specific recommendations on what this means. Who should be screening, and what should that screening look like? Should we use a biologic screen, a standardized screening tool, or simply ask patients whether they use illicit substances?
Screening tools seem advantageous in that they are low cost, noninvasive, potentially comprehensive, and not subject to false-positive results as biologic screens can be – but which tool or tools are best? There are several validated screening tools that can be used outside of pregnancy to determine an individual’s use of illicit substances and whether or not that use is problematic, but previous studies have not used biologic markers to validate substance use screeners in pregnancy. Nor have studies compared screeners in pregnancy.
In our prenatal population in Baltimore, we have not been getting the answers we want using various nonvalidated screening tools. Approximately 30% of patients are positive for cannabis by urine screen, but only half tell us about their use.
Through research in our two prenatal care practices (one serving mostly privately insured and the other serving primarily Medicaid-eligible patients), we assessed both the accuracy and the acceptability of three substance use screening tools that are brief and that have been validated (for the general population) by the World Health Organization for screening of multiple substances: the 4P’s Plus (Parents, Partner, Past, and Pregnancy), the National Institute on Drug Abuse Quick Screen–ASSIST (Modified Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test), and the SURP-P (Substance Use Risk Profile–Pregnancy) scale.
In one study, published in May 2019 in Obstetrics & Gynecology, we recruited 500 pregnant women and administered these three tests to each of them.5 We then compared results with those of urine and hair drug testing, and checked the test-retest reliability of each test by readministering them (albeit by telephone) a week later. Although hair testing is not an indicator of current substance use, we used it to validate the screening tools on less-recent use.
The tests with the highest sensitivity and negative predictive values – the qualities we most want for screening – were the SURP-P and the 4P’s Plus (sensitivity of 92.4% and 90.2%, respectively). Overall they were highly sensitive screening tools across all trimesters, races, and age groups, making them more ideal screening tests than the NIDA Quick Screen–ASSIST.
Of the two tests, the 4P’s Plus screening tool was the one preferred by staff from both practices. In a companion qualitative study, we conducted focus-group discussions with 40 practice staff who were responsible for administering or overseeing patient screening.6 The staff, who were unaware of the sensitivity findings, were asked what they thought about the acceptability to patients of each of the three tools and their usability in practice.
Most of the participating staff preferred the 4P’s Plus screening tool for several reasons: It is easy to understand, is brief and to the point, and it has nonjudgmental language and tone. The screener first asks the patient about her parents’ and her partner’s use of alcohol and drugs, and then asks the patient about her own use of alcohol and tobacco. Affirmative responses to these questions lead to additional questions.
The premise is that one’s genetics, history, and current exposures – as well as one’s own use of tobacco and alcohol – are significantly associated with the use of illicit substances. If the patient reports no parental history or partner usage, and has never drank or smoked before, it’s extremely unlikely that she is using other drugs. The progression of questions does indeed seem less judgmental than immediately asking: “Do you use drugs?”
For us, the insight from this staff perception study combined with the findings on accuracy mean that the 4P’s Plus may be the most useful and acceptable screening tool for routine use in prenatal care.
Talking with our patients
The increase in the use of cannabis before and after pregnancy parallels the movement toward state legalization and decriminalization. Historically, clinicians often have relied on illegality as their main focus of counseling when giving recommendations for cessation and abstinence in pregnancy.2 This approach not only leads to punitive counseling, which can fracture the doctor-patient relationship, but increasingly it is no longer valid. In our changing legal climate, we need to provide medically based counseling and be very clear with our patients that legalization does not equate to safety.
It is important that we neither minimize nor overstate the risks. The evidence base for adverse birth outcomes of cannabis use in pregnancy is quite robust, but the associations can be subtle and are moderated by other behaviors and environmental factors that continue to challenge researchers.
As with alcohol, there likely are dose-or trimester-dependent differences in perinatal outcomes, and it’s quite possible that different cannabis products and routes of consumption have different effects. At this point, however, we don’t know the full story, nor do we know the extent to which the literature is biased toward positive correlations – the reporting of adverse effects – compared with negative findings. It is our job as medical care providers to be comfortable in that gray area and to still counsel patients on what we do know, providing the best-possible medical advice based on the information available to us.
In talking with patients, I explain that cannabis may cause a spectrum of problems and that there certainly are risks. I also tell them that we’re uncertain about the conditions and magnitude of that risk and that some babies who are exposed to cannabis in utero may have no perceivable consequences. Such honesty is important for maintaining trust, especially as some patients may see friends and relatives who also are cannabis users have normal pregnancy outcomes.
Much of my concern about cannabis in pregnancy centers on its effect on the developing brain and on long-term neurologic development. I share this with patients – I tell them that cannabis crosses the placenta and may well affect their baby’s brain as it is developing. I explain that I do not know whether this effect would be big or small, but that it’s not a chance I’m willing to take for their baby.
It is also important to educate patients that cannabis products are untested and unregulated and that they may be contaminated with heavy metals, pesticides, and other toxins that may be harmful to themselves and their babies. Patients also should know that the potency of cannabis has been dramatically increasing; research shows that the tetrahydrocannabinol – the psychoactive component – concentration has tripled over the past 2 decades.7
Research tells us that women who use illicit drugs and alcohol categorically engage in some form of harm reduction once they learn they are pregnant, and the same is true for cannabis. This is seen in dramatically different rates of first- and third-trimester use in the new analysis of NSDUH data; third-trimester use is approximately halved.
Some women will not be able to discontinue use, however, or they may try to quit and fail in their attempts. As we should with substance use more broadly, we must meet patients where they are, view cannabis use as a chronic medical problem, offer our assistance in helping them reduce harms of their use, and understand that quitting is a process.
Screening for mental health disorders and trauma is, of course, especially important in patients who use cannabis and other substances recreationally. In cases of medical marijuana usage, I recommend, as ACOG and other have done, that we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing cannabis versus shifting to alternative medications if options exist.
All patients should be welcomed, congratulated on their pregnancy and on coming for prenatal care, and engaged in the overall process of optimizing their health and the health of their baby. Like any other health issue during pregnancy, cannabis use needs to be screened for and treated in an evidence-based manner, but it does not define the trajectory or success of a woman’s pregnancy or her ability to be a successful parent.
Dr. Mark is associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):145-52.
2. Preventive Medicine 2017 May 18;104:46-9.
3. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):167-9.
4. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e196471.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):952-61.
6. J. Addict Med. 2019 May 10. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000543.
7. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
A flurry of research papers published this year has simultaneously documented a rise in the use of cannabis during pregnancy and offered more data about its potential harms. This confluence of findings is concerning and highlights the importance of screening our patients for cannabis use and engaging with them in a way in which we can maintain their trust and their commitment to prenatal care.
A retrospective cohort study involving 661,617 women in Ontario found a significant association between self-reported cannabis use in pregnancy and an increased risk of preterm birth (relative risk, 1.41), as well as a greater likelihood of small-for-gestational-age babies (RR, 1.53), placental abruption (RR, 1.72), and transfer to neonatal intensive care (RR, 1.40).1 The study, reported in JAMA in July 2019, carefully matched users with nonusers who had the same characteristics – for example, tobacco use or not.
This new information builds upon other meta-analyses that have demonstrated a decrease in birth weight and greater admittance to the neonatal ICU associated with cannabis use in pregnancy – and it supplements what some research suggests about long-term neurologic development and a potentially increased risk of attention and behavioral problems. Other outcomes that have been noted in long-term neurologic studies of children who were exposed to cannabis in utero include impaired visual acuity, verbal reasoning and comprehension, and short-term memory.2
Increases in use were recently documented in two studies. One, an analysis of data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) published in JAMA in June 2019, showed that, between 2002-2003 and 2016-2017, the use of cannabis “in the past month” increased from 3.4% to 7.0% among pregnant women overall, and from 6% to 12% during the first trimester.3
The use of cannabis on a daily or near-daily basis, moreover, increased from 0.9% to 3% among pregnant women overall and from 2% to 5% during the first trimester. The data were collected during face-to-face interviews and were adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, and family income.
In the second study – a cross-sectional study of 367,403 pregnancies among women who filled out a questionnaire on cannabis use during standard prenatal care at Kaiser Permanente Northern California – the adjusted prevalence of use in the year before pregnancy increased from 7% in 2009 to 13% in 2017, and the adjusted prevalence during pregnancy increased from 2% to 3%.4
As in the NSDUH analysis, daily use increased most rapidly (compared with weekly or monthly) such that, by 2017, 25% of those who reported using cannabis in the year before pregnancy – and 21% of those who used cannabis during pregnancy – were daily users. It is notable that Kaiser’s population is diverse in all respects, and that the annual relative rates of increase in cannabis use before and during pregnancy (at each level of frequency) were consistent across racial/ethnic and household income groups.
It’s also worth noting that, in earlier research covering a similar time period (2009-2016), the investigators found significant increases in use via urine toxicology testing that occurs at the first prenatal visit at Kaiser. The increase found through questionnaires, therefore, reflects more than a greater willingness to self-report.
Choosing a screening tool
Universal prenatal substance use screening is recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but we don’t have any specific recommendations on what this means. Who should be screening, and what should that screening look like? Should we use a biologic screen, a standardized screening tool, or simply ask patients whether they use illicit substances?
Screening tools seem advantageous in that they are low cost, noninvasive, potentially comprehensive, and not subject to false-positive results as biologic screens can be – but which tool or tools are best? There are several validated screening tools that can be used outside of pregnancy to determine an individual’s use of illicit substances and whether or not that use is problematic, but previous studies have not used biologic markers to validate substance use screeners in pregnancy. Nor have studies compared screeners in pregnancy.
In our prenatal population in Baltimore, we have not been getting the answers we want using various nonvalidated screening tools. Approximately 30% of patients are positive for cannabis by urine screen, but only half tell us about their use.
Through research in our two prenatal care practices (one serving mostly privately insured and the other serving primarily Medicaid-eligible patients), we assessed both the accuracy and the acceptability of three substance use screening tools that are brief and that have been validated (for the general population) by the World Health Organization for screening of multiple substances: the 4P’s Plus (Parents, Partner, Past, and Pregnancy), the National Institute on Drug Abuse Quick Screen–ASSIST (Modified Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test), and the SURP-P (Substance Use Risk Profile–Pregnancy) scale.
In one study, published in May 2019 in Obstetrics & Gynecology, we recruited 500 pregnant women and administered these three tests to each of them.5 We then compared results with those of urine and hair drug testing, and checked the test-retest reliability of each test by readministering them (albeit by telephone) a week later. Although hair testing is not an indicator of current substance use, we used it to validate the screening tools on less-recent use.
The tests with the highest sensitivity and negative predictive values – the qualities we most want for screening – were the SURP-P and the 4P’s Plus (sensitivity of 92.4% and 90.2%, respectively). Overall they were highly sensitive screening tools across all trimesters, races, and age groups, making them more ideal screening tests than the NIDA Quick Screen–ASSIST.
Of the two tests, the 4P’s Plus screening tool was the one preferred by staff from both practices. In a companion qualitative study, we conducted focus-group discussions with 40 practice staff who were responsible for administering or overseeing patient screening.6 The staff, who were unaware of the sensitivity findings, were asked what they thought about the acceptability to patients of each of the three tools and their usability in practice.
Most of the participating staff preferred the 4P’s Plus screening tool for several reasons: It is easy to understand, is brief and to the point, and it has nonjudgmental language and tone. The screener first asks the patient about her parents’ and her partner’s use of alcohol and drugs, and then asks the patient about her own use of alcohol and tobacco. Affirmative responses to these questions lead to additional questions.
The premise is that one’s genetics, history, and current exposures – as well as one’s own use of tobacco and alcohol – are significantly associated with the use of illicit substances. If the patient reports no parental history or partner usage, and has never drank or smoked before, it’s extremely unlikely that she is using other drugs. The progression of questions does indeed seem less judgmental than immediately asking: “Do you use drugs?”
For us, the insight from this staff perception study combined with the findings on accuracy mean that the 4P’s Plus may be the most useful and acceptable screening tool for routine use in prenatal care.
Talking with our patients
The increase in the use of cannabis before and after pregnancy parallels the movement toward state legalization and decriminalization. Historically, clinicians often have relied on illegality as their main focus of counseling when giving recommendations for cessation and abstinence in pregnancy.2 This approach not only leads to punitive counseling, which can fracture the doctor-patient relationship, but increasingly it is no longer valid. In our changing legal climate, we need to provide medically based counseling and be very clear with our patients that legalization does not equate to safety.
It is important that we neither minimize nor overstate the risks. The evidence base for adverse birth outcomes of cannabis use in pregnancy is quite robust, but the associations can be subtle and are moderated by other behaviors and environmental factors that continue to challenge researchers.
As with alcohol, there likely are dose-or trimester-dependent differences in perinatal outcomes, and it’s quite possible that different cannabis products and routes of consumption have different effects. At this point, however, we don’t know the full story, nor do we know the extent to which the literature is biased toward positive correlations – the reporting of adverse effects – compared with negative findings. It is our job as medical care providers to be comfortable in that gray area and to still counsel patients on what we do know, providing the best-possible medical advice based on the information available to us.
In talking with patients, I explain that cannabis may cause a spectrum of problems and that there certainly are risks. I also tell them that we’re uncertain about the conditions and magnitude of that risk and that some babies who are exposed to cannabis in utero may have no perceivable consequences. Such honesty is important for maintaining trust, especially as some patients may see friends and relatives who also are cannabis users have normal pregnancy outcomes.
Much of my concern about cannabis in pregnancy centers on its effect on the developing brain and on long-term neurologic development. I share this with patients – I tell them that cannabis crosses the placenta and may well affect their baby’s brain as it is developing. I explain that I do not know whether this effect would be big or small, but that it’s not a chance I’m willing to take for their baby.
It is also important to educate patients that cannabis products are untested and unregulated and that they may be contaminated with heavy metals, pesticides, and other toxins that may be harmful to themselves and their babies. Patients also should know that the potency of cannabis has been dramatically increasing; research shows that the tetrahydrocannabinol – the psychoactive component – concentration has tripled over the past 2 decades.7
Research tells us that women who use illicit drugs and alcohol categorically engage in some form of harm reduction once they learn they are pregnant, and the same is true for cannabis. This is seen in dramatically different rates of first- and third-trimester use in the new analysis of NSDUH data; third-trimester use is approximately halved.
Some women will not be able to discontinue use, however, or they may try to quit and fail in their attempts. As we should with substance use more broadly, we must meet patients where they are, view cannabis use as a chronic medical problem, offer our assistance in helping them reduce harms of their use, and understand that quitting is a process.
Screening for mental health disorders and trauma is, of course, especially important in patients who use cannabis and other substances recreationally. In cases of medical marijuana usage, I recommend, as ACOG and other have done, that we discuss the risks and benefits of continuing cannabis versus shifting to alternative medications if options exist.
All patients should be welcomed, congratulated on their pregnancy and on coming for prenatal care, and engaged in the overall process of optimizing their health and the health of their baby. Like any other health issue during pregnancy, cannabis use needs to be screened for and treated in an evidence-based manner, but it does not define the trajectory or success of a woman’s pregnancy or her ability to be a successful parent.
Dr. Mark is associate professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
References
1. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):145-52.
2. Preventive Medicine 2017 May 18;104:46-9.
3. JAMA. 2019 Jul 9;322(2):167-9.
4. JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e196471.
5. Obstet Gynecol. 2019 May;133(5):952-61.
6. J. Addict Med. 2019 May 10. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000543.
7. Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 1;79(7):613-9.
Experts address barriers to genetic screening
WASHINGTON – Early diagnosis and intervention for genetic diseases using the latest carrier screening can allow families to be prepared and informed prior to pregnancy, said Aishwarya Arjunan, MS, MPH, a clinical product specialist for carrier screening at Myriad Women’s Health, part of a diagnostic testing company based in Salt Lake City, Utah.
“Rare diseases are responsible for 35% of deaths in the first year of life,” she said in a panel discussion at the Rare Diseases and Orphan Products Breakthrough Summit sponsored by the National Organization for Rare Disorders.
Most patients with rare diseases go through a “diagnostic odyssey” lasting an average of 8 years before they receive an accurate diagnosis, she said. During this time, data suggest that they have likely been misdiagnosed three times and have seen more than 10 specialists, she added.
Barriers to genetic screening include limited access to genetics professionals, lack of patient and provider education about screening, issues of insurance coverage and reimbursement, coding challenges, and misperceptions about the perceived impact of screening, noted Jodie Vento, manager of the Center for Rare Disease Therapy at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh.
The genetic carrier screening options, often referred to as panethnic expanded carrier screening, represents a change from previous screening protocols based on ethnicity, said Ms. Arjunan. However, guidelines for screening based on ethnicity “misses a significant percentage of pregnancies affected by serious conditions and widens the health disparity gap,” she said.
By contrast, expanded carrier screening allows for standardization of care that gives couples and families information to make decisions and preparations.
Current genetic testing strategies include single gene testing, in which a single gene of interest is tested; multigene panel testing, in which a subset of clinically important genes are tested; whole-exome sequencing, in which the DNA responsible for coding proteins is tested; and whole-genome sequencing, in which the entire human genome is tested for genetic disorders.
Improving access to genetic testing involves a combination of provider education, changes in payer policies, action by advocacy groups, and adjustment of societal guidelines, said Ms. Arjunan. However, the advantages of expanded carrier screening are many and include guiding patients to expert care early and setting up plans for long-term care and follow-up, she noted. In addition, early identification through screening can help patients reduce or eliminate the diagnostic odyssey and connect with advocacy and community groups for support, she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Early diagnosis and intervention for genetic diseases using the latest carrier screening can allow families to be prepared and informed prior to pregnancy, said Aishwarya Arjunan, MS, MPH, a clinical product specialist for carrier screening at Myriad Women’s Health, part of a diagnostic testing company based in Salt Lake City, Utah.
“Rare diseases are responsible for 35% of deaths in the first year of life,” she said in a panel discussion at the Rare Diseases and Orphan Products Breakthrough Summit sponsored by the National Organization for Rare Disorders.
Most patients with rare diseases go through a “diagnostic odyssey” lasting an average of 8 years before they receive an accurate diagnosis, she said. During this time, data suggest that they have likely been misdiagnosed three times and have seen more than 10 specialists, she added.
Barriers to genetic screening include limited access to genetics professionals, lack of patient and provider education about screening, issues of insurance coverage and reimbursement, coding challenges, and misperceptions about the perceived impact of screening, noted Jodie Vento, manager of the Center for Rare Disease Therapy at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh.
The genetic carrier screening options, often referred to as panethnic expanded carrier screening, represents a change from previous screening protocols based on ethnicity, said Ms. Arjunan. However, guidelines for screening based on ethnicity “misses a significant percentage of pregnancies affected by serious conditions and widens the health disparity gap,” she said.
By contrast, expanded carrier screening allows for standardization of care that gives couples and families information to make decisions and preparations.
Current genetic testing strategies include single gene testing, in which a single gene of interest is tested; multigene panel testing, in which a subset of clinically important genes are tested; whole-exome sequencing, in which the DNA responsible for coding proteins is tested; and whole-genome sequencing, in which the entire human genome is tested for genetic disorders.
Improving access to genetic testing involves a combination of provider education, changes in payer policies, action by advocacy groups, and adjustment of societal guidelines, said Ms. Arjunan. However, the advantages of expanded carrier screening are many and include guiding patients to expert care early and setting up plans for long-term care and follow-up, she noted. In addition, early identification through screening can help patients reduce or eliminate the diagnostic odyssey and connect with advocacy and community groups for support, she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
WASHINGTON – Early diagnosis and intervention for genetic diseases using the latest carrier screening can allow families to be prepared and informed prior to pregnancy, said Aishwarya Arjunan, MS, MPH, a clinical product specialist for carrier screening at Myriad Women’s Health, part of a diagnostic testing company based in Salt Lake City, Utah.
“Rare diseases are responsible for 35% of deaths in the first year of life,” she said in a panel discussion at the Rare Diseases and Orphan Products Breakthrough Summit sponsored by the National Organization for Rare Disorders.
Most patients with rare diseases go through a “diagnostic odyssey” lasting an average of 8 years before they receive an accurate diagnosis, she said. During this time, data suggest that they have likely been misdiagnosed three times and have seen more than 10 specialists, she added.
Barriers to genetic screening include limited access to genetics professionals, lack of patient and provider education about screening, issues of insurance coverage and reimbursement, coding challenges, and misperceptions about the perceived impact of screening, noted Jodie Vento, manager of the Center for Rare Disease Therapy at the Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh.
The genetic carrier screening options, often referred to as panethnic expanded carrier screening, represents a change from previous screening protocols based on ethnicity, said Ms. Arjunan. However, guidelines for screening based on ethnicity “misses a significant percentage of pregnancies affected by serious conditions and widens the health disparity gap,” she said.
By contrast, expanded carrier screening allows for standardization of care that gives couples and families information to make decisions and preparations.
Current genetic testing strategies include single gene testing, in which a single gene of interest is tested; multigene panel testing, in which a subset of clinically important genes are tested; whole-exome sequencing, in which the DNA responsible for coding proteins is tested; and whole-genome sequencing, in which the entire human genome is tested for genetic disorders.
Improving access to genetic testing involves a combination of provider education, changes in payer policies, action by advocacy groups, and adjustment of societal guidelines, said Ms. Arjunan. However, the advantages of expanded carrier screening are many and include guiding patients to expert care early and setting up plans for long-term care and follow-up, she noted. In addition, early identification through screening can help patients reduce or eliminate the diagnostic odyssey and connect with advocacy and community groups for support, she concluded.
The presenters had no financial conflicts to disclose.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM NORD 2019
Click for Credit: Long-term antibiotics & stroke, CHD; Postvaccination seizures; more
Here are 5 articles from the November issue of Clinician Reviews (individual articles are valid for one year from date of publication—expiration dates below):
1. Poor response to statins hikes risk of cardiovascular events
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2MVHlDR
Expires April 17, 2020
2. Postvaccination febrile seizures are no more severe than other febrile seizures
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2VUJzaE
Expires April 19, 2020
3. Hydroxychloroquine adherence in SLE: worse than you thought
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2oT00Z9
Expires April 22, 2020
4. Long-term antibiotic use may heighten stroke, CHD risk
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2OUUVu5
Expires April 28, 2020
5. Knowledge gaps about long-term osteoporosis drug therapy benefits, risks remain large
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2Msgqkb
Expires May 1, 2020
Here are 5 articles from the November issue of Clinician Reviews (individual articles are valid for one year from date of publication—expiration dates below):
1. Poor response to statins hikes risk of cardiovascular events
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2MVHlDR
Expires April 17, 2020
2. Postvaccination febrile seizures are no more severe than other febrile seizures
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2VUJzaE
Expires April 19, 2020
3. Hydroxychloroquine adherence in SLE: worse than you thought
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2oT00Z9
Expires April 22, 2020
4. Long-term antibiotic use may heighten stroke, CHD risk
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2OUUVu5
Expires April 28, 2020
5. Knowledge gaps about long-term osteoporosis drug therapy benefits, risks remain large
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2Msgqkb
Expires May 1, 2020
Here are 5 articles from the November issue of Clinician Reviews (individual articles are valid for one year from date of publication—expiration dates below):
1. Poor response to statins hikes risk of cardiovascular events
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2MVHlDR
Expires April 17, 2020
2. Postvaccination febrile seizures are no more severe than other febrile seizures
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2VUJzaE
Expires April 19, 2020
3. Hydroxychloroquine adherence in SLE: worse than you thought
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2oT00Z9
Expires April 22, 2020
4. Long-term antibiotic use may heighten stroke, CHD risk
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2OUUVu5
Expires April 28, 2020
5. Knowledge gaps about long-term osteoporosis drug therapy benefits, risks remain large
To take the posttest, go to: https://bit.ly/2Msgqkb
Expires May 1, 2020
Disparity in endometrial cancer outcomes: What can we do?
While the incidence of most cancers is falling, endometrial cancer rates continue to rise, in large part because of increasing life expectancy and obesity rates. However, what is even more alarming is the observation that there is a clear disparity in outcomes between black and white women with this disease. But there are things that all health care providers, including nononcologists, can do to help to overcome this disparity.
Black women are nearly twice as likely as non-Hispanic white women to die from the endometrial cancer. The 5-year survival for stage III and IV cancer is 43% for non-Hispanic white women, yet only 25% for black women.1 For a long time, this survival disparity was assumed to be a function of the more aggressive cancer histologies, such as serous, which are more commonly seen in black women. These high-grade cancers are more likely to present in advanced stages and with poorer responses to treatments; however, the predisposition to aggressive cancers tells only part of the story of racial disparities in endometrial cancer and their presentation at later stages. Indeed, fueling the problem are the findings that black women report symptoms less, experience more delays in diagnosis or more frequent deviations from guideline-directed diagnostics, undergo more morbid surgical approaches, receive less surgical staging, are enrolled less in clinical trials, have lower socioeconomic status and lower rates of health insurance, and receive less differential administration of adjuvant therapies, as well as have a background of higher all-cause mortality and comorbidities. While this array of contributing factors may seem overwhelming, it also can be considered a guide for health care providers because most of these factors, unlike histologic cell type, are modifiable, and it is important that we all consider what role we can play in dismantling them.
Black women are less likely to receive guideline-recommended care upon presentation. Research by Kemi M. Doll, MD, from the University of Washington, Seattle, demonstrated that, among women with endometrial cancers, black women were less likely to have documented histories of postmenopausal bleeding within 2 years of the diagnosis, presumably because of factors related to underreporting and inadequate ascertainment by medical professionals of whether or not they had experienced postmenopausal bleeding.2 Additionally, when postmenopausal bleeding was reported by these women, they were less likely to receive the appropriate diagnostic work-up as described by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, and their bleeding was more likely to be ascribed to nonmalignant pathologies. Her work raises the important question about how black women view the health care profession and their willingness to engage early in good faith that their concerns will be met. These concerns are understandable given the documented different responsiveness of providers to black patients’ symptoms such as pain.3
both of which are considered the standard of care.1,4 Lower rates of minimally invasive surgery expose black women to increased morbidity and are deleterious to quality of life, return to work, and functionality. If surgical staging is omitted, which is more common for these women, clinicians are less able to appropriately prescribe adjuvant therapies which might prevent lethal recurrences from unrecognized advanced cancer or they may overtreat early-stage cancers with adjuvant therapy to make up for gaps in staging information.1,5 However, adjuvant therapy is not a benign intervention, and itself is associated with morbidity.
As mentioned earlier, black women are at a higher risk for developing more aggressive cancer subtypes, and this phenomenon may appear unmodifiable. However, important research is looking at the concept of epigenetics and how modifiable environmental factors may contribute to the development of more aggressive types of cancer through gene expression. Additionally, differences in the gene mutations and gene expression of cancers more frequently acquired by black women may negatively influence how these cancers respond to conventional therapies. In the GOG210 study, which evaluated the outcomes of women with comprehensively staged endometrial cancer, black women demonstrated worse survival from cancer, even though they were more likely to receive chemotherapy.5 One explanation for this finding is that these women’s cancers were less responsive to conventional chemotherapy agents.
This raises a critical issue of disparity in clinical trial inclusion. Black women are underrepresented in clinical trials in the United States. There is a dark history in medical research and minority populations, particularly African American populations, which continues to be remembered and felt. However, not all of this underrepresentation may be from unwillingness to participate: For black women, issues of lack of access to or being considered for clinical trials is also a factor. But without adequate representation in trials of novel agents, we will not know whether they are effective for all populations, and indeed it would appear that we should not assume they are equally effective based on the results to date.
So how can we all individually help to overcome these disparities in endometrial cancer outcomes? To begin with, it is important to acknowledge that black women commonly report negative experiences with reproductive health care. From early in their lives, we must sensitively engage all of our patients and ensure they all feel heard and valued. They should know that their symptoms, including pain or bleeding, are taken and treated seriously. If we can do better with this throughout a woman’s earlier reproductive health care experiences, perhaps later in her life, when she experiences postmenopausal bleeding, she will feel comfortable raising this issue with her health care provider who in turn must take this symptom seriously and expeditiously engage all of the appropriate diagnostic resources. Health care delivery is about more than simply offering the best treatment. We also are responsible for education and shared decision making to ensure that we can deliver the best treatment.
We also can support organizations such as ECANA (Endometrial Cancer Action Network for African Americans) which serves to inform black women in their communities about the threat that endometrial cancer plays and empowers them through education about its symptoms and the need to seek care.
Systematically we must ensure black women have access to the same standards in surgical and nonsurgical management of these cancers. This includes referral of all women with cancer, including minorities, to high-volume centers with oncology specialists and explaining to those who may be reluctant to travel that this is associated with improved outcomes in the short and long term. We also must actively consider our black patients for clinical trials, sensitively educate them about their benefits, and overcome barriers to access. One simple way to do this is to explain that the treatments that we have developed for endometrial cancer have mostly been tested on white women, which may explain in part why they do not work so well for nonwhite women.
The racial disparity in endometrial cancer outcomes cannot entirely be attributed to the passive phenomenon of patient and tumor genetics, particularly with consideration that race is a social construct rather than a biological phenomenon. We can all make a difference through advocacy, access, education, and heightened awareness to combat this inequity and overcome these disparate outcomes.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Oct;143(1):98-104.
2. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Dec;219(6):593.e1-14.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun 1;30(16):1980-8.
4. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;128(3):526-34.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Nov;219(5):459.e1-11.
While the incidence of most cancers is falling, endometrial cancer rates continue to rise, in large part because of increasing life expectancy and obesity rates. However, what is even more alarming is the observation that there is a clear disparity in outcomes between black and white women with this disease. But there are things that all health care providers, including nononcologists, can do to help to overcome this disparity.
Black women are nearly twice as likely as non-Hispanic white women to die from the endometrial cancer. The 5-year survival for stage III and IV cancer is 43% for non-Hispanic white women, yet only 25% for black women.1 For a long time, this survival disparity was assumed to be a function of the more aggressive cancer histologies, such as serous, which are more commonly seen in black women. These high-grade cancers are more likely to present in advanced stages and with poorer responses to treatments; however, the predisposition to aggressive cancers tells only part of the story of racial disparities in endometrial cancer and their presentation at later stages. Indeed, fueling the problem are the findings that black women report symptoms less, experience more delays in diagnosis or more frequent deviations from guideline-directed diagnostics, undergo more morbid surgical approaches, receive less surgical staging, are enrolled less in clinical trials, have lower socioeconomic status and lower rates of health insurance, and receive less differential administration of adjuvant therapies, as well as have a background of higher all-cause mortality and comorbidities. While this array of contributing factors may seem overwhelming, it also can be considered a guide for health care providers because most of these factors, unlike histologic cell type, are modifiable, and it is important that we all consider what role we can play in dismantling them.
Black women are less likely to receive guideline-recommended care upon presentation. Research by Kemi M. Doll, MD, from the University of Washington, Seattle, demonstrated that, among women with endometrial cancers, black women were less likely to have documented histories of postmenopausal bleeding within 2 years of the diagnosis, presumably because of factors related to underreporting and inadequate ascertainment by medical professionals of whether or not they had experienced postmenopausal bleeding.2 Additionally, when postmenopausal bleeding was reported by these women, they were less likely to receive the appropriate diagnostic work-up as described by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, and their bleeding was more likely to be ascribed to nonmalignant pathologies. Her work raises the important question about how black women view the health care profession and their willingness to engage early in good faith that their concerns will be met. These concerns are understandable given the documented different responsiveness of providers to black patients’ symptoms such as pain.3
both of which are considered the standard of care.1,4 Lower rates of minimally invasive surgery expose black women to increased morbidity and are deleterious to quality of life, return to work, and functionality. If surgical staging is omitted, which is more common for these women, clinicians are less able to appropriately prescribe adjuvant therapies which might prevent lethal recurrences from unrecognized advanced cancer or they may overtreat early-stage cancers with adjuvant therapy to make up for gaps in staging information.1,5 However, adjuvant therapy is not a benign intervention, and itself is associated with morbidity.
As mentioned earlier, black women are at a higher risk for developing more aggressive cancer subtypes, and this phenomenon may appear unmodifiable. However, important research is looking at the concept of epigenetics and how modifiable environmental factors may contribute to the development of more aggressive types of cancer through gene expression. Additionally, differences in the gene mutations and gene expression of cancers more frequently acquired by black women may negatively influence how these cancers respond to conventional therapies. In the GOG210 study, which evaluated the outcomes of women with comprehensively staged endometrial cancer, black women demonstrated worse survival from cancer, even though they were more likely to receive chemotherapy.5 One explanation for this finding is that these women’s cancers were less responsive to conventional chemotherapy agents.
This raises a critical issue of disparity in clinical trial inclusion. Black women are underrepresented in clinical trials in the United States. There is a dark history in medical research and minority populations, particularly African American populations, which continues to be remembered and felt. However, not all of this underrepresentation may be from unwillingness to participate: For black women, issues of lack of access to or being considered for clinical trials is also a factor. But without adequate representation in trials of novel agents, we will not know whether they are effective for all populations, and indeed it would appear that we should not assume they are equally effective based on the results to date.
So how can we all individually help to overcome these disparities in endometrial cancer outcomes? To begin with, it is important to acknowledge that black women commonly report negative experiences with reproductive health care. From early in their lives, we must sensitively engage all of our patients and ensure they all feel heard and valued. They should know that their symptoms, including pain or bleeding, are taken and treated seriously. If we can do better with this throughout a woman’s earlier reproductive health care experiences, perhaps later in her life, when she experiences postmenopausal bleeding, she will feel comfortable raising this issue with her health care provider who in turn must take this symptom seriously and expeditiously engage all of the appropriate diagnostic resources. Health care delivery is about more than simply offering the best treatment. We also are responsible for education and shared decision making to ensure that we can deliver the best treatment.
We also can support organizations such as ECANA (Endometrial Cancer Action Network for African Americans) which serves to inform black women in their communities about the threat that endometrial cancer plays and empowers them through education about its symptoms and the need to seek care.
Systematically we must ensure black women have access to the same standards in surgical and nonsurgical management of these cancers. This includes referral of all women with cancer, including minorities, to high-volume centers with oncology specialists and explaining to those who may be reluctant to travel that this is associated with improved outcomes in the short and long term. We also must actively consider our black patients for clinical trials, sensitively educate them about their benefits, and overcome barriers to access. One simple way to do this is to explain that the treatments that we have developed for endometrial cancer have mostly been tested on white women, which may explain in part why they do not work so well for nonwhite women.
The racial disparity in endometrial cancer outcomes cannot entirely be attributed to the passive phenomenon of patient and tumor genetics, particularly with consideration that race is a social construct rather than a biological phenomenon. We can all make a difference through advocacy, access, education, and heightened awareness to combat this inequity and overcome these disparate outcomes.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Oct;143(1):98-104.
2. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Dec;219(6):593.e1-14.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun 1;30(16):1980-8.
4. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;128(3):526-34.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Nov;219(5):459.e1-11.
While the incidence of most cancers is falling, endometrial cancer rates continue to rise, in large part because of increasing life expectancy and obesity rates. However, what is even more alarming is the observation that there is a clear disparity in outcomes between black and white women with this disease. But there are things that all health care providers, including nononcologists, can do to help to overcome this disparity.
Black women are nearly twice as likely as non-Hispanic white women to die from the endometrial cancer. The 5-year survival for stage III and IV cancer is 43% for non-Hispanic white women, yet only 25% for black women.1 For a long time, this survival disparity was assumed to be a function of the more aggressive cancer histologies, such as serous, which are more commonly seen in black women. These high-grade cancers are more likely to present in advanced stages and with poorer responses to treatments; however, the predisposition to aggressive cancers tells only part of the story of racial disparities in endometrial cancer and their presentation at later stages. Indeed, fueling the problem are the findings that black women report symptoms less, experience more delays in diagnosis or more frequent deviations from guideline-directed diagnostics, undergo more morbid surgical approaches, receive less surgical staging, are enrolled less in clinical trials, have lower socioeconomic status and lower rates of health insurance, and receive less differential administration of adjuvant therapies, as well as have a background of higher all-cause mortality and comorbidities. While this array of contributing factors may seem overwhelming, it also can be considered a guide for health care providers because most of these factors, unlike histologic cell type, are modifiable, and it is important that we all consider what role we can play in dismantling them.
Black women are less likely to receive guideline-recommended care upon presentation. Research by Kemi M. Doll, MD, from the University of Washington, Seattle, demonstrated that, among women with endometrial cancers, black women were less likely to have documented histories of postmenopausal bleeding within 2 years of the diagnosis, presumably because of factors related to underreporting and inadequate ascertainment by medical professionals of whether or not they had experienced postmenopausal bleeding.2 Additionally, when postmenopausal bleeding was reported by these women, they were less likely to receive the appropriate diagnostic work-up as described by American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists guidelines, and their bleeding was more likely to be ascribed to nonmalignant pathologies. Her work raises the important question about how black women view the health care profession and their willingness to engage early in good faith that their concerns will be met. These concerns are understandable given the documented different responsiveness of providers to black patients’ symptoms such as pain.3
both of which are considered the standard of care.1,4 Lower rates of minimally invasive surgery expose black women to increased morbidity and are deleterious to quality of life, return to work, and functionality. If surgical staging is omitted, which is more common for these women, clinicians are less able to appropriately prescribe adjuvant therapies which might prevent lethal recurrences from unrecognized advanced cancer or they may overtreat early-stage cancers with adjuvant therapy to make up for gaps in staging information.1,5 However, adjuvant therapy is not a benign intervention, and itself is associated with morbidity.
As mentioned earlier, black women are at a higher risk for developing more aggressive cancer subtypes, and this phenomenon may appear unmodifiable. However, important research is looking at the concept of epigenetics and how modifiable environmental factors may contribute to the development of more aggressive types of cancer through gene expression. Additionally, differences in the gene mutations and gene expression of cancers more frequently acquired by black women may negatively influence how these cancers respond to conventional therapies. In the GOG210 study, which evaluated the outcomes of women with comprehensively staged endometrial cancer, black women demonstrated worse survival from cancer, even though they were more likely to receive chemotherapy.5 One explanation for this finding is that these women’s cancers were less responsive to conventional chemotherapy agents.
This raises a critical issue of disparity in clinical trial inclusion. Black women are underrepresented in clinical trials in the United States. There is a dark history in medical research and minority populations, particularly African American populations, which continues to be remembered and felt. However, not all of this underrepresentation may be from unwillingness to participate: For black women, issues of lack of access to or being considered for clinical trials is also a factor. But without adequate representation in trials of novel agents, we will not know whether they are effective for all populations, and indeed it would appear that we should not assume they are equally effective based on the results to date.
So how can we all individually help to overcome these disparities in endometrial cancer outcomes? To begin with, it is important to acknowledge that black women commonly report negative experiences with reproductive health care. From early in their lives, we must sensitively engage all of our patients and ensure they all feel heard and valued. They should know that their symptoms, including pain or bleeding, are taken and treated seriously. If we can do better with this throughout a woman’s earlier reproductive health care experiences, perhaps later in her life, when she experiences postmenopausal bleeding, she will feel comfortable raising this issue with her health care provider who in turn must take this symptom seriously and expeditiously engage all of the appropriate diagnostic resources. Health care delivery is about more than simply offering the best treatment. We also are responsible for education and shared decision making to ensure that we can deliver the best treatment.
We also can support organizations such as ECANA (Endometrial Cancer Action Network for African Americans) which serves to inform black women in their communities about the threat that endometrial cancer plays and empowers them through education about its symptoms and the need to seek care.
Systematically we must ensure black women have access to the same standards in surgical and nonsurgical management of these cancers. This includes referral of all women with cancer, including minorities, to high-volume centers with oncology specialists and explaining to those who may be reluctant to travel that this is associated with improved outcomes in the short and long term. We also must actively consider our black patients for clinical trials, sensitively educate them about their benefits, and overcome barriers to access. One simple way to do this is to explain that the treatments that we have developed for endometrial cancer have mostly been tested on white women, which may explain in part why they do not work so well for nonwhite women.
The racial disparity in endometrial cancer outcomes cannot entirely be attributed to the passive phenomenon of patient and tumor genetics, particularly with consideration that race is a social construct rather than a biological phenomenon. We can all make a difference through advocacy, access, education, and heightened awareness to combat this inequity and overcome these disparate outcomes.
Dr. Rossi is assistant professor in the division of gynecologic oncology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at obnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Oct;143(1):98-104.
2. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Dec;219(6):593.e1-14.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2012 Jun 1;30(16):1980-8.
4. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Sep;128(3):526-34.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Nov;219(5):459.e1-11.
STI update: Testing, treatment, and emerging threats
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis are still increasing in incidence and probably will continue to do so in the near future. Moreover, drug-resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae are emerging, as are less-known organisms such as Mycoplasma genitalium.
Now the good news: new tests for STIs are available or are coming! Based on nucleic acid amplification, these tests can be performed at the point of care, so that patients can leave the clinic with an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment for themselves and their sexual partners. Also, the tests can be run on samples collected by the patients themselves, either swabs or urine collections, eliminating the need for invasive sampling and making doctor-shy patients more likely to come in to be treated.1 We hope that by using these sensitive and accurate tests we can begin to bend the upward curve of STIs and be better antimicrobial stewards.2
This article reviews current issues surrounding STI control, and provides detailed guidance on recognizing, testing for, and treating gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection.
STI RATES ARE HIGH AND RISING
STIs are among the most common acute infectious diseases worldwide, with an estimated 1 million new curable cases every day.3 Further, STIs have major impacts on sexual, reproductive, and psychological health.
In the United States, rates of reportable STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis) are rising.4 In addition, more-sensitive tests for trichomoniasis, which is not a reportable infection in any state, have revealed it to be more prevalent than previously thought.5
BARRIERS AND CHALLENGES TO DIAGNOSIS
The medical system does not fully meet the needs of some populations, including young people and men who have sex with men, regarding their sexual and reproductive health.
Ongoing barriers among young people include reluctance to use available health services, limited access to STI testing, worries about confidentiality, and the shame and stigma associated with STIs.6
Men who have sex with men have a higher incidence of STIs than other groups. Since STIs are associated with a higher risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, it is important to detect, diagnose, and manage STIs in this group—and in all high-risk groups. Rectal STIs are an independent risk factor for incident HIV infection.7 In addition, many men who have sex with men face challenges navigating the emotional, physical, and cognitive aspects of adolescence, a voyage further complicated by mental health issues, unprotected sexual encounters, and substance abuse in many, especially among minority youth.8 These same factors also impair their ability to access resources for preventing and treating HIV and other STIs.
STI diagnosis is often missed
Most people who have STIs feel no symptoms, which increases the importance of risk-based screening to detect these infections.9,10 In many other cases, STIs manifest with nonspecific genitourinary symptoms that are mistaken for urinary tract infection. Tomas et al11 found that of 264 women who presented to an emergency department with genitourinary symptoms or were being treated for urinary tract infection, 175 were given a diagnosis of a urinary tract infection. Of these, 100 (57%) were treated without performing a urine culture; 60 (23%) of the 264 women had 1 or more positive STI tests, 22 (37%) of whom did not receive treatment for an STI.
Poor follow-up of patients and partners
Patients with STIs need to be retested 3 months after treatment to make sure the treatment was effective. Another reason for follow-up is that these patients are at higher risk of another infection within a year.12
Although treating patients’ partners has been shown to reduce reinfection rates, fewer than one-third of STIs (including HIV infections) were recognized through partner notification between 2010 and 2012 in a Dutch study, in men who have sex with men and in women.13 Challenges included partners who could not be identified among men who have sex with men, failure of heterosexual men to notify their partners, and lower rates of partner notification for HIV.
In the United States, “expedited partner therapy” allows healthcare providers to provide a prescription or medications to partners of patients diagnosed with chlamydia or gonorrhea without examining the partner.14 While this approach is legal in most states, implementation can be challenging.15
STI EVALUATION
History and physical examination
A complete sexual history helps in estimating the patient’s risk of an STI and applying appropriate risk-based screening. Factors such as sexual practices, use of barrier protection, and history of STIs should be discussed.
Physical examination is also important. Although some patients may experience discomfort during a genital or pelvic examination, omitting this step may lead to missed diagnoses in women with STIs.16
Laboratory testing
Laboratory testing for STIs helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. Empiric treatment without testing could give a patient a false sense of health by missing an infection that is not currently causing symptoms but that could later worsen or have lasting complications. Failure to test patients also misses the opportunity for partner notification, linkage to services, and follow-up testing.
Many of the most common STIs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis, can be detected using vaginal, cervical, or urethral swabs or first-catch urine (from the initial urine stream). In studies that compared various sampling methods,17 self-collected urine samples for gonorrhea in men were nearly as good as clinician-collected swabs of the urethra. In women, self-collected vaginal swabs for gonorrhea and chlamydia were nearly as good as clinician-collected vaginal swabs. While urine specimens are acceptable for chlamydia testing in women, their sensitivity may be slightly lower than with vaginal and endocervical swab specimens.18,19
A major advantage of urine specimens for STI testing is that collection is noninvasive and is therefore more likely to be acceptable to patients. Urine testing can also be conducted in a variety of nonclinical settings such as health fairs, pharmacy-based screening programs, and express STI testing sites, thus increasing availability.
To prevent further transmission and morbidity and to aid in public health efforts, it is critical to recognize the cause of infectious cervicitis and urethritis and to screen for STIs according to guidelines.12 Table 1 summarizes current screening and laboratory testing recommendations.
GONORRHEA AND CHLAMYDIA
Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the 2 most frequently reported STIs in the United States, with more than 550,000 cases of gonorrhea and 1.7 million cases of chlamydia reported in 2017.4
Both infections present similarly: cervicitis or urethritis characterized by discharge (mucopurulent discharge with gonorrhea) and dysuria. Untreated, they can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammation, and infertility.
Extragenital infections can be asymptomatic or cause exudative pharyngitis or proctitis. Most people in whom chlamydia is detected from pharyngeal specimens are asymptomatic. When pharyngeal symptoms exist secondary to gonorrheal infection, they typically include sore throat and pharyngeal exudates. However, Komaroff et al,20 in a study of 192 men and women who presented with sore throat, found that only 2 (1%) tested positive for N gonorrhoeae.
Screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia
Best practices include screening for gonorrhea and chlamydia as follows21–23:
- Every year in sexually active women through age 25 (including during pregnancy) and in older women who have risk factors for infection12
- At least every year in men who have sex with men, at all sites of sexual contact (urethra, pharynx, rectum), along with testing for HIV and syphilis
- Every 3 to 6 months in men who have sex with men who have multiple or anonymous partners, who are sexually active and use illicit drugs, or who have partners who use illicit drugs
- Possibly every year in young men who live in high-prevalence areas or who are seen in certain clinical settings, such as STI and adolescent clinics.
Specimens. A vaginal swab is preferred for screening in women. Several studies have shown that self-collected swabs have clinical sensitivity and specificity comparable to that of provider-collected samples.17,24 First-catch urine or endocervical swabs have similar performance characteristics and are also acceptable. In men, urethral swabs or first-catch urine samples are appropriate for screening for urogenital infections.
Testing methods. Testing for both pathogens should be done simultaneously with a nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT). Commercially available NAATs are more sensitive than culture and antigen testing for detecting gonorrhea and chlamydia.25–27
Most assays are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for testing vaginal, urethral, cervical, and urine specimens. Until recently, no commercial assay was cleared for testing extragenital sites, but recommendations for screening extragenital sites prompted many clinical laboratories to validate throat and rectal swabs for use with NAATs, which are more sensitive than culture at these sites.25,28 The recent FDA approval of extragenital specimen types for 2 commercially available assays may increase the availability of testing for these sites.
Data on the utility of NAATs for detecting chlamydia and gonorrhea in children are limited, and many clinical laboratories have not validated molecular methods for testing in children. Current guidelines specific to this population should be followed regarding test methods and preferred specimen types.12,29,30
Although gonococcal infection is usually diagnosed with culture-independent molecular methods, antimicrobial resistance is emerging. Thus, failure of the combination of ceftriaxone and azithromycin should prompt culture-based follow-up testing to determine antimicrobial susceptibility.
Strategies for treatment and control
Historically, people treated for gonorrhea have been treated for chlamydia at the same time, as these diseases tend to go together. This can be with a single intramuscular dose of ceftriaxone for the gonorrhea plus a single oral dose of azithromycin for the chlamydia.12 For patients who have only gonorrhea, this double regimen may help prevent the development of resistant gonorrhea strains.
All the patient’s sexual partners in the previous 60 days should be tested and treated, and expedited partner therapy should be offered if possible. Patients should be advised to have no sexual contact until they complete the treatment, or 7 days after single-dose treatment. Testing should be repeated 3 months after treatment.
M GENITALIUM IS EMERGING
A member of the Mycoplasmataceae family, M genitalium was originally identified as a pathogen in the early 1980s but has only recently emerged as an important cause of STI. Studies indicate that it is responsible for 10% to 20% of cases of nongonococcal urethritis and 10% to 30% of cases of cervicitis.31–33 Additionally, 2% to 22% of cases of pelvic inflammatory disease have evidence of M genitalium.34,35
However, data on M genitalium prevalence are suspect because the organism is hard to identify—lacking a cell wall, it is undetectable by Gram stain.36 Although it has been isolated in respiratory and synovial fluids, it has so far been recognized to be clinically important only in the urogenital tract. It can persist for years in infected patients by exploiting specialized cell-surface structures to invade cells.36 Once inside a cell, it triggers secretion of mycoplasmal toxins and destructive metabolites such as hydrogen peroxide, evading the host immune system as it does so.37
Testing guidelines for M genitalium
Current guidelines do not recommend routine screening for M genitalium, and no commercial test was available until recently.12 Although evidence suggests that M genitalium is independently associated with preterm birth and miscarriages,38 routine screening of pregnant women is not recommended.12
Testing for M genitalium should be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent nongonococcal urethritis in patients who test negative for gonorrhea and chlamydia or for whom treatment has failed.12 Many isolates exhibit genotypic resistance to macrolide antibiotics, which are often the first-line therapy for nongonococcal urethritis.39
Further study is needed to evaluate the potential impact of routine screening for M genitalium on the reproductive and sexual health of at-risk populations.
Diagnostic tests for M genitalium
Awareness of M genitalium as a cause of nongonococcal urethritis has been hampered by a dearth of diagnostic tests.40 The organism’s fastidious requirements and extremely slow growth preclude culture as a practical method of diagnosis.41 Serologic assays are dogged by cross-reactivity and poor sensitivity.42,43 Thus, molecular assays for detecting M genitalium and associated resistance markers are preferred for diagnosis.12
Several molecular tests are approved, available, and in use in Europe for diagnosing M genitalium infection,40 and in January 2019 the FDA approved a molecular test that can detect M genitalium in urine specimens and vaginal, endocervical, urethral, and penile meatal swabs. Although vaginal swabs are preferred for this assay because they have higher sensitivity (92% for provider-collected and 99% for patient-collected swabs), urine specimens are acceptable, with a sensitivity of 78%.44
At least 1 company is seeking FDA clearance for another molecular diagnostic assay for detecting M genitalium and markers of macrolide resistance in urine and genital swab specimens. Such assays may facilitate appropriate treatment.
Clinicians should stay abreast of diagnostic testing options, which are likely to become more readily available soon.
A high rate of macrolide resistance
Because M genitalium lacks a cell wall, antibiotics such as beta-lactams that target cell wall synthesis are ineffective.
Regimens for treating M genitalium are outlined in Table 2.12 Azithromycin is more effective than doxycycline. However, as many as 50% of strains were macrolide-resistant in a cohort of US female patients.45 Given the high incidence of treatment failure with azithromycin 1 g, it is thought that this regimen might select for resistance. For cases in which symptoms persist, a 1- to 2-week course of moxifloxacin is recommended.12 However, this has not been validated by clinical trials, and failures of the 7-day regimen have been reported.46
Partners of patients who test positive for M genitalium should also be tested and undergo clinically applicable screening for nongonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease.12
TRICHOMONIASIS
Trichomoniasis, caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, is the most prevalent nonviral STI in the United States. It disproportionately affects black women, in whom the prevalence is 13%, compared with 1% in non-Hispanic white women.47 It is also present in 26% of women with symptoms who are seen in STI clinics and is highly prevalent in incarcerated populations. It is uncommon in men who have sex with men.48
In men, trichomoniasis manifests as urethritis, epididymitis, or prostatitis. While most infected women have no symptoms, they may experience vaginitis with discharge that is diffuse, frothy, pruritic, malodorous, or yellow-green. Vaginal and cervical erythema (“strawberry cervix”) can also occur.
Screening for trichomoniasis
Current guidelines of the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend testing for T vaginalis in women who have symptoms and routinely screening in women who are HIV-positive, regardless of symptoms. There is no evidence to support routine screening of pregnant women without symptoms, and pregnant women who do have symptoms should be evaluated according to the same guidelines as for nonpregnant women.12 Testing can be considered in patients who have no symptoms but who engage in high-risk behaviors and in areas of high prevalence.
A lack of studies using sensitive methods for T vaginalis detection has hampered a true estimation of disease burden and at-risk populations. Screening recommendations may evolve in upcoming clinical guidelines as the field advances.
As infection can recur, women should be retested 3 months after initial diagnosis.12
NAAT is the preferred test for trichomoniasis
Commercially available diagnostic tests for trichomoniasis include culture, antigen testing, and NAAT.49 While many clinicians do their own wet-mount microscopy for a rapid result, this method has low sensitivity.50 Similarly, antigen testing and culture perform poorly compared with NAATs, which are the gold standard for detection.51,52 A major advantage of NAATs for T vaginalis detection is that they combine high sensitivity and fast results, facilitating diagnosis and appropriate treatment of patients and their partners.
In spite of these benefits, adoption of molecular diagnostic testing for T vaginalis has lagged behind that for chlamydia and gonorrhea.53 FDA-cleared NAATs are available for testing vaginal, cervical, or urine specimens from women, but until recently, there were no approved assays for testing in men. The Cepheid Xpert TV assay, which is valid for male urine specimens to diagnose other sexually transmitted diseases, has demonstrated excellent diagnostic sensitivity for T vaginalis in men and women.54 Interestingly, a large proportion of male patients in this study had no symptoms, suggesting that screening of men in high-risk groups may be warranted.
7-day metronidazole treatment beats single-dose treatment
The first-line treatment for trichomoniasis has been a single dose of metronidazole 2 g by mouth, but in a recent randomized controlled trial,55 a course of 500 mg by mouth twice a day for 7 days was 45% more effective at 4 weeks than a single dose, and it should now be the preferred regimen.
In clinical trials,56 a single dose of tinidazole 2 g orally was equivalent or superior to metronidazole 2 g and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects, but it is more expensive.
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
- Harding-Esch EM, Nori AV, Hegazi A, et al. Impact of deploying multiple point-of-care tests with a ‘sample first’ approach on a sexual health clinical care pathway. A service evaluation. Sex Transm Infect 2017; 93(6):424–429. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2016-052988
- Unemo M, Bradshaw CS, Hocking JS, et al. Sexually transmitted infections: challenges ahead. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17(8):e235–e279. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30310-9
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015; 10(12):e0143304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143304
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance 2017. www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/toc.htm. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Ginocchio CC, Chapin K, Smith JS, et al. Prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis and coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United States as determined by the Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis nucleic acid amplification assay. J Clin Microbiol 2012; 50(8):2601–2608. doi:10.1128/JCM.00748-12
- Newton-Levinson A, Leichliter JS, Chandra-Mouli V. Sexually transmitted infection services for adolescents and youth in low- and middle-income countries: perceived and experienced barriers to accessing care. J Adolesc Health 2016; 59(1):7–16.
doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.03.014 - Barbee LA, Khosropour CM, Dombrowksi JC, Golden MR. New human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis independently associated with rectal gonorrhea and chlamydia in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(7):385–389. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000614
- Halkitis PN, Kapadia F, Bub KL, Barton S, Moreira AD, Stults CB. A longitudinal investigation of syndemic conditions among young gay, bisexual, and other MSM: the P18 cohort study. AIDS Behav 2015; 19(6):970–980. doi:10.1007/s10461-014-0892-y
- Farley TA, Cohen DA, Elkins W. Asymptomatic sexually transmitted diseases: the case for screening. Prev Med 2003; 36(4):502–509. pmid:12649059
- Patel P, Bush T, Mayer K, et al; SUN Study Investigators. Routine brief risk-reduction counseling with biannual STD testing reduces STD incidence among HIV-infected men who have sex with men in care. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):470–474. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31824b3110
- Tomas ME, Getman D, Donskey CJ, Hecker MT. Overdiagnosis of urinary tract infection and underdiagnosis of sexually transmitted infection in adult women presenting to an emergency department. J Clin Microbiol 2015; 53(8):2686–2692. doi:10.1128/JCM.00670-15
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR Recomm Rep 2015; 64(RR–03): 1–137. pmid:26042815
- van Aar F, van Weert Y, Spijker R, Gotz H, Op de Coul E; Partner Notification Group. Partner notification among men who have sex with men and heterosexuals with STI/HIV: different outcomes and challenges. Int J STD AIDS 2015; 26(8):565–573. doi:10.1177/0956462414547398
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDa): expedited partner therapy. www.cdc.gov/std/ept/. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Jamison CD, Chang T, Mmeje O. Expedited partner therapy: combating record high sexually transmitted infection rates. Am J Public Health 2018; 108(10):1325–1327. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2018.304570
- Singh RH, Zenilman JM, Brown KM, Madden T, Gaydos C, Ghanem KG. The role of physical examination in diagnosing common causes of vaginitis: a prospective study. Sex Transm Infect 2013; 89(3):185–190. doi:10.1136/sextrans-2012-050550
- Lunny C, Taylor D, Hoang L, et al. Self-collected versus clinician-collected sampling for chlamydia and gonorrhea screening: a systemic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015; 10(7):e0132776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132776
- Michel CE, Sonnex C, Carne CA, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis load at matched anatomic sites: implications for screening strategies. J Clin Microbiol 2007; 45(5):1395–1402. doi:10.1128/JCM.00100-07
- Schachter J, Chernesky MA, Willis DE, et al. Vaginal swabs are the specimens of choice when screening for Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results from a multicenter evaluation of the APTIMA assays for both infections. Sex Transm Dis 2005; 32(12):725–728. pmid:16314767
- Komaroff AL, Aronson MD, Pass TM, Ervin CT. Prevalence of pharyngeal gonorrhea in general medical patients with sore throats. Sex Transm Dis 1980; 7(3):116–119. pmid:6777884
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinic-based testing for rectal and pharyngeal Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis infections by community-based organizations—five cities, United States, 2007. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2009; 58(26):716–719. pmid:19590491
- Chesson HW, Bernstein KT, Gift TL, Marcus JL, Pipkin S, Kent CK. The cost-effectiveness of screening men who have sex with men for rectal chlamydial and gonococcal infection to prevent HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis 2013; 40(5):366–471. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318284e544
- Park J, Marcus JL, Pandori M, Snell A, Philip SS, Bernstein KT. Sentinel surveillance for pharyngeal chlamydia and gonorrhea among men who have sex with men—San Francisco, 2010. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(6):482–484. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3182495e2f
- Masek BJ, Arora N, Quinn N, et al. Performance of three nucleic acid amplification tests for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae by use of self-collected vaginal swabs obtained via an internet-based screening program. J Clin Microbiol 2009; 47(6):1663–1667. doi:10.1128/JCM.02387-08
- Bachmann LH, Johnson RE, Cheng H, et al. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis rectal infections. J Clin Microbiol 2010; 48(5):1827–1832. doi:10.1128/JCM.02398-09
- Mimiaga MJ, Mayer KH, Reisner SL, et al. Asymptomatic gonorrhea and chlamydial infections detected by nucleic acid amplification tests among Boston area men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(5):495–498. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31816471ae
- Schachter J, Moncada J, Liska S, Shayevich C, Klausner JD. Nucleic acid amplification tests in the diagnosis of chlamydial and gonococcal infections of the oropharynx and rectum in men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(7):637–642. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31817bdd7e
- Cornelisse VJ, Chow EP, Huffam S, et al. Increased detection of pharyngeal and rectal gonorrhea in men who have sex with men after transition from culture to nucleic acid amplification testing. Sex Transm Dis 2017; 44(2):114–117. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000553
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the laboratory-based detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae—2014. MMWR Recomm Rep 2014; 63(RR–02):1–19. pmid:24622331
- Hammerschlag MR, Gaydos CA. Guidelines for the use of molecular biological methods to detect sexually transmitted pathogens in cases of suspected sexual abuse in children. Methods Mol Biol 2012; 903:307–317. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-937-2_21
- Huppert JS, Mortensen JE, Reed JL, Kahn JA, Rich KD, Hobbs MM. Mycoplasma genitalium detected by transcription-mediated amplification is associated with Chlamydia trachomatis in adolescent women. Sex Transm Dis 2008; 35(3):250–254. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e31815abac6
- Pond MJ, Nori AV, Witney AA, Lopeman RC, Butcher PD, Sadiq ST. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Mycoplasma genitalium in nongonococcal urethritis: the need for routine testing and the inadequacy of current treatment options. Clin Infect Dis 2014; 58(5):631–637. doi:10.1093/cid/cit752
- Seña AC, Lee JY, Schwebke J, et al. A silent epidemic: the prevalence, incidence and persistence of Mycoplasma genitalium among young, asymptomatic high-risk women in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2018; 67(1):73–79. doi:10.1093/cid/ciy025
- Bjartling C, Osser S, Persson K. The association between Mycoplasma genitalium and pelvic inflammatory disease after termination of pregnancy. BJOG 2010; 117(3):361–364. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2009.02455.x
- Cohen CR, Manhart LE, Bukusi EA, et al. Association between Mycoplasma genitalium and acute endometritis. Lancet 2002; 359(9308):765–766. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07848-0
- Taylor-Robinson D, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium: from chrysalis to multicolored butterfly. Clin Microbiol Rev 2011; 24(3):498–514. doi:10.1128/CMR.00006-11
- Ross JD, Jensen JS. Mycoplasma genitalium as a sexually transmitted infection: implications for screening, testing, and treatment. Sex Transm Infect 2006; 82(4):269–271. doi:10.1136/sti.2005.017368
- Donders GG, Ruban K, Bellen G, Petricevic L. Mycoplasma/ureaplasma infection in pregnancy: to screen or not to screen. J Perinat Med 2017; 45(5):505–515. doi:10.1515/jpm-2016-0111
- Allan-Blitz LT, Mokany E, Miller S, Wee R, Shannon C, Klausner JD. Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and azithromycin-resistant infections among remnant clinical specimens, Los Angeles. Sex Transm Dis 2018; 45(9):632–635. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000829
- Munson E. Molecular diagnostics update for the emerging (if not already widespread) sexually transmitted infection agent Mycoplasma genitalium: just about ready for prime time. J Clin Microbio. 2017; 55(10):2894–2902. doi:10.1128/JCM.00818-17
- Waites KB, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. In: Jorgensen JH, Pfaller MA, Carroll KC, American Society for Microbiology, eds. Manual of Clinical Microbiology. 11th ed. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2015:1088–1105.
- Cimolai N, Bryan LE, To M, Woods DE. Immunological cross-reactivity of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae membrane-associated protein antigen with Mycoplasma genitalium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Clin Microbiol 1987; 25(11):2136–2139. pmid:2447119
- Ma L, Mancuso M, Williams JA, et al. Extensive variation and rapid shift of the MG192 sequence in Mycoplasma genitalium strains from patients with chronic infection. Infect Immun 2014; 82(3):1326–1334. doi:10.1128/IAI.01526-13
- Hologic. Aptima Mycoplasma genitalium assay.www.hologic.com/sites/default/files/package-insert/AW-14170-001_005_01.pdf. Accessed October 7, 2019.
- Getman D, Jiang A, O’Donnell M, Cohen S. Mycoplasma genitalium prevalence, coinfection, and macrolide antibiotic resistance frequency in a multicenter clinical study cohort in the United States. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(9):2278–2283. doi:10.1128/JCM.01053-16
- Li Y, Le WJ, Li S, Cao YP, Su XH. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of moxifloxacin in treating Mycoplasma genitalium infection. Int J STD AIDS 2017; 28(11):1106–1114. doi:10.1177/0956462416688562
- Sutton M, Sternberg M, Koumans EH, McQuillan G, Berman S, Markowitz L. The prevalence of Trichomonas vaginalis infection among reproductive-age women in the United States, 2001–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45(10):1319–1326. doi:10.1086/522532
- Kelley CF, Rosenberg ES, O’Hara BM, Sanchez T, del Rio C, Sullivan PS. Prevalence of urethral Trichomonas vaginalis in black and white men who have sex with men. Sex Transm Dis 2012; 39(9):739. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0b013e318264248b
- Van Der Pol B. Clinical and laboratory testing for T vaginalis infection. J Clin Microbiol 2016; 54(1):7–12. doi:10.1128/JCM.02025-15
- Nye MB, Schwebke JR, Body BA. Comparison of APTIMA Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification to wet mount microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of trichomoniasis in men and women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2009; 200(2):188.e1–e7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2008.10.005
- Andrea SB, Chapin KC. Comparison of Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis transcription-mediated amplification assay and BD affirm VPIII for detection of T. vaginalis in symptomatic women: performance parameters and epidemiological implications. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(3):866–869. doi:10.1128/JCM.02367-10
- Schwebke JR, Hobbs MM, Taylor SN, et al. Molecular testing for Trichomonas vaginalis in women: results from a prospective U.S. clinical trial. J Clin Microbiol 2011; 49(12):4106–4111. doi:10.1128/JCM.01291-11
- College of American Pathologists. CAP surveys, Trichomonas vaginalis molecular, set TVAG-A. https://documents.cap.org/documents/2018-surveys-anatomic-pathology-ed-programs-catalog.pdf. Accessed October 31, 2019.
- Schwebke JR, Gaydos CA, Davis T, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert TV assay for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis with prospectively collected specimens from men and women. J Clin Microbiol 2018; 56(2). doi:10.1128/JCM.01091-17
- Kissinger P, Muzny CA, Mena LA, et al. Single-dose versus 7-day-dose metronidazole for the treatment of trichomoniasis in women: an open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2018; 18(11):1251–1259. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30423-7
- Forna F, Gulmezoglu AM. Interventions for treating trichomoniasis in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003; (2):CD000218. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000218
KEY POINTS
- Screen for gonorrhea and chlamydia annually—and more frequently for those at highest risk—in sexually active women age 25 and younger and in men who have sex with men, who should also be screened at the same time for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and syphilis.
- Test for Trichomonas vaginalis in women who have symptoms suggesting it, and routinely screen for this pathogen in women who are HIV-positive.
- Nucleic acid amplification is the preferred test for gonorrhea, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, and M genitalium infection; the use of urine specimens is acceptable.
- Consider M genitalium if therapy for gonorrhea and chlamydia fails or tests for those diseases are negative.
- Single-dose antibiotic therapy is preferred for chlamydia and uncomplicated gonorrhea. It is also available for trichomoniasis, although metronidazole 500 mg twice a day for 7 days has a higher cure rate.
SEEDS for success: Lifestyle management in migraine
Migraine is the second leading cause of years of life lived with a disability globally.1 It affects people of all ages, but particularly during the years associated with the highest productivity in terms of work and family life.
Migraine is a genetic neurologic disease that can be influenced or triggered by environmental factors. However, triggers do not cause migraine. For example, stress does not cause migraine, but it can exacerbate it.
Primary care physicians can help patients reduce the likelihood of a migraine attack, the severity of symptoms, or both by offering lifestyle counseling centered around the mnemonic SEEDS: sleep, exercise, eat, diary, and stress. In this article, each factor is discussed individually for its current support in the literature along with best-practice recommendations.
S IS FOR SLEEP
Before optimizing sleep hygiene, screen for sleep apnea, especially in those who have chronic daily headache upon awakening. An excellent tool is the STOP-Bang screening questionnaire5 (www.stopbang.ca/osa/screening.php). Patients respond “yes” or “no” to the following questions:
- Snoring: Do you snore loudly (louder than talking or loud enough to be heard through closed doors)?
- Tired: Do you often feel tired, fatigued, or sleepy during the daytime?
- Observed: Has anyone observed you stop breathing during your sleep?
- Pressure: Do you have or are you being treated for high blood pressure?
- Body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2?
- Age over 50?
- Neck circumference larger than 40 cm (females) or 42 cm (males)?
- Gender—male?
Each “yes” answer is scored as 1 point. A score less than 3 indicates low risk of obstructive sleep apnea; 3 to 4 indicates moderate risk; and 5 or more indicates high risk. Optimization of sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure therapy can improve sleep apnea headache.6 The improved sleep from reduced arousals may also mitigate migraine symptoms.
Behavioral modification for sleep hygiene can convert chronic migraine to episodic migraine.7 One such program is stimulus control therapy, which focuses on using cues to initiate sleep (Table 1). Patients are encouraged to keep the bedroom quiet, dark, and cool, and to go to sleep at the same time every night. Importantly, the bed should be associated only with sleep. If patients are unable to fall asleep within 20 to 30 minutes, they should leave the room so they do not associate the bed with frustration and anxiety. Use of phones, tablets, and television in the bedroom is discouraged as these devices may make it more difficult to fall asleep.8
The next option is sleep restriction, which is useful for comorbid insomnia. Patients keep a sleep diary to better understand their sleep-wake cycle. The goal is 90% sleep efficiency, meaning that 90% of the time in bed (TIB) is spent asleep. For example, if the patient is in bed 8 hours but asleep only 4 hours, sleep efficiency is 50%. The goal is to reduce TIB to match the time asleep and to agree on a prescribed daily wake-up time. When the patient is consistently sleeping 90% of the TIB, add 30-minute increments until he or she is appropriately sleeping 7 to 8 hours at night.9 Naps are not recommended.
Let patients know that their migraine may worsen until a new routine sleep pattern emerges. This method is not recommended for patients with untreated sleep apnea.
E IS FOR EXERCISE
Exercise is broadly recommended for a healthy lifestyle; some evidence suggests that it can also be useful in the management of migraine.10 Low levels of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle are associated with migraine.11 It is unclear if patients with migraine are less likely to exercise because they want to avoid triggering a migraine or if a sedentary lifestyle increases their risk.
Exercise has been studied for its prophylactic benefits in migraine, and one hypothesis relates to beta-endorphins. Levels of beta-endorphins are reduced in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine.12 Exercise programs may increase levels while reducing headache frequency and duration.13 One study showed that pain thresholds do not change with exercise programs, suggesting that it is avoidance behavior that is positively altered rather than the underlying pain pathways.14
A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 5 randomized controlled trials and 1 nonrandomized controlled clinical trial showed that exercise reduced monthly migraine days by only 0.6 (± 0.3) days, but the data also suggested that as the exercise intensity increased, so did the positive effects.10
Some data suggest that exercise may also reduce migraine duration and severity as well as the need for abortive medication.10 Two studies in this systematic review15,16 showed that exercise benefits were equivalent to those of migraine preventives such as amitriptyline and topiramate; the combination of amitriptyline and exercise was more beneficial than exercise alone. Multiple types of exercise were beneficial, including walking, jogging, cross-training, and cycling when done for least 6 weeks and for 30 to 50 minutes 3 to 5 times a week.
These findings are in line with the current recommendations for general health from the American College of Sports Medicine, ie, moderate to vigorous cardiorespiratory exercise for 30 to 60 minutes 3 to 5 times a week (or 150 minutes per week). The daily exercise can be continuous or done in intervals of less than 20 minutes. For those with a sedentary lifestyle, as is seen in a significant proportion of the migraine population, light to moderate exercise for less than 20 minutes is still beneficial.17
Based on this evidence, the best current recommendation for patients with migraine is to engage in graded moderate cardiorespiratory exercise, although any exercise is better than none. If a patient is sedentary or has poor exercise tolerance, or both, exercising once a week for shorter time periods may be a manageable place to start.
Some patients may identify exercise as a trigger or exacerbating factor in migraine. These patients may need appropriate prophylactic and abortive therapies before starting an exercise regimen.
THE SECOND E IS FOR EAT (FOOD AND DRINK)
Many patients believe that some foods trigger migraine attacks, but further study is needed. The most consistent food triggers appear to be red wine and caffeine (withdrawal).18,19 Interestingly, patients with migraine report low levels of alcohol consumption,20 but it is unclear if that is because alcohol has a protective effect or if patients avoid it.
Some patients may crave certain foods in the prodromal phase of an attack, eat the food, experience the attack, and falsely conclude that the food caused the attack.21 Premonitory symptoms include fatigue, cognitive changes, homeostatic changes, sensory hyperresponsiveness, and food cravings.21 It is difficult to distinguish between premonitory phase food cravings and true triggers because premonitory symptoms can precede headache by 48 to 72 hours, and the timing for a trigger to be considered causal is not known.22
Chocolate is often thought to be a migraine trigger, but the evidence argues against this and even suggests that sweet cravings are a part of the premonitory phase.23 Monosodium glutamate is often identified as a trigger as well, but the literature is inconsistent and does not support a causal relationship.24 Identifying true food triggers in migraine is difficult, and patients with migraine may have poor quality diets, with some foods acting as true triggers for certain patients.25 These possibilities have led to the development of many “migraine diets,” including elimination diets.
Elimination diets
Elimination diets involve avoiding specific food items over a period of time and then adding them back in one at a time to gauge whether they cause a reaction in the body. A number of these diets have been studied for their effects on headache and migraine:
Gluten-free diets restrict foods that contain wheat, rye, and barley. A systematic review of gluten-free diets in patients with celiac disease found that headache or migraine frequency decreased by 51.6% to 100% based on multiple cohort studies (N = 42,388).26 There are no studies on the use of a gluten-free diet for migraine in patients without celiac disease.
Immunoglobulin G-elimination diets restrict foods that serve as antigens for IgG. However, data supporting these diets are inconsistent. Two small randomized controlled trials found that the diets improved migraine symptoms, but a larger study found no improvement in the number of migraine days at 12 weeks, although there was an initially significant effect at 4 weeks.27–29
Antihistamine diets restrict foods that have high levels of histamines, including fermented dairy, vegetables, soy products, wine, beer, alcohol, and those that cause histamine release regardless of IgE testing results. A prospective single-arm study of antihistamine diets in patients with chronic headache reported symptom improvement, which could be applied to certain comorbidities such as mast cell activation syndrome.30 Another prospective nonrandomized controlled study eliminated foods based on positive IgE skin-prick testing for allergy in patients with recurrent migraine and found that it reduced headache frequency.31
Tyramine-free diets are often recommended due to the presumption that tyramine-containing foods (eg, aged cheese, cured or smoked meats and fish, and beer) are triggers. However, multiple studies have reviewed this theory with inconsistent results,32 and the only study of a tyramine-free diet was negative.33 In addition, commonly purported high-tyramine foods have lower tyramine levels than previously thought.34
Low-fat diets in migraine are supported by 2 small randomized controlled trials and a prospective study showing a decrease in symptom severity; the results for frequency are inconsistent.35–37
Low-glycemic index diets are supported in migraine by 1 randomized controlled trial that showed improvement in migraine frequency in a diet group and in a control group of patients who took a standard migraine-preventive medication to manage their symptoms.38
Other migraine diets
Diets high in certain foods or ingredient ratios, as opposed to elimination diets, have also been studied in patients with migraine. One promising diet containing high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and low levels of omega-6 fatty acids was shown in a systematic review to reduce the duration of migraine but not the frequency or severity.39 A more recent randomized controlled trial of this diet in chronic migraine also showed that it decreased migraine frequency.40
The ketogenic diet (high fat, low carbohydrate) had promising results in a randomized controlled trial in overweight women with migraine and in a prospective study.41,42 However, a prospective study of the Atkins diet in teenagers with chronic daily headaches showed no benefit.43 The ketogenic diet is difficult to follow and may work in part due to weight loss alone, although ketogenesis itself may also play a role.41,44
Sodium levels have been shown to be higher in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine than in controls, particularly during an attack.45 For a prehypertensive population or an elderly population, a low-sodium diet may be beneficial based on 2 prospective trials.46,47 However, a younger female population without hypertension and low-to-normal body mass index had a reduced probability of migraine while consuming a high-sodium diet.48
Counseling about sodium intake should be tailored to specific patient populations. For example, a diet low in sodium may be appropriate for patients with vascular risk factors such as hypertension, whereas a high-sodium diet may be appropriate in patients with comorbidities like postural tachycardia syndrome or in those with a propensity for low blood pressure or low body mass index.
Encourage routine meals and hydration
The standard advice for patients with migraine is to consume regular meals. Headaches have been associated with fasting, and those with migraine are predisposed to attacks in the setting of fasting.49,50 Migraine is more common when meals are skipped, particularly breakfast.51
It is unclear how fasting lowers the migraine threshold. Nutritional studies show that skipping meals, particularly breakfast, increases low-grade inflammation and impairs glucose metabolism by affecting insulin and fat oxidation metabolism.52 However, hypoglycemia itself is not a consistent cause of headache or migraine attacks.53 As described above, a randomized controlled trial of a low-glycemic index diet actually decreased migraine frequency and severity.38 Skipping meals also reduces energy and is associated with reduced physical activity, perhaps leading to multiple compounding triggers that further lower the migraine threshold.54,55
When counseling patients about the need to eat breakfast, consider what they normally consume (eg, is breakfast just a cup of coffee?). Replacing simple carbohydrates with protein, fats, and fiber may be beneficial for general health, but the effects on migraine are not known, nor is the optimal composition of breakfast foods.55
The optimal timing of breakfast relative to awakening is also unclear, but in general, it should be eaten within 30 to 60 minutes of rising. Also consider patients’ work hours—delayed-phase or shift workers have altered sleep cycles.
Recommendations vary in regard to hydration. Headache is associated with fluid restriction and dehydration,56,57 but only a few studies suggest that rehydration and increased hydration status can improve migraine.58 In fact, a single post hoc analysis of a metoclopramide study showed that intravenous fluid alone for patients with migraine in the emergency room did not improve pain outcomes.59
The amount of water patients should drink daily in the setting of migraine is also unknown, but a study showed benefit with 4 L, which equates to a daily intake of 16 eight-ounce glasses.60 One review on general health that could be extrapolated given the low risk of the intervention indicated that 1.8 L daily (7 to 8 eight-ounce glasses) promoted a euhydration status in most people, although many factors contribute to hydration status.61
Caffeine intake is also a major consideration. Caffeine is a nonspecific adenosine receptor antagonist that modulates adenosine receptors like the pronociceptive 2A receptor, leading to changes integral to the neuropathophysiology of migraine.62 Caffeine has analgesic properties at doses greater than 65 to 200 mg and augments the effects of analgesics such as acetaminophen and aspirin. Chronic caffeine use can lead to withdrawal symptoms when intake is stopped abruptly; this is thought to be due to upregulation of adenosine receptors, but the effect varies based on genetic predisposition.19
The risk of chronic daily headache may relate to high use of caffeine preceding the onset of chronification, and caffeine abstinence may improve response to acute migraine treatment.19,63 There is a dose-dependent risk of headache.64,65 Current recommendations suggest limiting caffeine consumption to less than 200 mg per day or stopping caffeine consumption altogether based on the quantity required for caffeine-withdrawal headache.66 Varying the caffeine dose from day to day may also trigger headache due to the high sensitivity to caffeine withdrawal.
While many diets have shown potential benefit in patients with migraine, more studies are needed before any one “migraine diet” can be recommended. Caution should be taken, as there is risk of adverse effects from nutrient deficiencies or excess levels, especially if the patient is not under the care of a healthcare professional who is familiar with the diet.
Whether it is beneficial to avoid specific food triggers at this time is unclear and still controversial even within the migraine community because some of these foods may be misattributed as triggers instead of premonitory cravings driven by the hypothalamus. It is important to counsel patients with migraine to eat a healthy diet with consistent meals, to maintain adequate hydration, and to keep their caffeine intake low or at least consistent, although these teachings are predominantly based on limited studies with extrapolation from nutrition research.
D IS FOR DIARY
A headache diary is a recommended part of headache management and may enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and assist in treatment modifications. Paper and electronic diaries have been used. Electronic diaries may be more accurate for real-time use, but patients may be more likely to complete a paper one.67 Patients prefer electronic diaries over long paper forms,68 but a practical issue to consider is easy electronic access.
Patients can start keeping a headache diary before the initial consultation to assist with diagnosis, or early in their management. A first-appointment diary mailed with instructions is a feasible option.69 These types of diaries ask detailed questions to help diagnose all major primary headache types including menstrual migraine and to identify concomitant medication-overuse headache. Physicians and patients generally report improved communication with use of a diary.70
Some providers distinguish between a headache diary and a calendar. In standard practice, a headache diary is the general term referring to both, but the literature differentiates between the two. Both should at least include headache frequency, with possible inclusion of other factors such as headache duration, headache intensity, analgesic use, headache impact on function, and absenteeism. Potential triggers including menses can also be tracked. The calendar version can fit on a single page and can be used for simple tracking of headache frequency and analgesia use.
One of the simplest calendars to use is the “stoplight” calendar. Red days are when a patient is completely debilitated in bed. On a yellow day, function at work, school, or daily activities is significantly reduced by migraine, but the patient is not bedbound. A green day is when headache is present but function is not affected. No color is placed if the patient is 100% headache-free.
Acute treatment use can be written in or, to improve compliance, a checkmark can be placed on days of treatment. Patients who are tracking menses circle the days of menstruation. The calendar-diary should be brought to every appointment to track treatment response and medication use.
THE SECOND S IS FOR STRESS
Behavioral management such as cognitive behavioral therapy in migraine has been shown to decrease catastrophizing, migraine disability, and headache severity and frequency.74 Both depression and anxiety can improve along with migraine.75 Cognitive behavioral therapy can be provided in individualized sessions or group sessions, either in person or online.74,76,77 The effects become more prominent about 5 weeks into treatment.78
Biofeedback, which uses behavioral techniques paired with physiologic autonomic measures, has been extensively studied, and shows benefit in migraine, including in meta-analysis.79 The types of biofeedback measurements used include electromyography, electroencephalography, temperature, sweat sensors, heart rate, blood volume pulse feedback, and respiration bands. While biofeedback is generally done under the guidance of a therapist, it can still be useful with minimal therapist contact and supplemental audio.80
Mindfulness, or the awareness of thoughts, feelings, and sensations in the present moment without judgment, is a behavioral technique that can be done alone or paired with another technique. It is often taught through a mindfulness-based stress-reduction program, which relies on a standardized approach. A meta-analysis showed that mindfulness improves pain intensity, headache frequency, disability, self-efficacy, and quality of life.81 It may work by encouraging pain acceptance.82
Relaxation techniques are also employed in migraine management, either alone or in conjunction with techniques mentioned above, such as mindfulness. They include progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing. Relaxation has been shown to be effective when done by professional trainers as well as lay trainers in both individual and group settings.83,84
In patients with intractable headache, more-intensive inpatient and outpatient programs have been tried. Inpatient admissions with multidisciplinary programs that include a focus on behavioral techniques often paired with lifestyle education and sometimes pharmacologic management can be beneficial.85,86 These programs have also been successfully conducted as multiple outpatient sessions.86–88
Stress management is an important aspect of migraine management. These treatments often involve homework and require active participation.
LIFESTYLE FOR ALL
All patients with migraine should initiate lifestyle modifications (see Advice to patients with migraine: SEEDS for success). Modifications with the highest level of evidence, specifically behavioral techniques, have had the most reproducible results. A headache diary is an essential tool to identify patterns and needs for optimization of acute or preventive treatment regimens. The strongest evidence is for the behavioral management techniques for stress reduction.
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017; 390(10100):1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2
- Vgontzas A, Pavlovic JM. Sleep diorders and migraine: review of literature and potential pathophysiology mechanisms. Headache 2018; 58(7):1030–1039. doi:10.1111/head.13358
- Lund N, Westergaard ML, Barloese M, Glumer C, Jensen RH. Epidemiology of concurrent headache and sleep problems in Denmark. Cephalalgia 2014; 34(10):833–845. doi:10.1177/0333102414543332
- Woldeamanuel YW, Cowan RP. The impact of regular lifestyle behavior in migraine: a prevalence case-referent study. J Neurol 2016; 263(4):669–676. doi:10.1007/s00415-016-8031-5
- Chung F, Abdullah HR, Liao P. STOP-Bang questionnaire: a practical approach to screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2016; 149(3):631–638. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0903
- Johnson KG, Ziemba AM, Garb JL. Improvement in headaches with continuous positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea: a retrospective analysis. Headache 2013; 53(2):333–343. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02251.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S. Behavioral sleep modification may revert transformed migraine to episodic migraine. Headache 2007; 47(8):1178–1183. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00780.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S, Finkel AG, Kahn KA, Mann JD. The prevalence and spectrum of sleep problems in women with transformed migraine. Headache 2006; 46(4):604–610. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00410.x
- Rains JC. Optimizing circadian cycles and behavioral insomnia treatment in migraine. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(3):213–219. pmid:18796272
- Lemmens J, De Pauw J, Van Soom T, et al. The effect of aerobic exercise on the number of migraine days, duration and pain intensity in migraine: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Headache Pain 2019; 20(1):16. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-0961-8
- Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, et al; European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). The association between migraine and physical exercise. J Headache Pain 2018; 19(1):83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y
- Genazzani AR, Nappi G, Facchinetti F, et al. Progressive impairment of CSF beta-EP levels in migraine sufferers. Pain 1984; 18:127-133. pmid:6324056
- Hindiyeh NA, Krusz JC, Cowan RP. Does exercise make migraines worse and tension type headaches better? Curr Pain Headache Rep 2013;17:380. pmid:24234818
- Kroll LS, Sjodahl Hammarlund C, Gard G, Jensen RH, Bendtsen L. Has aerobic exercise effect on pain perception in persons with migraine and coexisting tension-type headache and neck pain? A randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Eur J Pain 2018; 10:10. pmid:29635806
- Santiago MD, Carvalho Dde S, Gabbai AA, Pinto MM, Moutran AR, Villa TR. Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2014; 72(11):851-855. pmid:25410451
- Varkey E, Cider A, Carlsson J, Linde M. Exercise as migraine prophylaxis: a randomized study using relaxation and topiramate as controls. Cephalalgia 2011; 31(14):1428-1438. pmid:21890526
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, et al. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011; 43(7):1334-1359. pmid:21694556
- Guarnieri P, Radnitz CL, Blanchard EB. Assessment of dietary risk factors in chronic headache. Biofeedback Self Regul 1990; 15(1):15–25. pmid:2361144
- Shapiro RE. Caffeine and headaches. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(4):311–315. pmid:18625110
- Yokoyama M, Yokoyama T, Funazu K, et al. Associations between headache and stress, alcohol drinking, exercise, sleep, and comorbid health conditions in a Japanese population. J Headache Pain 2009; 10(3):177–185. doi:10.1007/s10194-009-0113-7
- Karsan N, Bose P, Goadsby PJ. The migraine premonitory phase. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2018; 24(4, Headache):996–1008. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000624
- Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB. Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies. Headache 2014; 54(10):1670–1679. doi:10.1111/head.12468
- Marcus DA, Scharff L, Turk D, Gourley LM. A double-blind provocative study of chocolate as a trigger of headache. Cephalalgia 1997; 17(8):855–862. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.1997.1708855.x
- Obayashi Y, Nagamura Y. Does monosodium glutamate really cause headache? A systematic review of human studies. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:54. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0639-4
- Evans EW, Lipton RB, Peterlin BL, et al. Dietary intake patterns and diet quality in a nationally representative sample of women with and without severe headache or migraine. Headache 2015; 55(4):550–561. doi:10.1111/head.12527
- Zis P, Julian T, Hadjivassiliou M. Headache associated with coeliac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018; 10(10). doi:10.3390/nu10101445
- Alpay K, Ertas M, Orhan EK, Ustay DK, Lieners C, Baykan B. Diet restriction in migraine, based on IgG against foods: a clinical double-blind, randomised, cross-over trial. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(7):829–837. doi:10.1177/0333102410361404
- Aydinlar EI, Dikmen PY, Tiftikci A, et al. IgG-based elimination diet in migraine plus irritable bowel syndrome. Headache 2013; 53(3):514–525. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02296.x
- Mitchell N, Hewitt CE, Jayakody S, et al. Randomised controlled trial of food elimination diet based on IgG antibodies for the prevention of migraine like headaches. Nutr J 2011; 10:85. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-85
- Wantke F, Gotz M, Jarisch R. Histamine-free diet: treatment of choice for histamine-induced food intolerance and supporting treatment for chronic headaches. Clin Exp Allergy 1993; 23(12):982–985. pmid:10779289
- Mansfield LE, Vaughan TR, Waller SF, Haverly RW, Ting S. Food allergy and adult migraine: double-blind and mediator confirmation of an allergic etiology. Ann Allergy 1985; 55(2):126–129. pmid:4025956
- Kohlenberg RJ. Tyramine sensitivity in dietary migraine: a critical review. Headache 1982; 22(1):30–34. pmid:17152742
- Medina JL, Diamond S. The role of diet in migraine. Headache 1978; 18(1):31–34. pmid:649377
- Mosnaim AD, Freitag F, Ignacio R, et al. Apparent lack of correlation between tyramine and phenylethylamine content and the occurrence of food-precipitated migraine. Reexamination of a variety of food products frequently consumed in the United States and commonly restricted in tyramine-free diets. Headache Quarterly. Current Treatment and Research 1996; 7(3):239–249.
- Ferrara LA, Pacioni D, Di Fronzo V, et al. Low-lipid diet reduces frequency and severity of acute migraine attacks. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2015; 25(4):370–375. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2014.12.006
- Bic Z, Blix GG, Hopp HP, Leslie FM, Schell MJ. The influence of a low-fat diet on incidence and severity of migraine headaches. J Womens Health Gend Based Med 1999; 8(5):623–630. doi:10.1089/jwh.1.1999.8.623
- Bunner AE, Agarwal U, Gonzales JF, Valente F, Barnard ND. Nutrition intervention for migraine: a randomized crossover trial. J Headache Pain 2014; 15:69. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-69
- Evcili G, Utku U, Ogun MN, Ozdemir G. Early and long period follow-up results of low glycemic index diet for migraine prophylaxis. Agri 2018; 30(1):8–11. doi:10.5505/agri.2017.62443
- Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L, Mansoori A, Abed R, Shishehbor F. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on the frequency, severity, and duration of migraine attacks: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(9):614–623. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1344371
- Soares AA, Loucana PMC, Nasi EP, Sousa KMH, Sa OMS, Silva-Neto RP. A double- blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (OPFA Ω-3) for the prevention of migraine in chronic migraine patients using amitriptyline. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(3):219–223. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2016.1266133
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Sirianni G, et al. Migraine improvement during short lasting ketogenesis: a proof-of-concept study. Eur J Neurol 2015; 22(1):170–177. doi:10.1111/ene.12550
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Bracaglia M, et al. Cortical functional correlates of responsiveness to short-lasting preventive intervention with ketogenic diet in migraine: a multimodal evoked potentials study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:58. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0650-9
- Kossoff EH, Huffman J, Turner Z, Gladstein J. Use of the modified Atkins diet for adolescents with chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(8):1014–1016. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.02016.x
- Slavin M, Ailani J. A clinical approach to addressing diet with migraine patients. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2017; 17(2):17. doi:10.1007/s11910-017-0721-6
- Amer M, Woodward M, Appel LJ. Effects of dietary sodium and the DASH diet on the occurrence of headaches: results from randomised multicentre DASH-sodium clinical trial. BMJ Open 2014; 4(12):e006671. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006671
- Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen W, Whelton PK, Appel LJ. Lower sodium intake and risk of headaches: results from the trial of nonpharmacologic interventions in the elderly. Am J Public Health 2016; 106(7):1270–1275. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303143
- Pogoda JM, Gross NB, Arakaki X, Fonteh AN, Cowan RP, Harrington MG. Severe headache or migraine history is inversely correlated with dietary sodium intake: NHANES 1999–2004. Headache 2016; 56(4):688–698. doi:10.1111/head.12792
- Awada A, al Jumah M. The first-of-Ramadan headache. Headache 1999; 39(7):490–493. pmid:11279933
- Abu-Salameh I, Plakht Y, Ifergane G. Migraine exacerbation during Ramadan fasting. J Headache Pain 2010; 11(6):513–517. doi:10.1007/s10194-010-0242-z
- Nazari F, Safavi M, Mahmudi M. Migraine and its relation with lifestyle in women. Pain Pract 2010; 10(3):228–234. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2009.00343.x
- Nas A, Mirza N, Hagele F, et al. Impact of breakfast skipping compared with dinner skipping on regulation of energy balance and metabolic risk. Am J Clin Nutr 2017; 105(6):1351–1361. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151332
- Torelli P, Manzoni GC. Fasting headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2010; 14(4):284–291. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0119-5
- Yoshimura E, Hatamoto Y, Yonekura S, Tanaka H. Skipping breakfast reduces energy intake and physical activity in healthy women who are habitual breakfast eaters: a randomized crossover trial. Physiol Behav 2017; 174:89–94. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.008
- Pendergast FJ, Livingstone KM, Worsley A, McNaughton SA. Correlates of meal skipping in young adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2016; 13(1):125. doi:10.1186/s12966-016-0451-1
- Maki KC, Phillips-Eakley AK, Smith KN. The effects of breakfast consumption and composition on metabolic wellness with a focus on carbohydrate metabolism. Adv Nutr 2016; 7(3):613S–621S. doi:10.3945/an.115.010314
- Shirreffs SM, Merson SJ, Fraser SM, Archer DT. The effects of fluid restriction on hydration status and subjective feelings in man. Br J Nutr 2004; 91(6):951–958. doi:10.1079/BJN20041149
- Blau JN. Water deprivation: a new migraine precipitant. Headache 2005; 45(6):757–759. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05143_3.x
- Price A, Burls A. Increased water intake to reduce headache: learning from a critical appraisal. J Eval Clin Pract 2015; 21(6):1212–1218. doi:10.1111/jep.12413
- Balbin JE, Nerenberg R, Baratloo A, Friedman BW. Intravenous fluids for migraine: a post hoc analysis of clinical trial data. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34(4):713–716. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.12.080
- Spigt M, Weerkamp N, Troost J, van Schayck CP, Knottnerus JA. A randomized trial on the effects of regular water intake in patients with recurrent headaches. Fam Pract 2012; 29(4):370–375. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmr112
- Armstrong LE, Johnson EC. Water intake, water balance, and the elusive daily water requirement. Nutrients 2018; 10(12). doi:10.3390/nu10121928
- Fried NT, Elliott MB, Oshinsky ML. The role of adenosine signaling in headache: a review. Brain Sci 2017; 7(3). doi:10.3390/brainsci7030030
- Lee MJ, Choi HA, Choi H, Chung CS. Caffeine discontinuation improves acute migraine treatment: a prospective clinic-based study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17(1):71. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0662-5
- Shirlow MJ, Mathers CD. A study of caffeine consumption and symptoms; indigestion, palpitations, tremor, headache and insomnia. Int J Epidemiol 1985; 14(2):239–248. doi:10.1093/ije/14.2.239
- Silverman K, Evans SM, Strain EC, Griffiths RR. Withdrawal syndrome after the double-blind cessation of caffeine consumption. N Engl J Med 1992; 327(16):1109–1114. doi:10.1056/NEJM199210153271601
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018; 38(1):1–211. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202
- Krogh AB, Larsson B, Salvesen O, Linde M. A comparison between prospective Internet-based and paper diary recordings of headache among adolescents in the general population. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(4):335–345. doi:10.1177/0333102415591506
- Bandarian-Balooch S, Martin PR, McNally B, Brunelli A, Mackenzie S. Electronic-diary for recording headaches, triggers, and medication use: development and evaluation. Headache 2017; 57(10):1551–1569. doi:10.1111/head.13184
- Tassorelli C, Sances G, Allena M, et al. The usefulness and applicability of a basic headache diary before first consultation: results of a pilot study conducted in two centres. Cephalalgia 2008; 28(10):1023–1030. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01639.x
- Baos V, Ester F, Castellanos A, et al. Use of a structured migraine diary improves patient and physician communication about migraine disability and treatment outcomes. Int J Clin Pract 2005; 59(3):281–286. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00469.x
- Martin PR, MacLeod C. Behavioral management of headache triggers: avoidance of triggers is an inadequate strategy. Clin Psychol Rev 2009; 29(6):483–495. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.05.002
- Giannini G, Zanigni S, Grimaldi D, et al. Cephalalgiaphobia as a feature of high-frequency migraine: a pilot study. J Headache Pain 2013; 14:49. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-14-49
- Westergaard ML, Glumer C, Hansen EH, Jensen RH. Medication overuse, healthy lifestyle behaviour and stress in chronic headache: results from a population-based representative survey. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(1):15–28. doi:10.1177/0333102415578430
- Christiansen S, Jurgens TP, Klinger R. Outpatient combined group and individual cognitive-behavioral treatment for patients with migraine and tension-type headache in a routine clinical setting. Headache 2015; 55(8):1072–1091. doi:10.1111/head.12626
- Martin PR, Aiello R, Gilson K, Meadows G, Milgrom J, Reece J. Cognitive behavior therapy for comorbid migraine and/or tension-type headache and major depressive disorder: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Behav Res Ther 2015; 73:8–18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2015.07.005
- Nash JM, Park ER, Walker BB, Gordon N, Nicholson RA. Cognitive-behavioral group treatment for disabling headache. Pain Med 2004; 5(2):178–186. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2004.04031.x
- Sorbi MJ, Balk Y, Kleiboer AM, Couturier EG. Follow-up over 20 months confirms gains of online behavioural training in frequent episodic migraine. Cephalalgia 2017; 37(3):236–250. doi:10.1177/0333102416657145
- Thorn BE, Pence LB, Ward LC, et al. A randomized clinical trial of targeted cognitive behavioral treatment to reduce catastrophizing in chronic headache sufferers. J Pain 2007; 8(12):938–949. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2007.06.010
- Nestoriuc Y, Martin A. Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis. Pain 2007; 128(1–2):111–127. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007
- Blanchard EB, Appelbaum KA, Nicholson NL, et al. A controlled evaluation of the addition of cognitive therapy to a home-based biofeedback and relaxation treatment of vascular headache. Headache 1990; 30(6):371–376. pmid:2196240
- Gu Q, Hou JC, Fang XM. Mindfulness meditation for primary headache pain: a meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2018; 131(7):829–838. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.228242
- Day MA, Thorn BE. The mediating role of pain acceptance during mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for headache. Complement Ther Med 2016; 25:51–54. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2016.01.002
- Williamson DA, Monguillot JE, Jarrell MP, Cohen RA, Pratt JM, Blouin DC. Relaxation for the treatment of headache. Controlled evaluation of two group programs. Behav Modif 1984; 8(3):407–424. doi:10.1177/01454455840083007
- Merelle SY, Sorbi MJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Passchier J. Qualities and health of lay trainers with migraine for behavioral attack prevention. Headache 2010; 50(4):613–625. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01241.x
- Gaul C, van Doorn C, Webering N, et al. Clinical outcome of a headache-specific multidisciplinary treatment program and adherence to treatment recommendations in a tertiary headache center: an observational study. J Headache Pain 2011; 12(4):475–483. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0348-y
- Wallasch TM, Kropp P. Multidisciplinary integrated headache care: a prospective 12-month follow-up observational study. J Headache Pain 2012; 13(7):521–529. doi:10.1007/s10194-012-0469-y
- Lemstra M, Stewart B, Olszynski WP. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary intervention in the treatment of migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Headache 2002; 42(9):845–854. pmid:12390609
- Krause SJ, Stillman MJ, Tepper DE, Zajac D. A prospective cohort study of outpatient interdisciplinary rehabilitation of chronic headache patients. Headache 2017; 57(3):428–440. doi:10.1111/head.13020
Migraine is the second leading cause of years of life lived with a disability globally.1 It affects people of all ages, but particularly during the years associated with the highest productivity in terms of work and family life.
Migraine is a genetic neurologic disease that can be influenced or triggered by environmental factors. However, triggers do not cause migraine. For example, stress does not cause migraine, but it can exacerbate it.
Primary care physicians can help patients reduce the likelihood of a migraine attack, the severity of symptoms, or both by offering lifestyle counseling centered around the mnemonic SEEDS: sleep, exercise, eat, diary, and stress. In this article, each factor is discussed individually for its current support in the literature along with best-practice recommendations.
S IS FOR SLEEP
Before optimizing sleep hygiene, screen for sleep apnea, especially in those who have chronic daily headache upon awakening. An excellent tool is the STOP-Bang screening questionnaire5 (www.stopbang.ca/osa/screening.php). Patients respond “yes” or “no” to the following questions:
- Snoring: Do you snore loudly (louder than talking or loud enough to be heard through closed doors)?
- Tired: Do you often feel tired, fatigued, or sleepy during the daytime?
- Observed: Has anyone observed you stop breathing during your sleep?
- Pressure: Do you have or are you being treated for high blood pressure?
- Body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2?
- Age over 50?
- Neck circumference larger than 40 cm (females) or 42 cm (males)?
- Gender—male?
Each “yes” answer is scored as 1 point. A score less than 3 indicates low risk of obstructive sleep apnea; 3 to 4 indicates moderate risk; and 5 or more indicates high risk. Optimization of sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure therapy can improve sleep apnea headache.6 The improved sleep from reduced arousals may also mitigate migraine symptoms.
Behavioral modification for sleep hygiene can convert chronic migraine to episodic migraine.7 One such program is stimulus control therapy, which focuses on using cues to initiate sleep (Table 1). Patients are encouraged to keep the bedroom quiet, dark, and cool, and to go to sleep at the same time every night. Importantly, the bed should be associated only with sleep. If patients are unable to fall asleep within 20 to 30 minutes, they should leave the room so they do not associate the bed with frustration and anxiety. Use of phones, tablets, and television in the bedroom is discouraged as these devices may make it more difficult to fall asleep.8
The next option is sleep restriction, which is useful for comorbid insomnia. Patients keep a sleep diary to better understand their sleep-wake cycle. The goal is 90% sleep efficiency, meaning that 90% of the time in bed (TIB) is spent asleep. For example, if the patient is in bed 8 hours but asleep only 4 hours, sleep efficiency is 50%. The goal is to reduce TIB to match the time asleep and to agree on a prescribed daily wake-up time. When the patient is consistently sleeping 90% of the TIB, add 30-minute increments until he or she is appropriately sleeping 7 to 8 hours at night.9 Naps are not recommended.
Let patients know that their migraine may worsen until a new routine sleep pattern emerges. This method is not recommended for patients with untreated sleep apnea.
E IS FOR EXERCISE
Exercise is broadly recommended for a healthy lifestyle; some evidence suggests that it can also be useful in the management of migraine.10 Low levels of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle are associated with migraine.11 It is unclear if patients with migraine are less likely to exercise because they want to avoid triggering a migraine or if a sedentary lifestyle increases their risk.
Exercise has been studied for its prophylactic benefits in migraine, and one hypothesis relates to beta-endorphins. Levels of beta-endorphins are reduced in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine.12 Exercise programs may increase levels while reducing headache frequency and duration.13 One study showed that pain thresholds do not change with exercise programs, suggesting that it is avoidance behavior that is positively altered rather than the underlying pain pathways.14
A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 5 randomized controlled trials and 1 nonrandomized controlled clinical trial showed that exercise reduced monthly migraine days by only 0.6 (± 0.3) days, but the data also suggested that as the exercise intensity increased, so did the positive effects.10
Some data suggest that exercise may also reduce migraine duration and severity as well as the need for abortive medication.10 Two studies in this systematic review15,16 showed that exercise benefits were equivalent to those of migraine preventives such as amitriptyline and topiramate; the combination of amitriptyline and exercise was more beneficial than exercise alone. Multiple types of exercise were beneficial, including walking, jogging, cross-training, and cycling when done for least 6 weeks and for 30 to 50 minutes 3 to 5 times a week.
These findings are in line with the current recommendations for general health from the American College of Sports Medicine, ie, moderate to vigorous cardiorespiratory exercise for 30 to 60 minutes 3 to 5 times a week (or 150 minutes per week). The daily exercise can be continuous or done in intervals of less than 20 minutes. For those with a sedentary lifestyle, as is seen in a significant proportion of the migraine population, light to moderate exercise for less than 20 minutes is still beneficial.17
Based on this evidence, the best current recommendation for patients with migraine is to engage in graded moderate cardiorespiratory exercise, although any exercise is better than none. If a patient is sedentary or has poor exercise tolerance, or both, exercising once a week for shorter time periods may be a manageable place to start.
Some patients may identify exercise as a trigger or exacerbating factor in migraine. These patients may need appropriate prophylactic and abortive therapies before starting an exercise regimen.
THE SECOND E IS FOR EAT (FOOD AND DRINK)
Many patients believe that some foods trigger migraine attacks, but further study is needed. The most consistent food triggers appear to be red wine and caffeine (withdrawal).18,19 Interestingly, patients with migraine report low levels of alcohol consumption,20 but it is unclear if that is because alcohol has a protective effect or if patients avoid it.
Some patients may crave certain foods in the prodromal phase of an attack, eat the food, experience the attack, and falsely conclude that the food caused the attack.21 Premonitory symptoms include fatigue, cognitive changes, homeostatic changes, sensory hyperresponsiveness, and food cravings.21 It is difficult to distinguish between premonitory phase food cravings and true triggers because premonitory symptoms can precede headache by 48 to 72 hours, and the timing for a trigger to be considered causal is not known.22
Chocolate is often thought to be a migraine trigger, but the evidence argues against this and even suggests that sweet cravings are a part of the premonitory phase.23 Monosodium glutamate is often identified as a trigger as well, but the literature is inconsistent and does not support a causal relationship.24 Identifying true food triggers in migraine is difficult, and patients with migraine may have poor quality diets, with some foods acting as true triggers for certain patients.25 These possibilities have led to the development of many “migraine diets,” including elimination diets.
Elimination diets
Elimination diets involve avoiding specific food items over a period of time and then adding them back in one at a time to gauge whether they cause a reaction in the body. A number of these diets have been studied for their effects on headache and migraine:
Gluten-free diets restrict foods that contain wheat, rye, and barley. A systematic review of gluten-free diets in patients with celiac disease found that headache or migraine frequency decreased by 51.6% to 100% based on multiple cohort studies (N = 42,388).26 There are no studies on the use of a gluten-free diet for migraine in patients without celiac disease.
Immunoglobulin G-elimination diets restrict foods that serve as antigens for IgG. However, data supporting these diets are inconsistent. Two small randomized controlled trials found that the diets improved migraine symptoms, but a larger study found no improvement in the number of migraine days at 12 weeks, although there was an initially significant effect at 4 weeks.27–29
Antihistamine diets restrict foods that have high levels of histamines, including fermented dairy, vegetables, soy products, wine, beer, alcohol, and those that cause histamine release regardless of IgE testing results. A prospective single-arm study of antihistamine diets in patients with chronic headache reported symptom improvement, which could be applied to certain comorbidities such as mast cell activation syndrome.30 Another prospective nonrandomized controlled study eliminated foods based on positive IgE skin-prick testing for allergy in patients with recurrent migraine and found that it reduced headache frequency.31
Tyramine-free diets are often recommended due to the presumption that tyramine-containing foods (eg, aged cheese, cured or smoked meats and fish, and beer) are triggers. However, multiple studies have reviewed this theory with inconsistent results,32 and the only study of a tyramine-free diet was negative.33 In addition, commonly purported high-tyramine foods have lower tyramine levels than previously thought.34
Low-fat diets in migraine are supported by 2 small randomized controlled trials and a prospective study showing a decrease in symptom severity; the results for frequency are inconsistent.35–37
Low-glycemic index diets are supported in migraine by 1 randomized controlled trial that showed improvement in migraine frequency in a diet group and in a control group of patients who took a standard migraine-preventive medication to manage their symptoms.38
Other migraine diets
Diets high in certain foods or ingredient ratios, as opposed to elimination diets, have also been studied in patients with migraine. One promising diet containing high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and low levels of omega-6 fatty acids was shown in a systematic review to reduce the duration of migraine but not the frequency or severity.39 A more recent randomized controlled trial of this diet in chronic migraine also showed that it decreased migraine frequency.40
The ketogenic diet (high fat, low carbohydrate) had promising results in a randomized controlled trial in overweight women with migraine and in a prospective study.41,42 However, a prospective study of the Atkins diet in teenagers with chronic daily headaches showed no benefit.43 The ketogenic diet is difficult to follow and may work in part due to weight loss alone, although ketogenesis itself may also play a role.41,44
Sodium levels have been shown to be higher in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine than in controls, particularly during an attack.45 For a prehypertensive population or an elderly population, a low-sodium diet may be beneficial based on 2 prospective trials.46,47 However, a younger female population without hypertension and low-to-normal body mass index had a reduced probability of migraine while consuming a high-sodium diet.48
Counseling about sodium intake should be tailored to specific patient populations. For example, a diet low in sodium may be appropriate for patients with vascular risk factors such as hypertension, whereas a high-sodium diet may be appropriate in patients with comorbidities like postural tachycardia syndrome or in those with a propensity for low blood pressure or low body mass index.
Encourage routine meals and hydration
The standard advice for patients with migraine is to consume regular meals. Headaches have been associated with fasting, and those with migraine are predisposed to attacks in the setting of fasting.49,50 Migraine is more common when meals are skipped, particularly breakfast.51
It is unclear how fasting lowers the migraine threshold. Nutritional studies show that skipping meals, particularly breakfast, increases low-grade inflammation and impairs glucose metabolism by affecting insulin and fat oxidation metabolism.52 However, hypoglycemia itself is not a consistent cause of headache or migraine attacks.53 As described above, a randomized controlled trial of a low-glycemic index diet actually decreased migraine frequency and severity.38 Skipping meals also reduces energy and is associated with reduced physical activity, perhaps leading to multiple compounding triggers that further lower the migraine threshold.54,55
When counseling patients about the need to eat breakfast, consider what they normally consume (eg, is breakfast just a cup of coffee?). Replacing simple carbohydrates with protein, fats, and fiber may be beneficial for general health, but the effects on migraine are not known, nor is the optimal composition of breakfast foods.55
The optimal timing of breakfast relative to awakening is also unclear, but in general, it should be eaten within 30 to 60 minutes of rising. Also consider patients’ work hours—delayed-phase or shift workers have altered sleep cycles.
Recommendations vary in regard to hydration. Headache is associated with fluid restriction and dehydration,56,57 but only a few studies suggest that rehydration and increased hydration status can improve migraine.58 In fact, a single post hoc analysis of a metoclopramide study showed that intravenous fluid alone for patients with migraine in the emergency room did not improve pain outcomes.59
The amount of water patients should drink daily in the setting of migraine is also unknown, but a study showed benefit with 4 L, which equates to a daily intake of 16 eight-ounce glasses.60 One review on general health that could be extrapolated given the low risk of the intervention indicated that 1.8 L daily (7 to 8 eight-ounce glasses) promoted a euhydration status in most people, although many factors contribute to hydration status.61
Caffeine intake is also a major consideration. Caffeine is a nonspecific adenosine receptor antagonist that modulates adenosine receptors like the pronociceptive 2A receptor, leading to changes integral to the neuropathophysiology of migraine.62 Caffeine has analgesic properties at doses greater than 65 to 200 mg and augments the effects of analgesics such as acetaminophen and aspirin. Chronic caffeine use can lead to withdrawal symptoms when intake is stopped abruptly; this is thought to be due to upregulation of adenosine receptors, but the effect varies based on genetic predisposition.19
The risk of chronic daily headache may relate to high use of caffeine preceding the onset of chronification, and caffeine abstinence may improve response to acute migraine treatment.19,63 There is a dose-dependent risk of headache.64,65 Current recommendations suggest limiting caffeine consumption to less than 200 mg per day or stopping caffeine consumption altogether based on the quantity required for caffeine-withdrawal headache.66 Varying the caffeine dose from day to day may also trigger headache due to the high sensitivity to caffeine withdrawal.
While many diets have shown potential benefit in patients with migraine, more studies are needed before any one “migraine diet” can be recommended. Caution should be taken, as there is risk of adverse effects from nutrient deficiencies or excess levels, especially if the patient is not under the care of a healthcare professional who is familiar with the diet.
Whether it is beneficial to avoid specific food triggers at this time is unclear and still controversial even within the migraine community because some of these foods may be misattributed as triggers instead of premonitory cravings driven by the hypothalamus. It is important to counsel patients with migraine to eat a healthy diet with consistent meals, to maintain adequate hydration, and to keep their caffeine intake low or at least consistent, although these teachings are predominantly based on limited studies with extrapolation from nutrition research.
D IS FOR DIARY
A headache diary is a recommended part of headache management and may enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and assist in treatment modifications. Paper and electronic diaries have been used. Electronic diaries may be more accurate for real-time use, but patients may be more likely to complete a paper one.67 Patients prefer electronic diaries over long paper forms,68 but a practical issue to consider is easy electronic access.
Patients can start keeping a headache diary before the initial consultation to assist with diagnosis, or early in their management. A first-appointment diary mailed with instructions is a feasible option.69 These types of diaries ask detailed questions to help diagnose all major primary headache types including menstrual migraine and to identify concomitant medication-overuse headache. Physicians and patients generally report improved communication with use of a diary.70
Some providers distinguish between a headache diary and a calendar. In standard practice, a headache diary is the general term referring to both, but the literature differentiates between the two. Both should at least include headache frequency, with possible inclusion of other factors such as headache duration, headache intensity, analgesic use, headache impact on function, and absenteeism. Potential triggers including menses can also be tracked. The calendar version can fit on a single page and can be used for simple tracking of headache frequency and analgesia use.
One of the simplest calendars to use is the “stoplight” calendar. Red days are when a patient is completely debilitated in bed. On a yellow day, function at work, school, or daily activities is significantly reduced by migraine, but the patient is not bedbound. A green day is when headache is present but function is not affected. No color is placed if the patient is 100% headache-free.
Acute treatment use can be written in or, to improve compliance, a checkmark can be placed on days of treatment. Patients who are tracking menses circle the days of menstruation. The calendar-diary should be brought to every appointment to track treatment response and medication use.
THE SECOND S IS FOR STRESS
Behavioral management such as cognitive behavioral therapy in migraine has been shown to decrease catastrophizing, migraine disability, and headache severity and frequency.74 Both depression and anxiety can improve along with migraine.75 Cognitive behavioral therapy can be provided in individualized sessions or group sessions, either in person or online.74,76,77 The effects become more prominent about 5 weeks into treatment.78
Biofeedback, which uses behavioral techniques paired with physiologic autonomic measures, has been extensively studied, and shows benefit in migraine, including in meta-analysis.79 The types of biofeedback measurements used include electromyography, electroencephalography, temperature, sweat sensors, heart rate, blood volume pulse feedback, and respiration bands. While biofeedback is generally done under the guidance of a therapist, it can still be useful with minimal therapist contact and supplemental audio.80
Mindfulness, or the awareness of thoughts, feelings, and sensations in the present moment without judgment, is a behavioral technique that can be done alone or paired with another technique. It is often taught through a mindfulness-based stress-reduction program, which relies on a standardized approach. A meta-analysis showed that mindfulness improves pain intensity, headache frequency, disability, self-efficacy, and quality of life.81 It may work by encouraging pain acceptance.82
Relaxation techniques are also employed in migraine management, either alone or in conjunction with techniques mentioned above, such as mindfulness. They include progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing. Relaxation has been shown to be effective when done by professional trainers as well as lay trainers in both individual and group settings.83,84
In patients with intractable headache, more-intensive inpatient and outpatient programs have been tried. Inpatient admissions with multidisciplinary programs that include a focus on behavioral techniques often paired with lifestyle education and sometimes pharmacologic management can be beneficial.85,86 These programs have also been successfully conducted as multiple outpatient sessions.86–88
Stress management is an important aspect of migraine management. These treatments often involve homework and require active participation.
LIFESTYLE FOR ALL
All patients with migraine should initiate lifestyle modifications (see Advice to patients with migraine: SEEDS for success). Modifications with the highest level of evidence, specifically behavioral techniques, have had the most reproducible results. A headache diary is an essential tool to identify patterns and needs for optimization of acute or preventive treatment regimens. The strongest evidence is for the behavioral management techniques for stress reduction.
Migraine is the second leading cause of years of life lived with a disability globally.1 It affects people of all ages, but particularly during the years associated with the highest productivity in terms of work and family life.
Migraine is a genetic neurologic disease that can be influenced or triggered by environmental factors. However, triggers do not cause migraine. For example, stress does not cause migraine, but it can exacerbate it.
Primary care physicians can help patients reduce the likelihood of a migraine attack, the severity of symptoms, or both by offering lifestyle counseling centered around the mnemonic SEEDS: sleep, exercise, eat, diary, and stress. In this article, each factor is discussed individually for its current support in the literature along with best-practice recommendations.
S IS FOR SLEEP
Before optimizing sleep hygiene, screen for sleep apnea, especially in those who have chronic daily headache upon awakening. An excellent tool is the STOP-Bang screening questionnaire5 (www.stopbang.ca/osa/screening.php). Patients respond “yes” or “no” to the following questions:
- Snoring: Do you snore loudly (louder than talking or loud enough to be heard through closed doors)?
- Tired: Do you often feel tired, fatigued, or sleepy during the daytime?
- Observed: Has anyone observed you stop breathing during your sleep?
- Pressure: Do you have or are you being treated for high blood pressure?
- Body mass index greater than 35 kg/m2?
- Age over 50?
- Neck circumference larger than 40 cm (females) or 42 cm (males)?
- Gender—male?
Each “yes” answer is scored as 1 point. A score less than 3 indicates low risk of obstructive sleep apnea; 3 to 4 indicates moderate risk; and 5 or more indicates high risk. Optimization of sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure therapy can improve sleep apnea headache.6 The improved sleep from reduced arousals may also mitigate migraine symptoms.
Behavioral modification for sleep hygiene can convert chronic migraine to episodic migraine.7 One such program is stimulus control therapy, which focuses on using cues to initiate sleep (Table 1). Patients are encouraged to keep the bedroom quiet, dark, and cool, and to go to sleep at the same time every night. Importantly, the bed should be associated only with sleep. If patients are unable to fall asleep within 20 to 30 minutes, they should leave the room so they do not associate the bed with frustration and anxiety. Use of phones, tablets, and television in the bedroom is discouraged as these devices may make it more difficult to fall asleep.8
The next option is sleep restriction, which is useful for comorbid insomnia. Patients keep a sleep diary to better understand their sleep-wake cycle. The goal is 90% sleep efficiency, meaning that 90% of the time in bed (TIB) is spent asleep. For example, if the patient is in bed 8 hours but asleep only 4 hours, sleep efficiency is 50%. The goal is to reduce TIB to match the time asleep and to agree on a prescribed daily wake-up time. When the patient is consistently sleeping 90% of the TIB, add 30-minute increments until he or she is appropriately sleeping 7 to 8 hours at night.9 Naps are not recommended.
Let patients know that their migraine may worsen until a new routine sleep pattern emerges. This method is not recommended for patients with untreated sleep apnea.
E IS FOR EXERCISE
Exercise is broadly recommended for a healthy lifestyle; some evidence suggests that it can also be useful in the management of migraine.10 Low levels of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle are associated with migraine.11 It is unclear if patients with migraine are less likely to exercise because they want to avoid triggering a migraine or if a sedentary lifestyle increases their risk.
Exercise has been studied for its prophylactic benefits in migraine, and one hypothesis relates to beta-endorphins. Levels of beta-endorphins are reduced in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine.12 Exercise programs may increase levels while reducing headache frequency and duration.13 One study showed that pain thresholds do not change with exercise programs, suggesting that it is avoidance behavior that is positively altered rather than the underlying pain pathways.14
A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 5 randomized controlled trials and 1 nonrandomized controlled clinical trial showed that exercise reduced monthly migraine days by only 0.6 (± 0.3) days, but the data also suggested that as the exercise intensity increased, so did the positive effects.10
Some data suggest that exercise may also reduce migraine duration and severity as well as the need for abortive medication.10 Two studies in this systematic review15,16 showed that exercise benefits were equivalent to those of migraine preventives such as amitriptyline and topiramate; the combination of amitriptyline and exercise was more beneficial than exercise alone. Multiple types of exercise were beneficial, including walking, jogging, cross-training, and cycling when done for least 6 weeks and for 30 to 50 minutes 3 to 5 times a week.
These findings are in line with the current recommendations for general health from the American College of Sports Medicine, ie, moderate to vigorous cardiorespiratory exercise for 30 to 60 minutes 3 to 5 times a week (or 150 minutes per week). The daily exercise can be continuous or done in intervals of less than 20 minutes. For those with a sedentary lifestyle, as is seen in a significant proportion of the migraine population, light to moderate exercise for less than 20 minutes is still beneficial.17
Based on this evidence, the best current recommendation for patients with migraine is to engage in graded moderate cardiorespiratory exercise, although any exercise is better than none. If a patient is sedentary or has poor exercise tolerance, or both, exercising once a week for shorter time periods may be a manageable place to start.
Some patients may identify exercise as a trigger or exacerbating factor in migraine. These patients may need appropriate prophylactic and abortive therapies before starting an exercise regimen.
THE SECOND E IS FOR EAT (FOOD AND DRINK)
Many patients believe that some foods trigger migraine attacks, but further study is needed. The most consistent food triggers appear to be red wine and caffeine (withdrawal).18,19 Interestingly, patients with migraine report low levels of alcohol consumption,20 but it is unclear if that is because alcohol has a protective effect or if patients avoid it.
Some patients may crave certain foods in the prodromal phase of an attack, eat the food, experience the attack, and falsely conclude that the food caused the attack.21 Premonitory symptoms include fatigue, cognitive changes, homeostatic changes, sensory hyperresponsiveness, and food cravings.21 It is difficult to distinguish between premonitory phase food cravings and true triggers because premonitory symptoms can precede headache by 48 to 72 hours, and the timing for a trigger to be considered causal is not known.22
Chocolate is often thought to be a migraine trigger, but the evidence argues against this and even suggests that sweet cravings are a part of the premonitory phase.23 Monosodium glutamate is often identified as a trigger as well, but the literature is inconsistent and does not support a causal relationship.24 Identifying true food triggers in migraine is difficult, and patients with migraine may have poor quality diets, with some foods acting as true triggers for certain patients.25 These possibilities have led to the development of many “migraine diets,” including elimination diets.
Elimination diets
Elimination diets involve avoiding specific food items over a period of time and then adding them back in one at a time to gauge whether they cause a reaction in the body. A number of these diets have been studied for their effects on headache and migraine:
Gluten-free diets restrict foods that contain wheat, rye, and barley. A systematic review of gluten-free diets in patients with celiac disease found that headache or migraine frequency decreased by 51.6% to 100% based on multiple cohort studies (N = 42,388).26 There are no studies on the use of a gluten-free diet for migraine in patients without celiac disease.
Immunoglobulin G-elimination diets restrict foods that serve as antigens for IgG. However, data supporting these diets are inconsistent. Two small randomized controlled trials found that the diets improved migraine symptoms, but a larger study found no improvement in the number of migraine days at 12 weeks, although there was an initially significant effect at 4 weeks.27–29
Antihistamine diets restrict foods that have high levels of histamines, including fermented dairy, vegetables, soy products, wine, beer, alcohol, and those that cause histamine release regardless of IgE testing results. A prospective single-arm study of antihistamine diets in patients with chronic headache reported symptom improvement, which could be applied to certain comorbidities such as mast cell activation syndrome.30 Another prospective nonrandomized controlled study eliminated foods based on positive IgE skin-prick testing for allergy in patients with recurrent migraine and found that it reduced headache frequency.31
Tyramine-free diets are often recommended due to the presumption that tyramine-containing foods (eg, aged cheese, cured or smoked meats and fish, and beer) are triggers. However, multiple studies have reviewed this theory with inconsistent results,32 and the only study of a tyramine-free diet was negative.33 In addition, commonly purported high-tyramine foods have lower tyramine levels than previously thought.34
Low-fat diets in migraine are supported by 2 small randomized controlled trials and a prospective study showing a decrease in symptom severity; the results for frequency are inconsistent.35–37
Low-glycemic index diets are supported in migraine by 1 randomized controlled trial that showed improvement in migraine frequency in a diet group and in a control group of patients who took a standard migraine-preventive medication to manage their symptoms.38
Other migraine diets
Diets high in certain foods or ingredient ratios, as opposed to elimination diets, have also been studied in patients with migraine. One promising diet containing high levels of omega-3 fatty acids and low levels of omega-6 fatty acids was shown in a systematic review to reduce the duration of migraine but not the frequency or severity.39 A more recent randomized controlled trial of this diet in chronic migraine also showed that it decreased migraine frequency.40
The ketogenic diet (high fat, low carbohydrate) had promising results in a randomized controlled trial in overweight women with migraine and in a prospective study.41,42 However, a prospective study of the Atkins diet in teenagers with chronic daily headaches showed no benefit.43 The ketogenic diet is difficult to follow and may work in part due to weight loss alone, although ketogenesis itself may also play a role.41,44
Sodium levels have been shown to be higher in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with migraine than in controls, particularly during an attack.45 For a prehypertensive population or an elderly population, a low-sodium diet may be beneficial based on 2 prospective trials.46,47 However, a younger female population without hypertension and low-to-normal body mass index had a reduced probability of migraine while consuming a high-sodium diet.48
Counseling about sodium intake should be tailored to specific patient populations. For example, a diet low in sodium may be appropriate for patients with vascular risk factors such as hypertension, whereas a high-sodium diet may be appropriate in patients with comorbidities like postural tachycardia syndrome or in those with a propensity for low blood pressure or low body mass index.
Encourage routine meals and hydration
The standard advice for patients with migraine is to consume regular meals. Headaches have been associated with fasting, and those with migraine are predisposed to attacks in the setting of fasting.49,50 Migraine is more common when meals are skipped, particularly breakfast.51
It is unclear how fasting lowers the migraine threshold. Nutritional studies show that skipping meals, particularly breakfast, increases low-grade inflammation and impairs glucose metabolism by affecting insulin and fat oxidation metabolism.52 However, hypoglycemia itself is not a consistent cause of headache or migraine attacks.53 As described above, a randomized controlled trial of a low-glycemic index diet actually decreased migraine frequency and severity.38 Skipping meals also reduces energy and is associated with reduced physical activity, perhaps leading to multiple compounding triggers that further lower the migraine threshold.54,55
When counseling patients about the need to eat breakfast, consider what they normally consume (eg, is breakfast just a cup of coffee?). Replacing simple carbohydrates with protein, fats, and fiber may be beneficial for general health, but the effects on migraine are not known, nor is the optimal composition of breakfast foods.55
The optimal timing of breakfast relative to awakening is also unclear, but in general, it should be eaten within 30 to 60 minutes of rising. Also consider patients’ work hours—delayed-phase or shift workers have altered sleep cycles.
Recommendations vary in regard to hydration. Headache is associated with fluid restriction and dehydration,56,57 but only a few studies suggest that rehydration and increased hydration status can improve migraine.58 In fact, a single post hoc analysis of a metoclopramide study showed that intravenous fluid alone for patients with migraine in the emergency room did not improve pain outcomes.59
The amount of water patients should drink daily in the setting of migraine is also unknown, but a study showed benefit with 4 L, which equates to a daily intake of 16 eight-ounce glasses.60 One review on general health that could be extrapolated given the low risk of the intervention indicated that 1.8 L daily (7 to 8 eight-ounce glasses) promoted a euhydration status in most people, although many factors contribute to hydration status.61
Caffeine intake is also a major consideration. Caffeine is a nonspecific adenosine receptor antagonist that modulates adenosine receptors like the pronociceptive 2A receptor, leading to changes integral to the neuropathophysiology of migraine.62 Caffeine has analgesic properties at doses greater than 65 to 200 mg and augments the effects of analgesics such as acetaminophen and aspirin. Chronic caffeine use can lead to withdrawal symptoms when intake is stopped abruptly; this is thought to be due to upregulation of adenosine receptors, but the effect varies based on genetic predisposition.19
The risk of chronic daily headache may relate to high use of caffeine preceding the onset of chronification, and caffeine abstinence may improve response to acute migraine treatment.19,63 There is a dose-dependent risk of headache.64,65 Current recommendations suggest limiting caffeine consumption to less than 200 mg per day or stopping caffeine consumption altogether based on the quantity required for caffeine-withdrawal headache.66 Varying the caffeine dose from day to day may also trigger headache due to the high sensitivity to caffeine withdrawal.
While many diets have shown potential benefit in patients with migraine, more studies are needed before any one “migraine diet” can be recommended. Caution should be taken, as there is risk of adverse effects from nutrient deficiencies or excess levels, especially if the patient is not under the care of a healthcare professional who is familiar with the diet.
Whether it is beneficial to avoid specific food triggers at this time is unclear and still controversial even within the migraine community because some of these foods may be misattributed as triggers instead of premonitory cravings driven by the hypothalamus. It is important to counsel patients with migraine to eat a healthy diet with consistent meals, to maintain adequate hydration, and to keep their caffeine intake low or at least consistent, although these teachings are predominantly based on limited studies with extrapolation from nutrition research.
D IS FOR DIARY
A headache diary is a recommended part of headache management and may enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and assist in treatment modifications. Paper and electronic diaries have been used. Electronic diaries may be more accurate for real-time use, but patients may be more likely to complete a paper one.67 Patients prefer electronic diaries over long paper forms,68 but a practical issue to consider is easy electronic access.
Patients can start keeping a headache diary before the initial consultation to assist with diagnosis, or early in their management. A first-appointment diary mailed with instructions is a feasible option.69 These types of diaries ask detailed questions to help diagnose all major primary headache types including menstrual migraine and to identify concomitant medication-overuse headache. Physicians and patients generally report improved communication with use of a diary.70
Some providers distinguish between a headache diary and a calendar. In standard practice, a headache diary is the general term referring to both, but the literature differentiates between the two. Both should at least include headache frequency, with possible inclusion of other factors such as headache duration, headache intensity, analgesic use, headache impact on function, and absenteeism. Potential triggers including menses can also be tracked. The calendar version can fit on a single page and can be used for simple tracking of headache frequency and analgesia use.
One of the simplest calendars to use is the “stoplight” calendar. Red days are when a patient is completely debilitated in bed. On a yellow day, function at work, school, or daily activities is significantly reduced by migraine, but the patient is not bedbound. A green day is when headache is present but function is not affected. No color is placed if the patient is 100% headache-free.
Acute treatment use can be written in or, to improve compliance, a checkmark can be placed on days of treatment. Patients who are tracking menses circle the days of menstruation. The calendar-diary should be brought to every appointment to track treatment response and medication use.
THE SECOND S IS FOR STRESS
Behavioral management such as cognitive behavioral therapy in migraine has been shown to decrease catastrophizing, migraine disability, and headache severity and frequency.74 Both depression and anxiety can improve along with migraine.75 Cognitive behavioral therapy can be provided in individualized sessions or group sessions, either in person or online.74,76,77 The effects become more prominent about 5 weeks into treatment.78
Biofeedback, which uses behavioral techniques paired with physiologic autonomic measures, has been extensively studied, and shows benefit in migraine, including in meta-analysis.79 The types of biofeedback measurements used include electromyography, electroencephalography, temperature, sweat sensors, heart rate, blood volume pulse feedback, and respiration bands. While biofeedback is generally done under the guidance of a therapist, it can still be useful with minimal therapist contact and supplemental audio.80
Mindfulness, or the awareness of thoughts, feelings, and sensations in the present moment without judgment, is a behavioral technique that can be done alone or paired with another technique. It is often taught through a mindfulness-based stress-reduction program, which relies on a standardized approach. A meta-analysis showed that mindfulness improves pain intensity, headache frequency, disability, self-efficacy, and quality of life.81 It may work by encouraging pain acceptance.82
Relaxation techniques are also employed in migraine management, either alone or in conjunction with techniques mentioned above, such as mindfulness. They include progressive muscle relaxation and deep breathing. Relaxation has been shown to be effective when done by professional trainers as well as lay trainers in both individual and group settings.83,84
In patients with intractable headache, more-intensive inpatient and outpatient programs have been tried. Inpatient admissions with multidisciplinary programs that include a focus on behavioral techniques often paired with lifestyle education and sometimes pharmacologic management can be beneficial.85,86 These programs have also been successfully conducted as multiple outpatient sessions.86–88
Stress management is an important aspect of migraine management. These treatments often involve homework and require active participation.
LIFESTYLE FOR ALL
All patients with migraine should initiate lifestyle modifications (see Advice to patients with migraine: SEEDS for success). Modifications with the highest level of evidence, specifically behavioral techniques, have had the most reproducible results. A headache diary is an essential tool to identify patterns and needs for optimization of acute or preventive treatment regimens. The strongest evidence is for the behavioral management techniques for stress reduction.
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017; 390(10100):1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2
- Vgontzas A, Pavlovic JM. Sleep diorders and migraine: review of literature and potential pathophysiology mechanisms. Headache 2018; 58(7):1030–1039. doi:10.1111/head.13358
- Lund N, Westergaard ML, Barloese M, Glumer C, Jensen RH. Epidemiology of concurrent headache and sleep problems in Denmark. Cephalalgia 2014; 34(10):833–845. doi:10.1177/0333102414543332
- Woldeamanuel YW, Cowan RP. The impact of regular lifestyle behavior in migraine: a prevalence case-referent study. J Neurol 2016; 263(4):669–676. doi:10.1007/s00415-016-8031-5
- Chung F, Abdullah HR, Liao P. STOP-Bang questionnaire: a practical approach to screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2016; 149(3):631–638. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0903
- Johnson KG, Ziemba AM, Garb JL. Improvement in headaches with continuous positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea: a retrospective analysis. Headache 2013; 53(2):333–343. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02251.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S. Behavioral sleep modification may revert transformed migraine to episodic migraine. Headache 2007; 47(8):1178–1183. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00780.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S, Finkel AG, Kahn KA, Mann JD. The prevalence and spectrum of sleep problems in women with transformed migraine. Headache 2006; 46(4):604–610. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00410.x
- Rains JC. Optimizing circadian cycles and behavioral insomnia treatment in migraine. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(3):213–219. pmid:18796272
- Lemmens J, De Pauw J, Van Soom T, et al. The effect of aerobic exercise on the number of migraine days, duration and pain intensity in migraine: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Headache Pain 2019; 20(1):16. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-0961-8
- Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, et al; European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). The association between migraine and physical exercise. J Headache Pain 2018; 19(1):83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y
- Genazzani AR, Nappi G, Facchinetti F, et al. Progressive impairment of CSF beta-EP levels in migraine sufferers. Pain 1984; 18:127-133. pmid:6324056
- Hindiyeh NA, Krusz JC, Cowan RP. Does exercise make migraines worse and tension type headaches better? Curr Pain Headache Rep 2013;17:380. pmid:24234818
- Kroll LS, Sjodahl Hammarlund C, Gard G, Jensen RH, Bendtsen L. Has aerobic exercise effect on pain perception in persons with migraine and coexisting tension-type headache and neck pain? A randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Eur J Pain 2018; 10:10. pmid:29635806
- Santiago MD, Carvalho Dde S, Gabbai AA, Pinto MM, Moutran AR, Villa TR. Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2014; 72(11):851-855. pmid:25410451
- Varkey E, Cider A, Carlsson J, Linde M. Exercise as migraine prophylaxis: a randomized study using relaxation and topiramate as controls. Cephalalgia 2011; 31(14):1428-1438. pmid:21890526
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, et al. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011; 43(7):1334-1359. pmid:21694556
- Guarnieri P, Radnitz CL, Blanchard EB. Assessment of dietary risk factors in chronic headache. Biofeedback Self Regul 1990; 15(1):15–25. pmid:2361144
- Shapiro RE. Caffeine and headaches. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(4):311–315. pmid:18625110
- Yokoyama M, Yokoyama T, Funazu K, et al. Associations between headache and stress, alcohol drinking, exercise, sleep, and comorbid health conditions in a Japanese population. J Headache Pain 2009; 10(3):177–185. doi:10.1007/s10194-009-0113-7
- Karsan N, Bose P, Goadsby PJ. The migraine premonitory phase. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2018; 24(4, Headache):996–1008. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000624
- Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB. Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies. Headache 2014; 54(10):1670–1679. doi:10.1111/head.12468
- Marcus DA, Scharff L, Turk D, Gourley LM. A double-blind provocative study of chocolate as a trigger of headache. Cephalalgia 1997; 17(8):855–862. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.1997.1708855.x
- Obayashi Y, Nagamura Y. Does monosodium glutamate really cause headache? A systematic review of human studies. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:54. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0639-4
- Evans EW, Lipton RB, Peterlin BL, et al. Dietary intake patterns and diet quality in a nationally representative sample of women with and without severe headache or migraine. Headache 2015; 55(4):550–561. doi:10.1111/head.12527
- Zis P, Julian T, Hadjivassiliou M. Headache associated with coeliac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018; 10(10). doi:10.3390/nu10101445
- Alpay K, Ertas M, Orhan EK, Ustay DK, Lieners C, Baykan B. Diet restriction in migraine, based on IgG against foods: a clinical double-blind, randomised, cross-over trial. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(7):829–837. doi:10.1177/0333102410361404
- Aydinlar EI, Dikmen PY, Tiftikci A, et al. IgG-based elimination diet in migraine plus irritable bowel syndrome. Headache 2013; 53(3):514–525. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02296.x
- Mitchell N, Hewitt CE, Jayakody S, et al. Randomised controlled trial of food elimination diet based on IgG antibodies for the prevention of migraine like headaches. Nutr J 2011; 10:85. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-85
- Wantke F, Gotz M, Jarisch R. Histamine-free diet: treatment of choice for histamine-induced food intolerance and supporting treatment for chronic headaches. Clin Exp Allergy 1993; 23(12):982–985. pmid:10779289
- Mansfield LE, Vaughan TR, Waller SF, Haverly RW, Ting S. Food allergy and adult migraine: double-blind and mediator confirmation of an allergic etiology. Ann Allergy 1985; 55(2):126–129. pmid:4025956
- Kohlenberg RJ. Tyramine sensitivity in dietary migraine: a critical review. Headache 1982; 22(1):30–34. pmid:17152742
- Medina JL, Diamond S. The role of diet in migraine. Headache 1978; 18(1):31–34. pmid:649377
- Mosnaim AD, Freitag F, Ignacio R, et al. Apparent lack of correlation between tyramine and phenylethylamine content and the occurrence of food-precipitated migraine. Reexamination of a variety of food products frequently consumed in the United States and commonly restricted in tyramine-free diets. Headache Quarterly. Current Treatment and Research 1996; 7(3):239–249.
- Ferrara LA, Pacioni D, Di Fronzo V, et al. Low-lipid diet reduces frequency and severity of acute migraine attacks. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2015; 25(4):370–375. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2014.12.006
- Bic Z, Blix GG, Hopp HP, Leslie FM, Schell MJ. The influence of a low-fat diet on incidence and severity of migraine headaches. J Womens Health Gend Based Med 1999; 8(5):623–630. doi:10.1089/jwh.1.1999.8.623
- Bunner AE, Agarwal U, Gonzales JF, Valente F, Barnard ND. Nutrition intervention for migraine: a randomized crossover trial. J Headache Pain 2014; 15:69. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-69
- Evcili G, Utku U, Ogun MN, Ozdemir G. Early and long period follow-up results of low glycemic index diet for migraine prophylaxis. Agri 2018; 30(1):8–11. doi:10.5505/agri.2017.62443
- Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L, Mansoori A, Abed R, Shishehbor F. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on the frequency, severity, and duration of migraine attacks: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(9):614–623. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1344371
- Soares AA, Loucana PMC, Nasi EP, Sousa KMH, Sa OMS, Silva-Neto RP. A double- blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (OPFA Ω-3) for the prevention of migraine in chronic migraine patients using amitriptyline. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(3):219–223. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2016.1266133
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Sirianni G, et al. Migraine improvement during short lasting ketogenesis: a proof-of-concept study. Eur J Neurol 2015; 22(1):170–177. doi:10.1111/ene.12550
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Bracaglia M, et al. Cortical functional correlates of responsiveness to short-lasting preventive intervention with ketogenic diet in migraine: a multimodal evoked potentials study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:58. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0650-9
- Kossoff EH, Huffman J, Turner Z, Gladstein J. Use of the modified Atkins diet for adolescents with chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(8):1014–1016. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.02016.x
- Slavin M, Ailani J. A clinical approach to addressing diet with migraine patients. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2017; 17(2):17. doi:10.1007/s11910-017-0721-6
- Amer M, Woodward M, Appel LJ. Effects of dietary sodium and the DASH diet on the occurrence of headaches: results from randomised multicentre DASH-sodium clinical trial. BMJ Open 2014; 4(12):e006671. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006671
- Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen W, Whelton PK, Appel LJ. Lower sodium intake and risk of headaches: results from the trial of nonpharmacologic interventions in the elderly. Am J Public Health 2016; 106(7):1270–1275. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303143
- Pogoda JM, Gross NB, Arakaki X, Fonteh AN, Cowan RP, Harrington MG. Severe headache or migraine history is inversely correlated with dietary sodium intake: NHANES 1999–2004. Headache 2016; 56(4):688–698. doi:10.1111/head.12792
- Awada A, al Jumah M. The first-of-Ramadan headache. Headache 1999; 39(7):490–493. pmid:11279933
- Abu-Salameh I, Plakht Y, Ifergane G. Migraine exacerbation during Ramadan fasting. J Headache Pain 2010; 11(6):513–517. doi:10.1007/s10194-010-0242-z
- Nazari F, Safavi M, Mahmudi M. Migraine and its relation with lifestyle in women. Pain Pract 2010; 10(3):228–234. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2009.00343.x
- Nas A, Mirza N, Hagele F, et al. Impact of breakfast skipping compared with dinner skipping on regulation of energy balance and metabolic risk. Am J Clin Nutr 2017; 105(6):1351–1361. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151332
- Torelli P, Manzoni GC. Fasting headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2010; 14(4):284–291. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0119-5
- Yoshimura E, Hatamoto Y, Yonekura S, Tanaka H. Skipping breakfast reduces energy intake and physical activity in healthy women who are habitual breakfast eaters: a randomized crossover trial. Physiol Behav 2017; 174:89–94. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.008
- Pendergast FJ, Livingstone KM, Worsley A, McNaughton SA. Correlates of meal skipping in young adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2016; 13(1):125. doi:10.1186/s12966-016-0451-1
- Maki KC, Phillips-Eakley AK, Smith KN. The effects of breakfast consumption and composition on metabolic wellness with a focus on carbohydrate metabolism. Adv Nutr 2016; 7(3):613S–621S. doi:10.3945/an.115.010314
- Shirreffs SM, Merson SJ, Fraser SM, Archer DT. The effects of fluid restriction on hydration status and subjective feelings in man. Br J Nutr 2004; 91(6):951–958. doi:10.1079/BJN20041149
- Blau JN. Water deprivation: a new migraine precipitant. Headache 2005; 45(6):757–759. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05143_3.x
- Price A, Burls A. Increased water intake to reduce headache: learning from a critical appraisal. J Eval Clin Pract 2015; 21(6):1212–1218. doi:10.1111/jep.12413
- Balbin JE, Nerenberg R, Baratloo A, Friedman BW. Intravenous fluids for migraine: a post hoc analysis of clinical trial data. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34(4):713–716. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.12.080
- Spigt M, Weerkamp N, Troost J, van Schayck CP, Knottnerus JA. A randomized trial on the effects of regular water intake in patients with recurrent headaches. Fam Pract 2012; 29(4):370–375. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmr112
- Armstrong LE, Johnson EC. Water intake, water balance, and the elusive daily water requirement. Nutrients 2018; 10(12). doi:10.3390/nu10121928
- Fried NT, Elliott MB, Oshinsky ML. The role of adenosine signaling in headache: a review. Brain Sci 2017; 7(3). doi:10.3390/brainsci7030030
- Lee MJ, Choi HA, Choi H, Chung CS. Caffeine discontinuation improves acute migraine treatment: a prospective clinic-based study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17(1):71. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0662-5
- Shirlow MJ, Mathers CD. A study of caffeine consumption and symptoms; indigestion, palpitations, tremor, headache and insomnia. Int J Epidemiol 1985; 14(2):239–248. doi:10.1093/ije/14.2.239
- Silverman K, Evans SM, Strain EC, Griffiths RR. Withdrawal syndrome after the double-blind cessation of caffeine consumption. N Engl J Med 1992; 327(16):1109–1114. doi:10.1056/NEJM199210153271601
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018; 38(1):1–211. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202
- Krogh AB, Larsson B, Salvesen O, Linde M. A comparison between prospective Internet-based and paper diary recordings of headache among adolescents in the general population. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(4):335–345. doi:10.1177/0333102415591506
- Bandarian-Balooch S, Martin PR, McNally B, Brunelli A, Mackenzie S. Electronic-diary for recording headaches, triggers, and medication use: development and evaluation. Headache 2017; 57(10):1551–1569. doi:10.1111/head.13184
- Tassorelli C, Sances G, Allena M, et al. The usefulness and applicability of a basic headache diary before first consultation: results of a pilot study conducted in two centres. Cephalalgia 2008; 28(10):1023–1030. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01639.x
- Baos V, Ester F, Castellanos A, et al. Use of a structured migraine diary improves patient and physician communication about migraine disability and treatment outcomes. Int J Clin Pract 2005; 59(3):281–286. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00469.x
- Martin PR, MacLeod C. Behavioral management of headache triggers: avoidance of triggers is an inadequate strategy. Clin Psychol Rev 2009; 29(6):483–495. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.05.002
- Giannini G, Zanigni S, Grimaldi D, et al. Cephalalgiaphobia as a feature of high-frequency migraine: a pilot study. J Headache Pain 2013; 14:49. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-14-49
- Westergaard ML, Glumer C, Hansen EH, Jensen RH. Medication overuse, healthy lifestyle behaviour and stress in chronic headache: results from a population-based representative survey. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(1):15–28. doi:10.1177/0333102415578430
- Christiansen S, Jurgens TP, Klinger R. Outpatient combined group and individual cognitive-behavioral treatment for patients with migraine and tension-type headache in a routine clinical setting. Headache 2015; 55(8):1072–1091. doi:10.1111/head.12626
- Martin PR, Aiello R, Gilson K, Meadows G, Milgrom J, Reece J. Cognitive behavior therapy for comorbid migraine and/or tension-type headache and major depressive disorder: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Behav Res Ther 2015; 73:8–18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2015.07.005
- Nash JM, Park ER, Walker BB, Gordon N, Nicholson RA. Cognitive-behavioral group treatment for disabling headache. Pain Med 2004; 5(2):178–186. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2004.04031.x
- Sorbi MJ, Balk Y, Kleiboer AM, Couturier EG. Follow-up over 20 months confirms gains of online behavioural training in frequent episodic migraine. Cephalalgia 2017; 37(3):236–250. doi:10.1177/0333102416657145
- Thorn BE, Pence LB, Ward LC, et al. A randomized clinical trial of targeted cognitive behavioral treatment to reduce catastrophizing in chronic headache sufferers. J Pain 2007; 8(12):938–949. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2007.06.010
- Nestoriuc Y, Martin A. Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis. Pain 2007; 128(1–2):111–127. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007
- Blanchard EB, Appelbaum KA, Nicholson NL, et al. A controlled evaluation of the addition of cognitive therapy to a home-based biofeedback and relaxation treatment of vascular headache. Headache 1990; 30(6):371–376. pmid:2196240
- Gu Q, Hou JC, Fang XM. Mindfulness meditation for primary headache pain: a meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2018; 131(7):829–838. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.228242
- Day MA, Thorn BE. The mediating role of pain acceptance during mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for headache. Complement Ther Med 2016; 25:51–54. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2016.01.002
- Williamson DA, Monguillot JE, Jarrell MP, Cohen RA, Pratt JM, Blouin DC. Relaxation for the treatment of headache. Controlled evaluation of two group programs. Behav Modif 1984; 8(3):407–424. doi:10.1177/01454455840083007
- Merelle SY, Sorbi MJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Passchier J. Qualities and health of lay trainers with migraine for behavioral attack prevention. Headache 2010; 50(4):613–625. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01241.x
- Gaul C, van Doorn C, Webering N, et al. Clinical outcome of a headache-specific multidisciplinary treatment program and adherence to treatment recommendations in a tertiary headache center: an observational study. J Headache Pain 2011; 12(4):475–483. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0348-y
- Wallasch TM, Kropp P. Multidisciplinary integrated headache care: a prospective 12-month follow-up observational study. J Headache Pain 2012; 13(7):521–529. doi:10.1007/s10194-012-0469-y
- Lemstra M, Stewart B, Olszynski WP. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary intervention in the treatment of migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Headache 2002; 42(9):845–854. pmid:12390609
- Krause SJ, Stillman MJ, Tepper DE, Zajac D. A prospective cohort study of outpatient interdisciplinary rehabilitation of chronic headache patients. Headache 2017; 57(3):428–440. doi:10.1111/head.13020
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017; 390(10100):1211–1259. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2
- Vgontzas A, Pavlovic JM. Sleep diorders and migraine: review of literature and potential pathophysiology mechanisms. Headache 2018; 58(7):1030–1039. doi:10.1111/head.13358
- Lund N, Westergaard ML, Barloese M, Glumer C, Jensen RH. Epidemiology of concurrent headache and sleep problems in Denmark. Cephalalgia 2014; 34(10):833–845. doi:10.1177/0333102414543332
- Woldeamanuel YW, Cowan RP. The impact of regular lifestyle behavior in migraine: a prevalence case-referent study. J Neurol 2016; 263(4):669–676. doi:10.1007/s00415-016-8031-5
- Chung F, Abdullah HR, Liao P. STOP-Bang questionnaire: a practical approach to screen for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2016; 149(3):631–638. doi:10.1378/chest.15-0903
- Johnson KG, Ziemba AM, Garb JL. Improvement in headaches with continuous positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea: a retrospective analysis. Headache 2013; 53(2):333–343. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02251.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S. Behavioral sleep modification may revert transformed migraine to episodic migraine. Headache 2007; 47(8):1178–1183. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.00780.x
- Calhoun AH, Ford S, Finkel AG, Kahn KA, Mann JD. The prevalence and spectrum of sleep problems in women with transformed migraine. Headache 2006; 46(4):604–610. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00410.x
- Rains JC. Optimizing circadian cycles and behavioral insomnia treatment in migraine. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(3):213–219. pmid:18796272
- Lemmens J, De Pauw J, Van Soom T, et al. The effect of aerobic exercise on the number of migraine days, duration and pain intensity in migraine: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J Headache Pain 2019; 20(1):16. doi:10.1186/s10194-019-0961-8
- Amin FM, Aristeidou S, Baraldi C, et al; European Headache Federation School of Advanced Studies (EHF-SAS). The association between migraine and physical exercise. J Headache Pain 2018; 19(1):83. doi:10.1186/s10194-018-0902-y
- Genazzani AR, Nappi G, Facchinetti F, et al. Progressive impairment of CSF beta-EP levels in migraine sufferers. Pain 1984; 18:127-133. pmid:6324056
- Hindiyeh NA, Krusz JC, Cowan RP. Does exercise make migraines worse and tension type headaches better? Curr Pain Headache Rep 2013;17:380. pmid:24234818
- Kroll LS, Sjodahl Hammarlund C, Gard G, Jensen RH, Bendtsen L. Has aerobic exercise effect on pain perception in persons with migraine and coexisting tension-type headache and neck pain? A randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Eur J Pain 2018; 10:10. pmid:29635806
- Santiago MD, Carvalho Dde S, Gabbai AA, Pinto MM, Moutran AR, Villa TR. Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2014; 72(11):851-855. pmid:25410451
- Varkey E, Cider A, Carlsson J, Linde M. Exercise as migraine prophylaxis: a randomized study using relaxation and topiramate as controls. Cephalalgia 2011; 31(14):1428-1438. pmid:21890526
- Garber CE, Blissmer B, Deschenes MR, et al. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011; 43(7):1334-1359. pmid:21694556
- Guarnieri P, Radnitz CL, Blanchard EB. Assessment of dietary risk factors in chronic headache. Biofeedback Self Regul 1990; 15(1):15–25. pmid:2361144
- Shapiro RE. Caffeine and headaches. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2008; 12(4):311–315. pmid:18625110
- Yokoyama M, Yokoyama T, Funazu K, et al. Associations between headache and stress, alcohol drinking, exercise, sleep, and comorbid health conditions in a Japanese population. J Headache Pain 2009; 10(3):177–185. doi:10.1007/s10194-009-0113-7
- Karsan N, Bose P, Goadsby PJ. The migraine premonitory phase. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2018; 24(4, Headache):996–1008. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000624
- Pavlovic JM, Buse DC, Sollars CM, Haut S, Lipton RB. Trigger factors and premonitory features of migraine attacks: summary of studies. Headache 2014; 54(10):1670–1679. doi:10.1111/head.12468
- Marcus DA, Scharff L, Turk D, Gourley LM. A double-blind provocative study of chocolate as a trigger of headache. Cephalalgia 1997; 17(8):855–862. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.1997.1708855.x
- Obayashi Y, Nagamura Y. Does monosodium glutamate really cause headache? A systematic review of human studies. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:54. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0639-4
- Evans EW, Lipton RB, Peterlin BL, et al. Dietary intake patterns and diet quality in a nationally representative sample of women with and without severe headache or migraine. Headache 2015; 55(4):550–561. doi:10.1111/head.12527
- Zis P, Julian T, Hadjivassiliou M. Headache associated with coeliac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2018; 10(10). doi:10.3390/nu10101445
- Alpay K, Ertas M, Orhan EK, Ustay DK, Lieners C, Baykan B. Diet restriction in migraine, based on IgG against foods: a clinical double-blind, randomised, cross-over trial. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(7):829–837. doi:10.1177/0333102410361404
- Aydinlar EI, Dikmen PY, Tiftikci A, et al. IgG-based elimination diet in migraine plus irritable bowel syndrome. Headache 2013; 53(3):514–525. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02296.x
- Mitchell N, Hewitt CE, Jayakody S, et al. Randomised controlled trial of food elimination diet based on IgG antibodies for the prevention of migraine like headaches. Nutr J 2011; 10:85. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-10-85
- Wantke F, Gotz M, Jarisch R. Histamine-free diet: treatment of choice for histamine-induced food intolerance and supporting treatment for chronic headaches. Clin Exp Allergy 1993; 23(12):982–985. pmid:10779289
- Mansfield LE, Vaughan TR, Waller SF, Haverly RW, Ting S. Food allergy and adult migraine: double-blind and mediator confirmation of an allergic etiology. Ann Allergy 1985; 55(2):126–129. pmid:4025956
- Kohlenberg RJ. Tyramine sensitivity in dietary migraine: a critical review. Headache 1982; 22(1):30–34. pmid:17152742
- Medina JL, Diamond S. The role of diet in migraine. Headache 1978; 18(1):31–34. pmid:649377
- Mosnaim AD, Freitag F, Ignacio R, et al. Apparent lack of correlation between tyramine and phenylethylamine content and the occurrence of food-precipitated migraine. Reexamination of a variety of food products frequently consumed in the United States and commonly restricted in tyramine-free diets. Headache Quarterly. Current Treatment and Research 1996; 7(3):239–249.
- Ferrara LA, Pacioni D, Di Fronzo V, et al. Low-lipid diet reduces frequency and severity of acute migraine attacks. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2015; 25(4):370–375. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2014.12.006
- Bic Z, Blix GG, Hopp HP, Leslie FM, Schell MJ. The influence of a low-fat diet on incidence and severity of migraine headaches. J Womens Health Gend Based Med 1999; 8(5):623–630. doi:10.1089/jwh.1.1999.8.623
- Bunner AE, Agarwal U, Gonzales JF, Valente F, Barnard ND. Nutrition intervention for migraine: a randomized crossover trial. J Headache Pain 2014; 15:69. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-15-69
- Evcili G, Utku U, Ogun MN, Ozdemir G. Early and long period follow-up results of low glycemic index diet for migraine prophylaxis. Agri 2018; 30(1):8–11. doi:10.5505/agri.2017.62443
- Maghsoumi-Norouzabad L, Mansoori A, Abed R, Shishehbor F. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on the frequency, severity, and duration of migraine attacks: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(9):614–623. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2017.1344371
- Soares AA, Loucana PMC, Nasi EP, Sousa KMH, Sa OMS, Silva-Neto RP. A double- blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled clinical trial with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (OPFA Ω-3) for the prevention of migraine in chronic migraine patients using amitriptyline. Nutr Neurosci 2018; 21(3):219–223. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2016.1266133
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Sirianni G, et al. Migraine improvement during short lasting ketogenesis: a proof-of-concept study. Eur J Neurol 2015; 22(1):170–177. doi:10.1111/ene.12550
- Di Lorenzo C, Coppola G, Bracaglia M, et al. Cortical functional correlates of responsiveness to short-lasting preventive intervention with ketogenic diet in migraine: a multimodal evoked potentials study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17:58. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0650-9
- Kossoff EH, Huffman J, Turner Z, Gladstein J. Use of the modified Atkins diet for adolescents with chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia 2010; 30(8):1014–1016. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.02016.x
- Slavin M, Ailani J. A clinical approach to addressing diet with migraine patients. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2017; 17(2):17. doi:10.1007/s11910-017-0721-6
- Amer M, Woodward M, Appel LJ. Effects of dietary sodium and the DASH diet on the occurrence of headaches: results from randomised multicentre DASH-sodium clinical trial. BMJ Open 2014; 4(12):e006671. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006671
- Chen L, Zhang Z, Chen W, Whelton PK, Appel LJ. Lower sodium intake and risk of headaches: results from the trial of nonpharmacologic interventions in the elderly. Am J Public Health 2016; 106(7):1270–1275. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2016.303143
- Pogoda JM, Gross NB, Arakaki X, Fonteh AN, Cowan RP, Harrington MG. Severe headache or migraine history is inversely correlated with dietary sodium intake: NHANES 1999–2004. Headache 2016; 56(4):688–698. doi:10.1111/head.12792
- Awada A, al Jumah M. The first-of-Ramadan headache. Headache 1999; 39(7):490–493. pmid:11279933
- Abu-Salameh I, Plakht Y, Ifergane G. Migraine exacerbation during Ramadan fasting. J Headache Pain 2010; 11(6):513–517. doi:10.1007/s10194-010-0242-z
- Nazari F, Safavi M, Mahmudi M. Migraine and its relation with lifestyle in women. Pain Pract 2010; 10(3):228–234. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2009.00343.x
- Nas A, Mirza N, Hagele F, et al. Impact of breakfast skipping compared with dinner skipping on regulation of energy balance and metabolic risk. Am J Clin Nutr 2017; 105(6):1351–1361. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.151332
- Torelli P, Manzoni GC. Fasting headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2010; 14(4):284–291. doi:10.1007/s11916-010-0119-5
- Yoshimura E, Hatamoto Y, Yonekura S, Tanaka H. Skipping breakfast reduces energy intake and physical activity in healthy women who are habitual breakfast eaters: a randomized crossover trial. Physiol Behav 2017; 174:89–94. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.03.008
- Pendergast FJ, Livingstone KM, Worsley A, McNaughton SA. Correlates of meal skipping in young adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2016; 13(1):125. doi:10.1186/s12966-016-0451-1
- Maki KC, Phillips-Eakley AK, Smith KN. The effects of breakfast consumption and composition on metabolic wellness with a focus on carbohydrate metabolism. Adv Nutr 2016; 7(3):613S–621S. doi:10.3945/an.115.010314
- Shirreffs SM, Merson SJ, Fraser SM, Archer DT. The effects of fluid restriction on hydration status and subjective feelings in man. Br J Nutr 2004; 91(6):951–958. doi:10.1079/BJN20041149
- Blau JN. Water deprivation: a new migraine precipitant. Headache 2005; 45(6):757–759. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2005.05143_3.x
- Price A, Burls A. Increased water intake to reduce headache: learning from a critical appraisal. J Eval Clin Pract 2015; 21(6):1212–1218. doi:10.1111/jep.12413
- Balbin JE, Nerenberg R, Baratloo A, Friedman BW. Intravenous fluids for migraine: a post hoc analysis of clinical trial data. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34(4):713–716. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2015.12.080
- Spigt M, Weerkamp N, Troost J, van Schayck CP, Knottnerus JA. A randomized trial on the effects of regular water intake in patients with recurrent headaches. Fam Pract 2012; 29(4):370–375. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmr112
- Armstrong LE, Johnson EC. Water intake, water balance, and the elusive daily water requirement. Nutrients 2018; 10(12). doi:10.3390/nu10121928
- Fried NT, Elliott MB, Oshinsky ML. The role of adenosine signaling in headache: a review. Brain Sci 2017; 7(3). doi:10.3390/brainsci7030030
- Lee MJ, Choi HA, Choi H, Chung CS. Caffeine discontinuation improves acute migraine treatment: a prospective clinic-based study. J Headache Pain 2016; 17(1):71. doi:10.1186/s10194-016-0662-5
- Shirlow MJ, Mathers CD. A study of caffeine consumption and symptoms; indigestion, palpitations, tremor, headache and insomnia. Int J Epidemiol 1985; 14(2):239–248. doi:10.1093/ije/14.2.239
- Silverman K, Evans SM, Strain EC, Griffiths RR. Withdrawal syndrome after the double-blind cessation of caffeine consumption. N Engl J Med 1992; 327(16):1109–1114. doi:10.1056/NEJM199210153271601
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018; 38(1):1–211. doi:10.1177/0333102417738202
- Krogh AB, Larsson B, Salvesen O, Linde M. A comparison between prospective Internet-based and paper diary recordings of headache among adolescents in the general population. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(4):335–345. doi:10.1177/0333102415591506
- Bandarian-Balooch S, Martin PR, McNally B, Brunelli A, Mackenzie S. Electronic-diary for recording headaches, triggers, and medication use: development and evaluation. Headache 2017; 57(10):1551–1569. doi:10.1111/head.13184
- Tassorelli C, Sances G, Allena M, et al. The usefulness and applicability of a basic headache diary before first consultation: results of a pilot study conducted in two centres. Cephalalgia 2008; 28(10):1023–1030. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01639.x
- Baos V, Ester F, Castellanos A, et al. Use of a structured migraine diary improves patient and physician communication about migraine disability and treatment outcomes. Int J Clin Pract 2005; 59(3):281–286. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2005.00469.x
- Martin PR, MacLeod C. Behavioral management of headache triggers: avoidance of triggers is an inadequate strategy. Clin Psychol Rev 2009; 29(6):483–495. doi:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.05.002
- Giannini G, Zanigni S, Grimaldi D, et al. Cephalalgiaphobia as a feature of high-frequency migraine: a pilot study. J Headache Pain 2013; 14:49. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-14-49
- Westergaard ML, Glumer C, Hansen EH, Jensen RH. Medication overuse, healthy lifestyle behaviour and stress in chronic headache: results from a population-based representative survey. Cephalalgia 2016; 36(1):15–28. doi:10.1177/0333102415578430
- Christiansen S, Jurgens TP, Klinger R. Outpatient combined group and individual cognitive-behavioral treatment for patients with migraine and tension-type headache in a routine clinical setting. Headache 2015; 55(8):1072–1091. doi:10.1111/head.12626
- Martin PR, Aiello R, Gilson K, Meadows G, Milgrom J, Reece J. Cognitive behavior therapy for comorbid migraine and/or tension-type headache and major depressive disorder: an exploratory randomized controlled trial. Behav Res Ther 2015; 73:8–18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2015.07.005
- Nash JM, Park ER, Walker BB, Gordon N, Nicholson RA. Cognitive-behavioral group treatment for disabling headache. Pain Med 2004; 5(2):178–186. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4637.2004.04031.x
- Sorbi MJ, Balk Y, Kleiboer AM, Couturier EG. Follow-up over 20 months confirms gains of online behavioural training in frequent episodic migraine. Cephalalgia 2017; 37(3):236–250. doi:10.1177/0333102416657145
- Thorn BE, Pence LB, Ward LC, et al. A randomized clinical trial of targeted cognitive behavioral treatment to reduce catastrophizing in chronic headache sufferers. J Pain 2007; 8(12):938–949. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2007.06.010
- Nestoriuc Y, Martin A. Efficacy of biofeedback for migraine: a meta-analysis. Pain 2007; 128(1–2):111–127. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.007
- Blanchard EB, Appelbaum KA, Nicholson NL, et al. A controlled evaluation of the addition of cognitive therapy to a home-based biofeedback and relaxation treatment of vascular headache. Headache 1990; 30(6):371–376. pmid:2196240
- Gu Q, Hou JC, Fang XM. Mindfulness meditation for primary headache pain: a meta-analysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2018; 131(7):829–838. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.228242
- Day MA, Thorn BE. The mediating role of pain acceptance during mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for headache. Complement Ther Med 2016; 25:51–54. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2016.01.002
- Williamson DA, Monguillot JE, Jarrell MP, Cohen RA, Pratt JM, Blouin DC. Relaxation for the treatment of headache. Controlled evaluation of two group programs. Behav Modif 1984; 8(3):407–424. doi:10.1177/01454455840083007
- Merelle SY, Sorbi MJ, Duivenvoorden HJ, Passchier J. Qualities and health of lay trainers with migraine for behavioral attack prevention. Headache 2010; 50(4):613–625. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01241.x
- Gaul C, van Doorn C, Webering N, et al. Clinical outcome of a headache-specific multidisciplinary treatment program and adherence to treatment recommendations in a tertiary headache center: an observational study. J Headache Pain 2011; 12(4):475–483. doi:10.1007/s10194-011-0348-y
- Wallasch TM, Kropp P. Multidisciplinary integrated headache care: a prospective 12-month follow-up observational study. J Headache Pain 2012; 13(7):521–529. doi:10.1007/s10194-012-0469-y
- Lemstra M, Stewart B, Olszynski WP. Effectiveness of multidisciplinary intervention in the treatment of migraine: a randomized clinical trial. Headache 2002; 42(9):845–854. pmid:12390609
- Krause SJ, Stillman MJ, Tepper DE, Zajac D. A prospective cohort study of outpatient interdisciplinary rehabilitation of chronic headache patients. Headache 2017; 57(3):428–440. doi:10.1111/head.13020
KEY POINTS
- Sleep: Standard sleep hygiene recommendations to maximize sleep quantity and quality.
- Exercise: 30 to 60 minutes 3 to 5 times a week.
- Eat: Regular healthy meals, adequate hydration, and low or stable caffeine intake.
- Diary: Establish a baseline pattern, assess response to treatment, and monitor analgesia to improve accuracy of migraine diagnosis.
- Stress: Cognitive behavioral therapy, mindfulness, relaxation, biofeedback, and provider-patient trust to minimize anxiety.
2019 Update on minimally invasive gynecologic surgery
Through the years, the surgical approach to hysterectomy has expanded from its early beginnings of being performed only through an abdominal or transvaginal route with traditional surgical clamps and suture. The late 1980s saw the advent of the laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH), and from that point forward several additional hysterectomy methods evolved, including today’s robotic approaches.
Although clinical evidence and societal endorsements support vaginal hysterectomy as a superior high-value modality, it remains one of the least performed among all available routes.1-3 In an analysis of inpatient hysterectomies published by Wright and colleagues in 2013, 16.7% of hysterectomies were performed vaginally, a number that essentially has remained steady throughout the ensuing years.4
Attempts to improve the application of vaginal hysterectomy have been made.5 These include the development of various curriculum and simulation-based medical education programs on vaginal surgical skills training and acquisition in the hopes of improving utilization.6 An interesting recent development is the rethinking of vaginal hysterectomy by several surgeons globally who are applying facets of the various hysterectomy methods to a transvaginal approach known as vaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (vNOTES).7,8 Unique to this thinking is the incorporation of conventional laparoscopic instrumentation.
Although I have not yet incorporated this approach in my surgical armamentarium at Columbia University Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, I am intrigued by the possibility that this technique may serve as a rescue for vaginal hysterectomies that are at risk of conversion or of not being performed at all.9
At this time, vNOTES is not a standard of care and should be performed only by highly specialized surgeons. However, in the spirit of this Update on minimally invasive surgery and to keep our readers abreast of burgeoning techniques, I am delighted to bring you this overview by Dr. Xiaoming Guan, one of the pioneers of this surgical approach, and Dr. Tamisa Koythong and Dr. Juan Liu. I hope you find this recent development in hysterectomy of interest.
—Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Continue to: Development and evolution of NOTES...
Development and evolution of NOTES
Over the past few decades, emphasis has shifted from laparotomy to minimally invasive surgery because of its proven significant advantages in patient care, such as improved cosmesis, shorter hospital stay, shorter postoperative recovery, and decreased postoperative pain and blood loss.10 Advances in laparoendoscopic surgery and instrumentation, including robot-assisted laparoscopy (RAL), single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS), and most recently natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), reflect ongoing innovative developments in the field of minimally invasive surgery.
Here, we provide a brief literature review of the NOTES technique, focus on its application in gynecologic surgery, and describe how we perform NOTES at our institution.
NOTES application in gynecology
With NOTES, peritoneal access is gained through a natural orifice (such as the mouth, vagina, urethra, or anus) to perform endoscopic surgery, occasionally without requiring an abdominal incision. First described in 2004, transgastric peritoneoscopy was performed in a porcine model, and shortly thereafter the first transgastric appendectomy was performed in humans.11,12 The technique has further been adopted in cholecystectomy, appendectomy, gastrectomy, and nephrectomy procedures.13
Given rapid interest in a possible paradigm shift in the field of minimally invasive surgery, the Natural Orifice Surgery Consortiumfor Assessment and Research (NOSCAR) was formed, and the group published an article on potential barriers to accepted practice and adoption of NOTES as a realistic alternative to traditional laparoscopic surgery.14
While transgastric and transanal access to the peritoneum were initially more popular, the risk of anastomotic leaks associated with incomplete closure and subsequent infection were thought to be prohibitively high.15 Transvaginal access was considered a safer and simpler alternative, allowing for complete closure without increased risk of infection, and this is now the route through which the majority of NOTES procedures are completed.16,17
The eventual application of NOTES in the field of gynecology seemed inevitable. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists stated that transvaginal surgery is the most minimally invasive and preferred surgical route in the management of patients with benign gynecologic diseases.18 However, performing it can be challenging at times due to limited visualization and lack of the required skills for single-site surgery. NOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon to improve visualization through the use of laparoendoscopic instruments and to complete surgery through a transvaginal route.
In 2012, Ahn and colleagues demonstrated the feasibility of the NOTES technique in gynecologic surgery after using it to successfully complete benign adnexal surgery in 10 patients.19 Vaginal NOTES (vNOTES) has since been further developed to include successful hysterectomy, myomectomy, sacrocolpopexy, tubal anastomosis, and even lymphadenectomy in the treatment of early- stage endometrial carcinoma.20-26 vNOTES also can be considered a rescue approach for traditional vaginal hysterectomy in instances in which it is necessary to evaluate adnexal pathology.9 Most recently, vNOTES hysterectomy has been reported with da Vinci Si or Xi robotic platforms.27,28
Continue to: Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients...
Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients
Few studies have compared outcomes with vNOTES to those with traditional laparoscopy. In 2016, Wang and colleagues compared surgical outcomes between NOTES-assisted ovarian cystectomy (NAOC) and laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (LOC) in a case-matched study that included 277 patients.29 Although mean (SD) blood loss in patients who underwent LOC was significantly less compared with those who underwent NAOC (21.4 [14.7] mL vs 31.6 [24.1] mL; P = .028), absolute blood loss in both groups was deemed minimal. Additionally, mean (SD) operative time and postoperative stay were significantly less in patients undergoing NAOC compared with those having LOC (38.23 [10.19] minutes vs 53.82 [18.61] minutes; P≤.001; and 1.38 [0.55] days vs 1.82 [0.52] days; P≤.001; respectively).29
How vNOTES hysterectomy stacked up against TLH
In 2018, Baekelandt and colleagues compared outcomes between vNOTES hysterectomy and total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) in a noninferiority single-blinded trial of 70 women.8 Compared with TLH, vNOTES hysterectomy was associated with shorter operative time (41 vs 75 minutes; P<.001), shorter hospital stay (0.8 vs 1.3 days; P = .004), and lower postoperative analgesic requirement (8 vs 14 U; P = .006). Additionally, there were no differences between the 2 groups in postoperative infection rate, intraoperative complications, or hospital readmissions within 6 weeks.8
Clearly, vNOTES is the next exciting development in minimally invasive surgery, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction with truly scarless surgery. Compared with traditional transvaginal surgery, vNOTES has the advantage of improved visualization with laparoendoscopic guidance, and it may be beneficial even for patients previously thought to have relative contraindications to successful completion of transvaginal surgery, such as nulliparity or a narrow introitus.
Approach for performing vNOTES procedures
At our institution, Baylor College of Medicine, the majority of gynecologic surgeries are performed via either transumbilical robot-assisted single-incision laparoscopy or vNOTES. Preoperative selection of appropriate candidates for vNOTES includes:
- low suspicion for or prior diagnosis of endometriosis with obliteration of the posterior cul-de-sac
- no surgical history suggestive of severe adhesive disease, and
- adequate vaginal sidewall access and sufficient descent for instrumentation for entry into the peritoneal cavity.
In general, a key concept in vNOTES is "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push," which means that the surgeon must pull the cervix while performing vaginal entry and then push the uterus back in the peritoneal cavity to increase surgical space during laparoscopic surgery.
Continue to: Overview of vNOTES steps...
Overview of vNOTES steps
Below we break down a description of vNOTES in 6 sections. Our patients are always placed in dorsal lithotomy position with TrenGuard (D.A. Surgical) Trendelenburg restraint. We prep the abdomen in case we need to convert to transabdominal surgery via transumbilical single-incision laparoscopic surgery or traditional laparoscopic surgery.
1. Vaginal entry
Accessing the peritoneal cavity through the vagina initially proceeds like a vaginal hysterectomy. We inject dilute vasopressin (20 U in 20 mL of normal saline) circumferentially in the cervix (for hysterectomy) or in the posterior cervix in the cervicovaginal junction (for adnexal surgery without hysterectomy) for vasoconstriction and hydrodissection.
We then incise the vaginal mucosa circumferentially with electrosurgical cautery and follow with posterior colpotomy. We find that reapproximating the posterior peritoneum to the posterior vagina with either figure-of-8 stitches or a running stitch of polyglactin 910 suture (2-0 Vicryl) assists in port placement, bleeding at the peritoneal edge, and closure of the cuff or colpotomy at the end of the case. We tag this suture with a curved hemostat.
Depending on whether a hysterectomy is being performed, anterior colpotomy is made. Again, the anterior peritoneum is then tagged to the anterior vaginal cuff in similar fashion, and this suture is tagged with a different instrument; we typically use a straight hemostat or Sarot clamp (FIGURE 1).
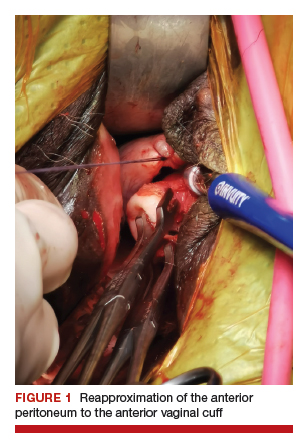
2. Traditional vaginal hysterectomy
After colpotomy, we prefer to perform progressive clamping of the broad ligament from the uterosacral and cardinal ligaments to the level of uterine artery as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy, if feasible.
3. Single-site port placement
The assembled GelPOINT Mini advanced access platform (Applied Medical) (FIGURE 2) is introduced through the vagina after the Alexis wound protector (included with the kit) is first placed through the colpotomy with assistance of Babcock clamps (FIGURE 3).
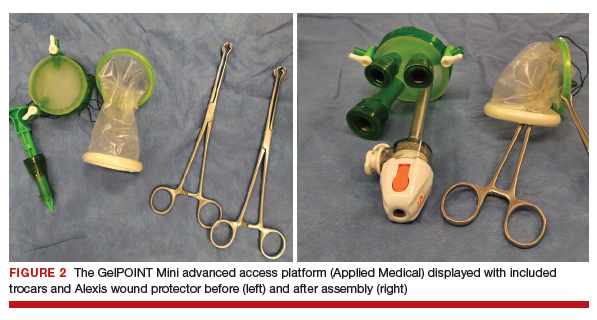

After ensuring that the green rigid ring of the Alexis wound protector is contained and completely expanded within the peritoneal cavity, we cross our previously tagged sutures as we find this helps with preventing the GelPOINT Mini access platform from inadvertently shifting out of the peritoneal cavity during surgery. The GelSeal cap is then secured and pneumoperitoneum is established (FIGURE 4).
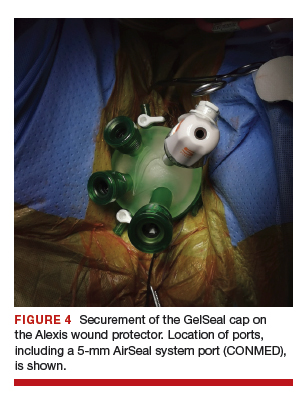
Continue to: 4. Laparoendoscopic surgery...
4. Laparoendoscopic surgery
Instruments used in our surgeries include a 10-mm rigid 30° 43-cm working length laparoscope; a 44-cm LigaSure device (Medtronic); a 5-mm, 37-cm laparoscopic cobra grasping forceps and fenestrated grasper (Karl Storz); and a 5-mm, 45-cm laparoscopic suction with hydrodissection tip (Stryker) (FIGURE 5).
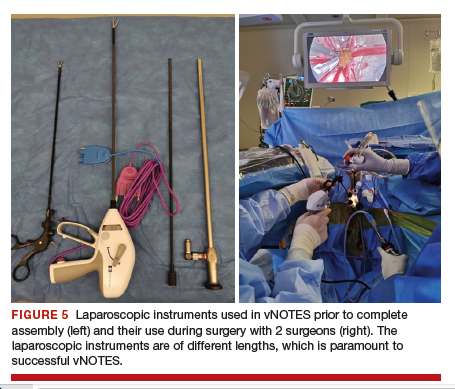
vNOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon the unique ability to survey the upper abdomen. The remainder of the surgery proceeds using basic laparoscopic single-site skills.
During vNOTES, as with all single-site surgical procedures, understanding the optimal placement of crossed instruments is important for successful completion. For example, when securing the right uterine artery, the surgeon needs to push the cervix toward the patient's left and slightly into the peritoneal cavity using a laparoscopic cobra grasper with his or her left hand while then securing the uterine pedicle using the LigaSure device with his or her right hand. This is then reversed when securing the left uterine artery, where the assistant surgeon pushes the cervix toward the patient's right while the surgeon secures the pedicle ("vaginal pull, laparoscopic push") (FIGURE 6).
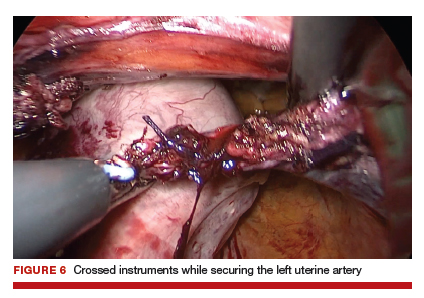
This again is reiterated in securing the ovarian pedicles, which are pushed into the peritoneal cavity while being secured with the LigaSure device.
5. Specimen removal
For large uteri or specimens that need morcellation, a 15-mm Endo Catch specimen retrieval bag (Medtronic) is introduced through the GelPOINT Mini system. The specimen is then placed in the bag and delivered to the vagina, where contained bag morcellation is performed in standard fashion (FIGURES 7 AND 8). We utilized the "big C" technique by first grasping the specimen with a penetrating clamp. The clamp is then held in our nondominant hand and a No. 10 blade scalpel is used to create a reverse c-incision, keeping one surface of the specimen intact. This is continued until the specimen can be completely delivered through the vagina.
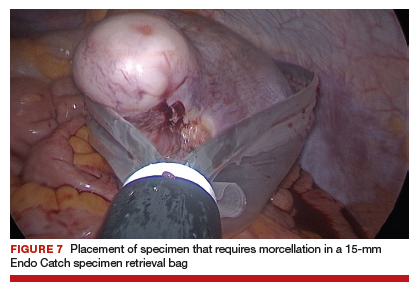
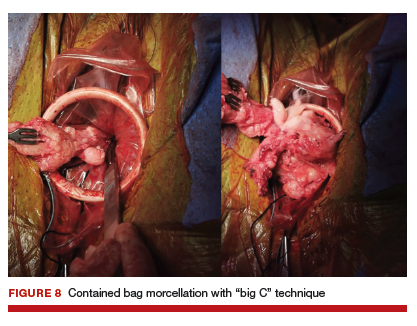
Specimens that do not require morcellation can be grasped laparoscopically, brought to the GelPOINT Mini port, which is quickly disassembled, and delivered. The GelSeal cap is then reassembled.
6. Vaginal cuff closure
The colpotomy or vaginal cuff is closed with barbed suture continuously, as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy cuff closure. Uterosacral ligament suspension should be performed for vaginal cuff support.
vNOTES is the most recent innovative development in the field of minimally invasive surgery, and it has demonstrated feasibility and safety in the fields of general surgery, urology, and gynecology. Adopting vNOTES in clinical practice can improve patient satisfaction and cosmesis as well as surgical outcomes. Gynecologic surgeons can think of vNOTES hysterectomy as "placing an eye" in the vagina while performing transvaginal hysterectomy. The surgical principle of "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push" facilitates the learning process.
1. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 444. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114:1156-1158.
2. AAGL Advancing Minimally Invasive Gynecology Worldwide. AAGL position statement: route of hysterectomy to treat benign uterine disease. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:1-3.
3. Whiteside JL, Kaeser CT, Ridgeway B. Achieving high value in the surgical approach to hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:242-245.
4. Wright JD, Herzog TJ, Tsui J, et al. Nationwide trends in the performance of inpatient hysterectomy in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(2 pt 1):233-241.
5. Moen M, Walter A, Harmanli O, et al. Considerations to improve the evidence-based use of vaginal hysterectomy in benign gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:585-588.
6. Balgobin S, Owens DM, Florian-Rodriguez ME, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy suturing skills training model and curriculum. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:553-558.
7. Baekelandt J. Total vaginal NOTES hysterectomy: a new approach to hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:1088-1094.
8. Baekelandt JF, De Mulder PA, Le Roy I, et al. Hysterectomy by transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery versus laparoscopy as a day-care procedure: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG. 2019;126:105-113.
9. Guan X, Bardawil E, Liu J, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery as a rescue for total vaginal hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:1135-1136.
10. Nieboer TE, Johnson N, Lethaby A, et al. Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;3:CD003677.
11. Kalloo AN, Singh VK, Jagannath SB, et al. Flexible transgastric peritoneoscopy: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:114-117.
12. Reddy N, Rao P. Per oral transgastric endoscopic appendectomy in human. Paper Presented at: 45th Annual Conference of the Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy of India; February 28-29, 2004; Jaipur, India.
13. Clark MP, Qayed ES, Kooby DA, et al. Natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery in humans: a review. Minim Invasive Surg. 2012;189296.
14. Rattner D, Kalloo A; ASGE/SAGES Working Group. ASGE/ SAGES Working Group on natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery, October 2005. Surg Endosc. 2006;20:329-333.
15. Autorino R, Yakoubi R, White WM, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): where are we going? A bibliometric assessment. BJU Int. 2013;111:11-16.
16. Santos BF, Hungness ES. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery: progress in humans since the white paper. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1655-1665.
17. Tolcher MC, Kalogera E, Hopkins MR, et al. Safety of culdotomy as a surgical approach: implications for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery. JSLS. 2012;16:413-420.
18. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 701. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2017:129:e155-e159.
19. Ahn KH, Song JY, Kim SH, et al. Transvaginal single-port natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for benign uterine adnexal pathologies. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:631-635.
20. Liu J, Kohn J, Sun B, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery sacrocolpopexy: tips and tricks. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:38-39.
21. Liu J, Kohn J, Fu H, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for sacrocolpopexy: a pilot study of 26 cases. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:748-753.
22. Su H, Yen CF, Wu KY, et al. Hysterectomy via transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): feasibility of an innovative approach. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51:217-221.
23. Lee CL, Huang CY, Wu KY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery myomectomy: an innovative approach to myomectomy. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:127-130.
24. Chen Y, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Transvaginal single-port laparoscopy sacrocolpopexy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:585- 588.
25. Lee CL, Wu KY, Tsao FY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery for endometrial cancer. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:89-92.
26. Leblanc E, Narducci F, Bresson L, et al. Fluorescence-assisted sentinel (SND) and pelvic node dissections by single-port transvaginal laparoscopic surgery, for the management of an endometrial carcinoma (EC) in an elderly obese patient. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143:686-687.
27. Lee CL, Wu KY, Su H, et al. Robot-assisted natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for hysterectomy. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;54:761-765.
28. Rezai S, Giovane RA, Johnson SN, et al. Robotic natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (R-NOTES) in gynecologic surgeries, a case report and review of literature. Obstet Gynecol Int J. 2019;10:287-289.
29. Wang CJ, Wu PY, Kuo HH, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery-assisted versus laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (NAOC vs. LOC): a case-matched study. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:1227-1234.
Through the years, the surgical approach to hysterectomy has expanded from its early beginnings of being performed only through an abdominal or transvaginal route with traditional surgical clamps and suture. The late 1980s saw the advent of the laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH), and from that point forward several additional hysterectomy methods evolved, including today’s robotic approaches.
Although clinical evidence and societal endorsements support vaginal hysterectomy as a superior high-value modality, it remains one of the least performed among all available routes.1-3 In an analysis of inpatient hysterectomies published by Wright and colleagues in 2013, 16.7% of hysterectomies were performed vaginally, a number that essentially has remained steady throughout the ensuing years.4
Attempts to improve the application of vaginal hysterectomy have been made.5 These include the development of various curriculum and simulation-based medical education programs on vaginal surgical skills training and acquisition in the hopes of improving utilization.6 An interesting recent development is the rethinking of vaginal hysterectomy by several surgeons globally who are applying facets of the various hysterectomy methods to a transvaginal approach known as vaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (vNOTES).7,8 Unique to this thinking is the incorporation of conventional laparoscopic instrumentation.
Although I have not yet incorporated this approach in my surgical armamentarium at Columbia University Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, I am intrigued by the possibility that this technique may serve as a rescue for vaginal hysterectomies that are at risk of conversion or of not being performed at all.9
At this time, vNOTES is not a standard of care and should be performed only by highly specialized surgeons. However, in the spirit of this Update on minimally invasive surgery and to keep our readers abreast of burgeoning techniques, I am delighted to bring you this overview by Dr. Xiaoming Guan, one of the pioneers of this surgical approach, and Dr. Tamisa Koythong and Dr. Juan Liu. I hope you find this recent development in hysterectomy of interest.
—Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Continue to: Development and evolution of NOTES...
Development and evolution of NOTES
Over the past few decades, emphasis has shifted from laparotomy to minimally invasive surgery because of its proven significant advantages in patient care, such as improved cosmesis, shorter hospital stay, shorter postoperative recovery, and decreased postoperative pain and blood loss.10 Advances in laparoendoscopic surgery and instrumentation, including robot-assisted laparoscopy (RAL), single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS), and most recently natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), reflect ongoing innovative developments in the field of minimally invasive surgery.
Here, we provide a brief literature review of the NOTES technique, focus on its application in gynecologic surgery, and describe how we perform NOTES at our institution.
NOTES application in gynecology
With NOTES, peritoneal access is gained through a natural orifice (such as the mouth, vagina, urethra, or anus) to perform endoscopic surgery, occasionally without requiring an abdominal incision. First described in 2004, transgastric peritoneoscopy was performed in a porcine model, and shortly thereafter the first transgastric appendectomy was performed in humans.11,12 The technique has further been adopted in cholecystectomy, appendectomy, gastrectomy, and nephrectomy procedures.13
Given rapid interest in a possible paradigm shift in the field of minimally invasive surgery, the Natural Orifice Surgery Consortiumfor Assessment and Research (NOSCAR) was formed, and the group published an article on potential barriers to accepted practice and adoption of NOTES as a realistic alternative to traditional laparoscopic surgery.14
While transgastric and transanal access to the peritoneum were initially more popular, the risk of anastomotic leaks associated with incomplete closure and subsequent infection were thought to be prohibitively high.15 Transvaginal access was considered a safer and simpler alternative, allowing for complete closure without increased risk of infection, and this is now the route through which the majority of NOTES procedures are completed.16,17
The eventual application of NOTES in the field of gynecology seemed inevitable. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists stated that transvaginal surgery is the most minimally invasive and preferred surgical route in the management of patients with benign gynecologic diseases.18 However, performing it can be challenging at times due to limited visualization and lack of the required skills for single-site surgery. NOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon to improve visualization through the use of laparoendoscopic instruments and to complete surgery through a transvaginal route.
In 2012, Ahn and colleagues demonstrated the feasibility of the NOTES technique in gynecologic surgery after using it to successfully complete benign adnexal surgery in 10 patients.19 Vaginal NOTES (vNOTES) has since been further developed to include successful hysterectomy, myomectomy, sacrocolpopexy, tubal anastomosis, and even lymphadenectomy in the treatment of early- stage endometrial carcinoma.20-26 vNOTES also can be considered a rescue approach for traditional vaginal hysterectomy in instances in which it is necessary to evaluate adnexal pathology.9 Most recently, vNOTES hysterectomy has been reported with da Vinci Si or Xi robotic platforms.27,28
Continue to: Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients...
Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients
Few studies have compared outcomes with vNOTES to those with traditional laparoscopy. In 2016, Wang and colleagues compared surgical outcomes between NOTES-assisted ovarian cystectomy (NAOC) and laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (LOC) in a case-matched study that included 277 patients.29 Although mean (SD) blood loss in patients who underwent LOC was significantly less compared with those who underwent NAOC (21.4 [14.7] mL vs 31.6 [24.1] mL; P = .028), absolute blood loss in both groups was deemed minimal. Additionally, mean (SD) operative time and postoperative stay were significantly less in patients undergoing NAOC compared with those having LOC (38.23 [10.19] minutes vs 53.82 [18.61] minutes; P≤.001; and 1.38 [0.55] days vs 1.82 [0.52] days; P≤.001; respectively).29
How vNOTES hysterectomy stacked up against TLH
In 2018, Baekelandt and colleagues compared outcomes between vNOTES hysterectomy and total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) in a noninferiority single-blinded trial of 70 women.8 Compared with TLH, vNOTES hysterectomy was associated with shorter operative time (41 vs 75 minutes; P<.001), shorter hospital stay (0.8 vs 1.3 days; P = .004), and lower postoperative analgesic requirement (8 vs 14 U; P = .006). Additionally, there were no differences between the 2 groups in postoperative infection rate, intraoperative complications, or hospital readmissions within 6 weeks.8
Clearly, vNOTES is the next exciting development in minimally invasive surgery, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction with truly scarless surgery. Compared with traditional transvaginal surgery, vNOTES has the advantage of improved visualization with laparoendoscopic guidance, and it may be beneficial even for patients previously thought to have relative contraindications to successful completion of transvaginal surgery, such as nulliparity or a narrow introitus.
Approach for performing vNOTES procedures
At our institution, Baylor College of Medicine, the majority of gynecologic surgeries are performed via either transumbilical robot-assisted single-incision laparoscopy or vNOTES. Preoperative selection of appropriate candidates for vNOTES includes:
- low suspicion for or prior diagnosis of endometriosis with obliteration of the posterior cul-de-sac
- no surgical history suggestive of severe adhesive disease, and
- adequate vaginal sidewall access and sufficient descent for instrumentation for entry into the peritoneal cavity.
In general, a key concept in vNOTES is "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push," which means that the surgeon must pull the cervix while performing vaginal entry and then push the uterus back in the peritoneal cavity to increase surgical space during laparoscopic surgery.
Continue to: Overview of vNOTES steps...
Overview of vNOTES steps
Below we break down a description of vNOTES in 6 sections. Our patients are always placed in dorsal lithotomy position with TrenGuard (D.A. Surgical) Trendelenburg restraint. We prep the abdomen in case we need to convert to transabdominal surgery via transumbilical single-incision laparoscopic surgery or traditional laparoscopic surgery.
1. Vaginal entry
Accessing the peritoneal cavity through the vagina initially proceeds like a vaginal hysterectomy. We inject dilute vasopressin (20 U in 20 mL of normal saline) circumferentially in the cervix (for hysterectomy) or in the posterior cervix in the cervicovaginal junction (for adnexal surgery without hysterectomy) for vasoconstriction and hydrodissection.
We then incise the vaginal mucosa circumferentially with electrosurgical cautery and follow with posterior colpotomy. We find that reapproximating the posterior peritoneum to the posterior vagina with either figure-of-8 stitches or a running stitch of polyglactin 910 suture (2-0 Vicryl) assists in port placement, bleeding at the peritoneal edge, and closure of the cuff or colpotomy at the end of the case. We tag this suture with a curved hemostat.
Depending on whether a hysterectomy is being performed, anterior colpotomy is made. Again, the anterior peritoneum is then tagged to the anterior vaginal cuff in similar fashion, and this suture is tagged with a different instrument; we typically use a straight hemostat or Sarot clamp (FIGURE 1).

2. Traditional vaginal hysterectomy
After colpotomy, we prefer to perform progressive clamping of the broad ligament from the uterosacral and cardinal ligaments to the level of uterine artery as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy, if feasible.
3. Single-site port placement
The assembled GelPOINT Mini advanced access platform (Applied Medical) (FIGURE 2) is introduced through the vagina after the Alexis wound protector (included with the kit) is first placed through the colpotomy with assistance of Babcock clamps (FIGURE 3).


After ensuring that the green rigid ring of the Alexis wound protector is contained and completely expanded within the peritoneal cavity, we cross our previously tagged sutures as we find this helps with preventing the GelPOINT Mini access platform from inadvertently shifting out of the peritoneal cavity during surgery. The GelSeal cap is then secured and pneumoperitoneum is established (FIGURE 4).

Continue to: 4. Laparoendoscopic surgery...
4. Laparoendoscopic surgery
Instruments used in our surgeries include a 10-mm rigid 30° 43-cm working length laparoscope; a 44-cm LigaSure device (Medtronic); a 5-mm, 37-cm laparoscopic cobra grasping forceps and fenestrated grasper (Karl Storz); and a 5-mm, 45-cm laparoscopic suction with hydrodissection tip (Stryker) (FIGURE 5).

vNOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon the unique ability to survey the upper abdomen. The remainder of the surgery proceeds using basic laparoscopic single-site skills.
During vNOTES, as with all single-site surgical procedures, understanding the optimal placement of crossed instruments is important for successful completion. For example, when securing the right uterine artery, the surgeon needs to push the cervix toward the patient's left and slightly into the peritoneal cavity using a laparoscopic cobra grasper with his or her left hand while then securing the uterine pedicle using the LigaSure device with his or her right hand. This is then reversed when securing the left uterine artery, where the assistant surgeon pushes the cervix toward the patient's right while the surgeon secures the pedicle ("vaginal pull, laparoscopic push") (FIGURE 6).

This again is reiterated in securing the ovarian pedicles, which are pushed into the peritoneal cavity while being secured with the LigaSure device.
5. Specimen removal
For large uteri or specimens that need morcellation, a 15-mm Endo Catch specimen retrieval bag (Medtronic) is introduced through the GelPOINT Mini system. The specimen is then placed in the bag and delivered to the vagina, where contained bag morcellation is performed in standard fashion (FIGURES 7 AND 8). We utilized the "big C" technique by first grasping the specimen with a penetrating clamp. The clamp is then held in our nondominant hand and a No. 10 blade scalpel is used to create a reverse c-incision, keeping one surface of the specimen intact. This is continued until the specimen can be completely delivered through the vagina.


Specimens that do not require morcellation can be grasped laparoscopically, brought to the GelPOINT Mini port, which is quickly disassembled, and delivered. The GelSeal cap is then reassembled.
6. Vaginal cuff closure
The colpotomy or vaginal cuff is closed with barbed suture continuously, as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy cuff closure. Uterosacral ligament suspension should be performed for vaginal cuff support.
vNOTES is the most recent innovative development in the field of minimally invasive surgery, and it has demonstrated feasibility and safety in the fields of general surgery, urology, and gynecology. Adopting vNOTES in clinical practice can improve patient satisfaction and cosmesis as well as surgical outcomes. Gynecologic surgeons can think of vNOTES hysterectomy as "placing an eye" in the vagina while performing transvaginal hysterectomy. The surgical principle of "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push" facilitates the learning process.
Through the years, the surgical approach to hysterectomy has expanded from its early beginnings of being performed only through an abdominal or transvaginal route with traditional surgical clamps and suture. The late 1980s saw the advent of the laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH), and from that point forward several additional hysterectomy methods evolved, including today’s robotic approaches.
Although clinical evidence and societal endorsements support vaginal hysterectomy as a superior high-value modality, it remains one of the least performed among all available routes.1-3 In an analysis of inpatient hysterectomies published by Wright and colleagues in 2013, 16.7% of hysterectomies were performed vaginally, a number that essentially has remained steady throughout the ensuing years.4
Attempts to improve the application of vaginal hysterectomy have been made.5 These include the development of various curriculum and simulation-based medical education programs on vaginal surgical skills training and acquisition in the hopes of improving utilization.6 An interesting recent development is the rethinking of vaginal hysterectomy by several surgeons globally who are applying facets of the various hysterectomy methods to a transvaginal approach known as vaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (vNOTES).7,8 Unique to this thinking is the incorporation of conventional laparoscopic instrumentation.
Although I have not yet incorporated this approach in my surgical armamentarium at Columbia University Medical Center/New York–Presbyterian Hospital, I am intrigued by the possibility that this technique may serve as a rescue for vaginal hysterectomies that are at risk of conversion or of not being performed at all.9
At this time, vNOTES is not a standard of care and should be performed only by highly specialized surgeons. However, in the spirit of this Update on minimally invasive surgery and to keep our readers abreast of burgeoning techniques, I am delighted to bring you this overview by Dr. Xiaoming Guan, one of the pioneers of this surgical approach, and Dr. Tamisa Koythong and Dr. Juan Liu. I hope you find this recent development in hysterectomy of interest.
—Arnold P. Advincula, MD
Continue to: Development and evolution of NOTES...
Development and evolution of NOTES
Over the past few decades, emphasis has shifted from laparotomy to minimally invasive surgery because of its proven significant advantages in patient care, such as improved cosmesis, shorter hospital stay, shorter postoperative recovery, and decreased postoperative pain and blood loss.10 Advances in laparoendoscopic surgery and instrumentation, including robot-assisted laparoscopy (RAL), single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS), and most recently natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), reflect ongoing innovative developments in the field of minimally invasive surgery.
Here, we provide a brief literature review of the NOTES technique, focus on its application in gynecologic surgery, and describe how we perform NOTES at our institution.
NOTES application in gynecology
With NOTES, peritoneal access is gained through a natural orifice (such as the mouth, vagina, urethra, or anus) to perform endoscopic surgery, occasionally without requiring an abdominal incision. First described in 2004, transgastric peritoneoscopy was performed in a porcine model, and shortly thereafter the first transgastric appendectomy was performed in humans.11,12 The technique has further been adopted in cholecystectomy, appendectomy, gastrectomy, and nephrectomy procedures.13
Given rapid interest in a possible paradigm shift in the field of minimally invasive surgery, the Natural Orifice Surgery Consortiumfor Assessment and Research (NOSCAR) was formed, and the group published an article on potential barriers to accepted practice and adoption of NOTES as a realistic alternative to traditional laparoscopic surgery.14
While transgastric and transanal access to the peritoneum were initially more popular, the risk of anastomotic leaks associated with incomplete closure and subsequent infection were thought to be prohibitively high.15 Transvaginal access was considered a safer and simpler alternative, allowing for complete closure without increased risk of infection, and this is now the route through which the majority of NOTES procedures are completed.16,17
The eventual application of NOTES in the field of gynecology seemed inevitable. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists stated that transvaginal surgery is the most minimally invasive and preferred surgical route in the management of patients with benign gynecologic diseases.18 However, performing it can be challenging at times due to limited visualization and lack of the required skills for single-site surgery. NOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon to improve visualization through the use of laparoendoscopic instruments and to complete surgery through a transvaginal route.
In 2012, Ahn and colleagues demonstrated the feasibility of the NOTES technique in gynecologic surgery after using it to successfully complete benign adnexal surgery in 10 patients.19 Vaginal NOTES (vNOTES) has since been further developed to include successful hysterectomy, myomectomy, sacrocolpopexy, tubal anastomosis, and even lymphadenectomy in the treatment of early- stage endometrial carcinoma.20-26 vNOTES also can be considered a rescue approach for traditional vaginal hysterectomy in instances in which it is necessary to evaluate adnexal pathology.9 Most recently, vNOTES hysterectomy has been reported with da Vinci Si or Xi robotic platforms.27,28
Continue to: Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients...
Operative time, post-op stay shorter in NAOC-treated patients
Few studies have compared outcomes with vNOTES to those with traditional laparoscopy. In 2016, Wang and colleagues compared surgical outcomes between NOTES-assisted ovarian cystectomy (NAOC) and laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (LOC) in a case-matched study that included 277 patients.29 Although mean (SD) blood loss in patients who underwent LOC was significantly less compared with those who underwent NAOC (21.4 [14.7] mL vs 31.6 [24.1] mL; P = .028), absolute blood loss in both groups was deemed minimal. Additionally, mean (SD) operative time and postoperative stay were significantly less in patients undergoing NAOC compared with those having LOC (38.23 [10.19] minutes vs 53.82 [18.61] minutes; P≤.001; and 1.38 [0.55] days vs 1.82 [0.52] days; P≤.001; respectively).29
How vNOTES hysterectomy stacked up against TLH
In 2018, Baekelandt and colleagues compared outcomes between vNOTES hysterectomy and total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH) in a noninferiority single-blinded trial of 70 women.8 Compared with TLH, vNOTES hysterectomy was associated with shorter operative time (41 vs 75 minutes; P<.001), shorter hospital stay (0.8 vs 1.3 days; P = .004), and lower postoperative analgesic requirement (8 vs 14 U; P = .006). Additionally, there were no differences between the 2 groups in postoperative infection rate, intraoperative complications, or hospital readmissions within 6 weeks.8
Clearly, vNOTES is the next exciting development in minimally invasive surgery, improving patient outcomes and satisfaction with truly scarless surgery. Compared with traditional transvaginal surgery, vNOTES has the advantage of improved visualization with laparoendoscopic guidance, and it may be beneficial even for patients previously thought to have relative contraindications to successful completion of transvaginal surgery, such as nulliparity or a narrow introitus.
Approach for performing vNOTES procedures
At our institution, Baylor College of Medicine, the majority of gynecologic surgeries are performed via either transumbilical robot-assisted single-incision laparoscopy or vNOTES. Preoperative selection of appropriate candidates for vNOTES includes:
- low suspicion for or prior diagnosis of endometriosis with obliteration of the posterior cul-de-sac
- no surgical history suggestive of severe adhesive disease, and
- adequate vaginal sidewall access and sufficient descent for instrumentation for entry into the peritoneal cavity.
In general, a key concept in vNOTES is "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push," which means that the surgeon must pull the cervix while performing vaginal entry and then push the uterus back in the peritoneal cavity to increase surgical space during laparoscopic surgery.
Continue to: Overview of vNOTES steps...
Overview of vNOTES steps
Below we break down a description of vNOTES in 6 sections. Our patients are always placed in dorsal lithotomy position with TrenGuard (D.A. Surgical) Trendelenburg restraint. We prep the abdomen in case we need to convert to transabdominal surgery via transumbilical single-incision laparoscopic surgery or traditional laparoscopic surgery.
1. Vaginal entry
Accessing the peritoneal cavity through the vagina initially proceeds like a vaginal hysterectomy. We inject dilute vasopressin (20 U in 20 mL of normal saline) circumferentially in the cervix (for hysterectomy) or in the posterior cervix in the cervicovaginal junction (for adnexal surgery without hysterectomy) for vasoconstriction and hydrodissection.
We then incise the vaginal mucosa circumferentially with electrosurgical cautery and follow with posterior colpotomy. We find that reapproximating the posterior peritoneum to the posterior vagina with either figure-of-8 stitches or a running stitch of polyglactin 910 suture (2-0 Vicryl) assists in port placement, bleeding at the peritoneal edge, and closure of the cuff or colpotomy at the end of the case. We tag this suture with a curved hemostat.
Depending on whether a hysterectomy is being performed, anterior colpotomy is made. Again, the anterior peritoneum is then tagged to the anterior vaginal cuff in similar fashion, and this suture is tagged with a different instrument; we typically use a straight hemostat or Sarot clamp (FIGURE 1).

2. Traditional vaginal hysterectomy
After colpotomy, we prefer to perform progressive clamping of the broad ligament from the uterosacral and cardinal ligaments to the level of uterine artery as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy, if feasible.
3. Single-site port placement
The assembled GelPOINT Mini advanced access platform (Applied Medical) (FIGURE 2) is introduced through the vagina after the Alexis wound protector (included with the kit) is first placed through the colpotomy with assistance of Babcock clamps (FIGURE 3).


After ensuring that the green rigid ring of the Alexis wound protector is contained and completely expanded within the peritoneal cavity, we cross our previously tagged sutures as we find this helps with preventing the GelPOINT Mini access platform from inadvertently shifting out of the peritoneal cavity during surgery. The GelSeal cap is then secured and pneumoperitoneum is established (FIGURE 4).

Continue to: 4. Laparoendoscopic surgery...
4. Laparoendoscopic surgery
Instruments used in our surgeries include a 10-mm rigid 30° 43-cm working length laparoscope; a 44-cm LigaSure device (Medtronic); a 5-mm, 37-cm laparoscopic cobra grasping forceps and fenestrated grasper (Karl Storz); and a 5-mm, 45-cm laparoscopic suction with hydrodissection tip (Stryker) (FIGURE 5).

vNOTES allows a gynecologic surgeon the unique ability to survey the upper abdomen. The remainder of the surgery proceeds using basic laparoscopic single-site skills.
During vNOTES, as with all single-site surgical procedures, understanding the optimal placement of crossed instruments is important for successful completion. For example, when securing the right uterine artery, the surgeon needs to push the cervix toward the patient's left and slightly into the peritoneal cavity using a laparoscopic cobra grasper with his or her left hand while then securing the uterine pedicle using the LigaSure device with his or her right hand. This is then reversed when securing the left uterine artery, where the assistant surgeon pushes the cervix toward the patient's right while the surgeon secures the pedicle ("vaginal pull, laparoscopic push") (FIGURE 6).

This again is reiterated in securing the ovarian pedicles, which are pushed into the peritoneal cavity while being secured with the LigaSure device.
5. Specimen removal
For large uteri or specimens that need morcellation, a 15-mm Endo Catch specimen retrieval bag (Medtronic) is introduced through the GelPOINT Mini system. The specimen is then placed in the bag and delivered to the vagina, where contained bag morcellation is performed in standard fashion (FIGURES 7 AND 8). We utilized the "big C" technique by first grasping the specimen with a penetrating clamp. The clamp is then held in our nondominant hand and a No. 10 blade scalpel is used to create a reverse c-incision, keeping one surface of the specimen intact. This is continued until the specimen can be completely delivered through the vagina.


Specimens that do not require morcellation can be grasped laparoscopically, brought to the GelPOINT Mini port, which is quickly disassembled, and delivered. The GelSeal cap is then reassembled.
6. Vaginal cuff closure
The colpotomy or vaginal cuff is closed with barbed suture continuously, as in traditional vaginal hysterectomy cuff closure. Uterosacral ligament suspension should be performed for vaginal cuff support.
vNOTES is the most recent innovative development in the field of minimally invasive surgery, and it has demonstrated feasibility and safety in the fields of general surgery, urology, and gynecology. Adopting vNOTES in clinical practice can improve patient satisfaction and cosmesis as well as surgical outcomes. Gynecologic surgeons can think of vNOTES hysterectomy as "placing an eye" in the vagina while performing transvaginal hysterectomy. The surgical principle of "vaginal pull, laparoscopic push" facilitates the learning process.
1. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 444. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114:1156-1158.
2. AAGL Advancing Minimally Invasive Gynecology Worldwide. AAGL position statement: route of hysterectomy to treat benign uterine disease. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:1-3.
3. Whiteside JL, Kaeser CT, Ridgeway B. Achieving high value in the surgical approach to hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:242-245.
4. Wright JD, Herzog TJ, Tsui J, et al. Nationwide trends in the performance of inpatient hysterectomy in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(2 pt 1):233-241.
5. Moen M, Walter A, Harmanli O, et al. Considerations to improve the evidence-based use of vaginal hysterectomy in benign gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:585-588.
6. Balgobin S, Owens DM, Florian-Rodriguez ME, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy suturing skills training model and curriculum. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:553-558.
7. Baekelandt J. Total vaginal NOTES hysterectomy: a new approach to hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:1088-1094.
8. Baekelandt JF, De Mulder PA, Le Roy I, et al. Hysterectomy by transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery versus laparoscopy as a day-care procedure: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG. 2019;126:105-113.
9. Guan X, Bardawil E, Liu J, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery as a rescue for total vaginal hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:1135-1136.
10. Nieboer TE, Johnson N, Lethaby A, et al. Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;3:CD003677.
11. Kalloo AN, Singh VK, Jagannath SB, et al. Flexible transgastric peritoneoscopy: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:114-117.
12. Reddy N, Rao P. Per oral transgastric endoscopic appendectomy in human. Paper Presented at: 45th Annual Conference of the Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy of India; February 28-29, 2004; Jaipur, India.
13. Clark MP, Qayed ES, Kooby DA, et al. Natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery in humans: a review. Minim Invasive Surg. 2012;189296.
14. Rattner D, Kalloo A; ASGE/SAGES Working Group. ASGE/ SAGES Working Group on natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery, October 2005. Surg Endosc. 2006;20:329-333.
15. Autorino R, Yakoubi R, White WM, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): where are we going? A bibliometric assessment. BJU Int. 2013;111:11-16.
16. Santos BF, Hungness ES. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery: progress in humans since the white paper. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1655-1665.
17. Tolcher MC, Kalogera E, Hopkins MR, et al. Safety of culdotomy as a surgical approach: implications for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery. JSLS. 2012;16:413-420.
18. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 701. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2017:129:e155-e159.
19. Ahn KH, Song JY, Kim SH, et al. Transvaginal single-port natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for benign uterine adnexal pathologies. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:631-635.
20. Liu J, Kohn J, Sun B, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery sacrocolpopexy: tips and tricks. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:38-39.
21. Liu J, Kohn J, Fu H, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for sacrocolpopexy: a pilot study of 26 cases. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:748-753.
22. Su H, Yen CF, Wu KY, et al. Hysterectomy via transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): feasibility of an innovative approach. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51:217-221.
23. Lee CL, Huang CY, Wu KY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery myomectomy: an innovative approach to myomectomy. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:127-130.
24. Chen Y, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Transvaginal single-port laparoscopy sacrocolpopexy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:585- 588.
25. Lee CL, Wu KY, Tsao FY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery for endometrial cancer. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:89-92.
26. Leblanc E, Narducci F, Bresson L, et al. Fluorescence-assisted sentinel (SND) and pelvic node dissections by single-port transvaginal laparoscopic surgery, for the management of an endometrial carcinoma (EC) in an elderly obese patient. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143:686-687.
27. Lee CL, Wu KY, Su H, et al. Robot-assisted natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for hysterectomy. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;54:761-765.
28. Rezai S, Giovane RA, Johnson SN, et al. Robotic natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (R-NOTES) in gynecologic surgeries, a case report and review of literature. Obstet Gynecol Int J. 2019;10:287-289.
29. Wang CJ, Wu PY, Kuo HH, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery-assisted versus laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (NAOC vs. LOC): a case-matched study. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:1227-1234.
1. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 444. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114:1156-1158.
2. AAGL Advancing Minimally Invasive Gynecology Worldwide. AAGL position statement: route of hysterectomy to treat benign uterine disease. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2011;18:1-3.
3. Whiteside JL, Kaeser CT, Ridgeway B. Achieving high value in the surgical approach to hysterectomy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;220:242-245.
4. Wright JD, Herzog TJ, Tsui J, et al. Nationwide trends in the performance of inpatient hysterectomy in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(2 pt 1):233-241.
5. Moen M, Walter A, Harmanli O, et al. Considerations to improve the evidence-based use of vaginal hysterectomy in benign gynecology. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;124:585-588.
6. Balgobin S, Owens DM, Florian-Rodriguez ME, et al. Vaginal hysterectomy suturing skills training model and curriculum. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:553-558.
7. Baekelandt J. Total vaginal NOTES hysterectomy: a new approach to hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2015;22:1088-1094.
8. Baekelandt JF, De Mulder PA, Le Roy I, et al. Hysterectomy by transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery versus laparoscopy as a day-care procedure: a randomised controlled trial. BJOG. 2019;126:105-113.
9. Guan X, Bardawil E, Liu J, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery as a rescue for total vaginal hysterectomy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:1135-1136.
10. Nieboer TE, Johnson N, Lethaby A, et al. Surgical approach to hysterectomy for benign gynaecological disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;3:CD003677.
11. Kalloo AN, Singh VK, Jagannath SB, et al. Flexible transgastric peritoneoscopy: a novel approach to diagnostic and therapeutic interventions in the peritoneal cavity. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60:114-117.
12. Reddy N, Rao P. Per oral transgastric endoscopic appendectomy in human. Paper Presented at: 45th Annual Conference of the Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy of India; February 28-29, 2004; Jaipur, India.
13. Clark MP, Qayed ES, Kooby DA, et al. Natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery in humans: a review. Minim Invasive Surg. 2012;189296.
14. Rattner D, Kalloo A; ASGE/SAGES Working Group. ASGE/ SAGES Working Group on natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery, October 2005. Surg Endosc. 2006;20:329-333.
15. Autorino R, Yakoubi R, White WM, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): where are we going? A bibliometric assessment. BJU Int. 2013;111:11-16.
16. Santos BF, Hungness ES. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery: progress in humans since the white paper. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1655-1665.
17. Tolcher MC, Kalogera E, Hopkins MR, et al. Safety of culdotomy as a surgical approach: implications for natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery. JSLS. 2012;16:413-420.
18. ACOG Committee on Gynecologic Practice. Committee opinion no. 701. Choosing the route of hysterectomy for benign disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2017:129:e155-e159.
19. Ahn KH, Song JY, Kim SH, et al. Transvaginal single-port natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for benign uterine adnexal pathologies. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:631-635.
20. Liu J, Kohn J, Sun B, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery sacrocolpopexy: tips and tricks. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:38-39.
21. Liu J, Kohn J, Fu H, et al. Transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for sacrocolpopexy: a pilot study of 26 cases. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:748-753.
22. Su H, Yen CF, Wu KY, et al. Hysterectomy via transvaginal natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): feasibility of an innovative approach. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51:217-221.
23. Lee CL, Huang CY, Wu KY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery myomectomy: an innovative approach to myomectomy. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:127-130.
24. Chen Y, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Transvaginal single-port laparoscopy sacrocolpopexy. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018;25:585- 588.
25. Lee CL, Wu KY, Tsao FY, et al. Natural orifice transvaginal endoscopic surgery for endometrial cancer. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2014;3:89-92.
26. Leblanc E, Narducci F, Bresson L, et al. Fluorescence-assisted sentinel (SND) and pelvic node dissections by single-port transvaginal laparoscopic surgery, for the management of an endometrial carcinoma (EC) in an elderly obese patient. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143:686-687.
27. Lee CL, Wu KY, Su H, et al. Robot-assisted natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery for hysterectomy. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;54:761-765.
28. Rezai S, Giovane RA, Johnson SN, et al. Robotic natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (R-NOTES) in gynecologic surgeries, a case report and review of literature. Obstet Gynecol Int J. 2019;10:287-289.
29. Wang CJ, Wu PY, Kuo HH, et al. Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery-assisted versus laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy (NAOC vs. LOC): a case-matched study. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:1227-1234.
FDA advisory committee supports birth control patch approval
Most of the committee members based their decisions on the need for additional contraceptive options for patients. However, most also expressed concerns about its efficacy and offered suggestions for product labeling that called attention to high rates of unintended pregnancies and increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in obese women.
The agency’s Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee reviewed safety and efficacy data for AG200-15, a combined hormonal contraceptive patch developed by Agile Therapeutics. The treatment regimen involves application of a patch to the abdomen, buttock, or upper torso, and the patch is changed weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week without a patch.
Elizabeth Garner, MD, consultant and former chief medical officer of Agile, presented study data on safety and effectiveness of the patch. The key study (known as Study 23) considered by the FDA included 1,736 women aged 35 years and younger. The primary efficacy endpoint was the pregnancy rate in the women who used the patch. Women reported sexual activity and back-up contraception use in e-diaries.
A total of 68 pregnancies occurred in the study population after 15,165 evaluable cycles, yielding an overall Pearl Index of 5.83 across all weight and body mass index groups. Historically, a Pearl Index of 5 has been the standard measure for effectiveness in contraceptive products, with lower being better. The index is defined as the number of pregnancies per 100 woman-years of product use. For example, a Pearl Index of 0.1 means that 1 in 1,000 women who use the same contraceptive method for 1 year becomes pregnant.
A subgroup analysis showed reduced efficacy in women with a higher BMI. The Pearl Index for women with a BMI of less than 30 kg/m2 (defined as nonobese) was 4.34, whereas in women with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 and higher (defined as obese), the index was 8.64, nearly double that of nonobese women. No significant differences in the index were noted based on race/ethnicity.
The company described the patch as filling a niche and providing an additional alternative for women seeking a noninvasive method of contraception. It proposed a limitation of use (LOU) as part of the product label that would provide detailed information on efficacy based on the Pearl Index for the different categories of BMI and would suggest that the patch may be less effective for women with obesity. Most of the committee members favored use of a LOU statement on the label, but some noted that it might limit prescriptions to nonobese women.
The committee expressed concern over the Pearl data in the study. The FDA has never approved a contraceptive product with a Pearl Index of greater than 5, said Yun Tang, PhD, a statistical reviewer for the agency’s Office of Translational Sciences, who presented the evaluation of the effectiveness of AG200-15.
Key safety concerns raised in discussion included the risk of venous thromboembolism and the risk of unscheduled bleeding. Both of those issues were significantly more common among obese women, said Nneka McNeal-Jackson, MD, clinical reviewer for the FDA, who presented details on the safety profile and risk-benefit considerations for the patch.
Overall, in Study 23, the incidence rate of VTE was 28/10,000 women-years, with cases in five participants. Four of those were deemed related to the patch, and all occurred in obese women.
Virginia C. “Jennie” Leslie, MD, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, voted no to recommending approval of the patch mainly because of efficacy concerns. “My goal is to do no harm, and I have concerns regarding efficacy and giving our patients a false sense of hope,” she said.
Even those members who voted yes expressed concerns about the efficacy data and VTE risk in obese women and recommended postmarketing studies and appropriate labeling to help clinicians in shared decision making with their patients.
Esther Eisenberg, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, noted that the patch fills a need, certainly for women with a BMI less than 30 kg/m2, and suggested that use be limited to women in that lower BMI category.
Other committee members suggested that the product not be restricted based on BMI, but rather that the LOU provide clear explanations of how effectiveness decreases as BMI increases.
David J. Margolis, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, opted to abstain from voting, in part based on concerns about the study design and a lack of additional data from the company.
Most of the committee members based their decisions on the need for additional contraceptive options for patients. However, most also expressed concerns about its efficacy and offered suggestions for product labeling that called attention to high rates of unintended pregnancies and increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in obese women.
The agency’s Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee reviewed safety and efficacy data for AG200-15, a combined hormonal contraceptive patch developed by Agile Therapeutics. The treatment regimen involves application of a patch to the abdomen, buttock, or upper torso, and the patch is changed weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week without a patch.
Elizabeth Garner, MD, consultant and former chief medical officer of Agile, presented study data on safety and effectiveness of the patch. The key study (known as Study 23) considered by the FDA included 1,736 women aged 35 years and younger. The primary efficacy endpoint was the pregnancy rate in the women who used the patch. Women reported sexual activity and back-up contraception use in e-diaries.
A total of 68 pregnancies occurred in the study population after 15,165 evaluable cycles, yielding an overall Pearl Index of 5.83 across all weight and body mass index groups. Historically, a Pearl Index of 5 has been the standard measure for effectiveness in contraceptive products, with lower being better. The index is defined as the number of pregnancies per 100 woman-years of product use. For example, a Pearl Index of 0.1 means that 1 in 1,000 women who use the same contraceptive method for 1 year becomes pregnant.
A subgroup analysis showed reduced efficacy in women with a higher BMI. The Pearl Index for women with a BMI of less than 30 kg/m2 (defined as nonobese) was 4.34, whereas in women with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 and higher (defined as obese), the index was 8.64, nearly double that of nonobese women. No significant differences in the index were noted based on race/ethnicity.
The company described the patch as filling a niche and providing an additional alternative for women seeking a noninvasive method of contraception. It proposed a limitation of use (LOU) as part of the product label that would provide detailed information on efficacy based on the Pearl Index for the different categories of BMI and would suggest that the patch may be less effective for women with obesity. Most of the committee members favored use of a LOU statement on the label, but some noted that it might limit prescriptions to nonobese women.
The committee expressed concern over the Pearl data in the study. The FDA has never approved a contraceptive product with a Pearl Index of greater than 5, said Yun Tang, PhD, a statistical reviewer for the agency’s Office of Translational Sciences, who presented the evaluation of the effectiveness of AG200-15.
Key safety concerns raised in discussion included the risk of venous thromboembolism and the risk of unscheduled bleeding. Both of those issues were significantly more common among obese women, said Nneka McNeal-Jackson, MD, clinical reviewer for the FDA, who presented details on the safety profile and risk-benefit considerations for the patch.
Overall, in Study 23, the incidence rate of VTE was 28/10,000 women-years, with cases in five participants. Four of those were deemed related to the patch, and all occurred in obese women.
Virginia C. “Jennie” Leslie, MD, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, voted no to recommending approval of the patch mainly because of efficacy concerns. “My goal is to do no harm, and I have concerns regarding efficacy and giving our patients a false sense of hope,” she said.
Even those members who voted yes expressed concerns about the efficacy data and VTE risk in obese women and recommended postmarketing studies and appropriate labeling to help clinicians in shared decision making with their patients.
Esther Eisenberg, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, noted that the patch fills a need, certainly for women with a BMI less than 30 kg/m2, and suggested that use be limited to women in that lower BMI category.
Other committee members suggested that the product not be restricted based on BMI, but rather that the LOU provide clear explanations of how effectiveness decreases as BMI increases.
David J. Margolis, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, opted to abstain from voting, in part based on concerns about the study design and a lack of additional data from the company.
Most of the committee members based their decisions on the need for additional contraceptive options for patients. However, most also expressed concerns about its efficacy and offered suggestions for product labeling that called attention to high rates of unintended pregnancies and increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in obese women.
The agency’s Bone, Reproductive and Urologic Drugs Advisory Committee reviewed safety and efficacy data for AG200-15, a combined hormonal contraceptive patch developed by Agile Therapeutics. The treatment regimen involves application of a patch to the abdomen, buttock, or upper torso, and the patch is changed weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 1 week without a patch.
Elizabeth Garner, MD, consultant and former chief medical officer of Agile, presented study data on safety and effectiveness of the patch. The key study (known as Study 23) considered by the FDA included 1,736 women aged 35 years and younger. The primary efficacy endpoint was the pregnancy rate in the women who used the patch. Women reported sexual activity and back-up contraception use in e-diaries.
A total of 68 pregnancies occurred in the study population after 15,165 evaluable cycles, yielding an overall Pearl Index of 5.83 across all weight and body mass index groups. Historically, a Pearl Index of 5 has been the standard measure for effectiveness in contraceptive products, with lower being better. The index is defined as the number of pregnancies per 100 woman-years of product use. For example, a Pearl Index of 0.1 means that 1 in 1,000 women who use the same contraceptive method for 1 year becomes pregnant.
A subgroup analysis showed reduced efficacy in women with a higher BMI. The Pearl Index for women with a BMI of less than 30 kg/m2 (defined as nonobese) was 4.34, whereas in women with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 and higher (defined as obese), the index was 8.64, nearly double that of nonobese women. No significant differences in the index were noted based on race/ethnicity.
The company described the patch as filling a niche and providing an additional alternative for women seeking a noninvasive method of contraception. It proposed a limitation of use (LOU) as part of the product label that would provide detailed information on efficacy based on the Pearl Index for the different categories of BMI and would suggest that the patch may be less effective for women with obesity. Most of the committee members favored use of a LOU statement on the label, but some noted that it might limit prescriptions to nonobese women.
The committee expressed concern over the Pearl data in the study. The FDA has never approved a contraceptive product with a Pearl Index of greater than 5, said Yun Tang, PhD, a statistical reviewer for the agency’s Office of Translational Sciences, who presented the evaluation of the effectiveness of AG200-15.
Key safety concerns raised in discussion included the risk of venous thromboembolism and the risk of unscheduled bleeding. Both of those issues were significantly more common among obese women, said Nneka McNeal-Jackson, MD, clinical reviewer for the FDA, who presented details on the safety profile and risk-benefit considerations for the patch.
Overall, in Study 23, the incidence rate of VTE was 28/10,000 women-years, with cases in five participants. Four of those were deemed related to the patch, and all occurred in obese women.
Virginia C. “Jennie” Leslie, MD, of Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, voted no to recommending approval of the patch mainly because of efficacy concerns. “My goal is to do no harm, and I have concerns regarding efficacy and giving our patients a false sense of hope,” she said.
Even those members who voted yes expressed concerns about the efficacy data and VTE risk in obese women and recommended postmarketing studies and appropriate labeling to help clinicians in shared decision making with their patients.
Esther Eisenberg, MD, of the National Institutes of Health, noted that the patch fills a need, certainly for women with a BMI less than 30 kg/m2, and suggested that use be limited to women in that lower BMI category.
Other committee members suggested that the product not be restricted based on BMI, but rather that the LOU provide clear explanations of how effectiveness decreases as BMI increases.
David J. Margolis, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, opted to abstain from voting, in part based on concerns about the study design and a lack of additional data from the company.
FROM THE FDA
Judge blocks Alabama abortion ban
A federal judge has temporarily barred Alabama’s near total abortion ban from taking effect.
In an Oct. 29 decision, Myron H. Thompson, District Court Judge for the Middle District of Alabama, North Division, wrote . Judge Thompson halted the measure, which was scheduled to take effect on Nov. 15, while the lawsuit continues through the courts.
“As stated previously, banning abortion before viability violates Supreme Court precedent,” Judge Thompson wrote in the opinion. “No alleged state interest can overcome this clear mandate. Thus, as a ban on pre-viability abortion, the act contravenes established law.”
Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey (R) signed the “Human Life Protection Act” into law on May 15. The measure bans abortion at every pregnancy stage and penalizes physicians with a Class A felony for performing an abortion and charges them with a Class C felony for attempting to perform an abortion. The law includes an exception if a woman’s life is at risk, but not for cases of rape or incest.
The federal court’s decision affirms that women have a right to access safe, legal abortion, Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO of Planned Parenthood Federation of America said in a statement. Planned Parenthood Federation of America, The American Civil Liberties Union, and the ACLU of Alabama are representing the plaintiffs in the lawsuit, which include Alabama physicians and patients.
“Politicians in Alabama, and across the country, are putting people’s health and lives at risk in their attempts to ban abortion outright in this country,” Ms. Johnson said in the statement. “Today’s victory means people can still access the health care they need across Alabama – for now. We will continue to fight to ensure that everyone can access health care – including safe, legal abortion.”
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the district court’s decision to temporarily halt the law was not unexpected.
“As we have stated before, the state’s objective is to advance our case to the U.S. Supreme Court where we intend to submit evidence that supports our argument that Roe and Casey were wrongly decided and that the Constitution does not prohibit states from protecting unborn children from abortion,” Mr. Marshall said in a statement.
The Alabama decision comes just weeks after the U.S. Supreme Court agreed to hear an abortion-related challenge out of Louisiana. June Medical Services v. Gee centers on the constitutionality of a Louisiana law that requires any doctor performing an abortion to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital. The high court likely will hear that case in early 2020.
A federal judge has temporarily barred Alabama’s near total abortion ban from taking effect.
In an Oct. 29 decision, Myron H. Thompson, District Court Judge for the Middle District of Alabama, North Division, wrote . Judge Thompson halted the measure, which was scheduled to take effect on Nov. 15, while the lawsuit continues through the courts.
“As stated previously, banning abortion before viability violates Supreme Court precedent,” Judge Thompson wrote in the opinion. “No alleged state interest can overcome this clear mandate. Thus, as a ban on pre-viability abortion, the act contravenes established law.”
Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey (R) signed the “Human Life Protection Act” into law on May 15. The measure bans abortion at every pregnancy stage and penalizes physicians with a Class A felony for performing an abortion and charges them with a Class C felony for attempting to perform an abortion. The law includes an exception if a woman’s life is at risk, but not for cases of rape or incest.
The federal court’s decision affirms that women have a right to access safe, legal abortion, Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO of Planned Parenthood Federation of America said in a statement. Planned Parenthood Federation of America, The American Civil Liberties Union, and the ACLU of Alabama are representing the plaintiffs in the lawsuit, which include Alabama physicians and patients.
“Politicians in Alabama, and across the country, are putting people’s health and lives at risk in their attempts to ban abortion outright in this country,” Ms. Johnson said in the statement. “Today’s victory means people can still access the health care they need across Alabama – for now. We will continue to fight to ensure that everyone can access health care – including safe, legal abortion.”
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the district court’s decision to temporarily halt the law was not unexpected.
“As we have stated before, the state’s objective is to advance our case to the U.S. Supreme Court where we intend to submit evidence that supports our argument that Roe and Casey were wrongly decided and that the Constitution does not prohibit states from protecting unborn children from abortion,” Mr. Marshall said in a statement.
The Alabama decision comes just weeks after the U.S. Supreme Court agreed to hear an abortion-related challenge out of Louisiana. June Medical Services v. Gee centers on the constitutionality of a Louisiana law that requires any doctor performing an abortion to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital. The high court likely will hear that case in early 2020.
A federal judge has temporarily barred Alabama’s near total abortion ban from taking effect.
In an Oct. 29 decision, Myron H. Thompson, District Court Judge for the Middle District of Alabama, North Division, wrote . Judge Thompson halted the measure, which was scheduled to take effect on Nov. 15, while the lawsuit continues through the courts.
“As stated previously, banning abortion before viability violates Supreme Court precedent,” Judge Thompson wrote in the opinion. “No alleged state interest can overcome this clear mandate. Thus, as a ban on pre-viability abortion, the act contravenes established law.”
Alabama Gov. Kay Ivey (R) signed the “Human Life Protection Act” into law on May 15. The measure bans abortion at every pregnancy stage and penalizes physicians with a Class A felony for performing an abortion and charges them with a Class C felony for attempting to perform an abortion. The law includes an exception if a woman’s life is at risk, but not for cases of rape or incest.
The federal court’s decision affirms that women have a right to access safe, legal abortion, Alexis McGill Johnson, president and CEO of Planned Parenthood Federation of America said in a statement. Planned Parenthood Federation of America, The American Civil Liberties Union, and the ACLU of Alabama are representing the plaintiffs in the lawsuit, which include Alabama physicians and patients.
“Politicians in Alabama, and across the country, are putting people’s health and lives at risk in their attempts to ban abortion outright in this country,” Ms. Johnson said in the statement. “Today’s victory means people can still access the health care they need across Alabama – for now. We will continue to fight to ensure that everyone can access health care – including safe, legal abortion.”
Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall said the district court’s decision to temporarily halt the law was not unexpected.
“As we have stated before, the state’s objective is to advance our case to the U.S. Supreme Court where we intend to submit evidence that supports our argument that Roe and Casey were wrongly decided and that the Constitution does not prohibit states from protecting unborn children from abortion,” Mr. Marshall said in a statement.
The Alabama decision comes just weeks after the U.S. Supreme Court agreed to hear an abortion-related challenge out of Louisiana. June Medical Services v. Gee centers on the constitutionality of a Louisiana law that requires any doctor performing an abortion to have admitting privileges at a nearby hospital. The high court likely will hear that case in early 2020.
Sleep problems in pregnancy presage postnatal depression
COPENHAGEN – Tiina Paunio, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think it is very important to understand that we need to screen pregnant women for sleep problems, even those without a history of depression, so we can have early treatment of insomnia – and also depression – because postnatal maternal depression is very much a risk for the child during a vulnerable period for development,” said Dr. Paunio, professor of psychiatry at the University of Helsinki.
She was a coinvestigator in a prospective study of the Finnish CHILD-SLEEP longitudinal birth cohort in which 1,398 women completed the Basic Nordic Sleep Questionnaire and the 10-item version of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) at about gestational week 32 and again around 3 months following delivery. Postnatal depressiveness as defined by a CES-D score of at least 10 points was present in 10.3% of the mothers. After adjusting for prenatal depressiveness and other potential confounders, the investigators found that tiredness during the day, poor general sleep quality, getting less than 6 hours of sleep, taking longer than 20 minutes to fall asleep, and sleep loss of 2 hours or more per night during pregnancy were each associated with clinically significant postnatal depressive symptoms, with odds ratios of 1.87-2.19.
The full details of the study have been published (Arch Womens Ment Health. 2019 Jun;22[3]:327-37).
The impetus for this study of sleep problems in pregnancy as a predictor of postnatal depressive symptoms was a body of evidence linking insomnia to depression in both men and women. But it turns out that insomnia is a significant predictor of later onset of a wide variety of psychiatric disorders, not only depression, as highlighted in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by an international team of investigators, Dr. Paunio observed.
Baseline insomnia symptoms were associated with a 183% increased risk of later onset of depression, a 223% increased risk of anxiety, a 35%greater risk of alcohol abuse, and a 28% increased risk of psychosis. However, the insomnia/psychosis link must be viewed as tentative, as it was examined in only a single published study. The investigators rated the overall risk of bias in the studies included in their meta-analysis as moderate (Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105).
For Dr. Paunio, these findings suggest that interventional studies of early and effective treatment of insomnia as a potential means of preventing psychiatric disorders are in order.
She reported receiving research funding from the Academy of Finland, the Gyllenberg Foundation, and Finska Lakaresallskapet.
COPENHAGEN – Tiina Paunio, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think it is very important to understand that we need to screen pregnant women for sleep problems, even those without a history of depression, so we can have early treatment of insomnia – and also depression – because postnatal maternal depression is very much a risk for the child during a vulnerable period for development,” said Dr. Paunio, professor of psychiatry at the University of Helsinki.
She was a coinvestigator in a prospective study of the Finnish CHILD-SLEEP longitudinal birth cohort in which 1,398 women completed the Basic Nordic Sleep Questionnaire and the 10-item version of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) at about gestational week 32 and again around 3 months following delivery. Postnatal depressiveness as defined by a CES-D score of at least 10 points was present in 10.3% of the mothers. After adjusting for prenatal depressiveness and other potential confounders, the investigators found that tiredness during the day, poor general sleep quality, getting less than 6 hours of sleep, taking longer than 20 minutes to fall asleep, and sleep loss of 2 hours or more per night during pregnancy were each associated with clinically significant postnatal depressive symptoms, with odds ratios of 1.87-2.19.
The full details of the study have been published (Arch Womens Ment Health. 2019 Jun;22[3]:327-37).
The impetus for this study of sleep problems in pregnancy as a predictor of postnatal depressive symptoms was a body of evidence linking insomnia to depression in both men and women. But it turns out that insomnia is a significant predictor of later onset of a wide variety of psychiatric disorders, not only depression, as highlighted in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by an international team of investigators, Dr. Paunio observed.
Baseline insomnia symptoms were associated with a 183% increased risk of later onset of depression, a 223% increased risk of anxiety, a 35%greater risk of alcohol abuse, and a 28% increased risk of psychosis. However, the insomnia/psychosis link must be viewed as tentative, as it was examined in only a single published study. The investigators rated the overall risk of bias in the studies included in their meta-analysis as moderate (Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105).
For Dr. Paunio, these findings suggest that interventional studies of early and effective treatment of insomnia as a potential means of preventing psychiatric disorders are in order.
She reported receiving research funding from the Academy of Finland, the Gyllenberg Foundation, and Finska Lakaresallskapet.
COPENHAGEN – Tiina Paunio, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology.
“I think it is very important to understand that we need to screen pregnant women for sleep problems, even those without a history of depression, so we can have early treatment of insomnia – and also depression – because postnatal maternal depression is very much a risk for the child during a vulnerable period for development,” said Dr. Paunio, professor of psychiatry at the University of Helsinki.
She was a coinvestigator in a prospective study of the Finnish CHILD-SLEEP longitudinal birth cohort in which 1,398 women completed the Basic Nordic Sleep Questionnaire and the 10-item version of the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) at about gestational week 32 and again around 3 months following delivery. Postnatal depressiveness as defined by a CES-D score of at least 10 points was present in 10.3% of the mothers. After adjusting for prenatal depressiveness and other potential confounders, the investigators found that tiredness during the day, poor general sleep quality, getting less than 6 hours of sleep, taking longer than 20 minutes to fall asleep, and sleep loss of 2 hours or more per night during pregnancy were each associated with clinically significant postnatal depressive symptoms, with odds ratios of 1.87-2.19.
The full details of the study have been published (Arch Womens Ment Health. 2019 Jun;22[3]:327-37).
The impetus for this study of sleep problems in pregnancy as a predictor of postnatal depressive symptoms was a body of evidence linking insomnia to depression in both men and women. But it turns out that insomnia is a significant predictor of later onset of a wide variety of psychiatric disorders, not only depression, as highlighted in a recent systematic review and meta-analysis conducted by an international team of investigators, Dr. Paunio observed.
Baseline insomnia symptoms were associated with a 183% increased risk of later onset of depression, a 223% increased risk of anxiety, a 35%greater risk of alcohol abuse, and a 28% increased risk of psychosis. However, the insomnia/psychosis link must be viewed as tentative, as it was examined in only a single published study. The investigators rated the overall risk of bias in the studies included in their meta-analysis as moderate (Sleep Med Rev. 2019 Feb;43:96-105).
For Dr. Paunio, these findings suggest that interventional studies of early and effective treatment of insomnia as a potential means of preventing psychiatric disorders are in order.
She reported receiving research funding from the Academy of Finland, the Gyllenberg Foundation, and Finska Lakaresallskapet.
REPORTING FROM ECNP 2019