User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Angioedema risk jumps when switching HF meds
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New renin-angiotensin-system (RAS) inhibitor therapy using sacubitril-valsartan (Entresto) is no more likely to cause angioedema than starting out with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB).
But the risk climbs when such patients start on an ACE inhibitor or ARB and then switch to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those prescribed the newer drug, the only available angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), in the first place.
Those findings and others from a large database analysis, by researchers at the Food and Drug Administration and Harvard Medical School, may clarify and help alleviate a residual safety concern about the ARNI – that it might promote angioedema – that persists after the drug’s major HF trials.
The angioedema risk increased the most right after the switch to the ARNI from one of the older RAS inhibitors. For example, the overall risk doubled for patients who started with an ARB then switched to sacubitril-valsartan, compared with those who started on the newer drug. But it went up about 2.5 times during the first 14 days after the switch.
A similar pattern emerged for ACE inhibitors, but the increased angioedema risk reached significance only within 2 weeks of the switch from an ACE inhibitor to sacubitril-valsartan compared to starting on the latter.
The analysis, based on data from the FDA’s Sentinel adverse event reporting system, was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
A rare complication, but ...
Angioedema was rare overall in the study, with an unadjusted rate of about 6.75 per 1,000 person-years for users of ACE inhibitors, less than half that rate for ARB users, and only one-fifth that rate for sacubitril-valsartan recipients.
But even a rare complication can be a worry for drugs as widely used as RAS inhibitors. And it’s not unusual for patients cautiously started on an ACE inhibitor or ARB to be switched to sacubitril-valsartan, which is only recently a core guideline–recommended therapy for HF with reduced ejection fraction.
Such patients transitioning to the ARNI, the current study suggests, should probably be watched closely for signs of angioedema for 2 weeks but especially during the first few days. Indeed, the study’s event curves show most of the extra risk “popping up” right after the switch to sacubitril-valsartan, lead author Efe Eworuke, PhD, told this news organization.
The ARNI’s labeling, which states the drug should follow ACE inhibitors only after 36-hour washout period, “has done justice to this issue,” she said. But “whether clinicians are adhering to that, we can’t tell.”
Potentially, patients who miss the 36-hour washout between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and sacubitril-valsartan may account for the excess angioedema risk seen in the analysis, said Dr. Eworuke, with the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Silver Spring, Md.
But the analysis doesn’t nail down the window of excess risk to only 36 hours. It suggests that patients switching to the ARNI – even those pausing for 36 hours in between drugs – should probably be monitored “2 weeks or longer,” she said. “They could still have angioedema after the washout period.”
Indeed, the “timing of the switch may be critical,” according to an editorial accompanying the report. “Perhaps a longer initial exposure period of ACE inhibitor or ARB,” beyond 2 weeks, “should be considered before switching to an ARNI,” contended Robert L. Page II, PharmD, MSPH, University of Colorado Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Aurora.
Moreover, he wrote, the study suggests that “initiation of an ARNI de novo may be safer compared with trialing an ACE inhibitor or ARB then switching to an ARNI,” and “should be a consideration when beginning guideline-directed medical therapy for patients with HF.”
New RAS inhibition with ARNI ‘protective’
Compared with ARNI “new users” who had not received any RAS inhibitor in the prior 6 months, patients in the study who switched from an ACE inhibitor to ARNI (41,548 matched pairs) showed a hazard ratio (HR) for angioedema of 1.62 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.91-2.89), that is, only a “trend,” the report states.
But that trend became significant when the analysis considered only angioedema cases in the first 14 days after the drug switch: HR, 1.98 (95% CI, 1.11-3.53).
Those switching from an ARB to ARNI, compared with ARNI new users (37,893 matched pairs), showed a significant HR for angioedema of 2.03 (95% CI, 1.16-3.54). The effect was more pronounced when considering only angioedema arising in the first 2 weeks: HR, 2.45 (95% CI, 1.36-4.43).
Compared with new use of ACE inhibitors, new ARNI use (41,998 matched pairs) was “protective,” the report states, with an HR for angioedema of 0.18 (95% CI, 0.11-0.29). So was a switch from ACE inhibitors to the ARNI (69,639 matched pairs), with an HR of 0.31 (95% CI, 0.23-0.43).
But compared with starting with an ARB, ARNI new use (43,755 matched pairs) had a null effect on angioedema risk, HR, 0.59 (95% CI, 0.35-1.01); as did switching from an ARB to ARNI (49,137 matched pairs), HR, 0.85 (95% CI, 0.58-1.26).
The analysis has limitations, Dr. Eworuke acknowledged. The comparator groups probably differed in unknown ways given the limits of propensity matching, for example, and because the FDA’s Sentinel system data can reflect only cases that are reported, the study probably underestimates the true prevalence of angioedema.
For example, a patient may see a clinician for a milder case that resolves without a significant intervention, she noted. But “those types of angioedema would not have been captured by our study.”
Dr. Eworuke disclosed that her comments reflect her views and are not those of the Food and Drug Administration; she and the other authors, as well as editorialist Dr. Page, report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
Even one head injury boosts all-cause mortality risk
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An analysis of more than 13,000 adult participants in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study showed a dose-response pattern in which one head injury was linked to a 66% increased risk for all-cause mortality, and two or more head injuries were associated with twice the risk in comparison with no head injuries.
These findings underscore the importance of preventing head injuries and of swift clinical intervention once a head injury occurs, lead author Holly Elser, MD, PhD, department of neurology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Clinicians should counsel patients who are at risk for falls about head injuries and ensure patients are promptly evaluated in the hospital setting if they do have a fall – especially with loss of consciousness or other symptoms, such as headache or dizziness,” Dr. Elser added.
The findings were published online in JAMA Neurology.
Consistent evidence
There is “pretty consistent evidence” that mortality rates are increased in the short term after head injury, predominantly among hospitalized patients, Dr. Elser noted.
“But there’s less evidence about the long-term mortality implications of head injuries and less evidence from adults living in the community,” she added.
The analysis included 13,037 participants in the ARIC study, an ongoing study involving adults aged 45-65 years who were recruited from four geographically and racially diverse U.S. communities. The mean age at baseline (1987-1989) was 54 years; 57.7% were women; and 27.9% were Black.
Study participants are followed at routine in-person visits and semiannually via telephone.
Data on head injuries came from hospital diagnostic codes and self-reports. These reports included information on the number of injuries and whether the injury required medical care and involved loss of consciousness.
During the 27-year follow-up, 18.4% of the study sample had at least one head injury. Injuries occurred more frequently among women, which may reflect the predominance of women in the study population, said Dr. Elser.
Overall, about 56% of participants died during the study period. The estimated median amount of survival time after head injury was 4.7 years.
The most common causes of death were neoplasm, cardiovascular disease, and neurologic disorders. Regarding specific neurologic causes of death, the researchers found that 62.2% of deaths were due to neurodegenerative disease among individuals with head injury, vs. 51.4% among those without head injury.
This, said Dr. Elser, raises the possibility of reverse causality. “If you have a neurodegenerative disorder like Alzheimer’s disease dementia or Parkinson’s disease that leads to difficulty walking, you may be more likely to fall and have a head injury. The head injury in turn may lead to increased mortality,” she noted.
However, she stressed that the data on cause-specific mortality are exploratory. “Our research motivates future studies that really examine this time-dependent relationship between neurodegenerative disease and head injuries,” Dr. Elser said.
Dose-dependent response
In the unadjusted analysis, the hazard ratio of mortality among individuals with head injury was 2.21 (95% confidence interval, 2.09-2.34) compared with those who did not have head injury.
The association remained significant with adjustment for sociodemographic factors (HR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.88-2.11) and with additional adjustment for vascular risk factors (HR, 1.92; 95% CI, 1.81-2.03).
The findings also showed a dose-response pattern in the association of head injuries with mortality. Compared with participants who did not have head injury, the HR was 1.66 (95% CI, 1.56-1.77) for those with one head injury and 2.11 (95% CI, 1.89-2.37) for those with two or more head injuries.
“It’s not as though once you’ve had one head injury, you’ve accrued all the damage you possibly can. We see pretty clearly here that recurrent head injury further increased the rate of deaths from all causes,” said Dr. Elser.
Injury severity was determined from hospital diagnostic codes using established algorithms. Results showed that mortality rates were increased with even mild head injury.
Interestingly, the association between head injury and all-cause mortality was weaker among those whose injuries were self-reported. One possibility is that these injuries were less severe, Dr. Elser noted.
“If you have head injury that’s mild enough that you don’t need to go to the hospital, it’s probably going to confer less long-term health risks than one that’s severe enough that you needed to be examined in an acute care setting,” she said.
Results were similar by race and for sex. “Even though there were more women with head injuries, the rate of mortality associated with head injury doesn’t differ from the rate among men,” Dr. Elser reported.
However, the association was stronger among those younger than 54 years at baseline (HR, 2.26) compared with older individuals (HR, 2.0) in the model that adjusted for demographics and lifestyle factors.
This may be explained by the reference group (those without a head injury) – the mortality rate was in general higher for the older participants, said Dr. Elser. It could also be that younger adults are more likely to have severe head injuries from, for example, motor vehicle accidents or violence, she added.
These new findings underscore the importance of public health measures, such as seatbelt laws, to reduce head injuries, the investigators note.
They add that clinicians with patients at risk for head injuries may recommend steps to lessen the risk of falls, such as having access to durable medical equipment, and ensuring driver safety.
Shorter life span
Commenting for this news organization, Frank Conidi, MD, director of the Florida Center for Headache and Sports Neurology in Port St. Lucie and past president of the Florida Society of Neurology, said the large number of participants “adds validity” to the finding that individuals with head injury are likely to have a shorter life span than those who do not suffer head trauma – and that this “was not purely by chance or from other causes.”
However, patients may not have accurately reported head injuries, in which case the rate of injury in the self-report subgroup would not reflect the actual incidence, noted Dr. Conidi, who was not involved with the research.
“In my practice, most patients have little knowledge as to the signs and symptoms of concussion and traumatic brain injury. Most think there needs to be some form of loss of consciousness to have a head injury, which is of course not true,” he said.
Dr. Conidi added that the finding of a higher incidence of death from neurodegenerative disorders supports the generally accepted consensus view that about 30% of patients with traumatic brain injury experience progression of symptoms and are at risk for early dementia.
The ARIC study is supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Elser and Dr. Conidi have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Noninvasive liver test may help select asymptomatic candidates for heart failure tests
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
The 2021 NAFLD clinical care pathway is a shining example of how a simple score like the fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index – paired sequentially with a second noninvasive test like vibration-controlled elastography – can provide an accurate, cost-effective screening tool and risk stratification and further limit invasive testing such as liver biopsy.
Broader use of FIB-4 by cardiovascular and hepatology providers may increase earlier identification of NAFLD or HFpEF or both.
Anand S. Shah, MD, is director of hepatology at Atlanta VA Healthcare and assistant professor of medicine, division of digestive disease, department of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta. He has no financial conflicts.
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
A noninvasive test for liver disease may be a useful, low-cost screening tool to select asymptomatic candidates for a detailed examination of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), say authors of a report published in Gastro Hep Advances.
The fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk, wrote Chisato Okamoto, MD, of the department of medical biochemistry at Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine and the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan, and colleagues.
“Recognition of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction at an early stage in mass screening is desirable, but difficult to achieve,” the authors wrote. “The FIB-4 index is calculated using only four parameters that are routinely evaluated in general health check-up programs.”
HFpEF is an emerging disease in recent years with a poor prognosis, they wrote. Early diagnosis can be challenging for several reasons, particularly because HFpEF patients are often asymptomatic until late in the disease process and have normal left ventricular filling pressures at rest. By using a tool to select probable cases from subclinical participants in a health check-up program, clinicians can refer patients for a diastolic stress test, which is considered the gold standard for diagnosing HFpEF.
Previous studies have found that the FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool to estimate liver stiffness and fibrosis, is associated with a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with HFpEF. In addition, patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have a twofold higher prevalence of HFpEF than the general population.
Dr. Okamoto and colleagues examined the association between the FIB-4 index and HFpEF risk based on the Heart Failure Association’s diagnostic algorithm for HFpEF in patients with breathlessness (HFA-PEFF). The researchers looked at the prognostic impact of the FIB-4 index in 710 patients who participated in a health check-up program in the rural community of Arita-cho, Japan, between 2006 and 2007. They excluded participants with a history of cardiovascular disease or reduced left ventricular systolic function (LVEF < 50%). Researchers calculated the FIB-4 index and HFA-PEFF score for all participants.
First, using the HFA-PEFF scores, the researchers sorted participants into five groups by HFpEF risk: 215 (30%) with zero points, 100 (14%) with 1 point, 171 (24%) with 2 points, 163 (23%) with 3 points, and 61 (9%) with 4-6 points. Participants in the high-risk group (scores 4-6) were older, mostly men, and had higher blood pressure, alcohol intake, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and liver disease. The higher the HFpEF risk group, the higher the rates of all-cause mortality, hospitalization for heart failure, and MACE.
Overall, the FIB-4 index was correlated with the HFpEF risk groups and showed a stepwise increase across the groups, with .94 for the low-risk group, 1.45 for the intermediate-risk group, and 1.99 for the high-risk group, the authors wrote. The FIB-4 index also correlated with markers associated with components of the HFA-PEFF scoring system.
Using multivariate logistic regression analysis, the FIB-4 index was associated with a high HFpEF risk, and an increase in FIB-4 was associated with increased odds of high HFpEF risk. The association remained significant across four separate models that accounted for risk factors associated with lifestyle-related diseases, blood parameters associated with liver disease, and chronic conditions such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and liver disease.
In additional area under the curve (AUC) analyses, the FIB-4 index was a significant predictor of high HFpEF risk. At cutoff values typically used for advanced liver fibrosis in NAFLD, a FIB-4 cutoff of 1.3 or less had a sensitivity of 85.2%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of 2.67 or higher had a specificity of 94.8%. At alternate cutoff values typically used for patients with HIV/hepatitis C virus infection, a FIB-4 cutoff of less than 1.45 had a sensitivity of 75.4%, while a FIB-4 cutoff of greater than 3.25 had a specificity of 98%.
Using cutoffs of 1.3 and 2.67, a higher FIB-4 was associated with higher rates of clinical events and MACE, as well as a higher HFpEF risk. Using the alternate cutoffs of 1.45 and 3.25, prognostic stratification of clinical events and MACE was also possible.
When all variables were included in the multivariate model, the FIB-4 index remained a significant prognostic predictor. The FIB-4 index stratified clinical prognosis was also an independent predictor of all-cause mortality and hospitalization for heart failure.
Although additional studies are needed to reveal the interaction between liver and heart function, the study authors wrote, the findings provide valuable insights that can help discover the cardiohepatic interaction to reduce the development of HFpEF.
“Since it can be easily, quickly, and inexpensively measured, routine or repeated measurements of the FIB-4 index could help in selecting preferred candidates for detailed examination of HFpEF risk, which may improve clinical outcomes by diagnosing HFpEF at an early stage,” they wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Osaka Medical Research Foundation for Intractable Disease, the Japan Arteriosclerosis Prevention Fund, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Japan Heart Foundation. The authors disclosed no conflicts.
FROM GASTRO HEP ADVANCES
Novel resuscitation for patients with nonshockable rhythms in cardiac arrest
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. with a remarkable increase in neurologically intact survival. Welcome, gentlemen.
Dr. Pepe, I’d like to start off by thanking you for taking time to join us to discuss this novel concept of head-up or what you now refer to as a neuroprotective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) bundle. Can you define what this entails and why it is referred to as a neuroprotective CPR bundle?
Paul E. Pepe, MD, MPH: CPR has been life saving for 60 years the way we’ve performed it, but probably only in a very small percentage of cases. That’s one of the problems. We have almost a thousand people a day who have sudden cardiac arrest out in the community alone and more in the hospital.
We know that early defibrillation and early CPR can contribute, but it’s still a small percentage of those. About 75%-85% of the cases that we go out to see will have nonshockable rhythms and flatlines. Some cases are what we call “pulseless electrical activity,” meaning that it looks like there is some kind of organized complex, but there is no pulse associated with it.
That’s why it’s a problem, because they don’t come back. Part of the reason why we see poor outcomes is not only that these cases tend to be people who, say, were in ventricular fibrillation and then just went on over time and were not witnessed or resuscitated or had a long response time. They basically either go into flatline or autoconvert into these bizarre rhythms.
The other issue is the way we perform CPR. CPR has been lifesaving, but it only generates about 20% and maybe 15% in some cases of normal blood flow, and particularly, cerebral perfusion pressure. We’ve looked at this nicely in the laboratory.
For example, during chest compressions, we’re hoping during the recoil phase to pull blood down and back into the right heart. The problem is that you’re not only setting a pressure rate up here to the arterial side but also, you’re setting back pressure wave on the venous side. Obviously, the arterial side always wins out, but it’s just not as efficient as it could be, at 20% or 30%.
What does this entail? It entails several independent mechanisms in terms of how they work, but they all do the same thing, which is they help to pull blood out of the brain and back into the right heart by basically manipulating intrathoracic pressure and creating more of a vacuum to get blood back there.
It’s so important that people do quality CPR. You have to have a good release and that helps us suck a little bit of blood and sucks the air in. As soon as the air rushes in, it neutralizes the pressure and there’s no more vacuum and nothing else is happening until the next squeeze.
What we have found is that we can cap the airway just for a second with a little pop-up valve. It acts like when you’re sucking a milkshake through a straw and it creates more of a vacuum in the chest. Just a little pop-up valve that pulls a little bit more blood out of the brain and the rest of the body and into the right heart.
We’ve shown in a human study that, for example, the systolic blood pressure almost doubles. It really goes from 40 mm Hg during standard CPR up to 80 mm Hg, and that would be sustained for 14-15 minutes. That was a nice little study that was done in Milwaukee a few years ago.
The other thing that happens is, if you add on something else, it’s like a toilet plunger. I think many people have seen it; it’s called “active compression-decompression.” It not only compresses, but it decompresses. Where it becomes even more effective is that if you had broken bones or stiff bones as you get older or whatever it may be, as you do the CPR, you’re still getting the push down and then you’re getting the pull out. It helps on several levels. More importantly, when you put the two together, they’re very synergistic.
We, have already done the clinical trial that is the proof of concept, and that was published in The Lancet about 10 years ago. In that study, we found that the combination of those two dramatically improved survival rates by 50%, with 1-year survival neurologically intact. That got us on the right track.
The interesting thing is that someone said, “Can we lift the head up a little bit?” We did a large amount of work in the laboratory over 10 years, fine tuning it. When do you first lift the head? How soon is too soon? It’s probably bad if you just go right to it.
We had to get the pump primed a little bit with these other things to get the flow going better, not only pulling blood out of the brain but now, you have a better flow this way. You have to prime at first for a couple of minutes, and we worked out the timing: Is it 3 or 4 minutes? It seems the timing is right at about 2 minutes, then you gradually elevate the head over about 2 minutes. We’re finding that seems to be the optimal way to do it. About 2 minutes of priming with those other two devices, the adjuncts, and then gradually elevate the head over 2 minutes.
When we do that in the laboratory, we’re getting normalized cerebral perfusion pressures. You’re normalizing the flow back again with that. We’re seeing profound differences in outcome as a result, even in these cases of the nonshockables.
Dr. Glatter: What you’re doing basically is resulting in an increase in cardiac output, essentially. That really is important, especially in these nonshockable rhythms, correct?
Dr. Pepe: Absolutely. As you’re doing this compression and you’re getting these intracranial pulse waves that are going up because they’re colliding up there. It could be even damaging in itself, but we’re seeing these intracranial raises. The intracranial pressure starts going up more and more over time. Also, peripherally in most people, you’re not getting good flow out there; then, your vasculature starts to relax. The arterials are starting to not get oxygen, so they don’t go out.
With this technique where we’re returning the pressure, we’re getting to 40% of normal now with the active compression-decompression CPR plus an impedance threshold device (ACD+ITD CPR) approach. Now, you add this, and you’re almost normalizing. In humans, even in these asystole patients, we’re seeing end-title CO2s which are generally in the 15-20 range with standard CPR are now up with ACD+ITD CPR in the 30%-40% range, where we’re getting through 30 or 40 end-tidal CO2s. Now, we’re seeing even the end-tidal CO2s moving up into the 40s and 50s. We know there’s a surrogate marker telling us that we are generating much better flows not only to the rest of the body, but most importantly, to the brain.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, could you tell us about the approach in terms of on scene, what you’re doing and how you use the device itself? Maybe you could talk about the backpack that you developed with your fire department?
Ryan P. Quinn, BS, EMS: Our approach has always been to get to the patient quickly, like everybody’s approach on a cardiac arrest when you’re responding. We are an advanced life-support paramedic ambulance service through the fire department – we’re all cross-trained firefighter paramedics. Our first vehicle from the fire department is typically the ambulance. It’s smaller and a little quicker than the fire engine. Two paramedics are going to jump out with two backpacks. One has the automated compressive device (we use the Lucas), and the other one is the sequential patient lifting device, the EleGARD.
Our two paramedics are quick to the patient’s side, and once they make contact with the patient to verify pulseless cardiac arrest, they will unpack. One person will go right to compressions if there’s nobody on compressions already. Sometimes we have a first responder police officer with an automated external defibrillator (AED). We go right to the patient’s side, concentrate on compressions, and within 90 seconds to 2 minutes, we have our bags unpacked, we’ve got the devices turned on, patient lifted up, slid under the device, and we have a supraglottic airway that is placed within 15 seconds already premade with the ITD on top. We have a sealed airway that we can continue to compress with Dr. Pepe’s original discussion of building on what’s previously been shown to work.
Dr. Pepe: Let me make a comment about this. This is so important, what Ryan is saying, because it’s something we found during the study. It’s really a true pit-crew approach. You’re not only getting these materials, which you think you need a medical Sherpa for, but you don’t. They set it up and then when they open it up, it’s all laid out just exactly as you need it. It’s not just how fast you get there; it’s how fast you get this done.
When we look at all cases combined against high-performance systems that had some of the highest survival rates around, when we compare it to those, we found that overall, even if you looked at the ones that had over 20-minute responses, the odds ratios were still three to four times higher. It was impressive.
If you looked at it under 15 minutes, which is really reasonable for most systems that get there by the way, the average time that people start CPR in any system in these studies has been about 8 minutes if you actually start this thing, which takes about 2 minutes more for this new bundle of care with this triad, it’s almost 12-14 times higher in terms of the odds ratio. I’ve never seen anything like that where the higher end is over 100 in terms of your confidence intervals.
Ryan’s system did really well and is one of those with even higher levels of outcomes, mostly because they got it on quickly. It’s like the AED for nonshockables but better because you have a wider range of efficacy where it will work.
Dr. Glatter: When the elapsed time was less than 11 minutes, that seemed to be an inflection point in the study, is that correct? You saw that 11-fold higher incidence in terms of neurologically intact survival, is that correct?
Dr. Pepe: We picked that number because that was the median time to get it on board. Half the people were getting it within that time period. The fact that you have a larger window, we’re talking about 13- almost 14-fold improvements in outcome if it was under 15 minutes. It doesn’t matter about the 11 or the 12. It’s the faster you get it on board, the better off you are.
Dr. Glatter: What’s the next step in the process of doing trials and having implementation on a larger scale based on your Annals of Emergency Medicine study? Where do you go from here?
Dr. Pepe: I’ve come to find out there are many confounding variables. What was the quality of CPR? How did people ventilate? Did they give the breath and hold it? Did they give a large enough breath so that blood can go across the transpulmonary system? There are many confounding variables. That’s why I think, in the future, it’s going to be more of looking at things like propensity score matching because we know all the variables that change outcomes. I think that’s going to be a way for me.
The other thing is that we were looking at only 380 cases here. When this doubles up in numbers, as we accrue more cases around the country of people who are implementing this, these numbers I just quoted are going to go up much higher. Unwitnessed asystole is considered futile, and you just don’t get them back. To be able to get these folks back now, even if it’s a small percentage, and the fact that we know that we’re producing this better flow, is pretty striking.
I’m really impressed, and the main thing is to make sure people are educated about it. Number two is that they understand that it has to be done right. It cannot be done wrong or you’re not going to see the differences. Getting it done right is not only following the procedures, the sequence, and how you do it, but it also has to do with getting there quickly, including assigning the right people to put it on and having well-trained people who know what they’re doing.
Dr. Glatter: In general, the lay public obviously should not attempt this in the field lifting someone’s head up in the sense of trying to do chest compressions. I think that message is important that you just said. It’s not ready for prime time yet in any way. It has to be done right.
Dr. Pepe: Bystanders have to learn CPR – they will buy us time and we’ll have better outcomes when they do that. That’s number one. Number two is that as more and more systems adopt this, you’re going to see more people coming back. If you think about what we’re doing now, if we only get back 5% of these nonshockable vs. less than 1%, it’s 5% of 800 people a day because a thousand people a day die. Several dozens of lives can be saved on a daily basis, coming back neurologically intact. That’s the key thing.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, can you comment about your experience in the field? Is there anything in terms of your current approach that you think would be ideal to change at this point?
Mr. Quinn: We’ve established that this is the approach that we want to take and we’re just fine tuning it to be more efficient. Using the choreography of which person is going to do which role, we have clearly defined roles and clearly defined command of the scene so we’re not missing anything. Training is extremely important.
Dr. Glatter: Paul, I want to ask you about your anecdotal experience of people waking up quickly and talking after elevating their heads and going through this process. Having people talk about it and waking up is really fascinating. Maybe you can comment further on this.
Dr. Pepe: That’s a great point that you bring up because a 40- to 50-year-old guy who got saved with this approach, when he came around, he said he was hearing what people were saying. When he came out of it, he found out he had been getting CPR for about 25 minutes because he had persistent recurring ventricular fibrillation. He said, “How could I have survived that that long?”
When we told him about the new approach, he added, “Well, that’s like neuroprotective.” He’s right, because in the laboratory, we showed it was neuroprotective and we’re also getting better flows back there. It goes along with everything else, and so we’ve adopted the name because it is.
These are really high-powered systems we are comparing against, and we have the same level of return of spontaneous circulation. The major difference was when you started talking about the neurointact survival. We don’t have enough numbers yet, but next go around, we’re going to look at cerebral performance category (CPC) – CPC1 vs. the CPC2 – which were both considered intact, but CPC1 is actually better. We’re seeing many more of those, anecdotally.
I also wanted to mention that people do bring this up and say, “Well, let’s do a trial.” As far as we’re concerned, the trial’s been done in terms of The Lancet study 10 years ago that showed that the active compression-decompression had tremendously better outcomes. We show in the laboratories that you augment that a little bit. These are all [Food and Drug Administration] approved. You can go out and buy it tomorrow and get it done. I have no conflicts of interest, by the way, with any of this.
To have this device that’s going to have the potential of saving so many more lives is really an exciting breakthrough. More importantly, we’re understanding more now about the physiology of CPR and why it works. It could work much better with the approaches that we’ve been developing over the last 20 years or so.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. I want to thank both of you gentlemen. It’s been really an incredible experience to learn more about an advance in resuscitation that could truly be lifesaving. Thank you again for taking time to join us.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician in the department of emergency medicine, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York. Dr. Pepe is professor, department of management, policy, and community health, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston. Mr. Quinn is EMS Chief, Edina (Minn.) Fire Department. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared Jan. 26 on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. with a remarkable increase in neurologically intact survival. Welcome, gentlemen.
Dr. Pepe, I’d like to start off by thanking you for taking time to join us to discuss this novel concept of head-up or what you now refer to as a neuroprotective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) bundle. Can you define what this entails and why it is referred to as a neuroprotective CPR bundle?
Paul E. Pepe, MD, MPH: CPR has been life saving for 60 years the way we’ve performed it, but probably only in a very small percentage of cases. That’s one of the problems. We have almost a thousand people a day who have sudden cardiac arrest out in the community alone and more in the hospital.
We know that early defibrillation and early CPR can contribute, but it’s still a small percentage of those. About 75%-85% of the cases that we go out to see will have nonshockable rhythms and flatlines. Some cases are what we call “pulseless electrical activity,” meaning that it looks like there is some kind of organized complex, but there is no pulse associated with it.
That’s why it’s a problem, because they don’t come back. Part of the reason why we see poor outcomes is not only that these cases tend to be people who, say, were in ventricular fibrillation and then just went on over time and were not witnessed or resuscitated or had a long response time. They basically either go into flatline or autoconvert into these bizarre rhythms.
The other issue is the way we perform CPR. CPR has been lifesaving, but it only generates about 20% and maybe 15% in some cases of normal blood flow, and particularly, cerebral perfusion pressure. We’ve looked at this nicely in the laboratory.
For example, during chest compressions, we’re hoping during the recoil phase to pull blood down and back into the right heart. The problem is that you’re not only setting a pressure rate up here to the arterial side but also, you’re setting back pressure wave on the venous side. Obviously, the arterial side always wins out, but it’s just not as efficient as it could be, at 20% or 30%.
What does this entail? It entails several independent mechanisms in terms of how they work, but they all do the same thing, which is they help to pull blood out of the brain and back into the right heart by basically manipulating intrathoracic pressure and creating more of a vacuum to get blood back there.
It’s so important that people do quality CPR. You have to have a good release and that helps us suck a little bit of blood and sucks the air in. As soon as the air rushes in, it neutralizes the pressure and there’s no more vacuum and nothing else is happening until the next squeeze.
What we have found is that we can cap the airway just for a second with a little pop-up valve. It acts like when you’re sucking a milkshake through a straw and it creates more of a vacuum in the chest. Just a little pop-up valve that pulls a little bit more blood out of the brain and the rest of the body and into the right heart.
We’ve shown in a human study that, for example, the systolic blood pressure almost doubles. It really goes from 40 mm Hg during standard CPR up to 80 mm Hg, and that would be sustained for 14-15 minutes. That was a nice little study that was done in Milwaukee a few years ago.
The other thing that happens is, if you add on something else, it’s like a toilet plunger. I think many people have seen it; it’s called “active compression-decompression.” It not only compresses, but it decompresses. Where it becomes even more effective is that if you had broken bones or stiff bones as you get older or whatever it may be, as you do the CPR, you’re still getting the push down and then you’re getting the pull out. It helps on several levels. More importantly, when you put the two together, they’re very synergistic.
We, have already done the clinical trial that is the proof of concept, and that was published in The Lancet about 10 years ago. In that study, we found that the combination of those two dramatically improved survival rates by 50%, with 1-year survival neurologically intact. That got us on the right track.
The interesting thing is that someone said, “Can we lift the head up a little bit?” We did a large amount of work in the laboratory over 10 years, fine tuning it. When do you first lift the head? How soon is too soon? It’s probably bad if you just go right to it.
We had to get the pump primed a little bit with these other things to get the flow going better, not only pulling blood out of the brain but now, you have a better flow this way. You have to prime at first for a couple of minutes, and we worked out the timing: Is it 3 or 4 minutes? It seems the timing is right at about 2 minutes, then you gradually elevate the head over about 2 minutes. We’re finding that seems to be the optimal way to do it. About 2 minutes of priming with those other two devices, the adjuncts, and then gradually elevate the head over 2 minutes.
When we do that in the laboratory, we’re getting normalized cerebral perfusion pressures. You’re normalizing the flow back again with that. We’re seeing profound differences in outcome as a result, even in these cases of the nonshockables.
Dr. Glatter: What you’re doing basically is resulting in an increase in cardiac output, essentially. That really is important, especially in these nonshockable rhythms, correct?
Dr. Pepe: Absolutely. As you’re doing this compression and you’re getting these intracranial pulse waves that are going up because they’re colliding up there. It could be even damaging in itself, but we’re seeing these intracranial raises. The intracranial pressure starts going up more and more over time. Also, peripherally in most people, you’re not getting good flow out there; then, your vasculature starts to relax. The arterials are starting to not get oxygen, so they don’t go out.
With this technique where we’re returning the pressure, we’re getting to 40% of normal now with the active compression-decompression CPR plus an impedance threshold device (ACD+ITD CPR) approach. Now, you add this, and you’re almost normalizing. In humans, even in these asystole patients, we’re seeing end-title CO2s which are generally in the 15-20 range with standard CPR are now up with ACD+ITD CPR in the 30%-40% range, where we’re getting through 30 or 40 end-tidal CO2s. Now, we’re seeing even the end-tidal CO2s moving up into the 40s and 50s. We know there’s a surrogate marker telling us that we are generating much better flows not only to the rest of the body, but most importantly, to the brain.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, could you tell us about the approach in terms of on scene, what you’re doing and how you use the device itself? Maybe you could talk about the backpack that you developed with your fire department?
Ryan P. Quinn, BS, EMS: Our approach has always been to get to the patient quickly, like everybody’s approach on a cardiac arrest when you’re responding. We are an advanced life-support paramedic ambulance service through the fire department – we’re all cross-trained firefighter paramedics. Our first vehicle from the fire department is typically the ambulance. It’s smaller and a little quicker than the fire engine. Two paramedics are going to jump out with two backpacks. One has the automated compressive device (we use the Lucas), and the other one is the sequential patient lifting device, the EleGARD.
Our two paramedics are quick to the patient’s side, and once they make contact with the patient to verify pulseless cardiac arrest, they will unpack. One person will go right to compressions if there’s nobody on compressions already. Sometimes we have a first responder police officer with an automated external defibrillator (AED). We go right to the patient’s side, concentrate on compressions, and within 90 seconds to 2 minutes, we have our bags unpacked, we’ve got the devices turned on, patient lifted up, slid under the device, and we have a supraglottic airway that is placed within 15 seconds already premade with the ITD on top. We have a sealed airway that we can continue to compress with Dr. Pepe’s original discussion of building on what’s previously been shown to work.
Dr. Pepe: Let me make a comment about this. This is so important, what Ryan is saying, because it’s something we found during the study. It’s really a true pit-crew approach. You’re not only getting these materials, which you think you need a medical Sherpa for, but you don’t. They set it up and then when they open it up, it’s all laid out just exactly as you need it. It’s not just how fast you get there; it’s how fast you get this done.
When we look at all cases combined against high-performance systems that had some of the highest survival rates around, when we compare it to those, we found that overall, even if you looked at the ones that had over 20-minute responses, the odds ratios were still three to four times higher. It was impressive.
If you looked at it under 15 minutes, which is really reasonable for most systems that get there by the way, the average time that people start CPR in any system in these studies has been about 8 minutes if you actually start this thing, which takes about 2 minutes more for this new bundle of care with this triad, it’s almost 12-14 times higher in terms of the odds ratio. I’ve never seen anything like that where the higher end is over 100 in terms of your confidence intervals.
Ryan’s system did really well and is one of those with even higher levels of outcomes, mostly because they got it on quickly. It’s like the AED for nonshockables but better because you have a wider range of efficacy where it will work.
Dr. Glatter: When the elapsed time was less than 11 minutes, that seemed to be an inflection point in the study, is that correct? You saw that 11-fold higher incidence in terms of neurologically intact survival, is that correct?
Dr. Pepe: We picked that number because that was the median time to get it on board. Half the people were getting it within that time period. The fact that you have a larger window, we’re talking about 13- almost 14-fold improvements in outcome if it was under 15 minutes. It doesn’t matter about the 11 or the 12. It’s the faster you get it on board, the better off you are.
Dr. Glatter: What’s the next step in the process of doing trials and having implementation on a larger scale based on your Annals of Emergency Medicine study? Where do you go from here?
Dr. Pepe: I’ve come to find out there are many confounding variables. What was the quality of CPR? How did people ventilate? Did they give the breath and hold it? Did they give a large enough breath so that blood can go across the transpulmonary system? There are many confounding variables. That’s why I think, in the future, it’s going to be more of looking at things like propensity score matching because we know all the variables that change outcomes. I think that’s going to be a way for me.
The other thing is that we were looking at only 380 cases here. When this doubles up in numbers, as we accrue more cases around the country of people who are implementing this, these numbers I just quoted are going to go up much higher. Unwitnessed asystole is considered futile, and you just don’t get them back. To be able to get these folks back now, even if it’s a small percentage, and the fact that we know that we’re producing this better flow, is pretty striking.
I’m really impressed, and the main thing is to make sure people are educated about it. Number two is that they understand that it has to be done right. It cannot be done wrong or you’re not going to see the differences. Getting it done right is not only following the procedures, the sequence, and how you do it, but it also has to do with getting there quickly, including assigning the right people to put it on and having well-trained people who know what they’re doing.
Dr. Glatter: In general, the lay public obviously should not attempt this in the field lifting someone’s head up in the sense of trying to do chest compressions. I think that message is important that you just said. It’s not ready for prime time yet in any way. It has to be done right.
Dr. Pepe: Bystanders have to learn CPR – they will buy us time and we’ll have better outcomes when they do that. That’s number one. Number two is that as more and more systems adopt this, you’re going to see more people coming back. If you think about what we’re doing now, if we only get back 5% of these nonshockable vs. less than 1%, it’s 5% of 800 people a day because a thousand people a day die. Several dozens of lives can be saved on a daily basis, coming back neurologically intact. That’s the key thing.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, can you comment about your experience in the field? Is there anything in terms of your current approach that you think would be ideal to change at this point?
Mr. Quinn: We’ve established that this is the approach that we want to take and we’re just fine tuning it to be more efficient. Using the choreography of which person is going to do which role, we have clearly defined roles and clearly defined command of the scene so we’re not missing anything. Training is extremely important.
Dr. Glatter: Paul, I want to ask you about your anecdotal experience of people waking up quickly and talking after elevating their heads and going through this process. Having people talk about it and waking up is really fascinating. Maybe you can comment further on this.
Dr. Pepe: That’s a great point that you bring up because a 40- to 50-year-old guy who got saved with this approach, when he came around, he said he was hearing what people were saying. When he came out of it, he found out he had been getting CPR for about 25 minutes because he had persistent recurring ventricular fibrillation. He said, “How could I have survived that that long?”
When we told him about the new approach, he added, “Well, that’s like neuroprotective.” He’s right, because in the laboratory, we showed it was neuroprotective and we’re also getting better flows back there. It goes along with everything else, and so we’ve adopted the name because it is.
These are really high-powered systems we are comparing against, and we have the same level of return of spontaneous circulation. The major difference was when you started talking about the neurointact survival. We don’t have enough numbers yet, but next go around, we’re going to look at cerebral performance category (CPC) – CPC1 vs. the CPC2 – which were both considered intact, but CPC1 is actually better. We’re seeing many more of those, anecdotally.
I also wanted to mention that people do bring this up and say, “Well, let’s do a trial.” As far as we’re concerned, the trial’s been done in terms of The Lancet study 10 years ago that showed that the active compression-decompression had tremendously better outcomes. We show in the laboratories that you augment that a little bit. These are all [Food and Drug Administration] approved. You can go out and buy it tomorrow and get it done. I have no conflicts of interest, by the way, with any of this.
To have this device that’s going to have the potential of saving so many more lives is really an exciting breakthrough. More importantly, we’re understanding more now about the physiology of CPR and why it works. It could work much better with the approaches that we’ve been developing over the last 20 years or so.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. I want to thank both of you gentlemen. It’s been really an incredible experience to learn more about an advance in resuscitation that could truly be lifesaving. Thank you again for taking time to join us.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician in the department of emergency medicine, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York. Dr. Pepe is professor, department of management, policy, and community health, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston. Mr. Quinn is EMS Chief, Edina (Minn.) Fire Department. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared Jan. 26 on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. with a remarkable increase in neurologically intact survival. Welcome, gentlemen.
Dr. Pepe, I’d like to start off by thanking you for taking time to join us to discuss this novel concept of head-up or what you now refer to as a neuroprotective cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) bundle. Can you define what this entails and why it is referred to as a neuroprotective CPR bundle?
Paul E. Pepe, MD, MPH: CPR has been life saving for 60 years the way we’ve performed it, but probably only in a very small percentage of cases. That’s one of the problems. We have almost a thousand people a day who have sudden cardiac arrest out in the community alone and more in the hospital.
We know that early defibrillation and early CPR can contribute, but it’s still a small percentage of those. About 75%-85% of the cases that we go out to see will have nonshockable rhythms and flatlines. Some cases are what we call “pulseless electrical activity,” meaning that it looks like there is some kind of organized complex, but there is no pulse associated with it.
That’s why it’s a problem, because they don’t come back. Part of the reason why we see poor outcomes is not only that these cases tend to be people who, say, were in ventricular fibrillation and then just went on over time and were not witnessed or resuscitated or had a long response time. They basically either go into flatline or autoconvert into these bizarre rhythms.
The other issue is the way we perform CPR. CPR has been lifesaving, but it only generates about 20% and maybe 15% in some cases of normal blood flow, and particularly, cerebral perfusion pressure. We’ve looked at this nicely in the laboratory.
For example, during chest compressions, we’re hoping during the recoil phase to pull blood down and back into the right heart. The problem is that you’re not only setting a pressure rate up here to the arterial side but also, you’re setting back pressure wave on the venous side. Obviously, the arterial side always wins out, but it’s just not as efficient as it could be, at 20% or 30%.
What does this entail? It entails several independent mechanisms in terms of how they work, but they all do the same thing, which is they help to pull blood out of the brain and back into the right heart by basically manipulating intrathoracic pressure and creating more of a vacuum to get blood back there.
It’s so important that people do quality CPR. You have to have a good release and that helps us suck a little bit of blood and sucks the air in. As soon as the air rushes in, it neutralizes the pressure and there’s no more vacuum and nothing else is happening until the next squeeze.
What we have found is that we can cap the airway just for a second with a little pop-up valve. It acts like when you’re sucking a milkshake through a straw and it creates more of a vacuum in the chest. Just a little pop-up valve that pulls a little bit more blood out of the brain and the rest of the body and into the right heart.
We’ve shown in a human study that, for example, the systolic blood pressure almost doubles. It really goes from 40 mm Hg during standard CPR up to 80 mm Hg, and that would be sustained for 14-15 minutes. That was a nice little study that was done in Milwaukee a few years ago.
The other thing that happens is, if you add on something else, it’s like a toilet plunger. I think many people have seen it; it’s called “active compression-decompression.” It not only compresses, but it decompresses. Where it becomes even more effective is that if you had broken bones or stiff bones as you get older or whatever it may be, as you do the CPR, you’re still getting the push down and then you’re getting the pull out. It helps on several levels. More importantly, when you put the two together, they’re very synergistic.
We, have already done the clinical trial that is the proof of concept, and that was published in The Lancet about 10 years ago. In that study, we found that the combination of those two dramatically improved survival rates by 50%, with 1-year survival neurologically intact. That got us on the right track.
The interesting thing is that someone said, “Can we lift the head up a little bit?” We did a large amount of work in the laboratory over 10 years, fine tuning it. When do you first lift the head? How soon is too soon? It’s probably bad if you just go right to it.
We had to get the pump primed a little bit with these other things to get the flow going better, not only pulling blood out of the brain but now, you have a better flow this way. You have to prime at first for a couple of minutes, and we worked out the timing: Is it 3 or 4 minutes? It seems the timing is right at about 2 minutes, then you gradually elevate the head over about 2 minutes. We’re finding that seems to be the optimal way to do it. About 2 minutes of priming with those other two devices, the adjuncts, and then gradually elevate the head over 2 minutes.
When we do that in the laboratory, we’re getting normalized cerebral perfusion pressures. You’re normalizing the flow back again with that. We’re seeing profound differences in outcome as a result, even in these cases of the nonshockables.
Dr. Glatter: What you’re doing basically is resulting in an increase in cardiac output, essentially. That really is important, especially in these nonshockable rhythms, correct?
Dr. Pepe: Absolutely. As you’re doing this compression and you’re getting these intracranial pulse waves that are going up because they’re colliding up there. It could be even damaging in itself, but we’re seeing these intracranial raises. The intracranial pressure starts going up more and more over time. Also, peripherally in most people, you’re not getting good flow out there; then, your vasculature starts to relax. The arterials are starting to not get oxygen, so they don’t go out.
With this technique where we’re returning the pressure, we’re getting to 40% of normal now with the active compression-decompression CPR plus an impedance threshold device (ACD+ITD CPR) approach. Now, you add this, and you’re almost normalizing. In humans, even in these asystole patients, we’re seeing end-title CO2s which are generally in the 15-20 range with standard CPR are now up with ACD+ITD CPR in the 30%-40% range, where we’re getting through 30 or 40 end-tidal CO2s. Now, we’re seeing even the end-tidal CO2s moving up into the 40s and 50s. We know there’s a surrogate marker telling us that we are generating much better flows not only to the rest of the body, but most importantly, to the brain.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, could you tell us about the approach in terms of on scene, what you’re doing and how you use the device itself? Maybe you could talk about the backpack that you developed with your fire department?
Ryan P. Quinn, BS, EMS: Our approach has always been to get to the patient quickly, like everybody’s approach on a cardiac arrest when you’re responding. We are an advanced life-support paramedic ambulance service through the fire department – we’re all cross-trained firefighter paramedics. Our first vehicle from the fire department is typically the ambulance. It’s smaller and a little quicker than the fire engine. Two paramedics are going to jump out with two backpacks. One has the automated compressive device (we use the Lucas), and the other one is the sequential patient lifting device, the EleGARD.
Our two paramedics are quick to the patient’s side, and once they make contact with the patient to verify pulseless cardiac arrest, they will unpack. One person will go right to compressions if there’s nobody on compressions already. Sometimes we have a first responder police officer with an automated external defibrillator (AED). We go right to the patient’s side, concentrate on compressions, and within 90 seconds to 2 minutes, we have our bags unpacked, we’ve got the devices turned on, patient lifted up, slid under the device, and we have a supraglottic airway that is placed within 15 seconds already premade with the ITD on top. We have a sealed airway that we can continue to compress with Dr. Pepe’s original discussion of building on what’s previously been shown to work.
Dr. Pepe: Let me make a comment about this. This is so important, what Ryan is saying, because it’s something we found during the study. It’s really a true pit-crew approach. You’re not only getting these materials, which you think you need a medical Sherpa for, but you don’t. They set it up and then when they open it up, it’s all laid out just exactly as you need it. It’s not just how fast you get there; it’s how fast you get this done.
When we look at all cases combined against high-performance systems that had some of the highest survival rates around, when we compare it to those, we found that overall, even if you looked at the ones that had over 20-minute responses, the odds ratios were still three to four times higher. It was impressive.
If you looked at it under 15 minutes, which is really reasonable for most systems that get there by the way, the average time that people start CPR in any system in these studies has been about 8 minutes if you actually start this thing, which takes about 2 minutes more for this new bundle of care with this triad, it’s almost 12-14 times higher in terms of the odds ratio. I’ve never seen anything like that where the higher end is over 100 in terms of your confidence intervals.
Ryan’s system did really well and is one of those with even higher levels of outcomes, mostly because they got it on quickly. It’s like the AED for nonshockables but better because you have a wider range of efficacy where it will work.
Dr. Glatter: When the elapsed time was less than 11 minutes, that seemed to be an inflection point in the study, is that correct? You saw that 11-fold higher incidence in terms of neurologically intact survival, is that correct?
Dr. Pepe: We picked that number because that was the median time to get it on board. Half the people were getting it within that time period. The fact that you have a larger window, we’re talking about 13- almost 14-fold improvements in outcome if it was under 15 minutes. It doesn’t matter about the 11 or the 12. It’s the faster you get it on board, the better off you are.
Dr. Glatter: What’s the next step in the process of doing trials and having implementation on a larger scale based on your Annals of Emergency Medicine study? Where do you go from here?
Dr. Pepe: I’ve come to find out there are many confounding variables. What was the quality of CPR? How did people ventilate? Did they give the breath and hold it? Did they give a large enough breath so that blood can go across the transpulmonary system? There are many confounding variables. That’s why I think, in the future, it’s going to be more of looking at things like propensity score matching because we know all the variables that change outcomes. I think that’s going to be a way for me.
The other thing is that we were looking at only 380 cases here. When this doubles up in numbers, as we accrue more cases around the country of people who are implementing this, these numbers I just quoted are going to go up much higher. Unwitnessed asystole is considered futile, and you just don’t get them back. To be able to get these folks back now, even if it’s a small percentage, and the fact that we know that we’re producing this better flow, is pretty striking.
I’m really impressed, and the main thing is to make sure people are educated about it. Number two is that they understand that it has to be done right. It cannot be done wrong or you’re not going to see the differences. Getting it done right is not only following the procedures, the sequence, and how you do it, but it also has to do with getting there quickly, including assigning the right people to put it on and having well-trained people who know what they’re doing.
Dr. Glatter: In general, the lay public obviously should not attempt this in the field lifting someone’s head up in the sense of trying to do chest compressions. I think that message is important that you just said. It’s not ready for prime time yet in any way. It has to be done right.
Dr. Pepe: Bystanders have to learn CPR – they will buy us time and we’ll have better outcomes when they do that. That’s number one. Number two is that as more and more systems adopt this, you’re going to see more people coming back. If you think about what we’re doing now, if we only get back 5% of these nonshockable vs. less than 1%, it’s 5% of 800 people a day because a thousand people a day die. Several dozens of lives can be saved on a daily basis, coming back neurologically intact. That’s the key thing.
Dr. Glatter: Ryan, can you comment about your experience in the field? Is there anything in terms of your current approach that you think would be ideal to change at this point?
Mr. Quinn: We’ve established that this is the approach that we want to take and we’re just fine tuning it to be more efficient. Using the choreography of which person is going to do which role, we have clearly defined roles and clearly defined command of the scene so we’re not missing anything. Training is extremely important.
Dr. Glatter: Paul, I want to ask you about your anecdotal experience of people waking up quickly and talking after elevating their heads and going through this process. Having people talk about it and waking up is really fascinating. Maybe you can comment further on this.
Dr. Pepe: That’s a great point that you bring up because a 40- to 50-year-old guy who got saved with this approach, when he came around, he said he was hearing what people were saying. When he came out of it, he found out he had been getting CPR for about 25 minutes because he had persistent recurring ventricular fibrillation. He said, “How could I have survived that that long?”
When we told him about the new approach, he added, “Well, that’s like neuroprotective.” He’s right, because in the laboratory, we showed it was neuroprotective and we’re also getting better flows back there. It goes along with everything else, and so we’ve adopted the name because it is.
These are really high-powered systems we are comparing against, and we have the same level of return of spontaneous circulation. The major difference was when you started talking about the neurointact survival. We don’t have enough numbers yet, but next go around, we’re going to look at cerebral performance category (CPC) – CPC1 vs. the CPC2 – which were both considered intact, but CPC1 is actually better. We’re seeing many more of those, anecdotally.
I also wanted to mention that people do bring this up and say, “Well, let’s do a trial.” As far as we’re concerned, the trial’s been done in terms of The Lancet study 10 years ago that showed that the active compression-decompression had tremendously better outcomes. We show in the laboratories that you augment that a little bit. These are all [Food and Drug Administration] approved. You can go out and buy it tomorrow and get it done. I have no conflicts of interest, by the way, with any of this.
To have this device that’s going to have the potential of saving so many more lives is really an exciting breakthrough. More importantly, we’re understanding more now about the physiology of CPR and why it works. It could work much better with the approaches that we’ve been developing over the last 20 years or so.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. I want to thank both of you gentlemen. It’s been really an incredible experience to learn more about an advance in resuscitation that could truly be lifesaving. Thank you again for taking time to join us.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician in the department of emergency medicine, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York. Dr. Pepe is professor, department of management, policy, and community health, University of Texas Health Sciences Center, Houston. Mr. Quinn is EMS Chief, Edina (Minn.) Fire Department. No conflicts of interest were reported.
A version of this article first appeared Jan. 26 on Medscape.com.
Don’t cross the friends line with patients
All that moving can make it hard to maintain friendships. Factor in the challenges from the pandemic, and a physician’s life can be lonely. So, when a patient invites you for coffee or a game of pickleball, do you accept? For almost one-third of the physicians who responded to the Medscape Physician Friendships: The Joys and Challenges 2022, the answer might be yes.
About 29% said they develop friendships with patients. However, a lot depends on the circumstances. As one physician in the report said: “I have been a pediatrician for 35 years, and my patients have grown up and become productive adults in our small, rural, isolated area. You can’t help but know almost everyone.”
As the daughter of a cardiologist, Nishi Mehta, MD, a radiologist and founder of the largest physician-only Facebook group in the country, grew up with that small-town-everyone-knows-the-doctor model.
“When I was a kid, I’d go to the mall, and my friends and I would play a game: How long before a patient [of my dad’s] comes up to me?” she said. At the time, Dr. Mehta was embarrassed, but now she marvels that her dad knew his patients so well that they would recognize his daughter in crowded suburban mall.
In other instances, a physician may develop a friendly relationship after a patient leaves their care. For example, Leo Nissola, MD, now a full-time researcher and immunotherapy scientist in San Francisco, has stayed in touch with some of the patients he treated while at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Dr. Nissola said it was important to stay connected with the patients he had meaningful relationships with. “It becomes challenging, though, when a former patient asks for medical advice.” At that moment, “you have to be explicitly clear that the relationship has changed.”
A hard line in the sand
The blurring of lines is one reason many doctors refuse to befriend patients, even after they are no longer treating them. The American College of Physicians Ethics Manual advises against treating anyone with whom you have a close relationship, including family and friends.
“Friendships can get in the way of patients being honest with you, which can interfere with medical care,” Dr. Mehta said. “If a patient has a concern related to something they wouldn’t want you to know as friends, it can get awkward. They may elect not to tell you.”
And on the flip side, friendship can provide a view into your private life that you may not welcome in the exam room.
“Let’s say you go out for drinks [with a patient], and you’re up late, but you have surgery the next day,” said Brandi Ring, MD, an ob.gyn. and the associate medical director at the Center for Children and Women in Houston. Now, one of your patients knows you were out until midnight when you had to be in the OR at 5:00 a.m.
Worse still, your relationship could color your decisions about a patient’s care, even unconsciously. It can be hard to maintain objectivity when you have an emotional investment in someone’s well-being.
“We don’t necessarily treat family and friends to the standards of medical care,” said Dr. Ring. “We go above and beyond. We might order more tests and more scans. We don’t always follow the guidelines, especially in critical illness.”
For all these reasons and more, the ACP advises against treating friends.
Put physician before friend
But adhering to those guidelines can lead physicians to make some painful decisions. Cutting yourself off from the possibility of friendship is never easy, and the Medscape report found that physicians tend to have fewer friends than the average American.
“Especially earlier in my practice, when I was a young parent, and I would see a lot of other young parents in the same stage in life, I’d think, ‘In other circumstances, I would be hanging out at the park with this person,’ “ said Kathleen Rowland, MD, a family medicine physician and vice chair of education in the department of family medicine at Rush University, Chicago. “But the hard part is, the doctor-patient relationship always comes first.”
To a certain extent, one’s specialty may determine the feasibility of becoming friends with a patient. While Dr. Mehta has never done so, as a radiologist, she doesn’t usually see patients repeatedly. Likewise, a young gerontologist may have little in common with his octogenarian patients. And an older pediatrician is not in the same life stage as his patients’ sleep-deprived new parents, possibly making them less attractive friends.
However, practicing family medicine is all about long-term physician-patient relationships. Getting to know patients and their families over many years can lead to a certain intimacy. Dr. Rowland said that, while a wonderful part of being a physician is getting that unique trust whereby patients tell you all sorts of things about their lives, she’s never gone down the friendship path.
“There’s the assumption I’ll take care of someone for a long period of time, and their partner and their kids, maybe another generation or two,” Dr. Rowland said. “People really do rely on that relationship to contribute to their health.”
Worse, nowadays, when people may be starved for connection, many patients want to feel emotionally close and cared for by their doctor, so it’d be easy to cross the line. While patients deserve a compassionate, caring doctor, the physician is left to walk the line between those boundaries. Dr. Rowland said, “It’s up to the clinician to say: ‘My role is as a doctor. You deserve caring friends, but I have to order your mammogram and your blood counts. My role is different.’ ”
Friendly but not friends
It can be tricky to navigate the boundary between a cordial, warm relationship with a patient and that patient inviting you to their daughter’s wedding.
“People may mistake being pleasant and friendly for being friends,” said Larry Blosser, MD, chief medical officer at Central Ohio Primary Care, Westerville. In his position, he sometimes hears from patients who have misunderstood their relationship with a doctor in the practice. When that happens, he advises the physician to consider the persona they’re presenting to the patient. If you’re overly friendly, there’s the potential for confusion, but you can’t be aloof and cold, he said.
Maintaining that awareness helps to prevent a patient’s offhand invitation to catch a movie or go on a hike. And verbalizing it to your patients can make your relationship clear from the get-go.
“I tell patients we’re a team. I’m the captain, and they’re my MVP. When the match is over, whatever the results, we’re done,” said Karenne Fru, MD, PhD, a fertility specialist at Oma Fertility Atlanta. Making deep connections is essential to her practice, so Dr. Fru structures her patient interactions carefully. “Infertility is such an isolating experience. While you’re with us, we care about what’s going on in your life, your pets, and your mom’s chemo. We need mutual trust for you to be compliant with the care.”
However, that approach won’t work when you see patients regularly, as with family practice or specialties that see the same patients repeatedly throughout the year. In those circumstances, the match is never over but one in which the onus is on the physician to establish a friendly yet professional rapport without letting your self-interest, loneliness, or lack of friends interfere.
“It’s been a very difficult couple of years for a lot of us. Depending on what kind of clinical work we do, some of us took care of healthy people that got very sick or passed away,” Dr. Rowland said. “Having the chance to reconnect with people and reestablish some of that closeness, both physical and emotional, is going to be good for us.”
Just continue conveying warm, trusting compassion for your patients without blurring the friend lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All that moving can make it hard to maintain friendships. Factor in the challenges from the pandemic, and a physician’s life can be lonely. So, when a patient invites you for coffee or a game of pickleball, do you accept? For almost one-third of the physicians who responded to the Medscape Physician Friendships: The Joys and Challenges 2022, the answer might be yes.
About 29% said they develop friendships with patients. However, a lot depends on the circumstances. As one physician in the report said: “I have been a pediatrician for 35 years, and my patients have grown up and become productive adults in our small, rural, isolated area. You can’t help but know almost everyone.”
As the daughter of a cardiologist, Nishi Mehta, MD, a radiologist and founder of the largest physician-only Facebook group in the country, grew up with that small-town-everyone-knows-the-doctor model.
“When I was a kid, I’d go to the mall, and my friends and I would play a game: How long before a patient [of my dad’s] comes up to me?” she said. At the time, Dr. Mehta was embarrassed, but now she marvels that her dad knew his patients so well that they would recognize his daughter in crowded suburban mall.
In other instances, a physician may develop a friendly relationship after a patient leaves their care. For example, Leo Nissola, MD, now a full-time researcher and immunotherapy scientist in San Francisco, has stayed in touch with some of the patients he treated while at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Dr. Nissola said it was important to stay connected with the patients he had meaningful relationships with. “It becomes challenging, though, when a former patient asks for medical advice.” At that moment, “you have to be explicitly clear that the relationship has changed.”
A hard line in the sand
The blurring of lines is one reason many doctors refuse to befriend patients, even after they are no longer treating them. The American College of Physicians Ethics Manual advises against treating anyone with whom you have a close relationship, including family and friends.
“Friendships can get in the way of patients being honest with you, which can interfere with medical care,” Dr. Mehta said. “If a patient has a concern related to something they wouldn’t want you to know as friends, it can get awkward. They may elect not to tell you.”
And on the flip side, friendship can provide a view into your private life that you may not welcome in the exam room.
“Let’s say you go out for drinks [with a patient], and you’re up late, but you have surgery the next day,” said Brandi Ring, MD, an ob.gyn. and the associate medical director at the Center for Children and Women in Houston. Now, one of your patients knows you were out until midnight when you had to be in the OR at 5:00 a.m.
Worse still, your relationship could color your decisions about a patient’s care, even unconsciously. It can be hard to maintain objectivity when you have an emotional investment in someone’s well-being.
“We don’t necessarily treat family and friends to the standards of medical care,” said Dr. Ring. “We go above and beyond. We might order more tests and more scans. We don’t always follow the guidelines, especially in critical illness.”
For all these reasons and more, the ACP advises against treating friends.
Put physician before friend
But adhering to those guidelines can lead physicians to make some painful decisions. Cutting yourself off from the possibility of friendship is never easy, and the Medscape report found that physicians tend to have fewer friends than the average American.
“Especially earlier in my practice, when I was a young parent, and I would see a lot of other young parents in the same stage in life, I’d think, ‘In other circumstances, I would be hanging out at the park with this person,’ “ said Kathleen Rowland, MD, a family medicine physician and vice chair of education in the department of family medicine at Rush University, Chicago. “But the hard part is, the doctor-patient relationship always comes first.”
To a certain extent, one’s specialty may determine the feasibility of becoming friends with a patient. While Dr. Mehta has never done so, as a radiologist, she doesn’t usually see patients repeatedly. Likewise, a young gerontologist may have little in common with his octogenarian patients. And an older pediatrician is not in the same life stage as his patients’ sleep-deprived new parents, possibly making them less attractive friends.
However, practicing family medicine is all about long-term physician-patient relationships. Getting to know patients and their families over many years can lead to a certain intimacy. Dr. Rowland said that, while a wonderful part of being a physician is getting that unique trust whereby patients tell you all sorts of things about their lives, she’s never gone down the friendship path.
“There’s the assumption I’ll take care of someone for a long period of time, and their partner and their kids, maybe another generation or two,” Dr. Rowland said. “People really do rely on that relationship to contribute to their health.”
Worse, nowadays, when people may be starved for connection, many patients want to feel emotionally close and cared for by their doctor, so it’d be easy to cross the line. While patients deserve a compassionate, caring doctor, the physician is left to walk the line between those boundaries. Dr. Rowland said, “It’s up to the clinician to say: ‘My role is as a doctor. You deserve caring friends, but I have to order your mammogram and your blood counts. My role is different.’ ”
Friendly but not friends
It can be tricky to navigate the boundary between a cordial, warm relationship with a patient and that patient inviting you to their daughter’s wedding.
“People may mistake being pleasant and friendly for being friends,” said Larry Blosser, MD, chief medical officer at Central Ohio Primary Care, Westerville. In his position, he sometimes hears from patients who have misunderstood their relationship with a doctor in the practice. When that happens, he advises the physician to consider the persona they’re presenting to the patient. If you’re overly friendly, there’s the potential for confusion, but you can’t be aloof and cold, he said.
Maintaining that awareness helps to prevent a patient’s offhand invitation to catch a movie or go on a hike. And verbalizing it to your patients can make your relationship clear from the get-go.
“I tell patients we’re a team. I’m the captain, and they’re my MVP. When the match is over, whatever the results, we’re done,” said Karenne Fru, MD, PhD, a fertility specialist at Oma Fertility Atlanta. Making deep connections is essential to her practice, so Dr. Fru structures her patient interactions carefully. “Infertility is such an isolating experience. While you’re with us, we care about what’s going on in your life, your pets, and your mom’s chemo. We need mutual trust for you to be compliant with the care.”
However, that approach won’t work when you see patients regularly, as with family practice or specialties that see the same patients repeatedly throughout the year. In those circumstances, the match is never over but one in which the onus is on the physician to establish a friendly yet professional rapport without letting your self-interest, loneliness, or lack of friends interfere.
“It’s been a very difficult couple of years for a lot of us. Depending on what kind of clinical work we do, some of us took care of healthy people that got very sick or passed away,” Dr. Rowland said. “Having the chance to reconnect with people and reestablish some of that closeness, both physical and emotional, is going to be good for us.”
Just continue conveying warm, trusting compassion for your patients without blurring the friend lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
All that moving can make it hard to maintain friendships. Factor in the challenges from the pandemic, and a physician’s life can be lonely. So, when a patient invites you for coffee or a game of pickleball, do you accept? For almost one-third of the physicians who responded to the Medscape Physician Friendships: The Joys and Challenges 2022, the answer might be yes.
About 29% said they develop friendships with patients. However, a lot depends on the circumstances. As one physician in the report said: “I have been a pediatrician for 35 years, and my patients have grown up and become productive adults in our small, rural, isolated area. You can’t help but know almost everyone.”
As the daughter of a cardiologist, Nishi Mehta, MD, a radiologist and founder of the largest physician-only Facebook group in the country, grew up with that small-town-everyone-knows-the-doctor model.
“When I was a kid, I’d go to the mall, and my friends and I would play a game: How long before a patient [of my dad’s] comes up to me?” she said. At the time, Dr. Mehta was embarrassed, but now she marvels that her dad knew his patients so well that they would recognize his daughter in crowded suburban mall.
In other instances, a physician may develop a friendly relationship after a patient leaves their care. For example, Leo Nissola, MD, now a full-time researcher and immunotherapy scientist in San Francisco, has stayed in touch with some of the patients he treated while at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
Dr. Nissola said it was important to stay connected with the patients he had meaningful relationships with. “It becomes challenging, though, when a former patient asks for medical advice.” At that moment, “you have to be explicitly clear that the relationship has changed.”
A hard line in the sand
The blurring of lines is one reason many doctors refuse to befriend patients, even after they are no longer treating them. The American College of Physicians Ethics Manual advises against treating anyone with whom you have a close relationship, including family and friends.
“Friendships can get in the way of patients being honest with you, which can interfere with medical care,” Dr. Mehta said. “If a patient has a concern related to something they wouldn’t want you to know as friends, it can get awkward. They may elect not to tell you.”
And on the flip side, friendship can provide a view into your private life that you may not welcome in the exam room.
“Let’s say you go out for drinks [with a patient], and you’re up late, but you have surgery the next day,” said Brandi Ring, MD, an ob.gyn. and the associate medical director at the Center for Children and Women in Houston. Now, one of your patients knows you were out until midnight when you had to be in the OR at 5:00 a.m.
Worse still, your relationship could color your decisions about a patient’s care, even unconsciously. It can be hard to maintain objectivity when you have an emotional investment in someone’s well-being.
“We don’t necessarily treat family and friends to the standards of medical care,” said Dr. Ring. “We go above and beyond. We might order more tests and more scans. We don’t always follow the guidelines, especially in critical illness.”
For all these reasons and more, the ACP advises against treating friends.
Put physician before friend
But adhering to those guidelines can lead physicians to make some painful decisions. Cutting yourself off from the possibility of friendship is never easy, and the Medscape report found that physicians tend to have fewer friends than the average American.
“Especially earlier in my practice, when I was a young parent, and I would see a lot of other young parents in the same stage in life, I’d think, ‘In other circumstances, I would be hanging out at the park with this person,’ “ said Kathleen Rowland, MD, a family medicine physician and vice chair of education in the department of family medicine at Rush University, Chicago. “But the hard part is, the doctor-patient relationship always comes first.”
To a certain extent, one’s specialty may determine the feasibility of becoming friends with a patient. While Dr. Mehta has never done so, as a radiologist, she doesn’t usually see patients repeatedly. Likewise, a young gerontologist may have little in common with his octogenarian patients. And an older pediatrician is not in the same life stage as his patients’ sleep-deprived new parents, possibly making them less attractive friends.
However, practicing family medicine is all about long-term physician-patient relationships. Getting to know patients and their families over many years can lead to a certain intimacy. Dr. Rowland said that, while a wonderful part of being a physician is getting that unique trust whereby patients tell you all sorts of things about their lives, she’s never gone down the friendship path.
“There’s the assumption I’ll take care of someone for a long period of time, and their partner and their kids, maybe another generation or two,” Dr. Rowland said. “People really do rely on that relationship to contribute to their health.”
Worse, nowadays, when people may be starved for connection, many patients want to feel emotionally close and cared for by their doctor, so it’d be easy to cross the line. While patients deserve a compassionate, caring doctor, the physician is left to walk the line between those boundaries. Dr. Rowland said, “It’s up to the clinician to say: ‘My role is as a doctor. You deserve caring friends, but I have to order your mammogram and your blood counts. My role is different.’ ”
Friendly but not friends
It can be tricky to navigate the boundary between a cordial, warm relationship with a patient and that patient inviting you to their daughter’s wedding.
“People may mistake being pleasant and friendly for being friends,” said Larry Blosser, MD, chief medical officer at Central Ohio Primary Care, Westerville. In his position, he sometimes hears from patients who have misunderstood their relationship with a doctor in the practice. When that happens, he advises the physician to consider the persona they’re presenting to the patient. If you’re overly friendly, there’s the potential for confusion, but you can’t be aloof and cold, he said.
Maintaining that awareness helps to prevent a patient’s offhand invitation to catch a movie or go on a hike. And verbalizing it to your patients can make your relationship clear from the get-go.
“I tell patients we’re a team. I’m the captain, and they’re my MVP. When the match is over, whatever the results, we’re done,” said Karenne Fru, MD, PhD, a fertility specialist at Oma Fertility Atlanta. Making deep connections is essential to her practice, so Dr. Fru structures her patient interactions carefully. “Infertility is such an isolating experience. While you’re with us, we care about what’s going on in your life, your pets, and your mom’s chemo. We need mutual trust for you to be compliant with the care.”
However, that approach won’t work when you see patients regularly, as with family practice or specialties that see the same patients repeatedly throughout the year. In those circumstances, the match is never over but one in which the onus is on the physician to establish a friendly yet professional rapport without letting your self-interest, loneliness, or lack of friends interfere.
“It’s been a very difficult couple of years for a lot of us. Depending on what kind of clinical work we do, some of us took care of healthy people that got very sick or passed away,” Dr. Rowland said. “Having the chance to reconnect with people and reestablish some of that closeness, both physical and emotional, is going to be good for us.”
Just continue conveying warm, trusting compassion for your patients without blurring the friend lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More type 2 diabetes deaths from cancer than heart disease
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.
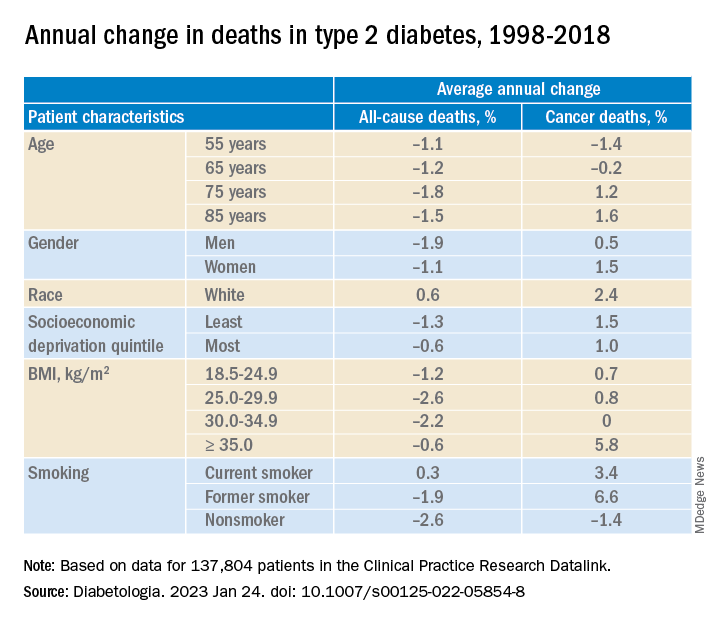
In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.

In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer appears to have overtaken cardiovascular disease (CVD) as a leading cause of death in adults with type 2 diabetes, a 20-year population study in England suggests.
The researchers found that, from 1998 to 2018, in more than 130,000 adults aged 35 and older with type 2 diabetes, all-cause mortality declined for all ages, but cancer mortality increased for those aged 75 and older; people with type 2 diabetes who were smokers had higher and steadily increasing cancer mortality rates; and people with type 2 diabetes had more than twice the rate of colorectal, pancreatic, liver, and endometrial cancer mortality than age- and sex-matched individuals in the general population.
The findings suggest that “cancer prevention strategies therefore deserve at least a similar level of attention as cardiovascular disease prevention, particularly in older people and for some cancers such as liver, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Tailored cancer prevention and early-detection strategies are needed to address persistent inequalities in the older population, the most deprived, and smokers, they added.
Breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes rising
According to the researchers, “early cancer detection through changes to existing screening [programs], or more in-depth investigations for suspected/nonspecific symptoms, may reduce the number of avoidable cancer deaths in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Moreover, breast cancer rates in younger women with type 2 diabetes are rising by 4.1% per year, they wrote, which suggests such women are high risk and should be screened at a younger age, but screening age would need to be determined in cost-effectiveness analyses.
The study by Suping Ling, PhD, and colleagues was published online in Diabetologia.
Results challenge belief that preventing CVD is priority in type 2 diabetes
“The prevention of cardiovascular disease has been, and is still considered, a priority in people with diabetes,” the researchers wrote.
“Our results challenge this view by showing that cancer may have overtaken cardiovascular disease as a leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
“The proportion of cancer deaths out of all-cause deaths remains high (> 30%) in young ages, and it was steadily increasing in older ages,” Dr. Ling, from the department of noncommunicable disease epidemiology, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said in a comment.
“Combined with previous studies reporting decreasing CVD mortality rates,” she said, “we concluded that cancer might have overtaken CVD as the leading cause of death in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Many evidence-based cancer-prevention strategies related to lifestyle (such as being physically active, being a healthy weight, eating a better diet, stopping smoking, as summarized by the World Cancer Research Fund), are helpful for preventing both cancer and CVD, Ling observed.
However, in the medical community, many additional efforts were made for monitoring, early detection, and innovating medications for CVD, she noted. “Therefore, we would like to propose a similar level of attention and effort for cancer in people with type 2 diabetes.”
Deaths from cancer vs. all causes in patients with diabetes
The researchers identified 137,804 patients aged 35 and older who were newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes from 1998 to 2018 in general practices in the UK that were part of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink.
Patients were a median age of 64 years and 45% were women. Most (83%) were White, followed by South Asian (3.5%), Black (2.0%), and other (3%); 8.4% had missing information for race. Patients had a median body mass index (BMI) of 30.6 kg/m2.
Researchers divided patients into socioeconomic quintiles of most to least deprived based on income, employment, education, and other factors. During a median follow-up of 8.4 years, there were 39,212 deaths (28.5%).
Cancer mortality in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes
Researchers analyzed annual deaths from cancer and from all causes over 20 years in subgroups of patients with type 2 diabetes.

In adults with type 2 diabetes, the average percentage change in cancer mortality per year, from 1998 to 2018 decreased in people aged 55 and 65 (–1.4% and –0.2%, respectively), but increased in people aged 75 and 85 (1.2% and 1.6%, respectively); increased more in women than in men (1.5% vs 1.0%), although women had lower cancer mortality than men; and increased more in the least deprived (wealthiest) individuals than in the most deprived (1.5% vs 1.0%). Cancer mortality rates were consistently higher in the most deprived individuals, Dr. Ling noted.
Cancer mortality also increased more in people with class III obesity (BMI ≥ 35) versus normal weight (5.8% vs 0.7%) and versus other weights. In addition, there was an upward trend in cancer mortality in people who were White or former/current smokers.
Deaths from specific cancers in diabetes vs. general population
Next, researchers determined cancer mortality ratios – the cancer mortality of the patients with diabetes divided by the cancer mortality of the general population.
They determined this for all cancers, the four most common cancers in the United Kingdom (lung, colorectal, breast, and prostate), and cancers caused by type 2 diabetes (pancreatic, liver, gallbladder, and endometrial cancer), standardized by sex and age.
Mortality from all cancer was 18% higher in patients with type 2 diabetes, compared with the general population.
Overall, mortality from colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and liver cancer was 2.4 times, 2.12 times, and 2.13 times higher, respectively, in patients with type 2 diabetes than in the general population.
Mortality from breast cancer was 9% higher and mortality from endometrial cancer was 2.08 times higher in women with type 2 diabetes than in women in the general population.
There was a constant upward trend for mortality rates for pancreatic, liver, and lung cancer at all ages, colorectal cancer at most ages, breast cancer at younger ages, and prostate and endometrial cancer at older ages.
The study was funded by Hope Against Cancer. Dr. Ling reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETOLOGIA
STS, new president apologize for predecessor’s speech amid Twitter backlash
The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) and its newly installed president have posted an apology for a speech delivered by its outgoing president that appeared, in part, to disparage affirmative action as a means to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in the field.
The speech, entitled “Three Score & More,” presented Jan. 22 at the STS 58th annual meeting in San Diego by John H. Calhoon, MD, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, unleashed a cascade of tweets, some circumspect but many expressing outrage and dismay.
Many of the tweets were from individuals who acknowledged not hearing the speech but who had seen at least one accompanying slide which, by then, had been widely circulated on the platform. It contained phrases such as “Affirmative Action is not equal opportunity” and “Defining people by color, gender, religion only tends to ingrain bias and discrimination,” all under the heading of “Virtuous Ideals.”
Reactions on Twitter included comments such as “This is bad beyond description” and a description of the slide’s content as “the blueprint & thought process for those actively maintaining Whiteness & the Patriarchy in medicine.”
Following an early onslaught of such tweets, the STS and new president Thomas E. MacGillivray, MD, MedStar Health, Washington, issued a statement disowning at least the controversial parts of Dr. Calhoon’s presentation, stating they were “inconsistent with STS’s core values of diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
The post continues, “The STS apologizes for these remarks. We know these comments were hurtful and we regret the pain they have caused to so many valued colleagues.” It then states, “Diversity, equity, and inclusion are central principles of our Society, and what we strive for in our profession and our practice. STS is committed to learning from this experience and taking action to reinforce our commitment to these values.”
“I believe that either the slide and/or my remarks were misinterpreted by some. I don’t want to hurt anybody. I’m profoundly sorry and apologize,” Dr. Calhoon said in an interview.
“I’m proud of my own group’s record on diversity and using equity and inclusion to get there,” he said. “We’re committed to it. We’ve had a wonderfully diverse group. I tried to highlight that in my remarks.”
About the Twitter response to the slide in question, Dr. Calhoon said, “I have no idea how they were thinking.” He added, “I can only comment that I’m really proud of our record and, for that matter, the STS’s record on diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) and its newly installed president have posted an apology for a speech delivered by its outgoing president that appeared, in part, to disparage affirmative action as a means to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in the field.
The speech, entitled “Three Score & More,” presented Jan. 22 at the STS 58th annual meeting in San Diego by John H. Calhoon, MD, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, unleashed a cascade of tweets, some circumspect but many expressing outrage and dismay.
Many of the tweets were from individuals who acknowledged not hearing the speech but who had seen at least one accompanying slide which, by then, had been widely circulated on the platform. It contained phrases such as “Affirmative Action is not equal opportunity” and “Defining people by color, gender, religion only tends to ingrain bias and discrimination,” all under the heading of “Virtuous Ideals.”
Reactions on Twitter included comments such as “This is bad beyond description” and a description of the slide’s content as “the blueprint & thought process for those actively maintaining Whiteness & the Patriarchy in medicine.”
Following an early onslaught of such tweets, the STS and new president Thomas E. MacGillivray, MD, MedStar Health, Washington, issued a statement disowning at least the controversial parts of Dr. Calhoon’s presentation, stating they were “inconsistent with STS’s core values of diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
The post continues, “The STS apologizes for these remarks. We know these comments were hurtful and we regret the pain they have caused to so many valued colleagues.” It then states, “Diversity, equity, and inclusion are central principles of our Society, and what we strive for in our profession and our practice. STS is committed to learning from this experience and taking action to reinforce our commitment to these values.”
“I believe that either the slide and/or my remarks were misinterpreted by some. I don’t want to hurt anybody. I’m profoundly sorry and apologize,” Dr. Calhoon said in an interview.
“I’m proud of my own group’s record on diversity and using equity and inclusion to get there,” he said. “We’re committed to it. We’ve had a wonderfully diverse group. I tried to highlight that in my remarks.”
About the Twitter response to the slide in question, Dr. Calhoon said, “I have no idea how they were thinking.” He added, “I can only comment that I’m really proud of our record and, for that matter, the STS’s record on diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) and its newly installed president have posted an apology for a speech delivered by its outgoing president that appeared, in part, to disparage affirmative action as a means to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion in the field.
The speech, entitled “Three Score & More,” presented Jan. 22 at the STS 58th annual meeting in San Diego by John H. Calhoon, MD, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, unleashed a cascade of tweets, some circumspect but many expressing outrage and dismay.
Many of the tweets were from individuals who acknowledged not hearing the speech but who had seen at least one accompanying slide which, by then, had been widely circulated on the platform. It contained phrases such as “Affirmative Action is not equal opportunity” and “Defining people by color, gender, religion only tends to ingrain bias and discrimination,” all under the heading of “Virtuous Ideals.”
Reactions on Twitter included comments such as “This is bad beyond description” and a description of the slide’s content as “the blueprint & thought process for those actively maintaining Whiteness & the Patriarchy in medicine.”
Following an early onslaught of such tweets, the STS and new president Thomas E. MacGillivray, MD, MedStar Health, Washington, issued a statement disowning at least the controversial parts of Dr. Calhoon’s presentation, stating they were “inconsistent with STS’s core values of diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
The post continues, “The STS apologizes for these remarks. We know these comments were hurtful and we regret the pain they have caused to so many valued colleagues.” It then states, “Diversity, equity, and inclusion are central principles of our Society, and what we strive for in our profession and our practice. STS is committed to learning from this experience and taking action to reinforce our commitment to these values.”
“I believe that either the slide and/or my remarks were misinterpreted by some. I don’t want to hurt anybody. I’m profoundly sorry and apologize,” Dr. Calhoon said in an interview.
“I’m proud of my own group’s record on diversity and using equity and inclusion to get there,” he said. “We’re committed to it. We’ve had a wonderfully diverse group. I tried to highlight that in my remarks.”
About the Twitter response to the slide in question, Dr. Calhoon said, “I have no idea how they were thinking.” He added, “I can only comment that I’m really proud of our record and, for that matter, the STS’s record on diversity, equity, and inclusion.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is preeclampsia a cardiovascular time bomb for mothers?
Women who experience preeclampsia during pregnancy are almost twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth as pregnant women who did not, according to a new study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. The risks are especially high in the first decade after giving birth, the researchers found.
Preeclampsia is the onset of high blood pressure after the 20th week of pregnancy combined with signs of organ damage, such as excess protein in the urine. It can occur in up to 8% of pregnancies, and the association between preeclampsia and long-term cardiac risks is well-known. But new research suggests these risks appear much earlier in life than expected – as early as age 30 – at a time when women are often not screened for signs of heart trouble
“Targeted interventions cannot wait until women with preeclampsia become eligible for conventional screening programs in middle age,” Sara Hallum, PhD, a coauthor of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Hallum, who was an epidemiologist at the University of Copenhagen at the time of the study, and colleagues evaluated the medical histories of more than 1.1 million women in Denmark who became pregnant once or twice between 1978 and 2017. Of this group, 3% had experienced preeclampsia. They compared rates of heart attack and stroke between the two groups over time.
While 1.2% of the entire study population had experienced a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth, 2% of the women with a history of preeclampsia had such an event. Within the first decade after delivery, women with a history of preeclampsia were four times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as other women.
Women aged 30-39 with a history of preeclampsia were nearly five times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as similar-aged women. And if a woman gave birth twice and had preeclampsia only during the second pregnancy, she was at especially high risk for a heart attack, the researchers found.
“Women with a history of preeclampsia should be monitored routinely for modifiable risk factors, particularly for increased blood pressure,” Dr. Hallum said.
The Danish study population is racially homogeneous, so the researchers were not able to distinguish the effects of preeclampsia by racial group. In the United States, strong evidence shows that Black women experience the effects of preeclampsia more than others.
A useful clue to cardiac risk
Ellen Seely, MD, an endocrinologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who specializes in preeclampsia, said physicians are less likely to ask women who have been pregnant if they had experienced preeclampsia than to ask if they smoke or have a family history of heart attacks. As a result, they may miss a looming cardiovascular event, especially in younger women who appear healthy.
“Emerging high blood pressure shouldn’t be ignored” in a seemingly healthy young woman, Dr. Seely said, particularly if that woman has divulged a history of preeclampsia. The doctor’s first step should be to verify hypertension, Dr. Seely said. If high blood pressure is evident, immediate treatment – such as encouraging more physical activity and a healthier diet – should follow. Watchful waiting in such cases is inappropriate, she added.
Although the experience of having preeclampsia is unpleasant and scary, Dr. Seely noted that in at least one way it can prove advantageous. Some women who did not experience preeclampsia will end up having a heart attack, sometimes with no prior warning that anything was amiss. At least a history of preeclampsia provides a clue that women should take care of their hearts.
“The patient carries their history with them wherever they go,” Dr. Seely said. For now, this reality often requires women to mention their pregnancy history even if a provider doesn’t ask. Someday, Dr. Seely said, asking about that history will become just as routine for providers as asking about family history.
The study was funded by the Danish Heart Foundation. Dr. Hallum and Dr. Seely have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women who experience preeclampsia during pregnancy are almost twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth as pregnant women who did not, according to a new study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. The risks are especially high in the first decade after giving birth, the researchers found.
Preeclampsia is the onset of high blood pressure after the 20th week of pregnancy combined with signs of organ damage, such as excess protein in the urine. It can occur in up to 8% of pregnancies, and the association between preeclampsia and long-term cardiac risks is well-known. But new research suggests these risks appear much earlier in life than expected – as early as age 30 – at a time when women are often not screened for signs of heart trouble
“Targeted interventions cannot wait until women with preeclampsia become eligible for conventional screening programs in middle age,” Sara Hallum, PhD, a coauthor of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Hallum, who was an epidemiologist at the University of Copenhagen at the time of the study, and colleagues evaluated the medical histories of more than 1.1 million women in Denmark who became pregnant once or twice between 1978 and 2017. Of this group, 3% had experienced preeclampsia. They compared rates of heart attack and stroke between the two groups over time.
While 1.2% of the entire study population had experienced a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth, 2% of the women with a history of preeclampsia had such an event. Within the first decade after delivery, women with a history of preeclampsia were four times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as other women.
Women aged 30-39 with a history of preeclampsia were nearly five times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as similar-aged women. And if a woman gave birth twice and had preeclampsia only during the second pregnancy, she was at especially high risk for a heart attack, the researchers found.
“Women with a history of preeclampsia should be monitored routinely for modifiable risk factors, particularly for increased blood pressure,” Dr. Hallum said.
The Danish study population is racially homogeneous, so the researchers were not able to distinguish the effects of preeclampsia by racial group. In the United States, strong evidence shows that Black women experience the effects of preeclampsia more than others.
A useful clue to cardiac risk
Ellen Seely, MD, an endocrinologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who specializes in preeclampsia, said physicians are less likely to ask women who have been pregnant if they had experienced preeclampsia than to ask if they smoke or have a family history of heart attacks. As a result, they may miss a looming cardiovascular event, especially in younger women who appear healthy.
“Emerging high blood pressure shouldn’t be ignored” in a seemingly healthy young woman, Dr. Seely said, particularly if that woman has divulged a history of preeclampsia. The doctor’s first step should be to verify hypertension, Dr. Seely said. If high blood pressure is evident, immediate treatment – such as encouraging more physical activity and a healthier diet – should follow. Watchful waiting in such cases is inappropriate, she added.
Although the experience of having preeclampsia is unpleasant and scary, Dr. Seely noted that in at least one way it can prove advantageous. Some women who did not experience preeclampsia will end up having a heart attack, sometimes with no prior warning that anything was amiss. At least a history of preeclampsia provides a clue that women should take care of their hearts.
“The patient carries their history with them wherever they go,” Dr. Seely said. For now, this reality often requires women to mention their pregnancy history even if a provider doesn’t ask. Someday, Dr. Seely said, asking about that history will become just as routine for providers as asking about family history.
The study was funded by the Danish Heart Foundation. Dr. Hallum and Dr. Seely have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women who experience preeclampsia during pregnancy are almost twice as likely to have a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth as pregnant women who did not, according to a new study published in the European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. The risks are especially high in the first decade after giving birth, the researchers found.
Preeclampsia is the onset of high blood pressure after the 20th week of pregnancy combined with signs of organ damage, such as excess protein in the urine. It can occur in up to 8% of pregnancies, and the association between preeclampsia and long-term cardiac risks is well-known. But new research suggests these risks appear much earlier in life than expected – as early as age 30 – at a time when women are often not screened for signs of heart trouble
“Targeted interventions cannot wait until women with preeclampsia become eligible for conventional screening programs in middle age,” Sara Hallum, PhD, a coauthor of the study, told this news organization.
Dr. Hallum, who was an epidemiologist at the University of Copenhagen at the time of the study, and colleagues evaluated the medical histories of more than 1.1 million women in Denmark who became pregnant once or twice between 1978 and 2017. Of this group, 3% had experienced preeclampsia. They compared rates of heart attack and stroke between the two groups over time.
While 1.2% of the entire study population had experienced a heart attack or stroke within 20 years of giving birth, 2% of the women with a history of preeclampsia had such an event. Within the first decade after delivery, women with a history of preeclampsia were four times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as other women.
Women aged 30-39 with a history of preeclampsia were nearly five times as likely to have a heart attack and three times as likely to have a stroke as similar-aged women. And if a woman gave birth twice and had preeclampsia only during the second pregnancy, she was at especially high risk for a heart attack, the researchers found.
“Women with a history of preeclampsia should be monitored routinely for modifiable risk factors, particularly for increased blood pressure,” Dr. Hallum said.
The Danish study population is racially homogeneous, so the researchers were not able to distinguish the effects of preeclampsia by racial group. In the United States, strong evidence shows that Black women experience the effects of preeclampsia more than others.
A useful clue to cardiac risk
Ellen Seely, MD, an endocrinologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, who specializes in preeclampsia, said physicians are less likely to ask women who have been pregnant if they had experienced preeclampsia than to ask if they smoke or have a family history of heart attacks. As a result, they may miss a looming cardiovascular event, especially in younger women who appear healthy.
“Emerging high blood pressure shouldn’t be ignored” in a seemingly healthy young woman, Dr. Seely said, particularly if that woman has divulged a history of preeclampsia. The doctor’s first step should be to verify hypertension, Dr. Seely said. If high blood pressure is evident, immediate treatment – such as encouraging more physical activity and a healthier diet – should follow. Watchful waiting in such cases is inappropriate, she added.
Although the experience of having preeclampsia is unpleasant and scary, Dr. Seely noted that in at least one way it can prove advantageous. Some women who did not experience preeclampsia will end up having a heart attack, sometimes with no prior warning that anything was amiss. At least a history of preeclampsia provides a clue that women should take care of their hearts.
“The patient carries their history with them wherever they go,” Dr. Seely said. For now, this reality often requires women to mention their pregnancy history even if a provider doesn’t ask. Someday, Dr. Seely said, asking about that history will become just as routine for providers as asking about family history.
The study was funded by the Danish Heart Foundation. Dr. Hallum and Dr. Seely have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PREVENTIVE CARDIOLOGY
High HDL-C levels linked to increased fracture risk
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Medicare policy tweak on LVADs may reduce access to transplant
A recent change in Medicare policy designed to increase access to left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) may have had the unintended consequence of increasing inequalities in access to heart transplant for patients with advanced heart failure.
In December 2020, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services relaxed restrictions on centers that implant LVADs but don’t perform heart transplants. Specifically, they dropped the requirement that LVAD-only centers obtain permission from a Medicare-approved heart transplant center authorizing LVAD implantation with “bridge-to-transplant” (BTT) intent, meaning the patient is a transplant candidate.
While the relaxed requirement has the potential to increase access to LVADs for appropriate patients, a look back at 22,221 LVAD recipients found that patients who received LVADs at transplant-capable centers had a 79% higher likelihood of receiving a BTT LVAD designation.
The 2-year heart transplant rate following LVAD implant was 25.6% for patients who received an LVAD at a heart transplant center, compared with 11.9% at LVAD-only centers.
Thomas Cascino, MD, with University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reported their findings in JAMA Network Open.
Differential assessment?
Nontransplant LVAD centers are increasing in number in the United States now that the CMS has made establishing an LVAD-only center easier.
“Although there should be enthusiasm for the potential of LVAD-only centers to increase access to LVAD, it appears that receiving an LVAD at a center that does not perform transplants results in differential assessment of transplant eligibility at the time of LVAD implant and inequities in receipt of transplant,” Dr. Cascino and colleagues said.
“Being cared for at a center that does not perform heart transplant should not result in a lesser chance to receive a heart transplant,” Dr. Cascino added in a university news release. “Our study shows that this disparity existed before the policy change, and we think it will likely grow larger now that there is less collaboration.”
The CMS policy will likely “further challenge equity in access to transplant for patients seeking care at nontransplant centers and may have the unintended consequence of contributing to increasing inequities in access to transplants, as has been feared,” the researchers wrote.
They also note that recent changes in the adult heart allocation system under the United Network for Organ Sharing have significantly reduced the likelihood of transplant after durable LVAD implant unless candidates are listed as being at higher urgency status owing to an LVAD complication or clinical deterioration.
“The reality is that durable LVADs are much less likely to be a bridge to the best therapy (that is, transplant) in the current allocation system. As a result, there is a critical need to select appropriate durable LVAD and transplant candidates at the initial evaluation,” the authors said.
“This puts the onus on the transplant community to select appropriate LVAD and transplant candidates during the initial evaluation. We need a system in which any patient can walk into the same hospital and get the right therapy for them,” Dr. Cascino added in the news release.
The research was supported in part through funding from the University of Michigan Health department of cardiac surgery and the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Cascino has received grants from Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent change in Medicare policy designed to increase access to left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) may have had the unintended consequence of increasing inequalities in access to heart transplant for patients with advanced heart failure.
In December 2020, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services relaxed restrictions on centers that implant LVADs but don’t perform heart transplants. Specifically, they dropped the requirement that LVAD-only centers obtain permission from a Medicare-approved heart transplant center authorizing LVAD implantation with “bridge-to-transplant” (BTT) intent, meaning the patient is a transplant candidate.
While the relaxed requirement has the potential to increase access to LVADs for appropriate patients, a look back at 22,221 LVAD recipients found that patients who received LVADs at transplant-capable centers had a 79% higher likelihood of receiving a BTT LVAD designation.
The 2-year heart transplant rate following LVAD implant was 25.6% for patients who received an LVAD at a heart transplant center, compared with 11.9% at LVAD-only centers.
Thomas Cascino, MD, with University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reported their findings in JAMA Network Open.
Differential assessment?
Nontransplant LVAD centers are increasing in number in the United States now that the CMS has made establishing an LVAD-only center easier.
“Although there should be enthusiasm for the potential of LVAD-only centers to increase access to LVAD, it appears that receiving an LVAD at a center that does not perform transplants results in differential assessment of transplant eligibility at the time of LVAD implant and inequities in receipt of transplant,” Dr. Cascino and colleagues said.
“Being cared for at a center that does not perform heart transplant should not result in a lesser chance to receive a heart transplant,” Dr. Cascino added in a university news release. “Our study shows that this disparity existed before the policy change, and we think it will likely grow larger now that there is less collaboration.”
The CMS policy will likely “further challenge equity in access to transplant for patients seeking care at nontransplant centers and may have the unintended consequence of contributing to increasing inequities in access to transplants, as has been feared,” the researchers wrote.
They also note that recent changes in the adult heart allocation system under the United Network for Organ Sharing have significantly reduced the likelihood of transplant after durable LVAD implant unless candidates are listed as being at higher urgency status owing to an LVAD complication or clinical deterioration.
“The reality is that durable LVADs are much less likely to be a bridge to the best therapy (that is, transplant) in the current allocation system. As a result, there is a critical need to select appropriate durable LVAD and transplant candidates at the initial evaluation,” the authors said.
“This puts the onus on the transplant community to select appropriate LVAD and transplant candidates during the initial evaluation. We need a system in which any patient can walk into the same hospital and get the right therapy for them,” Dr. Cascino added in the news release.
The research was supported in part through funding from the University of Michigan Health department of cardiac surgery and the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Cascino has received grants from Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent change in Medicare policy designed to increase access to left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) may have had the unintended consequence of increasing inequalities in access to heart transplant for patients with advanced heart failure.
In December 2020, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services relaxed restrictions on centers that implant LVADs but don’t perform heart transplants. Specifically, they dropped the requirement that LVAD-only centers obtain permission from a Medicare-approved heart transplant center authorizing LVAD implantation with “bridge-to-transplant” (BTT) intent, meaning the patient is a transplant candidate.
While the relaxed requirement has the potential to increase access to LVADs for appropriate patients, a look back at 22,221 LVAD recipients found that patients who received LVADs at transplant-capable centers had a 79% higher likelihood of receiving a BTT LVAD designation.
The 2-year heart transplant rate following LVAD implant was 25.6% for patients who received an LVAD at a heart transplant center, compared with 11.9% at LVAD-only centers.
Thomas Cascino, MD, with University of Michigan Health Frankel Cardiovascular Center, Ann Arbor, and colleagues reported their findings in JAMA Network Open.
Differential assessment?
Nontransplant LVAD centers are increasing in number in the United States now that the CMS has made establishing an LVAD-only center easier.
“Although there should be enthusiasm for the potential of LVAD-only centers to increase access to LVAD, it appears that receiving an LVAD at a center that does not perform transplants results in differential assessment of transplant eligibility at the time of LVAD implant and inequities in receipt of transplant,” Dr. Cascino and colleagues said.
“Being cared for at a center that does not perform heart transplant should not result in a lesser chance to receive a heart transplant,” Dr. Cascino added in a university news release. “Our study shows that this disparity existed before the policy change, and we think it will likely grow larger now that there is less collaboration.”
The CMS policy will likely “further challenge equity in access to transplant for patients seeking care at nontransplant centers and may have the unintended consequence of contributing to increasing inequities in access to transplants, as has been feared,” the researchers wrote.
They also note that recent changes in the adult heart allocation system under the United Network for Organ Sharing have significantly reduced the likelihood of transplant after durable LVAD implant unless candidates are listed as being at higher urgency status owing to an LVAD complication or clinical deterioration.
“The reality is that durable LVADs are much less likely to be a bridge to the best therapy (that is, transplant) in the current allocation system. As a result, there is a critical need to select appropriate durable LVAD and transplant candidates at the initial evaluation,” the authors said.
“This puts the onus on the transplant community to select appropriate LVAD and transplant candidates during the initial evaluation. We need a system in which any patient can walk into the same hospital and get the right therapy for them,” Dr. Cascino added in the news release.
The research was supported in part through funding from the University of Michigan Health department of cardiac surgery and the National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Cascino has received grants from Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN