User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Minimizing atrial pacing no benefit in sinus node disease: DANPACE II
suggest results of a trial that randomly assigned patients with SND who had received their first pacemaker implant to one of two pacing programs.
Over 2 years of follow-up with remote monitoring, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of time to first device-detected episode of AF lasting more than 6 minutes, reported Max Brix Kronborg, MD, PhD, department of cardiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
The study, DANPACE II, excluded patients with permanent or persistent AF or persistent bradycardia prior to or at the time of enrollment.
The findings were presented at annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and were published online simultaneously in the European Heart Journal.
The 539 participants in the trial were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to a pacing program of 60 beats/minute with rate-adaptive pacing (DDR-60) or 40 beats/minute without rate-adaptive pacing (DDD-40). All patients were equipped with remote monitoring and were followed for 2 years. Tracings were adjudicated for atrial high-rate episodes by experienced device specialists, Dr. Kronborg said.
No difference seen in primary outcome
When graphed, curves for the primary outcome in the two groups were essentially superimposable. For the secondary outcomes of AF lasting more than 6 hours and AF lasting more than 24 hours, there was a modest but progressive separation in the lines favoring the DDR-60 group for both. However, the P value did not approach significance in the first of these endpoints (P = .35) and remained only a trend (P = .08) in the second.
There were no substantial differences in results when patients were stratified by age (> 73 years vs. younger), gender (women represented 50% of patients), PR interval (> 150 milliseconds vs. less), or history of AF prior to study entry; the latter group represented approximately 40% of the trial participants.
There was a between-group difference in the primary composite safety endpoint of syncope and presyncope. By 2 years, 13% of those in the DDR-60 group had experienced one of these safety events, vs. 22% (P = .01) of the DDD-40 group.
The study was not designed to determine a cause for these episodes, but Dr. Kronborg reported that bradycardia was suspected in the majority of cases.
Crossovers more common on minimal pacing
Crossovers were permitted, and 26% of patients did so at some point in the trial. Of these, about one-third were switched to the opposite arm in response to syncope. Almost all of the others crossed over because of chronotropic incompetence. The greater crossover rate in the DDD-40 group (23% vs. 3%; P < .001) was highly significant.
Quality of life was measured with the SF36 tool, and physical function was evaluated with the 6-minute walk distance test (6MWD). Results on these measures did not differ significantly between groups. For 6MWD, the mean gain from baseline was 8 m in both groups.
The results of this study are important because they challenge what has been a widely held perception among electrophysiologists, according to Cecilia Linde, MD, PhD, a professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
“I think many of us involved in pacing thought for many years that minimizing pacing would be beneficial, and this clearly shows it is not,” said Dr. Linde, who was the moderator of the scientific session in which these results were presented.
Results appear definitive
The ESC-invited discussant, Jose L. Merino, MD, PhD, director of arrhythmia and electrophysiology research, La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, concurred. He said these results are convincing.
On the basis of these findings, which not only failed to show a benefit but showed in the experimental arm a higher incidence of syncope and chronotropic incompetence, Dr. Merino concluded, “Programming intended to minimize atrial pacing should not be used as routine in unselected patients with SND.”
A trend for protection from DDR-60 over DDD-40 from the longest episodes of AF caught Dr. Merino’s attention, leading him to question whether the optimal rate of pacing might be even higher than 60 beats/minute in SND, but he said that is a separate issue. DANPACE was not powered to examine the effect in long duration episodes.
Ultimately, while Dr. Merino characterized the increased risk of syncope with minimized pacing as “an important finding” in regard to dissuading clinicians to pursue this strategy, he said that the underlying question of the DANPACE trial remains unanswered.
Pacing remains “a treatment of choice” in SND, but further investigation is needed “about the optimal pacing rate to minimize AF and syncope” in this population, he said.
Dr. Kronborg reports a financial relationship with Abbott. Dr. Linde reports financial relationships with Cardio 3, Medtronic, St. Jude, and Vifor. Dr. Merino reports financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Microport.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggest results of a trial that randomly assigned patients with SND who had received their first pacemaker implant to one of two pacing programs.
Over 2 years of follow-up with remote monitoring, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of time to first device-detected episode of AF lasting more than 6 minutes, reported Max Brix Kronborg, MD, PhD, department of cardiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
The study, DANPACE II, excluded patients with permanent or persistent AF or persistent bradycardia prior to or at the time of enrollment.
The findings were presented at annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and were published online simultaneously in the European Heart Journal.
The 539 participants in the trial were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to a pacing program of 60 beats/minute with rate-adaptive pacing (DDR-60) or 40 beats/minute without rate-adaptive pacing (DDD-40). All patients were equipped with remote monitoring and were followed for 2 years. Tracings were adjudicated for atrial high-rate episodes by experienced device specialists, Dr. Kronborg said.
No difference seen in primary outcome
When graphed, curves for the primary outcome in the two groups were essentially superimposable. For the secondary outcomes of AF lasting more than 6 hours and AF lasting more than 24 hours, there was a modest but progressive separation in the lines favoring the DDR-60 group for both. However, the P value did not approach significance in the first of these endpoints (P = .35) and remained only a trend (P = .08) in the second.
There were no substantial differences in results when patients were stratified by age (> 73 years vs. younger), gender (women represented 50% of patients), PR interval (> 150 milliseconds vs. less), or history of AF prior to study entry; the latter group represented approximately 40% of the trial participants.
There was a between-group difference in the primary composite safety endpoint of syncope and presyncope. By 2 years, 13% of those in the DDR-60 group had experienced one of these safety events, vs. 22% (P = .01) of the DDD-40 group.
The study was not designed to determine a cause for these episodes, but Dr. Kronborg reported that bradycardia was suspected in the majority of cases.
Crossovers more common on minimal pacing
Crossovers were permitted, and 26% of patients did so at some point in the trial. Of these, about one-third were switched to the opposite arm in response to syncope. Almost all of the others crossed over because of chronotropic incompetence. The greater crossover rate in the DDD-40 group (23% vs. 3%; P < .001) was highly significant.
Quality of life was measured with the SF36 tool, and physical function was evaluated with the 6-minute walk distance test (6MWD). Results on these measures did not differ significantly between groups. For 6MWD, the mean gain from baseline was 8 m in both groups.
The results of this study are important because they challenge what has been a widely held perception among electrophysiologists, according to Cecilia Linde, MD, PhD, a professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
“I think many of us involved in pacing thought for many years that minimizing pacing would be beneficial, and this clearly shows it is not,” said Dr. Linde, who was the moderator of the scientific session in which these results were presented.
Results appear definitive
The ESC-invited discussant, Jose L. Merino, MD, PhD, director of arrhythmia and electrophysiology research, La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, concurred. He said these results are convincing.
On the basis of these findings, which not only failed to show a benefit but showed in the experimental arm a higher incidence of syncope and chronotropic incompetence, Dr. Merino concluded, “Programming intended to minimize atrial pacing should not be used as routine in unselected patients with SND.”
A trend for protection from DDR-60 over DDD-40 from the longest episodes of AF caught Dr. Merino’s attention, leading him to question whether the optimal rate of pacing might be even higher than 60 beats/minute in SND, but he said that is a separate issue. DANPACE was not powered to examine the effect in long duration episodes.
Ultimately, while Dr. Merino characterized the increased risk of syncope with minimized pacing as “an important finding” in regard to dissuading clinicians to pursue this strategy, he said that the underlying question of the DANPACE trial remains unanswered.
Pacing remains “a treatment of choice” in SND, but further investigation is needed “about the optimal pacing rate to minimize AF and syncope” in this population, he said.
Dr. Kronborg reports a financial relationship with Abbott. Dr. Linde reports financial relationships with Cardio 3, Medtronic, St. Jude, and Vifor. Dr. Merino reports financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Microport.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggest results of a trial that randomly assigned patients with SND who had received their first pacemaker implant to one of two pacing programs.
Over 2 years of follow-up with remote monitoring, there was no difference in the primary endpoint of time to first device-detected episode of AF lasting more than 6 minutes, reported Max Brix Kronborg, MD, PhD, department of cardiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark.
The study, DANPACE II, excluded patients with permanent or persistent AF or persistent bradycardia prior to or at the time of enrollment.
The findings were presented at annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and were published online simultaneously in the European Heart Journal.
The 539 participants in the trial were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to a pacing program of 60 beats/minute with rate-adaptive pacing (DDR-60) or 40 beats/minute without rate-adaptive pacing (DDD-40). All patients were equipped with remote monitoring and were followed for 2 years. Tracings were adjudicated for atrial high-rate episodes by experienced device specialists, Dr. Kronborg said.
No difference seen in primary outcome
When graphed, curves for the primary outcome in the two groups were essentially superimposable. For the secondary outcomes of AF lasting more than 6 hours and AF lasting more than 24 hours, there was a modest but progressive separation in the lines favoring the DDR-60 group for both. However, the P value did not approach significance in the first of these endpoints (P = .35) and remained only a trend (P = .08) in the second.
There were no substantial differences in results when patients were stratified by age (> 73 years vs. younger), gender (women represented 50% of patients), PR interval (> 150 milliseconds vs. less), or history of AF prior to study entry; the latter group represented approximately 40% of the trial participants.
There was a between-group difference in the primary composite safety endpoint of syncope and presyncope. By 2 years, 13% of those in the DDR-60 group had experienced one of these safety events, vs. 22% (P = .01) of the DDD-40 group.
The study was not designed to determine a cause for these episodes, but Dr. Kronborg reported that bradycardia was suspected in the majority of cases.
Crossovers more common on minimal pacing
Crossovers were permitted, and 26% of patients did so at some point in the trial. Of these, about one-third were switched to the opposite arm in response to syncope. Almost all of the others crossed over because of chronotropic incompetence. The greater crossover rate in the DDD-40 group (23% vs. 3%; P < .001) was highly significant.
Quality of life was measured with the SF36 tool, and physical function was evaluated with the 6-minute walk distance test (6MWD). Results on these measures did not differ significantly between groups. For 6MWD, the mean gain from baseline was 8 m in both groups.
The results of this study are important because they challenge what has been a widely held perception among electrophysiologists, according to Cecilia Linde, MD, PhD, a professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm.
“I think many of us involved in pacing thought for many years that minimizing pacing would be beneficial, and this clearly shows it is not,” said Dr. Linde, who was the moderator of the scientific session in which these results were presented.
Results appear definitive
The ESC-invited discussant, Jose L. Merino, MD, PhD, director of arrhythmia and electrophysiology research, La Paz University Hospital, Madrid, concurred. He said these results are convincing.
On the basis of these findings, which not only failed to show a benefit but showed in the experimental arm a higher incidence of syncope and chronotropic incompetence, Dr. Merino concluded, “Programming intended to minimize atrial pacing should not be used as routine in unselected patients with SND.”
A trend for protection from DDR-60 over DDD-40 from the longest episodes of AF caught Dr. Merino’s attention, leading him to question whether the optimal rate of pacing might be even higher than 60 beats/minute in SND, but he said that is a separate issue. DANPACE was not powered to examine the effect in long duration episodes.
Ultimately, while Dr. Merino characterized the increased risk of syncope with minimized pacing as “an important finding” in regard to dissuading clinicians to pursue this strategy, he said that the underlying question of the DANPACE trial remains unanswered.
Pacing remains “a treatment of choice” in SND, but further investigation is needed “about the optimal pacing rate to minimize AF and syncope” in this population, he said.
Dr. Kronborg reports a financial relationship with Abbott. Dr. Linde reports financial relationships with Cardio 3, Medtronic, St. Jude, and Vifor. Dr. Merino reports financial relationships with Abbott, Medtronic, and Microport.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2023
The most important study from ESC: FRAIL-AF
One of the hardest tasks of a clinician is applying evidence from trials to the person in your office. At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, the surprising and unexpected results of the FRAIL-AF trial confirm the massive challenge of evidence translation.
FRAIL-AF investigators set out to study the question of whether frail, elderly patients with atrial fibrillation who were doing well with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) should be switched to direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Senior author Geert-Jan Geersing, MD, PhD, from the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands), told me that frustration led him to design this study. He was frustrated that colleagues assumed that evidence in nonfrail patients can always be translated to frail patients.
Dr. Geersing offered two reasons why common wisdom may be wrong. First was that the large DOAC versus warfarin trials included few elderly patients with frailty. Second, first author Linda Joosten, MD, made it clear in her presentation that frailty is a lot more than aging. It is a clinical syndrome, which entails a “high burden of comorbidities, dependency on others, and a reduced ability to resist stressors.”
The FRAIL-AF trial
The investigators recruited elderly, frail patients with fibrillation who were treated with VKAs and had stable international normalized ratios from outpatient clinics throughout the Netherlands. They screened about 2,600 patients and enrolled nearly 1,400. Most were excluded for not being frail.
Half the group was randomized to switching to a DOAC – drug choice was left to the treating clinician – and the other half remained on VKAs. Patients were 83 years of age on average with a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4. All four classes of DOAC were used in the switching arm.
The primary endpoint was major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, whichever came first, accounting for death as a competing risk. Follow-up was 1 year.
The results for switching to DOAC vs. VKA
Dr. Joosten started her presentation with this: “The results turned out to be different than we expected.” The authors designed the trial with the idea that switching to DOACs would be superior in safety to remaining on VKAs.
But the trial was halted after an interim analysis found a rate of major bleeding in the switching arm of 15.3% versus 9.4% in the arm staying on VKA (hazard ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.32; P = .0012).
The Kaplan-Meier event curves reveal that the excess risk of bleeding occurred after 100 days and increased with time. This argued against an early effect from transitioning the drugs.
An analysis looking at specific DOAC drugs revealed similar hazards for the two most common ones used – apixaban and rivaroxaban.
Thrombotic events were a secondary endpoint and were low in absolute numbers, 2.4% versus 2.0%, for remaining on VKA and switching to DOAC, respectively (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 0.60-2.61).
The time in therapeutic range in FRAIL-AF was similar to that in the seminal DOAC trials.
Comments
Three reasons lead me to choose FRAIL-AF as the most important study from the 2023 ESC congress.
First is the specific lesson about switching drugs. Note that FRAIL-AF did not address the question of starting anticoagulation. The trial results show that if you have a frail older patient who is doing well on VKA, don’t change to a DOAC. That is important to know, but it is not what gives this study its heft.
The second reason centers on the investigators choice to do this trial. Dr. Geersing had a feeling that common wisdom was wrong. He did not try to persuade colleagues with anecdote or plausibility or meta-analyses of observational studies. He set out to answer a question in the correct way – with a randomized trial.
This is the path forward in medicine. I’ve often heard proponents of observational research declare that many topics in medicine cannot be studied with trials. I could hear people arguing that it’s not feasible to study mostly home-bound, elderly frail patients. And the fact that there exist so few trials in this space would support that argument.
But the FRAIL-AF authors showed that it is possible. This is the kind of science that medicine should celebrate. There were no soft endpoints, financial conflicts, or spin. If medical science had science as its incentive, rather than attention, FRAIL-AF easily wins top honors.
The third reason FRAIL-AF is so important is that it teaches us the humility required in translating evidence in our clinics. I like to say evidence is what separates doctors from palm readers. But using this evidence requires thinking hard about how average effects in trial environments apply to our patient.
Yes, of course, there is clear evidence from tens of thousands of patients in the DOAC versus warfarin trials, that, for those patients, on average, DOACs compare favorably with VKA. The average age of patients in these trials was 70-73 years; the average age in FRAIL-AF was 83 years. And that is just age. A substudy of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 trial found that only 360 of more than 20,000 patients in the trial had severe frailty.
That lesson extends to nearly every common therapy in medicine today. It also casts great doubt on the soft-thinking idea of using evidence from trials to derive quality metrics. As if the nuance of evidence translation can be captured in an electronic health record.
The skillful use of evidence will be one of the main challenges of the next generation of clinicians. Thanks to advances in medical science, more patients will live long enough to become frail. And the so-called “guideline-directed” therapies may not apply to them.
Dr. Joosten, Dr. Geersing, and the FRAIL-AF team have taught us specific lessons about anticoagulation, but their greatest contribution has been to demonstrate the value of humility in science and the practice of evidence-based medicine.
If you treat patients, no trial at this meeting is more important.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the hardest tasks of a clinician is applying evidence from trials to the person in your office. At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, the surprising and unexpected results of the FRAIL-AF trial confirm the massive challenge of evidence translation.
FRAIL-AF investigators set out to study the question of whether frail, elderly patients with atrial fibrillation who were doing well with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) should be switched to direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Senior author Geert-Jan Geersing, MD, PhD, from the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands), told me that frustration led him to design this study. He was frustrated that colleagues assumed that evidence in nonfrail patients can always be translated to frail patients.
Dr. Geersing offered two reasons why common wisdom may be wrong. First was that the large DOAC versus warfarin trials included few elderly patients with frailty. Second, first author Linda Joosten, MD, made it clear in her presentation that frailty is a lot more than aging. It is a clinical syndrome, which entails a “high burden of comorbidities, dependency on others, and a reduced ability to resist stressors.”
The FRAIL-AF trial
The investigators recruited elderly, frail patients with fibrillation who were treated with VKAs and had stable international normalized ratios from outpatient clinics throughout the Netherlands. They screened about 2,600 patients and enrolled nearly 1,400. Most were excluded for not being frail.
Half the group was randomized to switching to a DOAC – drug choice was left to the treating clinician – and the other half remained on VKAs. Patients were 83 years of age on average with a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4. All four classes of DOAC were used in the switching arm.
The primary endpoint was major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, whichever came first, accounting for death as a competing risk. Follow-up was 1 year.
The results for switching to DOAC vs. VKA
Dr. Joosten started her presentation with this: “The results turned out to be different than we expected.” The authors designed the trial with the idea that switching to DOACs would be superior in safety to remaining on VKAs.
But the trial was halted after an interim analysis found a rate of major bleeding in the switching arm of 15.3% versus 9.4% in the arm staying on VKA (hazard ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.32; P = .0012).
The Kaplan-Meier event curves reveal that the excess risk of bleeding occurred after 100 days and increased with time. This argued against an early effect from transitioning the drugs.
An analysis looking at specific DOAC drugs revealed similar hazards for the two most common ones used – apixaban and rivaroxaban.
Thrombotic events were a secondary endpoint and were low in absolute numbers, 2.4% versus 2.0%, for remaining on VKA and switching to DOAC, respectively (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 0.60-2.61).
The time in therapeutic range in FRAIL-AF was similar to that in the seminal DOAC trials.
Comments
Three reasons lead me to choose FRAIL-AF as the most important study from the 2023 ESC congress.
First is the specific lesson about switching drugs. Note that FRAIL-AF did not address the question of starting anticoagulation. The trial results show that if you have a frail older patient who is doing well on VKA, don’t change to a DOAC. That is important to know, but it is not what gives this study its heft.
The second reason centers on the investigators choice to do this trial. Dr. Geersing had a feeling that common wisdom was wrong. He did not try to persuade colleagues with anecdote or plausibility or meta-analyses of observational studies. He set out to answer a question in the correct way – with a randomized trial.
This is the path forward in medicine. I’ve often heard proponents of observational research declare that many topics in medicine cannot be studied with trials. I could hear people arguing that it’s not feasible to study mostly home-bound, elderly frail patients. And the fact that there exist so few trials in this space would support that argument.
But the FRAIL-AF authors showed that it is possible. This is the kind of science that medicine should celebrate. There were no soft endpoints, financial conflicts, or spin. If medical science had science as its incentive, rather than attention, FRAIL-AF easily wins top honors.
The third reason FRAIL-AF is so important is that it teaches us the humility required in translating evidence in our clinics. I like to say evidence is what separates doctors from palm readers. But using this evidence requires thinking hard about how average effects in trial environments apply to our patient.
Yes, of course, there is clear evidence from tens of thousands of patients in the DOAC versus warfarin trials, that, for those patients, on average, DOACs compare favorably with VKA. The average age of patients in these trials was 70-73 years; the average age in FRAIL-AF was 83 years. And that is just age. A substudy of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 trial found that only 360 of more than 20,000 patients in the trial had severe frailty.
That lesson extends to nearly every common therapy in medicine today. It also casts great doubt on the soft-thinking idea of using evidence from trials to derive quality metrics. As if the nuance of evidence translation can be captured in an electronic health record.
The skillful use of evidence will be one of the main challenges of the next generation of clinicians. Thanks to advances in medical science, more patients will live long enough to become frail. And the so-called “guideline-directed” therapies may not apply to them.
Dr. Joosten, Dr. Geersing, and the FRAIL-AF team have taught us specific lessons about anticoagulation, but their greatest contribution has been to demonstrate the value of humility in science and the practice of evidence-based medicine.
If you treat patients, no trial at this meeting is more important.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the hardest tasks of a clinician is applying evidence from trials to the person in your office. At the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, the surprising and unexpected results of the FRAIL-AF trial confirm the massive challenge of evidence translation.
FRAIL-AF investigators set out to study the question of whether frail, elderly patients with atrial fibrillation who were doing well with vitamin K antagonists (VKA) should be switched to direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOAC).
Senior author Geert-Jan Geersing, MD, PhD, from the University Medical Center Utrecht (the Netherlands), told me that frustration led him to design this study. He was frustrated that colleagues assumed that evidence in nonfrail patients can always be translated to frail patients.
Dr. Geersing offered two reasons why common wisdom may be wrong. First was that the large DOAC versus warfarin trials included few elderly patients with frailty. Second, first author Linda Joosten, MD, made it clear in her presentation that frailty is a lot more than aging. It is a clinical syndrome, which entails a “high burden of comorbidities, dependency on others, and a reduced ability to resist stressors.”
The FRAIL-AF trial
The investigators recruited elderly, frail patients with fibrillation who were treated with VKAs and had stable international normalized ratios from outpatient clinics throughout the Netherlands. They screened about 2,600 patients and enrolled nearly 1,400. Most were excluded for not being frail.
Half the group was randomized to switching to a DOAC – drug choice was left to the treating clinician – and the other half remained on VKAs. Patients were 83 years of age on average with a mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4. All four classes of DOAC were used in the switching arm.
The primary endpoint was major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, whichever came first, accounting for death as a competing risk. Follow-up was 1 year.
The results for switching to DOAC vs. VKA
Dr. Joosten started her presentation with this: “The results turned out to be different than we expected.” The authors designed the trial with the idea that switching to DOACs would be superior in safety to remaining on VKAs.
But the trial was halted after an interim analysis found a rate of major bleeding in the switching arm of 15.3% versus 9.4% in the arm staying on VKA (hazard ratio, 1.69; 95% confidence interval, 1.23-2.32; P = .0012).
The Kaplan-Meier event curves reveal that the excess risk of bleeding occurred after 100 days and increased with time. This argued against an early effect from transitioning the drugs.
An analysis looking at specific DOAC drugs revealed similar hazards for the two most common ones used – apixaban and rivaroxaban.
Thrombotic events were a secondary endpoint and were low in absolute numbers, 2.4% versus 2.0%, for remaining on VKA and switching to DOAC, respectively (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 0.60-2.61).
The time in therapeutic range in FRAIL-AF was similar to that in the seminal DOAC trials.
Comments
Three reasons lead me to choose FRAIL-AF as the most important study from the 2023 ESC congress.
First is the specific lesson about switching drugs. Note that FRAIL-AF did not address the question of starting anticoagulation. The trial results show that if you have a frail older patient who is doing well on VKA, don’t change to a DOAC. That is important to know, but it is not what gives this study its heft.
The second reason centers on the investigators choice to do this trial. Dr. Geersing had a feeling that common wisdom was wrong. He did not try to persuade colleagues with anecdote or plausibility or meta-analyses of observational studies. He set out to answer a question in the correct way – with a randomized trial.
This is the path forward in medicine. I’ve often heard proponents of observational research declare that many topics in medicine cannot be studied with trials. I could hear people arguing that it’s not feasible to study mostly home-bound, elderly frail patients. And the fact that there exist so few trials in this space would support that argument.
But the FRAIL-AF authors showed that it is possible. This is the kind of science that medicine should celebrate. There were no soft endpoints, financial conflicts, or spin. If medical science had science as its incentive, rather than attention, FRAIL-AF easily wins top honors.
The third reason FRAIL-AF is so important is that it teaches us the humility required in translating evidence in our clinics. I like to say evidence is what separates doctors from palm readers. But using this evidence requires thinking hard about how average effects in trial environments apply to our patient.
Yes, of course, there is clear evidence from tens of thousands of patients in the DOAC versus warfarin trials, that, for those patients, on average, DOACs compare favorably with VKA. The average age of patients in these trials was 70-73 years; the average age in FRAIL-AF was 83 years. And that is just age. A substudy of the ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 trial found that only 360 of more than 20,000 patients in the trial had severe frailty.
That lesson extends to nearly every common therapy in medicine today. It also casts great doubt on the soft-thinking idea of using evidence from trials to derive quality metrics. As if the nuance of evidence translation can be captured in an electronic health record.
The skillful use of evidence will be one of the main challenges of the next generation of clinicians. Thanks to advances in medical science, more patients will live long enough to become frail. And the so-called “guideline-directed” therapies may not apply to them.
Dr. Joosten, Dr. Geersing, and the FRAIL-AF team have taught us specific lessons about anticoagulation, but their greatest contribution has been to demonstrate the value of humility in science and the practice of evidence-based medicine.
If you treat patients, no trial at this meeting is more important.
Dr. Mandrola is a clinical electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates, Louisville, Ky. He reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five ways to avert a malpractice lawsuit with better EHR techniques
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although most physicians have gotten used to working with EHRs, despite their irritations, the use of EHRs has contributed to a growing number of malpractice lawsuits. Defense attorneys say that
According to a study in the Journal of Patient Safety, more than 30% of all EHR-related malpractice cases are associated with medication errors; 28% with diagnosis; and 31% with a complication of treatment, such as entering wrong information, entering information in the wrong place, and overlooking EHR flags and warnings for interactions or contraindications.
The study gave these examples of EHR-related errors that led to patient harm and ultimately to malpractice lawsuits:
- A discharge order omitted a patient’s medication that prevented strokes; the patient had a stroke days later.
- An electronic order for morphine failed to state the upper dose limit; the patient died.
- A physician meant to click on “discontinue” for an anticoagulant but mistakenly clicked on “continue” for home use.
Catching potential issues such as drug interactions or critical medical history that should inform treatment is more important than ever. “We know from safety engineering principles that just relying on vigilance is not a long-term safety strategy,” says Aaron Zach Hettinger, MD, chief research information officer at MedStar Health Research Institute, Washington, D.C. “So, it’s critical that we design these safe systems and leverage the data that’s in them.”
Here are five smart EHR practices to help protect your patients’ health and your own liability.
1. Double-check dropdown boxes
When it comes to user error, it’s easy to click the wrong choice from a drop-down menu. Better to take the time to explain your answer in a box, even if it takes a few more minutes. Or if you are choosing from a menu, proofread any information it auto-fills in the chart.
Dr. Hettinger says you can strike a balance between these templated approaches to diagnosis and long-term care by working with third-party systems and your organization or vendor IT department to help with follow-up questions to keep populated data in check.
“Make sure you have a back-end system that can help monitor that structured data,” says Dr. Hettinger. Structured data are the patient’s demographic information, like name, address, age, height, weight, vital signs, and data elements like diagnosis, medications, and lab results. “Wherever you can leverage the underlying tools that are part of the electronic health record to make sure that we’re constantly checking the right results, that helps reduce the workload so that clinicians can focus on taking care of the patients and doing the right thing and not be as focused on entering data into the system.”
2. Supplement EHR notes with direct communication
The failure to diagnose cancer because one physician doesn’t know what another physician saw in an imaging report is one of the most common claims in the cases he tries, says Aaron Boeder, a plaintiff’s medical negligence lawyer in Chicago.
Physicians often assume that if they put a note in the electronic chart, others will look for it, but Mr. Boeder says it’s far more prudent to communicate directly.
“Let’s say a radiologist interprets a scan and sees what might be cancer,” he says. “If the ordering doctor is an orthopedist who’s ordered a CT scan for DVT, there’s going to be a report for that scan. It’s going to get auto-populated back into that physician’s note,” says Mr. Boeder.
The physician may or may not look at it, but it will be in their note, and they’re supposed to follow up on it because they ordered the scan. “But they may not follow up on it, and they may not get a call from the radiologist,” he says.
“Next thing you know, 2 or 3 years later, that patient is diagnosed with very advanced cancer.”
3. Tailor auto-fill information to your common practices
Suppose, as a physician, you find that you need to change a default setting time and time again. Dr. Hettinger says it’s worth your time to take an extra couple of minutes to work with your vendor or your health system to try and make changes to auto-population settings that align with your practices.
“Let’s say a default dose of 20 milligrams of a medication is what automatically pops up, but in reality, your practice is to use a smaller dose because it’s safer, even though they’re all within the acceptable realm of what you would order,” he says. “Rather than have the default to the higher dose, see if you can change the default to a lower dose. And that way, you don’t have to catch yourself every time.”
If your auto-fills are amounts that constantly need changing, an interruption could easily knock you off course before you make that correction.
“If there are ways to have the system defaults be safer or more in line with your clinical practice, and especially across a group, then you’re designing a safer system and not relying on vigilance or memory prone to interruptions,” says Dr. Hettinger.
4. Curb the copy and paste
It’s tempting to copy a note from a previous patient visit and make only minimal changes as needed, but you risk including outdated information if you do. Even if you’re repeating questions asked by the intake nurse, it is safer to not to rely on that information, says Beth Kanik, a defense medical malpractice attorney in Atlanta.
“If it later goes into litigation, the argument then becomes that it looks like you didn’t do your job,” says Ms. Kanik. “Instead, try to ask questions in a way that would elicit responses that may be a little different than what the nurse got, so that it’s clear you asked the questions and didn’t just simply rely upon someone else’s information.”
5. Separate typing from listening
While EHR may be an excellent tool for data collection and safety checking, it’s not a stand-in for doctor-patient interaction. As technology practices push medicine toward more and more efficiency, Mr. Boeder says it’s most often listening over all else that makes the difference in the quality of care. And good listening requires full attention.
“A real concern for physicians is the number of visits they’re expected to accomplish in a set amount of time,” says Mr. Boeder. “Often this translates into a doctor talking to a patient while typing notes or while reading a note from the last time the patient was in.”
Taking the time to pause after entering data and briefly reviewing your understanding of what your patient has told you can be invaluable and may save you – and your patient – problems later.
“In so many cases, it comes down to people not being heard,” says Mr. Boeder. “So listen to what your patients are saying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-dose aspirin cuts type 2 diabetes risk in over-65s
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data come from a secondary analysis of ASPREE, a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of healthy adults aged 65 years or older, showing that 100 mg of aspirin taken daily for about 5 years did not provide a cardiovascular benefit but did significantly raise the risk for bleeding.
This new analysis shows that individuals taking aspirin had a 15% lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes and that the medication slowed the rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose, compared with placebo, during follow-up.
However, lead author Sophia Zoungas, MBBS, PhD, head of the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, said: “Major prescribing guidelines now recommend older adults take daily aspirin only when there is a medical reason to do so, such as after a heart attack. ... Although these new findings are of interest, they do not change the clinical advice about aspirin use in older people at this time.”
Nonetheless, she said in an interview, “at this time, our findings are exploratory but ignite the debate of the important role that anti-inflammatory approaches may play in preventing diabetes. Further work is currently underway to understand which subpopulations may be better targeted and to understand the balance of risk versus benefit.”
The results are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, taking place Oct. 2-6 in Hamburg, Germany.
New findings not robust enough to change current practice
Asked to comment, Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, said: “Given the post hoc secondary nature of the analysis, the findings should be considered hypothesis generating and not definitive… At this time, based on prospective randomized studies, the risks of aspirin outweigh the benefits for aspirin in older adults.”
Among those studies was an ASPREE substudy showing failure of low-dose aspirin to reduce fracture risk while increasing the risk for serious falls, and two other trials, ARRIVE and ASCEND, also showing that harms of aspirin outweigh the benefits in people with cardiovascular risk but not diabetes, and in those with diabetes, respectively, said Dr. Mukherjee, professor and chair of the department of internal medicine at Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center at El Paso.
And, Mukherjee noted, in 2019 the American College of Cardiology updated its practice guidelines to say that low-dose aspirin should not be administered on a routine basis for the primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in adults over age 70. In 2021, the American Diabetes Association seconded that recommendation.
Asked whether these newest findings might change current practice for any higher-risk subgroup, such as people with prediabetes, Dr. Mukherjee replied: “Unless there is a prospective randomized trial that validates these findings in those with prediabetes, the findings should not change practice. There are also no data [showing] that another antiplatelet agent would be indicated or would be beneficial. Instead, I would recommend lifestyle changes including regular exercise and a healthy diet to minimize risk of diabetes.”
The 16,209 ASPREE participants were community dwelling and did not have diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or dementia at baseline. They were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive 100 mg/d of enteric-coated aspirin or placebo. Over a median follow-up of 4.7 years, the proportions developing type 2 diabetes were 5.7% with aspirin versus 6.6% with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.85; P = .01).
The annual rate of increase in fasting plasma glucose over the follow-up period was slowed by 0.006 mmol/L with aspirin, compared with placebo, also a significant difference (P = .004).
According to Dr. Zoungas, “the potential for anti-inflammatory agents like aspirin to prevent type 2 diabetes or improve glucose levels needs further study.”
The ASPREE trial was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, Monash University, and the Victorian Cancer Agency. Dr. Zoungas and Dr. Mukherjee have no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2023
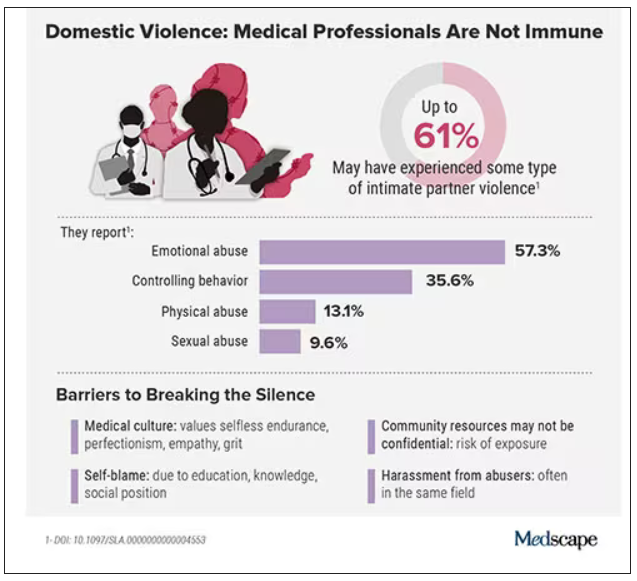
Domestic violence in health care is real and underreported
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To protect survivors’ identities, some names have been changed or shortened.
Natasha Abadilla, MD, met the man who would become her abuser while working abroad for a public health nonprofit. When he began emotionally and physically abusing her, she did everything she could to hide it.
“My coworkers knew nothing of the abuse. I became an expert in applying makeup to hide the bruises,” recalls Dr. Abadilla, now a second-year resident and pediatric neurologist at Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford.
Dr. Abadilla says she strongly identifies as a hard worker and – to this day – hopes her work did not falter despite her partner’s constant drain on her. But the impact of the abuse continued to affect her for years. Like many survivors of domestic violence, she struggled with PTSD and depression.
Health care workers are often the first point of contact for survivors of domestic violence. Experts and advocates continue to push for more training for clinicians to identify and respond to signs among their patients. Often missing from this conversation is the reality that those tasked with screening can also be victims of intimate partner violence themselves.
What’s more: The very strengths that medical professionals often pride themselves on – perfectionism, empathy, grit – can make it harder for them to identify abuse in their own relationships and push through humiliation and shame to seek help.
Dr. Abadilla is exceptional among survivors in the medical field. Rather than keep her experience quiet, she has shared it publicly.
Awareness, she believes, can save lives.
An understudied problem in an underserved group
The majority of research on health care workers in this area has focused on workplace violence, which 62% experience worldwide. But intimate partner violence remains understudied and underdiscussed. Some medical professionals are even saddled with a “double burden,” facing trauma at work and at home, note the authors of a 2022 meta-analysis published in the journal Trauma, Violence, & Abuse.
The problem has had dire consequences. In recent years, many health care workers have been killed by their abusers:
- In 2016, Casey M. Drawert, MD, a Texas-based critical care anesthesiologist, was fatally shot by her husband in a murder-suicide.
- In 2018, Tamara O’Neal, MD, an ER physician, and Dayna Less, a first-year pharmacy resident, were killed by Dr. O’Neal’s ex-fiancé at Mercy Hospital in Chicago.
- In 2019, Sarah Hawley, MD, a first-year University of Utah resident, was fatally shot by her boyfriend in a murder-suicide.
- In 2021, Moria Kinsey, a nurse practitioner in Tahlequah, Okla., was murdered by a physician.
- In July of 2023, Gwendolyn Lavonne Riddick, DO, an ob.gyn. in North Carolina, was fatally shot by the father of her 3-year-old son.
There are others.
In the wake of these tragedies, calls for health care workers to screen each other as well as patients have grown. But for an untold number of survivors, breaking the silence is still not possible due to concerns about their reputation, professional consequences, the threat of harassment from abusers who are often in the same field, a medical culture of selfless endurance, and a lack of appropriate resources.
While the vast majority have stayed silent, those who have spoken out say there’s a need for targeted interventions to educate medical professionals as well as more supportive policies throughout the health care system.
Are health care workers more at risk?
Although more studies are needed, research indicates health care workers experience domestic violence at rates comparable to those of other populations, whereas some data suggest rates may be higher.
In the United States, more than one in three women and one in four men experience some form of intimate partner violence in their lifetime. Similarly, a 2020 study found that 24% of 400 physicians responding to a survey reported a history of domestic violence, with 15% reporting verbal abuse, 8% reporting physical violence, 4% reporting sexual abuse, and 4% reporting stalking.
Meanwhile, in an anonymous survey completed by 882 practicing surgeons and trainees in the United States from late 2018 to early 2019, more than 60% reported experiencing some type of intimate partner violence, most commonly emotional abuse.
Recent studies in the United Kingdom, Australia, and elsewhere show that significant numbers of medical professionals are fighting this battle. A 2019 study of more than 2,000 nurses, midwives, and health care assistants in the United Kingdom found that nurses were three times more likely to experience domestic violence than the average person.
What would help solve this problem: More study of health care worker-survivors as a unique group with unique risk factors. In general, domestic violence is most prevalent among women and people in marginalized groups. But young adults, such as medical students and trainees, can face an increased risk due to economic strain. Major life changes, such as relocating for residency, can also drive up stress and fray social connections, further isolating victims.
Why it’s so much harder for medical professionals to reveal abuse
For medical professionals accustomed to being strong and forging on, identifying as a victim of abuse can seem like a personal contradiction. It can feel easier to separate their personal and professional lives rather than face a complex reality.
In a personal essay on KevinMD.com, medical student Chloe N. L. Lee describes this emotional turmoil. “As an aspiring psychiatrist, I questioned my character judgment (how did I end up with a misogynistic abuser?) and wondered if I ought to have known better. I worried that my colleagues would deem me unfit to care for patients. And I thought that this was not supposed to happen to women like me,” Ms. Lee writes.
Kimberly, a licensed therapist, experienced a similar pattern of self-blame when her partner began exhibiting violent behavior. “For a long time, I felt guilty because I said to myself, You’re a therapist. You’re supposed to know this,” she recalls. At the same time, she felt driven to help him and sought couples therapy as his violence escalated.
Whitney, a pharmacist, recognized the “hallmarks” of abuse in her relationship, but she coped by compartmentalizing. Whitney says she was vulnerable to her abuser as a young college student who struggled financially. As he showered her with gifts, she found herself waving away red flags like aggressiveness or overprotectiveness.
After Whitney graduated, her partner’s emotional manipulation escalated into frequent physical assaults. When he gave her a black eye, she could not bring herself to go into work. She quit her job without notice. Despite a spotless record, none of her coworkers ever reached out to investigate her sudden departure.
It would take 8 years for Whitney to acknowledge the abuse and seize a moment to escape. She fled with just her purse and started over in a new city, rebuilding her life in the midst of harassment and threats from her ex. She says she’s grateful to be alive.
An imperfect system doesn’t help
Health care workers rarely ask for support or disclose abuse at work. Some have cited stigma, a lack of confidentiality (especially when the abuser is also in health care), fears about colleagues’ judgment, and a culture that doesn’t prioritize self-care.
Sometimes policies get in the way: In a 2021 qualitative study of interviews with 21 female physician-survivors in the United Kingdom, many said that despite the intense stress of abuse and recovery, they were unable to take any time off.
Of 180 UK-based midwife-survivors interviewed in a 2018 study, only 60 sought support at work and 30 received it. Many said their supervisors pressured them to report the abuse and get back to work, called social services behind their back, or reported them to their professional regulator. “I was treated like the perpetrator,” one said. Barbara Hernandez, PhD, a researcher who studies physician-survivors and director of physician vitality at Loma Linda University in southern California, says workplace violence and mistreatment from patients or colleagues – and a poor institutional response – can make those in health care feel like they have to “shut up and put up,” priming them to also tolerate abuse at home.
When survivors do reach out, there can be a disconnect between the resources they need and those they’re offered, Dr. Hernandez adds. In a recent survey of 400 physicians she conducted, respondents typically said they would advise a physician-survivor to “get to a shelter quickly.” But when roles were reversed, they admitted going to a shelter was the least feasible option. Support groups can also be problematic in smaller communities where physicians might be recognized or see their own patients.
Complicating matters further, the violence often comes from within the medical community. This can lead to particularly malicious abuse tactics like sending false accusations to a victim’s regulatory college or board; prolonged court and custody battles to drain them of all resources and their ability to hold a job; or even sabotage, harassment, or violence at work. The sheen of the abuser’s public persona, on the other hand, can guard them from any accountability.
For example, one physician-survivor said her ex-partner, a psychiatrist, coerced her into believing she was mentally ill, claimed she was “psychotic” in order to take back their children after she left, and had numerous colleagues serve as character witnesses in court for him, “saying he couldn’t have done any of these things, how great he is, and what a wonderful father he is.”
Slow progress is still progress
After Sherilyn M. Gordon-Burroughs, MD, a Texas-based transplant surgeon, mother, and educator, was killed by her husband in a murder-suicide in 2017, her friends Barbara Lee Bass, MD, president of the American College of Surgeons, and Patricia L. Turner, MD, were spurred into action. Together, they founded the ACS Intimate Partner Violence Task Force. Their mission is to educate surgeons to identify the signs of intimate partner violence (IPV) in themselves and their colleagues and connect them with resources.
“There is a concerted effort to close that gap,” says D’Andrea K. Joseph, MD, cochair of the task force and chief of trauma and acute care surgery at NYU Langone in New York. In the future, Dr. Joseph predicts, “making this a part of the curriculum, that it’s standardized for residents and trainees, that there is a safe place for victims ... and that we can band together and really recognize and assist our colleagues who are in trouble.”
Resources created by the ACS IPV task force, such as the toolkit and curriculum, provide a model for other health care leaders. But there have been few similar initiatives aimed at increasing IPV intervention within the medical system.
What you can do in your workplace
In her essay, Ms. Lee explains that a major turning point came when a physician friend explicitly asked if she was experiencing abuse. He then gently confirmed she was, and asked without judgment how he could support her, an approach that mirrors advice from the National Domestic Violence Hotline.
“Having a physician validate that this was, indeed, an abusive situation helped enormously ... I believe it may have saved my life,” she writes.
That validation can be crucial, and Dr. Abadilla urges other physicians to regularly check in with colleagues, especially those who seem particularly positive with a go-getter attitude and yet may not seem themselves. That was how she presented when she was struggling the most.
Supporting systemic changes within your organization and beyond is also important. The authors of the 2022 meta-analysis stress the need for domestic violence training, legislative changes, paid leave, and union support.
Finding strength in recovery
Over a decade after escaping her abuser, Whitney says she’s only just begun to share her experience, but what she’s learned has made her a better pharmacist. She says she’s more attuned to subtle signs something could be off with patients and coworkers. When someone makes comments about feeling anxious or that they can’t do anything right, it’s important to ask why, she says.
Recently, Kimberly has opened up to her mentor and other therapists, many of whom have shared that they’re also survivors.
“The last thing I said to [my abuser] is you think you’ve won and you’re hurting me, but what you’ve done to me – I’m going to utilize this and I’m going to help other people,” Kimberly says. “This pain that I have will go away, and I’m going to save the lives of others.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in five doctors with long COVID can no longer work: Survey
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Crippling symptoms, lost careers, and eroded incomes: This is the harsh reality for doctors suffering with long COVID, according to the first major survey of physicians with the condition.
The survey, conducted by the British Medical Association and the Long COVID Doctors for Action support group, sheds light on the lingering effects of long COVID on more than 600 chronically ill and disabled doctors with the condition. It also spotlights what they describe as a lack of medical and financial support from their government and employers at the National Health Service.
“We feel betrayed and abandoned,” said Kelly Fearnley, MBChB, chair and cofounder of Long COVID Doctors for Action. “At a time of national crisis, when health care workers were asked to step up, we did. When the nation needed us, we stepped up. We put our lives on the line. We put our families’ lives on the line. And now that we are injured after knowingly being unprotected and deliberately and repeatedly exposed to a level 3 biohazard, we now find ourselves in this position.”
Dr. Fearnley fell ill while working in a hospital’s COVID ward in November 2020. She is one of an estimated 2 million people in the United Kingdom – including thousands of NHS employees – with long COVID. She hasn’t been able to return to work in nearly 3 years.
Long COVID affects more than 65 million people worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 10 people infected with the virus develop long-term symptoms. In the United Kingdom, health care and social care workers are seven times more likely to have had severe COVID-19 than other types of employees.
Doctors responding to the BMA survey reported a wide range of long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, muscular pain, nerve damage, joint pain, and respiratory problems.
Among the survey’s key findings, 60% of doctors said long COVID has affected their ability to carry out day-to-day tasks on a regular basis. Almost one in five (18%) said they were no longer able to work, while fewer than one in three (31%) were working full time. This compares with more than half (57%) of respondents working full time before the onset of their COVID illness – a decline of 46%.
Nearly half (48%) of respondents said they have experienced some form of loss of earnings as a result of long COVID, and almost half of the doctors were never referred to an NHS long COVID clinic. The survey included the following first-person accounts from doctors living with the condition.
- One doctor said: “I nearly lost my life, my home, my partner and my career. I have received little support to help keep these. The impact on my mental health nearly cost [me] my life again.”
- A senior consulting physician commented: “Life is absolutely miserable. Every day is a struggle. I wake up exhausted, the insomnia and night terrors are horrendous as I live through my worst fears every night. Any activity such as eating meals, washing, etc., will mean I have to go to bed for a few hours. I am unable to look after myself or my child, exercise or maintain social relationships. I have no financial security. Long COVID has totally destroyed my life.”
- A salaried general practitioner said: “I can no longer work, finances are ruined. I didn’t have employment protection so am now unemployed and penniless.”
Calls for action from the BMA include the following:
- Financial support for doctors and health care staff with long COVID.
- The recognition of long COVID as an occupational disease among health care workers, along with a definition of the condition that covers all of the debilitating disease’s symptoms.
- Improved access to physical and mental health services to help comprehensive assessment, investigations, and treatment.
- Greater workplace protection for health care staff who risk their lives for others.
- Better support for long COVID sufferers to return to work safely if they can, including a flexible approach to the use of workplace adjustments.
“One would think, given the circumstances under which we fell ill and current workforce shortages, NHS employers would be eager to do everything to facilitate the return to work of people with long COVID,” said Dr. Fearnley. “However, NHS employers are legally required to implement only ‘reasonable adjustments,’ and so things such as extended phased return or adjustments to shift patterns are not always being facilitated. Instead, an increasing number of employers are choosing to terminate contracts.”
Raymond Agius, the BMA’s occupational medicine committee cochair, also put the blame on inadequate safety measures for doctors. Those inadequate measures persist to this day, inasmuch as U.K. hospitals have dropped masking requirements.
“During the COVID-19 pandemic, doctors were left exposed and unprotected at work,” he said in a BMA press release. “They often did not have access to the right PPE. ... Too many risk assessments of workplaces and especially of vulnerable doctors were not undertaken.”
A small minority of doctors who were surveyed said they had access to respiratory protective equipment about the time they contracted COVID-19. Only 11% had access to an FFP2 respirator (the equivalent of an N95 mask); 16% had an FFP3 respirator (the equivalent of an N99 mask).
To date, the British government hasn’t issued much of a response to the survey, saying only that it has invested more than ₤50 million to better understand long COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Resident creates AI alternative to U.S. News med school ranking
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For decades, pre-med students depended on the annual medical school rankings by U.S. News and World Report to decide where to apply for physician education. But after several prominent med schools pulled out of the rankings, one resident began experimenting with artificial intelligence (AI) to create an alternative.
Brandon Turner MD, MSc, a radiation oncology resident at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, developed a free do-it-yourself tool using AI that allows prospective students to rank medical schools based on considerations that are most important to them. His research was published online in JAMA Network Open.
“One of the flaws with conventional ranking systems is that the metrics used in these tools are weighted based on the preferences and views of the people who developed these rankings, but those may not work for everyone,” Dr. Turner told this news organization.
He explained that there are different types of metrics used in the U.S. News ranking: one for research and the other for primary care. “The research rankings carry the most prestige and are the ones that most people know about,” he explained. These metrics take into account factors such as how many grant dollars the medical school receives and the average size of those grants per faculty member, Dr. Turner said.
Admission metrics are also included – for example, the median grade point average or MCAT scores of students who have been accepted. “These don’t tell you anything about the research output of the school, only about how selective the school is,” he said.
Primary care metrics might focus on how many graduates of a given school go into primary care, or how other schools rate the quality of primary care training at a given school – a process called peer assessment, Dr. Turner said.
But even though these might be helpful, students may be more interested in the cost of attendance, average debt, representation of minorities, and how many graduates pass their boards, he said. “U.S. News metrics don’t capture these things, but I included them in my algorithm.”
A U.S. News spokesperson said that the publication continues to help students and their families make decisions about their future education. The spokesperson cited U.S. News’ explanation of how it calculates its rankings. “A school’s overall Best Medical Schools rank should be one consideration and not the lone determinant in where a student applies and accepts,” the article states.
Dr. Turner agreed ranking systems are a good starting point when researching med schools, “but the values reflected in the ranking may not reflect an individual’s goals.”
Tyra-Lee Brett, a premed student at the University of South Florida, Tampa, believes an additional tool for students to evaluate medical schools is needed – and she could potentially see herself using Dr. Turner’s creation.
Still, Ms. Brett, a premed trustee of the American Medical Student Association, doesn’t regard any ranking tool as the “be all and end all.” Rather, she feels that the most effective tool would be based on students’ lived experiences. The AMSA is developing a scorecard in which students grade schools based on their opinions about such issues as housing, family planning, and environmental health, she said.
No prior judgments
To develop his algorithm, Dr. Turner used a branch of AI called “unsupervised learning.” It doesn’t make a prior judgment about what the data should look like, Dr. Turner explained.
“You’re just analyzing natural trends within the data.”
The algorithm tries to find and discover clusters or patterns within the data. “It’s like saying to the algorithm: ‘I want you to tell me what schools you think should be grouped together based on the data I feed you,’ which is the data that the user selects based on his or her personal preferences.”
U.S. News has been transparent about the metrics it uses, Dr. Turner notes. “When I started looking into how rankings are developed, I saw that there was transparency, and the reasoning for choosing the metrics used to develop the ranking was pretty sound,” he said.
“But I didn’t see any justification as to why they chose the particular metrics and weighted them in the way that they did.”
Dr. Turner extracted data from the 2023 U.S. News report, which ranked 109 allopathic medical schools, and applied several scenarios to the results to create his alternative ranking system.
In one scenario, he used the same research metrics used by U.S. News, such as a peer research assessment, median federal research activity per full-time faculty member, median GPA, median MCAT, acceptance rate, and faculty-student ratio.
In another scenario, he included four additional metrics: debt, in-state cost of attendance, USMLE Step 1 passing rate, and percentage of underrepresented students with minority race or ethnicity at the school.
For example, a user can rank the importance of the diversity of the class, amount of debt students expect to incur, and amount of research funding the medical school receives. After selecting those factors, the tool generates tiered results displayed in a circle, a shape chosen to avoid the appearance of the hierarchy associated with traditional rankings, Dr. Turner said.
“A prospective student might not care about acceptance rates and MCAT scores, and instead cares about diversity and debt,” Dr. Turner said. He looks forward to extending this approach to the ranking of colleges as well.
‘Imperfect measures’
“The model and interesting online tool that Dr. Turner created allows a premed [student] to generate custom rankings that are in line with their own priorities,” said Christopher Worsham, MD, MPH, a critical care physician in Mass General’s division of pulmonary and critical care medicine.
But Dr. Worsham, also a teaching associate at Harvard Medical School’s department of health care policy, expressed concern that factors figuring into the rankings by U.S. News and Dr. Turner’s alternative “are imperfect measures of medical school quality.”
For example, a student interested in research might favor federal research funding in their customized rankings with Dr. Turner’s model. “But higher research funding doesn’t necessarily translate into a better education for students, particularly when differentiating between two major research systems,” Dr. Worsham noted.
Dr. Worsham added that neither ranking system accurately predicts the quality of doctors graduating from the schools. Instead, he’d like to see ranking systems based on which schools’ graduates deliver the best patient outcomes, whether that’s through direct patient care, impactful research, or leadership within the health care system.
Michael Sauder, PhD, professor of sociology at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, said the model could offer a valuable alternative to the U.S. News ranking system. It might help users develop their own criteria for determining the ranking of medical schools, which is a big improvement over a “one-size-fits-all” approach, Dr. Sauder said.
And Hanna Stotland, an admission consultant based in Chicago, noted that most students rely on rankings because they “don’t have the luxury of advisers who know the ins and outs of different medical schools.” Given the role that rankings play, Ms. Stotland expects that every new ranking tool will have some influence on students.
This tool in particular “has the potential to be useful for students who have identified values they want their medical school to share.” For example, students who care about racial diversity “could use it to easily identify schools that are successful on that metric,” Ms. Stotland said.
Sujay Ratna, a 2nd-year med student at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, said he considered the U.S. News ranking his “go-to tool” when he was applying to med school.
But after reading Dr. Turner’s article, the AMSA membership vice president tried the algorithm. “I definitely would have used it had it existed when I was thinking of what schools to apply to and what [schools] to attend.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Turner, Dr. Worsham, Dr. Sauder, Ms. Stotland, Ms. Brett, and Mr. Ratna report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Q&A: What to know about the new BA 2.86 COVID variant
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Health Organization have dubbed the BA 2.86 variant of COVID-19 as a variant to watch.
So far, only 26 cases of “Pirola,” as the new variant is being called, have been identified: 10 in Denmark, four each in Sweden and the United States, three in South Africa, two in Portugal, and one each the United Kingdom, Israel, and Canada. BA 2.86 is a subvariant of Omicron, but according to reports from the CDC, the strain has many more mutations than the ones that came before it.
With so many facts still unknown about this new variant, this news organization asked experts what people need to be aware of as it continues to spread.
What is unique about the BA 2.86 variant?
“It is unique in that it has more than three mutations on the spike protein,” said Purvi S. Parikh, MD, an infectious disease expert at New York University’s Langone Health. The virus uses the spike proteins to enter our cells.
This “may mean it will be more transmissible, cause more severe disease, and/or our vaccines and treatments may not work as well, as compared to other variants,” she said.
What do we need to watch with BA 2.86 going forward?
“We don’t know if this variant will be associated with a change in the disease severity. We currently see increased numbers of cases in general, even though we don’t yet see the BA.2.86 in our system,” said Heba Mostafa, PhD, director of the molecular virology laboratory at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
“It is important to monitor BA.2.86 (and other variants) and understand how its evolution impacts the number of cases and disease outcomes,” she said. “We should all be aware of the current increase in cases, though, and try to get tested and be treated as soon as possible, as antivirals should be effective against the circulating variants.”
What should doctors know?
Dr. Parikh said doctors should generally expect more COVID cases in their clinics and make sure to screen patients even if their symptoms are mild.
“We have tools that can be used – antivirals like Paxlovid are still efficacious with current dominant strains such as EG.5,” she said. “And encourage your patients to get their boosters, mask, wash hands, and social distance.”
How well can our vaccines fight BA 2.86?
“Vaccine coverage for the BA.2.86 is an area of uncertainty right now,” said Dr. Mostafa.
In its report, the CDC said scientists are still figuring out how well the updated COVID vaccine works. It’s expected to be available in the fall, and for now, they believe the new shot will still make infections less severe, new variants and all.
Prior vaccinations and infections have created antibodies in many people, and that will likely provide some protection, Dr. Mostafa said. “When we experienced the Omicron wave in December 2021, even though the variant was distant from what circulated before its emergence and was associated with a very large increase in the number of cases, vaccinations were still protective against severe disease.”
What is the most important thing to keep track of when it comes to this variant?
According to Dr. Parikh, “it’s most important to monitor how transmissible [BA 2.86] is, how severe it is, and if our current treatments and vaccines work.”
Dr. Mostafa said how well the new variants escape existing antibody protection should also be studied and watched closely.
What does this stage of the virus mutation tell us about where we are in the pandemic?
The history of the coronavirus over the past few years shows that variants with many changes evolve and can spread very quickly, Dr. Mostafa said. “Now that the virus is endemic, it is essential to monitor, update vaccinations if necessary, diagnose, treat, and implement infection control measures when necessary.”
With the limited data we have so far, experts seem to agree that while the variant’s makeup raises some red flags, it is too soon to jump to any conclusions about how easy it is to catch it and the ways it may change how the virus impacts those who contract it.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
NPs, PAs, and physicians hope to join doctors’ union in rare alliance
Advanced practice providers (APPs) such as nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) have long been at odds with doctor groups over scope of practice issues. But in a rare alliance, in late September. If successful, the Allina group will join the Doctors Council SEIU, Local 10MD.
The Allina health care providers share concerns about their working conditions, such as understaffing and inadequate resources, limited decision-making authority, and health systems valuing productivity and profit over patient care.
Although doctors and APPs have said that they generally work well together, the relationship has been strained in recent years as APPs argue for greater scope of practice. Meanwhile, physician groups, such as the American Medical Association, believe that APPs need more oversight.
An Allina union organizer, Britta V. Kasmarik, CNP, acknowledges the tension between physicians and APPs. But she said in an interview that the union effort helped bond this group of health care providers. “We share common goals of providing high-quality care for patients in a safe way, and we see the same things day in and day out with our patients.”
Matt Hoffman, MD, a primary care physician at Allina, told this news organization that APPs in his specialty perform the same job as doctors “and the working conditions are really identical. In our view, that means we should be unionizing together.”
The decision to hold a union vote follows similar action by nearly 150 Allina Mercy Hospital physicians in March. Allina Health appealed the vote.
In response to a New York Times investigation, the Minnesota Attorney General’s office began reviewing reports of aggressive billing practices and denied care at Allina Health.
The Allina Health system, which reports $4 billion in annual revenue, cut off nonemergency services to patients, including children, if their medical debt exceeded $4,500, according to the New York Times article. For Allina’s physicians and APPs, that meant leaving patients’ illnesses untreated.
Less than a week after the attorney general announced its investigation, the health system ended this practice.
In a prepared statement to this news organization, Allina Health said that its providers are “critical members of our teams. … We deeply value and share their commitment to providing high-quality care to our patients.”
The health system said it planned to make operational improvements, implement new communication tools, and provide additional well-being resources and enhanced employee benefits “to improve the provider experience.” In addition, it hoped to continue to “foster a culture of collaboration with all our employees.”
Having a union will allow health care providers to advocate for their patients and give health care providers more decision-making power instead of corporate leaders maintaining full authority, Ms. Kasmarik told this news organization.
Union organizers are also concerned with changes to the daily practice of medicine. “We don’t want to be spending our time doing paperwork and calling insurance companies and filling out forms,” said Dr. Hoffman. “We want to be in the exam room with a patient.”
The Allina providers organized after multiple requests to corporate managers failed to address their concerns. Their demands include increased staffing and help with nonclinical work so that clinicians can spend more time with their patients.
“What I’m really excited about is that we will be able to work with the other unionized groups to make change ... by being involved in health care policy at a state or national level,” Dr. Hoffman said. For example, that involvement might include challenging insurance company decisions.
Doctors Council bills itself as the largest union for attending physicians in the country, with 3,500 members, according to Joe Crane, national organizing director.
Despite an increase in union efforts since the pandemic, health care workers – particularly doctors – have been slow to join unions. Mr. Crane estimated that only about 3% of U.S. physicians are currently union members. He cited union campaigns in Massachusetts, New York, and Washington, DC. For comparison, a minority of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) (9%) report union membership, according to Medscape’s APRN compensation report last year.
Dr. Hoffman is confident the Allina health care providers will have enough votes to win the election to join the union. “We should have done this years ago.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Advanced practice providers (APPs) such as nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) have long been at odds with doctor groups over scope of practice issues. But in a rare alliance, in late September. If successful, the Allina group will join the Doctors Council SEIU, Local 10MD.
The Allina health care providers share concerns about their working conditions, such as understaffing and inadequate resources, limited decision-making authority, and health systems valuing productivity and profit over patient care.
Although doctors and APPs have said that they generally work well together, the relationship has been strained in recent years as APPs argue for greater scope of practice. Meanwhile, physician groups, such as the American Medical Association, believe that APPs need more oversight.
An Allina union organizer, Britta V. Kasmarik, CNP, acknowledges the tension between physicians and APPs. But she said in an interview that the union effort helped bond this group of health care providers. “We share common goals of providing high-quality care for patients in a safe way, and we see the same things day in and day out with our patients.”
Matt Hoffman, MD, a primary care physician at Allina, told this news organization that APPs in his specialty perform the same job as doctors “and the working conditions are really identical. In our view, that means we should be unionizing together.”
The decision to hold a union vote follows similar action by nearly 150 Allina Mercy Hospital physicians in March. Allina Health appealed the vote.
In response to a New York Times investigation, the Minnesota Attorney General’s office began reviewing reports of aggressive billing practices and denied care at Allina Health.
The Allina Health system, which reports $4 billion in annual revenue, cut off nonemergency services to patients, including children, if their medical debt exceeded $4,500, according to the New York Times article. For Allina’s physicians and APPs, that meant leaving patients’ illnesses untreated.
Less than a week after the attorney general announced its investigation, the health system ended this practice.
In a prepared statement to this news organization, Allina Health said that its providers are “critical members of our teams. … We deeply value and share their commitment to providing high-quality care to our patients.”
The health system said it planned to make operational improvements, implement new communication tools, and provide additional well-being resources and enhanced employee benefits “to improve the provider experience.” In addition, it hoped to continue to “foster a culture of collaboration with all our employees.”
Having a union will allow health care providers to advocate for their patients and give health care providers more decision-making power instead of corporate leaders maintaining full authority, Ms. Kasmarik told this news organization.
Union organizers are also concerned with changes to the daily practice of medicine. “We don’t want to be spending our time doing paperwork and calling insurance companies and filling out forms,” said Dr. Hoffman. “We want to be in the exam room with a patient.”
The Allina providers organized after multiple requests to corporate managers failed to address their concerns. Their demands include increased staffing and help with nonclinical work so that clinicians can spend more time with their patients.
“What I’m really excited about is that we will be able to work with the other unionized groups to make change ... by being involved in health care policy at a state or national level,” Dr. Hoffman said. For example, that involvement might include challenging insurance company decisions.
Doctors Council bills itself as the largest union for attending physicians in the country, with 3,500 members, according to Joe Crane, national organizing director.
Despite an increase in union efforts since the pandemic, health care workers – particularly doctors – have been slow to join unions. Mr. Crane estimated that only about 3% of U.S. physicians are currently union members. He cited union campaigns in Massachusetts, New York, and Washington, DC. For comparison, a minority of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) (9%) report union membership, according to Medscape’s APRN compensation report last year.
Dr. Hoffman is confident the Allina health care providers will have enough votes to win the election to join the union. “We should have done this years ago.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Advanced practice providers (APPs) such as nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs) have long been at odds with doctor groups over scope of practice issues. But in a rare alliance, in late September. If successful, the Allina group will join the Doctors Council SEIU, Local 10MD.
The Allina health care providers share concerns about their working conditions, such as understaffing and inadequate resources, limited decision-making authority, and health systems valuing productivity and profit over patient care.
Although doctors and APPs have said that they generally work well together, the relationship has been strained in recent years as APPs argue for greater scope of practice. Meanwhile, physician groups, such as the American Medical Association, believe that APPs need more oversight.
An Allina union organizer, Britta V. Kasmarik, CNP, acknowledges the tension between physicians and APPs. But she said in an interview that the union effort helped bond this group of health care providers. “We share common goals of providing high-quality care for patients in a safe way, and we see the same things day in and day out with our patients.”
Matt Hoffman, MD, a primary care physician at Allina, told this news organization that APPs in his specialty perform the same job as doctors “and the working conditions are really identical. In our view, that means we should be unionizing together.”
The decision to hold a union vote follows similar action by nearly 150 Allina Mercy Hospital physicians in March. Allina Health appealed the vote.
In response to a New York Times investigation, the Minnesota Attorney General’s office began reviewing reports of aggressive billing practices and denied care at Allina Health.
The Allina Health system, which reports $4 billion in annual revenue, cut off nonemergency services to patients, including children, if their medical debt exceeded $4,500, according to the New York Times article. For Allina’s physicians and APPs, that meant leaving patients’ illnesses untreated.
Less than a week after the attorney general announced its investigation, the health system ended this practice.
In a prepared statement to this news organization, Allina Health said that its providers are “critical members of our teams. … We deeply value and share their commitment to providing high-quality care to our patients.”
The health system said it planned to make operational improvements, implement new communication tools, and provide additional well-being resources and enhanced employee benefits “to improve the provider experience.” In addition, it hoped to continue to “foster a culture of collaboration with all our employees.”
Having a union will allow health care providers to advocate for their patients and give health care providers more decision-making power instead of corporate leaders maintaining full authority, Ms. Kasmarik told this news organization.
Union organizers are also concerned with changes to the daily practice of medicine. “We don’t want to be spending our time doing paperwork and calling insurance companies and filling out forms,” said Dr. Hoffman. “We want to be in the exam room with a patient.”
The Allina providers organized after multiple requests to corporate managers failed to address their concerns. Their demands include increased staffing and help with nonclinical work so that clinicians can spend more time with their patients.
“What I’m really excited about is that we will be able to work with the other unionized groups to make change ... by being involved in health care policy at a state or national level,” Dr. Hoffman said. For example, that involvement might include challenging insurance company decisions.
Doctors Council bills itself as the largest union for attending physicians in the country, with 3,500 members, according to Joe Crane, national organizing director.
Despite an increase in union efforts since the pandemic, health care workers – particularly doctors – have been slow to join unions. Mr. Crane estimated that only about 3% of U.S. physicians are currently union members. He cited union campaigns in Massachusetts, New York, and Washington, DC. For comparison, a minority of advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) (9%) report union membership, according to Medscape’s APRN compensation report last year.
Dr. Hoffman is confident the Allina health care providers will have enough votes to win the election to join the union. “We should have done this years ago.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA to step up oversight of cosmetics, assess ‘forever chemicals’
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
They are also preparing to assess potential risks of so-called forever chemicals in these products.
The Food and Drug Administration last year gained new authority over cosmetics when Congress passed the Modernization of Cosmetics Regulation Act of 2022 (MoCRA) by adding this bill to a December budget package.
“On average, consumers in the U.S. use six to 12 cosmetics products daily. But, until recently the FDA didn’t have the authority to require manufacturers to submit cosmetic product listings, including a list of ingredients used in these products, or register the facilities where they were produced,” Namandjé Bumpus, PhD, FDA’s chief scientist, said in a press release.
In the statement, the FDA announced the release of a draft guidance document that is intended to help companies comply with the transparency requirements slated to kick in this December. The agency is accepting comments on this draft guidance through Sept. 7.
“Later this year, registration and listing of cosmetic product facilities and products will become a requirement, making information about cosmetic products, including the ingredients used in products and the facilities where they are produced, readily available to the agency,” Dr. Bumpus said.
The products, according to the FDA statement, include makeup, nail polishes, shaving creams, other grooming products, perfumes, face and body cleansers, hair products, moisturizers, and other skin care items.
MoCRA “represents a sea change in how FDA regulates the cosmetics industry,” attorneys Frederick R. Ball, Alyson Walker Lotman, and Kelly A. Bonner, wrote in an article for the Food and Drug Law Institute published in spring 2023.
The FDA has called the MoCRA law “the most significant expansion” of its authority to regulate cosmetics since the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act was passed in 1938.
The agency is in the process of expanding its staff to carry out newly authorized duties, including the tracking of adverse events. The FDA budget request for fiscal 2024, which begins Oct. 1, seeks $5 million for work needed to implement MoCRA.
PFAS, or ‘forever chemicals’
Some of the requested FDA funding is intended to prepare the agency to assess the use of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetics.
MoCRA sets a 3-year deadline for the FDA to issue an assessment of the use and potential risks of PFAS in cosmetics products. PFAS are sometimes added as ingredients in some cosmetic products, including lotions, cleansers, nail polish, shaving cream, foundation, lipstick, eyeliner, eyeshadow, and mascara, according to the FDA. Sometimes the presence of PFAS in cosmetics is unintentional and is the result of impurities in raw materials or is due to the breakdown of ingredients, the FDA said.
The FDA’s website says that so far, the available research doesn’t allow for “definitive conclusions about the potential health risks of PFAS in cosmetics.”
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has stated that research has suggested potential links between high levels of certain PFAS, in general, with increased cholesterol levels, changes in liver enzyme levels, increased risk of hypertension or preeclampsia in pregnant women, and increased risk of kidney or testicular cancer.
PFAS compounds often are used to resist grease, oil, water, and heat in industrial settings. They are used in thousands of products, from nonstick cookware to firefighting foams and protective gear, because they can reduce friction, according to a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine report on PFAS that was issued last year.
PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they contain a carbon-fluorine bond, which does not break naturally. Even when PFAS are transformed in the body, they can assume other forms of PFAS that preserve the troublesome carbon-fluorine bond. With PFAS, the human body is confronted with a substance it doesn’t have the tools to process.
This is in contrast to proteins and carbohydrates, which are in a sense prepackaged for relatively easy disassembly in the human body. Many of these compounds have weak links that enzymes and stomach acid can take apart, such as sulfur-to-sulfur (disulfide) bonds. That’s why protein-based biotech drugs are injected instead of administered as pills. The ultimate goal of this digestion is for the body to gain energy from these compounds.
But with PFAS, the body faces the challenge of carbon-fluorine bonds that are very hard to break down, and there is no payoff for these efforts, Graham F. Peaslee, PhD, professor of physics at the University of Notre Dame (Indiana), told this news organization.
“Nothing will naturally eat it because when you break the bond, it’s like eating celery,” he said. “You use more calories to eat the celery than you gain back from it.”
Interest from a U.S. senator
Dr. Peaslee was one of the authors of a 2021 article about PFAS in cosmetics that appeared in the journal Environmental Science and Technology Letters.
In the article, Dr. Peaslee and colleagues reported on their screening of 231 cosmetic products purchased in the United States and Canada using particle-induced gamma-ray emission spectroscopy. They found cases of undisclosed PFAS in cosmetic products. Foundations, mascaras, and lip products were noted as being especially problematic.
Sen. Susan Collins (R-ME) cited Dr. Peaslee’s article in a 2021 floor speech as she argued for having the FDA ban the intentional addition of PFAS to cosmetics.
“The findings of this study are particularly alarming, as many of these products are subject to direct human exposure,” Sen. Collins said. “For example, lipstick is often inadvertently ingested, and mascara is sometimes absorbed through tear ducts.”
In addition, workers at cosmetics plants may be exposed to PFAS and discarded cosmetics that have these compounds, which could potentially contaminate drinking water, Sen. Collins said. In 2021, she introduced legislation seeking a ban on PFAS that are intentionally added to cosmetics. That legislation did not advance through the Senate.
But the Senate Appropriations Committee, on which Sen. Collins is the ranking Republican, wants the FDA to keep a ban on PFAS in mind.
The Senate Agriculture Appropriations subcommittee, which oversees the FDA’s budget, raised the issue of PFAS and cosmetics in a June report. The FDA should develop a plan outlining research needed to inform “regulatory decision making, including potential development of a proposed rule to ban intentionally added PFAS substances in cosmetics,” the subcommittee said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.