User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
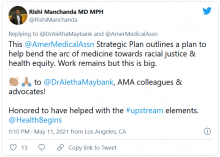
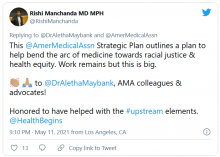
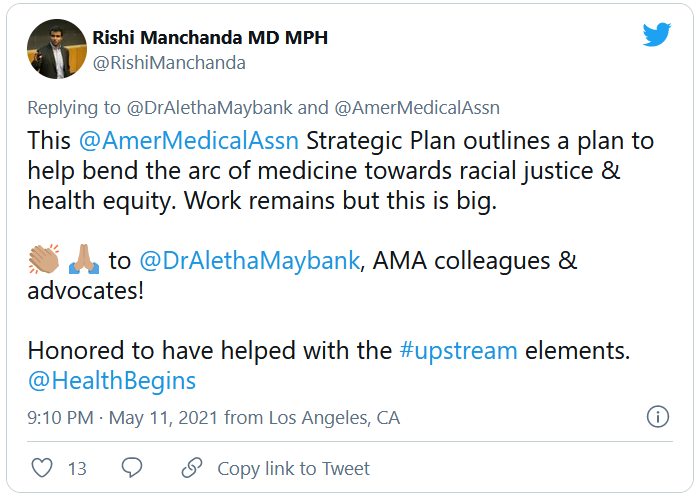
AMA announces major commitment to health equity
The 82-page report, which was created by the association’s Center for Health Equity, argues for both internal changes at the AMA and changes in how the association addresses race-based inequities in general.
The report was released just 2 months after this news organization reported that a podcast hosted by AMA’s top journal was lambasted as racist and out of touch. In the podcast – entitled “Stuctural Racism for Doctors – What Is It?” – one JAMA editor argued that structural racism doesn’t exist. He eventually resigned and the journal’s top editor was placed on administration leave.
The new AMA report’s strategic framework “is driven by the immense need for equity-centered solutions to confront harms produced by systemic racism and other forms of oppression for Black, Latinx, Indigenous, Asian, and other people of color, as well as people who identify as LGBTQ+ and people with disabilities,” the AMA said in a news release. “Its urgency is underscored by ongoing circumstances including inequities exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, ongoing police brutality, and hate crimes targeting Asian, Black, and Brown communities.”
The plan includes five main approaches to addressing inequities in health care and the AMA:
- Implement antiracist equity strategies through AMA practices, programming, policies, and culture.
- Build alliances with marginalized doctors and other stakeholders to elevate the experiences and ideas of historically marginalized and minority health care leaders.
- Strengthen, empower, and equip doctors with the knowledge and tools to dismantle structural and social health inequities.
- Ensure equitable opportunities in innovation.
- Foster truth, racial healing, reconciliation, and transformation for AMA’s past by accounting for how policies and processes excluded, discriminated, and harmed communities.
As the report acknowledges, the AMA has a long history of exclusion of and discrimination against Black physicians, for which the association publicly apologized in 2008. Within the past year, the AMA has reaffirmed its commitment to addressing this legacy and to be proactive on health equity.
Among other things, the association has described racism as a public health crisis, stated that race has nothing to do with biology, said police brutality is a product of structural racism, and called on the federal government to collect and release COVID-19 race/ethnicity data. It also removed the name of AMA founder Nathan Davis, MD, from an annual award and display because of his contribution to explicit racist practices.
Equity-centered solutions
The AMA launched its Center for Health Equity in 2019 with a mandate “to embed health equity across the organization.” Aletha Maybank, MD, was named the AMA’s chief health equity officer to lead the center.
In the report that Dr. Maybank helped write, the AMA discusses the consequences of individual and systemic injustice toward minorities. Among these consequences, the report said, is “segregated and inequitable health care systems.”
The “equity-centered solutions” listed in the report include:
- End segregated health care.
- Establish national health care equity and racial justice standards.
- End the use of race-based clinical decision models.
- Eliminate all forms of discrimination, exclusion and oppression in medical and physician education, training, hiring, and promotion.
- Prevent exclusion of and ensure equal representation of Black, Indigenous and Latinx people in medical school admissions as well as medical school and hospital leadership ranks.
- Ensure equity in innovation, including design, development, implementation along with support for equitable innovation opportunities and entrepreneurship.
- Solidify connections and coordination between health care and public health.
- Acknowledge and repair past harms committed by institutions.
Changing medical education
In an exclusive interview, Gerald E. Harmon, MD, president-elect of the AMA, singled out medical education as an area that is ripe for change. “One of the most threatened phenotypes on the planet is the Black male physician,” he said. “Their numbers among medical school applicants continue to drop. We have increasing numbers of women in medical schools – over 50% of trainees are women – and more Black women are entering medical school, but Black men in medical school are an endangered species.
“We’re trying to get the physician workforce to look like the patient workforce.”
Dr. Harmon cited the “pipeline program” at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta and the AMA’s “doctors back to school” program as examples of efforts to attract minority high school students to health care careers. Much more needs to be done, he added. “We have to put equity and representation into our medical workforce so we can provide better high quality, more reliable care for underrepresented patients.”
Putting the AMA’s house in order
In its report, the AMA also makes recommendations about how it can improve equity within its own organization. Over the next 3 years, among other things, the association plans to improve the diversity of leadership at the AMA and its journal, JAMA; train all staff on equity requirements; and develop a plan to recruit more racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ people, and disabled people.
Dr. Maybank, the AMA’s chief health equity officer, said in an interview that she wouldn’t describe these efforts as affirmative action. “This is beyond affirmative action. It’s about intentional activity and action to ensure equity and justice within the AMA.”
The AMA has to thoroughly examine its own processes and determine “how inequity shows up on a day-to-day basis,” she said. “Whether it’s through hiring, innovation, publishing or communications, everybody needs to know how inequity shows up and how their own mental models can exacerbate inequities. People need tools to challenge themselves and ask themselves critical questions about racism in their processes and what they can do to mitigate those.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The 82-page report, which was created by the association’s Center for Health Equity, argues for both internal changes at the AMA and changes in how the association addresses race-based inequities in general.
The report was released just 2 months after this news organization reported that a podcast hosted by AMA’s top journal was lambasted as racist and out of touch. In the podcast – entitled “Stuctural Racism for Doctors – What Is It?” – one JAMA editor argued that structural racism doesn’t exist. He eventually resigned and the journal’s top editor was placed on administration leave.
The new AMA report’s strategic framework “is driven by the immense need for equity-centered solutions to confront harms produced by systemic racism and other forms of oppression for Black, Latinx, Indigenous, Asian, and other people of color, as well as people who identify as LGBTQ+ and people with disabilities,” the AMA said in a news release. “Its urgency is underscored by ongoing circumstances including inequities exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, ongoing police brutality, and hate crimes targeting Asian, Black, and Brown communities.”
The plan includes five main approaches to addressing inequities in health care and the AMA:
- Implement antiracist equity strategies through AMA practices, programming, policies, and culture.
- Build alliances with marginalized doctors and other stakeholders to elevate the experiences and ideas of historically marginalized and minority health care leaders.
- Strengthen, empower, and equip doctors with the knowledge and tools to dismantle structural and social health inequities.
- Ensure equitable opportunities in innovation.
- Foster truth, racial healing, reconciliation, and transformation for AMA’s past by accounting for how policies and processes excluded, discriminated, and harmed communities.
As the report acknowledges, the AMA has a long history of exclusion of and discrimination against Black physicians, for which the association publicly apologized in 2008. Within the past year, the AMA has reaffirmed its commitment to addressing this legacy and to be proactive on health equity.
Among other things, the association has described racism as a public health crisis, stated that race has nothing to do with biology, said police brutality is a product of structural racism, and called on the federal government to collect and release COVID-19 race/ethnicity data. It also removed the name of AMA founder Nathan Davis, MD, from an annual award and display because of his contribution to explicit racist practices.
Equity-centered solutions
The AMA launched its Center for Health Equity in 2019 with a mandate “to embed health equity across the organization.” Aletha Maybank, MD, was named the AMA’s chief health equity officer to lead the center.
In the report that Dr. Maybank helped write, the AMA discusses the consequences of individual and systemic injustice toward minorities. Among these consequences, the report said, is “segregated and inequitable health care systems.”
The “equity-centered solutions” listed in the report include:
- End segregated health care.
- Establish national health care equity and racial justice standards.
- End the use of race-based clinical decision models.
- Eliminate all forms of discrimination, exclusion and oppression in medical and physician education, training, hiring, and promotion.
- Prevent exclusion of and ensure equal representation of Black, Indigenous and Latinx people in medical school admissions as well as medical school and hospital leadership ranks.
- Ensure equity in innovation, including design, development, implementation along with support for equitable innovation opportunities and entrepreneurship.
- Solidify connections and coordination between health care and public health.
- Acknowledge and repair past harms committed by institutions.
Changing medical education
In an exclusive interview, Gerald E. Harmon, MD, president-elect of the AMA, singled out medical education as an area that is ripe for change. “One of the most threatened phenotypes on the planet is the Black male physician,” he said. “Their numbers among medical school applicants continue to drop. We have increasing numbers of women in medical schools – over 50% of trainees are women – and more Black women are entering medical school, but Black men in medical school are an endangered species.
“We’re trying to get the physician workforce to look like the patient workforce.”
Dr. Harmon cited the “pipeline program” at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta and the AMA’s “doctors back to school” program as examples of efforts to attract minority high school students to health care careers. Much more needs to be done, he added. “We have to put equity and representation into our medical workforce so we can provide better high quality, more reliable care for underrepresented patients.”
Putting the AMA’s house in order
In its report, the AMA also makes recommendations about how it can improve equity within its own organization. Over the next 3 years, among other things, the association plans to improve the diversity of leadership at the AMA and its journal, JAMA; train all staff on equity requirements; and develop a plan to recruit more racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ people, and disabled people.
Dr. Maybank, the AMA’s chief health equity officer, said in an interview that she wouldn’t describe these efforts as affirmative action. “This is beyond affirmative action. It’s about intentional activity and action to ensure equity and justice within the AMA.”
The AMA has to thoroughly examine its own processes and determine “how inequity shows up on a day-to-day basis,” she said. “Whether it’s through hiring, innovation, publishing or communications, everybody needs to know how inequity shows up and how their own mental models can exacerbate inequities. People need tools to challenge themselves and ask themselves critical questions about racism in their processes and what they can do to mitigate those.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The 82-page report, which was created by the association’s Center for Health Equity, argues for both internal changes at the AMA and changes in how the association addresses race-based inequities in general.
The report was released just 2 months after this news organization reported that a podcast hosted by AMA’s top journal was lambasted as racist and out of touch. In the podcast – entitled “Stuctural Racism for Doctors – What Is It?” – one JAMA editor argued that structural racism doesn’t exist. He eventually resigned and the journal’s top editor was placed on administration leave.
The new AMA report’s strategic framework “is driven by the immense need for equity-centered solutions to confront harms produced by systemic racism and other forms of oppression for Black, Latinx, Indigenous, Asian, and other people of color, as well as people who identify as LGBTQ+ and people with disabilities,” the AMA said in a news release. “Its urgency is underscored by ongoing circumstances including inequities exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, ongoing police brutality, and hate crimes targeting Asian, Black, and Brown communities.”
The plan includes five main approaches to addressing inequities in health care and the AMA:
- Implement antiracist equity strategies through AMA practices, programming, policies, and culture.
- Build alliances with marginalized doctors and other stakeholders to elevate the experiences and ideas of historically marginalized and minority health care leaders.
- Strengthen, empower, and equip doctors with the knowledge and tools to dismantle structural and social health inequities.
- Ensure equitable opportunities in innovation.
- Foster truth, racial healing, reconciliation, and transformation for AMA’s past by accounting for how policies and processes excluded, discriminated, and harmed communities.
As the report acknowledges, the AMA has a long history of exclusion of and discrimination against Black physicians, for which the association publicly apologized in 2008. Within the past year, the AMA has reaffirmed its commitment to addressing this legacy and to be proactive on health equity.
Among other things, the association has described racism as a public health crisis, stated that race has nothing to do with biology, said police brutality is a product of structural racism, and called on the federal government to collect and release COVID-19 race/ethnicity data. It also removed the name of AMA founder Nathan Davis, MD, from an annual award and display because of his contribution to explicit racist practices.
Equity-centered solutions
The AMA launched its Center for Health Equity in 2019 with a mandate “to embed health equity across the organization.” Aletha Maybank, MD, was named the AMA’s chief health equity officer to lead the center.
In the report that Dr. Maybank helped write, the AMA discusses the consequences of individual and systemic injustice toward minorities. Among these consequences, the report said, is “segregated and inequitable health care systems.”
The “equity-centered solutions” listed in the report include:
- End segregated health care.
- Establish national health care equity and racial justice standards.
- End the use of race-based clinical decision models.
- Eliminate all forms of discrimination, exclusion and oppression in medical and physician education, training, hiring, and promotion.
- Prevent exclusion of and ensure equal representation of Black, Indigenous and Latinx people in medical school admissions as well as medical school and hospital leadership ranks.
- Ensure equity in innovation, including design, development, implementation along with support for equitable innovation opportunities and entrepreneurship.
- Solidify connections and coordination between health care and public health.
- Acknowledge and repair past harms committed by institutions.
Changing medical education
In an exclusive interview, Gerald E. Harmon, MD, president-elect of the AMA, singled out medical education as an area that is ripe for change. “One of the most threatened phenotypes on the planet is the Black male physician,” he said. “Their numbers among medical school applicants continue to drop. We have increasing numbers of women in medical schools – over 50% of trainees are women – and more Black women are entering medical school, but Black men in medical school are an endangered species.
“We’re trying to get the physician workforce to look like the patient workforce.”
Dr. Harmon cited the “pipeline program” at the Morehouse School of Medicine in Atlanta and the AMA’s “doctors back to school” program as examples of efforts to attract minority high school students to health care careers. Much more needs to be done, he added. “We have to put equity and representation into our medical workforce so we can provide better high quality, more reliable care for underrepresented patients.”
Putting the AMA’s house in order
In its report, the AMA also makes recommendations about how it can improve equity within its own organization. Over the next 3 years, among other things, the association plans to improve the diversity of leadership at the AMA and its journal, JAMA; train all staff on equity requirements; and develop a plan to recruit more racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ people, and disabled people.
Dr. Maybank, the AMA’s chief health equity officer, said in an interview that she wouldn’t describe these efforts as affirmative action. “This is beyond affirmative action. It’s about intentional activity and action to ensure equity and justice within the AMA.”
The AMA has to thoroughly examine its own processes and determine “how inequity shows up on a day-to-day basis,” she said. “Whether it’s through hiring, innovation, publishing or communications, everybody needs to know how inequity shows up and how their own mental models can exacerbate inequities. People need tools to challenge themselves and ask themselves critical questions about racism in their processes and what they can do to mitigate those.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Photoprotection recommended for people of color
and applying a tinted sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater to exposed areas, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
In addition, “with rigorous photoprotection, vitamin D supplementation should be advised to patients,” Dr. Lim, a former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “One multivitamin a day should be sufficient for most patients. This is especially relevant because we do know that skin of color patients tend to have lower vitamin D levels to start with.”
Photoprotection for people of color helps minimize the development of photodermatoses, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, polymorphous light eruption, and chronic actinic dermatitis, he said. In a retrospective chart review of 1,080 people conducted at four academic medical centers in the United States, Dr. Lim and colleagues found a higher proportion of polymorphous light eruption and chronic actinic dermatitis in Black individuals, and a higher proportion of photoallergic contact dermatitis, phototoxic drug eruptions, phytophotodermatitis, porphyria, and solar urticaria in White individuals.
“Another pediatric photodermatosis, actinic prurigo, tends to occur most often in Mestizo individuals, patients of American Indian heritage,” he added. “This is a significant issue, especially in Latin America.”
In a systematic review of 20 studies in the medical literature, researchers assessed the quality of life and psychological impact of photodermatoses in affected patients. Studies included in the review drew from 2,487 adults and 119 children. Among adults, the self-administered Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) revealed that photodermatoses adversely affected employment, education, and leisure activities in adults. Among children, the condition adversely affected outdoor activities and exacerbated symptoms in those with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP).
As for skin cancer risk, the association between UV light exposure and the development of melanoma is not as strong in people with skin of color, compared with light-skinned individuals. In a recent systematic review of 13 studies on the topic, 11 showed no association, one showed a small positive relationship in Black males and 1 showed a weak association in Hispanic males.
“The conclusion from this review is that UV protection for melanoma prevention in people of color is not supported by most studies,” said Dr. Lim, who was not affiliated with the review. “The authors also noted, however, that the evidence is of moderate to low quality. Larger studies should be done.”
The association between UV exposure and the development to squamous cell cancer in skin of color is also not strong. “However, we do know that sun exposure is associated with the development of basal cell carcinoma in this population,” he said.
Sunscreen ingredient studies
Dr. Lim also highlighted findings from two studies related to the effect of sunscreen application on plasma concentration of sunscreen active ingredients, both in adults. In the most recent analysis, scientists at the Food and Drug Administration and colleagues conducted a randomized clinical trial in 48 individuals with skin types II-IV.
Participants applied sunscreen at 2 mg/cm2 to 75% of body surface area at 0 hours on day 1 and 4 times on day 2 through day 4 at 2-hour intervals. Over the course of 21 days, the researchers collected 34 blood samples from each participant, and evaluated six active ingredients in four sunscreen products: avobenzone, oxybenzone, octocrylene, homosalate, octisalate, and octinoxate.
For all active ingredients, levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected after a single application on day 1. Levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected up to day 7, and up to day 21 for oxybenzone. All were detected in skin on days 7 and 14 via tape stripping. The authors called for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings and emphasized that the results “do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.”
The FDA is asking for additional studies on the safety of these 12 filters, noted Dr. Lim, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. On Feb. 26, 2019, the FDA issued a proposed rule regarding sunscreen drug products for over-the-counter human use. It proposes that the 16 UV filters be classified into one of 3 categories. Category I would include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective (GRASE). Category II would include PABA and trolamine salicylate, which are not used in the United States and are not GRASE. Category III would include 12 filters that lack insufficient safety data to make a determination regarding GRASE.
The final FDA rule was scheduled to be released in September of 2020, but a result of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the FDA “will be moving from a laborious rulemaking process to an administrative order process, which means it should not take as long to implement a monograph,” Dr. Lim said. “The FDA has decided that there will not be a final rule regarding sunscreen drug products,” but is required to issue a proposed administrative order by Sept. 27, 2021, he said.
When the final administrative order has been issued, manufacturers would have at least 1 year to comply with sunscreen products offered in the United States. “The approximate timeline is probably going to be 2023,” he said.
Dr. Lim disclosed that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oreal, Pfizer, and the Patient-centered Outcomes Research Institute, and a consultant for Pierre Fabre, ISDIN, Ferndale, La Roche–Posay, and Beiersdorf. He has been a speaker at general educational sessions sponsored by La Roche–Posay and Cantabria Labs.
and applying a tinted sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater to exposed areas, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
In addition, “with rigorous photoprotection, vitamin D supplementation should be advised to patients,” Dr. Lim, a former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “One multivitamin a day should be sufficient for most patients. This is especially relevant because we do know that skin of color patients tend to have lower vitamin D levels to start with.”
Photoprotection for people of color helps minimize the development of photodermatoses, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, polymorphous light eruption, and chronic actinic dermatitis, he said. In a retrospective chart review of 1,080 people conducted at four academic medical centers in the United States, Dr. Lim and colleagues found a higher proportion of polymorphous light eruption and chronic actinic dermatitis in Black individuals, and a higher proportion of photoallergic contact dermatitis, phototoxic drug eruptions, phytophotodermatitis, porphyria, and solar urticaria in White individuals.
“Another pediatric photodermatosis, actinic prurigo, tends to occur most often in Mestizo individuals, patients of American Indian heritage,” he added. “This is a significant issue, especially in Latin America.”
In a systematic review of 20 studies in the medical literature, researchers assessed the quality of life and psychological impact of photodermatoses in affected patients. Studies included in the review drew from 2,487 adults and 119 children. Among adults, the self-administered Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) revealed that photodermatoses adversely affected employment, education, and leisure activities in adults. Among children, the condition adversely affected outdoor activities and exacerbated symptoms in those with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP).
As for skin cancer risk, the association between UV light exposure and the development of melanoma is not as strong in people with skin of color, compared with light-skinned individuals. In a recent systematic review of 13 studies on the topic, 11 showed no association, one showed a small positive relationship in Black males and 1 showed a weak association in Hispanic males.
“The conclusion from this review is that UV protection for melanoma prevention in people of color is not supported by most studies,” said Dr. Lim, who was not affiliated with the review. “The authors also noted, however, that the evidence is of moderate to low quality. Larger studies should be done.”
The association between UV exposure and the development to squamous cell cancer in skin of color is also not strong. “However, we do know that sun exposure is associated with the development of basal cell carcinoma in this population,” he said.
Sunscreen ingredient studies
Dr. Lim also highlighted findings from two studies related to the effect of sunscreen application on plasma concentration of sunscreen active ingredients, both in adults. In the most recent analysis, scientists at the Food and Drug Administration and colleagues conducted a randomized clinical trial in 48 individuals with skin types II-IV.
Participants applied sunscreen at 2 mg/cm2 to 75% of body surface area at 0 hours on day 1 and 4 times on day 2 through day 4 at 2-hour intervals. Over the course of 21 days, the researchers collected 34 blood samples from each participant, and evaluated six active ingredients in four sunscreen products: avobenzone, oxybenzone, octocrylene, homosalate, octisalate, and octinoxate.
For all active ingredients, levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected after a single application on day 1. Levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected up to day 7, and up to day 21 for oxybenzone. All were detected in skin on days 7 and 14 via tape stripping. The authors called for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings and emphasized that the results “do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.”
The FDA is asking for additional studies on the safety of these 12 filters, noted Dr. Lim, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. On Feb. 26, 2019, the FDA issued a proposed rule regarding sunscreen drug products for over-the-counter human use. It proposes that the 16 UV filters be classified into one of 3 categories. Category I would include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective (GRASE). Category II would include PABA and trolamine salicylate, which are not used in the United States and are not GRASE. Category III would include 12 filters that lack insufficient safety data to make a determination regarding GRASE.
The final FDA rule was scheduled to be released in September of 2020, but a result of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the FDA “will be moving from a laborious rulemaking process to an administrative order process, which means it should not take as long to implement a monograph,” Dr. Lim said. “The FDA has decided that there will not be a final rule regarding sunscreen drug products,” but is required to issue a proposed administrative order by Sept. 27, 2021, he said.
When the final administrative order has been issued, manufacturers would have at least 1 year to comply with sunscreen products offered in the United States. “The approximate timeline is probably going to be 2023,” he said.
Dr. Lim disclosed that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oreal, Pfizer, and the Patient-centered Outcomes Research Institute, and a consultant for Pierre Fabre, ISDIN, Ferndale, La Roche–Posay, and Beiersdorf. He has been a speaker at general educational sessions sponsored by La Roche–Posay and Cantabria Labs.
and applying a tinted sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or greater to exposed areas, according to Henry W. Lim, MD.
In addition, “with rigorous photoprotection, vitamin D supplementation should be advised to patients,” Dr. Lim, a former chair of the department of dermatology at Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “One multivitamin a day should be sufficient for most patients. This is especially relevant because we do know that skin of color patients tend to have lower vitamin D levels to start with.”
Photoprotection for people of color helps minimize the development of photodermatoses, postinflammatory hyperpigmentation, polymorphous light eruption, and chronic actinic dermatitis, he said. In a retrospective chart review of 1,080 people conducted at four academic medical centers in the United States, Dr. Lim and colleagues found a higher proportion of polymorphous light eruption and chronic actinic dermatitis in Black individuals, and a higher proportion of photoallergic contact dermatitis, phototoxic drug eruptions, phytophotodermatitis, porphyria, and solar urticaria in White individuals.
“Another pediatric photodermatosis, actinic prurigo, tends to occur most often in Mestizo individuals, patients of American Indian heritage,” he added. “This is a significant issue, especially in Latin America.”
In a systematic review of 20 studies in the medical literature, researchers assessed the quality of life and psychological impact of photodermatoses in affected patients. Studies included in the review drew from 2,487 adults and 119 children. Among adults, the self-administered Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) revealed that photodermatoses adversely affected employment, education, and leisure activities in adults. Among children, the condition adversely affected outdoor activities and exacerbated symptoms in those with erythropoietic protoporphyria (EPP).
As for skin cancer risk, the association between UV light exposure and the development of melanoma is not as strong in people with skin of color, compared with light-skinned individuals. In a recent systematic review of 13 studies on the topic, 11 showed no association, one showed a small positive relationship in Black males and 1 showed a weak association in Hispanic males.
“The conclusion from this review is that UV protection for melanoma prevention in people of color is not supported by most studies,” said Dr. Lim, who was not affiliated with the review. “The authors also noted, however, that the evidence is of moderate to low quality. Larger studies should be done.”
The association between UV exposure and the development to squamous cell cancer in skin of color is also not strong. “However, we do know that sun exposure is associated with the development of basal cell carcinoma in this population,” he said.
Sunscreen ingredient studies
Dr. Lim also highlighted findings from two studies related to the effect of sunscreen application on plasma concentration of sunscreen active ingredients, both in adults. In the most recent analysis, scientists at the Food and Drug Administration and colleagues conducted a randomized clinical trial in 48 individuals with skin types II-IV.
Participants applied sunscreen at 2 mg/cm2 to 75% of body surface area at 0 hours on day 1 and 4 times on day 2 through day 4 at 2-hour intervals. Over the course of 21 days, the researchers collected 34 blood samples from each participant, and evaluated six active ingredients in four sunscreen products: avobenzone, oxybenzone, octocrylene, homosalate, octisalate, and octinoxate.
For all active ingredients, levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected after a single application on day 1. Levels of greater than 0.5 ng/mL were detected up to day 7, and up to day 21 for oxybenzone. All were detected in skin on days 7 and 14 via tape stripping. The authors called for further studies to determine the clinical significance of these findings and emphasized that the results “do not indicate that individuals should refrain from the use of sunscreen.”
The FDA is asking for additional studies on the safety of these 12 filters, noted Dr. Lim, who is a past president of the American Academy of Dermatology. On Feb. 26, 2019, the FDA issued a proposed rule regarding sunscreen drug products for over-the-counter human use. It proposes that the 16 UV filters be classified into one of 3 categories. Category I would include zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which are generally recognized as safe and effective (GRASE). Category II would include PABA and trolamine salicylate, which are not used in the United States and are not GRASE. Category III would include 12 filters that lack insufficient safety data to make a determination regarding GRASE.
The final FDA rule was scheduled to be released in September of 2020, but a result of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, the FDA “will be moving from a laborious rulemaking process to an administrative order process, which means it should not take as long to implement a monograph,” Dr. Lim said. “The FDA has decided that there will not be a final rule regarding sunscreen drug products,” but is required to issue a proposed administrative order by Sept. 27, 2021, he said.
When the final administrative order has been issued, manufacturers would have at least 1 year to comply with sunscreen products offered in the United States. “The approximate timeline is probably going to be 2023,” he said.
Dr. Lim disclosed that he is an investigator for Incyte, L’Oreal, Pfizer, and the Patient-centered Outcomes Research Institute, and a consultant for Pierre Fabre, ISDIN, Ferndale, La Roche–Posay, and Beiersdorf. He has been a speaker at general educational sessions sponsored by La Roche–Posay and Cantabria Labs.
FROM THE SPD PRE-AAD MEETING
The case for molecular classification of vascular anomalies presented
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
according to Beth Drolet, MD.
“We now know that 75%-80% of vascular malformations have gene mutations that make the cells either live longer, grow faster, or make them bigger in size,” Dr. Drolet, professor and chair of dermatology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, said during the Society for Pediatric Dermatology pre-AAD meeting. “The basic binary premise of the current ISSVA [International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies] classification dividing vascular anomalies into tumors and malformations is wrong; the biology is not that straightforward. It may be helpful to differentiate between an infantile hemangioma and a capillary malformation during infancy as the hemangioma will grow in the next month, but we now know that patients with capillary malformations also have significant overgrowth of their tissue. We’ve all seen that; it just takes years, not months for us to notice it.”
The change in thinking about the root causes of vascular anomalies, she noted, stems from scientific advances in the understanding of embryonic mosaicism, DNA variation that happens after the zygote is formed, but before birth. “We know that each cell in a zygote will undergo 40 cell divisions before a baby is born,” she said. “Those cell divisions are not as neat as we thought they were. That cell and DNA duplication is actually quite messy, so there are mutations that happen purely because of embryonic cell division.”
Everyone is born with 120 somatic mutations per cell, she continued, “so we have multiple genomes in one human. Not all of those mutations are going to cause disease. Not all of those are going to be functional. About 10% of those mutations will actually be in a coding region of the gene and have the potential to change the function of the protein. If it changes the function of the protein so that the cell can’t survive, that cell dies off, but it gives the cell an advantage. It grows a little bit faster, let’s say. That cell survives, divides, producing a line of cells that can cause disease.”
In 2011, Dr. Drolet and colleagues from the Hemangioma Investigator Group and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance (PeDRA) launched a multisite collaborative group to investigate the role of mosaic genetics in patients with vascular anomalies and discrepancy of growth. To date, 365 patients are enrolled, and the researchers have sequenced 97 of 165 affected tissue samples collected. “What’s nice about the registry is that we enrolled a wide spectrum of diseases: very mild diseases that might be treated by dermatologists to complex, syndromic diseases that might end up in an interdisciplinary vascular anomalies clinic,” she said.
For gene sequencing, the researchers drew from solid tumor biology and used next-generation sequencing with semi-target hybrid capture, “so we’re only looking at a subset of genes,” she said. “Right now, the chip we’re using has 180 cancer-related genes. It sequences the entire exome of the gene with a high depth of coverage, usually over 1,000 X. We use a specific pipeline that can detect very low allele frequency mutation: down to 1%, and robust criteria to determine variant pathogenicity.”
In 75% of tissue samples so far, the researchers have found a gene mutation in one of 13 genes: AKT1, AKT3, BRAF, GNA11, GNAQ, KRAS, MAP2K1, NRAS, PIK3CA, PIK3R1, PTPN11, RASA1, and TEK. According to Dr. Drolet, the common thread in these 13 genes is that they are implicated in cancer and have direct control over the cell cycle. “They’re intracellular proteins that control the cell cycle,” she explained. “These are proteins that are in the cell but interact with transmembrane proteins that receive extracellular messengers of cell growth”.
Understanding and recognizing genetic conditions is complicated, she said, because it involves determining which gene is altered, where in the DNA the gene is altered, how the gene variation will influence the function of the protein, and what tissue expresses that gene. “Then you get your phenotype,” Dr. Drolet said. “If you add mosaicism onto that, you have several additional variables. You need to know: When in embryogenesis did the mutation occur? What region of the body is affected? What cell lineage is affected? That predicts what phenotype you’re going to have.”
While molecular classification efforts continue to be refined, Dr. Drolet incorporates genotyping at every opportunity, like when she counsels parents of a baby born with a vascular stain on its face. “What can we tell them about what else might be wrong? What can we tell them about how this will change over time? What can we tell them about how we can treat it? I think genotyping absolutely helps to clarify that for me,” she said. “I can’t use that alone, but it gives me another piece of evidence to help do a better job in predicting when I need to screen, what I need to screen for, and what might happen in the future. If you combine your genotype with your clinical exam, I really do believe we can start to offer some prognostication for our families, to say, ‘this is the degree of overgrowth we may see over time; these are the complications I predict that you might have.’ ”
Even the vascular stain can give you a clue. “If it’s light and lacey, you probably don’t have a lot of cell cycle activation,” Dr. Drolet said. “If it’s dark and there’s blebs and you’ve got some bleeding at a young age, you’ve got a highly activated mutation, and there’s everything in between.”
Dr. Drolet disclosed that she is a consultant for Venthera and Novartis and is a board member for the Isthmus Project. She also holds intellectual property rights in and is a patent holder for Peds Derm Development Group. Dr. Drolet has also received funding from the Spirit Foundation, Kayleigh’s Crew Endowment, the SPD, PeDRA, and the National Institutes of Health.
FROM THE SPD PRE-AAD MEETING
CDC recommends use of Pfizer’s COVID vaccine in 12- to 15-year-olds
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s director Rochelle Walensky, MD, signed off on an advisory panel’s recommendation May 12 endorsing the use of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents aged 12-15 years.
Earlier in the day the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices voted 14-0 in favor of the safety and effectiveness of the vaccine in younger teens.
Dr. Walensky said in an official statement.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 issued an emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19 in individuals 12-15 years old. The FDA first cleared the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine through an EUA in December 2020 for those ages 16 and older. Pfizer this month also initiated steps with the FDA toward a full approval of its vaccine.
Dr. Walenksy urged parents to seriously consider vaccinating their children.
“Understandably, some parents want more information before their children receive a vaccine,” she said. “I encourage parents with questions to talk to your child’s healthcare provider or your family doctor to learn more about the vaccine.”
Vaccine “safe and effective”
Separately, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued a statement May 12 in support of vaccinating all children ages 12 and older who are eligible for the federally authorized COVID-19 vaccine.
“As a pediatrician and a parent, I have looked forward to getting my own children and patients vaccinated, and I am thrilled that those ages 12 and older can now be protected,” said AAP President Lee Savio Beers, MD, in a statement. “The data continue to show that this vaccine is safe and effective. I urge all parents to call their pediatrician to learn more about how to get their children and teens vaccinated.”
The expanded clearance for the Pfizer vaccine is seen as a critical step for allowing teens to resume activities on which they missed out during the pandemic.
“We’ve seen the harm done to children’s mental and emotional health as they’ve missed out on so many experiences during the pandemic,” Dr. Beers said. “Vaccinating children will protect them and allow them to fully engage in all of the activities – school, sports, socializing with friends and family – that are so important to their health and development.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Reassuring data on impact of mild COVID-19 on the heart
Six months after mild SARS-CoV-2 infection in a representative health care workforce, no long-term cardiovascular sequelae were detected, compared with a matched SARS-CoV-2 seronegative group.
“Mild COVID-19 left no measurable cardiovascular impact on LV structure, function, scar burden, aortic stiffness, or serum biomarkers,” the researchers reported in an article published online May 8 in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“We provide societal reassurance and support for the position that screening in asymptomatic individuals following mild disease is not indicated,” first author George Joy, MBBS, University College London, said in presenting the results at EuroCMR, the annual CMR congress of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI).
Briefing comoderator Leyla Elif Sade, MD, University of Baskent, Ankara, Turkey, said, “This is the hot topic of our time because of obvious reasons and I think [this] study is quite important to avoid unnecessary further testing, surveillance testing, and to avoid a significant burden of health care costs.”
‘Alarming’ early data
Early cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) studies in patients recovered from mild COVID-19 were “alarming,” Dr. Joy said.
As previously reported, one study showed cardiac abnormalities after mild COVID-19 in up to 78% of patients, with evidence of ongoing myocardial inflammation in 60%. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
To investigate further, Dr. Joy and colleagues did a nested case-control study within the COVIDsortium, a prospective study of 731 health care workers from three London hospitals who underwent weekly symptom, polymerase chain reaction, and serology assessment over 4 months during the first wave of the pandemic.
A total of 157 (21.5%) participants seroconverted during the study period.
Six months after infection, 74 seropositive (median age, 39; 62% women) and 75 age-, sex-, and ethnicity-matched seronegative controls underwent cardiovascular phenotyping (comprehensive phantom-calibrated CMR and blood biomarkers). The analysis was blinded, using objective artificial intelligence analytics when available.
The results showed no statistically significant differences between seropositive and seronegative participants in cardiac structure (left ventricular volumes, mass, atrial area), function (ejection fraction, global longitudinal shortening, aortic distensibility), tissue characterization (T1, T2, extracellular volume fraction mapping, late gadolinium enhancement) or biomarkers (troponin, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide).
Cardiovascular abnormalities were no more common in seropositive than seronegative otherwise healthy health care workers 6 months post mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. Measured abnormalities were “evenly distributed between both groups,” Dr. Joy said.
Therefore, it’s “important to reassure patients with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection regarding its cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Joy and colleagues concluded.
Limitations and caveats
They caution, however, that the study provides insight only into the short- to medium-term sequelae of patients aged 18-69 with mild COVID-19 who did not require hospitalization and had low numbers of comorbidities.
The study does not address the cardiovascular effects after severe COVID-19 infection requiring hospitalization or in those with multiple comorbid conditions, they noted. It also does not prove that apparently mild SARS-CoV-2 never causes chronic myocarditis.
“The study design would not distinguish between people who had sustained completely healed myocarditis and pericarditis and those in whom the heart had never been affected,” the researchers noted.
They pointed to a recent cross-sectional study of athletes 1-month post mild COVID-19 that found significant pericardial involvement (late enhancement and/or pericardial effusion), although no baseline pre-COVID-19 imaging was performed. In the current study at 6 months post infection the pericardium was normal.
The coauthors of a linked editorial say this study provides “welcome, reassuring information that in healthy individuals who experience mild infection with COVID-19, persisting evidence of cardiovascular complications is very uncommon. The results do not support cardiovascular screening in individuals with mild or asymptomatic infection with COVID-19.”
Colin Berry, PhD, and Kenneth Mangion, PhD, both from University of Glasgow, cautioned that the population is restricted to health care workers; therefore, the findings may not necessarily be generalized to a community population .
“Healthcare workers do not reflect the population of individuals most clinically affected by COVID-19 illness. The severity of acute COVID-19 infection is greatest in older individuals and those with preexisting health problems. Healthcare workers are not representative of the wider, unselected, at-risk, community population,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular risk factors and concomitant health problems (heart and respiratory disease) may be more common in the community than in health care workers, and prior studies have highlighted their potential impact for disease pathogenesis in COVID-19.
Dr. Berry and Dr. Mangion also noted that women made up nearly two-thirds of the seropositive group. This may reflect a selection bias or may naturally reflect the fact that proportionately more women are asymptomatic or have milder forms of illness, whereas severe SARS-CoV-2 infection requiring hospitalization affects men to a greater degree.
COVIDsortium funding was donated by individuals, charitable trusts, and corporations including Goldman Sachs, Citadel and Citadel Securities, The Guy Foundation, GW Pharmaceuticals, Kusuma Trust, and Jagclif Charitable Trust, and enabled by Barts Charity with support from UCLH Charity. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six months after mild SARS-CoV-2 infection in a representative health care workforce, no long-term cardiovascular sequelae were detected, compared with a matched SARS-CoV-2 seronegative group.
“Mild COVID-19 left no measurable cardiovascular impact on LV structure, function, scar burden, aortic stiffness, or serum biomarkers,” the researchers reported in an article published online May 8 in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“We provide societal reassurance and support for the position that screening in asymptomatic individuals following mild disease is not indicated,” first author George Joy, MBBS, University College London, said in presenting the results at EuroCMR, the annual CMR congress of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI).
Briefing comoderator Leyla Elif Sade, MD, University of Baskent, Ankara, Turkey, said, “This is the hot topic of our time because of obvious reasons and I think [this] study is quite important to avoid unnecessary further testing, surveillance testing, and to avoid a significant burden of health care costs.”
‘Alarming’ early data
Early cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) studies in patients recovered from mild COVID-19 were “alarming,” Dr. Joy said.
As previously reported, one study showed cardiac abnormalities after mild COVID-19 in up to 78% of patients, with evidence of ongoing myocardial inflammation in 60%. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
To investigate further, Dr. Joy and colleagues did a nested case-control study within the COVIDsortium, a prospective study of 731 health care workers from three London hospitals who underwent weekly symptom, polymerase chain reaction, and serology assessment over 4 months during the first wave of the pandemic.
A total of 157 (21.5%) participants seroconverted during the study period.
Six months after infection, 74 seropositive (median age, 39; 62% women) and 75 age-, sex-, and ethnicity-matched seronegative controls underwent cardiovascular phenotyping (comprehensive phantom-calibrated CMR and blood biomarkers). The analysis was blinded, using objective artificial intelligence analytics when available.
The results showed no statistically significant differences between seropositive and seronegative participants in cardiac structure (left ventricular volumes, mass, atrial area), function (ejection fraction, global longitudinal shortening, aortic distensibility), tissue characterization (T1, T2, extracellular volume fraction mapping, late gadolinium enhancement) or biomarkers (troponin, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide).
Cardiovascular abnormalities were no more common in seropositive than seronegative otherwise healthy health care workers 6 months post mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. Measured abnormalities were “evenly distributed between both groups,” Dr. Joy said.
Therefore, it’s “important to reassure patients with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection regarding its cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Joy and colleagues concluded.
Limitations and caveats
They caution, however, that the study provides insight only into the short- to medium-term sequelae of patients aged 18-69 with mild COVID-19 who did not require hospitalization and had low numbers of comorbidities.
The study does not address the cardiovascular effects after severe COVID-19 infection requiring hospitalization or in those with multiple comorbid conditions, they noted. It also does not prove that apparently mild SARS-CoV-2 never causes chronic myocarditis.
“The study design would not distinguish between people who had sustained completely healed myocarditis and pericarditis and those in whom the heart had never been affected,” the researchers noted.
They pointed to a recent cross-sectional study of athletes 1-month post mild COVID-19 that found significant pericardial involvement (late enhancement and/or pericardial effusion), although no baseline pre-COVID-19 imaging was performed. In the current study at 6 months post infection the pericardium was normal.
The coauthors of a linked editorial say this study provides “welcome, reassuring information that in healthy individuals who experience mild infection with COVID-19, persisting evidence of cardiovascular complications is very uncommon. The results do not support cardiovascular screening in individuals with mild or asymptomatic infection with COVID-19.”
Colin Berry, PhD, and Kenneth Mangion, PhD, both from University of Glasgow, cautioned that the population is restricted to health care workers; therefore, the findings may not necessarily be generalized to a community population .
“Healthcare workers do not reflect the population of individuals most clinically affected by COVID-19 illness. The severity of acute COVID-19 infection is greatest in older individuals and those with preexisting health problems. Healthcare workers are not representative of the wider, unselected, at-risk, community population,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular risk factors and concomitant health problems (heart and respiratory disease) may be more common in the community than in health care workers, and prior studies have highlighted their potential impact for disease pathogenesis in COVID-19.
Dr. Berry and Dr. Mangion also noted that women made up nearly two-thirds of the seropositive group. This may reflect a selection bias or may naturally reflect the fact that proportionately more women are asymptomatic or have milder forms of illness, whereas severe SARS-CoV-2 infection requiring hospitalization affects men to a greater degree.
COVIDsortium funding was donated by individuals, charitable trusts, and corporations including Goldman Sachs, Citadel and Citadel Securities, The Guy Foundation, GW Pharmaceuticals, Kusuma Trust, and Jagclif Charitable Trust, and enabled by Barts Charity with support from UCLH Charity. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six months after mild SARS-CoV-2 infection in a representative health care workforce, no long-term cardiovascular sequelae were detected, compared with a matched SARS-CoV-2 seronegative group.
“Mild COVID-19 left no measurable cardiovascular impact on LV structure, function, scar burden, aortic stiffness, or serum biomarkers,” the researchers reported in an article published online May 8 in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
“We provide societal reassurance and support for the position that screening in asymptomatic individuals following mild disease is not indicated,” first author George Joy, MBBS, University College London, said in presenting the results at EuroCMR, the annual CMR congress of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI).
Briefing comoderator Leyla Elif Sade, MD, University of Baskent, Ankara, Turkey, said, “This is the hot topic of our time because of obvious reasons and I think [this] study is quite important to avoid unnecessary further testing, surveillance testing, and to avoid a significant burden of health care costs.”
‘Alarming’ early data
Early cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) studies in patients recovered from mild COVID-19 were “alarming,” Dr. Joy said.
As previously reported, one study showed cardiac abnormalities after mild COVID-19 in up to 78% of patients, with evidence of ongoing myocardial inflammation in 60%. The CMR findings correlated with elevations in troponin T by high-sensitivity assay (hs-TnT).
To investigate further, Dr. Joy and colleagues did a nested case-control study within the COVIDsortium, a prospective study of 731 health care workers from three London hospitals who underwent weekly symptom, polymerase chain reaction, and serology assessment over 4 months during the first wave of the pandemic.
A total of 157 (21.5%) participants seroconverted during the study period.
Six months after infection, 74 seropositive (median age, 39; 62% women) and 75 age-, sex-, and ethnicity-matched seronegative controls underwent cardiovascular phenotyping (comprehensive phantom-calibrated CMR and blood biomarkers). The analysis was blinded, using objective artificial intelligence analytics when available.
The results showed no statistically significant differences between seropositive and seronegative participants in cardiac structure (left ventricular volumes, mass, atrial area), function (ejection fraction, global longitudinal shortening, aortic distensibility), tissue characterization (T1, T2, extracellular volume fraction mapping, late gadolinium enhancement) or biomarkers (troponin, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide).
Cardiovascular abnormalities were no more common in seropositive than seronegative otherwise healthy health care workers 6 months post mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. Measured abnormalities were “evenly distributed between both groups,” Dr. Joy said.
Therefore, it’s “important to reassure patients with mild SARS-CoV-2 infection regarding its cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Joy and colleagues concluded.
Limitations and caveats
They caution, however, that the study provides insight only into the short- to medium-term sequelae of patients aged 18-69 with mild COVID-19 who did not require hospitalization and had low numbers of comorbidities.
The study does not address the cardiovascular effects after severe COVID-19 infection requiring hospitalization or in those with multiple comorbid conditions, they noted. It also does not prove that apparently mild SARS-CoV-2 never causes chronic myocarditis.
“The study design would not distinguish between people who had sustained completely healed myocarditis and pericarditis and those in whom the heart had never been affected,” the researchers noted.
They pointed to a recent cross-sectional study of athletes 1-month post mild COVID-19 that found significant pericardial involvement (late enhancement and/or pericardial effusion), although no baseline pre-COVID-19 imaging was performed. In the current study at 6 months post infection the pericardium was normal.
The coauthors of a linked editorial say this study provides “welcome, reassuring information that in healthy individuals who experience mild infection with COVID-19, persisting evidence of cardiovascular complications is very uncommon. The results do not support cardiovascular screening in individuals with mild or asymptomatic infection with COVID-19.”
Colin Berry, PhD, and Kenneth Mangion, PhD, both from University of Glasgow, cautioned that the population is restricted to health care workers; therefore, the findings may not necessarily be generalized to a community population .
“Healthcare workers do not reflect the population of individuals most clinically affected by COVID-19 illness. The severity of acute COVID-19 infection is greatest in older individuals and those with preexisting health problems. Healthcare workers are not representative of the wider, unselected, at-risk, community population,” they pointed out.
Cardiovascular risk factors and concomitant health problems (heart and respiratory disease) may be more common in the community than in health care workers, and prior studies have highlighted their potential impact for disease pathogenesis in COVID-19.
Dr. Berry and Dr. Mangion also noted that women made up nearly two-thirds of the seropositive group. This may reflect a selection bias or may naturally reflect the fact that proportionately more women are asymptomatic or have milder forms of illness, whereas severe SARS-CoV-2 infection requiring hospitalization affects men to a greater degree.
COVIDsortium funding was donated by individuals, charitable trusts, and corporations including Goldman Sachs, Citadel and Citadel Securities, The Guy Foundation, GW Pharmaceuticals, Kusuma Trust, and Jagclif Charitable Trust, and enabled by Barts Charity with support from UCLH Charity. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What to know about COVID-19 vaccines and skin reactions
The good news is that these side effects tend to be minor and vanish within a few days, Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, said in a presentation at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
“The reality is actually very reassuring,” Dr. Freeman said, especially in light of what is currently known about when the rashes occur and how anaphylaxis is extremely uncommon. Now, she added, dermatologists can tell patients who had reactions to their initial vaccination that “we know you had this big reaction, and we know that it was upsetting and uncomfortable. But it may not happen the second time around. And if it does, [the reaction is] probably going to be smaller.”
Dr. Freeman, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, highlighted a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology that she coauthored with dermatologists across the United States. The researchers tracked 414 cutaneous reactions to the Moderna (83%) and Pfizer (17%) COVID-19 vaccines in a group of patients, which was 90% female, 78% White, and mostly from the United States. Their average age was 44 years. The cases were reported to the AAD–International League of Dermatological Societies registry of COVID-19 cutaneous manifestations.
While most were women, “it’s a little hard to know if this is really going to end up being a true finding,” said Dr. Freeman, the registry’s principal investigator and a member of the AAD’s COVID-19 Ad Hoc Task Force. “If you think about who got vaccinated early, it was health care providers, and the American health care workforce is over 70% female. So I think there’s a little bit of bias here. There may also be a bias because women may be slightly more likely to report or go to their health care provider for a rash.”
Delayed large local reactions were the most common, accounting for 66% (175 cases) of the 267 skin reactions reported after the first Moderna vaccine dose and 30% (31 cases) of the 102 reactions reported after the second dose. These reactions represented 15% (5 cases) of the 34 skin reactions reported after the first Pfizer vaccine dose and 18% (7 cases) of the 40 reactions after the second dose.
There are two peaks with that first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “There’s a peak around day 2 or 3. And there’s another peak around day 7 or 8 with some of these reactions. Only 27% who had a reaction with the first dose had the same reaction with the second.” She added that these reactions “are not cellulitis and don’t require antibiotics.”
Other more common reactions included local injection-site reactions (swelling, erythema, and pain), urticaria (after 24 hours in almost all cases, occurring at a higher rate in patients who received the Pfizer vaccine), and morbilliform eruptions.
Dr. Freeman said that patients may experience redness and swelling in the hands and feet that can be “very uncomfortable.” She described one patient “who was having a hard time actually closing his fist, just because of the amount of swelling and redness in his hand. It did resolve, and it’s important to reassure your patients it will go away.”
According to this study, less common reports of other cutaneous findings with both vaccines included 9 reports of swelling at the site of cosmetic fillers, 8 reports of pernio/chilblains, 10 reports of varicella zoster, 4 reports of herpes simplex flares, 4 pityriasis rosea–like reactions, and 4 rashes in infants of vaccinated breastfeeding mothers.
The study noted that “patients responded well to topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and/or pain-relieving medications. These reactions resolved after a median of 3-4 days.”
It’s important to understand that none of the patients developed anaphylaxis after the second dose even if they’d had a reaction to the first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “But I should point out that we’re talking about reactions that have started more than 4 hours after the vaccine. If a rash such as a urticaria specifically starts within 4 hours of vaccination, that’s in a different category. Those are considered more immediate allergic reactions, and those patients need to be seen by allergy before a second dose.”
Dr. Freeman added that “it’s really interesting to think about how our bodies are really reacting to the vaccine in a way that’s mimicking our body’s reactions to COVID-19.” For example, some patients who got vaccinated developed chilblains similar to the “COVID toes” described in infected patients, apparently as part of the body’s immune response to the virus. “We’ve seen this in patients who actually had COVID and had prior COVID toes and then actually got a flare with their vaccine. And then we’ve also seen it in patients who never had COVID.”
In regard to general advice for patients, she said, “I do still encourage my patients who previously had COVID to go ahead and get the vaccine even if they had a skin manifestation with COVID.”
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has have seen only a handful of cases of delayed large local reactions and local injection site reactions after COVID-19 vaccination. “I have seen a significant number of cases of acute urticaria following the first and second doses,” she said in an interview. “However, it is important to keep in mind that we cannot determine cause and effect for the cases of acute urticaria. They may or may not be vaccine related.”
Fortunately, none of the adverse effects she’s seen have been severe. “It is important that dermatologists educate the public and their patients that most people do not develop any skin reaction in response to the vaccine,” she said. In the minority who do, “reactions tend to be mild and are not life-threatening. Many of these skin reactions resolve on their own without treatment.”
She added that “patients with pernio/chilblains or herpes zoster following vaccination should be referred by a board-certified dermatologist for prompt treatment and to avoid sequelae.”
‘COVID vaccine arm’
Delayed local reactions to the Moderna vaccine were also described in a report published online on May 12, 2021, in JAMA Dermatology, after the AAD meeting, in 16 patients referred to the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital Dermatology service who experienced delayed localized cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions a median of 7 days after receiving the vaccine (range, 2-12 days), from Jan. 20 to Feb. 12, 2021. No such cases were reported in Pfizer vaccine recipients.
Of the 16 patients, whose median age was 38 years and who were mostly women, 15 developed the reaction after the first dose, described as “pruritic and variably painful erythematous reactions near the injection site,” which lasted a median of 5 days (range, 1-21 days). After the second dose, 12 of the 16 patients developed injection-site reactions (including one patient who had no reaction after dose 1), a median of 2 days after the vaccine was administered (range, 0-5 days). Histologic results of a biopsy in one patient with a reaction to the second dose “ demonstrated mild predominantly perivascular and focal interstitial mixed infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils consistent with a dermal hypersensitivity reaction,” wrote Alicia J. Little, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, and coauthors.
Compared with immediate hypersensitivity reactions, occurring within 4 hours of vaccination, such as anaphylaxis and urticaria, they concluded that “these delayed localized hypersensitivity reactions are not a contraindication to subsequent vaccination,” and they proposed that they be named “COVID vaccine arm.”
Dr. Freeman reported no disclosures. Dr. Lipner also had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Little reported receiving a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science and a Women’s Health Career Development Award from the Dermatology Foundation while the study was conducted; another author reported equity in Johnson & Johnson in his spouse’s retirement fund outside the submitted work.
The good news is that these side effects tend to be minor and vanish within a few days, Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, said in a presentation at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
“The reality is actually very reassuring,” Dr. Freeman said, especially in light of what is currently known about when the rashes occur and how anaphylaxis is extremely uncommon. Now, she added, dermatologists can tell patients who had reactions to their initial vaccination that “we know you had this big reaction, and we know that it was upsetting and uncomfortable. But it may not happen the second time around. And if it does, [the reaction is] probably going to be smaller.”
Dr. Freeman, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, highlighted a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology that she coauthored with dermatologists across the United States. The researchers tracked 414 cutaneous reactions to the Moderna (83%) and Pfizer (17%) COVID-19 vaccines in a group of patients, which was 90% female, 78% White, and mostly from the United States. Their average age was 44 years. The cases were reported to the AAD–International League of Dermatological Societies registry of COVID-19 cutaneous manifestations.
While most were women, “it’s a little hard to know if this is really going to end up being a true finding,” said Dr. Freeman, the registry’s principal investigator and a member of the AAD’s COVID-19 Ad Hoc Task Force. “If you think about who got vaccinated early, it was health care providers, and the American health care workforce is over 70% female. So I think there’s a little bit of bias here. There may also be a bias because women may be slightly more likely to report or go to their health care provider for a rash.”
Delayed large local reactions were the most common, accounting for 66% (175 cases) of the 267 skin reactions reported after the first Moderna vaccine dose and 30% (31 cases) of the 102 reactions reported after the second dose. These reactions represented 15% (5 cases) of the 34 skin reactions reported after the first Pfizer vaccine dose and 18% (7 cases) of the 40 reactions after the second dose.
There are two peaks with that first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “There’s a peak around day 2 or 3. And there’s another peak around day 7 or 8 with some of these reactions. Only 27% who had a reaction with the first dose had the same reaction with the second.” She added that these reactions “are not cellulitis and don’t require antibiotics.”
Other more common reactions included local injection-site reactions (swelling, erythema, and pain), urticaria (after 24 hours in almost all cases, occurring at a higher rate in patients who received the Pfizer vaccine), and morbilliform eruptions.
Dr. Freeman said that patients may experience redness and swelling in the hands and feet that can be “very uncomfortable.” She described one patient “who was having a hard time actually closing his fist, just because of the amount of swelling and redness in his hand. It did resolve, and it’s important to reassure your patients it will go away.”
According to this study, less common reports of other cutaneous findings with both vaccines included 9 reports of swelling at the site of cosmetic fillers, 8 reports of pernio/chilblains, 10 reports of varicella zoster, 4 reports of herpes simplex flares, 4 pityriasis rosea–like reactions, and 4 rashes in infants of vaccinated breastfeeding mothers.
The study noted that “patients responded well to topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and/or pain-relieving medications. These reactions resolved after a median of 3-4 days.”
It’s important to understand that none of the patients developed anaphylaxis after the second dose even if they’d had a reaction to the first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “But I should point out that we’re talking about reactions that have started more than 4 hours after the vaccine. If a rash such as a urticaria specifically starts within 4 hours of vaccination, that’s in a different category. Those are considered more immediate allergic reactions, and those patients need to be seen by allergy before a second dose.”
Dr. Freeman added that “it’s really interesting to think about how our bodies are really reacting to the vaccine in a way that’s mimicking our body’s reactions to COVID-19.” For example, some patients who got vaccinated developed chilblains similar to the “COVID toes” described in infected patients, apparently as part of the body’s immune response to the virus. “We’ve seen this in patients who actually had COVID and had prior COVID toes and then actually got a flare with their vaccine. And then we’ve also seen it in patients who never had COVID.”
In regard to general advice for patients, she said, “I do still encourage my patients who previously had COVID to go ahead and get the vaccine even if they had a skin manifestation with COVID.”
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has have seen only a handful of cases of delayed large local reactions and local injection site reactions after COVID-19 vaccination. “I have seen a significant number of cases of acute urticaria following the first and second doses,” she said in an interview. “However, it is important to keep in mind that we cannot determine cause and effect for the cases of acute urticaria. They may or may not be vaccine related.”
Fortunately, none of the adverse effects she’s seen have been severe. “It is important that dermatologists educate the public and their patients that most people do not develop any skin reaction in response to the vaccine,” she said. In the minority who do, “reactions tend to be mild and are not life-threatening. Many of these skin reactions resolve on their own without treatment.”
She added that “patients with pernio/chilblains or herpes zoster following vaccination should be referred by a board-certified dermatologist for prompt treatment and to avoid sequelae.”
‘COVID vaccine arm’
Delayed local reactions to the Moderna vaccine were also described in a report published online on May 12, 2021, in JAMA Dermatology, after the AAD meeting, in 16 patients referred to the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital Dermatology service who experienced delayed localized cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions a median of 7 days after receiving the vaccine (range, 2-12 days), from Jan. 20 to Feb. 12, 2021. No such cases were reported in Pfizer vaccine recipients.
Of the 16 patients, whose median age was 38 years and who were mostly women, 15 developed the reaction after the first dose, described as “pruritic and variably painful erythematous reactions near the injection site,” which lasted a median of 5 days (range, 1-21 days). After the second dose, 12 of the 16 patients developed injection-site reactions (including one patient who had no reaction after dose 1), a median of 2 days after the vaccine was administered (range, 0-5 days). Histologic results of a biopsy in one patient with a reaction to the second dose “ demonstrated mild predominantly perivascular and focal interstitial mixed infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils consistent with a dermal hypersensitivity reaction,” wrote Alicia J. Little, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, and coauthors.
Compared with immediate hypersensitivity reactions, occurring within 4 hours of vaccination, such as anaphylaxis and urticaria, they concluded that “these delayed localized hypersensitivity reactions are not a contraindication to subsequent vaccination,” and they proposed that they be named “COVID vaccine arm.”
Dr. Freeman reported no disclosures. Dr. Lipner also had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Little reported receiving a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science and a Women’s Health Career Development Award from the Dermatology Foundation while the study was conducted; another author reported equity in Johnson & Johnson in his spouse’s retirement fund outside the submitted work.
The good news is that these side effects tend to be minor and vanish within a few days, Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, said in a presentation at the American Academy of Dermatology Virtual Meeting Experience.
“The reality is actually very reassuring,” Dr. Freeman said, especially in light of what is currently known about when the rashes occur and how anaphylaxis is extremely uncommon. Now, she added, dermatologists can tell patients who had reactions to their initial vaccination that “we know you had this big reaction, and we know that it was upsetting and uncomfortable. But it may not happen the second time around. And if it does, [the reaction is] probably going to be smaller.”
Dr. Freeman, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, highlighted a study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology that she coauthored with dermatologists across the United States. The researchers tracked 414 cutaneous reactions to the Moderna (83%) and Pfizer (17%) COVID-19 vaccines in a group of patients, which was 90% female, 78% White, and mostly from the United States. Their average age was 44 years. The cases were reported to the AAD–International League of Dermatological Societies registry of COVID-19 cutaneous manifestations.
While most were women, “it’s a little hard to know if this is really going to end up being a true finding,” said Dr. Freeman, the registry’s principal investigator and a member of the AAD’s COVID-19 Ad Hoc Task Force. “If you think about who got vaccinated early, it was health care providers, and the American health care workforce is over 70% female. So I think there’s a little bit of bias here. There may also be a bias because women may be slightly more likely to report or go to their health care provider for a rash.”
Delayed large local reactions were the most common, accounting for 66% (175 cases) of the 267 skin reactions reported after the first Moderna vaccine dose and 30% (31 cases) of the 102 reactions reported after the second dose. These reactions represented 15% (5 cases) of the 34 skin reactions reported after the first Pfizer vaccine dose and 18% (7 cases) of the 40 reactions after the second dose.
There are two peaks with that first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “There’s a peak around day 2 or 3. And there’s another peak around day 7 or 8 with some of these reactions. Only 27% who had a reaction with the first dose had the same reaction with the second.” She added that these reactions “are not cellulitis and don’t require antibiotics.”
Other more common reactions included local injection-site reactions (swelling, erythema, and pain), urticaria (after 24 hours in almost all cases, occurring at a higher rate in patients who received the Pfizer vaccine), and morbilliform eruptions.
Dr. Freeman said that patients may experience redness and swelling in the hands and feet that can be “very uncomfortable.” She described one patient “who was having a hard time actually closing his fist, just because of the amount of swelling and redness in his hand. It did resolve, and it’s important to reassure your patients it will go away.”
According to this study, less common reports of other cutaneous findings with both vaccines included 9 reports of swelling at the site of cosmetic fillers, 8 reports of pernio/chilblains, 10 reports of varicella zoster, 4 reports of herpes simplex flares, 4 pityriasis rosea–like reactions, and 4 rashes in infants of vaccinated breastfeeding mothers.
The study noted that “patients responded well to topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines, and/or pain-relieving medications. These reactions resolved after a median of 3-4 days.”
It’s important to understand that none of the patients developed anaphylaxis after the second dose even if they’d had a reaction to the first dose, Dr. Freeman said. “But I should point out that we’re talking about reactions that have started more than 4 hours after the vaccine. If a rash such as a urticaria specifically starts within 4 hours of vaccination, that’s in a different category. Those are considered more immediate allergic reactions, and those patients need to be seen by allergy before a second dose.”
Dr. Freeman added that “it’s really interesting to think about how our bodies are really reacting to the vaccine in a way that’s mimicking our body’s reactions to COVID-19.” For example, some patients who got vaccinated developed chilblains similar to the “COVID toes” described in infected patients, apparently as part of the body’s immune response to the virus. “We’ve seen this in patients who actually had COVID and had prior COVID toes and then actually got a flare with their vaccine. And then we’ve also seen it in patients who never had COVID.”
In regard to general advice for patients, she said, “I do still encourage my patients who previously had COVID to go ahead and get the vaccine even if they had a skin manifestation with COVID.”
Shari Lipner, MD, PhD, associate professor of clinical dermatology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, said she has have seen only a handful of cases of delayed large local reactions and local injection site reactions after COVID-19 vaccination. “I have seen a significant number of cases of acute urticaria following the first and second doses,” she said in an interview. “However, it is important to keep in mind that we cannot determine cause and effect for the cases of acute urticaria. They may or may not be vaccine related.”
Fortunately, none of the adverse effects she’s seen have been severe. “It is important that dermatologists educate the public and their patients that most people do not develop any skin reaction in response to the vaccine,” she said. In the minority who do, “reactions tend to be mild and are not life-threatening. Many of these skin reactions resolve on their own without treatment.”
She added that “patients with pernio/chilblains or herpes zoster following vaccination should be referred by a board-certified dermatologist for prompt treatment and to avoid sequelae.”
‘COVID vaccine arm’
Delayed local reactions to the Moderna vaccine were also described in a report published online on May 12, 2021, in JAMA Dermatology, after the AAD meeting, in 16 patients referred to the Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital Dermatology service who experienced delayed localized cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions a median of 7 days after receiving the vaccine (range, 2-12 days), from Jan. 20 to Feb. 12, 2021. No such cases were reported in Pfizer vaccine recipients.
Of the 16 patients, whose median age was 38 years and who were mostly women, 15 developed the reaction after the first dose, described as “pruritic and variably painful erythematous reactions near the injection site,” which lasted a median of 5 days (range, 1-21 days). After the second dose, 12 of the 16 patients developed injection-site reactions (including one patient who had no reaction after dose 1), a median of 2 days after the vaccine was administered (range, 0-5 days). Histologic results of a biopsy in one patient with a reaction to the second dose “ demonstrated mild predominantly perivascular and focal interstitial mixed infiltrate with lymphocytes and eosinophils consistent with a dermal hypersensitivity reaction,” wrote Alicia J. Little, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, and coauthors.
Compared with immediate hypersensitivity reactions, occurring within 4 hours of vaccination, such as anaphylaxis and urticaria, they concluded that “these delayed localized hypersensitivity reactions are not a contraindication to subsequent vaccination,” and they proposed that they be named “COVID vaccine arm.”
Dr. Freeman reported no disclosures. Dr. Lipner also had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Little reported receiving a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Science and a Women’s Health Career Development Award from the Dermatology Foundation while the study was conducted; another author reported equity in Johnson & Johnson in his spouse’s retirement fund outside the submitted work.
FROM AAD VMX 2021
Dr. Fauci: Feds may ease indoor mask mandates soon
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Federal guidance on indoor mask use may change soon, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said on May 9.
He was asked whether it’s time to start relaxing indoor mask requirements.
“I think so, and I think you’re going to probably be seeing that as we go along and as more people get vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said on ABC News’s This Week.Nearly 150 million adults in the United States – or about 58% of the adult population – have received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose, according to the latest CDC tally. About 113 million adults, or 44%, are considered fully vaccinated.
“The CDC will be, you know, almost in real time … updating their recommendations and their guidelines,” Dr. Fauci said.
In April, the CDC relaxed its guidance for those who have been vaccinated against COVID-19. Those who have gotten a shot don’t need to wear a mask outdoors or in small indoor gatherings with other vaccinated people, but both vaccinated and unvaccinated people are still advised to wear masks in indoor public spaces.
“We do need to start being more liberal as we get more people vaccinated,” Dr. Fauci said. “As you get more people vaccinated, the number of cases per day will absolutely go down.”
The United States is averaging about 43,000 cases per day, he said, adding that the cases need to be “much, much lower.” When the case numbers drop and vaccination numbers increase, the risk of infection will fall dramatically indoors and outdoors, he said.
Even after the pandemic, though, wearing masks could become a seasonal habit, Dr. Fauci said May 9 on NBC News’s Meet the Press.“I think people have gotten used to the fact that wearing masks, clearly if you look at the data, it diminishes respiratory diseases. We’ve had practically a nonexistent flu season this year,” he said.
“So it is conceivable that as we go on, a year or 2 or more from now, that during certain seasonal periods when you have respiratory-borne viruses like the flu, people might actually elect to wear masks to diminish the likelihood that you’ll spread these respiratory-borne diseases,” he said.
Dr. Fauci was asked about indoor mask guidelines on May 9 after former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, said face mask requirements should be relaxed.
“Certainly outdoors, we shouldn’t be putting limits on gatherings anymore,” Dr. Gottlieb said on CBS News’s Face the Nation.“The states where prevalence is low, vaccination rates are high, we have good testing in place, and we’re identifying infections, I think we could start lifting these restrictions indoors as well, on a broad basis,” he said.
Lifting pandemic-related restrictions in areas where they’re no longer necessary could also encourage people to implement them again if cases increase during future surges, such as this fall or winter, Dr. Gottlieb said.
At the same time, Americans should continue to follow CDC guidance and wait for new guidelines before changing their indoor mask use, Jeffrey Zients, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, said on CNN’s State of the Union on May 9.
“We all want to get back to a normal lifestyle,” he said. “I think we’re on the path to do that, but stay disciplined, and let’s take advantage of the new privilege of being vaccinated and not wearing masks outdoors, for example, unless you’re in a crowded place.”
Mr. Zients pointed to President Joe Biden’s goal for 70% of adults to receive at least one vaccine dose by July 4.
“As we all move toward that 70% goal, there will be more and more advantages to being vaccinated,” he said. “And if you’re not vaccinated, you’re not protected.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA authorizes Pfizer COVID vaccine for teens 12-15
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on May 10 granted emergency use authorization (EUA) for the Pfizer coronavirus vaccine to be given to children 12-15 years old.
The much-expected decision increases the likelihood that schools in the United States will fully reopen in the fall – a goal of both the Biden and Trump administrations.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, called the decision “a significant step” in “returning to a sense of normalcy.”
“Today’s action allows for a younger population to be protected from COVID-19, bringing us closer to returning to a sense of normalcy and to ending the pandemic,” she said in a statement. “Parents and guardians can rest assured that the agency undertook a rigorous and thorough review of all available data, as we have with all of our COVID-19 vaccine emergency use authorizations.”
The Pfizer adolescent vaccine is not yet a done deal, though.
Next, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices will decide on May 12 whether to recommend use of the vaccine in this age group. After that, CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, will decide whether to give the green light for the vaccine to be administered to that age group.
The FDA action on May 10 amends the Dec. 11, 2020, emergency use authorization that allowed the Pfizer vaccine to be given to people 16 and older. Pfizer was the first company to receive an EUA for its adult vaccine and is the first to receive authorization for its adolescent vaccine. Pfizer is conducting clinical trials on much younger children, too.
The Moderna and Johnson & Johnson vaccines are authorized for people 18 and up. Moderna also has launched clinical trials in children.
Most health experts have said the United States needs to vaccinate children before the COVID-19 pandemic can truly be brought under control. The 12- to 15-year-old group represents 17 million people, about 5% of the population. Thus far, 58% of U.S. adults have had at least one dose of a vaccine and 34.8% of all Americans are fully vaccinated.
American Academy of Pediatrics President Lee Savio Beers, MD, praised the agency’s decision, calling it a “critically important step in bringing life-saving vaccines to children and adolescents. Our youngest generations have shouldered heavy burdens over the past year, and the vaccine is a hopeful sign that they will be able to begin to experience all the activities that are so important for their health and development.”
President Joe Biden recently announced a new strategy for expanding vaccinations in which vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds was a key component. He said the administration was ready to ship the adolescent vaccine directly to pharmacies and pediatricians to speed up the vaccination rate.
In March, Anthony S. Fauci, MD, told a Senate committee, “We don’t really know what that magical point of herd immunity is, but we do know that if we get the overwhelming population vaccinated, we’re going to be in good shape. … We ultimately would like to get and have to get children into that mix.”
Pfizer submitted data to the FDA in late March showing its mRNA vaccine was 100% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection in children ages 12-15 in clinical trials.
Though most children have milder symptoms when infected with the coronavirus, about 1.5 million cases in children aged 11-17 were reported to the CDC between March 1, 2020, and April 30 of this year, the FDA news release said.
Albert Bourla, CEO of Pfizer, tweeted that “today brings very encouraging news for families and adolescents across the United States.
“While this is a meaningful step forward, we are still in a critical period of combating #COVID19 around the world. In the coming weeks, we hope to continue to receive authorizations from global regulators to support worldwide vaccination efforts,” he said.
“It’s essential for children to be vaccinated against COVID-19. According to data compiled by the AAP and Children’s Hospital Association, more than 3.8 million children have tested positive for COVID-19 in the United States since the start of the pandemic,” said Dr. Savio Beers. “While fewer children than adults have suffered the most severe disease, this is not a benign disease in children. Thousands of children have been hospitalized, and hundreds have died. We will soon have a very safe, highly effective vaccine that can prevent so much suffering. I encourage parents to talk with their pediatricians about how to get the vaccine for their adolescents as soon as they are eligible.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NSAIDs don’t make COVID-19 worse in hospitalized patients
NSAIDs don’t boost the risk of more severe disease or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, a new study finds.
“To our knowledge, our prospective study includes the largest number of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 to date, and adds to the literature on the safety of NSAIDs and in-hospital outcomes. NSAIDs do not appear to increase the risk of worse in-hospital outcomes ...” the study authors wrote. “NSAIDs are an important analgesic modality and have a vital opioid-sparing role in pain management. Patients and clinicians should be reassured by these findings that NSAIDs are safe in the context of the pandemic.”
The report was published online May 7 in The Lancet Rheumatology and led by clinical research fellow Thomas M. Drake, MBChB, of the University of Edinburgh’s Usher Institute.
For more than a year, researchers worldwide have debated about whether NSAIDs spell trouble for people at risk of COVID-19. In March 2020, French health officials announced that use of the painkillers such as NSAIDs may increase the severity of the disease, and they recommended that patients take acetaminophen instead. The National Health Service in the United Kingdom made a similar recommendation. But other agencies didn’t believe there was enough evidence to support ditching NSAIDs, and recent research studies published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases and PLoS Medicine suggested they may be right.
For the new study, researchers identified 72,179 patients who were treated for COVID-19 in British hospitals during January-August 2020. About 56% were men, 74% were White, and 6% took NSAIDs on a regular basis before they entered the hospital. The average age was 70.
The researchers examined whether the patients in either group were more or less likely to die in the hospital, be admitted into a critical care unit, need oxygen treatment, need a ventilator, or suffer kidney injury.
In terms of outcomes, there weren’t any major gaps between the groups overall. The differences in most comparisons were statistically insignificant. For example, 31% of those who didn’t take NSAIDs died vs. 30% of those who did (P = .227). In both groups, 14% required critical care admission (P = .476).
The researchers then focused on two matched groups of 4,205 patients: One group used NSAIDs regularly, and the other group didn’t. The difference in risk of death in those who took NSAIDs vs. those who didn’t was statistically insignificant (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.07; P = .35). Other comparisons were also statistically insignificant.
The findings offer insight into whether the use of NSAIDs might actually be helpful for patients who develop COVID-19. Scientists believe that COVID-19 is linked to inflammation in the body, and NSAIDs, of course, reduce inflammation. But the researchers didn’t turn up any sign of a benefit.
The new study has some weaknesses: It doesn’t say anything about whether NSAIDs have an impact on whether people get COVID-19 in the first place. Researchers don’t know if high use of NSAIDs may affect the severity of the disease. And it doesn’t examine the potential effect of acetaminophen, although other research suggests the drug also may not cause harm in patients with COVID-19.
Still, the researchers say the study is the largest of its kind to look at the use of NSAIDs by patients who are admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. “Considering all the evidence, if there was an extreme effect of NSAIDs on COVID-19 outcomes or severity, this would have been observed in one or more of the studies that have been done, including the present study,” they wrote.
In a commentary that accompanied the study, three physicians from hospitals in Denmark, led by Kristian Kragholm, MD, of Aalborg University Hospital, praised the research and wrote that it adds to “a growing body of evidence” that NSAIDs don’t make things worse for patients with COVID-19.
The study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and the U.K. Medical Research Council. The study and commentary authors reported no relevant disclosures.
NSAIDs don’t boost the risk of more severe disease or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, a new study finds.
“To our knowledge, our prospective study includes the largest number of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 to date, and adds to the literature on the safety of NSAIDs and in-hospital outcomes. NSAIDs do not appear to increase the risk of worse in-hospital outcomes ...” the study authors wrote. “NSAIDs are an important analgesic modality and have a vital opioid-sparing role in pain management. Patients and clinicians should be reassured by these findings that NSAIDs are safe in the context of the pandemic.”
The report was published online May 7 in The Lancet Rheumatology and led by clinical research fellow Thomas M. Drake, MBChB, of the University of Edinburgh’s Usher Institute.
For more than a year, researchers worldwide have debated about whether NSAIDs spell trouble for people at risk of COVID-19. In March 2020, French health officials announced that use of the painkillers such as NSAIDs may increase the severity of the disease, and they recommended that patients take acetaminophen instead. The National Health Service in the United Kingdom made a similar recommendation. But other agencies didn’t believe there was enough evidence to support ditching NSAIDs, and recent research studies published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases and PLoS Medicine suggested they may be right.
For the new study, researchers identified 72,179 patients who were treated for COVID-19 in British hospitals during January-August 2020. About 56% were men, 74% were White, and 6% took NSAIDs on a regular basis before they entered the hospital. The average age was 70.
The researchers examined whether the patients in either group were more or less likely to die in the hospital, be admitted into a critical care unit, need oxygen treatment, need a ventilator, or suffer kidney injury.
In terms of outcomes, there weren’t any major gaps between the groups overall. The differences in most comparisons were statistically insignificant. For example, 31% of those who didn’t take NSAIDs died vs. 30% of those who did (P = .227). In both groups, 14% required critical care admission (P = .476).
The researchers then focused on two matched groups of 4,205 patients: One group used NSAIDs regularly, and the other group didn’t. The difference in risk of death in those who took NSAIDs vs. those who didn’t was statistically insignificant (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.07; P = .35). Other comparisons were also statistically insignificant.
The findings offer insight into whether the use of NSAIDs might actually be helpful for patients who develop COVID-19. Scientists believe that COVID-19 is linked to inflammation in the body, and NSAIDs, of course, reduce inflammation. But the researchers didn’t turn up any sign of a benefit.
The new study has some weaknesses: It doesn’t say anything about whether NSAIDs have an impact on whether people get COVID-19 in the first place. Researchers don’t know if high use of NSAIDs may affect the severity of the disease. And it doesn’t examine the potential effect of acetaminophen, although other research suggests the drug also may not cause harm in patients with COVID-19.
Still, the researchers say the study is the largest of its kind to look at the use of NSAIDs by patients who are admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. “Considering all the evidence, if there was an extreme effect of NSAIDs on COVID-19 outcomes or severity, this would have been observed in one or more of the studies that have been done, including the present study,” they wrote.
In a commentary that accompanied the study, three physicians from hospitals in Denmark, led by Kristian Kragholm, MD, of Aalborg University Hospital, praised the research and wrote that it adds to “a growing body of evidence” that NSAIDs don’t make things worse for patients with COVID-19.
The study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and the U.K. Medical Research Council. The study and commentary authors reported no relevant disclosures.
NSAIDs don’t boost the risk of more severe disease or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, a new study finds.
“To our knowledge, our prospective study includes the largest number of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 to date, and adds to the literature on the safety of NSAIDs and in-hospital outcomes. NSAIDs do not appear to increase the risk of worse in-hospital outcomes ...” the study authors wrote. “NSAIDs are an important analgesic modality and have a vital opioid-sparing role in pain management. Patients and clinicians should be reassured by these findings that NSAIDs are safe in the context of the pandemic.”
The report was published online May 7 in The Lancet Rheumatology and led by clinical research fellow Thomas M. Drake, MBChB, of the University of Edinburgh’s Usher Institute.
For more than a year, researchers worldwide have debated about whether NSAIDs spell trouble for people at risk of COVID-19. In March 2020, French health officials announced that use of the painkillers such as NSAIDs may increase the severity of the disease, and they recommended that patients take acetaminophen instead. The National Health Service in the United Kingdom made a similar recommendation. But other agencies didn’t believe there was enough evidence to support ditching NSAIDs, and recent research studies published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases and PLoS Medicine suggested they may be right.
For the new study, researchers identified 72,179 patients who were treated for COVID-19 in British hospitals during January-August 2020. About 56% were men, 74% were White, and 6% took NSAIDs on a regular basis before they entered the hospital. The average age was 70.
The researchers examined whether the patients in either group were more or less likely to die in the hospital, be admitted into a critical care unit, need oxygen treatment, need a ventilator, or suffer kidney injury.
In terms of outcomes, there weren’t any major gaps between the groups overall. The differences in most comparisons were statistically insignificant. For example, 31% of those who didn’t take NSAIDs died vs. 30% of those who did (P = .227). In both groups, 14% required critical care admission (P = .476).
The researchers then focused on two matched groups of 4,205 patients: One group used NSAIDs regularly, and the other group didn’t. The difference in risk of death in those who took NSAIDs vs. those who didn’t was statistically insignificant (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.84-1.07; P = .35). Other comparisons were also statistically insignificant.
The findings offer insight into whether the use of NSAIDs might actually be helpful for patients who develop COVID-19. Scientists believe that COVID-19 is linked to inflammation in the body, and NSAIDs, of course, reduce inflammation. But the researchers didn’t turn up any sign of a benefit.
The new study has some weaknesses: It doesn’t say anything about whether NSAIDs have an impact on whether people get COVID-19 in the first place. Researchers don’t know if high use of NSAIDs may affect the severity of the disease. And it doesn’t examine the potential effect of acetaminophen, although other research suggests the drug also may not cause harm in patients with COVID-19.
Still, the researchers say the study is the largest of its kind to look at the use of NSAIDs by patients who are admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. “Considering all the evidence, if there was an extreme effect of NSAIDs on COVID-19 outcomes or severity, this would have been observed in one or more of the studies that have been done, including the present study,” they wrote.
In a commentary that accompanied the study, three physicians from hospitals in Denmark, led by Kristian Kragholm, MD, of Aalborg University Hospital, praised the research and wrote that it adds to “a growing body of evidence” that NSAIDs don’t make things worse for patients with COVID-19.
The study was funded by the U.K. National Institute for Health Research and the U.K. Medical Research Council. The study and commentary authors reported no relevant disclosures.
FROM THE LANCET RHEUMATOLOGY
‘Malicious peer review’ destroyed doc’s career, he says
Cardiothoracic surgeon J. Marvin Smith III, MD, had always thrived on a busy practice schedule, often performing 20-30 surgeries a week. A practicing surgeon for more than 40 years, Dr. Smith said he had no plans to slow down anytime soon.
But Dr. Smith said his career was derailed when leaders at Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio initiated a sudden peer review proceeding against him. The hospital system alleged certain surgeries performed by Dr. Smith had excessive mortality rates. When he proved the data inaccurate, Dr. Smith said administrators next claimed he was cognitively impaired and wasn’t safe to practice.
Dr. Smith has now been embroiled in a peer review dispute with the hospital system for more than 2 years and says the conflict has essentially forced him out of surgical practice. He believes the peer review was “malicious” and was really launched because of complaints he made about nurse staffing and other issues at the hospital.
“I think it is absolutely in bad faith and is disingenuous what they’ve told me along the way,” said Dr. Smith, 73. “It’s because I pointed out deficiencies in nursing care, and they want to get rid of me. It would be a lot easier for them if I had a contract and they could control me better. But the fact that I was independent, meant they had to resort to a malicious peer review to try and push me out.”
Dr. Smith had a peer review hearing with Methodist in March 2021, and in April, a panel found in Dr. Smith’s favor, according to Dr. Smith. The findings were sent to the hospital’s medical board for review, which issued a decision in early May.
Eric A. Pullen, an attorney for Dr. Smith, said he could not go into detail about the board’s decision for legal reasons, but that “the medical board’s decision did not completely resolve the matter, and Dr. Smith intends to exercise his procedural rights, which could include an appeal.”
Methodist Hospital Texsan and its parent company, Methodist Health System of San Antonio, did not respond to messages seeking comment about the case. Without hearing from the hospital system, its side is unknown and it is unclear if there is more to the story from Methodist’s view.
The problem is not new, but some experts, such as Lawrence Huntoon, MD, PhD, say the practice has become more common in recent years, particularly against independent doctors.
Dr. Huntoon believes there is a nationwide trend at many hospitals to get rid of independent physicians and replace them with employed doctors, he said.
However, because most sham peer reviews go on behind closed doors, there are no data to pinpoint its prevalence or measure its growth.
“Independent physicians are basically being purged from medical staffs across the United States,” said Dr. Huntoon, who is chair of the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons’ Committee to Combat Sham Peer Review. “The hospitals want more control over how physicians practice and who they refer to, and they do that by having employees.”
Anthony P. Weiss, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center said it has not been his experience that independent physicians are being targeted in such a way. Dr. Weiss responded to an inquiry sent to the American Hospital Association for this story.
“As the authority for peer review rests with the organized medical staff (i.e., physicians), and not formally with the hospital per se, the peer review lever is not typically available as a management tool for hospital administration,” said Dr. Weiss, who is a former member of the AHA’s Committee on Clinical Leadership, but who was speaking on behalf of himself.
A spokesman for the AHA said the organization stands behinds Dr. Weiss’ comments.
Peer review remains a foundational aspect of overseeing the safety and appropriateness of healthcare provided by physicians, Dr. Weiss said. Peer review likely varies from hospital to hospital, he added, although the Healthcare Quality Improvement Act provides some level of guidance as does the American Medical Association Code of Medical Ethics (section 9.4.1).
“In essence, both require that the evaluation be conducted in good faith with the intention to improve care, by physicians with adequate training and knowledge, using a process that is fair and inclusive of the physician under review,” he said. “I believe that most medical staffs abide by these ethical principles, but we have little data to confirm this supposition.”
Did hospital target doc for being vocal?
When members of Methodist’s medical staff first approached Dr. Smith with concerns about his surgery outcomes in November 2018, the physician says he was surprised, but that he was open to an assessment.
“They came to me and said they thought my numbers were bad, and I said: ‘Well my gosh, I certainly don’t want that to be the case. I need to see what numbers you are talking about,’ ” Dr. Smith recalled. “I’ve been president of the Bexar County Medical Society; I’ve been involved with standards and ethics for the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Quality health care means a whole lot to me.”
The statistical information provided by hospital administrators indicated that Dr. Smith’s mortality rates for coronary artery surgery in 2018 were “excessive” and that his rates for aortic surgery were “unacceptable,” according to a lawsuit Dr. Smith filed against the hospital system. Dr. Smith, who is double boarded with the American Board of Surgery and the American Board of Thoracic Surgery, said his outcomes had never come into question in the past. Dr. Smith said the timing was suspicious to him, however, considering he had recently raised concerns with the hospital through letters about nursing performance, staffing, and compensation.
A peer review investigation was initiated. In the meantime, Dr. Smith agreed to intensivist consults on his postoperative patients and consults with the hospital’s “Heart Team” on all preoperative cardiac, valve, and aortic cases. A vocal critic of the Heart Team, Dr. Smith had long contended the entity provided no meaningful benefit to his patients in most cases and, rather, increased hospital stays and raised medical expenses. Despite his agreement, Dr. Smith was later asked to voluntarily stop performing surgeries at the hospital.
“I agreed, convinced that we’d get this all settled,” he said.
Another report issued by the hospital in 2019 also indicated elevated mortality rates associated with some of Smith’s surgeries, although the document differed from the first report, according to the lawsuit. Dr. Smith says he was ignored when he pointed out problems with the data, including a lack of appropriate risk stratification in the report, departure from Society of Thoracic Surgeons data rules, and improper inclusion of his cases in the denominator of the ratio when a comparison was made of his outcomes with those hospitalwide. A subsequent report from Methodist in March 2019 indicated Dr. Smith’s surgery outcomes were “within the expected parameters of performance,” according to court documents.
The surgery accusations were dropped, but the peer review proceeding against Dr. Smith wasn’t over. The hospital next requested that Dr. Smith undergo a competency evaluation.
“When they realized the data was bad, they then changed their argument in the peer review proceeding and essentially started to argue that Dr. Smith had some sort of cognitive disability that prevented him from continuing to practice,” said Mr. Pullen. “The way I look at it, when the initial basis for the peer review was proven false, the hospital found something else and some other reason to try to keep Dr. Smith from practicing.”
Thus began a lengthy disagreement about which entity would conduct the evaluation, who would pay, and the type of acceptable assessment. An evaluation by the hospital’s preferred organization resulted in a finding of mild cognitive impairment, Dr. Smith said. He hired his own experts who conducted separate evaluations, finding no impairment and no basis for the former evaluation’s conclusion.
“Literally, the determinant as to whether I was normal or below normal on their test was one point, which was associated with a finding that I didn’t draw a clock correctly,” Dr. Smith claimed. “The reviewer said my minute hand was a little too short and docked me a point. It was purely subjective. To me, the gold standard of whether you are learned in thoracic surgery is the American Board of Thoracic Surgery’s test. The board’s test shows my cognitive ability is entirely in keeping with my practice. That contrasts with the one point off I got for drawing a clock wrong in somebody’s estimation.”
Conflict leads to legal case
In September 2020, Dr. Smith filed a lawsuit against Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio, alleging business disparagement by Methodist for allegedly publishing false and disparaging information about Dr. Smith and tortious interference with business relations. The latter claim stems from Methodist refusing to provide documents to other hospitals about the status of Dr. Smith’s privileges at Methodist, Mr. Pullen said.
Because Methodist refused to confirm his status, the renewal process for Baptist Health System could not be completed and Dr. Smith lost his privileges at Baptist Health System facilities, according to the lawsuit.
Notably, Dr. Smith’s legal challenge also asks the court to take a stance against alleged amendments by Methodist to its Unified Medical Staff Bylaws. The hospital allegedly proposed changes that would prevent physicians from seeking legal action against the hospital for malicious peer review, according to Dr. Smith’s lawsuit.
The amendments would make the peer review process itself the “sole and exclusive remedy with respect to any action or recommendation taken at the hospital affecting medical staff appointment and/or clinical privileges,” according to an excerpt of the proposed amendments included in Dr. Smith’s lawsuit. In addition, the changes would hold practitioners liable for lost revenues if the doctor initiates “any type of legal action challenging credentialing, privileging, or other medical peer review or professional review activity,” according to the lawsuit.
Dr. Smith’s lawsuit seeks a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws are “void as against public policy,” and a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws cannot take away physicians’ statutory right to bring litigation against Methodist for malicious peer review.
“The proposed amendments have a tendency to and will injure the public good,” Dr. Smith argued in the lawsuit. “The proposed amendments allow Methodist to act with malice and in bad faith in conducting peer review proceedings and face no legal repercussions.”
Regardless of the final outcome of the peer review proceeding, Mr. Pullen said the harm Dr. Smith has already endured cannot be reversed.
“Even if comes out in his favor, the damage is already done,” he said. “It will not remedy the damage Dr. Smith has incurred.”
Fighting sham peer review is difficult
Battling a malicious peer review has long been an uphill battle for physicians, according to Dr. Huntoon. That’s because the Health Care Quality Improvement Act (HCQIA), a federal law passed in 1986, provides near absolute immunity to hospitals and peer reviewers in legal disputes.
The HCQIA was created by Congress to extend immunity to good-faith peer review of doctors and to increase overall participation in peer review by removing fear of litigation. However, the act has also enabled abuse of peer review by shielding bad-faith reviewers from accountability, said Dr. Huntoon.
“The Health Care Quality Improvement Act presumes that what the hospital did was warranted and reasonable and shifts the burden to the physician to prove his innocence by a preponderance of evidence,” he said. “That’s an entirely foreign concept to most people who think a person should be considered innocent until proven guilty. Here, it’s the exact opposite.”
The HCQIA has been challenged numerous times over the years and tested at the appellate level, but continues to survive and remain settled law, added Richard B. Willner, DPM, founder and director of the Center for Peer Review Justice, which assists and counsels physicians about sham peer review.
In 2011, former Rep. Joe Heck, DO, (R-Nev.) introduced a bill that would have amended the HCQIA to prohibit a professional review entity from submitting a report to the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) while the doctor was still under investigation and before the doctor was afforded adequate notice and a hearing. Although the measure had 16 cosponsors and plenty of support from the physician community, it failed.
In addition to a heavy legal burden, physicians who experience malicious peer reviews also face ramifications from being reported to the NPDB. Peer review organizations are required to report certain negative actions or findings to the NPDB.
“A databank entry is a scarlet letter on your forehead,” Dr. Willner said. “The rules at a lot of institutions are not to take anyone who has been databanked, rightfully or wrongfully. And what is the evidence necessary to databank you? None. There’s no evidence needed to databank somebody.”
Despite the bleak landscape, experts say progress has been made on a case-by-case basis by physicians who have succeeded in fighting back against questionable peer reviews in recent years.
In January 2020, Indiana ob.gyn. Rebecca Denman, MD, prevailed in her defamation lawsuit against St Vincent Carmel Hospital and St Vincent Carmel Medical Group, winning $4.75 million in damages. Dr. Denman alleged administrators failed to conduct a proper peer review investigation after a false allegation by a nurse that she was under the influence while on the job.
Indianapolis attorney Kathleen A. DeLaney, who represented Dr. Denman, said hospital leaders misled Dr. Denman into believing a peer review had occurred when no formal peer review hearing or proceeding took place.
“The CMO of the medical group claimed that he performed a peer review ‘screening,’ but he never informed the other members of the peer review executive committee of the matter until after he had placed Dr. Denman on administrative leave,” Ms. DeLaney said. “He also neglected to tell the peer review executive committee that the substance abuse policy had not been followed, or that Dr. Denman had not been tested for alcohol use – due to the 12-hour delay in report.”
Dr. Denman was ultimately required to undergo an alcohol abuse evaluation, enter a treatment program, and sign a 5-year monitoring contract with the Indiana State Medical Association as a condition of her employment, according to the lawsuit. She claimed repercussions from the false allegation resulted in lost compensation, out-of-pocket expenses, emotional distress, and damage to her professional reputation.
She sued the hospital in July 2018, alleging fraud, defamation, tortious interference with an employment relationship, and negligent misrepresentation. After a 4-day trial, jurors found in her favor, awarding Dr. Denman $2 million for her defamation claims, $2 million for her claims of fraud and constructive fraud, $500,000 for her claim of tortious interference with an employment relationship, and $250,000 for her claim of negligent misrepresentation.
A hospital spokesperson said Ascension St Vincent is pursuing an appeal, and that it looks “forward to the opportunity to bring this matter before the Indiana Court of Appeals in June.”
In another case, South Dakota surgeon Linda Miller, MD, was awarded $1.1 million in 2017 after a federal jury found Huron Regional Medical Center breached her contract and violated her due process rights. Dr. Miller became the subject of a peer review at Huron Regional Medical Center when the hospital began analyzing some of her surgery outcomes.
Ken Barker, an attorney for Dr. Miller, said he feels it became evident at trial that the campaign to force Dr. Miller to either resign or lose her privileges was led by the lay board of directors of the hospital and upper-level administration at the hospital.
“They began the process by ordering an unprecedented 90-day review of her medical charts, looking for errors in the medical care she provided patients,” he said. “They could find nothing, so they did a second 90-day review, waiting for a patient’s ‘bad outcome.’ As any general surgeon will say, a ‘bad outcome’ is inevitable. And so it was. Upon that occurrence, they had a medical review committee review the patient’s chart and use it as an excuse to force her to reduce her privileges. Unbeknown to Dr. Miller, an external review had been conducted on another patient’s chart, in which the external review found her care above the standards and, in some measure, ‘exemplary.’ ”
Dr. Miller was eventually pressured to resign, according to her claim. Because of reports made to the NPDB by the medical center, including a patient complication that was allegedly falsified by the hospital, Dr. Miller said she was unable to find work as a general surgeon and went to work as a wound care doctor. At trial, jurors awarded Dr. Miller $586,617 in lost wages, $343,640 for lost future earning capacity, and $250,000 for mental anguish. (The mental anguish award was subsequently struck by a district court.)
Attorneys for Huron Regional Medical Center argued the jury improperly awarded damages and requested a new trial, which was denied by an appeals court.
In the end, the evidence came to light and the jury’s verdict spoke loudly that the hospital had taken unfair advantage of Dr. Miller, Mr. Barker said. But he emphasized that such cases often end differently.
“There are a handful of cases in which physicians like Dr. Miller have challenged the system and won,” he said. “In most cases, however, it is a ‘David vs. Goliath’ scenario where the giant prevails.”
What to do if faced with malicious peer review
An important step when doctors encounter a peer review that they believe is malicious is to consult with an experienced attorney as early as possible, Dr. Huntoon said. “Not all attorneys who set themselves out to be health law attorneys necessarily have knowledge and expertise in sham peer review. And before such a thing happens, I always encourage physicians to read their medical staff bylaws. That’s where everything is set forth, [such as] the corrective action section that tells how peer review is to take place.”
Mr. Barker added that documentation is also key in the event of a potential malicious peer review.
“When a physician senses [the] administration has targeted them, they should start documenting their conversations and actions very carefully, and if possible, recruit another ‘observer’ who can provide a third-party perspective, if necessary,” Mr. Barker said.
Dr. Huntoon recently wrote an article with advice about preparedness and defense of sham peer reviews. The guidance includes that physicians educate themselves about the tactics used by some hospitals to conduct sham peer reviews and the factors that place doctors more at risk. Factors that may raise a doctor’s danger of being targeted include being in solo practice or a small group, being new on staff, or being an older physician approaching retirement as some bad-actor hospitals may view older physicians as being less likely to fight back, said Dr. Huntoon.
Doctors should also keep detailed records and a timeline in the event of a malicious peer review and insist that an independent court reporter record all peer review hearings, even if that means the physician has to pay for the reporter him or herself, according to the guidance. An independent record is invaluable should the physician ultimately issue a future legal challenge against the hospital.
Mr. Willner encourages physicians to call the Center for Peer Review Justice hotline at (504) 621-1670 or visit the website for help with peer review and NPDB issues.
As for Dr. Smith, his days are much quieter and slower today, compared with the active practice he was accustomed to for more than half his life. He misses the fast pace, the patients, and the work that always brought him great joy.
“I hope to get back to doing surgeries eventually,” he said. “I graduated medical school in 1972. Practicing surgery has been my whole life and my career. They have taken my identity and my livelihood away from me based on false numbers and false premises. I want it back.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiothoracic surgeon J. Marvin Smith III, MD, had always thrived on a busy practice schedule, often performing 20-30 surgeries a week. A practicing surgeon for more than 40 years, Dr. Smith said he had no plans to slow down anytime soon.
But Dr. Smith said his career was derailed when leaders at Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio initiated a sudden peer review proceeding against him. The hospital system alleged certain surgeries performed by Dr. Smith had excessive mortality rates. When he proved the data inaccurate, Dr. Smith said administrators next claimed he was cognitively impaired and wasn’t safe to practice.
Dr. Smith has now been embroiled in a peer review dispute with the hospital system for more than 2 years and says the conflict has essentially forced him out of surgical practice. He believes the peer review was “malicious” and was really launched because of complaints he made about nurse staffing and other issues at the hospital.
“I think it is absolutely in bad faith and is disingenuous what they’ve told me along the way,” said Dr. Smith, 73. “It’s because I pointed out deficiencies in nursing care, and they want to get rid of me. It would be a lot easier for them if I had a contract and they could control me better. But the fact that I was independent, meant they had to resort to a malicious peer review to try and push me out.”
Dr. Smith had a peer review hearing with Methodist in March 2021, and in April, a panel found in Dr. Smith’s favor, according to Dr. Smith. The findings were sent to the hospital’s medical board for review, which issued a decision in early May.
Eric A. Pullen, an attorney for Dr. Smith, said he could not go into detail about the board’s decision for legal reasons, but that “the medical board’s decision did not completely resolve the matter, and Dr. Smith intends to exercise his procedural rights, which could include an appeal.”
Methodist Hospital Texsan and its parent company, Methodist Health System of San Antonio, did not respond to messages seeking comment about the case. Without hearing from the hospital system, its side is unknown and it is unclear if there is more to the story from Methodist’s view.
The problem is not new, but some experts, such as Lawrence Huntoon, MD, PhD, say the practice has become more common in recent years, particularly against independent doctors.
Dr. Huntoon believes there is a nationwide trend at many hospitals to get rid of independent physicians and replace them with employed doctors, he said.
However, because most sham peer reviews go on behind closed doors, there are no data to pinpoint its prevalence or measure its growth.
“Independent physicians are basically being purged from medical staffs across the United States,” said Dr. Huntoon, who is chair of the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons’ Committee to Combat Sham Peer Review. “The hospitals want more control over how physicians practice and who they refer to, and they do that by having employees.”
Anthony P. Weiss, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center said it has not been his experience that independent physicians are being targeted in such a way. Dr. Weiss responded to an inquiry sent to the American Hospital Association for this story.
“As the authority for peer review rests with the organized medical staff (i.e., physicians), and not formally with the hospital per se, the peer review lever is not typically available as a management tool for hospital administration,” said Dr. Weiss, who is a former member of the AHA’s Committee on Clinical Leadership, but who was speaking on behalf of himself.
A spokesman for the AHA said the organization stands behinds Dr. Weiss’ comments.
Peer review remains a foundational aspect of overseeing the safety and appropriateness of healthcare provided by physicians, Dr. Weiss said. Peer review likely varies from hospital to hospital, he added, although the Healthcare Quality Improvement Act provides some level of guidance as does the American Medical Association Code of Medical Ethics (section 9.4.1).
“In essence, both require that the evaluation be conducted in good faith with the intention to improve care, by physicians with adequate training and knowledge, using a process that is fair and inclusive of the physician under review,” he said. “I believe that most medical staffs abide by these ethical principles, but we have little data to confirm this supposition.”
Did hospital target doc for being vocal?
When members of Methodist’s medical staff first approached Dr. Smith with concerns about his surgery outcomes in November 2018, the physician says he was surprised, but that he was open to an assessment.
“They came to me and said they thought my numbers were bad, and I said: ‘Well my gosh, I certainly don’t want that to be the case. I need to see what numbers you are talking about,’ ” Dr. Smith recalled. “I’ve been president of the Bexar County Medical Society; I’ve been involved with standards and ethics for the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Quality health care means a whole lot to me.”
The statistical information provided by hospital administrators indicated that Dr. Smith’s mortality rates for coronary artery surgery in 2018 were “excessive” and that his rates for aortic surgery were “unacceptable,” according to a lawsuit Dr. Smith filed against the hospital system. Dr. Smith, who is double boarded with the American Board of Surgery and the American Board of Thoracic Surgery, said his outcomes had never come into question in the past. Dr. Smith said the timing was suspicious to him, however, considering he had recently raised concerns with the hospital through letters about nursing performance, staffing, and compensation.
A peer review investigation was initiated. In the meantime, Dr. Smith agreed to intensivist consults on his postoperative patients and consults with the hospital’s “Heart Team” on all preoperative cardiac, valve, and aortic cases. A vocal critic of the Heart Team, Dr. Smith had long contended the entity provided no meaningful benefit to his patients in most cases and, rather, increased hospital stays and raised medical expenses. Despite his agreement, Dr. Smith was later asked to voluntarily stop performing surgeries at the hospital.
“I agreed, convinced that we’d get this all settled,” he said.
Another report issued by the hospital in 2019 also indicated elevated mortality rates associated with some of Smith’s surgeries, although the document differed from the first report, according to the lawsuit. Dr. Smith says he was ignored when he pointed out problems with the data, including a lack of appropriate risk stratification in the report, departure from Society of Thoracic Surgeons data rules, and improper inclusion of his cases in the denominator of the ratio when a comparison was made of his outcomes with those hospitalwide. A subsequent report from Methodist in March 2019 indicated Dr. Smith’s surgery outcomes were “within the expected parameters of performance,” according to court documents.
The surgery accusations were dropped, but the peer review proceeding against Dr. Smith wasn’t over. The hospital next requested that Dr. Smith undergo a competency evaluation.
“When they realized the data was bad, they then changed their argument in the peer review proceeding and essentially started to argue that Dr. Smith had some sort of cognitive disability that prevented him from continuing to practice,” said Mr. Pullen. “The way I look at it, when the initial basis for the peer review was proven false, the hospital found something else and some other reason to try to keep Dr. Smith from practicing.”
Thus began a lengthy disagreement about which entity would conduct the evaluation, who would pay, and the type of acceptable assessment. An evaluation by the hospital’s preferred organization resulted in a finding of mild cognitive impairment, Dr. Smith said. He hired his own experts who conducted separate evaluations, finding no impairment and no basis for the former evaluation’s conclusion.
“Literally, the determinant as to whether I was normal or below normal on their test was one point, which was associated with a finding that I didn’t draw a clock correctly,” Dr. Smith claimed. “The reviewer said my minute hand was a little too short and docked me a point. It was purely subjective. To me, the gold standard of whether you are learned in thoracic surgery is the American Board of Thoracic Surgery’s test. The board’s test shows my cognitive ability is entirely in keeping with my practice. That contrasts with the one point off I got for drawing a clock wrong in somebody’s estimation.”
Conflict leads to legal case
In September 2020, Dr. Smith filed a lawsuit against Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio, alleging business disparagement by Methodist for allegedly publishing false and disparaging information about Dr. Smith and tortious interference with business relations. The latter claim stems from Methodist refusing to provide documents to other hospitals about the status of Dr. Smith’s privileges at Methodist, Mr. Pullen said.
Because Methodist refused to confirm his status, the renewal process for Baptist Health System could not be completed and Dr. Smith lost his privileges at Baptist Health System facilities, according to the lawsuit.
Notably, Dr. Smith’s legal challenge also asks the court to take a stance against alleged amendments by Methodist to its Unified Medical Staff Bylaws. The hospital allegedly proposed changes that would prevent physicians from seeking legal action against the hospital for malicious peer review, according to Dr. Smith’s lawsuit.
The amendments would make the peer review process itself the “sole and exclusive remedy with respect to any action or recommendation taken at the hospital affecting medical staff appointment and/or clinical privileges,” according to an excerpt of the proposed amendments included in Dr. Smith’s lawsuit. In addition, the changes would hold practitioners liable for lost revenues if the doctor initiates “any type of legal action challenging credentialing, privileging, or other medical peer review or professional review activity,” according to the lawsuit.
Dr. Smith’s lawsuit seeks a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws are “void as against public policy,” and a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws cannot take away physicians’ statutory right to bring litigation against Methodist for malicious peer review.
“The proposed amendments have a tendency to and will injure the public good,” Dr. Smith argued in the lawsuit. “The proposed amendments allow Methodist to act with malice and in bad faith in conducting peer review proceedings and face no legal repercussions.”
Regardless of the final outcome of the peer review proceeding, Mr. Pullen said the harm Dr. Smith has already endured cannot be reversed.
“Even if comes out in his favor, the damage is already done,” he said. “It will not remedy the damage Dr. Smith has incurred.”
Fighting sham peer review is difficult
Battling a malicious peer review has long been an uphill battle for physicians, according to Dr. Huntoon. That’s because the Health Care Quality Improvement Act (HCQIA), a federal law passed in 1986, provides near absolute immunity to hospitals and peer reviewers in legal disputes.
The HCQIA was created by Congress to extend immunity to good-faith peer review of doctors and to increase overall participation in peer review by removing fear of litigation. However, the act has also enabled abuse of peer review by shielding bad-faith reviewers from accountability, said Dr. Huntoon.
“The Health Care Quality Improvement Act presumes that what the hospital did was warranted and reasonable and shifts the burden to the physician to prove his innocence by a preponderance of evidence,” he said. “That’s an entirely foreign concept to most people who think a person should be considered innocent until proven guilty. Here, it’s the exact opposite.”
The HCQIA has been challenged numerous times over the years and tested at the appellate level, but continues to survive and remain settled law, added Richard B. Willner, DPM, founder and director of the Center for Peer Review Justice, which assists and counsels physicians about sham peer review.
In 2011, former Rep. Joe Heck, DO, (R-Nev.) introduced a bill that would have amended the HCQIA to prohibit a professional review entity from submitting a report to the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) while the doctor was still under investigation and before the doctor was afforded adequate notice and a hearing. Although the measure had 16 cosponsors and plenty of support from the physician community, it failed.
In addition to a heavy legal burden, physicians who experience malicious peer reviews also face ramifications from being reported to the NPDB. Peer review organizations are required to report certain negative actions or findings to the NPDB.
“A databank entry is a scarlet letter on your forehead,” Dr. Willner said. “The rules at a lot of institutions are not to take anyone who has been databanked, rightfully or wrongfully. And what is the evidence necessary to databank you? None. There’s no evidence needed to databank somebody.”
Despite the bleak landscape, experts say progress has been made on a case-by-case basis by physicians who have succeeded in fighting back against questionable peer reviews in recent years.
In January 2020, Indiana ob.gyn. Rebecca Denman, MD, prevailed in her defamation lawsuit against St Vincent Carmel Hospital and St Vincent Carmel Medical Group, winning $4.75 million in damages. Dr. Denman alleged administrators failed to conduct a proper peer review investigation after a false allegation by a nurse that she was under the influence while on the job.
Indianapolis attorney Kathleen A. DeLaney, who represented Dr. Denman, said hospital leaders misled Dr. Denman into believing a peer review had occurred when no formal peer review hearing or proceeding took place.
“The CMO of the medical group claimed that he performed a peer review ‘screening,’ but he never informed the other members of the peer review executive committee of the matter until after he had placed Dr. Denman on administrative leave,” Ms. DeLaney said. “He also neglected to tell the peer review executive committee that the substance abuse policy had not been followed, or that Dr. Denman had not been tested for alcohol use – due to the 12-hour delay in report.”
Dr. Denman was ultimately required to undergo an alcohol abuse evaluation, enter a treatment program, and sign a 5-year monitoring contract with the Indiana State Medical Association as a condition of her employment, according to the lawsuit. She claimed repercussions from the false allegation resulted in lost compensation, out-of-pocket expenses, emotional distress, and damage to her professional reputation.
She sued the hospital in July 2018, alleging fraud, defamation, tortious interference with an employment relationship, and negligent misrepresentation. After a 4-day trial, jurors found in her favor, awarding Dr. Denman $2 million for her defamation claims, $2 million for her claims of fraud and constructive fraud, $500,000 for her claim of tortious interference with an employment relationship, and $250,000 for her claim of negligent misrepresentation.
A hospital spokesperson said Ascension St Vincent is pursuing an appeal, and that it looks “forward to the opportunity to bring this matter before the Indiana Court of Appeals in June.”
In another case, South Dakota surgeon Linda Miller, MD, was awarded $1.1 million in 2017 after a federal jury found Huron Regional Medical Center breached her contract and violated her due process rights. Dr. Miller became the subject of a peer review at Huron Regional Medical Center when the hospital began analyzing some of her surgery outcomes.
Ken Barker, an attorney for Dr. Miller, said he feels it became evident at trial that the campaign to force Dr. Miller to either resign or lose her privileges was led by the lay board of directors of the hospital and upper-level administration at the hospital.
“They began the process by ordering an unprecedented 90-day review of her medical charts, looking for errors in the medical care she provided patients,” he said. “They could find nothing, so they did a second 90-day review, waiting for a patient’s ‘bad outcome.’ As any general surgeon will say, a ‘bad outcome’ is inevitable. And so it was. Upon that occurrence, they had a medical review committee review the patient’s chart and use it as an excuse to force her to reduce her privileges. Unbeknown to Dr. Miller, an external review had been conducted on another patient’s chart, in which the external review found her care above the standards and, in some measure, ‘exemplary.’ ”
Dr. Miller was eventually pressured to resign, according to her claim. Because of reports made to the NPDB by the medical center, including a patient complication that was allegedly falsified by the hospital, Dr. Miller said she was unable to find work as a general surgeon and went to work as a wound care doctor. At trial, jurors awarded Dr. Miller $586,617 in lost wages, $343,640 for lost future earning capacity, and $250,000 for mental anguish. (The mental anguish award was subsequently struck by a district court.)
Attorneys for Huron Regional Medical Center argued the jury improperly awarded damages and requested a new trial, which was denied by an appeals court.
In the end, the evidence came to light and the jury’s verdict spoke loudly that the hospital had taken unfair advantage of Dr. Miller, Mr. Barker said. But he emphasized that such cases often end differently.
“There are a handful of cases in which physicians like Dr. Miller have challenged the system and won,” he said. “In most cases, however, it is a ‘David vs. Goliath’ scenario where the giant prevails.”
What to do if faced with malicious peer review
An important step when doctors encounter a peer review that they believe is malicious is to consult with an experienced attorney as early as possible, Dr. Huntoon said. “Not all attorneys who set themselves out to be health law attorneys necessarily have knowledge and expertise in sham peer review. And before such a thing happens, I always encourage physicians to read their medical staff bylaws. That’s where everything is set forth, [such as] the corrective action section that tells how peer review is to take place.”
Mr. Barker added that documentation is also key in the event of a potential malicious peer review.
“When a physician senses [the] administration has targeted them, they should start documenting their conversations and actions very carefully, and if possible, recruit another ‘observer’ who can provide a third-party perspective, if necessary,” Mr. Barker said.
Dr. Huntoon recently wrote an article with advice about preparedness and defense of sham peer reviews. The guidance includes that physicians educate themselves about the tactics used by some hospitals to conduct sham peer reviews and the factors that place doctors more at risk. Factors that may raise a doctor’s danger of being targeted include being in solo practice or a small group, being new on staff, or being an older physician approaching retirement as some bad-actor hospitals may view older physicians as being less likely to fight back, said Dr. Huntoon.
Doctors should also keep detailed records and a timeline in the event of a malicious peer review and insist that an independent court reporter record all peer review hearings, even if that means the physician has to pay for the reporter him or herself, according to the guidance. An independent record is invaluable should the physician ultimately issue a future legal challenge against the hospital.
Mr. Willner encourages physicians to call the Center for Peer Review Justice hotline at (504) 621-1670 or visit the website for help with peer review and NPDB issues.
As for Dr. Smith, his days are much quieter and slower today, compared with the active practice he was accustomed to for more than half his life. He misses the fast pace, the patients, and the work that always brought him great joy.
“I hope to get back to doing surgeries eventually,” he said. “I graduated medical school in 1972. Practicing surgery has been my whole life and my career. They have taken my identity and my livelihood away from me based on false numbers and false premises. I want it back.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiothoracic surgeon J. Marvin Smith III, MD, had always thrived on a busy practice schedule, often performing 20-30 surgeries a week. A practicing surgeon for more than 40 years, Dr. Smith said he had no plans to slow down anytime soon.
But Dr. Smith said his career was derailed when leaders at Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio initiated a sudden peer review proceeding against him. The hospital system alleged certain surgeries performed by Dr. Smith had excessive mortality rates. When he proved the data inaccurate, Dr. Smith said administrators next claimed he was cognitively impaired and wasn’t safe to practice.
Dr. Smith has now been embroiled in a peer review dispute with the hospital system for more than 2 years and says the conflict has essentially forced him out of surgical practice. He believes the peer review was “malicious” and was really launched because of complaints he made about nurse staffing and other issues at the hospital.
“I think it is absolutely in bad faith and is disingenuous what they’ve told me along the way,” said Dr. Smith, 73. “It’s because I pointed out deficiencies in nursing care, and they want to get rid of me. It would be a lot easier for them if I had a contract and they could control me better. But the fact that I was independent, meant they had to resort to a malicious peer review to try and push me out.”
Dr. Smith had a peer review hearing with Methodist in March 2021, and in April, a panel found in Dr. Smith’s favor, according to Dr. Smith. The findings were sent to the hospital’s medical board for review, which issued a decision in early May.
Eric A. Pullen, an attorney for Dr. Smith, said he could not go into detail about the board’s decision for legal reasons, but that “the medical board’s decision did not completely resolve the matter, and Dr. Smith intends to exercise his procedural rights, which could include an appeal.”
Methodist Hospital Texsan and its parent company, Methodist Health System of San Antonio, did not respond to messages seeking comment about the case. Without hearing from the hospital system, its side is unknown and it is unclear if there is more to the story from Methodist’s view.
The problem is not new, but some experts, such as Lawrence Huntoon, MD, PhD, say the practice has become more common in recent years, particularly against independent doctors.
Dr. Huntoon believes there is a nationwide trend at many hospitals to get rid of independent physicians and replace them with employed doctors, he said.
However, because most sham peer reviews go on behind closed doors, there are no data to pinpoint its prevalence or measure its growth.
“Independent physicians are basically being purged from medical staffs across the United States,” said Dr. Huntoon, who is chair of the Association of American Physicians and Surgeons’ Committee to Combat Sham Peer Review. “The hospitals want more control over how physicians practice and who they refer to, and they do that by having employees.”
Anthony P. Weiss, MD, MBA, chief medical officer for Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center said it has not been his experience that independent physicians are being targeted in such a way. Dr. Weiss responded to an inquiry sent to the American Hospital Association for this story.
“As the authority for peer review rests with the organized medical staff (i.e., physicians), and not formally with the hospital per se, the peer review lever is not typically available as a management tool for hospital administration,” said Dr. Weiss, who is a former member of the AHA’s Committee on Clinical Leadership, but who was speaking on behalf of himself.
A spokesman for the AHA said the organization stands behinds Dr. Weiss’ comments.
Peer review remains a foundational aspect of overseeing the safety and appropriateness of healthcare provided by physicians, Dr. Weiss said. Peer review likely varies from hospital to hospital, he added, although the Healthcare Quality Improvement Act provides some level of guidance as does the American Medical Association Code of Medical Ethics (section 9.4.1).
“In essence, both require that the evaluation be conducted in good faith with the intention to improve care, by physicians with adequate training and knowledge, using a process that is fair and inclusive of the physician under review,” he said. “I believe that most medical staffs abide by these ethical principles, but we have little data to confirm this supposition.”
Did hospital target doc for being vocal?
When members of Methodist’s medical staff first approached Dr. Smith with concerns about his surgery outcomes in November 2018, the physician says he was surprised, but that he was open to an assessment.
“They came to me and said they thought my numbers were bad, and I said: ‘Well my gosh, I certainly don’t want that to be the case. I need to see what numbers you are talking about,’ ” Dr. Smith recalled. “I’ve been president of the Bexar County Medical Society; I’ve been involved with standards and ethics for the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Quality health care means a whole lot to me.”
The statistical information provided by hospital administrators indicated that Dr. Smith’s mortality rates for coronary artery surgery in 2018 were “excessive” and that his rates for aortic surgery were “unacceptable,” according to a lawsuit Dr. Smith filed against the hospital system. Dr. Smith, who is double boarded with the American Board of Surgery and the American Board of Thoracic Surgery, said his outcomes had never come into question in the past. Dr. Smith said the timing was suspicious to him, however, considering he had recently raised concerns with the hospital through letters about nursing performance, staffing, and compensation.
A peer review investigation was initiated. In the meantime, Dr. Smith agreed to intensivist consults on his postoperative patients and consults with the hospital’s “Heart Team” on all preoperative cardiac, valve, and aortic cases. A vocal critic of the Heart Team, Dr. Smith had long contended the entity provided no meaningful benefit to his patients in most cases and, rather, increased hospital stays and raised medical expenses. Despite his agreement, Dr. Smith was later asked to voluntarily stop performing surgeries at the hospital.
“I agreed, convinced that we’d get this all settled,” he said.
Another report issued by the hospital in 2019 also indicated elevated mortality rates associated with some of Smith’s surgeries, although the document differed from the first report, according to the lawsuit. Dr. Smith says he was ignored when he pointed out problems with the data, including a lack of appropriate risk stratification in the report, departure from Society of Thoracic Surgeons data rules, and improper inclusion of his cases in the denominator of the ratio when a comparison was made of his outcomes with those hospitalwide. A subsequent report from Methodist in March 2019 indicated Dr. Smith’s surgery outcomes were “within the expected parameters of performance,” according to court documents.
The surgery accusations were dropped, but the peer review proceeding against Dr. Smith wasn’t over. The hospital next requested that Dr. Smith undergo a competency evaluation.
“When they realized the data was bad, they then changed their argument in the peer review proceeding and essentially started to argue that Dr. Smith had some sort of cognitive disability that prevented him from continuing to practice,” said Mr. Pullen. “The way I look at it, when the initial basis for the peer review was proven false, the hospital found something else and some other reason to try to keep Dr. Smith from practicing.”
Thus began a lengthy disagreement about which entity would conduct the evaluation, who would pay, and the type of acceptable assessment. An evaluation by the hospital’s preferred organization resulted in a finding of mild cognitive impairment, Dr. Smith said. He hired his own experts who conducted separate evaluations, finding no impairment and no basis for the former evaluation’s conclusion.
“Literally, the determinant as to whether I was normal or below normal on their test was one point, which was associated with a finding that I didn’t draw a clock correctly,” Dr. Smith claimed. “The reviewer said my minute hand was a little too short and docked me a point. It was purely subjective. To me, the gold standard of whether you are learned in thoracic surgery is the American Board of Thoracic Surgery’s test. The board’s test shows my cognitive ability is entirely in keeping with my practice. That contrasts with the one point off I got for drawing a clock wrong in somebody’s estimation.”
Conflict leads to legal case
In September 2020, Dr. Smith filed a lawsuit against Methodist Healthcare System of San Antonio, alleging business disparagement by Methodist for allegedly publishing false and disparaging information about Dr. Smith and tortious interference with business relations. The latter claim stems from Methodist refusing to provide documents to other hospitals about the status of Dr. Smith’s privileges at Methodist, Mr. Pullen said.
Because Methodist refused to confirm his status, the renewal process for Baptist Health System could not be completed and Dr. Smith lost his privileges at Baptist Health System facilities, according to the lawsuit.
Notably, Dr. Smith’s legal challenge also asks the court to take a stance against alleged amendments by Methodist to its Unified Medical Staff Bylaws. The hospital allegedly proposed changes that would prevent physicians from seeking legal action against the hospital for malicious peer review, according to Dr. Smith’s lawsuit.
The amendments would make the peer review process itself the “sole and exclusive remedy with respect to any action or recommendation taken at the hospital affecting medical staff appointment and/or clinical privileges,” according to an excerpt of the proposed amendments included in Dr. Smith’s lawsuit. In addition, the changes would hold practitioners liable for lost revenues if the doctor initiates “any type of legal action challenging credentialing, privileging, or other medical peer review or professional review activity,” according to the lawsuit.
Dr. Smith’s lawsuit seeks a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws are “void as against public policy,” and a declaration that the proposed amendments to the bylaws cannot take away physicians’ statutory right to bring litigation against Methodist for malicious peer review.
“The proposed amendments have a tendency to and will injure the public good,” Dr. Smith argued in the lawsuit. “The proposed amendments allow Methodist to act with malice and in bad faith in conducting peer review proceedings and face no legal repercussions.”
Regardless of the final outcome of the peer review proceeding, Mr. Pullen said the harm Dr. Smith has already endured cannot be reversed.
“Even if comes out in his favor, the damage is already done,” he said. “It will not remedy the damage Dr. Smith has incurred.”
Fighting sham peer review is difficult
Battling a malicious peer review has long been an uphill battle for physicians, according to Dr. Huntoon. That’s because the Health Care Quality Improvement Act (HCQIA), a federal law passed in 1986, provides near absolute immunity to hospitals and peer reviewers in legal disputes.
The HCQIA was created by Congress to extend immunity to good-faith peer review of doctors and to increase overall participation in peer review by removing fear of litigation. However, the act has also enabled abuse of peer review by shielding bad-faith reviewers from accountability, said Dr. Huntoon.
“The Health Care Quality Improvement Act presumes that what the hospital did was warranted and reasonable and shifts the burden to the physician to prove his innocence by a preponderance of evidence,” he said. “That’s an entirely foreign concept to most people who think a person should be considered innocent until proven guilty. Here, it’s the exact opposite.”
The HCQIA has been challenged numerous times over the years and tested at the appellate level, but continues to survive and remain settled law, added Richard B. Willner, DPM, founder and director of the Center for Peer Review Justice, which assists and counsels physicians about sham peer review.
In 2011, former Rep. Joe Heck, DO, (R-Nev.) introduced a bill that would have amended the HCQIA to prohibit a professional review entity from submitting a report to the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) while the doctor was still under investigation and before the doctor was afforded adequate notice and a hearing. Although the measure had 16 cosponsors and plenty of support from the physician community, it failed.
In addition to a heavy legal burden, physicians who experience malicious peer reviews also face ramifications from being reported to the NPDB. Peer review organizations are required to report certain negative actions or findings to the NPDB.
“A databank entry is a scarlet letter on your forehead,” Dr. Willner said. “The rules at a lot of institutions are not to take anyone who has been databanked, rightfully or wrongfully. And what is the evidence necessary to databank you? None. There’s no evidence needed to databank somebody.”
Despite the bleak landscape, experts say progress has been made on a case-by-case basis by physicians who have succeeded in fighting back against questionable peer reviews in recent years.
In January 2020, Indiana ob.gyn. Rebecca Denman, MD, prevailed in her defamation lawsuit against St Vincent Carmel Hospital and St Vincent Carmel Medical Group, winning $4.75 million in damages. Dr. Denman alleged administrators failed to conduct a proper peer review investigation after a false allegation by a nurse that she was under the influence while on the job.
Indianapolis attorney Kathleen A. DeLaney, who represented Dr. Denman, said hospital leaders misled Dr. Denman into believing a peer review had occurred when no formal peer review hearing or proceeding took place.
“The CMO of the medical group claimed that he performed a peer review ‘screening,’ but he never informed the other members of the peer review executive committee of the matter until after he had placed Dr. Denman on administrative leave,” Ms. DeLaney said. “He also neglected to tell the peer review executive committee that the substance abuse policy had not been followed, or that Dr. Denman had not been tested for alcohol use – due to the 12-hour delay in report.”
Dr. Denman was ultimately required to undergo an alcohol abuse evaluation, enter a treatment program, and sign a 5-year monitoring contract with the Indiana State Medical Association as a condition of her employment, according to the lawsuit. She claimed repercussions from the false allegation resulted in lost compensation, out-of-pocket expenses, emotional distress, and damage to her professional reputation.
She sued the hospital in July 2018, alleging fraud, defamation, tortious interference with an employment relationship, and negligent misrepresentation. After a 4-day trial, jurors found in her favor, awarding Dr. Denman $2 million for her defamation claims, $2 million for her claims of fraud and constructive fraud, $500,000 for her claim of tortious interference with an employment relationship, and $250,000 for her claim of negligent misrepresentation.
A hospital spokesperson said Ascension St Vincent is pursuing an appeal, and that it looks “forward to the opportunity to bring this matter before the Indiana Court of Appeals in June.”
In another case, South Dakota surgeon Linda Miller, MD, was awarded $1.1 million in 2017 after a federal jury found Huron Regional Medical Center breached her contract and violated her due process rights. Dr. Miller became the subject of a peer review at Huron Regional Medical Center when the hospital began analyzing some of her surgery outcomes.
Ken Barker, an attorney for Dr. Miller, said he feels it became evident at trial that the campaign to force Dr. Miller to either resign or lose her privileges was led by the lay board of directors of the hospital and upper-level administration at the hospital.
“They began the process by ordering an unprecedented 90-day review of her medical charts, looking for errors in the medical care she provided patients,” he said. “They could find nothing, so they did a second 90-day review, waiting for a patient’s ‘bad outcome.’ As any general surgeon will say, a ‘bad outcome’ is inevitable. And so it was. Upon that occurrence, they had a medical review committee review the patient’s chart and use it as an excuse to force her to reduce her privileges. Unbeknown to Dr. Miller, an external review had been conducted on another patient’s chart, in which the external review found her care above the standards and, in some measure, ‘exemplary.’ ”
Dr. Miller was eventually pressured to resign, according to her claim. Because of reports made to the NPDB by the medical center, including a patient complication that was allegedly falsified by the hospital, Dr. Miller said she was unable to find work as a general surgeon and went to work as a wound care doctor. At trial, jurors awarded Dr. Miller $586,617 in lost wages, $343,640 for lost future earning capacity, and $250,000 for mental anguish. (The mental anguish award was subsequently struck by a district court.)
Attorneys for Huron Regional Medical Center argued the jury improperly awarded damages and requested a new trial, which was denied by an appeals court.
In the end, the evidence came to light and the jury’s verdict spoke loudly that the hospital had taken unfair advantage of Dr. Miller, Mr. Barker said. But he emphasized that such cases often end differently.
“There are a handful of cases in which physicians like Dr. Miller have challenged the system and won,” he said. “In most cases, however, it is a ‘David vs. Goliath’ scenario where the giant prevails.”
What to do if faced with malicious peer review
An important step when doctors encounter a peer review that they believe is malicious is to consult with an experienced attorney as early as possible, Dr. Huntoon said. “Not all attorneys who set themselves out to be health law attorneys necessarily have knowledge and expertise in sham peer review. And before such a thing happens, I always encourage physicians to read their medical staff bylaws. That’s where everything is set forth, [such as] the corrective action section that tells how peer review is to take place.”
Mr. Barker added that documentation is also key in the event of a potential malicious peer review.
“When a physician senses [the] administration has targeted them, they should start documenting their conversations and actions very carefully, and if possible, recruit another ‘observer’ who can provide a third-party perspective, if necessary,” Mr. Barker said.
Dr. Huntoon recently wrote an article with advice about preparedness and defense of sham peer reviews. The guidance includes that physicians educate themselves about the tactics used by some hospitals to conduct sham peer reviews and the factors that place doctors more at risk. Factors that may raise a doctor’s danger of being targeted include being in solo practice or a small group, being new on staff, or being an older physician approaching retirement as some bad-actor hospitals may view older physicians as being less likely to fight back, said Dr. Huntoon.
Doctors should also keep detailed records and a timeline in the event of a malicious peer review and insist that an independent court reporter record all peer review hearings, even if that means the physician has to pay for the reporter him or herself, according to the guidance. An independent record is invaluable should the physician ultimately issue a future legal challenge against the hospital.
Mr. Willner encourages physicians to call the Center for Peer Review Justice hotline at (504) 621-1670 or visit the website for help with peer review and NPDB issues.
As for Dr. Smith, his days are much quieter and slower today, compared with the active practice he was accustomed to for more than half his life. He misses the fast pace, the patients, and the work that always brought him great joy.
“I hope to get back to doing surgeries eventually,” he said. “I graduated medical school in 1972. Practicing surgery has been my whole life and my career. They have taken my identity and my livelihood away from me based on false numbers and false premises. I want it back.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.