User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


New cases of child COVID-19 drop for fifth straight week
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
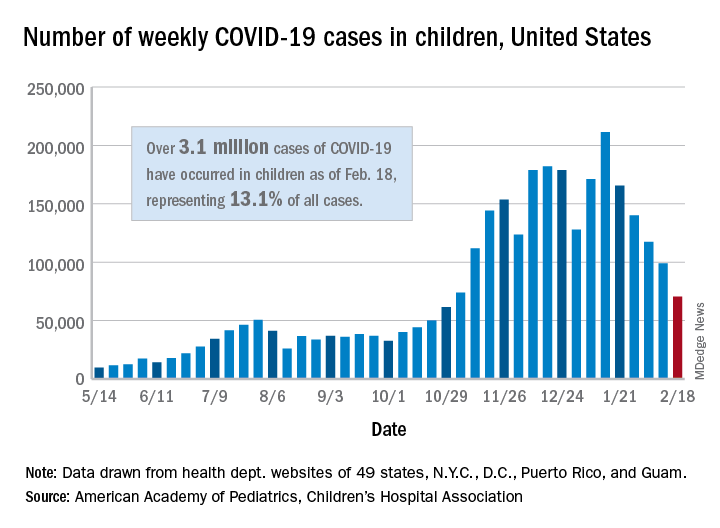
, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
The fifth consecutive week with a decline has the number of new COVID-19 cases in children at its lowest level since late October, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

, when 61,000 cases were reported, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID-19 report.
The cumulative number of COVID-19 cases in children is now just over 3.1 million, which represents 13.1% of cases among all ages in the United States, based on data gathered from the health departments of 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
More children in California (439,000) have been infected than in any other state, while Illinois (176,000), Florida (145,000), Tennessee (137,000), Arizona (127,000), Ohio (121,000), and Pennsylvania (111,000) are the only other states with more than 100,000 cases, the AAP/CHA report shows.
Proportionally, the children of Wyoming have been hardest hit: Pediatric cases represent 19.4% of all cases in the state. The other four states with proportions of 18% or more are Alaska, Vermont, South Carolina, and Tennessee. Cumulative rates, however, tell a somewhat different story, as North Dakota leads with just over 8,500 cases per 100,000 children, followed by Tennessee (7,700 per 100,000) and Rhode Island (7,000 per 100,000), the AAP and CHA said.
Deaths in children, which had not been following the trend of fewer new cases over the last few weeks, dropped below double digits for the first time in a month. The six deaths that occurred during the week of Feb. 12-18 bring the total to 247 since the start of the pandemic in the 43 states, along with New York City and Guam, that are reporting such data, according to the report.
Accessing data during EHR downtime
Reducing loss of efficiency
Electronic health record (EHR) implementations involve long downtimes, which are an under-recognized patient safety risk, as clinicians are forced to switch to completely manual, paper-based, and important unfamiliar workflows to care for their acutely ill patients, said Subha Airan-Javia, MD, FAMIA, a hospitalist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In this setting, we discovered an unanticipated benefit of our tool [Carelign, initially built to digitize the handoff process] as a clinical resource during EHR downtime, giving clinicians access to critical data as well as an electronic platform to collaborate as a team around the care of their patients,” she said.
There are two important takeaways from their study on this issue. “The first is that Carelign was able to give clinicians access to clinical data that would otherwise have been unavailable, including vitals, labs, medications, care plans and care team assignments,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “This undoubtedly mitigated patient safety risks during the EHR downtime.”
The second: “As many clinicians know, any change in workflow, even for a few hours, can make providing a high level of patient care very difficult,” she added. “During a downtime without a tool like Carelign, clinicians have to rely on paper and bedside charts, writing notes on paper and then re-typing them into the EHR when it is back up. This adds to the already excessive amount of administrative work that is burning clinicians out.” Using a tool like Carelign means no such loss in efficiency.
“A tool like Carelign, particularly because it is something that can be used without having to integrate it with the EHR, can put some control back into a hospitalist’s hands, to have a say in their workflow,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “In a world where EHRs are designed to optimize billing, it can be game-changer to have a tool like Carelign that was created by a practicing clinician, for clinicians. Anyone interested in this area is welcome to reach out to me at subhaairan@gmail.com for collaboration or more information.”
Reference
1. Airan-Javia SL, et al. Mind the gap: Revolutionizing the EHR downtime experience with an interoperable workflow tool. Abstract published at Hospital Medicine 2019, March 24-27, National Harbor, Md. Abstract 380. https://www.shmabstracts.com/abstract/mind-the-gap-revolutionizing-the-ehr-downtime-experience-with-an-interoperable-workflow-tool/. Accessed Dec 11, 2019.
Reducing loss of efficiency
Reducing loss of efficiency
Electronic health record (EHR) implementations involve long downtimes, which are an under-recognized patient safety risk, as clinicians are forced to switch to completely manual, paper-based, and important unfamiliar workflows to care for their acutely ill patients, said Subha Airan-Javia, MD, FAMIA, a hospitalist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In this setting, we discovered an unanticipated benefit of our tool [Carelign, initially built to digitize the handoff process] as a clinical resource during EHR downtime, giving clinicians access to critical data as well as an electronic platform to collaborate as a team around the care of their patients,” she said.
There are two important takeaways from their study on this issue. “The first is that Carelign was able to give clinicians access to clinical data that would otherwise have been unavailable, including vitals, labs, medications, care plans and care team assignments,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “This undoubtedly mitigated patient safety risks during the EHR downtime.”
The second: “As many clinicians know, any change in workflow, even for a few hours, can make providing a high level of patient care very difficult,” she added. “During a downtime without a tool like Carelign, clinicians have to rely on paper and bedside charts, writing notes on paper and then re-typing them into the EHR when it is back up. This adds to the already excessive amount of administrative work that is burning clinicians out.” Using a tool like Carelign means no such loss in efficiency.
“A tool like Carelign, particularly because it is something that can be used without having to integrate it with the EHR, can put some control back into a hospitalist’s hands, to have a say in their workflow,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “In a world where EHRs are designed to optimize billing, it can be game-changer to have a tool like Carelign that was created by a practicing clinician, for clinicians. Anyone interested in this area is welcome to reach out to me at subhaairan@gmail.com for collaboration or more information.”
Reference
1. Airan-Javia SL, et al. Mind the gap: Revolutionizing the EHR downtime experience with an interoperable workflow tool. Abstract published at Hospital Medicine 2019, March 24-27, National Harbor, Md. Abstract 380. https://www.shmabstracts.com/abstract/mind-the-gap-revolutionizing-the-ehr-downtime-experience-with-an-interoperable-workflow-tool/. Accessed Dec 11, 2019.
Electronic health record (EHR) implementations involve long downtimes, which are an under-recognized patient safety risk, as clinicians are forced to switch to completely manual, paper-based, and important unfamiliar workflows to care for their acutely ill patients, said Subha Airan-Javia, MD, FAMIA, a hospitalist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“In this setting, we discovered an unanticipated benefit of our tool [Carelign, initially built to digitize the handoff process] as a clinical resource during EHR downtime, giving clinicians access to critical data as well as an electronic platform to collaborate as a team around the care of their patients,” she said.
There are two important takeaways from their study on this issue. “The first is that Carelign was able to give clinicians access to clinical data that would otherwise have been unavailable, including vitals, labs, medications, care plans and care team assignments,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “This undoubtedly mitigated patient safety risks during the EHR downtime.”
The second: “As many clinicians know, any change in workflow, even for a few hours, can make providing a high level of patient care very difficult,” she added. “During a downtime without a tool like Carelign, clinicians have to rely on paper and bedside charts, writing notes on paper and then re-typing them into the EHR when it is back up. This adds to the already excessive amount of administrative work that is burning clinicians out.” Using a tool like Carelign means no such loss in efficiency.
“A tool like Carelign, particularly because it is something that can be used without having to integrate it with the EHR, can put some control back into a hospitalist’s hands, to have a say in their workflow,” Dr. Airan-Javia said. “In a world where EHRs are designed to optimize billing, it can be game-changer to have a tool like Carelign that was created by a practicing clinician, for clinicians. Anyone interested in this area is welcome to reach out to me at subhaairan@gmail.com for collaboration or more information.”
Reference
1. Airan-Javia SL, et al. Mind the gap: Revolutionizing the EHR downtime experience with an interoperable workflow tool. Abstract published at Hospital Medicine 2019, March 24-27, National Harbor, Md. Abstract 380. https://www.shmabstracts.com/abstract/mind-the-gap-revolutionizing-the-ehr-downtime-experience-with-an-interoperable-workflow-tool/. Accessed Dec 11, 2019.
Variants spur new FDA guidance on COVID vaccines, tests, drugs
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The United States is currently facing three main variant threats, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: B.1.1.7, which originated in the United Kingdom; B.1.351 from South Africa; and the P.1 variant, which originated in Brazil.
Acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said on a telephone press briefing call Feb. 22 that the FDA has already been communicating with individual manufacturers as they assess the variants’ effect on their products, but these guidelines are issued for the sake of transparency and to welcome scientific input.
Tailoring may be necessary
Dr. Woodcock emphasized that, “at this time, available data suggest the FDA-authorized vaccines are effective in protecting circulating strains of SARS-CoV-2.” However, in the event the strains start to show resistance, it may be necessary to tailor the vaccine to the variant.
In that case, effectiveness of a modified vaccine should be determined by data from clinical immunogenicity studies, which would compare a recipient’s immune response with virus variants induced by the modified vaccine against the immune response to the authorized vaccine, the guidance states.
Manufacturers should also study the vaccine in both nonvaccinated people and people fully vaccinated with the authorized vaccine, according to the guidance.
Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said on the call that the clinical immunogenicity data is needed to understand, for instance, whether a new vaccine strain is able to cover the new and old strain or whether it just covers the new strain. Information is also needed to understand whether the modified vaccine, when given to someone fully vaccinated, will still promote a positive response without introducing safety concerns.
Further discussions will be necessary to decide whether future modified vaccines may be authorized without the need for clinical studies.
Variants and testing
The FDA’s updated guidance for test developers, Policy for Evaluating Impact of Viral Mutations on COVID-19 Tests, includes information that test performance can be influenced by the sequence of the variant, prevalence of the variant in the population, or design of the test. For example, molecular tests designed to detect multiple SARS-CoV-2 genetic targets are less susceptible to genetic variants than tests designed to detect a single genetic target.
The FDA already issued a safety alert on Jan. 8 to caution that genetic mutations to the virus in a patient sample can potentially change the performance of a diagnostic test. The FDA identified three tests that had been granted emergency-use authorization (EUA) that are known to be affected.
However, Dr. Woodcock said on the call, “at this time the impact does not appear to be significant.”
Updated guidance for therapeutics
The FDA has issued new guidance on the effect of variants on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“The FDA is aware that some of the monoclonal antibodies that have been authorized are less active against some of the SARS-CoV-2 variants that have emerged,” the FDA noted in its press release. “This guidance provides recommendations on efficient approaches to the generation of ... manufacturing and controls data that could potentially support an EUA for monoclonal antibody products that may be effective against emerging variants.”
While the FDA is monitoring the effects of variants, manufacturers bear a lot of the responsibility as well.
The FDA added: “With these guidances, the FDA is encouraging developers of drugs or biological products targeting SARS-CoV-2 to continuously monitor genomic databases for emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and evaluate phenotypically any specific variants in the product target that are becoming prevalent or could potentially impact its activity.”
Dr.Woodcock added that “we urge all Americans to continue to get tested, get their vaccines when available, and follow important heath measures such as handwashing, masking, and social distancing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New light cast on type 2 MI aims to sharpen diagnosis, therapy
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.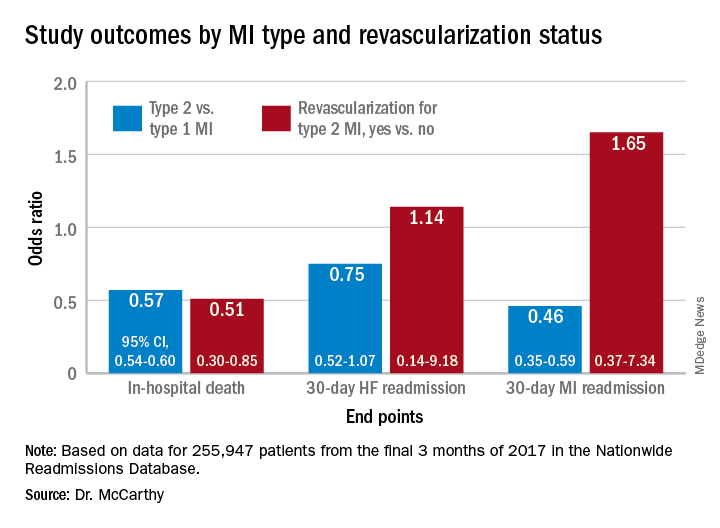
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The hospital and postdischarge course of patients diagnosed with type 2 myocardial infarction, triggered when myocardial oxygen demand outstrips supply, differs in telling ways from those with the more common atherothrombotic type 1 MI, suggests a new registry analysis that aims to lift a cloud of confusion surrounding their management.
The observational study of more than 250,000 patients with either form of MI, said to be the largest of its kind, points to widespread unfamiliarity with distinctions between the two, and the diagnostic and therapeutic implications of misclassification. It suggests, in particular, that type 2 MI may be grossly underdiagnosed and undertreated.
The minority of patients with type 2 MI were more likely female and to have heart failure (HF), renal disease, valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, and less likely to have a lipid disorder, compared with those with type 1 MI. They were one-fifth as likely to be referred for coronary angiography and 20 times less likely to undergo revascularization.
Indeed, only about 2% of the type 2 cohort ultimately underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary bypass surgery (CABG). Yet the analysis suggests that cardiovascular risk climbs regardless of MI type and that in patients with type 2 MI, coronary revascularization might well cut the risk of death in half over the short term.
There were also disparities in clinical outcomes in the analysis, based on data from the final 3 months of 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database, which reportedly documents almost 60% of hospitalizations in the United States.
For example, those with type 1 or type 2 MI – as characterized in the then-current third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction and today’s UDMI-4 – were comparably at risk for both 30-day all-cause readmission and HF readmission. But type 2 patients were less likely to die in the hospital or be readmitted within 30 days for recurrent MI.
Revascularization uncertainty
Importantly, the study’s 3-month observation period immediately followed the debut of a code specifically for type 2 MI in the ICD-10-CM system.
Type 2 accounted for about 15% of MIs during that period, the percentage climbing sharply from the first to the third month. That suggests clinicians were still getting used to the code during the early weeks, “undercoding” for type-2 MI at first but less so after some experience, Cian P. McCarthy, MB, BCh, BAO, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“I can imagine that as people become more aware of the coding, using it more often, the proportion of type 2 MI relative to the total MI cases will probably be much higher,” said McCarthy, lead author on the study published online Feb. 15, 2021, in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
What had been understood about type 2 MI came largely from single-center studies, he said. This “first national study of type-2 MI in the United States” sought to determine whether such findings are hospital specific or “representative of what people are doing nationally.”
The new analysis largely confirms that patients with type 2 MI are typically burdened with multiple comorbidities, Dr. McCarthy said, but also suggests that type 2 often was, and likely still is, incorrectly classified as type 1. So, it was “surprising” that they were rarely referred for angiography. “Only 1 in 50 received revascularization.”
Those diagnosed with type-2 MI were far less likely to receive coronary angiography (10.9% vs. 57.3%), PCI (1.7% vs. 38.5%), or CABG (0.4% vs. 7.8%) (P < .001 for all three differences), the report noted.
That, Dr. McCarthy said, “clearly shows that clinicians are uncertain about whether revascularization is beneficial” in type 2 MI.
Coding not in sync with UDMI
If there is confusion in practice about differentiating type 2 from type 1 MI, it likely has multiple sources, and one may be inconsistencies in how the UDMI and relevant ICD codes are applied in practice.
For example, the coding mandate is always to classify ST-segment elevation MI and non-STEMI as type 1, yet UDMI-4 itself states that a type 2 MI may be either STEMI or non-STEMI, noted Dr. McCarthy, as well as an editorial accompanying the report.
“It also can be difficult at times to distinguish type 2 MI from the diagnosis of myocardial injury,” both of which are partly defined by elevated cardiac troponin (cTn), adds the editorial, from Kristian Thygesen, MD, DSc, Aarhus (Denmark) University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark, and Allan S. Jaffe, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Crucially, but potentially sometimes overlooked, a diagnosis of infarction requires evidence of ischemia along with the biomarker elevation, whereas myocardial injury is defined by raised cTn without evidence of ischemia. Yet there is no ICD-10-CM code for “nonischemic myocardial injury,” Dr. Thygesen and Dr. Jaffe observed.
“Instead, the new ICD-10-CM coding includes a proxy called ‘non-MI troponin elevation due to an underlying cause,’ ” they wrote. “Unfortunately, although some have advocated using this code for myocardial injury, it is not specific for an elevated cTn value and could represent any abnormal laboratory measurements.” The code could be “misleading” and thus worsen the potential for miscoding and “misattribution of MI diagnoses.”
In the current study, 84.6% of the cohort were classified with type 1 MI, 14.8% with type 2, and 0.6% with both types. Of those with type 1 MI, 22.1% had STEMI, 76.4% had non-STEMI with the remainder “unspecified.”
“I think the introduction of ICD codes for type-2 MI is helpful in that we can study type 2 MI more broadly, across institutions, and try and get a better sense of its outcomes and how these patients are treated,” Dr. McCarthy said. But the coding system’s deficiencies may often lead to misclassification of patients. Especially, patients with type 2 STEMI may be miscoded as having type-1 STEMI, and those with only myocardial injury may be miscoded as having type 2 MI.
Most type 2 MI is a complication
A profile of patients with type 2 MI may be helpful for making distinctions. The analysis showed that, compared with patients with type 1 MI, they were slightly but significantly older and more likely to have clinical depression, alcohol or other substance abuse disorder, and to be female. They also had more heart failure (27.9% vs. 10.9%), kidney disease (35.7% vs. 25.7%), atrial fibrillation (31% vs. 21%), and anemia (26% vs. 18.9%) (P < .001 for all differences).
Type 2 patients were less likely to have CV risk factors usually associated with plaque instability and atherothrombosis, including a history of smoking, dyslipidemia, MI, PCI, or CABG (P < .001 for all differences), the group noted.
Of the 37,765 patients with type 2 MI, 91% received the diagnosis as secondary to another condition, including sepsis in 24.5%, hypertension in 16.9%, arrhythmias in 6.1%, respiratory failure in 4.3%, and pneumonia in 2.8% of cases.
In multivariate analyses, patients with type 2 MI, compared with type 1, showed lower risks of in-hospital death and readmission for MI within 30 days. Their 30-day risks of readmission from any cause and from MI were similar.
In-hospital mortality was lower for patients with type 2 MI who underwent revascularization, compared with those who did not, “but they were a very select, small proportion of the patient group. I would say there are probably unmeasured confounders,” Dr. McCarthy said.
“There’s a real kind of equipoise, so I think we desperately need a trial to guide us on whether revascularization is beneficial.”
Dr. McCarthy has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Thygesen disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jaffe disclosed serving as a consultant for Abbott, Roche, Siemens, Beckman-Coulter, Radiometer, ET Healthcare, Sphingotec, Brava, Quidel, Amgen, Novartis, and Medscape for educational activities.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Six-month follow-up shows continuing morbidity for COVID-19 survivors
In December 2019, a cluster of cases of what was first identified as a “mysterious pneumonia” was reported in the central Chinese city of Wuhan. Within a few short months, the disease had spread all over the world.
Wuhan was essentially “ground zero” for the novel coronavirus, or COVID-19, and now researchers report that many of the early survivors continue to experience a variety of lingering health issues.
At 6 months, for example, pulmonary and immune function have still not returned to normal in many of the patients who had been critically ill, said Zhiyong Peng, MD, PhD, an intensivist and medical researcher, in the department of critical care medicine, Zhonnan Hospital, Wuhan.
In addition, many are still experiencing varying degrees of psychiatric disability and physical morbidity.
The results of the report were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In 2020, Dr. Peng and colleagues conducted a single-center case series involving 138 patients with coronavirus pneumonia in order to describe the clinical characteristics of this new disease. Within this group, 26% of patients required admission to the intensive care unit and 4.3% died. As of Feb. 3, 2020, 26% required ICU care, 34.1% were discharged, 4.3% died, and 61.6% remained hospitalized. (JAMA. 2020 Mar 17;323[11]:1061-69) Not surprisingly, those requiring critical care experienced a higher rate of severe complications, including shock, arrythmias, acute cardiac injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, compared with non-ICU patients.
“However, the long-term outcomes of survivors were unknown,” said Dr. Peng. Thus, the goal of the current study was to analyze the outcomes based on pulmonary function, physical morbidity, immunological status, health-related quality of life, cognitive impairment, and psychiatric disability.
The cohort included patients from four hospitals in Wuhan, who had been treated in the adult ICU and required mechanical ventilation (invasive or noninvasive), or had a high FiO2 concentration, or needed an intravenous infusion of vasopressors.
In all, 171 critically ill patients were admitted to the four designated hospitals, and of this group, 110 were discharged from ICU and 106 survived. At the 3-month follow-up, 92 patients were evaluated and at 6 months, 72 were evaluated.
Pulmonary function tests were performed, and all patients received a chest CT scan, and did the “6-minute walk test.” For immune function, lymphocyte counts and function assays were performed. The SF-36 questionnaire was used to evaluate health related quality of life, and cognitive and psychological assessments were conducted with a variety of tools including the Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal Cognitive Assessment. Depression and anxiety were measured with Zung’s Self-Rating Anxiety Scale and the Hamilton Rating Scale.
At 3 months, 5 patients (5.4%) were seropositive for IgM and 9 (9.8%) were seronegative, while at 6 months, 9 patients (12.9%) tested seropositive for IgM and 12 (16.67%) tested seronegative.
A high proportion of patients also reported tachypnea after exercising (54%), heart palpitations (51.8%), fatigue (44.6%), and joint pain (20.5%).
In terms of lung function, survivors who had been intubated scored worse on pulmonary function tests and had a significant decrease in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), compared with those who had not been intubated.
At 6 months, the DLCO remained at 76% of the predicted level, but the walking test and chest CT scan improved over time. “In multivariate analysis tracheostomy was a risk factor associated with distance walked in 6 minutes,” said Dr. Peng.
Other results showed that B cells were lower in survivors who had been intubated, compared with those who weren’t, and they were still low at 3 and 6 months, compared with normal values. T-cell subsets were also persistently low.
“Hyperfunction of T lymphocytes and hypofunction of NK cells were detected, which had not improved at 6 months,” said Dr. Peng.
Cognitive dysfunction and depression were reported in some survivors. Cognitive dysfunction at 3 months affected 12.8% of survivors, but it improved by 6 months, affecting on only 2.9% of the cohort (P = .029). However, rates of depression more than doubled from 3 to 6 months (20% vs. 47.8%, P < .001), and anxiety showed a slight increase (15.6% vs. 17.6%, P = .726).
“Further follow-up will be performed to confirm these findings,” Dr. Peng concluded.
Rahul Kashyap, MBBS, MBA, a research scientist and assistant professor of anesthesiology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that currently the research from Wuhan is showing the follow-up for 6 months, but it takes time to gather and analyze the data. “I suspect we will be seeing results from the 1-year follow-up by June,” he said.
Dr. Kashyap, who was approached for an independent comment, also pointed out that in follow-up of SARS patients, some of them recovered but went on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome which is characterized by extreme fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest. “So the scientific community is contemplating if this will be true for patients with COVID-19 infection as well,” he said. “We have already seen that some of the ‘long haulers’ continue to have symptoms such as shortness of breath, joint pain, fatigue, loss of smell and taste, and even hearing loss in extreme cases.”
Some research is also confirming what has been reported from Wuhan. “Data from Ireland, that looked at 150 survivors, showed that almost 60% said they did not feel they were back to full health, regardless of the severity of the disease,” Dr. Kashyap said. “So, aside from Wuhan, we are now getting data from other sources that is similar. But what is interesting about the data from Ireland is that not all of the patients had severe illness or were in ICU.”
He added that data continue to come in from the United States and other countries, looking at long-term effects. “More and more patients are surviving as the care is getting better,” he said. “But beyond a year, we just don’t know yet.”
There was no outside sponsor listed. Dr. Peng and Dr. Kashyap have no disclosures.
In December 2019, a cluster of cases of what was first identified as a “mysterious pneumonia” was reported in the central Chinese city of Wuhan. Within a few short months, the disease had spread all over the world.
Wuhan was essentially “ground zero” for the novel coronavirus, or COVID-19, and now researchers report that many of the early survivors continue to experience a variety of lingering health issues.
At 6 months, for example, pulmonary and immune function have still not returned to normal in many of the patients who had been critically ill, said Zhiyong Peng, MD, PhD, an intensivist and medical researcher, in the department of critical care medicine, Zhonnan Hospital, Wuhan.
In addition, many are still experiencing varying degrees of psychiatric disability and physical morbidity.
The results of the report were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In 2020, Dr. Peng and colleagues conducted a single-center case series involving 138 patients with coronavirus pneumonia in order to describe the clinical characteristics of this new disease. Within this group, 26% of patients required admission to the intensive care unit and 4.3% died. As of Feb. 3, 2020, 26% required ICU care, 34.1% were discharged, 4.3% died, and 61.6% remained hospitalized. (JAMA. 2020 Mar 17;323[11]:1061-69) Not surprisingly, those requiring critical care experienced a higher rate of severe complications, including shock, arrythmias, acute cardiac injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, compared with non-ICU patients.
“However, the long-term outcomes of survivors were unknown,” said Dr. Peng. Thus, the goal of the current study was to analyze the outcomes based on pulmonary function, physical morbidity, immunological status, health-related quality of life, cognitive impairment, and psychiatric disability.
The cohort included patients from four hospitals in Wuhan, who had been treated in the adult ICU and required mechanical ventilation (invasive or noninvasive), or had a high FiO2 concentration, or needed an intravenous infusion of vasopressors.
In all, 171 critically ill patients were admitted to the four designated hospitals, and of this group, 110 were discharged from ICU and 106 survived. At the 3-month follow-up, 92 patients were evaluated and at 6 months, 72 were evaluated.
Pulmonary function tests were performed, and all patients received a chest CT scan, and did the “6-minute walk test.” For immune function, lymphocyte counts and function assays were performed. The SF-36 questionnaire was used to evaluate health related quality of life, and cognitive and psychological assessments were conducted with a variety of tools including the Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal Cognitive Assessment. Depression and anxiety were measured with Zung’s Self-Rating Anxiety Scale and the Hamilton Rating Scale.
At 3 months, 5 patients (5.4%) were seropositive for IgM and 9 (9.8%) were seronegative, while at 6 months, 9 patients (12.9%) tested seropositive for IgM and 12 (16.67%) tested seronegative.
A high proportion of patients also reported tachypnea after exercising (54%), heart palpitations (51.8%), fatigue (44.6%), and joint pain (20.5%).
In terms of lung function, survivors who had been intubated scored worse on pulmonary function tests and had a significant decrease in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), compared with those who had not been intubated.
At 6 months, the DLCO remained at 76% of the predicted level, but the walking test and chest CT scan improved over time. “In multivariate analysis tracheostomy was a risk factor associated with distance walked in 6 minutes,” said Dr. Peng.
Other results showed that B cells were lower in survivors who had been intubated, compared with those who weren’t, and they were still low at 3 and 6 months, compared with normal values. T-cell subsets were also persistently low.
“Hyperfunction of T lymphocytes and hypofunction of NK cells were detected, which had not improved at 6 months,” said Dr. Peng.
Cognitive dysfunction and depression were reported in some survivors. Cognitive dysfunction at 3 months affected 12.8% of survivors, but it improved by 6 months, affecting on only 2.9% of the cohort (P = .029). However, rates of depression more than doubled from 3 to 6 months (20% vs. 47.8%, P < .001), and anxiety showed a slight increase (15.6% vs. 17.6%, P = .726).
“Further follow-up will be performed to confirm these findings,” Dr. Peng concluded.
Rahul Kashyap, MBBS, MBA, a research scientist and assistant professor of anesthesiology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that currently the research from Wuhan is showing the follow-up for 6 months, but it takes time to gather and analyze the data. “I suspect we will be seeing results from the 1-year follow-up by June,” he said.
Dr. Kashyap, who was approached for an independent comment, also pointed out that in follow-up of SARS patients, some of them recovered but went on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome which is characterized by extreme fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest. “So the scientific community is contemplating if this will be true for patients with COVID-19 infection as well,” he said. “We have already seen that some of the ‘long haulers’ continue to have symptoms such as shortness of breath, joint pain, fatigue, loss of smell and taste, and even hearing loss in extreme cases.”
Some research is also confirming what has been reported from Wuhan. “Data from Ireland, that looked at 150 survivors, showed that almost 60% said they did not feel they were back to full health, regardless of the severity of the disease,” Dr. Kashyap said. “So, aside from Wuhan, we are now getting data from other sources that is similar. But what is interesting about the data from Ireland is that not all of the patients had severe illness or were in ICU.”
He added that data continue to come in from the United States and other countries, looking at long-term effects. “More and more patients are surviving as the care is getting better,” he said. “But beyond a year, we just don’t know yet.”
There was no outside sponsor listed. Dr. Peng and Dr. Kashyap have no disclosures.
In December 2019, a cluster of cases of what was first identified as a “mysterious pneumonia” was reported in the central Chinese city of Wuhan. Within a few short months, the disease had spread all over the world.
Wuhan was essentially “ground zero” for the novel coronavirus, or COVID-19, and now researchers report that many of the early survivors continue to experience a variety of lingering health issues.
At 6 months, for example, pulmonary and immune function have still not returned to normal in many of the patients who had been critically ill, said Zhiyong Peng, MD, PhD, an intensivist and medical researcher, in the department of critical care medicine, Zhonnan Hospital, Wuhan.
In addition, many are still experiencing varying degrees of psychiatric disability and physical morbidity.
The results of the report were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
In 2020, Dr. Peng and colleagues conducted a single-center case series involving 138 patients with coronavirus pneumonia in order to describe the clinical characteristics of this new disease. Within this group, 26% of patients required admission to the intensive care unit and 4.3% died. As of Feb. 3, 2020, 26% required ICU care, 34.1% were discharged, 4.3% died, and 61.6% remained hospitalized. (JAMA. 2020 Mar 17;323[11]:1061-69) Not surprisingly, those requiring critical care experienced a higher rate of severe complications, including shock, arrythmias, acute cardiac injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, compared with non-ICU patients.
“However, the long-term outcomes of survivors were unknown,” said Dr. Peng. Thus, the goal of the current study was to analyze the outcomes based on pulmonary function, physical morbidity, immunological status, health-related quality of life, cognitive impairment, and psychiatric disability.
The cohort included patients from four hospitals in Wuhan, who had been treated in the adult ICU and required mechanical ventilation (invasive or noninvasive), or had a high FiO2 concentration, or needed an intravenous infusion of vasopressors.
In all, 171 critically ill patients were admitted to the four designated hospitals, and of this group, 110 were discharged from ICU and 106 survived. At the 3-month follow-up, 92 patients were evaluated and at 6 months, 72 were evaluated.
Pulmonary function tests were performed, and all patients received a chest CT scan, and did the “6-minute walk test.” For immune function, lymphocyte counts and function assays were performed. The SF-36 questionnaire was used to evaluate health related quality of life, and cognitive and psychological assessments were conducted with a variety of tools including the Mini-Mental State Examination and Montreal Cognitive Assessment. Depression and anxiety were measured with Zung’s Self-Rating Anxiety Scale and the Hamilton Rating Scale.
At 3 months, 5 patients (5.4%) were seropositive for IgM and 9 (9.8%) were seronegative, while at 6 months, 9 patients (12.9%) tested seropositive for IgM and 12 (16.67%) tested seronegative.
A high proportion of patients also reported tachypnea after exercising (54%), heart palpitations (51.8%), fatigue (44.6%), and joint pain (20.5%).
In terms of lung function, survivors who had been intubated scored worse on pulmonary function tests and had a significant decrease in diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), compared with those who had not been intubated.
At 6 months, the DLCO remained at 76% of the predicted level, but the walking test and chest CT scan improved over time. “In multivariate analysis tracheostomy was a risk factor associated with distance walked in 6 minutes,” said Dr. Peng.
Other results showed that B cells were lower in survivors who had been intubated, compared with those who weren’t, and they were still low at 3 and 6 months, compared with normal values. T-cell subsets were also persistently low.
“Hyperfunction of T lymphocytes and hypofunction of NK cells were detected, which had not improved at 6 months,” said Dr. Peng.
Cognitive dysfunction and depression were reported in some survivors. Cognitive dysfunction at 3 months affected 12.8% of survivors, but it improved by 6 months, affecting on only 2.9% of the cohort (P = .029). However, rates of depression more than doubled from 3 to 6 months (20% vs. 47.8%, P < .001), and anxiety showed a slight increase (15.6% vs. 17.6%, P = .726).
“Further follow-up will be performed to confirm these findings,” Dr. Peng concluded.
Rahul Kashyap, MBBS, MBA, a research scientist and assistant professor of anesthesiology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that currently the research from Wuhan is showing the follow-up for 6 months, but it takes time to gather and analyze the data. “I suspect we will be seeing results from the 1-year follow-up by June,” he said.
Dr. Kashyap, who was approached for an independent comment, also pointed out that in follow-up of SARS patients, some of them recovered but went on to develop chronic fatigue syndrome which is characterized by extreme fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest. “So the scientific community is contemplating if this will be true for patients with COVID-19 infection as well,” he said. “We have already seen that some of the ‘long haulers’ continue to have symptoms such as shortness of breath, joint pain, fatigue, loss of smell and taste, and even hearing loss in extreme cases.”
Some research is also confirming what has been reported from Wuhan. “Data from Ireland, that looked at 150 survivors, showed that almost 60% said they did not feel they were back to full health, regardless of the severity of the disease,” Dr. Kashyap said. “So, aside from Wuhan, we are now getting data from other sources that is similar. But what is interesting about the data from Ireland is that not all of the patients had severe illness or were in ICU.”
He added that data continue to come in from the United States and other countries, looking at long-term effects. “More and more patients are surviving as the care is getting better,” he said. “But beyond a year, we just don’t know yet.”
There was no outside sponsor listed. Dr. Peng and Dr. Kashyap have no disclosures.
FROM CCC50
How do you run a hospital with no running water?
It’s bad enough that this month’s historic snowstorm left ordinary Texans scrambling for heat and resorting to melted snow for drinking, washing, and flushing. But what about hospitals, where sanitation is paramount and ample water is a sine qua non?
As pipes burst, pumps froze, and water pressure plummeted, patient care was affected as well as maintenance, food preparation, laundry, and heat. To counter the problems, several Texas hospitals stepped up to the plate with inventive responses.
“At the worst point, two of our hospitals, Houston Methodist West and Houston Methodist Baytown, had no city water supply, one for over 48 hours and the other for 72 hours,” said Marc L. Boom, MD, MBA, Houston Methodist’s president and CEO.
Although the main hospital had a reserve supply of potable water, a supply of water for laundry, cooking, and cleaning was another matter. “We introduced significant water restrictions and had to have 6,000-gallon tankers bring in extra water,” Dr. Boom said.
One hospital in the network got creative. When it rained the day after the ice storm, the staff rigged up a rain collection system using the huge bins that move linens around the hospital to collect nonpotable water for cleaning and flushing toilets, Dr. Boom said. Another hospital was able to provide showers for staff by bringing in bathroom trailers with self-contained water supplies of the kind used at some sporting events.
And at some facilities, patients were discharged into the lobby as they could not return home with transportation, electricity, and water systems crippled. With widespread challenges continuing, even as temperatures warmed, President Biden signed a major disaster declaration Feb. 20 that will provide emergency assistance to residents and businesses in more than a third of Texas counties, including those surrounding Houston, Dallas, and Austin.
Although conditions forced the rescheduling of some nonemergent surgeries, the water shortage had no impact on COVID-19 care, except for the unavailability of showers in the case of mobile patients. “At the worst, they just had to use bucket flushing for the toilets,” Dr. Boom said.
And in an unexpected win, when a Harris County freezer for COVID-19 vaccine storage failed and threatened to spoil 8,400 precious doses, Dr. Boom’s center was able to take delivery on 1,000 doses and administer them in 3 hours at a hastily set up ad hoc immunization center.
In all this, the lessons of the pandemic had a positive preparatory role. “2020 taught us to be agile as things change and to align our goals across different medical teams,” said Ben Saldana, MD, medical director of Houston Methodist’s emergency care centers. “And we were prepared for hurricanes, but not for snow.”
Increased pressure on emergency departments
As the outages continued and stress levels in the community rose, the network started seeing exacerbations of chronic conditions after the power shut-down incapacitated electrical devices running machines for heart assistance, oxygen delivery, and sleep apnea. “We started seeing food-borne illness and carbon monoxide poisoning, as well as more heart attacks, strokes, and sepsis,” Dr. Saldana said.
One serious strain on the network’s main hospital was the sudden need to accommodate large numbers of patients on dialysis, a procedure that uses a lot of water and is typically performed in small, vulnerable community facilities with limited infrastructure and no generators. “The hospitals are their backup and act as a safety net for them,” Boom said. Some hospital areas generally used for other types of conditions had to be marshaled for renal care.
Emergency rooms became pop-up dialysis centers, Dr. Saldana said. “And if the water pressure dropped, we had to cut dialysis time from the standard 4 hours to 2. That’s like putting a band-aid on patients.”
Fortunately, municipal water pressure in the Houston area has steadily risen and is almost back to normal. And according to Dr. Boom, the brutal storm may yet have a silver lining: a decline in county coronavirus cases as the storm and icy road conditions forced people to stay sequestered at home.
Further north in Austin, a number of hospitals lost municipal water pressure, creating a series of problems. Among them was St. David’s South Austin Medical Center, at which, according to reports in the Austin American-Statesman, staff members were at one point asked to use trash bags to remove waste from toilets, to refrain from showering, and to clean their hands only with sanitizer.
A statement issued by David Huffstutler, CEO of St. David’s HealthCare, acknowledged that the heating system is based on a water-fed boiler. When the building lost heat owing to lack of water, some patients had to be transferred elsewhere or discharged. The hospital distributed jugs and bottles of water for handwashing and drinking, and was working with city officials to obtain portable toilets.
Meanwhile, officials at Austin’s Dell Children’s Medical Center acknowledged in a memo that its toilets no longer had “flushing capabilities.” Other area hospitals in the Ascension Seton network were also suffering from compromised water supplies last week, according to local news reports.
Washroom facilities were affected elsewhere as well. A post on a medical association Facebook page referred to a memo ordering staff to use a single toilet in an outpatient area for bowel movements and warned them to limit their time there. No paper or other products were to be used in other toilets designated for urination.
‘The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm’
Some hospitals fared better. Along the Coastal Bend, Corpus Christi Medical Center managed to maintain its electricity and water supply to ensure continuity of hospital services after the storm, according to a statement.
But back in Houston, Liz Youngblood, MBA, RN, president of Baylor St. Luke’s Medical Center, said a number of hospitals in her network experienced low water pressure after the storm.
“Fortunately, we had water conservation measures and low-water alerts in place for such emergencies,” she said. “And we rely on water tankers to help maintain enough pressure for the basics.”
Some of the challenges posed by the storm are quite similar to what St. Luke’s faced after Hurricane Harvey in 2017. “We had already made plans to address them and so we felt prepared,” Ms. Youngblood said.
And thanks to COVID-19, Texas hospitals have been operating in crisis mode for the past year. “The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm,” said Gina Blocker, MD, a St. Luke’s ED physician, “so we had measures and teams in place. We did have some reduction in water pressure, though the pressure was still good.”
But the hospital was inundated with patients looking for shelter. “Some were just scared about what might happen to them if their heat didn’t come back on and they wanted to be where they could get care,” Dr. Blocker said. Others came in with expected storm-related injuries such as hypothermia and carbon monoxide poisoning.
According to Ms. Youngblood, little compromise in patient care was necessary except for the cancellation of some operations and vaccinations owing to the treacherous travel conditions. “But one of the biggest remaining issues is that we need plenty of blood, so we’re encouraging people to donate at their local centers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
It’s bad enough that this month’s historic snowstorm left ordinary Texans scrambling for heat and resorting to melted snow for drinking, washing, and flushing. But what about hospitals, where sanitation is paramount and ample water is a sine qua non?
As pipes burst, pumps froze, and water pressure plummeted, patient care was affected as well as maintenance, food preparation, laundry, and heat. To counter the problems, several Texas hospitals stepped up to the plate with inventive responses.
“At the worst point, two of our hospitals, Houston Methodist West and Houston Methodist Baytown, had no city water supply, one for over 48 hours and the other for 72 hours,” said Marc L. Boom, MD, MBA, Houston Methodist’s president and CEO.
Although the main hospital had a reserve supply of potable water, a supply of water for laundry, cooking, and cleaning was another matter. “We introduced significant water restrictions and had to have 6,000-gallon tankers bring in extra water,” Dr. Boom said.
One hospital in the network got creative. When it rained the day after the ice storm, the staff rigged up a rain collection system using the huge bins that move linens around the hospital to collect nonpotable water for cleaning and flushing toilets, Dr. Boom said. Another hospital was able to provide showers for staff by bringing in bathroom trailers with self-contained water supplies of the kind used at some sporting events.
And at some facilities, patients were discharged into the lobby as they could not return home with transportation, electricity, and water systems crippled. With widespread challenges continuing, even as temperatures warmed, President Biden signed a major disaster declaration Feb. 20 that will provide emergency assistance to residents and businesses in more than a third of Texas counties, including those surrounding Houston, Dallas, and Austin.
Although conditions forced the rescheduling of some nonemergent surgeries, the water shortage had no impact on COVID-19 care, except for the unavailability of showers in the case of mobile patients. “At the worst, they just had to use bucket flushing for the toilets,” Dr. Boom said.
And in an unexpected win, when a Harris County freezer for COVID-19 vaccine storage failed and threatened to spoil 8,400 precious doses, Dr. Boom’s center was able to take delivery on 1,000 doses and administer them in 3 hours at a hastily set up ad hoc immunization center.
In all this, the lessons of the pandemic had a positive preparatory role. “2020 taught us to be agile as things change and to align our goals across different medical teams,” said Ben Saldana, MD, medical director of Houston Methodist’s emergency care centers. “And we were prepared for hurricanes, but not for snow.”
Increased pressure on emergency departments
As the outages continued and stress levels in the community rose, the network started seeing exacerbations of chronic conditions after the power shut-down incapacitated electrical devices running machines for heart assistance, oxygen delivery, and sleep apnea. “We started seeing food-borne illness and carbon monoxide poisoning, as well as more heart attacks, strokes, and sepsis,” Dr. Saldana said.
One serious strain on the network’s main hospital was the sudden need to accommodate large numbers of patients on dialysis, a procedure that uses a lot of water and is typically performed in small, vulnerable community facilities with limited infrastructure and no generators. “The hospitals are their backup and act as a safety net for them,” Boom said. Some hospital areas generally used for other types of conditions had to be marshaled for renal care.
Emergency rooms became pop-up dialysis centers, Dr. Saldana said. “And if the water pressure dropped, we had to cut dialysis time from the standard 4 hours to 2. That’s like putting a band-aid on patients.”
Fortunately, municipal water pressure in the Houston area has steadily risen and is almost back to normal. And according to Dr. Boom, the brutal storm may yet have a silver lining: a decline in county coronavirus cases as the storm and icy road conditions forced people to stay sequestered at home.
Further north in Austin, a number of hospitals lost municipal water pressure, creating a series of problems. Among them was St. David’s South Austin Medical Center, at which, according to reports in the Austin American-Statesman, staff members were at one point asked to use trash bags to remove waste from toilets, to refrain from showering, and to clean their hands only with sanitizer.
A statement issued by David Huffstutler, CEO of St. David’s HealthCare, acknowledged that the heating system is based on a water-fed boiler. When the building lost heat owing to lack of water, some patients had to be transferred elsewhere or discharged. The hospital distributed jugs and bottles of water for handwashing and drinking, and was working with city officials to obtain portable toilets.
Meanwhile, officials at Austin’s Dell Children’s Medical Center acknowledged in a memo that its toilets no longer had “flushing capabilities.” Other area hospitals in the Ascension Seton network were also suffering from compromised water supplies last week, according to local news reports.
Washroom facilities were affected elsewhere as well. A post on a medical association Facebook page referred to a memo ordering staff to use a single toilet in an outpatient area for bowel movements and warned them to limit their time there. No paper or other products were to be used in other toilets designated for urination.
‘The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm’
Some hospitals fared better. Along the Coastal Bend, Corpus Christi Medical Center managed to maintain its electricity and water supply to ensure continuity of hospital services after the storm, according to a statement.
But back in Houston, Liz Youngblood, MBA, RN, president of Baylor St. Luke’s Medical Center, said a number of hospitals in her network experienced low water pressure after the storm.
“Fortunately, we had water conservation measures and low-water alerts in place for such emergencies,” she said. “And we rely on water tankers to help maintain enough pressure for the basics.”
Some of the challenges posed by the storm are quite similar to what St. Luke’s faced after Hurricane Harvey in 2017. “We had already made plans to address them and so we felt prepared,” Ms. Youngblood said.
And thanks to COVID-19, Texas hospitals have been operating in crisis mode for the past year. “The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm,” said Gina Blocker, MD, a St. Luke’s ED physician, “so we had measures and teams in place. We did have some reduction in water pressure, though the pressure was still good.”
But the hospital was inundated with patients looking for shelter. “Some were just scared about what might happen to them if their heat didn’t come back on and they wanted to be where they could get care,” Dr. Blocker said. Others came in with expected storm-related injuries such as hypothermia and carbon monoxide poisoning.
According to Ms. Youngblood, little compromise in patient care was necessary except for the cancellation of some operations and vaccinations owing to the treacherous travel conditions. “But one of the biggest remaining issues is that we need plenty of blood, so we’re encouraging people to donate at their local centers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
It’s bad enough that this month’s historic snowstorm left ordinary Texans scrambling for heat and resorting to melted snow for drinking, washing, and flushing. But what about hospitals, where sanitation is paramount and ample water is a sine qua non?
As pipes burst, pumps froze, and water pressure plummeted, patient care was affected as well as maintenance, food preparation, laundry, and heat. To counter the problems, several Texas hospitals stepped up to the plate with inventive responses.
“At the worst point, two of our hospitals, Houston Methodist West and Houston Methodist Baytown, had no city water supply, one for over 48 hours and the other for 72 hours,” said Marc L. Boom, MD, MBA, Houston Methodist’s president and CEO.
Although the main hospital had a reserve supply of potable water, a supply of water for laundry, cooking, and cleaning was another matter. “We introduced significant water restrictions and had to have 6,000-gallon tankers bring in extra water,” Dr. Boom said.
One hospital in the network got creative. When it rained the day after the ice storm, the staff rigged up a rain collection system using the huge bins that move linens around the hospital to collect nonpotable water for cleaning and flushing toilets, Dr. Boom said. Another hospital was able to provide showers for staff by bringing in bathroom trailers with self-contained water supplies of the kind used at some sporting events.
And at some facilities, patients were discharged into the lobby as they could not return home with transportation, electricity, and water systems crippled. With widespread challenges continuing, even as temperatures warmed, President Biden signed a major disaster declaration Feb. 20 that will provide emergency assistance to residents and businesses in more than a third of Texas counties, including those surrounding Houston, Dallas, and Austin.
Although conditions forced the rescheduling of some nonemergent surgeries, the water shortage had no impact on COVID-19 care, except for the unavailability of showers in the case of mobile patients. “At the worst, they just had to use bucket flushing for the toilets,” Dr. Boom said.
And in an unexpected win, when a Harris County freezer for COVID-19 vaccine storage failed and threatened to spoil 8,400 precious doses, Dr. Boom’s center was able to take delivery on 1,000 doses and administer them in 3 hours at a hastily set up ad hoc immunization center.
In all this, the lessons of the pandemic had a positive preparatory role. “2020 taught us to be agile as things change and to align our goals across different medical teams,” said Ben Saldana, MD, medical director of Houston Methodist’s emergency care centers. “And we were prepared for hurricanes, but not for snow.”
Increased pressure on emergency departments
As the outages continued and stress levels in the community rose, the network started seeing exacerbations of chronic conditions after the power shut-down incapacitated electrical devices running machines for heart assistance, oxygen delivery, and sleep apnea. “We started seeing food-borne illness and carbon monoxide poisoning, as well as more heart attacks, strokes, and sepsis,” Dr. Saldana said.
One serious strain on the network’s main hospital was the sudden need to accommodate large numbers of patients on dialysis, a procedure that uses a lot of water and is typically performed in small, vulnerable community facilities with limited infrastructure and no generators. “The hospitals are their backup and act as a safety net for them,” Boom said. Some hospital areas generally used for other types of conditions had to be marshaled for renal care.
Emergency rooms became pop-up dialysis centers, Dr. Saldana said. “And if the water pressure dropped, we had to cut dialysis time from the standard 4 hours to 2. That’s like putting a band-aid on patients.”
Fortunately, municipal water pressure in the Houston area has steadily risen and is almost back to normal. And according to Dr. Boom, the brutal storm may yet have a silver lining: a decline in county coronavirus cases as the storm and icy road conditions forced people to stay sequestered at home.
Further north in Austin, a number of hospitals lost municipal water pressure, creating a series of problems. Among them was St. David’s South Austin Medical Center, at which, according to reports in the Austin American-Statesman, staff members were at one point asked to use trash bags to remove waste from toilets, to refrain from showering, and to clean their hands only with sanitizer.
A statement issued by David Huffstutler, CEO of St. David’s HealthCare, acknowledged that the heating system is based on a water-fed boiler. When the building lost heat owing to lack of water, some patients had to be transferred elsewhere or discharged. The hospital distributed jugs and bottles of water for handwashing and drinking, and was working with city officials to obtain portable toilets.
Meanwhile, officials at Austin’s Dell Children’s Medical Center acknowledged in a memo that its toilets no longer had “flushing capabilities.” Other area hospitals in the Ascension Seton network were also suffering from compromised water supplies last week, according to local news reports.
Washroom facilities were affected elsewhere as well. A post on a medical association Facebook page referred to a memo ordering staff to use a single toilet in an outpatient area for bowel movements and warned them to limit their time there. No paper or other products were to be used in other toilets designated for urination.
‘The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm’
Some hospitals fared better. Along the Coastal Bend, Corpus Christi Medical Center managed to maintain its electricity and water supply to ensure continuity of hospital services after the storm, according to a statement.
But back in Houston, Liz Youngblood, MBA, RN, president of Baylor St. Luke’s Medical Center, said a number of hospitals in her network experienced low water pressure after the storm.
“Fortunately, we had water conservation measures and low-water alerts in place for such emergencies,” she said. “And we rely on water tankers to help maintain enough pressure for the basics.”
Some of the challenges posed by the storm are quite similar to what St. Luke’s faced after Hurricane Harvey in 2017. “We had already made plans to address them and so we felt prepared,” Ms. Youngblood said.
And thanks to COVID-19, Texas hospitals have been operating in crisis mode for the past year. “The pandemic was the prelude to the ice storm,” said Gina Blocker, MD, a St. Luke’s ED physician, “so we had measures and teams in place. We did have some reduction in water pressure, though the pressure was still good.”
But the hospital was inundated with patients looking for shelter. “Some were just scared about what might happen to them if their heat didn’t come back on and they wanted to be where they could get care,” Dr. Blocker said. Others came in with expected storm-related injuries such as hypothermia and carbon monoxide poisoning.
According to Ms. Youngblood, little compromise in patient care was necessary except for the cancellation of some operations and vaccinations owing to the treacherous travel conditions. “But one of the biggest remaining issues is that we need plenty of blood, so we’re encouraging people to donate at their local centers.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
Akathisia: “Ants in the Pants”
Potentially poor outcome if untreated
Case
The patient is a 65-year-old female with increasing anxiety and agitation. She completed cycle 2 of chemotherapy for breast cancer several hours ago. Her premedication was Reglan (metoclopramide); her only other medication is tamoxifen. Other than breast cancer, she suffers only from osteoarthritis.
She is found pacing about the ward – almost uncontrollably. She feels she must move, only to have to stop and, shortly afterwards, feels the urge to move again. This has never happened to her before. She must move despite being fatigued. She also complains of an odd overall feeling; something akin to “ant in the pants.” She is nervous and exhausted. What is her diagnosis and what clues to it are in her presentation?
Background
The word “akathisia” is derived from the Greek language and means “unable to sit.” It is thought to occur as a consequence of dopaminergic blockade in the midbrain region. The decrease in dopaminergic activity leads to a subsequent decrease in inhibitory motor control which, in turn, manifests as involuntary movements.
In this malady, the patient is seen as perpetually in motion. The patient feels the need to move until they must stop. But once static, they have the urge to move again. They pace, they rock and they ‘fidget’ – they just cannot sit still. This feeling has been likened to having “ants in the pants.” Patients become anxious, agitated, and suffer from insomnia. They cannot rest.
If left unresolved akathisia can torment patients to sheer exhaustion. For some it serves as a harbinger of suicide. This toxicity is more commonly seen in the psychiatric pharmacy with the most common offender being haloperidol. The causative agents of the least notoriety are the non-antipsychotics.
Diagnosis and treatment
Akathisia is an extrapyramidal symptom found largely but NOT exclusively with psychiatric medications. There are drugs in the non-psychiatric field that can also cause it, including antiemetics (e.g., metoclopramide), antihypertensives (e.g., diltiazem), and narcotics (e.g., cocaine). Metoclopramide is given under circumstances ranging from diabetic gastroparesis to premedicating chemotherapy. It is a peripheral and centrally acting dopamine antagonist. There are no lab tests or radiographic workups to diagnose akathisia. Its manifestations are erratic and disturbing, and the prognosis is doleful if unresolved.
The primary intervention for the treatment of akathisia is its recognition and the discontinuation of the offending drug. Beyond this, for symptomatic care, there is a compendium of case reports and small studies supporting many drugs, but only a few have received consistent recommendation. Beta-adrenergic antagonists, such as propranolol, are considered the gold standard, the first choice for the treatment of akathisia. Their toxicities include orthostatic hypotension and bradycardia. Additionally, they are contraindicated in the setting of asthma.
Anticholinergics, such as benztropine (cogentin) and trihexylphenidyl (artane) are considered in the literature as 2nd line treatments, behind beta-blockers. However, the data advocating their use is limited. They have multiple side-effects including sedation, memory impairment, visual impairment, and urinary retention. They are also contraindicated in patients with closed-angle glaucoma.
An equivalent alternative to beta-blockers could also be the 5HT2a receptor antagonists such as mirtazapine (remeron) and cyproheptadine (periactin). This class of medications is thought to act by an inhibitory control of dopaminergic neurons. Sedation and weight gain are the primary toxicities, and they are contraindicated in patients who are breastfeeding.
Benzodiazepines, such as clonazepam (klonopin), have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms but the data is very limited. The risk of tolerance and dependence, coupled with the problems of sedation impacting the elderly, prompts their placement in reserve. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), when given in a high dose format, causes significant improvement in akathisia. However, it can cause headache and nausea. Chronic administration of high doses has also been found to cause a severe and irreversible sensory neuropathy as well as lead to seizures. Many other agents have been studied, but the data are too small to warrant recommendation.
Conclusion
Akathisia remains an extreme reaction to drugs not always in the psychotropic class. The hospitalist will likely deal with the acute onset, a dramatic form, and a potentially poor outcome if untreated. The patient’s only true defense is the physician’s clinical acumen and their ability to recognize it.
Dr. Killeen is a physician in Tampa, Fla. He practices internal medicine, hematology, and oncology, and has worked in hospice and hospital medicine.
Recommended reading
Van Gool AR, Doorduijn JK, Sevnaeve C. Severe akathisia as a side effect of metoclopramide. Pharm World Sci. 2010; 32(6):704-706.
Loonen AJM, Stahl SM. The mechanism of drug-induced akathisia. CNS Spectr. 2010;15(11):491-494.
Forcen FE, Matsoukas K, Alici Y. Antipsychotic-induced akathisia in delirium: A systemic review. Palliat Support Care. 2016;14(1):77-84.
Sethuram K, Gedzior J. Akathisia: Case presentation and review of newer treatment agents. Psychiatric Annals. 2014;44(8):391-396.
Pringsheim T, et al. The assessment and treatment of antipsychotic-induced akathisia. Can J Psychiatry. 2018;63(11): 719-729.
Tachere RO, Mandana M. Beyond anxiety and agitation: A clinical approach to akathisia. Royal Australian Coll Gen Practitioners. 2017;46(5): 296-298.
Key points
- Although associated more with psychiatric medications, akathisia can occur with non-psychotropics as well.
- To recognize the illness, the clinician must notice the repetitive involuntary movements and pacing as well as the “ants in the pants” fidgeting involved.
- Primary treatment consists of medication discontinuation with pharmaceutical intervention as a backup.
- Recognition is the key to successful treatment.
Classic signs of akathisia
- Fidgeting – “ants in the pants”
- Swinging the legs while seated
- Rocking from foot to foot
- Walking while in a static position
- Inability to sit or stand still – pacing
- Onset appears with the initiation or dose adjustment of an offending drug
Quiz
1. Which of the following findings occur in Akathisia?
A. Fidgeting
B. Pacing
C. Swinging the legs while seated
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia is manifest as involuntary hyperactivity of the extremities, particularly the lower extremities. People feel the urge to move, to continue endlessly in motion, stopping only when fatigue sets in. The fidgeting has been described by patients as feeling like “ants in the pants.”
2. Which of the following interventions are used to treat akathisia?
A. Drug discontinuation
B. Propranolol
C. Mirtazapine
D. All the above
Answer: D
All the interventions mentioned are used to treat akathisia. The foremost is to stop the offending drug. Failing this, propranolol is the “gold standard” while 5HT2a antagonists, such as mirtazapine, are favored when beta-blockers either fail or are contraindicated.
3. The use of pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) in the treatment of akathisia is associated with what toxicities?
A. Headache
B. Nausea
C. Seizures
D. All the above
Answer: D
The use of Vitamin B6 in the treatment of akathisia has several drawbacks. Its administration is associated with headache and nausea, and high dose usage increases the risk of seizure.
4. If unresolved, akathisia can lead to which of the following?
A. Insomnia
B. Suicide
C. Physical exhaustion
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia, left unrecognized and untreated, can eventually lead to physical exhaustion, and is compounded by difficulties in trying to rest, hence insomnia. The physical and mental torment of this malady can lead to suicide.
Potentially poor outcome if untreated
Potentially poor outcome if untreated
Case
The patient is a 65-year-old female with increasing anxiety and agitation. She completed cycle 2 of chemotherapy for breast cancer several hours ago. Her premedication was Reglan (metoclopramide); her only other medication is tamoxifen. Other than breast cancer, she suffers only from osteoarthritis.
She is found pacing about the ward – almost uncontrollably. She feels she must move, only to have to stop and, shortly afterwards, feels the urge to move again. This has never happened to her before. She must move despite being fatigued. She also complains of an odd overall feeling; something akin to “ant in the pants.” She is nervous and exhausted. What is her diagnosis and what clues to it are in her presentation?
Background
The word “akathisia” is derived from the Greek language and means “unable to sit.” It is thought to occur as a consequence of dopaminergic blockade in the midbrain region. The decrease in dopaminergic activity leads to a subsequent decrease in inhibitory motor control which, in turn, manifests as involuntary movements.
In this malady, the patient is seen as perpetually in motion. The patient feels the need to move until they must stop. But once static, they have the urge to move again. They pace, they rock and they ‘fidget’ – they just cannot sit still. This feeling has been likened to having “ants in the pants.” Patients become anxious, agitated, and suffer from insomnia. They cannot rest.
If left unresolved akathisia can torment patients to sheer exhaustion. For some it serves as a harbinger of suicide. This toxicity is more commonly seen in the psychiatric pharmacy with the most common offender being haloperidol. The causative agents of the least notoriety are the non-antipsychotics.
Diagnosis and treatment
Akathisia is an extrapyramidal symptom found largely but NOT exclusively with psychiatric medications. There are drugs in the non-psychiatric field that can also cause it, including antiemetics (e.g., metoclopramide), antihypertensives (e.g., diltiazem), and narcotics (e.g., cocaine). Metoclopramide is given under circumstances ranging from diabetic gastroparesis to premedicating chemotherapy. It is a peripheral and centrally acting dopamine antagonist. There are no lab tests or radiographic workups to diagnose akathisia. Its manifestations are erratic and disturbing, and the prognosis is doleful if unresolved.
The primary intervention for the treatment of akathisia is its recognition and the discontinuation of the offending drug. Beyond this, for symptomatic care, there is a compendium of case reports and small studies supporting many drugs, but only a few have received consistent recommendation. Beta-adrenergic antagonists, such as propranolol, are considered the gold standard, the first choice for the treatment of akathisia. Their toxicities include orthostatic hypotension and bradycardia. Additionally, they are contraindicated in the setting of asthma.
Anticholinergics, such as benztropine (cogentin) and trihexylphenidyl (artane) are considered in the literature as 2nd line treatments, behind beta-blockers. However, the data advocating their use is limited. They have multiple side-effects including sedation, memory impairment, visual impairment, and urinary retention. They are also contraindicated in patients with closed-angle glaucoma.
An equivalent alternative to beta-blockers could also be the 5HT2a receptor antagonists such as mirtazapine (remeron) and cyproheptadine (periactin). This class of medications is thought to act by an inhibitory control of dopaminergic neurons. Sedation and weight gain are the primary toxicities, and they are contraindicated in patients who are breastfeeding.
Benzodiazepines, such as clonazepam (klonopin), have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms but the data is very limited. The risk of tolerance and dependence, coupled with the problems of sedation impacting the elderly, prompts their placement in reserve. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), when given in a high dose format, causes significant improvement in akathisia. However, it can cause headache and nausea. Chronic administration of high doses has also been found to cause a severe and irreversible sensory neuropathy as well as lead to seizures. Many other agents have been studied, but the data are too small to warrant recommendation.
Conclusion
Akathisia remains an extreme reaction to drugs not always in the psychotropic class. The hospitalist will likely deal with the acute onset, a dramatic form, and a potentially poor outcome if untreated. The patient’s only true defense is the physician’s clinical acumen and their ability to recognize it.
Dr. Killeen is a physician in Tampa, Fla. He practices internal medicine, hematology, and oncology, and has worked in hospice and hospital medicine.
Recommended reading
Van Gool AR, Doorduijn JK, Sevnaeve C. Severe akathisia as a side effect of metoclopramide. Pharm World Sci. 2010; 32(6):704-706.
Loonen AJM, Stahl SM. The mechanism of drug-induced akathisia. CNS Spectr. 2010;15(11):491-494.
Forcen FE, Matsoukas K, Alici Y. Antipsychotic-induced akathisia in delirium: A systemic review. Palliat Support Care. 2016;14(1):77-84.
Sethuram K, Gedzior J. Akathisia: Case presentation and review of newer treatment agents. Psychiatric Annals. 2014;44(8):391-396.
Pringsheim T, et al. The assessment and treatment of antipsychotic-induced akathisia. Can J Psychiatry. 2018;63(11): 719-729.
Tachere RO, Mandana M. Beyond anxiety and agitation: A clinical approach to akathisia. Royal Australian Coll Gen Practitioners. 2017;46(5): 296-298.
Key points
- Although associated more with psychiatric medications, akathisia can occur with non-psychotropics as well.
- To recognize the illness, the clinician must notice the repetitive involuntary movements and pacing as well as the “ants in the pants” fidgeting involved.
- Primary treatment consists of medication discontinuation with pharmaceutical intervention as a backup.
- Recognition is the key to successful treatment.
Classic signs of akathisia
- Fidgeting – “ants in the pants”
- Swinging the legs while seated
- Rocking from foot to foot
- Walking while in a static position
- Inability to sit or stand still – pacing
- Onset appears with the initiation or dose adjustment of an offending drug
Quiz
1. Which of the following findings occur in Akathisia?
A. Fidgeting
B. Pacing
C. Swinging the legs while seated
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia is manifest as involuntary hyperactivity of the extremities, particularly the lower extremities. People feel the urge to move, to continue endlessly in motion, stopping only when fatigue sets in. The fidgeting has been described by patients as feeling like “ants in the pants.”
2. Which of the following interventions are used to treat akathisia?
A. Drug discontinuation
B. Propranolol
C. Mirtazapine
D. All the above
Answer: D
All the interventions mentioned are used to treat akathisia. The foremost is to stop the offending drug. Failing this, propranolol is the “gold standard” while 5HT2a antagonists, such as mirtazapine, are favored when beta-blockers either fail or are contraindicated.
3. The use of pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) in the treatment of akathisia is associated with what toxicities?
A. Headache
B. Nausea
C. Seizures
D. All the above
Answer: D
The use of Vitamin B6 in the treatment of akathisia has several drawbacks. Its administration is associated with headache and nausea, and high dose usage increases the risk of seizure.
4. If unresolved, akathisia can lead to which of the following?
A. Insomnia
B. Suicide
C. Physical exhaustion
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia, left unrecognized and untreated, can eventually lead to physical exhaustion, and is compounded by difficulties in trying to rest, hence insomnia. The physical and mental torment of this malady can lead to suicide.
Case
The patient is a 65-year-old female with increasing anxiety and agitation. She completed cycle 2 of chemotherapy for breast cancer several hours ago. Her premedication was Reglan (metoclopramide); her only other medication is tamoxifen. Other than breast cancer, she suffers only from osteoarthritis.
She is found pacing about the ward – almost uncontrollably. She feels she must move, only to have to stop and, shortly afterwards, feels the urge to move again. This has never happened to her before. She must move despite being fatigued. She also complains of an odd overall feeling; something akin to “ant in the pants.” She is nervous and exhausted. What is her diagnosis and what clues to it are in her presentation?
Background
The word “akathisia” is derived from the Greek language and means “unable to sit.” It is thought to occur as a consequence of dopaminergic blockade in the midbrain region. The decrease in dopaminergic activity leads to a subsequent decrease in inhibitory motor control which, in turn, manifests as involuntary movements.
In this malady, the patient is seen as perpetually in motion. The patient feels the need to move until they must stop. But once static, they have the urge to move again. They pace, they rock and they ‘fidget’ – they just cannot sit still. This feeling has been likened to having “ants in the pants.” Patients become anxious, agitated, and suffer from insomnia. They cannot rest.
If left unresolved akathisia can torment patients to sheer exhaustion. For some it serves as a harbinger of suicide. This toxicity is more commonly seen in the psychiatric pharmacy with the most common offender being haloperidol. The causative agents of the least notoriety are the non-antipsychotics.
Diagnosis and treatment
Akathisia is an extrapyramidal symptom found largely but NOT exclusively with psychiatric medications. There are drugs in the non-psychiatric field that can also cause it, including antiemetics (e.g., metoclopramide), antihypertensives (e.g., diltiazem), and narcotics (e.g., cocaine). Metoclopramide is given under circumstances ranging from diabetic gastroparesis to premedicating chemotherapy. It is a peripheral and centrally acting dopamine antagonist. There are no lab tests or radiographic workups to diagnose akathisia. Its manifestations are erratic and disturbing, and the prognosis is doleful if unresolved.
The primary intervention for the treatment of akathisia is its recognition and the discontinuation of the offending drug. Beyond this, for symptomatic care, there is a compendium of case reports and small studies supporting many drugs, but only a few have received consistent recommendation. Beta-adrenergic antagonists, such as propranolol, are considered the gold standard, the first choice for the treatment of akathisia. Their toxicities include orthostatic hypotension and bradycardia. Additionally, they are contraindicated in the setting of asthma.
Anticholinergics, such as benztropine (cogentin) and trihexylphenidyl (artane) are considered in the literature as 2nd line treatments, behind beta-blockers. However, the data advocating their use is limited. They have multiple side-effects including sedation, memory impairment, visual impairment, and urinary retention. They are also contraindicated in patients with closed-angle glaucoma.
An equivalent alternative to beta-blockers could also be the 5HT2a receptor antagonists such as mirtazapine (remeron) and cyproheptadine (periactin). This class of medications is thought to act by an inhibitory control of dopaminergic neurons. Sedation and weight gain are the primary toxicities, and they are contraindicated in patients who are breastfeeding.
Benzodiazepines, such as clonazepam (klonopin), have shown some efficacy in improving symptoms but the data is very limited. The risk of tolerance and dependence, coupled with the problems of sedation impacting the elderly, prompts their placement in reserve. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), when given in a high dose format, causes significant improvement in akathisia. However, it can cause headache and nausea. Chronic administration of high doses has also been found to cause a severe and irreversible sensory neuropathy as well as lead to seizures. Many other agents have been studied, but the data are too small to warrant recommendation.
Conclusion
Akathisia remains an extreme reaction to drugs not always in the psychotropic class. The hospitalist will likely deal with the acute onset, a dramatic form, and a potentially poor outcome if untreated. The patient’s only true defense is the physician’s clinical acumen and their ability to recognize it.
Dr. Killeen is a physician in Tampa, Fla. He practices internal medicine, hematology, and oncology, and has worked in hospice and hospital medicine.
Recommended reading
Van Gool AR, Doorduijn JK, Sevnaeve C. Severe akathisia as a side effect of metoclopramide. Pharm World Sci. 2010; 32(6):704-706.
Loonen AJM, Stahl SM. The mechanism of drug-induced akathisia. CNS Spectr. 2010;15(11):491-494.
Forcen FE, Matsoukas K, Alici Y. Antipsychotic-induced akathisia in delirium: A systemic review. Palliat Support Care. 2016;14(1):77-84.
Sethuram K, Gedzior J. Akathisia: Case presentation and review of newer treatment agents. Psychiatric Annals. 2014;44(8):391-396.
Pringsheim T, et al. The assessment and treatment of antipsychotic-induced akathisia. Can J Psychiatry. 2018;63(11): 719-729.
Tachere RO, Mandana M. Beyond anxiety and agitation: A clinical approach to akathisia. Royal Australian Coll Gen Practitioners. 2017;46(5): 296-298.
Key points
- Although associated more with psychiatric medications, akathisia can occur with non-psychotropics as well.
- To recognize the illness, the clinician must notice the repetitive involuntary movements and pacing as well as the “ants in the pants” fidgeting involved.
- Primary treatment consists of medication discontinuation with pharmaceutical intervention as a backup.
- Recognition is the key to successful treatment.
Classic signs of akathisia
- Fidgeting – “ants in the pants”
- Swinging the legs while seated
- Rocking from foot to foot
- Walking while in a static position
- Inability to sit or stand still – pacing
- Onset appears with the initiation or dose adjustment of an offending drug
Quiz
1. Which of the following findings occur in Akathisia?
A. Fidgeting
B. Pacing
C. Swinging the legs while seated
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia is manifest as involuntary hyperactivity of the extremities, particularly the lower extremities. People feel the urge to move, to continue endlessly in motion, stopping only when fatigue sets in. The fidgeting has been described by patients as feeling like “ants in the pants.”
2. Which of the following interventions are used to treat akathisia?
A. Drug discontinuation
B. Propranolol
C. Mirtazapine
D. All the above
Answer: D
All the interventions mentioned are used to treat akathisia. The foremost is to stop the offending drug. Failing this, propranolol is the “gold standard” while 5HT2a antagonists, such as mirtazapine, are favored when beta-blockers either fail or are contraindicated.
3. The use of pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) in the treatment of akathisia is associated with what toxicities?
A. Headache
B. Nausea
C. Seizures
D. All the above
Answer: D
The use of Vitamin B6 in the treatment of akathisia has several drawbacks. Its administration is associated with headache and nausea, and high dose usage increases the risk of seizure.
4. If unresolved, akathisia can lead to which of the following?
A. Insomnia
B. Suicide
C. Physical exhaustion
D. All the above
Answer: D
Akathisia, left unrecognized and untreated, can eventually lead to physical exhaustion, and is compounded by difficulties in trying to rest, hence insomnia. The physical and mental torment of this malady can lead to suicide.
More from DAPA-HF: Dapagliflozin quickly reduces heart failure events
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
Dapagliflozin’s benefits in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction appeared quickly after treatment began, and patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within the prior year got the biggest boost from the drug, according to secondary analyses of the more than 4,700-patient DAPA-HF trial.
Dapagliflozin’s significant reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure became apparent in DAPA-HF within 28 days after patients started treatment, by which time those on the study drug had a 49% cut in this combined endpoint, compared with patients on placebo, David D. Berg, MD, and associates said in a recent report published in JAMA Cardiology.
Their analyses also showed that the absolute reduction linked with dapagliflozin treatment for this primary endpoint of the study (which classified worsening heart failure as either hospitalization for heart failure or an urgent visit because of heart failure that required intravenous therapy) was greatest, 10% during 2 years of follow-up, among the roughly one-quarter of enrolled patients who had been hospitalized for heart failure within 12 months of entering the study. Patients previously hospitalized for heart failure more than 12 months before they entered DAPA-HF had a 4% absolute cut in their primary-outcome events during the trial, and those who had never been hospitalized for heart failure had a 2% absolute benefit, compared with placebo, during 2 years of follow-up.
These findings were consistent with the timing of benefits for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) in recent studies of two other drugs from the same class, the sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitors, including empagliflozin (Jardiance, which inhibits SGLT-2) in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial, and sotagliflozin (Zynquista, which inhibits both SGLT1 and -2) in the SOLOIST-WHF trial, noted Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, and Clyde W. Yancy, MD, in an editor’s note that accompanied the new report.
The new findings show “the opportunity to expeditiously implement this remarkable class of therapy for HFrEF is now compelling and deserves disruptive efforts to ensure comprehensive treatment and the best patient outcomes,” wrote Dr. Fonarow, a professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, and Dr. Yancy, a professor of medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
But despite these new findings, their exact meaning remains unclear in terms of when to start dapagliflozin (or a different drug from the same class), compared with the other drug classes that have proven highly effective in patients with HFrEF, and exactly how long after hospitalization for heart failure dapagliflozin can safely and effectively begin.
Data needed on starting an SGLT inhibitor soon after hospitalization in patients without diabetes
“DAPA-HF showed that, in patients with or without diabetes, an SGLT2 inhibitor reduced the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with stable HFrEF. SOLOIST-WHF looked strictly at patients with diabetes, and showed that a combined SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor could reduce the risk of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure in patients with recently decompensated heart failure,” Dr. Berg, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, noted in an interview. “What we don’t have is a trial focused exclusively on enrolling patients while hospitalized with acute heart failure, irrespective of whether they have diabetes, and testing the immediate clinical efficacy and safety of starting an SGLT2 inhibitor. That is what we are testing with the ongoing DAPA ACT HF-TIMI 68 trial.”
In addition, updated recommendations from the American College of Cardiology on initiating drug therapy in patients newly diagnosed with HFrEF that appeared in early 2021 promoted a sequence that starts most patients on sacubitril/valsartan (Entresto) and a beta-blocker, followed by a diuretic (when needed), a mineralocorticoid receptor agonist, and then an SGLT inhibitor. The recommendations note that starting a patient on all these drug classes could take 3-6 months.
“There are intense debates about the optimal sequence for introducing these therapies, and I don’t think we have solid data to suggest that one sequence is clearly better than another,” noted Dr. Berg. “A one-size-fits-all approach probably doesn’t make sense. For example, each of these therapies has a different set of effects on heart rate and blood pressure, and each has a unique side effect profile, so clinicians will often need to tailor the treatment approach to the patient. And, of course, cost is an important consideration. Although the optimal time to start an SGLT2 inhibitor remains uncertain, the results of our analysis suggest that waiting may result in preventable adverse heart failure events.”
DAPA-HF randomized 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class II-IV at 410 sites in 20 countries. The incidence of the primary, combined endpoint fell by 26% with dapagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo, during a median 18-month follow-up. Among the study cohort 27% of patients had been hospitalized for heart failure within a year of their entry, 20% had been hospitalized for heart failure more than 1 year before entry, and 53% had no history of a hospitalization for heart failure.
DAPA-HF was sponsored by AstraZeneca, the company that markets dapagliflozin (Farxiga). Dr. Berg has received research support through his institution from AstraZeneca. Dr. Fonarow has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and from numerous other companies. Dr. Yancy’s spouse works for Abbott Laboratories.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Ivabradine knocks down heart rate, symptoms in POTS
The heart failure drug ivabradine (Corlanor) can provide relief from the elevated heart rate and often debilitating symptoms associated with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), a new study suggests.
Ivabradine significantly lowered standing heart rate, compared with placebo (77.9 vs. 94.2 beats/min; P < .001). The typical surge in heart rate that occurs upon standing in these patients was also blunted, compared with baseline (13.0 vs. 21.4 beats/min; P = .001).
“There are really not a lot of great options for patients with POTS and, mechanistically, ivabradine just make sense because it’s a drug that lowers heart rate very selectively and doesn’t lower blood pressure,” lead study author Pam R. Taub, MD, told this news organization.
Surprisingly, the reduction in heart rate translated into improved physical (P = .008) and social (P = .021) functioning after just 1 month of ivabradine, without any other background POTS medications or a change in nonpharmacologic therapies, she said. “What’s really nice to see is when you tackle a really significant part of the disease, which is the elevated heart rate, just how much better they feel.”
POTS patients are mostly healthy, active young women, who after some inciting event – such as viral infection, trauma, or surgery – experience an increase in heart rate of at least 30 beats/min upon standing accompanied by a range of symptoms, including dizziness, palpitations, brain fog, and fatigue.
A COVID connection?
The study enrolled patients with hyperadrenergic POTS as the predominant subtype, but another group to keep in mind that might benefit is the post-COVID POTS patient, said Dr. Taub, from the University of California, San Diego.
“We’re seeing an incredible number of patients post COVID that meet the criteria for POTS, and a lot of these patients also have COVID fatigue,” she said. “So clinically, myself and many other cardiologists who understand ivabradine have been using it off-label for the COVID patients, as long as they meet the criteria. You don’t want to use it in every COVID patient, but if someone’s predominant complaint is that their heart rate is going up when they’re standing and they’re debilitated by it, this is a drug to consider.”
Anecdotal findings in patients with long-hauler COVID need to be translated into rigorous research protocols, but mechanistically, whether it’s POTS from COVID or from another type of infection – like Lyme disease or some other viral syndrome – it should work the same, Dr. Taub said. “POTS is POTS.”
There are no first-line drugs for POTS, and current class IIb recommendations include midodrine, which increases blood pressure and can make people feel awful, and fludrocortisone, which can cause a lot of weight gain and fluid retention, she observed. Other agents that lower heart rate, like beta-blockers, also lower blood pressure and can aggravate depression and fatigue.
Ivabradine regulates heart rate by specifically blocking the Ifunny channel of the sinoatrial node. It was approved in 2015 in the United States to reduce hospitalizations in patients with systolic heart failure, and it also has a second class IIb recommendation for inappropriate sinus tachycardia.
The present study, reported in the Feb. 23 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, is the first randomized clinical trial using ivabradine to treat POTS.
A total of 26 patients with POTS were started on ivabradine 5 mg or placebo twice daily for 1 month, then were crossed over to the other treatment for 1 month after a 1-week washout period. Six patients were started on a 2.5-mg twice-daily dose. Doses were adjusted during the study based on the patient’s heart rate response and tolerance. Patients had seven clinic visits in which norepinephrine (NE) levels were measured and head-up tilt testing conducted.
Four patients in the ivabradine arm withdrew because of adverse effects, and one withdrew during crossover.
Among the 22 patients who completed the study, exploratory analyses showed a strong trend for greater reduction in plasma NE upon standing with ivabradine (P = .056). The effect was also more profound in patients with very high baseline standing NE levels (at least 1,000 pg/mL) than in those with lower NE levels (600 to 1,000 pg/mL).
“It makes sense because that means their sympathetic nervous system is more overactive; they have a higher heart rate,” Dr. Taub said. “So it’s a potential clinical tool that people can use in their practice to determine, ‘okay, is this a patient I should be considering ivabradine on?’ ”
Although the present study had only 22 patients, “it should definitely be looked at as a step forward, both in terms of ivabradine specifically and in terms of setting the standard for the types of studies we want to see in our patients,” Satish R. Raj, MD, MSCI, University of Calgary (Alta.), said in an interview.
In a related editorial, however, Dr. Raj and coauthor Robert S. Sheldon, MD, PhD, also from the University of Calgary, point out that the standing heart rate in the placebo phase was only 94 beats/min, “suggesting that these patients may be affected only mildly by their POTS.”
Asked about the point, Dr. Taub said: “I don’t know if I agree with that.” She noted that the diagnosis of POTS was confirmed by tilt-table testing and NE levels and that patients’ symptoms vary from day to day. “The standard deviation was plus or minus 16.8, so there’s variability.”
Both Dr. Raj and Dr. Taub said they expect the results will be included in the next scientific statement for POTS, but in the meantime, it may be a struggle to get the drug covered by insurance.
“The challenge is that this is a very off-label use for this medication, and the medication’s not cheap,” Dr. Raj observed. The price for 60 tablets, which is about a 1-month supply, is $485 on GoodRx.
Another question going forward, he said, is whether ivabradine is superior to beta-blockers, which will be studied in a 20-patient crossover trial sponsored by the University of Calgary that is about to launch. The primary completion date is set for 2024.
The study was supported by a grant from Amgen. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA. Dr. Raj has received a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and research grants from Dysautonomia International to address the pathophysiology of POTS. Dr. Sheldon has received a research grant from Dysautonomia International for a clinical trial assessing ivabradine and propranolol for the treatment of POTS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The heart failure drug ivabradine (Corlanor) can provide relief from the elevated heart rate and often debilitating symptoms associated with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), a new study suggests.
Ivabradine significantly lowered standing heart rate, compared with placebo (77.9 vs. 94.2 beats/min; P < .001). The typical surge in heart rate that occurs upon standing in these patients was also blunted, compared with baseline (13.0 vs. 21.4 beats/min; P = .001).
“There are really not a lot of great options for patients with POTS and, mechanistically, ivabradine just make sense because it’s a drug that lowers heart rate very selectively and doesn’t lower blood pressure,” lead study author Pam R. Taub, MD, told this news organization.
Surprisingly, the reduction in heart rate translated into improved physical (P = .008) and social (P = .021) functioning after just 1 month of ivabradine, without any other background POTS medications or a change in nonpharmacologic therapies, she said. “What’s really nice to see is when you tackle a really significant part of the disease, which is the elevated heart rate, just how much better they feel.”
POTS patients are mostly healthy, active young women, who after some inciting event – such as viral infection, trauma, or surgery – experience an increase in heart rate of at least 30 beats/min upon standing accompanied by a range of symptoms, including dizziness, palpitations, brain fog, and fatigue.
A COVID connection?
The study enrolled patients with hyperadrenergic POTS as the predominant subtype, but another group to keep in mind that might benefit is the post-COVID POTS patient, said Dr. Taub, from the University of California, San Diego.
“We’re seeing an incredible number of patients post COVID that meet the criteria for POTS, and a lot of these patients also have COVID fatigue,” she said. “So clinically, myself and many other cardiologists who understand ivabradine have been using it off-label for the COVID patients, as long as they meet the criteria. You don’t want to use it in every COVID patient, but if someone’s predominant complaint is that their heart rate is going up when they’re standing and they’re debilitated by it, this is a drug to consider.”
Anecdotal findings in patients with long-hauler COVID need to be translated into rigorous research protocols, but mechanistically, whether it’s POTS from COVID or from another type of infection – like Lyme disease or some other viral syndrome – it should work the same, Dr. Taub said. “POTS is POTS.”
There are no first-line drugs for POTS, and current class IIb recommendations include midodrine, which increases blood pressure and can make people feel awful, and fludrocortisone, which can cause a lot of weight gain and fluid retention, she observed. Other agents that lower heart rate, like beta-blockers, also lower blood pressure and can aggravate depression and fatigue.
Ivabradine regulates heart rate by specifically blocking the Ifunny channel of the sinoatrial node. It was approved in 2015 in the United States to reduce hospitalizations in patients with systolic heart failure, and it also has a second class IIb recommendation for inappropriate sinus tachycardia.
The present study, reported in the Feb. 23 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, is the first randomized clinical trial using ivabradine to treat POTS.
A total of 26 patients with POTS were started on ivabradine 5 mg or placebo twice daily for 1 month, then were crossed over to the other treatment for 1 month after a 1-week washout period. Six patients were started on a 2.5-mg twice-daily dose. Doses were adjusted during the study based on the patient’s heart rate response and tolerance. Patients had seven clinic visits in which norepinephrine (NE) levels were measured and head-up tilt testing conducted.
Four patients in the ivabradine arm withdrew because of adverse effects, and one withdrew during crossover.
Among the 22 patients who completed the study, exploratory analyses showed a strong trend for greater reduction in plasma NE upon standing with ivabradine (P = .056). The effect was also more profound in patients with very high baseline standing NE levels (at least 1,000 pg/mL) than in those with lower NE levels (600 to 1,000 pg/mL).
“It makes sense because that means their sympathetic nervous system is more overactive; they have a higher heart rate,” Dr. Taub said. “So it’s a potential clinical tool that people can use in their practice to determine, ‘okay, is this a patient I should be considering ivabradine on?’ ”
Although the present study had only 22 patients, “it should definitely be looked at as a step forward, both in terms of ivabradine specifically and in terms of setting the standard for the types of studies we want to see in our patients,” Satish R. Raj, MD, MSCI, University of Calgary (Alta.), said in an interview.
In a related editorial, however, Dr. Raj and coauthor Robert S. Sheldon, MD, PhD, also from the University of Calgary, point out that the standing heart rate in the placebo phase was only 94 beats/min, “suggesting that these patients may be affected only mildly by their POTS.”
Asked about the point, Dr. Taub said: “I don’t know if I agree with that.” She noted that the diagnosis of POTS was confirmed by tilt-table testing and NE levels and that patients’ symptoms vary from day to day. “The standard deviation was plus or minus 16.8, so there’s variability.”
Both Dr. Raj and Dr. Taub said they expect the results will be included in the next scientific statement for POTS, but in the meantime, it may be a struggle to get the drug covered by insurance.
“The challenge is that this is a very off-label use for this medication, and the medication’s not cheap,” Dr. Raj observed. The price for 60 tablets, which is about a 1-month supply, is $485 on GoodRx.
Another question going forward, he said, is whether ivabradine is superior to beta-blockers, which will be studied in a 20-patient crossover trial sponsored by the University of Calgary that is about to launch. The primary completion date is set for 2024.
The study was supported by a grant from Amgen. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA. Dr. Raj has received a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and research grants from Dysautonomia International to address the pathophysiology of POTS. Dr. Sheldon has received a research grant from Dysautonomia International for a clinical trial assessing ivabradine and propranolol for the treatment of POTS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The heart failure drug ivabradine (Corlanor) can provide relief from the elevated heart rate and often debilitating symptoms associated with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS), a new study suggests.
Ivabradine significantly lowered standing heart rate, compared with placebo (77.9 vs. 94.2 beats/min; P < .001). The typical surge in heart rate that occurs upon standing in these patients was also blunted, compared with baseline (13.0 vs. 21.4 beats/min; P = .001).
“There are really not a lot of great options for patients with POTS and, mechanistically, ivabradine just make sense because it’s a drug that lowers heart rate very selectively and doesn’t lower blood pressure,” lead study author Pam R. Taub, MD, told this news organization.
Surprisingly, the reduction in heart rate translated into improved physical (P = .008) and social (P = .021) functioning after just 1 month of ivabradine, without any other background POTS medications or a change in nonpharmacologic therapies, she said. “What’s really nice to see is when you tackle a really significant part of the disease, which is the elevated heart rate, just how much better they feel.”
POTS patients are mostly healthy, active young women, who after some inciting event – such as viral infection, trauma, or surgery – experience an increase in heart rate of at least 30 beats/min upon standing accompanied by a range of symptoms, including dizziness, palpitations, brain fog, and fatigue.
A COVID connection?
The study enrolled patients with hyperadrenergic POTS as the predominant subtype, but another group to keep in mind that might benefit is the post-COVID POTS patient, said Dr. Taub, from the University of California, San Diego.
“We’re seeing an incredible number of patients post COVID that meet the criteria for POTS, and a lot of these patients also have COVID fatigue,” she said. “So clinically, myself and many other cardiologists who understand ivabradine have been using it off-label for the COVID patients, as long as they meet the criteria. You don’t want to use it in every COVID patient, but if someone’s predominant complaint is that their heart rate is going up when they’re standing and they’re debilitated by it, this is a drug to consider.”
Anecdotal findings in patients with long-hauler COVID need to be translated into rigorous research protocols, but mechanistically, whether it’s POTS from COVID or from another type of infection – like Lyme disease or some other viral syndrome – it should work the same, Dr. Taub said. “POTS is POTS.”
There are no first-line drugs for POTS, and current class IIb recommendations include midodrine, which increases blood pressure and can make people feel awful, and fludrocortisone, which can cause a lot of weight gain and fluid retention, she observed. Other agents that lower heart rate, like beta-blockers, also lower blood pressure and can aggravate depression and fatigue.
Ivabradine regulates heart rate by specifically blocking the Ifunny channel of the sinoatrial node. It was approved in 2015 in the United States to reduce hospitalizations in patients with systolic heart failure, and it also has a second class IIb recommendation for inappropriate sinus tachycardia.
The present study, reported in the Feb. 23 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, is the first randomized clinical trial using ivabradine to treat POTS.
A total of 26 patients with POTS were started on ivabradine 5 mg or placebo twice daily for 1 month, then were crossed over to the other treatment for 1 month after a 1-week washout period. Six patients were started on a 2.5-mg twice-daily dose. Doses were adjusted during the study based on the patient’s heart rate response and tolerance. Patients had seven clinic visits in which norepinephrine (NE) levels were measured and head-up tilt testing conducted.
Four patients in the ivabradine arm withdrew because of adverse effects, and one withdrew during crossover.
Among the 22 patients who completed the study, exploratory analyses showed a strong trend for greater reduction in plasma NE upon standing with ivabradine (P = .056). The effect was also more profound in patients with very high baseline standing NE levels (at least 1,000 pg/mL) than in those with lower NE levels (600 to 1,000 pg/mL).
“It makes sense because that means their sympathetic nervous system is more overactive; they have a higher heart rate,” Dr. Taub said. “So it’s a potential clinical tool that people can use in their practice to determine, ‘okay, is this a patient I should be considering ivabradine on?’ ”
Although the present study had only 22 patients, “it should definitely be looked at as a step forward, both in terms of ivabradine specifically and in terms of setting the standard for the types of studies we want to see in our patients,” Satish R. Raj, MD, MSCI, University of Calgary (Alta.), said in an interview.
In a related editorial, however, Dr. Raj and coauthor Robert S. Sheldon, MD, PhD, also from the University of Calgary, point out that the standing heart rate in the placebo phase was only 94 beats/min, “suggesting that these patients may be affected only mildly by their POTS.”
Asked about the point, Dr. Taub said: “I don’t know if I agree with that.” She noted that the diagnosis of POTS was confirmed by tilt-table testing and NE levels and that patients’ symptoms vary from day to day. “The standard deviation was plus or minus 16.8, so there’s variability.”
Both Dr. Raj and Dr. Taub said they expect the results will be included in the next scientific statement for POTS, but in the meantime, it may be a struggle to get the drug covered by insurance.
“The challenge is that this is a very off-label use for this medication, and the medication’s not cheap,” Dr. Raj observed. The price for 60 tablets, which is about a 1-month supply, is $485 on GoodRx.
Another question going forward, he said, is whether ivabradine is superior to beta-blockers, which will be studied in a 20-patient crossover trial sponsored by the University of Calgary that is about to launch. The primary completion date is set for 2024.
The study was supported by a grant from Amgen. Dr. Taub has served as a consultant for Amgen, Bayer, Esperion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; is a shareholder in Epirium Bio; and has received research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Department of Homeland Security/FEMA. Dr. Raj has received a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and research grants from Dysautonomia International to address the pathophysiology of POTS. Dr. Sheldon has received a research grant from Dysautonomia International for a clinical trial assessing ivabradine and propranolol for the treatment of POTS.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Quick byte: Curing diabetes
Harvard biologist Doug Melton, PhD, is exploring the use of stem cells to create replacement beta cells that produce insulin, according to Time magazine.
In 2014, he co-founded Semma Therapeutics to develop the technology, which was acquired by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
“The company has created a small, implantable device that holds millions of replacement beta cells, letting glucose and insulin through but keeping immune cells out. ‘If it works in people as well as it does in animals, it’s possible that people will not be diabetic,’ said Dr. Melton, co-director of the Harvard Stem Cell Institute and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. ‘They will eat and drink and play like those of us who are not.’”
Reference
Steinberg D. 12 innovations that will change health care and medicine in the 2020s. Time. 2019 Oct 25. https://time.com/5710295/top-health-innovations/ Accessed Dec 5, 2019.
Harvard biologist Doug Melton, PhD, is exploring the use of stem cells to create replacement beta cells that produce insulin, according to Time magazine.
In 2014, he co-founded Semma Therapeutics to develop the technology, which was acquired by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
“The company has created a small, implantable device that holds millions of replacement beta cells, letting glucose and insulin through but keeping immune cells out. ‘If it works in people as well as it does in animals, it’s possible that people will not be diabetic,’ said Dr. Melton, co-director of the Harvard Stem Cell Institute and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. ‘They will eat and drink and play like those of us who are not.’”
Reference
Steinberg D. 12 innovations that will change health care and medicine in the 2020s. Time. 2019 Oct 25. https://time.com/5710295/top-health-innovations/ Accessed Dec 5, 2019.
Harvard biologist Doug Melton, PhD, is exploring the use of stem cells to create replacement beta cells that produce insulin, according to Time magazine.
In 2014, he co-founded Semma Therapeutics to develop the technology, which was acquired by Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
“The company has created a small, implantable device that holds millions of replacement beta cells, letting glucose and insulin through but keeping immune cells out. ‘If it works in people as well as it does in animals, it’s possible that people will not be diabetic,’ said Dr. Melton, co-director of the Harvard Stem Cell Institute and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. ‘They will eat and drink and play like those of us who are not.’”
Reference
Steinberg D. 12 innovations that will change health care and medicine in the 2020s. Time. 2019 Oct 25. https://time.com/5710295/top-health-innovations/ Accessed Dec 5, 2019.













