User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
COVID-19: Delirium first, depression, anxiety, insomnia later?
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Severe COVID-19 may cause delirium in the acute stage of illness, followed by the possibility of depression, anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) over the longer term, new research suggests.
Results from “the first systematic review and meta-analysis of the psychiatric consequences of coronavirus infection” showed that previous coronavirus epidemics were associated with a significant psychiatric burden in both the acute and post-illness stages.
“Most people with COVID-19 will not develop any mental health problems, even among those with severe cases requiring hospitalization, but given the huge numbers of people getting sick, the global impact on mental health could be considerable,” co–lead investigator Jonathan Rogers, MRCPsych, Department of Psychiatry, University College London, United Kingdom, said in a news release.
The study was published online May 18 in Lancet Psychiatry.
Need for Monitoring, Support
The researchers analyzed 65 peer-reviewed studies and seven preprint articles with data on acute and post-illness psychiatric and neuropsychiatric features of patients who had been hospitalized with COVID-19, as well as two other diseases caused by coronaviruses – severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), in 2002–2004, and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), in 2012.
“Our main findings are that signs suggestive of delirium are common in the acute stage of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19; there is evidence of depression, anxiety, fatigue, and post-traumatic stress disorder in the post-illness stage of previous coronavirus epidemics, but there are few data yet on COVID-19,” the investigators write.
The data show that among patients acutely ill with SARS and MERS, 28% experienced confusion, 33% had depressed mood, 36% had anxiety, 34% suffered from impaired memory, and 42% had insomnia.
After recovery from SARS and MERS, sleep disorder, frequent recall of traumatic memories, emotional lability, impaired concentration, fatigue, and impaired memory were reported in more than 15% of patients during a follow-up period that ranged from 6 weeks to 39 months.
In a meta-analysis, the point prevalence in the post-illness stage was 32% for PTSD and about 15% for depression and anxiety.
In patients acutely ill with severe COVID-19, available data suggest that 65% experience delirium, 69% have agitation after withdrawal of sedation, and 21% have altered consciousness.
In one study, 33% of patients had a dysexecutive syndrome at discharge, characterized by symptoms such as inattention, disorientation, or poorly organized movements in response to command. Currently, data are very limited regarding patients who have recovered from COVID-19, the investigators caution.
“, and monitored after they recover to ensure they do not develop mental illnesses, and are able to access treatment if needed,” senior author Anthony David, FMedSci, from UCL Institute of Mental Health, said in a news release.
“While most people with COVID-19 will recover without experiencing mental illness, we need to research which factors may contribute to enduring mental health problems, and develop interventions to prevent and treat them,” he added.
Be Prepared
The coauthors of a linked commentary say it makes sense, from a biological perspective, to merge data on these three coronavirus diseases, given the degree to which they resemble each other.
They caution, however, that treatment of COVID-19 seems to be different from treatment of SARS and MERS. In addition, the social and economic situation of COVID-19 survivors’ return is completely different from that of SARS and MERS survivors.
Findings from previous coronavirus outbreaks are “useful, but might not be exact predictors of prevalences of psychiatric complications for patients with COVID-19,” write Iris Sommer, MD, PhD, from University Medical Center Groningen, the Netherlands, and P. Roberto Bakker, MD, PhD, from Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands.
“The warning from [this study] that we should prepare to treat large numbers of patients with COVID-19 who go on to develop delirium, post-traumatic stress disorder, anxiety, and depression is an important message for the psychiatric community,” they add.
Sommer and Bakker also say the reported estimates of prevalence in this study should be interpreted with caution, “as true numbers of both acute and long-term psychiatric disorders for patients with COVID-19 might be considerably higher.”
Funding for the study was provided by the Wellcome Trust, the UK National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), the UK Medical Research Council, the NIHR Biomedical Research Center at the University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and the University College London. The authors of the study and the commentary have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
To fast or not to fast before elective cardiac catheterization
No restriction of oral food intake prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization is as safe as the current traditional NPO [nothing by mouth] strategy, results from a large, single-center, randomized controlled trial showed.
According to lead investigator Abhishek Mishra, MD, NPO after midnight has been a standard practice before major surgery requiring general anesthesia since Mendelson Syndrome was first described in 1946. “The rational for keeping NPO after midnight has been to keep the stomach empty, to reduce gastric contents and acidity – which would reduce emesis – and eventually reduce the risk of aspiration,” Dr. Mishra, a cardiologist at the Heart and Vascular Institute at Vidant Health in Greenville, N.C., said at the at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions virtual annual scientific sessions. “The rationale of NPO in the setting of cardiac catheterization is to reduce the risk of aspiration, and more so, of a patient needing emergent cardiac surgery.” The clinical question was, do we really need to keep our patients NPO prior to elective cardiac catheterization? So far, no large randomized study has been done to answer this question.”
To find out, Dr. Mishra and colleagues carried out CHOW NOW (Can We Safely Have Our Patients Eat With Cardiac Catheterization – Nix or Allow), a single-center, prospective, randomized, single-blinded study that compared the safety of a nonfasting strategy with the current fasting protocol strategies in 599 patients who underwent nonemergent cardiac catheterization at The Guthrie Clinic/Robert Packer Hospital in Sayre, Pa.
Patients in the fasting group were instructed to be NPO after midnight, but could have clear liquids up to 2 hours prior to the procedure, while those in the nonfasting group had no restriction of oral intake, irrespective of time of cardiac catheterization. The primary outcome was a composite of aspiration pneumonia, preprocedural hypertension, preprocedural hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, incidence of nausea/vomiting, and contrast-induced neuropathy. Secondary outcomes included total cost of the index hospitalization, patient satisfaction via a questionnaire containing seven questions, and in-hospital mortality.
Of the 599 patients, 306 were assigned to the standard fasting group and the remaining 293 to the nonfasting group. Their mean age was 67 years, 45% were on a proton pump inhibitor or H2 blockers, and 33% had diabetes. In addition, 40% had acute coronary syndrome, and 23% underwent percutaneous intervention.
The researchers observed no statistically significant difference in the primary or secondary outcomes between the study groups. In the nonfasting group, 11.3% of patients met the primary endpoint, compared with 9.8% of the patients in the standard fasting group (P = .65). In addition, the nonfasting strategy was found to be noninferior to the standard fasting strategy for the primary outcome at a noninferiority margin threshold of 0.059.
Dr. Mishra and colleagues observed no differences between the standard fasting and nonfasting groups with respect to in-hospital mortality (0.3% vs. 0.7%, respectively; P = .616), patient satisfaction score (a mean of 4.4 vs. a mean of 4.5; P = .257), and mean total cost of hospitalization ($8,446 vs. $6,960; P = .654).
“In this randomized, controlled trial, we found that there was no significant difference in the rate of overall adverse events with an approach of unrestricted oral intake prior to cardiac catheterization compared to strict fasting, and it was associated with better patient satisfaction and lower cost of care, especially for hospitalized patients,” concluded Dr. Mishra, who conducted the research during his fellowship at The Guthrie Clinic.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including the fact that results are applicable only to cardiac catheterization procedures, including coronary angiographies, percutaneous coronary interventions, and left heart catheterizations. “These results are not applicable to certain high-risk coronary procedures that required the use of a large-bore access or any valve procedures,” he said.
One of the session’s invited panelists, Cindy L. Grines, MD,, said that she and other interventional cardiologists have “gone around and around” on the issue of NPO prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization. “I actually let my patients get fluids up until the time they’re put on the cath lab table,” said Dr. Grines, chief scientific officer of the Northside Cardiovascular Institute in Atlanta. “I haven’t been giving them solid food like this, though.”
Another panelist, Timothy D. Henry, MD, said that in his clinical experience, “patients don’t like being NPO, and I think we’ve all seen cases where patients are actually volume-depleted in the morning.” Dr. Henry, medical director of The Carl and Edyth Lindner Center for Research and Education at The Christ Hospital in Cincinnati, pointed out that most NPO policy “is not dictated by us as interventional cardiologists; it’s dictated by hospital policies or by anesthesiologists. Will [the results of this study] change what we do?”
The Donald Guthrie Research Foundation funded the study. Daniel P. Sporn, MD, FACC, was the study’s principal investigator. Dr. Mishra reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mishra A et al., SCAI 2020, abstract 11758.
No restriction of oral food intake prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization is as safe as the current traditional NPO [nothing by mouth] strategy, results from a large, single-center, randomized controlled trial showed.
According to lead investigator Abhishek Mishra, MD, NPO after midnight has been a standard practice before major surgery requiring general anesthesia since Mendelson Syndrome was first described in 1946. “The rational for keeping NPO after midnight has been to keep the stomach empty, to reduce gastric contents and acidity – which would reduce emesis – and eventually reduce the risk of aspiration,” Dr. Mishra, a cardiologist at the Heart and Vascular Institute at Vidant Health in Greenville, N.C., said at the at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions virtual annual scientific sessions. “The rationale of NPO in the setting of cardiac catheterization is to reduce the risk of aspiration, and more so, of a patient needing emergent cardiac surgery.” The clinical question was, do we really need to keep our patients NPO prior to elective cardiac catheterization? So far, no large randomized study has been done to answer this question.”
To find out, Dr. Mishra and colleagues carried out CHOW NOW (Can We Safely Have Our Patients Eat With Cardiac Catheterization – Nix or Allow), a single-center, prospective, randomized, single-blinded study that compared the safety of a nonfasting strategy with the current fasting protocol strategies in 599 patients who underwent nonemergent cardiac catheterization at The Guthrie Clinic/Robert Packer Hospital in Sayre, Pa.
Patients in the fasting group were instructed to be NPO after midnight, but could have clear liquids up to 2 hours prior to the procedure, while those in the nonfasting group had no restriction of oral intake, irrespective of time of cardiac catheterization. The primary outcome was a composite of aspiration pneumonia, preprocedural hypertension, preprocedural hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, incidence of nausea/vomiting, and contrast-induced neuropathy. Secondary outcomes included total cost of the index hospitalization, patient satisfaction via a questionnaire containing seven questions, and in-hospital mortality.
Of the 599 patients, 306 were assigned to the standard fasting group and the remaining 293 to the nonfasting group. Their mean age was 67 years, 45% were on a proton pump inhibitor or H2 blockers, and 33% had diabetes. In addition, 40% had acute coronary syndrome, and 23% underwent percutaneous intervention.
The researchers observed no statistically significant difference in the primary or secondary outcomes between the study groups. In the nonfasting group, 11.3% of patients met the primary endpoint, compared with 9.8% of the patients in the standard fasting group (P = .65). In addition, the nonfasting strategy was found to be noninferior to the standard fasting strategy for the primary outcome at a noninferiority margin threshold of 0.059.
Dr. Mishra and colleagues observed no differences between the standard fasting and nonfasting groups with respect to in-hospital mortality (0.3% vs. 0.7%, respectively; P = .616), patient satisfaction score (a mean of 4.4 vs. a mean of 4.5; P = .257), and mean total cost of hospitalization ($8,446 vs. $6,960; P = .654).
“In this randomized, controlled trial, we found that there was no significant difference in the rate of overall adverse events with an approach of unrestricted oral intake prior to cardiac catheterization compared to strict fasting, and it was associated with better patient satisfaction and lower cost of care, especially for hospitalized patients,” concluded Dr. Mishra, who conducted the research during his fellowship at The Guthrie Clinic.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including the fact that results are applicable only to cardiac catheterization procedures, including coronary angiographies, percutaneous coronary interventions, and left heart catheterizations. “These results are not applicable to certain high-risk coronary procedures that required the use of a large-bore access or any valve procedures,” he said.
One of the session’s invited panelists, Cindy L. Grines, MD,, said that she and other interventional cardiologists have “gone around and around” on the issue of NPO prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization. “I actually let my patients get fluids up until the time they’re put on the cath lab table,” said Dr. Grines, chief scientific officer of the Northside Cardiovascular Institute in Atlanta. “I haven’t been giving them solid food like this, though.”
Another panelist, Timothy D. Henry, MD, said that in his clinical experience, “patients don’t like being NPO, and I think we’ve all seen cases where patients are actually volume-depleted in the morning.” Dr. Henry, medical director of The Carl and Edyth Lindner Center for Research and Education at The Christ Hospital in Cincinnati, pointed out that most NPO policy “is not dictated by us as interventional cardiologists; it’s dictated by hospital policies or by anesthesiologists. Will [the results of this study] change what we do?”
The Donald Guthrie Research Foundation funded the study. Daniel P. Sporn, MD, FACC, was the study’s principal investigator. Dr. Mishra reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mishra A et al., SCAI 2020, abstract 11758.
No restriction of oral food intake prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization is as safe as the current traditional NPO [nothing by mouth] strategy, results from a large, single-center, randomized controlled trial showed.
According to lead investigator Abhishek Mishra, MD, NPO after midnight has been a standard practice before major surgery requiring general anesthesia since Mendelson Syndrome was first described in 1946. “The rational for keeping NPO after midnight has been to keep the stomach empty, to reduce gastric contents and acidity – which would reduce emesis – and eventually reduce the risk of aspiration,” Dr. Mishra, a cardiologist at the Heart and Vascular Institute at Vidant Health in Greenville, N.C., said at the at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions virtual annual scientific sessions. “The rationale of NPO in the setting of cardiac catheterization is to reduce the risk of aspiration, and more so, of a patient needing emergent cardiac surgery.” The clinical question was, do we really need to keep our patients NPO prior to elective cardiac catheterization? So far, no large randomized study has been done to answer this question.”
To find out, Dr. Mishra and colleagues carried out CHOW NOW (Can We Safely Have Our Patients Eat With Cardiac Catheterization – Nix or Allow), a single-center, prospective, randomized, single-blinded study that compared the safety of a nonfasting strategy with the current fasting protocol strategies in 599 patients who underwent nonemergent cardiac catheterization at The Guthrie Clinic/Robert Packer Hospital in Sayre, Pa.
Patients in the fasting group were instructed to be NPO after midnight, but could have clear liquids up to 2 hours prior to the procedure, while those in the nonfasting group had no restriction of oral intake, irrespective of time of cardiac catheterization. The primary outcome was a composite of aspiration pneumonia, preprocedural hypertension, preprocedural hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, incidence of nausea/vomiting, and contrast-induced neuropathy. Secondary outcomes included total cost of the index hospitalization, patient satisfaction via a questionnaire containing seven questions, and in-hospital mortality.
Of the 599 patients, 306 were assigned to the standard fasting group and the remaining 293 to the nonfasting group. Their mean age was 67 years, 45% were on a proton pump inhibitor or H2 blockers, and 33% had diabetes. In addition, 40% had acute coronary syndrome, and 23% underwent percutaneous intervention.
The researchers observed no statistically significant difference in the primary or secondary outcomes between the study groups. In the nonfasting group, 11.3% of patients met the primary endpoint, compared with 9.8% of the patients in the standard fasting group (P = .65). In addition, the nonfasting strategy was found to be noninferior to the standard fasting strategy for the primary outcome at a noninferiority margin threshold of 0.059.
Dr. Mishra and colleagues observed no differences between the standard fasting and nonfasting groups with respect to in-hospital mortality (0.3% vs. 0.7%, respectively; P = .616), patient satisfaction score (a mean of 4.4 vs. a mean of 4.5; P = .257), and mean total cost of hospitalization ($8,446 vs. $6,960; P = .654).
“In this randomized, controlled trial, we found that there was no significant difference in the rate of overall adverse events with an approach of unrestricted oral intake prior to cardiac catheterization compared to strict fasting, and it was associated with better patient satisfaction and lower cost of care, especially for hospitalized patients,” concluded Dr. Mishra, who conducted the research during his fellowship at The Guthrie Clinic.
He acknowledged certain limitations of the trial, including the fact that results are applicable only to cardiac catheterization procedures, including coronary angiographies, percutaneous coronary interventions, and left heart catheterizations. “These results are not applicable to certain high-risk coronary procedures that required the use of a large-bore access or any valve procedures,” he said.
One of the session’s invited panelists, Cindy L. Grines, MD,, said that she and other interventional cardiologists have “gone around and around” on the issue of NPO prior to nonemergent cardiac catheterization. “I actually let my patients get fluids up until the time they’re put on the cath lab table,” said Dr. Grines, chief scientific officer of the Northside Cardiovascular Institute in Atlanta. “I haven’t been giving them solid food like this, though.”
Another panelist, Timothy D. Henry, MD, said that in his clinical experience, “patients don’t like being NPO, and I think we’ve all seen cases where patients are actually volume-depleted in the morning.” Dr. Henry, medical director of The Carl and Edyth Lindner Center for Research and Education at The Christ Hospital in Cincinnati, pointed out that most NPO policy “is not dictated by us as interventional cardiologists; it’s dictated by hospital policies or by anesthesiologists. Will [the results of this study] change what we do?”
The Donald Guthrie Research Foundation funded the study. Daniel P. Sporn, MD, FACC, was the study’s principal investigator. Dr. Mishra reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Mishra A et al., SCAI 2020, abstract 11758.
REPORTING FROM SCAI 2020
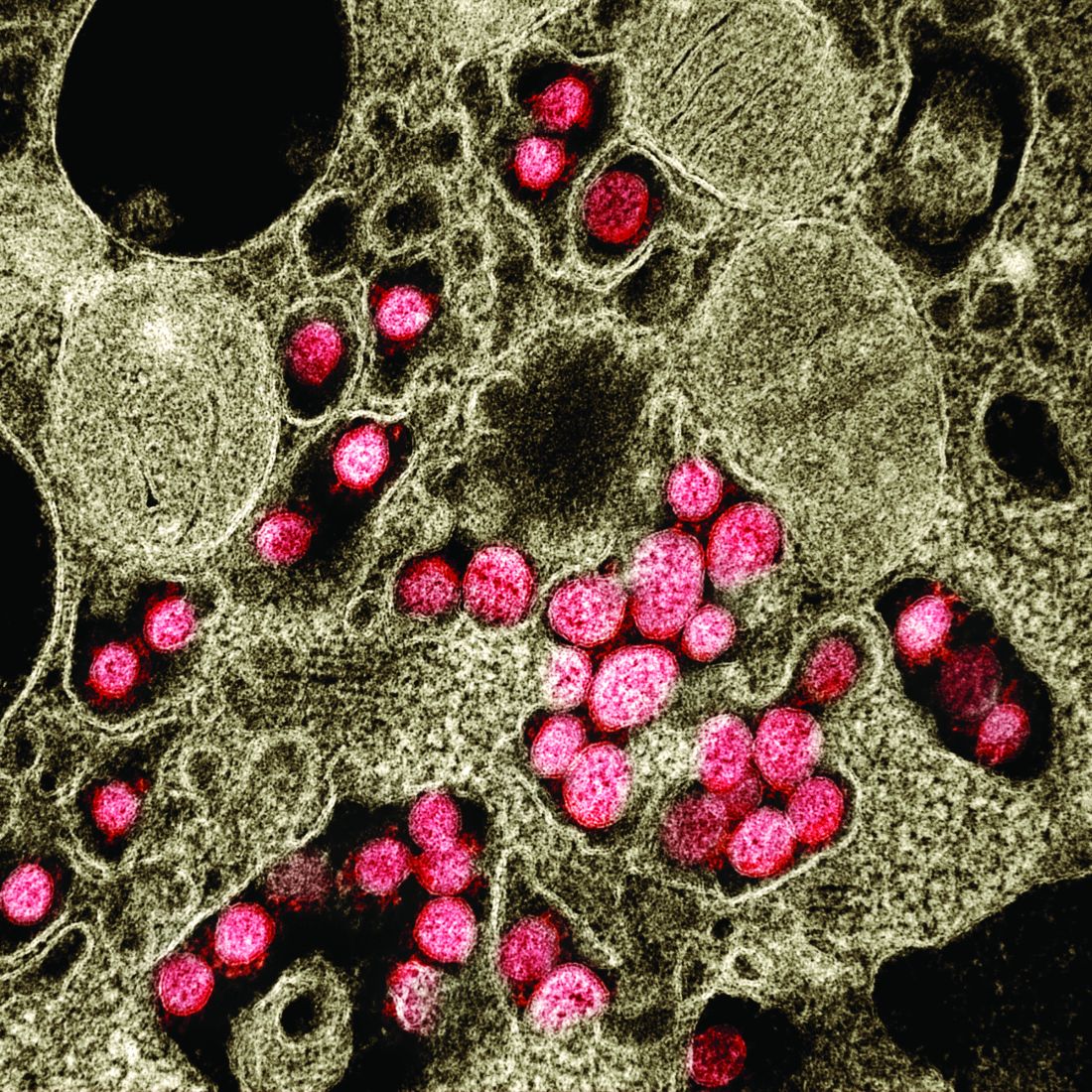
Chilblain-like lesions reported in children thought to have COVID-19
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
Two and elsewhere.
These symptoms should be considered a sign of infection with the virus, but the symptoms themselves typically don’t require treatment, according to the authors of the two new reports, from hospitals in Milan and Madrid, published in Pediatric Dermatology.
In the first study, Cristiana Colonna, MD, and colleagues at Hospital Maggiore Polyclinic in Milan described four cases of chilblain-like lesions in children ages 5-11 years with mild COVID-19 symptoms.
In the second, David Andina, MD, and colleagues in the ED and the departments of dermatology and pathology at the Child Jesus University Children’s Hospital in Madrid published a retrospective study of 22 cases in children and adolescents ages 6-17 years who reported to the hospital ED from April 6 to 17, the peak of the pandemic in Madrid.
In all four of the Milan cases, the skin lesions appeared several days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, although all four patients initially tested negative for COVID-19. However, Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote that, “given the fact that the sensitivity and specificity of both nasopharyngeal swabs and antibody tests for COVID-19 (when available) are not 100% reliable, the question of the origin of these strange chilblain-like lesions is still elusive.” Until further studies are available, they emphasized that clinicians should be “alert to the presentation of chilblain-like findings” in children with mild symptoms “as a possible sign of COVID-19 infection.”
All the patients had lesions on their feet or toes, and a 5-year-old boy also had lesions on the right hand. One patient, an 11-year-old girl, had a biopsy that revealed dense lymphocytic perivascular cuffing and periadnexal infiltration.
“The finding of an elevated d-dimer in one of our patients, along with the clinical features suggestive of a vasoocclusive phenomenon, supports consideration of laboratory evaluation for coagulation defects in asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic children with acrovasculitis-like findings,” Dr. Colonna and colleagues wrote. None of the four cases in Milan required treatment, with three cases resolving within 5 days.
Like the Milan cases, all 22 patients in the Madrid series had foot or toe lesions and three had lesions on the fingers. This larger series also reported more detailed symptoms about the lesions: pruritus in nine patients (41%) and mild pain in seven (32%). A total of 10 patients had systemic symptoms of COVID-19, predominantly cough and rhinorrhea in 9 patients (41%), but 2 (9%) had abdominal pain and diarrhea. These symptoms, the authors said, appeared a median of 14 days (range, 1-28 days) before they developed chilblains.
A total of 19 patients were tested for COVID-19, but only 1 was positive.
This retrospective study also included contact information, with one patient having household contact with a single confirmed case of COVID-19; 12 patients recalled household contact who were considered probable cases of COVID-19, with respiratory symptoms.
Skin biopsies were obtained from the acral lesions in six patients, all showing similar results, although with varying degrees of intensity. All biopsies showed features of lymphocytic vasculopathy. Some cases showed mild dermal and perieccrine mucinosis, lymphocytic eccrine hidradenitis, vascular ectasia, red cell extravasation and focal thrombosis described as “mostly confined to scattered papillary dermal capillaries, but also in vessels of the reticular dermis.”
The only treatments Dr. Andina and colleagues reported were oral analgesics for pain and oral antihistamines for pruritus when needed. One patient was given topical corticosteroids and another a short course of oral steroids, both for erythema multiforme.
Dr. Andina and colleagues wrote that the skin lesions in these patients “were unequivocally categorized as chilblains, both clinically and histopathologically,” and, after 7-10 days, began to fade. None of the patients had complications, and had an “excellent outcome,” they noted.
Dr. Colonna and colleagues had no conflicts of interest to declare. Dr. Andina and colleagues provided no disclosure statement.
SOURCES: Colonna C et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1111/pde.14210; Andina D et al. Ped Derm. 2020 May 9. doi: 10.1111/pde.14215.
FROM PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Today’s top news highlights: Risks & benefits of universal masking, prostate cancer rising
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively. As reported in Science, previous randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses have shown no added protection, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors. Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus. On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects found that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” READ MORE
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Biomarkers for inflammation and thrombosis may predict deaths from COVID-19 among critically ill patients, researchers said. Their prospective cohort study of 1,150 patients hospitalized in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality. “Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York, said in a press release. The study was published in The Lancet. READ MORE
Advanced prostate cancers still rising in U.S.
The incidence of advanced prostate cancers in the United States “persistently” increased annually for 5 years after the United States Preventive Services Task Force controversially advised in 2012 against prostate-specific antigen screening in men of all ages. “These data illustrate the trade-off between higher screening rates and more early-stage disease diagnoses (possibly overdiagnosis and overtreatment) and lower screening rates and more late-stage (possibly fatal) disease,” the authors of the study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, commented. “What is a surprise is that it’s every year,” said Ahmad Shabsigh, MD, a urologic oncologist at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center. “To see it so clearly in this study is sad." READ MORE
Testicular sperm may improve IVF outcomes
Use of testicular sperm in nonazoospermic couples who had prior in vitro fertilization failure using ejaculated sperm appears to improve embryo development and rates of clinical pregnancy and live birth, a retrospective observational study has found. The findings offer more evidence “that this might be something we can offer patients who’ve had multiple failures and no other reason as to why,” said M. Blake Evans, DO, a clinical fellow in reproductive endocrinology and infertility. The study, which won the college’s Donald F. Richardson Memorial Prize Research Paper award, was released ahead of a scheduled presentation at the annual American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists meeting. READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news coverage is available on MDedge.com.
Large COVID-19 dataset: Kidney injury in >35% of those in hospital
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As a new report shows that over a third of U.S. patients hospitalized with COVID-19 developed acute kidney injury (AKI), and nearly 15% of these patients needed dialysis, experts in the field are calling for more robust research into multiple aspects of this increasingly important issue.
Among 5,449 patients admitted to 13 Northwell Health New York–based hospitals between March and April 2020, 36.6% (1,993) developed AKI.
– the rate of kidney injury was 89.7% among ventilated patients, compared with 21.7% among other patients.
AKI in COVID-19 was also linked to a poor prognosis: 35% of those who developed AKI had died at the time of publication.
The study includes the largest defined cohort of hospitalized COVID-19 patients to date with a focus on AKI, says Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, of Northwell Health in Great Neck, N.Y., and colleagues in their article published online in Kidney International.
The findings track with those of a study of New York hospitals published online in The Lancet. In that dataset, just under a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and needed dialysis.
Both of these studies help solidify the experiences of clinicians on the ground, with many U.S. hospitals in the early phases of the pandemic underestimating the problem of AKI and having to scramble to find enough dialysis machines and dialysate solution to treat the most severely affected patients.
“We hope to learn more about the COVID-19–related AKI in the coming weeks, and that by sharing what we have learned from our patients, other doctors and their patients can benefit,” said senior author of the new study, Kenar D. Jhaveri, MD, associated chief of nephrology at Hofstra/Northwell.
The new report also comes as scientists from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases highlighted the importance of AKI as a sequela of COVID-19 in an editorial published in Diabetes Care.
They, too, said that it is vitally important to better understand what is happening, as more and more hospitals will face COVID-19 patients with this complication.
“The natural history and heterogeneity of the kidney disease caused by COVID-19 need to be unraveled,” one of the authors, Robert A. Star, MD, director of the division of kidney, urologic, and hematologic diseases at NIDDK, said in an interview.
Such research is key because “low kidney function is an exclusion criterion in current studies” examining antiviral medications in COVID-19, he said. “Clinical trials are needed to test therapeutic interventions to prevent or treat COVID-19–induced AKI.”
Extremely ill patients develop AKI as their condition deteriorates
Identifying risk factors for the development of AKI in COVID-19 will be critical in helping shed more light on diagnostic and predictive biomarkers, Dr. Star said.
Dr. Hirsch and colleagues said that extremely ill patients often develop kidney failure as their condition deteriorates, and this happens quickly. Indeed, the clearest risk factors for the development of AKI were “the need for ventilator support or vasopressor drug treatment.”
Other independent predictors of AKI were older age, black race, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease.
Of those on mechanical ventilation overall in the more than 5,000-patient study, almost a quarter (23.2%) developed AKI and needed renal replacement therapy, which consisted of either intermittent or continuous hemodialysis.
Dr. Star and associates wrote that these numbers are important because of the knock-on effects.
“Hemodialysis in critically ill infected patients is associated with significant clotting complications and mortality as well as increased infection risk to staff,” they pointed out.
Dr. Star said that “the incidence rate of AKI reported in this study is higher than what had been previously reported by others in the United States and China and may reflect differences in population demographics, severity of illness, prevalence of comorbidities, socioeconomic factors, patient volume overwhelming hospital capacity, or other factors not yet determined.
“It may be caused by dehydration (volume depletion), heart failure, the inflammatory response to the virus (cytokine storm), respiratory failure, clotting of blood vessels (hypercoagulation), muscle tissue breakdown (rhabdomyolysis), and/or a direct viral infection of the kidney,” he said.
Renal biopsies from patients with AKI may help shed some light
The editorialists went on to say that findings from kidney biopsies of COVID-19 patients with AKI may help shed some light on this condition.
“While difficult to perform, kidney biopsies from patients with early AKI could help us understand the underlying pathophysiologies at the cellular and molecular level and begin to target specific treatments to specific subgroups of patients,” they wrote.
The authors noted that, as part of funding opportunities provided by the National Institutes of Health for COVID-19 research, the NIDDK has published a Notice of Special Interest outlining the most urgent areas in need of research, with one of the focuses being on the kidney.
“As the research community emerges from the crisis situation, there should be renewed efforts for multidisciplinary research to conduct integrated basic, translational, and clinical studies aimed at greatly increasing the knowledge base to understand how both the current COVID-19 threat and future health threats affect both healthy people and people with chronic diseases and conditions,” the editorials noted.
The authors of the Diabetes Care editorial have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Jhaveri has reported being a consultant for Astex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AAN publishes ethical guidance on patient care during the pandemic
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
The document, which was published online May 15 in Neurology, reviews adaptations to the inpatient and outpatient settings and addresses the need to develop protocols for the allocation of scarce medical resources. The guidance is the product of a joint committee of the AAN, the American Neurological Association, the Child Neurology Society, and the Neurocritical Care Society Ethics Committee.
“Now is one of the most challenging times of our careers as neurologists,” said James C. Stevens, MD, president of the AAN, in a press release. “Clinics and hospitals are adapting to caring for the most ill, managing scarce resources, and trying to protect people without the disease. As neurologists, we must continue to adapt our daily practice, continue to care for our most ill neurology patients, and help contribute to the care of those afflicted with COVID-19.”
The role of telehealth
The authors recommended that ordinary appointments be held using telehealth, which, they say, already has become part of patient care. Telehealth enables neurologists to continue providing care while reducing the risk of exposure to and spread of SARS-CoV-2. The disadvantages of telehealth are that it limits physical examinations and behavioral health examinations, the authors acknowledged. “Each clinician should decide, in concert with his or her patient, if an in-person evaluation warrants the risk of an encounter,” according to the guidance.
Neurologists also should advise their patients that their neurologic condition could affect their relative risk of hospitalization and death resulting from COVID-19. Patients with multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis, for example, may be receiving corticosteroids or immunomodulatory therapies that make them more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection. “Even if desired services are available, neurologists and their patients ought to consider whether their care plans can safely be delayed in order to mitigate risk,” wrote the authors. Neurologists must try to maintain the customary standard of care, however, for patients with neurologic disease severe enough to warrant hospitalization, such as stroke or epilepsy.
The potential need for triage
Resources such as ventilators and ICU beds are limited, and health care facilities have had to triage them during the pandemic. Patients with a neurologic disease that decreases their likelihood of survival from a respiratory illness may not be offered these resources. Neurologists should discuss with patients and decision makers the ways in which reduced resources might affect patient care. Neurologists must “be aware of the burden of disease in their local community and how healthcare leaders plan on coping with a surge,” according to the guidance.
Advance directives, which should be a standard part of clinical care, take on increased importance during the pandemic. Patients who have not completed advance care planning documents should be encouraged to do so, according to the authors. These documents include patients’ preferences for “do not attempt resuscitation” status. Nevertheless, “we must assure patients with chronic illness that diminished resources in this healthcare crisis will not restrict their access to comfort and palliative care,” the document states.
Scarce resource allocation protocols
In the event that a surge in patients overwhelms a hospital’s contingencies and forces it to operate in crisis mode, it should have a scarce resource allocation protocol in place.
“This will surely be the most challenging aspect of patient care during this pandemic public health emergency,” wrote the authors. To ensure transparency and to mitigate the emotional effect of these decisions on patients and clinicians, scarce resource allocation protocols should be developed by teams that include intensivists, clinical ethicists, and nursing representatives who are not directly involved in the care of the critically ill patients. The goal of these protocols is to maximize the number of lives saved. They generally include an initial patient assessment followed by regular reevaluations to determine whether patients using scarce resources are benefiting less than other patients who need the same resources. The protocols should consider not only patients with COVID-19 infection, but also patients with stroke, traumatic injury, influenza, and heart failure who may need the same resources. Race, gender, ethnicity, socioeconomics, and perceived social worth should not influence care decisions, according to the guidance. Validated mortality prediction scales, such as the Glasgow Outcome Scale, can contribute to care decisions. Obtaining community input into these protocols will ensure trust in the health care system.
“If the situation necessitates hard decisions, we need to be fair, objective, transparent, and adamantly preserve our professional integrity,” wrote the authors. “Through it all, we owe it to our patients and families, as well as ourselves, to maintain our own health and wellness.”
The guidance was developed without funding, and the authors reported no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Rubin MA et al. Neurology. 2020 May 15. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009744.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Inflammation, thrombosis biomarkers tied to COVID-19 deaths
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Their prospective cohort study of 1150 patients hospitalized with the disease in New York City also revealed a high proportion of racial and ethnic minorities, and confirmed high rates of critical illness and mortality.
“Of particular interest is the finding that over three quarters of critically ill patients required a ventilator and almost one third required renal dialysis support,” Max O’Donnell, MD, MPH, assistant professor of medicine and epidemiology at Columbia University in New York City, said in a press release.
O’Donnell and colleagues published the results of their study online today in The Lancet. It is the largest prospective cohort study published in the United States, they said.
“Although the clinical spectrum of disease has been characterised in reports from China and Italy, until now, detailed understanding of how the virus is affecting critically ill patients in the US has been limited to reports from a small number of cases,” said Natalie Yip, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Columbia University.
In the cohort, drawn from two NewYork-Presbyterian hospitals, the researchers focused on the 257 (22%) patients who required intensive care. When they estimated inflammation through interleukin-6 (IL-6) concentrations and thrombosis through D-dimer concentrations, they found a 10% increased risk for death with every 10% increase of IL-6 (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02–1.20) or D-dimer concentration (aHR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01–1.19).
“The association of mortality with higher concentrations of IL-6 and d-dimer is particularly relevant for two reasons,” write Giacomo Grasselli, from the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospediale Maggiore Policlinico, and Alberto Zanella, from the University of Milan, Italy, in an accompanying commentary.
“First, it confirms the key pathogenic role played by the activation of systemic inflammation and endothelial-vascular damage in the development of organ dysfunction,” they write. “Second, it provides the rationale for the design of clinical trials for measuring the efficacy of treatment with immunomodulating and anticoagulant drugs.”
Seventeen percent of patients received interleukin receptor antagonists and 26% received corticosteroids, but the authors did not report any data on the effects of these treatments, or any data about anticoagulant therapies administered.
Severe disease common
The study also highlighted a high proportion of ethnic and racial minorities. Sixty-two percent of the critically ill patients were Hispanic or Latinx, 19% Black, 32% White, and 3% Asian.
Their median age was 62 years and 67% were men. Eighty-two percent had at least one chronic illness, most commonly hypertension (63%), followed by diabetes (36%). Forty-six percent were obese.
As of April 28, 2020, 101 (39%) of the critically ill patients had died following a median of 9 days (interquartile range (IQR), 5–15) in the hospital and 94 (37%) remained hospitalized. Of the 203 patients who received invasive mechanical ventilation, 84 (41%) had died.
The poor prognosis of patients requiring ventilation is consistent with data from a report on patients treated in National Health Service intensive care units in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland through May 15. Overall, 11,292 patients with COVID-19 required critical care, and 4855 needed advanced respiratory support. Approximately half of the patients receiving mechanical ventilation had died 30 days after starting critical care.
In the New York study, patients spent an average of 18 days on a ventilator (IQR, 9–28 days). This is a longer period than reported in smaller studies of cases from Washington state, but corresponds with a recent report from Italy, the researchers said.
Remarkably, O’Donnell and colleagues report that almost a third (31%) of critically ill patients developed severe kidney damage and required dialysis.
Mortality was associated with several baseline factors, including older age (aHR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.09–1.57] per 10-year increase), chronic cardiac disease (aHR, 1.76; 95% CI, 1.08–2·86), and chronic pulmonary disease (aHR, 2.94; 95% CI, 1.48–5.84).
Authors of the New York study reported financial relationships to ICE Neurosystems, ALung Technologies, Baxter, BREETHE, Xenios, Hemovent, Gilead Sciences, Amazon, and Karyopharm Therapeutics. Grasselli reports personal fees from Biotest, Draeger, Fisher & Paykel, Maquet, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Pfizer, all outside the area of work commented on here. Zanella has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
DOACs linked to lower fracture risk versus warfarin in AFib patients
results of a recent population-based cohort study show.
The choice of direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) didn’t appear to have an impact, as each individual agent yielded a substantially lower risk of fracture versus the vitamin K antagonist, with risk reductions ranging from 38% to 48%, according to the study authors.
This is one of the latest reports to suggest DOACs could have an edge over warfarin for preventing fractures, providing new evidence that “may help inform the benefit risk assessment” when it comes to choosing an anticoagulant for a patient with atrial fibrillation (AFib) in the clinic, wrote the authors, led by Wallis C.Y. Lau, PhD, with the University College London.
“There exists a compelling case for evaluating whether the risk for osteoporotic fractures should be considered at the point of prescribing an oral anticoagulant to minimize fracture risk,” Dr. Lau and coauthors wrote in a report on the study that appears in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The case is especially compelling since fracture risk is “often neglected” when choosing an anticoagulant, the authors wrote. Surgeries to treat fracture are difficult because of the need for perioperative management of anticoagulation as “a balance between the risk for stroke and excessive bleeding must be achieved,” they added.
Based on these data, physicians should strongly consider DOACs as an alternative to vitamin K antagonists to reduce the risk of osteoporosis over the long term in patients with AFib, according to Victor Lawrence Roberts, MD, a Florida endocrinologist.
“Osteoporosis takes years, sometimes decades to develop, and if you then overlay warfarin on top of a readily evolving metabolic bone disease, you probably accelerate that process, said Dr. Roberts, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and editorial advisory board member of Internal Medicine News.
There’s a considerable amount of concerning preclinical data that warfarin could increase osteoporotic fracture risk. Of note, vitamin K antagonists modulate osteocalcin, a calcium-binding bone matrix protein, Dr. Roberts said.
“Osteocalcin is important for bone metabolism and health, and inhibiting osteocalcin will inhibit the ability to have a healthy bone matrix,” he explained.
The impact of anticoagulants on fracture risk is particularly relevant to patients with AFib, according to Dr. Lau and colleagues, who referenced one 2017 report showing a higher incidence of hip fracture among AFib patients versus those without AFib.
In their more recent study, Dr. Lau and colleagues reviewed electronic health records in a Hong Kong database for 23,515 older adults with a new diagnosis of AFib who received a new prescription of warfarin or DOACs including apixaban, dabigatran, or rivaroxaban.
DOAC use was consistently associated with a lower risk of osteoporotic fractures versus warfarin, regardless of the DOAC considered. The hazard ratios were 0.62 (95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.94) for apixaban, 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86) for dabigatran, and 0.52 (95% CI, 0.37-0.73) for rivaroxaban versus warfarin, the report showed.
Head-to-head comparisons between DOACS didn’t yield any statistically significant differences, though the analyses were underpowered in this respect, according to the investigators.
“This study can only rule out more than a twofold higher or a 50% lower relative risk for osteoporotic fractures between individual DOACs,” they wrote. “However, any absolute risk differences were small and would likely be of minor clinical significance.”
The reduced risk of fracture for DOACs versus warfarin was consistent in men and women with AFib, suggesting that women may particularly benefit from DOACs, given that they have a higher risk of fracture than men, the investigators added.
The results of this study suggest yet another benefit of DOACs over warfarin in patients with AFib, according to internist Noel Deep, MD, who is the chief medical officer of Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wisconsin.
“The lower risk of osteoporotic fractures with DOACS, in addition to other advantages such as lower risk of intracranial bleeding, once- or twice-daily consistent dosing, no dietary restrictions, and no blood tests to regulate the dose might be another reason that physicians may favor them over warfarin in older individuals requiring anticoagulation,” Dr. Deep said in an interview.
Results of this and several other recent studies may help in recommending DOACs to internal medicine patients who have a diagnosis of AFib requiring anticoagulation, according to Dr. Deep, who is also a physician at Aspirus Antigo Clinic and a member of Internal Medicine News’ editorial advisory board. These include a 2019 U.S.-based study of more than 167,000 patients with AFib (JAMA Intern Med. 2019;180[2]:245‐253) showing that use of DOACs, particularly apixaban, were linked to lower fracture risk versus warfarin use. Similarly, a Danish national registry study also published in 2019 showed that the absolute risk of osteoporotic fractures was low overall and significantly lower in patients who received DOACs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74[17]:2150-2158).
Funding for the study came from the University of Hong Kong and University College London Strategic Planning Fund. The study authors reported disclosures related to Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Janssen, Amgen, Takeda, IQVIA, and others.
SOURCE: Lau WCY et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.7326/M19-3671.
results of a recent population-based cohort study show.
The choice of direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) didn’t appear to have an impact, as each individual agent yielded a substantially lower risk of fracture versus the vitamin K antagonist, with risk reductions ranging from 38% to 48%, according to the study authors.
This is one of the latest reports to suggest DOACs could have an edge over warfarin for preventing fractures, providing new evidence that “may help inform the benefit risk assessment” when it comes to choosing an anticoagulant for a patient with atrial fibrillation (AFib) in the clinic, wrote the authors, led by Wallis C.Y. Lau, PhD, with the University College London.
“There exists a compelling case for evaluating whether the risk for osteoporotic fractures should be considered at the point of prescribing an oral anticoagulant to minimize fracture risk,” Dr. Lau and coauthors wrote in a report on the study that appears in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The case is especially compelling since fracture risk is “often neglected” when choosing an anticoagulant, the authors wrote. Surgeries to treat fracture are difficult because of the need for perioperative management of anticoagulation as “a balance between the risk for stroke and excessive bleeding must be achieved,” they added.
Based on these data, physicians should strongly consider DOACs as an alternative to vitamin K antagonists to reduce the risk of osteoporosis over the long term in patients with AFib, according to Victor Lawrence Roberts, MD, a Florida endocrinologist.
“Osteoporosis takes years, sometimes decades to develop, and if you then overlay warfarin on top of a readily evolving metabolic bone disease, you probably accelerate that process, said Dr. Roberts, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and editorial advisory board member of Internal Medicine News.
There’s a considerable amount of concerning preclinical data that warfarin could increase osteoporotic fracture risk. Of note, vitamin K antagonists modulate osteocalcin, a calcium-binding bone matrix protein, Dr. Roberts said.
“Osteocalcin is important for bone metabolism and health, and inhibiting osteocalcin will inhibit the ability to have a healthy bone matrix,” he explained.
The impact of anticoagulants on fracture risk is particularly relevant to patients with AFib, according to Dr. Lau and colleagues, who referenced one 2017 report showing a higher incidence of hip fracture among AFib patients versus those without AFib.
In their more recent study, Dr. Lau and colleagues reviewed electronic health records in a Hong Kong database for 23,515 older adults with a new diagnosis of AFib who received a new prescription of warfarin or DOACs including apixaban, dabigatran, or rivaroxaban.
DOAC use was consistently associated with a lower risk of osteoporotic fractures versus warfarin, regardless of the DOAC considered. The hazard ratios were 0.62 (95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.94) for apixaban, 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86) for dabigatran, and 0.52 (95% CI, 0.37-0.73) for rivaroxaban versus warfarin, the report showed.
Head-to-head comparisons between DOACS didn’t yield any statistically significant differences, though the analyses were underpowered in this respect, according to the investigators.
“This study can only rule out more than a twofold higher or a 50% lower relative risk for osteoporotic fractures between individual DOACs,” they wrote. “However, any absolute risk differences were small and would likely be of minor clinical significance.”
The reduced risk of fracture for DOACs versus warfarin was consistent in men and women with AFib, suggesting that women may particularly benefit from DOACs, given that they have a higher risk of fracture than men, the investigators added.
The results of this study suggest yet another benefit of DOACs over warfarin in patients with AFib, according to internist Noel Deep, MD, who is the chief medical officer of Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wisconsin.
“The lower risk of osteoporotic fractures with DOACS, in addition to other advantages such as lower risk of intracranial bleeding, once- or twice-daily consistent dosing, no dietary restrictions, and no blood tests to regulate the dose might be another reason that physicians may favor them over warfarin in older individuals requiring anticoagulation,” Dr. Deep said in an interview.
Results of this and several other recent studies may help in recommending DOACs to internal medicine patients who have a diagnosis of AFib requiring anticoagulation, according to Dr. Deep, who is also a physician at Aspirus Antigo Clinic and a member of Internal Medicine News’ editorial advisory board. These include a 2019 U.S.-based study of more than 167,000 patients with AFib (JAMA Intern Med. 2019;180[2]:245‐253) showing that use of DOACs, particularly apixaban, were linked to lower fracture risk versus warfarin use. Similarly, a Danish national registry study also published in 2019 showed that the absolute risk of osteoporotic fractures was low overall and significantly lower in patients who received DOACs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74[17]:2150-2158).
Funding for the study came from the University of Hong Kong and University College London Strategic Planning Fund. The study authors reported disclosures related to Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Janssen, Amgen, Takeda, IQVIA, and others.
SOURCE: Lau WCY et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.7326/M19-3671.
results of a recent population-based cohort study show.
The choice of direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) didn’t appear to have an impact, as each individual agent yielded a substantially lower risk of fracture versus the vitamin K antagonist, with risk reductions ranging from 38% to 48%, according to the study authors.
This is one of the latest reports to suggest DOACs could have an edge over warfarin for preventing fractures, providing new evidence that “may help inform the benefit risk assessment” when it comes to choosing an anticoagulant for a patient with atrial fibrillation (AFib) in the clinic, wrote the authors, led by Wallis C.Y. Lau, PhD, with the University College London.
“There exists a compelling case for evaluating whether the risk for osteoporotic fractures should be considered at the point of prescribing an oral anticoagulant to minimize fracture risk,” Dr. Lau and coauthors wrote in a report on the study that appears in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The case is especially compelling since fracture risk is “often neglected” when choosing an anticoagulant, the authors wrote. Surgeries to treat fracture are difficult because of the need for perioperative management of anticoagulation as “a balance between the risk for stroke and excessive bleeding must be achieved,” they added.
Based on these data, physicians should strongly consider DOACs as an alternative to vitamin K antagonists to reduce the risk of osteoporosis over the long term in patients with AFib, according to Victor Lawrence Roberts, MD, a Florida endocrinologist.
“Osteoporosis takes years, sometimes decades to develop, and if you then overlay warfarin on top of a readily evolving metabolic bone disease, you probably accelerate that process, said Dr. Roberts, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and editorial advisory board member of Internal Medicine News.
There’s a considerable amount of concerning preclinical data that warfarin could increase osteoporotic fracture risk. Of note, vitamin K antagonists modulate osteocalcin, a calcium-binding bone matrix protein, Dr. Roberts said.
“Osteocalcin is important for bone metabolism and health, and inhibiting osteocalcin will inhibit the ability to have a healthy bone matrix,” he explained.
The impact of anticoagulants on fracture risk is particularly relevant to patients with AFib, according to Dr. Lau and colleagues, who referenced one 2017 report showing a higher incidence of hip fracture among AFib patients versus those without AFib.
In their more recent study, Dr. Lau and colleagues reviewed electronic health records in a Hong Kong database for 23,515 older adults with a new diagnosis of AFib who received a new prescription of warfarin or DOACs including apixaban, dabigatran, or rivaroxaban.
DOAC use was consistently associated with a lower risk of osteoporotic fractures versus warfarin, regardless of the DOAC considered. The hazard ratios were 0.62 (95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.94) for apixaban, 0.65 (95% CI, 0.49-0.86) for dabigatran, and 0.52 (95% CI, 0.37-0.73) for rivaroxaban versus warfarin, the report showed.
Head-to-head comparisons between DOACS didn’t yield any statistically significant differences, though the analyses were underpowered in this respect, according to the investigators.
“This study can only rule out more than a twofold higher or a 50% lower relative risk for osteoporotic fractures between individual DOACs,” they wrote. “However, any absolute risk differences were small and would likely be of minor clinical significance.”
The reduced risk of fracture for DOACs versus warfarin was consistent in men and women with AFib, suggesting that women may particularly benefit from DOACs, given that they have a higher risk of fracture than men, the investigators added.
The results of this study suggest yet another benefit of DOACs over warfarin in patients with AFib, according to internist Noel Deep, MD, who is the chief medical officer of Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo, Wisconsin.
“The lower risk of osteoporotic fractures with DOACS, in addition to other advantages such as lower risk of intracranial bleeding, once- or twice-daily consistent dosing, no dietary restrictions, and no blood tests to regulate the dose might be another reason that physicians may favor them over warfarin in older individuals requiring anticoagulation,” Dr. Deep said in an interview.
Results of this and several other recent studies may help in recommending DOACs to internal medicine patients who have a diagnosis of AFib requiring anticoagulation, according to Dr. Deep, who is also a physician at Aspirus Antigo Clinic and a member of Internal Medicine News’ editorial advisory board. These include a 2019 U.S.-based study of more than 167,000 patients with AFib (JAMA Intern Med. 2019;180[2]:245‐253) showing that use of DOACs, particularly apixaban, were linked to lower fracture risk versus warfarin use. Similarly, a Danish national registry study also published in 2019 showed that the absolute risk of osteoporotic fractures was low overall and significantly lower in patients who received DOACs (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74[17]:2150-2158).
Funding for the study came from the University of Hong Kong and University College London Strategic Planning Fund. The study authors reported disclosures related to Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Janssen, Amgen, Takeda, IQVIA, and others.
SOURCE: Lau WCY et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 May 18. doi: 10.7326/M19-3671.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Maskomania: Masks and COVID-19
A comprehensive review
On April 3, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued an advisory that the general public wear cloth face masks when outside, particularly those residing in areas with significant severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) community transmission.1 Recent research reveals several factors related to the nature of the virus as well as the epidemiologic spread of the illness that may have led to this decision.
However, controversy still prevails whether this recommendation will alleviate or aggravate disease progression. With many hospitals across America lacking sufficient personal protective equipment (PPE) and scrambling for supplies, universal masking may create more chaos, especially with certain states imposing monetary fines on individuals spotted outdoors without a mask. With new information being discovered each day about COVID-19, it is more imperative than ever to update existing strategies and formulate more effective methods to flatten the curve.
Airborne vs. droplet transmission
According to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization, there have been studies with mixed evidence and opinions regarding the presence of COVID-19 ribonucleic acid (RNA) in air samples.2 In medRxiv, Santarpia et al., from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, detected viral RNA in samples taken from beneath a patient’s bed and from a window ledge, both areas in which neither the patient nor health care personnel had any direct contact. They also found that 66.7% of air samples taken from a hospital hallway carried virus-containing particles.3 It is worth noting that certain aerosol-generating procedures (AGP) may increase the likelihood of airborne dissemination. Whether airborne transmission is a major mode of COVID-19 spread in the community and routine clinical settings (with no aerosol-generating procedures) is still a debatable question without a definitive answer.
We should consider the epidemiology of COVID-19 thus far in the pandemic to determine if transmission patterns are more consistent with that of other common respiratory viral pathogens or more consistent with that of the agents we classically consider to be transmitted by the airborne route (measles, varicella zoster virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The attack rates in various settings (household, health care, and the public) as well as the expected number of secondary cases from a single infected individual in a susceptible population (R0) are more consistent with those of a droplet spread pathogen.
For measles, the R0 is 12-18, and the secondary household attack rates are ≥ 90%. In case of the varicella zoster virus, the R0 is ~10, and the secondary household attack rate is 85%. The R0 for pulmonary tuberculosis is up to 10 (per year) and the secondary household attack rate has been reported to be >50%. With COVID-19, the R0 appears to be around 2.5-3 and secondary household attack rates are ~ 10% from data available so far, similar to that of influenza viruses. This discrepancy suggests that droplet transmission may be more likely. The dichotomy of airborne versus droplet mode of spread may be better described as a continuum, as pointed out in a recent article in the JAMA. Infectious droplets form turbulent gas clouds allowing the virus particles to travel further and remain in the air longer.4 The necessary precautions for an airborne illness should be chosen over droplet precautions, especially when there is concern for an AGP.
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively since the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. According to public health authorities, significant exposure is defined as “face-to-face contact within 6 feet with a patient with symptomatic COVID-19” in the range of a few minutes up to 30 minutes.5 The researchers wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine that the chance of catching COVID-19 from a passing interaction in a public space is therefore minimal, and it may seem unnecessary to wear a mask at all times in public.
As reported in Science, randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses in the past have shown no added protection conferred by wearing a mask, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors to their validity.6 On the contrary, mask wearing has been enforced in many parts of Asia, including Hong Kong and Singapore with promising results.5 Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. Also, universal masking would reduce the stigma around symptomatic individuals covering their faces. It has become a cultural phenomenon in many southeast Asian countries and has been cited as one of the reasons for relatively successful containment in Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. The most important benefit of universal masking is protection attained by preventing spread from asymptomatic, mildly symptomatic, and presymptomatic carriers.7
In a study in the New England Journal of Medicine that estimated viral loads during various stages of COVID-19, researchers found that asymptomatic patients had similar viral loads to symptomatic patients, thereby suggesting high potential for transmission.8 Furthermore, numerous cases are being reported concerning the spread of illness from asymptomatic carriers.9-12 In an outbreak at a skilled nursing facility in Washington outlined in MMWR, 13 of 23 residents with positive test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and of those, 3 never developed any symptoms.12
Many hospitals are now embracing the policy of universal masking. A mask is a critical component of the personal protective equipment (PPE) clinicians need when caring for symptomatic patients with respiratory viral infections, in conjunction with a gown, gloves, and eye protection. Masking in this context is already part of routine operations in most hospitals. There are two scenarios in which there may be possible benefits. One scenario is the lower likelihood of transmission from asymptomatic and minimally symptomatic health care workers with COVID-19 to other providers and patients. The other less plausible benefit of universal masking among health care workers is that it may provide some protection in the possibility of caring for an unrecognized COVID-19 patient. However, universal masking should be coupled with other favorable practices like temperature checks and symptom screening on a daily basis to avail the maximum benefit from masking. Despite varied opinions on the outcomes of universal masking, this measure helps improve health care workers’ safety, psychological well-being, trust in their hospital, and decreases anxiety of acquiring the illness.
Efficacy of various types of masks
With the possibility of airborne transmission of the virus, are cloth masks as recommended by the CDC truly helpful in preventing infection? A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus (comparable to coronavirus in size and physical characteristics). The homemade mask was created using one layer of polyester cloth and a four-layered kitchen filter paper.13
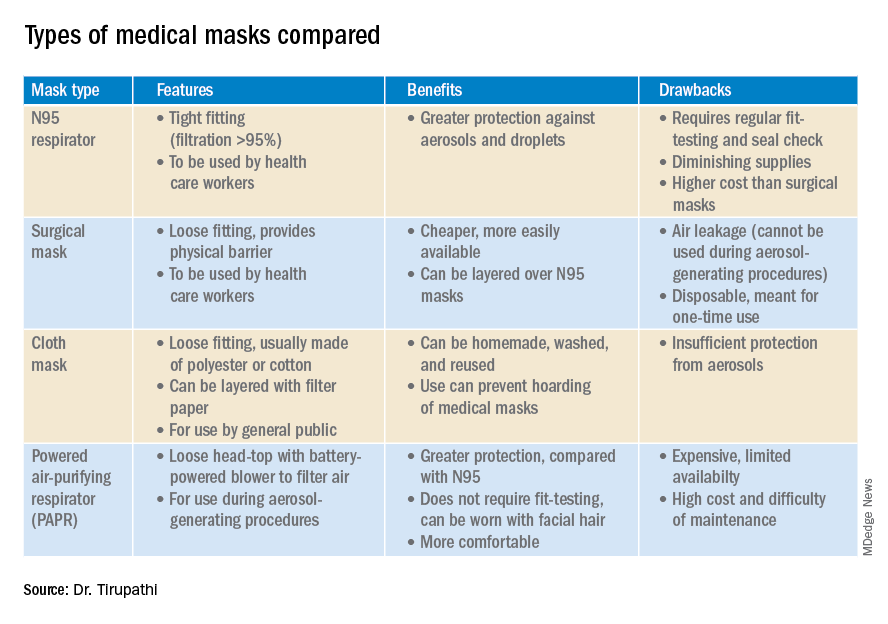
N95 masks (equivalent to FFP/P2 in European countries) are made of electrostatically charged polypropylene microfibers designed to filter particles measuring 100-300nm in diameter with 95% efficacy. A single SARS-CoV-2 molecule measures 125 nm approximately. N99 (FFP3) and N100 (P3) masks are also available, though not as widely used, with 99% and 99.7% efficacy respectively for the same size range. Though cloth masks are the clear-cut last resort for medical professionals, a few studies state no clinically proven difference in protection between surgical masks and N95 respirators.14,15 Even aerosolized droplets (< 5 mcm) were found to be blocked by surgical masks in a Nature Medicine study in which 4/10 subjects tested positive for coronavirus in exhaled breath samples without masks and 0/10 subjects with masks.16
On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” In fact, more contamination was found on the outer surface of the masks when compared to the inner surface, probably owing to the masks’ aerodynamic properties.17 Because of limitations present in the above-mentioned studies, further research is necessary to conclusively determine which types of masks are efficacious in preventing infection by the virus. In a scarcity of surgical masks and respirators for health care personnel, suboptimal masks can be of some use provided there is adherent use, minimal donning and doffing, and it is to be accompanied by adequate hand washing practices.14
In case of severe infections with high viral loads or patients undergoing aerosol-generating procedures, powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) also are advisable as they confer greater protection than N95 respirators, according to a study in the Annals of Work Exposures and Health. Despite being more comfortable for long-term use and accommodative of facial hair, their use is limited because of high cost and difficult maintenance.18 3-D printing also is being used to combat the current shortage of masks worldwide. However, a study from the International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery reported that virologic testing for leakage between the two reusable components and contamination of the components themselves after one or multiple disinfection cycles is essential before application in real-life situations.19
Ongoing issues
WHO estimates a monthly requirement of nearly 90 million masks exclusively for health care workers to protect themselves against COVID-19.20 In spite of increasing the production rate by 40%, if the general public hoards masks and respirators, the results could be disastrous. Personal protective equipment is currently at 100 times the usual demand and 20 times the usual cost, with stocks backlogged by 4-6 months. The appropriate order of priority in distribution to health care professionals first, followed by those caring for infected patients is critical.20 In a survey conducted by the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, results revealed that 48% of the U.S. health care facilities that responded were either out or nearly out of respirators as of March 25. 21
The gravest risk behind the universal masking policy is the likely depletion of medical resources.22 A possible solution to this issue could be to modify the policy to stagger the requirement based on the severity of community transmission in that area of residence. In the article appropriately titled “Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic” published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, researchers described how the Chinese population was classified into moderate, low, and very-low risk of infection categories and advised to wear a surgical or disposable mask, disposable mask, and no mask respectively.23 This curbs widespread panic and eagerness by the general public to stock up on essential medical equipment when it may not even be necessary.
Reuse, extended use, and sterilization
Several studies have been conducted to identify the viability of the COVID-19 on various surfaces.24-25 The CDC and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) guidelines state that an N95 respirator can be used up to 8 hours with intermittent or continuous use, though this number is not fixed and heavily depends upon the extent of exposure, risk of contamination, and frequency of donning and doffing26,27. Though traditionally meant for single-time usage, after 8 hours, the mask can be decontaminated and reused. The CDC defines extended use as the “practice of wearing the same N95 respirator for repeated close-contact encounters with several patients, without removing the respirator between patient encounters.” Reuse is defined as “using the same N95 respirator for multiple encounters with patients but removing it (‘doffing’) after each encounter. The respirator is stored in between encounters to be put on again (‘donned’) prior to the next encounter with a patient.”
It has been established that extended use is more advisable than reuse given the lower risk of self-inoculation. Furthermore, health care professionals are urged to wear a cleanable face shield or disposable mask over the respirator to minimize contamination and practice diligent hand hygiene before and after handling the respirator. N95 respirators are to be discarded following aerosol-generating procedures or if they come in contact with blood, respiratory secretions, or bodily fluids. They should also be discarded in case of close contact with an infected patient or if they cause breathing difficulties to the wearer.27 This may not always be possible given the unprecedented shortage of PPE, hence decontamination techniques and repurposing are the need of the hour.
In Anesthesia & Analgesia, Naveen Nathan, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends recycling four masks in a series, using one per day, keeping the mask in a dry, clean environment, and then repeating use of the first mask on the 5th day, the second on the 6th day, and so forth. This ensures clearance of the virus particles by the next use. Alternatively, respirators can be sterilized between uses by heating to 70º C (158º F) for 30 minutes. Liquid disinfectants such as alcohol and bleach as well as ultraviolet rays in sunlight tend to damage masks.28 Steam sterilization is the most commonly utilized technique in hospitals. Other methods, described by the N95/PPE Working Group, report include gamma irradiation at 20kGy (2MRad) for large-scale sterilization (though the facilities may not be widely available), vaporized hydrogen peroxide, ozone decontamination, ultraviolet germicidal irradiation, and ethylene oxide.29 Though a discussion on various considerations of decontamination techniques is out of the scope of this article, detailed guidelines have been published by the CDC30 and the COVID-19 Healthcare Coalition.30
Conclusion
A recent startling discovery reported on in Emerging Infectious Diseases suggests that the basic COVID-19 reproductive number (R0) is actually much higher than previously thought. Using expanded data, updated epidemiologic parameters, and the current outbreak dynamics in Wuhan, the team came to the conclusion that the R0 for the novel coronavirus is actually 5.7 (95% CI 3.8-8.9), compared with an initial estimate of 2.2-2.7.31 Concern for transmissibility demands heightened prevention strategies until more data evolves. The latest recommendation by the CDC regarding cloth masking in the public may help slow the progression of the pandemic. However, it is of paramount importance to keep in mind that masks alone are not enough to control the disease and must be coupled with other nonpharmacologic interventions such as social distancing, quarantining/isolation, and diligent hand hygiene.
Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. He also is the lead physician for antibiotic stewardship at these hospitals. Dr. Bharathidasan is a recent medical graduate from India with an interest in public health and community research; she plans to pursue residency training in the United States. Ms. Freshman is currently the regional director of infection prevention for WellSpan Health and has 35 years of experience in nursing. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendation regarding the use of cloth face coverings.
2. World Health Organization. Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19 : implications for IPC precaution recommendations. Sci Br. 2020 Mar 29:1-3.
3. Santarpia JL et al. Transmission potential of SARS-CoV-2 in viral shedding observed at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. 2020 Mar 26. medRxiv. 2020;2020.03.23.20039446.
4. Bourouiba L. Turbulent gas clouds and respiratory pathogen emissions: Potential implications for reducing transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4756.
5. Klompas M et al. Universal masking in hospitals in the Covid-19 era. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2006372.
6. Servick K. Would everyone wearing face masks help us slow the pandemic? Science 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9371.
7. Leung CC et al. Mass masking in the COVID-19 epidemic: People need guidance. Lancet 2020 Mar 21;395(10228):945. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30520-1.
8. Zou L et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 19;382(12):1177-9.
9. Pan X et al. Asymptomatic cases in a family cluster with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;20(4):410-1.
10. Bai Y et al. Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Feb 21;323(14):1406-7.
11. Wei WE et al. Presymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 – Singapore, Jan. 23–March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:411-5.
12. Kimball A et al. Asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections in residents of a long-term care skilled nursing facility – King County, Washington, March 2020. 2020 Apr 3. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:377-81.
13. Ma Q-X et al. Potential utilities of mask wearing and instant hand hygiene for fighting SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol. 2020 Mar 31;10.1002/jmv.25805. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25805.
14. Abd-Elsayed A et al. Utility of substandard face mask options for health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31;10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841.
15. Long Y et al. Effectiveness of N95 respirators versus surgical masks against influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Evid Based Med. 2020 Mar 13;10.1111/jebm.12381. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12381.
16. Leung NHL et al. Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks. Nat Med. 2020 May;26(5):676-80.
17. Bae S et al. Effectiveness of surgical and cotton masks in blocking SARS-CoV-2: A controlled comparison in 4 patients. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6;M20-1342. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
18. Brosseau LM. Are powered air purifying respirators a solution for protecting healthcare workers from emerging aerosol-transmissible diseases? Ann Work Expo Health. 2020 Apr 30;64(4):339-41.
19. Swennen GRJ et al. Custom-made 3D-printed face masks in case of pandemic crisis situations with a lack of commercially available FFP2/3 masks. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 May;49(5):673-7.
20. Mahase E. Coronavirus: Global stocks of protective gear are depleted, with demand at “100 times” normal level, WHO warns. BMJ. 2020 Feb 10;368:m543. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m543.
21. National survey shows dire shortages of PPE, hand sanitizer across the U.S. 2020 Mar 27. Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) press briefing.
22. Wu HL et al. Facemask shortage and the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak: Reflections on public health measures. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Apr 3:100329. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100329.
23. Feng S et al. Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 May;8(5):434-6.
24. Chin AWH et al. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental. The Lancet Microbe. 2020 May 1;5247(20):2004973. doi. org/10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3.
25. van Doremalen N et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 16;382(16):1564-7.
26. NIOSH – Workplace Safety and Health Topics: Recommended guidance for extended use and limited reuse of n95 filtering facepiece respirators in healthcare settings.
27. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 decontamination and reuse of filtering facepiece respirators. 2020 Apr 15.
28. Nathan N. Waste not, want not: The re-usability of N95 masks. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31.doi: 10.1213/ane.0000000000004843.
29. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control technical report. Cloth masks and mask sterilisation as options in case of shortage of surgical masks and respirators. 2020 Mar.
30. N95/PPE Working Group report. Evaluation of decontamination techniques for the reuse of N95 respirators. 2020 Apr 3;2:1-7.
31. Sanche Set al. High contagiousness and rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Jul. doi. org/10.3201/eid2607.200282.
A comprehensive review
A comprehensive review
On April 3, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued an advisory that the general public wear cloth face masks when outside, particularly those residing in areas with significant severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) community transmission.1 Recent research reveals several factors related to the nature of the virus as well as the epidemiologic spread of the illness that may have led to this decision.
However, controversy still prevails whether this recommendation will alleviate or aggravate disease progression. With many hospitals across America lacking sufficient personal protective equipment (PPE) and scrambling for supplies, universal masking may create more chaos, especially with certain states imposing monetary fines on individuals spotted outdoors without a mask. With new information being discovered each day about COVID-19, it is more imperative than ever to update existing strategies and formulate more effective methods to flatten the curve.
Airborne vs. droplet transmission
According to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization, there have been studies with mixed evidence and opinions regarding the presence of COVID-19 ribonucleic acid (RNA) in air samples.2 In medRxiv, Santarpia et al., from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, detected viral RNA in samples taken from beneath a patient’s bed and from a window ledge, both areas in which neither the patient nor health care personnel had any direct contact. They also found that 66.7% of air samples taken from a hospital hallway carried virus-containing particles.3 It is worth noting that certain aerosol-generating procedures (AGP) may increase the likelihood of airborne dissemination. Whether airborne transmission is a major mode of COVID-19 spread in the community and routine clinical settings (with no aerosol-generating procedures) is still a debatable question without a definitive answer.
We should consider the epidemiology of COVID-19 thus far in the pandemic to determine if transmission patterns are more consistent with that of other common respiratory viral pathogens or more consistent with that of the agents we classically consider to be transmitted by the airborne route (measles, varicella zoster virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The attack rates in various settings (household, health care, and the public) as well as the expected number of secondary cases from a single infected individual in a susceptible population (R0) are more consistent with those of a droplet spread pathogen.
For measles, the R0 is 12-18, and the secondary household attack rates are ≥ 90%. In case of the varicella zoster virus, the R0 is ~10, and the secondary household attack rate is 85%. The R0 for pulmonary tuberculosis is up to 10 (per year) and the secondary household attack rate has been reported to be >50%. With COVID-19, the R0 appears to be around 2.5-3 and secondary household attack rates are ~ 10% from data available so far, similar to that of influenza viruses. This discrepancy suggests that droplet transmission may be more likely. The dichotomy of airborne versus droplet mode of spread may be better described as a continuum, as pointed out in a recent article in the JAMA. Infectious droplets form turbulent gas clouds allowing the virus particles to travel further and remain in the air longer.4 The necessary precautions for an airborne illness should be chosen over droplet precautions, especially when there is concern for an AGP.
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively since the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. According to public health authorities, significant exposure is defined as “face-to-face contact within 6 feet with a patient with symptomatic COVID-19” in the range of a few minutes up to 30 minutes.5 The researchers wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine that the chance of catching COVID-19 from a passing interaction in a public space is therefore minimal, and it may seem unnecessary to wear a mask at all times in public.
As reported in Science, randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses in the past have shown no added protection conferred by wearing a mask, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors to their validity.6 On the contrary, mask wearing has been enforced in many parts of Asia, including Hong Kong and Singapore with promising results.5 Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. Also, universal masking would reduce the stigma around symptomatic individuals covering their faces. It has become a cultural phenomenon in many southeast Asian countries and has been cited as one of the reasons for relatively successful containment in Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. The most important benefit of universal masking is protection attained by preventing spread from asymptomatic, mildly symptomatic, and presymptomatic carriers.7
In a study in the New England Journal of Medicine that estimated viral loads during various stages of COVID-19, researchers found that asymptomatic patients had similar viral loads to symptomatic patients, thereby suggesting high potential for transmission.8 Furthermore, numerous cases are being reported concerning the spread of illness from asymptomatic carriers.9-12 In an outbreak at a skilled nursing facility in Washington outlined in MMWR, 13 of 23 residents with positive test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and of those, 3 never developed any symptoms.12
Many hospitals are now embracing the policy of universal masking. A mask is a critical component of the personal protective equipment (PPE) clinicians need when caring for symptomatic patients with respiratory viral infections, in conjunction with a gown, gloves, and eye protection. Masking in this context is already part of routine operations in most hospitals. There are two scenarios in which there may be possible benefits. One scenario is the lower likelihood of transmission from asymptomatic and minimally symptomatic health care workers with COVID-19 to other providers and patients. The other less plausible benefit of universal masking among health care workers is that it may provide some protection in the possibility of caring for an unrecognized COVID-19 patient. However, universal masking should be coupled with other favorable practices like temperature checks and symptom screening on a daily basis to avail the maximum benefit from masking. Despite varied opinions on the outcomes of universal masking, this measure helps improve health care workers’ safety, psychological well-being, trust in their hospital, and decreases anxiety of acquiring the illness.
Efficacy of various types of masks
With the possibility of airborne transmission of the virus, are cloth masks as recommended by the CDC truly helpful in preventing infection? A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus (comparable to coronavirus in size and physical characteristics). The homemade mask was created using one layer of polyester cloth and a four-layered kitchen filter paper.13

N95 masks (equivalent to FFP/P2 in European countries) are made of electrostatically charged polypropylene microfibers designed to filter particles measuring 100-300nm in diameter with 95% efficacy. A single SARS-CoV-2 molecule measures 125 nm approximately. N99 (FFP3) and N100 (P3) masks are also available, though not as widely used, with 99% and 99.7% efficacy respectively for the same size range. Though cloth masks are the clear-cut last resort for medical professionals, a few studies state no clinically proven difference in protection between surgical masks and N95 respirators.14,15 Even aerosolized droplets (< 5 mcm) were found to be blocked by surgical masks in a Nature Medicine study in which 4/10 subjects tested positive for coronavirus in exhaled breath samples without masks and 0/10 subjects with masks.16
On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” In fact, more contamination was found on the outer surface of the masks when compared to the inner surface, probably owing to the masks’ aerodynamic properties.17 Because of limitations present in the above-mentioned studies, further research is necessary to conclusively determine which types of masks are efficacious in preventing infection by the virus. In a scarcity of surgical masks and respirators for health care personnel, suboptimal masks can be of some use provided there is adherent use, minimal donning and doffing, and it is to be accompanied by adequate hand washing practices.14
In case of severe infections with high viral loads or patients undergoing aerosol-generating procedures, powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) also are advisable as they confer greater protection than N95 respirators, according to a study in the Annals of Work Exposures and Health. Despite being more comfortable for long-term use and accommodative of facial hair, their use is limited because of high cost and difficult maintenance.18 3-D printing also is being used to combat the current shortage of masks worldwide. However, a study from the International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery reported that virologic testing for leakage between the two reusable components and contamination of the components themselves after one or multiple disinfection cycles is essential before application in real-life situations.19
Ongoing issues
WHO estimates a monthly requirement of nearly 90 million masks exclusively for health care workers to protect themselves against COVID-19.20 In spite of increasing the production rate by 40%, if the general public hoards masks and respirators, the results could be disastrous. Personal protective equipment is currently at 100 times the usual demand and 20 times the usual cost, with stocks backlogged by 4-6 months. The appropriate order of priority in distribution to health care professionals first, followed by those caring for infected patients is critical.20 In a survey conducted by the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, results revealed that 48% of the U.S. health care facilities that responded were either out or nearly out of respirators as of March 25. 21
The gravest risk behind the universal masking policy is the likely depletion of medical resources.22 A possible solution to this issue could be to modify the policy to stagger the requirement based on the severity of community transmission in that area of residence. In the article appropriately titled “Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic” published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, researchers described how the Chinese population was classified into moderate, low, and very-low risk of infection categories and advised to wear a surgical or disposable mask, disposable mask, and no mask respectively.23 This curbs widespread panic and eagerness by the general public to stock up on essential medical equipment when it may not even be necessary.
Reuse, extended use, and sterilization
Several studies have been conducted to identify the viability of the COVID-19 on various surfaces.24-25 The CDC and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) guidelines state that an N95 respirator can be used up to 8 hours with intermittent or continuous use, though this number is not fixed and heavily depends upon the extent of exposure, risk of contamination, and frequency of donning and doffing26,27. Though traditionally meant for single-time usage, after 8 hours, the mask can be decontaminated and reused. The CDC defines extended use as the “practice of wearing the same N95 respirator for repeated close-contact encounters with several patients, without removing the respirator between patient encounters.” Reuse is defined as “using the same N95 respirator for multiple encounters with patients but removing it (‘doffing’) after each encounter. The respirator is stored in between encounters to be put on again (‘donned’) prior to the next encounter with a patient.”
It has been established that extended use is more advisable than reuse given the lower risk of self-inoculation. Furthermore, health care professionals are urged to wear a cleanable face shield or disposable mask over the respirator to minimize contamination and practice diligent hand hygiene before and after handling the respirator. N95 respirators are to be discarded following aerosol-generating procedures or if they come in contact with blood, respiratory secretions, or bodily fluids. They should also be discarded in case of close contact with an infected patient or if they cause breathing difficulties to the wearer.27 This may not always be possible given the unprecedented shortage of PPE, hence decontamination techniques and repurposing are the need of the hour.
In Anesthesia & Analgesia, Naveen Nathan, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends recycling four masks in a series, using one per day, keeping the mask in a dry, clean environment, and then repeating use of the first mask on the 5th day, the second on the 6th day, and so forth. This ensures clearance of the virus particles by the next use. Alternatively, respirators can be sterilized between uses by heating to 70º C (158º F) for 30 minutes. Liquid disinfectants such as alcohol and bleach as well as ultraviolet rays in sunlight tend to damage masks.28 Steam sterilization is the most commonly utilized technique in hospitals. Other methods, described by the N95/PPE Working Group, report include gamma irradiation at 20kGy (2MRad) for large-scale sterilization (though the facilities may not be widely available), vaporized hydrogen peroxide, ozone decontamination, ultraviolet germicidal irradiation, and ethylene oxide.29 Though a discussion on various considerations of decontamination techniques is out of the scope of this article, detailed guidelines have been published by the CDC30 and the COVID-19 Healthcare Coalition.30
Conclusion
A recent startling discovery reported on in Emerging Infectious Diseases suggests that the basic COVID-19 reproductive number (R0) is actually much higher than previously thought. Using expanded data, updated epidemiologic parameters, and the current outbreak dynamics in Wuhan, the team came to the conclusion that the R0 for the novel coronavirus is actually 5.7 (95% CI 3.8-8.9), compared with an initial estimate of 2.2-2.7.31 Concern for transmissibility demands heightened prevention strategies until more data evolves. The latest recommendation by the CDC regarding cloth masking in the public may help slow the progression of the pandemic. However, it is of paramount importance to keep in mind that masks alone are not enough to control the disease and must be coupled with other nonpharmacologic interventions such as social distancing, quarantining/isolation, and diligent hand hygiene.
Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. He also is the lead physician for antibiotic stewardship at these hospitals. Dr. Bharathidasan is a recent medical graduate from India with an interest in public health and community research; she plans to pursue residency training in the United States. Ms. Freshman is currently the regional director of infection prevention for WellSpan Health and has 35 years of experience in nursing. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendation regarding the use of cloth face coverings.
2. World Health Organization. Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19 : implications for IPC precaution recommendations. Sci Br. 2020 Mar 29:1-3.
3. Santarpia JL et al. Transmission potential of SARS-CoV-2 in viral shedding observed at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. 2020 Mar 26. medRxiv. 2020;2020.03.23.20039446.
4. Bourouiba L. Turbulent gas clouds and respiratory pathogen emissions: Potential implications for reducing transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4756.
5. Klompas M et al. Universal masking in hospitals in the Covid-19 era. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2006372.
6. Servick K. Would everyone wearing face masks help us slow the pandemic? Science 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9371.
7. Leung CC et al. Mass masking in the COVID-19 epidemic: People need guidance. Lancet 2020 Mar 21;395(10228):945. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30520-1.
8. Zou L et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 19;382(12):1177-9.
9. Pan X et al. Asymptomatic cases in a family cluster with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;20(4):410-1.
10. Bai Y et al. Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Feb 21;323(14):1406-7.
11. Wei WE et al. Presymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 – Singapore, Jan. 23–March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:411-5.
12. Kimball A et al. Asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections in residents of a long-term care skilled nursing facility – King County, Washington, March 2020. 2020 Apr 3. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:377-81.
13. Ma Q-X et al. Potential utilities of mask wearing and instant hand hygiene for fighting SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol. 2020 Mar 31;10.1002/jmv.25805. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25805.
14. Abd-Elsayed A et al. Utility of substandard face mask options for health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31;10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841.
15. Long Y et al. Effectiveness of N95 respirators versus surgical masks against influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Evid Based Med. 2020 Mar 13;10.1111/jebm.12381. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12381.
16. Leung NHL et al. Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks. Nat Med. 2020 May;26(5):676-80.
17. Bae S et al. Effectiveness of surgical and cotton masks in blocking SARS-CoV-2: A controlled comparison in 4 patients. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6;M20-1342. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
18. Brosseau LM. Are powered air purifying respirators a solution for protecting healthcare workers from emerging aerosol-transmissible diseases? Ann Work Expo Health. 2020 Apr 30;64(4):339-41.
19. Swennen GRJ et al. Custom-made 3D-printed face masks in case of pandemic crisis situations with a lack of commercially available FFP2/3 masks. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 May;49(5):673-7.
20. Mahase E. Coronavirus: Global stocks of protective gear are depleted, with demand at “100 times” normal level, WHO warns. BMJ. 2020 Feb 10;368:m543. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m543.
21. National survey shows dire shortages of PPE, hand sanitizer across the U.S. 2020 Mar 27. Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) press briefing.
22. Wu HL et al. Facemask shortage and the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak: Reflections on public health measures. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Apr 3:100329. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100329.
23. Feng S et al. Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 May;8(5):434-6.
24. Chin AWH et al. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental. The Lancet Microbe. 2020 May 1;5247(20):2004973. doi. org/10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3.
25. van Doremalen N et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 16;382(16):1564-7.
26. NIOSH – Workplace Safety and Health Topics: Recommended guidance for extended use and limited reuse of n95 filtering facepiece respirators in healthcare settings.
27. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 decontamination and reuse of filtering facepiece respirators. 2020 Apr 15.
28. Nathan N. Waste not, want not: The re-usability of N95 masks. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31.doi: 10.1213/ane.0000000000004843.
29. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control technical report. Cloth masks and mask sterilisation as options in case of shortage of surgical masks and respirators. 2020 Mar.
30. N95/PPE Working Group report. Evaluation of decontamination techniques for the reuse of N95 respirators. 2020 Apr 3;2:1-7.
31. Sanche Set al. High contagiousness and rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Jul. doi. org/10.3201/eid2607.200282.
On April 3, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued an advisory that the general public wear cloth face masks when outside, particularly those residing in areas with significant severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) community transmission.1 Recent research reveals several factors related to the nature of the virus as well as the epidemiologic spread of the illness that may have led to this decision.
However, controversy still prevails whether this recommendation will alleviate or aggravate disease progression. With many hospitals across America lacking sufficient personal protective equipment (PPE) and scrambling for supplies, universal masking may create more chaos, especially with certain states imposing monetary fines on individuals spotted outdoors without a mask. With new information being discovered each day about COVID-19, it is more imperative than ever to update existing strategies and formulate more effective methods to flatten the curve.
Airborne vs. droplet transmission
According to a scientific brief released by the World Health Organization, there have been studies with mixed evidence and opinions regarding the presence of COVID-19 ribonucleic acid (RNA) in air samples.2 In medRxiv, Santarpia et al., from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, detected viral RNA in samples taken from beneath a patient’s bed and from a window ledge, both areas in which neither the patient nor health care personnel had any direct contact. They also found that 66.7% of air samples taken from a hospital hallway carried virus-containing particles.3 It is worth noting that certain aerosol-generating procedures (AGP) may increase the likelihood of airborne dissemination. Whether airborne transmission is a major mode of COVID-19 spread in the community and routine clinical settings (with no aerosol-generating procedures) is still a debatable question without a definitive answer.
We should consider the epidemiology of COVID-19 thus far in the pandemic to determine if transmission patterns are more consistent with that of other common respiratory viral pathogens or more consistent with that of the agents we classically consider to be transmitted by the airborne route (measles, varicella zoster virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis). The attack rates in various settings (household, health care, and the public) as well as the expected number of secondary cases from a single infected individual in a susceptible population (R0) are more consistent with those of a droplet spread pathogen.
For measles, the R0 is 12-18, and the secondary household attack rates are ≥ 90%. In case of the varicella zoster virus, the R0 is ~10, and the secondary household attack rate is 85%. The R0 for pulmonary tuberculosis is up to 10 (per year) and the secondary household attack rate has been reported to be >50%. With COVID-19, the R0 appears to be around 2.5-3 and secondary household attack rates are ~ 10% from data available so far, similar to that of influenza viruses. This discrepancy suggests that droplet transmission may be more likely. The dichotomy of airborne versus droplet mode of spread may be better described as a continuum, as pointed out in a recent article in the JAMA. Infectious droplets form turbulent gas clouds allowing the virus particles to travel further and remain in the air longer.4 The necessary precautions for an airborne illness should be chosen over droplet precautions, especially when there is concern for an AGP.
Universal masking: Risks and benefits
The idea of universal masking has been debated extensively since the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. According to public health authorities, significant exposure is defined as “face-to-face contact within 6 feet with a patient with symptomatic COVID-19” in the range of a few minutes up to 30 minutes.5 The researchers wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine that the chance of catching COVID-19 from a passing interaction in a public space is therefore minimal, and it may seem unnecessary to wear a mask at all times in public.
As reported in Science, randomized clinical studies performed on other viruses in the past have shown no added protection conferred by wearing a mask, though small sample sizes and noncompliance are limiting factors to their validity.6 On the contrary, mask wearing has been enforced in many parts of Asia, including Hong Kong and Singapore with promising results.5 Leung et al. stated in The Lancet that the lack of proof that masks are effective should not rule them as ineffective. Also, universal masking would reduce the stigma around symptomatic individuals covering their faces. It has become a cultural phenomenon in many southeast Asian countries and has been cited as one of the reasons for relatively successful containment in Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan. The most important benefit of universal masking is protection attained by preventing spread from asymptomatic, mildly symptomatic, and presymptomatic carriers.7
In a study in the New England Journal of Medicine that estimated viral loads during various stages of COVID-19, researchers found that asymptomatic patients had similar viral loads to symptomatic patients, thereby suggesting high potential for transmission.8 Furthermore, numerous cases are being reported concerning the spread of illness from asymptomatic carriers.9-12 In an outbreak at a skilled nursing facility in Washington outlined in MMWR, 13 of 23 residents with positive test results were asymptomatic at the time of testing, and of those, 3 never developed any symptoms.12
Many hospitals are now embracing the policy of universal masking. A mask is a critical component of the personal protective equipment (PPE) clinicians need when caring for symptomatic patients with respiratory viral infections, in conjunction with a gown, gloves, and eye protection. Masking in this context is already part of routine operations in most hospitals. There are two scenarios in which there may be possible benefits. One scenario is the lower likelihood of transmission from asymptomatic and minimally symptomatic health care workers with COVID-19 to other providers and patients. The other less plausible benefit of universal masking among health care workers is that it may provide some protection in the possibility of caring for an unrecognized COVID-19 patient. However, universal masking should be coupled with other favorable practices like temperature checks and symptom screening on a daily basis to avail the maximum benefit from masking. Despite varied opinions on the outcomes of universal masking, this measure helps improve health care workers’ safety, psychological well-being, trust in their hospital, and decreases anxiety of acquiring the illness.
Efficacy of various types of masks
With the possibility of airborne transmission of the virus, are cloth masks as recommended by the CDC truly helpful in preventing infection? A study in the Journal of Medical Virology demonstrates 99.98%, 97.14%, and 95.15% efficacy for N95, surgical, and homemade masks, respectively, in blocking the avian influenza virus (comparable to coronavirus in size and physical characteristics). The homemade mask was created using one layer of polyester cloth and a four-layered kitchen filter paper.13

N95 masks (equivalent to FFP/P2 in European countries) are made of electrostatically charged polypropylene microfibers designed to filter particles measuring 100-300nm in diameter with 95% efficacy. A single SARS-CoV-2 molecule measures 125 nm approximately. N99 (FFP3) and N100 (P3) masks are also available, though not as widely used, with 99% and 99.7% efficacy respectively for the same size range. Though cloth masks are the clear-cut last resort for medical professionals, a few studies state no clinically proven difference in protection between surgical masks and N95 respirators.14,15 Even aerosolized droplets (< 5 mcm) were found to be blocked by surgical masks in a Nature Medicine study in which 4/10 subjects tested positive for coronavirus in exhaled breath samples without masks and 0/10 subjects with masks.16
On the contrary, an Annals of Internal Medicine study of four COVID-19 positive subjects that “neither surgical masks nor cloth masks effectively filtered SARS-CoV-2 during coughs of infected patients.” In fact, more contamination was found on the outer surface of the masks when compared to the inner surface, probably owing to the masks’ aerodynamic properties.17 Because of limitations present in the above-mentioned studies, further research is necessary to conclusively determine which types of masks are efficacious in preventing infection by the virus. In a scarcity of surgical masks and respirators for health care personnel, suboptimal masks can be of some use provided there is adherent use, minimal donning and doffing, and it is to be accompanied by adequate hand washing practices.14
In case of severe infections with high viral loads or patients undergoing aerosol-generating procedures, powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) also are advisable as they confer greater protection than N95 respirators, according to a study in the Annals of Work Exposures and Health. Despite being more comfortable for long-term use and accommodative of facial hair, their use is limited because of high cost and difficult maintenance.18 3-D printing also is being used to combat the current shortage of masks worldwide. However, a study from the International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery reported that virologic testing for leakage between the two reusable components and contamination of the components themselves after one or multiple disinfection cycles is essential before application in real-life situations.19
Ongoing issues
WHO estimates a monthly requirement of nearly 90 million masks exclusively for health care workers to protect themselves against COVID-19.20 In spite of increasing the production rate by 40%, if the general public hoards masks and respirators, the results could be disastrous. Personal protective equipment is currently at 100 times the usual demand and 20 times the usual cost, with stocks backlogged by 4-6 months. The appropriate order of priority in distribution to health care professionals first, followed by those caring for infected patients is critical.20 In a survey conducted by the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, results revealed that 48% of the U.S. health care facilities that responded were either out or nearly out of respirators as of March 25. 21
The gravest risk behind the universal masking policy is the likely depletion of medical resources.22 A possible solution to this issue could be to modify the policy to stagger the requirement based on the severity of community transmission in that area of residence. In the article appropriately titled “Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic” published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, researchers described how the Chinese population was classified into moderate, low, and very-low risk of infection categories and advised to wear a surgical or disposable mask, disposable mask, and no mask respectively.23 This curbs widespread panic and eagerness by the general public to stock up on essential medical equipment when it may not even be necessary.
Reuse, extended use, and sterilization
Several studies have been conducted to identify the viability of the COVID-19 on various surfaces.24-25 The CDC and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) guidelines state that an N95 respirator can be used up to 8 hours with intermittent or continuous use, though this number is not fixed and heavily depends upon the extent of exposure, risk of contamination, and frequency of donning and doffing26,27. Though traditionally meant for single-time usage, after 8 hours, the mask can be decontaminated and reused. The CDC defines extended use as the “practice of wearing the same N95 respirator for repeated close-contact encounters with several patients, without removing the respirator between patient encounters.” Reuse is defined as “using the same N95 respirator for multiple encounters with patients but removing it (‘doffing’) after each encounter. The respirator is stored in between encounters to be put on again (‘donned’) prior to the next encounter with a patient.”
It has been established that extended use is more advisable than reuse given the lower risk of self-inoculation. Furthermore, health care professionals are urged to wear a cleanable face shield or disposable mask over the respirator to minimize contamination and practice diligent hand hygiene before and after handling the respirator. N95 respirators are to be discarded following aerosol-generating procedures or if they come in contact with blood, respiratory secretions, or bodily fluids. They should also be discarded in case of close contact with an infected patient or if they cause breathing difficulties to the wearer.27 This may not always be possible given the unprecedented shortage of PPE, hence decontamination techniques and repurposing are the need of the hour.
In Anesthesia & Analgesia, Naveen Nathan, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, recommends recycling four masks in a series, using one per day, keeping the mask in a dry, clean environment, and then repeating use of the first mask on the 5th day, the second on the 6th day, and so forth. This ensures clearance of the virus particles by the next use. Alternatively, respirators can be sterilized between uses by heating to 70º C (158º F) for 30 minutes. Liquid disinfectants such as alcohol and bleach as well as ultraviolet rays in sunlight tend to damage masks.28 Steam sterilization is the most commonly utilized technique in hospitals. Other methods, described by the N95/PPE Working Group, report include gamma irradiation at 20kGy (2MRad) for large-scale sterilization (though the facilities may not be widely available), vaporized hydrogen peroxide, ozone decontamination, ultraviolet germicidal irradiation, and ethylene oxide.29 Though a discussion on various considerations of decontamination techniques is out of the scope of this article, detailed guidelines have been published by the CDC30 and the COVID-19 Healthcare Coalition.30
Conclusion
A recent startling discovery reported on in Emerging Infectious Diseases suggests that the basic COVID-19 reproductive number (R0) is actually much higher than previously thought. Using expanded data, updated epidemiologic parameters, and the current outbreak dynamics in Wuhan, the team came to the conclusion that the R0 for the novel coronavirus is actually 5.7 (95% CI 3.8-8.9), compared with an initial estimate of 2.2-2.7.31 Concern for transmissibility demands heightened prevention strategies until more data evolves. The latest recommendation by the CDC regarding cloth masking in the public may help slow the progression of the pandemic. However, it is of paramount importance to keep in mind that masks alone are not enough to control the disease and must be coupled with other nonpharmacologic interventions such as social distancing, quarantining/isolation, and diligent hand hygiene.
Dr. Tirupathi is the medical director of Keystone Infectious Diseases/HIV in Chambersburg, Pa., and currently chair of infection prevention at Wellspan Chambersburg and Waynesboro (Pa.) Hospitals. He also is the lead physician for antibiotic stewardship at these hospitals. Dr. Bharathidasan is a recent medical graduate from India with an interest in public health and community research; she plans to pursue residency training in the United States. Ms. Freshman is currently the regional director of infection prevention for WellSpan Health and has 35 years of experience in nursing. Dr. Palabindala is the medical director, utilization management and physician advisory services, at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson. He is an associate professor of medicine and academic hospitalist in the UMMC School of Medicine.
References
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendation regarding the use of cloth face coverings.
2. World Health Organization. Modes of transmission of virus causing COVID-19 : implications for IPC precaution recommendations. Sci Br. 2020 Mar 29:1-3.
3. Santarpia JL et al. Transmission potential of SARS-CoV-2 in viral shedding observed at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. 2020 Mar 26. medRxiv. 2020;2020.03.23.20039446.
4. Bourouiba L. Turbulent gas clouds and respiratory pathogen emissions: Potential implications for reducing transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4756.
5. Klompas M et al. Universal masking in hospitals in the Covid-19 era. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2006372.
6. Servick K. Would everyone wearing face masks help us slow the pandemic? Science 2020 Mar 28. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9371.
7. Leung CC et al. Mass masking in the COVID-19 epidemic: People need guidance. Lancet 2020 Mar 21;395(10228):945. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30520-1.
8. Zou L et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 19;382(12):1177-9.
9. Pan X et al. Asymptomatic cases in a family cluster with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;20(4):410-1.
10. Bai Y et al. Presumed asymptomatic carrier transmission of COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Feb 21;323(14):1406-7.
11. Wei WE et al. Presymptomatic transmission of SARS-CoV-2 – Singapore, Jan. 23–March 16, 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:411-5.
12. Kimball A et al. Asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections in residents of a long-term care skilled nursing facility – King County, Washington, March 2020. 2020 Apr 3. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2020;69:377-81.
13. Ma Q-X et al. Potential utilities of mask wearing and instant hand hygiene for fighting SARS-CoV-2. J Med Virol. 2020 Mar 31;10.1002/jmv.25805. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25805.
14. Abd-Elsayed A et al. Utility of substandard face mask options for health care workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31;10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004841.
15. Long Y et al. Effectiveness of N95 respirators versus surgical masks against influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Evid Based Med. 2020 Mar 13;10.1111/jebm.12381. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12381.
16. Leung NHL et al. Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks. Nat Med. 2020 May;26(5):676-80.
17. Bae S et al. Effectiveness of surgical and cotton masks in blocking SARS-CoV-2: A controlled comparison in 4 patients. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Apr 6;M20-1342. doi: 10.7326/M20-1342.
18. Brosseau LM. Are powered air purifying respirators a solution for protecting healthcare workers from emerging aerosol-transmissible diseases? Ann Work Expo Health. 2020 Apr 30;64(4):339-41.
19. Swennen GRJ et al. Custom-made 3D-printed face masks in case of pandemic crisis situations with a lack of commercially available FFP2/3 masks. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020 May;49(5):673-7.
20. Mahase E. Coronavirus: Global stocks of protective gear are depleted, with demand at “100 times” normal level, WHO warns. BMJ. 2020 Feb 10;368:m543. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m543.
21. National survey shows dire shortages of PPE, hand sanitizer across the U.S. 2020 Mar 27. Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) press briefing.
22. Wu HL et al. Facemask shortage and the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak: Reflections on public health measures. EClinicalMedicine. 2020 Apr 3:100329. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100329.
23. Feng S et al. Rational use of face masks in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 May;8(5):434-6.
24. Chin AWH et al. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental. The Lancet Microbe. 2020 May 1;5247(20):2004973. doi. org/10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3.
25. van Doremalen N et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS-CoV-2 as compared with SARS-CoV-1. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 16;382(16):1564-7.
26. NIOSH – Workplace Safety and Health Topics: Recommended guidance for extended use and limited reuse of n95 filtering facepiece respirators in healthcare settings.
27. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 decontamination and reuse of filtering facepiece respirators. 2020 Apr 15.
28. Nathan N. Waste not, want not: The re-usability of N95 masks. Anesth Analg. 2020 Mar 31.doi: 10.1213/ane.0000000000004843.
29. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control technical report. Cloth masks and mask sterilisation as options in case of shortage of surgical masks and respirators. 2020 Mar.
30. N95/PPE Working Group report. Evaluation of decontamination techniques for the reuse of N95 respirators. 2020 Apr 3;2:1-7.
31. Sanche Set al. High contagiousness and rapid spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020 Jul. doi. org/10.3201/eid2607.200282.
Today’s top news highlights: COVID-19 in kids, addiction-related suicide
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-19 in kids
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illess after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but infants and teens are most likely to be hospitalized, according to retrospective data from 177 children and young adults at a single center. “One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Pediatrics. READ MORE
Avoiding ageism in COVID resource allocation
The American Geriatrics Society has issued new policy recommendations for resource allocation during the COVID-19 pandemic that are aimed at protecting seniors for ageism. When allocating scarce resources in an emergency, officials should equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term mortality, the group wrote. “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies,” AGS officials wrote in the statement. READ MORE
Preventing addiction-related suicide
Individuals with substance use disorders are at a significant risk for suicide, but there have been few evidence-based options for their treatment. Now a single intervention is showing promise for this high-risk group. In a large, multicenter randomized effectiveness study, a single 3-hour-long group psychosocial intervention resulted in significantly improved knowledge and attitudes regarding suicide that persisted at 6 months of follow-up. The intervention to prevent future suicide was designed specifically for patients who were in intensive outpatient programs for addiction treatment. “We’ve shown that suicide prevention in intensive outpatient program addiction groups is feasible, easy to train, and highly rated by counselors, and I’d say it’s very adaptable, easy to go national in almost any addiction treatment program, right out of the box,” said Richard K. Ries, MD, director of outpatient psychiatry as well as the psychiatry addiction division at Harborview Medical Center. READ MORE
TNF inhibitors may hamper COVID-19 severity
Early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry has produced an intriguing result: Patients on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for their rheumatic disease are less likely to require hospitalization when infected with COVID-19. The registry data also show that taking hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization. “A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” said Jinoos Yazdany, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital. READ MORE
Audrey Hepburn’s lessons in pandemic grace
There are a lot of new skills required for praticing medicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. In his latest MDedge column, Jeffrey Benabio, MD, explains that grace is one of them. Dr. Benabio, director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego, looks to Audrey Hepburn for inspiration. “Effort is also required for telephone and video visits,” he writes. “In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.” READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-19 in kids
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illess after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but infants and teens are most likely to be hospitalized, according to retrospective data from 177 children and young adults at a single center. “One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Pediatrics. READ MORE
Avoiding ageism in COVID resource allocation
The American Geriatrics Society has issued new policy recommendations for resource allocation during the COVID-19 pandemic that are aimed at protecting seniors for ageism. When allocating scarce resources in an emergency, officials should equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term mortality, the group wrote. “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies,” AGS officials wrote in the statement. READ MORE
Preventing addiction-related suicide
Individuals with substance use disorders are at a significant risk for suicide, but there have been few evidence-based options for their treatment. Now a single intervention is showing promise for this high-risk group. In a large, multicenter randomized effectiveness study, a single 3-hour-long group psychosocial intervention resulted in significantly improved knowledge and attitudes regarding suicide that persisted at 6 months of follow-up. The intervention to prevent future suicide was designed specifically for patients who were in intensive outpatient programs for addiction treatment. “We’ve shown that suicide prevention in intensive outpatient program addiction groups is feasible, easy to train, and highly rated by counselors, and I’d say it’s very adaptable, easy to go national in almost any addiction treatment program, right out of the box,” said Richard K. Ries, MD, director of outpatient psychiatry as well as the psychiatry addiction division at Harborview Medical Center. READ MORE
TNF inhibitors may hamper COVID-19 severity
Early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry has produced an intriguing result: Patients on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for their rheumatic disease are less likely to require hospitalization when infected with COVID-19. The registry data also show that taking hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization. “A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” said Jinoos Yazdany, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital. READ MORE
Audrey Hepburn’s lessons in pandemic grace
There are a lot of new skills required for praticing medicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. In his latest MDedge column, Jeffrey Benabio, MD, explains that grace is one of them. Dr. Benabio, director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego, looks to Audrey Hepburn for inspiration. “Effort is also required for telephone and video visits,” he writes. “In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.” READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
COVID-19 in kids
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illess after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but infants and teens are most likely to be hospitalized, according to retrospective data from 177 children and young adults at a single center. “One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, of Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues reported in the Journal of Pediatrics. READ MORE
Avoiding ageism in COVID resource allocation
The American Geriatrics Society has issued new policy recommendations for resource allocation during the COVID-19 pandemic that are aimed at protecting seniors for ageism. When allocating scarce resources in an emergency, officials should equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term mortality, the group wrote. “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies,” AGS officials wrote in the statement. READ MORE
Preventing addiction-related suicide
Individuals with substance use disorders are at a significant risk for suicide, but there have been few evidence-based options for their treatment. Now a single intervention is showing promise for this high-risk group. In a large, multicenter randomized effectiveness study, a single 3-hour-long group psychosocial intervention resulted in significantly improved knowledge and attitudes regarding suicide that persisted at 6 months of follow-up. The intervention to prevent future suicide was designed specifically for patients who were in intensive outpatient programs for addiction treatment. “We’ve shown that suicide prevention in intensive outpatient program addiction groups is feasible, easy to train, and highly rated by counselors, and I’d say it’s very adaptable, easy to go national in almost any addiction treatment program, right out of the box,” said Richard K. Ries, MD, director of outpatient psychiatry as well as the psychiatry addiction division at Harborview Medical Center. READ MORE
TNF inhibitors may hamper COVID-19 severity
Early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry has produced an intriguing result: Patients on tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for their rheumatic disease are less likely to require hospitalization when infected with COVID-19. The registry data also show that taking hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization. “A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” said Jinoos Yazdany, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital. READ MORE
Audrey Hepburn’s lessons in pandemic grace
There are a lot of new skills required for praticing medicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. In his latest MDedge column, Jeffrey Benabio, MD, explains that grace is one of them. Dr. Benabio, director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego, looks to Audrey Hepburn for inspiration. “Effort is also required for telephone and video visits,” he writes. “In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.” READ MORE
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.