User login
Rituximab Not Inferior to Cyclophosphamide in Pediatric Vasculitis
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
and those who received rituximab required a significantly lower steroid dose than those who received cyclophosphamide or a combination therapy.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the efficacy of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, or a combination of both in pediatric patients diagnosed with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) or microscopic polyangiitis.
- A total of 104 patients (median age at diagnosis, 14 years; 67% girls) were included from A Registry of Childhood Vasculitis; the majority had a diagnosis of GPA (81%) and renal involvement (87%). Overall, induction therapy involved rituximab for 43%, cyclophosphamide for 46%, and a combination of both for 11% patients.
- The primary endpoint was the rate of achieving remission (Pediatric Vasculitis Activity Score [PVAS] of 0) or low disease activity (PVAS ≤ 2) at the post-induction visit (4-6 months after diagnosis).
- The secondary endpoints were the degree of disease-related damage at 12- and 24-month visits and rates of drug-related hospitalization occurring between the diagnosis and post-induction visits.
TAKEAWAY:
- At the post-induction visit, 63% patients achieved remission or low disease activity, with the rates being similar between patients who received rituximab and those who received cyclophosphamide (64% vs 62%).
- Patients treated with rituximab required a significantly lower median steroid dose (0.13 mg/kg per day) than those treated with cyclophosphamide (0.3 mg/kg per day) or the combination therapy (0.3 mg/kg per day; P < .001) at the post-induction visit.
- Overall, 61% and 56% patients receiving rituximab and cyclophosphamide, respectively, had disease-related damage measure on the Pediatric Vasculitis Damage Index at the 12-month visit; however, the degree of damage was low.
- The percentage of patients requiring hospitalization was higher in the rituximab group than in the cyclophosphamide group (22% vs 10%), primarily stemming from drug- or infection-related causes (11% vs 2%).
IN PRACTICE:
“The results of this study may assist with current clinical decision-making with regard to the choice of induction medications in childhood-onset AAV and will complement the ongoing [Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance] prospective [consensus treatment plans] study,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Samuel J. Gagne, MD, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center in Pennsylvania, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
Study limitations included the inconsistencies in glucocorticoid dosing, which may have affected remission rates. Moreover, data on the adverse events not requiring hospitalization and long-term adverse events were not captured.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received funding through a Nationwide Children’s Hospital intramural grant award. The authors reported no potential conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Fall Vaccine Updates From the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices: New Recommendations
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This episode of Medicine Matters reviews highlights from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ (ACIP’s) October 2024 meeting, with new recommendations for pneumococcal, COVID, and meningococcal B (Men B) vaccines, as well as a safety update for maternal RSV vaccination.
Pneumococcal Vaccination and New Lower Age-Based Recommendations
New age-based recommendation. ACIP has lowered the age for routine vaccination with the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) from age 65 down to age 50, but only with PCV. Review of data revealed that more than half of those in the 50- to 64-year-old age group already had a risk indication to receive a PCV dose. In addition, rates of invasive pneumococcal disease peak at younger ages in Black patients compared with White patients. The rate of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) among Black adults aged 50 or older exceeds the average rate of IPD for all adults aged 65 or older. The goal of this age-based change is to reduce disease in demographic groups with the highest burden of disease.
The new expanded age-based recommendation applies only to vaccination with PCV. Conjugate vaccines trigger memory B-cell production and therefore induce greater long-term immunity. New research is now focusing on higher-valent PCV vaccines. Two 24-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines and one 31-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine are now in advanced stages of development.
Risk-based recommendation. A risk-based recommendation for ages 19 through 49 years still applies to those with certain medical conditions, including diabetes; chronic heart, lung, liver, or kidney disease; and also for those with immunocompromising conditions. Risk-based recommendations are harder to implement particularly because many vaccines are now administered in pharmacies and pharmacists don’t know the patients as well as their physicians do, so it’s harder for them to know who should get the vaccine if the recommendation is based on risk.
COVID-19 Vaccines With Additional Dose Recommendations
Everyone 6 months or older is recommended to receive a dose of the updated 2024-2025 COVID vaccine. An additional updated COVID vaccine dose is now recommended for everyone aged 65 or older, and for those aged 6 months or older with immunocompromising (moderate or severe) conditions. Review of data revealed that 1 in 6 patients hospitalized with COVID have an immunocompromising condition, and 70% of COVID hospitalizations are in those aged 65 or older. This older age group also has the highest death rates due to COVID-19. We know that vaccination protection wanes with time. Data from previous studies show that additional vaccine doses provide additional protection. Additional doses are now being recommended for those at highest risk.
Timing of additional doses. This second dose is recommended at 6 months after the last updated COVID-19 vaccine dose. However, the additional dose can be given as early as 2 months after the last dose. Those who recently had COVID-19 can wait 3 months before getting an additional vaccine dose. This flexibility allows patients to maximize additional protection by timing additional doses around travel and life events, such as weddings, family get-togethers, or chemotherapy.
Those with immunocompromising conditions may receive more doses. Patients with immunocompromising conditions can receive even more additional doses, if recommended by their physician, under shared clinical decision-making.
Meningococcal Vaccines
Meningococcal disease is rare but deadly. The disease can progress rapidly. As many as 10%-15% of people with meningococcal infection die, even with appropriate antibiotic therapy. And for those who survive, about 20% suffer long-term sequalae (cognitive deficits, hearing loss, limb amputations).
Aligning Men B vaccine dosing intervals. The new ACIP vote applies only to Men B vaccines, of which there are two: one by GSK (brand name Bexsero), and the other by Wyeth, a Pfizer subsidiary (brand name Trumenba). The two MenB vaccine products are not interchangeable. The same type of MenB vaccine has to be used to complete the series.
The MenB vaccines initially had different dosing schedules and now they don’t. ACIP voted to harmonize and align the dosing schedule for the two different MenB products to mirror recent FDA (Food and Drug Administration) labeling updates. So now the dosing recommendations for both MenB vaccines are the same: either two doses given 6 months apart to healthy adolescents and young adults, or a three-dose series given at zero, 1-2 months, and 6 months for those at high risk or for those who want to optimize rapid protection (for example, if they are starting the series within 6 months of going off to college). But understand that the current recommendation for MenB vaccination for healthy adolescents and young adults is based on shared clinical decision-making, preferably for those aged 16-18.
MenACWY. Two doses of MenACWY are routinely recommended, with the first dose at age 11-12 and a second dose at age 16. The MenACWY vaccines are interchangeable.
Implementation challenges and new pentavalent vaccines. Having to use the same MenB vaccine product for all doses in a patient’s series is difficult. It’s even more difficult when the patient needs both MenACWY and MenB vaccinations.
Adding to the complexity is a new pentavalent vaccine from Pfizer (brand name Penbraya) that combines MenACWY with the MenB vaccine. And another pentavalent vaccine version by GSK is up for regulatory decision in February 2025.
The work group did say that they plan to take a fresh look at the meningococcal vaccination schedule. Let’s hope it gets simpler, so more to come on that.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccines
Current RSV vaccine recommendations for older adults. RSV vaccine has both age- and risk-based recommendations. Now, everyone aged 75 or older needs a dose of RSV vaccine. Adults aged 60-75 with risk factors for severe RSV are also recommended to receive a dose of RSV vaccine, but not adults without these risk factors. The conditions associated with increased risk for severe RSV disease include lung disease, heart disease, immune compromise, diabetes, obesity with BMI (body mass index) of 40 or higher, neurologic or neuromuscular conditions, chronic kidney disease, liver disorders, and hematologic disorders. Frailty, as well as living in a nursing home or other long-term care facility, are other risk factors for severe RSV disease. Those aged 60-75 without these risk factors are no longer recommended to receive it.
Three RSV vaccines. We now have three RSV vaccine to choose from. Two are protein subunit vaccines. One is by Pfizer (brand name Abrysvo) that does not contain an adjuvant. The other protein-based RSV vaccine by GSK (brand name Arexvy) does contain an adjuvant. The third RSV vaccine by Moderna (brand name mRESVIA) uses an mRNA platform, and durability of protection is still unclear. However, recent studies now suggest that the RSV protein subunit vaccines confer 36 months of protection rather than only 24 months.
All three RSV vaccines are licensed for those aged 60 or older. The age indication for GSK’s RSV vaccine, Arexvy, has already been lowered by the FDA to age 50. FDA recently lowered the age approval for Abrysvo to age 18 for those at high risk. However, ACIP has not yet expanded its age recommendations for getting these vaccines. One of the main hesitations is vaccine safety concerns. FDA›s safety update presented to ACIP still suggests an increased risk for Guillain-Barré syndrome with both protein-based RSV vaccines among those aged 65 or older. Fortunately, the risk is rare: less than 10 cases per million vaccinations.
RSV immunization for infant protection. RSV season starts in October and goes through March. We now have two new ways to protect babies. One is a maternal RSV vaccine, given at 32-36 weeks of pregnancy to moms who will deliver their babies during RSV season. But only Pfizer’s RSV vaccine (brand name Abrysvo, without an adjuvant) can be given during pregnancy.
A maternal RSV vaccine safety update, presented at ACIP, was reassuring. Abrysvo was not associated with increased risk for preterm birth or small gestational age at birth.
Nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, can be given to infants. Nirsevimab is indicated for all babies under 8 months of age entering their first RSV season.
People who received a maternal RSV vaccine during a previous pregnancy are not recommended to receive additional doses during subsequent pregnancies. However, infants born to women who were vaccinated during a prior pregnancy should receive nirsevimab.
Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, has disclosed conflicts of interest with the American Medical Association, the Medical Association of Atlanta, ACIP, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This episode of Medicine Matters reviews highlights from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ (ACIP’s) October 2024 meeting, with new recommendations for pneumococcal, COVID, and meningococcal B (Men B) vaccines, as well as a safety update for maternal RSV vaccination.
Pneumococcal Vaccination and New Lower Age-Based Recommendations
New age-based recommendation. ACIP has lowered the age for routine vaccination with the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) from age 65 down to age 50, but only with PCV. Review of data revealed that more than half of those in the 50- to 64-year-old age group already had a risk indication to receive a PCV dose. In addition, rates of invasive pneumococcal disease peak at younger ages in Black patients compared with White patients. The rate of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) among Black adults aged 50 or older exceeds the average rate of IPD for all adults aged 65 or older. The goal of this age-based change is to reduce disease in demographic groups with the highest burden of disease.
The new expanded age-based recommendation applies only to vaccination with PCV. Conjugate vaccines trigger memory B-cell production and therefore induce greater long-term immunity. New research is now focusing on higher-valent PCV vaccines. Two 24-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines and one 31-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine are now in advanced stages of development.
Risk-based recommendation. A risk-based recommendation for ages 19 through 49 years still applies to those with certain medical conditions, including diabetes; chronic heart, lung, liver, or kidney disease; and also for those with immunocompromising conditions. Risk-based recommendations are harder to implement particularly because many vaccines are now administered in pharmacies and pharmacists don’t know the patients as well as their physicians do, so it’s harder for them to know who should get the vaccine if the recommendation is based on risk.
COVID-19 Vaccines With Additional Dose Recommendations
Everyone 6 months or older is recommended to receive a dose of the updated 2024-2025 COVID vaccine. An additional updated COVID vaccine dose is now recommended for everyone aged 65 or older, and for those aged 6 months or older with immunocompromising (moderate or severe) conditions. Review of data revealed that 1 in 6 patients hospitalized with COVID have an immunocompromising condition, and 70% of COVID hospitalizations are in those aged 65 or older. This older age group also has the highest death rates due to COVID-19. We know that vaccination protection wanes with time. Data from previous studies show that additional vaccine doses provide additional protection. Additional doses are now being recommended for those at highest risk.
Timing of additional doses. This second dose is recommended at 6 months after the last updated COVID-19 vaccine dose. However, the additional dose can be given as early as 2 months after the last dose. Those who recently had COVID-19 can wait 3 months before getting an additional vaccine dose. This flexibility allows patients to maximize additional protection by timing additional doses around travel and life events, such as weddings, family get-togethers, or chemotherapy.
Those with immunocompromising conditions may receive more doses. Patients with immunocompromising conditions can receive even more additional doses, if recommended by their physician, under shared clinical decision-making.
Meningococcal Vaccines
Meningococcal disease is rare but deadly. The disease can progress rapidly. As many as 10%-15% of people with meningococcal infection die, even with appropriate antibiotic therapy. And for those who survive, about 20% suffer long-term sequalae (cognitive deficits, hearing loss, limb amputations).
Aligning Men B vaccine dosing intervals. The new ACIP vote applies only to Men B vaccines, of which there are two: one by GSK (brand name Bexsero), and the other by Wyeth, a Pfizer subsidiary (brand name Trumenba). The two MenB vaccine products are not interchangeable. The same type of MenB vaccine has to be used to complete the series.
The MenB vaccines initially had different dosing schedules and now they don’t. ACIP voted to harmonize and align the dosing schedule for the two different MenB products to mirror recent FDA (Food and Drug Administration) labeling updates. So now the dosing recommendations for both MenB vaccines are the same: either two doses given 6 months apart to healthy adolescents and young adults, or a three-dose series given at zero, 1-2 months, and 6 months for those at high risk or for those who want to optimize rapid protection (for example, if they are starting the series within 6 months of going off to college). But understand that the current recommendation for MenB vaccination for healthy adolescents and young adults is based on shared clinical decision-making, preferably for those aged 16-18.
MenACWY. Two doses of MenACWY are routinely recommended, with the first dose at age 11-12 and a second dose at age 16. The MenACWY vaccines are interchangeable.
Implementation challenges and new pentavalent vaccines. Having to use the same MenB vaccine product for all doses in a patient’s series is difficult. It’s even more difficult when the patient needs both MenACWY and MenB vaccinations.
Adding to the complexity is a new pentavalent vaccine from Pfizer (brand name Penbraya) that combines MenACWY with the MenB vaccine. And another pentavalent vaccine version by GSK is up for regulatory decision in February 2025.
The work group did say that they plan to take a fresh look at the meningococcal vaccination schedule. Let’s hope it gets simpler, so more to come on that.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccines
Current RSV vaccine recommendations for older adults. RSV vaccine has both age- and risk-based recommendations. Now, everyone aged 75 or older needs a dose of RSV vaccine. Adults aged 60-75 with risk factors for severe RSV are also recommended to receive a dose of RSV vaccine, but not adults without these risk factors. The conditions associated with increased risk for severe RSV disease include lung disease, heart disease, immune compromise, diabetes, obesity with BMI (body mass index) of 40 or higher, neurologic or neuromuscular conditions, chronic kidney disease, liver disorders, and hematologic disorders. Frailty, as well as living in a nursing home or other long-term care facility, are other risk factors for severe RSV disease. Those aged 60-75 without these risk factors are no longer recommended to receive it.
Three RSV vaccines. We now have three RSV vaccine to choose from. Two are protein subunit vaccines. One is by Pfizer (brand name Abrysvo) that does not contain an adjuvant. The other protein-based RSV vaccine by GSK (brand name Arexvy) does contain an adjuvant. The third RSV vaccine by Moderna (brand name mRESVIA) uses an mRNA platform, and durability of protection is still unclear. However, recent studies now suggest that the RSV protein subunit vaccines confer 36 months of protection rather than only 24 months.
All three RSV vaccines are licensed for those aged 60 or older. The age indication for GSK’s RSV vaccine, Arexvy, has already been lowered by the FDA to age 50. FDA recently lowered the age approval for Abrysvo to age 18 for those at high risk. However, ACIP has not yet expanded its age recommendations for getting these vaccines. One of the main hesitations is vaccine safety concerns. FDA›s safety update presented to ACIP still suggests an increased risk for Guillain-Barré syndrome with both protein-based RSV vaccines among those aged 65 or older. Fortunately, the risk is rare: less than 10 cases per million vaccinations.
RSV immunization for infant protection. RSV season starts in October and goes through March. We now have two new ways to protect babies. One is a maternal RSV vaccine, given at 32-36 weeks of pregnancy to moms who will deliver their babies during RSV season. But only Pfizer’s RSV vaccine (brand name Abrysvo, without an adjuvant) can be given during pregnancy.
A maternal RSV vaccine safety update, presented at ACIP, was reassuring. Abrysvo was not associated with increased risk for preterm birth or small gestational age at birth.
Nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, can be given to infants. Nirsevimab is indicated for all babies under 8 months of age entering their first RSV season.
People who received a maternal RSV vaccine during a previous pregnancy are not recommended to receive additional doses during subsequent pregnancies. However, infants born to women who were vaccinated during a prior pregnancy should receive nirsevimab.
Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, has disclosed conflicts of interest with the American Medical Association, the Medical Association of Atlanta, ACIP, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
This episode of Medicine Matters reviews highlights from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices’ (ACIP’s) October 2024 meeting, with new recommendations for pneumococcal, COVID, and meningococcal B (Men B) vaccines, as well as a safety update for maternal RSV vaccination.
Pneumococcal Vaccination and New Lower Age-Based Recommendations
New age-based recommendation. ACIP has lowered the age for routine vaccination with the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) from age 65 down to age 50, but only with PCV. Review of data revealed that more than half of those in the 50- to 64-year-old age group already had a risk indication to receive a PCV dose. In addition, rates of invasive pneumococcal disease peak at younger ages in Black patients compared with White patients. The rate of invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) among Black adults aged 50 or older exceeds the average rate of IPD for all adults aged 65 or older. The goal of this age-based change is to reduce disease in demographic groups with the highest burden of disease.
The new expanded age-based recommendation applies only to vaccination with PCV. Conjugate vaccines trigger memory B-cell production and therefore induce greater long-term immunity. New research is now focusing on higher-valent PCV vaccines. Two 24-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines and one 31-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine are now in advanced stages of development.
Risk-based recommendation. A risk-based recommendation for ages 19 through 49 years still applies to those with certain medical conditions, including diabetes; chronic heart, lung, liver, or kidney disease; and also for those with immunocompromising conditions. Risk-based recommendations are harder to implement particularly because many vaccines are now administered in pharmacies and pharmacists don’t know the patients as well as their physicians do, so it’s harder for them to know who should get the vaccine if the recommendation is based on risk.
COVID-19 Vaccines With Additional Dose Recommendations
Everyone 6 months or older is recommended to receive a dose of the updated 2024-2025 COVID vaccine. An additional updated COVID vaccine dose is now recommended for everyone aged 65 or older, and for those aged 6 months or older with immunocompromising (moderate or severe) conditions. Review of data revealed that 1 in 6 patients hospitalized with COVID have an immunocompromising condition, and 70% of COVID hospitalizations are in those aged 65 or older. This older age group also has the highest death rates due to COVID-19. We know that vaccination protection wanes with time. Data from previous studies show that additional vaccine doses provide additional protection. Additional doses are now being recommended for those at highest risk.
Timing of additional doses. This second dose is recommended at 6 months after the last updated COVID-19 vaccine dose. However, the additional dose can be given as early as 2 months after the last dose. Those who recently had COVID-19 can wait 3 months before getting an additional vaccine dose. This flexibility allows patients to maximize additional protection by timing additional doses around travel and life events, such as weddings, family get-togethers, or chemotherapy.
Those with immunocompromising conditions may receive more doses. Patients with immunocompromising conditions can receive even more additional doses, if recommended by their physician, under shared clinical decision-making.
Meningococcal Vaccines
Meningococcal disease is rare but deadly. The disease can progress rapidly. As many as 10%-15% of people with meningococcal infection die, even with appropriate antibiotic therapy. And for those who survive, about 20% suffer long-term sequalae (cognitive deficits, hearing loss, limb amputations).
Aligning Men B vaccine dosing intervals. The new ACIP vote applies only to Men B vaccines, of which there are two: one by GSK (brand name Bexsero), and the other by Wyeth, a Pfizer subsidiary (brand name Trumenba). The two MenB vaccine products are not interchangeable. The same type of MenB vaccine has to be used to complete the series.
The MenB vaccines initially had different dosing schedules and now they don’t. ACIP voted to harmonize and align the dosing schedule for the two different MenB products to mirror recent FDA (Food and Drug Administration) labeling updates. So now the dosing recommendations for both MenB vaccines are the same: either two doses given 6 months apart to healthy adolescents and young adults, or a three-dose series given at zero, 1-2 months, and 6 months for those at high risk or for those who want to optimize rapid protection (for example, if they are starting the series within 6 months of going off to college). But understand that the current recommendation for MenB vaccination for healthy adolescents and young adults is based on shared clinical decision-making, preferably for those aged 16-18.
MenACWY. Two doses of MenACWY are routinely recommended, with the first dose at age 11-12 and a second dose at age 16. The MenACWY vaccines are interchangeable.
Implementation challenges and new pentavalent vaccines. Having to use the same MenB vaccine product for all doses in a patient’s series is difficult. It’s even more difficult when the patient needs both MenACWY and MenB vaccinations.
Adding to the complexity is a new pentavalent vaccine from Pfizer (brand name Penbraya) that combines MenACWY with the MenB vaccine. And another pentavalent vaccine version by GSK is up for regulatory decision in February 2025.
The work group did say that they plan to take a fresh look at the meningococcal vaccination schedule. Let’s hope it gets simpler, so more to come on that.
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccines
Current RSV vaccine recommendations for older adults. RSV vaccine has both age- and risk-based recommendations. Now, everyone aged 75 or older needs a dose of RSV vaccine. Adults aged 60-75 with risk factors for severe RSV are also recommended to receive a dose of RSV vaccine, but not adults without these risk factors. The conditions associated with increased risk for severe RSV disease include lung disease, heart disease, immune compromise, diabetes, obesity with BMI (body mass index) of 40 or higher, neurologic or neuromuscular conditions, chronic kidney disease, liver disorders, and hematologic disorders. Frailty, as well as living in a nursing home or other long-term care facility, are other risk factors for severe RSV disease. Those aged 60-75 without these risk factors are no longer recommended to receive it.
Three RSV vaccines. We now have three RSV vaccine to choose from. Two are protein subunit vaccines. One is by Pfizer (brand name Abrysvo) that does not contain an adjuvant. The other protein-based RSV vaccine by GSK (brand name Arexvy) does contain an adjuvant. The third RSV vaccine by Moderna (brand name mRESVIA) uses an mRNA platform, and durability of protection is still unclear. However, recent studies now suggest that the RSV protein subunit vaccines confer 36 months of protection rather than only 24 months.
All three RSV vaccines are licensed for those aged 60 or older. The age indication for GSK’s RSV vaccine, Arexvy, has already been lowered by the FDA to age 50. FDA recently lowered the age approval for Abrysvo to age 18 for those at high risk. However, ACIP has not yet expanded its age recommendations for getting these vaccines. One of the main hesitations is vaccine safety concerns. FDA›s safety update presented to ACIP still suggests an increased risk for Guillain-Barré syndrome with both protein-based RSV vaccines among those aged 65 or older. Fortunately, the risk is rare: less than 10 cases per million vaccinations.
RSV immunization for infant protection. RSV season starts in October and goes through March. We now have two new ways to protect babies. One is a maternal RSV vaccine, given at 32-36 weeks of pregnancy to moms who will deliver their babies during RSV season. But only Pfizer’s RSV vaccine (brand name Abrysvo, without an adjuvant) can be given during pregnancy.
A maternal RSV vaccine safety update, presented at ACIP, was reassuring. Abrysvo was not associated with increased risk for preterm birth or small gestational age at birth.
Nirsevimab, a long-acting monoclonal antibody, can be given to infants. Nirsevimab is indicated for all babies under 8 months of age entering their first RSV season.
People who received a maternal RSV vaccine during a previous pregnancy are not recommended to receive additional doses during subsequent pregnancies. However, infants born to women who were vaccinated during a prior pregnancy should receive nirsevimab.
Sandra Adamson Fryhofer, Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Georgia, has disclosed conflicts of interest with the American Medical Association, the Medical Association of Atlanta, ACIP, and Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Multidisciplinary Amputation Prevention at the DeBakey VA Hospital: Our First Decade
Individuals with diabetes are at risk for developing foot ulcers or full-thickness defects in the epithelium of the foot. These defects can lead to bacterial invasion and foot infection, potentially resulting in leg amputation (Figure 1). Effective treatment to prevent leg amputation, known as limb salvage, requires management across multiple medical specialties including podiatry, vascular surgery, and infectious diseases. The multidisciplinary team approach to limb salvage was introduced in Boston in 1928 and has been the prevailing approach to this cross-specialty medical problem for at least a decade.1,2
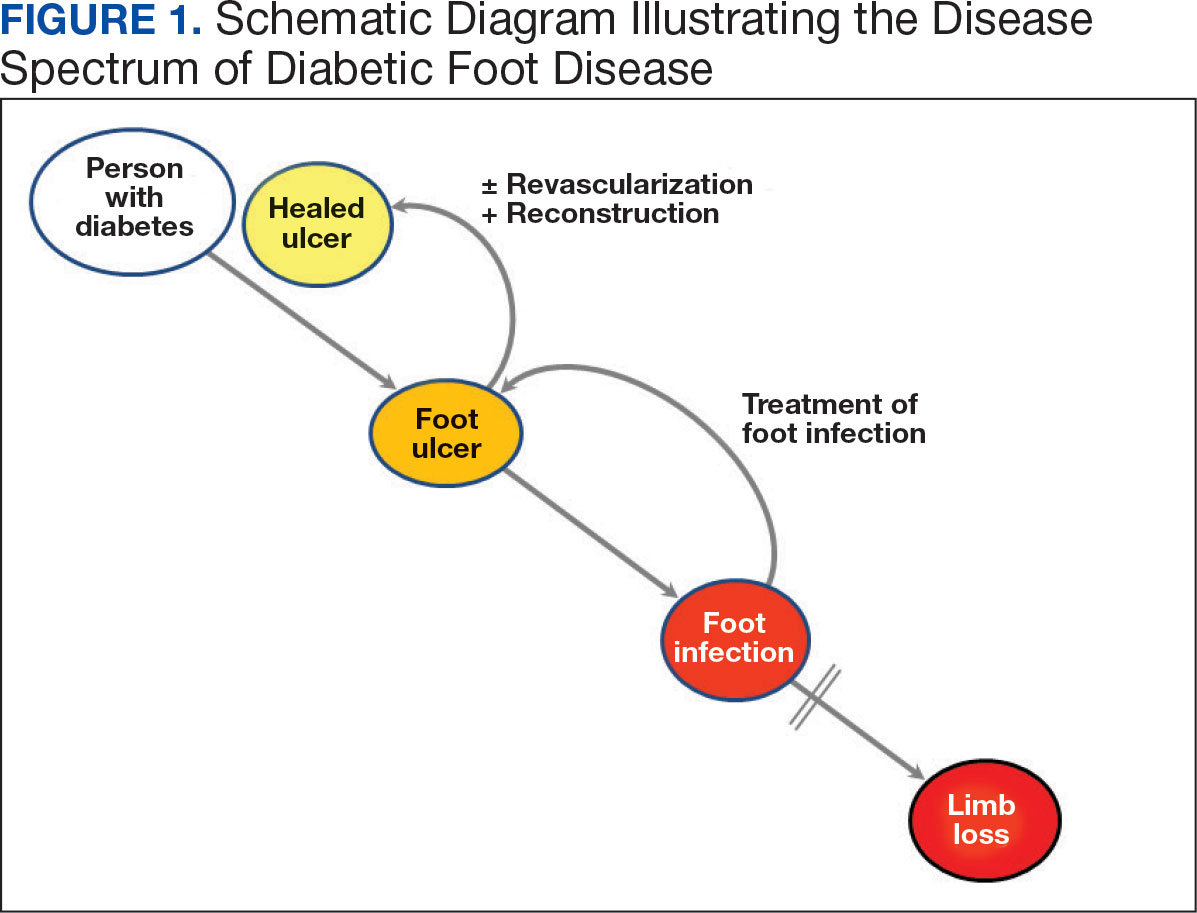
The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) has established an inpatient limb salvage program—a group of dedicated clinicians working collaboratively to provide evidence-guided management of patients hospitalized with foot ulcers, foot gangrene or any superimposed infection with the goal of avoiding leg amputations. We have seen a significant and durable reduction in the incidence of leg amputations among veterans at MEDVAMC.
This article describes the evolution and outcomes of the MEDVAMC limb salvage program over more than a decade. It includes changes to team structure and workflow, as well as past and present successes and challenges. The eAppendix provides a narrative summary with examples of how our clinical practice and research efforts have informed one another and how these findings are applied to clinical management. This process is part of the larger efforts of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) to create a learning health system in which “internal data and experience are systematically integrated with external evidence, and that knowledge is put into practice.”3
Methods
Data from the VHA Support Service Center were used to obtain monthly major (leg) and minor (toe and partial foot) amputation records at MEDVAMC from October 2000 through May 2023. Yearly totals for the number of persons with diabetes and foot ulcers at MEDVAMC were also obtained from the support service center. Annual patient population sizes and number of persons with foot ulcers were converted to monthly estimates using cubic spline interpolation. Rates were calculated as 12-month rolling averages. Trend lines were created with locally weighted running line smoothing that used a span α of 0.1.
We characterized the patient population using data from cohorts of veterans treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at MEDVAMC. To compare the contemporary veteran population with nonveteran inpatients treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at other hospitals, we created a 2:1 nonveteran to veteran cohort matched by sex and zip code, using publicly available hospital admission data from the Texas Department of Health and State Health Services. Veterans used for this cohort comparison are consistent with the 100 consecutive patients who underwent angiography for limb salvage in 2022.
This research was approved by the Baylor College of Medicine Institutional Review Board (protocol H-34858) and the MEDVAMC Research Committee (IRBNet protocol 15A12. HB). All analyses used deidentified data in the R programming language version 4.2.2 using RStudio version 2022.06.0 Build 421.
Program Description
MEDVAMC is a 350-bed teaching hospital located in central Houston. Its hospital system includes 11 outpatient clinics, ranging from 28 to 126 miles (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure A) from MEDVAMC. MEDVAMC provides vascular, orthopedic, and podiatric surgery services, as well as many other highly specialized services such as liver and heart transplants. The hospital’s risk-adjusted rates of operative morbidity and mortality (observed-to-expected ratios) are significantly lower than expected.
Despite this, the incidence rate of leg amputations at MEDVAMC in early 2011 was nearly 3-times higher than the VHA average. The inpatient management of veterans with infected foot ulcers was fragmented, with the general, orthopedic, and vascular surgery teams separately providing siloed care. Delays in treatment were common. There was much service- and practitioner-level practice heterogeneity. No diagnostic or treatment protocols were used, and standard treatment components were sporadically provided.
Patient Population
Compared to the matched non-VHA patient cohort (Supplemental Table 1), veterans treated at MEDVAMC for limb salvage are older. Nearly half (46%) identify as Black, which is associated with a 2-fold higher riskadjusted rate of leg amputations.4 MEDVAMC patients also have significantly higher rates of diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and systolic heart failure. About 22% travel > 40 miles for treatment at MEDVAMC, double that of the matched cohort (10.7%). Additionally, 35% currently smoke and 37% have moderate to severe peripheral artery disease (PAD).5
Program Design
In late 2011, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team led limb salvage efforts by implementing a single team model, which involved assuming the primary role of managing foot ulcers for all veterans, both infected and uninfected (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure B). Consultations were directed to a dedicated limb salvage pager. The vascular team provided interdisciplinary limb salvage management across the spectrum of disease, including the surgical treatment of infection, assessment for PAD, open surgical operations and endovascular interventions to treat PAD, and foot reconstruction (debridement, minor or partial foot amputations, and skin grafting). This care was complemented by frequent consultation with the infectious disease, vascular medicine, podiatry, and geriatric wound care teams. This approach streamlined the delivery of consistent multidisciplinary care.
This collaborative effort aimed to develop ideal multidisciplinary care plans through research spanning the spectrum of the diabetic foot infection disease process (eAppendix, Supplemental Table 1). Some of the most impactful practices were: (1) a proclivity towards surgical treatment of foot infections, especially osteomyelitis5; (2) improved identification of PAD6,7; (3) early surgical closure of foot wounds following revascularization8,9; and (4) palliative wound care as an alternative to leg amputation in veterans who are not candidates for revascularization and limb salvage.10 Initally, the vascular surgery team held monthly multidisciplinary limb salvage meetings to coordinate patient management, identify ways to streamline care and avoid waste, discuss research findings, and review the 12-month rolling average of the MEDVAMC leg amputation incidence rate.
During the study period, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team consisted of 2 to 5 board certified vascular or general surgeons, 2 or 3 nurse practitioners, and 3 vascular ultrasound technologists. Associated specialists included 2 podiatrists, 3 geriatricians with wound care certification, as well as additional infectious diseases, vascular medicine, orthopedics, and general surgery specialists.
Program Assessment
We noted a significant and sustained decrease in the MEDVAMC leg amputation rate after implementing multidisciplinary meetings and a single- team model from early 2012 through 2017 (Figure 2). The amputation incidence rate decreased steadily over the period from a maximum of 160 per 100,000 per year in February 2012 to a nadir of 66 per 100,000 per year in April 2017, an overall 60% decrease. Increases were noted in early 2018 after ceasing the single- team model, and in the summer of 2022, following periods of bed shortages after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Tracking this metric allowed clinicians to make course corrections.
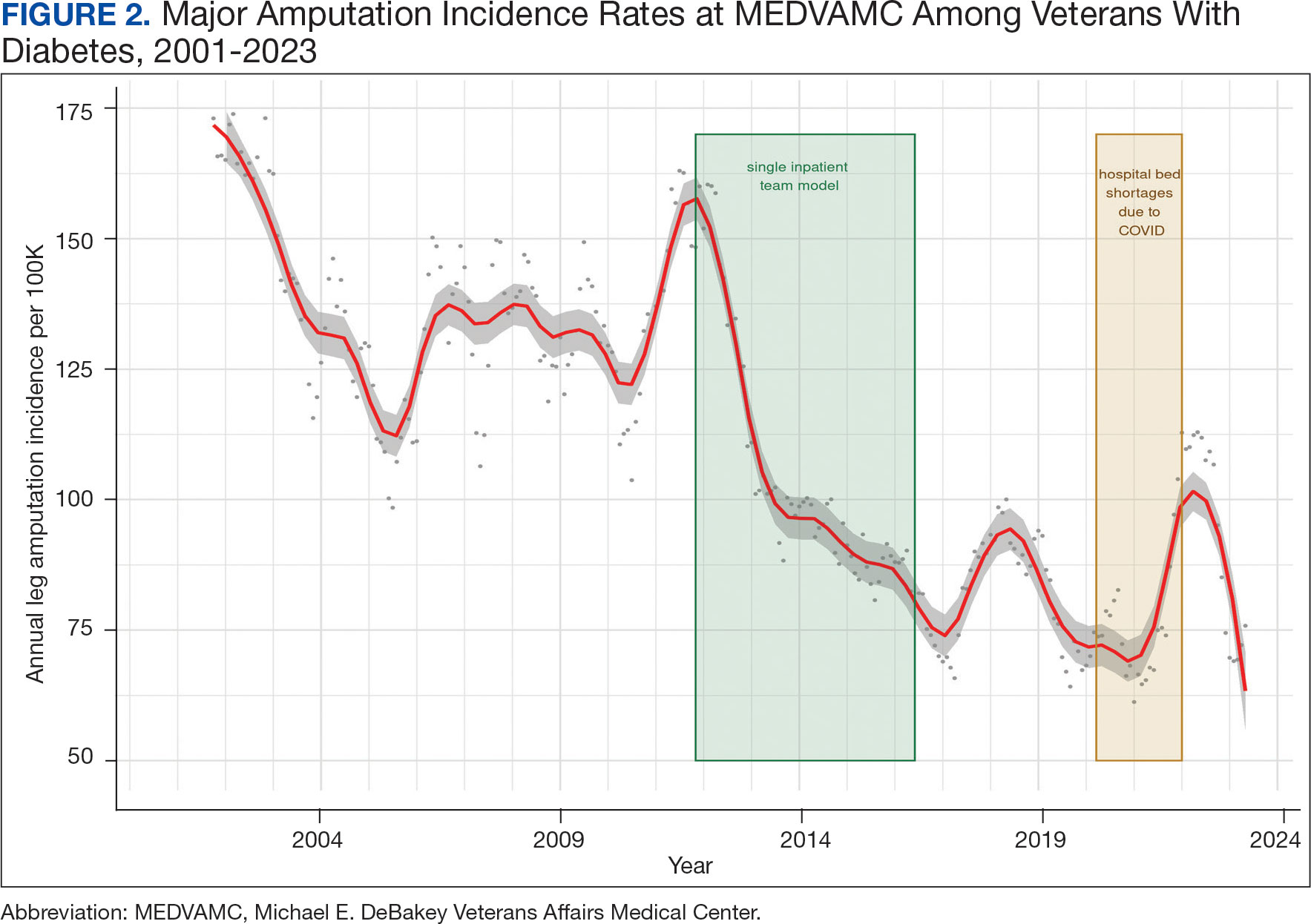
The decreased leg amputation rate at MEDVAMC does not seem to be mirroring national or regional trends. During this 10-year period, the VHA annualized amputation rate decreased minimally, from 58 to 54 per 100,000 (eAppendix Supplemental Figure C). Leg amputation incidence at non-VHA hospitals in Texas slightly increased over the same period.11
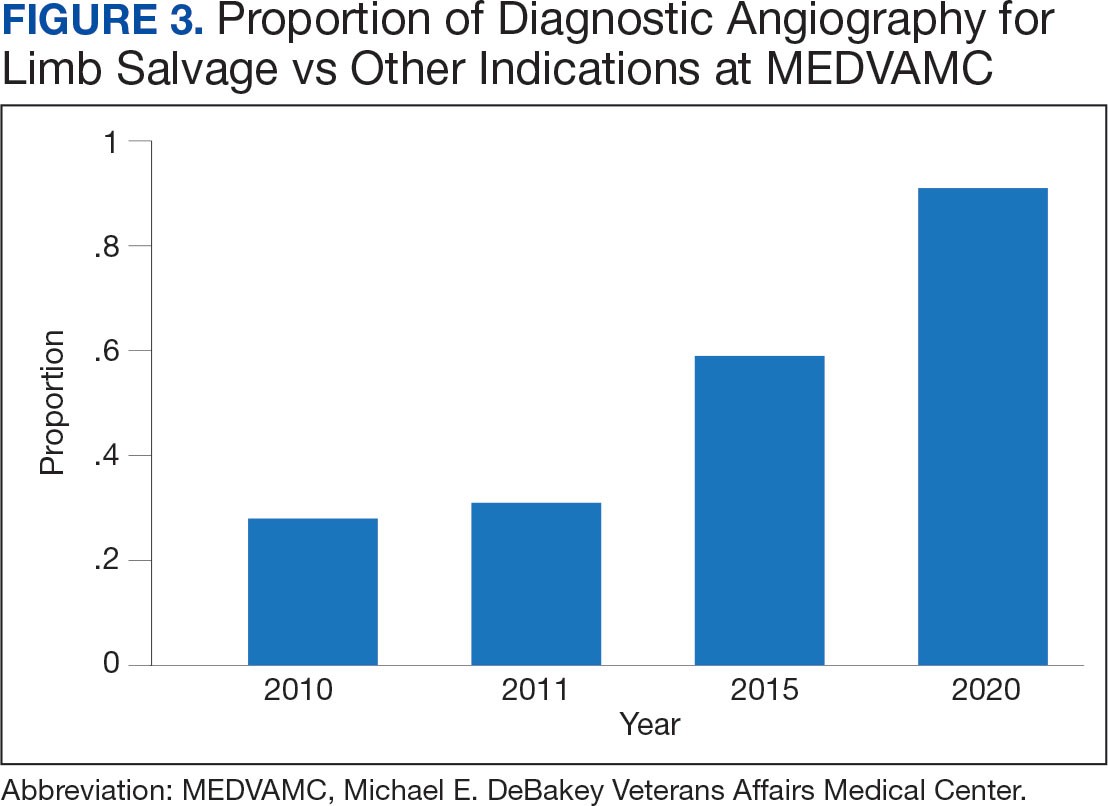
Value was also reflected in other metrics. MEDVAMC improved safety through a bundled strategy that reduced the risk-adjusted rate of surgical wound infections by 95%.12 MEDVAMC prioritized limb salvage when selecting patients for angiography and nearly eliminated using stent-grafts, cryopreserved allogeneic saphenous vein grafts, and expensive surgical and endovascular implants, which were identified as more expensive and less effective than other options (Figure 3).13-15 The MEDVAMC team achieved a > 90% patient trust rating on the Veterans Signals survey in fiscal years 2021 and 2022.
Challenges
A significant increase in the patient-physician ratio occurred 5 years into the program. In 2016, 2 vascular surgeons left MEDVAMC and a planned renovation of 1 of the 2 vascular surgery-assigned hybrid working facilities began even as the number of MEDVAMC patients with diabetes grew 120% (from 89,400 to 107,746 between 2010 and 2016), and the incidence rate of foot ulcers grew 300% (from 392 in 2010 to 1183 in 2016 per 100,000). The net result was a higher clinical workload among the remaining vascular surgeons with less operating room availability.
To stabilize surgeon retention, MEDVAMC reverted from the single team model back to inpatient care being distributed among general surgery, orthopedic surgery, and vascular surgery. After noting an increase in the leg amputation incidence rate, we adjusted the focus from multidisciplinary to interdisciplinary care (ie, majority of limb salvage clinical care can be provided by practitioners of any involved specialties). We worked to establish a local, written, interdisciplinary consensus on evaluating and managing veterans with nonhealing foot ulcers to mitigate the loss of a consolidated inpatient approach. Despite frequent staff turnover, ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from the core specialties of vascular surgery, podiatry, and infectious diseases remained throughout the study period.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a shortage of hospital beds. This was followed by more bed shortages due to decreased nursing staff. Our health care system also had a period of restricted outpatient encounters early in the pandemic. During this time, we noted a delayed presentation of veterans with advanced infections and another increase in leg amputation incidence rate.
Like many health systems, MEDVAMC pivoted to telephone- and video-based outpatient encounters. Our team also used publicly available Texas hospitalization data to identify zip codes with particularly high leg amputation incidence rates, and > 3500 educational mailings to veterans categorized as moderate and high risk for leg amputation in these zip codes. These mailings provided information on recognizing foot ulcers and infections, emphasized timely evaluation, and named the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team as a point-of-contact. More recently, we have seen a further decrease in the MEDVAMC incidences of leg amputation to its lowest rate in > 20 years.
Discussion
A learning organization that directs its research based on clinical observations and informs its clinical care with research findings can produce palpable improvements in outcomes. Understanding the disease process and trying to better understand management across the entire range of this disease process has allowed our team to make consistent and systematic changes in care (Table). Consolidating inpatient care in a single team model seems to have been effective in reducing amputation rates among veterans with diabetes. The role the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team served for limb salvage patients may have been particularly beneficial because of the large impact untreated or unidentified PAD can have and because of the high prevalence of PAD among the limb salvage population seen at MEDVAMC. To be sustainable, though, a single-team model needs resources. A multiteam model can also be effective if the degree of multidisciplinary involvement for any given veteran is appropriate to the individual's clinical needs, teams are engaged and willing to contribute in a defined role within their specialty, and lines of communication remain open.
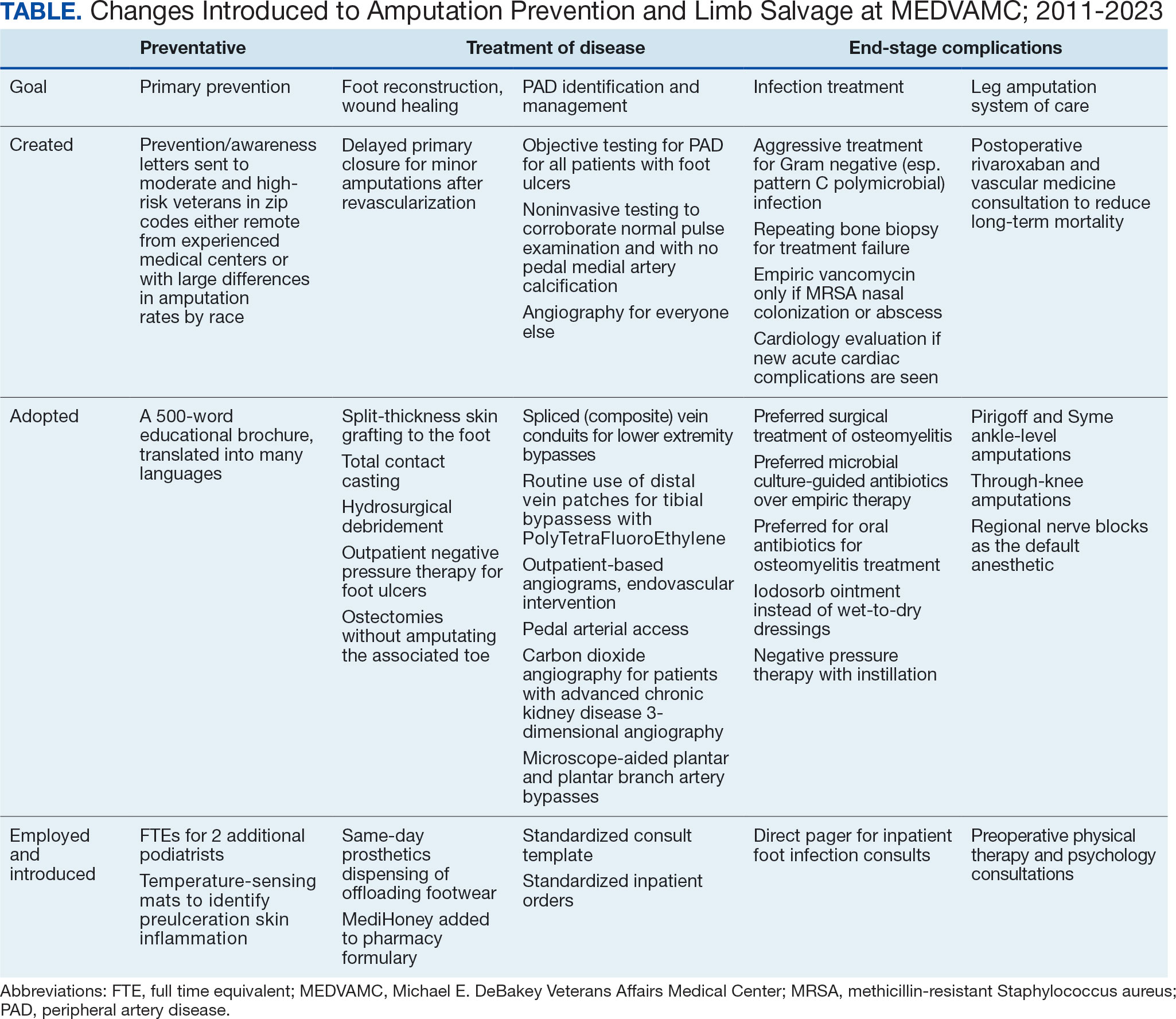
The primary challenge at MEDVAMC has been, and will continue to be, the retention of physicians and surgeons. MEDVAMC has excellent leadership and a collegial working environment, but better access to operating rooms for elective and time-sensitive operations, additional clinical staff support, and higher salary at non-VA positions have been the basis for many of physicians— especially surgeons—leaving MEDVAMC. Despite high staff turnover and a constant flow of resident and fellow trainees, MEDVAMC has been able to keep the clinical approach relatively consistent due to the use of written protocols and continuity of care as ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from each of the 4 main teams remained engaged with limb salvage throughout the entire period.
Going forward, we will work to ensure that all requirements of the 2022 Prevention of Amputation in Veterans Everywhere directive are incorporated into care.8 We plan to standardize MEDVAMC management algorithms further, both to streamline care and reduce the opportunity for disparities in treatment. More prophylactic podiatric procedures, surgical forms of offloading, and a shared multidisciplinary clinic space may also further help patients.
Conclusions
The introduction of multidisciplinary limb salvage at MEDVAMC has led to significant and sustained reductions in leg amputation incidence. These reductions do not seem dependent upon a specific team structure for inpatient care. To improve patient outcomes, efforts should focus on making improvements across the entire disease spectrum. For limb salvage, this includes primary prevention of foot ulcers, the treatment of foot infections, identification and management of PAD, surgical reconstruction/optimal wound healing, and care for patients who undergo leg amputation.
- Sanders LJ, Robbins JM, Edmonds ME. History of the team approach to amputation prevention: pioneers and milestones. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(5):317- 334. doi:10.7547/1000317
- Sumpio BE, Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Andros G. The role of interdisciplinary team approach in the management of the diabetic foot: a joint statement from the society for vascular surgery and the American podiatric medical association. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(4):309-311. doi:10.7547/1000309
- About learning health systems. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Published March 2019. Updated May 2019. Accessed October 9, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/learning-health-systems/about.html
- Barshes NR, Minc SD. Healthcare disparities in vascular surgery: a critical review. J Vasc Surg. 2021;74(2S):6S-14S.
- Barshes NR, Mindru C, Ashong C, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Trautner BW. Treatment failure and leg amputation among patients with foot osteomyelitis. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2016;15(4):303-312. doi:10.1177/1534734616661058
- Barshes NR, Flores E, Belkin M, Kougias P, Armstrong DG, Mills JL Sr. The accuracy and cost-effectiveness of strategies used to identify peripheral artery disease among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(6):1682-1690.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.056 e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2021.03.055
- Choi JC, Miranda J, Greenleaf E, et al. Lower-extremity pressure, staging, and grading thresholds to identify chronic limb-threatening ischemia. Vasc Med. 2023;28(1):45-53. doi:10.1177/1358863X221147945
- Barshes NR, Chambers JD, Cohen J, Belkin M; Model To Optimize Healthcare Value in Ischemic Extremities 1 (MOVIE) Study Collaborators. Cost-effectiveness in the contemporary management of critical limb ischemia with tissue loss. J Vasc Surg. 2012;56(4):1015-24.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.02.069
- Barshes NR, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Preliminary experiences with early primary closure of foot wounds after lower extremity revascularization. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28(1):48-52. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2013.06.012
- Barshes NR, Gold B, Garcia A, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Minor amputation and palliative wound care as a strategy to avoid major amputation in patients with foot infections and severe peripheral arterial disease. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2014;13(3):211-219. doi:10.1177/1534734614543663
- Garcia M, Hernandez B, Ellington TG, et al. A lack of decline in major nontraumatic amputations in Texas: contemporary trends, risk factor associations, and impact of revascularization. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(6):1061-1066. doi:10.2337/dc19-0078
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Vo E, Awad SS, Kougias P, Barshes NR. A multi-component strategy to decrease wound complications after open infra-inguinal re-vascularization. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2018;19(1):87-94. doi:10.1089/sur.2017.193
- Barshes NR, Ozaki CK, Kougias P, Belkin M. A costeffectiveness analysis of infrainguinal bypass in the absence of great saphenous vein conduit. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57(6):1466-1470. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.11.115
- Zamani N, Sharath S, Browder R, et al. PC158 longterm outcomes after endovascular stent placement for symptomatic, long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(6):182S-183S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.03.344
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Browder RC, et al. Outcomes after endovascular stent placement for long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021;71:298-307. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2020.08.124
Individuals with diabetes are at risk for developing foot ulcers or full-thickness defects in the epithelium of the foot. These defects can lead to bacterial invasion and foot infection, potentially resulting in leg amputation (Figure 1). Effective treatment to prevent leg amputation, known as limb salvage, requires management across multiple medical specialties including podiatry, vascular surgery, and infectious diseases. The multidisciplinary team approach to limb salvage was introduced in Boston in 1928 and has been the prevailing approach to this cross-specialty medical problem for at least a decade.1,2

The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) has established an inpatient limb salvage program—a group of dedicated clinicians working collaboratively to provide evidence-guided management of patients hospitalized with foot ulcers, foot gangrene or any superimposed infection with the goal of avoiding leg amputations. We have seen a significant and durable reduction in the incidence of leg amputations among veterans at MEDVAMC.
This article describes the evolution and outcomes of the MEDVAMC limb salvage program over more than a decade. It includes changes to team structure and workflow, as well as past and present successes and challenges. The eAppendix provides a narrative summary with examples of how our clinical practice and research efforts have informed one another and how these findings are applied to clinical management. This process is part of the larger efforts of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) to create a learning health system in which “internal data and experience are systematically integrated with external evidence, and that knowledge is put into practice.”3
Methods
Data from the VHA Support Service Center were used to obtain monthly major (leg) and minor (toe and partial foot) amputation records at MEDVAMC from October 2000 through May 2023. Yearly totals for the number of persons with diabetes and foot ulcers at MEDVAMC were also obtained from the support service center. Annual patient population sizes and number of persons with foot ulcers were converted to monthly estimates using cubic spline interpolation. Rates were calculated as 12-month rolling averages. Trend lines were created with locally weighted running line smoothing that used a span α of 0.1.
We characterized the patient population using data from cohorts of veterans treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at MEDVAMC. To compare the contemporary veteran population with nonveteran inpatients treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at other hospitals, we created a 2:1 nonveteran to veteran cohort matched by sex and zip code, using publicly available hospital admission data from the Texas Department of Health and State Health Services. Veterans used for this cohort comparison are consistent with the 100 consecutive patients who underwent angiography for limb salvage in 2022.
This research was approved by the Baylor College of Medicine Institutional Review Board (protocol H-34858) and the MEDVAMC Research Committee (IRBNet protocol 15A12. HB). All analyses used deidentified data in the R programming language version 4.2.2 using RStudio version 2022.06.0 Build 421.
Program Description
MEDVAMC is a 350-bed teaching hospital located in central Houston. Its hospital system includes 11 outpatient clinics, ranging from 28 to 126 miles (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure A) from MEDVAMC. MEDVAMC provides vascular, orthopedic, and podiatric surgery services, as well as many other highly specialized services such as liver and heart transplants. The hospital’s risk-adjusted rates of operative morbidity and mortality (observed-to-expected ratios) are significantly lower than expected.
Despite this, the incidence rate of leg amputations at MEDVAMC in early 2011 was nearly 3-times higher than the VHA average. The inpatient management of veterans with infected foot ulcers was fragmented, with the general, orthopedic, and vascular surgery teams separately providing siloed care. Delays in treatment were common. There was much service- and practitioner-level practice heterogeneity. No diagnostic or treatment protocols were used, and standard treatment components were sporadically provided.
Patient Population
Compared to the matched non-VHA patient cohort (Supplemental Table 1), veterans treated at MEDVAMC for limb salvage are older. Nearly half (46%) identify as Black, which is associated with a 2-fold higher riskadjusted rate of leg amputations.4 MEDVAMC patients also have significantly higher rates of diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and systolic heart failure. About 22% travel > 40 miles for treatment at MEDVAMC, double that of the matched cohort (10.7%). Additionally, 35% currently smoke and 37% have moderate to severe peripheral artery disease (PAD).5
Program Design
In late 2011, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team led limb salvage efforts by implementing a single team model, which involved assuming the primary role of managing foot ulcers for all veterans, both infected and uninfected (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure B). Consultations were directed to a dedicated limb salvage pager. The vascular team provided interdisciplinary limb salvage management across the spectrum of disease, including the surgical treatment of infection, assessment for PAD, open surgical operations and endovascular interventions to treat PAD, and foot reconstruction (debridement, minor or partial foot amputations, and skin grafting). This care was complemented by frequent consultation with the infectious disease, vascular medicine, podiatry, and geriatric wound care teams. This approach streamlined the delivery of consistent multidisciplinary care.
This collaborative effort aimed to develop ideal multidisciplinary care plans through research spanning the spectrum of the diabetic foot infection disease process (eAppendix, Supplemental Table 1). Some of the most impactful practices were: (1) a proclivity towards surgical treatment of foot infections, especially osteomyelitis5; (2) improved identification of PAD6,7; (3) early surgical closure of foot wounds following revascularization8,9; and (4) palliative wound care as an alternative to leg amputation in veterans who are not candidates for revascularization and limb salvage.10 Initally, the vascular surgery team held monthly multidisciplinary limb salvage meetings to coordinate patient management, identify ways to streamline care and avoid waste, discuss research findings, and review the 12-month rolling average of the MEDVAMC leg amputation incidence rate.
During the study period, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team consisted of 2 to 5 board certified vascular or general surgeons, 2 or 3 nurse practitioners, and 3 vascular ultrasound technologists. Associated specialists included 2 podiatrists, 3 geriatricians with wound care certification, as well as additional infectious diseases, vascular medicine, orthopedics, and general surgery specialists.
Program Assessment
We noted a significant and sustained decrease in the MEDVAMC leg amputation rate after implementing multidisciplinary meetings and a single- team model from early 2012 through 2017 (Figure 2). The amputation incidence rate decreased steadily over the period from a maximum of 160 per 100,000 per year in February 2012 to a nadir of 66 per 100,000 per year in April 2017, an overall 60% decrease. Increases were noted in early 2018 after ceasing the single- team model, and in the summer of 2022, following periods of bed shortages after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Tracking this metric allowed clinicians to make course corrections.

The decreased leg amputation rate at MEDVAMC does not seem to be mirroring national or regional trends. During this 10-year period, the VHA annualized amputation rate decreased minimally, from 58 to 54 per 100,000 (eAppendix Supplemental Figure C). Leg amputation incidence at non-VHA hospitals in Texas slightly increased over the same period.11
Value was also reflected in other metrics. MEDVAMC improved safety through a bundled strategy that reduced the risk-adjusted rate of surgical wound infections by 95%.12 MEDVAMC prioritized limb salvage when selecting patients for angiography and nearly eliminated using stent-grafts, cryopreserved allogeneic saphenous vein grafts, and expensive surgical and endovascular implants, which were identified as more expensive and less effective than other options (Figure 3).13-15 The MEDVAMC team achieved a > 90% patient trust rating on the Veterans Signals survey in fiscal years 2021 and 2022.

Challenges
A significant increase in the patient-physician ratio occurred 5 years into the program. In 2016, 2 vascular surgeons left MEDVAMC and a planned renovation of 1 of the 2 vascular surgery-assigned hybrid working facilities began even as the number of MEDVAMC patients with diabetes grew 120% (from 89,400 to 107,746 between 2010 and 2016), and the incidence rate of foot ulcers grew 300% (from 392 in 2010 to 1183 in 2016 per 100,000). The net result was a higher clinical workload among the remaining vascular surgeons with less operating room availability.
To stabilize surgeon retention, MEDVAMC reverted from the single team model back to inpatient care being distributed among general surgery, orthopedic surgery, and vascular surgery. After noting an increase in the leg amputation incidence rate, we adjusted the focus from multidisciplinary to interdisciplinary care (ie, majority of limb salvage clinical care can be provided by practitioners of any involved specialties). We worked to establish a local, written, interdisciplinary consensus on evaluating and managing veterans with nonhealing foot ulcers to mitigate the loss of a consolidated inpatient approach. Despite frequent staff turnover, ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from the core specialties of vascular surgery, podiatry, and infectious diseases remained throughout the study period.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a shortage of hospital beds. This was followed by more bed shortages due to decreased nursing staff. Our health care system also had a period of restricted outpatient encounters early in the pandemic. During this time, we noted a delayed presentation of veterans with advanced infections and another increase in leg amputation incidence rate.
Like many health systems, MEDVAMC pivoted to telephone- and video-based outpatient encounters. Our team also used publicly available Texas hospitalization data to identify zip codes with particularly high leg amputation incidence rates, and > 3500 educational mailings to veterans categorized as moderate and high risk for leg amputation in these zip codes. These mailings provided information on recognizing foot ulcers and infections, emphasized timely evaluation, and named the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team as a point-of-contact. More recently, we have seen a further decrease in the MEDVAMC incidences of leg amputation to its lowest rate in > 20 years.
Discussion
A learning organization that directs its research based on clinical observations and informs its clinical care with research findings can produce palpable improvements in outcomes. Understanding the disease process and trying to better understand management across the entire range of this disease process has allowed our team to make consistent and systematic changes in care (Table). Consolidating inpatient care in a single team model seems to have been effective in reducing amputation rates among veterans with diabetes. The role the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team served for limb salvage patients may have been particularly beneficial because of the large impact untreated or unidentified PAD can have and because of the high prevalence of PAD among the limb salvage population seen at MEDVAMC. To be sustainable, though, a single-team model needs resources. A multiteam model can also be effective if the degree of multidisciplinary involvement for any given veteran is appropriate to the individual's clinical needs, teams are engaged and willing to contribute in a defined role within their specialty, and lines of communication remain open.

The primary challenge at MEDVAMC has been, and will continue to be, the retention of physicians and surgeons. MEDVAMC has excellent leadership and a collegial working environment, but better access to operating rooms for elective and time-sensitive operations, additional clinical staff support, and higher salary at non-VA positions have been the basis for many of physicians— especially surgeons—leaving MEDVAMC. Despite high staff turnover and a constant flow of resident and fellow trainees, MEDVAMC has been able to keep the clinical approach relatively consistent due to the use of written protocols and continuity of care as ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from each of the 4 main teams remained engaged with limb salvage throughout the entire period.
Going forward, we will work to ensure that all requirements of the 2022 Prevention of Amputation in Veterans Everywhere directive are incorporated into care.8 We plan to standardize MEDVAMC management algorithms further, both to streamline care and reduce the opportunity for disparities in treatment. More prophylactic podiatric procedures, surgical forms of offloading, and a shared multidisciplinary clinic space may also further help patients.
Conclusions
The introduction of multidisciplinary limb salvage at MEDVAMC has led to significant and sustained reductions in leg amputation incidence. These reductions do not seem dependent upon a specific team structure for inpatient care. To improve patient outcomes, efforts should focus on making improvements across the entire disease spectrum. For limb salvage, this includes primary prevention of foot ulcers, the treatment of foot infections, identification and management of PAD, surgical reconstruction/optimal wound healing, and care for patients who undergo leg amputation.
Individuals with diabetes are at risk for developing foot ulcers or full-thickness defects in the epithelium of the foot. These defects can lead to bacterial invasion and foot infection, potentially resulting in leg amputation (Figure 1). Effective treatment to prevent leg amputation, known as limb salvage, requires management across multiple medical specialties including podiatry, vascular surgery, and infectious diseases. The multidisciplinary team approach to limb salvage was introduced in Boston in 1928 and has been the prevailing approach to this cross-specialty medical problem for at least a decade.1,2

The Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MEDVAMC) has established an inpatient limb salvage program—a group of dedicated clinicians working collaboratively to provide evidence-guided management of patients hospitalized with foot ulcers, foot gangrene or any superimposed infection with the goal of avoiding leg amputations. We have seen a significant and durable reduction in the incidence of leg amputations among veterans at MEDVAMC.
This article describes the evolution and outcomes of the MEDVAMC limb salvage program over more than a decade. It includes changes to team structure and workflow, as well as past and present successes and challenges. The eAppendix provides a narrative summary with examples of how our clinical practice and research efforts have informed one another and how these findings are applied to clinical management. This process is part of the larger efforts of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) to create a learning health system in which “internal data and experience are systematically integrated with external evidence, and that knowledge is put into practice.”3
Methods
Data from the VHA Support Service Center were used to obtain monthly major (leg) and minor (toe and partial foot) amputation records at MEDVAMC from October 2000 through May 2023. Yearly totals for the number of persons with diabetes and foot ulcers at MEDVAMC were also obtained from the support service center. Annual patient population sizes and number of persons with foot ulcers were converted to monthly estimates using cubic spline interpolation. Rates were calculated as 12-month rolling averages. Trend lines were created with locally weighted running line smoothing that used a span α of 0.1.
We characterized the patient population using data from cohorts of veterans treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at MEDVAMC. To compare the contemporary veteran population with nonveteran inpatients treated for foot ulcers and foot infections at other hospitals, we created a 2:1 nonveteran to veteran cohort matched by sex and zip code, using publicly available hospital admission data from the Texas Department of Health and State Health Services. Veterans used for this cohort comparison are consistent with the 100 consecutive patients who underwent angiography for limb salvage in 2022.
This research was approved by the Baylor College of Medicine Institutional Review Board (protocol H-34858) and the MEDVAMC Research Committee (IRBNet protocol 15A12. HB). All analyses used deidentified data in the R programming language version 4.2.2 using RStudio version 2022.06.0 Build 421.
Program Description
MEDVAMC is a 350-bed teaching hospital located in central Houston. Its hospital system includes 11 outpatient clinics, ranging from 28 to 126 miles (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure A) from MEDVAMC. MEDVAMC provides vascular, orthopedic, and podiatric surgery services, as well as many other highly specialized services such as liver and heart transplants. The hospital’s risk-adjusted rates of operative morbidity and mortality (observed-to-expected ratios) are significantly lower than expected.
Despite this, the incidence rate of leg amputations at MEDVAMC in early 2011 was nearly 3-times higher than the VHA average. The inpatient management of veterans with infected foot ulcers was fragmented, with the general, orthopedic, and vascular surgery teams separately providing siloed care. Delays in treatment were common. There was much service- and practitioner-level practice heterogeneity. No diagnostic or treatment protocols were used, and standard treatment components were sporadically provided.
Patient Population
Compared to the matched non-VHA patient cohort (Supplemental Table 1), veterans treated at MEDVAMC for limb salvage are older. Nearly half (46%) identify as Black, which is associated with a 2-fold higher riskadjusted rate of leg amputations.4 MEDVAMC patients also have significantly higher rates of diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and systolic heart failure. About 22% travel > 40 miles for treatment at MEDVAMC, double that of the matched cohort (10.7%). Additionally, 35% currently smoke and 37% have moderate to severe peripheral artery disease (PAD).5
Program Design
In late 2011, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team led limb salvage efforts by implementing a single team model, which involved assuming the primary role of managing foot ulcers for all veterans, both infected and uninfected (eAppendix, Supplemental Figure B). Consultations were directed to a dedicated limb salvage pager. The vascular team provided interdisciplinary limb salvage management across the spectrum of disease, including the surgical treatment of infection, assessment for PAD, open surgical operations and endovascular interventions to treat PAD, and foot reconstruction (debridement, minor or partial foot amputations, and skin grafting). This care was complemented by frequent consultation with the infectious disease, vascular medicine, podiatry, and geriatric wound care teams. This approach streamlined the delivery of consistent multidisciplinary care.
This collaborative effort aimed to develop ideal multidisciplinary care plans through research spanning the spectrum of the diabetic foot infection disease process (eAppendix, Supplemental Table 1). Some of the most impactful practices were: (1) a proclivity towards surgical treatment of foot infections, especially osteomyelitis5; (2) improved identification of PAD6,7; (3) early surgical closure of foot wounds following revascularization8,9; and (4) palliative wound care as an alternative to leg amputation in veterans who are not candidates for revascularization and limb salvage.10 Initally, the vascular surgery team held monthly multidisciplinary limb salvage meetings to coordinate patient management, identify ways to streamline care and avoid waste, discuss research findings, and review the 12-month rolling average of the MEDVAMC leg amputation incidence rate.
During the study period, the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team consisted of 2 to 5 board certified vascular or general surgeons, 2 or 3 nurse practitioners, and 3 vascular ultrasound technologists. Associated specialists included 2 podiatrists, 3 geriatricians with wound care certification, as well as additional infectious diseases, vascular medicine, orthopedics, and general surgery specialists.
Program Assessment
We noted a significant and sustained decrease in the MEDVAMC leg amputation rate after implementing multidisciplinary meetings and a single- team model from early 2012 through 2017 (Figure 2). The amputation incidence rate decreased steadily over the period from a maximum of 160 per 100,000 per year in February 2012 to a nadir of 66 per 100,000 per year in April 2017, an overall 60% decrease. Increases were noted in early 2018 after ceasing the single- team model, and in the summer of 2022, following periods of bed shortages after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Tracking this metric allowed clinicians to make course corrections.

The decreased leg amputation rate at MEDVAMC does not seem to be mirroring national or regional trends. During this 10-year period, the VHA annualized amputation rate decreased minimally, from 58 to 54 per 100,000 (eAppendix Supplemental Figure C). Leg amputation incidence at non-VHA hospitals in Texas slightly increased over the same period.11
Value was also reflected in other metrics. MEDVAMC improved safety through a bundled strategy that reduced the risk-adjusted rate of surgical wound infections by 95%.12 MEDVAMC prioritized limb salvage when selecting patients for angiography and nearly eliminated using stent-grafts, cryopreserved allogeneic saphenous vein grafts, and expensive surgical and endovascular implants, which were identified as more expensive and less effective than other options (Figure 3).13-15 The MEDVAMC team achieved a > 90% patient trust rating on the Veterans Signals survey in fiscal years 2021 and 2022.

Challenges
A significant increase in the patient-physician ratio occurred 5 years into the program. In 2016, 2 vascular surgeons left MEDVAMC and a planned renovation of 1 of the 2 vascular surgery-assigned hybrid working facilities began even as the number of MEDVAMC patients with diabetes grew 120% (from 89,400 to 107,746 between 2010 and 2016), and the incidence rate of foot ulcers grew 300% (from 392 in 2010 to 1183 in 2016 per 100,000). The net result was a higher clinical workload among the remaining vascular surgeons with less operating room availability.
To stabilize surgeon retention, MEDVAMC reverted from the single team model back to inpatient care being distributed among general surgery, orthopedic surgery, and vascular surgery. After noting an increase in the leg amputation incidence rate, we adjusted the focus from multidisciplinary to interdisciplinary care (ie, majority of limb salvage clinical care can be provided by practitioners of any involved specialties). We worked to establish a local, written, interdisciplinary consensus on evaluating and managing veterans with nonhealing foot ulcers to mitigate the loss of a consolidated inpatient approach. Despite frequent staff turnover, ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from the core specialties of vascular surgery, podiatry, and infectious diseases remained throughout the study period.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a shortage of hospital beds. This was followed by more bed shortages due to decreased nursing staff. Our health care system also had a period of restricted outpatient encounters early in the pandemic. During this time, we noted a delayed presentation of veterans with advanced infections and another increase in leg amputation incidence rate.
Like many health systems, MEDVAMC pivoted to telephone- and video-based outpatient encounters. Our team also used publicly available Texas hospitalization data to identify zip codes with particularly high leg amputation incidence rates, and > 3500 educational mailings to veterans categorized as moderate and high risk for leg amputation in these zip codes. These mailings provided information on recognizing foot ulcers and infections, emphasized timely evaluation, and named the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team as a point-of-contact. More recently, we have seen a further decrease in the MEDVAMC incidences of leg amputation to its lowest rate in > 20 years.
Discussion
A learning organization that directs its research based on clinical observations and informs its clinical care with research findings can produce palpable improvements in outcomes. Understanding the disease process and trying to better understand management across the entire range of this disease process has allowed our team to make consistent and systematic changes in care (Table). Consolidating inpatient care in a single team model seems to have been effective in reducing amputation rates among veterans with diabetes. The role the MEDVAMC vascular surgery team served for limb salvage patients may have been particularly beneficial because of the large impact untreated or unidentified PAD can have and because of the high prevalence of PAD among the limb salvage population seen at MEDVAMC. To be sustainable, though, a single-team model needs resources. A multiteam model can also be effective if the degree of multidisciplinary involvement for any given veteran is appropriate to the individual's clinical needs, teams are engaged and willing to contribute in a defined role within their specialty, and lines of communication remain open.

The primary challenge at MEDVAMC has been, and will continue to be, the retention of physicians and surgeons. MEDVAMC has excellent leadership and a collegial working environment, but better access to operating rooms for elective and time-sensitive operations, additional clinical staff support, and higher salary at non-VA positions have been the basis for many of physicians— especially surgeons—leaving MEDVAMC. Despite high staff turnover and a constant flow of resident and fellow trainees, MEDVAMC has been able to keep the clinical approach relatively consistent due to the use of written protocols and continuity of care as ≥ 1 physician or surgeon from each of the 4 main teams remained engaged with limb salvage throughout the entire period.
Going forward, we will work to ensure that all requirements of the 2022 Prevention of Amputation in Veterans Everywhere directive are incorporated into care.8 We plan to standardize MEDVAMC management algorithms further, both to streamline care and reduce the opportunity for disparities in treatment. More prophylactic podiatric procedures, surgical forms of offloading, and a shared multidisciplinary clinic space may also further help patients.
Conclusions
The introduction of multidisciplinary limb salvage at MEDVAMC has led to significant and sustained reductions in leg amputation incidence. These reductions do not seem dependent upon a specific team structure for inpatient care. To improve patient outcomes, efforts should focus on making improvements across the entire disease spectrum. For limb salvage, this includes primary prevention of foot ulcers, the treatment of foot infections, identification and management of PAD, surgical reconstruction/optimal wound healing, and care for patients who undergo leg amputation.
- Sanders LJ, Robbins JM, Edmonds ME. History of the team approach to amputation prevention: pioneers and milestones. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(5):317- 334. doi:10.7547/1000317
- Sumpio BE, Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Andros G. The role of interdisciplinary team approach in the management of the diabetic foot: a joint statement from the society for vascular surgery and the American podiatric medical association. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(4):309-311. doi:10.7547/1000309
- About learning health systems. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Published March 2019. Updated May 2019. Accessed October 9, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/learning-health-systems/about.html
- Barshes NR, Minc SD. Healthcare disparities in vascular surgery: a critical review. J Vasc Surg. 2021;74(2S):6S-14S.
- Barshes NR, Mindru C, Ashong C, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Trautner BW. Treatment failure and leg amputation among patients with foot osteomyelitis. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2016;15(4):303-312. doi:10.1177/1534734616661058
- Barshes NR, Flores E, Belkin M, Kougias P, Armstrong DG, Mills JL Sr. The accuracy and cost-effectiveness of strategies used to identify peripheral artery disease among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(6):1682-1690.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.056 e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2021.03.055
- Choi JC, Miranda J, Greenleaf E, et al. Lower-extremity pressure, staging, and grading thresholds to identify chronic limb-threatening ischemia. Vasc Med. 2023;28(1):45-53. doi:10.1177/1358863X221147945
- Barshes NR, Chambers JD, Cohen J, Belkin M; Model To Optimize Healthcare Value in Ischemic Extremities 1 (MOVIE) Study Collaborators. Cost-effectiveness in the contemporary management of critical limb ischemia with tissue loss. J Vasc Surg. 2012;56(4):1015-24.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.02.069
- Barshes NR, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Preliminary experiences with early primary closure of foot wounds after lower extremity revascularization. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28(1):48-52. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2013.06.012
- Barshes NR, Gold B, Garcia A, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Minor amputation and palliative wound care as a strategy to avoid major amputation in patients with foot infections and severe peripheral arterial disease. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2014;13(3):211-219. doi:10.1177/1534734614543663
- Garcia M, Hernandez B, Ellington TG, et al. A lack of decline in major nontraumatic amputations in Texas: contemporary trends, risk factor associations, and impact of revascularization. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(6):1061-1066. doi:10.2337/dc19-0078
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Vo E, Awad SS, Kougias P, Barshes NR. A multi-component strategy to decrease wound complications after open infra-inguinal re-vascularization. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2018;19(1):87-94. doi:10.1089/sur.2017.193
- Barshes NR, Ozaki CK, Kougias P, Belkin M. A costeffectiveness analysis of infrainguinal bypass in the absence of great saphenous vein conduit. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57(6):1466-1470. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.11.115
- Zamani N, Sharath S, Browder R, et al. PC158 longterm outcomes after endovascular stent placement for symptomatic, long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(6):182S-183S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.03.344
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Browder RC, et al. Outcomes after endovascular stent placement for long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021;71:298-307. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2020.08.124
- Sanders LJ, Robbins JM, Edmonds ME. History of the team approach to amputation prevention: pioneers and milestones. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(5):317- 334. doi:10.7547/1000317
- Sumpio BE, Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Andros G. The role of interdisciplinary team approach in the management of the diabetic foot: a joint statement from the society for vascular surgery and the American podiatric medical association. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2010;100(4):309-311. doi:10.7547/1000309
- About learning health systems. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Published March 2019. Updated May 2019. Accessed October 9, 2024. https://www.ahrq.gov/learning-health-systems/about.html
- Barshes NR, Minc SD. Healthcare disparities in vascular surgery: a critical review. J Vasc Surg. 2021;74(2S):6S-14S.
- Barshes NR, Mindru C, Ashong C, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Trautner BW. Treatment failure and leg amputation among patients with foot osteomyelitis. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2016;15(4):303-312. doi:10.1177/1534734616661058
- Barshes NR, Flores E, Belkin M, Kougias P, Armstrong DG, Mills JL Sr. The accuracy and cost-effectiveness of strategies used to identify peripheral artery disease among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64(6):1682-1690.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.056 e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2021.03.055
- Choi JC, Miranda J, Greenleaf E, et al. Lower-extremity pressure, staging, and grading thresholds to identify chronic limb-threatening ischemia. Vasc Med. 2023;28(1):45-53. doi:10.1177/1358863X221147945
- Barshes NR, Chambers JD, Cohen J, Belkin M; Model To Optimize Healthcare Value in Ischemic Extremities 1 (MOVIE) Study Collaborators. Cost-effectiveness in the contemporary management of critical limb ischemia with tissue loss. J Vasc Surg. 2012;56(4):1015-24.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.02.069
- Barshes NR, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Preliminary experiences with early primary closure of foot wounds after lower extremity revascularization. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28(1):48-52. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2013.06.012
- Barshes NR, Gold B, Garcia A, Bechara CF, Pisimisis G, Kougias P. Minor amputation and palliative wound care as a strategy to avoid major amputation in patients with foot infections and severe peripheral arterial disease. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2014;13(3):211-219. doi:10.1177/1534734614543663
- Garcia M, Hernandez B, Ellington TG, et al. A lack of decline in major nontraumatic amputations in Texas: contemporary trends, risk factor associations, and impact of revascularization. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(6):1061-1066. doi:10.2337/dc19-0078
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Vo E, Awad SS, Kougias P, Barshes NR. A multi-component strategy to decrease wound complications after open infra-inguinal re-vascularization. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2018;19(1):87-94. doi:10.1089/sur.2017.193
- Barshes NR, Ozaki CK, Kougias P, Belkin M. A costeffectiveness analysis of infrainguinal bypass in the absence of great saphenous vein conduit. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57(6):1466-1470. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2012.11.115
- Zamani N, Sharath S, Browder R, et al. PC158 longterm outcomes after endovascular stent placement for symptomatic, long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(6):182S-183S. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.03.344
- Zamani N, Sharath SE, Browder RC, et al. Outcomes after endovascular stent placement for long-segment superficial femoral artery lesions. Ann Vasc Surg. 2021;71:298-307. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2020.08.124
Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis Presaged by Changes in Gut Microbiome
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Individuals at an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have a unique gut microbial composition, characterized by a notable increase in certain strains of Prevotella bacteria. These changes begin approximately 10 months prior to the onset of RA.
METHODOLOGY:
- In this cross-sectional and longitudinal observational study, researchers aimed to identify microbial associations in the early stages of RA, focusing specifically on Prevotellaceae strains.
- The cross-sectional analysis assessed the gut microbiome profiles of 124 individuals at risk of developing RA, 7 patients with newly diagnosed RA, and 22 healthy control individuals free of musculoskeletal symptoms at five different time points over a period of 15 months; 30 patients progressed to RA during the study period.
- The longitudinal analysis was performed in 19 individuals at risk of developing RA, of whom 5 progressed to the condition.
- The risk of developing RA was identified by the presence of anti–cyclic citrullinated protein (anti-CCP) antibodies and the onset of musculoskeletal pain in the preceding 3 months.
- Gut microbiome taxonomic alterations were investigated using 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing and confirmed with shotgun metagenomic DNA sequencing of 49 samples.
TAKEAWAY:
- Gut microbial diversity, particularly alpha diversity, was notably reduced in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA vs healthy control individuals (P = .012). Recognized risk factors for RA development such as the presence of rheumatoid factor antibodies and the human leukocyte antigen shared epitope, were significantly linked to diminished gut microbial diversity, in addition to steroid use.
- A specific Prevotellaceae strain (ASV2058) was found to be overabundant in CCP+ individuals at risk of developing RA and in those newly diagnosed with the condition but not in healthy control individuals. Further analysis showed that enrichment and depletion of three and five strains of Prevotellaceae, respectively, were associated with the progression to RA in CCP+ individuals.
- CCP+ individuals who progressed to RA were found to have substantial fluctuations in gut microbiome profiles around 10 months before clinical diagnosis; however, these profiles were relatively stable 10-15 months before the onset of RA, suggesting that changes in the microbiome occur at a later stage.
- Patients with new-onset RA were found to have distinct metabolic shifts, particularly in pathways related to amino acid and energy metabolism.
IN PRACTICE:
“Individuals at risk of RA harbor a distinctive gut microbial composition, including but not limited to an overabundance of Prevotellaceae species. This microbial signature is consistent and correlates with traditional RA risk factors,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Christopher M. Rooney, MD, PhD, University of Leeds in England. It was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small longitudinal sample size and lack of a 1:1 longitudinal comparison between CCP+ individuals at risk for RA and healthy control individuals were major limitations of this study. The new-onset RA cohort was heterogeneous, reflecting the practical constraints of recruitment from standard care clinics. Integrated transcriptomic or metabolomic data were unavailable, restricting interpretation to potential rather than confirmed metabolic activity.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by personal fellowships received by the lead author from Versus Arthritis, Leeds Cares, and a National Institute for Health Research Clinical Lectureship. Some authors disclosed receiving grants, funding, consulting fees, or honoraria from various pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Are GLP-1s the Newest Fertility Treatment?
First, there were “Ozempic babies.” Now, there is also Ozempic-before-baby.
Unplanned pregnancies are still regularly being reported among people using glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) drugs, and now fertility specialists are increasingly incorporating the medicines into preconception care plans.
The specialists say their colleagues in other areas of medicine may have an opportunity, too, to talk about weight loss using these new drugs in terms of reproductive health. Motivation and compliance can transform when the goal isn’t simply weight loss but having children.
“We have this really special moment to help patients be healthier, in order to be healthier for their kids,” said Christina Boots, MD, MSci, an associate professor of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. “And I think that’s also a very motivating moment. It may be hard to get up and go for a run to make my jeans fit better, but when I think about it in terms of, ‘this might someday help my future daughter,’ that is a whole different level of motivation.”
Here’s why, what to know about the current lengthy list of unknowns and risks, and some options for approaching the topic with patients.
What Fertility Docs Are Doing
While overweight and obesity are consistently linked to fertility and pregnancy outcomes, Boots predicts the biggest impact of GLP-1 weight loss for fertility among women will be a specific subset: Those who are not cycling regularly, such as those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
“The women who are cycling regularly who have very unexplained infertility and no other comorbidities like high blood pressure or something else going on, I don’t think it’s going to help their fertility very much at all,” she said “It might, but I think there’s probably something else going on in her tubes or with her eggs or his sperm, but it has nothing to do with her metabolic health.
Women who aren’t cycling regularly will benefit, but those with truly unexplained fertility probably won’t, she said.
In their recent narrative review on treating obesity and fertility with GLP-1 RAs that appeared in Fertility and Sterility, Boots and co-author Alyse S. Goldberg, MD, an endocrinologist with the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, advocate for the use of GLP-1s as a go-to treatment for obesity as part of preconception care by reproductive endocrinologists, calling the drugs “the most effective, least invasive means of weight loss.”
The paper is timely and necessary because use of GLP-1s is only going to increase, Patricia Jimenez, MD, an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, said in an email to this news organization.
“GLP-1 RAs are becoming a larger part of my practice. More patients are either using them already or interested in using them,” said Jimenez, who is board certified in reproductive endocrinology, obstetrics and gynecology, and obesity medicine. “I specifically see patients to discuss this and do prescribe antiobesity medications, not only GLP-1 RAs. Often this is with people with PCOS who are not planning to conceive soon or patients willing to delay fertility treatment [by] 3-6 months.”
Treating obesity is also important for women who are seeking in vitro fertilization, Boots said, because many IVF clinics have a body mass index cutoff of 40 kg/m2.
Like Jimenez’s approach, Boots and Goldberg call for comprehensive obesity care beyond the use of medication, including nutritional counseling and mental health support. Those supports are important during the transition off of GLP-1 medications, which poses a risk for rapid weight regain. That’s even with the potential support of taking metformin, which Boots often prescribes as a bridge.
Semaglutide should be stopped at least 2 months prior to conception, and tirzepatide should be stopped 1 month prior to conception, according to the manufacturers. (Boots and Goldberg listed the Canadian label recommendation for stopping tirzepatide, noting there is no suggested timeline for stopping prior to conception on the US label.)
Numerous studies have shown rapid weight regain is common when stopping GLP-1s, which presents a unique set of risks for pregnant women including early pregnancy loss, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and nonelective cesarean delivery.
Weighing Risks, Benefits, and Unknowns
Early looks at small human data sets, mostly involving semaglutide and earlier short-acting GLP-1s, and their impact on the risk for birth defects are “reassuring,” Boots said.
“But birth defects are just one small aspect. There’s also metabolic health and things like that long-term. Understanding what it does to the growing baby and the proximity of that medication to that growing baby is really important to see, and can’t be answered with animal studies, not perfectly anyway,” Boots said.
There are no published reports, from clinical trials nor case collections, examining the use of tirzepatide among pregnant people.
“One of the most important questions we need to answer is the preconception safety of these medications, and that includes safety for men,” Joshua Halpern, MD, MS, an adjunct assistant professor of urology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, and chief scientific officer for Posterity Health, said in an email to this news organization.
“For example, a recent study found that men who were taking metformin, another popular medication for diabetes, were more likely to have children with birth defects, compared with those who were not taking the medication,” Halpern said. “Further studies are needed to determine whether a similar effect might hold true for the GLP-1 agonists.”
Small early studies on sperm are encouraging, Halpern said, suggesting that GLP-1 use may be beneficial, but a better understanding of direct effects is needed.
Among women, there may be cases where continuing use of a GLP-1 during pregnancy may offer benefits that outweigh risks, Boots suggested. Manufacturers have also created pregnancy exposure registries to measure the safety of their therapies during pregnancy.
“I have a group of patients whose sugars are so well controlled on these medications, but as soon as they come off, they get weight regain and their glucose is just so poorly controlled,” she said. “There may be a group of women where the benefits of glucose control outweigh the risks of being on the medication the whole pregnancy.”
The list of important unknowns also includes a need to examine how rapid weight loss may impact ovulation rates and spontaneous conception, as well as miscarriage rates, birth weight, and metabolic health of the child.
More detailed rebound weight gain data is coming next year, with additional analysis expected as well on birth weight and pregnancy outcomes, said Jacqueline Maya, MD, first author of the research abstract presented at this year’s American Diabetes Association conference that examined gestational weight gain among people with preexisting type 2 diabetes who were exposed to GLP-1s during pregnancy. The study included 47 exposed pregnancies (based on prescription records and electronic chart information) and compared gestational weight gain to 141 unexposed matched pregnancies. Among the exposed group, 62% exceeded recommended weight gain, compared with 41% in the unexposed group. On average, gestational weight gain in exposed pregnancies exceeded that among matched unexposed pregnancies by about 6 pounds.
The team is now working with an additional data set to examine exposed pregnancies among people with obesity, said Maya, an instructor of pediatrics at Mass General Hospital and Harvard School of Medicine. She is particularly interested in examining weight trajectories during pregnancy to see how they may affect fetal outcomes. Her team’s current project also will likely include analysis to examine other variables like postpartum weight gain and adiposity characteristics of the baby.
Maya said the team hopes to have more to report at the American Diabetes Association conference in June next year.
Offer the Conversation
Using a GLP-1 for weight loss takes time, usually around 1 year to reach a plateau. Boots encouraged nonfertility providers to ask patients of reproductive age about their family plans as an opening.
“I hope for all primary care doctors and gynecologists, that with any patient of reproductive age, you should be bringing this up, asking, ‘Have you thought about having kids? Are you thinking about it soon?’ And if they say they are sometime in the near future, then you can say, ‘Is it OK if I bring up your weight?’ And you should ask permission.”
If the patient declines, it’s OK to bring it up again at a future visit.
“People with obesity have often experienced negative weight bias that impacts their care,” Jimenez said. “Treat obesity as a disease, not a personal failing. Ask permission to discuss weight with the patient beforehand. If they say no, respect that answer. This goes a long way in developing a positive relationship, so they return for care and may be willing to discuss later.”
When patients are open to the conversation, Boots suggests not focusing on the potential for poor outcomes, and instead perhaps saying, “If you’re thinking about having a baby in 5 years, optimizing your health now will not only make your pregnancy healthier, but your child healthier long-term.”
Discussing contraception plans remains important. People starting semaglutide or tirzepatide should use contraception other than oral birth control for 4 weeks while starting the medicine and for 4 weeks after each dose increase.
Boots said that the contraception conversation is particularly important because many people have come to deeply believe that they are infertile and, thus, may perhaps think contraception advice doesn’t apply to them. Maya hypothesized that behavioral changes following weight loss may also be a pathway toward pregnancy.
“Pregnancy while on GLP-1 RAs does happen. I always have a discussion about this possibility and contraception. This can sometimes be challenging for people with infertility to consider,” Jimenez said. “Explaining the risks, benefits, and unknowns can help. As the [Fertility and Sterility] paper describes, the limited data available has not shown increased fetal or maternal complications. We need more high quality data to better understand the impact of exposure or use around the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
It’s also important to introduce the idea to patients that they may someday need to come off the medications, such as when they are ready to have children, and how important lifestyle and behavioral changes will be at that time, Maya said.
“We do know what the alternative is, and we do know what the risks of obesity are,” she said. “So, it’s a tug and pull. We’re not starting off with healthy. We’re starting off with a disease that is physically and emotionally very difficult for the patient, especially when it starts in childhood.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
First, there were “Ozempic babies.” Now, there is also Ozempic-before-baby.
Unplanned pregnancies are still regularly being reported among people using glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) drugs, and now fertility specialists are increasingly incorporating the medicines into preconception care plans.
The specialists say their colleagues in other areas of medicine may have an opportunity, too, to talk about weight loss using these new drugs in terms of reproductive health. Motivation and compliance can transform when the goal isn’t simply weight loss but having children.
“We have this really special moment to help patients be healthier, in order to be healthier for their kids,” said Christina Boots, MD, MSci, an associate professor of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. “And I think that’s also a very motivating moment. It may be hard to get up and go for a run to make my jeans fit better, but when I think about it in terms of, ‘this might someday help my future daughter,’ that is a whole different level of motivation.”
Here’s why, what to know about the current lengthy list of unknowns and risks, and some options for approaching the topic with patients.
What Fertility Docs Are Doing
While overweight and obesity are consistently linked to fertility and pregnancy outcomes, Boots predicts the biggest impact of GLP-1 weight loss for fertility among women will be a specific subset: Those who are not cycling regularly, such as those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
“The women who are cycling regularly who have very unexplained infertility and no other comorbidities like high blood pressure or something else going on, I don’t think it’s going to help their fertility very much at all,” she said “It might, but I think there’s probably something else going on in her tubes or with her eggs or his sperm, but it has nothing to do with her metabolic health.
Women who aren’t cycling regularly will benefit, but those with truly unexplained fertility probably won’t, she said.
In their recent narrative review on treating obesity and fertility with GLP-1 RAs that appeared in Fertility and Sterility, Boots and co-author Alyse S. Goldberg, MD, an endocrinologist with the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, advocate for the use of GLP-1s as a go-to treatment for obesity as part of preconception care by reproductive endocrinologists, calling the drugs “the most effective, least invasive means of weight loss.”
The paper is timely and necessary because use of GLP-1s is only going to increase, Patricia Jimenez, MD, an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, said in an email to this news organization.
“GLP-1 RAs are becoming a larger part of my practice. More patients are either using them already or interested in using them,” said Jimenez, who is board certified in reproductive endocrinology, obstetrics and gynecology, and obesity medicine. “I specifically see patients to discuss this and do prescribe antiobesity medications, not only GLP-1 RAs. Often this is with people with PCOS who are not planning to conceive soon or patients willing to delay fertility treatment [by] 3-6 months.”
Treating obesity is also important for women who are seeking in vitro fertilization, Boots said, because many IVF clinics have a body mass index cutoff of 40 kg/m2.
Like Jimenez’s approach, Boots and Goldberg call for comprehensive obesity care beyond the use of medication, including nutritional counseling and mental health support. Those supports are important during the transition off of GLP-1 medications, which poses a risk for rapid weight regain. That’s even with the potential support of taking metformin, which Boots often prescribes as a bridge.
Semaglutide should be stopped at least 2 months prior to conception, and tirzepatide should be stopped 1 month prior to conception, according to the manufacturers. (Boots and Goldberg listed the Canadian label recommendation for stopping tirzepatide, noting there is no suggested timeline for stopping prior to conception on the US label.)
Numerous studies have shown rapid weight regain is common when stopping GLP-1s, which presents a unique set of risks for pregnant women including early pregnancy loss, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and nonelective cesarean delivery.
Weighing Risks, Benefits, and Unknowns
Early looks at small human data sets, mostly involving semaglutide and earlier short-acting GLP-1s, and their impact on the risk for birth defects are “reassuring,” Boots said.
“But birth defects are just one small aspect. There’s also metabolic health and things like that long-term. Understanding what it does to the growing baby and the proximity of that medication to that growing baby is really important to see, and can’t be answered with animal studies, not perfectly anyway,” Boots said.
There are no published reports, from clinical trials nor case collections, examining the use of tirzepatide among pregnant people.
“One of the most important questions we need to answer is the preconception safety of these medications, and that includes safety for men,” Joshua Halpern, MD, MS, an adjunct assistant professor of urology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, and chief scientific officer for Posterity Health, said in an email to this news organization.
“For example, a recent study found that men who were taking metformin, another popular medication for diabetes, were more likely to have children with birth defects, compared with those who were not taking the medication,” Halpern said. “Further studies are needed to determine whether a similar effect might hold true for the GLP-1 agonists.”
Small early studies on sperm are encouraging, Halpern said, suggesting that GLP-1 use may be beneficial, but a better understanding of direct effects is needed.
Among women, there may be cases where continuing use of a GLP-1 during pregnancy may offer benefits that outweigh risks, Boots suggested. Manufacturers have also created pregnancy exposure registries to measure the safety of their therapies during pregnancy.
“I have a group of patients whose sugars are so well controlled on these medications, but as soon as they come off, they get weight regain and their glucose is just so poorly controlled,” she said. “There may be a group of women where the benefits of glucose control outweigh the risks of being on the medication the whole pregnancy.”
The list of important unknowns also includes a need to examine how rapid weight loss may impact ovulation rates and spontaneous conception, as well as miscarriage rates, birth weight, and metabolic health of the child.
More detailed rebound weight gain data is coming next year, with additional analysis expected as well on birth weight and pregnancy outcomes, said Jacqueline Maya, MD, first author of the research abstract presented at this year’s American Diabetes Association conference that examined gestational weight gain among people with preexisting type 2 diabetes who were exposed to GLP-1s during pregnancy. The study included 47 exposed pregnancies (based on prescription records and electronic chart information) and compared gestational weight gain to 141 unexposed matched pregnancies. Among the exposed group, 62% exceeded recommended weight gain, compared with 41% in the unexposed group. On average, gestational weight gain in exposed pregnancies exceeded that among matched unexposed pregnancies by about 6 pounds.
The team is now working with an additional data set to examine exposed pregnancies among people with obesity, said Maya, an instructor of pediatrics at Mass General Hospital and Harvard School of Medicine. She is particularly interested in examining weight trajectories during pregnancy to see how they may affect fetal outcomes. Her team’s current project also will likely include analysis to examine other variables like postpartum weight gain and adiposity characteristics of the baby.
Maya said the team hopes to have more to report at the American Diabetes Association conference in June next year.
Offer the Conversation
Using a GLP-1 for weight loss takes time, usually around 1 year to reach a plateau. Boots encouraged nonfertility providers to ask patients of reproductive age about their family plans as an opening.
“I hope for all primary care doctors and gynecologists, that with any patient of reproductive age, you should be bringing this up, asking, ‘Have you thought about having kids? Are you thinking about it soon?’ And if they say they are sometime in the near future, then you can say, ‘Is it OK if I bring up your weight?’ And you should ask permission.”
If the patient declines, it’s OK to bring it up again at a future visit.
“People with obesity have often experienced negative weight bias that impacts their care,” Jimenez said. “Treat obesity as a disease, not a personal failing. Ask permission to discuss weight with the patient beforehand. If they say no, respect that answer. This goes a long way in developing a positive relationship, so they return for care and may be willing to discuss later.”
When patients are open to the conversation, Boots suggests not focusing on the potential for poor outcomes, and instead perhaps saying, “If you’re thinking about having a baby in 5 years, optimizing your health now will not only make your pregnancy healthier, but your child healthier long-term.”
Discussing contraception plans remains important. People starting semaglutide or tirzepatide should use contraception other than oral birth control for 4 weeks while starting the medicine and for 4 weeks after each dose increase.
Boots said that the contraception conversation is particularly important because many people have come to deeply believe that they are infertile and, thus, may perhaps think contraception advice doesn’t apply to them. Maya hypothesized that behavioral changes following weight loss may also be a pathway toward pregnancy.
“Pregnancy while on GLP-1 RAs does happen. I always have a discussion about this possibility and contraception. This can sometimes be challenging for people with infertility to consider,” Jimenez said. “Explaining the risks, benefits, and unknowns can help. As the [Fertility and Sterility] paper describes, the limited data available has not shown increased fetal or maternal complications. We need more high quality data to better understand the impact of exposure or use around the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
It’s also important to introduce the idea to patients that they may someday need to come off the medications, such as when they are ready to have children, and how important lifestyle and behavioral changes will be at that time, Maya said.
“We do know what the alternative is, and we do know what the risks of obesity are,” she said. “So, it’s a tug and pull. We’re not starting off with healthy. We’re starting off with a disease that is physically and emotionally very difficult for the patient, especially when it starts in childhood.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
First, there were “Ozempic babies.” Now, there is also Ozempic-before-baby.
Unplanned pregnancies are still regularly being reported among people using glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) drugs, and now fertility specialists are increasingly incorporating the medicines into preconception care plans.
The specialists say their colleagues in other areas of medicine may have an opportunity, too, to talk about weight loss using these new drugs in terms of reproductive health. Motivation and compliance can transform when the goal isn’t simply weight loss but having children.
“We have this really special moment to help patients be healthier, in order to be healthier for their kids,” said Christina Boots, MD, MSci, an associate professor of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago. “And I think that’s also a very motivating moment. It may be hard to get up and go for a run to make my jeans fit better, but when I think about it in terms of, ‘this might someday help my future daughter,’ that is a whole different level of motivation.”
Here’s why, what to know about the current lengthy list of unknowns and risks, and some options for approaching the topic with patients.
What Fertility Docs Are Doing
While overweight and obesity are consistently linked to fertility and pregnancy outcomes, Boots predicts the biggest impact of GLP-1 weight loss for fertility among women will be a specific subset: Those who are not cycling regularly, such as those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
“The women who are cycling regularly who have very unexplained infertility and no other comorbidities like high blood pressure or something else going on, I don’t think it’s going to help their fertility very much at all,” she said “It might, but I think there’s probably something else going on in her tubes or with her eggs or his sperm, but it has nothing to do with her metabolic health.
Women who aren’t cycling regularly will benefit, but those with truly unexplained fertility probably won’t, she said.
In their recent narrative review on treating obesity and fertility with GLP-1 RAs that appeared in Fertility and Sterility, Boots and co-author Alyse S. Goldberg, MD, an endocrinologist with the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, advocate for the use of GLP-1s as a go-to treatment for obesity as part of preconception care by reproductive endocrinologists, calling the drugs “the most effective, least invasive means of weight loss.”
The paper is timely and necessary because use of GLP-1s is only going to increase, Patricia Jimenez, MD, an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, said in an email to this news organization.
“GLP-1 RAs are becoming a larger part of my practice. More patients are either using them already or interested in using them,” said Jimenez, who is board certified in reproductive endocrinology, obstetrics and gynecology, and obesity medicine. “I specifically see patients to discuss this and do prescribe antiobesity medications, not only GLP-1 RAs. Often this is with people with PCOS who are not planning to conceive soon or patients willing to delay fertility treatment [by] 3-6 months.”
Treating obesity is also important for women who are seeking in vitro fertilization, Boots said, because many IVF clinics have a body mass index cutoff of 40 kg/m2.
Like Jimenez’s approach, Boots and Goldberg call for comprehensive obesity care beyond the use of medication, including nutritional counseling and mental health support. Those supports are important during the transition off of GLP-1 medications, which poses a risk for rapid weight regain. That’s even with the potential support of taking metformin, which Boots often prescribes as a bridge.
Semaglutide should be stopped at least 2 months prior to conception, and tirzepatide should be stopped 1 month prior to conception, according to the manufacturers. (Boots and Goldberg listed the Canadian label recommendation for stopping tirzepatide, noting there is no suggested timeline for stopping prior to conception on the US label.)
Numerous studies have shown rapid weight regain is common when stopping GLP-1s, which presents a unique set of risks for pregnant women including early pregnancy loss, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and nonelective cesarean delivery.
Weighing Risks, Benefits, and Unknowns
Early looks at small human data sets, mostly involving semaglutide and earlier short-acting GLP-1s, and their impact on the risk for birth defects are “reassuring,” Boots said.
“But birth defects are just one small aspect. There’s also metabolic health and things like that long-term. Understanding what it does to the growing baby and the proximity of that medication to that growing baby is really important to see, and can’t be answered with animal studies, not perfectly anyway,” Boots said.
There are no published reports, from clinical trials nor case collections, examining the use of tirzepatide among pregnant people.
“One of the most important questions we need to answer is the preconception safety of these medications, and that includes safety for men,” Joshua Halpern, MD, MS, an adjunct assistant professor of urology at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine, and chief scientific officer for Posterity Health, said in an email to this news organization.
“For example, a recent study found that men who were taking metformin, another popular medication for diabetes, were more likely to have children with birth defects, compared with those who were not taking the medication,” Halpern said. “Further studies are needed to determine whether a similar effect might hold true for the GLP-1 agonists.”
Small early studies on sperm are encouraging, Halpern said, suggesting that GLP-1 use may be beneficial, but a better understanding of direct effects is needed.
Among women, there may be cases where continuing use of a GLP-1 during pregnancy may offer benefits that outweigh risks, Boots suggested. Manufacturers have also created pregnancy exposure registries to measure the safety of their therapies during pregnancy.
“I have a group of patients whose sugars are so well controlled on these medications, but as soon as they come off, they get weight regain and their glucose is just so poorly controlled,” she said. “There may be a group of women where the benefits of glucose control outweigh the risks of being on the medication the whole pregnancy.”
The list of important unknowns also includes a need to examine how rapid weight loss may impact ovulation rates and spontaneous conception, as well as miscarriage rates, birth weight, and metabolic health of the child.
More detailed rebound weight gain data is coming next year, with additional analysis expected as well on birth weight and pregnancy outcomes, said Jacqueline Maya, MD, first author of the research abstract presented at this year’s American Diabetes Association conference that examined gestational weight gain among people with preexisting type 2 diabetes who were exposed to GLP-1s during pregnancy. The study included 47 exposed pregnancies (based on prescription records and electronic chart information) and compared gestational weight gain to 141 unexposed matched pregnancies. Among the exposed group, 62% exceeded recommended weight gain, compared with 41% in the unexposed group. On average, gestational weight gain in exposed pregnancies exceeded that among matched unexposed pregnancies by about 6 pounds.
The team is now working with an additional data set to examine exposed pregnancies among people with obesity, said Maya, an instructor of pediatrics at Mass General Hospital and Harvard School of Medicine. She is particularly interested in examining weight trajectories during pregnancy to see how they may affect fetal outcomes. Her team’s current project also will likely include analysis to examine other variables like postpartum weight gain and adiposity characteristics of the baby.
Maya said the team hopes to have more to report at the American Diabetes Association conference in June next year.
Offer the Conversation
Using a GLP-1 for weight loss takes time, usually around 1 year to reach a plateau. Boots encouraged nonfertility providers to ask patients of reproductive age about their family plans as an opening.
“I hope for all primary care doctors and gynecologists, that with any patient of reproductive age, you should be bringing this up, asking, ‘Have you thought about having kids? Are you thinking about it soon?’ And if they say they are sometime in the near future, then you can say, ‘Is it OK if I bring up your weight?’ And you should ask permission.”
If the patient declines, it’s OK to bring it up again at a future visit.
“People with obesity have often experienced negative weight bias that impacts their care,” Jimenez said. “Treat obesity as a disease, not a personal failing. Ask permission to discuss weight with the patient beforehand. If they say no, respect that answer. This goes a long way in developing a positive relationship, so they return for care and may be willing to discuss later.”
When patients are open to the conversation, Boots suggests not focusing on the potential for poor outcomes, and instead perhaps saying, “If you’re thinking about having a baby in 5 years, optimizing your health now will not only make your pregnancy healthier, but your child healthier long-term.”
Discussing contraception plans remains important. People starting semaglutide or tirzepatide should use contraception other than oral birth control for 4 weeks while starting the medicine and for 4 weeks after each dose increase.
Boots said that the contraception conversation is particularly important because many people have come to deeply believe that they are infertile and, thus, may perhaps think contraception advice doesn’t apply to them. Maya hypothesized that behavioral changes following weight loss may also be a pathway toward pregnancy.
“Pregnancy while on GLP-1 RAs does happen. I always have a discussion about this possibility and contraception. This can sometimes be challenging for people with infertility to consider,” Jimenez said. “Explaining the risks, benefits, and unknowns can help. As the [Fertility and Sterility] paper describes, the limited data available has not shown increased fetal or maternal complications. We need more high quality data to better understand the impact of exposure or use around the time of conception and during pregnancy.”
It’s also important to introduce the idea to patients that they may someday need to come off the medications, such as when they are ready to have children, and how important lifestyle and behavioral changes will be at that time, Maya said.
“We do know what the alternative is, and we do know what the risks of obesity are,” she said. “So, it’s a tug and pull. We’re not starting off with healthy. We’re starting off with a disease that is physically and emotionally very difficult for the patient, especially when it starts in childhood.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Patients on Anti-Obesity Drugs Decrease Alcohol Use?
SAN ANTONIO —
The findings, from surveys of more than 14,000 participants in WeightWatchers’ telehealth weight management program, were presented on November 6 at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2024 meeting by the company’s Chief Nutrition Officer, Michelle I. Cardel, PhD, RD, based in Gainesville, Florida.
Similar reductions in alcohol consumption were seen in people taking different classes of AOMs, suggesting “an additional mechanism by which AOMs reduce energy intake, and also signal a potential role for these medications to reduce alcohol use,” Cardel said, adding “Clinicians treating individuals for obesity may consider anti-obesity medications particularly among those who report higher alcohol intake.”
Asked to comment, session moderator and obesity researcher Joseph A. Skelton, MD, professor of pediatrics at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said, “I think there are some overlapping pathways there, possibly a reward system or something like that in the brain. I don’t think we know exactly what the end result will be as a potential use of the medications. But there’s a signal that needs to be investigated more.”
Cardel noted that there was one previous large cohort study finding that semaglutide was associated with a lower risk for alcohol use disorder, and another study that analyzed social media threads of people saying they’d quit drinking after starting a GLP-1 drug. But this new study is the first to examine the relationship with different classes of AOMs and to quantify the amount of alcohol consumed.
About Half Reported Reduced Alcohol Consumption, Regardless the AOM Class
The study included 14,053 WeightWatchers’ telehealth program participants who initiated an AOM between January 2022 and August 2023 and refilled the same AOM between October and November 2023. Those who had previously used AOMs before coming to the program or who had undergone bariatric surgery were excluded.
Participants had a mean age of 43 years, were 86% women, were 60% White, and had a mean body mass index of 36. They were surveyed about their weekly alcohol use prior to AOM initiation and again at the time of AOM refill.
At baseline, they were divided into categories of 0 (no alcohol use; n = 6562), category 1 (one to three drinks for women and one to six for men; n = 5948), category 2 (4-6 for women and 7-14 for men; n = 1216), and category 3 (≥ 7 for women and ≥ 15 for men; n = 327).
At the second survey, 24% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 71% reported no change, and 4% reported increased drinking (P < .0001). But when just the 7491 individuals who reported any alcohol use at baseline were included, 45% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 52% reported no change, and only 2% reported increased drinking.
The decrease in drinking with AOM use rose with greater alcohol use at baseline, from 37% for category 1, 76% for category 2, and 91% for category 3. The proportions reporting increased drinking were just 3%, 1%, and 0%, respectively. The adjusted odds ratios (ORs) for decreasing drinking were 5.97 for category 2 (P < .0001) and 19.18 for category 3 (P < .0001) vs category 1.
The proportions reporting reduced drinking were similar across AOM classes: 51% for metformin, 46% for bupropion/naltrexone, 46% for first-generation GLP-1s (Saxenda, Trulicity, and Victoza), and 45% for the second-generation GLP-1 drugs (Mounjaro, Ozempic, Rybelsus, Wegovy, and Zepbound). All were statistically significant at P < .0001.
The highest proportion reporting increased drinking was 4% for bupropion/naltrexone. Compared with women, men were significantly more likely to report decreased drinking with AOM use (adjusted OR, 0.74; P < .001), but there were no differences by race/ethnicity or age.
Compared with those who had overweight, those in obesity classes I, II, and III were all more likely to decrease drinking with AOM use, with adjusted ORs of 1.26 (P = .0045), 1.49 (P < .001), and 1.63 (P < .001), respectively.
Mechanisms Appear Both Biological and Behavioral
During the discussion, Cardel said that qualitative assessments with participants suggest that there are at least two mechanisms behind this phenomenon: One biological and the other intentional.
“What we hear from them is twofold, one, particularly amongst those folks on GLP-1 medications, we’re hearing that physiologically, they feel different with the medications, that their cravings for alcohol are decreased, and that when they do choose to drink that there’s often a very much a negative reinforcement ... I’ve had a patient tell me, ‘I used to be able to have two or three margaritas, and maybe I didn’t feel like the best I’d ever felt in the morning, but I was okay. And now if I have two or three drinks, I will be throwing up for 5 hours, and it’s the worst hangover I’ve ever had in my life.’ And so it very much creates that negative reinforcement loop.”
But at the same time, “folks who are coming to us and seeking these medications are very much on a on a health-based journey. That’s what they tell us. The majority of our patients are there to improve their health. We rarely hear about the vanity or aesthetic part of it. So perhaps it’s that, in terms of trying to improve their health, they’re also trying to reduce their alcohol consumption, either just for their overall health or also as a means of trying to decrease their overall calorie consumption.”
In future research, Cardel said, “we want to examine whether the anti-obesity medications are more successful at reducing alcohol use compared to non-pharmacological weight management interventions, as we know that people often reduce their alcohol consumption on a weight management journey as a means of prioritizing their calories for food and decreasing the calories from alcohol.”
Cardel and all the study coauthors were employees and shareholders at WeightWatchers at the time the research was conducted. Skelton is editor in chief of the journal Childhood Obesity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO —
The findings, from surveys of more than 14,000 participants in WeightWatchers’ telehealth weight management program, were presented on November 6 at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2024 meeting by the company’s Chief Nutrition Officer, Michelle I. Cardel, PhD, RD, based in Gainesville, Florida.
Similar reductions in alcohol consumption were seen in people taking different classes of AOMs, suggesting “an additional mechanism by which AOMs reduce energy intake, and also signal a potential role for these medications to reduce alcohol use,” Cardel said, adding “Clinicians treating individuals for obesity may consider anti-obesity medications particularly among those who report higher alcohol intake.”
Asked to comment, session moderator and obesity researcher Joseph A. Skelton, MD, professor of pediatrics at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said, “I think there are some overlapping pathways there, possibly a reward system or something like that in the brain. I don’t think we know exactly what the end result will be as a potential use of the medications. But there’s a signal that needs to be investigated more.”
Cardel noted that there was one previous large cohort study finding that semaglutide was associated with a lower risk for alcohol use disorder, and another study that analyzed social media threads of people saying they’d quit drinking after starting a GLP-1 drug. But this new study is the first to examine the relationship with different classes of AOMs and to quantify the amount of alcohol consumed.
About Half Reported Reduced Alcohol Consumption, Regardless the AOM Class
The study included 14,053 WeightWatchers’ telehealth program participants who initiated an AOM between January 2022 and August 2023 and refilled the same AOM between October and November 2023. Those who had previously used AOMs before coming to the program or who had undergone bariatric surgery were excluded.
Participants had a mean age of 43 years, were 86% women, were 60% White, and had a mean body mass index of 36. They were surveyed about their weekly alcohol use prior to AOM initiation and again at the time of AOM refill.
At baseline, they were divided into categories of 0 (no alcohol use; n = 6562), category 1 (one to three drinks for women and one to six for men; n = 5948), category 2 (4-6 for women and 7-14 for men; n = 1216), and category 3 (≥ 7 for women and ≥ 15 for men; n = 327).
At the second survey, 24% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 71% reported no change, and 4% reported increased drinking (P < .0001). But when just the 7491 individuals who reported any alcohol use at baseline were included, 45% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 52% reported no change, and only 2% reported increased drinking.
The decrease in drinking with AOM use rose with greater alcohol use at baseline, from 37% for category 1, 76% for category 2, and 91% for category 3. The proportions reporting increased drinking were just 3%, 1%, and 0%, respectively. The adjusted odds ratios (ORs) for decreasing drinking were 5.97 for category 2 (P < .0001) and 19.18 for category 3 (P < .0001) vs category 1.
The proportions reporting reduced drinking were similar across AOM classes: 51% for metformin, 46% for bupropion/naltrexone, 46% for first-generation GLP-1s (Saxenda, Trulicity, and Victoza), and 45% for the second-generation GLP-1 drugs (Mounjaro, Ozempic, Rybelsus, Wegovy, and Zepbound). All were statistically significant at P < .0001.
The highest proportion reporting increased drinking was 4% for bupropion/naltrexone. Compared with women, men were significantly more likely to report decreased drinking with AOM use (adjusted OR, 0.74; P < .001), but there were no differences by race/ethnicity or age.
Compared with those who had overweight, those in obesity classes I, II, and III were all more likely to decrease drinking with AOM use, with adjusted ORs of 1.26 (P = .0045), 1.49 (P < .001), and 1.63 (P < .001), respectively.
Mechanisms Appear Both Biological and Behavioral
During the discussion, Cardel said that qualitative assessments with participants suggest that there are at least two mechanisms behind this phenomenon: One biological and the other intentional.
“What we hear from them is twofold, one, particularly amongst those folks on GLP-1 medications, we’re hearing that physiologically, they feel different with the medications, that their cravings for alcohol are decreased, and that when they do choose to drink that there’s often a very much a negative reinforcement ... I’ve had a patient tell me, ‘I used to be able to have two or three margaritas, and maybe I didn’t feel like the best I’d ever felt in the morning, but I was okay. And now if I have two or three drinks, I will be throwing up for 5 hours, and it’s the worst hangover I’ve ever had in my life.’ And so it very much creates that negative reinforcement loop.”
But at the same time, “folks who are coming to us and seeking these medications are very much on a on a health-based journey. That’s what they tell us. The majority of our patients are there to improve their health. We rarely hear about the vanity or aesthetic part of it. So perhaps it’s that, in terms of trying to improve their health, they’re also trying to reduce their alcohol consumption, either just for their overall health or also as a means of trying to decrease their overall calorie consumption.”
In future research, Cardel said, “we want to examine whether the anti-obesity medications are more successful at reducing alcohol use compared to non-pharmacological weight management interventions, as we know that people often reduce their alcohol consumption on a weight management journey as a means of prioritizing their calories for food and decreasing the calories from alcohol.”
Cardel and all the study coauthors were employees and shareholders at WeightWatchers at the time the research was conducted. Skelton is editor in chief of the journal Childhood Obesity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN ANTONIO —
The findings, from surveys of more than 14,000 participants in WeightWatchers’ telehealth weight management program, were presented on November 6 at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2024 meeting by the company’s Chief Nutrition Officer, Michelle I. Cardel, PhD, RD, based in Gainesville, Florida.
Similar reductions in alcohol consumption were seen in people taking different classes of AOMs, suggesting “an additional mechanism by which AOMs reduce energy intake, and also signal a potential role for these medications to reduce alcohol use,” Cardel said, adding “Clinicians treating individuals for obesity may consider anti-obesity medications particularly among those who report higher alcohol intake.”
Asked to comment, session moderator and obesity researcher Joseph A. Skelton, MD, professor of pediatrics at Wake Forest University School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina, said, “I think there are some overlapping pathways there, possibly a reward system or something like that in the brain. I don’t think we know exactly what the end result will be as a potential use of the medications. But there’s a signal that needs to be investigated more.”
Cardel noted that there was one previous large cohort study finding that semaglutide was associated with a lower risk for alcohol use disorder, and another study that analyzed social media threads of people saying they’d quit drinking after starting a GLP-1 drug. But this new study is the first to examine the relationship with different classes of AOMs and to quantify the amount of alcohol consumed.
About Half Reported Reduced Alcohol Consumption, Regardless the AOM Class
The study included 14,053 WeightWatchers’ telehealth program participants who initiated an AOM between January 2022 and August 2023 and refilled the same AOM between October and November 2023. Those who had previously used AOMs before coming to the program or who had undergone bariatric surgery were excluded.
Participants had a mean age of 43 years, were 86% women, were 60% White, and had a mean body mass index of 36. They were surveyed about their weekly alcohol use prior to AOM initiation and again at the time of AOM refill.
At baseline, they were divided into categories of 0 (no alcohol use; n = 6562), category 1 (one to three drinks for women and one to six for men; n = 5948), category 2 (4-6 for women and 7-14 for men; n = 1216), and category 3 (≥ 7 for women and ≥ 15 for men; n = 327).
At the second survey, 24% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 71% reported no change, and 4% reported increased drinking (P < .0001). But when just the 7491 individuals who reported any alcohol use at baseline were included, 45% reported decreased drinking after starting an AOM, 52% reported no change, and only 2% reported increased drinking.
The decrease in drinking with AOM use rose with greater alcohol use at baseline, from 37% for category 1, 76% for category 2, and 91% for category 3. The proportions reporting increased drinking were just 3%, 1%, and 0%, respectively. The adjusted odds ratios (ORs) for decreasing drinking were 5.97 for category 2 (P < .0001) and 19.18 for category 3 (P < .0001) vs category 1.
The proportions reporting reduced drinking were similar across AOM classes: 51% for metformin, 46% for bupropion/naltrexone, 46% for first-generation GLP-1s (Saxenda, Trulicity, and Victoza), and 45% for the second-generation GLP-1 drugs (Mounjaro, Ozempic, Rybelsus, Wegovy, and Zepbound). All were statistically significant at P < .0001.
The highest proportion reporting increased drinking was 4% for bupropion/naltrexone. Compared with women, men were significantly more likely to report decreased drinking with AOM use (adjusted OR, 0.74; P < .001), but there were no differences by race/ethnicity or age.
Compared with those who had overweight, those in obesity classes I, II, and III were all more likely to decrease drinking with AOM use, with adjusted ORs of 1.26 (P = .0045), 1.49 (P < .001), and 1.63 (P < .001), respectively.
Mechanisms Appear Both Biological and Behavioral
During the discussion, Cardel said that qualitative assessments with participants suggest that there are at least two mechanisms behind this phenomenon: One biological and the other intentional.
“What we hear from them is twofold, one, particularly amongst those folks on GLP-1 medications, we’re hearing that physiologically, they feel different with the medications, that their cravings for alcohol are decreased, and that when they do choose to drink that there’s often a very much a negative reinforcement ... I’ve had a patient tell me, ‘I used to be able to have two or three margaritas, and maybe I didn’t feel like the best I’d ever felt in the morning, but I was okay. And now if I have two or three drinks, I will be throwing up for 5 hours, and it’s the worst hangover I’ve ever had in my life.’ And so it very much creates that negative reinforcement loop.”
But at the same time, “folks who are coming to us and seeking these medications are very much on a on a health-based journey. That’s what they tell us. The majority of our patients are there to improve their health. We rarely hear about the vanity or aesthetic part of it. So perhaps it’s that, in terms of trying to improve their health, they’re also trying to reduce their alcohol consumption, either just for their overall health or also as a means of trying to decrease their overall calorie consumption.”
In future research, Cardel said, “we want to examine whether the anti-obesity medications are more successful at reducing alcohol use compared to non-pharmacological weight management interventions, as we know that people often reduce their alcohol consumption on a weight management journey as a means of prioritizing their calories for food and decreasing the calories from alcohol.”
Cardel and all the study coauthors were employees and shareholders at WeightWatchers at the time the research was conducted. Skelton is editor in chief of the journal Childhood Obesity.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM OBESITY WEEK 2024
Infliximab vs Adalimumab: Which Is Best for Behçet Syndrome?
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both infliximab and adalimumab are safe and effective in achieving remission in patients with severe mucocutaneous Behçet syndrome, with adalimumab demonstrating a quicker response time; both drugs also improve quality of life and disease activity scores.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a phase 3 prospective study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of the anti–tumor necrosis factor–alpha agents infliximab and adalimumab in patients with Behçet syndrome presenting with mucocutaneous manifestations and inadequate response to prior treatments who were recruited from four Italian tertiary referral centers specializing in Behçet syndrome.
- Patients were randomly assigned to receive either 5 mg/kg intravenous infliximab at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 6-8 weeks (n = 22; mean age, 46 years; 32% women) or 40 mg subcutaneous adalimumab every 2 weeks (n = 18; mean age, 48 years; 28% women) for 24 weeks.
- Patients were followed-up for an additional 12 weeks after the treatment period, with regular assessments of disease activity, safety, and adherence to treatment.
- The primary outcome was the time to response of mucocutaneous manifestations over 6 months; the secondary outcomes included relapse rates; quality of life, assessed using the Short-Form Health Survey 36; and disease activity, assessed using the Behçet Disease Current Activity Form.
- The safety and tolerability of the drugs were evaluated as the frequency of treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) and serious AEs, monitored every 2 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- The resolution of mucocutaneous manifestations was achieved significantly more quickly with adalimumab than with infliximab, with a median time to response of 42 vs 152 days (P = .001); the proportion of responders was also higher in the adalimumab group than in the infliximab group (94% vs 64%; P = .023).
- Patients in the infliximab group had a higher risk for nonresponse (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 3.33; P = .012) and relapse (adjusted HR, 7.57; P = .036) than those in the adalimumab group.
- Both infliximab and adalimumab significantly improved the quality of life in all dimensions (P < .05 for all) and disease activity scores (P < .001 for both) from baseline to the end of the study period, with no significant differences found between the groups.
- Two AEs were reported in the adalimumab group, one of which was serious (myocardial infarction); three nonserious AEs were reported in the infliximab group.
IN PRACTICE:
“ADA [adalimumab] and IFX [infliximab] were generally well tolerated and efficacious in patients with BS [Behçet syndrome] who showed an inadequate response to prior treatments with at least AZA [azathioprine] or CyA [cyclosporine],” the authors wrote. “Although a more detailed treat-to-target profile is yet to be better defined, [the study] results are also crucial in terms of prescriptiveness (currently off label), not only in Italy but also beyond national borders, as the evidence coming from real life still needs to be confirmed by growing data from clinical trials.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Rosaria Talarico, MD, PhD, University of Pisa in Italy, and was published online in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
The small sample size and the distinctive study design may have limited the generalizability of the findings.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded through a grant from the Italian Medicines Agency. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Asymptomatic Papules on the Neck
THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).
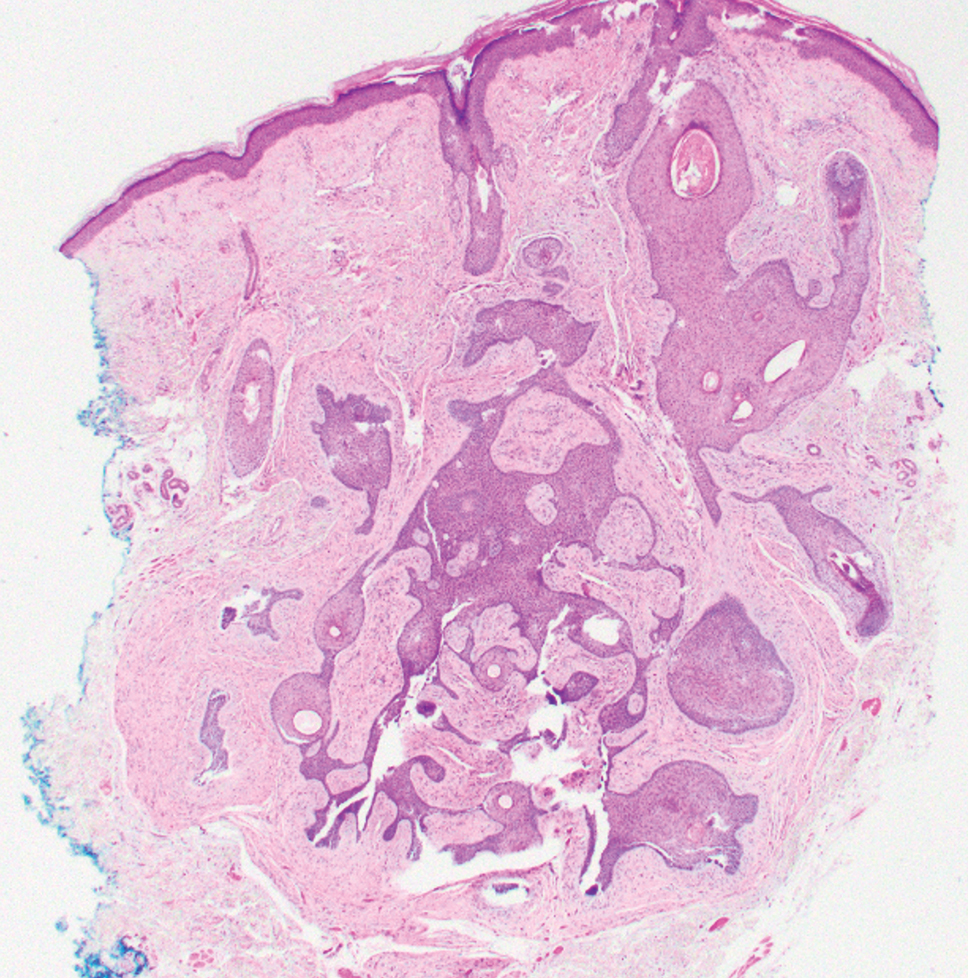
Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).
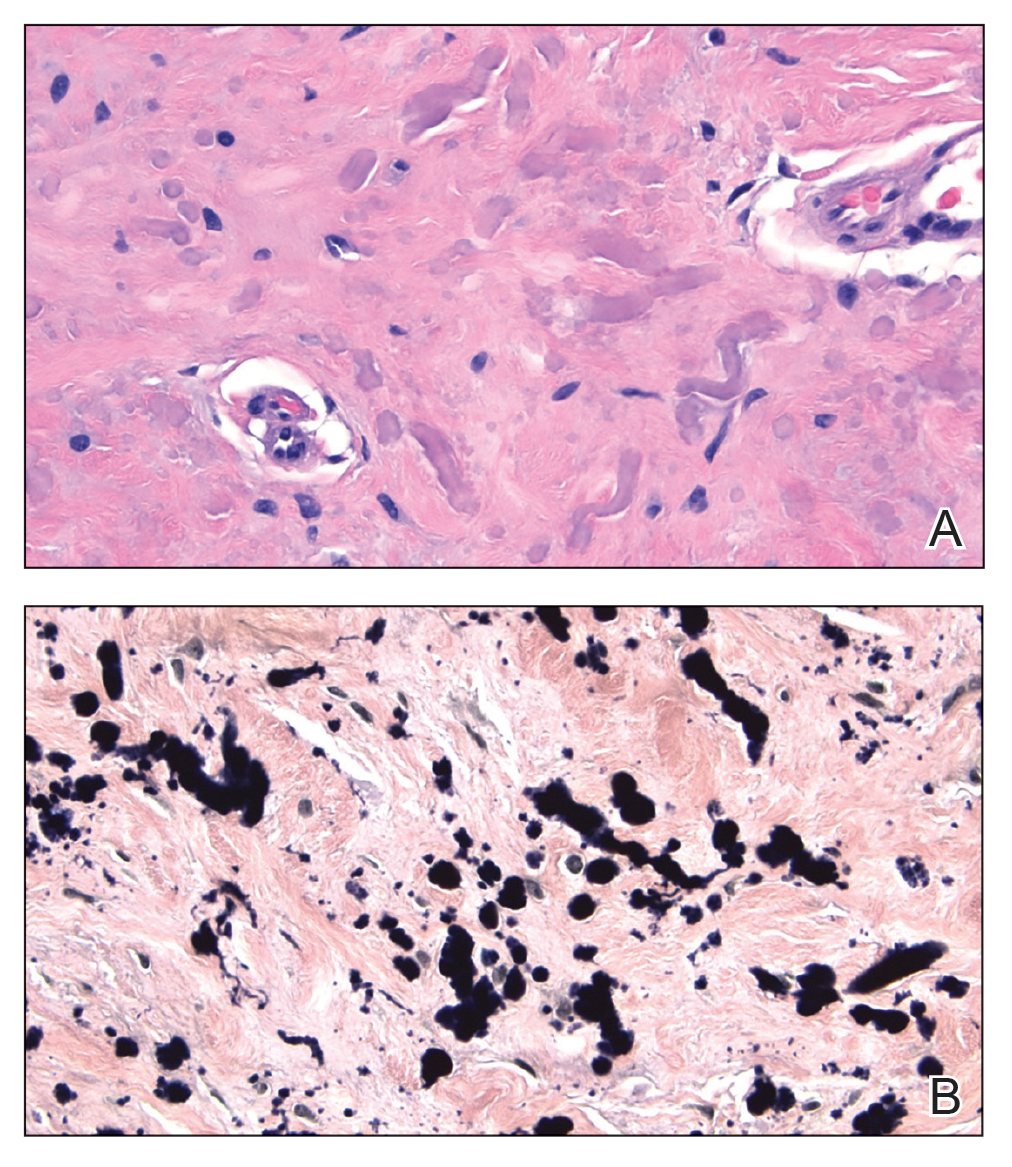
Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).
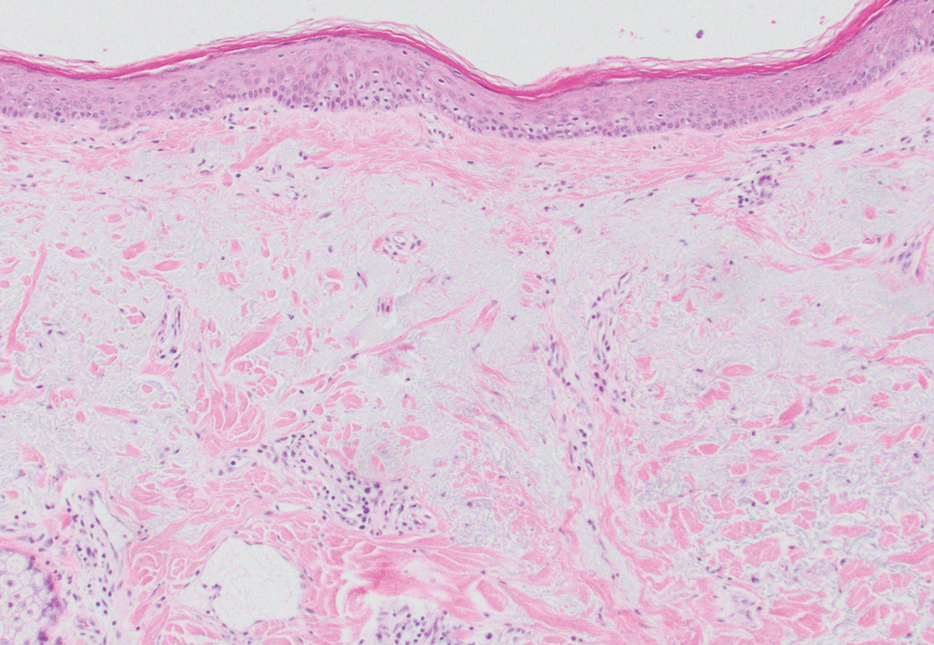
- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).

Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).

Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).

THE DIAGNOSIS: White Fibrous Papulosis
Given the histopathology findings, location on a sun-exposed site, lack of any additional systemic signs or symptoms, and no family history of similar lesions to suggest an underlying genetic condition, a diagnosis of white fibrous papulosis (WFP) was made. White fibrous papulosis is a relatively rare cutaneous disorder that was first reported by Shimizu et al1 in 1985. It is characterized by numerous grouped, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules that in most cases are confined to the neck in middle-aged to elderly individuals; however, cases involving the upper trunk and axillae also have been reported.1-3 The etiology of this condition is unclear but is thought to be related to aging and chronic exposure to UV light. Although treatment is not required, various modalities including tretinoin, excision, and laser therapy have been trialed with varying success.2,4 Our patient elected not to proceed with treatment.
Histologically, WFP may manifest similarly to connective tissue nevi; the overall architecture is nonspecific with focally thickened collagen and often elastic fibers that may be normal to reduced and/or fragmented, as well as an overall decrease in superficial dermal elastic tissue.3,5 Therefore, the differential diagnosis may include connective tissue nevi and require clinical correlation to make a correct diagnosis.
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is an autosomalrecessive disorder most commonly related to mutations in the ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 6 (ABCC6) gene that tends to manifest clinically on the neck and flexural extremities.6 This disease affects elastic fibers, which may become calcified over time. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is associated with ocular complications relating to the Bruch membrane of the retina and angioid streaks; choroidal neovascularization involving the damaged Bruch membrane and episodes of acute retinopathy may result in vision loss in later stages of the disease.7 Involvement of the elastic laminae of arteries can be associated with cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications such as stroke, coronary artery disease, claudication, and aneurysms. Involvement of the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tracts also may occur and most commonly manifests with bleeding. Pathologic alterations in the elastic fibers of the lungs also have been reported in patients with PXE.8 Histologically, PXE exhibits increased abnormally clumped and fragmented elastic fibers in the superficial dermis, often with calcification (Figure 1). Pseudo-PXE related to D-penicillamine use often lacks calcification and has a bramble bush appearance.9

Fibrofolliculomas may manifest alone or in association with an underlying condition such as Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, in which lesions are most frequently seen scattered on the scalp, face, ears, neck, or upper trunk.10 This condition is related to a folliculin (FLCN) gene germline mutation. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome also may be associated with acrochordons, trichodiscomas, renal cancer, and lung cysts with or without spontaneous pneumothorax. Less frequently noted findings include oral papules, epidermal cysts, angiofibromas, lipomas/angiolipomas, parotid gland tumors, and thyroid neoplasms. Connective tissue nevi/collagenomas can appear clinically similar to fibrofolliculomas; true connective tissue nevi are reported less commonly in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome.11 Histologically, a fibrofolliculoma manifests with epidermal strands originating from a hair follicle associated with prominent surrounding connective tissue (Figure 2).

Elastofibroma dorsi is a benign tumor of connective tissue that most commonly manifests clinically as a solitary subcutaneous mass on the back near the inferior angle of the scapula; it typically develops below the rhomboid major and latissimus dorsi muscles.12 The pathogenesis is uncertain, but some patients have reported a family history of the condition or a history of repetitive shoulder movement/trauma prior to onset; the mass may be asymptomatic or associated with pain and/or swelling. Those affected tend to be older than 50 years.13 Histologically, thickened and rounded to beaded elastic fibers are seen admixed with collagen (Figure 3).

Actinic (solar) elastosis frequently is encountered in many skin biopsies and is caused by chronic photodamage. More hypertrophic variants, such as papular or nodular solar elastosis, may clinically manifest similarly to WFP.14 Histologically, actinic elastosis manifests as a considerable increase in elastic tissue in the papillary and superficial reticular dermis (Figure 4).

- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
- Shimizu H, Nishikawa T, Kimura S. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: review of our 16 cases. Nihon Hifuka Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;95:1077-1084.
- Teo W, Pang S. White fibrous papulosis of the chest and back. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:AB33.
- Dokic Y, Tschen J. White fibrous papulosis of the axillae and neck. Cureus. 2020;12:E7635.
- Lueangarun S, Panchaprateep R. White fibrous papulosis of the neck treated with fractionated 1550-nm erbium glass laser: a case report. J Lasers Med Sci. 2016;7:256-258.
- Rios-Gomez M, Ramos-Garibay JA, Perez-Santana ME, et al. White fibrous papulosis of the neck: a case report. Cureus. 2022;14:E25661.
- Váradi A, Szabó Z, Pomozi V, et al. ABCC6 as a target in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Curr Drug Targets. 2011;12:671-682.
- Gliem M, Birtel J, Müller PL, et al. Acute retinopathy in pseudoxanthoma elasticum. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137:1165-1173.
- Germain DP. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017;12:85. doi:10.1186/s13023-017-0639-8
- Chisti MA, Binamer Y, Alfadley A, et al. D-penicillamine-induced pseudo-pseudoxanthoma elasticum and extensive elastosis perforans serpiginosa with excellent response to acitretin. Ann Saudi Med. 2019;39:56-60.
- Criscito MC, Mu EW, Meehan SA, et al. Dermoscopic features of a solitary fibrofolliculoma on the left cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(2 suppl 1):S8-S9.
- Sattler EC, Steinlein OK. Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. In: Adam MP, Everman DB, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Updated January 30, 2020. Accessed February 23, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1522
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Settipalli S, et al. Elastofibroma: an uncommon tumor revisited. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2016;9:34-37. doi:10.4103/0974- 2077.178543
- Chandrasekar CR, Grimer RJ, Carter SR, et al. Elastofibroma dorsi: an uncommon benign pseudotumour. Sarcoma. 2008;2008:756565. doi:10.1155/2008/756565
- Kwittken J. Papular elastosis. Cutis. 2000;66:81-83.
A 70-year-old woman with a history of osteoporosis and breast cancer presented for evaluation of asymptomatic, 2- to 3-mm, white to flesh-colored papules concentrated on the inferior occipital scalp and posterior neck (inset) for at least several months. She had no additional systemic signs or symptoms, and there was no family history of similar skin findings. A punch biopsy was performed.
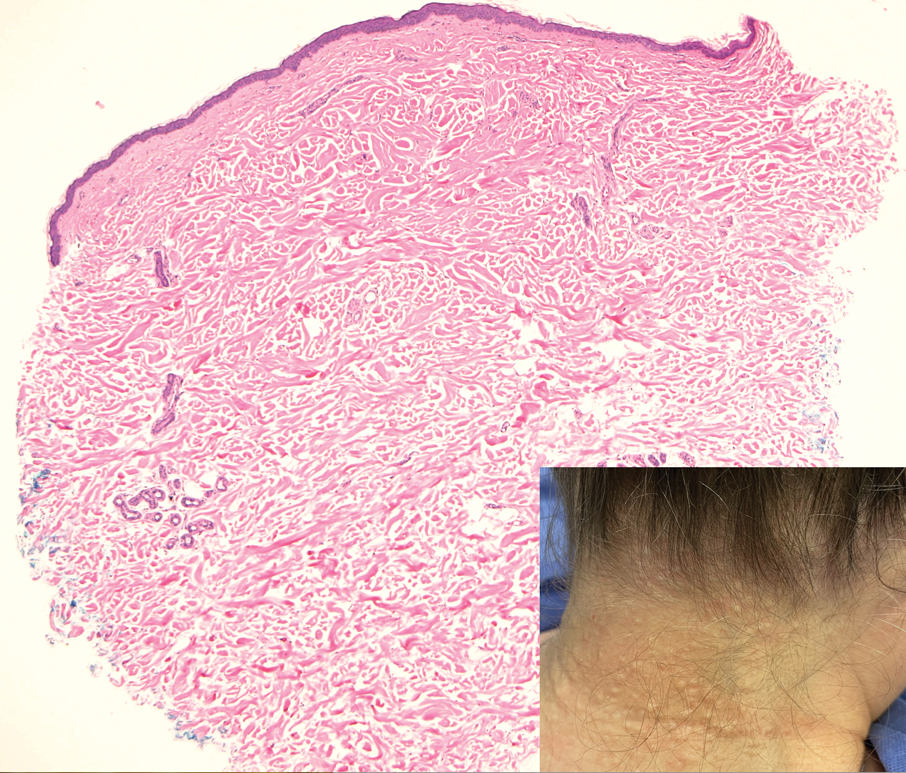
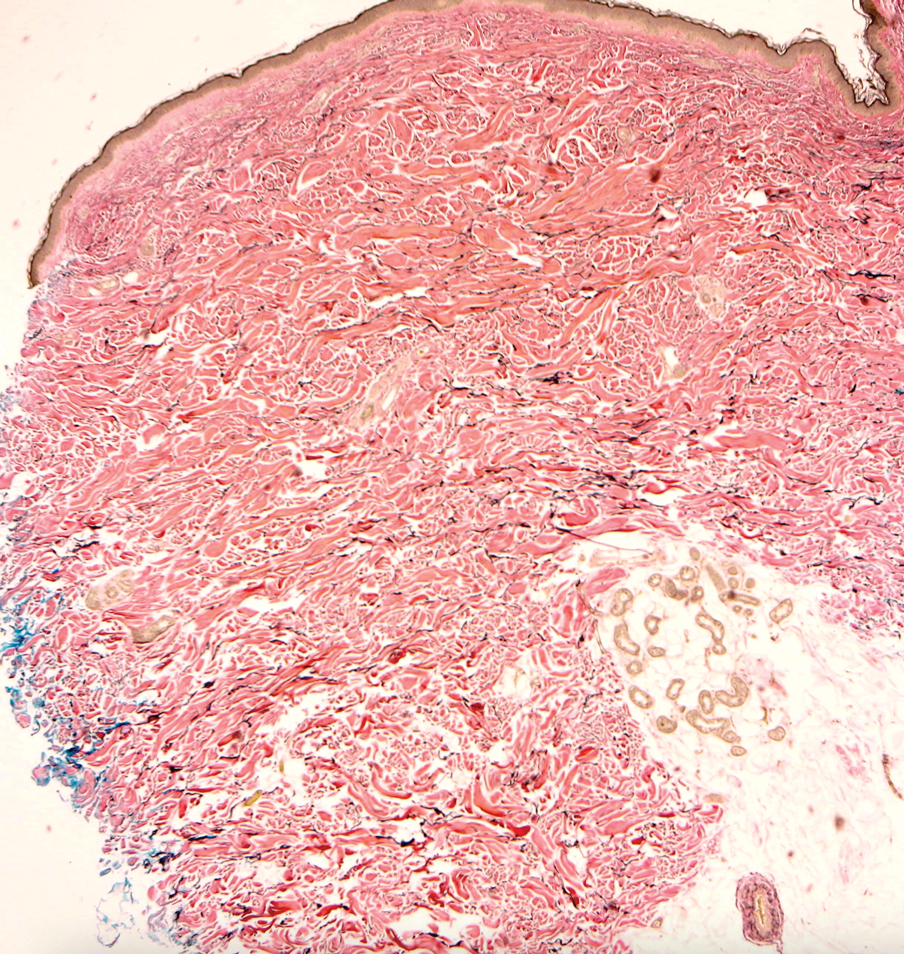
Eating Disorder Risk Factors and the Impact of Obesity in Patients With Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).
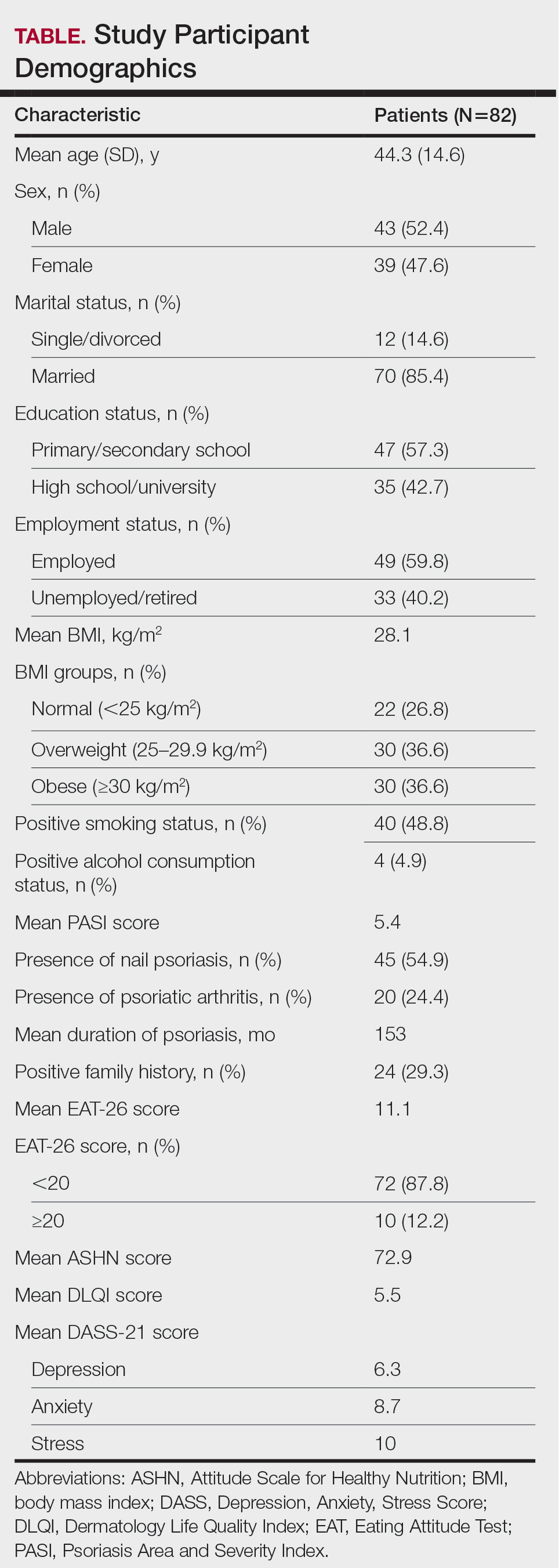
Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.
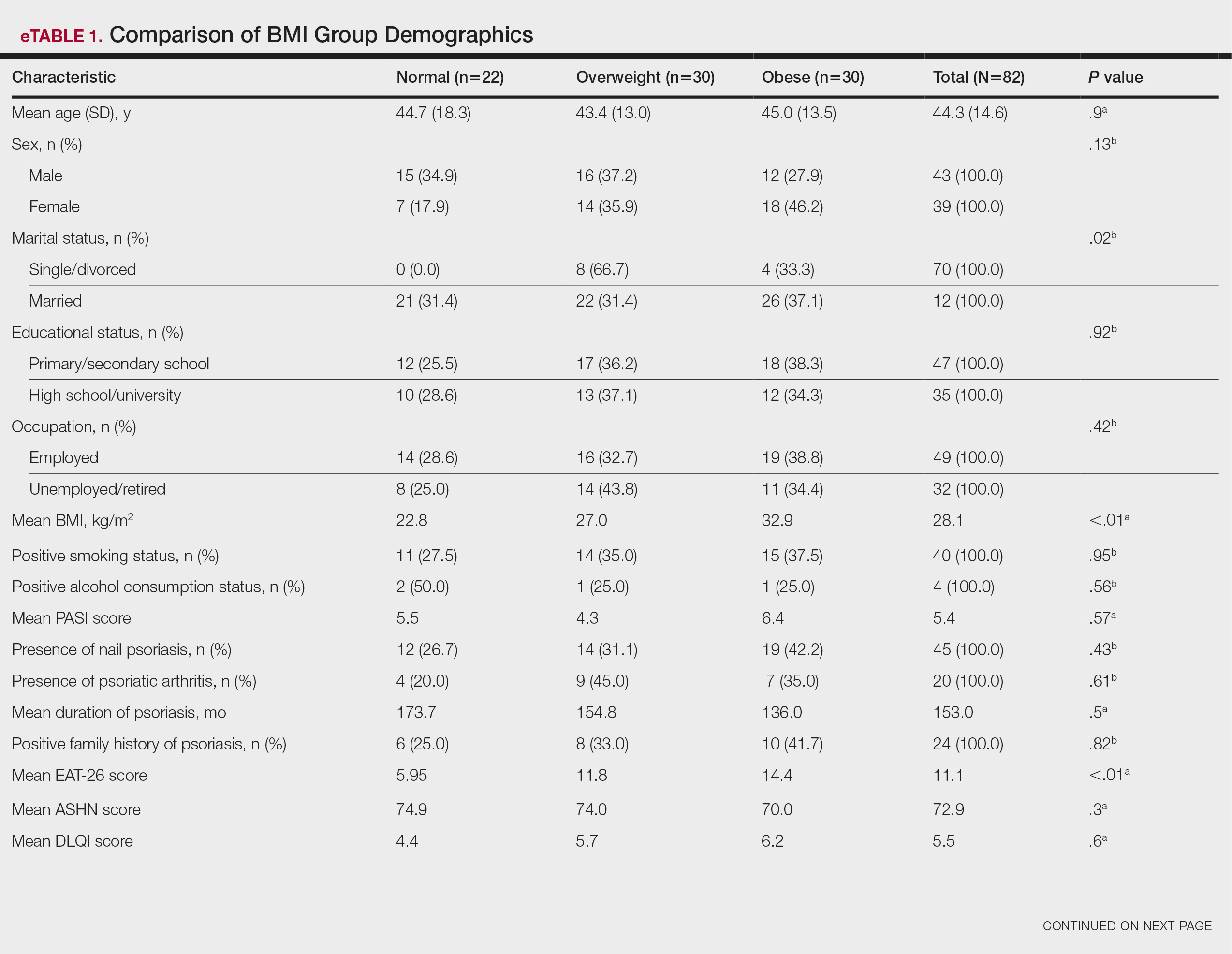
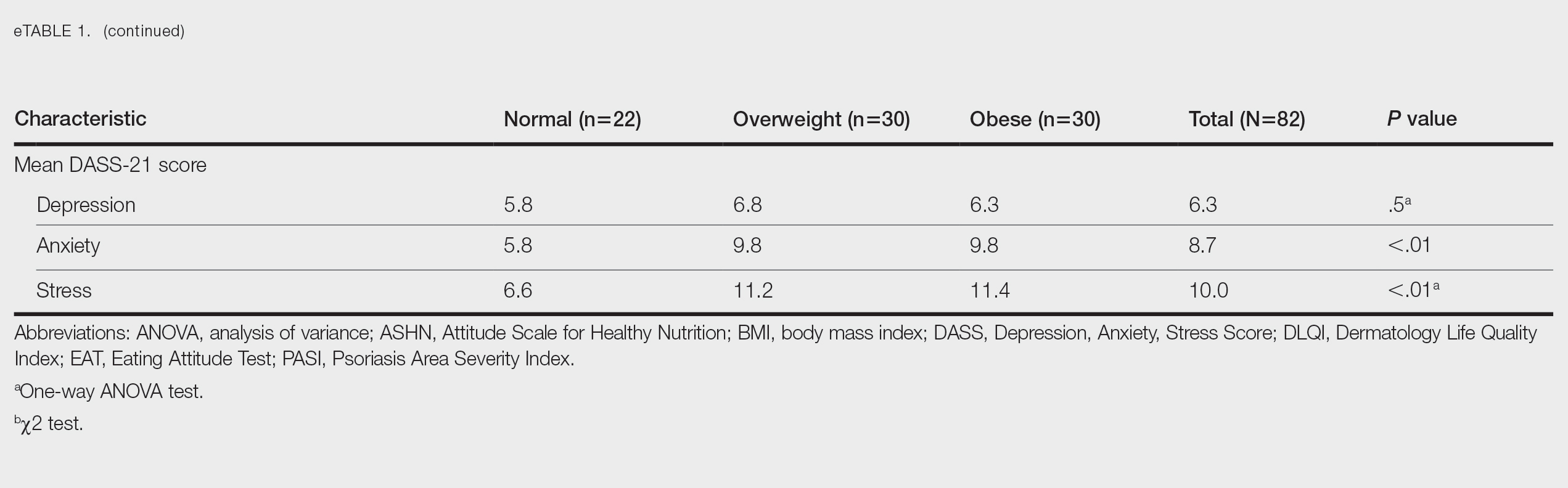
Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).
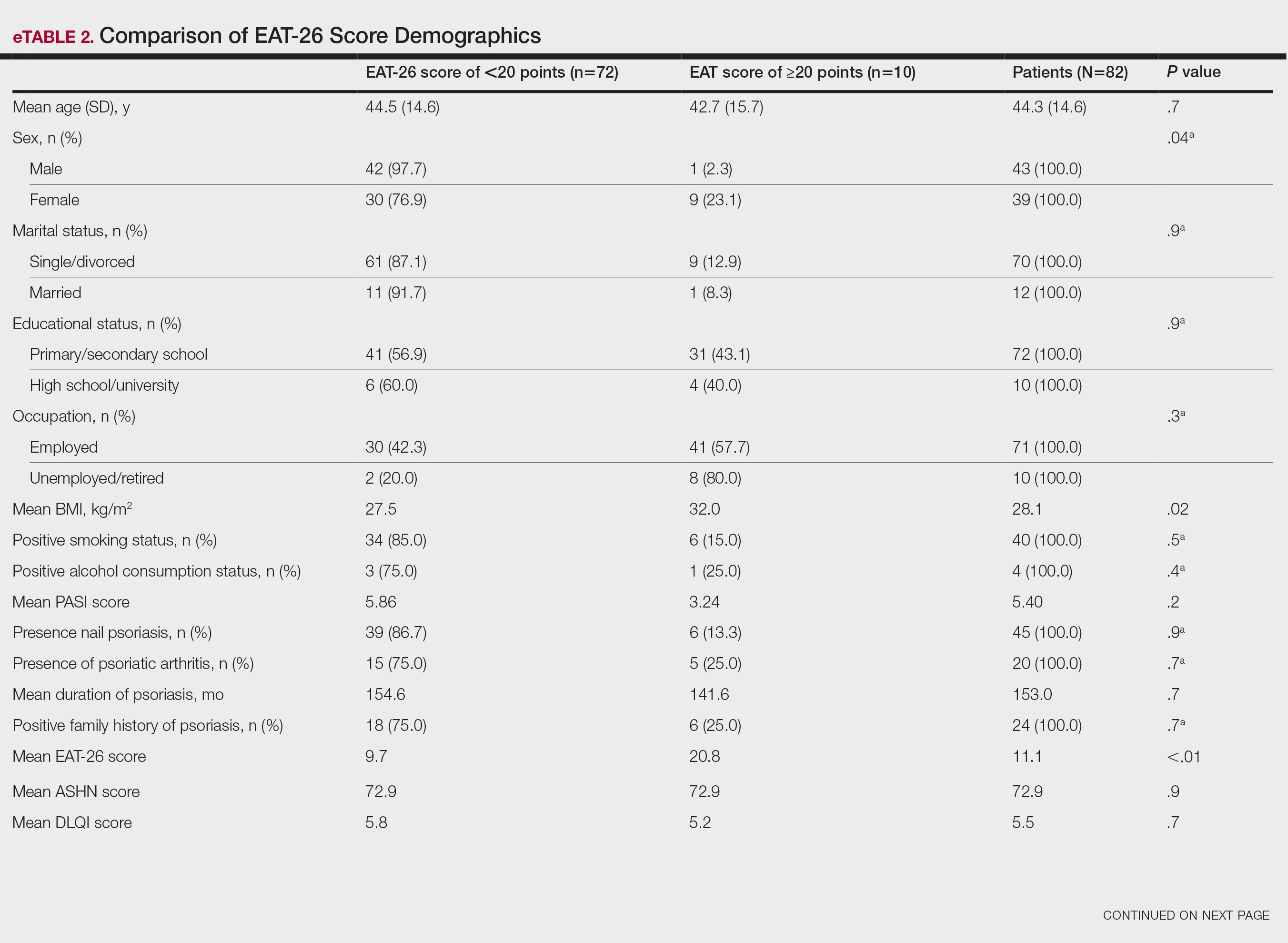
Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).
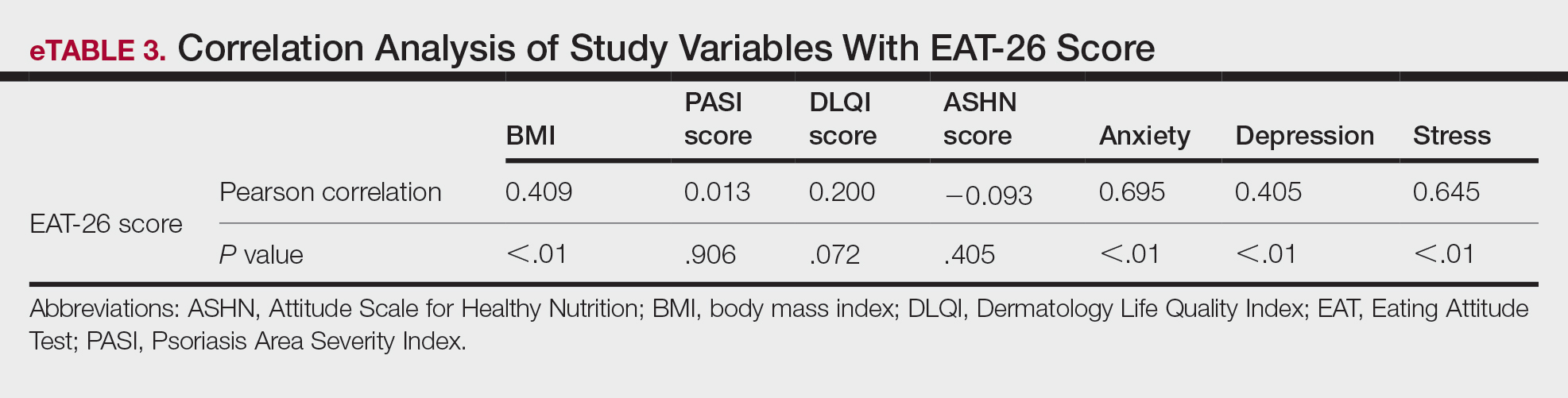
Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).

Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.


Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).


Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).

Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
Psoriasis is a chronic multisystemic inflammatory skin disease with a worldwide prevalence of 2% to 3%.1 Psoriasis can be accompanied by other conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerotic disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and anxiety/depression. It is important to manage comorbidities of psoriasis in addition to treating the cutaneous manifestations of the disease.1
Obesity is a major public health concern worldwide. Numerous observational and epidemiologic studies have reported a high prevalence of obesity among patients with psoriasis.2 Current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate or worsen psoriasis; furthermore, it is important to note that obesity may negatively impact the effectiveness of psoriasis-specific treatments or increase the incidence of adverse effects. Therefore, managing obesity is crucial in the treatment of psoriasis.3 Numerous studies have investigated the association between psoriasis and obesity, and they commonly conclude that both conditions share the same genetic metabolic pathways.2-4 However, it is important to consider environmental factors such as dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle—all of which are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to the development of obesity.5 Because of the effects of obesity in psoriasis patients, factors that impact the development of obesity have become a popular research topic.
Eating disorders (EDs) are a crucial risk factor for both developing and maintaining obesity. In particular, two EDs that are associated with obesity include binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa.6 According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition,7 binge eating disorder can be diagnosed when a patient has at least 1 episode of binge eating per week over a 3-month period. Bulimia nervosa can be diagnosed when a patient is excessively concerned with their body weight and shape and engages in behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, forced vomiting, excessive use of laxatives).7 Psychiatrists who specialize in EDs make diagnoses based on these criteria. In daily practice, there are several quick and simple questionnaires available to screen for EDs that can be used by nonpsychiatrist physicians, including the commonly used 26-item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26).8 The EAT-26 has been used to screen for EDs in patients with inflammatory disorders.9
The aim of this study was to screen for EDs in patients with psoriasis to identify potential risk factors for development of obesity.
Materials and Methods
This study included patients with psoriasis who were screened for EDs at a tertiary dermatology clinic in Turkey between January 2021 and December 2023. This study was approved by the local ethics committee and was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (decision number E-93471371-514.99-225000079).
Study Design and Patient Inclusion Criteria—This quantitative cross-sectional study utilized EAT-26, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition (ASHN), and Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scores. All the questionnaire scales used in the study were adapted and validated in Turkey.8,10-12 The inclusion criteria consisted of being older than 18 years of age, being literate, having psoriasis for at least 1 year that was not treated topically or systemically, and having no psychiatric diseases outside an ED. The questionnaires were presented in written format following the clinical examination. Literacy was an inclusion criterion in this study due to the absence of auxiliary health personnel.
Study Variables—The study variables included age, sex, marital status (single/divorced or married), education status (primary/secondary school or high school/university), employment status (employed or unemployed/retired), body mass index (BMI), smoking status, alcohol-consumption status, Psoriasis Area Severity Index score, presence of nail psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, duration of psoriasis, family history of psoriasis, EAT-26 score, ASHN score, DLQI score, and DASS-21 score. Body mass index was calculated by taking a participant’s weight in kilograms and dividing it by their height in meters squared. The BMI values were classified into 3 categories: normal (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obese (≥30 kg/m2).13
Questionnaires—The EAT-26 questionnaire includes 26 questions that are used to detect EDs. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “always,” “usually,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” and “never.”) Patients with scores of 20 points or higher (range, 0–78) are classified as high risk for EDs.8 In our study, EAT-26 scores were grouped into 2 categories: patients scoring less than 20 points and those scoring 20 points or higher.
The DLQI questionnaire includes 10 questions to measure dermatologic symptoms and qualiy of life. Responses to each question include Likert-type answer options (ie, “not at all,” “a little,” “a lot,” or “very much.”) On the DLQI scale, the higher the score, the lower the quality of life (score range, 0–30).10
The ASHN questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure attitudes toward healthy nutrition with 5 possible answer options (“strongly disagree,” “disagree,” “undecided,” “agree,” and “strongly agree”). On this scale, higher scores indicate the participant is more knowledgeable about healthy nutrition (score range, 0–78).11
The DASS-21 questionnaire includes 21 questions that measure the severity of a range of symptoms common to depression, anxiety, and stress. Responses include Likert-type answer options (eg, “never,” “sometimes,” “often,” and “almost always.”) On this scale, a higher score (range of 0–21 for each) indicates higher levels of depression, anxiety, and stress.12
Statistical Analysis—Descriptive statistics were analyzed using SPSS software version 22.0 (IBM). The Shapiro-Wilk test was applied to determine whether the data were normally distributed. For categorical variables, frequency differences among groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test. A t test was used to compare the means of 2 independent groups with a normal distribution. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey Honest Significant Difference post hoc analysis were used to test whether there was a statistically significant difference among the normally distributed means of independent groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine whether there was a linear relationship between 2 numeric measurements and, if so, to determine the direction and severity of this relationship. P<.05 indicated statistical significance in this study.
Results
Study Participant Demographics—This study included 82 participants with a mean age of 44.3 years; 52.4% (43/82) were female, and 85.4% (70/82) were married. The questionnaire took an average of 4.2 minutes for participants to complete. A total of 57.3% (47/82) of patients had completed primary/secondary education and 59.8% (49/82) were employed. The mean BMI was 28.1 kg/m2. According to the BMI classification, 26.8% (22/82) participants had a normal weight, 36.6% (30/82) were overweight, and 43.9% (36/82) were obese. A total of 48.8% (40/82) of participants smoked, and 4.9% (4/82) consumed alcohol. The mean Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was 5.4. A total of 54.9% (45/82) of participants had nail psoriasis, and 24.4% (20/82) had psoriatic arthritis. The mean duration of psoriasis was 153 months. A total of 29.3% (24/82) of participants had a positive family history of psoriasis. The mean EAT-26 score was 11.1. A total of 12.2% (10/82) of participants had an EAT-26 score of 20 points or higher and were considered at high risk for an ED. The mean ASHN score was 72.9; the mean DLQI score was 5.5; and on the DASS-21 scale, mean scores for depression, anxiety, and stress were 6.3, 8.7, and 10.0, respectively (Table).

Comparative Evaluation of the BMI Groups—The only statistically significant differences among the 3 BMI groups were related to marital status, EAT-26 score, and anxiety and stress scores (P=.02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively)(eTable 1). The number of single/divorced participants in the overweight group was significantly (P=.02) greater than in the normal weight group. The mean EAT-26 score for the normal weight group was significantly (P<.01) lower than for the overweight and obese groups; there was no significant difference in mean EAT-26 scores between the overweight and obese groups. The mean anxiety score was significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group compared with the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean depression score. The mean stress and anxiety scores were significantly (P<.01) lower in the normal weight group than in the overweight and obese groups. There was no significant difference between the overweight and obese groups according to the mean anxiety score.


Comparative Evaluation of the EAT-26 Scores—There were statistically significant differences among the EAT-26 scores related to sex; BMI; and depression, anxiety, and stress scores (P=.04, .02, <.01, <.01, and <.01, respectively). The number of females in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.04) less than that in the group scoring less than 20 points. The mean BMI in the group with a score of 20 points or higher was significantly (P=.02) greater than in group scoring less than 20 points. The mean depression, anxiety, and stress scores of the group scoring 20 points or higher were significantly (P<.01 for all) greater than in the group scoring less than 20 points (eTable 2).


Correlation Analysis of the Study Variables—The EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress (P<.01 for all)(eTable 3).

Comment
Eating disorders are psychiatric conditions that require a multidisciplinary approach. Nonpsychiatric medical departments may be involved due to the severe consequences (eg, various skin changes14) of these disorders. Psoriasis is not known to be directly affected by the presence of an ED; however, it is possible that EDs could indirectly affect patients with psoriasis by influencing obesity. Therefore, this study aimed to examine the relationship between ED risk factors and obesity in this population.
The relationship between psoriasis and obesity has been a popular research topic in dermatology since the 1990s.15 Epidemiologic and observational studies have reported that patients with psoriasis are more likely to be overweight or have obesity, which is an independent risk factor for psoriasis.3,16 However, the causal relationship between psoriasis and obesity remains unclear. In a comprehensive review, Barros et al17 emphasized the causal relationship between obesity and psoriasis under several headings. Firstly, a higher BMI increases the risk for psoriasis by promoting cytokine release and immune system dysregulation. Secondly, a Western diet (eg, processed foods and fast food) triggers obesity and psoriasis by increasing adipose tissue. Thirdly, the alteration of the skin and gut microbiota triggers chronic inflammation as a result of bacterial translocation in patients with obesity. Fourthly, a high-fat diet and palmitic acid disrupt the intestinal integrity of the gut and increase the risk for psoriasis and obesity by triggering chronic inflammation of bacterial fragments that pass into the blood. Finally, the decrease in the amount of adiponectin and the increase in the amount of leptin in patients with obesity may cause psoriasis by increasing proinflammatory cytokines, which are similar to those involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.17 Additionally, psoriatic inflammation can cause insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction, leading to obesity.18 The relationship between psoriasis and obesity cannot be solely explained by metabolic pathways. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle all are associated with psoriasis and also can contribute to obesity.5 Our study revealed no significant difference in smoking or alcohol consumption between the normal weight and overweight/obesity groups. Based on our data, we determined that smoking and alcohol consumption did not affect obesity in our patients with psoriasis.
Observational and epidemiologic studies have shown that patients with psoriasis experience increased rates of depression, anxiety, and stress.19 In studies of pathogenesis, a connection between depression and psoriatic inflammation has been established.20 It is known that inflammatory cytokines similar to those in psoriasis are involved in the development of obesity.18 In addition, depression and anxiety can lead to binge eating, unhealthy food choices, and a more sedentary lifestyle.5 All of these variables may contribute to the associations between depression and anxiety with psoriasis and obesity. Zafiriou et al21 conducted a study to investigate the relationship between psoriasis, obesity, and depression through inflammatory pathways with a focus on the importance of IL-17. Data showing that IL-17–producing Th17-cell subgroups play a considerable role in the development of obesity and depression prompted the authors to suggest that psoriasis, obesity, and anxiety/depression may be interconnected manifestations of immune dysregulation, potentially linked to IL-17 and its associated cells.21 Mrowietz et al22 also suggested that metabolic inflammation may contribute to obesity and depression in patients with psoriasis and highlighted the importance of several cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17, and IL-23. Our study revealed no significant differences in depression scores between BMI groups. Another meta-analysis reported conflicting findings on the incidence of depression in obese patients with psoriasis.23 Some of the studies had a small number of participants. Compared to depression, anxiety has received less attention in studies of patients with obesity with psoriasis. However, these studies have shown a positive correlation between anxiety scores and BMI in patients with psoriasis.24,25 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, overweight patients and those with obesitywho have psoriasis had significantly (P<.01) greater anxiety and stress scores than did normal weight patients with psoriasis.
Obesity should be assessed in patients with psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that takes into account genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.26 Eating disorders are considered to be one of the factors contributing to obesity. Numerous studies in the literature have demonstrated a greater incidence of EDs in patients with obesity vs those without obesity.5,6,27 Obesity and EDs have a bidirectional relationship: individuals with obesity are at risk for EDs due to body dissatisfaction, dieting habits, and depressive states. Conversely, poor eating behaviors in individuals with a normal weight can lead to obesity.28
There are few studies in the literature exploring the relationship between psoriasis and EDs. Crosta et al29 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis had impaired results on ED screening tests and that these scores deteriorated further as BMI increased. Moreover, Altunay et al30 demonstrated that patients with psoriasis and metabolic syndrome had higher scores on the ED screening test. In this study, patients with higher scores also exhibited high levels of anxiety.30 In our study, similar to the findings of previous studies, patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity had significantly (P<.01) greater EAT-26 scores than those in the normal weight group. Patients with high EAT-26 scores also exhibited elevated levels of depression, anxiety, and stress. Additionally, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI, anxiety, depression, and stress scores. Our study as well as other studies in the literature indicate that additional research is needed to determine the associations between EDs and obesity in psoriasis.
Conclusion
Managing obesity is crucial for patients with psoriasis. This study showed that EAT-26 scores were higher in patients with psoriasis who were overweight or had obesity than in those who were normal weight. Participants with high EAT-26 scores (≥20 points) were more likely to be female and have higher anxiety and stress scores. In addition, EAT-26 scores were positively correlated with BMI as well as depression, anxiety, and stress scores. Eating disorders may contribute to the development of obesity in patients with psoriasis. Although our study was limited by a small sample size, the results suggest that there is a need for large-scale multicenter studies to investigate the relationship between psoriasis and EDs.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
- Kalkan G. Comorbidities in psoriasis: the recognition of psoriasis as a systemic disease and current management. Turkderm-Turk Arch Dermatol Venereol. 2017;51:71-77.
- Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ. The association between psoriasis and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes. 2012;2:E54.
- Jensen P, Skov L. Psoriasis and obesity. Dermatology. 2016;232:633-639.
- Mirghani H, Altemani AT, Altemani ST, et al. The cross talk between psoriasis, obesity, and dyslipidemia: a meta-analysis. Cureus. 2023;15:e49253.
- Roehring M, Mashep MR, White MA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and behavioral correlates in obese patients with binge disorders. Obesity. 2009;17:481-486.
- da Luz FQ, Hay P, Touyz S, et al. Obesity with comorbid eating disorders: associated health risks and treatment approaches. Nutrients. 2018;10:829.
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
- Ergüney Okumus¸ FE, Sertel Berk HÖ. The psychometric properties of the Eating Attitudes Test short form (EAT-26) in a college sample. Stud Psychol. 2020;40:57-78.
- Stoleru G, Leopold A, Auerbach A, et al. Female gender, dissatisfaction with weight, and number of IBD related surgeries as independent risk factors for eating disorders among patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:438.
- Öztürkcan S, Ermertcan AT, Eser E, et al. Cross validation of the Turkish version of dermatology life quality index. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:1300-1307.
- Demir GT, Ciciog˘lu HI˙. Attitude scale for healthy nutrition (ASHN): validity and reliability study. Gaziantep Univ J Sport Sci. 2019;4:256-274.
- Yılmaz O, Boz H, Arslan A. The validity and reliability of depression stress and anxiety scale (DASS 21) Turkish short form. Res Financial Econ Soc Stud. 2017;2:78-91.
- Nuttall FQ. Body mass index: obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutr Today. 2015;50:117-128.
- Strumia R, Manzata E, Gualandi M. Is there a role for dermatologists in eating disorders? Expert Rev Dermatol. 2017; 2:109-112.
- Henseler T, Christophers E. Disease concomitance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;32:982-986.
- Naldi L, Addis A, Chimenti S, et al. Impact of body mass index and obesity on clinical response to systemic treatment for psoriasis. evidence from the Psocare project. Dermatology. 2008;217:365-373.
- Barros G, Duran P, Vera I, et al. Exploring the links between obesity and psoriasis: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:7499.
- Hao Y, Zhu YJ, Zou S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and psoriasis: mechanisms and future directions. Front Immunol. 2021;12:711060.
- Jing D, Xiao H, Shen M, et al. Association of psoriasis with anxiety and depression: a case–control study in Chinese patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:771645.
- Sahi FM, Masood A, Danawar NA, et al. Association between psoriasis and depression: a traditional review. Cureus. 2020;12:E9708.
- Zafiriou E, Daponte AI, Siokas V, et al. Depression and obesity in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: is IL-17–mediated immune dysregulation the connecting link? Front Immunol. 2021;12:699848.
- Mrowietz U, Sümbül M, Gerdes S. Depression, a major comorbidity of psoriatic disease, is caused by metabolic inflammation. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023;37:1731-1738.
- Pavlova NT, Kioskli K, Smith C, et al. Psychosocial aspects of obesity in adults with psoriasis: a systematic review. Skin Health Dis. 2021;1:E33.
- Innamorati M, Quinto RM, Imperatori C, et al. Health-related quality of life and its association with alexithymia and difficulties in emotion regulation in patients with psoriasis. Compr Psychiatry. 2016;70:200-208.
- Tabolli S, Naldi L, Pagliarello C, et al. Evaluation of the impact of writing exercises interventions on quality of life in patients with psoriasis undergoing systemic treatments. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1254‐1264.
- Albuquerque D, Nóbrega C, Manco L, et al. The contribution of genetics and environment to obesity. Br Med Bull. 2017;123:159‐173.
- Balantekin KN, Grammer AC, Fitzsimmons-Craft EE, et al. Overweight and obesity are associated with increased eating disorder correlates and general psychopathology in university women with eating disorders. Eat Behav. 2021;41:101482.
- Jebeile H, Lister NB, Baur LA, et al. Eating disorder risk in adolescents with obesity. Obes Rev. 2021;22:E13173.
- Crosta ML, Caldarola G, Fraietta S, et al. Psychopathology and eating disorders in patients with psoriasis. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2014;149:355-361.
- Altunay I, Demirci GT, Ates B, et al. Do eating disorders accompany metabolic syndrome in psoriasis patients? results of a preliminary study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2011;4:139-143.
Practice Points
- Eating disorders are considered a contributing factor in obesity.
- Obesity is prevalent in patients with psoriasis, and current evidence indicates that obesity may initiate psoriasis or worsen existing disease.
- Obesity should be considered as contributory to the development of psoriasis via a biopsychosocial approach that accounts for genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors.
Scurvy: A Diagnosis Still Relevant Today
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
“Petechial rash often prompts further investigation into hematological, dermatological, or vasculitis causes. However, if the above investigations are negative and skin biopsy has not revealed a cause, there is a Renaissance-era diagnosis that is often overlooked but is easily investigated and treated,” wrote Andrew Dermawan, MD, and colleagues from Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Nedlands, Australia, in BMJ Case Reports. The diagnosis they highlight is scurvy, a disease that has faded from common medical concern but is reemerging, partly because of the rise in bariatric surgery.
Diagnosing Scurvy in the 2020s
In their article, Dermawan and colleagues present the case of a 50-year-old man with a bilateral petechial rash on his lower limbs, without any history of trauma. The patient, who exhibited no infectious symptoms, also had gross hematuria, microcytic anemia, mild neutropenia, and lymphopenia. Tests for autoimmune and hematological diseases were negative, as were abdominal and leg CT scans, ruling out abdominal hemorrhage and vasculitis. Additionally, a skin biopsy showed no causative findings.
The doctors noted that the patient had undergone sleeve gastrectomy, prompting them to inquire about his diet. They discovered that, because of financial difficulties, his diet primarily consisted of processed foods with little to no fruits or vegetables, and he had stopped taking supplements recommended by his gastroenterologist. Further tests revealed a vitamin D deficiency and a severe deficiency in vitamin C. With the diagnosis of scurvy confirmed, the doctors treated the patient with 1000 mg of ascorbic acid daily, along with cholecalciferol, folic acid, and a multivitamin complex, leading to a complete resolution of his symptoms.
Risk Factors Then and Now
It can cause mucosal and gastric hemorrhages, and if left untreated, it can lead to fatal bleeding.
Historically known as “sailors’ disease,” scurvy plagued men on long voyages who lacked access to fresh fruits or vegetables and thus did not get enough vitamin C. In 1747, James Lind, a British physician in the Royal Navy, demonstrated that the consumption of oranges and lemons could combat scurvy.
Today’s risk factors for scurvy include malnutrition, gastrointestinal disorders (eg, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases), alcohol and tobacco use, eating disorders, psychiatric illnesses, dialysis, and the use of medications that reduce the absorption of ascorbic acid (such as corticosteroids and proton pump inhibitors).
Scurvy remains more common among individuals with unfavorable socioeconomic conditions. The authors of the study emphasize how the rising cost of living — specifically in Australia but applicable elsewhere — is changing eating habits, leading to a high consumption of low-cost, nutritionally poor foods.
Poverty has always been a risk factor for scurvy, but today there may be an additional cause: bariatric surgery. Patients undergoing these procedures are at a risk for deficiencies in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and if their diet is inadequate, they may also experience a vitamin C deficiency. Awareness of this can facilitate the timely diagnosis of scurvy in these patients.
This story was translated from Univadis Italy using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.