User login
Researchers Take Aim at Genetic Influence on Asthma and Allergy
The impact of maternal factors on allergy and asthma is the subject of new research in the wake of a grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to a team at Indiana University School of Medicine, according to a university press release.
Researchers led by Joan Cook-Mills, PhD, will examine the mechanisms behind the development of asthma, food allergies, and allergic diseases in children whose mothers had allergies.
“Research from the Cook-Mills lab revealed mothers with allergies have elevated levels of a specific lipid within the eicosanoid class of lipids, suggesting this lipid may have a potential influence on their offspring also developing allergies,” according to the press release.
A 5-year grant for $3.9 million was awarded to extend work by the Cook-Mills lab, and the research will focus on four areas, according to the university:
The potential impact of higher levels of lipid from mothers’ lungs may affect infants’ risk for allergy and whether this lipid is transmitted to infants during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The potential impact of elevated levels of a specific eicosanoid in mothers with allergies promotes the creation of more dendritic cells by fetal bone marrow and how this might affect allergy risk for infants.
, potentially leading to altered lung bacteria, which can affect immune cell responses to allergies and asthma.
The potential impact of elevated eicosanoids on whether the altered lung microbiome “actively changes the production of this eicosanoid in the lungs of allergic mothers,” according to the press release.
“Allergies and asthma cause a significant burden of disease in our pediatric population, which is further complicated by limited therapies and interventions to combat these diseases, let alone prevent their development,” Anne C. Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at Maine Medical Center, Portland, said in an interview.
“The work by Cook-Mills and her colleagues will expand our understanding of the role maternal health may have on allergies and asthma and opportunities to mitigate it,” she said. The key implications of the research are the potential to facilitate the development of future clinical studies and trials that could yield novel targeted treatments for significant allergies, Dr. Coates told this news organization.
The research by Cook-Mills and her team had “the potential for the development of transformative approaches to allergy prevention and management, which could improve the health and quality of life for scores of individuals worldwide,” she said.
Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose but served on the Editorial Advisory Board of Chest Physician.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The impact of maternal factors on allergy and asthma is the subject of new research in the wake of a grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to a team at Indiana University School of Medicine, according to a university press release.
Researchers led by Joan Cook-Mills, PhD, will examine the mechanisms behind the development of asthma, food allergies, and allergic diseases in children whose mothers had allergies.
“Research from the Cook-Mills lab revealed mothers with allergies have elevated levels of a specific lipid within the eicosanoid class of lipids, suggesting this lipid may have a potential influence on their offspring also developing allergies,” according to the press release.
A 5-year grant for $3.9 million was awarded to extend work by the Cook-Mills lab, and the research will focus on four areas, according to the university:
The potential impact of higher levels of lipid from mothers’ lungs may affect infants’ risk for allergy and whether this lipid is transmitted to infants during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The potential impact of elevated levels of a specific eicosanoid in mothers with allergies promotes the creation of more dendritic cells by fetal bone marrow and how this might affect allergy risk for infants.
, potentially leading to altered lung bacteria, which can affect immune cell responses to allergies and asthma.
The potential impact of elevated eicosanoids on whether the altered lung microbiome “actively changes the production of this eicosanoid in the lungs of allergic mothers,” according to the press release.
“Allergies and asthma cause a significant burden of disease in our pediatric population, which is further complicated by limited therapies and interventions to combat these diseases, let alone prevent their development,” Anne C. Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at Maine Medical Center, Portland, said in an interview.
“The work by Cook-Mills and her colleagues will expand our understanding of the role maternal health may have on allergies and asthma and opportunities to mitigate it,” she said. The key implications of the research are the potential to facilitate the development of future clinical studies and trials that could yield novel targeted treatments for significant allergies, Dr. Coates told this news organization.
The research by Cook-Mills and her team had “the potential for the development of transformative approaches to allergy prevention and management, which could improve the health and quality of life for scores of individuals worldwide,” she said.
Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose but served on the Editorial Advisory Board of Chest Physician.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The impact of maternal factors on allergy and asthma is the subject of new research in the wake of a grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to a team at Indiana University School of Medicine, according to a university press release.
Researchers led by Joan Cook-Mills, PhD, will examine the mechanisms behind the development of asthma, food allergies, and allergic diseases in children whose mothers had allergies.
“Research from the Cook-Mills lab revealed mothers with allergies have elevated levels of a specific lipid within the eicosanoid class of lipids, suggesting this lipid may have a potential influence on their offspring also developing allergies,” according to the press release.
A 5-year grant for $3.9 million was awarded to extend work by the Cook-Mills lab, and the research will focus on four areas, according to the university:
The potential impact of higher levels of lipid from mothers’ lungs may affect infants’ risk for allergy and whether this lipid is transmitted to infants during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The potential impact of elevated levels of a specific eicosanoid in mothers with allergies promotes the creation of more dendritic cells by fetal bone marrow and how this might affect allergy risk for infants.
, potentially leading to altered lung bacteria, which can affect immune cell responses to allergies and asthma.
The potential impact of elevated eicosanoids on whether the altered lung microbiome “actively changes the production of this eicosanoid in the lungs of allergic mothers,” according to the press release.
“Allergies and asthma cause a significant burden of disease in our pediatric population, which is further complicated by limited therapies and interventions to combat these diseases, let alone prevent their development,” Anne C. Coates, MD, a pediatric pulmonologist at Maine Medical Center, Portland, said in an interview.
“The work by Cook-Mills and her colleagues will expand our understanding of the role maternal health may have on allergies and asthma and opportunities to mitigate it,” she said. The key implications of the research are the potential to facilitate the development of future clinical studies and trials that could yield novel targeted treatments for significant allergies, Dr. Coates told this news organization.
The research by Cook-Mills and her team had “the potential for the development of transformative approaches to allergy prevention and management, which could improve the health and quality of life for scores of individuals worldwide,” she said.
Dr. Coates had no financial conflicts to disclose but served on the Editorial Advisory Board of Chest Physician.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why GLP-1 Drugs Stop Working, and What to Do About It
There’s no question that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists represent a major advance in the treatment of obesity for patients with or without diabetes. In clinical trials, participants lost 15%-20% of their body weight, depending on the drug.
But studies also have shown that once people stop taking these drugs — either by choice, because of shortage, or lack of access — they regain most, if not all, the weight they lost.
Arguably more frustrating is the fact that those who continue on the drug eventually reach a plateau, at which point, the body seemingly stubbornly refuses to lose more weight. Essentially, it stabilizes at its set point, said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, MBA, an obesity medicine physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
‘Tug of War’
Every study of weight loss drugs done over the past 40 years or so shows a plateau, Dr. Stanford told this news organization. “If you look at the phentermine/topiramate studies, there’s a plateau. If you look at the bupropion/naltrexone studies, there’s a plateau. Or if we look at bariatric surgery, there’s a plateau. And it’s the same for the newer GLP-1 drugs.”
The reason? “It really depends on where the body gets to,” Dr. Stanford said. “The body knows what it needs to do to maintain itself, and the brain knows where it’s supposed to be. And when you lose weight and reach what you feel is a lower set point, the body resists.”
When the body goes below its set point, the hunger hormone ghrelin, which is housed in the brain, gets reactivated and gradually starts to reemerge, she explained. GLP-1, which is housed in the distal portion of the small intestine and in the colon, also starts to reemerge over time.
“It becomes kind of a tug of war” between the body and whatever weight loss strategy is being implemented, from drugs to surgery to lifestyle changes, Dr. Stanford said. “The patient will start to notice changes in how their body is responding. Usually, they’ll say they don’t feel like the treatment is working the same. But the treatment is working the same as it’s always been working — except their body is now acclimated to it.”
Anne L. Peters, MD, CDE, professor and clinical scholar, Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, and director, agreed that in the simplest terms, a plateau occurs because “the body becomes more and more used to” the weight loss intervention.
However, when you lose weight, you lose both fat mass and lean body mass, and lean body mass is the metabolically active part of your body, explained Dr. Peters. “That’s what burns and basically makes up your basal metabolic rate.”
With weight loss, the metabolism slows down, she said. If patients need 2000 calories a day to survive at a certain weight and then lose 50 pounds, they may then need only a 1000 calories a day. “With any obesity treatment, you reach a point at which your metabolic rate and your daily caloric requirements become equal, and you stop losing weight, even though your daily caloric requirement is less than it was when your weight was higher.”
Managing the Plateau
Several strategies can be used to help patients break through a plateau. One is to try multiple weight loss agents with different targets — something often done in the real world, Dr. Stanford said. “You don’t see this in the studies, which are focused on just one drug, but many of our patients are on combination therapy. They’re on a GLP-1 drug plus phentermine/topiramate plus metformin, and more. They’re usually on three, four, five drugs, similar to what we would see with resistant hypertension.”
If a patient plateaus on a GLP-1 drug, Dr. Stanford might add phentermine. When the patient reaches a plateau on phentermine, she would switch again to another agent. “The goal is to use agents that treat different receptors in the brain,” she said. “You would never use two GLP-1 agonists; you would use the GLP-1, and then something that treats norepinephrine, for example.”
At the same time, Dr. Peters noted, “try to get them off the drugs that cause weight gain, like insulin and sulfonylurea agents.”
Tapering the GLP-1 dose can also help, Dr. Peters said. However, she added, “If I’m using a GLP-1 drug for type 2 diabetes, it’s different than if I’m using it just for weight loss. With type 2 diabetes, if you taper too much, the blood sugar and weight will go back up, so you need to reach a balance.”
Dr. Peters has successfully tapered patients from a 2-mg dose down to 1 mg. She has also changed the strategy for some — ie, the patient takes the drug every other week instead of every week. “I even have a patient or two who just take it once a month and that seems to be enough,” she said. “You want to help them be at the dose that maintains their weight and keeps them healthy with the least possible medication.”
Emphasizing lifestyle changes is also important, she said. Although resistance training won’t necessarily help with weight loss, “it’s critical to maintaining lean body mass. If people keep losing and regaining weight, they’re going to lose more and more lean body mass and gain the weight back primarily as fat mass. So, their exercise should include about half aerobic activity and half resistance training.”
Long-term Journey
Setting appropriate expectations is a key part of helping patients accept and deal with a plateau. “This is long-term, lifelong journey,” Dr. Stanford said. “We need to think about obesity as a complex, multifactorial chronic disease, like we think about hypertension or type 2 diabetes or hyperlipidemia.”
Furthermore, and in keeping with that perspective, emerging evidence is demonstrating that GLP-1 drugs also have important nonglycemic benefits that can be achieved and maintained, Dr. Peters said. “Obviously weight loss matters, and weight loss is good for you if you’re overweight or obese. But now we know that GLP-1 drugs have wonderful benefits for the heart as well as renal function.” These are reasons to continue the drugs even in the face of a plateau.
One of Dr. Peters’ patients, a physician with type 2 diabetes, had “fought with her weight her whole life. She’s been on one or another GLP-1 drug for more than 15 years, and while none seem to impact her weight, she’s gone from having relatively poorly controlled to now beautifully controlled diabetes,” Dr. Peters said. “Even if she hasn’t lost, she’s maintained her weight, a benefit since people tend to gain weight as they get older, and she hasn’t gained.”
Another patient was disabled, on oxygen, and had recurrent pulmonary embolisms. “She weighed 420 pounds, and I put her on semaglutide because she was too sick to be considered for bariatric surgery.” When that didn’t work, Dr. Peters switched her to tirzepatide, gradually increasing the dose; the patient lost 80 pounds, her emboli are gone, she can walk down the street, and went back to work.
“Part of why she could do that is that she started exercising,” Dr. Peters noted. “She felt so much better from the drug-related weight loss that she began to do things that help enhance weight loss. She became happier because she was no longer homebound.”
This points to another element that can help patients break through a plateau over time, Dr. Peters said — namely, behavioral health. “The more people lose weight, the more they feel better about themselves, and that may mean that they take better care of themselves. The psychological part of this journey is as important as anything else. Not everyone has the same response to these agents, and there are all sorts of issues behind why people are overweight that physicians can’t ignore.
“So, in addition to managing the drugs and lifestyle, it’s important to make sure that people access the behavioral health help they need, and that once they break through a plateau, they don’t develop an eating disorder or go to the opposite extreme and become too thin, which has happened with some of my patients,” she said. “We need to remember that we’re not just giving patients a miraculous weight loss. We’re helping them to be healthier, mentally as well as physically.”
Dr. Stanford disclosed that she had been a consultant for Calibrate, GoodRx, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Vida Health, Life Force, Ilant Health, Melli Cell, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Peters disclosed that she had been a consultant for Vertex, Medscape Medical News, and Lilly; received funding from Abbott and Insulet; and had stock options in Omada Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
There’s no question that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists represent a major advance in the treatment of obesity for patients with or without diabetes. In clinical trials, participants lost 15%-20% of their body weight, depending on the drug.
But studies also have shown that once people stop taking these drugs — either by choice, because of shortage, or lack of access — they regain most, if not all, the weight they lost.
Arguably more frustrating is the fact that those who continue on the drug eventually reach a plateau, at which point, the body seemingly stubbornly refuses to lose more weight. Essentially, it stabilizes at its set point, said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, MBA, an obesity medicine physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
‘Tug of War’
Every study of weight loss drugs done over the past 40 years or so shows a plateau, Dr. Stanford told this news organization. “If you look at the phentermine/topiramate studies, there’s a plateau. If you look at the bupropion/naltrexone studies, there’s a plateau. Or if we look at bariatric surgery, there’s a plateau. And it’s the same for the newer GLP-1 drugs.”
The reason? “It really depends on where the body gets to,” Dr. Stanford said. “The body knows what it needs to do to maintain itself, and the brain knows where it’s supposed to be. And when you lose weight and reach what you feel is a lower set point, the body resists.”
When the body goes below its set point, the hunger hormone ghrelin, which is housed in the brain, gets reactivated and gradually starts to reemerge, she explained. GLP-1, which is housed in the distal portion of the small intestine and in the colon, also starts to reemerge over time.
“It becomes kind of a tug of war” between the body and whatever weight loss strategy is being implemented, from drugs to surgery to lifestyle changes, Dr. Stanford said. “The patient will start to notice changes in how their body is responding. Usually, they’ll say they don’t feel like the treatment is working the same. But the treatment is working the same as it’s always been working — except their body is now acclimated to it.”
Anne L. Peters, MD, CDE, professor and clinical scholar, Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, and director, agreed that in the simplest terms, a plateau occurs because “the body becomes more and more used to” the weight loss intervention.
However, when you lose weight, you lose both fat mass and lean body mass, and lean body mass is the metabolically active part of your body, explained Dr. Peters. “That’s what burns and basically makes up your basal metabolic rate.”
With weight loss, the metabolism slows down, she said. If patients need 2000 calories a day to survive at a certain weight and then lose 50 pounds, they may then need only a 1000 calories a day. “With any obesity treatment, you reach a point at which your metabolic rate and your daily caloric requirements become equal, and you stop losing weight, even though your daily caloric requirement is less than it was when your weight was higher.”
Managing the Plateau
Several strategies can be used to help patients break through a plateau. One is to try multiple weight loss agents with different targets — something often done in the real world, Dr. Stanford said. “You don’t see this in the studies, which are focused on just one drug, but many of our patients are on combination therapy. They’re on a GLP-1 drug plus phentermine/topiramate plus metformin, and more. They’re usually on three, four, five drugs, similar to what we would see with resistant hypertension.”
If a patient plateaus on a GLP-1 drug, Dr. Stanford might add phentermine. When the patient reaches a plateau on phentermine, she would switch again to another agent. “The goal is to use agents that treat different receptors in the brain,” she said. “You would never use two GLP-1 agonists; you would use the GLP-1, and then something that treats norepinephrine, for example.”
At the same time, Dr. Peters noted, “try to get them off the drugs that cause weight gain, like insulin and sulfonylurea agents.”
Tapering the GLP-1 dose can also help, Dr. Peters said. However, she added, “If I’m using a GLP-1 drug for type 2 diabetes, it’s different than if I’m using it just for weight loss. With type 2 diabetes, if you taper too much, the blood sugar and weight will go back up, so you need to reach a balance.”
Dr. Peters has successfully tapered patients from a 2-mg dose down to 1 mg. She has also changed the strategy for some — ie, the patient takes the drug every other week instead of every week. “I even have a patient or two who just take it once a month and that seems to be enough,” she said. “You want to help them be at the dose that maintains their weight and keeps them healthy with the least possible medication.”
Emphasizing lifestyle changes is also important, she said. Although resistance training won’t necessarily help with weight loss, “it’s critical to maintaining lean body mass. If people keep losing and regaining weight, they’re going to lose more and more lean body mass and gain the weight back primarily as fat mass. So, their exercise should include about half aerobic activity and half resistance training.”
Long-term Journey
Setting appropriate expectations is a key part of helping patients accept and deal with a plateau. “This is long-term, lifelong journey,” Dr. Stanford said. “We need to think about obesity as a complex, multifactorial chronic disease, like we think about hypertension or type 2 diabetes or hyperlipidemia.”
Furthermore, and in keeping with that perspective, emerging evidence is demonstrating that GLP-1 drugs also have important nonglycemic benefits that can be achieved and maintained, Dr. Peters said. “Obviously weight loss matters, and weight loss is good for you if you’re overweight or obese. But now we know that GLP-1 drugs have wonderful benefits for the heart as well as renal function.” These are reasons to continue the drugs even in the face of a plateau.
One of Dr. Peters’ patients, a physician with type 2 diabetes, had “fought with her weight her whole life. She’s been on one or another GLP-1 drug for more than 15 years, and while none seem to impact her weight, she’s gone from having relatively poorly controlled to now beautifully controlled diabetes,” Dr. Peters said. “Even if she hasn’t lost, she’s maintained her weight, a benefit since people tend to gain weight as they get older, and she hasn’t gained.”
Another patient was disabled, on oxygen, and had recurrent pulmonary embolisms. “She weighed 420 pounds, and I put her on semaglutide because she was too sick to be considered for bariatric surgery.” When that didn’t work, Dr. Peters switched her to tirzepatide, gradually increasing the dose; the patient lost 80 pounds, her emboli are gone, she can walk down the street, and went back to work.
“Part of why she could do that is that she started exercising,” Dr. Peters noted. “She felt so much better from the drug-related weight loss that she began to do things that help enhance weight loss. She became happier because she was no longer homebound.”
This points to another element that can help patients break through a plateau over time, Dr. Peters said — namely, behavioral health. “The more people lose weight, the more they feel better about themselves, and that may mean that they take better care of themselves. The psychological part of this journey is as important as anything else. Not everyone has the same response to these agents, and there are all sorts of issues behind why people are overweight that physicians can’t ignore.
“So, in addition to managing the drugs and lifestyle, it’s important to make sure that people access the behavioral health help they need, and that once they break through a plateau, they don’t develop an eating disorder or go to the opposite extreme and become too thin, which has happened with some of my patients,” she said. “We need to remember that we’re not just giving patients a miraculous weight loss. We’re helping them to be healthier, mentally as well as physically.”
Dr. Stanford disclosed that she had been a consultant for Calibrate, GoodRx, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Vida Health, Life Force, Ilant Health, Melli Cell, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Peters disclosed that she had been a consultant for Vertex, Medscape Medical News, and Lilly; received funding from Abbott and Insulet; and had stock options in Omada Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
There’s no question that glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists represent a major advance in the treatment of obesity for patients with or without diabetes. In clinical trials, participants lost 15%-20% of their body weight, depending on the drug.
But studies also have shown that once people stop taking these drugs — either by choice, because of shortage, or lack of access — they regain most, if not all, the weight they lost.
Arguably more frustrating is the fact that those who continue on the drug eventually reach a plateau, at which point, the body seemingly stubbornly refuses to lose more weight. Essentially, it stabilizes at its set point, said Fatima Cody Stanford, MD, MPH, MPA, MBA, an obesity medicine physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and associate professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
‘Tug of War’
Every study of weight loss drugs done over the past 40 years or so shows a plateau, Dr. Stanford told this news organization. “If you look at the phentermine/topiramate studies, there’s a plateau. If you look at the bupropion/naltrexone studies, there’s a plateau. Or if we look at bariatric surgery, there’s a plateau. And it’s the same for the newer GLP-1 drugs.”
The reason? “It really depends on where the body gets to,” Dr. Stanford said. “The body knows what it needs to do to maintain itself, and the brain knows where it’s supposed to be. And when you lose weight and reach what you feel is a lower set point, the body resists.”
When the body goes below its set point, the hunger hormone ghrelin, which is housed in the brain, gets reactivated and gradually starts to reemerge, she explained. GLP-1, which is housed in the distal portion of the small intestine and in the colon, also starts to reemerge over time.
“It becomes kind of a tug of war” between the body and whatever weight loss strategy is being implemented, from drugs to surgery to lifestyle changes, Dr. Stanford said. “The patient will start to notice changes in how their body is responding. Usually, they’ll say they don’t feel like the treatment is working the same. But the treatment is working the same as it’s always been working — except their body is now acclimated to it.”
Anne L. Peters, MD, CDE, professor and clinical scholar, Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, and director, agreed that in the simplest terms, a plateau occurs because “the body becomes more and more used to” the weight loss intervention.
However, when you lose weight, you lose both fat mass and lean body mass, and lean body mass is the metabolically active part of your body, explained Dr. Peters. “That’s what burns and basically makes up your basal metabolic rate.”
With weight loss, the metabolism slows down, she said. If patients need 2000 calories a day to survive at a certain weight and then lose 50 pounds, they may then need only a 1000 calories a day. “With any obesity treatment, you reach a point at which your metabolic rate and your daily caloric requirements become equal, and you stop losing weight, even though your daily caloric requirement is less than it was when your weight was higher.”
Managing the Plateau
Several strategies can be used to help patients break through a plateau. One is to try multiple weight loss agents with different targets — something often done in the real world, Dr. Stanford said. “You don’t see this in the studies, which are focused on just one drug, but many of our patients are on combination therapy. They’re on a GLP-1 drug plus phentermine/topiramate plus metformin, and more. They’re usually on three, four, five drugs, similar to what we would see with resistant hypertension.”
If a patient plateaus on a GLP-1 drug, Dr. Stanford might add phentermine. When the patient reaches a plateau on phentermine, she would switch again to another agent. “The goal is to use agents that treat different receptors in the brain,” she said. “You would never use two GLP-1 agonists; you would use the GLP-1, and then something that treats norepinephrine, for example.”
At the same time, Dr. Peters noted, “try to get them off the drugs that cause weight gain, like insulin and sulfonylurea agents.”
Tapering the GLP-1 dose can also help, Dr. Peters said. However, she added, “If I’m using a GLP-1 drug for type 2 diabetes, it’s different than if I’m using it just for weight loss. With type 2 diabetes, if you taper too much, the blood sugar and weight will go back up, so you need to reach a balance.”
Dr. Peters has successfully tapered patients from a 2-mg dose down to 1 mg. She has also changed the strategy for some — ie, the patient takes the drug every other week instead of every week. “I even have a patient or two who just take it once a month and that seems to be enough,” she said. “You want to help them be at the dose that maintains their weight and keeps them healthy with the least possible medication.”
Emphasizing lifestyle changes is also important, she said. Although resistance training won’t necessarily help with weight loss, “it’s critical to maintaining lean body mass. If people keep losing and regaining weight, they’re going to lose more and more lean body mass and gain the weight back primarily as fat mass. So, their exercise should include about half aerobic activity and half resistance training.”
Long-term Journey
Setting appropriate expectations is a key part of helping patients accept and deal with a plateau. “This is long-term, lifelong journey,” Dr. Stanford said. “We need to think about obesity as a complex, multifactorial chronic disease, like we think about hypertension or type 2 diabetes or hyperlipidemia.”
Furthermore, and in keeping with that perspective, emerging evidence is demonstrating that GLP-1 drugs also have important nonglycemic benefits that can be achieved and maintained, Dr. Peters said. “Obviously weight loss matters, and weight loss is good for you if you’re overweight or obese. But now we know that GLP-1 drugs have wonderful benefits for the heart as well as renal function.” These are reasons to continue the drugs even in the face of a plateau.
One of Dr. Peters’ patients, a physician with type 2 diabetes, had “fought with her weight her whole life. She’s been on one or another GLP-1 drug for more than 15 years, and while none seem to impact her weight, she’s gone from having relatively poorly controlled to now beautifully controlled diabetes,” Dr. Peters said. “Even if she hasn’t lost, she’s maintained her weight, a benefit since people tend to gain weight as they get older, and she hasn’t gained.”
Another patient was disabled, on oxygen, and had recurrent pulmonary embolisms. “She weighed 420 pounds, and I put her on semaglutide because she was too sick to be considered for bariatric surgery.” When that didn’t work, Dr. Peters switched her to tirzepatide, gradually increasing the dose; the patient lost 80 pounds, her emboli are gone, she can walk down the street, and went back to work.
“Part of why she could do that is that she started exercising,” Dr. Peters noted. “She felt so much better from the drug-related weight loss that she began to do things that help enhance weight loss. She became happier because she was no longer homebound.”
This points to another element that can help patients break through a plateau over time, Dr. Peters said — namely, behavioral health. “The more people lose weight, the more they feel better about themselves, and that may mean that they take better care of themselves. The psychological part of this journey is as important as anything else. Not everyone has the same response to these agents, and there are all sorts of issues behind why people are overweight that physicians can’t ignore.
“So, in addition to managing the drugs and lifestyle, it’s important to make sure that people access the behavioral health help they need, and that once they break through a plateau, they don’t develop an eating disorder or go to the opposite extreme and become too thin, which has happened with some of my patients,” she said. “We need to remember that we’re not just giving patients a miraculous weight loss. We’re helping them to be healthier, mentally as well as physically.”
Dr. Stanford disclosed that she had been a consultant for Calibrate, GoodRx, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gelesis, Vida Health, Life Force, Ilant Health, Melli Cell, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Peters disclosed that she had been a consultant for Vertex, Medscape Medical News, and Lilly; received funding from Abbott and Insulet; and had stock options in Omada Health.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
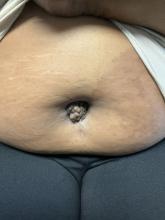
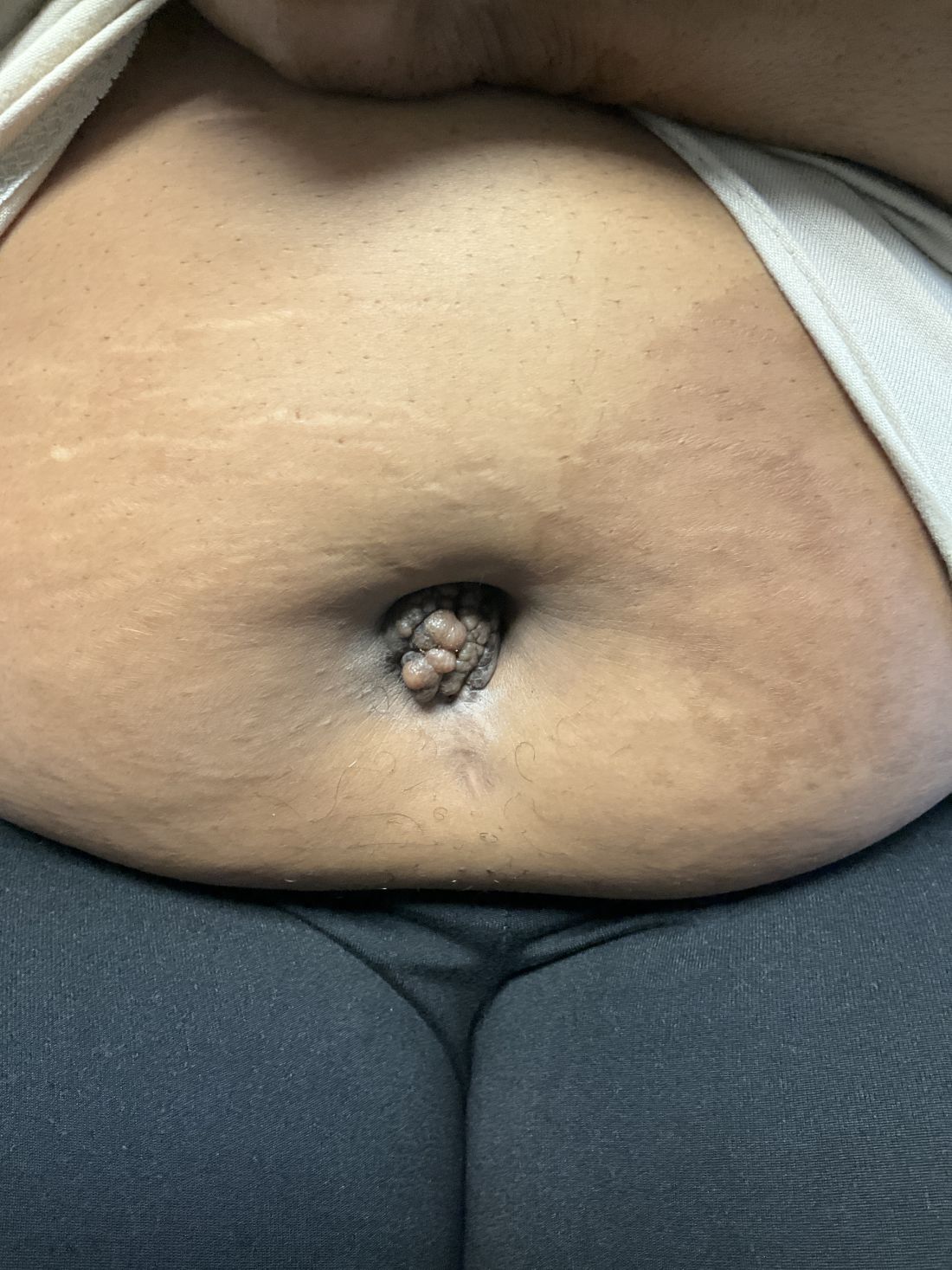
A 27-year-old Haitian woman presented with a painful umbilical mass which had been growing in size for 5 months
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity, commonly occurring in women of reproductive age. The condition usually affects the adnexa (ovaries, Fallopian tubes, and associated ligaments and connective tissue) but can also be seen in extrapelvic structures.
Cutaneous endometriosis is an uncommon subtype that accounts for 1% of endometriosis cases and occurs when endometrial tissue is found on the surface of the skin. It is divided into primary and secondary cutaneous endometriosis. The that may lead to seeding of endometrial tissue on the skin. In the case of our patient, it appears that her laparoscopic procedure 2 years ago was the cause of endometrial seeding in the umbilicus.
Clinically, the condition may present with a palpable mass, cyclic pain, and bloody discharge from the affected area. Due to the rarity of cutaneous endometriosis, it may be hard to distinguish from other diagnoses such as keloids, dermatofibromas, hernias, or cutaneous metastasis of cancers (Sister Mary Joseph nodules).
The definitive diagnosis can be made by biopsy and histopathological assessment showing a mixture of endometrial glands and stromal tissue. Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scan and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are helpful in excluding more common diagnoses such as hernia or cutaneous metastasis. In this patient, the mass was surgically excised. Histopathological assessment established the diagnosis of cutaneous endometriosis.
Treatment options include surgical excision and medical therapy. Medical therapy entails the use of hormonal agents such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, danazol (a pituitary gonadotropin inhibitor), and oral contraceptives, which reduce the cyclical proliferation of endothelial tissue. These agents can be used preoperatively to reduce the size of the cutaneous mass before surgical excision, or as an alternative treatment for patients who wish to avoid surgery. The rate of recurrence is observed to be higher with medical therapy rather than surgical treatment.
The case and photo were submitted by Mina Ahmed, MBBS, Brooke Resh Sateesh MD, and Nathan Uebelhoer MD, of San Diego Family Dermatology, San Diego, California. The column was edited by Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Florida. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Gonzalez RH et al. Am J Case Rep. 2021;22:e932493-1–e932493-4.
2. Raffi L et al. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2019 Dec;5(5):384-386.
3. Sharma A, Apostol R. Cutaneous endometriosis. Treasure Island, Fla: Statpearls Publishing, 2023.
Lipids and Dementia: A Complex and Evolving Story
The relationship between lipid levels and the development of dementia is an evolving but confusing landscape.
“This is an incredibly complex area, and there really isn’t a clear consensus on this subject because different lipid classes reflect different things,” according to Betsy Mills, PhD, assistant director of aging and Alzheimer’s prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Some studies suggest that excessive lipid levels may increase the risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Others imply that elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol or even triglycerides may offer some protection against subsequent dementia whereas higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, hitherto thought to be protective, may have a deleterious effect.
“It depends on what lipids you’re measuring, what you’re using to measure those lipids, what age the person is, and multiple other factors,” Dr. Mills told this news organization.
Teasing out the variables and potential mechanisms for the association between lipids and dementia risk necessitates understanding the role that lipids play in the healthy brain, the negative impact of brain lipid dysregulation, and the interplay between cholesterol in the central nervous system (CNS) and the cholesterol in the rest of the body.
Beyond Amyloid
The role of lipids in AD risk has historically been “overlooked,” says Scott Hansen, PhD, associate professor, Department of Molecular Medicine, Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation and Technology, Florida.
“The common narrative is that amyloid is the culprit in AD and certainly that’s the case in familial AD,” he told this news organization. “It’s been assumed that because amyloid deposits are also found in the brains of people with late-onset AD — which is the vast majority of cases — amyloid is the cause, but that’s not clear at all.”
The “limited clinical success” of aducanumab, its “extremely small efficacy” — despite its obvious success in eradicating the amyloid plaques — suggests there’s “much more to the story than amyloid.”
He and a growing community of scientists recognize the role of inflammation and lipids. “The major finding of my lab is that cholesterol actually drives the synthesis of amyloid via inflammation. In other words, amyloid is downstream of cholesterol. Cholesterol drives the inflammation, and the inflammation drives amyloid,” he said.
‘Lipid Invasion Model’
Because the brain is an incredibly lipid-rich organ, Dr. Mills said that “any dysregulation in lipid homeostasis will impact the brain because cholesterol is needed for the myelin sheaths, cell membranes, and other functions.”
A healthy brain relies upon healthy lipid regulation, and “since the first description of AD over 100 years ago, the disease has been associated with altered lipids in the brain,” Dr. Hansen noted.
He cited the “ lipid invasion model” as a way of understanding brain lipid dysregulation. This hypothesis posits that AD is driven by external lipids that enter the brain as a result of damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
“Cholesterol in the brain and cholesterol in the periphery — meaning, in the rest of the body, outside the brain — are separate,” Dr. Hansen explained. “The brain produces its own cholesterol and keeps tight control of it.”
Under normal circumstances, cholesterol from the diet doesn’t enter the brain. “Each pool of cholesterol — in the brain and in the periphery — has its own distinct regulatory mechanisms, target cells, and transport mechanisms.”
When the BBB has been compromised, it becomes permeable, allowing LDL cholesterol to enter the brain, said Dr. Hansen. Then the brain’s own lipoproteins transport the invading cholesterol, allowing it to be taken up by neurons. In turn, this causes neuronal amyloid levels to rise, ultimately leading to the creation of amyloid-b plaques. It also plays a role in tau phosphorylation. Both are key features of AD pathology.
Elevated levels of cholesterol and other lipids have been found in amyloid plaques, Dr. Hansen noted. Moreover, studies of brains of patients with AD have pointed to BBB damage.
And the risk factors for AD overlap with the risk factors for damage to the BBB (such as, aging, brain trauma, hypertension, stress, sleep deprivation, smoking, excess alcohol, obesity, diabetes, and APOE4 genotype), according to the lipid invasion model paper cited by Dr. Hansen.
‘Chicken and Egg’
“There is a strong link between the brain and the heart, and we know that cardiovascular risk factors have an overlap with dementia risk factors — especially vascular dementia,” said Dr. Mills.
She explained that an atherogenic lipid profile results in narrowing of the arteries, with less blood reaching the brain. “This can lead to stress in the brain, which drives inflammation and pathology.”
But cholesterol itself plays an important role in inflammation, Dr. Hansen said. In the periphery, it is “part of an integral response to tissue damage and infection.”
In the brain, once cholesterol is synthesized by the astrocytes, it is transported to neurons via the apolipoprotein E (APOE) protein, which plays a role in brain cholesterol homeostasis, Dr. Mills explained. Those with the ε4 allele of APOE (APOE4) tend to have faultier transport and storage of lipids in the brain, relative to the other APOE variants.
It’s known that individuals with APOE4 are particularly vulnerable to late-onset AD, Dr. Hansen observed. By contrast, APOE2 has a more protective effect. “Most people have APOE3, which is ‘in between,’ ” he said.
When there is neuronal uptake of “invading cholesterol,” not only is amyloid produced but also neuroinflammatory cytokines, further driving inflammation. A vicious cycle ensues: Cholesterol induces cytokine release; and cytokine release, in turn, induces cholesterol synthesis — which “suggests an autocatalytic function of cholesterol in the escalation of inflammation,” Dr. Hansen suggested. He noted that permeability of the BBB also allows inflammatory cytokines from elsewhere in the body to invade the brain, further driving inflammation.
Dr. Mills elaborated: “We know that generally, in dementia, there appear to be some changes in cholesterol metabolism in the brain, but it’s a chicken-and-egg question. We know that as the disease progresses, neurons are dying and getting remodeled. Do these changes have to do with the degenerative process, or are the changes in the cholesterol metabolism actually driving the degenerative disease process? It’s probably a combination, but it’s unclear at this point.”
Lipids in Plasma vs CSF
Dr. Mills explained that HDL particles in the brain differ from those in the periphery. “In the CNS, you have ‘HDL-like particles,’ which are similar in size and composition [to HDL in the periphery] but aren’t the same particles.” The brain itself generates HDL-like lipoproteins, which are produced by astrocytes and other glial cells and found in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Dyslipidemia in the periphery can be a marker for cardiovascular pathology. In the brain, “it can be an indication that there is active damage going on, depending on which compartment you’re looking at.”
She noted that plasma lipid levels and brain CSF lipid levels are “very different.” Research suggests that HDL in the CSF exhibits similar heterogeneity to plasma HDL, but these CSF lipoproteins present at 100-fold lower concentrations, compared to plasma HDL and have unique combinations of protein subpopulations. Lipidomics analysis studies show that these compartments “get very different readings, in terms of the predominant lipid disease state, and they are regulated differently from the way lipids in the periphery are regulated.”
In the brain, the cholesterol “needs to get shuttled from glial cells to neurons,” so defects in the transport process can disrupt overall brain homeostasis, said Dr. Mills. But since the brain system is separate from the peripheral system, measuring plasma lipids is more likely to point to cardiovascular risks, while changes reflected in CSF lipids are “more indicative of alteration in lipid homeostasis in the brain.”
HDL and Triglycerides: A Complicated Story
Dr. Mills noted that HDL in the periphery is “very complicated,” and the idea that HDL, as a measure on its own, is “necessarily ‘good’ isn’t particularly informative.” Rather, HDL is “extremely heterogeneous, very diverse, has different lipid compositions, different classes, and different modifications.” For example, like oxidized LDL, oxidized HDL is also “bad,” preventing the HDL from having protective functions.
Similarly, the apolipoproteins associated with HDL can affect the function of the HDL. “Our understanding of the HDL-like particles in the CNS is limited, but we do understand the APOE4 link,” Dr. Mills said. “It seems that the HDL-like particles containing APOE2 or APOE3 are larger and are more effective at transferring the lipids and cholesterol linked to them relative to APOE4-containing particles.”
Because HDL is more complex than simply being “good,” measuring HDL doesn’t “give you the full story,” said Dr. Mills. She speculates that this may be why there are studies suggesting that high levels of HDL might not have protective benefits and might even be detrimental. This makes it difficult to look at population studies, where the different subclasses of HDL are not necessarily captured in depth.
Dr. Mills pointed to another confounding factor, which is that much of the risk for the development of AD appears to be related to the interaction of HDL, LDL, and triglycerides. “When you look at each of these individually, you get a lot of heterogeneity, and it’s unclear what’s driving what,” she said.
An advantage of observational studies is that they give information about which of these markers are associated with trends and disease risks in specific groups vs others.
“For example, higher levels of triglycerides are associated with cardiovascular risk more in women, relative to men,” she said. And the triglyceride-to-HDL ratio seems “particularly robust” as a measure of cardiovascular health and risk.
The interpretation of associations with triglycerides can be “tricky” and “confusing” because results differ so much between studies, she said. “There are differences between middle age and older age, which have to do with age-related changes in metabolism and lipid metabolism and not necessarily that the markers are indicating something different,” she said.
Some research has suggested that triglycerides may have a protective effect against dementia, noted Uma Naidoo, MD, director of nutritional and lifestyle psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, and director of nutritional psychiatry at MGH Academy.
This may be because the brain “runs mostly on energy from burning triglycerides,” suggested Dr. Naidoo, author of the books Calm Your Mind With Food and This Is Your Brain on Food.
In addition, having higher levels of triglycerides may be linked with having overall healthier behaviors, Dr. Naidoo told this news organization.
Dr. Mills said that in middle-aged individuals, high levels of LDL-C and triglycerides are “often indicative of more atherogenic particles and risk to cardiovascular health, which is a generally negative trajectory. But in older individuals, things become more complicated because there are differences in terms of clearance of some of these particles, tissue clearance and distribution, and nutrient status. So for older individuals, it seems that fluctuations in either direction—either too high or too low—tend to be more informative that some overall dysregulation is going on the system.”
She emphasized that, in this “emerging area, looking at only one or two studies is confusing. But if you look at the spectrum of studies, you can see a pattern, which is that the regulation gets ‘off,’ as people age.”
The Potential Role of Statins
Dr. Mills speculated that there may be “neuroprotective benefits for some of the statins which appear to be related to cardiovascular benefits. But at this point, we don’t have any clear data whether statins actually directly impact brain cholesterol, since it’s a separate pool.”
They could help “by increasing blood flow and reducing narrowing of the arteries, but any direct impact on the brain is still under investigation.”
Dr. Hansen pointed to research suggesting statins taken at midlife appear to be cardioprotective and may be protective of brain health as well, whereas statins initiated in older age do not appear to have these benefits.
He speculated that one reason statins seem less helpful when initiated later in life is that the BBB has already been damaged by systemic inflammation in the periphery, and the neuroinflammatory process resulting in neuronal destruction is already underway. “I think statins aren’t going to fix that problem, so although lowering cholesterol can be helpful in some respects, it might be too late to affect cognition because the nerves have already died and won’t grow back.”
Can Dietary Approaches Help?
Dr. Naidoo said that when looking at neurologic and psychiatric disease, “it’s important to think about the ‘long game’ — how can we improve our blood and cardiovascular health earlier in life to help potentiate healthy aging?”
From a nutritional psychiatry standpoint, Dr. Naidoo focuses on nourishing the gut microbiome and decreasing inflammation. “A healthy and balanced microbiome supports cognition, while the composition of gut bacteria is actually drastically different in patients with neurological diseases, such as AD.”
She recommends a nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory diet including probiotic-rich foods (such as kimchi, sauerkraut, plain yogurt, and miso). Moreover, “the quality and structure of our fatty acids may be relevant as well: Increasing our intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids and avoiding processed fats like trans fats and hydrogenated oils may benefit our overall brain health.”
Dr. Naidoo recommends extra-virgin olive oil as a source of healthy fat. Its consumption is linked to lower incidence of AD by way of encouraging autophagy, which she calls “our own process of “cellular cleanup.’”
Dr. Naidoo believes that clinicians’ guidance to patients should “focus on healthy nutrition and other lifestyle practices, such as exercise, outdoor time, good sleep, and stress reduction.”
Dr. Mills notes the importance of omega-3 fatty acids, such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) , for brain health. “DHA is a major lipid component of neuronal membranes,” she said. “Because of inefficiencies in metabolism with APOE4, people tend to metabolize more of the lipids on the membranes themselves, so they have higher lipid membrane turnover and a greater need to supplement. Supplementing particularly through diet, with foods such as fatty fish rich in omega-3, can help boost the levels to help keep neuronal membranes intact.”
What This Means for the Clinician
“At this point, we see all of these associations between lipids and dementia, but we haven’t worked out exactly what it means on the individual level for an individual patient,” said Dr. Mills. Certainly, the picture is complex, and the understanding is growing and shifting. “The clinical applications remain unclear.”
One potential clinical take-home is that clinicians might consider tracking lipid levels over time. “If you follow a patient and see an increase or decrease [in lipid levels], that can be informative.” Looking at ratios of lipids might be more useful than looking only at a change in a single measure. “If you see trends in a variety of measures that track with one another, it might be more of a sign that something is potentially wrong.”
Whether the patient should first try a lifestyle intervention or might need medication is a “personalized clinical decision, depending on the individual, their risk factors, and how their levels are going,” said Dr. Mills.
Dr. Mills, Dr. Hansen, and Dr. Naidoo declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The relationship between lipid levels and the development of dementia is an evolving but confusing landscape.
“This is an incredibly complex area, and there really isn’t a clear consensus on this subject because different lipid classes reflect different things,” according to Betsy Mills, PhD, assistant director of aging and Alzheimer’s prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Some studies suggest that excessive lipid levels may increase the risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Others imply that elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol or even triglycerides may offer some protection against subsequent dementia whereas higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, hitherto thought to be protective, may have a deleterious effect.
“It depends on what lipids you’re measuring, what you’re using to measure those lipids, what age the person is, and multiple other factors,” Dr. Mills told this news organization.
Teasing out the variables and potential mechanisms for the association between lipids and dementia risk necessitates understanding the role that lipids play in the healthy brain, the negative impact of brain lipid dysregulation, and the interplay between cholesterol in the central nervous system (CNS) and the cholesterol in the rest of the body.
Beyond Amyloid
The role of lipids in AD risk has historically been “overlooked,” says Scott Hansen, PhD, associate professor, Department of Molecular Medicine, Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation and Technology, Florida.
“The common narrative is that amyloid is the culprit in AD and certainly that’s the case in familial AD,” he told this news organization. “It’s been assumed that because amyloid deposits are also found in the brains of people with late-onset AD — which is the vast majority of cases — amyloid is the cause, but that’s not clear at all.”
The “limited clinical success” of aducanumab, its “extremely small efficacy” — despite its obvious success in eradicating the amyloid plaques — suggests there’s “much more to the story than amyloid.”
He and a growing community of scientists recognize the role of inflammation and lipids. “The major finding of my lab is that cholesterol actually drives the synthesis of amyloid via inflammation. In other words, amyloid is downstream of cholesterol. Cholesterol drives the inflammation, and the inflammation drives amyloid,” he said.
‘Lipid Invasion Model’
Because the brain is an incredibly lipid-rich organ, Dr. Mills said that “any dysregulation in lipid homeostasis will impact the brain because cholesterol is needed for the myelin sheaths, cell membranes, and other functions.”
A healthy brain relies upon healthy lipid regulation, and “since the first description of AD over 100 years ago, the disease has been associated with altered lipids in the brain,” Dr. Hansen noted.
He cited the “ lipid invasion model” as a way of understanding brain lipid dysregulation. This hypothesis posits that AD is driven by external lipids that enter the brain as a result of damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
“Cholesterol in the brain and cholesterol in the periphery — meaning, in the rest of the body, outside the brain — are separate,” Dr. Hansen explained. “The brain produces its own cholesterol and keeps tight control of it.”
Under normal circumstances, cholesterol from the diet doesn’t enter the brain. “Each pool of cholesterol — in the brain and in the periphery — has its own distinct regulatory mechanisms, target cells, and transport mechanisms.”
When the BBB has been compromised, it becomes permeable, allowing LDL cholesterol to enter the brain, said Dr. Hansen. Then the brain’s own lipoproteins transport the invading cholesterol, allowing it to be taken up by neurons. In turn, this causes neuronal amyloid levels to rise, ultimately leading to the creation of amyloid-b plaques. It also plays a role in tau phosphorylation. Both are key features of AD pathology.
Elevated levels of cholesterol and other lipids have been found in amyloid plaques, Dr. Hansen noted. Moreover, studies of brains of patients with AD have pointed to BBB damage.
And the risk factors for AD overlap with the risk factors for damage to the BBB (such as, aging, brain trauma, hypertension, stress, sleep deprivation, smoking, excess alcohol, obesity, diabetes, and APOE4 genotype), according to the lipid invasion model paper cited by Dr. Hansen.
‘Chicken and Egg’
“There is a strong link between the brain and the heart, and we know that cardiovascular risk factors have an overlap with dementia risk factors — especially vascular dementia,” said Dr. Mills.
She explained that an atherogenic lipid profile results in narrowing of the arteries, with less blood reaching the brain. “This can lead to stress in the brain, which drives inflammation and pathology.”
But cholesterol itself plays an important role in inflammation, Dr. Hansen said. In the periphery, it is “part of an integral response to tissue damage and infection.”
In the brain, once cholesterol is synthesized by the astrocytes, it is transported to neurons via the apolipoprotein E (APOE) protein, which plays a role in brain cholesterol homeostasis, Dr. Mills explained. Those with the ε4 allele of APOE (APOE4) tend to have faultier transport and storage of lipids in the brain, relative to the other APOE variants.
It’s known that individuals with APOE4 are particularly vulnerable to late-onset AD, Dr. Hansen observed. By contrast, APOE2 has a more protective effect. “Most people have APOE3, which is ‘in between,’ ” he said.
When there is neuronal uptake of “invading cholesterol,” not only is amyloid produced but also neuroinflammatory cytokines, further driving inflammation. A vicious cycle ensues: Cholesterol induces cytokine release; and cytokine release, in turn, induces cholesterol synthesis — which “suggests an autocatalytic function of cholesterol in the escalation of inflammation,” Dr. Hansen suggested. He noted that permeability of the BBB also allows inflammatory cytokines from elsewhere in the body to invade the brain, further driving inflammation.
Dr. Mills elaborated: “We know that generally, in dementia, there appear to be some changes in cholesterol metabolism in the brain, but it’s a chicken-and-egg question. We know that as the disease progresses, neurons are dying and getting remodeled. Do these changes have to do with the degenerative process, or are the changes in the cholesterol metabolism actually driving the degenerative disease process? It’s probably a combination, but it’s unclear at this point.”
Lipids in Plasma vs CSF
Dr. Mills explained that HDL particles in the brain differ from those in the periphery. “In the CNS, you have ‘HDL-like particles,’ which are similar in size and composition [to HDL in the periphery] but aren’t the same particles.” The brain itself generates HDL-like lipoproteins, which are produced by astrocytes and other glial cells and found in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Dyslipidemia in the periphery can be a marker for cardiovascular pathology. In the brain, “it can be an indication that there is active damage going on, depending on which compartment you’re looking at.”
She noted that plasma lipid levels and brain CSF lipid levels are “very different.” Research suggests that HDL in the CSF exhibits similar heterogeneity to plasma HDL, but these CSF lipoproteins present at 100-fold lower concentrations, compared to plasma HDL and have unique combinations of protein subpopulations. Lipidomics analysis studies show that these compartments “get very different readings, in terms of the predominant lipid disease state, and they are regulated differently from the way lipids in the periphery are regulated.”
In the brain, the cholesterol “needs to get shuttled from glial cells to neurons,” so defects in the transport process can disrupt overall brain homeostasis, said Dr. Mills. But since the brain system is separate from the peripheral system, measuring plasma lipids is more likely to point to cardiovascular risks, while changes reflected in CSF lipids are “more indicative of alteration in lipid homeostasis in the brain.”
HDL and Triglycerides: A Complicated Story
Dr. Mills noted that HDL in the periphery is “very complicated,” and the idea that HDL, as a measure on its own, is “necessarily ‘good’ isn’t particularly informative.” Rather, HDL is “extremely heterogeneous, very diverse, has different lipid compositions, different classes, and different modifications.” For example, like oxidized LDL, oxidized HDL is also “bad,” preventing the HDL from having protective functions.
Similarly, the apolipoproteins associated with HDL can affect the function of the HDL. “Our understanding of the HDL-like particles in the CNS is limited, but we do understand the APOE4 link,” Dr. Mills said. “It seems that the HDL-like particles containing APOE2 or APOE3 are larger and are more effective at transferring the lipids and cholesterol linked to them relative to APOE4-containing particles.”
Because HDL is more complex than simply being “good,” measuring HDL doesn’t “give you the full story,” said Dr. Mills. She speculates that this may be why there are studies suggesting that high levels of HDL might not have protective benefits and might even be detrimental. This makes it difficult to look at population studies, where the different subclasses of HDL are not necessarily captured in depth.
Dr. Mills pointed to another confounding factor, which is that much of the risk for the development of AD appears to be related to the interaction of HDL, LDL, and triglycerides. “When you look at each of these individually, you get a lot of heterogeneity, and it’s unclear what’s driving what,” she said.
An advantage of observational studies is that they give information about which of these markers are associated with trends and disease risks in specific groups vs others.
“For example, higher levels of triglycerides are associated with cardiovascular risk more in women, relative to men,” she said. And the triglyceride-to-HDL ratio seems “particularly robust” as a measure of cardiovascular health and risk.
The interpretation of associations with triglycerides can be “tricky” and “confusing” because results differ so much between studies, she said. “There are differences between middle age and older age, which have to do with age-related changes in metabolism and lipid metabolism and not necessarily that the markers are indicating something different,” she said.
Some research has suggested that triglycerides may have a protective effect against dementia, noted Uma Naidoo, MD, director of nutritional and lifestyle psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, and director of nutritional psychiatry at MGH Academy.
This may be because the brain “runs mostly on energy from burning triglycerides,” suggested Dr. Naidoo, author of the books Calm Your Mind With Food and This Is Your Brain on Food.
In addition, having higher levels of triglycerides may be linked with having overall healthier behaviors, Dr. Naidoo told this news organization.
Dr. Mills said that in middle-aged individuals, high levels of LDL-C and triglycerides are “often indicative of more atherogenic particles and risk to cardiovascular health, which is a generally negative trajectory. But in older individuals, things become more complicated because there are differences in terms of clearance of some of these particles, tissue clearance and distribution, and nutrient status. So for older individuals, it seems that fluctuations in either direction—either too high or too low—tend to be more informative that some overall dysregulation is going on the system.”
She emphasized that, in this “emerging area, looking at only one or two studies is confusing. But if you look at the spectrum of studies, you can see a pattern, which is that the regulation gets ‘off,’ as people age.”
The Potential Role of Statins
Dr. Mills speculated that there may be “neuroprotective benefits for some of the statins which appear to be related to cardiovascular benefits. But at this point, we don’t have any clear data whether statins actually directly impact brain cholesterol, since it’s a separate pool.”
They could help “by increasing blood flow and reducing narrowing of the arteries, but any direct impact on the brain is still under investigation.”
Dr. Hansen pointed to research suggesting statins taken at midlife appear to be cardioprotective and may be protective of brain health as well, whereas statins initiated in older age do not appear to have these benefits.
He speculated that one reason statins seem less helpful when initiated later in life is that the BBB has already been damaged by systemic inflammation in the periphery, and the neuroinflammatory process resulting in neuronal destruction is already underway. “I think statins aren’t going to fix that problem, so although lowering cholesterol can be helpful in some respects, it might be too late to affect cognition because the nerves have already died and won’t grow back.”
Can Dietary Approaches Help?
Dr. Naidoo said that when looking at neurologic and psychiatric disease, “it’s important to think about the ‘long game’ — how can we improve our blood and cardiovascular health earlier in life to help potentiate healthy aging?”
From a nutritional psychiatry standpoint, Dr. Naidoo focuses on nourishing the gut microbiome and decreasing inflammation. “A healthy and balanced microbiome supports cognition, while the composition of gut bacteria is actually drastically different in patients with neurological diseases, such as AD.”
She recommends a nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory diet including probiotic-rich foods (such as kimchi, sauerkraut, plain yogurt, and miso). Moreover, “the quality and structure of our fatty acids may be relevant as well: Increasing our intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids and avoiding processed fats like trans fats and hydrogenated oils may benefit our overall brain health.”
Dr. Naidoo recommends extra-virgin olive oil as a source of healthy fat. Its consumption is linked to lower incidence of AD by way of encouraging autophagy, which she calls “our own process of “cellular cleanup.’”
Dr. Naidoo believes that clinicians’ guidance to patients should “focus on healthy nutrition and other lifestyle practices, such as exercise, outdoor time, good sleep, and stress reduction.”
Dr. Mills notes the importance of omega-3 fatty acids, such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) , for brain health. “DHA is a major lipid component of neuronal membranes,” she said. “Because of inefficiencies in metabolism with APOE4, people tend to metabolize more of the lipids on the membranes themselves, so they have higher lipid membrane turnover and a greater need to supplement. Supplementing particularly through diet, with foods such as fatty fish rich in omega-3, can help boost the levels to help keep neuronal membranes intact.”
What This Means for the Clinician
“At this point, we see all of these associations between lipids and dementia, but we haven’t worked out exactly what it means on the individual level for an individual patient,” said Dr. Mills. Certainly, the picture is complex, and the understanding is growing and shifting. “The clinical applications remain unclear.”
One potential clinical take-home is that clinicians might consider tracking lipid levels over time. “If you follow a patient and see an increase or decrease [in lipid levels], that can be informative.” Looking at ratios of lipids might be more useful than looking only at a change in a single measure. “If you see trends in a variety of measures that track with one another, it might be more of a sign that something is potentially wrong.”
Whether the patient should first try a lifestyle intervention or might need medication is a “personalized clinical decision, depending on the individual, their risk factors, and how their levels are going,” said Dr. Mills.
Dr. Mills, Dr. Hansen, and Dr. Naidoo declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The relationship between lipid levels and the development of dementia is an evolving but confusing landscape.
“This is an incredibly complex area, and there really isn’t a clear consensus on this subject because different lipid classes reflect different things,” according to Betsy Mills, PhD, assistant director of aging and Alzheimer’s prevention at the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation.
Some studies suggest that excessive lipid levels may increase the risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Others imply that elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol or even triglycerides may offer some protection against subsequent dementia whereas higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, hitherto thought to be protective, may have a deleterious effect.
“It depends on what lipids you’re measuring, what you’re using to measure those lipids, what age the person is, and multiple other factors,” Dr. Mills told this news organization.
Teasing out the variables and potential mechanisms for the association between lipids and dementia risk necessitates understanding the role that lipids play in the healthy brain, the negative impact of brain lipid dysregulation, and the interplay between cholesterol in the central nervous system (CNS) and the cholesterol in the rest of the body.
Beyond Amyloid
The role of lipids in AD risk has historically been “overlooked,” says Scott Hansen, PhD, associate professor, Department of Molecular Medicine, Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation and Technology, Florida.
“The common narrative is that amyloid is the culprit in AD and certainly that’s the case in familial AD,” he told this news organization. “It’s been assumed that because amyloid deposits are also found in the brains of people with late-onset AD — which is the vast majority of cases — amyloid is the cause, but that’s not clear at all.”
The “limited clinical success” of aducanumab, its “extremely small efficacy” — despite its obvious success in eradicating the amyloid plaques — suggests there’s “much more to the story than amyloid.”
He and a growing community of scientists recognize the role of inflammation and lipids. “The major finding of my lab is that cholesterol actually drives the synthesis of amyloid via inflammation. In other words, amyloid is downstream of cholesterol. Cholesterol drives the inflammation, and the inflammation drives amyloid,” he said.
‘Lipid Invasion Model’
Because the brain is an incredibly lipid-rich organ, Dr. Mills said that “any dysregulation in lipid homeostasis will impact the brain because cholesterol is needed for the myelin sheaths, cell membranes, and other functions.”
A healthy brain relies upon healthy lipid regulation, and “since the first description of AD over 100 years ago, the disease has been associated with altered lipids in the brain,” Dr. Hansen noted.
He cited the “ lipid invasion model” as a way of understanding brain lipid dysregulation. This hypothesis posits that AD is driven by external lipids that enter the brain as a result of damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
“Cholesterol in the brain and cholesterol in the periphery — meaning, in the rest of the body, outside the brain — are separate,” Dr. Hansen explained. “The brain produces its own cholesterol and keeps tight control of it.”
Under normal circumstances, cholesterol from the diet doesn’t enter the brain. “Each pool of cholesterol — in the brain and in the periphery — has its own distinct regulatory mechanisms, target cells, and transport mechanisms.”
When the BBB has been compromised, it becomes permeable, allowing LDL cholesterol to enter the brain, said Dr. Hansen. Then the brain’s own lipoproteins transport the invading cholesterol, allowing it to be taken up by neurons. In turn, this causes neuronal amyloid levels to rise, ultimately leading to the creation of amyloid-b plaques. It also plays a role in tau phosphorylation. Both are key features of AD pathology.
Elevated levels of cholesterol and other lipids have been found in amyloid plaques, Dr. Hansen noted. Moreover, studies of brains of patients with AD have pointed to BBB damage.
And the risk factors for AD overlap with the risk factors for damage to the BBB (such as, aging, brain trauma, hypertension, stress, sleep deprivation, smoking, excess alcohol, obesity, diabetes, and APOE4 genotype), according to the lipid invasion model paper cited by Dr. Hansen.
‘Chicken and Egg’
“There is a strong link between the brain and the heart, and we know that cardiovascular risk factors have an overlap with dementia risk factors — especially vascular dementia,” said Dr. Mills.
She explained that an atherogenic lipid profile results in narrowing of the arteries, with less blood reaching the brain. “This can lead to stress in the brain, which drives inflammation and pathology.”
But cholesterol itself plays an important role in inflammation, Dr. Hansen said. In the periphery, it is “part of an integral response to tissue damage and infection.”
In the brain, once cholesterol is synthesized by the astrocytes, it is transported to neurons via the apolipoprotein E (APOE) protein, which plays a role in brain cholesterol homeostasis, Dr. Mills explained. Those with the ε4 allele of APOE (APOE4) tend to have faultier transport and storage of lipids in the brain, relative to the other APOE variants.
It’s known that individuals with APOE4 are particularly vulnerable to late-onset AD, Dr. Hansen observed. By contrast, APOE2 has a more protective effect. “Most people have APOE3, which is ‘in between,’ ” he said.
When there is neuronal uptake of “invading cholesterol,” not only is amyloid produced but also neuroinflammatory cytokines, further driving inflammation. A vicious cycle ensues: Cholesterol induces cytokine release; and cytokine release, in turn, induces cholesterol synthesis — which “suggests an autocatalytic function of cholesterol in the escalation of inflammation,” Dr. Hansen suggested. He noted that permeability of the BBB also allows inflammatory cytokines from elsewhere in the body to invade the brain, further driving inflammation.
Dr. Mills elaborated: “We know that generally, in dementia, there appear to be some changes in cholesterol metabolism in the brain, but it’s a chicken-and-egg question. We know that as the disease progresses, neurons are dying and getting remodeled. Do these changes have to do with the degenerative process, or are the changes in the cholesterol metabolism actually driving the degenerative disease process? It’s probably a combination, but it’s unclear at this point.”
Lipids in Plasma vs CSF
Dr. Mills explained that HDL particles in the brain differ from those in the periphery. “In the CNS, you have ‘HDL-like particles,’ which are similar in size and composition [to HDL in the periphery] but aren’t the same particles.” The brain itself generates HDL-like lipoproteins, which are produced by astrocytes and other glial cells and found in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Dyslipidemia in the periphery can be a marker for cardiovascular pathology. In the brain, “it can be an indication that there is active damage going on, depending on which compartment you’re looking at.”
She noted that plasma lipid levels and brain CSF lipid levels are “very different.” Research suggests that HDL in the CSF exhibits similar heterogeneity to plasma HDL, but these CSF lipoproteins present at 100-fold lower concentrations, compared to plasma HDL and have unique combinations of protein subpopulations. Lipidomics analysis studies show that these compartments “get very different readings, in terms of the predominant lipid disease state, and they are regulated differently from the way lipids in the periphery are regulated.”
In the brain, the cholesterol “needs to get shuttled from glial cells to neurons,” so defects in the transport process can disrupt overall brain homeostasis, said Dr. Mills. But since the brain system is separate from the peripheral system, measuring plasma lipids is more likely to point to cardiovascular risks, while changes reflected in CSF lipids are “more indicative of alteration in lipid homeostasis in the brain.”
HDL and Triglycerides: A Complicated Story
Dr. Mills noted that HDL in the periphery is “very complicated,” and the idea that HDL, as a measure on its own, is “necessarily ‘good’ isn’t particularly informative.” Rather, HDL is “extremely heterogeneous, very diverse, has different lipid compositions, different classes, and different modifications.” For example, like oxidized LDL, oxidized HDL is also “bad,” preventing the HDL from having protective functions.
Similarly, the apolipoproteins associated with HDL can affect the function of the HDL. “Our understanding of the HDL-like particles in the CNS is limited, but we do understand the APOE4 link,” Dr. Mills said. “It seems that the HDL-like particles containing APOE2 or APOE3 are larger and are more effective at transferring the lipids and cholesterol linked to them relative to APOE4-containing particles.”
Because HDL is more complex than simply being “good,” measuring HDL doesn’t “give you the full story,” said Dr. Mills. She speculates that this may be why there are studies suggesting that high levels of HDL might not have protective benefits and might even be detrimental. This makes it difficult to look at population studies, where the different subclasses of HDL are not necessarily captured in depth.
Dr. Mills pointed to another confounding factor, which is that much of the risk for the development of AD appears to be related to the interaction of HDL, LDL, and triglycerides. “When you look at each of these individually, you get a lot of heterogeneity, and it’s unclear what’s driving what,” she said.
An advantage of observational studies is that they give information about which of these markers are associated with trends and disease risks in specific groups vs others.
“For example, higher levels of triglycerides are associated with cardiovascular risk more in women, relative to men,” she said. And the triglyceride-to-HDL ratio seems “particularly robust” as a measure of cardiovascular health and risk.
The interpretation of associations with triglycerides can be “tricky” and “confusing” because results differ so much between studies, she said. “There are differences between middle age and older age, which have to do with age-related changes in metabolism and lipid metabolism and not necessarily that the markers are indicating something different,” she said.
Some research has suggested that triglycerides may have a protective effect against dementia, noted Uma Naidoo, MD, director of nutritional and lifestyle psychiatry, Massachusetts General Hospital, and director of nutritional psychiatry at MGH Academy.
This may be because the brain “runs mostly on energy from burning triglycerides,” suggested Dr. Naidoo, author of the books Calm Your Mind With Food and This Is Your Brain on Food.
In addition, having higher levels of triglycerides may be linked with having overall healthier behaviors, Dr. Naidoo told this news organization.
Dr. Mills said that in middle-aged individuals, high levels of LDL-C and triglycerides are “often indicative of more atherogenic particles and risk to cardiovascular health, which is a generally negative trajectory. But in older individuals, things become more complicated because there are differences in terms of clearance of some of these particles, tissue clearance and distribution, and nutrient status. So for older individuals, it seems that fluctuations in either direction—either too high or too low—tend to be more informative that some overall dysregulation is going on the system.”
She emphasized that, in this “emerging area, looking at only one or two studies is confusing. But if you look at the spectrum of studies, you can see a pattern, which is that the regulation gets ‘off,’ as people age.”
The Potential Role of Statins
Dr. Mills speculated that there may be “neuroprotective benefits for some of the statins which appear to be related to cardiovascular benefits. But at this point, we don’t have any clear data whether statins actually directly impact brain cholesterol, since it’s a separate pool.”
They could help “by increasing blood flow and reducing narrowing of the arteries, but any direct impact on the brain is still under investigation.”
Dr. Hansen pointed to research suggesting statins taken at midlife appear to be cardioprotective and may be protective of brain health as well, whereas statins initiated in older age do not appear to have these benefits.
He speculated that one reason statins seem less helpful when initiated later in life is that the BBB has already been damaged by systemic inflammation in the periphery, and the neuroinflammatory process resulting in neuronal destruction is already underway. “I think statins aren’t going to fix that problem, so although lowering cholesterol can be helpful in some respects, it might be too late to affect cognition because the nerves have already died and won’t grow back.”
Can Dietary Approaches Help?
Dr. Naidoo said that when looking at neurologic and psychiatric disease, “it’s important to think about the ‘long game’ — how can we improve our blood and cardiovascular health earlier in life to help potentiate healthy aging?”
From a nutritional psychiatry standpoint, Dr. Naidoo focuses on nourishing the gut microbiome and decreasing inflammation. “A healthy and balanced microbiome supports cognition, while the composition of gut bacteria is actually drastically different in patients with neurological diseases, such as AD.”
She recommends a nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory diet including probiotic-rich foods (such as kimchi, sauerkraut, plain yogurt, and miso). Moreover, “the quality and structure of our fatty acids may be relevant as well: Increasing our intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids and avoiding processed fats like trans fats and hydrogenated oils may benefit our overall brain health.”
Dr. Naidoo recommends extra-virgin olive oil as a source of healthy fat. Its consumption is linked to lower incidence of AD by way of encouraging autophagy, which she calls “our own process of “cellular cleanup.’”
Dr. Naidoo believes that clinicians’ guidance to patients should “focus on healthy nutrition and other lifestyle practices, such as exercise, outdoor time, good sleep, and stress reduction.”
Dr. Mills notes the importance of omega-3 fatty acids, such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) , for brain health. “DHA is a major lipid component of neuronal membranes,” she said. “Because of inefficiencies in metabolism with APOE4, people tend to metabolize more of the lipids on the membranes themselves, so they have higher lipid membrane turnover and a greater need to supplement. Supplementing particularly through diet, with foods such as fatty fish rich in omega-3, can help boost the levels to help keep neuronal membranes intact.”
What This Means for the Clinician
“At this point, we see all of these associations between lipids and dementia, but we haven’t worked out exactly what it means on the individual level for an individual patient,” said Dr. Mills. Certainly, the picture is complex, and the understanding is growing and shifting. “The clinical applications remain unclear.”
One potential clinical take-home is that clinicians might consider tracking lipid levels over time. “If you follow a patient and see an increase or decrease [in lipid levels], that can be informative.” Looking at ratios of lipids might be more useful than looking only at a change in a single measure. “If you see trends in a variety of measures that track with one another, it might be more of a sign that something is potentially wrong.”
Whether the patient should first try a lifestyle intervention or might need medication is a “personalized clinical decision, depending on the individual, their risk factors, and how their levels are going,” said Dr. Mills.
Dr. Mills, Dr. Hansen, and Dr. Naidoo declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Transcranial Electrical Stimulation Effective for Insomnia
TOPLINE:
Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), a noninvasive technique that uses low-intensity electrical currents to modulate brain activity, is an effective intervention for treating chronic insomnia, especially in older people, results of a relatively large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blind study included 124 adults with chronic insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep and early morning awakening occurring at least three times a week over 3 or more months), mean age about 51 years, from two centers in China who were randomized to receive either tACS (active group) or sham tACS (control group).
- Patients underwent 20 40-minute sessions over 4 weeks; the tACS intervention involved positioning three electrodes on the scalp and applying a current of 15 mA at a frequency of 77.5 Hz, whereas the control group received no stimulation.
- Primary outcome measures included total score on the Chinese version of the self-report Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), sleep onset latency, total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency, sleep quality, and daily disturbances (such as fatigue and attention deficits).
- Secondary outcomes included Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), and Clinical Global Impression scale (including Clinical Global Impression Severity of Illness [CGI-SI], Clinical Global Impression Global Improvement [CGI-GI], and Clinical Global Impression Efficacy Index [CGI-EI]).
- As rates of chronic insomnia increase with age, researchers explored the influence of age on treatment benefits by dividing participants into two age groups (< 50 years and ≥ 50 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the 120 participants who completed the trial, tACS resulted in a statistically significant decrease in insomnia severity compared with the control group (estimated advantage [number of points on PSQI scale], 2.61; 95% CI, 1.47-3.75; P < .001).
- There were also statistically significant estimated advantages of tACS for TST (−0.65; 95% CI, −1.06 to −0.24; P = .002), sleep efficiency (1.05; 95% CI, 0.48-1.62; P < .001), sleep quality (0.82; 95% CI, 0.29-1.34; P = .003), and daily disturbances (0.91; 95% CI, 0.58-1.25; P < .001).
- tACS exhibited significant effects on CGI-SI (0.84; 95% CI, 0.38-1.30; P < .001), CGI-GI (0.74; 95% CI, 0.42-1.06; P < .001), and CGI-EI (−0.71; 95% CI, −1.02 to −0.39; P < .001) but not on total scores of HAMD and HAMA, possibly because of the relatively low baseline levels of depression and anxiety among study subjects, said the authors.
- In the older, but not younger, group, tACS treatment had a significant benefit in sleep quality, sleep efficiency, PSQI total score, CGI-SI, CGI-GI, and CGI-EI.
IN PRACTICE:
“These significant findings contribute substantially to promoting evidence-based practices and facilitating the development of innovative treatment strategies for chronic insomnia,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Xiaolin Zhu, Beijing Huilongguan Hospital, Peking University Huilongguan Clinical Medical School, Beijing, China, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The follow-up period was limited to 8 weeks, so longer follow-up studies are needed to explore the sustained effects of tACS on chronic insomnia. Severity of chronic insomnia was limited by using the self-report PSQI, and not objective measures of insomnia such as polysomnography and wrist actigraphy. The age of study subjects ranged from 22 to only 65 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), a noninvasive technique that uses low-intensity electrical currents to modulate brain activity, is an effective intervention for treating chronic insomnia, especially in older people, results of a relatively large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blind study included 124 adults with chronic insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep and early morning awakening occurring at least three times a week over 3 or more months), mean age about 51 years, from two centers in China who were randomized to receive either tACS (active group) or sham tACS (control group).
- Patients underwent 20 40-minute sessions over 4 weeks; the tACS intervention involved positioning three electrodes on the scalp and applying a current of 15 mA at a frequency of 77.5 Hz, whereas the control group received no stimulation.
- Primary outcome measures included total score on the Chinese version of the self-report Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), sleep onset latency, total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency, sleep quality, and daily disturbances (such as fatigue and attention deficits).
- Secondary outcomes included Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), and Clinical Global Impression scale (including Clinical Global Impression Severity of Illness [CGI-SI], Clinical Global Impression Global Improvement [CGI-GI], and Clinical Global Impression Efficacy Index [CGI-EI]).
- As rates of chronic insomnia increase with age, researchers explored the influence of age on treatment benefits by dividing participants into two age groups (< 50 years and ≥ 50 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the 120 participants who completed the trial, tACS resulted in a statistically significant decrease in insomnia severity compared with the control group (estimated advantage [number of points on PSQI scale], 2.61; 95% CI, 1.47-3.75; P < .001).
- There were also statistically significant estimated advantages of tACS for TST (−0.65; 95% CI, −1.06 to −0.24; P = .002), sleep efficiency (1.05; 95% CI, 0.48-1.62; P < .001), sleep quality (0.82; 95% CI, 0.29-1.34; P = .003), and daily disturbances (0.91; 95% CI, 0.58-1.25; P < .001).
- tACS exhibited significant effects on CGI-SI (0.84; 95% CI, 0.38-1.30; P < .001), CGI-GI (0.74; 95% CI, 0.42-1.06; P < .001), and CGI-EI (−0.71; 95% CI, −1.02 to −0.39; P < .001) but not on total scores of HAMD and HAMA, possibly because of the relatively low baseline levels of depression and anxiety among study subjects, said the authors.
- In the older, but not younger, group, tACS treatment had a significant benefit in sleep quality, sleep efficiency, PSQI total score, CGI-SI, CGI-GI, and CGI-EI.
IN PRACTICE:
“These significant findings contribute substantially to promoting evidence-based practices and facilitating the development of innovative treatment strategies for chronic insomnia,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Xiaolin Zhu, Beijing Huilongguan Hospital, Peking University Huilongguan Clinical Medical School, Beijing, China, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The follow-up period was limited to 8 weeks, so longer follow-up studies are needed to explore the sustained effects of tACS on chronic insomnia. Severity of chronic insomnia was limited by using the self-report PSQI, and not objective measures of insomnia such as polysomnography and wrist actigraphy. The age of study subjects ranged from 22 to only 65 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), a noninvasive technique that uses low-intensity electrical currents to modulate brain activity, is an effective intervention for treating chronic insomnia, especially in older people, results of a relatively large study suggested.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blind study included 124 adults with chronic insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep and early morning awakening occurring at least three times a week over 3 or more months), mean age about 51 years, from two centers in China who were randomized to receive either tACS (active group) or sham tACS (control group).
- Patients underwent 20 40-minute sessions over 4 weeks; the tACS intervention involved positioning three electrodes on the scalp and applying a current of 15 mA at a frequency of 77.5 Hz, whereas the control group received no stimulation.
- Primary outcome measures included total score on the Chinese version of the self-report Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), sleep onset latency, total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency, sleep quality, and daily disturbances (such as fatigue and attention deficits).
- Secondary outcomes included Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), and Clinical Global Impression scale (including Clinical Global Impression Severity of Illness [CGI-SI], Clinical Global Impression Global Improvement [CGI-GI], and Clinical Global Impression Efficacy Index [CGI-EI]).
- As rates of chronic insomnia increase with age, researchers explored the influence of age on treatment benefits by dividing participants into two age groups (< 50 years and ≥ 50 years).
TAKEAWAY:
- Among the 120 participants who completed the trial, tACS resulted in a statistically significant decrease in insomnia severity compared with the control group (estimated advantage [number of points on PSQI scale], 2.61; 95% CI, 1.47-3.75; P < .001).
- There were also statistically significant estimated advantages of tACS for TST (−0.65; 95% CI, −1.06 to −0.24; P = .002), sleep efficiency (1.05; 95% CI, 0.48-1.62; P < .001), sleep quality (0.82; 95% CI, 0.29-1.34; P = .003), and daily disturbances (0.91; 95% CI, 0.58-1.25; P < .001).
- tACS exhibited significant effects on CGI-SI (0.84; 95% CI, 0.38-1.30; P < .001), CGI-GI (0.74; 95% CI, 0.42-1.06; P < .001), and CGI-EI (−0.71; 95% CI, −1.02 to −0.39; P < .001) but not on total scores of HAMD and HAMA, possibly because of the relatively low baseline levels of depression and anxiety among study subjects, said the authors.
- In the older, but not younger, group, tACS treatment had a significant benefit in sleep quality, sleep efficiency, PSQI total score, CGI-SI, CGI-GI, and CGI-EI.
IN PRACTICE:
“These significant findings contribute substantially to promoting evidence-based practices and facilitating the development of innovative treatment strategies for chronic insomnia,” the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Xiaolin Zhu, Beijing Huilongguan Hospital, Peking University Huilongguan Clinical Medical School, Beijing, China, and colleagues. It was published online in the Journal of Psychiatric Research.
LIMITATIONS:
The follow-up period was limited to 8 weeks, so longer follow-up studies are needed to explore the sustained effects of tACS on chronic insomnia. Severity of chronic insomnia was limited by using the self-report PSQI, and not objective measures of insomnia such as polysomnography and wrist actigraphy. The age of study subjects ranged from 22 to only 65 years.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Panel Recommends Small Bump in 2025 Medicare Physician Pay
An influential panel is seeking an increase in Medicare’s 2025 payments for clinicians, adding to pressure on Congress to reconsider how the largest US purchaser of health services pays for office visits and related care of the nation’s older citizens and those with disabilities.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) on Thursday voted unanimously in favor of a two-part recommendation on changes to the 2025 physician fee schedule:
- An increase in the base rate equal to half of the projected change in the Medicare Economic Index (MEI). Recent estimates have projected a 2.6% increase in MEI for 2025, which is intended to show how inflation affects the costs of running a medical practice.
- The creation of a safety-net add-on payment under the physician fee schedule to cover care of people with low incomes.
These recommendations echo the calls MedPAC made in a 2023 report to Congress.
Lawmakers and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) rely on MedPAC’s work in deciding how much to pay for services. About 1.3 million clinicians bill Medicare for their work, including about 670,000 physicians.
Thursday’s MedPAC vote comes amid continuing uncertainty about how much the federal government will actually pay clinicians this year through the physician fee schedule.
There are serious efforts underway to undo cuts already demanded by previously passed federal law. In an email, Rep. Larry Buchson, MD, (R-IN) said he remains committed to “eliminating the full 3.37% cut this year while also working toward a permanent solution to halt the downward spiral of physician reimbursement.”
“The Medicare payment cut to physicians will impede patients’ access to care and further accelerate the current path toward consolidation, physician burnout, and closure of medical practices,” Buchson told this news organization. “It’s past time that Congress provides much needed and deserved stability for America’s doctors.”
Congress this month is attempting to complete overdue budget legislation needed to fund federal operations for fiscal 2024, which began October 1, 2023. The pending expiration of a short-term stopgap continuing resolution could provide a vehicle that could also carry legislation that would address the physician fee schedule.
In a Thursday statement, Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, commended MedPAC for its recommendations and urged lawmakers to act.
“Long-term reforms from Congress are overdue to close the unsustainable gap between what Medicare pays physicians and the actual costs of delivering high-quality care,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “When adjusted for inflation in practice costs, Medicare physician pay declined 26% from 2001 to 2023.”
Continual Struggles
Congress has struggled for years in its attempts to set Medicare payments for office visits and other services covered by the physician fee schedule. A 1990s budget law set the stage for what proved to be untenable reductions in payment through the sustainable growth rate mechanism.
Between 2003 through April 2014, lawmakers passed “doc-fix” legislation 17 times to block the slated cuts, according to the Congressional Research Service. In 2015, Congress passed an intended overhaul of the physician fee schedule through the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA). As part of this law, Congress eliminated a base automatic inflation adjuster for the physician fee schedule.
In recent years, Congress has acted repeatedly to address MACRA’s mandates for flat base pay. MedPAC and members of both parties in Congress have called for a broad new look at how Medicare pays physicians.
At Thursday’s meeting, MedPAC member Lawrence Casalino, MD, PhD, MPH, noted that the struggles to keep up with inflation and the “unpredictability of what the payment rates are going to be from year to year really do affect physician morale.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An influential panel is seeking an increase in Medicare’s 2025 payments for clinicians, adding to pressure on Congress to reconsider how the largest US purchaser of health services pays for office visits and related care of the nation’s older citizens and those with disabilities.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) on Thursday voted unanimously in favor of a two-part recommendation on changes to the 2025 physician fee schedule:
- An increase in the base rate equal to half of the projected change in the Medicare Economic Index (MEI). Recent estimates have projected a 2.6% increase in MEI for 2025, which is intended to show how inflation affects the costs of running a medical practice.
- The creation of a safety-net add-on payment under the physician fee schedule to cover care of people with low incomes.
These recommendations echo the calls MedPAC made in a 2023 report to Congress.
Lawmakers and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) rely on MedPAC’s work in deciding how much to pay for services. About 1.3 million clinicians bill Medicare for their work, including about 670,000 physicians.
Thursday’s MedPAC vote comes amid continuing uncertainty about how much the federal government will actually pay clinicians this year through the physician fee schedule.
There are serious efforts underway to undo cuts already demanded by previously passed federal law. In an email, Rep. Larry Buchson, MD, (R-IN) said he remains committed to “eliminating the full 3.37% cut this year while also working toward a permanent solution to halt the downward spiral of physician reimbursement.”
“The Medicare payment cut to physicians will impede patients’ access to care and further accelerate the current path toward consolidation, physician burnout, and closure of medical practices,” Buchson told this news organization. “It’s past time that Congress provides much needed and deserved stability for America’s doctors.”
Congress this month is attempting to complete overdue budget legislation needed to fund federal operations for fiscal 2024, which began October 1, 2023. The pending expiration of a short-term stopgap continuing resolution could provide a vehicle that could also carry legislation that would address the physician fee schedule.
In a Thursday statement, Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, commended MedPAC for its recommendations and urged lawmakers to act.
“Long-term reforms from Congress are overdue to close the unsustainable gap between what Medicare pays physicians and the actual costs of delivering high-quality care,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “When adjusted for inflation in practice costs, Medicare physician pay declined 26% from 2001 to 2023.”
Continual Struggles
Congress has struggled for years in its attempts to set Medicare payments for office visits and other services covered by the physician fee schedule. A 1990s budget law set the stage for what proved to be untenable reductions in payment through the sustainable growth rate mechanism.
Between 2003 through April 2014, lawmakers passed “doc-fix” legislation 17 times to block the slated cuts, according to the Congressional Research Service. In 2015, Congress passed an intended overhaul of the physician fee schedule through the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA). As part of this law, Congress eliminated a base automatic inflation adjuster for the physician fee schedule.
In recent years, Congress has acted repeatedly to address MACRA’s mandates for flat base pay. MedPAC and members of both parties in Congress have called for a broad new look at how Medicare pays physicians.
At Thursday’s meeting, MedPAC member Lawrence Casalino, MD, PhD, MPH, noted that the struggles to keep up with inflation and the “unpredictability of what the payment rates are going to be from year to year really do affect physician morale.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An influential panel is seeking an increase in Medicare’s 2025 payments for clinicians, adding to pressure on Congress to reconsider how the largest US purchaser of health services pays for office visits and related care of the nation’s older citizens and those with disabilities.
The Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) on Thursday voted unanimously in favor of a two-part recommendation on changes to the 2025 physician fee schedule:
- An increase in the base rate equal to half of the projected change in the Medicare Economic Index (MEI). Recent estimates have projected a 2.6% increase in MEI for 2025, which is intended to show how inflation affects the costs of running a medical practice.
- The creation of a safety-net add-on payment under the physician fee schedule to cover care of people with low incomes.
These recommendations echo the calls MedPAC made in a 2023 report to Congress.
Lawmakers and the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) rely on MedPAC’s work in deciding how much to pay for services. About 1.3 million clinicians bill Medicare for their work, including about 670,000 physicians.
Thursday’s MedPAC vote comes amid continuing uncertainty about how much the federal government will actually pay clinicians this year through the physician fee schedule.
There are serious efforts underway to undo cuts already demanded by previously passed federal law. In an email, Rep. Larry Buchson, MD, (R-IN) said he remains committed to “eliminating the full 3.37% cut this year while also working toward a permanent solution to halt the downward spiral of physician reimbursement.”
“The Medicare payment cut to physicians will impede patients’ access to care and further accelerate the current path toward consolidation, physician burnout, and closure of medical practices,” Buchson told this news organization. “It’s past time that Congress provides much needed and deserved stability for America’s doctors.”
Congress this month is attempting to complete overdue budget legislation needed to fund federal operations for fiscal 2024, which began October 1, 2023. The pending expiration of a short-term stopgap continuing resolution could provide a vehicle that could also carry legislation that would address the physician fee schedule.
In a Thursday statement, Jesse M. Ehrenfeld, MD, MPH, president of the American Medical Association, commended MedPAC for its recommendations and urged lawmakers to act.
“Long-term reforms from Congress are overdue to close the unsustainable gap between what Medicare pays physicians and the actual costs of delivering high-quality care,” Dr. Ehrenfeld said. “When adjusted for inflation in practice costs, Medicare physician pay declined 26% from 2001 to 2023.”
Continual Struggles
Congress has struggled for years in its attempts to set Medicare payments for office visits and other services covered by the physician fee schedule. A 1990s budget law set the stage for what proved to be untenable reductions in payment through the sustainable growth rate mechanism.
Between 2003 through April 2014, lawmakers passed “doc-fix” legislation 17 times to block the slated cuts, according to the Congressional Research Service. In 2015, Congress passed an intended overhaul of the physician fee schedule through the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA). As part of this law, Congress eliminated a base automatic inflation adjuster for the physician fee schedule.
In recent years, Congress has acted repeatedly to address MACRA’s mandates for flat base pay. MedPAC and members of both parties in Congress have called for a broad new look at how Medicare pays physicians.
At Thursday’s meeting, MedPAC member Lawrence Casalino, MD, PhD, MPH, noted that the struggles to keep up with inflation and the “unpredictability of what the payment rates are going to be from year to year really do affect physician morale.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Do Plant-based Psychedelics Offer a New Option for TBI Treatment?
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Oneirogens are substances that produce or enhance dreamlike states of consciousness—could one of those, ibogaine, be key to relieving the sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in veterans?
An extract from the root bark of Tabernanthe iboga, an African shrub, ibogaine has both pharmacological and psychological effects. Acting on opioid receptors and the serotonin and dopamine systems, it can relieve withdrawal symptoms and reduce drug cravings—reportedly, often, in just a few hours—and reduce the risk of regular use. The results can last for weeks, months, or sometimes longer.
In the US, ibogaine is a Schedule I drug. Few controlled studies of ibogaine are available; most data come from anecdotal reports and case studies. Clinical research into ibogaine stalled due to legal restrictions that come with a Schedule I drug, as well as concerns about possible cardiac consequences. For example, some reports have described QT interval prolongation, with instances of subsequent fatal arrhythmia.
That may change now, with findings from the Magnesium–Ibogaine: the Stanford Traumatic Injury to the CNS protocol (MISTIC), which took place at a treatment center in Mexico. Researchers from Stanford School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System combined prophylactic intravenous magnesium with ibogaine, in hopes of mitigating the cardiac risks. Magnesium supplementation has been shown to protect against QT interval prolongation when coadministered with medications that ordinarily would have such an effect.
The researchers studied 30 male Special Operations Forces veterans (SOVs) who had predominantly mild TBI. Of those, 15 participants met the criteria for major depressive disorder, 14 for an anxiety disorder, and 23 for PTSD; 19 had past suicidal ideation and 7 had attempted suicide.
Special Operations Forces, the researchers note, are “deployed at a greater pace and to higher intensity combat than conventional military, exposing them to greater allostatic load and risk of injury, including from blast exposure.” This, they say, may result in a “unique pattern” of physical, cognitive, behavioral, psychiatric, and endocrine-related problems across several domains.
Participants received a mean (SD) of 12.1 (1.2) mg kg-1 of oral ibogaine. The researchers assessed changes in the World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule at baseline, immediately after treatment, and 1 month after treatment. They also assessed changes in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
The treatment significantly improved functioning both immediately and at 1 month after treatment and PTSD, depression, and anxiety at 1 month after treatment. There were no unexpected or serious treatment-emergent adverse effects, nor were there instances of bradycardia, tachycardia, clinically meaningful QT prolongation, or hemodynamic instability. All participants experienced transient cerebellar signs, such as mild ataxia and intention tremor, that resolved within 24 hours. While experiencing oneirogenic effects, 12 participants were treated for headache, 7 for nausea, 3 for anxiety, 2 for hypertension, and 1 for insomnia.
At 1 month, suicidal ideation had declined from 47% to 7%—a statistically significant change. “Given the alarming rates of suicide in veterans, as well as evidence that military-related TBI increases the risk of suicide,” the researchers say, “the substantial reduction in SI that we observed—which must be interpreted cautiously as an exploratory analysis—is noteworthy.” TBI also is associated with increased impulsivity, a well-known risk factor for suicide, they note. MISTIC resulted in a measurable improvement in cognitive inhibition.
Results of a neuropsychological battery indicated statistically significant improvements in processing speed and executive functioning (including inhibition, cognitive flexibility, problem-solving, phonemic fluency, and working memory), both immediately after treatment and at 1 month. No declines were noted across any performance domain.
Interestingly, mean performances on these tests moved from the average to the high average score range relative to same-age peers and, in all but one instance, phonemic fluency was high average at baseline and improved to the superior range relative to same-age peers at the 1-month follow-up. Learning and memory tests showed a significant improvement in visual memory and verbal memory. Sustained attention showed a significant improvement in accuracy (detection) and a weak but significant slowing of reaction time, consistent with a prioritization of accuracy over speed and reduced impulsivity.
In a Scientific American article, lead researcher Nolan Williams said he suspects the powerful effects of psychedelics have to do with their “profound ability to increase plasticity in the brain” by “bringing it back to a more juvenile state where reorganization can occur.” People often experience a life review that appears in their minds almost like a slideshow. “It somehow drives a particular sort of psychological phenomenon that you don’t achieve through guidance,” Williams said.
The data from the MISTIC trial in Mexico may spur more research in the US. The National Defense Authorization Act, signed by President Joe Biden last December, authorizes service members diagnosed with PTSD or TBI to take part in clinical studies of any “qualified plant-based alternative therapies.”
“It’s all really timely,” Williams said. “From my perspective, we should have some traction to make a strong argument that the risk-benefit is right.”
Lump in breast
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
Given clinical and imaging outcomes, as well as results on IHC assay, this patient is diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer and is referred for further consultation with a multidisciplinary care team.
Triple-negative breast cancer accounts for 15% of all female breast cancer cases. The term "triple-negative" refers to the absence of estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) targets and the HER2 target for treatment. Otherwise, triple-negative breast cancer is highly heterogeneous and includes multiple molecular subtypes. Typically, triple-negative breast cancer occurs in younger patients, has a higher grade, a greater tumor size, a higher clinical stage at diagnosis, and a poorer prognosis than non–triple-negative breast cancers.
Biopsy samples from patients with a new primary or newly metastatic breast cancer diagnosis should undergo HR testing, both ER and PR, as well as HER2 receptor testing. Results of ER and PR testing are negative if a validated IHC assay shows 0% to < 1% of nuclei stain, according to the latest American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) HR testing guideline. HER2 results are negative if a validated IHC assay shows weak to moderate complete membrane staining in < 10% of tumor cells, according to ASCO/CAP guidelines. If HER2 results of a primary tumor are negative and specific clinical criteria suggest further testing, the oncologist may choose to order another IHC assay or a validated dual probe in situ hybridization (ISH) assay to aid in clinical decision-making.
Pathologic classification of triple-negative breast cancers includes multiple subgroups determined by therapeutic possibilities: low-risk histologic types (salivary gland–like carcinomas, fibromatosis-like carcinoma, low-grade adenosquamous breast carcinoma), immune activation (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, CD8, programmed death–ligand 1, tumor mutational burden), HER2-low status (IHC score 1+/2+ nonamplified), associated germline BRCA mutations, and other targets (trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2, HER3).
Family history is the most common risk factor for developing breast cancer. If a person's mother or sister had breast cancer, the lifetime risk for that individual is four times greater than that of the general population. Risk for breast cancer grows even more if two or more first-degree relatives are diagnosed, or if one first-degree relative was diagnosed with breast cancer at ≤ 50 years of age. About 25% of triple-negative breast cancer cases have accompanying germline BRCA mutations. A recent study by Ahearn and colleagues found that 85 variants were linked to one or more tumor feature of ER-negative disease, and 32 of those variants were associated with triple-negative disease.
For a breast cancer diagnosis, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommends multidisciplinary care as well as the development of a personalized survivorship treatment plan, which includes a customized summary of possible long-term treatment toxicities. In addition, multidisciplinary care coordination encourages close follow-up that helps patients adhere to their medications and stay current with ongoing screening.
Because triple-negative breast cancer lacks HR and HER2 therapeutic targets, it can be difficult to treat. Standard therapy for high-risk triple-negative tumors includes chemotherapy with taxanes (paclitaxel or docetaxel) plus anthracycline-based treatment (cyclophosphamide plus doxorubicin). Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is recommended for patients with stage 2 and 3 tumors to reduce locoregional surgical extension and to allow for personalized treatment based on pathologic response. In 2018, two poly ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors, olaparib and talazoparib, were approved for use in select patients with triple-negative breast cancer, significantly changing the treatment paradigm for this disease. Other promising treatments have emerged recently in clinical trials for triple-negative disease, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors, and cytotoxin-conjugated antibodies.
Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, is Medical Director of Thoracic Oncology, St. Catherine of Siena Medical Center, Catholic Health Services, Smithtown, New York.
Dr. Schwartz serve(d) as a member of the following medical societies:
American College of Chest Physicians, American College of Surgeons, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, Western Thoracic Surgical Association.
Disclosure: Daniel S. Schwartz, MD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Image Quizzes are fictional or fictionalized clinical scenarios intended to provide evidence-based educational takeaways.
A 34-year-old woman visits her primary care physician after detecting a lump in her right breast. The physician conducts a physical exam and finds a hard, poorly mobile mass in the outer upper quadrant. Ultrasonography reveals an irregular hypoechoic mass of 22.1 x 15.1 mm with several abnormal axillary lymph nodes. MRI of the right breast shows an irregularly shaped and lobulated mass in the outer upper quadrant with enlarged axillary lymph nodes. On further radiologic examination, there is no detectable metastatic spread to the brain, chest, or upper abdomen. The patient undergoes a core needle biopsy of the tumor, which confirms ductal carcinoma and right axillary lymph node metastasis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay of the sample is negative for hormone receptor (HR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2).
Ozempic is Appealing, but Not Cost-Effective, for Obesity Treatment
, according to a modeling study that compared the drugs with surgery and endoscopy.
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) for moderate to severe (class II/III) obesity and the less invasive endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) for mild (class I) obesity were both cost effective strategies to reduce obesity, the researchers report.
“SG should be offered as the first-line treatment for class II and class III obesity,” write Monica Saumoy, MD, of the Center for Digestive Health, Penn Medicine Princeton Medical Center, Plainsboro, N.J., and coauthors. “ESG is an effective and cost-effective nonsurgical treatment for class I, class II and class III obesity, and more efforts are needed to ensure that patients have access to this procedure.
“While semaglutide is highly effective for weight loss, and there is substantial patient interest, it is not currently cost-effective due to its high cost,” they add. “With methods to reduce semaglutide’s annual cost, it may provide an effective and cost-effective method to reduce the morbidity related to obesity.”
The study was published in Gut.
Cost Concerns
One in two Americans will likely be obese by 2030, according to current models, and nearly one in four adults will be severely obese.
Several weight-loss therapies exist to treat obesity. Evidence shows bariatric surgery is effective in reducing weight, metabolic comorbidities, and mortality in people with obesity compared with lifestyle intervention alone, but surgery has risks, adverse events, and poor national uptake. Patients are likely more interested in less invasive options, the authors write.
Recent trials have reported effective weight loss from less invasive options. A five-year follow-up of the randomized controlled MERIT trial found that ESG was associated with a 13.6% total body weight loss for people with mild to moderate obesity.
On the pharmaceutical front, other randomized controlled trials have shown that semaglutide is linked with as much as 17% total body weight loss at two years. Also, recent guidance from the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) states that long-term treatment with a semaglutide is the preferred strategy for weight loss.
“However, concerns about the cost and the cost-effectiveness of these [less invasive] interventions have limited their usage in the USA,” the study authors write.
The aim of the study was to perform a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing SG, ESG, semaglutide, and lifestyle interventions (LI) for patients with obesity in class I (defined as BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2), class II (35-29.9 kg/m2), and class III (>40kg/m2) obesity.
Researchers used a state-transition, semi-Markov microsimulation model to analyze the effectiveness of ESG, SG, semaglutide, and LI in a simulated 40-year-old with three different base-case scenarios of class I, II, or III obesity. They then performed a detailed threshold and sensitivity analysis to change the cost of treatment modalities and the semaglutide adherence rate. Outcome measures included a willingness-to-pay threshold of US $100,000/quality-adjusted life years (QALY) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
Cost-Effectiveness of Treatments
When the treatment modalities were compared with each other, findings showed that for class I obesity, ESG was cost effective (US $4,105/QALY). For class II and III obesity, SG was cost-effective as well (US $5,883/QALY) and (US $7,821/QALY), respectively.
In all classes of obesity, SG and ESG were cost-effective compared with LI. Semaglutide was not cost-effective compared with LI for class I, II, and III obesity (ICER US $508,414/QALY, $420,483/QALY, and $350,637/QALY, respectively).
“For semaglutide to be cost-effective when compared with ESG, it would have to cost less than US $1,879 (class III), US $1,204 (class II), or US $297 (class I) annually,” the authors note.
The authors addressed recent guidelines to consider bariatric surgery in all obese patients. They recommend SG remain the standard of care for patients with severe obesity.
But national projections show that SG would address only 0.5% of life-years lost due to obesity.
“Barring a dramatic increase in patient adherence, bariatric surgery will not likely successfully mitigate the harm from the obesity epidemic,” they write.
“ESG may fill this gap and provide an additional option for patients with obesity as it demonstrated sustained weight loss at 2-5 years.” While insurance coverage is limited, they write, “our model demonstrates that payer coverage for ESG would provide an alternative tool to combat the obesity epidemic as part of a multidisciplinary approach.”
Semaglutide shows sustained weight loss in trials for up to two years but has a substantial annual cost, the authors note.
At lower prices, semaglutide can make a “major impact on the obesity pandemic as it can be prescribed in multiple healthcare settings and due to increased patient interested in non-invasive obesity treatment,” they write.
One limitation to the study is a lack of long-term data available for ESG and semaglutide. Authors were also not able to use a lifetime horizon because of a lack of long-term weight loss.
One study author reports financial relationships with BSC, Cook Medical, Surgical Intuitive, and Olympus America. Another author reports relationships with ACI, AGA-Varia, BSC, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, Medtronic, Olympus, Virgo Systems; equity: AGA-Varia, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, EndoSound, and Virgo Systems. The rest of the authors have no conflicts to disclose.
, according to a modeling study that compared the drugs with surgery and endoscopy.
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) for moderate to severe (class II/III) obesity and the less invasive endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) for mild (class I) obesity were both cost effective strategies to reduce obesity, the researchers report.
“SG should be offered as the first-line treatment for class II and class III obesity,” write Monica Saumoy, MD, of the Center for Digestive Health, Penn Medicine Princeton Medical Center, Plainsboro, N.J., and coauthors. “ESG is an effective and cost-effective nonsurgical treatment for class I, class II and class III obesity, and more efforts are needed to ensure that patients have access to this procedure.
“While semaglutide is highly effective for weight loss, and there is substantial patient interest, it is not currently cost-effective due to its high cost,” they add. “With methods to reduce semaglutide’s annual cost, it may provide an effective and cost-effective method to reduce the morbidity related to obesity.”
The study was published in Gut.
Cost Concerns
One in two Americans will likely be obese by 2030, according to current models, and nearly one in four adults will be severely obese.
Several weight-loss therapies exist to treat obesity. Evidence shows bariatric surgery is effective in reducing weight, metabolic comorbidities, and mortality in people with obesity compared with lifestyle intervention alone, but surgery has risks, adverse events, and poor national uptake. Patients are likely more interested in less invasive options, the authors write.
Recent trials have reported effective weight loss from less invasive options. A five-year follow-up of the randomized controlled MERIT trial found that ESG was associated with a 13.6% total body weight loss for people with mild to moderate obesity.
On the pharmaceutical front, other randomized controlled trials have shown that semaglutide is linked with as much as 17% total body weight loss at two years. Also, recent guidance from the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) states that long-term treatment with a semaglutide is the preferred strategy for weight loss.
“However, concerns about the cost and the cost-effectiveness of these [less invasive] interventions have limited their usage in the USA,” the study authors write.
The aim of the study was to perform a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing SG, ESG, semaglutide, and lifestyle interventions (LI) for patients with obesity in class I (defined as BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2), class II (35-29.9 kg/m2), and class III (>40kg/m2) obesity.
Researchers used a state-transition, semi-Markov microsimulation model to analyze the effectiveness of ESG, SG, semaglutide, and LI in a simulated 40-year-old with three different base-case scenarios of class I, II, or III obesity. They then performed a detailed threshold and sensitivity analysis to change the cost of treatment modalities and the semaglutide adherence rate. Outcome measures included a willingness-to-pay threshold of US $100,000/quality-adjusted life years (QALY) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
Cost-Effectiveness of Treatments
When the treatment modalities were compared with each other, findings showed that for class I obesity, ESG was cost effective (US $4,105/QALY). For class II and III obesity, SG was cost-effective as well (US $5,883/QALY) and (US $7,821/QALY), respectively.
In all classes of obesity, SG and ESG were cost-effective compared with LI. Semaglutide was not cost-effective compared with LI for class I, II, and III obesity (ICER US $508,414/QALY, $420,483/QALY, and $350,637/QALY, respectively).
“For semaglutide to be cost-effective when compared with ESG, it would have to cost less than US $1,879 (class III), US $1,204 (class II), or US $297 (class I) annually,” the authors note.
The authors addressed recent guidelines to consider bariatric surgery in all obese patients. They recommend SG remain the standard of care for patients with severe obesity.
But national projections show that SG would address only 0.5% of life-years lost due to obesity.
“Barring a dramatic increase in patient adherence, bariatric surgery will not likely successfully mitigate the harm from the obesity epidemic,” they write.
“ESG may fill this gap and provide an additional option for patients with obesity as it demonstrated sustained weight loss at 2-5 years.” While insurance coverage is limited, they write, “our model demonstrates that payer coverage for ESG would provide an alternative tool to combat the obesity epidemic as part of a multidisciplinary approach.”
Semaglutide shows sustained weight loss in trials for up to two years but has a substantial annual cost, the authors note.
At lower prices, semaglutide can make a “major impact on the obesity pandemic as it can be prescribed in multiple healthcare settings and due to increased patient interested in non-invasive obesity treatment,” they write.
One limitation to the study is a lack of long-term data available for ESG and semaglutide. Authors were also not able to use a lifetime horizon because of a lack of long-term weight loss.
One study author reports financial relationships with BSC, Cook Medical, Surgical Intuitive, and Olympus America. Another author reports relationships with ACI, AGA-Varia, BSC, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, Medtronic, Olympus, Virgo Systems; equity: AGA-Varia, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, EndoSound, and Virgo Systems. The rest of the authors have no conflicts to disclose.
, according to a modeling study that compared the drugs with surgery and endoscopy.
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) for moderate to severe (class II/III) obesity and the less invasive endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) for mild (class I) obesity were both cost effective strategies to reduce obesity, the researchers report.
“SG should be offered as the first-line treatment for class II and class III obesity,” write Monica Saumoy, MD, of the Center for Digestive Health, Penn Medicine Princeton Medical Center, Plainsboro, N.J., and coauthors. “ESG is an effective and cost-effective nonsurgical treatment for class I, class II and class III obesity, and more efforts are needed to ensure that patients have access to this procedure.
“While semaglutide is highly effective for weight loss, and there is substantial patient interest, it is not currently cost-effective due to its high cost,” they add. “With methods to reduce semaglutide’s annual cost, it may provide an effective and cost-effective method to reduce the morbidity related to obesity.”
The study was published in Gut.
Cost Concerns
One in two Americans will likely be obese by 2030, according to current models, and nearly one in four adults will be severely obese.
Several weight-loss therapies exist to treat obesity. Evidence shows bariatric surgery is effective in reducing weight, metabolic comorbidities, and mortality in people with obesity compared with lifestyle intervention alone, but surgery has risks, adverse events, and poor national uptake. Patients are likely more interested in less invasive options, the authors write.
Recent trials have reported effective weight loss from less invasive options. A five-year follow-up of the randomized controlled MERIT trial found that ESG was associated with a 13.6% total body weight loss for people with mild to moderate obesity.
On the pharmaceutical front, other randomized controlled trials have shown that semaglutide is linked with as much as 17% total body weight loss at two years. Also, recent guidance from the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) states that long-term treatment with a semaglutide is the preferred strategy for weight loss.
“However, concerns about the cost and the cost-effectiveness of these [less invasive] interventions have limited their usage in the USA,” the study authors write.
The aim of the study was to perform a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing SG, ESG, semaglutide, and lifestyle interventions (LI) for patients with obesity in class I (defined as BMI 30-34.9 kg/m2), class II (35-29.9 kg/m2), and class III (>40kg/m2) obesity.
Researchers used a state-transition, semi-Markov microsimulation model to analyze the effectiveness of ESG, SG, semaglutide, and LI in a simulated 40-year-old with three different base-case scenarios of class I, II, or III obesity. They then performed a detailed threshold and sensitivity analysis to change the cost of treatment modalities and the semaglutide adherence rate. Outcome measures included a willingness-to-pay threshold of US $100,000/quality-adjusted life years (QALY) and incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs).
Cost-Effectiveness of Treatments
When the treatment modalities were compared with each other, findings showed that for class I obesity, ESG was cost effective (US $4,105/QALY). For class II and III obesity, SG was cost-effective as well (US $5,883/QALY) and (US $7,821/QALY), respectively.
In all classes of obesity, SG and ESG were cost-effective compared with LI. Semaglutide was not cost-effective compared with LI for class I, II, and III obesity (ICER US $508,414/QALY, $420,483/QALY, and $350,637/QALY, respectively).
“For semaglutide to be cost-effective when compared with ESG, it would have to cost less than US $1,879 (class III), US $1,204 (class II), or US $297 (class I) annually,” the authors note.
The authors addressed recent guidelines to consider bariatric surgery in all obese patients. They recommend SG remain the standard of care for patients with severe obesity.
But national projections show that SG would address only 0.5% of life-years lost due to obesity.
“Barring a dramatic increase in patient adherence, bariatric surgery will not likely successfully mitigate the harm from the obesity epidemic,” they write.
“ESG may fill this gap and provide an additional option for patients with obesity as it demonstrated sustained weight loss at 2-5 years.” While insurance coverage is limited, they write, “our model demonstrates that payer coverage for ESG would provide an alternative tool to combat the obesity epidemic as part of a multidisciplinary approach.”
Semaglutide shows sustained weight loss in trials for up to two years but has a substantial annual cost, the authors note.
At lower prices, semaglutide can make a “major impact on the obesity pandemic as it can be prescribed in multiple healthcare settings and due to increased patient interested in non-invasive obesity treatment,” they write.
One limitation to the study is a lack of long-term data available for ESG and semaglutide. Authors were also not able to use a lifetime horizon because of a lack of long-term weight loss.
One study author reports financial relationships with BSC, Cook Medical, Surgical Intuitive, and Olympus America. Another author reports relationships with ACI, AGA-Varia, BSC, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, Medtronic, Olympus, Virgo Systems; equity: AGA-Varia, Dark Canyon Labs, Endiatx, EndoSound, and Virgo Systems. The rest of the authors have no conflicts to disclose.
FROM GUT
Pet Peeves About the State of Primary Care – Part 2
I have received lots of notes from readers about other pet peeves they have about practicing primary care in our current environment and wanted to share some of them. I appreciate all the emails I received on this topic.
- The rapid increase in the number of hospital administrators in the last 50 years
This has increased health system costs without providing any relief for practicing physicians, and often has led to policies that have been harmful and detrimental. This would be a great place to start cutting back to get true savings without affecting quality of care.
- Emergency physicians and specialists who refer my patient elsewhere for a service we provide in our office
It is expensive for patients to go to a specialty provider for a simple procedure that can be easily done in a primary care practice, or to be referred to see a specialist for a problem that does not need specialty care. This creates further problems accessing specialists.
- Online reviews of practices, including reviews from people who have never been patients
I am concerned about the accuracy and intent of online reviews. If a patient is upset because they did not receive an antibiotic or narcotic, they can vent their frustration in a review, when what the medical professional was actually doing was good medicine. More concerning to me is that some organizations use these reviews to determine compensation, promotion, and support. These reviews are not evidence based or accurately collected.
- Offices and organizations being dropped by insurance carriers
Insurance companies are running amok. They make their own rules, which can devastate practices and patients. They can change fees paid unilaterally, and drop practices without explanation or valid reasons. Patients suffer terribly because they now cannot see their long-time physicians or they have to pay much more to see them as they are suddenly “out of network.”
- The lack of appreciation by organizations as well as the general public of the enormous cost savings primary care professionals contribute to the healthcare system
There are many studies showing that patients who see a primary care physician save the system money and have better health outcomes. US adults who regularly see a primary care physician have 33% lower healthcare costs and 19% lower odds of dying prematurely than those who see only a specialist.1
In one study, for every $1 invested in primary care, there was $13 in savings in healthcare costs.2 I had a patient a few years ago complain about the “enormous” bill she received for a visit where I had done an annual exam, cryotherapy for three actinic keratoses, and a steroid injection for her ailing knee. The cost savings was well over $700 (the new patient cost for two specialty visits). There is no doubt that patients who have stable primary care save money themselves and for the whole medical system.
- The stress of being witness to a dysfunctional system
It is really hard to see the hurt and difficulty our patients go through on a daily basis while trying to navigate a broken system. We bear witness to them and listen to all the stories when things have gone wrong. This also takes its toll on us, as we are part of the system, and our patients’ frustrations sometimes boil over. We are also the ones who care for the whole patient, so every bad experience with a specialty clinic is shared with us.
Many thanks extended to those who wrote to share their ideas (Drs. Sylvia Androne, Bhawna Bahethi, Pierre Ghassibi, Richard Katz, Louis Kasunic, Rebecca Keenan, David Kosnosky, Gregory Miller, and James Wilkens).
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the Division of General Internal Medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington, Seattle. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Forbes.com. Why Primary Care Matters, and What We Can Do To Increase It. 2023 Nov 27.
2. Washingtonpost.com. A Health Care Solution We Can’t Afford to Ignore: Primary Care.
I have received lots of notes from readers about other pet peeves they have about practicing primary care in our current environment and wanted to share some of them. I appreciate all the emails I received on this topic.
- The rapid increase in the number of hospital administrators in the last 50 years
This has increased health system costs without providing any relief for practicing physicians, and often has led to policies that have been harmful and detrimental. This would be a great place to start cutting back to get true savings without affecting quality of care.
- Emergency physicians and specialists who refer my patient elsewhere for a service we provide in our office
It is expensive for patients to go to a specialty provider for a simple procedure that can be easily done in a primary care practice, or to be referred to see a specialist for a problem that does not need specialty care. This creates further problems accessing specialists.
- Online reviews of practices, including reviews from people who have never been patients
I am concerned about the accuracy and intent of online reviews. If a patient is upset because they did not receive an antibiotic or narcotic, they can vent their frustration in a review, when what the medical professional was actually doing was good medicine. More concerning to me is that some organizations use these reviews to determine compensation, promotion, and support. These reviews are not evidence based or accurately collected.
- Offices and organizations being dropped by insurance carriers
Insurance companies are running amok. They make their own rules, which can devastate practices and patients. They can change fees paid unilaterally, and drop practices without explanation or valid reasons. Patients suffer terribly because they now cannot see their long-time physicians or they have to pay much more to see them as they are suddenly “out of network.”
- The lack of appreciation by organizations as well as the general public of the enormous cost savings primary care professionals contribute to the healthcare system
There are many studies showing that patients who see a primary care physician save the system money and have better health outcomes. US adults who regularly see a primary care physician have 33% lower healthcare costs and 19% lower odds of dying prematurely than those who see only a specialist.1
In one study, for every $1 invested in primary care, there was $13 in savings in healthcare costs.2 I had a patient a few years ago complain about the “enormous” bill she received for a visit where I had done an annual exam, cryotherapy for three actinic keratoses, and a steroid injection for her ailing knee. The cost savings was well over $700 (the new patient cost for two specialty visits). There is no doubt that patients who have stable primary care save money themselves and for the whole medical system.
- The stress of being witness to a dysfunctional system
It is really hard to see the hurt and difficulty our patients go through on a daily basis while trying to navigate a broken system. We bear witness to them and listen to all the stories when things have gone wrong. This also takes its toll on us, as we are part of the system, and our patients’ frustrations sometimes boil over. We are also the ones who care for the whole patient, so every bad experience with a specialty clinic is shared with us.
Many thanks extended to those who wrote to share their ideas (Drs. Sylvia Androne, Bhawna Bahethi, Pierre Ghassibi, Richard Katz, Louis Kasunic, Rebecca Keenan, David Kosnosky, Gregory Miller, and James Wilkens).
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the Division of General Internal Medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington, Seattle. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Forbes.com. Why Primary Care Matters, and What We Can Do To Increase It. 2023 Nov 27.
2. Washingtonpost.com. A Health Care Solution We Can’t Afford to Ignore: Primary Care.
I have received lots of notes from readers about other pet peeves they have about practicing primary care in our current environment and wanted to share some of them. I appreciate all the emails I received on this topic.
- The rapid increase in the number of hospital administrators in the last 50 years
This has increased health system costs without providing any relief for practicing physicians, and often has led to policies that have been harmful and detrimental. This would be a great place to start cutting back to get true savings without affecting quality of care.
- Emergency physicians and specialists who refer my patient elsewhere for a service we provide in our office
It is expensive for patients to go to a specialty provider for a simple procedure that can be easily done in a primary care practice, or to be referred to see a specialist for a problem that does not need specialty care. This creates further problems accessing specialists.
- Online reviews of practices, including reviews from people who have never been patients
I am concerned about the accuracy and intent of online reviews. If a patient is upset because they did not receive an antibiotic or narcotic, they can vent their frustration in a review, when what the medical professional was actually doing was good medicine. More concerning to me is that some organizations use these reviews to determine compensation, promotion, and support. These reviews are not evidence based or accurately collected.
- Offices and organizations being dropped by insurance carriers
Insurance companies are running amok. They make their own rules, which can devastate practices and patients. They can change fees paid unilaterally, and drop practices without explanation or valid reasons. Patients suffer terribly because they now cannot see their long-time physicians or they have to pay much more to see them as they are suddenly “out of network.”
- The lack of appreciation by organizations as well as the general public of the enormous cost savings primary care professionals contribute to the healthcare system
There are many studies showing that patients who see a primary care physician save the system money and have better health outcomes. US adults who regularly see a primary care physician have 33% lower healthcare costs and 19% lower odds of dying prematurely than those who see only a specialist.1
In one study, for every $1 invested in primary care, there was $13 in savings in healthcare costs.2 I had a patient a few years ago complain about the “enormous” bill she received for a visit where I had done an annual exam, cryotherapy for three actinic keratoses, and a steroid injection for her ailing knee. The cost savings was well over $700 (the new patient cost for two specialty visits). There is no doubt that patients who have stable primary care save money themselves and for the whole medical system.
- The stress of being witness to a dysfunctional system
It is really hard to see the hurt and difficulty our patients go through on a daily basis while trying to navigate a broken system. We bear witness to them and listen to all the stories when things have gone wrong. This also takes its toll on us, as we are part of the system, and our patients’ frustrations sometimes boil over. We are also the ones who care for the whole patient, so every bad experience with a specialty clinic is shared with us.
Many thanks extended to those who wrote to share their ideas (Drs. Sylvia Androne, Bhawna Bahethi, Pierre Ghassibi, Richard Katz, Louis Kasunic, Rebecca Keenan, David Kosnosky, Gregory Miller, and James Wilkens).
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the Division of General Internal Medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington, Seattle. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Forbes.com. Why Primary Care Matters, and What We Can Do To Increase It. 2023 Nov 27.
2. Washingtonpost.com. A Health Care Solution We Can’t Afford to Ignore: Primary Care.