User login
A Cardiac Tumor Traced to Merkel Cell Carcinoma
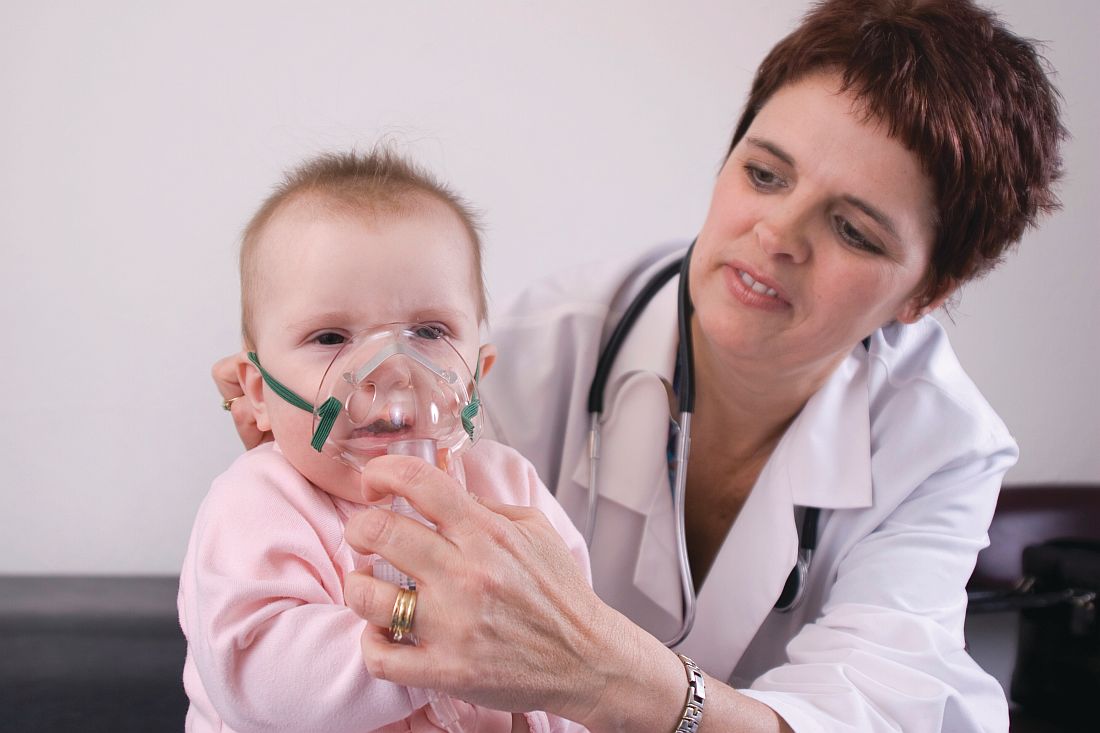
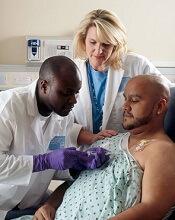
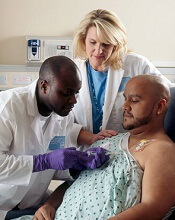
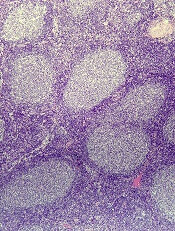
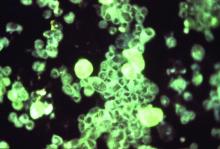
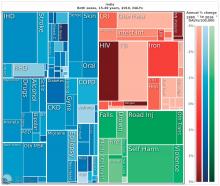
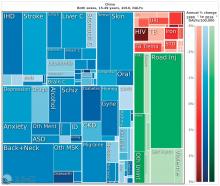
A patient with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) came to Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Perth, Australia, after 2 weeks of dyspnea. He was diagnosed with cardiac tamponade and received urgent pericardiocentesis. An echocardiogram and computer tomography scan showed a large infiltrating mass in the heart. Immunohistochemistry of the pericardial fluid revealed MCC. The MCC had metastasized to his heart—the tenth such reported case, and the second case reported of MCC causing cardiac tamponade.
The clinicians report on several “important illustrative aspects” that appeared while they were unraveling the clues to the patient’s condition. One aspect was the challenge of the histopathologic diagnosis itself. The majority of patients with MCC present with localized disease, they note. Only 4% of patients have distant metastases, usually to lymph nodes, lung, central nervous system, and bone. MCC metastases to the heart are extremely rare. Most commonly, a cancer that spreads to the heart has started in the lungs, esophagus, or breast, or has begun as lymphoma, melanoma, or leukemia.
However, it’s “exponentially more likely,” the clinicians say, for a cardiac tumor to be a metastasis than a primary cardiac tumor, and it is uncommon for the heart to be the only site of metastatic disease from a noncardiac malignancy. Thus, the patient represented a unique case: apart from an internal mammary lymph node, the heart was the only site of distant metastatic spread.
This patient’s case highlights the importance of early and accurate diagnosis of MCC with aggressive surgical treatment for localized disease, the clinicians say. New cardiac symptoms in the setting of malignancy should raise suspicion of cardiac metastasis.
Source:
Di Loreto M, Francis R. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. pii: bcr-2017-221311.
doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221311.
A patient with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) came to Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Perth, Australia, after 2 weeks of dyspnea. He was diagnosed with cardiac tamponade and received urgent pericardiocentesis. An echocardiogram and computer tomography scan showed a large infiltrating mass in the heart. Immunohistochemistry of the pericardial fluid revealed MCC. The MCC had metastasized to his heart—the tenth such reported case, and the second case reported of MCC causing cardiac tamponade.
The clinicians report on several “important illustrative aspects” that appeared while they were unraveling the clues to the patient’s condition. One aspect was the challenge of the histopathologic diagnosis itself. The majority of patients with MCC present with localized disease, they note. Only 4% of patients have distant metastases, usually to lymph nodes, lung, central nervous system, and bone. MCC metastases to the heart are extremely rare. Most commonly, a cancer that spreads to the heart has started in the lungs, esophagus, or breast, or has begun as lymphoma, melanoma, or leukemia.
However, it’s “exponentially more likely,” the clinicians say, for a cardiac tumor to be a metastasis than a primary cardiac tumor, and it is uncommon for the heart to be the only site of metastatic disease from a noncardiac malignancy. Thus, the patient represented a unique case: apart from an internal mammary lymph node, the heart was the only site of distant metastatic spread.
This patient’s case highlights the importance of early and accurate diagnosis of MCC with aggressive surgical treatment for localized disease, the clinicians say. New cardiac symptoms in the setting of malignancy should raise suspicion of cardiac metastasis.
Source:
Di Loreto M, Francis R. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. pii: bcr-2017-221311.
doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221311.
A patient with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) came to Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Perth, Australia, after 2 weeks of dyspnea. He was diagnosed with cardiac tamponade and received urgent pericardiocentesis. An echocardiogram and computer tomography scan showed a large infiltrating mass in the heart. Immunohistochemistry of the pericardial fluid revealed MCC. The MCC had metastasized to his heart—the tenth such reported case, and the second case reported of MCC causing cardiac tamponade.
The clinicians report on several “important illustrative aspects” that appeared while they were unraveling the clues to the patient’s condition. One aspect was the challenge of the histopathologic diagnosis itself. The majority of patients with MCC present with localized disease, they note. Only 4% of patients have distant metastases, usually to lymph nodes, lung, central nervous system, and bone. MCC metastases to the heart are extremely rare. Most commonly, a cancer that spreads to the heart has started in the lungs, esophagus, or breast, or has begun as lymphoma, melanoma, or leukemia.
However, it’s “exponentially more likely,” the clinicians say, for a cardiac tumor to be a metastasis than a primary cardiac tumor, and it is uncommon for the heart to be the only site of metastatic disease from a noncardiac malignancy. Thus, the patient represented a unique case: apart from an internal mammary lymph node, the heart was the only site of distant metastatic spread.
This patient’s case highlights the importance of early and accurate diagnosis of MCC with aggressive surgical treatment for localized disease, the clinicians say. New cardiac symptoms in the setting of malignancy should raise suspicion of cardiac metastasis.
Source:
Di Loreto M, Francis R. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. pii: bcr-2017-221311.
doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221311.
High symptom burden in advanced cancer patients
New research indicates that hospitalized patients with advanced cancer have a high burden of physical and psychological symptoms, and this burden is linked to longer hospital stays and a greater risk for unplanned hospital readmissions and death.
Researchers said these findings highlight the need to develop and test interventions to lessen patients’ symptoms.
Ryan Nipp, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and his colleagues reported the findings in Cancer.
The researchers noted that patients with advanced cancer often experience frequent and prolonged hospitalizations for reasons that have not been fully explored.
To investigate, the team collected information from 1036 patients with advanced cancer as they were being admitted for an unplanned hospitalization.
The Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) was used to assess patients’ physical symptoms, and the Patient Health Questionnaire 4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess their psychological symptoms.
The researchers examined the relationship between patients’ symptom burden and the duration of their hospital stay, risk of readmission, and death.
Many patients reported moderate or severe fatigue (86.7%), poor well-being (74.2%), drowsiness (71.7%), pain (67.7%), and lack of appetite (67.3%). Nearly 30% of patients had clinically significant symptoms of depression (28.8%) and anxiety (28.0%).
The patients’ mean hospital stay was 6.3 days, the readmission rate within 90 days of discharge was 43.1%, and the 90-day mortality rate was 41.6%.
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.040), and depression symptoms (P=0.017) were significantly associated with longer hospital stays, but anxiety symptoms were not (P=0.190).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.072), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.045) were significantly associated with a higher likelihood of readmission within 90 days, but depression symptoms were not (P=0.219).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P<0.001), depression symptoms (P<0.001), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.012) were all significantly associated with a higher likelihood of death or readmission within 90 days.
“We demonstrated that many hospitalized patients with advanced cancer experience an immense physical and psychological symptom burden,” Dr Nipp said.
“Interventions to identify and treat symptomatic patients hold great potential for improving patients’ experience with their illness, enhancing their quality of life, and reducing their healthcare utilization.” ![]()
New research indicates that hospitalized patients with advanced cancer have a high burden of physical and psychological symptoms, and this burden is linked to longer hospital stays and a greater risk for unplanned hospital readmissions and death.
Researchers said these findings highlight the need to develop and test interventions to lessen patients’ symptoms.
Ryan Nipp, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and his colleagues reported the findings in Cancer.
The researchers noted that patients with advanced cancer often experience frequent and prolonged hospitalizations for reasons that have not been fully explored.
To investigate, the team collected information from 1036 patients with advanced cancer as they were being admitted for an unplanned hospitalization.
The Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) was used to assess patients’ physical symptoms, and the Patient Health Questionnaire 4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess their psychological symptoms.
The researchers examined the relationship between patients’ symptom burden and the duration of their hospital stay, risk of readmission, and death.
Many patients reported moderate or severe fatigue (86.7%), poor well-being (74.2%), drowsiness (71.7%), pain (67.7%), and lack of appetite (67.3%). Nearly 30% of patients had clinically significant symptoms of depression (28.8%) and anxiety (28.0%).
The patients’ mean hospital stay was 6.3 days, the readmission rate within 90 days of discharge was 43.1%, and the 90-day mortality rate was 41.6%.
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.040), and depression symptoms (P=0.017) were significantly associated with longer hospital stays, but anxiety symptoms were not (P=0.190).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.072), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.045) were significantly associated with a higher likelihood of readmission within 90 days, but depression symptoms were not (P=0.219).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P<0.001), depression symptoms (P<0.001), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.012) were all significantly associated with a higher likelihood of death or readmission within 90 days.
“We demonstrated that many hospitalized patients with advanced cancer experience an immense physical and psychological symptom burden,” Dr Nipp said.
“Interventions to identify and treat symptomatic patients hold great potential for improving patients’ experience with their illness, enhancing their quality of life, and reducing their healthcare utilization.” ![]()
New research indicates that hospitalized patients with advanced cancer have a high burden of physical and psychological symptoms, and this burden is linked to longer hospital stays and a greater risk for unplanned hospital readmissions and death.
Researchers said these findings highlight the need to develop and test interventions to lessen patients’ symptoms.
Ryan Nipp, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, and his colleagues reported the findings in Cancer.
The researchers noted that patients with advanced cancer often experience frequent and prolonged hospitalizations for reasons that have not been fully explored.
To investigate, the team collected information from 1036 patients with advanced cancer as they were being admitted for an unplanned hospitalization.
The Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS) was used to assess patients’ physical symptoms, and the Patient Health Questionnaire 4 (PHQ-4) was used to assess their psychological symptoms.
The researchers examined the relationship between patients’ symptom burden and the duration of their hospital stay, risk of readmission, and death.
Many patients reported moderate or severe fatigue (86.7%), poor well-being (74.2%), drowsiness (71.7%), pain (67.7%), and lack of appetite (67.3%). Nearly 30% of patients had clinically significant symptoms of depression (28.8%) and anxiety (28.0%).
The patients’ mean hospital stay was 6.3 days, the readmission rate within 90 days of discharge was 43.1%, and the 90-day mortality rate was 41.6%.
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.040), and depression symptoms (P=0.017) were significantly associated with longer hospital stays, but anxiety symptoms were not (P=0.190).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P=0.072), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.045) were significantly associated with a higher likelihood of readmission within 90 days, but depression symptoms were not (P=0.219).
Physical symptoms (P<0.001), total ESAS score (P<0.001), total PHQ-4 score (P<0.001), depression symptoms (P<0.001), and anxiety symptoms (P=0.012) were all significantly associated with a higher likelihood of death or readmission within 90 days.
“We demonstrated that many hospitalized patients with advanced cancer experience an immense physical and psychological symptom burden,” Dr Nipp said.
“Interventions to identify and treat symptomatic patients hold great potential for improving patients’ experience with their illness, enhancing their quality of life, and reducing their healthcare utilization.” ![]()
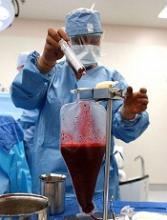
Antibody can treat HSCT-TMA and GVHD, case suggests
GRANADA, SPAIN—A monoclonal antibody can resolve co-existing hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), according to a case study.
The antibody is OMS721, and it targets MASP-2, a pro-inflammatory protein target involved in activation of the complement system.
The case of OMS721 ameliorating HSCT-TMA and GVHD was presented at the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Crash Course on Diagnosis and Treatment of Noninfectious Complications after HCT.
The patient was a participant in an ongoing phase 2 trial of thrombotic microangiopathies, including HSCT-TMA. The trial is sponsored by Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721.
The patient was an adult male with post-transplant TMA persisting at least 2 weeks following calcineurin inhibitor modification.
The patient had undergone HSCT for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. His post-transplant course was complicated by multiple episodes of steroid-refractory grade 4 GVHD, cytomegalovirus infection, and HSCT-TMA.
After 2 prior episodes of GVHD, the patient presented with bloody diarrhea. Intestinal biopsy demonstrated both HSCT-TMA and GVHD. No infections were identified.
The patient also had new-onset neurological symptoms of paresthesias, tetraparesis, and a neurogenic bladder, which have been reported as neurological manifestations of GVHD and TMA.
The patient was unable to walk due to the tetraparesis and required blood transfusions at least once daily. Hematological markers demonstrated HSCT-TMA with thrombocytopenia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and schistocytes.
Two weeks prior to starting OMS721, the patient’s immunosuppression (cyclosporine) had been decreased, and, given his history of steroid-refractory GVHD, he was receiving only low-dose corticosteroids. He received no other GVHD treatment.
After 2 OMS721 doses, the patient’s bloody diarrhea resolved, and his hematological markers improved. After 4 OMS721 doses, he was able to walk with help.
The patient completed 8 weeks of OMS721 treatment and has been doing well at home. All signs and symptoms of HSCT-TMA and all clinical symptoms of GVHD have resolved. His neurological symptoms have continued to improve.
“This patient’s marked response to OMS721 treatment was very gratifying,” said Anna Grassi, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Papa Giovanni XXIII in Bergamo, Italy.
“The cause of his neurological symptoms is not clear but may be a manifestation of GVHD or other endothelial injury. Prior to OMS721 treatment, this patient was deteriorating and at high risk for early death. The improvement of GVHD, H[S]CT-TMA, and the neurological symptoms following OMS721 treatment is promising.” ![]()
GRANADA, SPAIN—A monoclonal antibody can resolve co-existing hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), according to a case study.
The antibody is OMS721, and it targets MASP-2, a pro-inflammatory protein target involved in activation of the complement system.
The case of OMS721 ameliorating HSCT-TMA and GVHD was presented at the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Crash Course on Diagnosis and Treatment of Noninfectious Complications after HCT.
The patient was a participant in an ongoing phase 2 trial of thrombotic microangiopathies, including HSCT-TMA. The trial is sponsored by Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721.
The patient was an adult male with post-transplant TMA persisting at least 2 weeks following calcineurin inhibitor modification.
The patient had undergone HSCT for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. His post-transplant course was complicated by multiple episodes of steroid-refractory grade 4 GVHD, cytomegalovirus infection, and HSCT-TMA.
After 2 prior episodes of GVHD, the patient presented with bloody diarrhea. Intestinal biopsy demonstrated both HSCT-TMA and GVHD. No infections were identified.
The patient also had new-onset neurological symptoms of paresthesias, tetraparesis, and a neurogenic bladder, which have been reported as neurological manifestations of GVHD and TMA.
The patient was unable to walk due to the tetraparesis and required blood transfusions at least once daily. Hematological markers demonstrated HSCT-TMA with thrombocytopenia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and schistocytes.
Two weeks prior to starting OMS721, the patient’s immunosuppression (cyclosporine) had been decreased, and, given his history of steroid-refractory GVHD, he was receiving only low-dose corticosteroids. He received no other GVHD treatment.
After 2 OMS721 doses, the patient’s bloody diarrhea resolved, and his hematological markers improved. After 4 OMS721 doses, he was able to walk with help.
The patient completed 8 weeks of OMS721 treatment and has been doing well at home. All signs and symptoms of HSCT-TMA and all clinical symptoms of GVHD have resolved. His neurological symptoms have continued to improve.
“This patient’s marked response to OMS721 treatment was very gratifying,” said Anna Grassi, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Papa Giovanni XXIII in Bergamo, Italy.
“The cause of his neurological symptoms is not clear but may be a manifestation of GVHD or other endothelial injury. Prior to OMS721 treatment, this patient was deteriorating and at high risk for early death. The improvement of GVHD, H[S]CT-TMA, and the neurological symptoms following OMS721 treatment is promising.” ![]()
GRANADA, SPAIN—A monoclonal antibody can resolve co-existing hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (HSCT-TMA) and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), according to a case study.
The antibody is OMS721, and it targets MASP-2, a pro-inflammatory protein target involved in activation of the complement system.
The case of OMS721 ameliorating HSCT-TMA and GVHD was presented at the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Crash Course on Diagnosis and Treatment of Noninfectious Complications after HCT.
The patient was a participant in an ongoing phase 2 trial of thrombotic microangiopathies, including HSCT-TMA. The trial is sponsored by Omeros Corporation, the company developing OMS721.
The patient was an adult male with post-transplant TMA persisting at least 2 weeks following calcineurin inhibitor modification.
The patient had undergone HSCT for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. His post-transplant course was complicated by multiple episodes of steroid-refractory grade 4 GVHD, cytomegalovirus infection, and HSCT-TMA.
After 2 prior episodes of GVHD, the patient presented with bloody diarrhea. Intestinal biopsy demonstrated both HSCT-TMA and GVHD. No infections were identified.
The patient also had new-onset neurological symptoms of paresthesias, tetraparesis, and a neurogenic bladder, which have been reported as neurological manifestations of GVHD and TMA.
The patient was unable to walk due to the tetraparesis and required blood transfusions at least once daily. Hematological markers demonstrated HSCT-TMA with thrombocytopenia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase, and schistocytes.
Two weeks prior to starting OMS721, the patient’s immunosuppression (cyclosporine) had been decreased, and, given his history of steroid-refractory GVHD, he was receiving only low-dose corticosteroids. He received no other GVHD treatment.
After 2 OMS721 doses, the patient’s bloody diarrhea resolved, and his hematological markers improved. After 4 OMS721 doses, he was able to walk with help.
The patient completed 8 weeks of OMS721 treatment and has been doing well at home. All signs and symptoms of HSCT-TMA and all clinical symptoms of GVHD have resolved. His neurological symptoms have continued to improve.
“This patient’s marked response to OMS721 treatment was very gratifying,” said Anna Grassi, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Papa Giovanni XXIII in Bergamo, Italy.
“The cause of his neurological symptoms is not clear but may be a manifestation of GVHD or other endothelial injury. Prior to OMS721 treatment, this patient was deteriorating and at high risk for early death. The improvement of GVHD, H[S]CT-TMA, and the neurological symptoms following OMS721 treatment is promising.” ![]()
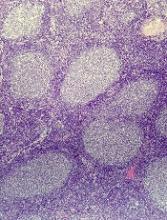
EMA recommends orphan designation for G100 to treat FL
The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA’s) Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products has recommended orphan designation for G100 for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL).
G100 contains the synthetic small molecule toll-like receptor-4 agonist glucopyranosyl lipid A.
G100 works by activating innate and adaptive immunity in the tumor microenvironment to generate an immune response against the tumor’s pre-existing antigens.
Clinical and preclinical data have demonstrated G100’s ability to activate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and promote antigen-presentation and the recruitment of T cells to the tumor.
The induction of local and systemic immune responses has been shown in preclinical studies to result in local and abscopal tumor control.
Immune Design, the company developing G100, is currently evaluating G100 plus local radiation, with or without pembrolizumab, in a phase 1/2 trial of FL patients.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7537). Nine patients who received G100 (3 patients each at the 5, 10, or 20 μg dose) with radiation (but not pembrolizumab) were evaluable for safety and efficacy.
The overall response rate was 44%, and all of these were partial responses (n=4). Thirty-three percent of patients had stable disease (n=3).
Among the responders, tumor regression ranged from 58% to 89%, which included up to 56% shrinkage of abscopal sites. Tumor biopsies showed increased inflammatory responses and T-cell infiltrates in abscopal tumors.
An additional 13 patients treated at the 10 μg dose were evaluable for safety. There were no dose-limiting toxicities, serious adverse events (AEs), or grade 3/4 AEs observed.
Common AEs included injection site disorders, abdominal pain/discomfort, nausea, pruritus, and decrease in lymphocytes.
Immune Design said that, if this trial produces a sufficiently robust clinical benefit for patients, the company may pursue FL as the first indication for regulatory approval of G100.
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval.
The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The commission typically makes a decision within 30 days of the submission. ![]()
The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA’s) Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products has recommended orphan designation for G100 for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL).
G100 contains the synthetic small molecule toll-like receptor-4 agonist glucopyranosyl lipid A.
G100 works by activating innate and adaptive immunity in the tumor microenvironment to generate an immune response against the tumor’s pre-existing antigens.
Clinical and preclinical data have demonstrated G100’s ability to activate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and promote antigen-presentation and the recruitment of T cells to the tumor.
The induction of local and systemic immune responses has been shown in preclinical studies to result in local and abscopal tumor control.
Immune Design, the company developing G100, is currently evaluating G100 plus local radiation, with or without pembrolizumab, in a phase 1/2 trial of FL patients.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7537). Nine patients who received G100 (3 patients each at the 5, 10, or 20 μg dose) with radiation (but not pembrolizumab) were evaluable for safety and efficacy.
The overall response rate was 44%, and all of these were partial responses (n=4). Thirty-three percent of patients had stable disease (n=3).
Among the responders, tumor regression ranged from 58% to 89%, which included up to 56% shrinkage of abscopal sites. Tumor biopsies showed increased inflammatory responses and T-cell infiltrates in abscopal tumors.
An additional 13 patients treated at the 10 μg dose were evaluable for safety. There were no dose-limiting toxicities, serious adverse events (AEs), or grade 3/4 AEs observed.
Common AEs included injection site disorders, abdominal pain/discomfort, nausea, pruritus, and decrease in lymphocytes.
Immune Design said that, if this trial produces a sufficiently robust clinical benefit for patients, the company may pursue FL as the first indication for regulatory approval of G100.
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval.
The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The commission typically makes a decision within 30 days of the submission. ![]()
The European Medicines Agency’s (EMA’s) Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products has recommended orphan designation for G100 for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL).
G100 contains the synthetic small molecule toll-like receptor-4 agonist glucopyranosyl lipid A.
G100 works by activating innate and adaptive immunity in the tumor microenvironment to generate an immune response against the tumor’s pre-existing antigens.
Clinical and preclinical data have demonstrated G100’s ability to activate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and promote antigen-presentation and the recruitment of T cells to the tumor.
The induction of local and systemic immune responses has been shown in preclinical studies to result in local and abscopal tumor control.
Immune Design, the company developing G100, is currently evaluating G100 plus local radiation, with or without pembrolizumab, in a phase 1/2 trial of FL patients.
Results from this trial were presented at the 2017 ASCO Annual Meeting (abstract 7537). Nine patients who received G100 (3 patients each at the 5, 10, or 20 μg dose) with radiation (but not pembrolizumab) were evaluable for safety and efficacy.
The overall response rate was 44%, and all of these were partial responses (n=4). Thirty-three percent of patients had stable disease (n=3).
Among the responders, tumor regression ranged from 58% to 89%, which included up to 56% shrinkage of abscopal sites. Tumor biopsies showed increased inflammatory responses and T-cell infiltrates in abscopal tumors.
An additional 13 patients treated at the 10 μg dose were evaluable for safety. There were no dose-limiting toxicities, serious adverse events (AEs), or grade 3/4 AEs observed.
Common AEs included injection site disorders, abdominal pain/discomfort, nausea, pruritus, and decrease in lymphocytes.
Immune Design said that, if this trial produces a sufficiently robust clinical benefit for patients, the company may pursue FL as the first indication for regulatory approval of G100.
About orphan designation
Orphan designation provides regulatory and financial incentives for companies to develop and market therapies that treat life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting no more than 5 in 10,000 people in the European Union, and where no satisfactory treatment is available.
Orphan designation provides a 10-year period of marketing exclusivity if the drug receives regulatory approval.
The designation also provides incentives for companies seeking protocol assistance from the EMA during the product development phase and direct access to the centralized authorization procedure.
The EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products adopts an opinion on the granting of orphan drug designation, and that opinion is submitted to the European Commission for a final decision. The commission typically makes a decision within 30 days of the submission. ![]()
Intellectual impairment seems not a risk of asymptomatic cCMV
Infants with congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) who were asymptomatic at birth with normal hearing by age 2 years were not at higher risk of intellectual impairment or low academic achievement, compared with controls, but patients with sensorineural hearing loss may experience more difficulty, according to a longitudinal study.
Full-scale intelligence, language, and academic achievement was evaluated in 78 adolescents with cCMV and normal hearing, 11 with cCMV and sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) by age 2 years, and 40 controls. Mean full-scale intelligence scores did not vary among the patients with normal hearing and the controls, said Adriana S. Lopez of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and her coauthors. Each group scored a mean 108 (95% confidence interval, 105-110 and 104-111, respectively) at age 5 years and 111 (95% CI, 108-114 and 107-104, respectively) at age 18 years (P = .96). The scores of the patients with SNHL, however, were 7 points lower at both times (P less than .05).
In the other categories (expressive vocabulary and academic achievement in math and reading), the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant (P less than .05 for all three categories), suggesting that the other scores may underestimate the full intellectual potential of cCMV patients with SNHL, according to the researchers (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1517).
“Findings from our study suggest that and, therefore, may not need long-term monitoring for cognitive impairment and/or disabilities,” Dr. Lopez and her coauthors wrote. “This information could provide reassurance to parents.”
“Further studies are needed to better understand the impact of asymptomatic congenital CMV infection on behavior and specific cognitive domains such as attention, perception, and memory,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and was supported in other ways by a number of other organizations. Dr. Lopez and her coauthors reported no financial disclosures.
Congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection is a leading nongenetic cause of hearing loss and neurodevelopmental disability, with the number of infants experiencing these symptoms approaching that of those with Down Syndrome and exceeding that of those with fetal alcohol syndrome, spina bifida, and childhood infections such as HIV. Most infected infants are asymptomatic, and the majority are not recognized at birth.
Yet little is known about intellectual outcomes and academic performance in these children. Lopez et al. provide encouraging findings and new insights that begin to bridge this gap in knowledge about children with asymptomatic cCMV up into adolescence.
There were some challenges in this study, including the large percentage of children whose mothers have medium to high socioeconomic status and the selection of appropriate controls. Although the controls were born within 6 days of the infants with cCMV, they were not matched for other demographic factors. It will be important to confirm these findings in children with families of lower socioeconomic status.
That said, this study is helpful in defining the disease burden from this common prenatal infection and in reassuring patients and doctors that these infants are not at increased risk for disabilities in terms of intellectual attainment and academic performance.
Suresh B. Boppana, MD, is a professor of pediatrics and microbiology, and Karen B. Fowler, DrPH, is a professor of epidemiology. Both practice at the University of Alabama in Birmingham. These remarks accompanied the Lopez et al. article (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2526). Neither author reported any financial disclosures.
Congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection is a leading nongenetic cause of hearing loss and neurodevelopmental disability, with the number of infants experiencing these symptoms approaching that of those with Down Syndrome and exceeding that of those with fetal alcohol syndrome, spina bifida, and childhood infections such as HIV. Most infected infants are asymptomatic, and the majority are not recognized at birth.
Yet little is known about intellectual outcomes and academic performance in these children. Lopez et al. provide encouraging findings and new insights that begin to bridge this gap in knowledge about children with asymptomatic cCMV up into adolescence.
There were some challenges in this study, including the large percentage of children whose mothers have medium to high socioeconomic status and the selection of appropriate controls. Although the controls were born within 6 days of the infants with cCMV, they were not matched for other demographic factors. It will be important to confirm these findings in children with families of lower socioeconomic status.
That said, this study is helpful in defining the disease burden from this common prenatal infection and in reassuring patients and doctors that these infants are not at increased risk for disabilities in terms of intellectual attainment and academic performance.
Suresh B. Boppana, MD, is a professor of pediatrics and microbiology, and Karen B. Fowler, DrPH, is a professor of epidemiology. Both practice at the University of Alabama in Birmingham. These remarks accompanied the Lopez et al. article (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2526). Neither author reported any financial disclosures.
Congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) infection is a leading nongenetic cause of hearing loss and neurodevelopmental disability, with the number of infants experiencing these symptoms approaching that of those with Down Syndrome and exceeding that of those with fetal alcohol syndrome, spina bifida, and childhood infections such as HIV. Most infected infants are asymptomatic, and the majority are not recognized at birth.
Yet little is known about intellectual outcomes and academic performance in these children. Lopez et al. provide encouraging findings and new insights that begin to bridge this gap in knowledge about children with asymptomatic cCMV up into adolescence.
There were some challenges in this study, including the large percentage of children whose mothers have medium to high socioeconomic status and the selection of appropriate controls. Although the controls were born within 6 days of the infants with cCMV, they were not matched for other demographic factors. It will be important to confirm these findings in children with families of lower socioeconomic status.
That said, this study is helpful in defining the disease burden from this common prenatal infection and in reassuring patients and doctors that these infants are not at increased risk for disabilities in terms of intellectual attainment and academic performance.
Suresh B. Boppana, MD, is a professor of pediatrics and microbiology, and Karen B. Fowler, DrPH, is a professor of epidemiology. Both practice at the University of Alabama in Birmingham. These remarks accompanied the Lopez et al. article (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2526). Neither author reported any financial disclosures.
Infants with congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) who were asymptomatic at birth with normal hearing by age 2 years were not at higher risk of intellectual impairment or low academic achievement, compared with controls, but patients with sensorineural hearing loss may experience more difficulty, according to a longitudinal study.
Full-scale intelligence, language, and academic achievement was evaluated in 78 adolescents with cCMV and normal hearing, 11 with cCMV and sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) by age 2 years, and 40 controls. Mean full-scale intelligence scores did not vary among the patients with normal hearing and the controls, said Adriana S. Lopez of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and her coauthors. Each group scored a mean 108 (95% confidence interval, 105-110 and 104-111, respectively) at age 5 years and 111 (95% CI, 108-114 and 107-104, respectively) at age 18 years (P = .96). The scores of the patients with SNHL, however, were 7 points lower at both times (P less than .05).
In the other categories (expressive vocabulary and academic achievement in math and reading), the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant (P less than .05 for all three categories), suggesting that the other scores may underestimate the full intellectual potential of cCMV patients with SNHL, according to the researchers (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1517).
“Findings from our study suggest that and, therefore, may not need long-term monitoring for cognitive impairment and/or disabilities,” Dr. Lopez and her coauthors wrote. “This information could provide reassurance to parents.”
“Further studies are needed to better understand the impact of asymptomatic congenital CMV infection on behavior and specific cognitive domains such as attention, perception, and memory,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and was supported in other ways by a number of other organizations. Dr. Lopez and her coauthors reported no financial disclosures.
Infants with congenital cytomegalovirus (cCMV) who were asymptomatic at birth with normal hearing by age 2 years were not at higher risk of intellectual impairment or low academic achievement, compared with controls, but patients with sensorineural hearing loss may experience more difficulty, according to a longitudinal study.
Full-scale intelligence, language, and academic achievement was evaluated in 78 adolescents with cCMV and normal hearing, 11 with cCMV and sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) by age 2 years, and 40 controls. Mean full-scale intelligence scores did not vary among the patients with normal hearing and the controls, said Adriana S. Lopez of the National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and her coauthors. Each group scored a mean 108 (95% confidence interval, 105-110 and 104-111, respectively) at age 5 years and 111 (95% CI, 108-114 and 107-104, respectively) at age 18 years (P = .96). The scores of the patients with SNHL, however, were 7 points lower at both times (P less than .05).
In the other categories (expressive vocabulary and academic achievement in math and reading), the differences between the three groups were not statistically significant (P less than .05 for all three categories), suggesting that the other scores may underestimate the full intellectual potential of cCMV patients with SNHL, according to the researchers (Pediatrics. 2017. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1517).
“Findings from our study suggest that and, therefore, may not need long-term monitoring for cognitive impairment and/or disabilities,” Dr. Lopez and her coauthors wrote. “This information could provide reassurance to parents.”
“Further studies are needed to better understand the impact of asymptomatic congenital CMV infection on behavior and specific cognitive domains such as attention, perception, and memory,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and was supported in other ways by a number of other organizations. Dr. Lopez and her coauthors reported no financial disclosures.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: Infants with cCMV who were asymptomatic at birth with normal hearing by age 2 years were not at higher risk of intellectual impairment or low academic achievement, compared with controls, but patients with sensorineural hearing loss may experience more difficulty.
Major finding: The infants with cCMV with normal hearing at 2 years and the controls both scored a mean 108 at age 5 years and 111 at age 18 years (P = .96). The scores of the patients with SNHL, however, were 7 points lower (P less than .05).
Data source: A longitudinal study of 78 adolescents with cCMV and normal hearing, 11 with cCMV and SNHL by age 2 years, and 40 controls.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and was supported in other ways by a number of other organizations. Dr. Lopez and her coauthors reported no financial disclosures.
GIs take on Capitol Hill
During AGA’s annual Joint Committee weekend, 55 AGA members collectively attended 79 meetings with staff from the offices of their House representatives and senators, lobbying for the top concerns of gastroenterologists across the country, including:
- Continued coverage of patients through either the Affordable Care Act or another bill that has the patient’s best interests in mind. More specifically, one that provides coverage for those with pre-existing conditions and for children under their parents’ plan until 26 years of age, among many other important provisions.
- Changes in health care language that label a colonoscopy for cancer screening as “therapeutic,” which renders a large copay for patients.
- Increased funding for the NIH.
Participants shared experiences from their time on Capitol Hill in the AGA Community forum, and encouraged others to get involved. Here are some of their reasons why.
- Your voice matters: You are constituents – which translates to votes in the minds of representatives and senators – and providing face-to-face conversation with their staffers shows them that you care about your patients and their needs, explains Siddharth Singh, MD.
- Being consistent gets your foot in the door: Some staffers recognized and remembered previous Advocacy Day participants, like Peter Liang, MD, MPH. Personally connecting could lead to follow-up communication and advocacy efforts, says Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF.
- You’re indirectly (and sometimes directly) connecting with decision makers: Staff members from these offices work closely with the legislators who evaluate which policies to support or oppose. “So it’s important to come to Washington, build relationships, and make the case for our science, our specialty, and our patients,” says Kim Barrett, PhD, AGAF.
- Others could be advocating against you on the same issues: “I very strongly believe that it is important to keep letting our legislators know how we feel and what we believe in,” shares Deborah Proctor, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a rewarding experience: “Voice [your] concerns to your representatives who embrace the stories of how their decisions and policies affect your patients, practice, research, and institution,” explains Susan Ramdhaney, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a critical time to take action: With the current health care environment, gastroenterologists need to express the needs of their patients and profession, Dr. Streett explains.
View the full discussion and read updates from colleagues who visited with legislative staffers from California, New York, North Carolina, and Oregon in the forum, community.gastro.org.
Please contact agaadvocacy@gastro.org.
During AGA’s annual Joint Committee weekend, 55 AGA members collectively attended 79 meetings with staff from the offices of their House representatives and senators, lobbying for the top concerns of gastroenterologists across the country, including:
- Continued coverage of patients through either the Affordable Care Act or another bill that has the patient’s best interests in mind. More specifically, one that provides coverage for those with pre-existing conditions and for children under their parents’ plan until 26 years of age, among many other important provisions.
- Changes in health care language that label a colonoscopy for cancer screening as “therapeutic,” which renders a large copay for patients.
- Increased funding for the NIH.
Participants shared experiences from their time on Capitol Hill in the AGA Community forum, and encouraged others to get involved. Here are some of their reasons why.
- Your voice matters: You are constituents – which translates to votes in the minds of representatives and senators – and providing face-to-face conversation with their staffers shows them that you care about your patients and their needs, explains Siddharth Singh, MD.
- Being consistent gets your foot in the door: Some staffers recognized and remembered previous Advocacy Day participants, like Peter Liang, MD, MPH. Personally connecting could lead to follow-up communication and advocacy efforts, says Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF.
- You’re indirectly (and sometimes directly) connecting with decision makers: Staff members from these offices work closely with the legislators who evaluate which policies to support or oppose. “So it’s important to come to Washington, build relationships, and make the case for our science, our specialty, and our patients,” says Kim Barrett, PhD, AGAF.
- Others could be advocating against you on the same issues: “I very strongly believe that it is important to keep letting our legislators know how we feel and what we believe in,” shares Deborah Proctor, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a rewarding experience: “Voice [your] concerns to your representatives who embrace the stories of how their decisions and policies affect your patients, practice, research, and institution,” explains Susan Ramdhaney, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a critical time to take action: With the current health care environment, gastroenterologists need to express the needs of their patients and profession, Dr. Streett explains.
View the full discussion and read updates from colleagues who visited with legislative staffers from California, New York, North Carolina, and Oregon in the forum, community.gastro.org.
Please contact agaadvocacy@gastro.org.
During AGA’s annual Joint Committee weekend, 55 AGA members collectively attended 79 meetings with staff from the offices of their House representatives and senators, lobbying for the top concerns of gastroenterologists across the country, including:
- Continued coverage of patients through either the Affordable Care Act or another bill that has the patient’s best interests in mind. More specifically, one that provides coverage for those with pre-existing conditions and for children under their parents’ plan until 26 years of age, among many other important provisions.
- Changes in health care language that label a colonoscopy for cancer screening as “therapeutic,” which renders a large copay for patients.
- Increased funding for the NIH.
Participants shared experiences from their time on Capitol Hill in the AGA Community forum, and encouraged others to get involved. Here are some of their reasons why.
- Your voice matters: You are constituents – which translates to votes in the minds of representatives and senators – and providing face-to-face conversation with their staffers shows them that you care about your patients and their needs, explains Siddharth Singh, MD.
- Being consistent gets your foot in the door: Some staffers recognized and remembered previous Advocacy Day participants, like Peter Liang, MD, MPH. Personally connecting could lead to follow-up communication and advocacy efforts, says Sarah Streett, MD, AGAF.
- You’re indirectly (and sometimes directly) connecting with decision makers: Staff members from these offices work closely with the legislators who evaluate which policies to support or oppose. “So it’s important to come to Washington, build relationships, and make the case for our science, our specialty, and our patients,” says Kim Barrett, PhD, AGAF.
- Others could be advocating against you on the same issues: “I very strongly believe that it is important to keep letting our legislators know how we feel and what we believe in,” shares Deborah Proctor, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a rewarding experience: “Voice [your] concerns to your representatives who embrace the stories of how their decisions and policies affect your patients, practice, research, and institution,” explains Susan Ramdhaney, MD, AGAF.
- It’s a critical time to take action: With the current health care environment, gastroenterologists need to express the needs of their patients and profession, Dr. Streett explains.
View the full discussion and read updates from colleagues who visited with legislative staffers from California, New York, North Carolina, and Oregon in the forum, community.gastro.org.
Please contact agaadvocacy@gastro.org.
Localized wheezing differs from asthmatic, viral wheezing
CHICAGO – , explained Erik Hysinger, MD, MS, of the division of pulmonary medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Localized wheezing is not consistent with asthmatic or viral wheezing, which is typically diffuse and polyphonic, Dr. Hysinger emphasized at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“Localized wheezing is less common than diffuse wheezing and typically has a homophonous sound,” Dr. Hysinger said. It also usually arises from a central airway pathology. “High flow rates create loud amplitude sounds.”
Dr. Hysinger also covered management strategies for focal wheezing, starting with an initial trial of bronchodilators. Any wheezing resulting from a central airway problem, however, isn’t likely to respond to bronchodilators. Standard work-up for any of these causes is usually a chest x-ray, often paired with a bronchoscopy. Persistent wheezing likely needs a chest CT, and many of these conditions will require referral to a subspecialist.
Airway occlusion diagnoses
Four potential causes of an airway blockage are a foreign body, a bronchial cast, mucous plugs, or airway tumors.
A foreign body typically occurs with a cough, wheezing, stridor, and respiratory distress. It is most common in children under age 4 years, usually in those without a history of aspiration, yet providers initially misdiagnose more than 20% of patients with a foreign body. The foreign object – often coins, food, or batteries – frequently ends up in the right main bronchus and may go undetected up to a month, potentially leading to pneumonia, abscess, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, or airway erosion.
An endobronchial cast is rarer than a foreign body, but can be large enough to completely fill a lung with branching mucin, fibrin, and inflammatory cells. The wheezing sounds homophonous, with a barky or brassy cough accompanied by atelectasis. Dr. Hysinger recommended ordering chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and bronchoscopy. Although often idiopathic, these casts also can result from asthma or another disease: neutrophilic inflammation typically indicates a heart condition whereas asthma or influenza leads to eosinophilic inflammation.
Treatment should involve clearing the airway, followed by hypertonic saline, an inhaled tissue plasminogen activator, and a bronchoscopy for extraction.
Although distinct from endobronchial casts, a mucus plug also presents with wheezing, a cough, and atelectasis, and potentially respiratory distress or failure, and hypoxemia. Mucus plugs are diagnosed with a chest x-ray and flexible bronchoscopy, and then treated by removing the plug and clearing the airway, hypertonic saline, and mucolytics.
The rarest cause of an airway blockage is an airway tumor, often mistaken for asthma. Benign causes include papillomatosis, hemangioma, and hamartomas, while potentially malignant causes include a carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, inflammatory myofibromas, and granular cell tumors.
In addition to a chest x-ray and bronchoscopy, a chest CT scan plus a biopsy and resection are necessary to diagnose airway tumors. Treatment will depend on the specific type of tumor identified.
“Overall survival is excellent,” Dr. Hysinger said of children with airway tumors.
Airway narrowing diagnoses
Two possible diagnoses for an intrinsic airway narrowing include bronchomalacia, occurring in only 1 of 2,100 children, and bronchial stenosis.
In bronchomalacia – diagnosed primarily with bronchoscopy – the airway collapses from weakening of the cartilage and posterior membrane. Bronchomalacia sounds like homophonous wheezing with a barky or brassy cough, and it’s frequently accompanied by recurrent bronchitis and/or pneumonia. Intervention is rarely necessary when occurring on its own, but severe cases may require endobronchial stents. Dr. Hysinger also recommended considering ipratroprium instead of albuterol.
Bronchial stenosis involves a fixed narrowing of the bronchi and can be congenital – typically occurring with heart disease – or acquired after an intubation and suction trauma or bronchiolitis obliterans (“popcorn lung”). A chest x-ray and bronchoscopy again are standard, but MRI may be necessary as well. Aside from helping the patient clear the airway, bronchial stenosis typically needs limited management unless the patient is symptomatic. In that case, options include balloon dilation, endobronchial stents, or a slide bronchoplasty.
Airway compression diagnoses
An extrinsic airway compression could have a vascular cause or could result from pressure by an extrinsic mass or the axial skeleton.
Vascular compression usually occurs due to abnormal vasculature development, particularly with vascular stents, Dr. Hysinger said. The wheezing presents with stridor, feeding intolerance, recurrent infections, and cyanotic episodes. The work-up should include a chest x-ray, bronchoscopy, and a chest CT and/or MRI. A variety of interventions may be necessary to treat it, including an aortopexy, pulmonary artery trunk–pexy, arterioplasty, vessel implantation, or endobronchial stent. Residual malacia may remain after treatment, however.
The most common reasons for airway compression by some kind of mass is a reactive lymphadenopathy, a tumor, or an infection, including tuberculosis or histoplasmosis. Severe narrowing of the airway can lead to respiratory failure, but because the compression can develop slowly, the wheezing can be mistaken for asthma. In addition to a chest CT and bronchoscopy, a patient will need other work-ups depending on the cause. Possibilities include a biopsy, a gastric aspirate (for tuberculosis), a bronchoalveolar lavage, or antibody titers.
Similarly, because therapeutic intervention requires treating the underlying infection, specific treatments will vary. Tumors typically will need resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation – and, until the airway is fully cleared, the patient may need chronic mechanical ventilation.
Children with severe scoliosis or kyphosis are those most likely to experience airway compression resulting from pressure by the axial skeleton, in which the spine’s curvature directly presses on the airway. In addition to the wheeze, these patients may have respiratory distress or recurrent focal pneumonia, Dr. Hysinger said. The standard work-up involves a chest x-ray, chest CT, spinal MRI, and bronchoscopy.
Consider using spinal rods, but they can both help the condition or potentially exacerbate the compression, Dr. Hysinger said. Either way, children also will need help with airway clearance and coughing.
Dr. Hysinger concluded by reviewing what you may consider changing in your current practice, including the initial trial of bronchodilators, a chest x-ray, and a subspecialist referral.
No funding was used for this presentation, and Dr. Hysinger reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – , explained Erik Hysinger, MD, MS, of the division of pulmonary medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Localized wheezing is not consistent with asthmatic or viral wheezing, which is typically diffuse and polyphonic, Dr. Hysinger emphasized at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“Localized wheezing is less common than diffuse wheezing and typically has a homophonous sound,” Dr. Hysinger said. It also usually arises from a central airway pathology. “High flow rates create loud amplitude sounds.”
Dr. Hysinger also covered management strategies for focal wheezing, starting with an initial trial of bronchodilators. Any wheezing resulting from a central airway problem, however, isn’t likely to respond to bronchodilators. Standard work-up for any of these causes is usually a chest x-ray, often paired with a bronchoscopy. Persistent wheezing likely needs a chest CT, and many of these conditions will require referral to a subspecialist.
Airway occlusion diagnoses
Four potential causes of an airway blockage are a foreign body, a bronchial cast, mucous plugs, or airway tumors.
A foreign body typically occurs with a cough, wheezing, stridor, and respiratory distress. It is most common in children under age 4 years, usually in those without a history of aspiration, yet providers initially misdiagnose more than 20% of patients with a foreign body. The foreign object – often coins, food, or batteries – frequently ends up in the right main bronchus and may go undetected up to a month, potentially leading to pneumonia, abscess, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, or airway erosion.
An endobronchial cast is rarer than a foreign body, but can be large enough to completely fill a lung with branching mucin, fibrin, and inflammatory cells. The wheezing sounds homophonous, with a barky or brassy cough accompanied by atelectasis. Dr. Hysinger recommended ordering chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and bronchoscopy. Although often idiopathic, these casts also can result from asthma or another disease: neutrophilic inflammation typically indicates a heart condition whereas asthma or influenza leads to eosinophilic inflammation.
Treatment should involve clearing the airway, followed by hypertonic saline, an inhaled tissue plasminogen activator, and a bronchoscopy for extraction.
Although distinct from endobronchial casts, a mucus plug also presents with wheezing, a cough, and atelectasis, and potentially respiratory distress or failure, and hypoxemia. Mucus plugs are diagnosed with a chest x-ray and flexible bronchoscopy, and then treated by removing the plug and clearing the airway, hypertonic saline, and mucolytics.
The rarest cause of an airway blockage is an airway tumor, often mistaken for asthma. Benign causes include papillomatosis, hemangioma, and hamartomas, while potentially malignant causes include a carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, inflammatory myofibromas, and granular cell tumors.
In addition to a chest x-ray and bronchoscopy, a chest CT scan plus a biopsy and resection are necessary to diagnose airway tumors. Treatment will depend on the specific type of tumor identified.
“Overall survival is excellent,” Dr. Hysinger said of children with airway tumors.
Airway narrowing diagnoses
Two possible diagnoses for an intrinsic airway narrowing include bronchomalacia, occurring in only 1 of 2,100 children, and bronchial stenosis.
In bronchomalacia – diagnosed primarily with bronchoscopy – the airway collapses from weakening of the cartilage and posterior membrane. Bronchomalacia sounds like homophonous wheezing with a barky or brassy cough, and it’s frequently accompanied by recurrent bronchitis and/or pneumonia. Intervention is rarely necessary when occurring on its own, but severe cases may require endobronchial stents. Dr. Hysinger also recommended considering ipratroprium instead of albuterol.
Bronchial stenosis involves a fixed narrowing of the bronchi and can be congenital – typically occurring with heart disease – or acquired after an intubation and suction trauma or bronchiolitis obliterans (“popcorn lung”). A chest x-ray and bronchoscopy again are standard, but MRI may be necessary as well. Aside from helping the patient clear the airway, bronchial stenosis typically needs limited management unless the patient is symptomatic. In that case, options include balloon dilation, endobronchial stents, or a slide bronchoplasty.
Airway compression diagnoses
An extrinsic airway compression could have a vascular cause or could result from pressure by an extrinsic mass or the axial skeleton.
Vascular compression usually occurs due to abnormal vasculature development, particularly with vascular stents, Dr. Hysinger said. The wheezing presents with stridor, feeding intolerance, recurrent infections, and cyanotic episodes. The work-up should include a chest x-ray, bronchoscopy, and a chest CT and/or MRI. A variety of interventions may be necessary to treat it, including an aortopexy, pulmonary artery trunk–pexy, arterioplasty, vessel implantation, or endobronchial stent. Residual malacia may remain after treatment, however.
The most common reasons for airway compression by some kind of mass is a reactive lymphadenopathy, a tumor, or an infection, including tuberculosis or histoplasmosis. Severe narrowing of the airway can lead to respiratory failure, but because the compression can develop slowly, the wheezing can be mistaken for asthma. In addition to a chest CT and bronchoscopy, a patient will need other work-ups depending on the cause. Possibilities include a biopsy, a gastric aspirate (for tuberculosis), a bronchoalveolar lavage, or antibody titers.
Similarly, because therapeutic intervention requires treating the underlying infection, specific treatments will vary. Tumors typically will need resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation – and, until the airway is fully cleared, the patient may need chronic mechanical ventilation.
Children with severe scoliosis or kyphosis are those most likely to experience airway compression resulting from pressure by the axial skeleton, in which the spine’s curvature directly presses on the airway. In addition to the wheeze, these patients may have respiratory distress or recurrent focal pneumonia, Dr. Hysinger said. The standard work-up involves a chest x-ray, chest CT, spinal MRI, and bronchoscopy.
Consider using spinal rods, but they can both help the condition or potentially exacerbate the compression, Dr. Hysinger said. Either way, children also will need help with airway clearance and coughing.
Dr. Hysinger concluded by reviewing what you may consider changing in your current practice, including the initial trial of bronchodilators, a chest x-ray, and a subspecialist referral.
No funding was used for this presentation, and Dr. Hysinger reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – , explained Erik Hysinger, MD, MS, of the division of pulmonary medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
Localized wheezing is not consistent with asthmatic or viral wheezing, which is typically diffuse and polyphonic, Dr. Hysinger emphasized at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
“Localized wheezing is less common than diffuse wheezing and typically has a homophonous sound,” Dr. Hysinger said. It also usually arises from a central airway pathology. “High flow rates create loud amplitude sounds.”
Dr. Hysinger also covered management strategies for focal wheezing, starting with an initial trial of bronchodilators. Any wheezing resulting from a central airway problem, however, isn’t likely to respond to bronchodilators. Standard work-up for any of these causes is usually a chest x-ray, often paired with a bronchoscopy. Persistent wheezing likely needs a chest CT, and many of these conditions will require referral to a subspecialist.
Airway occlusion diagnoses
Four potential causes of an airway blockage are a foreign body, a bronchial cast, mucous plugs, or airway tumors.
A foreign body typically occurs with a cough, wheezing, stridor, and respiratory distress. It is most common in children under age 4 years, usually in those without a history of aspiration, yet providers initially misdiagnose more than 20% of patients with a foreign body. The foreign object – often coins, food, or batteries – frequently ends up in the right main bronchus and may go undetected up to a month, potentially leading to pneumonia, abscess, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, or airway erosion.
An endobronchial cast is rarer than a foreign body, but can be large enough to completely fill a lung with branching mucin, fibrin, and inflammatory cells. The wheezing sounds homophonous, with a barky or brassy cough accompanied by atelectasis. Dr. Hysinger recommended ordering chest x-ray, echocardiogram, and bronchoscopy. Although often idiopathic, these casts also can result from asthma or another disease: neutrophilic inflammation typically indicates a heart condition whereas asthma or influenza leads to eosinophilic inflammation.
Treatment should involve clearing the airway, followed by hypertonic saline, an inhaled tissue plasminogen activator, and a bronchoscopy for extraction.
Although distinct from endobronchial casts, a mucus plug also presents with wheezing, a cough, and atelectasis, and potentially respiratory distress or failure, and hypoxemia. Mucus plugs are diagnosed with a chest x-ray and flexible bronchoscopy, and then treated by removing the plug and clearing the airway, hypertonic saline, and mucolytics.
The rarest cause of an airway blockage is an airway tumor, often mistaken for asthma. Benign causes include papillomatosis, hemangioma, and hamartomas, while potentially malignant causes include a carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, inflammatory myofibromas, and granular cell tumors.
In addition to a chest x-ray and bronchoscopy, a chest CT scan plus a biopsy and resection are necessary to diagnose airway tumors. Treatment will depend on the specific type of tumor identified.
“Overall survival is excellent,” Dr. Hysinger said of children with airway tumors.
Airway narrowing diagnoses
Two possible diagnoses for an intrinsic airway narrowing include bronchomalacia, occurring in only 1 of 2,100 children, and bronchial stenosis.
In bronchomalacia – diagnosed primarily with bronchoscopy – the airway collapses from weakening of the cartilage and posterior membrane. Bronchomalacia sounds like homophonous wheezing with a barky or brassy cough, and it’s frequently accompanied by recurrent bronchitis and/or pneumonia. Intervention is rarely necessary when occurring on its own, but severe cases may require endobronchial stents. Dr. Hysinger also recommended considering ipratroprium instead of albuterol.
Bronchial stenosis involves a fixed narrowing of the bronchi and can be congenital – typically occurring with heart disease – or acquired after an intubation and suction trauma or bronchiolitis obliterans (“popcorn lung”). A chest x-ray and bronchoscopy again are standard, but MRI may be necessary as well. Aside from helping the patient clear the airway, bronchial stenosis typically needs limited management unless the patient is symptomatic. In that case, options include balloon dilation, endobronchial stents, or a slide bronchoplasty.
Airway compression diagnoses
An extrinsic airway compression could have a vascular cause or could result from pressure by an extrinsic mass or the axial skeleton.
Vascular compression usually occurs due to abnormal vasculature development, particularly with vascular stents, Dr. Hysinger said. The wheezing presents with stridor, feeding intolerance, recurrent infections, and cyanotic episodes. The work-up should include a chest x-ray, bronchoscopy, and a chest CT and/or MRI. A variety of interventions may be necessary to treat it, including an aortopexy, pulmonary artery trunk–pexy, arterioplasty, vessel implantation, or endobronchial stent. Residual malacia may remain after treatment, however.
The most common reasons for airway compression by some kind of mass is a reactive lymphadenopathy, a tumor, or an infection, including tuberculosis or histoplasmosis. Severe narrowing of the airway can lead to respiratory failure, but because the compression can develop slowly, the wheezing can be mistaken for asthma. In addition to a chest CT and bronchoscopy, a patient will need other work-ups depending on the cause. Possibilities include a biopsy, a gastric aspirate (for tuberculosis), a bronchoalveolar lavage, or antibody titers.
Similarly, because therapeutic intervention requires treating the underlying infection, specific treatments will vary. Tumors typically will need resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation – and, until the airway is fully cleared, the patient may need chronic mechanical ventilation.
Children with severe scoliosis or kyphosis are those most likely to experience airway compression resulting from pressure by the axial skeleton, in which the spine’s curvature directly presses on the airway. In addition to the wheeze, these patients may have respiratory distress or recurrent focal pneumonia, Dr. Hysinger said. The standard work-up involves a chest x-ray, chest CT, spinal MRI, and bronchoscopy.
Consider using spinal rods, but they can both help the condition or potentially exacerbate the compression, Dr. Hysinger said. Either way, children also will need help with airway clearance and coughing.
Dr. Hysinger concluded by reviewing what you may consider changing in your current practice, including the initial trial of bronchodilators, a chest x-ray, and a subspecialist referral.
No funding was used for this presentation, and Dr. Hysinger reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AAP 2017
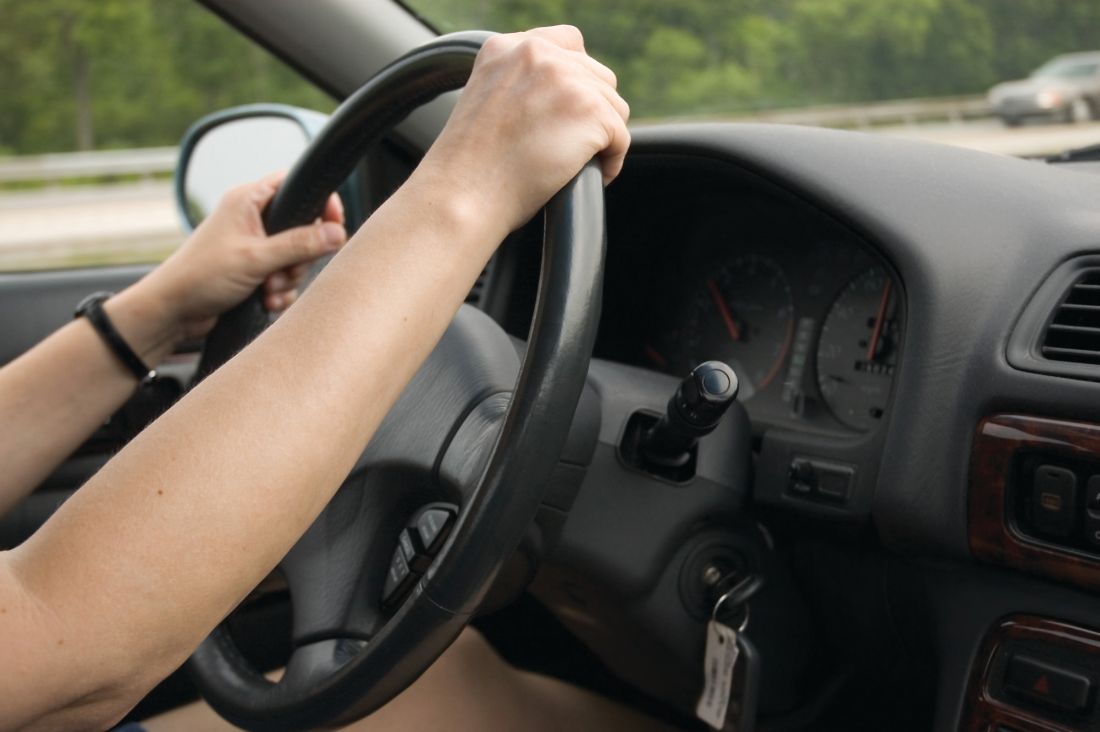
Driving ability of Parkinson’s patients can decline quickly
according to a longitudinal cohort study conducted by Urgun Uc, MD, and associates.
While some patients with Parkinson’s disease who took part in a test of driving skills on a standardized driving course performed significantly worse at a baseline assessment than did healthy control patients, the patients who performed at a similar level as the control group made a significantly higher number of driving mistakes 2 years later on a follow-up evaluation.
Among the original 67 Parkinson’s disease patients, the 28 who returned for repeat testing at 2 years had performed just as well at baseline as the 69 control group returnees. But at the 2-year follow-up, the Parkinson’s disease group made an average of 49.7 mistakes, while the control group made 34.6 mistakes.
In addition to an increase in overall driving errors, Parkinson’s disease patients also made a significantly higher number of lane observance, overtaking, turning, miscellaneous, and serious errors after 2 years than did the control group. Risk factors for worse performance after 2 years included greater error count and worse visual acuity at baseline, and worsening of global cognition, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale scores, executive function, visual-processing speed, and attention.
“Health care providers for patients with Parkinson’s disease should routinely inquire about driving status and make necessary referrals for evaluation of driving fitness as needed. Further research is needed to determine if improvement of underlying impairments in visual perception, executive function, and motor abilities through physical exercise and cognitive training can preserve driving ability in Parkinson’s disease for a longer time,” the investigators concluded.
Read the full study in Neurology (doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004629).
according to a longitudinal cohort study conducted by Urgun Uc, MD, and associates.
While some patients with Parkinson’s disease who took part in a test of driving skills on a standardized driving course performed significantly worse at a baseline assessment than did healthy control patients, the patients who performed at a similar level as the control group made a significantly higher number of driving mistakes 2 years later on a follow-up evaluation.
Among the original 67 Parkinson’s disease patients, the 28 who returned for repeat testing at 2 years had performed just as well at baseline as the 69 control group returnees. But at the 2-year follow-up, the Parkinson’s disease group made an average of 49.7 mistakes, while the control group made 34.6 mistakes.
In addition to an increase in overall driving errors, Parkinson’s disease patients also made a significantly higher number of lane observance, overtaking, turning, miscellaneous, and serious errors after 2 years than did the control group. Risk factors for worse performance after 2 years included greater error count and worse visual acuity at baseline, and worsening of global cognition, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale scores, executive function, visual-processing speed, and attention.
“Health care providers for patients with Parkinson’s disease should routinely inquire about driving status and make necessary referrals for evaluation of driving fitness as needed. Further research is needed to determine if improvement of underlying impairments in visual perception, executive function, and motor abilities through physical exercise and cognitive training can preserve driving ability in Parkinson’s disease for a longer time,” the investigators concluded.
Read the full study in Neurology (doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004629).
according to a longitudinal cohort study conducted by Urgun Uc, MD, and associates.
While some patients with Parkinson’s disease who took part in a test of driving skills on a standardized driving course performed significantly worse at a baseline assessment than did healthy control patients, the patients who performed at a similar level as the control group made a significantly higher number of driving mistakes 2 years later on a follow-up evaluation.
Among the original 67 Parkinson’s disease patients, the 28 who returned for repeat testing at 2 years had performed just as well at baseline as the 69 control group returnees. But at the 2-year follow-up, the Parkinson’s disease group made an average of 49.7 mistakes, while the control group made 34.6 mistakes.
In addition to an increase in overall driving errors, Parkinson’s disease patients also made a significantly higher number of lane observance, overtaking, turning, miscellaneous, and serious errors after 2 years than did the control group. Risk factors for worse performance after 2 years included greater error count and worse visual acuity at baseline, and worsening of global cognition, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale scores, executive function, visual-processing speed, and attention.
“Health care providers for patients with Parkinson’s disease should routinely inquire about driving status and make necessary referrals for evaluation of driving fitness as needed. Further research is needed to determine if improvement of underlying impairments in visual perception, executive function, and motor abilities through physical exercise and cognitive training can preserve driving ability in Parkinson’s disease for a longer time,” the investigators concluded.
Read the full study in Neurology (doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004629).
FROM NEUROLOGY
As nations advance economically, mental illnesses exact greater burdens
BERLIN – A vision perceived during America’s Great Depression has come to fruition across the globe, putting mental illness at the center of a devastating web of personal and economic costs.
In the 1930s, the Rockefeller Foundation’s director of medical science, Alan Gregg, MD, distilled an important notion from his decades of travel providing health care and advice to developing nations. As poor countries became richer, infectious diseases that had long ravaged their populations came under control. As people lived longer, however, they became subject to other disorders: chronic age-related illnesses for the old and, for the young, mental illnesses.
“We have a very, very low rate of infectious disease now, much as the Rockefeller Foundation predicted,” said Dr. Summergrad, the Dr. Frances S. Arkin Professor and chair of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. “But, in 2010, the biggest causes of morbidity and disability for U.S. residents aged 15-49 years old were major depressive disorder, dysthymia, drug and alcohol use, schizophrenia, and anxiety. These dwarf the impact of every other illness during that age period. …. They are the burdens of disease of the modern world.”
This shift from infectious disease to mental illness as a primary cause of disability has profound downstream health implications as well, Dr. Summergrad said. Mental disorders that emerge in adolescent and young adulthood are inextricably linked to the chronic diseases that develop in older people.
“Mental and behavioral disturbances are important risk factors for medical conditions that also exact a heavy burden,” he said, referring to a study in JAMA (2013 Aug 14;310[6]:591-608). The report, “The state of U.S. health, 1990-2010: Burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors,” found that more than half of the of the Top 17 risk factors for morbidity and mortality were directly or indirectly related to mental or behavioral disorders. These included direct causes like alcohol and drug use, and indirect causes that are highly correlated with mental illnesses: physical inactivity, tobacco use, glycemic abnormalities, hypertension, and obesity.
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle, illustrated these global trends in September, with a report published in the Lancet (2017;390:1423-59). Produced in collaboration with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the report focused on the U.N. Sustainable Development Goals, measured 37 of the 50 health-related SDG indicators from 1990-2016 in 188 countries, and projected the indicators to 2030.
China, on the other hand, looked very much like North America. The proportion of infectious diseases was much smaller than in sub-Saharan Africa or India, a finding Dr. Summergrad attributed to the Chinese government’s post–World War II determination to eradicate communicable diseases.
Unfortunately, Dr. Summergrad said, most countries are ill equipped to handle this shift in the burden of illness. Even in the United States, there are limited mental health hospital beds and a dearth of psychiatrists to handle the burgeoning patient load. And the shift toward higher rates of mental illness will likely continue, at a shocking financial cost.
A Harvard School of Public Health policy report, issued in 2011, paints a stark picture. In 2010, mental illness cost high-income countries about $5.5 trillion in lost income and productivity, narrowly beating out the burden imposed by cardivoascular disease ($5.4 trillion). By 2030, lost wages and productivity tied to mental illiness is expected to cost the United States $7.3 trillion.
“Globally, by 2030, we can expect the direct economic impact of mental illnesses to reach $16 trillion,” Dr. Summergrad said. “We have a limited workforce, limited outpatient facilities, limited hospital beds, and limited money, even here in the U.S. All of this is almost nonexistent in much of the world. The integration of care and workforce and facilities will be a huge challenge as we move forward. We need to think about long-term investment here, much in the same way that the Rockefeller Foundation thought about this in the 1930s.”
Dr. Summergrad had no relevant financial disclosures.
BERLIN – A vision perceived during America’s Great Depression has come to fruition across the globe, putting mental illness at the center of a devastating web of personal and economic costs.
In the 1930s, the Rockefeller Foundation’s director of medical science, Alan Gregg, MD, distilled an important notion from his decades of travel providing health care and advice to developing nations. As poor countries became richer, infectious diseases that had long ravaged their populations came under control. As people lived longer, however, they became subject to other disorders: chronic age-related illnesses for the old and, for the young, mental illnesses.
“We have a very, very low rate of infectious disease now, much as the Rockefeller Foundation predicted,” said Dr. Summergrad, the Dr. Frances S. Arkin Professor and chair of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. “But, in 2010, the biggest causes of morbidity and disability for U.S. residents aged 15-49 years old were major depressive disorder, dysthymia, drug and alcohol use, schizophrenia, and anxiety. These dwarf the impact of every other illness during that age period. …. They are the burdens of disease of the modern world.”
This shift from infectious disease to mental illness as a primary cause of disability has profound downstream health implications as well, Dr. Summergrad said. Mental disorders that emerge in adolescent and young adulthood are inextricably linked to the chronic diseases that develop in older people.
“Mental and behavioral disturbances are important risk factors for medical conditions that also exact a heavy burden,” he said, referring to a study in JAMA (2013 Aug 14;310[6]:591-608). The report, “The state of U.S. health, 1990-2010: Burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors,” found that more than half of the of the Top 17 risk factors for morbidity and mortality were directly or indirectly related to mental or behavioral disorders. These included direct causes like alcohol and drug use, and indirect causes that are highly correlated with mental illnesses: physical inactivity, tobacco use, glycemic abnormalities, hypertension, and obesity.
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle, illustrated these global trends in September, with a report published in the Lancet (2017;390:1423-59). Produced in collaboration with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the report focused on the U.N. Sustainable Development Goals, measured 37 of the 50 health-related SDG indicators from 1990-2016 in 188 countries, and projected the indicators to 2030.
China, on the other hand, looked very much like North America. The proportion of infectious diseases was much smaller than in sub-Saharan Africa or India, a finding Dr. Summergrad attributed to the Chinese government’s post–World War II determination to eradicate communicable diseases.
Unfortunately, Dr. Summergrad said, most countries are ill equipped to handle this shift in the burden of illness. Even in the United States, there are limited mental health hospital beds and a dearth of psychiatrists to handle the burgeoning patient load. And the shift toward higher rates of mental illness will likely continue, at a shocking financial cost.
A Harvard School of Public Health policy report, issued in 2011, paints a stark picture. In 2010, mental illness cost high-income countries about $5.5 trillion in lost income and productivity, narrowly beating out the burden imposed by cardivoascular disease ($5.4 trillion). By 2030, lost wages and productivity tied to mental illiness is expected to cost the United States $7.3 trillion.
“Globally, by 2030, we can expect the direct economic impact of mental illnesses to reach $16 trillion,” Dr. Summergrad said. “We have a limited workforce, limited outpatient facilities, limited hospital beds, and limited money, even here in the U.S. All of this is almost nonexistent in much of the world. The integration of care and workforce and facilities will be a huge challenge as we move forward. We need to think about long-term investment here, much in the same way that the Rockefeller Foundation thought about this in the 1930s.”
Dr. Summergrad had no relevant financial disclosures.
BERLIN – A vision perceived during America’s Great Depression has come to fruition across the globe, putting mental illness at the center of a devastating web of personal and economic costs.
In the 1930s, the Rockefeller Foundation’s director of medical science, Alan Gregg, MD, distilled an important notion from his decades of travel providing health care and advice to developing nations. As poor countries became richer, infectious diseases that had long ravaged their populations came under control. As people lived longer, however, they became subject to other disorders: chronic age-related illnesses for the old and, for the young, mental illnesses.
“We have a very, very low rate of infectious disease now, much as the Rockefeller Foundation predicted,” said Dr. Summergrad, the Dr. Frances S. Arkin Professor and chair of psychiatry at Tufts University, Boston. “But, in 2010, the biggest causes of morbidity and disability for U.S. residents aged 15-49 years old were major depressive disorder, dysthymia, drug and alcohol use, schizophrenia, and anxiety. These dwarf the impact of every other illness during that age period. …. They are the burdens of disease of the modern world.”
This shift from infectious disease to mental illness as a primary cause of disability has profound downstream health implications as well, Dr. Summergrad said. Mental disorders that emerge in adolescent and young adulthood are inextricably linked to the chronic diseases that develop in older people.
“Mental and behavioral disturbances are important risk factors for medical conditions that also exact a heavy burden,” he said, referring to a study in JAMA (2013 Aug 14;310[6]:591-608). The report, “The state of U.S. health, 1990-2010: Burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors,” found that more than half of the of the Top 17 risk factors for morbidity and mortality were directly or indirectly related to mental or behavioral disorders. These included direct causes like alcohol and drug use, and indirect causes that are highly correlated with mental illnesses: physical inactivity, tobacco use, glycemic abnormalities, hypertension, and obesity.
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle, illustrated these global trends in September, with a report published in the Lancet (2017;390:1423-59). Produced in collaboration with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the report focused on the U.N. Sustainable Development Goals, measured 37 of the 50 health-related SDG indicators from 1990-2016 in 188 countries, and projected the indicators to 2030.
China, on the other hand, looked very much like North America. The proportion of infectious diseases was much smaller than in sub-Saharan Africa or India, a finding Dr. Summergrad attributed to the Chinese government’s post–World War II determination to eradicate communicable diseases.
Unfortunately, Dr. Summergrad said, most countries are ill equipped to handle this shift in the burden of illness. Even in the United States, there are limited mental health hospital beds and a dearth of psychiatrists to handle the burgeoning patient load. And the shift toward higher rates of mental illness will likely continue, at a shocking financial cost.
A Harvard School of Public Health policy report, issued in 2011, paints a stark picture. In 2010, mental illness cost high-income countries about $5.5 trillion in lost income and productivity, narrowly beating out the burden imposed by cardivoascular disease ($5.4 trillion). By 2030, lost wages and productivity tied to mental illiness is expected to cost the United States $7.3 trillion.
“Globally, by 2030, we can expect the direct economic impact of mental illnesses to reach $16 trillion,” Dr. Summergrad said. “We have a limited workforce, limited outpatient facilities, limited hospital beds, and limited money, even here in the U.S. All of this is almost nonexistent in much of the world. The integration of care and workforce and facilities will be a huge challenge as we move forward. We need to think about long-term investment here, much in the same way that the Rockefeller Foundation thought about this in the 1930s.”
Dr. Summergrad had no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM WPA 2017
Hep C screening falling short in neonatal abstinence syndrome infants
SAN DIEGO – A review of care for neonates born with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) found that screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is low, based on Medicaid data from the state of Kentucky.
“These children are at high risk for HCV, and the screening rate should really be 100%. We think that it is important to get the message out there,” said Michael Smith, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the Duke University, Durham, N.C.
According to the Kentucky Medicaid data, the rates of NAS are not evenly distributed in the state. Stratifying the incidence rates by eight regions, Dr. Smith reported that 33% of the NAS births in 2016 were in region 8. Although region 8 is a rural Appalachian section on the eastern border of the state, the proportion in this region was more than 50% greater than any other region, including the more populated regions containing Louisville, the largest city, and Lexington, the capital.
Statewide, approximately one in three newborns with NAS were screened for HCV, but the rate was as low as 5% in some areas, and low rates were more common in those counties with the highest rates of opioid use and NAS, Dr. Smith said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. Although he acknowledged that rates of HCV screening in newborns with NAS appeared to be increasing when 2015 and 2012 data were compared, “there is still a long way to go.”
“Why is this important? There are a couple of reasons. One is that, if you get children into care early, you are more likely to have follow-up,” Dr. Smith said. Follow-up will be important if, as Dr. Smith predicted, HCV therapies become available for children. When providers know which children are infected, treatment can be initiated more efficiently, and this has implications for risk of transmission and, potentially, for outcomes.
At the University of Louisville, children with NAS are typically screened for HCV, HIV, and other transmissible infections that “travel together,” such as syphilis. The evaluation of the Medicaid data suggested that there were no differences in likelihood of HCV testing for sex and race, but Dr. Smith noted that children placed in foster care were significantly more likely to be tested, likely a reflection of processing regulations.
Overall, there are striking differences in the rates of opioid use, rates of NAS, and likelihood of HCV testing in NAS neonates in eastern Appalachian regions of Kentucky and those in regions in the center of the state closer to academic medical centers. The three regions near the University of Louisville, University of Kentucky in Lexington, and the Ohio River border with Cincinnati are known as “the Golden Triangle,” according to Dr. Smith; these regions are where HCV testing rates in neonates with NAS are higher, but testing still is not uniform.
Currently, HCV testing is mandated for adults in several states, but Dr. Smith emphasized that children with NAS are particularly “vulnerable.” He called for policy changes that would require testing in these children and urged HCV screening regardless of whether official policies are established.
SAN DIEGO – A review of care for neonates born with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) found that screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is low, based on Medicaid data from the state of Kentucky.
“These children are at high risk for HCV, and the screening rate should really be 100%. We think that it is important to get the message out there,” said Michael Smith, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the Duke University, Durham, N.C.
According to the Kentucky Medicaid data, the rates of NAS are not evenly distributed in the state. Stratifying the incidence rates by eight regions, Dr. Smith reported that 33% of the NAS births in 2016 were in region 8. Although region 8 is a rural Appalachian section on the eastern border of the state, the proportion in this region was more than 50% greater than any other region, including the more populated regions containing Louisville, the largest city, and Lexington, the capital.
Statewide, approximately one in three newborns with NAS were screened for HCV, but the rate was as low as 5% in some areas, and low rates were more common in those counties with the highest rates of opioid use and NAS, Dr. Smith said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. Although he acknowledged that rates of HCV screening in newborns with NAS appeared to be increasing when 2015 and 2012 data were compared, “there is still a long way to go.”
“Why is this important? There are a couple of reasons. One is that, if you get children into care early, you are more likely to have follow-up,” Dr. Smith said. Follow-up will be important if, as Dr. Smith predicted, HCV therapies become available for children. When providers know which children are infected, treatment can be initiated more efficiently, and this has implications for risk of transmission and, potentially, for outcomes.
At the University of Louisville, children with NAS are typically screened for HCV, HIV, and other transmissible infections that “travel together,” such as syphilis. The evaluation of the Medicaid data suggested that there were no differences in likelihood of HCV testing for sex and race, but Dr. Smith noted that children placed in foster care were significantly more likely to be tested, likely a reflection of processing regulations.
Overall, there are striking differences in the rates of opioid use, rates of NAS, and likelihood of HCV testing in NAS neonates in eastern Appalachian regions of Kentucky and those in regions in the center of the state closer to academic medical centers. The three regions near the University of Louisville, University of Kentucky in Lexington, and the Ohio River border with Cincinnati are known as “the Golden Triangle,” according to Dr. Smith; these regions are where HCV testing rates in neonates with NAS are higher, but testing still is not uniform.
Currently, HCV testing is mandated for adults in several states, but Dr. Smith emphasized that children with NAS are particularly “vulnerable.” He called for policy changes that would require testing in these children and urged HCV screening regardless of whether official policies are established.
SAN DIEGO – A review of care for neonates born with neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) found that screening for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is low, based on Medicaid data from the state of Kentucky.
“These children are at high risk for HCV, and the screening rate should really be 100%. We think that it is important to get the message out there,” said Michael Smith, MD, of the department of pediatrics at the Duke University, Durham, N.C.
According to the Kentucky Medicaid data, the rates of NAS are not evenly distributed in the state. Stratifying the incidence rates by eight regions, Dr. Smith reported that 33% of the NAS births in 2016 were in region 8. Although region 8 is a rural Appalachian section on the eastern border of the state, the proportion in this region was more than 50% greater than any other region, including the more populated regions containing Louisville, the largest city, and Lexington, the capital.
Statewide, approximately one in three newborns with NAS were screened for HCV, but the rate was as low as 5% in some areas, and low rates were more common in those counties with the highest rates of opioid use and NAS, Dr. Smith said at an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases. Although he acknowledged that rates of HCV screening in newborns with NAS appeared to be increasing when 2015 and 2012 data were compared, “there is still a long way to go.”
“Why is this important? There are a couple of reasons. One is that, if you get children into care early, you are more likely to have follow-up,” Dr. Smith said. Follow-up will be important if, as Dr. Smith predicted, HCV therapies become available for children. When providers know which children are infected, treatment can be initiated more efficiently, and this has implications for risk of transmission and, potentially, for outcomes.
At the University of Louisville, children with NAS are typically screened for HCV, HIV, and other transmissible infections that “travel together,” such as syphilis. The evaluation of the Medicaid data suggested that there were no differences in likelihood of HCV testing for sex and race, but Dr. Smith noted that children placed in foster care were significantly more likely to be tested, likely a reflection of processing regulations.
Overall, there are striking differences in the rates of opioid use, rates of NAS, and likelihood of HCV testing in NAS neonates in eastern Appalachian regions of Kentucky and those in regions in the center of the state closer to academic medical centers. The three regions near the University of Louisville, University of Kentucky in Lexington, and the Ohio River border with Cincinnati are known as “the Golden Triangle,” according to Dr. Smith; these regions are where HCV testing rates in neonates with NAS are higher, but testing still is not uniform.
Currently, HCV testing is mandated for adults in several states, but Dr. Smith emphasized that children with NAS are particularly “vulnerable.” He called for policy changes that would require testing in these children and urged HCV screening regardless of whether official policies are established.
AT ID WEEK 2017
Key clinical point: In Kentucky, which has one of the highest rates of neonates with NAS, screening rates for HCV remain low.
Major finding:
Data source: Retrospective data analysis of Kentucky Medicaid data.
Disclosures: Dr. Smith reported no financial relationships relevant to this study.