User login
Hospital floors are an overlooked reservoir for pathogens
Floors in hospital patients’ rooms are frequently contaminated with pathogens such as Clostridium difficile, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci, which are easily transmitted to the hands of patients, care providers, and visitors, according to a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Disinfection usually focuses on surfaces that are frequently touched by patients’ or health care workers’ hands, such as bed rails and call buttons. Floor disinfection has received limited attention.
However, floors are frequently touched by objects that are then handled, such as shoes and socks, said Abhishek Deshpande, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and his associates.
To examine the extent of floor contamination and the potential for transfer of pathogens to hands, the investigators surveyed five Cleveland-area hospitals.
They collected samples from 1-square-foot areas of floors adjacent to beds and in bathrooms in C. difficile isolation rooms, and in 2-3 randomly selected nonisolation rooms on the same wards. At least 30 rooms at each hospital were cultured for C. difficile, MRSA, and VRE, either during a patient stay or after the rooms had been cleaned at patient discharge.
In addition, the researchers performed a point-prevalence survey of the number and type of high-touch objects contacting floors in 10-25 randomly selected occupied patient rooms at each hospital. After they handled these objects, their hands also were cultured.
Floor contamination was common with all of the pathogens, particularly with C. difficile. The frequency of contamination was similar across the five hospitals, in both bedroom and bathroom sites, and even in the 50 rooms that had been cleaned at the last patient discharge.
C. difficile spores were recovered from the floors of 47%-55% of rooms, MRSA was recovered from the floors of 8%-32% of rooms, and VRE were recovered from the floors of 13%-30% of rooms.
In addition, 41 of 100 occupied rooms had 1-4 “high-touch” objects in direct contact with the floors, including personal items such as clothing, canes, or cellphone chargers; medical supplies or devices such as pulse oximeters, call buttons, heating pads, urinals, blood pressure cuffs, and wash basins; and linens such as bed sheets, pillows, and towels.
Of the 31 cultures taken from both bare and gloved hands that handled these items, MRSA was recovered from 18%, VRE were recovered from 6%, and C. difficile was recovered from 3%.
“These results suggest that floors in hospital rooms could be an underappreciated source for dissemination of pathogens,” Dr. Deshpande and his associates noted (Am J Infect Control. 2017 Mar 1;45[3]:336-8).
“It would be reasonable to educate health care personnel and patients that they should avoid placing high-touch objects on the floor when possible,” they added.
Moreover, the efficacy of current floor-cleaning and disinfection techniques should be reexamined, particularly with regard to eliminating C. difficile spores.
Other modes of transmission from floors also should be assessed, such as contamination of wheelchairs and wheeled equipment. And transmission of other pathogens, such as gram-negative organisms and viruses, should be examined, the investigators said.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs funded the study. Dr. Deshpande reported receiving research grants from 3M, Clorox, and Steris, and one of his associates reported receiving research grants from Clorox, Ecolab, GOJO, Merck, Pfizer, and Steris.
Floors in hospital patients’ rooms are frequently contaminated with pathogens such as Clostridium difficile, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci, which are easily transmitted to the hands of patients, care providers, and visitors, according to a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Disinfection usually focuses on surfaces that are frequently touched by patients’ or health care workers’ hands, such as bed rails and call buttons. Floor disinfection has received limited attention.
However, floors are frequently touched by objects that are then handled, such as shoes and socks, said Abhishek Deshpande, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and his associates.
To examine the extent of floor contamination and the potential for transfer of pathogens to hands, the investigators surveyed five Cleveland-area hospitals.
They collected samples from 1-square-foot areas of floors adjacent to beds and in bathrooms in C. difficile isolation rooms, and in 2-3 randomly selected nonisolation rooms on the same wards. At least 30 rooms at each hospital were cultured for C. difficile, MRSA, and VRE, either during a patient stay or after the rooms had been cleaned at patient discharge.
In addition, the researchers performed a point-prevalence survey of the number and type of high-touch objects contacting floors in 10-25 randomly selected occupied patient rooms at each hospital. After they handled these objects, their hands also were cultured.
Floor contamination was common with all of the pathogens, particularly with C. difficile. The frequency of contamination was similar across the five hospitals, in both bedroom and bathroom sites, and even in the 50 rooms that had been cleaned at the last patient discharge.
C. difficile spores were recovered from the floors of 47%-55% of rooms, MRSA was recovered from the floors of 8%-32% of rooms, and VRE were recovered from the floors of 13%-30% of rooms.
In addition, 41 of 100 occupied rooms had 1-4 “high-touch” objects in direct contact with the floors, including personal items such as clothing, canes, or cellphone chargers; medical supplies or devices such as pulse oximeters, call buttons, heating pads, urinals, blood pressure cuffs, and wash basins; and linens such as bed sheets, pillows, and towels.
Of the 31 cultures taken from both bare and gloved hands that handled these items, MRSA was recovered from 18%, VRE were recovered from 6%, and C. difficile was recovered from 3%.
“These results suggest that floors in hospital rooms could be an underappreciated source for dissemination of pathogens,” Dr. Deshpande and his associates noted (Am J Infect Control. 2017 Mar 1;45[3]:336-8).
“It would be reasonable to educate health care personnel and patients that they should avoid placing high-touch objects on the floor when possible,” they added.
Moreover, the efficacy of current floor-cleaning and disinfection techniques should be reexamined, particularly with regard to eliminating C. difficile spores.
Other modes of transmission from floors also should be assessed, such as contamination of wheelchairs and wheeled equipment. And transmission of other pathogens, such as gram-negative organisms and viruses, should be examined, the investigators said.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs funded the study. Dr. Deshpande reported receiving research grants from 3M, Clorox, and Steris, and one of his associates reported receiving research grants from Clorox, Ecolab, GOJO, Merck, Pfizer, and Steris.
Floors in hospital patients’ rooms are frequently contaminated with pathogens such as Clostridium difficile, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci, which are easily transmitted to the hands of patients, care providers, and visitors, according to a report published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
Disinfection usually focuses on surfaces that are frequently touched by patients’ or health care workers’ hands, such as bed rails and call buttons. Floor disinfection has received limited attention.
However, floors are frequently touched by objects that are then handled, such as shoes and socks, said Abhishek Deshpande, MD, PhD, of the Cleveland Clinic, and his associates.
To examine the extent of floor contamination and the potential for transfer of pathogens to hands, the investigators surveyed five Cleveland-area hospitals.
They collected samples from 1-square-foot areas of floors adjacent to beds and in bathrooms in C. difficile isolation rooms, and in 2-3 randomly selected nonisolation rooms on the same wards. At least 30 rooms at each hospital were cultured for C. difficile, MRSA, and VRE, either during a patient stay or after the rooms had been cleaned at patient discharge.
In addition, the researchers performed a point-prevalence survey of the number and type of high-touch objects contacting floors in 10-25 randomly selected occupied patient rooms at each hospital. After they handled these objects, their hands also were cultured.
Floor contamination was common with all of the pathogens, particularly with C. difficile. The frequency of contamination was similar across the five hospitals, in both bedroom and bathroom sites, and even in the 50 rooms that had been cleaned at the last patient discharge.
C. difficile spores were recovered from the floors of 47%-55% of rooms, MRSA was recovered from the floors of 8%-32% of rooms, and VRE were recovered from the floors of 13%-30% of rooms.
In addition, 41 of 100 occupied rooms had 1-4 “high-touch” objects in direct contact with the floors, including personal items such as clothing, canes, or cellphone chargers; medical supplies or devices such as pulse oximeters, call buttons, heating pads, urinals, blood pressure cuffs, and wash basins; and linens such as bed sheets, pillows, and towels.
Of the 31 cultures taken from both bare and gloved hands that handled these items, MRSA was recovered from 18%, VRE were recovered from 6%, and C. difficile was recovered from 3%.
“These results suggest that floors in hospital rooms could be an underappreciated source for dissemination of pathogens,” Dr. Deshpande and his associates noted (Am J Infect Control. 2017 Mar 1;45[3]:336-8).
“It would be reasonable to educate health care personnel and patients that they should avoid placing high-touch objects on the floor when possible,” they added.
Moreover, the efficacy of current floor-cleaning and disinfection techniques should be reexamined, particularly with regard to eliminating C. difficile spores.
Other modes of transmission from floors also should be assessed, such as contamination of wheelchairs and wheeled equipment. And transmission of other pathogens, such as gram-negative organisms and viruses, should be examined, the investigators said.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs funded the study. Dr. Deshpande reported receiving research grants from 3M, Clorox, and Steris, and one of his associates reported receiving research grants from Clorox, Ecolab, GOJO, Merck, Pfizer, and Steris.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF INFECTION CONTROL
Key clinical point: Floors in hospital patients’ rooms are frequently contaminated with pathogens that are easily transmitted to the hands of patients, care providers, and visitors.
Major finding: C. difficile spores were recovered from the floors of 47%-55% of rooms, MRSA was recovered from the floors of 8%-32% of rooms, and VRE were recovered from the floors of 13%-30% of rooms.
Data source: A survey of five Cleveland-area hospitals in which 318 samples were collected from floors in patient rooms and bathrooms.
Disclosures: The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs funded the study. Dr. Deshpande reported receiving research grants from 3M, Clorox, and Steris, and one of his associates reported receiving research grants from Clorox, Ecolab, Gojo, Merck, Pfizer, and Steris.
How to get the most out of methotrexate for psoriasis
WAILEA, HAWAII – In an era when affordable health insurance could become increasingly tough to come by, it’s worth emphasizing that methotrexate is the most cost-effective way to manage extensive psoriasis – and the liquid formulation designed for intramuscular injection can be taken orally to reduce the cost even further, according to Craig L. Leonardi, MD.
“The absolute cheapest way to manage the patient who has no insurance and has bad psoriasis is to put him on methotrexate and teach him how to draw the liquid solution up in a syringe, dump it in a cup of juice, and drink it,” Dr. Leonardi said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Research Foundation. “The bioavailability is equivalent to [that of] the tablets, and it’s only about one-tenth the cost.”
He urged his fellow dermatologists not to forget about methotrexate in the current flashy era of highly effective – and very expensive – biologic therapies for psoriasis.
“I was thinking methotrexate was going to go away, but it turns out I rely more on that drug than ever before. It’s very useful, and it’s safe if used correctly,” said Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University and a prominent clinical trialist.
He highlighted numerous clinical scenarios in which methotrexate remains a valuable treatment in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. He also touched on patient monitoring requirements, adverse events, and common reasons he receives referrals from physicians whose patients seem to be having problems on methotrexate – referrals that, in most cases, could be avoided, he said, if the referring physician had a fuller understanding of the drug.
“Patients are referred to me all the time for methotrexate intolerance,” Dr. Leonardi said. “When you take methotrexate, you get a brief, dramatic spike in transaminase levels that peaks within a day and then drops off. But, when you get lab tests in these patients, you want to look at trough levels. You want to see the best liver function test values for the week.
“That means you have to tell the patient what day to take the drug and what day to get labs drawn,” he continued. “I’m here to tell you that the vast majority of issues that I see where patients have elevated liver function tests involves them getting their testing done in the first 4 days after taking methotrexate. Take the time to ask about this, and I think you’ll be pleasantly surprised.
“If you just make an adjustment and get them on the right schedule, you’ll discover that the patient is tolerating the drug just fine,” Dr. Leonardi added. “We like getting labs on Monday and dosing on Tuesday.”
Methotrexate’s half-life is 3-15 hours. Psoriasis is often controlled at a methotrexate dose of about 15 mg/week.
Methotrexate’s advantages include ease of use. It’s a straightforward matter to start and stop the drug and to make small dose adjustments. Methotrexate comes in a variety of formulations: the 2.5-mg tablets, the 25 mg/mL solution for IM injection, and prefilled autoinjector devices for subcutaneous administration.
These preloaded pens for subcutaneous injection are just as effective as IM therapy, Dr. Leonardi said. Methotrexate is also better absorbed subcutaneously than it is orally. The bioavailability of oral methotrexate plateaus at a dose of about 22 mg/week, while subcutaneously delivered methotrexate does not. So, if a patient’s psoriasis isn’t adequately controlled on higher-dose oral therapy, it’s worth considering a switch to the preloaded pens.
“It’s a very simple injection, very cost-effective, and your patients may get more bang for the buck by doing that,” according to the dermatologist.
Also, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain have been shown to be significantly less frequent and intense with subcutaneous methotrexate than with the tablets. So, if a patient is experiencing limiting gastrointestinal issues on methotrexate tablets, a shift to subcutaneous therapy is often the solution.
What kind of efficacy can physicians expect with methotrexate monotherapy?
Dr. Leonardi cited the results of the European randomized, open-label RESTORE-1 trial (Br J Dermatol. 2011 Nov;165[5]:1109-17) as being consistent with his own extensive clinical experience: a week-16 PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index ) 75 response rate of 42% with methotrexate, compared with 78% for infliximab (Remicade).
Of course, some patients can’t receive a biologic agent because of their age, lack of insurance coverage, or medical contraindications.
“I use methotrexate a lot in Medicare patients, where, with Part D, it’s hard to get access to biologics without really good coinsurance. I think all of us who prescribe biologics understand that,” he observed.
In pediatric patients with extensive psoriasis, he turns to methotrexate as first-line systemic therapy. After 3 months, if the young patient hasn’t responded satisfactorily, Dr. Leonardi asks the insurance company for access to a biologic agent and usually gets it.
Methotrexate really shines in combination with a biologic agent. It inhibits formation of antibiologic antibodies, an important cause of loss of effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapy.
In one study, 28% of patients on adalimumab (Humira) developed antiadalimumab antibodies during the first 3 years of therapy. These patients were more likely to drop out of therapy for lack of effectiveness.
A key finding in this study was that two-thirds of patients who developed antiadalimumab antibodies did so during the first 28 weeks of therapy (JAMA. 2011 Apr 13;305[14]:1460-8). This time line has influenced Dr. Leonardi’s own clinical practice. He routinely keeps patients on methotrexate for their first 28-36 weeks on a biologic, then tapers the methotrexate in favor of biologic monotherapy.
Other benefits and guidelines
Methotrexate is also a boon in managing psoriasis flares in patients on a biologic.
“We’ve all had patients who are doing well on a biologic, they’re cruising along at 140 weeks, then they get strep throat or another infection, and, next thing you know, you have destabilized psoriasis,” Dr. Leonardi noted.
“One thing I’ll do is add methotrexate to the mix, try to get things under control, and, if we do, then we’ll try to taper the methotrexate,” he continued. “That whole episode might take 4-6 months to resolve before the patient might be able to tolerate biologic monotherapy, though. If they can’t at that point, you might consider rotating to another biologic.”
Current American Academy of Dermatology guidelines recommend that women on methotrexate limit their alcohol intake to one drink per day, two drinks for men. British Society for Rheumatology guidelines recommend a ceiling of 32 g to 64 g of ethanol per week.
“We don’t insist on abstinence. There’s no good evidence that it’s needed,” Dr. Leonardi noted. “If you dose this drug on Tuesday, you can be sure that it’s eliminated from the body on Friday, and that’s when I’ll generally green-light patients to socialize over the weekend. If you can make life a little more tolerable for your patients and they’re willing to follow your instructions, I think it’s a better deal all the way around.”
Prior to initiating methotrexate, he obtains a CBC with platelet count, liver function tests, serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, and screens for latent tuberculosis. In terms of on-treatment monitoring, he gets a CBC and liver function tests every 4-12 weeks and keeps an eye on renal function, especially in older patients, because methotrexate is eliminated renally.
“The guidelines have relaxed regarding the need for liver biopsies,” Dr. Leonardi said. “Most of us are not getting liver biopsies anymore, as is true of our friends in rheumatology.”
He reported having financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies. The SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
WAILEA, HAWAII – In an era when affordable health insurance could become increasingly tough to come by, it’s worth emphasizing that methotrexate is the most cost-effective way to manage extensive psoriasis – and the liquid formulation designed for intramuscular injection can be taken orally to reduce the cost even further, according to Craig L. Leonardi, MD.
“The absolute cheapest way to manage the patient who has no insurance and has bad psoriasis is to put him on methotrexate and teach him how to draw the liquid solution up in a syringe, dump it in a cup of juice, and drink it,” Dr. Leonardi said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Research Foundation. “The bioavailability is equivalent to [that of] the tablets, and it’s only about one-tenth the cost.”
He urged his fellow dermatologists not to forget about methotrexate in the current flashy era of highly effective – and very expensive – biologic therapies for psoriasis.
“I was thinking methotrexate was going to go away, but it turns out I rely more on that drug than ever before. It’s very useful, and it’s safe if used correctly,” said Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University and a prominent clinical trialist.
He highlighted numerous clinical scenarios in which methotrexate remains a valuable treatment in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. He also touched on patient monitoring requirements, adverse events, and common reasons he receives referrals from physicians whose patients seem to be having problems on methotrexate – referrals that, in most cases, could be avoided, he said, if the referring physician had a fuller understanding of the drug.
“Patients are referred to me all the time for methotrexate intolerance,” Dr. Leonardi said. “When you take methotrexate, you get a brief, dramatic spike in transaminase levels that peaks within a day and then drops off. But, when you get lab tests in these patients, you want to look at trough levels. You want to see the best liver function test values for the week.
“That means you have to tell the patient what day to take the drug and what day to get labs drawn,” he continued. “I’m here to tell you that the vast majority of issues that I see where patients have elevated liver function tests involves them getting their testing done in the first 4 days after taking methotrexate. Take the time to ask about this, and I think you’ll be pleasantly surprised.
“If you just make an adjustment and get them on the right schedule, you’ll discover that the patient is tolerating the drug just fine,” Dr. Leonardi added. “We like getting labs on Monday and dosing on Tuesday.”
Methotrexate’s half-life is 3-15 hours. Psoriasis is often controlled at a methotrexate dose of about 15 mg/week.
Methotrexate’s advantages include ease of use. It’s a straightforward matter to start and stop the drug and to make small dose adjustments. Methotrexate comes in a variety of formulations: the 2.5-mg tablets, the 25 mg/mL solution for IM injection, and prefilled autoinjector devices for subcutaneous administration.
These preloaded pens for subcutaneous injection are just as effective as IM therapy, Dr. Leonardi said. Methotrexate is also better absorbed subcutaneously than it is orally. The bioavailability of oral methotrexate plateaus at a dose of about 22 mg/week, while subcutaneously delivered methotrexate does not. So, if a patient’s psoriasis isn’t adequately controlled on higher-dose oral therapy, it’s worth considering a switch to the preloaded pens.
“It’s a very simple injection, very cost-effective, and your patients may get more bang for the buck by doing that,” according to the dermatologist.
Also, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain have been shown to be significantly less frequent and intense with subcutaneous methotrexate than with the tablets. So, if a patient is experiencing limiting gastrointestinal issues on methotrexate tablets, a shift to subcutaneous therapy is often the solution.
What kind of efficacy can physicians expect with methotrexate monotherapy?
Dr. Leonardi cited the results of the European randomized, open-label RESTORE-1 trial (Br J Dermatol. 2011 Nov;165[5]:1109-17) as being consistent with his own extensive clinical experience: a week-16 PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index ) 75 response rate of 42% with methotrexate, compared with 78% for infliximab (Remicade).
Of course, some patients can’t receive a biologic agent because of their age, lack of insurance coverage, or medical contraindications.
“I use methotrexate a lot in Medicare patients, where, with Part D, it’s hard to get access to biologics without really good coinsurance. I think all of us who prescribe biologics understand that,” he observed.
In pediatric patients with extensive psoriasis, he turns to methotrexate as first-line systemic therapy. After 3 months, if the young patient hasn’t responded satisfactorily, Dr. Leonardi asks the insurance company for access to a biologic agent and usually gets it.
Methotrexate really shines in combination with a biologic agent. It inhibits formation of antibiologic antibodies, an important cause of loss of effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapy.
In one study, 28% of patients on adalimumab (Humira) developed antiadalimumab antibodies during the first 3 years of therapy. These patients were more likely to drop out of therapy for lack of effectiveness.
A key finding in this study was that two-thirds of patients who developed antiadalimumab antibodies did so during the first 28 weeks of therapy (JAMA. 2011 Apr 13;305[14]:1460-8). This time line has influenced Dr. Leonardi’s own clinical practice. He routinely keeps patients on methotrexate for their first 28-36 weeks on a biologic, then tapers the methotrexate in favor of biologic monotherapy.
Other benefits and guidelines
Methotrexate is also a boon in managing psoriasis flares in patients on a biologic.
“We’ve all had patients who are doing well on a biologic, they’re cruising along at 140 weeks, then they get strep throat or another infection, and, next thing you know, you have destabilized psoriasis,” Dr. Leonardi noted.
“One thing I’ll do is add methotrexate to the mix, try to get things under control, and, if we do, then we’ll try to taper the methotrexate,” he continued. “That whole episode might take 4-6 months to resolve before the patient might be able to tolerate biologic monotherapy, though. If they can’t at that point, you might consider rotating to another biologic.”
Current American Academy of Dermatology guidelines recommend that women on methotrexate limit their alcohol intake to one drink per day, two drinks for men. British Society for Rheumatology guidelines recommend a ceiling of 32 g to 64 g of ethanol per week.
“We don’t insist on abstinence. There’s no good evidence that it’s needed,” Dr. Leonardi noted. “If you dose this drug on Tuesday, you can be sure that it’s eliminated from the body on Friday, and that’s when I’ll generally green-light patients to socialize over the weekend. If you can make life a little more tolerable for your patients and they’re willing to follow your instructions, I think it’s a better deal all the way around.”
Prior to initiating methotrexate, he obtains a CBC with platelet count, liver function tests, serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, and screens for latent tuberculosis. In terms of on-treatment monitoring, he gets a CBC and liver function tests every 4-12 weeks and keeps an eye on renal function, especially in older patients, because methotrexate is eliminated renally.
“The guidelines have relaxed regarding the need for liver biopsies,” Dr. Leonardi said. “Most of us are not getting liver biopsies anymore, as is true of our friends in rheumatology.”
He reported having financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies. The SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
WAILEA, HAWAII – In an era when affordable health insurance could become increasingly tough to come by, it’s worth emphasizing that methotrexate is the most cost-effective way to manage extensive psoriasis – and the liquid formulation designed for intramuscular injection can be taken orally to reduce the cost even further, according to Craig L. Leonardi, MD.
“The absolute cheapest way to manage the patient who has no insurance and has bad psoriasis is to put him on methotrexate and teach him how to draw the liquid solution up in a syringe, dump it in a cup of juice, and drink it,” Dr. Leonardi said at the Hawaii Dermatology Seminar provided by the Global Academy for Medical Education/Skin Disease Research Foundation. “The bioavailability is equivalent to [that of] the tablets, and it’s only about one-tenth the cost.”
He urged his fellow dermatologists not to forget about methotrexate in the current flashy era of highly effective – and very expensive – biologic therapies for psoriasis.
“I was thinking methotrexate was going to go away, but it turns out I rely more on that drug than ever before. It’s very useful, and it’s safe if used correctly,” said Dr. Leonardi, a dermatologist at Saint Louis University and a prominent clinical trialist.
He highlighted numerous clinical scenarios in which methotrexate remains a valuable treatment in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. He also touched on patient monitoring requirements, adverse events, and common reasons he receives referrals from physicians whose patients seem to be having problems on methotrexate – referrals that, in most cases, could be avoided, he said, if the referring physician had a fuller understanding of the drug.
“Patients are referred to me all the time for methotrexate intolerance,” Dr. Leonardi said. “When you take methotrexate, you get a brief, dramatic spike in transaminase levels that peaks within a day and then drops off. But, when you get lab tests in these patients, you want to look at trough levels. You want to see the best liver function test values for the week.
“That means you have to tell the patient what day to take the drug and what day to get labs drawn,” he continued. “I’m here to tell you that the vast majority of issues that I see where patients have elevated liver function tests involves them getting their testing done in the first 4 days after taking methotrexate. Take the time to ask about this, and I think you’ll be pleasantly surprised.
“If you just make an adjustment and get them on the right schedule, you’ll discover that the patient is tolerating the drug just fine,” Dr. Leonardi added. “We like getting labs on Monday and dosing on Tuesday.”
Methotrexate’s half-life is 3-15 hours. Psoriasis is often controlled at a methotrexate dose of about 15 mg/week.
Methotrexate’s advantages include ease of use. It’s a straightforward matter to start and stop the drug and to make small dose adjustments. Methotrexate comes in a variety of formulations: the 2.5-mg tablets, the 25 mg/mL solution for IM injection, and prefilled autoinjector devices for subcutaneous administration.
These preloaded pens for subcutaneous injection are just as effective as IM therapy, Dr. Leonardi said. Methotrexate is also better absorbed subcutaneously than it is orally. The bioavailability of oral methotrexate plateaus at a dose of about 22 mg/week, while subcutaneously delivered methotrexate does not. So, if a patient’s psoriasis isn’t adequately controlled on higher-dose oral therapy, it’s worth considering a switch to the preloaded pens.
“It’s a very simple injection, very cost-effective, and your patients may get more bang for the buck by doing that,” according to the dermatologist.
Also, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain have been shown to be significantly less frequent and intense with subcutaneous methotrexate than with the tablets. So, if a patient is experiencing limiting gastrointestinal issues on methotrexate tablets, a shift to subcutaneous therapy is often the solution.
What kind of efficacy can physicians expect with methotrexate monotherapy?
Dr. Leonardi cited the results of the European randomized, open-label RESTORE-1 trial (Br J Dermatol. 2011 Nov;165[5]:1109-17) as being consistent with his own extensive clinical experience: a week-16 PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index ) 75 response rate of 42% with methotrexate, compared with 78% for infliximab (Remicade).
Of course, some patients can’t receive a biologic agent because of their age, lack of insurance coverage, or medical contraindications.
“I use methotrexate a lot in Medicare patients, where, with Part D, it’s hard to get access to biologics without really good coinsurance. I think all of us who prescribe biologics understand that,” he observed.
In pediatric patients with extensive psoriasis, he turns to methotrexate as first-line systemic therapy. After 3 months, if the young patient hasn’t responded satisfactorily, Dr. Leonardi asks the insurance company for access to a biologic agent and usually gets it.
Methotrexate really shines in combination with a biologic agent. It inhibits formation of antibiologic antibodies, an important cause of loss of effectiveness of monoclonal antibody therapy.
In one study, 28% of patients on adalimumab (Humira) developed antiadalimumab antibodies during the first 3 years of therapy. These patients were more likely to drop out of therapy for lack of effectiveness.
A key finding in this study was that two-thirds of patients who developed antiadalimumab antibodies did so during the first 28 weeks of therapy (JAMA. 2011 Apr 13;305[14]:1460-8). This time line has influenced Dr. Leonardi’s own clinical practice. He routinely keeps patients on methotrexate for their first 28-36 weeks on a biologic, then tapers the methotrexate in favor of biologic monotherapy.
Other benefits and guidelines
Methotrexate is also a boon in managing psoriasis flares in patients on a biologic.
“We’ve all had patients who are doing well on a biologic, they’re cruising along at 140 weeks, then they get strep throat or another infection, and, next thing you know, you have destabilized psoriasis,” Dr. Leonardi noted.
“One thing I’ll do is add methotrexate to the mix, try to get things under control, and, if we do, then we’ll try to taper the methotrexate,” he continued. “That whole episode might take 4-6 months to resolve before the patient might be able to tolerate biologic monotherapy, though. If they can’t at that point, you might consider rotating to another biologic.”
Current American Academy of Dermatology guidelines recommend that women on methotrexate limit their alcohol intake to one drink per day, two drinks for men. British Society for Rheumatology guidelines recommend a ceiling of 32 g to 64 g of ethanol per week.
“We don’t insist on abstinence. There’s no good evidence that it’s needed,” Dr. Leonardi noted. “If you dose this drug on Tuesday, you can be sure that it’s eliminated from the body on Friday, and that’s when I’ll generally green-light patients to socialize over the weekend. If you can make life a little more tolerable for your patients and they’re willing to follow your instructions, I think it’s a better deal all the way around.”
Prior to initiating methotrexate, he obtains a CBC with platelet count, liver function tests, serum urea nitrogen, creatinine, and screens for latent tuberculosis. In terms of on-treatment monitoring, he gets a CBC and liver function tests every 4-12 weeks and keeps an eye on renal function, especially in older patients, because methotrexate is eliminated renally.
“The guidelines have relaxed regarding the need for liver biopsies,” Dr. Leonardi said. “Most of us are not getting liver biopsies anymore, as is true of our friends in rheumatology.”
He reported having financial relationships with more than a dozen pharmaceutical companies. The SDEF and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SDEF HAWAII DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Malpractice: Paid claims down, but average payment up
The rate of paid legal claims against physicians dropped by more than half between 1992 and 2014, but the average claim payment amount rose, according to an analysis of the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Adam C. Schaffer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues examined paid claims from the National Practitioner Data Bank from Jan. 1, 1992, to Dec. 31, 2014, accounting for specialty. Dollar amounts were inflation-adjusted to 2014 dollars using the Consumer Price Index.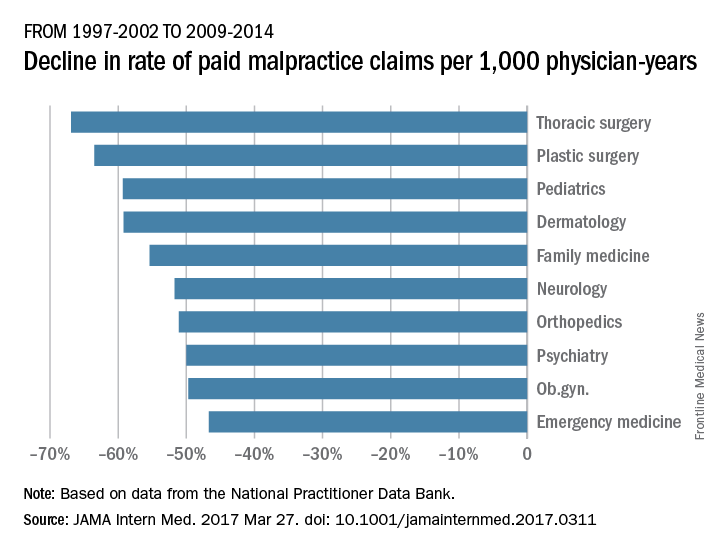
From 1992-1996 to 2009-2014, the rate of paid claims decreased by 56%, ranging from a 76% decrease in pediatrics to a 14% rate decrease in cardiology. The mean payment increased by 23% from $286,751 to $353,473 between 1992-1996 and 2009-2014. The increases ranged from $17,431 in general practice to $138,708 in pathology (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311).
The most common allegation was diagnostic error, followed by surgical error and medication or treatment error. The proportion of paid claims attributable to diagnostic error varied widely and was highest in pathology and radiology. Plastic surgery had the highest percentage of paid claims related to surgical errors. Specialties with the highest percentage of paid claims related to medication/treatment errors were psychiatry, general practice, and pulmonology.
While prior data have shown the overall trend of declining paid malpractice claims and increasing average payments, this study is the first to examine such trends by medical specialty, said Dr. Schaffer.
“We think it is important to try to understand the reasons for the variation among specialties in characteristics of paid malpractice claims, as understanding the reasons for this variation may provide insights about how we can provide the safest care possible,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Schaffer said that he hopes the findings make physicians more aware of the malpractice landscape and aid their future practice decisions.
“Medical malpractice is an issue that concerns many physicians, and physicians’ perceptions of their liability risk can influence the decisions they make in caring for their patients,” he said. “By performing an analysis of a national database of paid medical malpractice claims broken down by specialty, we hope to provide physicians with data that give them an accurate picture of the medical malpractice environment in which they are practicing.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
The rate of paid legal claims against physicians dropped by more than half between 1992 and 2014, but the average claim payment amount rose, according to an analysis of the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Adam C. Schaffer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues examined paid claims from the National Practitioner Data Bank from Jan. 1, 1992, to Dec. 31, 2014, accounting for specialty. Dollar amounts were inflation-adjusted to 2014 dollars using the Consumer Price Index.
From 1992-1996 to 2009-2014, the rate of paid claims decreased by 56%, ranging from a 76% decrease in pediatrics to a 14% rate decrease in cardiology. The mean payment increased by 23% from $286,751 to $353,473 between 1992-1996 and 2009-2014. The increases ranged from $17,431 in general practice to $138,708 in pathology (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311).
The most common allegation was diagnostic error, followed by surgical error and medication or treatment error. The proportion of paid claims attributable to diagnostic error varied widely and was highest in pathology and radiology. Plastic surgery had the highest percentage of paid claims related to surgical errors. Specialties with the highest percentage of paid claims related to medication/treatment errors were psychiatry, general practice, and pulmonology.
While prior data have shown the overall trend of declining paid malpractice claims and increasing average payments, this study is the first to examine such trends by medical specialty, said Dr. Schaffer.
“We think it is important to try to understand the reasons for the variation among specialties in characteristics of paid malpractice claims, as understanding the reasons for this variation may provide insights about how we can provide the safest care possible,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Schaffer said that he hopes the findings make physicians more aware of the malpractice landscape and aid their future practice decisions.
“Medical malpractice is an issue that concerns many physicians, and physicians’ perceptions of their liability risk can influence the decisions they make in caring for their patients,” he said. “By performing an analysis of a national database of paid medical malpractice claims broken down by specialty, we hope to provide physicians with data that give them an accurate picture of the medical malpractice environment in which they are practicing.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
The rate of paid legal claims against physicians dropped by more than half between 1992 and 2014, but the average claim payment amount rose, according to an analysis of the National Practitioner Data Bank.
Adam C. Schaffer, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and his colleagues examined paid claims from the National Practitioner Data Bank from Jan. 1, 1992, to Dec. 31, 2014, accounting for specialty. Dollar amounts were inflation-adjusted to 2014 dollars using the Consumer Price Index.
From 1992-1996 to 2009-2014, the rate of paid claims decreased by 56%, ranging from a 76% decrease in pediatrics to a 14% rate decrease in cardiology. The mean payment increased by 23% from $286,751 to $353,473 between 1992-1996 and 2009-2014. The increases ranged from $17,431 in general practice to $138,708 in pathology (JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Mar 27. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0311).
The most common allegation was diagnostic error, followed by surgical error and medication or treatment error. The proportion of paid claims attributable to diagnostic error varied widely and was highest in pathology and radiology. Plastic surgery had the highest percentage of paid claims related to surgical errors. Specialties with the highest percentage of paid claims related to medication/treatment errors were psychiatry, general practice, and pulmonology.
While prior data have shown the overall trend of declining paid malpractice claims and increasing average payments, this study is the first to examine such trends by medical specialty, said Dr. Schaffer.
“We think it is important to try to understand the reasons for the variation among specialties in characteristics of paid malpractice claims, as understanding the reasons for this variation may provide insights about how we can provide the safest care possible,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Schaffer said that he hopes the findings make physicians more aware of the malpractice landscape and aid their future practice decisions.
“Medical malpractice is an issue that concerns many physicians, and physicians’ perceptions of their liability risk can influence the decisions they make in caring for their patients,” he said. “By performing an analysis of a national database of paid medical malpractice claims broken down by specialty, we hope to provide physicians with data that give them an accurate picture of the medical malpractice environment in which they are practicing.”
agallegos@frontlinemedcom.com
On Twitter @legal_med
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Stroll Down the AmSECT Avenue
As the premier organization focused on extracorporeal circulation technology professionals, AmSECT encourages sharing of the latest trends and developments in the industry. When visiting the Exhibit Hall, stroll over to AmSECT Avenue and explore perfusion technologies and products – all in one place!
Walk the red carpet and meet with Abbott, Spectrum Medical, Medtronic, LivaNova, Terumo and more! See first-hand the latest in perfusion technology and advancements. You’ll gain knowledge of products that you can immediately take back to your facility, and other advancements that will help you remain current in the field of perfusion.
Stop by the AmSECT booth to discover how to keep learning after the conference concludes! AmSECT University provides a platform to facilitate perfusion-related education and earn continuing education units. The AmSECT team is available to answer your questions about AmSECT University and other benefits you will receive by becoming an AmSECT member.
As the premier organization focused on extracorporeal circulation technology professionals, AmSECT encourages sharing of the latest trends and developments in the industry. When visiting the Exhibit Hall, stroll over to AmSECT Avenue and explore perfusion technologies and products – all in one place!
Walk the red carpet and meet with Abbott, Spectrum Medical, Medtronic, LivaNova, Terumo and more! See first-hand the latest in perfusion technology and advancements. You’ll gain knowledge of products that you can immediately take back to your facility, and other advancements that will help you remain current in the field of perfusion.
Stop by the AmSECT booth to discover how to keep learning after the conference concludes! AmSECT University provides a platform to facilitate perfusion-related education and earn continuing education units. The AmSECT team is available to answer your questions about AmSECT University and other benefits you will receive by becoming an AmSECT member.
As the premier organization focused on extracorporeal circulation technology professionals, AmSECT encourages sharing of the latest trends and developments in the industry. When visiting the Exhibit Hall, stroll over to AmSECT Avenue and explore perfusion technologies and products – all in one place!
Walk the red carpet and meet with Abbott, Spectrum Medical, Medtronic, LivaNova, Terumo and more! See first-hand the latest in perfusion technology and advancements. You’ll gain knowledge of products that you can immediately take back to your facility, and other advancements that will help you remain current in the field of perfusion.
Stop by the AmSECT booth to discover how to keep learning after the conference concludes! AmSECT University provides a platform to facilitate perfusion-related education and earn continuing education units. The AmSECT team is available to answer your questions about AmSECT University and other benefits you will receive by becoming an AmSECT member.
Transplantation and ECMO feature prominently in Saturday session
Saturday’s course “Cardiothoracic Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support of Heart and Lung Failure: Mastery of the Management of End Stage Heart and Lung Disease” will explore novel techniques in heart and lung transplant, mechanical circulatory support, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). The course is co-chaired by Matthew D. Bacchetta, MD, of Columbia University, Carmelo A. Milano, of Duke University, and Rich Walczak, CCP, FPP, also of Duke University.
The first session will focus on heart transplants, and will cover topics such as perfusion storage for transplantation, maintaining an ex-vivo heart, primary graft dysfunction and a talk from Yoshifumi Naka, MD, of Columbia University, who will provide first-hand accounts of using the latest durable centrifugal left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
“We’re going to get a very comprehensive update on the use of donation after cardiac death (DCD) lung transplantation, which is obviously a hot topic in our field right now,” explained Dr. Bacchetta. DCD will also be discussed in relation to heart transplants.
After lunch, mechanical circulatory support will take center stage. Presentations will range from dealing with LVAD and BiVAD support, to avoiding and treating pump thrombosis, and techniques for troubleshooting implantable devices. The course will close with a session on ECMO with Dr. Bacchetta presenting on ECMO bridge to transplantation (BTT), while other talks consider artificial lung development, ECMO transport, management of ambulation during ECMO, and ex vivo lung perfusion.
Dr. Bacchetta said, “We’ll be getting really good reviews from some of the best centers around the world.”
Saturday’s course “Cardiothoracic Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support of Heart and Lung Failure: Mastery of the Management of End Stage Heart and Lung Disease” will explore novel techniques in heart and lung transplant, mechanical circulatory support, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). The course is co-chaired by Matthew D. Bacchetta, MD, of Columbia University, Carmelo A. Milano, of Duke University, and Rich Walczak, CCP, FPP, also of Duke University.
The first session will focus on heart transplants, and will cover topics such as perfusion storage for transplantation, maintaining an ex-vivo heart, primary graft dysfunction and a talk from Yoshifumi Naka, MD, of Columbia University, who will provide first-hand accounts of using the latest durable centrifugal left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
“We’re going to get a very comprehensive update on the use of donation after cardiac death (DCD) lung transplantation, which is obviously a hot topic in our field right now,” explained Dr. Bacchetta. DCD will also be discussed in relation to heart transplants.
After lunch, mechanical circulatory support will take center stage. Presentations will range from dealing with LVAD and BiVAD support, to avoiding and treating pump thrombosis, and techniques for troubleshooting implantable devices. The course will close with a session on ECMO with Dr. Bacchetta presenting on ECMO bridge to transplantation (BTT), while other talks consider artificial lung development, ECMO transport, management of ambulation during ECMO, and ex vivo lung perfusion.
Dr. Bacchetta said, “We’ll be getting really good reviews from some of the best centers around the world.”
Saturday’s course “Cardiothoracic Transplant and Mechanical Circulatory Support of Heart and Lung Failure: Mastery of the Management of End Stage Heart and Lung Disease” will explore novel techniques in heart and lung transplant, mechanical circulatory support, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). The course is co-chaired by Matthew D. Bacchetta, MD, of Columbia University, Carmelo A. Milano, of Duke University, and Rich Walczak, CCP, FPP, also of Duke University.
The first session will focus on heart transplants, and will cover topics such as perfusion storage for transplantation, maintaining an ex-vivo heart, primary graft dysfunction and a talk from Yoshifumi Naka, MD, of Columbia University, who will provide first-hand accounts of using the latest durable centrifugal left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
“We’re going to get a very comprehensive update on the use of donation after cardiac death (DCD) lung transplantation, which is obviously a hot topic in our field right now,” explained Dr. Bacchetta. DCD will also be discussed in relation to heart transplants.
After lunch, mechanical circulatory support will take center stage. Presentations will range from dealing with LVAD and BiVAD support, to avoiding and treating pump thrombosis, and techniques for troubleshooting implantable devices. The course will close with a session on ECMO with Dr. Bacchetta presenting on ECMO bridge to transplantation (BTT), while other talks consider artificial lung development, ECMO transport, management of ambulation during ECMO, and ex vivo lung perfusion.
Dr. Bacchetta said, “We’ll be getting really good reviews from some of the best centers around the world.”
The 20th Annual C. Walton Lillehei Forum Award
Attendees will have the opportunity to hear about exceptional cardiothoracic research at Monday afternoon’s 20th Annual C. Walton Lillehei Resident Forum, which showcases top research by residents.
Co-chairs Dao Nguyen, MD, of the University of Miami Health System and Frederick Y. Chen, MD, PhD, of Tufts Medical Center, along with members of the AATS Research Scholarship Committee reviewed the submitted manuscripts and will judge the oral presentations to select the winner of a prestigious $5,000 cash prize. The competition is limited to original work presented by residents in cardiothoracic surgery and/or residents in general surgical training programs who are working in a cardiothoracic surgical laboratory or clinical rotation in North America.
“The competition is fierce as all the abstracts were of the highest scientific caliber and the committee had a hard time selecting the final top six to include in the final program,” he said. “It is a great honor for resident trainees to give a podium presentation of their research works at the top international meeting in the field of cardiothoracic surgery, such as the AATS.”
The individual presentations are the work of one to three years in the laboratory and represent the specialties’ best non-clinical research, Dr. Chen added.
“The top prize is the most prestigious prize for any postdoctoral research fellow in thoracic surgery and marks them as someone who will likely become a leader in the field,” he said.
Attendees will get the chance to hear a wide diversity of research on Monday, including two abstracts focused on cardiac surgery research, one of which centers on the genetic basis of aortic aneurysm, and another that focuses on cell therapy to rescue heart function following ischemic injury, Dr. Nguyen said. Four abstracts focus on thoracic surgery research, one of which relates to oncology, one that focuses on tissue engineering, one that pertains to lung transplantation, and one that applies the concept of lung perfusion to rehabilitate borderline lung donor graft to restore lung function affected by sepsis.
“These research projects are at the cutting edge of innovation,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Monday’s forum will kick off with a research paper entitled “Mutations in ROBO4 Lead to the Development of Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Ascending Aortic Aneurysm,” presented by Hamza Aziz, MD, of Duke University.
Next, Jarrod Predina, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, will present research that describes how “Targeted Near-Infrared Intraoperative Molecular Imaging Can Identify Residual Disease During Pulmonary Resection,” followed by an analysis on how “Delivery of Endothelial Progenitor Cells with Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogels Maintains Ventricular Geometry and Normalizes Dynamic Strain to Stabilize Cardiac Function Following Ischemic Injury,” presented by Ann C. Gaffey, MD, also of the University of Pennsylvania.
Attendees will also hear a presentation entitled “Targeted Cell Replacement in Human Lung Bioengineering,” by Brandon A. Guenthart, MD, of Columbia University. Stephen Chiu, MD, of Northwestern University, will then present his research paper called “Donor-derived Non-Classical Monocytes Mediate Primary Lung Allograft Dysfunction by Recruiting Recipient Neutrophils via Toll-Like Receptor-dependent Production of MIP-2 .”
Finally, attendees will hear about how “In Vivo Lung Perfusion Rehabilitates Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury,” presented by J. Hunter Mehaffey, MD, of the University of Virginia.
Dr. Nguyen encourages all meeting attendees to attend the forum to learn about the forefront of cardiothoracic surgery research performed by the future generation of the specialty and to “give the trainees all the support and accolades that they and their lab mentors all deserve.”
Attendees will have the opportunity to hear about exceptional cardiothoracic research at Monday afternoon’s 20th Annual C. Walton Lillehei Resident Forum, which showcases top research by residents.
Co-chairs Dao Nguyen, MD, of the University of Miami Health System and Frederick Y. Chen, MD, PhD, of Tufts Medical Center, along with members of the AATS Research Scholarship Committee reviewed the submitted manuscripts and will judge the oral presentations to select the winner of a prestigious $5,000 cash prize. The competition is limited to original work presented by residents in cardiothoracic surgery and/or residents in general surgical training programs who are working in a cardiothoracic surgical laboratory or clinical rotation in North America.
“The competition is fierce as all the abstracts were of the highest scientific caliber and the committee had a hard time selecting the final top six to include in the final program,” he said. “It is a great honor for resident trainees to give a podium presentation of their research works at the top international meeting in the field of cardiothoracic surgery, such as the AATS.”
The individual presentations are the work of one to three years in the laboratory and represent the specialties’ best non-clinical research, Dr. Chen added.
“The top prize is the most prestigious prize for any postdoctoral research fellow in thoracic surgery and marks them as someone who will likely become a leader in the field,” he said.
Attendees will get the chance to hear a wide diversity of research on Monday, including two abstracts focused on cardiac surgery research, one of which centers on the genetic basis of aortic aneurysm, and another that focuses on cell therapy to rescue heart function following ischemic injury, Dr. Nguyen said. Four abstracts focus on thoracic surgery research, one of which relates to oncology, one that focuses on tissue engineering, one that pertains to lung transplantation, and one that applies the concept of lung perfusion to rehabilitate borderline lung donor graft to restore lung function affected by sepsis.
“These research projects are at the cutting edge of innovation,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Monday’s forum will kick off with a research paper entitled “Mutations in ROBO4 Lead to the Development of Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Ascending Aortic Aneurysm,” presented by Hamza Aziz, MD, of Duke University.
Next, Jarrod Predina, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, will present research that describes how “Targeted Near-Infrared Intraoperative Molecular Imaging Can Identify Residual Disease During Pulmonary Resection,” followed by an analysis on how “Delivery of Endothelial Progenitor Cells with Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogels Maintains Ventricular Geometry and Normalizes Dynamic Strain to Stabilize Cardiac Function Following Ischemic Injury,” presented by Ann C. Gaffey, MD, also of the University of Pennsylvania.
Attendees will also hear a presentation entitled “Targeted Cell Replacement in Human Lung Bioengineering,” by Brandon A. Guenthart, MD, of Columbia University. Stephen Chiu, MD, of Northwestern University, will then present his research paper called “Donor-derived Non-Classical Monocytes Mediate Primary Lung Allograft Dysfunction by Recruiting Recipient Neutrophils via Toll-Like Receptor-dependent Production of MIP-2 .”
Finally, attendees will hear about how “In Vivo Lung Perfusion Rehabilitates Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury,” presented by J. Hunter Mehaffey, MD, of the University of Virginia.
Dr. Nguyen encourages all meeting attendees to attend the forum to learn about the forefront of cardiothoracic surgery research performed by the future generation of the specialty and to “give the trainees all the support and accolades that they and their lab mentors all deserve.”
Attendees will have the opportunity to hear about exceptional cardiothoracic research at Monday afternoon’s 20th Annual C. Walton Lillehei Resident Forum, which showcases top research by residents.
Co-chairs Dao Nguyen, MD, of the University of Miami Health System and Frederick Y. Chen, MD, PhD, of Tufts Medical Center, along with members of the AATS Research Scholarship Committee reviewed the submitted manuscripts and will judge the oral presentations to select the winner of a prestigious $5,000 cash prize. The competition is limited to original work presented by residents in cardiothoracic surgery and/or residents in general surgical training programs who are working in a cardiothoracic surgical laboratory or clinical rotation in North America.
“The competition is fierce as all the abstracts were of the highest scientific caliber and the committee had a hard time selecting the final top six to include in the final program,” he said. “It is a great honor for resident trainees to give a podium presentation of their research works at the top international meeting in the field of cardiothoracic surgery, such as the AATS.”
The individual presentations are the work of one to three years in the laboratory and represent the specialties’ best non-clinical research, Dr. Chen added.
“The top prize is the most prestigious prize for any postdoctoral research fellow in thoracic surgery and marks them as someone who will likely become a leader in the field,” he said.
Attendees will get the chance to hear a wide diversity of research on Monday, including two abstracts focused on cardiac surgery research, one of which centers on the genetic basis of aortic aneurysm, and another that focuses on cell therapy to rescue heart function following ischemic injury, Dr. Nguyen said. Four abstracts focus on thoracic surgery research, one of which relates to oncology, one that focuses on tissue engineering, one that pertains to lung transplantation, and one that applies the concept of lung perfusion to rehabilitate borderline lung donor graft to restore lung function affected by sepsis.
“These research projects are at the cutting edge of innovation,” Dr. Nguyen said.
Monday’s forum will kick off with a research paper entitled “Mutations in ROBO4 Lead to the Development of Bicuspid Aortic Valve and Ascending Aortic Aneurysm,” presented by Hamza Aziz, MD, of Duke University.
Next, Jarrod Predina, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, will present research that describes how “Targeted Near-Infrared Intraoperative Molecular Imaging Can Identify Residual Disease During Pulmonary Resection,” followed by an analysis on how “Delivery of Endothelial Progenitor Cells with Injectable Shear-Thinning Hydrogels Maintains Ventricular Geometry and Normalizes Dynamic Strain to Stabilize Cardiac Function Following Ischemic Injury,” presented by Ann C. Gaffey, MD, also of the University of Pennsylvania.
Attendees will also hear a presentation entitled “Targeted Cell Replacement in Human Lung Bioengineering,” by Brandon A. Guenthart, MD, of Columbia University. Stephen Chiu, MD, of Northwestern University, will then present his research paper called “Donor-derived Non-Classical Monocytes Mediate Primary Lung Allograft Dysfunction by Recruiting Recipient Neutrophils via Toll-Like Receptor-dependent Production of MIP-2 .”
Finally, attendees will hear about how “In Vivo Lung Perfusion Rehabilitates Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury,” presented by J. Hunter Mehaffey, MD, of the University of Virginia.
Dr. Nguyen encourages all meeting attendees to attend the forum to learn about the forefront of cardiothoracic surgery research performed by the future generation of the specialty and to “give the trainees all the support and accolades that they and their lab mentors all deserve.”
Cardiac surgery symposium critiques challenging cases
“This year’s Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium will prove to be one of the most dynamic and liveliest to date,” said course chair Vinod H. Thourani, MD, in an interview. “Each session will have dedicated time for robust panel discussion and hopefully significant participant involvement,” he said.
Dr. Thourani, of Emory University, leads an expert roster of clinicians in the AATS/STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium entitled “Excellence Through Knowledge.” The all-day Sunday format allows for an in-depth exploration that can benefit clinicians with a range of perspectives. The talks will include not only examples from clinical experience, but also “will provide the audience with the most up-to-date literature on a variety of topics relevant to the practice of cardiac surgery,” Dr. Thourani said.
The topics scheduled for discussion will include the management of short-term circulatory support for acute cardiac decompensation, aortic and mitral valve surgery, coronary artery disease, and management of aorta diseases, Dr. Thourani said.
Dr. Thourani highlighted some of specific topics that he considers especially hot this year: “New Surgical and Transcatheter Therapies for Right Ventricular Failure,” by Edward G. Soltesz, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic; “TAVR for the Treatment of Aortic Stenosis: Here Comes the Tsunami!!!,” by Michael J. Mack, MD, of the Baylor Health Care System; “Indications for Concomitant Tricuspid Valve Repair,” by Gilles D. Dreyfus, MD, of the Cardio Thoracic Centre of Monaco; “Making the Heat Team a Reality in Choosing Between CABG and PCI,” by Farouc A. Jaffer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital; and “Root Aneurysm with Bicuspid Aortic Valve: Spare or Replace,” by Tirone E. David, MD of Toronto General Hospital.
After a break for lunch, the symposium continues with a session on “Controversies in Mitral Valve Surgery.” Topics include not only indications for concomitant tricuspid valve repair, but also determinants for mitral valve repair or replacement and a discussion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mitral valve disease.
“We are delighted that this symposium will not only have renowned surgeons, but also cardiologists and perfusionists that truly represent a heart team approach to these complex patients,” Dr. Thourani concluded.
“This year’s Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium will prove to be one of the most dynamic and liveliest to date,” said course chair Vinod H. Thourani, MD, in an interview. “Each session will have dedicated time for robust panel discussion and hopefully significant participant involvement,” he said.
Dr. Thourani, of Emory University, leads an expert roster of clinicians in the AATS/STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium entitled “Excellence Through Knowledge.” The all-day Sunday format allows for an in-depth exploration that can benefit clinicians with a range of perspectives. The talks will include not only examples from clinical experience, but also “will provide the audience with the most up-to-date literature on a variety of topics relevant to the practice of cardiac surgery,” Dr. Thourani said.
The topics scheduled for discussion will include the management of short-term circulatory support for acute cardiac decompensation, aortic and mitral valve surgery, coronary artery disease, and management of aorta diseases, Dr. Thourani said.
Dr. Thourani highlighted some of specific topics that he considers especially hot this year: “New Surgical and Transcatheter Therapies for Right Ventricular Failure,” by Edward G. Soltesz, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic; “TAVR for the Treatment of Aortic Stenosis: Here Comes the Tsunami!!!,” by Michael J. Mack, MD, of the Baylor Health Care System; “Indications for Concomitant Tricuspid Valve Repair,” by Gilles D. Dreyfus, MD, of the Cardio Thoracic Centre of Monaco; “Making the Heat Team a Reality in Choosing Between CABG and PCI,” by Farouc A. Jaffer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital; and “Root Aneurysm with Bicuspid Aortic Valve: Spare or Replace,” by Tirone E. David, MD of Toronto General Hospital.
After a break for lunch, the symposium continues with a session on “Controversies in Mitral Valve Surgery.” Topics include not only indications for concomitant tricuspid valve repair, but also determinants for mitral valve repair or replacement and a discussion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mitral valve disease.
“We are delighted that this symposium will not only have renowned surgeons, but also cardiologists and perfusionists that truly represent a heart team approach to these complex patients,” Dr. Thourani concluded.
“This year’s Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium will prove to be one of the most dynamic and liveliest to date,” said course chair Vinod H. Thourani, MD, in an interview. “Each session will have dedicated time for robust panel discussion and hopefully significant participant involvement,” he said.
Dr. Thourani, of Emory University, leads an expert roster of clinicians in the AATS/STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Symposium entitled “Excellence Through Knowledge.” The all-day Sunday format allows for an in-depth exploration that can benefit clinicians with a range of perspectives. The talks will include not only examples from clinical experience, but also “will provide the audience with the most up-to-date literature on a variety of topics relevant to the practice of cardiac surgery,” Dr. Thourani said.
The topics scheduled for discussion will include the management of short-term circulatory support for acute cardiac decompensation, aortic and mitral valve surgery, coronary artery disease, and management of aorta diseases, Dr. Thourani said.
Dr. Thourani highlighted some of specific topics that he considers especially hot this year: “New Surgical and Transcatheter Therapies for Right Ventricular Failure,” by Edward G. Soltesz, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic; “TAVR for the Treatment of Aortic Stenosis: Here Comes the Tsunami!!!,” by Michael J. Mack, MD, of the Baylor Health Care System; “Indications for Concomitant Tricuspid Valve Repair,” by Gilles D. Dreyfus, MD, of the Cardio Thoracic Centre of Monaco; “Making the Heat Team a Reality in Choosing Between CABG and PCI,” by Farouc A. Jaffer, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital; and “Root Aneurysm with Bicuspid Aortic Valve: Spare or Replace,” by Tirone E. David, MD of Toronto General Hospital.
After a break for lunch, the symposium continues with a session on “Controversies in Mitral Valve Surgery.” Topics include not only indications for concomitant tricuspid valve repair, but also determinants for mitral valve repair or replacement and a discussion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of mitral valve disease.
“We are delighted that this symposium will not only have renowned surgeons, but also cardiologists and perfusionists that truly represent a heart team approach to these complex patients,” Dr. Thourani concluded.
New devices improve outcomes for pediatric patients
The smallest patients get a full day’s focus in the “Congenital Heart Disease Symposium: Innovations and Controversies in the Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease,” session on Sunday, April 30.
“This symposium is designed for participants to get up-to-date information about cardiothoracic surgery,” said Katsuhide Maeda, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, in an interview.
The Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates (PumpKIN) trial is designed as a randomized, multicenter, two-arm study to evaluate an investigational ventricular assistance device (VAD) known as Jarvik 2015, comparing it to the EXCOR Pediatric VAD in children with heart failure. The study is designed to enroll 88 patients, 44 randomized to the Jarvik 2015 and 44 to the EXCOR.
The primary objectives of the PumpKIN trial, according to Clinicaltrials.gov description, are to determine the safety of the Jarvik 2015 based on evaluations of reported serious adverse events up to the first 180 days after implantation, and to assess benefits based on overall survival without severe neurologic impairment.
Symposium attendees can learn the latest information about outcomes as well as tips and techniques for device use in neonates and infants, Dr. Maeda said.
Some of the presentations featuring tips and techniques include “Device Innovations and Options for Biventrical Mechanical Circulatory Support,” by Mark Shepard, MD, of St. Louis Children’s Hospital; “Surgical Techniques for TAPVR,” by Christopher A. Caldarone, MD, of the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto; and “The “Tweener” Arch - Front vs. Side,” by Charles D. Fraser, MD, of Texas Children’s Hospital.
Looking ahead, Dr. Maeda advised clinicians to keep watching the PumpKIN trial, which is set to begin in seven institutions in the United States and Canada. “This device may open a new door,” for pediatric heart surgery, he noted.
The smallest patients get a full day’s focus in the “Congenital Heart Disease Symposium: Innovations and Controversies in the Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease,” session on Sunday, April 30.
“This symposium is designed for participants to get up-to-date information about cardiothoracic surgery,” said Katsuhide Maeda, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, in an interview.
The Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates (PumpKIN) trial is designed as a randomized, multicenter, two-arm study to evaluate an investigational ventricular assistance device (VAD) known as Jarvik 2015, comparing it to the EXCOR Pediatric VAD in children with heart failure. The study is designed to enroll 88 patients, 44 randomized to the Jarvik 2015 and 44 to the EXCOR.
The primary objectives of the PumpKIN trial, according to Clinicaltrials.gov description, are to determine the safety of the Jarvik 2015 based on evaluations of reported serious adverse events up to the first 180 days after implantation, and to assess benefits based on overall survival without severe neurologic impairment.
Symposium attendees can learn the latest information about outcomes as well as tips and techniques for device use in neonates and infants, Dr. Maeda said.
Some of the presentations featuring tips and techniques include “Device Innovations and Options for Biventrical Mechanical Circulatory Support,” by Mark Shepard, MD, of St. Louis Children’s Hospital; “Surgical Techniques for TAPVR,” by Christopher A. Caldarone, MD, of the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto; and “The “Tweener” Arch - Front vs. Side,” by Charles D. Fraser, MD, of Texas Children’s Hospital.
Looking ahead, Dr. Maeda advised clinicians to keep watching the PumpKIN trial, which is set to begin in seven institutions in the United States and Canada. “This device may open a new door,” for pediatric heart surgery, he noted.
The smallest patients get a full day’s focus in the “Congenital Heart Disease Symposium: Innovations and Controversies in the Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease,” session on Sunday, April 30.
“This symposium is designed for participants to get up-to-date information about cardiothoracic surgery,” said Katsuhide Maeda, MD, of Stanford University Medical Center, in an interview.
The Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates (PumpKIN) trial is designed as a randomized, multicenter, two-arm study to evaluate an investigational ventricular assistance device (VAD) known as Jarvik 2015, comparing it to the EXCOR Pediatric VAD in children with heart failure. The study is designed to enroll 88 patients, 44 randomized to the Jarvik 2015 and 44 to the EXCOR.
The primary objectives of the PumpKIN trial, according to Clinicaltrials.gov description, are to determine the safety of the Jarvik 2015 based on evaluations of reported serious adverse events up to the first 180 days after implantation, and to assess benefits based on overall survival without severe neurologic impairment.
Symposium attendees can learn the latest information about outcomes as well as tips and techniques for device use in neonates and infants, Dr. Maeda said.
Some of the presentations featuring tips and techniques include “Device Innovations and Options for Biventrical Mechanical Circulatory Support,” by Mark Shepard, MD, of St. Louis Children’s Hospital; “Surgical Techniques for TAPVR,” by Christopher A. Caldarone, MD, of the Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto; and “The “Tweener” Arch - Front vs. Side,” by Charles D. Fraser, MD, of Texas Children’s Hospital.
Looking ahead, Dr. Maeda advised clinicians to keep watching the PumpKIN trial, which is set to begin in seven institutions in the United States and Canada. “This device may open a new door,” for pediatric heart surgery, he noted.
Multidisciplinary Teams Create Systems of Care
Experts from a variety of disciplines will come together to discuss topics related to preoperative, perioperative and postoperative care for cardiovascular surgery patients during Sunday’s full-day symposium, “Improving Systems of Care, Quality and Safety.”
“The AATS recognizes that the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered cardiovascular care is best achieved through the use of proficient multidisciplinary teams,” said course co-chair Katherine J. Hoercher, RN, FAHA, of the Cleveland Clinic. “This symposium, with its focus on interprofessional education, is an important mechanism for developing team-based care competencies that form the underpinning of high-functioning teams.”
By bringing together faculty and learners from multiple cardiovascular surgery professions, attendees can learn how effective collaboration and utilization of standardized processes can improve outcomes in systems of care, quality and safety, Ms. Hoercher said.
“The session should provide the audience with nuts-and-bolts approaches to everyday problems through a global view of the difficulties we face in consistently delivering the highest quality medical care,” added course co-chair Glenn J.R. Whitman, MD, of The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
The morning session “will address a variety of common problems that we all face in managing cardiac surgical patients,” Dr. Whitman said. “The topics are varied and include, for example, informed consent, optimizing preoperative surgical readiness, as well as specific aspects of postoperative management such as goal-directed resuscitation and approach to the cardiac arrest patient.”
Included in the morning presentations are four talks on a team approach to minimizing transfusions, including preadmission use of epoetin; preoperative evaluation and intraoperative management; perioperative management of blood preservation; and risks, recognition and management of post cardiopulmonary bypass hemorrhage.
The afternoon portion of the symposium “will continue the morning objective and focus on specific postoperative morbidities, including hyperglycemia, perioperative myocardial infarctions and strokes,” Dr. Whitman said.
The session will conclude with presentations from five nationally-renowned speakers. Douglas R. Johnston, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, will discuss what surgical teams can learn from fighter pilots, special ops forces and other elite performers; Peter Pronovost, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine, and its Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality, will discuss organizational structure and process factors for improving cardiac surgery quality and safety; Don Goldmann, MD, of the Institute for Healthcare Improvement, will provide insights on the impact of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) on the delivery of cardiovascular care; David M. Shahian, MD, of Harvard Medical School, who oversees the Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ database, will talk about meaningful outcome measures in cardiac surgery; and Alex B. Haynes, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, will review surgical checklists and their association with decreased morbidity and mortality.
“This session should be of interest to all AATS meeting attendees as we navigate the ever-changing landscape of health care delivery,” Ms. Hoercher said. “The information presented will be something the audience can’t easily obtain elsewhere,” added Dr. Whitman.
“I hope many of the AATS meeting attendees, both surgeons and non-surgeons, will join us at what will be an excellent educational opportunity,” Ms. Hoercher said.
Experts from a variety of disciplines will come together to discuss topics related to preoperative, perioperative and postoperative care for cardiovascular surgery patients during Sunday’s full-day symposium, “Improving Systems of Care, Quality and Safety.”
“The AATS recognizes that the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered cardiovascular care is best achieved through the use of proficient multidisciplinary teams,” said course co-chair Katherine J. Hoercher, RN, FAHA, of the Cleveland Clinic. “This symposium, with its focus on interprofessional education, is an important mechanism for developing team-based care competencies that form the underpinning of high-functioning teams.”
By bringing together faculty and learners from multiple cardiovascular surgery professions, attendees can learn how effective collaboration and utilization of standardized processes can improve outcomes in systems of care, quality and safety, Ms. Hoercher said.
“The session should provide the audience with nuts-and-bolts approaches to everyday problems through a global view of the difficulties we face in consistently delivering the highest quality medical care,” added course co-chair Glenn J.R. Whitman, MD, of The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
The morning session “will address a variety of common problems that we all face in managing cardiac surgical patients,” Dr. Whitman said. “The topics are varied and include, for example, informed consent, optimizing preoperative surgical readiness, as well as specific aspects of postoperative management such as goal-directed resuscitation and approach to the cardiac arrest patient.”
Included in the morning presentations are four talks on a team approach to minimizing transfusions, including preadmission use of epoetin; preoperative evaluation and intraoperative management; perioperative management of blood preservation; and risks, recognition and management of post cardiopulmonary bypass hemorrhage.
The afternoon portion of the symposium “will continue the morning objective and focus on specific postoperative morbidities, including hyperglycemia, perioperative myocardial infarctions and strokes,” Dr. Whitman said.
The session will conclude with presentations from five nationally-renowned speakers. Douglas R. Johnston, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, will discuss what surgical teams can learn from fighter pilots, special ops forces and other elite performers; Peter Pronovost, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine, and its Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality, will discuss organizational structure and process factors for improving cardiac surgery quality and safety; Don Goldmann, MD, of the Institute for Healthcare Improvement, will provide insights on the impact of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) on the delivery of cardiovascular care; David M. Shahian, MD, of Harvard Medical School, who oversees the Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ database, will talk about meaningful outcome measures in cardiac surgery; and Alex B. Haynes, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, will review surgical checklists and their association with decreased morbidity and mortality.
“This session should be of interest to all AATS meeting attendees as we navigate the ever-changing landscape of health care delivery,” Ms. Hoercher said. “The information presented will be something the audience can’t easily obtain elsewhere,” added Dr. Whitman.
“I hope many of the AATS meeting attendees, both surgeons and non-surgeons, will join us at what will be an excellent educational opportunity,” Ms. Hoercher said.
Experts from a variety of disciplines will come together to discuss topics related to preoperative, perioperative and postoperative care for cardiovascular surgery patients during Sunday’s full-day symposium, “Improving Systems of Care, Quality and Safety.”
“The AATS recognizes that the delivery of high-quality, patient-centered cardiovascular care is best achieved through the use of proficient multidisciplinary teams,” said course co-chair Katherine J. Hoercher, RN, FAHA, of the Cleveland Clinic. “This symposium, with its focus on interprofessional education, is an important mechanism for developing team-based care competencies that form the underpinning of high-functioning teams.”
By bringing together faculty and learners from multiple cardiovascular surgery professions, attendees can learn how effective collaboration and utilization of standardized processes can improve outcomes in systems of care, quality and safety, Ms. Hoercher said.
“The session should provide the audience with nuts-and-bolts approaches to everyday problems through a global view of the difficulties we face in consistently delivering the highest quality medical care,” added course co-chair Glenn J.R. Whitman, MD, of The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
The morning session “will address a variety of common problems that we all face in managing cardiac surgical patients,” Dr. Whitman said. “The topics are varied and include, for example, informed consent, optimizing preoperative surgical readiness, as well as specific aspects of postoperative management such as goal-directed resuscitation and approach to the cardiac arrest patient.”
Included in the morning presentations are four talks on a team approach to minimizing transfusions, including preadmission use of epoetin; preoperative evaluation and intraoperative management; perioperative management of blood preservation; and risks, recognition and management of post cardiopulmonary bypass hemorrhage.
The afternoon portion of the symposium “will continue the morning objective and focus on specific postoperative morbidities, including hyperglycemia, perioperative myocardial infarctions and strokes,” Dr. Whitman said.
The session will conclude with presentations from five nationally-renowned speakers. Douglas R. Johnston, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, will discuss what surgical teams can learn from fighter pilots, special ops forces and other elite performers; Peter Pronovost, MD, of Johns Hopkins Medicine, and its Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality, will discuss organizational structure and process factors for improving cardiac surgery quality and safety; Don Goldmann, MD, of the Institute for Healthcare Improvement, will provide insights on the impact of the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act (MACRA) on the delivery of cardiovascular care; David M. Shahian, MD, of Harvard Medical School, who oversees the Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ database, will talk about meaningful outcome measures in cardiac surgery; and Alex B. Haynes, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, will review surgical checklists and their association with decreased morbidity and mortality.
“This session should be of interest to all AATS meeting attendees as we navigate the ever-changing landscape of health care delivery,” Ms. Hoercher said. “The information presented will be something the audience can’t easily obtain elsewhere,” added Dr. Whitman.
“I hope many of the AATS meeting attendees, both surgeons and non-surgeons, will join us at what will be an excellent educational opportunity,” Ms. Hoercher said.
ACC/AHA vs. USPSTF statin guidelines
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for preventive statin therapy would cover an estimated 9.3 million more U.S. adults than would the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidelines, according to a report published online April 18 in JAMA.
Most of this difference can be attributed to younger adults and those with diabetes, for whom the ACC/AHA guidelines recommend statin therapy but the USPSTF guidelines do not, said Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, of the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., and her associates.
They compared the proportion of patients who would be eligible for primary prevention statin therapy according to these two sets of guidelines by applying the eligibility criteria to a sample of 3,416 participants in the nationally representative 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). These participants were 40-75 years of age, were free of cardiovascular disease, and had triglyceride levels of 400 mg/dL or less. A total of 747 (21.5%) were taking lipid-lowering medication at the time of the survey.
If the USPSTF guidelines (JAMA. 2016 Nov 15;316[19]:1997-2007)were fully implemented in this cohort, 15.8% more of the participants would be taking statin therapy. In contrast, if the ACC/AHA guidelines (Circulation. 2014 Jun 24;129[25 Suppl 2]:S1-4) were fully implemented in this cohort, 24.3% more would be taking statins.
A total of 8.9% of the cohort would be recommended for statin therapy under the ACC/AHA guidelines but not the USPSTF guidelines. Most of this discrepancy could be attributed to the youngest adults and to those with diabetes. The ACC/AHA guidelines were much more likely to recommend statins to patients aged 40-59 years. Such patients have a relatively low 10-year risk of cardiovascular events (7.0%) but a much higher longer-term risk of 34.6% at 30 years, the investigators said.
“Given that half of all [cardiovascular] events in men and one-third in women occur before age 65 years, reliance on 10-year risk alone may miss many younger individuals who could potentially benefit from long-term statin therapy,” they noted (JAMA 2017 Apr 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3416).
Further analysis broke down which adults the ACC/AHA guidelines covered, in contrast to the USPSTF guidelines: younger male smokers, younger men with dyslipidemia, younger men with high LDL-cholesterol levels, younger women with obesity, and older men who didn’t have high LDL-cholesterol levels.
Extrapolating these findings to the general U.S. population, “there could be an estimated 17.1 million vs 26.4 million U.S. adults with a new recommendation for statin therapy, based on the USPSTF recommendations vs the ACC/AHA guideline recommendations, respectively – an estimated difference of 9.3 million individuals,” Dr. Pagidipati and her associates wrote.
“Alternative approaches to augmenting risk-based cholesterol guidelines, including those that explicitly incorporate potential benefit of therapy, should be considered,” they added.
This study was supported by the Duke Clinical Research Institute. Dr. Pagidipati reported having no relevant financial disclosures; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for preventive statin therapy would cover an estimated 9.3 million more U.S. adults than would the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidelines, according to a report published online April 18 in JAMA.
Most of this difference can be attributed to younger adults and those with diabetes, for whom the ACC/AHA guidelines recommend statin therapy but the USPSTF guidelines do not, said Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, of the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., and her associates.
They compared the proportion of patients who would be eligible for primary prevention statin therapy according to these two sets of guidelines by applying the eligibility criteria to a sample of 3,416 participants in the nationally representative 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). These participants were 40-75 years of age, were free of cardiovascular disease, and had triglyceride levels of 400 mg/dL or less. A total of 747 (21.5%) were taking lipid-lowering medication at the time of the survey.
If the USPSTF guidelines (JAMA. 2016 Nov 15;316[19]:1997-2007)were fully implemented in this cohort, 15.8% more of the participants would be taking statin therapy. In contrast, if the ACC/AHA guidelines (Circulation. 2014 Jun 24;129[25 Suppl 2]:S1-4) were fully implemented in this cohort, 24.3% more would be taking statins.
A total of 8.9% of the cohort would be recommended for statin therapy under the ACC/AHA guidelines but not the USPSTF guidelines. Most of this discrepancy could be attributed to the youngest adults and to those with diabetes. The ACC/AHA guidelines were much more likely to recommend statins to patients aged 40-59 years. Such patients have a relatively low 10-year risk of cardiovascular events (7.0%) but a much higher longer-term risk of 34.6% at 30 years, the investigators said.
“Given that half of all [cardiovascular] events in men and one-third in women occur before age 65 years, reliance on 10-year risk alone may miss many younger individuals who could potentially benefit from long-term statin therapy,” they noted (JAMA 2017 Apr 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3416).
Further analysis broke down which adults the ACC/AHA guidelines covered, in contrast to the USPSTF guidelines: younger male smokers, younger men with dyslipidemia, younger men with high LDL-cholesterol levels, younger women with obesity, and older men who didn’t have high LDL-cholesterol levels.
Extrapolating these findings to the general U.S. population, “there could be an estimated 17.1 million vs 26.4 million U.S. adults with a new recommendation for statin therapy, based on the USPSTF recommendations vs the ACC/AHA guideline recommendations, respectively – an estimated difference of 9.3 million individuals,” Dr. Pagidipati and her associates wrote.
“Alternative approaches to augmenting risk-based cholesterol guidelines, including those that explicitly incorporate potential benefit of therapy, should be considered,” they added.
This study was supported by the Duke Clinical Research Institute. Dr. Pagidipati reported having no relevant financial disclosures; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines for preventive statin therapy would cover an estimated 9.3 million more U.S. adults than would the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guidelines, according to a report published online April 18 in JAMA.
Most of this difference can be attributed to younger adults and those with diabetes, for whom the ACC/AHA guidelines recommend statin therapy but the USPSTF guidelines do not, said Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, of the Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., and her associates.
They compared the proportion of patients who would be eligible for primary prevention statin therapy according to these two sets of guidelines by applying the eligibility criteria to a sample of 3,416 participants in the nationally representative 2009-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). These participants were 40-75 years of age, were free of cardiovascular disease, and had triglyceride levels of 400 mg/dL or less. A total of 747 (21.5%) were taking lipid-lowering medication at the time of the survey.
If the USPSTF guidelines (JAMA. 2016 Nov 15;316[19]:1997-2007)were fully implemented in this cohort, 15.8% more of the participants would be taking statin therapy. In contrast, if the ACC/AHA guidelines (Circulation. 2014 Jun 24;129[25 Suppl 2]:S1-4) were fully implemented in this cohort, 24.3% more would be taking statins.
A total of 8.9% of the cohort would be recommended for statin therapy under the ACC/AHA guidelines but not the USPSTF guidelines. Most of this discrepancy could be attributed to the youngest adults and to those with diabetes. The ACC/AHA guidelines were much more likely to recommend statins to patients aged 40-59 years. Such patients have a relatively low 10-year risk of cardiovascular events (7.0%) but a much higher longer-term risk of 34.6% at 30 years, the investigators said.
“Given that half of all [cardiovascular] events in men and one-third in women occur before age 65 years, reliance on 10-year risk alone may miss many younger individuals who could potentially benefit from long-term statin therapy,” they noted (JAMA 2017 Apr 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.3416).
Further analysis broke down which adults the ACC/AHA guidelines covered, in contrast to the USPSTF guidelines: younger male smokers, younger men with dyslipidemia, younger men with high LDL-cholesterol levels, younger women with obesity, and older men who didn’t have high LDL-cholesterol levels.
Extrapolating these findings to the general U.S. population, “there could be an estimated 17.1 million vs 26.4 million U.S. adults with a new recommendation for statin therapy, based on the USPSTF recommendations vs the ACC/AHA guideline recommendations, respectively – an estimated difference of 9.3 million individuals,” Dr. Pagidipati and her associates wrote.
“Alternative approaches to augmenting risk-based cholesterol guidelines, including those that explicitly incorporate potential benefit of therapy, should be considered,” they added.
This study was supported by the Duke Clinical Research Institute. Dr. Pagidipati reported having no relevant financial disclosures; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
FROM JAMA
Key clinical point: The ACC/AHA guidelines for preventive statin therapy would cover an estimated 9 million more U.S. adults than the USPSTF guidelines.
Major finding: 8.9% of the 3,416 NHANES participants would be recommended for statin therapy under the ACC/AHA guidelines but not the USPSTF guidelines.
Data source: An analysis of the difference in eligibility for preventive statin therapy between two sets of guidelines using data for 3,416 participants in the nationally representative NHANES survey in 2009-2014.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Duke Clinical Research Institute. Dr. Pagidipati reported having no relevant financial disclosures; her associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.












