User login
Evolve your website
The past few years have seen major transformations in the way health care websites operate and interact with patients. .
In mid-2018, a major Google algorithm change, known to the IT community as the “Medic Update,” significantly changed search criteria for most health and wellness websites. Another big update went live in late 2021. Websites that have not evolved with these changes have dropped in search rankings and provide a poorer user experience all around.
Many potential patients are searching for your services online, so your website cannot be an afterthought. Not only does it need to be designed with your target audience in mind, but it is also important to consider the metrics Google and other search engines now use when assessing the quality of your website so that patients will find it in the first place.
Here are some features that you (or your website company) need to prioritize to keep your site current and atop search results in 2023 and beyond.
Begin with an understandable URL. Search engines use URLs to determine how well your site, or a portion of it, matches search criteria. URLs also need to make sense to searchers, especially when they link specific areas of expertise (more on that in a minute). For example, a URL like “jonesdermatology.com/?p=89021” is meaningless to anyone except programmers; but “jonesdermatology.com/psoriasistreatments” obviously leads to a page about psoriasis treatments. Search engines look for not only the most relevant, but also the most helpful and user-friendly answers to a user’s query.
Incidentally, if the URL for your site is not your own name, you should register your name as a separate domain name – even if you never use it – to be sure that a trickster or troll, or someone with the same name but a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Continue with a good meta description. That’s the grayish text that follows the title and URL in search results. Searchers will read it to confirm that your site is what they seek, so make sure it describes exactly what you do, including any areas of special expertise.
Make your practice approachable with photos. New patients are more comfortable when they know what you look like, so real photos of you and your staff are always more effective than stock photos of models. Photos or a video tour of your office will reassure prospective patients that they will be visiting a clean, modern, professional facility.
Describe your principal services in detail. You never know which specific service a prospective patient is searching for, so describe everything you offer. Don’t try to summarize everything on a single page; relevance is determined by how deeply a topic is covered, so each principal service should have a detailed description on its own page. Not only will your skills become more visible to search engines, but you can also use the space to enumerate your qualifications and expertise in each area. Whenever possible, write your descriptions in question-and-answer form. Searchers tend to ask questions (“what is the best ... ?”), particularly in voice searches. Search engines increasingly value sites that ask and answer common questions.
Make your site interactive. “Interactivity” is a major buzzword in modern search engine parlance. Once searchers make an appointment, they stop searching. If they have to wait until the next day to call your office, they may keep looking – and might find a competitor with online scheduling. HIPAA-compliant chatbots, secure messaging, and online patient portals to access medical records, lab results, and other important information will also set your site apart.
Testimonials are essential. Amazon.com taught us that candid reviews from customers go a long way toward building the trust necessary to buy products and services, and nowhere is that truer than for medical services. According to one study, when it comes to finding a doctor, 88% of people trust online reviews as much as a personal recommendation. Loyal patients will be happy to write you glowing reviews; feature them prominently.
How does your site look on small screens? More than half of all searches are now made on smartphones, so the more mobile-friendly your site is, the higher it will be ranked. Prospective patients who are forced to scroll forever, or zoom in to tap a link, are likely to become frustrated and move on. Mobile searchers prefer sites that provide the best experience for the least amount of effort, and rankings tend to reflect that preference. You can test how easily a visitor can use your website on a mobile device with Google’s free Mobile-Friendly Test..
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The past few years have seen major transformations in the way health care websites operate and interact with patients. .
In mid-2018, a major Google algorithm change, known to the IT community as the “Medic Update,” significantly changed search criteria for most health and wellness websites. Another big update went live in late 2021. Websites that have not evolved with these changes have dropped in search rankings and provide a poorer user experience all around.
Many potential patients are searching for your services online, so your website cannot be an afterthought. Not only does it need to be designed with your target audience in mind, but it is also important to consider the metrics Google and other search engines now use when assessing the quality of your website so that patients will find it in the first place.
Here are some features that you (or your website company) need to prioritize to keep your site current and atop search results in 2023 and beyond.
Begin with an understandable URL. Search engines use URLs to determine how well your site, or a portion of it, matches search criteria. URLs also need to make sense to searchers, especially when they link specific areas of expertise (more on that in a minute). For example, a URL like “jonesdermatology.com/?p=89021” is meaningless to anyone except programmers; but “jonesdermatology.com/psoriasistreatments” obviously leads to a page about psoriasis treatments. Search engines look for not only the most relevant, but also the most helpful and user-friendly answers to a user’s query.
Incidentally, if the URL for your site is not your own name, you should register your name as a separate domain name – even if you never use it – to be sure that a trickster or troll, or someone with the same name but a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Continue with a good meta description. That’s the grayish text that follows the title and URL in search results. Searchers will read it to confirm that your site is what they seek, so make sure it describes exactly what you do, including any areas of special expertise.
Make your practice approachable with photos. New patients are more comfortable when they know what you look like, so real photos of you and your staff are always more effective than stock photos of models. Photos or a video tour of your office will reassure prospective patients that they will be visiting a clean, modern, professional facility.
Describe your principal services in detail. You never know which specific service a prospective patient is searching for, so describe everything you offer. Don’t try to summarize everything on a single page; relevance is determined by how deeply a topic is covered, so each principal service should have a detailed description on its own page. Not only will your skills become more visible to search engines, but you can also use the space to enumerate your qualifications and expertise in each area. Whenever possible, write your descriptions in question-and-answer form. Searchers tend to ask questions (“what is the best ... ?”), particularly in voice searches. Search engines increasingly value sites that ask and answer common questions.
Make your site interactive. “Interactivity” is a major buzzword in modern search engine parlance. Once searchers make an appointment, they stop searching. If they have to wait until the next day to call your office, they may keep looking – and might find a competitor with online scheduling. HIPAA-compliant chatbots, secure messaging, and online patient portals to access medical records, lab results, and other important information will also set your site apart.
Testimonials are essential. Amazon.com taught us that candid reviews from customers go a long way toward building the trust necessary to buy products and services, and nowhere is that truer than for medical services. According to one study, when it comes to finding a doctor, 88% of people trust online reviews as much as a personal recommendation. Loyal patients will be happy to write you glowing reviews; feature them prominently.
How does your site look on small screens? More than half of all searches are now made on smartphones, so the more mobile-friendly your site is, the higher it will be ranked. Prospective patients who are forced to scroll forever, or zoom in to tap a link, are likely to become frustrated and move on. Mobile searchers prefer sites that provide the best experience for the least amount of effort, and rankings tend to reflect that preference. You can test how easily a visitor can use your website on a mobile device with Google’s free Mobile-Friendly Test..
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The past few years have seen major transformations in the way health care websites operate and interact with patients. .
In mid-2018, a major Google algorithm change, known to the IT community as the “Medic Update,” significantly changed search criteria for most health and wellness websites. Another big update went live in late 2021. Websites that have not evolved with these changes have dropped in search rankings and provide a poorer user experience all around.
Many potential patients are searching for your services online, so your website cannot be an afterthought. Not only does it need to be designed with your target audience in mind, but it is also important to consider the metrics Google and other search engines now use when assessing the quality of your website so that patients will find it in the first place.
Here are some features that you (or your website company) need to prioritize to keep your site current and atop search results in 2023 and beyond.
Begin with an understandable URL. Search engines use URLs to determine how well your site, or a portion of it, matches search criteria. URLs also need to make sense to searchers, especially when they link specific areas of expertise (more on that in a minute). For example, a URL like “jonesdermatology.com/?p=89021” is meaningless to anyone except programmers; but “jonesdermatology.com/psoriasistreatments” obviously leads to a page about psoriasis treatments. Search engines look for not only the most relevant, but also the most helpful and user-friendly answers to a user’s query.
Incidentally, if the URL for your site is not your own name, you should register your name as a separate domain name – even if you never use it – to be sure that a trickster or troll, or someone with the same name but a bad reputation, doesn’t get it.
Continue with a good meta description. That’s the grayish text that follows the title and URL in search results. Searchers will read it to confirm that your site is what they seek, so make sure it describes exactly what you do, including any areas of special expertise.
Make your practice approachable with photos. New patients are more comfortable when they know what you look like, so real photos of you and your staff are always more effective than stock photos of models. Photos or a video tour of your office will reassure prospective patients that they will be visiting a clean, modern, professional facility.
Describe your principal services in detail. You never know which specific service a prospective patient is searching for, so describe everything you offer. Don’t try to summarize everything on a single page; relevance is determined by how deeply a topic is covered, so each principal service should have a detailed description on its own page. Not only will your skills become more visible to search engines, but you can also use the space to enumerate your qualifications and expertise in each area. Whenever possible, write your descriptions in question-and-answer form. Searchers tend to ask questions (“what is the best ... ?”), particularly in voice searches. Search engines increasingly value sites that ask and answer common questions.
Make your site interactive. “Interactivity” is a major buzzword in modern search engine parlance. Once searchers make an appointment, they stop searching. If they have to wait until the next day to call your office, they may keep looking – and might find a competitor with online scheduling. HIPAA-compliant chatbots, secure messaging, and online patient portals to access medical records, lab results, and other important information will also set your site apart.
Testimonials are essential. Amazon.com taught us that candid reviews from customers go a long way toward building the trust necessary to buy products and services, and nowhere is that truer than for medical services. According to one study, when it comes to finding a doctor, 88% of people trust online reviews as much as a personal recommendation. Loyal patients will be happy to write you glowing reviews; feature them prominently.
How does your site look on small screens? More than half of all searches are now made on smartphones, so the more mobile-friendly your site is, the higher it will be ranked. Prospective patients who are forced to scroll forever, or zoom in to tap a link, are likely to become frustrated and move on. Mobile searchers prefer sites that provide the best experience for the least amount of effort, and rankings tend to reflect that preference. You can test how easily a visitor can use your website on a mobile device with Google’s free Mobile-Friendly Test..
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
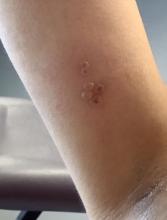
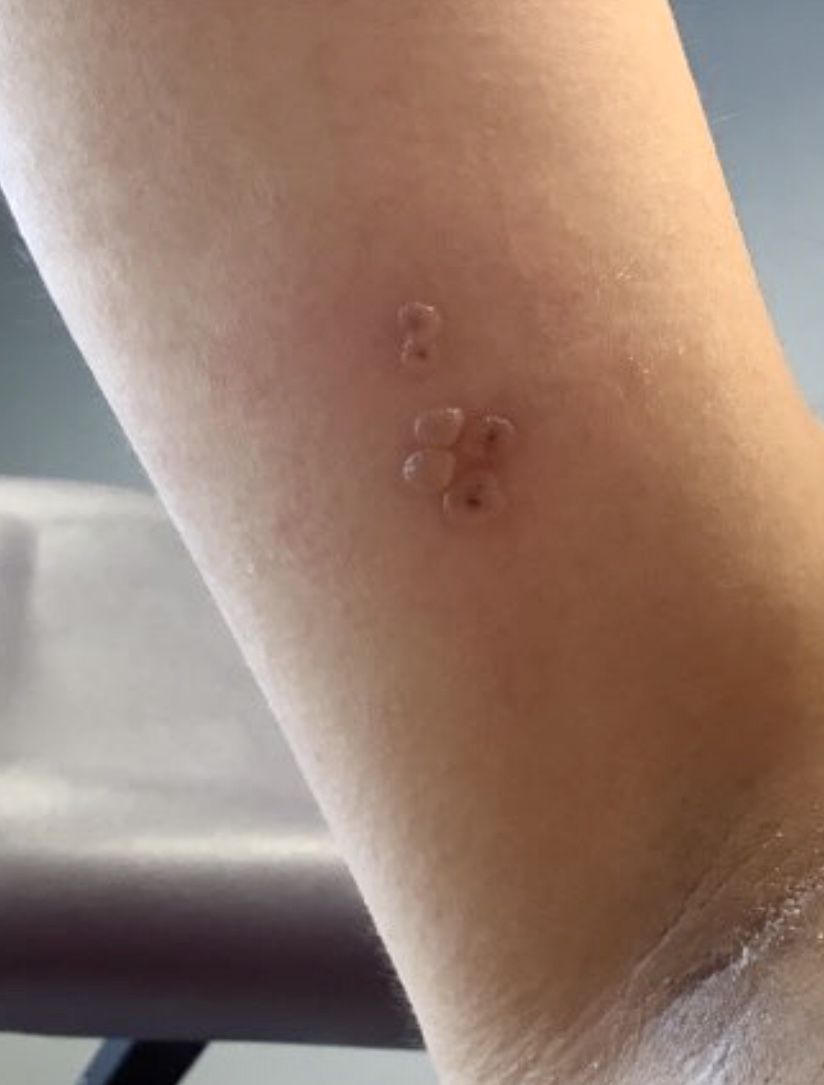
A healthy 36-year-old female presented with 4 days of itchy lesions on the right upper extremity
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Additionally, Orthopox DNA by PCR and Monkeypox (mpox) virus DNA by PCR were detected. Herpes simplex virus and bacterial viral cultures were negative. Valacyclovir was started at the time of presentation and the patient’s lesions resolved without sequelae.
Mpox is a zoonotic double-stranded DNA virus that is part of the Orthopoxvirus family, including the West African and Central African variants. This disease presents similarly to smallpox, so most mpox research was conducted around the time smallpox was eradicated. It was not until 1970, when the disease was isolated from a patient with suspected smallpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), that human mpox was considered a distinct disease. An epidemic outbreak in the United States occurred in 2003 related to infected prairie dogs, and travel-related outbreaks have been more recently reported up until May 2022, in which mpox was reported in nonendemic areas including North America, Europe, and Australia. Most cases in this outbreak occurred in men who have sex with men (MSM), but this is not always the case, and mpox is not necessarily considered a sexually transmitted infection. Mpox presents similarly to smallpox and VZV, so using laboratory tests is important in diagnosing and tracking this disease.
Although it is not easily transmitted, the disease can spread through bodily secretions both directly and indirectly. Mpox typically begins with a prodrome that includes fever, headache, myalgia, and fatigue. This is followed by lymphadenopathy that precedes and coincides with rash development. The lymph nodes are firm, tender, may be painful, and are a defining factor in presentation that differs from smallpox and varicella. The rash typically starts on the face, then presents on the body in a centrifugal distribution. However, cases related to sexual transmission present with anogenital lesions. The lesions are characterized by a progression from maculopapular to vesiculopustular, and can vary widely in quantity.
Notably, individuals are contagious from the onset of the prodrome until the lesions have scabbed over and fallen off. The eruptive nature of the later lesions poses a threat of secondary infection, and is often accompanied by a second febrile period that signifies deterioration of the patient’s condition. Other signs of secondary infection are variable and include pulmonary symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, ocular infections, and in rare cases, encephalitis. These sequelae are more common in unvaccinated and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term complications of mpox include pitted scarring from cutaneous lesions with children being more susceptible to severe disease. The mortality rate for the disease is very low. (As of May 10, 2023, there have been 30,395 mpox cases reported in the United States, and 42 deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
There are a variety of diagnostic tests that can aid in mpox identification, but they are most strongly supported when combined with clinical and epidemiological data. The best, least invasive method includes collection of lesion exudate or crust on a swab, and viral DNA is best preserved by keeping the specimen in a cool, dry, and dark environment. PCR is considered the standard, and electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry are valid tests, but all modalities require sophisticated technicians with the proper laboratory equipment. This is limiting because many cases present in underserved areas that lack the facilities for proper, real-time analysis. Antigen and antibody-based tests can be used, but cross-reactivity of other orthopoxviridae limits confirmation of mpox infection. Vaccination status, history and location must be considered.
Vaccination is the chief form of prevention for mpox, although it is not considered entirely protective. Smallpox vaccination provides protection, but widespread administration of the vaccine is no longer practiced, and an estimated 70% of the global population is no longer vaccinated. Vaccination is recommended for anyone at risk of exposure, but as this is a live, attenuated vaccine, the immune status of the patient is important to keep in mind. Tecovirimat and other antiviral medications including cidofovir and brincidofovir may be considered in severe cases.
This case is unique as our patient, who had no known risk factors for mpox, presented with mpox and VZV, simultaneously. Although clinical presentation and epidemiological patterns between these diseases differ, there have been a limited number of cases of coinfection reported in the literature, mainly in the DRC where mpox is endemic. Diagnosis must be made by separate laboratory tests and there are differences in presentation between independent and coinfection for these viruses. Notably, patients with mpox/VZV coinfection may be less likely to present with lesions on the face, thorax, arms, palms, and soles than those with only mpox but experience a higher lesion burden than those afflicted by only VZV. Coinfection may be related to reactivation of dormant VZV, or increased susceptibility to secondary infection when infected with one virus.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, of the Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine at Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, Fla., and Donna Bilu Martin, MD.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Macneil A et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 1;48(1):e6-8.
2. Di Gennaro F et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 12;10(8):1633.
3. Hughes CM et al. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Dec 7;104(2):604-11.
Fatigue is a monster for patients with pulmonary disease
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
If you’re looking for it, you’ll find fatigue almost everywhere. It’s so common that it hides in plain sight, never dealt with because it’s present for good reason: the inevitable consequence of age, whatever disease you’re treating, poor lifestyle choices, and the daily grind of twenty-first–century life. Its impact is so ubiquitous and pernicious that it’s considered acceptable.
Is it though? After all, fatigue can be debilitating. Not every symptom is worthy of a chronic syndrome bearing its name. Furthermore, what if its relationship to the disease you’re treating is bidirectional?
Outside of sleep medicine, I see little focus on fatigue among pulmonologists. This despite the existing data on fatigue related to sarcoidosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung disease. Even when we do pay it lip service, “addressing” fatigue or sleep is essentially a euphemism for ordering a sleep study.
As with fatigue, if you look for obstructive sleep apnea, it’ll be there, although with OSA, it’s related to the incredibly low, nonevidence-based threshold the American Academy of Sleep Medicine has established for making the diagnosis. With continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in hand, the patient has a new disease to worry about and a difficult behavioral change (wearing, cleaning, and resupplying their CPAP equipment) to make. Too often, the CPAP isn’t used – or is – and the fatigue persists. But it’s okay, because we followed somebody’s guideline.
The American Thoracic Society just published a research statement on cancer-related fatigue. It is comprehensive and highlights the high prevalence and poor recognition of cancer-related fatigue. The authors note that among cancers, those of the lung are associated with a higher comorbid disease burden, older age, and cigarette smoking. All these factors make patients with lung cancer particularly prone to fatigue. Interactions between these factors, lung cancer histology, and specific chemotherapy regimens are poorly understood. True to its title, the “research statement” serves more as a call to action than an evidence-based blueprint for diagnosis and management.
The cancer-related fatigue data that does exist suggests treatment starts with recognition followed by a focus on sleep, exercise, and nutrition. This should surprise no one. The data on fatigue in general (not specific to cancer-related fatigue) shows that although fatigue is not synonymous with poor quality or insufficient sleep, sleep is usually a major factor. The cancer-related conditions affecting sleep include anxiety, depression, insufficient sleep, insomnia, medication side effects, and OSA. The intersecting web is complex, but across underlying conditions (cancer or otherwise), the quickest most efficient method for mitigating fatigue is optimizing sleep.
Exercise and nutrition are also important. Again, across disease processes (interstitial lung disease, COPD, lung cancer, and so on), no drug comes close to aerobic exercise for reducing symptoms, including fatigue. If an exercise prescription could be delivered in pill-form, it’d be a blockbuster. But it can’t be, and the ATS lung cancer–related fatigue research statement nicely outlines the evidence for increased activity levels and the barriers to obtaining support and compliance. As is the case with exercise, support for improving nutrition is limited by cost, access, and patient education.
Perhaps most importantly, sleep, exercise, and nutrition require time for counseling and a behavior change for the physician and patient. Both are in short supply, and commitment is always ephemeral. Incentivization could perhaps be re-structured, but the ATS document notes this will be challenging. With respect to pulmonary rehabilitation (about 50% of patients with lung cancer have comorbid COPD), for example, reimbursement is poor, which serves as a disincentive. Their suggestions? Early integration and repeated introduction to rehabilitation and exercise concepts. Sounds great.
In summary, in my opinion, fatigue doesn’t receive the attention level commensurate with its impact. It’s easy to understand why, but I’m glad the ATS is highlighting the problem. Unbeknownst to me, multiple cancer guidelines already recommend screening for fatigue. The recent sarcoidosis treatment guideline published by the European Respiratory Society dedicated a PICO (Patients, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes) to the topic and recommended exercise (pulmonary rehabilitation). That said, consensus statements on COPD mention it only in passing in relation to severe disease and end-of-life care, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis guidelines ignore it entirely. So, recognition is improving, but we’ve got ways to go.
Dr. Holley is professor of medicine at Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Md., and a pulmonary/sleep and critical care medicine physician at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington. He disclosed ties with Metapharm, CHEST College, and WebMD.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Boys may carry the weight, or overweight, of adults’ infertility
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Overweight boy, infertile man?
When it comes to causes of infertility, history and science have generally focused on women. A lot of the research overlooks men, but some previous studies have suggested that male infertility contributes to about half of the cases of couple infertility. The reason for much of that male infertility, however, has been a mystery. Until now.
A group of Italian investigators looked at the declining trend in sperm counts over the past 40 years and the increase of childhood obesity. Is there a correlation? The researchers think so. Childhood obesity can be linked to multiple causes, but the researchers zeroed in on the effect that obesity has on metabolic rates and, therefore, testicular growth.
Collecting data on testicular volume, body mass index (BMI), and insulin resistance from 268 boys aged 2-18 years, the researchers discovered that those with normal weight and normal insulin levels had testicular volumes 1.5 times higher than their overweight counterparts and 1.5-2 times higher than those with hyperinsulinemia, building a case for obesity being a factor for infertility later in life.
Since low testicular volume is associated with lower sperm count and production as an adult, putting two and two together makes a compelling argument for childhood obesity being a major male infertility culprit. It also creates even more urgency for the health care industry and community decision makers to focus on childhood obesity.
It sure would be nice to be able to take one of the many risk factors for future human survival off the table. Maybe by taking something, like cake, off the table.
Fecal transplantation moves to the kitchen
Fecal microbiota transplantation is an effective way to treat Clostridioides difficile infection, but, in the end, it’s still a transplantation procedure involving a nasogastric or colorectal tube or rather large oral capsules with a demanding (30-40 capsules over 2 days) dosage. Please, Science, tell us there’s a better way.
Science, in the form of investigators at the University of Geneva and Lausanne University Hospital in Switzerland, has spoken, and there may be a better way. Presenting fecal beads: All the bacterial goodness of donor stool without the tubal insertions or massive quantities of giant capsules.
We know you’re scoffing out there, but it’s true. All you need is a little alginate, which is a “biocompatible polysaccharide isolated from brown algae” of the Phaeophyceae family. The donor feces is microencapsulated by mixing it with the alginate, dropping that mixture into water containing calcium chloride, turning it into a gel, and then freeze-drying the gel into small (just 2 mm), solid beads.
Sounds plausible enough, but what do you do with them? “These brownish beads can be easily dispersed in a liquid or food that is pleasant to eat. They also have no taste,” senior author Eric Allémann, PhD, said in a statement released by the University of Geneva.
Pleasant to eat? No taste? So which is it? If you really want to know, watch fecal beads week on the new season of “The Great British Baking Show,” when Paul and Prue judge poop baked into crumpets, crepes, and crostatas. Yum.
We’re on the low-oxygen diet
Nine out of ten doctors agree: Oxygen is more important to your continued well-being than food. After all, a human can go weeks without food, but just minutes without oxygen. However, ten out of ten doctors agree that the United States has an obesity problem. They all also agree that previous research has shown soldiers who train at high altitudes lose more weight than those training at lower altitudes.
So, on the one hand, we have a country full of overweight people, and on the other, we have low oxygen levels causing weight loss. The solution, then, is obvious: Stop breathing.
More specifically (and somewhat less facetiously), researchers from Louisiana have launched the Low Oxygen and Weight Status trial and are currently recruiting individuals with BMIs of 30-40 to, uh, suffocate themselves. No, no, it’s okay, it’s just when they’re sleeping.
Fine, straight face. Participants in the LOWS trial will undergo an 8-week period when they will consume a controlled weight-loss diet and spend their nights in a hypoxic sealed tent, where they will sleep in an environment with an oxygen level equivalent to 8,500 feet above sea level (roughly equivalent to Aspen, Colo.). They will be compared with people on the same diet who sleep in a normal, sea-level oxygen environment.
The study’s goal is to determine whether or not spending time in a low-oxygen environment will suppress appetite, increase energy expenditure, and improve weight loss and insulin sensitivity. Excessive weight loss in high-altitude environments isn’t a good thing for soldiers – they kind of need their muscles and body weight to do the whole soldiering thing – but it could be great for people struggling to lose those last few pounds. And it also may prove LOTME’s previous thesis: Air is not good.
Clinical trials: Top priority for long COVID
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Census Bureau estimate that 6.1% of the U.S. adult population is living with long COVID, with millions more debilitated worldwide. The demand for substantial treatment is enormous, but the urgency to fund and begin the necessary range of clinical trials has not met the severity of the problem.
While trials are slowly beginning to happen, the treatment choices and trial design require crucial nuances and understanding of viral-onset illnesses, and few research groups are creating strong trials that fully reflect the complexities of this landscape.
These recommendations recognize that roughly half of long COVID patients have new-onset myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and dysautonomia from COVID, which must be at the forefront of how trials are designed and conducted, and are additionally based on the current hypotheses about long COVID’s pathophysiologies.
1: Drugs proposed by experts in postviral fields should be prioritized
Upward of 50 drugs for viral-onset conditions like ME/CFS, dysautonomia, AIDS, and others have been waiting for years to go to trial, but have not had the funding to do so.
Treatments proposed by experts in viral-onset illnesses (such as ME/CFS and dysautonomia) should be prioritized (PM R. 2022 Oct;14[10]:1270-91), as outside researchers are not familiar with these fields and their potential treatment options.
2: Drugs targeting a wide range of mechanisms should be trialed
Treatments that should be trialed include anticoagulants/antiplatelets for clotting and vascular functioning, immunomodulators including JAK-STAT inhibitors, COVID-specific antivirals and antivirals against reactivated herpesviruses (Valcyte, Valacyclovir, EBV vaccine).
Other options include prescription mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen, cromolyn sodium), drugs that regulate microglial activation (low-dose naltrexone, low-dose aripiprazole), anti-CGRP medications, beta-blockers, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
Others include medications that target mitochondrial dysfunction; ivabradine; pyridostigmine;, DRP1 inhibitors; supplements showing success in patient communities including lactoferrin, ubiquinone, and nattokinase; and therapies targeting glymphatic/lymphatic dysfunction, microbiome therapies, and therapeutic peptides.
3: Use appropriate long COVID subtypes
Long COVID is an umbrella term that encompasses multiple new-onset and worsened conditions and symptoms after COVID. Roughly half of long COVID patients likely meet the criteria for ME/CFS and/or dysautonomia. Others may have new-onset diabetes, major clotting events, lung damage, neurological disorders, loss of smell or taste, and other manifestations.
Patients in different categories likely have different responses to treatments. It’s critical to identify appropriate subtypes for each trial, ideally performing detailed analyses to identify the treatments that work best, and don’t, for each subtype.
4: Behavioral treatments, especially those that have harmed similar populations, should not be trialed
Behavioral treatments including exercise, graded exercise therapy (GET), and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) should not be trialed, let alone prioritized, for long COVID.
In patients with postexertional malaise (PEM), one of the most common long COVID symptoms, exercise is actively harmful and causes dysfunctional metabolic patterns, cardiac preload failure, impaired systemic oxygen extraction, and more. GET and CBT have failed similar populations , and exercise is explicitly contraindicated by the World Health Organization, the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, the CDC, and other organizations.
Resources should instead be put toward the wide range of medications that have not yet adequately undergone clinical trials.
5: PCR and antibody tests should not be used as inclusion criteria for trial participants
Only an estimated 1%-3% of cases in the first wave of COVID were documented, and the CDC estimates that only 25% of cases through September 2021 were documented. Similarly, antibody tests are unreliable to determine past infection, as roughly a third of patients don’t seroconvert, and a similar proportion serorevert within a few months. Using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and antibody testing to determine who should be included in clinical trials limits who is eligible to participate in research, particularly those who have been ill for longer. Additionally, the majority of those who serorevert are women, so using antibody tests for inclusion introduces a selection bias and may miss mechanisms of immune system functioning that are part of long COVID.
PCR tests also have high false-negative rates and requiring them in research excludes people with lower viral loads with long COVID, which would confound findings.
These issues with testing also lead to COVID-infected people accidentally being included in control groups, which ruins the credibility of the research findings completely.
6: Include comparator groups
There are several common diagnoses that occur in people with long COVID, including ME/CFS, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, small-fiber neuropathy, mast cell activation syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Identifying people with these conditions within the trial cohort improves research across all fields, benefiting all groups, and helps clarify what types of patients benefit most from certain medications.
7: Identify the right endpoints; avoid the wrong ones
Even though our understanding of the pathophysiology of long COVID is still evolving, it’s still possible to do clinical trials by identifying strong endpoints and outcome measures.
Several tools have been designed for viral-onset conditions and should be used alongside other endpoints. Postexertional malaise and autonomic symptoms, which are some of the most common symptoms of long COVID, can be measured with the validated DSQ-PEM and COMPASS-31, respectively. Tools for cognitive dysfunction trials should capture specific and common types of impairment, like processing speed.
Endpoints should be high-impact and aim for large improvements that have clinical significance over small improvements that do not have clinical significance.
Objective tests should be incorporated where possible; some to consider include natural killer cell functioning, cerebral blood flow, T-cell functioning, levels of reactivated herpesviruses, blood lactate levels, and microclots, as testing becomes available.
Mental health outcomes shouldn’t be primary endpoints, except where a trial is targeting a specific mental health condition because of COVID (for example, premenstrual dysphoric disorder).
If mental health conditions are tracked secondarily, it’s vital not to use questionnaires that include physical symptoms like fatigue, difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, or palpitations, as these artificially increase depression and anxiety scores in chronically ill respondents. Tools that include physical symptoms (Patient Health Questionnaire–9, Beck Anxiety Inventory, Beck Depression Inventory) can be replaced with scales like the PHQ-2, General Anxiety Disorder–7, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, or PROMIS-29 subscales.
Because certain cytokines and other inflammatory markers may naturally decrease over time without corresponding improvement in the ME/CFS subtype, caution should be taken when using cytokines as endpoints.
8: Consider enrollment and objectives carefully
A proportion of people with long COVID will recover in the early months after infection. Ideally, clinical trials will primarily study treatments in patients who have been ill 6 months or longer, as some natural recovery will happen before that can bias studies.
But where resources are abundant, it is ideal for trials to additionally look at whether the treatments can help patients in the early months recover and prevent progression to the later stage.
9: Tracking illness duration is crucial
Research from ME/CFS shows that there may be an immune change in the first few years of the illness, where cytokines decrease without any corresponding change in symptom improvement.
Because of this and the possibility that other markers follow the same pattern, disease duration should be a core feature of all analyses and trial designs. Trial outcomes should be designed to answer the question of whether the medication helps patients at different durations of illness.
10: Prioritize patient populations less likely to recover without intervention
Some long COVID phenotypes seem less likely to recover without intervention. Trials should take care to focus on these patient populations, which include those with neurologic symptoms and those meeting ME/CFS criteria.
11: Account for the relapsing/remitting nature
Outcome measures need to be assessed in a way that can distinguish a temporary remission, which is part of the natural course of the disease, from a permanent cure.
Factors that can contribute to the relapsing/remitting nature include physical and cognitive postexertional malaise, menstrual cycle changes, and seasonal changes.
12: Trial participants should reflect the diversity of the long COVID population
Certain demographics are more likely to be affected by acute and long COVID and need to be appropriately recruited and reflected in research, including in patient engagement.
Trials must include high numbers of Hispanic/Latinx, Black, and indigenous communities, queer and transgender populations, and women. Trial materials and design need to incorporate linguistic diversity in addition to racial/ethnic diversity.
Upward of 75% of long COVID cases happen after mild acute cases; clinical researchers should ensure that nonhospitalized patients make up the bulk of trial participants.
13: Utilize meaningful engagement of patients, especially in treatment selection and study design
Meaningful patient engagement means engaging multiple patients at every step of the trial process, from treatment selection to study design to analysis to communication of the results.
Patient experiences are extremely valuable and contain information that researchers may not be familiar with, including the nature and patterns of the illness, insights into possible treatments, and barriers to documentation and care that may also impact research. Tapping into those patient experiences will make trials stronger.
Overall, the landscape of long COVID clinical trials is ripe for discovery, and researchers choosing to go down this path will be deeply appreciated by the patient community.
Hannah Davis is a long COVID patient-researcher and cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an organization studying the long-term effects of COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Census Bureau estimate that 6.1% of the U.S. adult population is living with long COVID, with millions more debilitated worldwide. The demand for substantial treatment is enormous, but the urgency to fund and begin the necessary range of clinical trials has not met the severity of the problem.
While trials are slowly beginning to happen, the treatment choices and trial design require crucial nuances and understanding of viral-onset illnesses, and few research groups are creating strong trials that fully reflect the complexities of this landscape.
These recommendations recognize that roughly half of long COVID patients have new-onset myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and dysautonomia from COVID, which must be at the forefront of how trials are designed and conducted, and are additionally based on the current hypotheses about long COVID’s pathophysiologies.
1: Drugs proposed by experts in postviral fields should be prioritized
Upward of 50 drugs for viral-onset conditions like ME/CFS, dysautonomia, AIDS, and others have been waiting for years to go to trial, but have not had the funding to do so.
Treatments proposed by experts in viral-onset illnesses (such as ME/CFS and dysautonomia) should be prioritized (PM R. 2022 Oct;14[10]:1270-91), as outside researchers are not familiar with these fields and their potential treatment options.
2: Drugs targeting a wide range of mechanisms should be trialed
Treatments that should be trialed include anticoagulants/antiplatelets for clotting and vascular functioning, immunomodulators including JAK-STAT inhibitors, COVID-specific antivirals and antivirals against reactivated herpesviruses (Valcyte, Valacyclovir, EBV vaccine).
Other options include prescription mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen, cromolyn sodium), drugs that regulate microglial activation (low-dose naltrexone, low-dose aripiprazole), anti-CGRP medications, beta-blockers, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
Others include medications that target mitochondrial dysfunction; ivabradine; pyridostigmine;, DRP1 inhibitors; supplements showing success in patient communities including lactoferrin, ubiquinone, and nattokinase; and therapies targeting glymphatic/lymphatic dysfunction, microbiome therapies, and therapeutic peptides.
3: Use appropriate long COVID subtypes
Long COVID is an umbrella term that encompasses multiple new-onset and worsened conditions and symptoms after COVID. Roughly half of long COVID patients likely meet the criteria for ME/CFS and/or dysautonomia. Others may have new-onset diabetes, major clotting events, lung damage, neurological disorders, loss of smell or taste, and other manifestations.
Patients in different categories likely have different responses to treatments. It’s critical to identify appropriate subtypes for each trial, ideally performing detailed analyses to identify the treatments that work best, and don’t, for each subtype.
4: Behavioral treatments, especially those that have harmed similar populations, should not be trialed
Behavioral treatments including exercise, graded exercise therapy (GET), and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) should not be trialed, let alone prioritized, for long COVID.
In patients with postexertional malaise (PEM), one of the most common long COVID symptoms, exercise is actively harmful and causes dysfunctional metabolic patterns, cardiac preload failure, impaired systemic oxygen extraction, and more. GET and CBT have failed similar populations , and exercise is explicitly contraindicated by the World Health Organization, the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, the CDC, and other organizations.
Resources should instead be put toward the wide range of medications that have not yet adequately undergone clinical trials.
5: PCR and antibody tests should not be used as inclusion criteria for trial participants
Only an estimated 1%-3% of cases in the first wave of COVID were documented, and the CDC estimates that only 25% of cases through September 2021 were documented. Similarly, antibody tests are unreliable to determine past infection, as roughly a third of patients don’t seroconvert, and a similar proportion serorevert within a few months. Using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and antibody testing to determine who should be included in clinical trials limits who is eligible to participate in research, particularly those who have been ill for longer. Additionally, the majority of those who serorevert are women, so using antibody tests for inclusion introduces a selection bias and may miss mechanisms of immune system functioning that are part of long COVID.
PCR tests also have high false-negative rates and requiring them in research excludes people with lower viral loads with long COVID, which would confound findings.
These issues with testing also lead to COVID-infected people accidentally being included in control groups, which ruins the credibility of the research findings completely.
6: Include comparator groups
There are several common diagnoses that occur in people with long COVID, including ME/CFS, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, small-fiber neuropathy, mast cell activation syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Identifying people with these conditions within the trial cohort improves research across all fields, benefiting all groups, and helps clarify what types of patients benefit most from certain medications.
7: Identify the right endpoints; avoid the wrong ones
Even though our understanding of the pathophysiology of long COVID is still evolving, it’s still possible to do clinical trials by identifying strong endpoints and outcome measures.
Several tools have been designed for viral-onset conditions and should be used alongside other endpoints. Postexertional malaise and autonomic symptoms, which are some of the most common symptoms of long COVID, can be measured with the validated DSQ-PEM and COMPASS-31, respectively. Tools for cognitive dysfunction trials should capture specific and common types of impairment, like processing speed.
Endpoints should be high-impact and aim for large improvements that have clinical significance over small improvements that do not have clinical significance.
Objective tests should be incorporated where possible; some to consider include natural killer cell functioning, cerebral blood flow, T-cell functioning, levels of reactivated herpesviruses, blood lactate levels, and microclots, as testing becomes available.
Mental health outcomes shouldn’t be primary endpoints, except where a trial is targeting a specific mental health condition because of COVID (for example, premenstrual dysphoric disorder).
If mental health conditions are tracked secondarily, it’s vital not to use questionnaires that include physical symptoms like fatigue, difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, or palpitations, as these artificially increase depression and anxiety scores in chronically ill respondents. Tools that include physical symptoms (Patient Health Questionnaire–9, Beck Anxiety Inventory, Beck Depression Inventory) can be replaced with scales like the PHQ-2, General Anxiety Disorder–7, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, or PROMIS-29 subscales.
Because certain cytokines and other inflammatory markers may naturally decrease over time without corresponding improvement in the ME/CFS subtype, caution should be taken when using cytokines as endpoints.
8: Consider enrollment and objectives carefully
A proportion of people with long COVID will recover in the early months after infection. Ideally, clinical trials will primarily study treatments in patients who have been ill 6 months or longer, as some natural recovery will happen before that can bias studies.
But where resources are abundant, it is ideal for trials to additionally look at whether the treatments can help patients in the early months recover and prevent progression to the later stage.
9: Tracking illness duration is crucial
Research from ME/CFS shows that there may be an immune change in the first few years of the illness, where cytokines decrease without any corresponding change in symptom improvement.
Because of this and the possibility that other markers follow the same pattern, disease duration should be a core feature of all analyses and trial designs. Trial outcomes should be designed to answer the question of whether the medication helps patients at different durations of illness.
10: Prioritize patient populations less likely to recover without intervention
Some long COVID phenotypes seem less likely to recover without intervention. Trials should take care to focus on these patient populations, which include those with neurologic symptoms and those meeting ME/CFS criteria.
11: Account for the relapsing/remitting nature
Outcome measures need to be assessed in a way that can distinguish a temporary remission, which is part of the natural course of the disease, from a permanent cure.
Factors that can contribute to the relapsing/remitting nature include physical and cognitive postexertional malaise, menstrual cycle changes, and seasonal changes.
12: Trial participants should reflect the diversity of the long COVID population
Certain demographics are more likely to be affected by acute and long COVID and need to be appropriately recruited and reflected in research, including in patient engagement.
Trials must include high numbers of Hispanic/Latinx, Black, and indigenous communities, queer and transgender populations, and women. Trial materials and design need to incorporate linguistic diversity in addition to racial/ethnic diversity.
Upward of 75% of long COVID cases happen after mild acute cases; clinical researchers should ensure that nonhospitalized patients make up the bulk of trial participants.
13: Utilize meaningful engagement of patients, especially in treatment selection and study design
Meaningful patient engagement means engaging multiple patients at every step of the trial process, from treatment selection to study design to analysis to communication of the results.
Patient experiences are extremely valuable and contain information that researchers may not be familiar with, including the nature and patterns of the illness, insights into possible treatments, and barriers to documentation and care that may also impact research. Tapping into those patient experiences will make trials stronger.
Overall, the landscape of long COVID clinical trials is ripe for discovery, and researchers choosing to go down this path will be deeply appreciated by the patient community.
Hannah Davis is a long COVID patient-researcher and cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an organization studying the long-term effects of COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Census Bureau estimate that 6.1% of the U.S. adult population is living with long COVID, with millions more debilitated worldwide. The demand for substantial treatment is enormous, but the urgency to fund and begin the necessary range of clinical trials has not met the severity of the problem.
While trials are slowly beginning to happen, the treatment choices and trial design require crucial nuances and understanding of viral-onset illnesses, and few research groups are creating strong trials that fully reflect the complexities of this landscape.
These recommendations recognize that roughly half of long COVID patients have new-onset myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and dysautonomia from COVID, which must be at the forefront of how trials are designed and conducted, and are additionally based on the current hypotheses about long COVID’s pathophysiologies.
1: Drugs proposed by experts in postviral fields should be prioritized
Upward of 50 drugs for viral-onset conditions like ME/CFS, dysautonomia, AIDS, and others have been waiting for years to go to trial, but have not had the funding to do so.
Treatments proposed by experts in viral-onset illnesses (such as ME/CFS and dysautonomia) should be prioritized (PM R. 2022 Oct;14[10]:1270-91), as outside researchers are not familiar with these fields and their potential treatment options.
2: Drugs targeting a wide range of mechanisms should be trialed
Treatments that should be trialed include anticoagulants/antiplatelets for clotting and vascular functioning, immunomodulators including JAK-STAT inhibitors, COVID-specific antivirals and antivirals against reactivated herpesviruses (Valcyte, Valacyclovir, EBV vaccine).
Other options include prescription mast cell stabilizers (ketotifen, cromolyn sodium), drugs that regulate microglial activation (low-dose naltrexone, low-dose aripiprazole), anti-CGRP medications, beta-blockers, and intravenous immunoglobulin.
Others include medications that target mitochondrial dysfunction; ivabradine; pyridostigmine;, DRP1 inhibitors; supplements showing success in patient communities including lactoferrin, ubiquinone, and nattokinase; and therapies targeting glymphatic/lymphatic dysfunction, microbiome therapies, and therapeutic peptides.
3: Use appropriate long COVID subtypes
Long COVID is an umbrella term that encompasses multiple new-onset and worsened conditions and symptoms after COVID. Roughly half of long COVID patients likely meet the criteria for ME/CFS and/or dysautonomia. Others may have new-onset diabetes, major clotting events, lung damage, neurological disorders, loss of smell or taste, and other manifestations.
Patients in different categories likely have different responses to treatments. It’s critical to identify appropriate subtypes for each trial, ideally performing detailed analyses to identify the treatments that work best, and don’t, for each subtype.
4: Behavioral treatments, especially those that have harmed similar populations, should not be trialed
Behavioral treatments including exercise, graded exercise therapy (GET), and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) should not be trialed, let alone prioritized, for long COVID.
In patients with postexertional malaise (PEM), one of the most common long COVID symptoms, exercise is actively harmful and causes dysfunctional metabolic patterns, cardiac preload failure, impaired systemic oxygen extraction, and more. GET and CBT have failed similar populations , and exercise is explicitly contraindicated by the World Health Organization, the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, the CDC, and other organizations.
Resources should instead be put toward the wide range of medications that have not yet adequately undergone clinical trials.
5: PCR and antibody tests should not be used as inclusion criteria for trial participants
Only an estimated 1%-3% of cases in the first wave of COVID were documented, and the CDC estimates that only 25% of cases through September 2021 were documented. Similarly, antibody tests are unreliable to determine past infection, as roughly a third of patients don’t seroconvert, and a similar proportion serorevert within a few months. Using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and antibody testing to determine who should be included in clinical trials limits who is eligible to participate in research, particularly those who have been ill for longer. Additionally, the majority of those who serorevert are women, so using antibody tests for inclusion introduces a selection bias and may miss mechanisms of immune system functioning that are part of long COVID.
PCR tests also have high false-negative rates and requiring them in research excludes people with lower viral loads with long COVID, which would confound findings.
These issues with testing also lead to COVID-infected people accidentally being included in control groups, which ruins the credibility of the research findings completely.
6: Include comparator groups
There are several common diagnoses that occur in people with long COVID, including ME/CFS, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, small-fiber neuropathy, mast cell activation syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Identifying people with these conditions within the trial cohort improves research across all fields, benefiting all groups, and helps clarify what types of patients benefit most from certain medications.
7: Identify the right endpoints; avoid the wrong ones
Even though our understanding of the pathophysiology of long COVID is still evolving, it’s still possible to do clinical trials by identifying strong endpoints and outcome measures.
Several tools have been designed for viral-onset conditions and should be used alongside other endpoints. Postexertional malaise and autonomic symptoms, which are some of the most common symptoms of long COVID, can be measured with the validated DSQ-PEM and COMPASS-31, respectively. Tools for cognitive dysfunction trials should capture specific and common types of impairment, like processing speed.
Endpoints should be high-impact and aim for large improvements that have clinical significance over small improvements that do not have clinical significance.
Objective tests should be incorporated where possible; some to consider include natural killer cell functioning, cerebral blood flow, T-cell functioning, levels of reactivated herpesviruses, blood lactate levels, and microclots, as testing becomes available.
Mental health outcomes shouldn’t be primary endpoints, except where a trial is targeting a specific mental health condition because of COVID (for example, premenstrual dysphoric disorder).
If mental health conditions are tracked secondarily, it’s vital not to use questionnaires that include physical symptoms like fatigue, difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, or palpitations, as these artificially increase depression and anxiety scores in chronically ill respondents. Tools that include physical symptoms (Patient Health Questionnaire–9, Beck Anxiety Inventory, Beck Depression Inventory) can be replaced with scales like the PHQ-2, General Anxiety Disorder–7, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, or PROMIS-29 subscales.
Because certain cytokines and other inflammatory markers may naturally decrease over time without corresponding improvement in the ME/CFS subtype, caution should be taken when using cytokines as endpoints.
8: Consider enrollment and objectives carefully
A proportion of people with long COVID will recover in the early months after infection. Ideally, clinical trials will primarily study treatments in patients who have been ill 6 months or longer, as some natural recovery will happen before that can bias studies.
But where resources are abundant, it is ideal for trials to additionally look at whether the treatments can help patients in the early months recover and prevent progression to the later stage.
9: Tracking illness duration is crucial
Research from ME/CFS shows that there may be an immune change in the first few years of the illness, where cytokines decrease without any corresponding change in symptom improvement.
Because of this and the possibility that other markers follow the same pattern, disease duration should be a core feature of all analyses and trial designs. Trial outcomes should be designed to answer the question of whether the medication helps patients at different durations of illness.
10: Prioritize patient populations less likely to recover without intervention
Some long COVID phenotypes seem less likely to recover without intervention. Trials should take care to focus on these patient populations, which include those with neurologic symptoms and those meeting ME/CFS criteria.
11: Account for the relapsing/remitting nature
Outcome measures need to be assessed in a way that can distinguish a temporary remission, which is part of the natural course of the disease, from a permanent cure.
Factors that can contribute to the relapsing/remitting nature include physical and cognitive postexertional malaise, menstrual cycle changes, and seasonal changes.
12: Trial participants should reflect the diversity of the long COVID population
Certain demographics are more likely to be affected by acute and long COVID and need to be appropriately recruited and reflected in research, including in patient engagement.
Trials must include high numbers of Hispanic/Latinx, Black, and indigenous communities, queer and transgender populations, and women. Trial materials and design need to incorporate linguistic diversity in addition to racial/ethnic diversity.
Upward of 75% of long COVID cases happen after mild acute cases; clinical researchers should ensure that nonhospitalized patients make up the bulk of trial participants.
13: Utilize meaningful engagement of patients, especially in treatment selection and study design
Meaningful patient engagement means engaging multiple patients at every step of the trial process, from treatment selection to study design to analysis to communication of the results.
Patient experiences are extremely valuable and contain information that researchers may not be familiar with, including the nature and patterns of the illness, insights into possible treatments, and barriers to documentation and care that may also impact research. Tapping into those patient experiences will make trials stronger.
Overall, the landscape of long COVID clinical trials is ripe for discovery, and researchers choosing to go down this path will be deeply appreciated by the patient community.
Hannah Davis is a long COVID patient-researcher and cofounder of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an organization studying the long-term effects of COVID.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosis of Indolent Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini Infections as Risk Factors for Cholangiocarcinoma: An Unmet Medical Need
Cholangiocarcinoma is a heterogeneous, highly aggressive cancer of the biliary tract epithelium with an overall 5-year relative survival rate of only 9%.1,2 Although surgical resection of localized, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is associated with improved overall survival, most patients present with advanced disease not amenable to surgery due to a late onset of symptoms.2 Recently, an increased incidence of cholangiocarcinoma has been reported in the United States.3 Although relatively rare in the US, cholangiocarcinoma is prevalent across large parts of Asia, including China, Vietnam, Thailand, South Korea, and Taiwan.2
Risk Factors
To date, risk factors for developing cholangiocarcinoma have not been elucidated. 4,5 However, a growing body of literature suggests that chronic infection of genetically susceptible human subjects with Clonorchis sinensis ( C sinensis ) and Opisthorchis viverrini ( O viverrini ) plays a role. 6,7 The life cycle of these food-borne zoonotic trematodes involves eggs discharged in the stool of infected humans, the definitive host. 6,7 In nature, these eggs are ingested by freshwater snails, the intermediate host, where they undergo several developmental stages to form cercariae. Once released from snails into the water, free-swimming cercariae come in contact and penetrate freshwater fish where they encyst as metacercariae. Infection of humans occurs by ingesting undercooked, salted, pickled, or smoked freshwater fish infested with metacercariae. After ingestion, metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater. They then mature into adult flukes that reside in small- and medium-sized intrahepatic biliary ducts. 6,7
Although most infected people remain asymptomatic, untreated indolent infections with C sinensis and O viverrini may persist in peripheral intrahepatic bile ducts for as long as 30 years, which is the lifespan of the trematodes.6,7 During this prolonged period, C sinensis and O viverrini feeding activities and their excretory-secretory products may damage bile duct epithelium and promote intense local inflammation.6,7 Conceivably, these pathological processes could then provoke the epithelial desquamation, adenomatous hyperplasia, goblet cell metaplasia, periductal fibrosis, and granuloma formation that are conducive to initiation and progression of cholangiocarcinoma in genetically susceptible people.8 Accordingly, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has determined that there is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini in humans and that chronic infections with these trematodes cause cholangiocarcinoma.9 The IARC concluded that chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).9
Diagnosis
Presently, the diagnosis of C sinensis and O viverrini infection is based on microscopic identification and enumeration of the parasites’ eggs in weighted stool specimens using a formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation concentration technique. 6,7 This approach requires a labor-intensive test that is conducted by an experienced technician. The test has low specificity and sensitivity because eggs could be confused with those of nonpathogenic intestinal flukes that are morphologically similar and because eggs are not present in feces during all stages of the infection. Although diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts by screening sonography is used to diagnose clonorchiasis in endemic areas, it has low sensitivity, particularly in patients with low-level C sinensis and O viverrin i infections. 10
To address the current diagnostic gap, several enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) have been developed for the diagnosis of C sinensis, including monoclonal antibody-based (mAb) ELISA and indirect antibody ELISA.11,12 However, both have important limitations. The mAb ELISA detects only active infections while indirect antibody ELISA cross-reacts with other liver flukes.11,12 Taken together, these data illustrate the difficulties in diagnosing asymptomatic individuals with low-burden C sinensis or O viverrini infections by existing laboratory methods.
Timely serodiagnosis of indolent C sinensis and O viverrini infections is important because these parasites have recently been raised as a risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma in veterans who served in Vietnam.13 The American War Library estimates that as of February 28, 2019, about 610,000 Americans who served on land in Vietnam or in the air over Vietnam between 1954 and 1975 are alive, and about 164,000 Americans who served at sea in Vietnam waters are alive.14 To that end, Psevdos and colleagues screened 97 US veterans who served in Vietnam and identified 50 who reported exposure to raw or undercooked fish while there.13 None had evidence of active C sinensis or O viverrini infection. Blood samples obtained from these veterans were analyzed for circulating C sinensis and O viverrini antibodies using an ELISA developed in South Korea and 12 blood samples tested positive for the trematodes. Imaging of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts was unyielding in all cases. One veteran diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma had repeated negative tests. However, the results of this study were challenged by several experts in this field because the authors did not report the sensitivity and specificity of the ELISA assay used.15
Serologic testing of US veterans who served in C sinensis and O viverrini–endemic countries for indolent infections with these parasites is not recommended at present.15 Nevertheless, there is an urgent need to develop sensitive and specific serologic assays, such as ELISA tests with recombinant antigens, to detect both acute and indolent infections caused by each biliary liver fluke in the US, including in patients diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma. We posit that testing and treatment of high-risk populations could lead to earlier detection and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma, leading to improved overall survival in the population at risk.
1. American Cancer Society. Survival rates for bile duct cancer. Updated March 1, 2023. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bile-duct-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-by-stage.html
2. Vij M, Puri Y, Rammohan A, et al. Pathological, molecular, and clinical characteristics of cholangiocarcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(3):607-627. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607
3. Yao KJ, Jabbour S, Parekh N, Lin Y, Moss RA. Increasing mortality in the United States from cholangiocarcinoma: an analysis of the National Center for Health Statistics Database. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16(1):117. Published 2016 Sep 21. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0527-z
4. Rustagi T, Dasanu CA. Risk factors for gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma: similarities, differences and updates. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2012;43(2):137-147. doi:10.1007/s12029-011-9284-y
5. Maemura K, Natsugoe S, Takao S. Molecular mechanism of cholangiocarcinoma carcinogenesis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(10):754-760. doi:10.1002/jhbp.126
6. Steele JA, Richter CH, Echaubard P, et al. Thinking beyond Opisthorchis viverrini for risk of cholangiocarcinoma in the lower Mekong region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7(1):44. Published 2018 May 17. doi:10.1186/s40249-018-0434-3.
7. Kim TS, Pak JH, Kim JB, Bahk YY. Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: a brief review. BMB Rep. 2016;49(11):590-597. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.11.109
8. Murata M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ Health Prev Med. 2018;23(1):50. Published 2018 Oct 20. doi:10.1186/s12199-018-0740-1
9. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Biological agents. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2012;100(pt B):1-441.
10. Mairiang E, Laha T, Bethony JM, et al. Ultrasonography assessment of hepatobiliary abnormalities in 3359 subjects with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in endemic areas of Thailand. Parasitol Int. 2012;61(1):208-211. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.07.009
11. Li HM, Qian MB, Yang YC, et al. Performance evaluation of existing immunoassays for Clonorchis sinensis infection in China. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11(1):35. Published 2018 Jan 15. doi:10.1186/s13071-018-2612-3
12. Hughes T, O’Connor T, Techasen A, et al. Opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma in Southeast Asia: an unresolved problem. Int J Gen Med. 2017;10:227-237. Published 2017 Aug 10. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S133292
13. Psevdos G, Ford FM, Hong ST. Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):208-210. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000611
14. American War Library. In harm’s way... How many real Vietnam vets are alive today? Updated February 28, 2019. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.americanwarlibrary.com/personnel/vietvet.htm
15. Nash TE, Sullivan D, Mitre E, et al. Comments on “Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war”. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):240-241. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000659
Cholangiocarcinoma is a heterogeneous, highly aggressive cancer of the biliary tract epithelium with an overall 5-year relative survival rate of only 9%.1,2 Although surgical resection of localized, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is associated with improved overall survival, most patients present with advanced disease not amenable to surgery due to a late onset of symptoms.2 Recently, an increased incidence of cholangiocarcinoma has been reported in the United States.3 Although relatively rare in the US, cholangiocarcinoma is prevalent across large parts of Asia, including China, Vietnam, Thailand, South Korea, and Taiwan.2
Risk Factors
To date, risk factors for developing cholangiocarcinoma have not been elucidated. 4,5 However, a growing body of literature suggests that chronic infection of genetically susceptible human subjects with Clonorchis sinensis ( C sinensis ) and Opisthorchis viverrini ( O viverrini ) plays a role. 6,7 The life cycle of these food-borne zoonotic trematodes involves eggs discharged in the stool of infected humans, the definitive host. 6,7 In nature, these eggs are ingested by freshwater snails, the intermediate host, where they undergo several developmental stages to form cercariae. Once released from snails into the water, free-swimming cercariae come in contact and penetrate freshwater fish where they encyst as metacercariae. Infection of humans occurs by ingesting undercooked, salted, pickled, or smoked freshwater fish infested with metacercariae. After ingestion, metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater. They then mature into adult flukes that reside in small- and medium-sized intrahepatic biliary ducts. 6,7
Although most infected people remain asymptomatic, untreated indolent infections with C sinensis and O viverrini may persist in peripheral intrahepatic bile ducts for as long as 30 years, which is the lifespan of the trematodes.6,7 During this prolonged period, C sinensis and O viverrini feeding activities and their excretory-secretory products may damage bile duct epithelium and promote intense local inflammation.6,7 Conceivably, these pathological processes could then provoke the epithelial desquamation, adenomatous hyperplasia, goblet cell metaplasia, periductal fibrosis, and granuloma formation that are conducive to initiation and progression of cholangiocarcinoma in genetically susceptible people.8 Accordingly, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has determined that there is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini in humans and that chronic infections with these trematodes cause cholangiocarcinoma.9 The IARC concluded that chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).9
Diagnosis
Presently, the diagnosis of C sinensis and O viverrini infection is based on microscopic identification and enumeration of the parasites’ eggs in weighted stool specimens using a formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation concentration technique. 6,7 This approach requires a labor-intensive test that is conducted by an experienced technician. The test has low specificity and sensitivity because eggs could be confused with those of nonpathogenic intestinal flukes that are morphologically similar and because eggs are not present in feces during all stages of the infection. Although diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts by screening sonography is used to diagnose clonorchiasis in endemic areas, it has low sensitivity, particularly in patients with low-level C sinensis and O viverrin i infections. 10
To address the current diagnostic gap, several enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) have been developed for the diagnosis of C sinensis, including monoclonal antibody-based (mAb) ELISA and indirect antibody ELISA.11,12 However, both have important limitations. The mAb ELISA detects only active infections while indirect antibody ELISA cross-reacts with other liver flukes.11,12 Taken together, these data illustrate the difficulties in diagnosing asymptomatic individuals with low-burden C sinensis or O viverrini infections by existing laboratory methods.
Timely serodiagnosis of indolent C sinensis and O viverrini infections is important because these parasites have recently been raised as a risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma in veterans who served in Vietnam.13 The American War Library estimates that as of February 28, 2019, about 610,000 Americans who served on land in Vietnam or in the air over Vietnam between 1954 and 1975 are alive, and about 164,000 Americans who served at sea in Vietnam waters are alive.14 To that end, Psevdos and colleagues screened 97 US veterans who served in Vietnam and identified 50 who reported exposure to raw or undercooked fish while there.13 None had evidence of active C sinensis or O viverrini infection. Blood samples obtained from these veterans were analyzed for circulating C sinensis and O viverrini antibodies using an ELISA developed in South Korea and 12 blood samples tested positive for the trematodes. Imaging of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts was unyielding in all cases. One veteran diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma had repeated negative tests. However, the results of this study were challenged by several experts in this field because the authors did not report the sensitivity and specificity of the ELISA assay used.15
Serologic testing of US veterans who served in C sinensis and O viverrini–endemic countries for indolent infections with these parasites is not recommended at present.15 Nevertheless, there is an urgent need to develop sensitive and specific serologic assays, such as ELISA tests with recombinant antigens, to detect both acute and indolent infections caused by each biliary liver fluke in the US, including in patients diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma. We posit that testing and treatment of high-risk populations could lead to earlier detection and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma, leading to improved overall survival in the population at risk.
Cholangiocarcinoma is a heterogeneous, highly aggressive cancer of the biliary tract epithelium with an overall 5-year relative survival rate of only 9%.1,2 Although surgical resection of localized, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma is associated with improved overall survival, most patients present with advanced disease not amenable to surgery due to a late onset of symptoms.2 Recently, an increased incidence of cholangiocarcinoma has been reported in the United States.3 Although relatively rare in the US, cholangiocarcinoma is prevalent across large parts of Asia, including China, Vietnam, Thailand, South Korea, and Taiwan.2
Risk Factors
To date, risk factors for developing cholangiocarcinoma have not been elucidated. 4,5 However, a growing body of literature suggests that chronic infection of genetically susceptible human subjects with Clonorchis sinensis ( C sinensis ) and Opisthorchis viverrini ( O viverrini ) plays a role. 6,7 The life cycle of these food-borne zoonotic trematodes involves eggs discharged in the stool of infected humans, the definitive host. 6,7 In nature, these eggs are ingested by freshwater snails, the intermediate host, where they undergo several developmental stages to form cercariae. Once released from snails into the water, free-swimming cercariae come in contact and penetrate freshwater fish where they encyst as metacercariae. Infection of humans occurs by ingesting undercooked, salted, pickled, or smoked freshwater fish infested with metacercariae. After ingestion, metacercariae excyst in the duodenum and ascend the biliary tract through the ampulla of Vater. They then mature into adult flukes that reside in small- and medium-sized intrahepatic biliary ducts. 6,7
Although most infected people remain asymptomatic, untreated indolent infections with C sinensis and O viverrini may persist in peripheral intrahepatic bile ducts for as long as 30 years, which is the lifespan of the trematodes.6,7 During this prolonged period, C sinensis and O viverrini feeding activities and their excretory-secretory products may damage bile duct epithelium and promote intense local inflammation.6,7 Conceivably, these pathological processes could then provoke the epithelial desquamation, adenomatous hyperplasia, goblet cell metaplasia, periductal fibrosis, and granuloma formation that are conducive to initiation and progression of cholangiocarcinoma in genetically susceptible people.8 Accordingly, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has determined that there is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini in humans and that chronic infections with these trematodes cause cholangiocarcinoma.9 The IARC concluded that chronic infections with C sinensis and O viverrini are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1).9
Diagnosis
Presently, the diagnosis of C sinensis and O viverrini infection is based on microscopic identification and enumeration of the parasites’ eggs in weighted stool specimens using a formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation concentration technique. 6,7 This approach requires a labor-intensive test that is conducted by an experienced technician. The test has low specificity and sensitivity because eggs could be confused with those of nonpathogenic intestinal flukes that are morphologically similar and because eggs are not present in feces during all stages of the infection. Although diffuse dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts by screening sonography is used to diagnose clonorchiasis in endemic areas, it has low sensitivity, particularly in patients with low-level C sinensis and O viverrin i infections. 10
To address the current diagnostic gap, several enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) have been developed for the diagnosis of C sinensis, including monoclonal antibody-based (mAb) ELISA and indirect antibody ELISA.11,12 However, both have important limitations. The mAb ELISA detects only active infections while indirect antibody ELISA cross-reacts with other liver flukes.11,12 Taken together, these data illustrate the difficulties in diagnosing asymptomatic individuals with low-burden C sinensis or O viverrini infections by existing laboratory methods.
Timely serodiagnosis of indolent C sinensis and O viverrini infections is important because these parasites have recently been raised as a risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma in veterans who served in Vietnam.13 The American War Library estimates that as of February 28, 2019, about 610,000 Americans who served on land in Vietnam or in the air over Vietnam between 1954 and 1975 are alive, and about 164,000 Americans who served at sea in Vietnam waters are alive.14 To that end, Psevdos and colleagues screened 97 US veterans who served in Vietnam and identified 50 who reported exposure to raw or undercooked fish while there.13 None had evidence of active C sinensis or O viverrini infection. Blood samples obtained from these veterans were analyzed for circulating C sinensis and O viverrini antibodies using an ELISA developed in South Korea and 12 blood samples tested positive for the trematodes. Imaging of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts was unyielding in all cases. One veteran diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma had repeated negative tests. However, the results of this study were challenged by several experts in this field because the authors did not report the sensitivity and specificity of the ELISA assay used.15
Serologic testing of US veterans who served in C sinensis and O viverrini–endemic countries for indolent infections with these parasites is not recommended at present.15 Nevertheless, there is an urgent need to develop sensitive and specific serologic assays, such as ELISA tests with recombinant antigens, to detect both acute and indolent infections caused by each biliary liver fluke in the US, including in patients diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma. We posit that testing and treatment of high-risk populations could lead to earlier detection and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma, leading to improved overall survival in the population at risk.
1. American Cancer Society. Survival rates for bile duct cancer. Updated March 1, 2023. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bile-duct-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-by-stage.html
2. Vij M, Puri Y, Rammohan A, et al. Pathological, molecular, and clinical characteristics of cholangiocarcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(3):607-627. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607
3. Yao KJ, Jabbour S, Parekh N, Lin Y, Moss RA. Increasing mortality in the United States from cholangiocarcinoma: an analysis of the National Center for Health Statistics Database. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16(1):117. Published 2016 Sep 21. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0527-z
4. Rustagi T, Dasanu CA. Risk factors for gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma: similarities, differences and updates. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2012;43(2):137-147. doi:10.1007/s12029-011-9284-y
5. Maemura K, Natsugoe S, Takao S. Molecular mechanism of cholangiocarcinoma carcinogenesis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(10):754-760. doi:10.1002/jhbp.126
6. Steele JA, Richter CH, Echaubard P, et al. Thinking beyond Opisthorchis viverrini for risk of cholangiocarcinoma in the lower Mekong region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7(1):44. Published 2018 May 17. doi:10.1186/s40249-018-0434-3.
7. Kim TS, Pak JH, Kim JB, Bahk YY. Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: a brief review. BMB Rep. 2016;49(11):590-597. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.11.109
8. Murata M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ Health Prev Med. 2018;23(1):50. Published 2018 Oct 20. doi:10.1186/s12199-018-0740-1
9. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Biological agents. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2012;100(pt B):1-441.
10. Mairiang E, Laha T, Bethony JM, et al. Ultrasonography assessment of hepatobiliary abnormalities in 3359 subjects with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in endemic areas of Thailand. Parasitol Int. 2012;61(1):208-211. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.07.009
11. Li HM, Qian MB, Yang YC, et al. Performance evaluation of existing immunoassays for Clonorchis sinensis infection in China. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11(1):35. Published 2018 Jan 15. doi:10.1186/s13071-018-2612-3
12. Hughes T, O’Connor T, Techasen A, et al. Opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma in Southeast Asia: an unresolved problem. Int J Gen Med. 2017;10:227-237. Published 2017 Aug 10. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S133292
13. Psevdos G, Ford FM, Hong ST. Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):208-210. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000611
14. American War Library. In harm’s way... How many real Vietnam vets are alive today? Updated February 28, 2019. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.americanwarlibrary.com/personnel/vietvet.htm
15. Nash TE, Sullivan D, Mitre E, et al. Comments on “Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war”. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):240-241. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000659
1. American Cancer Society. Survival rates for bile duct cancer. Updated March 1, 2023. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/bile-duct-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-by-stage.html
2. Vij M, Puri Y, Rammohan A, et al. Pathological, molecular, and clinical characteristics of cholangiocarcinoma: A comprehensive review. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;14(3):607-627. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v14.i3.607
3. Yao KJ, Jabbour S, Parekh N, Lin Y, Moss RA. Increasing mortality in the United States from cholangiocarcinoma: an analysis of the National Center for Health Statistics Database. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16(1):117. Published 2016 Sep 21. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0527-z
4. Rustagi T, Dasanu CA. Risk factors for gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma: similarities, differences and updates. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2012;43(2):137-147. doi:10.1007/s12029-011-9284-y
5. Maemura K, Natsugoe S, Takao S. Molecular mechanism of cholangiocarcinoma carcinogenesis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(10):754-760. doi:10.1002/jhbp.126
6. Steele JA, Richter CH, Echaubard P, et al. Thinking beyond Opisthorchis viverrini for risk of cholangiocarcinoma in the lower Mekong region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect Dis Poverty. 2018;7(1):44. Published 2018 May 17. doi:10.1186/s40249-018-0434-3.
7. Kim TS, Pak JH, Kim JB, Bahk YY. Clonorchis sinensis, an oriental liver fluke, as a human biological agent of cholangiocarcinoma: a brief review. BMB Rep. 2016;49(11):590-597. doi:10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.11.109
8. Murata M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ Health Prev Med. 2018;23(1):50. Published 2018 Oct 20. doi:10.1186/s12199-018-0740-1
9. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Biological agents. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2012;100(pt B):1-441.
10. Mairiang E, Laha T, Bethony JM, et al. Ultrasonography assessment of hepatobiliary abnormalities in 3359 subjects with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in endemic areas of Thailand. Parasitol Int. 2012;61(1):208-211. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2011.07.009
11. Li HM, Qian MB, Yang YC, et al. Performance evaluation of existing immunoassays for Clonorchis sinensis infection in China. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11(1):35. Published 2018 Jan 15. doi:10.1186/s13071-018-2612-3
12. Hughes T, O’Connor T, Techasen A, et al. Opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma in Southeast Asia: an unresolved problem. Int J Gen Med. 2017;10:227-237. Published 2017 Aug 10. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S133292
13. Psevdos G, Ford FM, Hong ST. Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):208-210. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000611
14. American War Library. In harm’s way... How many real Vietnam vets are alive today? Updated February 28, 2019. Accessed March 17, 2023. https://www.americanwarlibrary.com/personnel/vietvet.htm
15. Nash TE, Sullivan D, Mitre E, et al. Comments on “Screening US Vietnam veterans for liver fluke exposure 5 decades after the end of the war”. Infect Dis Clin Pract (Baltim Md). 2018;26(4):240-241. doi:10.1097/IPC.0000000000000659
The 30th-birthday gift that could save a life
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Milestone birthdays are always memorable – those ages when your life seems to fundamentally change somehow. Age 16: A license to drive. Age 18: You can vote to determine your own future and serve in the military. At 21, 3 years after adulthood, you are finally allowed to drink alcohol, for some reason. And then ... nothing much happens. At least until you turn 65 and become eligible for Medicare.
But imagine a future when turning 30 might be the biggest milestone birthday of all. Imagine a future when, at 30, you get your genome sequenced and doctors tell you what needs to be done to save your life.
That future may not be far off, as a new study shows us that
Getting your genome sequenced is a double-edged sword. Of course, there is the potential for substantial benefit; finding certain mutations allows for definitive therapy before it’s too late. That said, there are genetic diseases without a cure and without a treatment. Knowing about that destiny may do more harm than good.
Three conditions are described by the CDC as “Tier 1” conditions, genetic syndromes with a significant impact on life expectancy that also have definitive, effective therapies.
These include mutations like BRCA1/2, associated with a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer; mutations associated with Lynch syndrome, which confer an elevated risk for colon cancer; and mutations associated with familial hypercholesterolemia, which confer elevated risk for cardiovascular events.
In each of these cases, there is clear evidence that early intervention can save lives. Individuals at high risk for breast and ovarian cancer can get prophylactic mastectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy. Those with Lynch syndrome can get more frequent screening for colon cancer and polypectomy, and those with familial hypercholesterolemia can get aggressive lipid-lowering therapy.
I think most of us would probably want to know if we had one of these conditions. Most of us would use that information to take concrete steps to decrease our risk. But just because a rational person would choose to do something doesn’t mean it’s feasible. After all, we’re talking about tests and treatments that have significant costs.
In a recent issue of Annals of Internal Medicine, Josh Peterson and David Veenstra present a detailed accounting of the cost and benefit of a hypothetical nationwide, universal screening program for Tier 1 conditions. And in the end, it may actually be worth it.
Cost-benefit analyses work by comparing two independent policy choices: the status quo – in this case, a world in which some people get tested for these conditions, but generally only if they are at high risk based on strong family history; and an alternative policy – in this case, universal screening for these conditions starting at some age.
After that, it’s time to play the assumption game. Using the best available data, the authors estimated the percentage of the population that will have each condition, the percentage of those individuals who will definitively act on the information, and how effective those actions would be if taken.
The authors provide an example. First, they assume that the prevalence of mutations leading to a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer is around 0.7%, and that up to 40% of people who learn that they have one of these mutations would undergo prophylactic mastectomy, which would reduce the risk for breast cancer by around 94%. (I ran these numbers past my wife, a breast surgical oncologist, who agreed that they seem reasonable.)
Assumptions in place, it’s time to consider costs. The cost of the screening test itself: The authors use $250 as their average per-person cost. But we also have the cost of treatment – around $22,000 per person for a bilateral prophylactic mastectomy; the cost of statin therapy for those with familial hypercholesterolemia; or the cost of all of those colonoscopies for those with Lynch syndrome.
Finally, we assess quality of life. Obviously, living longer is generally considered better than living shorter, but marginal increases in life expectancy at the cost of quality of life might not be a rational choice.
You then churn these assumptions through a computer and see what comes out. How many dollars does it take to save one quality-adjusted life-year (QALY)? I’ll tell you right now that $50,000 per QALY used to be the unofficial standard for a “cost-effective” intervention in the United States. Researchers have more recently used $100,000 as that threshold.
Let’s look at some hard numbers.
If you screened 100,000 people at age 30 years, 1,500 would get news that something in their genetics was, more or less, a ticking time bomb. Some would choose to get definitive treatment and the authors estimate that the strategy would prevent 85 cases of cancer. You’d prevent nine heart attacks and five strokes by lowering cholesterol levels among those with familial hypercholesterolemia. Obviously, these aren’t huge numbers, but of course most people don’t have these hereditary risk factors. For your average 30-year-old, the genetic screening test will be completely uneventful, but for those 1,500 it will be life-changing, and potentially life-saving.
But is it worth it? The authors estimate that, at the midpoint of all their assumptions, the cost of this program would be $68,000 per QALY saved.
Of course, that depends on all those assumptions we talked about. Interestingly, the single factor that changes the cost-effectiveness the most in this analysis is the cost of the genetic test itself, which I guess makes sense, considering we’d be talking about testing a huge segment of the population. If the test cost $100 instead of $250, the cost per QALY would be $39,700 – well within the range that most policymakers would support. And given the rate at which the cost of genetic testing is decreasing, and the obvious economies of scale here, I think $100 per test is totally feasible.
The future will bring other changes as well. Right now, there are only three hereditary conditions designated as Tier 1 by the CDC. If conditions are added, that might also swing the calculation more heavily toward benefit.
This will represent a stark change from how we think about genetic testing currently, focusing on those whose pretest probability of an abnormal result is high due to family history or other risk factors. But for the 20-year-olds out there, I wouldn’t be surprised if your 30th birthday is a bit more significant than you have been anticipating.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Milestone birthdays are always memorable – those ages when your life seems to fundamentally change somehow. Age 16: A license to drive. Age 18: You can vote to determine your own future and serve in the military. At 21, 3 years after adulthood, you are finally allowed to drink alcohol, for some reason. And then ... nothing much happens. At least until you turn 65 and become eligible for Medicare.
But imagine a future when turning 30 might be the biggest milestone birthday of all. Imagine a future when, at 30, you get your genome sequenced and doctors tell you what needs to be done to save your life.
That future may not be far off, as a new study shows us that
Getting your genome sequenced is a double-edged sword. Of course, there is the potential for substantial benefit; finding certain mutations allows for definitive therapy before it’s too late. That said, there are genetic diseases without a cure and without a treatment. Knowing about that destiny may do more harm than good.
Three conditions are described by the CDC as “Tier 1” conditions, genetic syndromes with a significant impact on life expectancy that also have definitive, effective therapies.
These include mutations like BRCA1/2, associated with a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer; mutations associated with Lynch syndrome, which confer an elevated risk for colon cancer; and mutations associated with familial hypercholesterolemia, which confer elevated risk for cardiovascular events.
In each of these cases, there is clear evidence that early intervention can save lives. Individuals at high risk for breast and ovarian cancer can get prophylactic mastectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy. Those with Lynch syndrome can get more frequent screening for colon cancer and polypectomy, and those with familial hypercholesterolemia can get aggressive lipid-lowering therapy.
I think most of us would probably want to know if we had one of these conditions. Most of us would use that information to take concrete steps to decrease our risk. But just because a rational person would choose to do something doesn’t mean it’s feasible. After all, we’re talking about tests and treatments that have significant costs.
In a recent issue of Annals of Internal Medicine, Josh Peterson and David Veenstra present a detailed accounting of the cost and benefit of a hypothetical nationwide, universal screening program for Tier 1 conditions. And in the end, it may actually be worth it.
Cost-benefit analyses work by comparing two independent policy choices: the status quo – in this case, a world in which some people get tested for these conditions, but generally only if they are at high risk based on strong family history; and an alternative policy – in this case, universal screening for these conditions starting at some age.
After that, it’s time to play the assumption game. Using the best available data, the authors estimated the percentage of the population that will have each condition, the percentage of those individuals who will definitively act on the information, and how effective those actions would be if taken.
The authors provide an example. First, they assume that the prevalence of mutations leading to a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer is around 0.7%, and that up to 40% of people who learn that they have one of these mutations would undergo prophylactic mastectomy, which would reduce the risk for breast cancer by around 94%. (I ran these numbers past my wife, a breast surgical oncologist, who agreed that they seem reasonable.)
Assumptions in place, it’s time to consider costs. The cost of the screening test itself: The authors use $250 as their average per-person cost. But we also have the cost of treatment – around $22,000 per person for a bilateral prophylactic mastectomy; the cost of statin therapy for those with familial hypercholesterolemia; or the cost of all of those colonoscopies for those with Lynch syndrome.
Finally, we assess quality of life. Obviously, living longer is generally considered better than living shorter, but marginal increases in life expectancy at the cost of quality of life might not be a rational choice.
You then churn these assumptions through a computer and see what comes out. How many dollars does it take to save one quality-adjusted life-year (QALY)? I’ll tell you right now that $50,000 per QALY used to be the unofficial standard for a “cost-effective” intervention in the United States. Researchers have more recently used $100,000 as that threshold.
Let’s look at some hard numbers.
If you screened 100,000 people at age 30 years, 1,500 would get news that something in their genetics was, more or less, a ticking time bomb. Some would choose to get definitive treatment and the authors estimate that the strategy would prevent 85 cases of cancer. You’d prevent nine heart attacks and five strokes by lowering cholesterol levels among those with familial hypercholesterolemia. Obviously, these aren’t huge numbers, but of course most people don’t have these hereditary risk factors. For your average 30-year-old, the genetic screening test will be completely uneventful, but for those 1,500 it will be life-changing, and potentially life-saving.
But is it worth it? The authors estimate that, at the midpoint of all their assumptions, the cost of this program would be $68,000 per QALY saved.
Of course, that depends on all those assumptions we talked about. Interestingly, the single factor that changes the cost-effectiveness the most in this analysis is the cost of the genetic test itself, which I guess makes sense, considering we’d be talking about testing a huge segment of the population. If the test cost $100 instead of $250, the cost per QALY would be $39,700 – well within the range that most policymakers would support. And given the rate at which the cost of genetic testing is decreasing, and the obvious economies of scale here, I think $100 per test is totally feasible.
The future will bring other changes as well. Right now, there are only three hereditary conditions designated as Tier 1 by the CDC. If conditions are added, that might also swing the calculation more heavily toward benefit.
This will represent a stark change from how we think about genetic testing currently, focusing on those whose pretest probability of an abnormal result is high due to family history or other risk factors. But for the 20-year-olds out there, I wouldn’t be surprised if your 30th birthday is a bit more significant than you have been anticipating.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
Milestone birthdays are always memorable – those ages when your life seems to fundamentally change somehow. Age 16: A license to drive. Age 18: You can vote to determine your own future and serve in the military. At 21, 3 years after adulthood, you are finally allowed to drink alcohol, for some reason. And then ... nothing much happens. At least until you turn 65 and become eligible for Medicare.
But imagine a future when turning 30 might be the biggest milestone birthday of all. Imagine a future when, at 30, you get your genome sequenced and doctors tell you what needs to be done to save your life.
That future may not be far off, as a new study shows us that
Getting your genome sequenced is a double-edged sword. Of course, there is the potential for substantial benefit; finding certain mutations allows for definitive therapy before it’s too late. That said, there are genetic diseases without a cure and without a treatment. Knowing about that destiny may do more harm than good.
Three conditions are described by the CDC as “Tier 1” conditions, genetic syndromes with a significant impact on life expectancy that also have definitive, effective therapies.
These include mutations like BRCA1/2, associated with a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer; mutations associated with Lynch syndrome, which confer an elevated risk for colon cancer; and mutations associated with familial hypercholesterolemia, which confer elevated risk for cardiovascular events.
In each of these cases, there is clear evidence that early intervention can save lives. Individuals at high risk for breast and ovarian cancer can get prophylactic mastectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy. Those with Lynch syndrome can get more frequent screening for colon cancer and polypectomy, and those with familial hypercholesterolemia can get aggressive lipid-lowering therapy.
I think most of us would probably want to know if we had one of these conditions. Most of us would use that information to take concrete steps to decrease our risk. But just because a rational person would choose to do something doesn’t mean it’s feasible. After all, we’re talking about tests and treatments that have significant costs.
In a recent issue of Annals of Internal Medicine, Josh Peterson and David Veenstra present a detailed accounting of the cost and benefit of a hypothetical nationwide, universal screening program for Tier 1 conditions. And in the end, it may actually be worth it.
Cost-benefit analyses work by comparing two independent policy choices: the status quo – in this case, a world in which some people get tested for these conditions, but generally only if they are at high risk based on strong family history; and an alternative policy – in this case, universal screening for these conditions starting at some age.
After that, it’s time to play the assumption game. Using the best available data, the authors estimated the percentage of the population that will have each condition, the percentage of those individuals who will definitively act on the information, and how effective those actions would be if taken.
The authors provide an example. First, they assume that the prevalence of mutations leading to a high risk for breast and ovarian cancer is around 0.7%, and that up to 40% of people who learn that they have one of these mutations would undergo prophylactic mastectomy, which would reduce the risk for breast cancer by around 94%. (I ran these numbers past my wife, a breast surgical oncologist, who agreed that they seem reasonable.)
Assumptions in place, it’s time to consider costs. The cost of the screening test itself: The authors use $250 as their average per-person cost. But we also have the cost of treatment – around $22,000 per person for a bilateral prophylactic mastectomy; the cost of statin therapy for those with familial hypercholesterolemia; or the cost of all of those colonoscopies for those with Lynch syndrome.
Finally, we assess quality of life. Obviously, living longer is generally considered better than living shorter, but marginal increases in life expectancy at the cost of quality of life might not be a rational choice.
You then churn these assumptions through a computer and see what comes out. How many dollars does it take to save one quality-adjusted life-year (QALY)? I’ll tell you right now that $50,000 per QALY used to be the unofficial standard for a “cost-effective” intervention in the United States. Researchers have more recently used $100,000 as that threshold.
Let’s look at some hard numbers.
If you screened 100,000 people at age 30 years, 1,500 would get news that something in their genetics was, more or less, a ticking time bomb. Some would choose to get definitive treatment and the authors estimate that the strategy would prevent 85 cases of cancer. You’d prevent nine heart attacks and five strokes by lowering cholesterol levels among those with familial hypercholesterolemia. Obviously, these aren’t huge numbers, but of course most people don’t have these hereditary risk factors. For your average 30-year-old, the genetic screening test will be completely uneventful, but for those 1,500 it will be life-changing, and potentially life-saving.
But is it worth it? The authors estimate that, at the midpoint of all their assumptions, the cost of this program would be $68,000 per QALY saved.
Of course, that depends on all those assumptions we talked about. Interestingly, the single factor that changes the cost-effectiveness the most in this analysis is the cost of the genetic test itself, which I guess makes sense, considering we’d be talking about testing a huge segment of the population. If the test cost $100 instead of $250, the cost per QALY would be $39,700 – well within the range that most policymakers would support. And given the rate at which the cost of genetic testing is decreasing, and the obvious economies of scale here, I think $100 per test is totally feasible.
The future will bring other changes as well. Right now, there are only three hereditary conditions designated as Tier 1 by the CDC. If conditions are added, that might also swing the calculation more heavily toward benefit.
This will represent a stark change from how we think about genetic testing currently, focusing on those whose pretest probability of an abnormal result is high due to family history or other risk factors. But for the 20-year-olds out there, I wouldn’t be surprised if your 30th birthday is a bit more significant than you have been anticipating.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator in New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medications that scare me
An 85-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a syncopal episode. Her caregivers report a similar episode 2 weeks ago, but she recovered so quickly they did not seek evaluation for her.
Medications: Omeprazole 20 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, citalopram 10 mg, albuterol, donepezil 10 mg, isosorbide mononitrate 60 mg, and calcium. On exam, blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 55. ECG indicates bradycardia with normal intervals. What drug most likely caused her syncope?
A. Citalopram
B. Pravastatin
C. Donepezil
D. Isosorbide
E. Calcium
This woman’s syncope is likely caused by donepezil. Citalopram can lengthen the QT interval, especially in elderly patients, but the normal intervals on ECG eliminate this possibility. Donepezil can cause bradycardia, which can contribute to syncope.
Hernandez and colleagues evaluated a cohort of veterans with dementia over an 8-year period.1 They found that there was a 1.4-fold increased risk of bradycardia in patients with dementia treated with an acetylcholine inhibitor (compared with that in patients who were not taking these medications) and that there was a dose-dependent increase in risk for patients on donepezil.
Park-Wyllie et al. found in a study of 1.4 million older adults a greater than twofold risk of hospitalization for bradycardia in patients treated with a cholinesterase inhibitor.2 Gill and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study of 19,803 elderly patients with dementia who were prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors, and compared them to age-matched controls.3 They found increased hospital visits for syncope in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors (hazard ratio, 1.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-1.98). Other syncope-related events were also more common in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors, compared with controls: hospital visits for bradycardia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.32-2.15), permanent pacemaker insertion (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.12-2.00), and hip fracture (HR, 1.18; (95% CI, 1.04-1.34).
Nausea, vomiting, and weight loss are much more common than the rarer side effects of bradycardia and syncope. The frequency of gastroenterological side effects is up to 25%. Cholinesterase inhibitors have modest effects on cognitive function with a high number needed to treat (NNT) of 10, and an NNT as high as 100 for global function. The number needed to harm (NNH) is 4, when gastrointestinal symptoms are added in.4 Another important, problematic side effect of cholinesterase inhibitors is urinary incontinence. This often leads to patients receiving medications, to combat this side effect, that may worsen cognitive function.
Another commonly used medication that scares me in certain circumstances is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. My main concern is when it is used in patients who are elderly, have chronic kidney disease, or are taking other medications that can cause hyperkalemia (ACEIs, ARBs, potassium-sparing diuretics including spironolactone). Hyperkalemia is a real concern in these patient populations. Trimethoprim reduces renal potassium excretion through the competitive inhibition of sodium channels in the distal nephron, in a manner similar to the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride. Hospitalizations for hyperkalemia are more common in patients who take ACEIs and ARBs and are prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, compared with other antibiotics.5
Sudden cardiac death is also more common in patients who are taking ACEIs or ARBs and receive trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.6 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole also has a powerful interaction with warfarin, both displacing warfarin from albumin and inhibiting its metabolism. It raises the INR (international normalized ratio) in warfarin-treated patients much greater than do other antibiotics.7
Pearls
- Think carefully about the use of cholinesterase inhibitors because of the unfavorable NNH vs. NNT.
- Use caution prescribing trimethoprim for patients who are elderly, especially if they are on an ACEI, an ARB, or spironolactone, and in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Hernandez RK et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57:1997-2003.
2. Park-Wyllie LY et al. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000157.
3. Gill SS et al. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:867-73.
4. Peters KR. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jul;61(7):1170-4.
5. Antoniou TN et al. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170(12):1045-9.
6. Fralick M et al. BMJ. 2014 Oct 30;349:g6196.
7. Glasheen JJ et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2005 Jul;20(7):653-6.
An 85-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a syncopal episode. Her caregivers report a similar episode 2 weeks ago, but she recovered so quickly they did not seek evaluation for her.
Medications: Omeprazole 20 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, citalopram 10 mg, albuterol, donepezil 10 mg, isosorbide mononitrate 60 mg, and calcium. On exam, blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 55. ECG indicates bradycardia with normal intervals. What drug most likely caused her syncope?
A. Citalopram
B. Pravastatin
C. Donepezil
D. Isosorbide
E. Calcium
This woman’s syncope is likely caused by donepezil. Citalopram can lengthen the QT interval, especially in elderly patients, but the normal intervals on ECG eliminate this possibility. Donepezil can cause bradycardia, which can contribute to syncope.
Hernandez and colleagues evaluated a cohort of veterans with dementia over an 8-year period.1 They found that there was a 1.4-fold increased risk of bradycardia in patients with dementia treated with an acetylcholine inhibitor (compared with that in patients who were not taking these medications) and that there was a dose-dependent increase in risk for patients on donepezil.
Park-Wyllie et al. found in a study of 1.4 million older adults a greater than twofold risk of hospitalization for bradycardia in patients treated with a cholinesterase inhibitor.2 Gill and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study of 19,803 elderly patients with dementia who were prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors, and compared them to age-matched controls.3 They found increased hospital visits for syncope in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors (hazard ratio, 1.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-1.98). Other syncope-related events were also more common in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors, compared with controls: hospital visits for bradycardia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.32-2.15), permanent pacemaker insertion (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.12-2.00), and hip fracture (HR, 1.18; (95% CI, 1.04-1.34).
Nausea, vomiting, and weight loss are much more common than the rarer side effects of bradycardia and syncope. The frequency of gastroenterological side effects is up to 25%. Cholinesterase inhibitors have modest effects on cognitive function with a high number needed to treat (NNT) of 10, and an NNT as high as 100 for global function. The number needed to harm (NNH) is 4, when gastrointestinal symptoms are added in.4 Another important, problematic side effect of cholinesterase inhibitors is urinary incontinence. This often leads to patients receiving medications, to combat this side effect, that may worsen cognitive function.
Another commonly used medication that scares me in certain circumstances is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. My main concern is when it is used in patients who are elderly, have chronic kidney disease, or are taking other medications that can cause hyperkalemia (ACEIs, ARBs, potassium-sparing diuretics including spironolactone). Hyperkalemia is a real concern in these patient populations. Trimethoprim reduces renal potassium excretion through the competitive inhibition of sodium channels in the distal nephron, in a manner similar to the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride. Hospitalizations for hyperkalemia are more common in patients who take ACEIs and ARBs and are prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, compared with other antibiotics.5
Sudden cardiac death is also more common in patients who are taking ACEIs or ARBs and receive trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.6 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole also has a powerful interaction with warfarin, both displacing warfarin from albumin and inhibiting its metabolism. It raises the INR (international normalized ratio) in warfarin-treated patients much greater than do other antibiotics.7
Pearls
- Think carefully about the use of cholinesterase inhibitors because of the unfavorable NNH vs. NNT.
- Use caution prescribing trimethoprim for patients who are elderly, especially if they are on an ACEI, an ARB, or spironolactone, and in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Hernandez RK et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57:1997-2003.
2. Park-Wyllie LY et al. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000157.
3. Gill SS et al. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:867-73.
4. Peters KR. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jul;61(7):1170-4.
5. Antoniou TN et al. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170(12):1045-9.
6. Fralick M et al. BMJ. 2014 Oct 30;349:g6196.
7. Glasheen JJ et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2005 Jul;20(7):653-6.
An 85-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a syncopal episode. Her caregivers report a similar episode 2 weeks ago, but she recovered so quickly they did not seek evaluation for her.
Medications: Omeprazole 20 mg, pravastatin 40 mg, citalopram 10 mg, albuterol, donepezil 10 mg, isosorbide mononitrate 60 mg, and calcium. On exam, blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 55. ECG indicates bradycardia with normal intervals. What drug most likely caused her syncope?
A. Citalopram
B. Pravastatin
C. Donepezil
D. Isosorbide
E. Calcium
This woman’s syncope is likely caused by donepezil. Citalopram can lengthen the QT interval, especially in elderly patients, but the normal intervals on ECG eliminate this possibility. Donepezil can cause bradycardia, which can contribute to syncope.
Hernandez and colleagues evaluated a cohort of veterans with dementia over an 8-year period.1 They found that there was a 1.4-fold increased risk of bradycardia in patients with dementia treated with an acetylcholine inhibitor (compared with that in patients who were not taking these medications) and that there was a dose-dependent increase in risk for patients on donepezil.
Park-Wyllie et al. found in a study of 1.4 million older adults a greater than twofold risk of hospitalization for bradycardia in patients treated with a cholinesterase inhibitor.2 Gill and colleagues performed a population-based cohort study of 19,803 elderly patients with dementia who were prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors, and compared them to age-matched controls.3 They found increased hospital visits for syncope in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors (hazard ratio, 1.76; 95% confidence interval, 1.57-1.98). Other syncope-related events were also more common in people receiving cholinesterase inhibitors, compared with controls: hospital visits for bradycardia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.32-2.15), permanent pacemaker insertion (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.12-2.00), and hip fracture (HR, 1.18; (95% CI, 1.04-1.34).
Nausea, vomiting, and weight loss are much more common than the rarer side effects of bradycardia and syncope. The frequency of gastroenterological side effects is up to 25%. Cholinesterase inhibitors have modest effects on cognitive function with a high number needed to treat (NNT) of 10, and an NNT as high as 100 for global function. The number needed to harm (NNH) is 4, when gastrointestinal symptoms are added in.4 Another important, problematic side effect of cholinesterase inhibitors is urinary incontinence. This often leads to patients receiving medications, to combat this side effect, that may worsen cognitive function.
Another commonly used medication that scares me in certain circumstances is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. My main concern is when it is used in patients who are elderly, have chronic kidney disease, or are taking other medications that can cause hyperkalemia (ACEIs, ARBs, potassium-sparing diuretics including spironolactone). Hyperkalemia is a real concern in these patient populations. Trimethoprim reduces renal potassium excretion through the competitive inhibition of sodium channels in the distal nephron, in a manner similar to the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride. Hospitalizations for hyperkalemia are more common in patients who take ACEIs and ARBs and are prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, compared with other antibiotics.5
Sudden cardiac death is also more common in patients who are taking ACEIs or ARBs and receive trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.6 Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole also has a powerful interaction with warfarin, both displacing warfarin from albumin and inhibiting its metabolism. It raises the INR (international normalized ratio) in warfarin-treated patients much greater than do other antibiotics.7
Pearls
- Think carefully about the use of cholinesterase inhibitors because of the unfavorable NNH vs. NNT.
- Use caution prescribing trimethoprim for patients who are elderly, especially if they are on an ACEI, an ARB, or spironolactone, and in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. Contact Dr. Paauw at dpaauw@uw.edu.
References
1. Hernandez RK et al. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57:1997-2003.
2. Park-Wyllie LY et al. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000157.
3. Gill SS et al. Arch Intern Med 2009;169:867-73.
4. Peters KR. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jul;61(7):1170-4.
5. Antoniou TN et al. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170(12):1045-9.
6. Fralick M et al. BMJ. 2014 Oct 30;349:g6196.
7. Glasheen JJ et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2005 Jul;20(7):653-6.
Overcoming dental phobias
When I was medical student, world famous behaviorist Dr. Joseph Wolpe was my mentor and taught me a great deal about anxiety disorders and phobias in his clinic. I did some of the original research on agoraphobias in the mid-1970s and have used the experience to treat many patients with phobias over the last 40-plus years.
Some of these patients with phobias had marked functional impairments in their social functioning and their adaptive skills. One such example – dental phobia – is a fear of going to the dentist and is commonly found in the general population.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for more than 20 years, has seen this fear on a daily basis in her patients, ranging from mild to extreme. She says that most dental patients are able to overcome their fear and panic, but she estimates that about 5% have extreme dental phobias that prevented a patient from visiting the dentist. This can lead to poor dental health, affect self esteem, and destroy relationships.
The causes of dental phobia are multifactorial and as follows:
- Fear of pain and needles.
- Past bad experiences with dental procedures.
- Past history of abuse.
- Fear of loss of control in the dental chair.
- History of other phobias or anxiety disorders.
Dr. Cohen also states that the anticipatory anxiety of going to the dentist can be just as fearful as being in the dental chair. And she further states this anticipatory anxiety causes a great deal of noncompliance in keeping dental appointments. Patients missed dental appointments that were very necessary for their overall health. Dr. Cohen noticed that triggers to this specific dental anxiety are:
- Thoughts of being in the dental office.
- Thoughts of lying in the dental chair.
- Thoughts of hearing sounds of drills or seeing dental instruments.
- The smells of the dental office.
- Dental overhead lights.
Symptoms of dental phobias include chills, dizziness, hyperhidrosis, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, indigestion, and trembling. Dr. Cohen also notes that people with dental phobias can cry before visits, have insomnia, and experience panic attacks. These symptoms can further cause avoidance of visits, and can trigger anxiety and fears that do not match the danger.
Avoidance of treatment often leads to poor dental health, periodontal disease, tooth loss, and decayed teeth, but also may contribute to heart problems, diabetes, and undetected carcinomas. Noncompliance with dental care affects general well being and self esteem, and may cause chronic pain, sleep problems, and embarrassment. It may also affect performance in work and school, and can cause social isolation.
Exposure therapy in vivo and in vitro with systematic desensitization and flooding can decrease significantly the fears, panic, and avoidance some dental patients experience. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can change the way patients see and respond to the situations that trigger symptoms.
Additionally, acupuncture can reduce the anxiety that patients feel about dental visits, and distraction techniques such as music and television can be very helpful during dental appointments. Guided imagery using deep breathing exercises with relaxation, visualization, and positive suggestion can create a sense of well-being and calmness. Hypnosis has also been shown to decrease the stress of being in a dental office. Nitrous oxide and oral or IV sedation may be a helpful last resort.
It is important for a person with dental phobias to be referred to a caring dentist who is sensitive to anxiety, and choose a dentist who will listen to and help the patient come up with signals, such as raising their hand, to temporarily stop a dental procedure. This technique will help the dental patient to avoid experiencing a total loss of control and help them feel less overwhelmed.
Dr. Cohen also says that it is helpful to visit the dentist at a less busy time of the day so there are fewer dental sounds and anxiety triggers in the office.
I have found that behavior modification with systematic desensitization and flooding in vivo and in vitro is extremely helpful in helping patients with extreme dental phobias overcome their fears and become more compliant with their dental treatments. Through the use of these techniques, dental phobias – and their emotional and physical sequelae – may be alleviated together.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
When I was medical student, world famous behaviorist Dr. Joseph Wolpe was my mentor and taught me a great deal about anxiety disorders and phobias in his clinic. I did some of the original research on agoraphobias in the mid-1970s and have used the experience to treat many patients with phobias over the last 40-plus years.
Some of these patients with phobias had marked functional impairments in their social functioning and their adaptive skills. One such example – dental phobia – is a fear of going to the dentist and is commonly found in the general population.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for more than 20 years, has seen this fear on a daily basis in her patients, ranging from mild to extreme. She says that most dental patients are able to overcome their fear and panic, but she estimates that about 5% have extreme dental phobias that prevented a patient from visiting the dentist. This can lead to poor dental health, affect self esteem, and destroy relationships.
The causes of dental phobia are multifactorial and as follows:
- Fear of pain and needles.
- Past bad experiences with dental procedures.
- Past history of abuse.
- Fear of loss of control in the dental chair.
- History of other phobias or anxiety disorders.
Dr. Cohen also states that the anticipatory anxiety of going to the dentist can be just as fearful as being in the dental chair. And she further states this anticipatory anxiety causes a great deal of noncompliance in keeping dental appointments. Patients missed dental appointments that were very necessary for their overall health. Dr. Cohen noticed that triggers to this specific dental anxiety are:
- Thoughts of being in the dental office.
- Thoughts of lying in the dental chair.
- Thoughts of hearing sounds of drills or seeing dental instruments.
- The smells of the dental office.
- Dental overhead lights.
Symptoms of dental phobias include chills, dizziness, hyperhidrosis, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, indigestion, and trembling. Dr. Cohen also notes that people with dental phobias can cry before visits, have insomnia, and experience panic attacks. These symptoms can further cause avoidance of visits, and can trigger anxiety and fears that do not match the danger.
Avoidance of treatment often leads to poor dental health, periodontal disease, tooth loss, and decayed teeth, but also may contribute to heart problems, diabetes, and undetected carcinomas. Noncompliance with dental care affects general well being and self esteem, and may cause chronic pain, sleep problems, and embarrassment. It may also affect performance in work and school, and can cause social isolation.
Exposure therapy in vivo and in vitro with systematic desensitization and flooding can decrease significantly the fears, panic, and avoidance some dental patients experience. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can change the way patients see and respond to the situations that trigger symptoms.
Additionally, acupuncture can reduce the anxiety that patients feel about dental visits, and distraction techniques such as music and television can be very helpful during dental appointments. Guided imagery using deep breathing exercises with relaxation, visualization, and positive suggestion can create a sense of well-being and calmness. Hypnosis has also been shown to decrease the stress of being in a dental office. Nitrous oxide and oral or IV sedation may be a helpful last resort.
It is important for a person with dental phobias to be referred to a caring dentist who is sensitive to anxiety, and choose a dentist who will listen to and help the patient come up with signals, such as raising their hand, to temporarily stop a dental procedure. This technique will help the dental patient to avoid experiencing a total loss of control and help them feel less overwhelmed.
Dr. Cohen also says that it is helpful to visit the dentist at a less busy time of the day so there are fewer dental sounds and anxiety triggers in the office.
I have found that behavior modification with systematic desensitization and flooding in vivo and in vitro is extremely helpful in helping patients with extreme dental phobias overcome their fears and become more compliant with their dental treatments. Through the use of these techniques, dental phobias – and their emotional and physical sequelae – may be alleviated together.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.
When I was medical student, world famous behaviorist Dr. Joseph Wolpe was my mentor and taught me a great deal about anxiety disorders and phobias in his clinic. I did some of the original research on agoraphobias in the mid-1970s and have used the experience to treat many patients with phobias over the last 40-plus years.
Some of these patients with phobias had marked functional impairments in their social functioning and their adaptive skills. One such example – dental phobia – is a fear of going to the dentist and is commonly found in the general population.
Susan A. Cohen, DMD, a dentist who has practiced for more than 20 years, has seen this fear on a daily basis in her patients, ranging from mild to extreme. She says that most dental patients are able to overcome their fear and panic, but she estimates that about 5% have extreme dental phobias that prevented a patient from visiting the dentist. This can lead to poor dental health, affect self esteem, and destroy relationships.
The causes of dental phobia are multifactorial and as follows:
- Fear of pain and needles.
- Past bad experiences with dental procedures.
- Past history of abuse.
- Fear of loss of control in the dental chair.
- History of other phobias or anxiety disorders.
Dr. Cohen also states that the anticipatory anxiety of going to the dentist can be just as fearful as being in the dental chair. And she further states this anticipatory anxiety causes a great deal of noncompliance in keeping dental appointments. Patients missed dental appointments that were very necessary for their overall health. Dr. Cohen noticed that triggers to this specific dental anxiety are:
- Thoughts of being in the dental office.
- Thoughts of lying in the dental chair.
- Thoughts of hearing sounds of drills or seeing dental instruments.
- The smells of the dental office.
- Dental overhead lights.
Symptoms of dental phobias include chills, dizziness, hyperhidrosis, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, indigestion, and trembling. Dr. Cohen also notes that people with dental phobias can cry before visits, have insomnia, and experience panic attacks. These symptoms can further cause avoidance of visits, and can trigger anxiety and fears that do not match the danger.
Avoidance of treatment often leads to poor dental health, periodontal disease, tooth loss, and decayed teeth, but also may contribute to heart problems, diabetes, and undetected carcinomas. Noncompliance with dental care affects general well being and self esteem, and may cause chronic pain, sleep problems, and embarrassment. It may also affect performance in work and school, and can cause social isolation.
Exposure therapy in vivo and in vitro with systematic desensitization and flooding can decrease significantly the fears, panic, and avoidance some dental patients experience. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can change the way patients see and respond to the situations that trigger symptoms.
Additionally, acupuncture can reduce the anxiety that patients feel about dental visits, and distraction techniques such as music and television can be very helpful during dental appointments. Guided imagery using deep breathing exercises with relaxation, visualization, and positive suggestion can create a sense of well-being and calmness. Hypnosis has also been shown to decrease the stress of being in a dental office. Nitrous oxide and oral or IV sedation may be a helpful last resort.
It is important for a person with dental phobias to be referred to a caring dentist who is sensitive to anxiety, and choose a dentist who will listen to and help the patient come up with signals, such as raising their hand, to temporarily stop a dental procedure. This technique will help the dental patient to avoid experiencing a total loss of control and help them feel less overwhelmed.
Dr. Cohen also says that it is helpful to visit the dentist at a less busy time of the day so there are fewer dental sounds and anxiety triggers in the office.
I have found that behavior modification with systematic desensitization and flooding in vivo and in vitro is extremely helpful in helping patients with extreme dental phobias overcome their fears and become more compliant with their dental treatments. Through the use of these techniques, dental phobias – and their emotional and physical sequelae – may be alleviated together.
Dr. Richard W. Cohen is a psychiatrist who has been in private practice for more than 40 years and is on the editorial advisory board for Clinical Psychiatry News. Dr. Susan A. Cohen has practiced dentistry for over 20 years. The Cohens, who are married, are based in Philadelphia.