User login
MDedge conference coverage features onsite reporting of the latest study results and expert perspectives from leading researchers.
LDL lowering to specific targets may offset risk from high Lp(a)
MILAN – The increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events caused by elevated lipoprotein(a) levels can potentially be precisely offset by lowering LDL cholesterol to specific levels, suggests a novel study that underscores the importance or early intervention.
The results, derived from an analysis of data on Lp(a) and LDL cholesterol levels and associated genetic risk scores in almost 500,000 individuals from the United Kingdom, have been used to develop a series of age-related targets for lowering LDL cholesterol levels to counter the risk associated with lifetime Lp(a) exposure.
Measuring Lp(a) levels can “substantially refine individual estimates of absolute risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study presenter Brian A. Ference, MD, Centre for Naturally Randomized Trials, University of Cambridge (England).
This can “directly inform treatment decisions about the intensity of LDL lowering or other risk-factor modification needed to overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a).”
Dr. Ference said this will allow clinicians to personalize the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and identify people “who may benefit from potent Lp(a)-lowering therapies when they become available.”
The research was presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) 2022 congress on May 24.
In addition to producing a tabular version of the intensification of LDL-cholesterol reduction needed to overcome the increased cardiovascular risk at different levels of Lp(a), stratified by age, Dr. Ference is working with the EAS to develop an app to further deliver on that personalized prevention.
It will display an individual’s lifetime risk for myocardial infarction or stroke, with and without the inclusion of Lp(a) levels, and determine not only the percentage of increased risk caused by Lp(a), but also the amount by which LDL cholesterol needs to be lowered to overcome that risk.
“The whole rationale for this study was to say, how can we give practical advice on how to use Lp(a) to inform clinical decisions about how to individualize personal risk reduction,” Dr. Ference told this news organization.
“What the app will do is make it very easy for clinicians to, first, understand how much Lp(a) increases risk, but specifically how they can use that information to directly inform their treatment decisions.”
In addition, Dr. Ference said that it will “show patients why it’s important for them” to intensify LDL lowering to overcome their particular level of Lp(a).
Other key takeaways from the results is the importance of intervention as early as possible to minimize the impact of lifetime exposure to increased Lp(a), and that the reduction in LDL cholesterol required to achieve that remains relatively modest.
For Dr. Ference, this means ideally beginning comprehensive health checks at 30 years of age and starting lipid-lowering interventions immediately for those at risk.
“The good thing about LDL and other causes of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is it doesn’t really matter how you lower it,” he said, noting that it could be with diet, lifestyle interventions, or medication.
Handy tool
The new app could be a “handy tool to counsel patients,” Florian Kronenberg, MD, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, told this news organization.
“We can say, look, you have high Lp(a),” he said. “This is coming from nature, from your genetics, but here we have a point where we can act on your high risk by lowering LDL further. This is important to explain to the patient,” said Dr. Kronenberg, who was not involved in the study.
He emphasized that it is crucial to get across the idea of an individual’s global risk, with not just Lp(a) or cholesterol levels influencing their likelihood of cardiovascular events, but also their age, blood pressure, smoking status, and underlying genetic risk.
Dr. Kronenberg said the current data will be helpful in explaining to clinicians why they should lower LDL-cholesterol levels when a patients had high Lp(a), again centered on the idea of lowering their global risk.
During his presentation, Dr. Ference noted that an increase in Lp(a) levels is associated with a log-linear increase in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that is proportional to the absolute, rather than relative, magnitude of Lp(a) increase.
“Unfortunately, unlike other proteins,” he continued, diet and exercise do not affect levels, and there are currently no effective therapies to lower the risks associated with increased Lp(a) concentrations.
“For that reason,” he said, the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias, on which Dr. Ference was a coauthor, “recommend that we intensify life risk-factor modification in persons with elevated risks.”
However, he added, “this guidance is not specific enough to be useful, and that has created a great deal of inertia among clinicians,” with some concluding that they don’t need to measure Lp(a) “because there’s nothing they can do for it.”
Until the development of novel therapies that directly target Lp(a), the authors sought to quantify the amount of LDL lowering needed to “overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a),” he said.
They studied data on 455,765 individuals from the UK Biobank who did not have a history of cardiovascular events, diabetes, or any cancer before the age of 30. They also had LDL cholesterol levels below 5 mmol/L at the time of enrollment to exclude people with presumed familial hypercholesterolemia.
The researchers used an Lp(a) genetic risk score based on the variants rs10455872 and rs3798220 and an LDL instrumental variable genetic score comprised of 100 variants to randomly categorize individuals with average Lp(a) levels, higher Lp(a) levels, or higher Lp(a) and lower LDL-cholesterol levels.
The data showed that, with elevated absolute levels of measured Lp(a) and with elevated genetic risk scores, there was a progressive increase in the lifetime risk for major coronary events.
When looking at the combination of both increased Lp(a) levels and lower LDL-cholesterol levels, they found that the increase in risk for major coronary events at Lp(a) of 123 nmol/L could be offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 19.5 mg/dL.
For people with an Lp(a) level of 251 nmol/L, the increase in risk for major coronary events was offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 36.1 mg/dL.
Furthermore, the researchers found that the magnitude of intensification of LDL-cholesterol lowering needed to overcome the risk caused by elevated Lp(a) levels varied by age.
For example, in individuals with an Lp(a) level of 220 nmol/L, the reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels needed to offset the risk for major coronary events was calculated to be 0.8 mmol/L if lipid-lowering was started at 30 years of age, rising to 0.9 mmol/L if started at 40 years, 1.2 mmol/L if started at 50 years, and 1.5 mmol/L if started at 60 years.
This, Dr. Ference said, suggests that “diet and lifestyle modification is unlikely to be an effective strategy if started later.”
No funding was declared. Dr. Ference declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck, Esperion Therapeutics, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, The Medicines Company, Mylan, Daiichi Sankyo, Viatris, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, dalCOR, CiVi Pharma, and KrKa Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kronenberg declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, and Kaneka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – The increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events caused by elevated lipoprotein(a) levels can potentially be precisely offset by lowering LDL cholesterol to specific levels, suggests a novel study that underscores the importance or early intervention.
The results, derived from an analysis of data on Lp(a) and LDL cholesterol levels and associated genetic risk scores in almost 500,000 individuals from the United Kingdom, have been used to develop a series of age-related targets for lowering LDL cholesterol levels to counter the risk associated with lifetime Lp(a) exposure.
Measuring Lp(a) levels can “substantially refine individual estimates of absolute risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study presenter Brian A. Ference, MD, Centre for Naturally Randomized Trials, University of Cambridge (England).
This can “directly inform treatment decisions about the intensity of LDL lowering or other risk-factor modification needed to overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a).”
Dr. Ference said this will allow clinicians to personalize the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and identify people “who may benefit from potent Lp(a)-lowering therapies when they become available.”
The research was presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) 2022 congress on May 24.
In addition to producing a tabular version of the intensification of LDL-cholesterol reduction needed to overcome the increased cardiovascular risk at different levels of Lp(a), stratified by age, Dr. Ference is working with the EAS to develop an app to further deliver on that personalized prevention.
It will display an individual’s lifetime risk for myocardial infarction or stroke, with and without the inclusion of Lp(a) levels, and determine not only the percentage of increased risk caused by Lp(a), but also the amount by which LDL cholesterol needs to be lowered to overcome that risk.
“The whole rationale for this study was to say, how can we give practical advice on how to use Lp(a) to inform clinical decisions about how to individualize personal risk reduction,” Dr. Ference told this news organization.
“What the app will do is make it very easy for clinicians to, first, understand how much Lp(a) increases risk, but specifically how they can use that information to directly inform their treatment decisions.”
In addition, Dr. Ference said that it will “show patients why it’s important for them” to intensify LDL lowering to overcome their particular level of Lp(a).
Other key takeaways from the results is the importance of intervention as early as possible to minimize the impact of lifetime exposure to increased Lp(a), and that the reduction in LDL cholesterol required to achieve that remains relatively modest.
For Dr. Ference, this means ideally beginning comprehensive health checks at 30 years of age and starting lipid-lowering interventions immediately for those at risk.
“The good thing about LDL and other causes of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is it doesn’t really matter how you lower it,” he said, noting that it could be with diet, lifestyle interventions, or medication.
Handy tool
The new app could be a “handy tool to counsel patients,” Florian Kronenberg, MD, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, told this news organization.
“We can say, look, you have high Lp(a),” he said. “This is coming from nature, from your genetics, but here we have a point where we can act on your high risk by lowering LDL further. This is important to explain to the patient,” said Dr. Kronenberg, who was not involved in the study.
He emphasized that it is crucial to get across the idea of an individual’s global risk, with not just Lp(a) or cholesterol levels influencing their likelihood of cardiovascular events, but also their age, blood pressure, smoking status, and underlying genetic risk.
Dr. Kronenberg said the current data will be helpful in explaining to clinicians why they should lower LDL-cholesterol levels when a patients had high Lp(a), again centered on the idea of lowering their global risk.
During his presentation, Dr. Ference noted that an increase in Lp(a) levels is associated with a log-linear increase in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that is proportional to the absolute, rather than relative, magnitude of Lp(a) increase.
“Unfortunately, unlike other proteins,” he continued, diet and exercise do not affect levels, and there are currently no effective therapies to lower the risks associated with increased Lp(a) concentrations.
“For that reason,” he said, the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias, on which Dr. Ference was a coauthor, “recommend that we intensify life risk-factor modification in persons with elevated risks.”
However, he added, “this guidance is not specific enough to be useful, and that has created a great deal of inertia among clinicians,” with some concluding that they don’t need to measure Lp(a) “because there’s nothing they can do for it.”
Until the development of novel therapies that directly target Lp(a), the authors sought to quantify the amount of LDL lowering needed to “overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a),” he said.
They studied data on 455,765 individuals from the UK Biobank who did not have a history of cardiovascular events, diabetes, or any cancer before the age of 30. They also had LDL cholesterol levels below 5 mmol/L at the time of enrollment to exclude people with presumed familial hypercholesterolemia.
The researchers used an Lp(a) genetic risk score based on the variants rs10455872 and rs3798220 and an LDL instrumental variable genetic score comprised of 100 variants to randomly categorize individuals with average Lp(a) levels, higher Lp(a) levels, or higher Lp(a) and lower LDL-cholesterol levels.
The data showed that, with elevated absolute levels of measured Lp(a) and with elevated genetic risk scores, there was a progressive increase in the lifetime risk for major coronary events.
When looking at the combination of both increased Lp(a) levels and lower LDL-cholesterol levels, they found that the increase in risk for major coronary events at Lp(a) of 123 nmol/L could be offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 19.5 mg/dL.
For people with an Lp(a) level of 251 nmol/L, the increase in risk for major coronary events was offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 36.1 mg/dL.
Furthermore, the researchers found that the magnitude of intensification of LDL-cholesterol lowering needed to overcome the risk caused by elevated Lp(a) levels varied by age.
For example, in individuals with an Lp(a) level of 220 nmol/L, the reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels needed to offset the risk for major coronary events was calculated to be 0.8 mmol/L if lipid-lowering was started at 30 years of age, rising to 0.9 mmol/L if started at 40 years, 1.2 mmol/L if started at 50 years, and 1.5 mmol/L if started at 60 years.
This, Dr. Ference said, suggests that “diet and lifestyle modification is unlikely to be an effective strategy if started later.”
No funding was declared. Dr. Ference declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck, Esperion Therapeutics, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, The Medicines Company, Mylan, Daiichi Sankyo, Viatris, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, dalCOR, CiVi Pharma, and KrKa Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kronenberg declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, and Kaneka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN – The increased risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events caused by elevated lipoprotein(a) levels can potentially be precisely offset by lowering LDL cholesterol to specific levels, suggests a novel study that underscores the importance or early intervention.
The results, derived from an analysis of data on Lp(a) and LDL cholesterol levels and associated genetic risk scores in almost 500,000 individuals from the United Kingdom, have been used to develop a series of age-related targets for lowering LDL cholesterol levels to counter the risk associated with lifetime Lp(a) exposure.
Measuring Lp(a) levels can “substantially refine individual estimates of absolute risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” said study presenter Brian A. Ference, MD, Centre for Naturally Randomized Trials, University of Cambridge (England).
This can “directly inform treatment decisions about the intensity of LDL lowering or other risk-factor modification needed to overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a).”
Dr. Ference said this will allow clinicians to personalize the prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and identify people “who may benefit from potent Lp(a)-lowering therapies when they become available.”
The research was presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) 2022 congress on May 24.
In addition to producing a tabular version of the intensification of LDL-cholesterol reduction needed to overcome the increased cardiovascular risk at different levels of Lp(a), stratified by age, Dr. Ference is working with the EAS to develop an app to further deliver on that personalized prevention.
It will display an individual’s lifetime risk for myocardial infarction or stroke, with and without the inclusion of Lp(a) levels, and determine not only the percentage of increased risk caused by Lp(a), but also the amount by which LDL cholesterol needs to be lowered to overcome that risk.
“The whole rationale for this study was to say, how can we give practical advice on how to use Lp(a) to inform clinical decisions about how to individualize personal risk reduction,” Dr. Ference told this news organization.
“What the app will do is make it very easy for clinicians to, first, understand how much Lp(a) increases risk, but specifically how they can use that information to directly inform their treatment decisions.”
In addition, Dr. Ference said that it will “show patients why it’s important for them” to intensify LDL lowering to overcome their particular level of Lp(a).
Other key takeaways from the results is the importance of intervention as early as possible to minimize the impact of lifetime exposure to increased Lp(a), and that the reduction in LDL cholesterol required to achieve that remains relatively modest.
For Dr. Ference, this means ideally beginning comprehensive health checks at 30 years of age and starting lipid-lowering interventions immediately for those at risk.
“The good thing about LDL and other causes of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is it doesn’t really matter how you lower it,” he said, noting that it could be with diet, lifestyle interventions, or medication.
Handy tool
The new app could be a “handy tool to counsel patients,” Florian Kronenberg, MD, Institute of Genetic Epidemiology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria, told this news organization.
“We can say, look, you have high Lp(a),” he said. “This is coming from nature, from your genetics, but here we have a point where we can act on your high risk by lowering LDL further. This is important to explain to the patient,” said Dr. Kronenberg, who was not involved in the study.
He emphasized that it is crucial to get across the idea of an individual’s global risk, with not just Lp(a) or cholesterol levels influencing their likelihood of cardiovascular events, but also their age, blood pressure, smoking status, and underlying genetic risk.
Dr. Kronenberg said the current data will be helpful in explaining to clinicians why they should lower LDL-cholesterol levels when a patients had high Lp(a), again centered on the idea of lowering their global risk.
During his presentation, Dr. Ference noted that an increase in Lp(a) levels is associated with a log-linear increase in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that is proportional to the absolute, rather than relative, magnitude of Lp(a) increase.
“Unfortunately, unlike other proteins,” he continued, diet and exercise do not affect levels, and there are currently no effective therapies to lower the risks associated with increased Lp(a) concentrations.
“For that reason,” he said, the 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias, on which Dr. Ference was a coauthor, “recommend that we intensify life risk-factor modification in persons with elevated risks.”
However, he added, “this guidance is not specific enough to be useful, and that has created a great deal of inertia among clinicians,” with some concluding that they don’t need to measure Lp(a) “because there’s nothing they can do for it.”
Until the development of novel therapies that directly target Lp(a), the authors sought to quantify the amount of LDL lowering needed to “overcome the increased risk caused by Lp(a),” he said.
They studied data on 455,765 individuals from the UK Biobank who did not have a history of cardiovascular events, diabetes, or any cancer before the age of 30. They also had LDL cholesterol levels below 5 mmol/L at the time of enrollment to exclude people with presumed familial hypercholesterolemia.
The researchers used an Lp(a) genetic risk score based on the variants rs10455872 and rs3798220 and an LDL instrumental variable genetic score comprised of 100 variants to randomly categorize individuals with average Lp(a) levels, higher Lp(a) levels, or higher Lp(a) and lower LDL-cholesterol levels.
The data showed that, with elevated absolute levels of measured Lp(a) and with elevated genetic risk scores, there was a progressive increase in the lifetime risk for major coronary events.
When looking at the combination of both increased Lp(a) levels and lower LDL-cholesterol levels, they found that the increase in risk for major coronary events at Lp(a) of 123 nmol/L could be offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 19.5 mg/dL.
For people with an Lp(a) level of 251 nmol/L, the increase in risk for major coronary events was offset by a reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels of 36.1 mg/dL.
Furthermore, the researchers found that the magnitude of intensification of LDL-cholesterol lowering needed to overcome the risk caused by elevated Lp(a) levels varied by age.
For example, in individuals with an Lp(a) level of 220 nmol/L, the reduction in LDL-cholesterol levels needed to offset the risk for major coronary events was calculated to be 0.8 mmol/L if lipid-lowering was started at 30 years of age, rising to 0.9 mmol/L if started at 40 years, 1.2 mmol/L if started at 50 years, and 1.5 mmol/L if started at 60 years.
This, Dr. Ference said, suggests that “diet and lifestyle modification is unlikely to be an effective strategy if started later.”
No funding was declared. Dr. Ference declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, Merck, Esperion Therapeutics, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, The Medicines Company, Mylan, Daiichi Sankyo, Viatris, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, dalCOR, CiVi Pharma, and KrKa Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Kronenberg declared relationships with Amgen, Novartis, and Kaneka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EAS 2022
Hand outcomes similar with distal or proximal radial cardiac cath
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
The first randomized controlled study comparing the use of the emerging distal radial artery access to the traditional proximal access for cardiac catheterization has found no significant differences in postprocedure hand function and other secondary outcomes a month afterward, along with similar rates of bleeding and gaining successful RA access at the time of the procedure.
Karim Al-Azizi, MD, reported results of the single-center, Distal vs. Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions annual scientific sessions. DIPRA randomized 300 patients on a 1:1 basis to cardiac catheterization via either the distal or proximal RAs (dRA or pRA). The trial was conducted at the Baylor Scott & White Health The Heart Hospital–Plano in Richardson, Texas, where Dr. Al-Azizi is an interventional cardiologist and structural heart disease specialist.
“Distal radial artery access is a safe strategy for access for cardiovascular patients with a low complication rate,” Dr. Al-Azizi said. “Similarly, the success with distal vs. radial artery access was noted in the study: No significant bleeding or hematomas were noted in the dRA cohort.”
In an interview, Dr. Al-Azizi added, “Our study is the first of its kind and the first to evaluate the true hand function post distal/radial.”
He explained the rationale for the study. “One of the biggest criticisms that came up a few years ago when distal access was being developed and started gaining some momentum is the fact that it is yet unknown what would be the effect on hand function given the proximity to the fingers, proximity to the nerve, and despite that RA occlusion rates were lower.”
The final DIPRA analysis included 254 patients who completed their 30-day follow-up, 128 of whom were randomized to dRA access, 126 to pRA access. Demographics and procedural characteristics were balanced between both arms. The latter included similarities in sheath size used (6-French in 99.3% of both arms) and type of procedure (35.9% in the dRA and 32.9% in pRA arms had percutaneous coronary angioplasty).
To evaluate the primary outcome of hand function in the catheterization hand, the study used a composite of the Quick Disabilities of Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) questionnaire, hand-grip test, and thumb/forefinger pinch test. The composite score changed –.4 and .1 in the dRA and pRA arms, respectively (P = .07), which didn’t reach statistical significance, Dr. Al-Azizi said.
Outcomes at the time of intervention were similar. Successful RA access failed in six dRA patients, who were converted to pRA, and in two pRA patients. Overall rates for successful RA access were 96.7% in the distal arm and 98% in the proximal arm (P = .72). Bleeding rates were 0% and 1.4% in the respective arms (P = .25).
Dr. Al-Azizi said that he and his coinvestigators are collecting 1-year outcomes data that they will present next year.
The DIPRA findings “provide reassurance that hand function is not compromised regardless of access site,” Sunil V. Rao, MD, moderator of the session where Dr. Al-Azizi reported the results, said in an interview.
“Prior studies indicated no difference in hand function between radial and femoral access, and now these data indicate no difference between distal radial and proximal radial access.” Dr. Rao, the incoming SCAI president, is a professor at Duke University Medical Center in Durham, N.C., and cardiology section chief at Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
“We do need more patient-reported outcomes in percutaneous coronary intervention studies. The DIPRA study is a great example of this,” Dr. Rao added. “The DIPRA study adds to the body of literature indicating that access site choice is an important aspect of the PCI procedure. With meticulous procedural technique, patients can have an excellent outcome from PCI procedures.”
Dr. Al-Azizi disclosed consulting for Edwards Lifesciences and Phillips. Dr. Rao has no disclosures.
FROM SCAI 2022
New test might transform male infertility
A new study suggests that, at least for certain male patients, the answer to infertility might lie with epigenetics.
According to the study, a commercially available test of epigenetic anomalies – factors that affect how genes express themselves – can grade the likelihood that sperm are viable for conception.
“The uniqueness of epigenetics is that some of the abnormalities detected have the potential to be modified with lifestyle,” said Larry I. Lipshultz, MD, head of the Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who presented the new findings at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Urological Association.
For decades, semen analysis has been based on motility, morphology, and concentration. But these measures, while useful, are limited. Semen can still have low capacity for producing a pregnancy even when all three parameters are normal, Dr. Lipshultz told this news organization.
The test, called Path SpermQT (Inherent Biosciences) detects unstable gene promotors, which are the epigenetic markers for gene expression. In previous work with more than 1,300 gene samples, expression of the specific genes regulated by these promoters were linked to a wide variety of functions relevant to fertilization, such as spermatogenesis.
The test does not attempt to look for expression of specific unstable promoters but rather quantifies them to characterize sperm quality as excellent (≤ 10 unstable promoters), average (11-42), or poor (≥ 43).
In the studies that led to development of the SpermQT test, the number of unstable promoters correlated with pregnancy success. Pregnancy was achieved even among those in the group with poor sperm quality – but at very low rates.
Of the 172 semen samples collected so far in the ongoing analysis, sperm quality was characterized as excellent in 31%, average in 59%, and poor in 10%.
The stratifications for sperm quality were not significantly correlated with common measures of sperm viability, such as concentration, Dr. Lipshultz reported.
Certain patient characteristics were associated with greater sperm quality. These included use of antioxidant supplementation and low estrogen levels, as seen in men who had taken aromatase inhibitors.
So far, only one natural conception has occurred in the group with poor sperm versus eight in those with average or excellent quality.
The prognostic role of the test is only part of the picture.
“The exciting thing about this area of research is that epigenetics can be changed,” Dr. Lipshultz said in an interview. Based on the data so far, he said he is already starting to consider antioxidant supplementation and hormone modifications when sperm quality is poor.
The value of the Path SpermQT test for identifying treatment targets might eventually revolutionize the management of male infertility, Dr. Lipshultz said, but it has more immediate potential in helping couples decide whether to proceed with in vitro fertilization (IVF).
“We often see patients at an impasse when they are trying to decide to move to IVF,” he said. “A test like this could provide some direction. If sperm quality is good, the advice might be to keep trying. If poor, then a couple might want to move to IVF more quickly.”
A test of sperm quality on the basis of epigenetics “could change how we look at couples attempting to conceive,” agreed Peter N. Schlegel, MD, professor of urology and reproductive medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Schlegel praised several characteristics of the epigenetics test, including that 70%-80% of men with poor quality with SpermQT have normal results on standard assessments of semen. This finding suggests the tool is providing unique information about patients. He also noted that the studies so far indicate that sperm of poor quality for natural conception is still viable for IVF fertilization – which could be useful for couples weighing their options.
However, while the test is already available, Dr. Schlegel cautioned that much of the promise has yet to be documented.
“The results to date, despite being statistically significant, have only been gleaned from a small group of patients,” he said. “Much larger studies are needed before a change in practice is warranted.”
The value of SpermQT for identifying modifiable risks might be even further away.
“It is well recognized that environmental and lifestyle changes can affect methylation, but it is not known if the abnormalities seen so far could be influenced by lifestyle changes,” Dr. Schlegel said. Among the numerous steps needed to answer this question, he suggested that it might first be important “to evaluate why such changes in methylation occur.”
Dr. Lipshultz has financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including Inherent Biosciences, which is marketing the SpermQT test. Dr. Schlegel has financial relationships with Theralogix, Posterity Health, and Roman Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study suggests that, at least for certain male patients, the answer to infertility might lie with epigenetics.
According to the study, a commercially available test of epigenetic anomalies – factors that affect how genes express themselves – can grade the likelihood that sperm are viable for conception.
“The uniqueness of epigenetics is that some of the abnormalities detected have the potential to be modified with lifestyle,” said Larry I. Lipshultz, MD, head of the Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who presented the new findings at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Urological Association.
For decades, semen analysis has been based on motility, morphology, and concentration. But these measures, while useful, are limited. Semen can still have low capacity for producing a pregnancy even when all three parameters are normal, Dr. Lipshultz told this news organization.
The test, called Path SpermQT (Inherent Biosciences) detects unstable gene promotors, which are the epigenetic markers for gene expression. In previous work with more than 1,300 gene samples, expression of the specific genes regulated by these promoters were linked to a wide variety of functions relevant to fertilization, such as spermatogenesis.
The test does not attempt to look for expression of specific unstable promoters but rather quantifies them to characterize sperm quality as excellent (≤ 10 unstable promoters), average (11-42), or poor (≥ 43).
In the studies that led to development of the SpermQT test, the number of unstable promoters correlated with pregnancy success. Pregnancy was achieved even among those in the group with poor sperm quality – but at very low rates.
Of the 172 semen samples collected so far in the ongoing analysis, sperm quality was characterized as excellent in 31%, average in 59%, and poor in 10%.
The stratifications for sperm quality were not significantly correlated with common measures of sperm viability, such as concentration, Dr. Lipshultz reported.
Certain patient characteristics were associated with greater sperm quality. These included use of antioxidant supplementation and low estrogen levels, as seen in men who had taken aromatase inhibitors.
So far, only one natural conception has occurred in the group with poor sperm versus eight in those with average or excellent quality.
The prognostic role of the test is only part of the picture.
“The exciting thing about this area of research is that epigenetics can be changed,” Dr. Lipshultz said in an interview. Based on the data so far, he said he is already starting to consider antioxidant supplementation and hormone modifications when sperm quality is poor.
The value of the Path SpermQT test for identifying treatment targets might eventually revolutionize the management of male infertility, Dr. Lipshultz said, but it has more immediate potential in helping couples decide whether to proceed with in vitro fertilization (IVF).
“We often see patients at an impasse when they are trying to decide to move to IVF,” he said. “A test like this could provide some direction. If sperm quality is good, the advice might be to keep trying. If poor, then a couple might want to move to IVF more quickly.”
A test of sperm quality on the basis of epigenetics “could change how we look at couples attempting to conceive,” agreed Peter N. Schlegel, MD, professor of urology and reproductive medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Schlegel praised several characteristics of the epigenetics test, including that 70%-80% of men with poor quality with SpermQT have normal results on standard assessments of semen. This finding suggests the tool is providing unique information about patients. He also noted that the studies so far indicate that sperm of poor quality for natural conception is still viable for IVF fertilization – which could be useful for couples weighing their options.
However, while the test is already available, Dr. Schlegel cautioned that much of the promise has yet to be documented.
“The results to date, despite being statistically significant, have only been gleaned from a small group of patients,” he said. “Much larger studies are needed before a change in practice is warranted.”
The value of SpermQT for identifying modifiable risks might be even further away.
“It is well recognized that environmental and lifestyle changes can affect methylation, but it is not known if the abnormalities seen so far could be influenced by lifestyle changes,” Dr. Schlegel said. Among the numerous steps needed to answer this question, he suggested that it might first be important “to evaluate why such changes in methylation occur.”
Dr. Lipshultz has financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including Inherent Biosciences, which is marketing the SpermQT test. Dr. Schlegel has financial relationships with Theralogix, Posterity Health, and Roman Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study suggests that, at least for certain male patients, the answer to infertility might lie with epigenetics.
According to the study, a commercially available test of epigenetic anomalies – factors that affect how genes express themselves – can grade the likelihood that sperm are viable for conception.
“The uniqueness of epigenetics is that some of the abnormalities detected have the potential to be modified with lifestyle,” said Larry I. Lipshultz, MD, head of the Division of Male Reproductive Medicine and Surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, who presented the new findings at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Urological Association.
For decades, semen analysis has been based on motility, morphology, and concentration. But these measures, while useful, are limited. Semen can still have low capacity for producing a pregnancy even when all three parameters are normal, Dr. Lipshultz told this news organization.
The test, called Path SpermQT (Inherent Biosciences) detects unstable gene promotors, which are the epigenetic markers for gene expression. In previous work with more than 1,300 gene samples, expression of the specific genes regulated by these promoters were linked to a wide variety of functions relevant to fertilization, such as spermatogenesis.
The test does not attempt to look for expression of specific unstable promoters but rather quantifies them to characterize sperm quality as excellent (≤ 10 unstable promoters), average (11-42), or poor (≥ 43).
In the studies that led to development of the SpermQT test, the number of unstable promoters correlated with pregnancy success. Pregnancy was achieved even among those in the group with poor sperm quality – but at very low rates.
Of the 172 semen samples collected so far in the ongoing analysis, sperm quality was characterized as excellent in 31%, average in 59%, and poor in 10%.
The stratifications for sperm quality were not significantly correlated with common measures of sperm viability, such as concentration, Dr. Lipshultz reported.
Certain patient characteristics were associated with greater sperm quality. These included use of antioxidant supplementation and low estrogen levels, as seen in men who had taken aromatase inhibitors.
So far, only one natural conception has occurred in the group with poor sperm versus eight in those with average or excellent quality.
The prognostic role of the test is only part of the picture.
“The exciting thing about this area of research is that epigenetics can be changed,” Dr. Lipshultz said in an interview. Based on the data so far, he said he is already starting to consider antioxidant supplementation and hormone modifications when sperm quality is poor.
The value of the Path SpermQT test for identifying treatment targets might eventually revolutionize the management of male infertility, Dr. Lipshultz said, but it has more immediate potential in helping couples decide whether to proceed with in vitro fertilization (IVF).
“We often see patients at an impasse when they are trying to decide to move to IVF,” he said. “A test like this could provide some direction. If sperm quality is good, the advice might be to keep trying. If poor, then a couple might want to move to IVF more quickly.”
A test of sperm quality on the basis of epigenetics “could change how we look at couples attempting to conceive,” agreed Peter N. Schlegel, MD, professor of urology and reproductive medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York.
Dr. Schlegel praised several characteristics of the epigenetics test, including that 70%-80% of men with poor quality with SpermQT have normal results on standard assessments of semen. This finding suggests the tool is providing unique information about patients. He also noted that the studies so far indicate that sperm of poor quality for natural conception is still viable for IVF fertilization – which could be useful for couples weighing their options.
However, while the test is already available, Dr. Schlegel cautioned that much of the promise has yet to be documented.
“The results to date, despite being statistically significant, have only been gleaned from a small group of patients,” he said. “Much larger studies are needed before a change in practice is warranted.”
The value of SpermQT for identifying modifiable risks might be even further away.
“It is well recognized that environmental and lifestyle changes can affect methylation, but it is not known if the abnormalities seen so far could be influenced by lifestyle changes,” Dr. Schlegel said. Among the numerous steps needed to answer this question, he suggested that it might first be important “to evaluate why such changes in methylation occur.”
Dr. Lipshultz has financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including Inherent Biosciences, which is marketing the SpermQT test. Dr. Schlegel has financial relationships with Theralogix, Posterity Health, and Roman Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM 2022 AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
Studies address ibrutinib bleeding risk in patients with CLL receiving Mohs surgery
Patients receiving , new research shows.
“Our cohort of CLL patients on ibrutinib had a two-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those on anticoagulants and a nearly 40-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those patients on no anticoagulants or CLL therapy,” Kelsey E. Hirotsu, MD, first author of one of two studies on the issue presented at the American College of Mohs Surgery annual meeting, told this news organization.
“It was definitely surprising to see this doubled risk with ibrutinib relative to anticoagulants, and certainly highlights the clinically relevant increased bleeding risk in patients on ibrutinib,” said Dr. Hirotsu, a Mohs micrographic surgery fellow in the department of dermatology, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
With CLL associated with an increased risk for aggressive skin cancers, particularly squamous cell carcinoma, Mohs surgeons may commonly find themselves treating patients with these unique considerations. Surgical treatment of those cancers can be complicated not only because of potential underlying thrombocytopenia, which occurs in about 5% of untreated CLL patients, but also because of the increased risk for bleeding that is associated with the use of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, commonly used for CLL.
While the nature of the increased bleeding-related complications among patients with CLL undergoing Mohs surgery has been documented in some case reports, evidence from larger studies has been lacking.
In one of the studies presented at the ACMS meeting, Dr. Hirotsu and her colleagues evaluated data on patients with CLL who underwent at least one Mohs surgery procedure at UCSD Dermatologic Surgery over 10 years. Of the 362 Mohs cases among 98 patients with CLL, 32 cases had at least one complication. Patients on anticoagulants, including antiplatelet agents, Coumadin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), not surprisingly, had higher rates of complications, particularly bleeding.
However, those treated with ibrutinib had the highest rates of complications among all of the patients (40.6%), with all of their complications involving bleeding-related events. In comparison, the complication rates, for instance, of patients treated with antiplatelets were 21.9%; Coumadin, 6.2%; and DOACs, 15.6%.
The incidence of bleeding-related complications among the cases in the ibrutinib-treated patients was 30.2% compared with 13.2% among those on blood thinners and no CLL therapy (relative risk [RR], 2.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-5.11; P = .11). “Although not statistically significant, these results could trend toward significance with larger sample sizes,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
The risk for bleeding among patients on ibrutinib compared with patients on no medications, however, was significant, with a relative risk of 39.0 (95% CI, 2.35-646; P = .011).
Of note, among 12 patients on ibrutinib who experienced bleeding complications, 7 had previously undergone Mohs surgeries when they were not taking ibrutinib and no bleeding complications had occurred in those procedures. “This may further implicate ibrutinib as a cause of the bleeding-related complications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In investigating the role of thrombocytopenia at the time of Mohs surgery, the authors found that, among ibrutinib-treated patients who had no complications, 30% had thrombocytopenia, compared with 70% of those who did have bleeding while on ibrutinib at the time of surgery.
“It was interesting that thrombocytopenia is more common in ibrutinib patients with bleeding-related complications, but further research needs to be done to determine the clinical relevance and possible management implications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In a separate study presented at the meeting, 37 patients treated with ibrutinib for CLL while undergoing cutaneous surgery that included Mohs surgery and excisions had a significantly increased bleeding complication rate compared with a control group of 64 age- and sex-matched patients with CLL undergoing cutaneous surgery: 6 of 75 procedures (8%) versus 1 of 115 procedures (0.9%; P = .02).
Those with bleeding complications while on ibrutinib were all male, older (mean age, 82.7 vs. 73.0; P = .01), and had lower mean platelet counts (104 K/mcL vs. 150.5 K/mcL; P = .03).
There were no significant differences between the case and control groups in terms of anatomic site, type of procedure (Mohs versus excision), tumor diagnosis, lesion size, or type of reconstruction, while the control group was more likely to be on aspirin or other anticoagulants (P < .0001).
In an interview, senior author Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, a Mohs surgeon and dermatologic oncologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that “the take-home message is that patients on ibrutinib should be considered higher risk for bleeding events, regardless of whether they are having a simpler surgery [excision] or more involved skin surgery procedure [Mohs with flap].”
Holding treatment
To offset the bleeding risk, Dr. Vidal notes that holding the treatment is considered safe and that the manufacturer recommends holding ibrutinib for at least 3-7 days pre- and post surgery, “depending on type of surgery and risk of bleeding.”
“In our institution, with the hematologist/oncologist’s input, we hold ibrutinib for 5 days preop and 3 days post op, and have not had bleed complications in these patients,” she said, noting that there were no bleeding events in the patients in the study when ibrutinib was held.
Likewise, Dr. Hirotsu noted that at her center at UCSD, patients on ibrutinib are asked during the preop call to hold treatment for 3 days before and after Mohs surgery – but are advised to discuss the decision with their hematologist/oncologist for approval.
The measure isn’t always successful in preventing bleeding, however, as seen in a case study describing two patients who experienced bleeding complications following Mohs surgery despite being taken off ibrutinib 3 days prior to the procedure.
The senior author of that study, Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, department of dermatology, Weill Cornell/New York Presbyterian, New York, told this news organization that her team concluded that in those cases ibrutinib perhaps should have been held longer than 3 days.
“In some cases, especially if the Mohs surgery is a large procedure with a more advanced reconstruction, such as a large flap, it might be more prudent to continue it longer than 3 days,” Dr. Minkis said. She noted that the high bleeding risk observed in the studies at ACMS was notable – but not unexpected.
“I’m not that surprised because if you look at the hematologic literature, the risk is indeed pretty significant, so it makes sense that it would also occur with Mohs surgeries,” she said.
She underscored that a 3-day hold of ibrutinib should be considered the minimum, “and in some cases, it should be held up to 7 days prior to surgery, depending on the specific surgery,” with the important caveat of consulting with the patient’s hematology team.
“Multidisciplinary decision-making is necessary for these cases, and the interruption of therapy should always be discussed with their hematology team,” she added. That said, Dr. Minkis noted that “I’ve never had a hematologist who had any concerns for withholding ibrutinib even for a week around the time of a surgery.”
Dr. Hirotsu, Dr. Vidal, and Dr. Minkis reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving , new research shows.
“Our cohort of CLL patients on ibrutinib had a two-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those on anticoagulants and a nearly 40-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those patients on no anticoagulants or CLL therapy,” Kelsey E. Hirotsu, MD, first author of one of two studies on the issue presented at the American College of Mohs Surgery annual meeting, told this news organization.
“It was definitely surprising to see this doubled risk with ibrutinib relative to anticoagulants, and certainly highlights the clinically relevant increased bleeding risk in patients on ibrutinib,” said Dr. Hirotsu, a Mohs micrographic surgery fellow in the department of dermatology, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
With CLL associated with an increased risk for aggressive skin cancers, particularly squamous cell carcinoma, Mohs surgeons may commonly find themselves treating patients with these unique considerations. Surgical treatment of those cancers can be complicated not only because of potential underlying thrombocytopenia, which occurs in about 5% of untreated CLL patients, but also because of the increased risk for bleeding that is associated with the use of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, commonly used for CLL.
While the nature of the increased bleeding-related complications among patients with CLL undergoing Mohs surgery has been documented in some case reports, evidence from larger studies has been lacking.
In one of the studies presented at the ACMS meeting, Dr. Hirotsu and her colleagues evaluated data on patients with CLL who underwent at least one Mohs surgery procedure at UCSD Dermatologic Surgery over 10 years. Of the 362 Mohs cases among 98 patients with CLL, 32 cases had at least one complication. Patients on anticoagulants, including antiplatelet agents, Coumadin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), not surprisingly, had higher rates of complications, particularly bleeding.
However, those treated with ibrutinib had the highest rates of complications among all of the patients (40.6%), with all of their complications involving bleeding-related events. In comparison, the complication rates, for instance, of patients treated with antiplatelets were 21.9%; Coumadin, 6.2%; and DOACs, 15.6%.
The incidence of bleeding-related complications among the cases in the ibrutinib-treated patients was 30.2% compared with 13.2% among those on blood thinners and no CLL therapy (relative risk [RR], 2.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-5.11; P = .11). “Although not statistically significant, these results could trend toward significance with larger sample sizes,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
The risk for bleeding among patients on ibrutinib compared with patients on no medications, however, was significant, with a relative risk of 39.0 (95% CI, 2.35-646; P = .011).
Of note, among 12 patients on ibrutinib who experienced bleeding complications, 7 had previously undergone Mohs surgeries when they were not taking ibrutinib and no bleeding complications had occurred in those procedures. “This may further implicate ibrutinib as a cause of the bleeding-related complications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In investigating the role of thrombocytopenia at the time of Mohs surgery, the authors found that, among ibrutinib-treated patients who had no complications, 30% had thrombocytopenia, compared with 70% of those who did have bleeding while on ibrutinib at the time of surgery.
“It was interesting that thrombocytopenia is more common in ibrutinib patients with bleeding-related complications, but further research needs to be done to determine the clinical relevance and possible management implications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In a separate study presented at the meeting, 37 patients treated with ibrutinib for CLL while undergoing cutaneous surgery that included Mohs surgery and excisions had a significantly increased bleeding complication rate compared with a control group of 64 age- and sex-matched patients with CLL undergoing cutaneous surgery: 6 of 75 procedures (8%) versus 1 of 115 procedures (0.9%; P = .02).
Those with bleeding complications while on ibrutinib were all male, older (mean age, 82.7 vs. 73.0; P = .01), and had lower mean platelet counts (104 K/mcL vs. 150.5 K/mcL; P = .03).
There were no significant differences between the case and control groups in terms of anatomic site, type of procedure (Mohs versus excision), tumor diagnosis, lesion size, or type of reconstruction, while the control group was more likely to be on aspirin or other anticoagulants (P < .0001).
In an interview, senior author Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, a Mohs surgeon and dermatologic oncologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that “the take-home message is that patients on ibrutinib should be considered higher risk for bleeding events, regardless of whether they are having a simpler surgery [excision] or more involved skin surgery procedure [Mohs with flap].”
Holding treatment
To offset the bleeding risk, Dr. Vidal notes that holding the treatment is considered safe and that the manufacturer recommends holding ibrutinib for at least 3-7 days pre- and post surgery, “depending on type of surgery and risk of bleeding.”
“In our institution, with the hematologist/oncologist’s input, we hold ibrutinib for 5 days preop and 3 days post op, and have not had bleed complications in these patients,” she said, noting that there were no bleeding events in the patients in the study when ibrutinib was held.
Likewise, Dr. Hirotsu noted that at her center at UCSD, patients on ibrutinib are asked during the preop call to hold treatment for 3 days before and after Mohs surgery – but are advised to discuss the decision with their hematologist/oncologist for approval.
The measure isn’t always successful in preventing bleeding, however, as seen in a case study describing two patients who experienced bleeding complications following Mohs surgery despite being taken off ibrutinib 3 days prior to the procedure.
The senior author of that study, Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, department of dermatology, Weill Cornell/New York Presbyterian, New York, told this news organization that her team concluded that in those cases ibrutinib perhaps should have been held longer than 3 days.
“In some cases, especially if the Mohs surgery is a large procedure with a more advanced reconstruction, such as a large flap, it might be more prudent to continue it longer than 3 days,” Dr. Minkis said. She noted that the high bleeding risk observed in the studies at ACMS was notable – but not unexpected.
“I’m not that surprised because if you look at the hematologic literature, the risk is indeed pretty significant, so it makes sense that it would also occur with Mohs surgeries,” she said.
She underscored that a 3-day hold of ibrutinib should be considered the minimum, “and in some cases, it should be held up to 7 days prior to surgery, depending on the specific surgery,” with the important caveat of consulting with the patient’s hematology team.
“Multidisciplinary decision-making is necessary for these cases, and the interruption of therapy should always be discussed with their hematology team,” she added. That said, Dr. Minkis noted that “I’ve never had a hematologist who had any concerns for withholding ibrutinib even for a week around the time of a surgery.”
Dr. Hirotsu, Dr. Vidal, and Dr. Minkis reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients receiving , new research shows.
“Our cohort of CLL patients on ibrutinib had a two-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those on anticoagulants and a nearly 40-times greater risk of bleeding complications relative to those patients on no anticoagulants or CLL therapy,” Kelsey E. Hirotsu, MD, first author of one of two studies on the issue presented at the American College of Mohs Surgery annual meeting, told this news organization.
“It was definitely surprising to see this doubled risk with ibrutinib relative to anticoagulants, and certainly highlights the clinically relevant increased bleeding risk in patients on ibrutinib,” said Dr. Hirotsu, a Mohs micrographic surgery fellow in the department of dermatology, University of California, San Diego (UCSD).
With CLL associated with an increased risk for aggressive skin cancers, particularly squamous cell carcinoma, Mohs surgeons may commonly find themselves treating patients with these unique considerations. Surgical treatment of those cancers can be complicated not only because of potential underlying thrombocytopenia, which occurs in about 5% of untreated CLL patients, but also because of the increased risk for bleeding that is associated with the use of the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib, commonly used for CLL.
While the nature of the increased bleeding-related complications among patients with CLL undergoing Mohs surgery has been documented in some case reports, evidence from larger studies has been lacking.
In one of the studies presented at the ACMS meeting, Dr. Hirotsu and her colleagues evaluated data on patients with CLL who underwent at least one Mohs surgery procedure at UCSD Dermatologic Surgery over 10 years. Of the 362 Mohs cases among 98 patients with CLL, 32 cases had at least one complication. Patients on anticoagulants, including antiplatelet agents, Coumadin, and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), not surprisingly, had higher rates of complications, particularly bleeding.
However, those treated with ibrutinib had the highest rates of complications among all of the patients (40.6%), with all of their complications involving bleeding-related events. In comparison, the complication rates, for instance, of patients treated with antiplatelets were 21.9%; Coumadin, 6.2%; and DOACs, 15.6%.
The incidence of bleeding-related complications among the cases in the ibrutinib-treated patients was 30.2% compared with 13.2% among those on blood thinners and no CLL therapy (relative risk [RR], 2.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-5.11; P = .11). “Although not statistically significant, these results could trend toward significance with larger sample sizes,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
The risk for bleeding among patients on ibrutinib compared with patients on no medications, however, was significant, with a relative risk of 39.0 (95% CI, 2.35-646; P = .011).
Of note, among 12 patients on ibrutinib who experienced bleeding complications, 7 had previously undergone Mohs surgeries when they were not taking ibrutinib and no bleeding complications had occurred in those procedures. “This may further implicate ibrutinib as a cause of the bleeding-related complications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In investigating the role of thrombocytopenia at the time of Mohs surgery, the authors found that, among ibrutinib-treated patients who had no complications, 30% had thrombocytopenia, compared with 70% of those who did have bleeding while on ibrutinib at the time of surgery.
“It was interesting that thrombocytopenia is more common in ibrutinib patients with bleeding-related complications, but further research needs to be done to determine the clinical relevance and possible management implications,” Dr. Hirotsu said.
In a separate study presented at the meeting, 37 patients treated with ibrutinib for CLL while undergoing cutaneous surgery that included Mohs surgery and excisions had a significantly increased bleeding complication rate compared with a control group of 64 age- and sex-matched patients with CLL undergoing cutaneous surgery: 6 of 75 procedures (8%) versus 1 of 115 procedures (0.9%; P = .02).
Those with bleeding complications while on ibrutinib were all male, older (mean age, 82.7 vs. 73.0; P = .01), and had lower mean platelet counts (104 K/mcL vs. 150.5 K/mcL; P = .03).
There were no significant differences between the case and control groups in terms of anatomic site, type of procedure (Mohs versus excision), tumor diagnosis, lesion size, or type of reconstruction, while the control group was more likely to be on aspirin or other anticoagulants (P < .0001).
In an interview, senior author Nahid Y. Vidal, MD, a Mohs surgeon and dermatologic oncologist at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that “the take-home message is that patients on ibrutinib should be considered higher risk for bleeding events, regardless of whether they are having a simpler surgery [excision] or more involved skin surgery procedure [Mohs with flap].”
Holding treatment
To offset the bleeding risk, Dr. Vidal notes that holding the treatment is considered safe and that the manufacturer recommends holding ibrutinib for at least 3-7 days pre- and post surgery, “depending on type of surgery and risk of bleeding.”
“In our institution, with the hematologist/oncologist’s input, we hold ibrutinib for 5 days preop and 3 days post op, and have not had bleed complications in these patients,” she said, noting that there were no bleeding events in the patients in the study when ibrutinib was held.
Likewise, Dr. Hirotsu noted that at her center at UCSD, patients on ibrutinib are asked during the preop call to hold treatment for 3 days before and after Mohs surgery – but are advised to discuss the decision with their hematologist/oncologist for approval.
The measure isn’t always successful in preventing bleeding, however, as seen in a case study describing two patients who experienced bleeding complications following Mohs surgery despite being taken off ibrutinib 3 days prior to the procedure.
The senior author of that study, Kira Minkis, MD, PhD, department of dermatology, Weill Cornell/New York Presbyterian, New York, told this news organization that her team concluded that in those cases ibrutinib perhaps should have been held longer than 3 days.
“In some cases, especially if the Mohs surgery is a large procedure with a more advanced reconstruction, such as a large flap, it might be more prudent to continue it longer than 3 days,” Dr. Minkis said. She noted that the high bleeding risk observed in the studies at ACMS was notable – but not unexpected.
“I’m not that surprised because if you look at the hematologic literature, the risk is indeed pretty significant, so it makes sense that it would also occur with Mohs surgeries,” she said.
She underscored that a 3-day hold of ibrutinib should be considered the minimum, “and in some cases, it should be held up to 7 days prior to surgery, depending on the specific surgery,” with the important caveat of consulting with the patient’s hematology team.
“Multidisciplinary decision-making is necessary for these cases, and the interruption of therapy should always be discussed with their hematology team,” she added. That said, Dr. Minkis noted that “I’ve never had a hematologist who had any concerns for withholding ibrutinib even for a week around the time of a surgery.”
Dr. Hirotsu, Dr. Vidal, and Dr. Minkis reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE ACMS ANNUAL MEETING
Long COVID neuropsychiatric deficits greater than expected
NEW ORLEANS – , adding to mounting evidence of the significant toll the chronic condition can have on mental health.
“Many clinicians have observed the symptoms we describe in this study, however this report is among the first which identify the specific deficits using neuropsychological testing to better characterize the syndrome,” Sean T. Lynch, MD, first author of a study on the issue presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, said in an interview.
Dr. Lynch, of the department of psychiatry, Westchester Medical Center Health System, Valhalla, N.Y., and his colleagues enrolled 60 participants who had experienced acute COVID-19 disease 6-8 months earlier and had undergone neuropsychological, psychiatric, medical, functional, and quality-of-life assessments. Results from the study were published online in the Journal of the Academy of Consultation–Liaison Psychiatry (2022 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaclp.2022.01.003).
Among the study participants, 32 were seeking treatment for brain fog in a clinical program for survivors of COVID-19, while the remaining 28 were part of an ongoing longitudinal investigation of neuropsychological, medical, and psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19, but were not seeking care for the persistent symptoms.
Assessments for neurocognitive impairment included a battery of tests used in infectious and other diseases, including the Test of Premorbid Function, the Patient Assessment of Own Function, the Trail Making Test parts A and B, the Stroop Color and Word Test, and others.
Overall, the battery of assessments showed that 37 (62%) of participants had neuropsychological test impairment, with results below the 16th percentile in two tests, while 16 (27%) showed scores indicative of severe impairment (below the second percentile in at least one test and below the 16th percentile in one test).
Those reporting brain fog had scores that were even lower than expected on tests of attention, processing speed, memory, and executive function. And among those reporting brain fog, significantly more had scores reflecting severe impairment compared with the controls (38% vs. 14%; P < .04).
“Based on what we’ve observed in our patients and what others have previously reported, we did expect to find some impairment in this study sample,” Dr. Lynch noted.
“However, we were surprised to find that 27% of the study sample had extremely low neuropsychological test scores, meaning that they scored at least two standard deviations below the expected score on at least one neuropsychological test based on their age and level of education.”
The brain fog group also reported significantly higher levels of depression, fatigue, PTSD, and functional difficulties, and lower quality of life.
Severe impairment on the neuropsychological tests correlated with the extent of acute COVID-19 symptoms, as well as depression scores, number of medical comorbidities, and subjective cognitive complaints.
An analysis of serum levels of the inflammatory markers among 50 of the 60 participants showed that 45% of the patients had an elevated IL-6, 20% had elevated TNF-alpha, and 41% had elevated CRP, compared with reference ranges.
IL-6 levels were found to correlate with acute COVID-19 symptoms, the number of medical comorbidities, fatigue, and measures of executive function, while C-reactive protein (CRP) correlated with current COVID-19 symptoms and depression scores.
In terms of clinical factors that might predict low neuropsychological test scores, Dr. Lynch noted that the “markers that we found to be significant included severity of acute COVID-19 illness, current post-COVID-19 symptoms, measures of depression and anxiety, level of fatigue, and number of medical comorbidities.”
Dr. Lynch noted that the ongoing study will include up to 18-month follow-ups that are currently underway. “The [follow-ups] will examine if symptoms improve over time and evaluate if any intervention that took place was successful,” he said.
Survey supports findings
The detrimental effects of mental health symptoms in long COVID were further supported in another study at the APA meeting, an online survey of 787 survivors of acute COVID-19.
In the community survey, presented by Michael Van Ameringen, MD, a professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University, in Hamilton, Ont., all respondents (100%) reported having persistent symptoms of the virus, and as many as 68% indicated that they had not returned to normal functioning, despite only 15% of the respondents having been hospitalized with COVID-19.
A large proportion showed significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and the most commonly reported persistent symptoms were fatigue in 75.9% of respondents, brain fog in 67.9%, concentration difficulties in 61.1%, and weakness in 51.2%.
As many as 88.2% of patients said they experienced persistent neurocognitive symptoms, with poor memory and concentration; 56% reported problems with word finding; and 54.1% had slowed thinking.
The respondents showed high rates of anxiety (41.7%) as well as depression (61.4%) as determined by scores above 9 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 (GAD-7) and Patient Health Questionnaires (PHQ-9).
As many as 40.5% of respondents showed probable PTSD, with scores above 30 on the PTSD checklist (PCL-5). Their mean resilience score on the Brief Resilient Coping Scale was 13.5, suggesting low resilience.
Among the respondents, 43.3% said they had received past treatment for mental health, while 33.5% were currently receiving mental health treatment.
Dr. Van Ameringen noted the important limitation of the study being an online survey with no control group, but said the responses nevertheless raise the question of the role of prior psychiatric disorders in long COVID.
“In our sample, 40% of respondents had a past psychiatric history, so you wonder if that also makes you vulnerable to long COVID,” he said in an interview.
“About a third were getting psychiatric help, but I think the more impaired you are, the more likely you are to seek help.”
Those who were hospitalized with COVID-19 were at a higher risk of PTSD compared with those not hospitalized (P < .001), as were those under the age of 30 (P < .05) or between 31 and 50 vs. over 50 (P < .01).
Dr. Van Ameringen noted that the survey’s high rate of subjects who had not returned to normal functioning was especially striking.
“This is not a minor issue – these are people who are no longer functioning in society,” he said.
In pandemics, the brain tends to be ‘overlooked’
Further addressing the neurological effects of COVID-19 at the APA meeting, Avindra Nath, MD, clinical director of the National Institutes of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke in Bethesda, Md., noted that the persisting cognitive and psychiatric symptoms after illness, such as brain fog and depression and anxiety, are not necessarily unique to COVID-19.
“We have seen this before,” he said. “There have been at least seven or eight human coronaviruses, and the interesting thing is each one affects the brain and causes neurological complications.”
The effects are classified differently and have slightly different receptors, “but the consequences are the same.”
Of note, however, research published in The Lancet Psychiatry (2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366[21]00084-5) revealed that symptoms such as dementia, mood, and anxiety are significantly higher after COVID-19 compared with other respiratory infections, with the differences increasing at 180 days since the index event.
Dr. Nath noted that, over the decades, he has observed that in pandemics “the brain tends to get overlooked.” He explained that “what can be most important in the end is what happened in the brain, because those are the things that really cause the long-term consequences.”
“These patients are depressed; they have dementia, they have brain fog, and even now that we recognize these issues, we haven’t done a very good job of studying them,” he said. “There’s so much we still don’t know, and a lot of patients are left with these symptoms and nowhere to go.”
Dr. Lynch, Dr. Van Ameringen, and Dr. Nath had no disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS – , adding to mounting evidence of the significant toll the chronic condition can have on mental health.
“Many clinicians have observed the symptoms we describe in this study, however this report is among the first which identify the specific deficits using neuropsychological testing to better characterize the syndrome,” Sean T. Lynch, MD, first author of a study on the issue presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, said in an interview.
Dr. Lynch, of the department of psychiatry, Westchester Medical Center Health System, Valhalla, N.Y., and his colleagues enrolled 60 participants who had experienced acute COVID-19 disease 6-8 months earlier and had undergone neuropsychological, psychiatric, medical, functional, and quality-of-life assessments. Results from the study were published online in the Journal of the Academy of Consultation–Liaison Psychiatry (2022 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaclp.2022.01.003).
Among the study participants, 32 were seeking treatment for brain fog in a clinical program for survivors of COVID-19, while the remaining 28 were part of an ongoing longitudinal investigation of neuropsychological, medical, and psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19, but were not seeking care for the persistent symptoms.
Assessments for neurocognitive impairment included a battery of tests used in infectious and other diseases, including the Test of Premorbid Function, the Patient Assessment of Own Function, the Trail Making Test parts A and B, the Stroop Color and Word Test, and others.
Overall, the battery of assessments showed that 37 (62%) of participants had neuropsychological test impairment, with results below the 16th percentile in two tests, while 16 (27%) showed scores indicative of severe impairment (below the second percentile in at least one test and below the 16th percentile in one test).
Those reporting brain fog had scores that were even lower than expected on tests of attention, processing speed, memory, and executive function. And among those reporting brain fog, significantly more had scores reflecting severe impairment compared with the controls (38% vs. 14%; P < .04).
“Based on what we’ve observed in our patients and what others have previously reported, we did expect to find some impairment in this study sample,” Dr. Lynch noted.
“However, we were surprised to find that 27% of the study sample had extremely low neuropsychological test scores, meaning that they scored at least two standard deviations below the expected score on at least one neuropsychological test based on their age and level of education.”
The brain fog group also reported significantly higher levels of depression, fatigue, PTSD, and functional difficulties, and lower quality of life.
Severe impairment on the neuropsychological tests correlated with the extent of acute COVID-19 symptoms, as well as depression scores, number of medical comorbidities, and subjective cognitive complaints.
An analysis of serum levels of the inflammatory markers among 50 of the 60 participants showed that 45% of the patients had an elevated IL-6, 20% had elevated TNF-alpha, and 41% had elevated CRP, compared with reference ranges.
IL-6 levels were found to correlate with acute COVID-19 symptoms, the number of medical comorbidities, fatigue, and measures of executive function, while C-reactive protein (CRP) correlated with current COVID-19 symptoms and depression scores.
In terms of clinical factors that might predict low neuropsychological test scores, Dr. Lynch noted that the “markers that we found to be significant included severity of acute COVID-19 illness, current post-COVID-19 symptoms, measures of depression and anxiety, level of fatigue, and number of medical comorbidities.”
Dr. Lynch noted that the ongoing study will include up to 18-month follow-ups that are currently underway. “The [follow-ups] will examine if symptoms improve over time and evaluate if any intervention that took place was successful,” he said.
Survey supports findings
The detrimental effects of mental health symptoms in long COVID were further supported in another study at the APA meeting, an online survey of 787 survivors of acute COVID-19.
In the community survey, presented by Michael Van Ameringen, MD, a professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University, in Hamilton, Ont., all respondents (100%) reported having persistent symptoms of the virus, and as many as 68% indicated that they had not returned to normal functioning, despite only 15% of the respondents having been hospitalized with COVID-19.
A large proportion showed significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and the most commonly reported persistent symptoms were fatigue in 75.9% of respondents, brain fog in 67.9%, concentration difficulties in 61.1%, and weakness in 51.2%.
As many as 88.2% of patients said they experienced persistent neurocognitive symptoms, with poor memory and concentration; 56% reported problems with word finding; and 54.1% had slowed thinking.
The respondents showed high rates of anxiety (41.7%) as well as depression (61.4%) as determined by scores above 9 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 (GAD-7) and Patient Health Questionnaires (PHQ-9).
As many as 40.5% of respondents showed probable PTSD, with scores above 30 on the PTSD checklist (PCL-5). Their mean resilience score on the Brief Resilient Coping Scale was 13.5, suggesting low resilience.
Among the respondents, 43.3% said they had received past treatment for mental health, while 33.5% were currently receiving mental health treatment.
Dr. Van Ameringen noted the important limitation of the study being an online survey with no control group, but said the responses nevertheless raise the question of the role of prior psychiatric disorders in long COVID.
“In our sample, 40% of respondents had a past psychiatric history, so you wonder if that also makes you vulnerable to long COVID,” he said in an interview.
“About a third were getting psychiatric help, but I think the more impaired you are, the more likely you are to seek help.”
Those who were hospitalized with COVID-19 were at a higher risk of PTSD compared with those not hospitalized (P < .001), as were those under the age of 30 (P < .05) or between 31 and 50 vs. over 50 (P < .01).
Dr. Van Ameringen noted that the survey’s high rate of subjects who had not returned to normal functioning was especially striking.
“This is not a minor issue – these are people who are no longer functioning in society,” he said.
In pandemics, the brain tends to be ‘overlooked’
Further addressing the neurological effects of COVID-19 at the APA meeting, Avindra Nath, MD, clinical director of the National Institutes of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke in Bethesda, Md., noted that the persisting cognitive and psychiatric symptoms after illness, such as brain fog and depression and anxiety, are not necessarily unique to COVID-19.
“We have seen this before,” he said. “There have been at least seven or eight human coronaviruses, and the interesting thing is each one affects the brain and causes neurological complications.”
The effects are classified differently and have slightly different receptors, “but the consequences are the same.”
Of note, however, research published in The Lancet Psychiatry (2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366[21]00084-5) revealed that symptoms such as dementia, mood, and anxiety are significantly higher after COVID-19 compared with other respiratory infections, with the differences increasing at 180 days since the index event.
Dr. Nath noted that, over the decades, he has observed that in pandemics “the brain tends to get overlooked.” He explained that “what can be most important in the end is what happened in the brain, because those are the things that really cause the long-term consequences.”
“These patients are depressed; they have dementia, they have brain fog, and even now that we recognize these issues, we haven’t done a very good job of studying them,” he said. “There’s so much we still don’t know, and a lot of patients are left with these symptoms and nowhere to go.”
Dr. Lynch, Dr. Van Ameringen, and Dr. Nath had no disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS – , adding to mounting evidence of the significant toll the chronic condition can have on mental health.
“Many clinicians have observed the symptoms we describe in this study, however this report is among the first which identify the specific deficits using neuropsychological testing to better characterize the syndrome,” Sean T. Lynch, MD, first author of a study on the issue presented at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association, said in an interview.
Dr. Lynch, of the department of psychiatry, Westchester Medical Center Health System, Valhalla, N.Y., and his colleagues enrolled 60 participants who had experienced acute COVID-19 disease 6-8 months earlier and had undergone neuropsychological, psychiatric, medical, functional, and quality-of-life assessments. Results from the study were published online in the Journal of the Academy of Consultation–Liaison Psychiatry (2022 Jan 25. doi: 10.1016/j.jaclp.2022.01.003).
Among the study participants, 32 were seeking treatment for brain fog in a clinical program for survivors of COVID-19, while the remaining 28 were part of an ongoing longitudinal investigation of neuropsychological, medical, and psychiatric sequelae of COVID-19, but were not seeking care for the persistent symptoms.
Assessments for neurocognitive impairment included a battery of tests used in infectious and other diseases, including the Test of Premorbid Function, the Patient Assessment of Own Function, the Trail Making Test parts A and B, the Stroop Color and Word Test, and others.
Overall, the battery of assessments showed that 37 (62%) of participants had neuropsychological test impairment, with results below the 16th percentile in two tests, while 16 (27%) showed scores indicative of severe impairment (below the second percentile in at least one test and below the 16th percentile in one test).
Those reporting brain fog had scores that were even lower than expected on tests of attention, processing speed, memory, and executive function. And among those reporting brain fog, significantly more had scores reflecting severe impairment compared with the controls (38% vs. 14%; P < .04).
“Based on what we’ve observed in our patients and what others have previously reported, we did expect to find some impairment in this study sample,” Dr. Lynch noted.
“However, we were surprised to find that 27% of the study sample had extremely low neuropsychological test scores, meaning that they scored at least two standard deviations below the expected score on at least one neuropsychological test based on their age and level of education.”
The brain fog group also reported significantly higher levels of depression, fatigue, PTSD, and functional difficulties, and lower quality of life.
Severe impairment on the neuropsychological tests correlated with the extent of acute COVID-19 symptoms, as well as depression scores, number of medical comorbidities, and subjective cognitive complaints.
An analysis of serum levels of the inflammatory markers among 50 of the 60 participants showed that 45% of the patients had an elevated IL-6, 20% had elevated TNF-alpha, and 41% had elevated CRP, compared with reference ranges.
IL-6 levels were found to correlate with acute COVID-19 symptoms, the number of medical comorbidities, fatigue, and measures of executive function, while C-reactive protein (CRP) correlated with current COVID-19 symptoms and depression scores.
In terms of clinical factors that might predict low neuropsychological test scores, Dr. Lynch noted that the “markers that we found to be significant included severity of acute COVID-19 illness, current post-COVID-19 symptoms, measures of depression and anxiety, level of fatigue, and number of medical comorbidities.”
Dr. Lynch noted that the ongoing study will include up to 18-month follow-ups that are currently underway. “The [follow-ups] will examine if symptoms improve over time and evaluate if any intervention that took place was successful,” he said.
Survey supports findings
The detrimental effects of mental health symptoms in long COVID were further supported in another study at the APA meeting, an online survey of 787 survivors of acute COVID-19.
In the community survey, presented by Michael Van Ameringen, MD, a professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neurosciences at McMaster University, in Hamilton, Ont., all respondents (100%) reported having persistent symptoms of the virus, and as many as 68% indicated that they had not returned to normal functioning, despite only 15% of the respondents having been hospitalized with COVID-19.
A large proportion showed significant depression, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and the most commonly reported persistent symptoms were fatigue in 75.9% of respondents, brain fog in 67.9%, concentration difficulties in 61.1%, and weakness in 51.2%.
As many as 88.2% of patients said they experienced persistent neurocognitive symptoms, with poor memory and concentration; 56% reported problems with word finding; and 54.1% had slowed thinking.
The respondents showed high rates of anxiety (41.7%) as well as depression (61.4%) as determined by scores above 9 on the Generalized Anxiety Disorder–7 (GAD-7) and Patient Health Questionnaires (PHQ-9).
As many as 40.5% of respondents showed probable PTSD, with scores above 30 on the PTSD checklist (PCL-5). Their mean resilience score on the Brief Resilient Coping Scale was 13.5, suggesting low resilience.
Among the respondents, 43.3% said they had received past treatment for mental health, while 33.5% were currently receiving mental health treatment.
Dr. Van Ameringen noted the important limitation of the study being an online survey with no control group, but said the responses nevertheless raise the question of the role of prior psychiatric disorders in long COVID.
“In our sample, 40% of respondents had a past psychiatric history, so you wonder if that also makes you vulnerable to long COVID,” he said in an interview.
“About a third were getting psychiatric help, but I think the more impaired you are, the more likely you are to seek help.”
Those who were hospitalized with COVID-19 were at a higher risk of PTSD compared with those not hospitalized (P < .001), as were those under the age of 30 (P < .05) or between 31 and 50 vs. over 50 (P < .01).
Dr. Van Ameringen noted that the survey’s high rate of subjects who had not returned to normal functioning was especially striking.
“This is not a minor issue – these are people who are no longer functioning in society,” he said.
In pandemics, the brain tends to be ‘overlooked’
Further addressing the neurological effects of COVID-19 at the APA meeting, Avindra Nath, MD, clinical director of the National Institutes of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke in Bethesda, Md., noted that the persisting cognitive and psychiatric symptoms after illness, such as brain fog and depression and anxiety, are not necessarily unique to COVID-19.
“We have seen this before,” he said. “There have been at least seven or eight human coronaviruses, and the interesting thing is each one affects the brain and causes neurological complications.”
The effects are classified differently and have slightly different receptors, “but the consequences are the same.”
Of note, however, research published in The Lancet Psychiatry (2021 May. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366[21]00084-5) revealed that symptoms such as dementia, mood, and anxiety are significantly higher after COVID-19 compared with other respiratory infections, with the differences increasing at 180 days since the index event.
Dr. Nath noted that, over the decades, he has observed that in pandemics “the brain tends to get overlooked.” He explained that “what can be most important in the end is what happened in the brain, because those are the things that really cause the long-term consequences.”
“These patients are depressed; they have dementia, they have brain fog, and even now that we recognize these issues, we haven’t done a very good job of studying them,” he said. “There’s so much we still don’t know, and a lot of patients are left with these symptoms and nowhere to go.”
Dr. Lynch, Dr. Van Ameringen, and Dr. Nath had no disclosures to report.
AT APA 2022
Double the pleasure: Stim patch delays early ejaculation: Study
A wearable patch that delivers electrical stimulation to the perineum may postpone premature ejaculation, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association. The disposable device appears to work by helping men contract the muscles in the pelvic floor, allowing them to postpone climax.
Among 34 men with a lifelong history of premature ejaculation, average intravaginal ejaculatory latency time – the time from vaginal penetration to ejaculation – increased from about 67 seconds at baseline to 123 seconds when they used the device.
Another 17 participants received a sham treatment – stimulation they could feel but that did not activate muscles. In this group, time to ejaculation increased from 63 seconds to 81 seconds.
The longer duration with active treatment was statistically significant (P < .0001), whereas the increase in the control group was not (P = .1653), said Ege Can Serefoglu, MD, a researcher at Biruni University, Istanbul, and editor-in-chief of the International Journal of Impotence Research.
Dr. Serefoglu is a member of the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, a company in Hod Hasharon, Israel, that is developing the stimulator. Marketed as vPatch, the device is expected to be available in 2023, Dr. Serefoglu said. It was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in November and has CE-mark approval in Europe, according to the company.
Common problem, limited options
Research shows that 20%-30% of men are not happy with their time to ejaculation, Dr. Serefoglu said.
The International Society for Sexual Medicine defines premature ejaculation as ejaculation which always or almost always occurs within about 1 minute of penetration, the patient is unable to delay this occurrence, and the condition causes personal distress.
“Unfortunately, in spite of its high prevalence we do not really have any satisfying treatment options,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Topical anesthetics may be used to decrease the sensitivity of the glans penis, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may help delay ejaculation. But these options have limited efficacy and low adherence, he said.
Preclinical studies have shown that injection of botulinum toxin into the bulbospongiosus muscles is associated with a dose-dependent increase in ejaculation latency in rats.
Data on ClinicalTrials.gov show that this approach also may increase ejaculation latency in men, Dr. Serefoglu said. Although investigators found no safety concerns, drugmaker Allergan made a strategic business decision to stop developing this treatment approach, according to the registration entry for the study.
The idea for vPatch came from researchers wondering if instead of paralyzing the muscles with botulinum toxin, they used electrical stimulation to cause contraction of those muscles, Dr. Serefoglu said. A smaller proof-of-concept study demonstrated the feasibility and safety of this technique.
To further assess the safety and efficacy of a transcutaneous perineal electrical stimulator for the treatment of premature ejaculation, investigators conducted the randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial at Rambam Medical Centre, Haifa, Israel, and Villa Donatello Clinic, Florence, Italy.
The trial included males with premature ejaculation aged 18-60 years. Their female partners measured IELT using a stopwatch during four sexual intercourse sessions before treatment, and four times on treatment, at home.
In addition to the increased time to ejaculation, perceived control over ejaculation, satisfaction with sexual intercourse, personal distress related to ejaculation, and interpersonal difficulty related to ejaculation all significantly improved with vPatch, the researchers found.
Of participants who received active treatment, 73.5% reported a subjective sense of improvement versus 41.2% of the control group.
Potential reactions
No serious adverse events were observed, Dr. Serefoglu reported. Potential adverse reactions include redness, discomfort, and localized pain, according to the company’s website.
Men should not use vPatch if they have been diagnosed with pelvic cancer, or if they have an implanted electronic device, diabetes with peripheral neuropathy, or perineal dermatologic diseases, irritations, or lesions. Other precautions include avoiding use of the vPatch in water or humid environments. The device has not been tested on use with a pregnant partner.
The disposable patches are meant for one-time use. “The miniaturized perineal stimulation device may become an on-demand, drug-free therapeutic option,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Combining electrical stimulation with other treatment approaches may provide additional benefit, said Bradley Schwartz, DO, professor and chairman of urology at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, who moderated the session at the AUA meeting at which the results of the study were presented.
“You go from 1 to 2 minutes just with this device,” Dr. Schwartz said. “If you went from 2 to 3 minutes, you would essentially be tripling their pleasure or their time, which might make a significant difference.”
Serefoglu agreed that combining the stimulator with other treatment approaches such as topical anesthetics could increase patient satisfaction.
Comoderator Kelly Healy, MD, assistant professor of urology at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, highlighted a direction for future research: examining outcomes according to different types of relationships, as well as partner satisfaction.
“That is a perfect question that should also be considered in the future trials,” Dr. Serefoglu said. “This was mainly focused on the man’s satisfaction. But men are trying to delay their ejaculation to satisfy their partner.”
Dr. Serefoglu is on the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, which sponsored the study. Dr. Healy had no disclosures. Dr. Schwartz disclosed ties to Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A wearable patch that delivers electrical stimulation to the perineum may postpone premature ejaculation, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association. The disposable device appears to work by helping men contract the muscles in the pelvic floor, allowing them to postpone climax.
Among 34 men with a lifelong history of premature ejaculation, average intravaginal ejaculatory latency time – the time from vaginal penetration to ejaculation – increased from about 67 seconds at baseline to 123 seconds when they used the device.
Another 17 participants received a sham treatment – stimulation they could feel but that did not activate muscles. In this group, time to ejaculation increased from 63 seconds to 81 seconds.
The longer duration with active treatment was statistically significant (P < .0001), whereas the increase in the control group was not (P = .1653), said Ege Can Serefoglu, MD, a researcher at Biruni University, Istanbul, and editor-in-chief of the International Journal of Impotence Research.
Dr. Serefoglu is a member of the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, a company in Hod Hasharon, Israel, that is developing the stimulator. Marketed as vPatch, the device is expected to be available in 2023, Dr. Serefoglu said. It was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in November and has CE-mark approval in Europe, according to the company.
Common problem, limited options
Research shows that 20%-30% of men are not happy with their time to ejaculation, Dr. Serefoglu said.
The International Society for Sexual Medicine defines premature ejaculation as ejaculation which always or almost always occurs within about 1 minute of penetration, the patient is unable to delay this occurrence, and the condition causes personal distress.
“Unfortunately, in spite of its high prevalence we do not really have any satisfying treatment options,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Topical anesthetics may be used to decrease the sensitivity of the glans penis, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may help delay ejaculation. But these options have limited efficacy and low adherence, he said.
Preclinical studies have shown that injection of botulinum toxin into the bulbospongiosus muscles is associated with a dose-dependent increase in ejaculation latency in rats.
Data on ClinicalTrials.gov show that this approach also may increase ejaculation latency in men, Dr. Serefoglu said. Although investigators found no safety concerns, drugmaker Allergan made a strategic business decision to stop developing this treatment approach, according to the registration entry for the study.
The idea for vPatch came from researchers wondering if instead of paralyzing the muscles with botulinum toxin, they used electrical stimulation to cause contraction of those muscles, Dr. Serefoglu said. A smaller proof-of-concept study demonstrated the feasibility and safety of this technique.
To further assess the safety and efficacy of a transcutaneous perineal electrical stimulator for the treatment of premature ejaculation, investigators conducted the randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial at Rambam Medical Centre, Haifa, Israel, and Villa Donatello Clinic, Florence, Italy.
The trial included males with premature ejaculation aged 18-60 years. Their female partners measured IELT using a stopwatch during four sexual intercourse sessions before treatment, and four times on treatment, at home.
In addition to the increased time to ejaculation, perceived control over ejaculation, satisfaction with sexual intercourse, personal distress related to ejaculation, and interpersonal difficulty related to ejaculation all significantly improved with vPatch, the researchers found.
Of participants who received active treatment, 73.5% reported a subjective sense of improvement versus 41.2% of the control group.
Potential reactions
No serious adverse events were observed, Dr. Serefoglu reported. Potential adverse reactions include redness, discomfort, and localized pain, according to the company’s website.
Men should not use vPatch if they have been diagnosed with pelvic cancer, or if they have an implanted electronic device, diabetes with peripheral neuropathy, or perineal dermatologic diseases, irritations, or lesions. Other precautions include avoiding use of the vPatch in water or humid environments. The device has not been tested on use with a pregnant partner.
The disposable patches are meant for one-time use. “The miniaturized perineal stimulation device may become an on-demand, drug-free therapeutic option,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Combining electrical stimulation with other treatment approaches may provide additional benefit, said Bradley Schwartz, DO, professor and chairman of urology at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, who moderated the session at the AUA meeting at which the results of the study were presented.
“You go from 1 to 2 minutes just with this device,” Dr. Schwartz said. “If you went from 2 to 3 minutes, you would essentially be tripling their pleasure or their time, which might make a significant difference.”
Serefoglu agreed that combining the stimulator with other treatment approaches such as topical anesthetics could increase patient satisfaction.
Comoderator Kelly Healy, MD, assistant professor of urology at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, highlighted a direction for future research: examining outcomes according to different types of relationships, as well as partner satisfaction.
“That is a perfect question that should also be considered in the future trials,” Dr. Serefoglu said. “This was mainly focused on the man’s satisfaction. But men are trying to delay their ejaculation to satisfy their partner.”
Dr. Serefoglu is on the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, which sponsored the study. Dr. Healy had no disclosures. Dr. Schwartz disclosed ties to Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A wearable patch that delivers electrical stimulation to the perineum may postpone premature ejaculation, according to research presented at the annual meeting of the American Urological Association. The disposable device appears to work by helping men contract the muscles in the pelvic floor, allowing them to postpone climax.
Among 34 men with a lifelong history of premature ejaculation, average intravaginal ejaculatory latency time – the time from vaginal penetration to ejaculation – increased from about 67 seconds at baseline to 123 seconds when they used the device.
Another 17 participants received a sham treatment – stimulation they could feel but that did not activate muscles. In this group, time to ejaculation increased from 63 seconds to 81 seconds.
The longer duration with active treatment was statistically significant (P < .0001), whereas the increase in the control group was not (P = .1653), said Ege Can Serefoglu, MD, a researcher at Biruni University, Istanbul, and editor-in-chief of the International Journal of Impotence Research.
Dr. Serefoglu is a member of the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, a company in Hod Hasharon, Israel, that is developing the stimulator. Marketed as vPatch, the device is expected to be available in 2023, Dr. Serefoglu said. It was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in November and has CE-mark approval in Europe, according to the company.
Common problem, limited options
Research shows that 20%-30% of men are not happy with their time to ejaculation, Dr. Serefoglu said.
The International Society for Sexual Medicine defines premature ejaculation as ejaculation which always or almost always occurs within about 1 minute of penetration, the patient is unable to delay this occurrence, and the condition causes personal distress.
“Unfortunately, in spite of its high prevalence we do not really have any satisfying treatment options,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Topical anesthetics may be used to decrease the sensitivity of the glans penis, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may help delay ejaculation. But these options have limited efficacy and low adherence, he said.
Preclinical studies have shown that injection of botulinum toxin into the bulbospongiosus muscles is associated with a dose-dependent increase in ejaculation latency in rats.
Data on ClinicalTrials.gov show that this approach also may increase ejaculation latency in men, Dr. Serefoglu said. Although investigators found no safety concerns, drugmaker Allergan made a strategic business decision to stop developing this treatment approach, according to the registration entry for the study.
The idea for vPatch came from researchers wondering if instead of paralyzing the muscles with botulinum toxin, they used electrical stimulation to cause contraction of those muscles, Dr. Serefoglu said. A smaller proof-of-concept study demonstrated the feasibility and safety of this technique.
To further assess the safety and efficacy of a transcutaneous perineal electrical stimulator for the treatment of premature ejaculation, investigators conducted the randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial at Rambam Medical Centre, Haifa, Israel, and Villa Donatello Clinic, Florence, Italy.
The trial included males with premature ejaculation aged 18-60 years. Their female partners measured IELT using a stopwatch during four sexual intercourse sessions before treatment, and four times on treatment, at home.
In addition to the increased time to ejaculation, perceived control over ejaculation, satisfaction with sexual intercourse, personal distress related to ejaculation, and interpersonal difficulty related to ejaculation all significantly improved with vPatch, the researchers found.
Of participants who received active treatment, 73.5% reported a subjective sense of improvement versus 41.2% of the control group.
Potential reactions
No serious adverse events were observed, Dr. Serefoglu reported. Potential adverse reactions include redness, discomfort, and localized pain, according to the company’s website.
Men should not use vPatch if they have been diagnosed with pelvic cancer, or if they have an implanted electronic device, diabetes with peripheral neuropathy, or perineal dermatologic diseases, irritations, or lesions. Other precautions include avoiding use of the vPatch in water or humid environments. The device has not been tested on use with a pregnant partner.
The disposable patches are meant for one-time use. “The miniaturized perineal stimulation device may become an on-demand, drug-free therapeutic option,” Dr. Serefoglu said.
Combining electrical stimulation with other treatment approaches may provide additional benefit, said Bradley Schwartz, DO, professor and chairman of urology at Southern Illinois University, Springfield, who moderated the session at the AUA meeting at which the results of the study were presented.
“You go from 1 to 2 minutes just with this device,” Dr. Schwartz said. “If you went from 2 to 3 minutes, you would essentially be tripling their pleasure or their time, which might make a significant difference.”
Serefoglu agreed that combining the stimulator with other treatment approaches such as topical anesthetics could increase patient satisfaction.
Comoderator Kelly Healy, MD, assistant professor of urology at Columbia University Medical Center, New York, highlighted a direction for future research: examining outcomes according to different types of relationships, as well as partner satisfaction.
“That is a perfect question that should also be considered in the future trials,” Dr. Serefoglu said. “This was mainly focused on the man’s satisfaction. But men are trying to delay their ejaculation to satisfy their partner.”
Dr. Serefoglu is on the scientific advisory board for Virility Medical, which sponsored the study. Dr. Healy had no disclosures. Dr. Schwartz disclosed ties to Cook Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pilonidal disease, other conditions may benefit from laser treatment
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
SAN DIEGO – Pilonidal disease – a chronic inflammatory condition that can trigger the formation of cysts and sinuses in the superior portion of the intragluteal cleft or the sacrococcygeal area – remains challenging to manage, but mounting evidence supports the use of lasers to enhance treatment success.
“Draining sinuses or acute abscesses are usually associated with an underlying cyst and associated granulation tissue, fibrosis, and tufts of hair,” Catherine M. DiGiorgio, MD, said at the annual conference of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is why laser hair removal can help with the treatment of these patients.”
The suspected etiology is a foreign body reaction to the entrapped hairs, which are found in the sinuses in about 75% of cases. “The treatment for that is surgery,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, a laser and cosmetic dermatologist in Boston. Laser hair reduction decreases the recurrence of cyst formation and drainage, and is usually covered by insurance, she noted.
Supportive evidence
In a comparative study, French researchers retrospectively reviewed the efficacy of laser hair removal after surgery in reducing recurrence rate of pilonidal cysts, versus surgery alone. Of the 41 study participants, 12 had laser hair removal plus surgery and 29 had surgery alone. The rate of cyst recurrence was significantly lower in the laser hair removal plus surgery group, compared with the surgery only group (8.3% vs. 51.7%, respectively; P < .001).
In another study, researchers from the United Kingdom and The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, evaluated the use of the long-pulsed Alexandrite laser in 19 patients with recurrent pilonidal disease who had undergone multiple surgeries.They were treated with the laser for hair removal in the sinus area, requiring 4-12 sessions. The researchers found that 84.2% of patients had a reduction of hair density to less than 5 hairs/cm2, while 15.8% had a reduction of hair density to 5-10 hairs/cm2. They also noted a statistically significant increase in disease-free time in the laser-treated group compared with those treated with surgical management only (P < .01).
Lasers for pseudofolliculitis barbae, HS
Lasers also play a significant role in the treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae, a chronic, inflammatory disease that primarily affects the bearded area of men with thick hairs, usually those with a darker Fitzpatrick skin type. This can also occur in women, particularly those with polycystic ovary syndrome, Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In people with pseudofolliculitis barbae, the hair follicle is positioned at an acute angle to the skin surface and the sharp end of shaved hair reenters the skin, which results in the formation of pustules, papules, secondary infection, and keloids. Treatment involves a variety of medical therapies including retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics, and keratolytics, “but laser hair removal is the best way to get rid of this issue, and results in permanent reduction,” she said. “When treating male patients with laser hair removal in the bearded area, you have to tell them that they won’t be able to grow a beard going forward. Most of them are okay with that.”
A 2002 study, led by E. Victor Ross, MD, of the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, evaluated treatment of pseudofolliculitis barbae in patients with skin types IV, V, and VI with a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser. For the first phase of the study, the investigators tested epidermal tolerance on the thighs of 37 patients and determined that the laser was safe and effective. For the second phase 2 weeks later, they treated a 15x15-mm submental area with the highest fluence tolerated in phase 1 of the trial and used an adjacent site as the control.
After 90 days, the mean papule count was 6.95 for the control site compared with 1 for the laser-treated site. The researchers observed that miniaturization and elimination of hair shafts resulted in decreased inflamed papules. “We know that this works,” Dr. DiGiorgio said.
In another study from investigators at the Naval Medical Center, San Diego, 22 patients with skin types IV, V, and VI who had pseudofolliculitis barbae underwent 5 weekly treatments with a 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser. Topical anesthesia was not used, and 10 evaluators used a Global Assessment Scale (GAS) to assess treatment success from photos taken at baseline and at 4 weeks. At 4 weeks, 11 patients demonstrated 83% improvement on the GAS (P < .01), the investigators reported.
Laser and energy-based treatments can also be used to treat hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic condition that affects apocrine gland–bearing skin. “The hypothesized pathogenesis is that it’s an inflammatory disorder of the hair follicle, where the follicle rupture introduces its contents into the surrounding dermis,” Dr. DiGiorgio said. “The skin reacts with a chemotactic response and abscess formation. This results in inflammatory nodules and sterile abscesses, which can lead to sinus tracts and hypertrophic scars and chronic drainage, which can be foul-smelling. This frequently leads to depression and psychological distress for the patients.”
Possible laser and energy-based treatments for HS include follicular destruction with the Nd:YAG laser, the diode laser, the Alexandrite laser, microwave technology, or intense pulsed light, she said. Microwave technology or radiofrequency can be used for sweat gland destruction, while CO2 lasers can be used to debulk tissue, and the ablative fractional CO2 laser can be used to reduce scarring and improve range of motion.
In a prospective, randomized, intraindividual comparative trial conducted at eight centers in France, researchers evaluated the use of a long-pulsed Nd:YAG laser to treat 36 patients with mild to moderate HS; 27 had inguinal disease and 9 had axillary disease. They received four laser treatments at 6-week intervals; laser settings varied depending on the patient skin type.
At 1 month, there was a significant reduction in the number of inflammatory lesions on the areas treated with lasers, compared to the untreated areas, but the difference was not significant at 3 months. There was no significant difference in the number of flares between the treated and untreated sites at 1 or 3 months.
In a separate study, researchers found that the Nd:YAG laser in combination with topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin was significantly more effective than topical benzoyl peroxide and clindamycin alone for the treatment of HS in 22 patients with Hurley stage II disease. The patients received monthly treatments for 4 months and were followed up 2 months after the last treatment; the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Area and Severity Index was used to measure treatment response.
Statistically significant improvements were observed in the inguinal and axillary areas but not in the inframammary areas. Most patients (90%) reported less frequent breakouts while 10% reported no change. “In addition, 92% of subjects felt that the use of laser was more effective than other treatments they had tried but 8% stated it was equal to the other treatments they had tried,” said Dr. DiGiorgio, who was not affiliated with the study. “The researchers noted continued improvement with subsequent laser sessions,” she added.
According to 2019 guidelines from the United States and Canadian HS Foundations on the management of HS – in the section on light, laser, and energy sources – an Nd:YAG laser is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease on the basis of randomized, controlled trials and case series data, and in patients with Hurley stage I disease based on expert consensus. “Other wavelengths that are used for follicular destruction are recommended on the basis of lower-quality evidence,” the recommendations state.
The guidelines also state that CO2 laser excision “is recommended in patients with Hurley stage II or III disease with fibrotic sinus tracts” while “external beam radiation and PDT have a limited role in the management of patients with HS.”
Dr. DiGiorgio reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT ASLMS 2022
Fractional lasers appear to treat more than a fraction of skin, expert says
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
SAN DIEGO – Using the according to Molly Wanner, MD, MBA.
As a case in point, Dr. Wanner discussed the results of a trial of 48 people over aged 60 years with actinic damage, who received ablative fractional laser treatment on one arm and no treatment on the other arm, which served as the control. At 24 months, only two nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs) developed on the treated arms, compared with 26 on the treated arms.
“What I find interesting is that the treated arm did not develop basal cell carcinoma, only squamous cell carcinoma,” she said at the annual meeting of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “It appears that this is working through more than just treatment of the AK precursor lesions, for which fractional lasers are cleared for use. It appears to impact both types of NMSCs.”
The ablative fractional laser and other wounding therapies can modulate a response to UV light – a process that naturally diminishes with age, according to Dr. Wanner, a dermatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital’s Dermatology Laser and Cosmetic Center in Boston. “This ability to repair DNA is actually modulated by insulin-like growth factor 1,” she said. “IGF-1 is produced by papillary dermal fibroblasts and communicates with keratinocytes. If keratinocytes are exposed to UV light and there is no IGF-1 around, you get a mutated cell, and that keeps spreading, and you could potentially get a skin cancer.”
On the other hand, she continued, if IGF-1 is injected around the keratinocytes, they are able to respond. “Keratinocytes, which are the most superficial layer of the skin, are really active,” noted Dr. Wanner, who is also an assistant professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. “They’re dividing and replicating, whereas fibroblasts are more non-proliferative and more long-lived. They stick around for a long time. I think of them as the adults in the room, giving these new keratinocytes direction.”
In a review of wounding therapies for the prevention of photocarcinogenesis, she and her coauthors noted that IGF-1 increases nucleotide excision repair of damaged DNA, promotes checkpoint signaling and suppression of DNA synthesis, favors specialized polymerases that are better able to repair DNA damage, and enhances p53-dependent transcriptional responses to DNA damage.
“Older fibroblasts produce less IGF-1 and lead to a situation where keratinocytes can grow unchecked,” she said. “We can use fractional laser to help with this. Fractional laser increases fibroblast production and decreases senescent fibroblasts.”
In a 2017 review on the impact of age and IGF-1 on DNA damage responses in UV-irradiated skin, the authors noted the high levels of IGF-1 in the skin of younger individuals and lower levels in the skin of their older counterparts.
“But once older skin has been treated with either dermabrasion or fractional laser, the levels of IGF-1 are restored to that of a young adult,” Dr. Wanner said. “The restoration of IGF-1 then restores that level of appropriate response to UV light. So, what’s interesting is that fractional lasers treat more than a fraction [of skin]. Fractional lasers were developed to have an easier way to improve wound healing by leaving the skin intact around these columns [of treated skin]. It turns out that treatment of these columns of skin does not just impact the cells in that area. There is a true global effect that’s allowing us to almost normalize skin.”
Dr. Wanner now thinks of fractional lasers as stimulating a laser-cell biology interaction, not just a laser-tissue interaction. “It’s incredible that we can use these photons to not only impact the tissue itself but how the cells actually respond,” she said. “What’s going to be interesting for us in the next few years is to look at how lasers impact our cellular biology. How can we harness it to help our patients?”
She and her colleagues are conducting a trial of different wounding modalities to assess their impact on IGF-1. “Does depth matter? Does density matter? Does the wavelength matter?” she asked. “The bottom line is, it turns out that when the skin looks healthier, it is healthier. Cosmetic treatments can impact medical outcomes.”
Dr. Wanner disclosed that she is a consultant and advisor to Nu Skin. She has also received research funding and equipment from Solta.
AT ASLMS 2022
Psychological intervention looks promising in Crohn’s disease
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.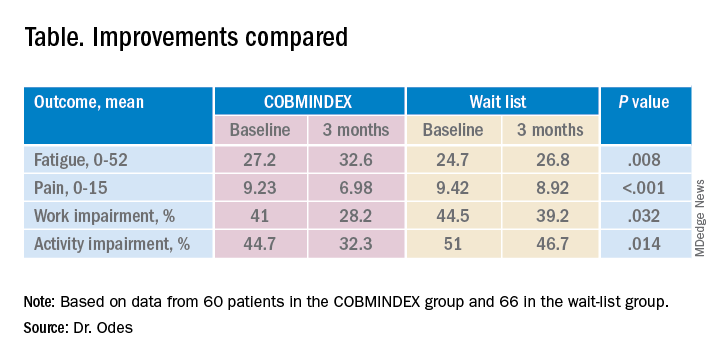
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
SAN DIEGO – A combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness meditation could reduce pain and fatigue from Crohn’s disease, researchers say.
Patients who followed the program not only felt better but were also more often able to show up for work and leisure activities, compared with a control group assigned to a wait list, said Shmuel Odes, MD, a professor of internal medicine at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He presented the finding at Digestive Diseases Week® (DDW) 2022.
Psychological and social factors affect the gut and vice versa, Dr. Odes said. Yet many inflammatory bowel disease clinics overlook psychological interventions.
To address these issues, Dr. Odes and colleagues developed cognitive-behavioral– and mindfulness-based stress reduction (COBMINDEX) training, which can be taught by clinical social workers over the Internet. “The patient learns to relax,” Dr. Odes told MDedge News. “He learns not to fight his condition.”
In a previous paper, published in the journal Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Dr. Odes and colleagues reported that patients who learned the technique showed improvement on a variety of psychological and quality-of-life measures, accompanied by changes in inflammatory cytokines and cortisol.
In a follow-up analysis presented here, the researchers looked at measures of pain and fatigue and then examined whether these were associated with productivity at work and other daily activities.
The study investigators randomly assigned 72 patients to an intervention group who got COBMINDEX training right away, and another 70 to a control group assigned to a wait list of 12 weeks before they could get the training. At baseline, the two groups were not significantly different in any demographic or clinical variable the researchers could find.
Social workers provided COBMINDEX training for the patients in seven 60-minute session over 12 weeks. Five of the sessions were devoted to cognitive-behavioral therapy and two to mindfulness-based stress reduction. The social workers asked the patients to do exercises at least once a day and report outcomes through an app.
Twelve patients dropped out of the COBMINDEX group and four dropped from the wait-list group because of lack of interest, time constraints, pregnancy, or illness.
The researchers created a composite score with a 0-15 scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain) from three pain items from the Harvey-Bradshaw Index for Crohn’s Disease, the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire, and the 12-Item Short Form Survey.
To measure fatigue, they used the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue, which has a 0-52 scale, with lower scores indicating greater fatigue.
To measure impairment while working and other daily activities, they used the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire: Crohn’s Disease. Scores on this measure are expressed as a percentage, with higher values indicating greater impairment.
Both the COBMINDEX and the wait-list groups improved on all these scales, but the improvements were significantly greater for the COBMINDEX group.
Through statistical analysis, the researchers found that the improvements in pain and fatigue indirectly caused the improvements in work and activity impairment, and that pain and fatigue improvements made independent contributions of similar magnitudes. COBMINDEX did not directly improve work or activity.
Psychological interventions are too often overlooked in Crohn’s disease, said the session comoderator Paul Moayyedi, MD, a professor of gastroenterology at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont. “We need to realize how important this is to patients and urgently make this available,” he told MDedge.
A variety of interventions are being researched, and this study makes an important contribution, he said. However, he questioned whether people on a wait list can serve as an adequate control. “If you have to wait for something, you tend to have more pain, and you could have less productivity just because of waiting,” he said. “Ideally they should do a randomized trial with a sham intervention, not a wait list.”
Dr. Odes responded that it is very difficult to recruit people to a trial if they only have a 50% chance of getting a real treatment. And he noted that the people on the wait list in this trial did not show any signs of increased symptoms.
Physicians wanting to provide psychological help to their Crohn’s disease patients can refer them to social workers or psychotherapists, Dr. Odes said, but these professionals may lack training for applying cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction to patients with Crohn’s disease. His team hopes to make an app publicly available soon.
Neither Dr. Odes nor Dr. Moayyedi reported any relevant financial interests. The study was supported by a grant from the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust.
AT DDW 2022
Medical trauma an under-recognized trigger for PTSD
NEW ORLEANS – Recent studies have confirmed that posttraumatic stress disorder can be triggered by health-related stress such as stints in the ICU and life-threatening medical emergencies, but most psychiatrists may not be aware of the latest research, according to an expert in mental trauma.
“This is true among children as well as adults, but it is not generally appreciated by psychiatrists and not at all by non-physicians,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas at Austin’s Dell Medical School, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “It’s something that we all need to educate our colleagues about.”
As Dr. Nemeroff noted in a wide-ranging discussion about the latest trends in PTSD diagnosis and treatment, the DSM-5 doesn’t yet mention medical trauma in its definition of PTSD but refers more vaguely to triggering events that involve “actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence.”
However, multiple recent studies have linked medical trauma to PTSD. A 2019 study in Intensive Care Medicine found that 25% of 99 patients who were treated for emergency respiratory or cardiovascular crises showed PTSD symptoms at 6 months, and the percentage of childhood cancer survivors with PTSD was estimated at as high as 22%, according to research published in Frontiers in Psychology.In 2013, a meta-analysis suggested that 23% of stroke survivors have PTSD symptoms within 1 year, and 11% after 1 year.
PTSD is unique
Dr. Nemeroff noted that PTSD is the only diagnosis in the DSM-5 that’s directly linked to an environmental event. Specifically, he said, PTSD is caused by “very unexpected traumatic events that occur outside the normal repertoire of human behavior.”
In response, “most people that have an acute stress disorder response will fundamentally extinguish it and end up returning to the baseline level of functioning,” he said. But those with PTSD do not recover.
Dr. Nemeroff recommends the use of the 20-question self-report tool known as PCL-5. “It’s your friend,” he said. “It takes a few minutes for the patients to fill out while in the front office, and it doesn’t cost anything. Most patients who have PTSD will have a score of 50-55, maybe 60. You’re going to try to get them down to below 30, and you’re going to give this to them every time they come to your office to follow their progress. It works like a charm.”
As for treatment, psychotherapy and medications remain standard, he said, although “PTSD is a tough disorder to treat.”
According to him, brief cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – 4-5 sessions – has shown the greatest benefit and highest level of evidence in support when initiated within 4-30 days of trauma. Group therapy may be helpful, while it’s not clear if spiritual support and “psychological first aid” are useful during this time period.
There’s no evidence that medications such as SSRIs and atypical antipsychotics will prevent PTSD from developing; typical antipsychotics are not recommended. Individual or group “debriefing” is highly not recommended, Dr. Nemeroff said, because the experience can re-traumatize patients, as researchers learned after 9/11 when encouraging people to relive their experiences triggered PTSD and heartbreak.
Also not recommended: Benzodiazepines and formal psychotherapy in people without symptoms.
Exposure-based CBT has been proven to be successful, Dr. Nemeroff said, but it must be provided by a trained professional. “Going for a weekend course isn’t sufficient,” he said, and research suggests that group CBT is not as helpfulas individual CBT.
As for medication over the longer term, research supports SNRIs and SSRIs such as sertaline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil). Dr. Nemeroff is a fan of venlafaxine (Effexor): “It has a wide dose range. I can go from 75 to 150 milligrams at the low end and 450 and even 600 milligrams at the high end. I’ve had some amazing successes.”
In addition, atypical antipsychotics can be helpful in non-responders or psychotic PTSD patients, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff said he’s skeptical of ketamine as a treatment for PTSD, but he’s most hopeful about MDMA-assisted therapy due to “impressive data” regarding PTSD that was released last year. A bid for FDA approval is in the works, he said.
He added that data is promising from trials examining transcranial magnetic stimulationand (in work by his own team) electroconvulsive therapy. Both therapies are worth considering, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff reported multiple disclosures including research/grant support, stock holdings, scientific advisory board service, consulting relationships, board of director service, and patents.
NEW ORLEANS – Recent studies have confirmed that posttraumatic stress disorder can be triggered by health-related stress such as stints in the ICU and life-threatening medical emergencies, but most psychiatrists may not be aware of the latest research, according to an expert in mental trauma.
“This is true among children as well as adults, but it is not generally appreciated by psychiatrists and not at all by non-physicians,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas at Austin’s Dell Medical School, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “It’s something that we all need to educate our colleagues about.”
As Dr. Nemeroff noted in a wide-ranging discussion about the latest trends in PTSD diagnosis and treatment, the DSM-5 doesn’t yet mention medical trauma in its definition of PTSD but refers more vaguely to triggering events that involve “actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence.”
However, multiple recent studies have linked medical trauma to PTSD. A 2019 study in Intensive Care Medicine found that 25% of 99 patients who were treated for emergency respiratory or cardiovascular crises showed PTSD symptoms at 6 months, and the percentage of childhood cancer survivors with PTSD was estimated at as high as 22%, according to research published in Frontiers in Psychology.In 2013, a meta-analysis suggested that 23% of stroke survivors have PTSD symptoms within 1 year, and 11% after 1 year.
PTSD is unique
Dr. Nemeroff noted that PTSD is the only diagnosis in the DSM-5 that’s directly linked to an environmental event. Specifically, he said, PTSD is caused by “very unexpected traumatic events that occur outside the normal repertoire of human behavior.”
In response, “most people that have an acute stress disorder response will fundamentally extinguish it and end up returning to the baseline level of functioning,” he said. But those with PTSD do not recover.
Dr. Nemeroff recommends the use of the 20-question self-report tool known as PCL-5. “It’s your friend,” he said. “It takes a few minutes for the patients to fill out while in the front office, and it doesn’t cost anything. Most patients who have PTSD will have a score of 50-55, maybe 60. You’re going to try to get them down to below 30, and you’re going to give this to them every time they come to your office to follow their progress. It works like a charm.”
As for treatment, psychotherapy and medications remain standard, he said, although “PTSD is a tough disorder to treat.”
According to him, brief cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – 4-5 sessions – has shown the greatest benefit and highest level of evidence in support when initiated within 4-30 days of trauma. Group therapy may be helpful, while it’s not clear if spiritual support and “psychological first aid” are useful during this time period.
There’s no evidence that medications such as SSRIs and atypical antipsychotics will prevent PTSD from developing; typical antipsychotics are not recommended. Individual or group “debriefing” is highly not recommended, Dr. Nemeroff said, because the experience can re-traumatize patients, as researchers learned after 9/11 when encouraging people to relive their experiences triggered PTSD and heartbreak.
Also not recommended: Benzodiazepines and formal psychotherapy in people without symptoms.
Exposure-based CBT has been proven to be successful, Dr. Nemeroff said, but it must be provided by a trained professional. “Going for a weekend course isn’t sufficient,” he said, and research suggests that group CBT is not as helpfulas individual CBT.
As for medication over the longer term, research supports SNRIs and SSRIs such as sertaline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil). Dr. Nemeroff is a fan of venlafaxine (Effexor): “It has a wide dose range. I can go from 75 to 150 milligrams at the low end and 450 and even 600 milligrams at the high end. I’ve had some amazing successes.”
In addition, atypical antipsychotics can be helpful in non-responders or psychotic PTSD patients, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff said he’s skeptical of ketamine as a treatment for PTSD, but he’s most hopeful about MDMA-assisted therapy due to “impressive data” regarding PTSD that was released last year. A bid for FDA approval is in the works, he said.
He added that data is promising from trials examining transcranial magnetic stimulationand (in work by his own team) electroconvulsive therapy. Both therapies are worth considering, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff reported multiple disclosures including research/grant support, stock holdings, scientific advisory board service, consulting relationships, board of director service, and patents.
NEW ORLEANS – Recent studies have confirmed that posttraumatic stress disorder can be triggered by health-related stress such as stints in the ICU and life-threatening medical emergencies, but most psychiatrists may not be aware of the latest research, according to an expert in mental trauma.
“This is true among children as well as adults, but it is not generally appreciated by psychiatrists and not at all by non-physicians,” said Charles B. Nemeroff, MD, PhD, professor and chair of the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the University of Texas at Austin’s Dell Medical School, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association. “It’s something that we all need to educate our colleagues about.”
As Dr. Nemeroff noted in a wide-ranging discussion about the latest trends in PTSD diagnosis and treatment, the DSM-5 doesn’t yet mention medical trauma in its definition of PTSD but refers more vaguely to triggering events that involve “actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence.”
However, multiple recent studies have linked medical trauma to PTSD. A 2019 study in Intensive Care Medicine found that 25% of 99 patients who were treated for emergency respiratory or cardiovascular crises showed PTSD symptoms at 6 months, and the percentage of childhood cancer survivors with PTSD was estimated at as high as 22%, according to research published in Frontiers in Psychology.In 2013, a meta-analysis suggested that 23% of stroke survivors have PTSD symptoms within 1 year, and 11% after 1 year.
PTSD is unique
Dr. Nemeroff noted that PTSD is the only diagnosis in the DSM-5 that’s directly linked to an environmental event. Specifically, he said, PTSD is caused by “very unexpected traumatic events that occur outside the normal repertoire of human behavior.”
In response, “most people that have an acute stress disorder response will fundamentally extinguish it and end up returning to the baseline level of functioning,” he said. But those with PTSD do not recover.
Dr. Nemeroff recommends the use of the 20-question self-report tool known as PCL-5. “It’s your friend,” he said. “It takes a few minutes for the patients to fill out while in the front office, and it doesn’t cost anything. Most patients who have PTSD will have a score of 50-55, maybe 60. You’re going to try to get them down to below 30, and you’re going to give this to them every time they come to your office to follow their progress. It works like a charm.”
As for treatment, psychotherapy and medications remain standard, he said, although “PTSD is a tough disorder to treat.”
According to him, brief cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – 4-5 sessions – has shown the greatest benefit and highest level of evidence in support when initiated within 4-30 days of trauma. Group therapy may be helpful, while it’s not clear if spiritual support and “psychological first aid” are useful during this time period.
There’s no evidence that medications such as SSRIs and atypical antipsychotics will prevent PTSD from developing; typical antipsychotics are not recommended. Individual or group “debriefing” is highly not recommended, Dr. Nemeroff said, because the experience can re-traumatize patients, as researchers learned after 9/11 when encouraging people to relive their experiences triggered PTSD and heartbreak.
Also not recommended: Benzodiazepines and formal psychotherapy in people without symptoms.
Exposure-based CBT has been proven to be successful, Dr. Nemeroff said, but it must be provided by a trained professional. “Going for a weekend course isn’t sufficient,” he said, and research suggests that group CBT is not as helpfulas individual CBT.
As for medication over the longer term, research supports SNRIs and SSRIs such as sertaline (Zoloft) and paroxetine (Paxil). Dr. Nemeroff is a fan of venlafaxine (Effexor): “It has a wide dose range. I can go from 75 to 150 milligrams at the low end and 450 and even 600 milligrams at the high end. I’ve had some amazing successes.”
In addition, atypical antipsychotics can be helpful in non-responders or psychotic PTSD patients, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff said he’s skeptical of ketamine as a treatment for PTSD, but he’s most hopeful about MDMA-assisted therapy due to “impressive data” regarding PTSD that was released last year. A bid for FDA approval is in the works, he said.
He added that data is promising from trials examining transcranial magnetic stimulationand (in work by his own team) electroconvulsive therapy. Both therapies are worth considering, he said.
Dr. Nemeroff reported multiple disclosures including research/grant support, stock holdings, scientific advisory board service, consulting relationships, board of director service, and patents.
at APA 2022














